- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides

MLA8 Citation Generator
Keep all of your citations in one safe place
Create an account to save all of your citations
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper
Consider your source's credibility. ask these questions:, contributor/author.
- Has the author written several articles on the topic, and do they have the credentials to be an expert in their field?
- Can you contact them? Do they have social media profiles?
- Have other credible individuals referenced this source or author?
- Book: What have reviews said about it?
- What do you know about the publisher/sponsor? Are they well-respected?
- Do they take responsibility for the content? Are they selective about what they publish?
- Take a look at their other content. Do these other articles generally appear credible?
- Does the author or the organization have a bias? Does bias make sense in relation to your argument?
- Is the purpose of the content to inform, entertain, or to spread an agenda? Is there commercial intent?
- Are there ads?
- When was the source published or updated? Is there a date shown?
- Does the publication date make sense in relation to the information presented to your argument?
- Does the source even have a date?
- Was it reproduced? If so, from where?
- If it was reproduced, was it done so with permission? Copyright/disclaimer included?
MLA Format: Everything You Need to Know and More
Filled with a wide variety of examples and visuals, our Citation Machine® MLA guide will help you master the citation process. Learn how to cite websites, books, journal articles, magazines, newspapers, films, social media, and more!
MLA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Comprehensive Guide to APA Format
Our Citation Machine® APA guide is a one-stop shop for learning how to cite in APA format. Read up on what APA is, or use our citing tools and APA examples to create citations for websites, books, journals, and more!
APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Everything You Need to Know About Chicago Style
Creating citations in Chicago style has never been easier thanks to our extensive Citation Machine® Chicago style guide and tools. Learn about footnotes, endnotes, and everything in between, or easily create citations for websites, books, journal articles, and more!
Chicago Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Citation Machine®’s Ultimate Writing Guides
Whether you’re a student, writer, foreign language learner, or simply looking to brush up on your grammar skills, our comprehensive grammar guides provide an extensive overview on over 50 grammar-related topics. Confused about reflexive verbs, demonstrative adjectives, or conjunctive adverbs? Look no further! Learn about these grammar topics and many, many more in our thorough and easy to understand reference guides!
Citing Sources Guide | Grammar Guide | Plagiarism Guide | Writing Tips
Student Blog
Stay up to date! Get research tips and citation information or just enjoy some fun posts from our student blog.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
- For educators
- Go to my projects
- Português (PT)
- Português (BR)
BibGuru MLA Citation Generator
Cite websites, books, articles, ...
Your Works Cited page in MLA
- A closer look at MLA's core elements
In-text citations in MLA
Formatting your paper in mla, helpful resources on mla style, the ultimate guide to citing in mla.
The MLA citation style was developed by the Modern Language Association of America, an association of scholars and teachers of language and literature.
The MLA publishes several academic journals, and the MLA Handbook , a citation guide for high school and undergrad students. The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for writing and documenting research, as well as tips for the use of the English language in your writing.
MLA is a very popular citation style. However, if you are unsure which citation style to use in your paper, ask your instructor. There are many different citation styles and using the style your instructor or institution has established correctly can have a positive impact on your grade.
This guide is based on the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook and aims at helping you cite correctly in MLA. The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for a large variety of sources and uses a two-part documentation system for citing sources:
- in-text parenthetical citations (author, page)
- a reference list at the end of paper with all literature used in text.
Each source that was cited in the text or notes of your paper should appear in a list at the end of the paper. MLA calls the reference list a "Works Cited" page.

I want to cite a ...
Your Works Cited list identifies the sources you cite in the body of your research project. Works that you consult during your research, but don't use and cite in your paper, are not included. Your Works Cited list is ordered alphabetically by the part of the author's name that comes first in each entry.
Entries in the list of works cited are made up of core elements given in a specific order, and there are optional elements that may be included. The core elements in your works cited list are the following, given in the order in which they should appear, followed by the correct punctuation mark. The final element in an MLA reference should end with a period:
- Title of source.
- Title of container,
- Contributor,
- Publication date,
To use this template of core elements, first evaluate what you are citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then list each element relevant to your source in the order given on the template. For a work containing another work (e.g. an article published in a journal and contained in a database), you can repeat the process by filling out the template again from Title of container to Location , listing all elements that apply to the container.
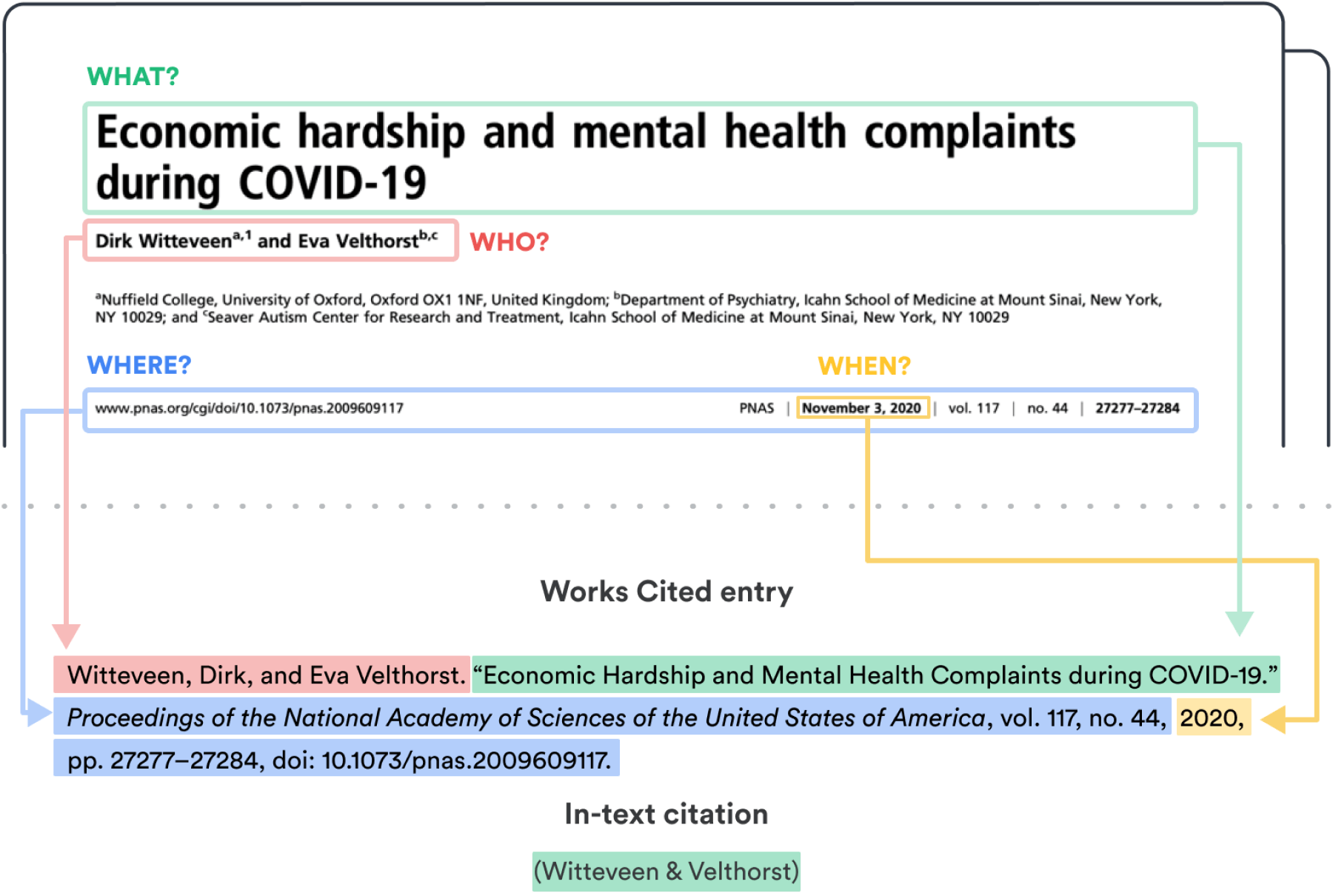
Step-by-step guide to create a Works Cited entry
Let's try this with a journal article. If you wanted to cite the article , “What Should We Do with a Doctor Here?”: Medical Authority in Austen’s Sanditon ," from the journal, Nineteenth-Century Contexts , the process would look like this:
- First, you would determine the author. In this case, that's Amy Mallory-Kani. so the first part of your reference would be: Mallory-Kani, Amy.
- Next, you'd want to include the title of the source in quotation marks, followed by a period: “What Should We Do with a Doctor Here?”: Medical Authority in Austen’s Sanditon."
- After the title of the source, you need to list the container. In this case, it's the journal's name, Nineteenth-Century Contexts , italicized and followed by a comma.
- For journal articles, the title of the container needs to be followed by version, or the volume number of the journal, separated by a comma from the issue number: vol. 39, no. 4,
- Since there is not typically a publisher listed for journal articles, the next step is to include the date, followed by a comma: 2017,
- Finally, you'll end your reference by adding the page numbers for the article, followed by an ending period: pp. 313-26.
If we put this all together, the full reference will look like this:
EXAMPLE Journal article
Mallory-Kani, Amy. “'What Should We Do with a Doctor Here?': Medical Authority in Austen’s Sanditon ”. Nineteenth-Century Contexts , vol. 39, no. 4, 2017, pp. 313-26.
MLA has a specific rule about how to structure page numbers in a works cited entry. Use pp. and then list the number. If the page range is within ten or one hundred digits, you don't need to repeat the first digit. For example, you would write pp. 51-8 or pp. 313-26.
The following section takes a deeper look at the core elements of an MLA works cited entry to help you get your citation right.
A closer look at MLA's core elements
When formatting the author element, make sure to follow these guidelines:
- When a work is published without an author's name, do not list it as Anonymous . Skip the author element instead and begin with the Title of source .
- Begin the entry with the last name of the author, so it can be alphabetized under this name. Follow the last name with a comma and the rest of the name as presented by the work.
- When a source has two authors, include them in the order in which they are presented in the work. Reverse the first of the names as described above.
- When a source has three or more authors, reverse the first of the names as described above and follow it with a comma and the abbreviation, et al.
EXAMPLE Source with two authors
Gabrielle, Matthew, and David M. Perry. The Bright Ages: A New History of Medieval Europe . Harper, 2021.
In the Title of Source element, you list the title of the work you are citing:
EXAMPLE Title of Source element
Cox, Taylor. Creating the Multicultural Organization: A Strategy for Capturing the Power of Diversity . Jossey-Bass, 2001.
In general, titles in your Works Cited list are given in full exactly as they are found in the source, except that capitalization, punctuation between the main title and a subtitle, and the styling of titles that normally appear in italic typeface are standardized. The Title of Source element is followed by a period unless the title ends in a question mark or exclamation point.
A container in the context of the MLA template is a work that contains another work. An example of a container can be:
- A periodical, such as a journal, magazine or newspaper is the container of an article published there.
- A website or database can be the container of a post, a review, a song, a film, or other media.
- An art exhibit is the container of an artwork featured in it.
In the example below, the Journal of Postsecondary Education and Disability is the container of the article “Vocabulary Knowledge of Deaf and Hearing Postsecondary Students”:
EXAMPLE Title of Container
Sarchet, Thomastine, et al. “Vocabulary Knowledge of Deaf and Hearing Postsecondary Students.” Journal of Postsecondary Education and Disability , vol. 27, no. 2, Summer 2014, pp. 161–178.
