- Good Writing
- Revising & Rewriting
- Nonfiction Writing
- Academic Writing
- Travel Writing
- Literary Agents
- Getting Published
- Fiction Writing
- Self-Publishing
- Marketing & Selling Books
- Building a Blog
- Making Money Blogging
- Boosting Blog Traffic
- Online Writing
- eZine Writing
- Making Money Online
- Non-Fiction Writing
- Magazine Writing
- Pitching Query Letters
- Working With Editors
- Professional Writers
- Newspaper Writing
- Making Money Writing
- Running a Writing Business

11 Most Popular Types of Articles to Write for Magazines
- September 4, 2023
- 31 Comments
Want to write for magazines? This list includes feature stories, roundups, profiles, research shorts, human interest, how-to articles and more. You’ll be surprised by how many types of online and print magazine articles you can write! Whether you’re an aspiring freelance writer or an established author you’ll find lots of ideas in this list.
Learning about the different types of magazine articles is one thing. More important is finding courage to write boldly and the strength to keep pitching ideas to editors! May you get published again and again. And, may you prepare yourself to do the work now — before the day ends and you lose your momentum.
The most important thing to remember when you’re looking for different types of magazine articles to write is your audience. Learn how to slant your writing to the target audience, publisher, and editor of the magazine or publication. Books like Writer’s Market: The Most Trusted Guide to Getting Published – are essential to your success. They reveal details and information for freelance writers that you won’t find online.
“You can’t sit in a rocking chair with a lily in your hand and wait for the Mood,” writes author Faith Baldwin in The Writer’s Handbook . “You have to work. You have to work hard and unremittingly, and sacrifice a great deal; and when you fall at, or fail to clear, an obstacle (usually an editor), you have to pick yourself up and go on.”
A crucial part of earning money as a freelance writer is knowing what to work hard on. Learning about the different types of magazine articles is an excellent way to start a freelance writing career, or even boost a faltering author’s yearly income. If you’re serious about selling your writing and making money writing, you need to be constantly learning about writing, getting published, and working with editors.
“Two types of articles continue to dominate the changing field of magazine publishing,” writes Nancy Hamilton in Magazine Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide to Success . “The personality profile and the how-to story with its self-help variant. Together, they account for an estimated 72% of magazine feature material.”
11 Different Types of Magazine Articles
I’ve been published in several different magazines (such as Reader’s Digest, Chatelaine, Women’s Health and More ) and have written each one of these different types of magazine articles…except for the exposé. My favorite is writing research shorts for magazines – but they are just that ( short ) and thus don’t pay much.
As you read through the following types of articles, think about which one you most like to read. This will help you decide what type of article to research and write. The best writing comes from writers who are enjoying their work and passionate about their topic, so don’t hesitate to choose the project that lights your fire.
1. “How To” Articles
“Easily the most popular and the shortest and easiest to write, the how-to article with its self-help variant gives instructions for how to do or be something or how to do it better,” writes Hamilton in Magazine Writing .
“How to” articles:
- Make a rousing promise of success
- Describe what you need in easy to follow instructions
- Give step-by-step directions (sometimes with subtitles)
- Include shortcomings or warnings
- Tell how to locate supplies
- Give proofs and promises
- Make referrals to other sources
Examples of “how to” articles are: “How to Write Magazine Articles That Editors Love to Publish” or “How Freelance Writers Earn a $100,000 Every Year” or How to Think Like a Magazine Editor – 8 Tips for Writers . “How to” articles are my favorite type of feature articles; they simply tell readers how to do something.
Tip for freelance writers: Some magazine or newspaper editors require writers to submit their own photos for how-to articles. Before you accept an assignment from an editor, ask what their photo policy is.
2. Profile and Interview Articles
This popular type of article describes a contemporary or historical person – but a profile doesn’t have to be about a human being! Animals, communities, nations, states, provinces, companies, associations, churches can all be profiled (but not necessarily interviewed).
Personality profiles and interview articles:
- Have different definitions. In a personality profile, you use additional sources, such as friends, family, kids, neighbors, colleagues. In an interview, you talk to the source him or herself – preferably in person.
- Can have a theme or focus.
- Can be presented as a “Q & A” or a written article.
- Require strong interviewing and perception skills for the “best” information
Examples of profiles or interview articles are: “The Real Natalie Goldberg and Her Real Writing Career” or “Anne Lamott Shares Her Secrets for Writing Different Types of Magazine Articles.” Profiles and interview are two different types of magazine articles to write.
About this type of magazine article Hamilton says, “The most successful personality profile allows the reader to experience the story directly without having to filter that experience through the ‘I’ of an unknown writer. Despite this common-sense perspective, many magazines today prefer the ‘I’ approach for personality profiles.” Why? Because most editors want to encourage a personal relationship between the magazine and the reader by addressing them personally.
3. Informative or Service Articles
Informative articles are also know as “survey articles.” They often offer information about a specific field, such as sports medicine, health writing, ocean currents, politics, etc. Service articles are similar, but often used as shorter fillers. Service articles offer a few pieces of good advice or tips, but aren’t usually long or involved.
Informative or service articles:
- Focus on one unique aspect, or the “handle”
- Describe what-to, how-to, when-to, why-to, etc.
- Answer the journalist’s who, what, when, where, why, and how questions
- Can end with a “how-to” piece as a sidebar
Examples of this type of magazine article include: “How to Write Query Letters for Magazines” or “ 10 Magazine Writing Tips From a Reader’s Digest Editor ” or “11 Types of Magazine Articles to Write for Magazines.”
The informative or service article is similar to the how-to type of magazine article. I’d love to write a service article for the SPCA, but I’m too busy with my blogs to pitch article ideas to editors.
4. The Alarmer-Exposé
“A Reader’s Digest staple, the alarmer-exposé is designed to alert and move the reader to action,” writes Hamilton in Magazine Writing . “Well-researched and heavy with documentation, this type of magazine article takes a stance and adopts a particular point of view on a timely and often controversial issue. Its purpose is to expose what’s wrong here.”
- Shocks or surprises readers
- Includes statistics, quotes, anecdotes
- Can range from how extension cords can kill to new info on Watergate
“This article is best written by an established writer who is skilled in reporting an issue and building a case without flagrant – and apparent – bias,” says Hamilton.
Examples of an exposé magazine article are: “Stephen King’s Ghostwriter Reveals Secret Writing Career” or “95% of Natalie Goldberg’s Writing is From a Ghostwriter!” Those aren’t actual feature articles that were written by freelance writers – they’re just examples of the different types of magazine articles.
5. Human Interest Magazine Articles:
- Usually start with an anecdote
- Are often chronologically organized
Examples of human interest magazine articles are: “Anne Lamott Shares Her Secrets to Success as a Single Mother and Bestselling Author” or “Mark Twain’s Great-Granddaughter Discovers a Brand New Type of Magazine Article.” This type of feature article interests the majority of readers of a specific, niched magazine.
People is currently one of the most popular magazines on the market, and it specializes in this type of article. If you find someone who has done or experienced something extraordinary – and if your writing skills are pretty good – you might consider sending a query letter to the editors at People .
6. Essay, Narrative, or Opinion Articles
This is my least favorite type of magazine article or blog post to write! I’m not a big writer of personal stories (nor do I like to read autobiographies, biographies, or personal blogs). I’d much rather encourage readers by sharing information – such as these 11 different types of articles to write magazines 🙂
Essay, narrative, or opinion articles:
- Usually revolve around an important or timely subject (if they’re to be published in a newspaper or “serious” magazine)
- Are harder to sell if you’re an unknown or unpublished writer
- Can be found on blogs all over the internet
Here’s some great writing advice from Hamilton: “The narrative uses fiction technique to recreate the tension, the setting, the emotion – the drama – of something that actually happened. The article must have implications and ramifications that are meaningful to a reader. It must be relevant to what’s going on today – one event that relates to the larger whole.”
Examples of this type of magazine article are: “What I Think of Natalie Goldberg’s Decision to Retire From Her Writing Career” or “Anne Lamott’s Most Famous Writing Mistakes.”
If you feel overwhelmed with all these types of magazine articles, read How to Write When You Have No Ideas .
7. Humor or Satire Articles
Humor or satire articles are really hard to write. I just read today – in the University of Alberta’s Trail magazine – that it takes the Simpsons’ writers and staff SIX MONTHS to write and produce a single episode! That’s because humor writing seems easy and fast, but it’s actually the hardest type of writing to learn…not to mention master.
Humor or satire articles:
- Usually have a specific audience, such as the readers of The Onion
- Are usually written on spec (that is, you submit the whole article before the editors or publishers will accept it for publication in the magazine)
Examples of humor or satire articles might include: “Ode to Stephen King’s Typewriter” or “What Margaret Laurence Ate the Day She Started Writing Articles for Magazines.”
8. Historical Articles
What can I say? A historical article describes a moment in time. Or an epoch. Or an era. Or an eon.
Historical articles:
- Reveal events of interest to millions (which means at least one of my examples wouldn’t work as this type of article)
- Focus on a single aspect of the subject
- Are organized chronologically
- Tell readers something new
- Go beyond history to make a current connection
Examples of this type of magazine article include: “The Typewriter Mark Twain First Used” or “How Freelance Writers Submitted Articles Before Typewriters Were Invented” or “How the Use of the Word ‘Tweet’ Evolved From 2005 to Now.”
9. Inspirational Magazine Articles
- Describe how to feel good or how to do good things
- Can describe how to feel good about yourself – this type of article can work for anyone from writers to plumbers to pilots
- Offer a moral message
- Focus on the inspirational point
Examples of different types of inspirational articles for magazines are: “How You Can Change the World With Your Writing Career” or “13 Tips to Improve Your Writing Confidence.”
This is probably my second most favorite type of feature article to write. It’s definitely the post I write most often on my Blossom blogs!
10. Round-Up Magazine Articles
- Gather a collection from many sources
- Focus on one theme
- Offer quotations, opinions, statistics, research studies, anecdotes, recipes, etc.
The Round-Up was one of my favorite types of magazine articles to write when I was freelancing. Examples of round up articles are: “ 12 Fiction Writing Tips From Authors and Editors ” or “1,001 Types of Articles to Write for Magazines.” I enjoy writing round-ups because I can squeeze in lots of information in 1,000 words.
11. Research Shorts
- Describe current scientific information
- Are usually less than 250 words long
- Are often written on spec (at least by me)
- Are fast, effective ways to earn money as a freelance writer – if you can find the right markets
Research Shorts for the “Front of the Book” are those little blurbs of scientific research you see at the beginning of many magazines. Examples of these types of articles for magazines include: “How Alliteration Affects Your Memory” or “What Anne Lamott’s Writing Does to Your Brain Waves.”
Shorts aren’t really a type of magazine article, but they’re a great way to get your foot in the door and learn what articles editors will pay to publish .
Types of Magazine Articles You Can Write
In 11 Most Popular Articles to Write for Magazines | Tips for Freelance Writers I share different types of articles to write, to help you get published in the right magazine.
My list includes feature length stories, roundups, personality profiles, research shorts, human interest pieces, and “how to” articles. I also included examples of magazines that publish each type of article. Whether you’re an aspiring freelance writer or an established author you’ll find lots of ideas in this list.
Here’s a tip from bestselling author Natalie Goldberg about being a successful writer: “I hear people say they’re going to write. I ask, when? They give me vague statements,” she writes in Thunder and Lightning: Cracking Open the Writer’s Craft . “Indefinite plans get dubious results.”
What are your writing goals, and how will you achieve them? Have you made a specific plan? After you read through these different types of articles to write for magazines, create goals for yourself.
Writer’s Digest Magazine
Writer’s Digest Magazine is my favorite periodical about writing; a subscription is both motivating and informative. The more you learn about freelance writing – including the business of writing – the easier it’ll be to remember the different types of magazine articles you can write for magazines.
If you want to be a freelance writer, you have to do more than just learn about the different types of magazine articles to write for magazines. You need to research professional writing organizations, learn how to write query letters for editors, and where to pitch your ideas.
If you have any thoughts or questions about writing these types of feature articles for magazines and other publications, feel free to share below.
She Blossoms Newsletter
Comments cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of new posts by email.
31 thoughts on “11 Most Popular Types of Articles to Write for Magazines”
What if you wrote a catchier title? I don’t want to tell you how to run your Successful Writers blog, but suppose you added something to possibly grab folk’s attention? I mean 11 Popular Magazine Articles That Editors Love to Publish is a little vanilla. You ought to peek at Yahoo’s home page and see how they create post titles to get viewers to click. You might try adding a video or a related pic or two to get readers interested about everything’ve got to say. Just my opinion, it could make your Successful Writers blog a little livelier.
Thank you , Laurie! I am just starting my online magazine UpMixed in a month so these tips are going to help me.
“By the time I was fourteen the nail in my wall would no longer support the weight of the rejection slips impaled upon it. I replaced the nail with a spike and went on writing.” ~ Stephen King
Most writers starts their publishing journey the wrong way. They want to start big. They want a book contract, a speaking tour, and all-around international fame and notoriety. But that’s not how this thing works. we need to start small. This is a blessing in disguise, actually, as you are probably not that good when you are just beginning. You need time to practice writing articles for magazines that are of publishable quality.
Dear Newbie Magazine Writer,
Here’s an article that will give you a few pointers:
How to Write a Query Letter and Get Your Article Published https://www.theadventurouswriter.com/blogwriting/how-to-write-query-letters-for-magazine-articles/
Let me know what happens after you pitch your query to the magazine editor! It sounds like a winner 🙂
I have a brilliant idea for an article, and I believe it’s perfect for the publication I have in mind. I just don’t know how to write a query letter to a magazine. Can you help me by giving me a formula or structure on how to pitch my idea to the editor? I haven’t done much research or reading, but I found this article on the different types of magazine articles helpful. Thank you for any direction you can offer!
Nice ☺☺☺ would give some topics of Articles. ..?
I also need some topics
Dear Lokesh,
Your first step is to learn how to write English really, really well. Take ESL courses, read books, practice writing, do whatever it takes to learn how to write English.
At the same time, you need to learn the business of freelance writing. It’s a career, not a hobby. It takes time, dedication, and energy.
Here’s one place to start:
How to Become a Freelance Writer https://www.theadventurouswriter.com/blogwriting/how-to-be-a-freelance-writer/
Read books about freelance writing, pitching articles to editors, and becoming a journalist. Rolling Stone is an amazing magazine and it’s difficult to get published in it — but you CAN do it!
Take it one step at a time. Keep learning English – you’re doing great so far – and keep reading articles, blogs, and books about becoming a freelance writer for magazines.
You can do it! Remember that nothing worth having is easy. Everything good in life takes hard work. If it was easy, everyone would do it.
Blessings, Laurie
Thanks for the help Ressa, I am just a student and I confuse for my future because every time I thinking a new Idea like what I want or which field is good for me and finnaly I diciede what I want….!! Article writer and for me I think it’s a very good choice but still I little confused that how I write my first artical, actually the problem is that my mind is confuse that what is a good topic for me…. cause I need a very new or u can say a “fresh” topic which is never be write buy anyone And unlucky my first problem is that I am not good in English as well as in grammar so, If u don’t mind any u tell me any idea how to start my dream work ???? And Yaa one more thing I want to tell my dream company also which I want to work with and the name is (rolling stone) so u think in future there is any chance to get or touch my dream???
Thanks Ressa, I appreciate your thoughts! A profile is one type of feature article, so I meant what I originally wrote 🙂
There sure are a lot of choices for magazine articles…but my favorite is still blogging. I love the freedom and immediacy of writing blog posts, without having to worry about pitching article ideas to editors. But, blogging doesn’t offer as much exposure as writing for magazines does. Unless of course you write for the HuffPost!
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Write a Magazine Article
Last Updated: October 11, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Gerald Posner . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 932,310 times.
Magazine articles can be a big boost for seasoned freelance writers or writers who are trying to jump-start their writing careers. In fact, there are no clear qualifications required for writing magazine articles except for a strong writing voice, a passion for research, and the ability to target your article pitches to the right publications. Though it may seem like magazines may be fading in the digital age, national magazines continue to thrive and can pay their writers $1 a word. [1] X Research source To write a good magazine article, you should focus on generating strong article ideas and crafting and revising the article with high attention to detail.
Generating Article Ideas

- Check if the bylines match the names on the masthead. If the names on the bylines do not match the masthead names, this may be an indication that the publication hires freelance writers to contribute to its issues.
- Look for the names and contact information of editors for specific areas. If you’re interested in writing about pop culture, identify the name and contact information of the arts editor. If you’re more interested in writing about current events, look for the name and contact information of the managing editor or the features editor. You should avoid contacting the executive editor or the editor-in-chief as they are too high up the chain and you will likely not interact with them as a freelance writer.
- Note recent topics or issues covered in the publication and the angle or spin on the topics. Does the publication seem to go for more controversial takes on a topic or a more objective approach? Does the publication seem open to experimentation in form and content or are they more traditional?
- Look at the headlines used by the publication and how the articles begin. Note if the headlines are shocking or vague. Check if the articles start with a quote, a statistic, or an anecdote. This will give you a good sense of the writing style that gets published in that particular publication.
- Note the types of sources quoted in the articles. Are they academic or more laymen? Are there many sources quoted, or many different types of sources quoted?
- Pay attention to how writers wrap up their articles in the publication. Do they end on a poignant quote? An interesting image? Or do they have a bold, concluding thought?