Importantly, a website or a database is not always automatically the container of a work that can be found there. If you click on a Facebook link that takes you to a New York Times article, Facebook is not the container of the article, but the New York Times website is. Be careful to make the distinction here.
The title of Container is normally italicized and followed by a comma.
People, groups, and organizations can be contributors to a work without being its primary creator. There can be a primary author, but a work can also be created by a group of people. Key contributors should always be listed in your entry. Other contributors can be listed on a case-by-case basis. Whenever you list a contributor, include a label describing the role. These kinds of contributors should always be listed in your entry:
- translators
- editors responsible for scholarly editions and anthologies
- editors responsible for edited collections of works by various primary authors from which you cite an individual contribution
EXAMPLE Translator of a work with a primary author
Chartier, Roger. The Order of Books: Readers, Authors, and Libraries in Europe between the Fourteenth and Eighteenth Centuries. Translated by Lydia G. Cochrane, Stanford UP, 1994.
It may be necessary to include other types of contributors if they shaped the overall presentation of the work. Use labels (in lowercase) to describe the contributor's role, such as:
- translated by
EXAMPLE Creator of a television show
"Strike Up the Band." The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel , created by Amy Sherman-Palladino, season 3, episode 1, Amazon Studios, 2019.
When a source has three or more contributors in the same role, list the first contributor, followed by et al.
EXAMPLE Three or more contributors
Balibar, Étienne. Politics and the Other Scene . Translated by Christine Jones et al., Verso, 2002.
If a source is a version of a work released in more than one form, you need to identify the version in your entry. For example, books are commonly issued in versions called editions .
When citing versions in your Works Cited list, write original numbers with arabic numerals and no superscript. Abbreviate revised (rev.) and edition (ed.) .
EXAMPLE Edition of a work
Black, Joseph, et al., editors. The Broadview Anthology of British Literature: The Victorian Era . 3rd ed., Broadview, 2021.
The source you are documenting may be part of a sequence, like a volume, issue, or episode. Include that number in your entry:
EXAMPLE Work with a number
Warren, R., et al. “The Projected Effect on Insects, Vertebrates, and Plants of Limiting Global Warming to 1.5°C Rather than 2°C.” Science (New York, N.Y.) , vol. 360, no. 6390, 2018, pp. 791–795, doi:10.1126/science.aar3646.
Always use arabic numerals in the Number element. If necessary, convert roman numerals or spelled out numerals to arabic numerals.
The publisher is the entity primarily responsible for making the work available to the public. The publisher element may include the following:
- book publisher
- studio, network, company, or distributor that produced or broadcast a television show
- institution responsible for creating website content
- agency that produced government publication
A publisher's name may be omitted when there is none, or when it doesn't need to be given, for example in:
- some periodicals (when publication is ongoing)
- works published by their authors or editors (self-published)
- websites not involved in producing the content they make available (e.g. Youtube)
This element tells your reader when the version of the book you are citing was published. In the example below, the book was published in 2018:
EXAMPLE Publication date
Lavelle, Christophe, editor. Molecular Motors: Methods and Protocols. 2nd ed., Humana Press, 2018, doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-8556-2.
If roman numerals are used, convert them to arabic numerals. Use the day-month-year style to minimize commas in your entry and use the most specific date you can find in your source. Include day, month, and year if your source does:
EXAMPLE Specific Publication date
Merrill, Stephen. "Teaching through a Pandemic: A Mindset for This Moment." Edutopia , 19 Mar. 2020, www.edutopia.org/article/teaching-through-pandemic-mindset-moment.
When time is given and helps define and locate the work, include it.
For paginated print or similar formats (e.g. PDFs), the location is the page range. In other cases, additional information may need to be included with the page numbers so that the work can be found. In this overview, you can see examples for locations:
As mentioned above, Works Cited list entries in MLA style are based on the template of core elements. In some cases, you may need or want to give additional information relevant to the work you are documenting. You can do so by adding supplements to the template. There are two sections where you can add supplements, either:
- after the Title of Source, or
- at the end of the entry.
A period should be placed after a supplemental element. Three pieces of information are the most likely to be placed after the Title of Source:
- A contributor other than the author
- The original publication date (for a work contained in another work)
- Generically labeled sections (if any part or section of the work has a unique title as well as generic label)
For example, inserting the contributors' roles and names after the Title of Source element tells the reader that Leila El Khalidi and Christopher Tingley translated only The Singing of the Stars , not all the other works in Short Arabic Plays :
EXAMPLE Supplemental elements
Fagih, Ahmed Ibrahim al-. The Singing of the Stars . Translated by Leila El Khalidi and Christopher Tingley. Short Arabic Plays: An Anthology , edited by Salma Khadra Jayyusi, Interlink Books, 2003, pp. 140-57.
If you need to clarify something about the entry as a whole, you can do it at the end of the entry , like:
- Date of access
- Medium of publication (when more than one version of a source is accessible on the same landing page and you are citing a version that is not the default version)
- Dissertations and theses
- Publication history
- Book series
- Columns, sections, and other recurring titled features
- Multivolume works
- Government documents
EXAMPLE Government documents
United States, Congress, House. Improving Broadband Access for Veterans Act of 2016. Congress.gov , www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/house-bill/6394/text. 114th Congress, 2nd session, House Resolution 6394, passed 6 Dec. 2016.
How to use Bibguru for MLA citations

In-text citations aim at directing the reader to the entry in your Works Cited list for the source. while creating the least possible interruption in the text. An in-text citation usually contains the author's name (or other first element in the entry in the works cited list) and a page number. The page number usually goes in a parenthesis, placed where there is a natural pause in the text.
A parenthetical citation that directly follows a quotation is placed after the closing quotation mark. No punctuation is used between the author's name (or the title) and a page number:
EXAMPLE Parenthetical citation
“It's silly not to hope. It's a sin he thought.” (Hemingway 96)
The author's name can appear in the text itself or before the page number in the parenthesis:
Cox names five strategies to implement Diversity Management in companies (50).
Here are some additional examples of in-text citations and their corresponding Works Cited entries:
EXAMPLE Citation in prose using author's name
Smith argues that Jane Eyre is a "feminist Künstlerroman " that narrativizes a woman's struggle to write herself into being (86).
Jane Eyre is a "feminist Künstlerroman " that narrativizes a woman's struggle to write herself into being (Smith 86).
EXAMPLE Works cited
Smith, Jane. Feminist Self-Definition in the Nineteenth-Century Novel . Cambridge UP, 2001.
How to correctly style your in-text citations
- If you are citing an author in your paper, give the full name at first mention and the last name alone thereafter.
- If you are citing a work with two authors, include both first and last names the first time you mention them in your paper. Then, in a following parenthetical citation, connect the two last names with and .
- If the source has three or more authors, you may list all the names or provide the name of the first collaborator followed by "and others" or "and colleagues". In a parenthetical citation, list the last name of the first author and et al .
Ditch the frustrations for stress-free citations
The MLA Handbook also provides guidelines on how to present your paper in a clear and consistent way. These are the general guidelines to format your paper correctly , according to MLA. For more details, refer to the MLA Handbook :
- Use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Font size should be 12 pt.
- Set the margins of your document to 1 inch on all sides.
- Double-space the entire text of your paper.
- Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks.
- Indent every new paragraph one half-inch from the left margin. You can use your tab bar for this.
- Create a header that numbers all pages consecutively in the upper right-hand corner, one half-inch from the top and flush with the right margin.
- Use italics for the titles of longer works.
- Do not make a title page for your paper unless specifically required.
- On the first page, make sure that the text is left-aligned. Then, list your name, the name of your teacher or professor, the course name and the date in separate lines.
- Center align your heading. Do not italicize, bold, or underline your title. Also, do not use a period after the title.
The MLA Handbook gives guidance for a multitude of different sources, like websites, television series, songs, articles, comic books, etc., and considers various types of contributors to these sources. BibGuru's MLA citation generator helps you create the fastest and most accurate MLA citations possible. If you want to learn more about MLA citations, check out our detailed MLA citation guides .
From our blog

More Bibguru MLA guides

Resources based on the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab (OWL)
- California State University, Northridge Library MLA Style Guide
- Columbia College Library MLA Style Guide
- McMaster University Library MLA Style Guide
- Spartanburg Community College Library MLA Style Guide
- Madison College Libraries MLA Style Guide
- California State University, Dominguez Hills Library MLA Style Guide
- University of Wisconsin-Parkside Library MLA Style Guide
The following resources are based on the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook , but still offer relevant insights on MLA style
- University of Washington Libraries MLA Style Guide
- University of North Texas Libraries MLA Style Guide
- Valencia College Library MLA Style Guide
- College of Southern Nevada Libraries MLA Style Guide
- University of Nevada, Reno Libraries MLA Style Guide
- Montana State University Library MLA Style Guide
- University of Michigan Library MLA Style Guide
- University of Vermont Libraries MLA Style Guide
- University of Illinois Library MLA Style Guide
- Hillsborough Community College Libraries MLA Style Guide
- Southern Connecticut State University Library MLA Style Guide
- Arizona State University Library MLA Style Guide
An in-text citation usually contains the author's name (or other first element in the entry in the works cited list) and a page number. The page number usually goes in a parenthesis, placed where there is a natural pause in the text.
In MLA style, audio-visual material uses the specific time of the audio/video for in-text citations. You need to cite the author's last name and the time or a short version of the title and the time within parentheses, e.g.:
The following scene exemplifies the performer's physical abilities (Thurman 00:15:43-00:20:07).
Anyone can use MLA style given its versatility. However, this format is often used by writers and students working in the arts and humanities, such as linguistics, literature, and history.
Yes, the BibGuru MLA citation generator is completely free and ready to use by students and writers adopting MLA guidelines.
The most recent version of the MLA guidelines is the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook, released in 2021. It is still very new so you should check with your instructor or institution to make sure you're using the right version.
Citation generators
Citation guides, alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
MLA Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What is Cite This For Me’s Citation Generator?
Are you looking for an easy and reliable way to cite your sources in the MLA format? Look no further because Cite This For Me’s MLA citation generator is designed to remove the hassle of citing. You can use it to save valuable time by auto-generating all of your citations.
The Cite This For Me citation machine accesses information from across the web, assembling all of the relevant material into a fully-formatted works cited MLA format page that clearly maps out all of the sources that have contributed to your paper. Using a generator simplifies the frustrating citing process, allowing you to focus on what’s important: completing your assignment to the best of your ability.
Have you encountered an unusual source, such as a microfiche or a handwritten manuscript, and are unsure how to accurately cite this in the MLA format? Or are you struggling with the dozens of different ways to cite a book? If you need a helping hand with creating your citations, Cite This For Me’s accurate and powerful generator and handy MLA format template for each source type will help to get you one step closer to the finishing line.
Continue reading our handy style guide to learn how to cite like a pro. Find out exactly what a citation generator is, how to implement the MLA style in your writing, and how to organize and present your work according to the guidelines.
Popular MLA Citation Examples
- Archive material
- Book Chapter
- Dictionary entry
- E-book or PDF
- Image online or video
- Presentation or lecture
- Video, film, or DVD
Why Do I Need To Cite?
Whenever you use someone else’s ideas or words in your own work, even if you have paraphrased or completely reworded the information, you must give credit where credit is due to avoid charges of plagiarism. There are many reasons why.