- These inspiring conversations do not need to be about global problems or a large issue. Having conversations with your neighbors, your friends, and your peers can allow you to discuss local topics that could then turn into an article idea for a local magazine.

- You should also look through your local newspaper for human interest stories that may have national relevance. You could then take the local story and pitch it to a magazine. You may come across a local story that feels incomplete or full of unanswered questions. This could then act as a story idea for a magazine article.

- You can also set your Google alerts to notify you if keywords on topics of interest appear online. If you have Twitter or Instagram, you can use the hashtag option to search trending topics or issues that you can turn into article ideas.

- For example, rather than write about the psychological problems of social media on teenagers, which has been done many times in many different magazines, perhaps you can focus on a demographic that is not often discussed about social media: seniors and the elderly. This will give you a fresh approach to the topic and ensure your article is not just regurgitating a familiar angle.
Crafting the Article

- Look for content written by experts in the field that relates to your article idea. If you are doing a magazine article on dying bee populations in California, for example, you should try to read texts written by at least two bee experts and/or a beekeeper who studies bee populations in California.
- You should ensure any texts you use as part of your research are credible and accurate. Be wary of websites online that contain lots of advertisements or those that are not affiliated with a professionally recognized association or field of study. Make sure you check if any of the claims made by an author have been disputed by other experts in the field or have been challenged by other experts. Try to present a well-rounded approach to your research so you do not appear biased or slanted in your research.

- You can also do an online search for individuals who may serve as good expert sources based in your area. If you need a legal source, you may ask other freelance writers who they use or ask for a contact at a police station or in the legal system.

- Prepare a list of questions before the interview. Research the source’s background and level of expertise. Be specific in your questions, as interviewees usually like to see that you have done previous research and are aware of the source’s background.
- Ask open-ended questions, avoid yes or no questions. For example, rather than asking, "Did you witness the test trials of this drug?" You can present an open-ended question, "What can you tell me about the test trials of this drug?" Be an active listener and try to minimize the amount of talking you do during the interview. The interview should be about the subject, not about you.
- Make sure you end the interview with the question: “Is there anything I haven’t asked you about this topic that I should know about?” You can also ask for referrals to other sources by asking, “Who disagrees with you on your stance on this issue?” and “Who else should I talk to about this issue?”
- Don’t be afraid to contact the source with follow-up questions as your research continues. As well, if you have any controversial or possibly offensive questions to ask the subject, save them for last.

- The best way to transcribe your interviews is to sit down with headphones plugged into your tape recorder and set aside a few hours to type out the interviews. There is no short and quick way to transcribe unless you decide to use a transcription service, which will charge you a fee for transcribing your interviews.

- Your outline should include the main point or angle of the article in the introduction, followed by supporting points in the article body, and a restatement or further development of your main point or angle in your conclusion section.
- The structure of your article will depend on the type of article you are writing. If you are writing an article on an interview with a noteworthy individual, your outline may be more straightforward and begin with the start of the interview and move to the end of the interview. But if you are writing an investigative report, you may start with the most relevant statements or statements that relate to recent news and work backward to the least relevant or more big picture statements. [10] X Research source
- Keep in mind the word count of the article, as specified by your editor. You should keep the first draft within the word count or just above the word count so you do not lose track of your main point. Most editors will be clear about the required word count of the article and will expect you not to go over the word count, for example, 500 words for smaller articles and 2,000-3,000 words for a feature article. Most magazines prefer short and sweet over long and overly detailed, with a maximum of 12 pages, including graphics and images. [11] X Research source
- You should also decide if you are going to include images or graphics in the article and where these graphics are going to come from. You may contribute your own photography or the publication may provide a photographer. If you are using graphics, you may need to have a graphic designer re create existing graphics or get permission to use the existing graphics.

- Use an interesting or surprising example: This could be a personal experience that relates to the article topic or a key moment in an interview with a source that relates to the article topic. For example, you may start an article on beekeeping in California by using a discussion you had with a source: "Darryl Bernhardt never thought he would end up becoming the foremost expert on beekeeping in California."
- Try a provocative quotation: This could be from a source from your research that raises interesting questions or introduces your angle on the topic. For example, you may quote a source who has a surprising stance on bee populations: "'Bees are more confused than ever,' Darryl Bernhart, the foremost expert in bees in California, tells me."
- Use a vivid anecdote: An anecdote is a short story that carries moral or symbolic weight. Think of an anecdote that might be a poetic or powerful way to open your article. For example, you may relate a short story about coming across abandoned bee hives in California with one of your sources, an expert in bee populations in California.
- Come up with a thought provoking question: Think of a question that will get your reader thinking and engaged in your topic, or that may surprise them. For example, for an article on beekeeping you may start with the question: "What if all the bees in California disappeared one day?"

- You want to avoid leaning too much on quotations to write the article for you. A good rule of thumb is to expand on a quotation once you use it and only use quotations when they feel necessary and impactful. The quotations should support the main angle of your article and back up any claims being made in the article.

- You may want to lean on a strong quote from a source that feels like it points to future developments relating to the topic or the ongoing nature of the topic. Ending the article on a quote may also give the article more credibility, as you are allowing your sources to provide context for the reader.
Revising the Article

- Having a conversation about the article with your editor can offer you a set of professional eyes who can make sure the article fits within the writing style of the publication and reaches its best possible draft. You should be open to editor feedback and work with your editor to improve the draft of the article.

- You should also get a copy of the publication’s style sheet or contributors guidelines and make sure the article follows these rules and guidelines. Your article should adhere to these guidelines to ensure it is ready for publication by your deadline.

- Most publications accept electronic submissions of articles. Talk with your editor to determine the best way to submit the revised article.
Sample Articles

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you'd like to learn more about writing an article, check out our in-depth interview with Gerald Posner .
- ↑ http://grammar.yourdictionary.com/grammar-rules-and-tips/tips-on-writing-a-good-feature-for-magazines.html
- ↑ https://www.writersdigest.com/writing-articles/20-ways-to-generate-article-ideas-in-20-minutes-or-less
- ↑ http://www.writerswrite.com/journal/jun03/eight-tips-for-getting-published-in-magazines-6036
- ↑ http://www.thepenmagazine.net/20-steps-to-write-a-good-article/
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0R5f2VV58pw
- ↑ https://www.writersdigest.com/write-better-nonfiction/how-many-different-kinds-of-articles-are-there
- ↑ http://libguides.unf.edu/c.php?g=177086&p=1163719
About This Article

To write a magazine article, start by researching your topic and interviewing experts in the field. Next, create an outline of the main points you want to cover so you don’t go off topic. Then, start the article with a hook that will grab the reader’s attention and keep them reading. As you write, incorporate quotes from your research, but be careful to stick to your editor’s word count, such as 500 words for a small article or 2,000 words for a feature. Finally, conclude with a statement that expands on your topic, but leaves the reader wanting to learn more. For tips on how to smoothly navigate the revision process with an editor, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Smriti Chauhan
Sep 20, 2016
Did this article help you?
Jasskaran Jolly
Sep 1, 2016
Emily Jensen
Apr 5, 2016
May 5, 2016
Ravi Sharma
Dec 25, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Structure of a Magazine Article: The Full Guide

The complete guide to the structure of a magazine article offers an in-depth look at creating enthralling magazine pieces, keeping the structure of a magazine article in focus.
Table of Contents
This comprehensive resource emphasizes the importance of mastering key elements to captivate your audience and produce high-quality content that effectively showcases the structural aspects of a well-crafted magazine article.
Introduction to the Structure of a Magazine Article: Laying the Foundation
Instead of a standard article, a magazine editorial often presents the writer’s opinion on a particular subject or issue. Although the content may be subjective, the structure of a magazine editorial should still follow a coherent and logical pattern. This ensures readers can easily follow the author’s argument and find the piece enjoyable.
The structure of a magazine editorial generally consists of several key components, including an attention-grabbing headline, an engaging lead, a well-organized body, and a firm conclusion. Each element plays a vital role in capturing the reader’s interest and effectively conveying the message.
The headline should be succinct yet powerful enough to pique the reader’s curiosity. It sets the tone for the entire editorial and helps readers decide whether to engage with the content further. A captivating lead follows the headline, briefly introducing the topic and drawing the reader into the heart of the editorial.
The body of the magazine editorial is where the author develops their argument or opinion. It is essential to present the information logically and coherently, using clear headings and subheadings to guide the reader through the narrative. Including compelling evidence, anecdotes, or quotes can also strengthen the writer’s argument and keep the reader interested.
Finally, a firm conclusion should summarize the editorial, summarizing the key points and providing a clear call to action or a thought-provoking statement. This creates a lasting impact on the reader and promotes further engagement with the topic.
Understanding the structure of a magazine editorial is vital for creating impactful and engaging content. By mastering the art of crafting powerful headlines, captivating leads, coherent body text, and firm conclusions, you can establish the groundwork for a successful magazine article that resonates with your audience and leaves a lasting impression.
Structure of a Magazine Article: Crafting Engaging Headlines and Subheadings
The power of an engaging headline and well-crafted subheadings cannot be understated when it comes to the success of a magazine article. These elements are instrumental in capturing the reader’s attention and guiding them through the content, playing a significant role in the overall magazine structure.
An enticing headline is the first point of contact between the reader and the article, and it can either facilitate or hinder their decision to delve further into the content. It should be short, impactful, and thought-provoking, effectively conveying the article’s essence in just a few words. Writing a captivating headline involves striking a balance between being informative and intriguing while remaining true to the subject.
Subheadings, on the other hand, break up the body of the article into digestible sections, making it easier for the reader to navigate through the content. They provide a clear roadmap of the article’s main points, helping the reader understand the flow of ideas and the magazine structure. Compelling subheadings should be concise, informative, and engaging, enticing the reader to continue reading and ensuring they can quickly grasp the key points being discussed.
In addition to their practical purposes, headlines and subheadings also contribute to the overall visual appeal of a magazine article. They help create a sense of hierarchy and organization, essential for maintaining the reader’s interest and making the content more accessible. By using varying font sizes, styles, and formatting techniques, designers can further emphasize the importance of these elements and enhance the article’s overall aesthetic.
Engaging headlines and subheadings are crucial to the magazine structure, serving functional and aesthetic purposes. By mastering the art of crafting these essential elements, writers and designers can ensure their magazine articles capture the reader’s attention, provide a straightforward and accessible narrative, and, ultimately, leave a lasting impression.

Structure of a Magazine Article: How to Hook Your Readers from the Start
In magazine writing, the lead is crucial in captivating readers from the outset. Serving as the opening paragraph, it establishes the foundation for the remainder of the content and is a vital component in the structure of articles. A well-crafted lead piques the reader’s interest and encourages them to continue reading the entire piece.
The primary objective of a leader is to provide a glimpse into the central theme or argument of the article while leaving the reader wanting more. It should be engaging, concise, and informative, offering just enough information to entice the reader without giving away all the details. Striking the right balance between mystery and clarity is essential in creating a compelling lead that successfully hooks readers.
The structure of articles often varies depending on the subject matter and the target audience. Nevertheless, there are several tried-and-true approaches to crafting compelling leads. One such approach is the anecdotal lead, which opens with a captivating story or personal experience that sets the tone for the article. Another popular option is the question lead, which poses a thought-provoking inquiry that piques the reader’s curiosity and encourages them to read on in search of an answer.
Regardless of the chosen approach, keeping the lead concise and relevant to the article’s central theme is essential. Additionally, the lead should transition seamlessly into the body of the article, maintaining a logical flow that maintains the reader’s interest and involvement in the content.
Structure of a Magazine Article: Building a Compelling Narrative
In magazine writing, the body text forms the backbone of the article, providing the substance and depth required to convey the author’s message or argument effectively. Drawing inspiration from magazine editorial examples can help writers build a compelling narrative that keeps readers engaged and maintains their interest throughout the article.
One of the essential aspects of crafting a captivating body text is maintaining a clear and coherent structure. This can be achieved by using subheadings to break the content into smaller, digestible sections, making it easier for readers to follow the narrative and absorb the information presented. Magazine editorial examples often demonstrate how effective subheadings can guide the reader through the article, ensuring they can easily comprehend the key points and arguments.
Another critical aspect of constructing an engaging body text is to vary the sentence structure and maintain a natural, conversational tone. This helps the content feel more approachable and enjoyable to read, as opposed to overly formal or rigid. Examining magazine editorial examples can provide valuable insights into how experienced writers maintain a consistent voice and style throughout their articles, fostering a connection with the reader and making the content more relatable.
Furthermore, using compelling evidence, anecdotes, quotes, or statistics can significantly enhance the credibility and impact of the body text. These elements not only lend weight to the author’s arguments but also help to keep the reader’s interest piqued, encouraging them to continue reading and engage with the content more deeply.

Structure of a Magazine Article: Visual Elements and Their Role
In magazine publishing, visual elements play a vital role in enhancing the reader’s experience and contributing to the overall structure of an article. As the adage states, “A picture is worth a thousand words,” and this concept holds true when considering the structure of an article. Images, graphics, and other visual components can bring the written content to life, adding depth, context, and appeal to the magazine piece.
Functions of Visual Elements
One of the primary functions of visual elements in a magazine article is to break up large blocks of text, making the content more digestible and visually appealing. By incorporating relevant images or graphics throughout the article, writers and designers can create a more engaging and enjoyable reading experience for the audience. This not only makes the content more accessible but also helps to maintain the reader’s interest and attention.
Another essential function of visual elements is to provide additional context or information that may be difficult to convey through text alone. For example, data visualizations, such as charts or infographics , can effectively present complex information or statistics in a more easily understandable format. This enhances the reader’s comprehension of the subject matter and strengthens the overall impact of the article.
Furthermore, visual elements can also contribute to a magazine article’s overall aesthetic and design. By strategically using color, typography, and other design elements, designers can create a cohesive visual language that complements the written content and reflects the article’s theme or mood. This adds to the reader’s enjoyment and reinforces the magazine’s brand identity and style.
Understanding the structure of an article is complete by considering the role of visual elements. By incorporating relevant images, graphics, and design elements, writers and designers can create a more engaging and visually appealing magazine piece that captures the reader’s attention and enhances their overall experience.
Structure of a Magazine Article: Crafting a Memorable Ending
A well-crafted conclusion is an essential component of any compelling magazine article. It reinforces the main points and ideas, leaving the reader with a lasting impression and closure. Understanding how to structure an article involves organizing the content logically and ensuring that the conclusion ties everything together, providing a strong and memorable finish.
When crafting a memorable ending, it is crucial to reiterate the key points discussed throughout the article, summarizing the central argument or message. However, this should be done concisely, avoiding repetition or regurgitation of information. Instead, the conclusion should offer a fresh perspective or insight that adds depth to the article and encourages readers to further reflect on the subject.
Another effective technique when considering how to structure an article is to end with a call to action, a thought-provoking question, or a prediction. This can inspire the reader to engage with the topic beyond the article, fostering a sense of curiosity and leaving them with something to ponder. The conclusion can impact the reader by provoking an emotional response or encouraging further exploration.
In addition, the tone of the conclusion should be consistent with the rest of the article, maintaining a sense of cohesion and harmony. Whether the article is informative, persuasive, or narrative-driven, the conclusion should reflect the same style and voice, ensuring a smooth and satisfying reading experience.
Mastering how to structure an article involves organizing the content effectively and crafting a powerful and memorable conclusion. By summarizing the key points, offering fresh insights, and provoking thought or action, writers can ensure that their magazine articles resonate with readers and leave a lasting impact. By incorporating these techniques, you can create a compelling, engaging magazine article that stands out.
What are the critical components of a magazine article structure?
The critical components of a magazine article structure include an attention-grabbing headline, an engaging lead, a well-organized body, and a firm conclusion.
How do I write a captivating headline for my magazine article?
A captivating headline should be short, impactful, and thought-provoking, conveying the article’s essence in just a few words. Strive to balance being informative and intriguing while remaining true to the subject.
What role do subheadings play in the structure of a magazine article?
Subheadings break up the body of the article into digestible sections, making it easier for the reader to navigate through the content. They provide a clear roadmap of the article’s main points, helping the reader understand the flow of ideas and the magazine structure.
How can I write an engaging lead for my magazine article?
To write an engaging lead, provide a glimpse into the central theme or argument of the article while leaving the reader wanting more. Keep it concise and relevant to the article’s theme, striking the right balance between mystery and clarity.
What are some tips for crafting a compelling body text?
Craft a compelling body text, maintain a clear and coherent structure, vary sentence structure, and maintain a natural, conversational tone. Use subheadings, compelling evidence, anecdotes, quotes, or statistics to enhance the credibility and impact of the content.

Learn How To Develop Launch-Ready Creative Products
Download How to Turn Your Creativity into a Product, a FREE starter kit.

Advertisement
Create a Memorable Social Media Experience
Get the content planner that makes social media 10x easier.

Invite Your Customers To A Whole New World
Create a unique user experience.

Maximize Your Brand and Make Your Mark
Custom brand assets will take you to new heights.

Business Ideas in Tech: How to Find Potential

Headlines: How to Craft for Social Media

Email Marketing vs. SMS Marketing: How to Choose

Side Hustle: How to Start One from Home

Storytelling: How to Use it for B2B Marketing

Press Release Distribution: How to Select One
ThemeGrill Blog
WordPress News, Trends and Information
21 Popular Types of Magazine Articles to Impress Your Audience in 2024
Are you looking for the best types of magazine articles to impress your online audience? Well, we’re here with over a dozen of them.
Say you’ve just started your magazine or blog, but you’re unsure what kind of articles you should write. And you want to look for some ideas that will help you decide.
That’s what we’ll help you within this article.
We’ll show you some of the best types of magazine articles that will impress your readers. Also, we’ll discuss briefly how you can easily create an online magazine.
Table of Contents
Types of Magazine Articles to Impress Your Online Audience
The best types of magazine articles are the ones that you enjoy writing. So, try to look for an idea you’ll enjoy the most.
People are always looking for something. They search for movies to watch, products to buy, games to play, companies to trust, and many more.
And you’ll surely impress your online audience with a good list of any of these.
For instance, if you’re an avid movie watcher, then you can write about the ones you found out to be hidden gems or have the best visuals.
Likewise, we’re WordPress lovers, so we have an article about the best plugins in WordPress .
With lists, you can also promote your products if you own a business. For example, let’s say you own a headphone brand. Then, you can talk about the best headphones brand and promote your product in that article.
For instance, we have some list articles on our blog where we write about our products as well. Check them out:
- 15 Best WordPress Form Builder Plugins for 2024
- 27 Best WooCommerce Plugins & Extensions for Your Business
2. ‘How-to’ Tutorials
Ten bucks say you’ve searched for a ‘how-to’ article at least once in your life. That’s how popular these types of magazine articles are.
Thus, a helpful tutorial is one of the most popular types of magazine articles to impress your online audience and teach them new skills.
On the ThemeGrill blog , we have lots of tutorials, like how to create a WordPress website .

There’s a vast area for ‘how-to’ articles. To name a few, you can publish recipes, i.e., how to cook something.
Also, you can write on helpful topics like how to register for an online course, how to clear your computer’s memory, and so many more.
Interested in exploring how-to articles? Take a moment to explore these informative articles:
- How to Delete a Theme in WordPress?
- How to Register a Domain Name for a New Website?
3. Cheat Sheet
Cheat Sheets are one of the best types of magazine articles. Because who doesn’t love shortcuts?
Cheat sheets are articles intended to help people memorize some kind of information more easily. If you help people cut corners and do something more quickly, they’ll return for more.
For example, this cheat sheet for calculus will make the audience come back for a cheat sheet for algebra as well.
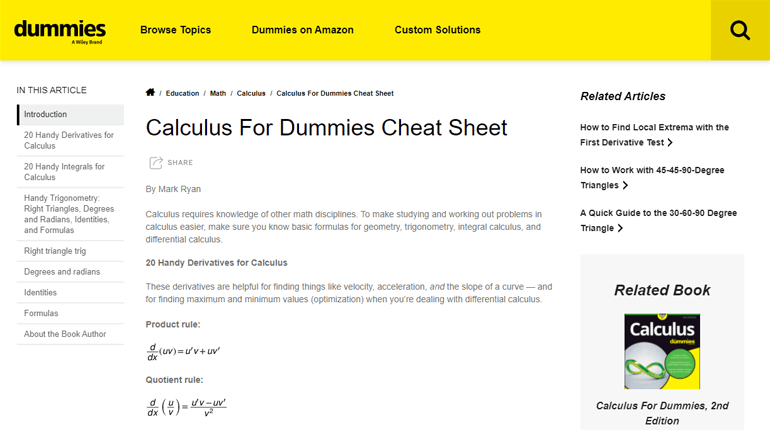
Cheat Sheets can be about many things, such as programming languages like C#, HTML, software like Photoshop, or even games.
Apart from that, you can also go for educational cheat sheets, like a list of formulae for trigonometry.
4. Comparisons (Versus Articles)
A versus article explains why one product is better than the other. And everyone loves to hear a good argument.
It works as a review as well. So it’s like inviting an audience with two purposes in a single article.
These types of magazine articles can be about anything. They can be about electric vs. petrol cars, Intel vs. AMD, Google Docs vs. Microsoft Word, Nike vs. Gucci, or anything else.
Like the article on our blog about WordPress vs. Drupal – which CMS is better for your website ?

Versus articles are also an excellent and clean way to promote your product or service.
Let’s say you own a clothing brand. You can tell your audience why they should choose your brand over the other ones.
Check this out. We compared some of the best WordPress products side by side:
- Kinsta vs SiteGround – Which Managed WordPress Hosting is Better?
- Divi vs. Elementor: Which is a Better Page Builder for WordPress?
Gossips are articles where you talk about famous people. It can be about their hobbies, lifestyle, net worth, or anything. The show biz is vast and never runs out of content.
There is good competition as well. But people never stop looking up for things about celebrities, so the traffic is always good.
For example, people aren’t stop looking up about Usain Bolt anytime soon.

Hence, you can publish posts about the lifestyle, net worth, and relationships of famous actors, actresses, and sports champions.
The point is there’s a lot of content, and it depends on what interests you.
6. Product Review
While the comparison articles work for two or more products, review articles focus on an in-depth analysis of a single product.
Corresponding to that, we have a review article on Bluehost that includes all the important details.

For instance, you put up a good review about Domain . com , a domain registration service for websites.
As a result, your audience will visit your website for many other website-related services and product reviews as well.
Explore our insightful product review articles, where we thoroughly evaluate the features and performance of popular tools for WordPress websites:
- Hostinger Review: Is it Good Web Hosting for WordPress?
- Rank Math Review: Is it a Good SEO WordPress Plugin?
7. Free Tools
People look up free tools all the time. Free tools introduce users to something new and unexplored.
For example, the free-to-use version of the Zakra theme introduces users to theme features and makes way to learn the premium benefits.
With a bit of research, you can find tons of free valuable stuff online. Then, you can write about them, such as the best free online tools to grow your online business, etc.
For example, we have a big list of free WordPress themes on our blog.

You can also promote your magazine by giving away some free stuff. Giveaways are a great way to invite a new audience and introduce your content to them.
Speaking of free tools, here are articles where we explore some of the best free products in WordPress:
- 31 Best Free WordPress Blog Themes for 2024
- 15 Best Free WordPress Hosting Services for Startups
8. Facts and Stats
We always love to know something we don’t, especially when it’s something interesting. Hence, publishing facts and stats in your magazine is an excellent way to increase engagement.
If you can pile up amazing facts and statistics, then it keeps the audience engaged.
For example, we made an ultimate list of over 100 WordPress stats and facts .

Similarly, you can write about the fastest cars with their top speed if you love cars.
Maybe a statistics report on the richest women throughout recent history. Maybe some amazing facts about the past, space, or the ocean. It’s up to you!
9. Personal Experience
Have you ever noticed that people find listening to someone else’s experience quite interesting?
Therefore, magazine articles about personal anecdotes never go out of style. And when the content is relatable, people are more likely to share it as well.
Remember, instead of a long piece, short and exciting experiences tend to be more engaging, like this list of paranormal experiences.

Moreover, asking your audience to share an unusual experience can increase engagement. Perhaps even share your own experience?
Other than that, you can even write about what celebrities say or experience. It’s bound to attract a larger audience.
10. Stories
Stories are a great way to engage your online audience. Moreover, when the story is real or relatable, your content is more likely to be shared and make people stay on your site.
You can publish someone’s success stories to inspire your audience. Like the inspiring stories of Malala Yousafzai, Jane Goodall, and more.
Or you can publish a story by someone, like the fictional story, ‘ Symbols and Signs’ by Vladimir Nabokov.
If you’re interested in history, you can write about historical events, but from a different perspective. Conversely, bedtime stories or stories for kids can also work.
Wiki is a type of article for your magazine that provides visitors with lots of information and resources. Wikipedia is the best example.
It’s one of the most significant websites on the internet. So, you know how powerful wikis can be.
Sometimes, letting your users add information to your site can exponentially increase engagement. Like this Harry Potter Wiki, where the community can also contribute.

Likewise, you can work on creating wikis of popular franchises or celebrities. Furthermore, you can also talk about how things work, like how jet planes work, airplanes fly, etc.
12. Transparency
Transparency articles are the types of magazine articles that talk about lesser-known things.
And no, we’re not saying you should stalk people and organizations for transparency. Instead, you can look at public data or surf online to find a lot of things.
For instance, you can write about little-known facts about something, maybe some movies like Star Wars.
Or, you can talk about data that have been revealed and provide your perspective, like this data reveal that shows inequities in federal funding.

You don’t even have to search elsewhere for content. You can tell your audience about things in your own business. Staying clean and transparent increases trust and grows your online business as well.
13. Discoveries
Another amazing idea – you can talk about a few discoveries and elaborate on them. If you can provide your audience with amusing discoveries, then they’re sure to be impressed.
Most of the time, the articles could be about scientific discoveries, outer space, the human body, or similar stuff.
But they can also be about unique things that people do, such as this article on what a man did to make his daughter a princess.

Not only the science stuff, but the article can also be about what someone found in a popular game, like the minus world in Super Mario Bros.
Or, to keep it interesting, you can talk about accidents that led to discoveries like Velcro and Microwave.
14. Daily Dose
As the title says, the article is about satisfying the daily appetite of your audience. Therefore, the content needs to be published regularly.
As a result, it increases audience engagement and keeps your traffic consistent.
A good thing about these types of magazine articles is that it makes your audience more loyal. And it’s better to choose a niche that’ll consistently provide you the content, such as motivational quotes.
If you don’t mind a good amount of media in your magazine, then you can publish a daily dose of memes. If not, how about a daily dose of amazing facts?
Maybe a daily dose of inspiring stories and quotes? You choose.
15. Predictions
In these types of magazine articles, you can talk about the predictions that some famous people made.
For instance, great minds like Stephen Hawking and Michio Kaku have predicted the future of climate change.
Articles about predictions work for all kinds of people, the religious ones, the science-headed, everyone.
Your article can also be about past predictions, like this article on some 100-year predictions that came true.

Apart from these, you can also put forward your own opinions. For example, you can talk about what you think artificial intelligence will bring or what the future of agriculture will hold.
16. Research-Based Articles
If you like to research, you’re in for a good treat. You can research popular topics and share your findings with your audience.
The good thing here is that these types of magazine articles have a vast audience. If you publish about things you find interesting, then you’ll attract a like-minded audience.
For example, an article about Roman architecture attracts architects and history lovers.

There’s no limit to what your research has to be about.
For instance, it can be about what discoveries helped make computers shrink. Or how Google owns a considerable chunk of the internet or what chain of events led to the Cold War.
17. Articles About Earnings
Magazine articles about how much someone made or earned can attract a large audience.
In these types of magazine articles, you can also talk about platforms that help people make money online, cryptocurrencies, and whatnot.
You’ll have an endless supply of exciting content, such as upcoming entrepreneurs or how people made a huge amount of money.

Moreover, a lot of the time, people are just click-baiting by publishing about earning platforms.
Thus, if you post an honest review of money-making platforms like Fiverr, you are sure to impress your audience.
18. News Articles
If you like keeping yourself updated about what’s happening globally, this is the type of magazine article for you.
At the same time, you can also grab a specific niche to communicate with your audience.
There are a lot of sectors to pick from. You can post about current situations like the pandemic, business news about stocks, or tech news.
For example, the article in the image talks about Google’s AI tech that can design computer chips faster than humans.

Moreover, you can provide your views on topics or give a different perspective to keep it interesting.
19. Comments and Feedback (Customer Response)
It’s no surprise that people trust consumer reviews more than flashy advertisements.
So, they’re always grateful for articles that put forward the opinions of customers about a specific product.
You can also present them as statistics so that the content is more scannable. Finally, you can talk about what consumer reports show and what they mean.
Apart from these options, you can also feature some great comments and feedback that your website received.
Doing so will motivate your audience to engage more in your content and the comment sections.
Trends are popular ideas that are developing quickly. New trends rise on the internet every day. And people like to know about those trends and follow them.
You don’t have to talk about new trends either. You can talk about popular trends like the chain wallets that took over the 90s and similar stuff.
Furthermore, you can talk about current trends that are hauling the internet, like the 20 trends from last year.
Popular styles and trends can rise from anywhere now. There are lots of platforms like YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, and Twitter for that.
And there’s always something, so don’t worry about running short of content with these types of magazine articles.
21. Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth analysis and observational examination of a particular real world.
The goal of a case study is to provide a thorough understanding of the complexities of a particular subject, problem, or phenomenon.