First, using information from a credible source lends credibility to your own thesis or argument. Your writing will be more convincing if you can connect it to information that has been well-researched or written by a credible author. For example, you could argue that “dogs are smart“ based on your own experiences, but it would be more convincing if you could cite scientific research that tested the intelligence of dogs.
Second, you should cite sources because it demonstrates that you are capable of writing on an academic or professional level. Citations show that your writing was thoughtfully researched and composed, something that you would not find in more casual writing.
Lastly, and most importantly, citing is the ethical thing to do. Imagine that you spent months of your life on a paper: researching it, writing it, and revising it. It came out great and you received many compliments on your thesis and ideas. How would you feel if someone took those ideas (or even the whole paper) and turned them in as their own work without citations? You’d probably feel terrible.
All of the source material that has contributed to your work must be acknowledged with an MLA in-text citation (also known as a parenthetical citation ) and be featured in your works cited list as full references.
Create citations, whether manually or by using the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator, to maintain accuracy and consistency throughout your project.
Do I Have to Cite Everything?
When writing a research paper, any information used from another source needs to be cited. The only exceptions to this rule are everyday phrases (e.g., all the world’s a stage) and common knowledge (e.g., President Kennedy was killed in 1963).
Also, your own work does not need to be cited. That includes your opinions, ideas, and visuals (e.g., graphs, photos, etc.) you created. However, you do need to cite your own work if you have previously published it or used it in another assignment. Otherwise it’s considered self plagiarism . For example, submitting a paper that you wrote and already turned in for another class is still plagiarism, even though it is your own work.
If you have any doubts about whether or not something you’ve written requires a citation, it’s always better to cite the source. While it may be a tedious process without an MLA citation machine, attributing your research is essential in validating the statements and conclusions you make in your work. What’s more, drawing on numerous sources elevates your understanding of the topic, and accurately citing these sources reflects the impressive research journey that you have embarked on.
Consequences of Not Citing
The importance of crediting your sources goes far beyond ensuring that you don’t lose points on your assignment for citing incorrectly. Plagiarism, even when done unintentionally, can be a serious offense in both the academic and professional world.
If you’re a student, possible consequences include a failing assignment or class grade, loss of scholarship, academic probation, or even expulsion. If you plagiarize while writing professionally, you may suffer legal ramifications as well, such as fines, penalties, or lawsuits.
The consequences of plagiarism extend beyond just the person who plagiarized: it can result in the spread of misinformation. When work is copied and/or improperly cited, the facts and information presented can get misinterpreted, misconstrued, and mis-paraphrased. It can also be more difficult or impossible for readers and peers to check the information and original sources, making your work less credible.
What is the MLA Format?
The MLA format was developed by the Modern Language Association as a consistent way of documenting sources used in academic writing. It is a concise style predominantly used in the liberal arts and humanities, first and foremost in research focused on languages, literature, and culture. The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook has the most current format guidelines. It was updated to reflect the expanding digital world and how researchers and writers cite more online sources. You can find out more here .
It is important to present your work consistently, regardless of the style you are using. Accurately and coherently crediting your source material both demonstrates your attention to detail and enhances the credibility of your written work. The MLA format provides a uniform framework for consistency across a scholarly document, and caters to a large variety of sources. So, whether you are citing a website, an article, or even a podcast, the style guide outlines everything you need to know to correctly format all of your MLA citations.* The style also provides specific guidelines for formatting your research paper, and useful tips on the use of the English language in your writing.
Cite This For Me’s style guide is based on (but not associated with) the 9th edition of the Modern Language Association Handbook for Writers of Research Papers. Our MLA generator also uses the 9th edition – allowing you to shift focus from the formatting of your citations to what’s important – how each source contributes to your work.
MLA has been widely adopted by scholars, professors, journal publishers, and both academic and commercial presses across the world. However, many academic institutions and disciplines prefer a specific style of referencing (or have even developed their own unique format) so be sure to check which style you should be using with your professor. Cite This For Me supports citing in thousands of styles, so the odds are good that we have tools for the citation style you need. Whichever style you’re using, be consistent!
So, if you’re battling to get your citations finished in time, you’ve come to the right MLA citation website. The generator above will can cite any source in 7,000+ styles. So, whether your discipline uses the APA citation style, or your institution requires you to cite in the Chicago style citation , simply go to Cite This For Me’s website to find generators and style guides for ASA , IEEE , AMA and many more.
*You may need to cite a source type that is not covered by the format manual – for these instances we have developed additional guidance and MLA format examples, which we believe stick as closely as possible to the spirit of the style. It is clearly indicated where examples are not covered in the official handbook.
How Do I Create and Format MLA In-text Citations?
The MLA format is generally simpler than other referencing styles as it was developed to emphasize brevity and clarity. The style uses a straightforward two-part documentation system for citing sources: parenthetical citations in the author-page format that are keyed to an alphabetically ordered works cited page. This means that the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text as a parenthetical citation, and a complete corresponding reference should appear in your works cited list.
Keep your MLA in-text citations brief, clear and accurate by only including the information needed to identify the sources. Furthermore, each parenthetical citation should be placed close to the idea or quote being cited, where a natural pause occurs – which is usually at the end of the sentence. Essentially you should be aiming to position your parenthetical citations where they minimize interruption to the reading flow, which is particularly important in an extensive piece of written work.
Check out the examples below…
Citation Examples
Parenthetical citation examples:
- Page specified, author mentioned in text:
If the author’s name already appears in the sentence itself then it does not need to appear in the parentheses. Only the page number appears in the citation. Here’s an MLA format example:
Sontag has theorized that collecting photographs is a way “to collect the world” (3).
- Page specified, author not mentioned in text:
Include the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken in a parenthetical citation after the quote. This way of citing foregrounds the information being cited.
“To collect photographs is to collect the world” (Sontag 3).
When the author is referred to more than once in the same paragraph, you may use a single MLA in-text citation at the end of the paragraph (as long as the work cannot be confused with others cited).
On Photography posits that “to collect photographs is to collect the world.” It intensifies that sentiment by saying photography “means putting oneself into a certain relation to the world that feels like knowledge—and, therefore, like power.” (Sontag 3, 4)
- Page specified, same author, different works:
If you are citing two works by the same author, you should put a comma after the author’s surname and add a shortened title to distinguish between them. Italicize book titles, put article titles within quotation marks. As with the above examples, if you mention the author in the text, they don’t need to be included in the parenthetical MLA citation.
In the line “Ask Benjy ef I did. I aint stud’in dat winder” ( The Sound 276), Faulkner employs spelling and diction to communicate the character background of Dilsey. He’s also seen doing this in other books. For example, “He kilt her.” ( As I Lay 54).
- Page specified, two authors, same last name:
In MLA citing, if there are two authors with the same surname, be sure to include their first initial in your citation to avoid confusion.
- Page specified, two authors, same work:
Each author’s name will be included in both the parenthetical and the full source reference in your MLA bibliography.
Crowley is in fact, the snake who convinced Eve to eat the apple in the Garden of Eden (Prattchett and Gaiman 4).
- Page specified, more than two authors, same work:
For any work with three authors or more, you’ll include the last name of the first author listed and the abbreviation “et al.” which is Latin for “and others.”
“The skills required to master high-stakes interactions are quite easy to spot and moderately easy to learn” (Patterson et al. 28).
- Websites and other online sources:
The MLA formatting examples below above are for information or quotes that have specified pages, usually from a book. If you are using information from a website or online source, the author rules below still apply but a page number is not needed. Instead, just include the first bit of identifiable information that will be shown in the source’s full reference (e.g., author name, video title, website name, etc.).
“Scientists speculate that this might be due to a large chunk of nickel and iron embedded beneath the crater – perhaps the remnants of the asteroid that created it” (Ravilious).
“There’s a flag on the flag; it’s bad design” (“In Defense of Bad Flags”)
Full citations/references MLA website citation:
One of the most common sources cited are websites, so it’s useful to know how to cite a website in MLA.
Ravilious, Kate. “Terrawatch: The Mysteries of the Moon’s Largest Crater.” The Guardian , 1 Oct 2019, www.theguardian.com/science/2019/oct/01/terrawatch-the-mysteries-of-the-moons-largest-crater.
Format for books:
Franke, Damon. Modernist Heresies: British Literary History, 1883-1924 . Ohio State UP, 2008.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography . Penguin, 2008.
MLA citation format for journal articles:
Stanton, Elizabeth Cady. “Progress of the American Woman.” The North American Review , vol. 171, no. 529, 1900, pp. 904–907. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/25105100.
Format for online videos:
“In Defense of Bad Flags.” YouTube , uploaded by Vlogbrothers, 4 Oct. 2019, www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkpAe3_qmq0.
Works cited / bibliography example:
Unlike an MLA in-text citation, you must include all of the publication information in your works cited entries.
Franke, Damon. Modernist Heresies: British Literary History, 1883-1924. Ohio State UP, 2008.
There’s a lot of formatting needed when you cite. Luckily for you, we know where the commas go, and our MLA citation maker will help you put them there.
If citing is giving you a headache, use Cite This For Me’s free, accurate and intuitive MLA citation generator to add all of your source material to your works cited page with just a click.
How Do I Format My MLA Works Cited Page?
A works cited page is a comprehensive list of all the sources that directly contributed to your work – each entry links to the brief parenthetical citations in the main body of your work. An in-text citation MLA only contains enough information to enable readers to find the source in the works cited list, so you’ll need to include the complete publication information for the source in your works cited entries.
Your works cited page in MLA should appear at the end of the main body of text on a separate page. Each entry should start at the left margin and be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name (note that if there is no author, you can alphabetize by title). For entries that run for more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) – this format is called a ‘hanging indentation.’
The title of the page should be neither italicized nor bold – it is simply center-aligned. Like the rest of your MLA format paper the list should be double-spaced, both between and within entries.
Sometimes your professor will ask you to also list the works that you have read throughout your research process, but didn’t directly cite in your paper. This list should be called ‘Work Cited and Consulted,’ and is an excellent opportunity to demonstrate the full extent of the research you have carried out.
As long as you clearly indicate all of your sources via both parenthetical citations and an MLA format works cited list, it is very unlikely that you will lose points for citing incorrectly.
Works cited examples:
Anderson, Benedict. Imagined Communities. Verso, 1983.
Fox, Claire F. The Fence and the River: Culture and Politics at the U.S.-Mexico Border. U of Minnesota P, 1999.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography. Penguin, 2008.
MLA Style Research
When you are gathering sources in your research phase, be sure to make note of the following bibliographical items that will later make up your works cited MLA.
- Name of original source owner: author, editor, translator, illustrator, or director …
- Titles: article or newspaper title, title of publication, series title …
- Important dates: date of publication, date of composition, issue date, event date, date accessed …
- Publishing information: publisher name
- Identifying information: number of volumes, volume number, issue number, edition, chapter, pages, lines …
If you’re still in your research phase, why not try out Cite This For Me for Chrome? It’s an intuitive and easy-to-use browser extension that enables you to instantly create and edit a citation for any online source while you browse the web.
Racing against the clock? If your deadline has crept up on you and you’re running out of time, the Cite This For Me MLA citation maker will collect and add any source to your bibliography with just a click.
In today’s digital age, source material comes in all shapes and sizes. Thanks to the Cite This For Me citation generator, citing is no longer a chore. The citation generator will help you accurately and easily cite any type of source in a heartbeat, whether it be a musical score, a work of art, or even a comic strip. Cite This For Me helps to elevate a student’s research to the next level by enabling them to cite a wide range of sources.