Case studies make content more concrete and compelling by providing real-world examples and proof points grounded in data.
With articles like these, readers get insights into how solutions would apply to real scenarios they might face themselves.
For reference, you can explore informative articles delving into case studies of specific topics, such as WordPress case studies and more.
Bonus Tips on How to Create an Online Magazine Easily?
Deciding on the types of magazine articles to write is not the only hurdle. You also need to create a magazine.
In this section, we’ll briefly talk about creating an online magazine, step by step.
So, once you’ve found the best domain registration and web hosting service , the next important step for your site is to choose a theme .
And we have just the suitable theme for your magazine.
Presenting the top magazine-styled theme for WordPress, ColorMag is the best deal you can get for your magazine. ColorMag suits newspapers, magazines, blogs, and more perfectly.
We recommend ColorMag because of its amazing features. Some of the significant features of ColorMag include:
- Advanced Typography, Color Options, and Multiple Widget Areas
- One-Click Demo Import of Dozens of Starter Demos
- Perfectly Compatible with WooCommerce
- Seamless Integration with Page Builders like Divi, Elementor
- Reliable and Dependable Support
And you’ll find more amazing features once you start using ColorMag.
Step 1: Set Up Your WordPress Site
First of all, you need to purchase a domain name and web hosting service. A domain name is your website’s name like themegrill.com is our site’s name.
Web hosting is a service that provides space to put your site’s files and makes your website appear online.
Choose a domain name suitable for your magazine and register it with a domain registrar. Or you can buy web hosting with Bluehost and get a free domain for 1 year.

After you purchase a domain and hosting, you’ll get access to your hosting control panel (commonly cPanel).
From there, you can install WordPress with a click. Next, you’ll get your WordPress dashboard from where you can manage your online magazine entirely.
To know the step-by-step process in detail, please check our article on how to create a WordPress site.
Step 2: Installing ColorMag
Now that we’ve chosen a theme, it’s now time to install it. For that, first, log in to your WordPress dashboard .
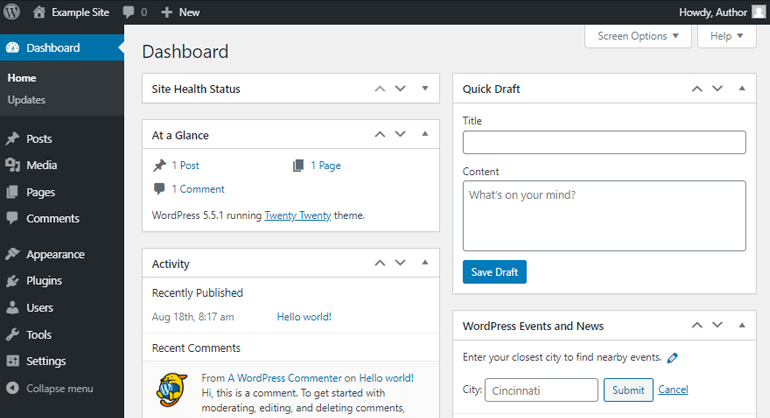
Then, go to Appearance >> Themes . This is a place where all your installed themes reside.
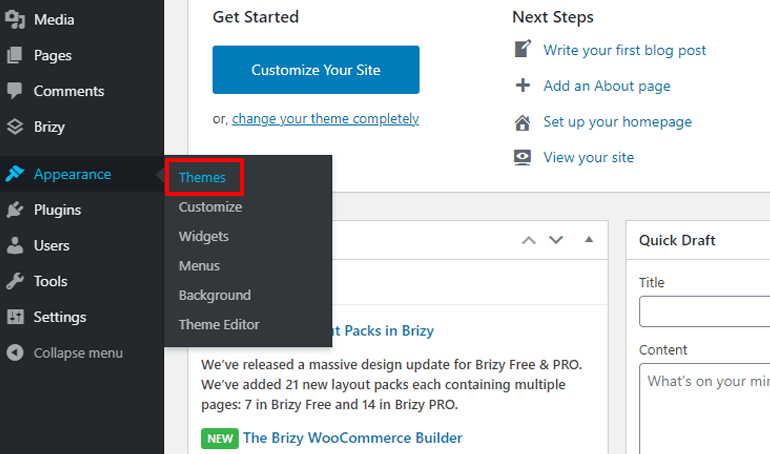
Next, click on the Add New button on the top left side to access all the themes in the WordPress repository.
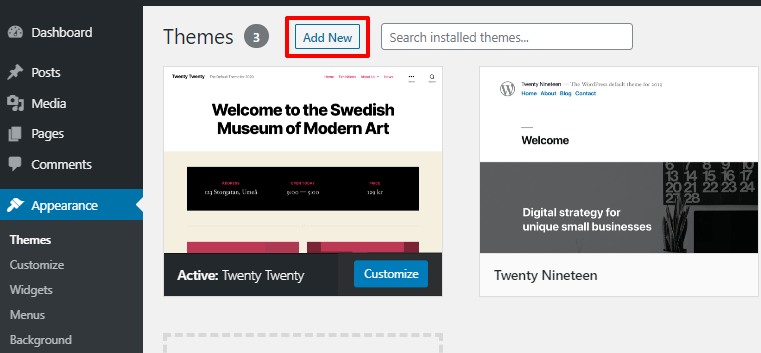
Now, in the search bar on the top right side, type ColorMag . And as soon as you type in ColorMag, the ColorMag theme will show up.
Hover over the panel of the ColorMag theme, and you’ll see the Install button. Click on it.
Once you install the theme, the Activate button will show up in the same place. Click on it.
There, you’ve installed the best magazine-styled theme on your website. If you want to know more about installing a theme or other ways to install a theme, then check out this article on installing a WordPress theme .
Step 3: Choosing a Demo
When you install ColorMag, it’ll greet you with a welcome message.
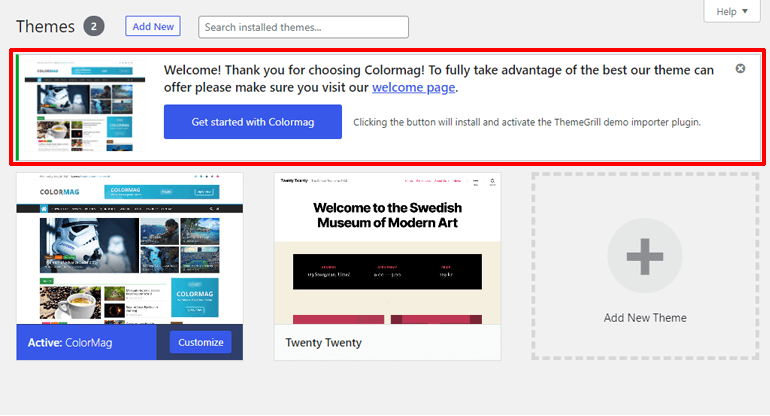
On that welcome message, click on Get Started with ColorMag to go to the templates library.

For now, let’s go with the first demo site. Hover over it, and click on Import .

When you click on the Import button, you’ll see a text about when to import a demo site and what happens when importing one. After you read the text, click on Confirm .

Importing a demo site takes some time, but it’s worth the wait. And once it’s done, so is most of your work.
To view your site, hover over the panel of your template and click on the Live Preview button.
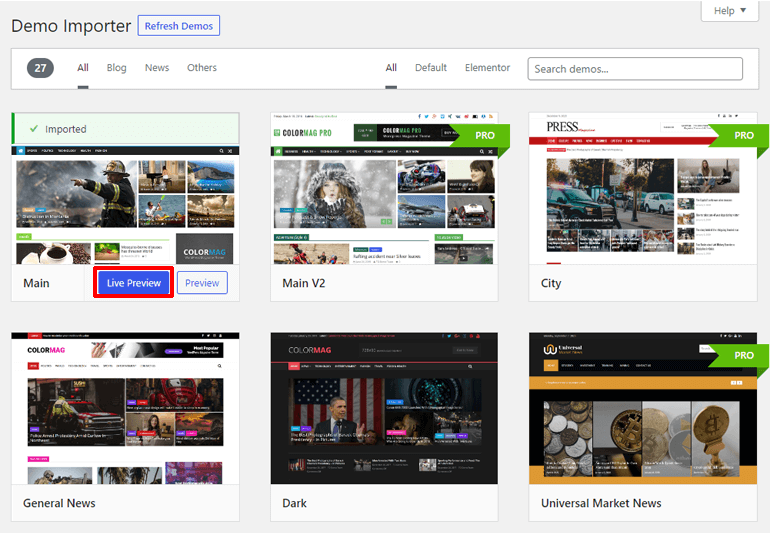
Step 4: Customizing Your Website
If you’ve noticed, ColorMag replaces the default logos and texts with placeholder texts and images. So to give your website its own identity, you need to customize it.
To customize your site, click on the Customize button on the left side of the top bar.
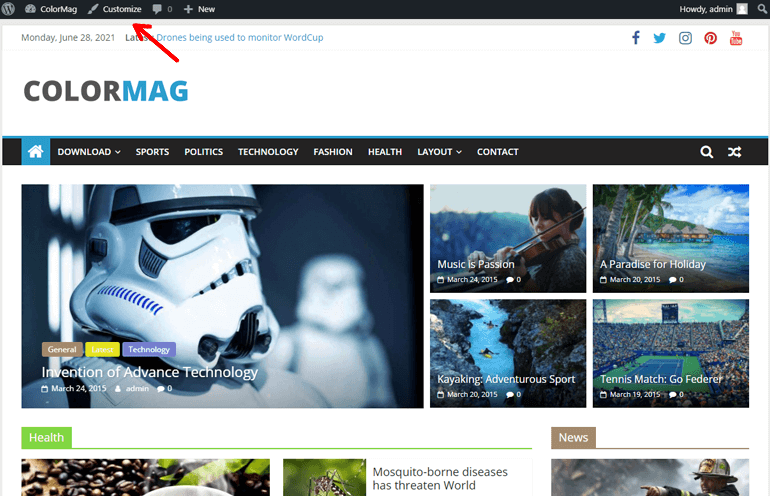
That’ll take you to the WordPress live customizer . On the left, you can see different options to customize various parts of your site. And on your right is the live preview.

The options are very self-explanatory, and you’ll have an easy time customizing your site. Moreover, you can also see the change you made on your right, so there’s nothing to fear.
You can also access specific customization options by clicking on the pencil icon on the right side of your screen.
Take your time, customize your site, and give the internet a professional and awesome website. And that’s it. Your online magazine is ready.
Also, if you want to know in detail about starting an online magazine, then look at this article on How to Create an Online Magazine in WordPress .
ColorMag Theme Free vs. Premium – Which one to use?
The free version of the ColorMag theme is powerful enough to create an impressive online magazine. You can get it for direct installation from WordPress.org.
With the premium version, you’ll be able to sail in an ocean of features and beautiful pro demo sites.

Some important features include integration with WooCommerce, payment gateways , email marketing services , etc.
ColorMag Pro also works perfectly with Elementor. Thus, you’ll unlock a new dimension of customization possibilities with Elementor blocks and templates.
So, if you want to explore the advanced features, you can try ColorMag’s premium version. You can visit the theme’s official website to purchase it.
Wrapping it Up!
There are hundreds of types of magazine articles on the internet. And the ones mentioned above seem to impress more online audiences.
Undoubtedly, they’re good for engaging visitors and getting higher rankings .
We spent quite some time searching for the best kinds of magazine articles. Our key take was this: apart from the content type, you also need to have a professional website and publish regular content.
So, set your website up, choose your interest, dive into it, and impress your online audience.
We hope that this article helped you to find your type of magazine article. If it did, share it on socials, let’s celebrate.
While we’re on the topic, check out our article on the best online magazine WordPress plugins ! It’s sure to prove resourceful for your magazine website.

ThemeGrill Author
We are a team of SEO copywriters and editors who work both individually and in the team. ThemeGrill author is where one of the editors here is working on one project personally. Write to us @themegrill_blog in Twitter.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You May Also Like

How to Learn WordPress? + (18 Best Ways to Learn Fast)

How to Make a Fitness Website? (In 5 Easy Steps)

How to Use ChatGPT for Marketing? 10 Incredible Ways

How to Build an Online Course in WordPress (Shockingly Fast!)

How Masteriyo was Born?
![styles of writing magazine articles Zakra 3.0 | Zakra Pro 2.0 Release [Major Updates!]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/g3rifl7kWvg/maxresdefault.jpg)
Zakra 3.0 | Zakra Pro 2.0 Release [Major Updates!]
Pin it on pinterest.
ThinkWritten
The 4 Main Types of Writing Styles and How to Use Them as a Writer
Understanding the 4 main types of writing styles can help you grow as a writer and attract an audience for your written work. Here’s how to identify each style of writing and tips for using each of the 4 common writing styles to develop your written skills.

We may receive a commission when you make a purchase from one of our links for products and services we recommend. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Thank you for support!
Sharing is caring!
One of the things that can help you grow as a writer is to learn the 4 main types of writing styles and use the characteristics of each to further develop your own personal voice as a writer.

By learning how to use the different writing styles in your work, you will not only improve your skills as writer, but also learn ways to better connect with your audience of readers.
In this post we’ll cover the 4 main types of writing styles and how to use them as a writer to create compelling books, stories, essays, poetry, articles and more.
What are Writing Styles?
Writing styles are basically another way of saying the form or type of written work you are creating. Think of it as a classification for being able to identify what kind of writing you are creating.
For example, if you are writing a cookbook, that is a completely different style of writing than if you were writing a steamy romance novel!
Each writing style has a different purpose – and therefore, different characteristics are present when you are writing each type of different work.
Now that we understand what a writing style is – let’s talk about the 4 main writing styles which are commonly talked about amongst writers and literary educators.
The 4 Main Writing Styles & What They Mean
The four main writing styles which are commonly recognized are expository , descriptive , narrative , and persuasive .
Style #1: Expository

The definition of expository is this: “intended to explain or describe something.”
Most types of written work that fall into this category explain something in more detail, or provide insight and instruction in regards to a particular topic.
What types of writing fall into this category of expository writing style?
While there are many different types of written work which can be categorized as expository style of writing, you can often identify this type of writing by noticing the purpose of the work.
- Does the work intend to explain something in more detail?
- Does the written piece inform?
- Does the written piece answer questions such as “what, how and why?”