MLA Citation Formatting Guidelines
Accurately citing sources for your assignment doesn’t just prevent the appearance of or accusations of plagiarism – presenting your source material in a clear and consistent way also ensures that your work is accessible to your reader. So, whether you’re following the MLA format citation guidelines or using the Cite This For Me citation generator, be sure to abide by the presentation rules on font type, margins, page headers, and line spacing.
For research papers, an MLA cover page or title page is not required. Still, some instructors request an MLA title page. In these cases, ask your instructor for an example of a title page so you know the format they want.
Instead of a cover page, headings are used on a paper’s first page to indicate details like the author’s name, instructor’s name, the class, and date written. Read on for more details.
General page and header formatting:
To format your research paper according to the MLA guidelines:
- Set the margins to 1 inch (or 2.5 cm) on all sides
- Choose an easily readable font, recommended Times New Roman
- Set font size to 12 point
- Set double space for your entire paper
- Indent every new paragraph by ½ inch – you can simply use your tab bar for this
- In the header section – on the top right corner of the pages – give your last name followed by the respective page number
For your headings (which replace the need for a cover page), do the following:
- On the first page, ensure that the text is left-aligned and then give your details: starting with your full name in line one, followed by the name of your teacher or professor, the course name and number, and the date in separate lines
- Center align your MLA format heading for the paper’s title – do not italicize, bold or underline, or use a period after the title
- The body of your text should start in the next line, left-aligned with an indentation

You’ll also need to include a running head on each page. It should include your last name and the page number. For example: Johnson 2. Place the running head in the upper right-hand corner of the paper, ½ inches from the top and 1 inch from the page’s right edge.

MLA Style 9th Edition - Changes From Previous Editions
It is worth bearing in mind that the MLA format is constantly evolving to meet the various challenges facing today’s researchers. Using the Cite This For Me citation generator will help you to stay ahead of the game without having to worry about the ways in which the style has changed.
Below is a list outlining the key ways in which MLA has developed since previous editions.
- Titles of independent works (such as books and periodicals) are now italicized rather than underlined .
- You are encouraged to include a source’s URL when citing a source from the internet, and you should no longer include “https://” at the beginning of the URL with the exception of DOIs.
- You are no longer required to include medium information at the end of your citation, i.e., Print, Web, etc.
- Including the city of publication is optional, and only encouraged if the version of the work changes based on location, or if it was published prior to 1900.
How Do I Cite My Sources With The Cite This For Me Citation Machine MLA?
If you’re frustrated by the time-consuming process of citing, the Cite This For Me multi-platform citation management tool will transform the way you conduct your research. Using this fast, accurate and accessible generator will give you more time to work on the content of your paper, so you can spend less time worrying about tedious references.
So if you’re having issues with accurately formatting your citations, sign up to Cite This For Me and let our MLA format generator do the grunt work for you.
To use the generator:
- Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g., website, book, journal & video)
- Enter the URL , DOI , ISBN , title, or other unique source information to locate your source
- Click the ‘Search’ button to begin looking for your source
- Look through the search results and click the ‘Cite’ button next to the correct source. Cite This For Me citation tool will automatically pull your sources data for you!
- Review the citation details and make sure that everything you need is included and accurate
- Click ‘Complete citation’
- Copy your fully-formatted citation into your MLA works cited list</li/>
- Repeat the same process for each source that has contributed to your work
As well as making use of the powerful generator, you can cite with our Chrome add-on or Word add-on.

Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool
Published October 1, 2015. Updated June 16, 2021.
There are many consequences for not providing a correct citation in MLA style. The biggest consequence is that without proper citations, your paper will lose marks for incorrect citations. In addition, your paper can also be considered plagiarism. The responsibility for using proper citations rests with the author of the paper. Failing to properly cite your sources implies that the information in the paper is solely yours when it is not.
While some instructors might be lenient about incorrect citations, others might not. Ultimately, this could land you in serious trouble with your school, organization, or institution. To avoid such issues, always ensure that you provide proper citations. If you are finding it difficult to provide proper citations, Chegg’s citation generator may help.
When citing multiple works by the same author, include the title (or a shortened version of the title) along with the author’s last name and page number in in-text citations.
You can include the author’s name and/or the title in the prose, or you can include all three pieces of information in the parenthetical citation.
(Last Name, Shortened Title page number)
(Sam, Notes to Live By 42)
(Sam, Pointers From a Friend 85)
If you’d like to shorten a title in parenthetical citations, the title can be condensed to the first noun phrase. In the examples above, the titles would be shortened to Notes and Pointers in the parenthetical citations.
When using MLA style to cite a source with two authors, the last names of both authors and the page number being referenced should be included in in-text citations. The names should be listed in the same order in which they appear on the works cited list and be separated by the word “and” in parenthetical citations. If mentioning the authors in the prose, be sure to use both authors’ first and last names on first reference.
Below are a template and example for how to create an in-text citation for a source with two authors in MLA style.
(Last Name 1 and Last Name 2 page number)
(Prusty and Patel 75)
When using MLA style to cite a source with more than two authors, include the last name of the first author listed on your works cited page along with “et. al” and the page number in your in-text citations.
You should only use “et. al” in your works cited list and parenthetical citations. If you include the authors’ names in your prose instead, you can list all the authors’ names or the name of the first author and a phrase like “and her co-authors,” “and others,” etc.
Below are a template and example for how to create an in-text citation for a source with more than two authors in MLA style.
(Author 1 Last Name et al. page number)
(Krishnaswamy et al. 75)
Sources may be cited for various reasons, including to provide credit to others’ ideas, to ensure that readers can find the right sources, and to improve a paper’s credibility. There are some situations when a citation might not be necessary. To avoid ambiguity, here are the situations in which you should include a citation in an MLA style paper:
- When you are directly quoting an expert or other source of information
- When you are paraphrasing a quotation, passage, or idea
- When you are summarizing another person’s ideas
- When you are specifically referencing a fact, phrase, or statistics found in another source
Things that may be considered common knowledge (like dates of historical events or widely known biographical facts) do not need to be cited. However, if you are unsure whether or not a source needs to be cited, it is always better to err on the side of caution and include a citation.
As per MLA standards, a title page is NOT required. In fact, MLA recommends using a header with all relevant information instead, including your name, instructor’s name, course name, date of submission, and title. However, when your instructor requires a title page or when you are authoring your paper as a group with other people, it is recommended to create a title page for your paper.
If you are creating a title page, you should include the below information:
- Name of the paper’s author(s)
- Names of the instructor(s)
- Course name and number
- Title of the paper
Since websites don’t usually have page numbers, include only the author’s last name within parentheses using the standard MLA format. If using a citation in prose, directly referring to the author’s name in the sentence, then there is no need to provide any additional parenthetical citation.
Plastics contribute to the single greatest pollutant source for oceans (Shimla).
Shimla states that plastics are the oceans’ greatest pollutant source. [No additional citation is needed since you include the author’s name in the citation in prose and there is no page number available.]
As per section 1.3 of the MLA 9 handbook, center the title of a paper and use double-spacing. Do NOT underline, italicize, bold, or use all capitals for the title. Instead, follow standard rules of capitalization. Any italicized words within the text (e.g., book titles or literary movements) would ALSO be italicized in the title. Don’t use a period after your paper’s title.
Usually, you nclude the paper title on your first page. Only when the instructor needs a specific title page or when the paper is a group paper necessitating a list of all authors should you provide a separate title page. Apart from these two situations, a title page is NOT required.
Below are some examples when you would need to italicize words in the title because they include names of books and/or literary movements.
Perspective Shift during the Baroque Period
Is Macbeth Relevant in 2022 and Beyond?
While the MLA handbook recommends using “an easily readable typeface” and a font size “between 11 and 13,” it also clarifies to follow a professor’s or instructor’s guidelines if they differ. The handbook advises using double-spacing and the same font and size throughout the paper.
Check with your instructor on their preferences, and in the absence of any such preference, use a decent and readable font, like Times New Roman, with font size 12, which is a good balance between readability and aesthetics. The most important thing is to use the same font and size consistently throughout your paper.
As per Sections 5 and 6 of the MLA 9 handbook, if you are referring multiple times to a single source in the same paragraph, you do not need to repeat the author’s name each time you make a reference. However, you must include the page number(s), or another applicable locator, if you are referring to different pages of the same source in the same paragraph. In the examples below, it is clear in the second sentence that you’re citing the same source, so you don’t need to include the author name again, only the page number you’re referring to.
However, if you quote or paraphrase a different source by a different author between mentions of a source by the same author in the same paragraph, you need to reintroduce the source and original author name to clarify who you’re citing.
Citation in Prose Example
According to Theodore Garner, “It is evident that Caucasian males have a proclivity toward thrift than their African counterparts” (352). This can be seen from the high saving levels over a decade (345).
Parenthetical Citation Example
“It is evident that Caucasian males have a proclivity toward thrift than their African counterparts” (Garner 352). This can be seen from the high saving levels over a decade (345).
If referring to different sources by the same author(s), include the source’s title in your in-text citation, so readers know which source you are referring to. You can style such citations in various ways, as shown below. The style remains the same for works with more than one author.
Example with the author’s name and the title in the citation in prose
Howitzer says it best when he talked about the Moonmakers in his poem (23). Howitzer does contradict himself at a later point in time in Sunchanters (46).
Example with the author’s name in prose and the title in a parenthetical citation
Shakespeare writes pessimistically about existence from Hamlet’s point of view (Hamlet 103) . In another work, Shakespeare writes, “Life is a tale told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing” ( Macbeth 55).
Example with the author’s name and the title in the parenthetical citation
A similar pessimism about existence is present in other works, for instance when Hamlet contemplates suicide (Shakespeare, Hamlet 103). Macbeth similarly claims, “Life is a tale told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing” (Shakespeare, Macbeth 55).
To format an MLA works-cited page, follow these fundamental steps:
Place the works-cited list at the end of the paper and after any endnotes, should they be used.
Set a one-inch margin all around (top, bottom, left, and right). Like the prose portion of the paper, use a left margin, not a justified margin.
Running head
Place a running head on the right side of the page in the one-inch header, one-half inch from the top of the page. The running head format includes Surname and page #. The page number continues from the last page of the prose portion of the paper.
Use an easily readable font in which the italics feature is clearly distinguishable. Use the same font as in the prose portion of the paper. Times New Roman and Helvetica are popular standard fonts. Use a font size between 11 and 13 points.
Title the heading “Works Cited”; do not use bold or italics. Align it to the center of the page. Then double-space to begin the first entry. Double-space throughout the page.
Begin the entries flush with the left margin. Indent the second and subsequent lines of each entry one-half inch from the left margin.
Arranging entries
Arrange the Works-cited-list entries alphabetically according to the name of the author, or title if there is no author. If there is more than one author, cite the author listed first on the title page of the work in the alphabetical entry.
A separate medium identification, such as “Print,” is no longer used; however, the medium usually can be identified by the information provided in the citation.
Gann, Ernest K. A Hostage to Fortune . Alfred A. Knopf, 1978.
Invest Answers [@InvestAnswers]. “Taking another run at $45,000.” Twitter , 2 Mar. 2022, twitter.com/invest_answers/status/1499033186734542850.
To include the URL in website citation in MLA style, copy the URL from the browser, but exclude the http:// or https:// unless it is used in a DOI. If the work has a DOI, it is used instead of the URL.