Here are some examples of the different types of writing pieces which can fall into the category of expository writing:
- Newspaper and Magazine Articles {not including editorials}
- Non-Fiction Books
- How-To Books
- Self Help Books
- Writing about Hobbies & Interests
- Recipes & Cookbooks
- Instructional Guides
- Scientific Research
- Textbooks & Educational Resources
- Business Articles & Books
- Medical Research, Journals and Articles
When you write expository style pieces, your main goal as a writer is to inform your readers with insight and facts that pertain to the subject of your piece.
For example, if you are writing about the history of ice cream, you would be including a lot of research and fun facts into your piece.
Note that this type of writing style is not intended to persuade or influence your audience. In writing your piece on the history of ice cream, you would NOT be trying to persuade your readers.
You would not want to say things like “Everybody should eat ice cream!” and “These 5 reasons will convince you forever to choose strawberry swirl flavored ice cream as your favorite flavor.”
Sometimes it can be confusing on whether an article is expository or persuasive. For example, an article called “The 5 Unexpected Health Benefits of Ice Cream” – would not fall into expository writing, even though it is providing information.
The word “benefits” has a positive connotation to the title. If you were to be writing an article on possible health benefits on ice cream, it would be very important that you as the writer keep your opinion separated from the facts and information if you plan for it to be an expository style piece. To be expository in nature, you would want to use a title such as “Scientists Research The Health Effects of Ice Cream.”
Books and articles that explain how to do something are also very popular examples of expository writing. Cookbooks are very popular, as they explain to others the tips, techniques, and recipes on how to cook something. How-to books for hobbies and crafts are also a good example of this type of writing.
Style #2: Descriptive Writing

Descriptive writing goes deeper than expository writing. While expository writing might have some descriptive details and factual information, descriptive writing will make use of many writing elements and literary devices such as metaphors and similes.
The purpose and goal of descriptive writing is to bring your reader into the written work as if the reader were to be experiencing it first hand.
Most fictional pieces fall under the category of descriptive writing, and even some non-fiction pieces such as memoirs and creative non-fiction can fall under the category of a descriptive writing style.
If you are writing fiction, the more descriptive you can be with your words, the more relatable your story will be to the reader.
For example, we recommend that writers ask their characters questions as one way to really intimately understand the details about a character. Details about the setting, events, and people present in a story will help your readers be able to imagine and understand the piece.
This style also includes poetry. If you browse through some of our poetry writing prompts , you will see there is a lot of attention put on using details to create a scene or feeling in writing a poem!
Here are some examples of types of descriptive writing pieces:
- Poetry & Prose
- Travel Diaries
- Personal Journals
- Lyrics in Music and Songwriting
Most pieces using only a descriptive writing style are not very long. It is uncommon for a fictional novel to be 100% fully descriptive without getting into our next writing style, which is narrative writing.
Style #3: Narrative Writing

Narrative writing is far more complex that simple descriptive writing.
While a poem for example may describe a scene or even events or people – generally you do not get into the deep inner thoughts of the characters or even get a full story with a clear middle, beginning, and end complete with conflict and dialogue.
Nearly all fiction novels fall into the case of narrative writing, as well as longer epic poems and sagas.
In narrative writing, there is a story to be told – a clear plot complete with setting, characters, dialogue, conflict and resolution. A narrative piece often has a timeline or sequence of events which further build to the point of conflict and resolution.
Here are some examples of the works which would be considered to have a narrative writing style:
- Fiction Novels
- Memoirs & Biographies
- Screenplays
- Myths, Legends, and Fables
- Historical accounts
- Essays which talk about a lesson learned or valuable insight from an experience
Narrative writing pieces are generally easy to identify, although sometimes it can be confused with descriptive writing styles. The key difference in determining which one a written work might be is whether or not there is a developed storyline or plot.
If there is a well developed plot and storyline, you are most likely reading narrative writing.
Style #4: Persuasive Writing

Persuasive writing is a type of writing style where the purpose is to influence someone into believing or doing something. As the word “persuasive” suggests – your goal is to persuade someone’s actions or thoughts to align with your own goals as the writer.
The persuasive writing essay is a popular homework assignment for many kids. For example, a student might be assigned to write an essay to convince their parents of something. “Why We Should Get a Pet Rabbit” and “5 Reasons You Should Not Make Me Clean My Room”.
Persuasive writing is intended to convince someone of something, and so it usually needs to have a good bit of research and logical analysis – but also should attempt to make an emotional connection to the desired audience as well.
A classic piece of writing which serves as an example of persuasive writing is Thomas Paine’s book Common Sense , which was written in the Colonial times of the American Revolutionary War, urging citizens that separating from England was of utmost importance.
Here are some examples of types of writing which are persuasive writing:
- Editorial & Opinion pieces in Newspapers and Magazines
- Essays on a specific belief or “hot button” topic
- Letters written to request an action or file a complaint
- Advertisements {Convincing you to buy something}
- Copywriting {Note, copywriting is different from copyright!}
- Company Brochures
- Business Proposals
- Political speeches
When the intention of the work is to convince the audience of something – this falls into persuasive writing.
How to Use the 4 Main Different Writing Styles as a Writer
Now that we know the different types of writing styles, you may be wondering how do you use each style?

The first thing to do is think about what you are planning to write and what the intention is. What is your goal and what type of message are you trying to communicate to your readers?
Expository Style Writing:
In this type of writing your goal is to inform your readers about research or data.
When writing expository style pieces, follow these guidelines:
- Avoid using words which have a positive or negative connotation
- Do not insert your opinion or attempt to persuade your audience into thinking, feeling, or doing something based on your beliefs
- Use research and cite your sources
- When writing online, link to additional resources or websites
- Use quotes, illustrations or informative graphics to highlight the information
- Give concise and clear directions
Descriptive Writing Style:
This type of writing has the goal to describe something and bring into your reader’s imaginations
Here are some tips for writing with descriptive writing styles:
- Use literary devices such as metaphors and similes.
- Use well thought out adjectives and adverbs to describe nouns and verbs.
- Bring attention to small details
- Use the 6 senses: sight, touch, taste, smell, sound, and feeling
Narrative Writing Style:
In narrative writing style, your goal is to convey a storyline to your readers.
Here is how to achieve this type of writing style:
- Outline a storyline, plot or timeline sequence of events
- Include detailed descriptions of your characters and scenes
- Give your readers insight into the inner thoughts or behind-the-scenes information to elements of your story
- Answer the 6 W questions in your writing: Who, What, When, Where, How, and Why?
- Make it so your piece of work conveys an important lesson or insight – what is the moral of the story? What was the outcome of this experience?
- Use concrete language which gives readers a specific image to visualize and relate to
Persuasive Writing Style:
When you are writing to persuade, your intention is to convince your readers to side with you. This can be as simple as convincing them to buy your latest new product, or even writing about important social and humanitarian issues.
Here are some tips for writing persuasively:
- Include information, data, and facts to back up your argument
- Cite your sources and give readers access to additional information
- Appeal to your readers on an emotional level – how will siding with your opinion connect with them and make them feel?
- Take into consideration your reader’s needs, wants, and desires and how your message will help your reader achieve these.
Understanding Writing Styles Can Help You Be a Better Writer
No matter what type of writing you enjoy creating – understanding the basic main 4 types of writing styles can help you become a better writer.
If you are writing a how-to article for example, you will be able to understand what types of elements to ensure your piece of work includes. If you’re writing a descriptive poem, knowing what type of language to use can help convey your message for abstract concepts.
Use these different writing styles as a fun writing exercise!
Even if you typically only write for one style, it can be a lot of fun to push yourself to try to write for the different types of styles. For example, try writing a persuasive essay, and then a descriptive essay on the same topic. It can also be fun to write a descriptive poem and then turn it into a narrative essay or short story.
Not sure what to write about using these different writing styles? We have TONS of ideas for you with many different writing prompts! Check out our list of 365 writing prompts ideas which are sure to inspire your creative muse!
Using prompts is a great way to help you start writing in different writing styles and push yourself to a new exciting challenge for your writing skills!
I hope this article about the different writing styles and how you can use them as a writer will be helpful for you in building and developing your written skillset.
What types of writing styles do you enjoy writing the most? Have any tips for writing in expository, descriptive, narrative or persuasive styles of writing? We’d love to hear your ideas and experiences in the comments section below!
Chelle Stein wrote her first embarrassingly bad novel at the age of 14 and hasn't stopped writing since. As the founder of ThinkWritten, she enjoys encouraging writers and creatives of all types.
Similar Posts

How to Mind Map a Novel Plot

How to Write a Short Story

10 Tips for Writing a Novel

How to Name Your Characters

What is an Antagonist?

How to Improve Your Vocabulary: 12 Ways to Learn New Words
15 comments.
Enjoyed reading this artice. I stumbled across this website by chance and I don’t regret it. Best thing I read today. I am sure this information will be pretty helpful for my Notes in future. Thank you. 👍
Thank you! Glad you found it helpful 🙂
I am grateful I came across this article. It will come in handy in my writing work
Great! This is very helpful.
I am glad it is helpful for you Nazz!
I teach English to non-native speakers and I stress, on a regular basis, about the value of being able to write as well as speak. So when I stumbled across this article I had to post it to my linkedIn page.
Very informative article! Thank you.
Wow! Very exciting article. This help me rebuild my bad foundation. I have really had hard times writing a piece to finish. I never get to communicate my message the way i intend to because i get to a cross road of how best to relate with my audience with clarity. Quite EXPOSITORY! thanks
It’s really helpful 😊 it’s worth.
very helpful
To which writing style would a conversational manner apply best?
A writing that talks about the cages people Live can be classified as what type?
Great work!
Thanks Very useful It will be very helpful for me as a writer. I really appreciate this words of wisdom and knowledge. It was very insightful.
An article one can easily connect with. It brings clarity and understanding to the different writing styles as discussed. Kudos.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Online Flipbook
- Online Catalog
- Online Magazine
- Online Brochure
- Digital Booklet
- Business Proposal
- Real Estate Flyer
- Multimedia Presentation
- Ebook Online
- Online Photo Album
- Online Portfolio
- Company Newsletter
- Lead Generation
- Document Tracking
- PDF Statistics
- Virtual Bookshelf
- Flipbook App
Knowledge Base > Magazines > How to Write a Magazine Article? 12 Golden Rules
How to Write a Magazine Article? 12 Golden Rules
Although the number of magazines is shrinking in the digital age, many magazines have moved online. Many magazines created by online magazine maker are still popular, and authors enjoy fame and respect. That’s why, for many freelance writers, writing articles in magazines is often a career goal – because the pay can be ten times more per word than writing articles or texts for the local newspaper.
Writing magazine articles requires a different skill set than writing blog posts, screenplays, or advertisements. What’s more, as a magazine writer, more than in any other industry, you need to specialize to succeed. You write articles about history differently, sports differently, and sports history in a different way still.
A talent for writing, a love of meticulous research, and flexibility in creating texts are vital skills you need to master. Therefore, many people are interested in creating and publishing their own magazine need to master this specific style and learn how to write a magazine article.
What is a magazine?
A magazine is a publication that is a collection of articles that appears regularly. The magazine articles can be about any topic, as well as topics that interest a specific group, such as sports fans, music fans, or board game enthusiasts.
A magazine can be published weekly, monthly, bimonthly, or only a few times a year. Most magazines are published once a week or once a month. Most magazine articles do not have a list of sources and are written by regular magazine editors and writers, rarely freelance writers.

Most magazine articles are easy to read and don’t take too long to read. They are often illustrated with photos or other images, and are written with simple but remarkable fonts . Today, magazines are increasingly being replaced by websites, but there are still many magazines on various topics.
What is a magazine article?
A magazine article is a specific text that can be found in a magazine or newspaper. It can be a report, a profile of an important person, an opinion piece, a discussion of a topic or a personal essay. Depending on the topic, a magazine article is usually 1,000 to 5,000 words long.
The magazine usually employs a group of editors who come up with a theme for each issue and relevant article ideas. This way, all the articles and features in the issue will have something in common. A sports magazine might talk about the start of a new season, a political magazine about an upcoming election, and a Valentine’s Day issue might be about romance.

How the format of a magazine article differs from that of a newspaper or other articles? In a newspaper that comes out every day, put the most important parts of the story first. Newspaper articles are usually read once and aren’t supposed to influence anyone. It has to be news, something you want to read.
On the other hand, a good magazine article should often start with a mystery, a question, or a situation that makes the reader want to read on. Daily newspaper articles should be unbiased descriptions of what happened, while magazine articles, often subjective, can cover a particular topic from a certain angle. To learn how to write a magazine article, you need to know what the magazine is about and how to appeal to its readers.

Create a digital magazine with Publuu
Today, more and more people are creating magazines in purely digital form. Publuu converts PDF files into interactive digital magazines that you can easily view and share online. With support for HTML5 and vector fonts, your articles will look beautiful on any device, without the need to download additional apps.
Publuu makes your magazine article look and sound like the printed versions. Converting a regular PDF file into a flipping e-magazine using this service is extremely easy and fast.
Publuu’s online magazine example
View more online magazine examples
MAKE YOUR OWN
With Publuu, your readers can flip through the pages just as they would with a real paper magazine, but that’s not all. Rich multimedia capabilities, analytics, and easy access make many people publish content for free on Publuu.
Your audience, and you, can embed your magazines in websites or emails, or share them on social media platforms. It only takes one click to go to your magazine and start reading interesting articles.
Types and examples of magazine articles
Magazine editors categorize articles by type and often mention them in publication’s submission guidelines, so knowing these types by name will help you communicate with the editor. These are: First Person Article, Opinion Piece, Information or Service Piece, Personality Profile, and Think Piece. Many news articles, how-to articles, and reviews can also be found in magazines, but they are slightly different, and many of these have moved online, to digital magazines . Articles can also feature essays or humor pieces.

First Person Article
First-person magazine articles are written in the first person because they are based on personal experience. Depending on their length and newsworthiness, they can be sold as feature articles or essays. They are frequently personal accounts, especially interesting if they are written by a well-known magazine writer or celebrity. Typically, the purpose of such an article is stated in the first line or paragraph to hook the magazine’s target audience, such as “I voted for this politician, and now I regret my life choices.” When you write a magazine article like this one, you should present an unpopular or overlooked point of view from a fresh perspective.
Opinion Piece
This kind of magazine writing piece or opinion essay is less personal than the First-Person Article, but it still requires a narrow focus on a specific topic. The reader’s main question is, “Why are you qualified to render an opinion?” Everyone has an opinion, but why should anyone read yours?
If you’re an expert on this subject, let the reader know right away. Don’t criticize music trends if you’re not a musician! Demonstrate your knowledge, and support your opinion with up-to-date information and credentials.
Information/Service Piece
An informational or service piece expands the reader’s understanding of a particular subject. This can be a guide, a list of important issues. You can either be the expert or interview one. These are extremely pertinent to a specific industry. In a sports magazine article, you can explain a complete history of a sports team and its roster for the upcoming season.
You can expect some in-depth knowledge if the article title contains the phrases like Myths about or Secrets of. Explain everything you know: magazine journalism is different than being a freelance writer in that you should have some industry knowledge already.
Personality profile
This type of magazine article can present a silhouette of an important or relevant person – a politician, a political activist, a sports legend… If you’re writing for a video game magazine you can showcase a famous game designer or even an entire article can be about a game character like Lara Croft or Guybrush Threepwood, if the fictional character is detailed enough! Explain why readers will find this person interesting or noteworthy.
Think Piece
Written in an investigative tone, the think piece frequently shows the downside or less popular ideas of a popular industry aspect. This magazine article could also explain why something is popular or why a political party lost elections. A think piece is more in-depth than most feature articles and necessitates credibility. Confirm your thesis by interviewing analysts and experts. This type of article can be also found in zines , self-published magazines in small circulation, which often focus on niche hobbies, counterculture groups, or subcultures. If you would like to expend your knowledge about interviewing, make sure to check our guide on how to write an interview article .
How to start a magazine article?
Most creative writing professionals would agree that the best way to start writing a magazine article is with a strong opening sentence. A feature article must draw the attention of your target audience, and grab them from the go.
You can start by asking the reader a question which you will answer in the text of the article – for instance “Did you know that most users of Windows never use 80% of their functions – and that’s a good thing?”. In the content of your magazine articles you will be able to answer this question.
Another example of a good magazine article beginning is storytelling – human brains are fascinated by stories. Starting your example with “20 years ago no one in the industry knew what a genitine was, but now their inventor is one of the most influential people” can draw attention and spike up curiosity.

A great example is also a shocking quote – a compelling idea that goes against the grain is sure to capture the reader’s attention.
Most creative magazine article ideas
Even the most experienced journalists can often be looking for ideas for great articles. How to write a magazine article if you don’t have the slightest idea? Here are some of our suggestions:
Take a look at your specialty. If you’re a freelance writer, it’s a good idea to write about what you know. Delve into a topic thoroughly, and you’ll eventually find your niche and you might move from freelance writing jobs to magazine writing! Why? Having a writing specialty will make magazine editors think of you when story ideas in that genre come up.
Check out what’s trending. When browsing popular stories on social networks, many freelancers choose to write about current events. Lists of popular articles can help you understand what to focus your efforts on. Keep in mind that an article for national magazines needs to be well researched, and what’s trending now may change before the magazine finally comes out.
Reach out to the classics. Nostalgia always sells well. You can go back to books or movies that people remember from their youth or, for example, summarize the last year. Lists and numbers always look good!
12 rules on how to write great magazine articles

1. Write what you know about
If your articles are really fascinating and you know what you are writing about, you have a better chance of getting published, whether in a local newspaper or in a major magazine. Writing requires researching your chosen issue thoroughly. Identify perspectives that have not been explored before – describe something from the perspective of a woman, a minority, or a worker.
2. Research how you should write
Check the writing style requirements or guidelines of the magazines to which you want to submit your work. Each magazine has its own set of guidelines on what topics, manner and tone to use. Check out Strunk and White Elements of Style for tips on writing styles, as this is what many magazines draw from.
3. Remember to be flexible
One of the most valuable writing talents a journalist can possess is flexibility. You may find that you discover completely new facts while writing a magazine article and completely change your approach. Maybe you’ll change your mind 180 degrees and instead of attacking someone, you’ll defend them – anything to attract attention.
4. Make connections and meet people
Networking is important in any business, especially for freelance writers who want to make a jump to magazine writing. Editors regularly quit one magazine to work for another. Therefore, remember to know the people first and foremost than the magazine they work for.
5. Prepare a query letter
A query letter tells the editors why your magazine article is important, whether you think someone will want to read it and why you feel obligated to write it. Add to it a text sample and some information about yourself as a writer. Even a local magazine might not be aware of who you are, after all.
6. Prepare an outline
Always before writing a text have an outline that you can use when composing your articles. It must contain the important ideas, the content of the article body and the summary, the points you will include in it. You will find that it is easier to fill such a framework with your own content.
7. Meet the experts
You need to know pundits in your industry. There are several methods of locating experts, from networking to calling organizations or agencies in your field of interest. If you want to meet a police officer, call the police station and ask if someone could talk to a journalist – many people are tempted if you promise them a feature article.
8. Talk to experts
Once you get a contact for an expert, do your best to make the expert look as good as possible. The more prominent the expert, the better your text. Make a list of questions in advance and compare it with the outline to make sure you don’t forget anything. Remember to accurately describe your expert’s achievements and personal data.
9. Create a memorable title
This step can occur at any point in the process of writing an article for a magazine. Sometimes the whole article starts with a good title! However, there is nothing wrong with waiting until the article is finished before coming up with a title. The most important thing is that the title is catchy – editors-in-chief love that!
10. To write, you have to read
You never know where you will come across an inspiring text. It’s your duty as a good writer to read everything that falls into your hands, whether it’s articles on the front pages of major publications or small blog posts. Learn about the various issues that may be useful to your magazine writing skills.
11. Add a strong ending
End with a strong concluding remark that informs or elaborates on the theme of your piece. The last paragraph should make the reader satisfied, but also curious about the future progress of the issue. He must wonder “what’s next?” and answer the important questions himself.
12. Don’t give up
Writers are rejected hundreds of times, especially when they are initially learning how to create articles for magazines. However, even a seasoned freelance writer and professional journalist can get rejected. The most successful authors simply keep writing – being rejected is part of magazine writing. Freelance writing is a good school of writing career – including coping with rejection.
Now you know how to write a magazine article that will be engaging and interesting. Despite the digitalization of the market, writing magazine articles still offers many possibilities to a freelance writer or a seasoned professional. The market of press and magazines is evolving fast, but the basic principles of journalistic integrity stay the same!
You may be also interested in:
How To Publish Digital Magazine? How to Make a Magazine Cover With a Template? 5 Reasons to Start Using a Magazine Maker
Jakub Osiejewski is an experienced freelance writer and editor. He has written for various publications, including magazines, newspapers and websites. He is also a skilled layout graphic designer and knows exactly how to create visually appealing and informative PDFs and flipbooks!
Recent posts

- Flipbook Expert (13)
- PDF Expert (20)
- Catalogs (33)
- Brochures (44)
- Magazines (29)
- Real Estates (17)
- Portfolios (15)
- Booklets (13)
- Presentations (19)
- Education (8)
- Newsletters (13)
- Photo Albums (7)
- Ebooks (28)
- Business Proposals (16)
- Marketing Tips (53)
Popular articles

Convert your PDF to flipbook today!
Go beyond boring PDF and create digital flipbook for free. Register with Publuu for free today and check out all the smart options we prepared for you!
This site uses cookies. Learn more about the purpose of their use and changing cookie settings in your browser. By using this website you agree to the use of cookies in accordance with your current browser settings.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, understanding the 4 writing styles: how to identify and use them.
General Education

A piece’s writing style can help you figure out what kind of writing it is, what its purpose is, and how the author’s voice is unique. With so many different types of writing, you may think it’s difficult to figure out the specific writing style of a piece or you'll need to search through a long list of writing styles.
However, there are actually just four main types of writing styles, and together they cover practically all the writing you see, from textbooks to novels, to billboards and more. Whether you’re studying writing styles for class or trying to develop your own writing style and looking for information, we’ve got you covered.
In this guide, we explain the four styles of writing, provide examples for each one, go over the one thing you need to know to identify writing style, and give tips to help you develop your own unique style of writing.
The 4 Types of Writing
There are four main different styles of writing. We discuss each of them below, list where you’re likely to see them, and include an example so you can see for yourself what each of the writing styles looks like.
Writers who use the narrative style are telling a story with a plot and characters. It’s the most common writing style for fiction, although nonfiction can also be narrative writing as long as its focus is on characters, what they do, and what happens to them.
Common Places You’d See Narrative Writing
- Biography or autobiography
- Short stories
- Journals or diaries
“We had luncheon in the dining-room, darkened too against the heat, and drank down nervous gayety with the cold ale. ‘What’ll we do with ourselves this afternoon?’ cried Daisy, ‘and the day after that, and the next thirty years?’ ‘Don’t be morbid,’ Jordan said. ‘Life starts all over again when it gets crisp in the fall.’ ‘But it’s so hot,’ insisted Daisy, on the verge of tears, ‘and everything’s so confused. Let’s all go to town!’ - The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
You can quickly tell that this passage from the novel The Great Gatsby is an example of narrative writing because it has the two key traits: characters and a plot. The group is discussing eating and drinking while trying to decide what to do for the rest of the day.
As in this example, narrative writing often has extended dialogue scenes since the dialogue is used to move the plot along and give readers greater insight into the characters.
Writers use the expository style when they are trying to explain a concept. Expository writing is fact-based and doesn’t include the author’s opinions or background. It’s basically giving facts from the writer to the reader.
Common Places You’d See Expository Writing
- Newspaper articles
- Academic journals
- Business memos
- Manuals for electronics
- How-to books and articles
“The 1995/1996 reintroduction of gray wolves (Canis lupus) into Yellowstone National Park after a 70 year absence has allowed for studies of tri-trophic cascades involving wolves, elk (Cervus elaphus), and plant species such as aspen (Populus tremuloides), cottonwoods (Populus spp.), and willows (Salix spp.). To investigate the status of this cascade, in September of 2010 we repeated an earlier survey of aspen and measured browsing and heights of young aspen in 97 stands along four streams in the Lamar River catchment of the park’s northern winter range. We found that browsing on the five tallest young aspen in each stand decreased from 100% of all measured leaders in 1998 to means of <25% in the uplands and <20% in riparian areas by 2010. Correspondingly, aspen recruitment (i.e., growth of seedlings/sprouts above the browse level of ungulates) increased as browsing decreased over time in these same stands.” -”Trophic cascades in Yellowstone: The first 15 years after wolf reintroduction” by William J. Ripple and Robert L. Beschta
This abstract from an academic journal article is clearly expository because it only focuses on facts. The authors aren’t giving their opinion of wolves of Yellowstone, they’re not telling a story about the wolves, and the only descriptions are number of trees, streams, etc. so readers can understand the study better.
Because expository writing is focused on facts, without any unnecessary details or stories, the writing can sometimes feel dense and dry to read.
Descriptive
Descriptive writing is, as you may guess, when the author describes something. The writer could be describing a place, person, or an object, but descriptive writing will always include lots of details so the reader can get a clear and complete idea of what is being written about.
Common Places You’d See Descriptive Writing
- Fiction passages that describe something
“In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit. Not a nasty, dirty, wet hole, filled with the ends of worms and an oozy smell, nor yet a dry, bare sandy hole with nothing in it to sit down on or eat: it was a hobbit hole and that means comfort. It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted...” - The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien
This is the opening passage of the novel The Hobbit . While The Hobbit is primarily an example of narrative writing, since it explores the adventures of the hobbit and his companions, this scene is definitely descriptive. There is no plot or action going on in this passage; the point is to explain to readers exactly what the hobbit’s home looks like so they can get a clear picture of it while they read. There are lots of details, including the color of the door and exactly where the doorknob is placed.
You won’t often find long pieces of writing that are purely descriptive writing, since they’d be pretty boring to read (nothing would happen in them), instead many pieces of writing, including The Hobbit , will primarily be one of the other writing styles with some descriptive writing passages scattered throughout.
When you’re trying to persuade the reader to think a certain way or do a certain thing, you’ll use persuasive writing to try to convince them. Your end goal could be to get the reader to purchase something you’re selling, give you a job, give an acquaintance of yours a job, or simply agree with your opinion on a topic.
Common Places You’d See Persuasive Writing
- Advertisements
- Cover letters
- Opinion articles/letters to the editor
- Letters of recommendation
- Reviews of books/movies/restaurants etc.
- Letter to a politician
“What General Weygand called the Battle of France is over. I expect that the battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilization. Upon it depends our own British life, and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink by the lights of perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves, that if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, ‘This was their finest hour.’ - “This was their finest hour” by Winston Churchill
In this excerpt from his famous “Their finest hour” speech, Prime Minister Winston Churchill is clearing trying to convince his audience to see his viewpoint, and he lays out the actions he thinks they should take. In this case, Churchill is speaking to the House of Commons (knowing many other British people would also hear the speech), and he’s trying to prepare the British for the coming war and convince them how important it is to fight.
He emphasizes how important the fight will be (“Upon this battle depends the survival of the Christian civilization.” and clearly spells out what he thinks his audience should do (“Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties…”).

Common Writing Styles to Know
Each of the four main types of writing styles has multiple subsets of styles within it. Here are nine of the most common and important types of writing you’ll see.
Narrative Writing
Character voice.
Character voice is a common writing style in novels. Instead of having an unknown narrator, the audience knows who is telling the story. This first-person narrator can help the reader relate more both to the narrator and the storyline since knowing who is telling a story can help the reader feel more connected to it. Sometimes the narrator is completely truthful in telling what happens, while other times they are an unreliable narrator and will mislead or outright lie to readers to make themselves look better.
To Kill a Mockingbird (Scout is the narrator) and The Hunger Games (Katniss is the narrator) are two examples of this writing style.
Stream-of-Consciousness
This writing style attempts to emulate the thought process of the character. Instead of only writing about what the character says or does, stream-of-consciousness will include all or most of the characters thoughts, even if they jump from one topic to another randomly or include incomplete thoughts.
For example, rather than writing “I decided to take a walk to the ice cream shop,” an author using the stream-of-consciousness writing style could write, “It’s pretty hot out, and I feel like I should eat something, but I’m not really that hungry. I wonder if we have leftovers of the burgers Mom made last night? Is Mom staying late at work tonight? I can’t remember if she said. Ice cream would be a good choice, and not too filling. I can’t drive there though because my car is still in for repairs. Why is the repair shop taking so long? I should have listened when David said to check for reviews online before choosing a place. I should text David later to see how he is. He’ll think I’m mad at him if I don’t. I guess I’ll just have to walk to the shop.”
James Joyce and William Faulkner are two of the most well-known writers to have regularly used the stream-of-consciousness writing style.
Epistolary writing uses a series of documents, such as letters, diary entries, newspaper articles, or even text messages to tell a story. They don’t have a narrator, there’s just whoever purportedly gathered the documents together. This writing style can provide different points of view because a different person can be the author of each document.
Well-known examples of epistolary writing include the novels Dracula (written as a series of letters, newspaper articles, and diary entries) and Frankenstein (written as a series of letters).
Expository Writing
You’ll find this style in textbooks or academic journal articles. It’ll focus on teaching a topic or discussing an experiment, be heavy on facts, and include any sources it cited to get the information. Academic writing often assumes some previous knowledge of the topic and is more focused on providing information than being entertaining, which can make it difficult to read and understand at times.
Business writing refers to the writing done in a workplace. It can include reports, memos, and press releases. Business writing typically has a formal tone and standard formatting rules. Because employees are presumably very busy at work, business writing is very concise and to the point, without any additional flourishes intended to make the writing more interesting.
You’ll see this writing style most commonly in newspaper articles. It focuses on giving the facts in a concise, clear, and easy-to-understand way. Journalists often try to balance covering all the key facts, keeping their articles brief, and making the audience interested in the story.
This writing style is used to give information to people in a specific field, such as an explanation of a new computer programming system to people who work in software, a description of how to install pipes within a house for plumbers, or a guide to new gene modifications for microbiologists.
Technical writing is highly specialized for a certain occupational field. It assumes a high level of knowledge on the topic, and it focuses on sharing large amounts of information with the reader. If you’re not in that field, technical writing can be nearly impossible to understand because of the jargon and references to topics and facts you likely don’t know.

Descriptive Writing
Poetry is one of the most challenging styles of writing to define since it can come in many forms. In general, poems use rhythmic language and careful word choice to express an idea. A poem can be an example of descriptive writing or narrative writing, depending on whether it’s describing something or telling a story. Poetry doesn’t need to rhyme, and it often won’t follow standard grammatical or structural rules. Line breaks can, and often do, occur in the middle of sentences.
Persuasive Writing
Copywriting.
Copywriting is writing that is done for advertising or marketing purposes. It’s attempting to get the reader to buy whatever the writer is trying to sell. Examples of copywriting include catalogs, billboards, ads in newspapers or magazines, and social media ads.
In an attempt to get the reader to spend their money, copywriters may use techniques such as descriptive language (“This vanilla was harvested from the lush and exotic island of Madagascar"), exciting language (Stop what you’re doing and learn about this new product that will transform your life!”) and exaggeration (“This is the best cup of coffee you will ever taste!”).
Opinion
People write opinion pieces for the purpose of stating their beliefs on a certain topic and to try to get readers to agree with them. You can see opinion pieces in newspaper opinion sections, certain blog posts, and some social media posts. The quality of opinion writing can vary widely. Some papers or sites will only publish opinion pieces if all the facts in them can be backed up by evidence, but other opinion pieces, especially those that are self-published online, don't go through any fact-checking process and can include inaccuracies and misinformation.
What If You’re Unsure of a Work’s Writing Style?
If you’re reading a piece of writing and are unsure of its main writing style, how can you figure which style it is? The best method is to think about what the purpose or main idea of the writing is. Each of the four main writing styles has a specific purpose:
- Descriptive: to describe things
- Expository: to give facts
- Narrative: to tell a story
- Persuasive: to convince the reader of something
Here’s an example of a passage with a somewhat ambiguous writing style:
It can be tricky to determine the writing style of many poems since poetry is so varied and can fit many styles. For this poem, you might at first think it has a narrative writing style, since it begins with a narrator mentioning a walk he took after church. Character + plot = narrative writing style, right?
Before you decide, you need to read the entire passage. Once you do, it’ll become clear that there really isn’t much narrative. There’s a narrator, and he’s taking a walk to get a birch from another man, but that’s about all we have for character development and plot. We don’t know anything about the narrator or his friend’s personality, what’s going to happen next, what his motivations are, etc.
The poem doesn’t devote any space to that, instead, the majority of the lines are spent describing the scene. The narrator mentions the heat, scent of sap, the sound of frogs, what the ground is like, etc. It’s clear that, since the majority of the piece is dedicated to describing the scene, this is an example of descriptive writing.