Woldermont, Slat. “Sharks Impacted by Great Atlantic Garbage.” The Atlantic Cleanup , 4 May 2020, www.theatlanticcleanup.com/updates/sharks-impacted-by-Great-Atlantic-Garbage.
Saunders, Judith P. “Philosophy and Fitness: Hemingway’s ‘A Clean, Well-Lighted Place’ and The Sun Also Rises .” American Classics: Evolutionary Perspectives , Academic Studies Press, 2018, pp. 204–25, https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv4v3226.15.
The 6 th , 7 th , 8 th , and 9 th editions of MLA style are available on the Cite This For Me citation generator . The default MLA edition is the 9 th edition, the most current edition.
For a webpage/website, journal article, or book, you’ll need 1-2 pieces of basic publication information. For example:
- Website : URL, page title, etc.
- Journal article : Article title, DOI number, author(s), etc.
- Book : Book title, author, date published, etc.
Using those pieces of information, you can search for the source in the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator and it will help you to create a citation.
Other source types (newspaper article, video, government document, etc.) will provide a form on which you provide all source information. Using that information, the citation generator will create a properly formatted MLA citation for you.
Omitting or making up sources are unethical actions that can lead to plagiarism. An MLA citation generator can help a writer create citations for their sources, which is an ethical step needed to avoid plagiarism.
An MLA citation generator can make it easier (and sometimes faster) for a writer to create citations versus manually making each citation. We recommend trying the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator and deciding for yourself.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA8 Citation Generator
- powered by chegg.
Keep all of your citations in one safe place
Create an account to save all of your citations
Check your paper before your teacher does!
Avoid plagiarism — quickly check for missing citations and check for writing mistakes., is this source credible consider the criteria below..
Is the purpose to entertain, sell, persuade, or inform/teach ? Journal articles are often designed to inform or teach. Books and websites could have any of these or a combination of the purposes above. So it is important to determine why the source was created and if it is appropriate for your research. For websites in particular, looking at their "About Us" page or "Mission Statement" can help you evaluate purpose.
Accuracy is the reliability and truthfulness of the source. Here are a few indicators of an accurate source:
- Citations or a works cited list. For websites, this can be links to other credible sites.
- Evidence that backs up claims made by the author(s).
- Text that is free of spelling and grammatical errors.
- Information that matches that in other, credible sources.
- Language that is unbiased and free of emotion.
Based on the above the source could be accurate, inaccurate, a mixture of accurate and inaccurate, or hard to tell.
Authority: Author
The author is the individual or organization who wrote the information in the book, in the journal article, or on the website. If no author is listed, there may be another contributor instead. For example, an editor or a translator. A credible author has:
- Written several articles or books on the topic.
- Provided contact information. For example, an email address, mailing address, social media account, etc.
- The experience or qualifications to be an expert on the topic.
Authority: Publisher
The credibility of the publisher can contribute to the authority of a source. The publisher can be a person, company or organization. Authoritative publishers:
- Accept responsibility for content.
- Are often well-known.
- Often publish multiple works on the same or related topics.
Relevance describes how related or important a source is to your topic. While a source may be credible, it does not necessarily mean it is relevant to your assignment. To determine relevance, you should:
- Determine the website's intended audience. Look at the level of the information and the tone of the writing. For example, is it meant for academics or the general public?
- Make sure that the information is related to your research topic.
- Make sure that the information helps you answer your research question.
A publication date is an important part of evaluating the credibility of a source and its appropriateness for your topic. It is generally best to use content that was recently published or updated, but depending on your assignment, it may be appropriate to use older information. For example, a journal entry from Abraham Lincoln during the Civil War is too outdated to use in a discussion about modern politics and war, but would be appropriate for a paper about the Civil War. Consider the following when evaluating currency:
- Was it published or updated recently? If a website, is there even a publication date listed?
- Is the date of the source appropriate or inappropriate for my assignment?
After analyzing your source, do you believe it is credible, not credible, partially credible, or are you unsure? If you are still unsure, it may help to ask your instructor a librarian for assistance.
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

Click menu buttons below to import citations.
Copy and paste your BibTex citation in the text box area below.
Automatically create your citations:
Enter the ISBN number in the field below and select database (checkbox) to auto-generate citations for books.
Enter the website address (URL) or DOI you wish to cite in the field below and click search.
Click menu items to see source types.
- Conference Notes
- Course Notes
- Dissertation
- Dissertation Database
- Learning Management System
- Translation
- Advertisement
- Annual Report
- Presentation
- Image, Graph, Or Table
- Music Score
- Performance
- Blu-ray & DVD
- Software & Games
- Sound Recording
- Legislation
- Generative AI
- Social Media
- Academic Journal
- Encyclopaedia
- Add CiteWeb
- Change Style
© MasterGraphics Pty Ltd 2009-2024 All Rights Reserved.
Welcome to CiteMaker! This site is designed to help you quickly prepare an entire bibliography or reference list in three simple steps:
1. Select your citation style by clicking one of the buttons above.
2. Automatically or manually create your citations after selecting a citation style.
3. Save or export your reference list to your paper. It’s that easy!
Whether you’re beginning your research or tidying up your paper the night before it’s due, CiteMaker is here for you - anywhere, anytime, online!
Our forms and automatic citation generation tools will guide you through the process and alert you of what information is needed. This means less guessing for you and more accurate citations! Nearly any information source you can think of is supported by CiteMaker, in APA, Chicago, Harvard, MLA and Oxford styles. As you create citations, each will appear in alphabetical order. In-text citations are also created for you.
When you’ve finished your reference list, copy and paste it into your paper or export it to email, MS Word, Google Docs, or PDF. If you register to use CiteMaker, you will be able to save as many reference lists as you want and retrieve them when required.
How do I create a citation in MLA8 Style?
- Title of source.
- Title of container (if applicable).
- Other contributors (if applicable).
- Version (if applicable).
- Number (if applicable).
- Publication date,
- Location (such as page numbers or URLs).
Here is a general format for common types of sources in MLA 8th edition:
- Books: Author(s). Title of Book . Publisher, Year.
- Articles from Journals: Author(s). "Title of Article." Title of Journal , vol. volume number, no. issue number, Year, pp. page numbers.
- Websites: Author(s) (if available). "Title of Webpage." Title of Website , Publisher (if different from website title), Publication Date (if available), URL
- In-Text Citations: For in-text citations, use the author's last name and the page number where the information can be found. For example: (Author's Last Name page number).
The above text was generated using Open AI. Open Ai reminds students to italicize the titles of larger works (books, journals) and use quotation marks for shorter works (articles, webpage titles). CiteMaker does this for you without prompting and automatically punctuates main and in-text citations automatically.
CiteMaker is the first citation generator to create Generative AI citations for MLA8. We can do this because CiteMaker does not use crowd-sourced code offering thousands of styles.
Your reference list is currently empty!
Your citations will be formatted below in MLA (8th Ed.) style as you complete the form fields in the left-hand panel.
To add your citation to your reference list click the "Save" button at the foot of the form in the left-hand panel.
- Save myCites
- GoogleDrive
Your references will appear below in alphabetical order after you click "Save" at the foot of forms in the left-hand panel.
Your in-text references will appear below as you enter information in the form panel.
Already registered with CiteMaker? Click Here

Register for a free 30 day trial period. At the end of your trial period a yearly subscription fee will apply.
195.190.12.77
I have read and agree to CiteMaker.com's Usage Policy
To register Click Here
To log in, use the e-mail address and password that was sent to the e-mail address when you registered. If you have lost your password, enter the e-mail address you registered with and click the lost password link at the foot of the form below.
*only works if you registered using your facebook account
Click here for your password
CiteMaker.com citation maker is the most accurate free MLA 8th edition online citation machine and bibliography generator with pre-formatted citation forms for creating automatic citations and manual references and footnotes. CiteMaker MLA 8 is the free alternative to easybib, bibme, refme, citaton machine, cite this for me, citethisforme, citefast, citationsy, and refme, Includes OCLC WorldCat, google scholar, and Bibtex automatic citation machine for creating MLA 8th edition bibliographies, MLA 8 style reference lists, and in-text citations for student assignments and term papers. CiteMaker's CiteWeb chrome extension for automatically creating citations is available from the google store
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / A Complete Guide to MLA 8th Edition
A Complete Guide to MLA 8th Edition
Key differences in mla 8th edition.
1. One standard citation format that applies to every source type
In previous editions of the MLA Handbook, researchers were required to locate the citation format for the source that they used. For example, if a magazine was used, researchers needed to locate the specific citation format for periodicals. Due to the various ways that information is now received, in books, websites, lectures, tweets, Facebook posts, etc, it has become unrealistic for MLA to create citation formats for every source type. Now, there is one standard, universal format that researchers can use to create their citations.
2. Inclusion of “containers” in citations.
Containers are the elements that “hold” the source. For example, if a television episode is watched on Netflix, Netflix is the container. Both the title of the source and its container are included in a MLA 8th edition citation.
3. The ability to use pseudonyms for author names
It is now acceptable to use online handles or screen names in place of authors’ names.
@WSJ. “Generation X went from the most successful in terms of homeownership rates in 2004 to the least successful by 2015.” Twitter , 8 Apr. 2016, 4:30 p.m., www.twitter.com/WSJ/status/718532887830753280
4. Adding the abbreviations vol. and no. to magazine and journal article citations.
In MLA 7, there was no indication that the numbers in periodical citations referred to the volume and issue numbers.
Example of a journal article citation in MLA 7th Edition:
DelGuidice, Margaux. “When a Leadership Opportunity Knocks, Answer!” Library Media Connection 30.2 (2011): 48-49. Print
An example of a journal article citation in MLA 8th edition:
DelGuidice, Margaux. “When a Leadership Opportunity Knocks, Answer!” Library Media Connection , vol. 30, no. 2, 2011, pp. 48-49.
5. Inclusion of URLS
In previous versions of the MLA handbook, it was up to the discretion of the instructor whether URLs should be included in a citation. In MLA 8, it is highly recommended to include a URL in the citation. Even if it becomes outdated, it is still possible to trace the information online from an older URL.
Omit “https://” or “https://” from the URL when including it in a MLA 8th edition citation.
6. Omitting the publisher from some source types
It is not necessary to include the publisher for periodicals or for a web site when the name of the site matches the name of the publisher. For periodicals, the name of the publisher is generally insignificant.
7. Omitting the city of publication
In previous versions of the MLA handbook, researchers included the city where the publisher was located. Today, this information generally serves little purpose and the city of publication can often be omitted.
Only include the city of publication if the version of the source differs when published in a different country (Example: British editions of books versus versions printed in the United States).
Features that have not changed, and are the same as MLA 7:
- The overall principles of citing and plagiarism
- The use of in-text citations and works cited pages
——————————————————————————————————————————
How to Format an MLA 8 Works Cited List
The purpose of a Works Cited list is to display the sources that were used for a project. Showcasing the sources that were used allows others to locate the original sources themselves. In addition, a Works Cited list gives credit to the original authors of the works that were consulted for a project.
Works Cited lists are typically found at the very end of a project. The last page of a research paper, the final slide of a presentation, and the last screen of a video are all appropriate places to display a Works Cited list.
Each source is displayed in a special format, called a citation. This guide explains how to create citations for the Works Cited page.
When starting to build your Works Cited page, start by consulting your list of core elements. Remember, your core elements are:
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Other contributors
- Publication date
Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the citation, which is typically the last name of the author.