How Can You Develop Your Own Writing Style?
A distinctive writing style is one of the hallmarks of a good writer, but how can you develop your own? Below are four tips to follow.
Read Many Different Styles of Writing
If you don’t read lots of different kinds of writing, you won’t be able to write in those styles, so before you try to get your own writing style, read different writing styles than what you’re used to. This doesn’t mean that, if you mostly read novels, you suddenly need to shift to reading computer manuals. Instead, you can try to read novels that use unreliable narrators, stream-of-consciousness writing, etc.
The more you read, the more writing styles you’ll be exposed to, and the easier it’ll be able to combine some of those into your own writing style.
Consider Combining Multiple Types of Writing Styles
There’s no rule that you can only use one style for a piece of writing. In fact, many longer works will include multiple styles. A novel may be primarily narrative, but it can also contain highly descriptive passages as well as expository parts when the author wants the readers to understand a new concept.
However, make sure you don’t jump around too much. A paper or book that goes from dense academic text to impassioned plea for a cause to a story about your childhood and back again will confuse readers and make it difficult for them to understand the point you’re trying to make.
Find a Balance Between Comfort and Boundary-Pushing
You should write in a style that feels natural to you, since that will be what comes most easily and what feels most authentic to the reader. An academic who never ventures outside the city trying to write a book from the perspective of a weathered, unschooled cowboy may end up with writing that seems fake and forced.
A great way to change up your writing and see where it can be improved is to rewrite certain parts in a new writing style. If you’ve been writing a novel with narrative voice, change a few scenes to stream-of-consciousness, then think about how it felt to be using that style and if you think it improved your writing or gave you any new ideas. If you’re worried that some writing you did is dull and lacking depth, add in a few passages that are purely descriptive and see if they help bring the writing to life.
You don’t always need to do this, and you don’t need to keep the new additions in what you wrote, but trying new things will help you get a better idea of what you want your own style to be like.
The best way to develop your own writing style is to expose yourself to numerous types of writing, both through reading and writing. As you come into contact with more writing styles and try them out for yourself, you’ll naturally begin to develop a writing style that you feel comfortable with.
Summary: The 4 Different Styles of Writing
There are four main writing styles, and each has a different purpose:
If you’re struggling to figure out the writing style of a piece, ask yourself what its purpose is and why the author wants you to read it.
To develop your own writing style, you should:
- Read widely
- Consider mixing styles
- Balance writing what you know and trying new things
What's Next?
Literary devices are also an important part of understanding writing styles. Learn the 24 literary devices you must know by reading our guide on literary devices.
Writing a research paper for school but not sure what to write about? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Are you reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Joni M. Fisher
Award winning author, types of articles.
by Joni M Fisher | Jul 27, 2015 | Craft of Writing , Journalism | 2 comments
Editors categorize articles by type, so it helps to know these types by name so you speak the same language as the editor. The types are: Hard News, First Person Article, Opinion Piece, Informational or Service Piece, How-To Article, Personality Profile, and Think Piece. Since most Hard News articles are assigned to full-time staff, we will skip this type of article. Let’s examine the characteristics and differences of the remaining types of articles for freelancers to use to break into the market.
FIRST PERSON ARTICLE
First person articles come from personal experience and are traditionally written in first person. They can be sold as feature articles or as essays, depending on their length and newsworthiness. Characteristics of a first person article with high market value:
- 750-1500 words
- setting-specific sensory details (taste, touch, smell, sight, sound), history
- characters are vivid, newsworthy, memorable, interesting, odd
- dialogue clearly reveals the unique character of the author
- details a turning point-realization, discovery, or change in one’s life
- voice is fresh, audacious, trustworthy, accurate, funny, or full of attitude
- states its purpose in first line or paragraph to hook the reader. Example: I had to teach my child to rebel and to question authority for his own safety.
Sources of first person articles and essays: Memory What unusual, unique experience or perspective can you offer? How did this event affect you? What recently triggered this memory? How can you relate your experience to others? Skill/talent Do I have a skill or talent that isn’t common or do I lack a skill everyone else seems to have? Examples: a male nanny, a woman pilot. The art of doing something well sets the skilled above the rest and this essay will explore the tell-tale signs that separate the novice from the expert. Or it could go the Dave Barry route, as a humorist who commentated on the Olympics, and show a klutz attempting something far out of his league. Comparison Why does everyone (speak Spanish, wear a size 5, whatever) but me? If only I had known then what I know now…. Compare the before and after of an experience, training, or change. Opinion Take a topic or event in the news and present the unpopular or neglected point of view. Example: Why does the media accept male bashing as funny but would scream like monkeys if the same joke were aimed at women? What makes you mad? What makes you laugh? What do you value? Dig deep to explore your answer. The reasons for your particular opinion need to be anchored and detailed from your personal experience. Are you an expert on this topic? Get to the WHY factor of your opinion on the topic. Observation Trends, behaviors, fashions. Go non-politically correct in the politically correct world. Go against type. See from a new perspective. Example: What happened when I took my daughter to a hockey game when neither of us understood the sport. What details capture the subject? What is the first impression? The second? My all-time favorite first-person article is Rick Reilly’s “On a Wing and a Prayer” that appeared in Sports Illustrated . In it he describes his thrill ride in an F-14 Tomcat. I double dare you not to laugh as this civilian, non-pilot describes his ride. Take a few minutes to read this masterpiece by clicking on his name above. To get ideas for essay and first person articles, try this exercise: write as quickly as possible at least 5 things you do well, 5 things you have strong opinions on and 5 memories from childhood. Pick something from this list and write. Now. The following example sources buy First Person Articles from new writers: The Christian Science Monitor seeks “upbeat, personal essays from 300 to 900 words” and pays $75-$160 on publication. Aim for humor and heartfelt personal stories. See their guidelines: http://www.csmonitor.com/aboutus/guidelines and read online archives for their tone and subject matter. Underwired is a website that seeks women’s personal essays of 800-1200 words. See their monthly themes so your submission suits the theme. They pay $100 per essay. See their guidelines: http://uwmag.com .
OPINION PIECE
An Opinion Piece or opinion essay is less personal than the First Person Article, but the piece still needs a tight focus. Writing about an entire industry will not set your writing apart from the bulk of writing on the topic. Find your niche, your sub-category. Narrow your focus by asking the journalistic questions: Who, What, When, Where, Why and How? To that, I add one more question that my editor in college always asked—“Who cares?” If the topic is interesting only to you, don’t expect editors to mail you a contract. Look at your essay or article from the reader’s point of view. The main question in the reader’s mind is—why are you qualified to render an opinion? We all have opinions, but why should anyone read yours? If you’re an expert on this topic, be sure to state it up front for the reader. Let’s say you want to write an opinion piece on weight problems in America. Are you a dietitian? A physician? An athletic coach? A chronic dieter who has tried all the fad diets? Give your opinion the weight it deserves by showing your credentials. If you plan to write often on a particular topic, and build a readership, consider syndication. Essayists can become syndicated and sell their work in multiple newspapers. Whether you write etiquette advice like Miss Manners, humor like Dave Barry, or political analysis like Charles Krauthammer, syndication means you write one essay per week and collect checks from multiple sources. The key is to find your true topic and voice and spread the word. Though Pulitzer-Prize winning humorist Dave Barry was employed by the Miami Herald , his essays were published simultaneously in newspapers around the country because the papers did not have competing readership. Perhaps in time, blogs will replace syndication, but many writers continue to profit from syndication in print media. It takes time to build a readership or following, but syndication multiplies the income you receive from every piece you write. Among the highest paying markets for individual essays and opinion pieces are:
- Contests. There are a few online directories of contests. Here is one: Poets & Writers
- The Smithsonian’s last page. ( Quirky contemporary culture.) You have to read back issues to understand what they buy.
INFORMATION OR SERVICE PIECE
An informational or service piece builds the reader’s knowledge on a specific subject. Always interview an expert or two to get a broader view of the subject. Consumer Reports magazine, for example, is all about comparing different brands of a product so the buyer can understand which features are available and how to price each feature. Which features are gimmicks? Which ones make the product valuable in the short run, in the long run? Consider writing for industry specific publications or publications devoted to a specific organization, club or group. Many of these smaller publications yearn for writers. They might not pay as well as the national magazines, but they can help you build readership and clips. Clips are basically examples of your published work. Start a file of them. Characteristics of an Information or Service Piece:
- Tend to be fact-driven and educational.
- Present quotes from experts. If controversial, present experts from opposing views.
- Inform readers about things that will affect their lives. This series is Informational—“10 Things You Need to Know About Writing for Magazines”.
- Show a fact or trend.
- Dispel rumors and misunderstandings.
- Revisit history with a then/now comparison.
- Have catchy titles like: Myths about ___. Secrets of ___. An Insider’s View of ___. Six Ways to___.
Always relate statistics or any enormous number with an image or put the number in human terms. For example, how can a writer make a number like a billion memorable or describe it in simple, human terms? A billion minutes ago, Jesus was alive. Pick up a copy of Reader’s Digest and just read the titles of the articles. Just so you know, Reader’s Digest pays well, but they buy all rights. This makes reprints impossible and can strangle your ability to write similar articles on the same topic. Lest the gentle reader believe that these types of articles are cut and dried and must forever remain separate entities, please note that the types can be, well, combined, mixed, or crossbred. I published a humor essay “Rocket Mom: Dreaming of the Right Stuff” that presented a comparison between the Space Shuttle and the average SUV in terms of mileage, features, speed and such. The structure of the essay mimicked a service piece, but the tone was purely first person. Here’s the link: https://jonimfisher.com/Rocket-mom/ .
HOW TO ARTICLE
How To Articles present a step-by-step explanation of a process, like wiring a home theatre. An entire series of books is built around the concept of explaining processes and topics to industry outsiders– Electronics For Dummies, SEO For Dummies , etc. Again, if you are an expert or quote an expert, show the reader your credentials.
- Assume the reader does not speak the special language of the trade or industry.
- Assume the reader is inexperienced and reads at the high-school level. Even if you write for an adult, educated readership, your readers will come from a variety of backgrounds, and some may read English as a second language. Also, keep in mind that people read comfortably four grades below their last year of formal education.
- Break your subject into its main points, explaining what each is and how it is accomplished.
- Note any points of common misunderstanding and mistakes to avoid.
- Use a breezy, straightforward, conversational tone.
- Make special terminology clear and memorable. My husband is a surgeon and a pilot, but if he decided to take up sailing, he wouldn’t know his aft from his halyard.
- Use anecdotes to illustrate points. Some How-To articles organize the steps with acronyms.
- Include charts, graphs, or artwork to illustrate your points.
- Narrow the focus of your article and give it an inviting title. Example titles: 7 Ways to improve your skin, 30 Minutes a Day to Ward Off A Heart Attack, or You Can Learn Magic Tricks at Home.
The How To approach can be hysterical when applied to a complex subject. Have you read the book 8 Simple Rules for Dating My Teenage Daughter ? You could also write a How-Not-To article.
PERSONALITY PROFILE
A personality profile should balance facts with an interview of subject to show this person’s character and personality and explore public image versus up-close impressions. To be accurate, it also requires interviewing friends, colleagues, family—those who know the person best. What has this person done to merit attention? Is this a future Nobel Laureate? Unsung hero? Political candidate? Sports figure? Nail down why readers would find this person interesting or notable. Be careful about choosing an anti-hero, a criminal will be likely to use publicity for revenge or to attempt to sway public opinion against the facts. Celebrities get jaded and tend to avoid journalists who want to interview them unless they have a new project on the horizon. They will want to deflect attention from themselves and promote their project. They will also tend to avoid unknown interviewers/writers. Say, for example, you want to do a profile on an actor. Rather than focusing on his life in film and television, how about focusing on why he became the spokesman for a charity or why he took up flying as a hobby? People are more open to discussing what they love than who they are.
THINK PIECE
Superb site you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any community forums that cover the same topics talked about here? I’d really like to be a part of online community where I can get comments from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Bless you!
Try http://hiveword.com/wkb/search this is a search site for writer’s websites and groups.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- 2024 Christian Indie Awards Recognize East of Evil
- Reading as a Writer
- Resources for the Serious Writer
- Wishing Shelf Book Awards Finalist
- East of Evil Shortlisted for Murder and Mayhem Awards
Recent Comments
Pin it on pinterest.