When there are two or more sources with the same author, only include the author’s name in the first citation. In the second or subsequent citations, use three hyphens in place of the author’s name, followed by a period.
Sparks, Nicholas. Dear John . Grand Central, 2007, p. 82.
– – -. A Walk to Remember . Warner, 1999.
If the individual is someone other than an author, such as a director or an editor, follow the three hyphens with a comma. Then, include the role of the individual after the comma. Place the citations in alphabetical order by the title of the work when there are multiple works by one author.
Allen, Woody. Getting Even . Vintage, 1978.
– – -, director. Midnight in Paris. Sony Pictures Classics, 2011.
The only instance when it is acceptable to include an author’s name more than once in a Works Cited Page is when the author is a coauthor with another individual or team.
Patterson, James, and Chris Grabenstein. House of Robots . Little, Brown and Co., 2014.
Patterson, James, and Chris Tebbetts. Middle School: Get Me Out of Here. Little, Brown and Co., 2012.
When there is no author listed for a source, place it in alphabetical order by the title. Omit words such as A, An, and The. If the title begins with a number, write the number out in word form.
Twenty-Eight Days Later. Directed by Danny Boyle, produced by Alex Garland, Fox Searchlight Pictures, 2002.
Example of an MLA Eighth Edition Works Cited Page:
– – – . A Walk to Remember . Warner, 1999.
How to Format the Author’s Name in an MLA 8th Edition Citation:
The author’s name is generally the first piece of information included in an MLA 8th edition citation. Start with the author’s last name, follow it with a comma, and add the rest of the author’s name exactly as it appears on the source. Immediately following the author’s name is a period.
Sparks, Nicholas. Stine, R.L. Brown, Margaret Wise. Seuss, Dr.
When two authors are included on a source, add them into the citation in the order that they appear on the source. The first author’s name is in reverse order: Last name, comma, and then the rest of the name as it appears on the source. Follow it with a comma and add the word “and.” For the second author’s name, write it exactly as it appears on the source.
Pratchett, Terry, and Neil Gaiman. Mortenson, Greg, and David Oliver Relin.
When three or more authors share responsibility for a work, include only the first author’s name. Write the first author’s name in reverse order: Last name, comma, and then the rest of the name as it appears on the source. After the first author’s name, add a comma, and write et al. This is a latin term meaning “and others.”
White, Karen, et al. Chan, Danny Elizabeth, et al.
An author may not always be the person responsible for a source. Often times, others, such as an editor or a translator can play the leading role.
When citing an edited book in its entirety, add a comma at the end of the editor(s) names and add the role of individual.
Hage, Ghassan, editor. Nielson, Frank, and Rajendra Bhatia, editors. Ashraf, M., et al., editors.
If a translated text was used, place the translator’s name in the “other contributors” section of the citation.
Viripaev, Ivan. Illusions . Translated by Cazimir Liske, Faber and Faber, 2012.
However, if the focus of your research revolves around the translation itself, place the translator’s name as the leading name in the citation.
Eshleman, Clayton, and Lucas Klein, translators. Endure. By Bei Dao, Black Widow Press, 2011.
For other works, such as film and tv shows, the individual that was the main focus of your research should be the leading name in the citation. Add a comma after the name of the individual and add a description of their role.
Parker, Sarah Jessica, actress. Girls Just Wanna Have Fun. New World Pictures, 1985.
If the focus was on the whole film or television show, and not an individual, start the citation with the title.
Girls Just Wanna Have Fun. Directed by Alan Metter, performance by Sarah Jessica Parker, New World Pictures, 1985.
It is acceptable to use online usernames or social media handles as the author’s name.
@BilldeBlasio. “A union gathers its strength from its workers. So does a company. I commend @Verizon and its employees for coming to a tentative agreement.” Twitter, 1 June 2016, 8:30 a.m., www.twitter.com/BilldeBlasio/status/737964964066004992.
Companies and organizations can also produce sources. Start the citation with the name of the company or organization.
United States, Food and Drug Administration. National Food Safety Education Month – Myths and Facts. June 4, 2014, www.fda.gov/Food/ResourcesForYou/ucm368393.htm.
How to Format the Title in MLA 8
Titles of sources are included in the citation as they appear on the source. They are generally located on the front or top of the source. Include all words in the title and any subtitles as well.
Viorst, Judith. Alexander and the Terrible, Horrible, No Good, Very Bad Day. Atheneum, 1987.
If a subtitle is given, place a colon in between the title and the subtitle.
Sheff, David. Game Over: How Nintendo Conquered the World. Vintage Books, 1994.
When a title stands alone, meaning it is not part of a larger work, place the title in italics. If it is indeed part of a larger work, such as a short story in an anthology, or a chapter in an edited book, place the title in quotations and the title of the larger work in italics.
Hughes, Langston. “Red-Headed Baby.” The Oxford Book of American Short Stories, edited by Joyce Carol Oates, Oxford UP, 1992, pp. 365-370.
*The exception to this rule is when a title that is found in a larger work normally stands alone. In this case, both titles are written in italics, without quotation marks.
Kipling, Rudyard. The Jungle Book. The Complete Children’s Short Stories, Wordsworth Editions, 2004, pp. 1-128.
For newspaper, magazine, and journal articles, the title of the article is placed in quotation marks and the name of the source is placed in italics. The same rule applies to other forms as well. Episodes of television shows are placed in quotation marks and the name of the television series is placed in italics. In addition, song titles are placed in quotation marks and the album names are placed in italics directly afterwards. Articles on web sites are placed in quotation marks and the title of the web site is placed in italics.
Example of an MLA 8th edition citation for Periodicals:
Martinson, Nichole. “Can I Cut Through a Murky German Tale to Find Grandma?” Ancestry, vol. 27, no. 1, January/February 2009, p. 63.
Example of an MLA 8th edition citation for television shows:
“Brave New World.” Grey’s Anatomy, directed by Eric Stoltz, season 5, episode 4, ABC, October 16, 2008.
Example of an MLA 8th edition citation for songs:
Rufus Du Sol. “Take Me.” Atlas, Sweat It Out, 2013.
Example of an MLA 8th edition citation for websites:
Provenzano, Nicholas. “Project Based Learning and the Great Gatsby.” The Nerdy Teacher, May 3, 2016. www.thenerdyteacher.com/2016/05/project-based-learning-and-great-gatsby.html.
When citing something that doesn’t have a title, it is acceptable to include a brief description of the source. Only capitalize the first letter in the first word of the description. Do not italicize or place the description in quotation marks.
Example of an MLA 8th edition citation with no title:
Kirschner, Ariel. Purple diagonal stripes painting. King Townhouse, New York.
When citing posts on social media, such as a Tweet, the title is the full posting, placed in quotation marks. For e-mail messages, the subject of the message is used as the title and placed in italics.
Examples of an MLA 8th edition citation for tweets:
@BilldeBlasio. “A union gathers its strength from its workers. So does a company. I commend @Verizon and its employees for coming to a tentative agreement.” Twitter , 1 June 2016, 8:30 a.m., www.twitter.com/BilldeBlasio/status/737964964066004992.
Taparia, Neal. “Team Meeting Reminder for Tomorrow.” Received by Michele Kirschenbaum, 4 May 2016.
How to Format the Title of the Container in MLA 8
Titles do not always stand alone. They are often found in a larger whole, or a container. Here are some examples of containers:
A chapter is placed in a container, which is the book it sits in. A song is placed in a container, which is the album it is on A television episode is placed in a container, which is the name of the show An online article sits in a container, which is the website
It is important to include the title of the container as it provides necessary information to help the reader locate the information themselves.
When a source has a container, place the title of the work in quotation marks and add a period directly afterwards. For the container, place it in italics and add a comma.
Examples of MLA 8th edition citations with containers:
Kivisto, Peter. “Marxism after Marx.” Key Ideas in Sociology, 3rd ed., 2011, pp. 28-33.
Rihanna. “Don’t Stop the Music.” Good Girl Gone Bad, track 3, Def Jam, 2007.
“Walk of Punishment.” Game of Thrones, season 3, episode 3, HBO, 14 Apr. 2013.
Ferlazzo, Larry. “Statistic of the Day: Many Students are Chronically Absent.” Larry Ferlazzo’s Websites of the Day, 10 June 2016, www.larryferlazzo.edublogs.org/2016/06/10/statistic-of-the-day-many-students-are-chronically-absent/.
There are instances when a source can sit in more than one container. It is possible to have two containers.
Here are some examples:
For a scholarly article, the first container is the title of the journal, the second container is the title of the database. For a television show watched online, the first container is the title of the show, the second container is the title of the web site that the show was watched on.
It is necessary to include information about both containers.
When formatting a citation with two containers, use the following template:
Author. Title of source. Title of first container, Other contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication date, Location. Title of second container, Other contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication Date, Location.
If any parts of the above citation are irrelevant to the reader, omit them from the citation.
Examples of MLA 8th edition citations for sources with two containers:
Rossetti, Christina. “Caterpillar.” The Random House Book of Poetry for Children: A Treasury of 572 Poems for Today’s Child, Random House, 1982, p. 76. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=zLF_sKMUYS8C&lpg=PP1&dq=poetry&pg=PA76#v=onepage&q=poetry&f=false.
In the above example, “Caterpillar” is the title of the poem, The Random House Book of Poetry for Children: A Treasury of 572 Poems for Today’s Child is the first container, and Google Books is the second container.
Notice that the title of the source is placed in quotation marks, while the titles of the first and second containers are placed in italics.
Here are a few more examples:
Stemmer, John, et al. “Investigating the Relationship of Library Usage to Student Outcomes.” College & Research Libraries, vol. 7, no. 3, May 2016, pp. 359-375. ERIC, dx.doi.org/10.5860/crl.77.3.359
Alesso. “Tear the Roof Up.” Forever , 2015, track 4. Spotify, open.spotify.com/track/2ze8tFyaI1W6db1pJBWBGq
How to Format Other Contributors in MLA 8:
While it is generally just the author of a work that is included in a citation, there can be times when there are other contributors that can be included, especially when their work played a large role in your research. “Other contributors” can include directors, performers, editors, translators, and many other roles.
When including another contributor in a citation, first include the role of that individual, add the word “by” and then place their name in standard form (First name Last name).
Some possible examples of contributors include phrases such as:
translated by directed by produced by illustrated by
Examples of MLA 8th edition citations for sources with more than one contributor:
“Daddy’s Home.” Full House, performance by Bob Saget, season 1, episode 6, ABC, 30 Oct. 1987.
Baum, L. Frank. “The Wizard of Oz.” Audible, narrated by Anne Hathaway, Audible Studios, 8 Mar. 2012, www.audible.com/pd?asin=B007BR5KZA&action_code=AUDORWS0424159DCE
Bessen, James, and Alessandro Nuvolari. “Knowledge Sharing Among Investors: Some Historical Perspectives.” Revolutionizing Innovation: Users, Communities, and Open Innovation, edited by Dietmar Harhoff and Karim R. Lakhani, MIT Press, 2016, pp. 135-156. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=RMqrCwAAQBAJ&lpg=PP1&dq=edited%20book&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false.
It is acceptable to include more than one contributor. In fact, it is acceptable to include many contributors if they all played an important part in your research. . You may want to include a performer and a director, or an editor and a translator, or two performers.
Titanic. Directed by James Cameron, performance by Leonardo DiCaprio and Kate Winslet, Paramount Pictures, 1997.
Puff Daddy and the Family. “Victory.” No Way Out, performance by The Notorious B.I.G and Busta Rhymes, Bad Boy, 1997, Track 2.
How to Format the Version in MLA 8:
Sources can be released in different versions, or forms. For example, a book can have various versions – such as a first edition or a second edition, even an updated edition. A song can have an extended version or a radio edit. A movie can have an unrated or an uncut version. It is important to communicate to the reader which version was used to help them locate the exact source themselves.
For books, the version can often be found on the front cover or on the verso page. If it is a numbered edition, type out the numeral and use the abbreviation “ed.” for edition.
If no specific version is mentioned or located, omit this information from the citation.
Examples of MLA 8 edition citations for sources with various versions:
Weinberger, Norman M. “The Auditory System and Elements of Music” The Psychology of Music, edited by Diana Deutsch, 2nd ed., Academic Press, 1999, p.61. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=A3jkobk4yMMC&lpg=PP1&dq=psychology&pg=PR6#v=onepage&q=psychology&f=false.
JFK. Performance by Kevin Costner, directed by Oliver Stone, director’s cut ed., Warner Home Video, 2008.
How to Format Numbers in MLA 8:
There are times when sources are given a number. For example, a print encyclopedia, which is part of a set, often has a volume number. In addition, lengthy books are sometimes split into a few volumes. Comic books, magazines, and journal issues are often given a volume number AND an issue number. Television episodes are often numbered, as well as their seasons, too.
If a book is given a volume number, it can generally be found on the spine, cover, or on the title page. Comic books, magazines, and journals often have their volume number and issue number printed on the front cover. For television show episodes and seasons, this information can usually be found on the packaging or by clicking on the information while watching the show.
For volume numbers, use the abbreviation “vol.” and for issue numbers, use the abbreviation “no” in the citation.
Examples of MLA 8 edition citations for sources that are numbered:
Fillipponi, Piero, and Herta T. Freitag. “For an Arbitrary Argument.” Applications of Fibonacci Numbers, Edited by G. E. Bergum, et al., vol. 4, Springer Science and Business Media, 1990, pp. 91-98. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=bszoCAAAQBAJ&lpg=PR1&dq=volume%20numbers&pg=PR5#v=onepage&q=volume%20numbers&f=false.
Sadler, Philip M., and Gerhard Sonnert. “Understanding Misconceptions: Teaching and Learning in Middle School Physical Science.” American Educator, vol. 40, no. 1, American Federation of Teachers, 2016, pp. 26-32.
Kanigher, Robert. “Stone Slayer.” Wonder Woman, illustrated by Harry G. Peter, vol. 1, no. 65, DC Comics, April 1954.
“Thirsty Bird.” Orange is the New Black, directed by Jodie Foster, season 2, episode 1, Netflix, 6 June 2014.
How to Format the Publisher in MLA 8:
The publisher is the company that was responsible for making the work available. There are numerous publishing companies that are responsible for the creation and the release of books, movies, television shows, and other sources. Web sites are often published by many different types of organizations and companies, such as museums or government agencies.
To locate the publisher of a book, look at the bottom of the title page or on the verso page. For films and television shows, the publisher can often be found on the packaging or in the credits. For web sites, the name of publisher is often next to the copyright symbol at the bottom of the page.
Here are some examples of how to include the publisher in an MLA 8 edition citation:
How to cite a book in MLA 8:
Grissom, Kathleen. The Kitchen House. Touchstone, 2010.
Touchstone is the name of the publisher for the book.
There are times when it is not necessary to include the publisher in a citation. For web sites, when the name of the site matches the name of the publisher, omit the publisher from the citation. This prevents the same information from being displayed twice in a citation. Also, it is not necessary to include the publisher for any magazines, periodicals, or journals. Often, the name of those sources match the name of the publisher.
Example of how to cite an article on a blog in MLA 8 (when the publisher matches one of the other components of the citation)
Chan, Magdalene. “Volunteering with NYC Department for the Aging.” New York Public Library, 29 June 2016, www.nypl.org/blog/2016/06/29/volunteering-nyc-dfta.
In the above example, the New York Public Library is the name of the web site, but also the name of the organization responsible for publishing the content. Therefore, New York Public Library was only included once in the citation.
How to Format the Publication Date in MLA 8:
The publication date, which is the date that the source was released, is a necessary component of an MLA 8 edition citation. Including this information helps the reader locate the specific source that was used, as often times there are numerous versions of sources that are released at different times.
When including the date of publication, there aren’t any set rules to how the date should be input into the citation. For example, you can use May 5, 2016 or 5 May 2016. What does matter is consistency. Whichever way the date is placed in one citation, the same format should be used in the other citations in your project.
Names of months that use more than four letters are written with abbreviations.
Examples: Jan. Sept. Nov.
In addition, sometimes the day and month might not be featured on a source. Include the information that is readily available.
Example of how to cite a movie in MLA 8:
Ratatouille. Directed by Brad Bird, Pixar, June 29, 2007.
How to Format the Location in MLA 8:
It’s often helpful to include the exact location of where you found your information so that the reader can locate it themselves. For example, let’s say that you used a quote from a book in your project. If the reader wanted to find the quote for themselves, it would be helpful to include the page number in the citation. Or, if you were to use a cover story from a magazine, including the page ranges helps the reader easily find the information. Additionally, web site addresses are extremely helpful to include.
When including a page or page range in your citation, use the abbreviation p. when including information about one page, and use pp. when including a page range.
When including web site addresses in a citation, omit the https:// or https:// of the citation, since the reader can assume that the beginning of the address includes that information.
Here are some examples of MLA 8 edition citations that include locations:
Mohr, Nicholasa. El Bronx Remembered: A Novella and Stories. Harper Trophy, 1975, p. 87.
Szabo, Liz. “Zika Could Hit People in Poverty Hardest.” USA Today, 30 June 2016, www.usatoday.com/story/news/2016/06/30/zika-could-hit-people-poverty-hardest/86358782/.
Since the following citation has two containers (the book itself and Google Books) there are two locations included, a page range and a web site address:
Kipling, Rudyard. The Jungle Book. Everyman’s Library, 1994, pp. 27-28. Google Books, www.books.google.com/books?id=Y3xXkWyQZggC&lpg=PP1&dq=the%20jungle%20book&pg=PA4#v=onepage&q=the%20jungle%20book&f=false.
How to Create In-Text Citations in MLA 8:
The overall purpose of in-text citations is to allow the reader to briefly see where the direct quote or paraphrase came from, and to be able to identify it later on, as a full citation, in the works cited list.
As stated in the first part of this guide, when using a direct quote or paraphrase, place an in-text citation after the borrowed information. Generally the in-text citation is found immediately following the direct quote or paraphrase, but it is acceptable to insert it in a place, soon after, that allows for a natural pause while reading.
In-text citations are generally made up of two items: the author’s last name and the page number. If there isn’t an author, use the first item in the full citation entry. Place the name of the author (or the first item found in the full citation entry) and the page number in parentheses. Do not include any commas in between the two pieces of information.
Example on an in-text citation found in the body of a project:
“Professor McGonagall’s voice trembled as she went on. ‘That’s not all. They’re saying he tried to kill the Potter’s son, Harry. But – he couldn’t. He couldn’t kill that little boy. No one knows why, or how, but they’re saying that when he couldn’t kill Harry Potter, Voldemort’s power somehow broke – and that’s why he’s gone” (Rowling 22).
In the works cited list, found at the end of the project, readers will be able to see the full citation in its entirety, and will be able to locate the source for themselves.
The full citation, on the works cited page, will look like this:
Rowling, J.K. Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone. Scholastic, 1999, p. 22.
How to format in-text citations for two authors:
When there are two authors, or coauthors, add both names to the in-text citation, with the word and between the two names.
(Johnson and Selleck 44)
How to format in-text citations for three authors or more:
For three or more authors, include the last name of the first author listed on the source. After the first author’s last name, place et al. afterwards. This is a Latin term which means “and others.”
Example of an in-text citation for three or more authors:
(Chan et al. 134)
How to format an in-text citation for corporate authors: When adding an in-text citation for corporate authors, place the name of the corporation or organization in parentheses, followed by the page number. If there is a common abbreviation in the name of the corporation, it is acceptable to use the abbreviated term:
Examples of in-text citations with corporate authors:
(American Lung Association 14) (Penn. Dept. of Motor Vehicles 62)
When an author’s name is not listed in the full citation, use the title in the in-text citation. It is acceptable to shorten or abbreviate the title. If the title starts with A, An, or The, exclude it from the in-text citation and include the first main word.
Full title: A Tree Grows in Brooklyn
In-Text citation: ( Tree Grows in Brooklyn )
Full title: Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone
In-Text citation: ( Harry Potter )
How to format page numbers in in-text citations:
For page numbers, use the same style that the source uses. If a source is numbered using Roman numerals, in the in-text citation, use Roman numerals for the page number.
(Franklin IV)
(Wall Street Journal B8)
When it comes to e-books, it can be difficult to determine the page number. Furthermore, the page number on one type of e-reader, such as a Kindle, might differ on another e-reader, like a Nook. Exclude page numbers from in-text citations if the page numbers differ across devices. Only include the page number from an e-book if it is consistent with other readers. It is acceptable to use a chapter number or division number if it is stable across devices.
(Rowling ch. 1)
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Fast and free citation generator APA 6th and 7th ed. • MLA 8th ed. • Chicago 16th ed.
- Create Title Page
- Style Guide
- Manage Bibliographies

Mindfullness & COVID-19
JavaScript is off. Please enable to use site.
Note: The default citation style is now APA 7. To use APA 6 ensure that the APA 6 button is selected.
Citefast had an sql injection attack on May 29, 2021 which deleted all saved citations and accounts. We apologize for the inconvenience this might cause you. We are working on ensuring does not happen again.
- Social media
- Online video
- Dissertation/Thesis
- Encyclopedia/Dictionary
- Government publication
- Audio/Podcast
- Television/Radio
Current citation (not saved)
You have no saved citations in this bibliography .

Want to keep your citations for longer and access them from other computers? It's easy and free! Sign up.
Copy the information below in your paper according to the Guide on the right. Use your own page numbers.
APA 7 In-text citation guide
In-text citations are required when you use someone else's ideas, theories or research in your paper.
Quick Guide
Examples: (choose depending if author and/or date is mentioned in text)
Quotation :
- "The bones were very fragile" (Cole, 2019, p. 13).
- Cole (2019) found that "The bones were very fragile" (p. 33).
- In 2019, Cole found that "The bones were very fragile" (p. 33).
Paraphrase :
- The bones broke easily because they were porous (Cole, 2011).
- Cole (2011) discovered that the bones broke easily.
- In 2011, Cole found that the bones were easily broken (p. 33).
Note: APA style encourages the inclusion of page numbers for paraphrases, but it is not mandatory. Include page or paragraph numbers if it will help reader find the information.
No authors : Use the title in place of author. Shorten title if needed. Use double quotation marks for title of an article, a chapter, or a web page. Use italics for title of a periodical, a book, a brochure or a report.
- the observations found ("Arctic Voyage," 2014)
- the book Vitamin Discoveries (2013)
Two authors : Within the text use the word and . If the authors' names are within parentheses use the & symbol.
- Cole and Dough (1998) argued ...
- ...if they were left to their own devices.(Cole & Dough, 1998)
Three or more authors: Include only the last name of the first author followed by "et al."
(Wasserstein et al., 2017)
Spell out the name in full the first time and abbreviate subsequent times only if abbreviation is well known.
- First time: American Psychological Association (2020) explained...
- Second time: APA (2020) proved ...
When quoting always provide author, year and specific page citation or paragraph number for nonpaginated material.
If the quotation is less than 40 words incorporate it into the text and enclose the quotation with quotation marks. Cite the source immediately after the close of the quotation marks.
If the authors are named in the text, they do not have to be used in the citation.
In fact, "a neurosis is characterized by anxiety" (Kristen & Warb, 2012, p. 157).
"A neurosis is characterized by anxiety," according to Kristen and Warb's (2012, p. 157) longitudinal study.
If the quotation is over 40 words, you must indent the entire quotation and start the quotation on a new line. No quotation marks are required. Cite the quoted source after the final punctuation mark.
Alberta is occasionally divided into two regions, Northern Alberta and Southern Alberta. The majority of Alberta's population is located in large urban cities, mostly located in the South. Alberta is Canada's most populous province of all three Canadian Prairie provinces. Edmonton is the Capital of Alberta. (Hern, 1996, p. 22)
Paraphrasing
APA style encourages the inclusion of page numbers, but it is not mandatory. Include page or paragraph numbers if it will help reader find the information.
- (Reiton, 2003, para. 3)
If the document does not contain page numbers, include paragraph numbers.
- (Reiton, 2003, para. 3).
If neither is available omit page and paragraph numbers. Do not count paragraph numbers.
When paraphrasing from multiple sources, include all authors name in parentheses in alphabetical order.
- (Cole, 2006; Mann & Arthur, 2011; Zigmung, 2000).
APA In-Text Citation Guide
- "The bones were very fragile" (Cole, 2011, p. 13).
- Cole (2011) found that "The bones were very fragile" (p. 33).
- In 2011, Cole found that "The bones were very fragile" (p. 33).
Note: APA style encourages the inclusion of page numbers for paraphrases, but it is not mandatory. Include page or paragraph numbers if it will help reader find the information.)
Two or more authors : Within the text use the word and . If the authors' names are within parentheses use the & symbol.
Three to five authors : Include all authors' last names the first time the citation is used. If you use the same citation again within the same paragraph, use only the first last name followed by 'et al'. If you used the citation again omit the year.
- First time: Cole, Dough and Ferris (1998) explained...
- Second time: Cole et al. (1998) proved ...
- Third time: Cole et al. demonstrated...
Six or more authors: Include only the last name of the first author followed by "et al."
(Wasserstein et al., 2010)
- First time: American Psychological Association (1998) explained...
- Second time: APA (1998) proved ...
Alberta is occasionally divided into two regions, Northern Alberta and Southern Alberta. The majority of Alberta's population is located in large urban cities, mostly located in the South. Alberta is Canada's most populous Province of all three Canadian prairie provinces. Edmonton is the Capital of Alberta. (Hern, 1996, p. 22)
In-Text Citations Parenthetical Citations
In-text citations are called parenthetical references in MLA. This involves placing information about the source in parentheses after a quote or a paraphrase. The information in the parenthetical references must match the corresponding information in the list of works cited.
The purpose of parenthetical references is to indicate to readers not only what works you used, but what you used from each source and where in the source you found the material. This can be done by inserting a parenthetical reference in your text at the spot where you have used the source's ideas or words.
You should keep parenthetical references as brief and as few as clarity and accuracy permit.
General Guidelines
- The Soviets were surrounded by enemies (Waters 119).
- Waters argues that the Soviets were surrounded by enemies (119).
Authors – Identification of source
- (Natl. Research Council 15)
- Do not use abbreviations such as ed. or trans.
- ("The evolving internet")
- (Black and Mondoux 123)
- (Eddison, Zhu, and Lalonde)
- (Becker et al. 13)
- (Becker, Lafontaine, Robins, Given, and Rush 13)
- (Feder, The Birth of a Nation 124)
Location of passage within source
- give relevant page number if available
- give volume and page number in a multivolume work
- if citing entire work omit page numbers
- (Louis par. 20)
- film, television, broadcasts cannot be cited by numbers
Placement of parenthetical reference in text
- Cole found that "The bones were very fragile" (33-34).
Alberta is occasionally divided into two regions, Northern Alberta and Southern Alberta. The majority of Alberta's population is located in large urban cities, mostly located in the South. Alberta is Canada's most populous Province of all three Canadian prairie provinces. Edmonton is the Capital of Alberta. (Herick 22)
- In Chicago style, footnotes or endnotes are used to reference pieces of work in the text.
- To cite from a source a superscript number is placed after a quote or a paraphrase.
- Citation numbers should appear in sequential order.
- Each number then corresponds to a citation, a footnote or to an endnote.
- Endnotes must appear on an endnotes page. The page should be titled Notes (centered at top). This page should appear immediately before the bibliography page.
- Footnotes must appear at the bottom of the page that they are referred to.
Example: Cole found that "The bones were very fragile" (33-34). 1
Each superscript then refers to a numbered citation in the footnotes or endnotes.
Footnotes/endnotes:
The first time the in-text reference is cited you must include, author's first name, author's last name, title, place of publication, publisher name, year and referenced pages. e.g.
1. James Smith, The first and last war , (New York, Hamilton, 2003), 2.
If the citation has already been cited it may be shortened to author's last name, shortened title, and page referenced number. e.g.
2. Smith, The first , 220-221.
If the citation has been referenced immediately prior, the note may be shortened even further to ibid with the page number. e.g.
3. Ibid., 786.
For each author-date citation in the text, there must be a corresponding entry in the reference list under the same name and date.
An author-date citation in running text or at the end of a block quotation consists of the last (family) name of the author, followed by the year of publication of the work in question. In this context, author may refer not only to one or more authors or an institution but also to one or more editors, translators, or compilers. No punctuation appears between author and date. Abbreviations such as ed. or trans. are omitted.
(Woodward 1987)
(Schuman and Scott 1987)
When a specific page, section, equation, or other division of the work is cited, it follows the date, preceded by a comma. When a volume as a whole is referred to, without a page number, vol. is used. For volume plus page, only a colon is needed. The n in the Fischer and Siple example below indicates "note" (see 14.164 ). The last example shows how one might cite a section of a work that contains no page or section numbers or other numerical signposts—the case for some electronic documents (see 15.8 ).
(Piaget 1980, 74)
(LaFree 2010, 413, 417–18)
(Johnson 1979, sec. 24)
Fowler and Hoyle 1965, eq. 87)
(García 1987, vol. 2)
(García 1987, 2:345)
(Barnes 1998, 2:354–55, 3:29)
(Fischer and Siple 1990, 212n3)
(Hellman 1998, under "The Battleground")
The following features have been recently added to Citefast:
- Edit and delete citations
- Copy and paste functionality
- Citations will be saved for 24 hours
- A short wizard to guide you through the site the first time you use it
- Updated interface for inputting citation information
- Ability to create In-text citations
- In-text guide for APA, MLA and Chicago citations
- Export your bibliography to Word
- Add editor and chapter information to bibliography for book
- More tool tips to make entering data easier
Thank you to all those who emailed us with their suggestions for improvements.
Login to Citefast
Not a member? Sign Up
Create a Citefast account
Already have an account? Login
Login with citation in progress
Do you want to save your citation? It will be saved to the account you login to .
Password assistance
Verifying that it's you.
For your security, we need to verify your identity. We've sent a code to the email . Please enter it below. Remember to check your junk mail folder if you do not see it in your inbox.
Do you want to save the citation you are working on?
Change style?
Change bibliographies.
You will lose the citation you are entering.
Change Account Settings
Reset password, go to citefast for schools - no ads.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Create citations in MLA8 format for websites, books, journals, and more with this free online tool. Learn how to cite sources, avoid plagiarism, and improve your writing skills with Citation Machine® guides and tips.
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically with MyBib, a software tool that supports MLA 8 and MLA 9 styles. Search for or enter the details of websites, books, journals, and more, and copy or download your Works Cited page.
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
EasyBib® has tools to help you create citations for over 50 source types in this style, as well as a guide to show you how an MLA paper should be formatted. Review the guide to learn how to format a paper's title page, paragraphs, margins, quotations, abbreviations, numbers, tables, and more! There are even tips on editing, as well as on the ...
This guide is based on the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook and aims at helping you cite correctly in MLA. The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for a large variety of sources and uses a two-part documentation system for citing sources: in-text parenthetical citations (author, page) a reference list at the end of paper with all literature used in ...
To use the generator: Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g., website, book, journal & video) Enter the URL, DOI, ISBN, title, or other unique source information to locate your source. Click the 'Search' button to begin looking for your source. Look through the search results and click the 'Cite' button next to the ...
Here are a few indicators of an accurate source: Citations or a works cited list. For websites, this can be links to other credible sites. Evidence that backs up claims made by the author (s). Text that is free of spelling and grammatical errors. Information that matches that in other, credible sources. Language that is unbiased and free of ...
Scan your paper for plagiarism mistakes. Get help for 7,000+ citation styles including APA 6. Check for 400+ advanced grammar errors. Create in-text citations and save them. Free 3-day trial. Cancel anytime.*. Try Easybib® Plus. Consider your source's credibility. Ask these questions:
This free online MLA 8th edition citation maker with footnotes generator includes automatic Worldcat OCLC, google scholar, and Bibtex citation generator for distance and remote learning! CiteMaker.com is the smarter citation machine and bibliography maker for formatting student assignment referencing in APA, Harvard, and MLA formats.
In MLA 8, it is highly recommended to include a URL in the citation. Even if it becomes outdated, it is still possible to trace the information online from an older URL. Omit "https://" or "https://" from the URL when including it in a MLA 8th edition citation. 6. Omitting the publisher from some source types.
Step 5: Put in the source's title—i.e., the name of the website, the name of the newspaper, or the name of the magazine. Step 6: Plug in the dates of publication. You can usually find this information on the website near the author's name. In a book, you'll have to go to the title page or to the copyright page. Step 7: Generate that ...
Citing a print book in MLA 8 style. Parenthetical in-text citation template and examples: (Author's Surname) (Weatherford) Reference list entry template and examples: Surname, First Name Middle Initial. Title of the Book. Publisher Name, Year Published. Weatherford, Jack.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Citefast automatically formats citations in APA 7th edition. Note: The default citation style is now APA 7. To use APA 6 ensure that the APA 6 button is selected. APA 7. APA 6. MLA 8. Chicago. To create a citation choose a source and enter details below. Note: APA 7th edition is now the starting choice for creating citations.
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
For the 8th edition, the biggest difference and most exciting update was the use of one standard format for all source types. In previous versions, scholars were required to locate the citation format for the specific source that they used. ... Don't forget, the Chegg Writing citation generator in MLA creates citations for you quickly and ...
Creating in-text citations using the previous (eighth) edition. Although the MLA handbook is currently in its ninth edition, some information about citing in the text using the older (eighth) edition is being retained. The in-text citation is a brief reference within your text that indicates the source you consulted.
Below are general rules MLA citation checklist: Paper should be typed on a computer and printed out using standard white 8.5 x 11 inches document. Text should be double-spaced. A recommended font used should be Times New Roman or Arial. A recommended font size is 12 pt.
Citations for e-books closely resemble those for physical books. Simply indicate that the book in question is an e-book by putting the term "e-book" in the "version" slot of the MLA template (i.e., after the author, the title of the source, the title of the container, and the names of any other contributors).
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.