Writing for Magazine: Types, Characteristics, Difference, Writing Styles
- Post author: Anuj Kumar
- Post published: 10 August 2021
- Post category: Journalism
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Table of Contents
- 1 What is Magazine?
- 2 Characteristics of Magazines
- 3.1 Size and Appearance
- 3.2 Content
- 3.4 Design and Layout
- 3.5 Target Audience
- 3.6 Readability
- 3.7 Display Ads
- 3.8 Visual Strength
- 3.9 Shelf Life
- 4 Basics of Magazine Writing
- 5.1 Tell a Story
- 5.2 The Beginning
- 5.3 The Middle
- 5.4 The Ending
- 5.5 Extra Credit
- 6.1 Narrative Writing
- 6.2 Serialised Narrative Writing
- 6.3 Descriptive Writing
- 6.4 Persuasive Writing
- 6.5 Imaginative Writing
- 6.6 Visual Writing
- 6.7 Multiple Inverted Pyramid
- 7.1 General Interest Magazines
- 7.2 Special Interest Magazines
- 7.3 Farm Magazines
- 7.4 Sports Magazines
- 7.5 Business Magazines
- 7.6 Environmental Magazines
- 7.7 Entertainment Magazines
- 7.8 Automobile Magazines
- 7.9 Children’s Magazines
- 7.10 Women’s Magazines
- 7.11 Men’s Magazines
- 7.12 Literary Magazines
- 8.1 What is the difference between newspaper and magazine?
- 8.2 What are the basics of magazine writing?
- 8.3 What are the types of magazines?
What is Magazine?
A magazine is a publication that is issued periodically. It generally contains essays, stories, poems, articles, fiction, recipes, images, etc. Magazines are directed at a general and special audience, often published on a weekly or monthly basis.
A magazine can also be considered as a cabinet of curiosities; i.e. a display case in which interesting, unusual, and occasionally ‘eccentric’ objects are collected and displayed as a conversation piece or an expression of the writer’s wide-ranging interests or tastes.
The readers are treated with a fascinating, mind-expanding, and unique set of wonders they had never dreamt of.
Characteristics of Magazines
Characteristics of magazines While popular magazines provide broad overviews of topics, scholarly journals provide in-depth analysis of topics and report the findings of the research, and trade magazines report on industry trends, new products, or techniques.
A popular magazine that caters to the general public uses non-technical language. The contents of these magazines include interviews, general interest articles, and various types of features. They usually cover a wide range of topics based on research, source comments, and generalizations.
Articles are usually written by a staff writer or a journalist; in some cases, interesting articles of freelancers are also encouraged. They generally contain many interesting and sometimes sensuous photographs to attract readers.
In general, magazine articles are easy to read, fairly brief in length, and may include illustrations or photographs. Magazines don’t necessarily follow a specific format or structure in writing the articles.
Its attractive appearance, eye-catching cover pictures, and illustrations on quality paper make it more appealing to the reading public. Magazines also contain many colorful and impressive advertisements.
Difference between Newspaper and Magazine
Newspapers and magazines are two important forms of print media that are read by millions of people around the world. Some of the most common differences between newspapers and magazines can be seen through their size and appearance, content, style, target audience, design and layout, readability, and advertisements.
Let’s discuss the difference between newspapers and magazines :
Size and Appearance
Design and layout, target audience, readability, display ads, visual strength.
Newspapers are bigger in size and they can be folded. A story above the middle fold on the front page of a newspaper is considered the most important story and one that appears just below the fold is generally the second most important story.
If there are many important stories on a newspaper page, then the treatment given to a story will decide its importance: such as photos/graphics with a more important story and with no visual elements in other stories. The eyes of a reader can scan an entire page without a fold.
A magazine tends to have a “book-type” size while the newspaper is really meant to be spread at arm’s length for the reader to grasp its contents.
Newspapers deal with reports clearly, briefly, and objectively. A magazine writer focuses on specialized topics and current issues of public interest. Newspapers remain the primary source of authentic, reliable, and latest information about what is happening around the world and even in one’s own locality.
But magazines are not sources of fresh content to the extent of publishing the breaking news. However, its content is specialized and recent in nature. Thus, we have various magazines such as entertainment, science, share markets, sports, glamour, and movies.
Newspapers are more versatile in content and hence they never fall short of content as there is always something happening in different parts of the world. On the other hand, magazine content is always based on the liking of readers of diverse backgrounds.
Newspapers focus on catchy headlines to create interest in the reader. Many reporters and editors are employed in newspapers to prepare specialized reports and interpretative articles. But magazines have lesser staff. A magazine writer has more freedom to express or has more room for subjectivity.
She/he has the tenacity and freedom to express things in a creative manner. It further enhances the writer’s mastery of the expression by imploring these seemingly circular methods of self-expression.
The newspaper writer on the other hand is compounded to a somewhat strict, strong, and straight writing mostly based on facts and figures.
Newspapers are known for their simple layout and design . While the content is usually in black and white, the style and font are fairly consistent throughout. Magazines have much more visual expression than newspapers because magazines are not subject to one consistent layout.
Magazines use lots of colors, and different types and sizes of fonts, and break up their articles with images and colors.
The main difference between a newspaper and a magazine is that newspapers are written for a general audience , while magazines are for specific types of audiences. A magazine attracts varied target audiences . A newspaper’s target audience is determined by its geography and its focus is broad.
Here, the editor determines what the people should read, what they want and desire. In contrast, a magazine’s target audience is determined by demographics and interests. (‘Demographics’ means the physical characteristics of the individual such as race, gender, interest, education level, etc.).
News stories are usually written in a matter-of-fact style. But magazines employ colorful language so as to make the content enjoyable.
The newspaper readability level corresponds to a difficult classification built around tight grammatical and syntactical rules. Linguistic subjectivity which relies on expressive adjectives enhances the readability of magazines.
Though magazines and newspapers both provide readers with information, their format and appeal differ considerably. Magazines are more advertiser-driven than newspapers. Newspapers are slightly different in this regard. Newspapers are driven more by readership than by advertisers.
They focus more on catchy headlines in an effort to capture the reader’s interest and get him to read the entire story. Part of the reason for this is that people often associate what they read with an ad they see near the piece. Our minds just naturally attach and group objects and associations together.
Advertising giants know this and place their ads exactly in proper alignment with stories and articles they want to associate with their products on those specialized magazines.
The visual strength of magazines is enhanced with the effective use of color in magazines. In magazines, we can also use a color background whereas newspapers normally have only a white background. This means you can present more attractive color contrasts in your magazine visuals.
Another strength of magazines is a longer life . Newspapers are read only once and then discarded. In contrast, magazines are commonly kept for several days, weeks, or months in magazine racks which provides for possible repeat reading.
Magazines use some of the highest-quality paper and ink to produce a visually appealing product meant to be kept and read longer than a newspaper. Magazines tend to focus on entertainment pieces, and provide how-to-do articles and features about certain subjects within their chosen marketing niche.
Magazines also have advertisements taking up large amounts of page space to balance the cost of production.
Basics of Magazine Writing
The joy of magazine writing lies in its variety. Anything from a celebrity interview to a food recipe can be the topic for magazine articles and this variety demands versatility. Coverage of events for magazines offers challenges as well as opportunities to journalists.
A creative flair and innovative skill may help in producing masterpieces and also in creating an everlasting impression on the reader’s mind. The language used depends, to a certain extent, on the objective of the magazine.
Literary style is generally preferred by the magazine press. Thus magazine writing requires a different way of thinking, writing, and structuring. Effective magazine writing is accessible, interesting, lively, colorful, grabbing, and relevant.
Whatever be the type of publication a journalist writes for, the basic approach is the same: write for your readers. However, good writing for magazines depends on the adherence to some well-known guidelines.
Though there are not many lengthy rules, there are guidelines a magazine writer should follow to produce a stylish copy. The most important among them can be summarized as follows:
- Know whom you are writing for, their interests and concerns.
- Know what you want to say and achieve.
- Always prefer the concrete to the abstract.
- Be accurate and readable.
- Have an attention grabbing intro.
- Spend considerable time thinking about fresh ways to ap-proach the subject.
- Keep materials and sentences short.
- Promote a vibrant style.
- Know the publication’s editorial policy to achieve your di-rection.
Magazine writers often develop a strong personal style that is opinionated, anecdotal, and gossipy while developing the content. The quality of the content and style are equally important. The wordplay and tricks of style make the piece entertaining to read.
How to Structure Magazine Article
As soon as you’re ready to write a magazine article, you need to think about structure. With magazine articles, you can move beyond the inverted pyramid style of news by scattering important points throughout the article .
Tell a Story
The beginning, extra credit.
The important thing to remember is that you’re telling a story to your readers. That means you need a beginning, a middle, and an end. It also means you need to think about where you’re taking your reader and create a logical path to that endpoint.
To get people to read your article, you need to find a way to grab them. For example, you can begin an article with a quote or an anecdote from a person’s life. However, you can also set the scene or use anything that will attract the reader’s attention.
With most magazine articles, you talk to a person or people. People like reading about other people, so if your interviewee says something good, use a quote rather than the reported speech. This makes your magazine article more interesting.
Finally, end with a bang. This could be in the form of an important point, a revelation, or another anecdote or quote. The idea is to satisfy your reader and to get that reader interested in your other writings as well.
When you do research for an article, you often have information left over that didn’t make it into the main piece. Don’t get rid of this. Use it to create a sidebar or table (editors will love this), or as the starting point for another article.
Magazine Writing Styles
Let us now discuss some of the common styles used by the magazines in their presentation of articles:
Narrative Writing
Serialised narrative writing, descriptive writing, persuasive writing, imaginative writing, visual writing, multiple inverted pyramid.
Narratives are works that provide an account of connected events. In a narrative style, you’ll need to tell a story in such a way that the audience learns a lesson or gains insight. Narrative writing is a type of writing in which the author places himself as the character and leads you to the story.
Here, is a narrative, a story or event is told through characters and dialogues. Narrative writing has definite and logical beginnings, intervals, and endings. Narrative writing uses many literary techniques to provide deeper meaning for the reader and it also helps the reader use his / her imagination to visualize situations.
Literary techniques include metaphors, similes, personification, imagery, hyperbole, alliteration, back story, flashback, flash-forward, foreshadowing, and narrative perspective or point of view.
In this style, you cannot find out what’s going to happen next. You have to wait. Here the writer really understands how to hold a reader by his/her side and make them stick on with the piece till the end. That’s the skill absolutely essential for this style of writing.
The first and most essential quality of a serial narrative is that it has to be immensely, intensely, and inescapably readable. They should have a powerful pull on all readers with the power of a delicious sense of enforced writing.
Descriptive writing focuses on describing a character, an event, or a place in great detail. It is sometimes poetic in nature in which the author specifies the details of the event rather than just the information of that event.
In a descriptive style, the writer needs to describe a person, object, or event so vividly that the reader feels like s/he could reach out and touch it. The writer attempts to convey as many of the senses related to the subject as possible for a clearer understanding of what is being described.
Descriptive writing has a unique power and appeal, as it evokes sensory description through sights, smells, sounds, textures, and tastes through the text to your reader.
This writing revolves around convincing someone. Persuasion requires great skill and effort to convince your readers to endorse your opinion or viewpoint. You write with the sole objective of persuading your readers. Persuasive writing utilizes the power of words to confidently and passionately convey a very important matter.
Such writings are usually written with precision and authority. Persuasive texts are set out to argue and prove a case by presenting ideas that follow a logical progression. It aims to convince a targeted audience of the validity of a viewpoint on an issue by presenting logical arguments.
Imaginative writings present ideas, issues, and arguments in an imaginative and credible way through the description, characters, settings, figurative language, the five senses, etc. Imaginative writing assumes the form of fiction, specifically short stories.
Depending on the idea, the imaginative article can discuss anything from space travel to civil rights. Because of this wide variation, some imaginative pieces require a very serious response, while others invite a much more light-hearted, fantastic one.
Usually, imaginative write-ups start with a hypothetical situation and ask how you would respond to it. It should be credible and plausible and must convey information through description and figurative language. Add sensory details and realistic conversation.
Also include imaginary interactions with the characters. The characters should be dynamic in nature and they should see things differently or act differently by the end of the story. Narrate and describe events, characters, and situations.
Visual writing is a good language for storytelling in any medium. It focuses on the mind, and distinctive details from the intricately interconnected experiences of the individual. Visual writing creates depth, quality, and pacing.
The visual style isn’t an extension of the writing, but it has to be embedded into the writing in a way that the reader may not even be aware of its presence. This means the visual style is not about adding more but enriching an already existing text.
Visual communication engages meaningful experiences and feelings within individuals through richly embedded image symbols which are conveyed either directly through text or indirectly through other senses.
In the field of magazine journalism , the term ‘multiple inverted pyramid approach’ refers to a style of writing which informs and entertains the readers through self-sufficiently built plots of information, each of which may be arranged in the form of an inverted pyramid.
The fact is that the idea of the whole story is spilled in the first paragraph itself. The reader can decide whether to continue reading the details or to go into something else. But even if the reader stops at a certain point, this form of writing may provide some essential facts to the readers.
Types of Magazines
Today, there are thousands of magazines worldwide. They inspire, inform, educate and entertain audiences across the globe. Nearly 600 years after the advent of the printing press, magazines continue to change the nature of things throughout the world.
The major types of magazines are briefly explained below:
General Interest Magazines
Special interest magazines, farm magazines, sports magazines, business magazines, environmental magazines, entertainment magazines, automobile magazines, children’s magazines, women’s magazines, men’s magazines, literary magazines.
This type of magazine is published for a wider audience to provide information, in a general manner and the focus is on many different subjects. The main purpose of a general interest magazine is to provide information for the general audience. No background knowledge or expertise is assumed.
Articles usually provide broad coverage of topics of current interest. They are written by journalists, freelance writers, or staff correspondents of the magazine. These periodicals may be quite attractive in appearance, with articles often heavily illustrated with photographs.
The language of these publications is geared to any educated audience. There is no especially assumed target audience. Mere interest and a certain level of intelligence are only required to read and enjoy such magazines.
These are usually published by commercial enterprises, though some are published by professional organizations. Examples of general-interest periodicals are Time, Newsweek, Outlook, India Today, and The Week.
Special interest publications are magazines directed at specific groups of readers with common interests. Most special interest magazines cater to any specific interests or pursuits. For instance, there are magazines that cover sports, news, fashion, business, music, and so on.
While some attempt to cover all aspects of a broad subject, others are concerned only with a particular element of the general subject. Sports Illustrated, for example, contains stories on practically any sport, but Golf Digest carries only stories related to golf.
Other special interest publications find their audiences through different demographic segmentation. There are magazines published primarily for men (Field and Stream, Gentlemen’s Quarterly (GQ), etc.), women (Woman’s World, Grihalekshmi, Vanitha, etc.), boys (Boys’ Life) and girls (Teen Vogue). Specialized periodicals also serve most professions, industries, and organizations.
These are magazines featuring news and information pertaining to the agricultural sector. It is a resource for farmers and vendors of farmers’ markets.
There are various farm magazines that contain information about various farming equipment, farming practices, ideas and technology suitable to small and big farms, raising unusual livestock, growing high-value crops, direct marketing of their products to bring in more income, the latest techniques for growing bountiful, nutritious crops and many more articles that could provide information to the farmers who are their target audience.
They also share the success stories of artisans and farmers, on government policies and programs, and also about how to promote their business by reaching new customers and develop value-added products.
A sports magazine usually features articles or segments on sports comprising of many photographic images and illustrations. Some magazines concentrate on all general sports news and related issues while others concentrate on specific sports or games such as football, baseball, athletics, etc.
But the common aim of any sports magazine is to take fans inside the game and provide a mix of columns, features, profiles of their favorite players, scores, statistics, and analysis of the game.
News and information about sports, reviews, interviews, expert advice, player profiles, season previews, predictions, and pre-game analysis as well as quality photos are some of the main ingredients in a sports magazine.
Most of these magazines are dedicated to the dissemination of information related to particular business areas like accounting, banking, finance, international business, management , marketing and sales, real estate, small business, etc.
They explore the latest news and reviews on current trends in the world of business. Business magazines offer readers an unparalleled look at business and economic news, with incomparable access to business drivers around the globe.
It also provides the most recent news about trends and developments in global business, financial markets, and personal finance.
The aim of this type of magazine is to provide information about environmental issues and to share ideas about our very diverse and dynamic environment so that readers can live more sustainable lives and connect themselves to ideas and ongoing efforts for change, as well as for building a more just and sustainable future.
They cover everything environmental – from the big issues like climate change, renewable energy, toxins, and health to the topics that directly impact the readers’ daily lives: population, poverty, consumption, and the environment in general.
In-depth reviews of major policy reports, conferences, environmental education initiatives, environmental reports, and photos from around the world with an emphasis on human involvement in an environmentally changed scenario are some of the highlighted features of environmental magazines .
Entertainment magazines are usually glossy in nature and provide entertainment. They usually carry news, original stories, scandals, gossips, and exclusives about celebrities in various entertainment fields such as film, music, TV, fashion, and related similar areas of the industry.
Cultural criticism, beauty, lifestyle trends, and shopping guides also find expression in such magazines. As its main focus is on celebrity fashion or lifestyle, it is graphically rich in nature, featuring many photographs or other images.
Automobile magazines offer a rich and varied examination of the automotive universe in all its forms, illustrated with vibrant photography. They present interesting automotive news in the industry and celebrate the automotive lifestyle and its personalities, past and present.
It also offers insights into emerging trends in the industry and also creates images of whatever comes next in the written and visual form.
Updates in the motor vehicle arena such as newly arrived cars and bikes, contemporary style of vehicles, recommendations to buyers, reviews of newly launched vehicles are some of the attractive elements in these magazines.
The main aim of children’s magazines is to engage children to learn new things through entertainment and to provide memories that last a lifetime. The content is delivered through colorful images, read-aloud stories, and various fun activities that both the parent as well as the child can enjoy together.
Children’s magazines are designed to set young children on the path to becoming curious, creative, caring, confident individuals through reading, thinking, and learning with a wide variety of stories, puzzles, crafts, games, and activities. 3D children’s magazines are now on sale in Kerala.
Women’s magazines play a variety of roles as educators, family counselors, beauty specialists,s and lifestyle experts. Women’s magazines, on many occasions, have become an arena for debate and promotion of education for women.
The personal nature of the content also makes it a unique material specifically for women. The gorgeous photographs, engaging designs, and innovative styles make them attractive.
The outlook of a women’s magazine is an intelligent perspective that is focused on personal style – the way women actually look, think and dress. They reflect the spirit of today’s woman – changing with the times, moving with trends, styles, and fashion.
Men’s magazines bring the latest style tips, travel guides, lifestyle improvement, offering advice and information useful to men on a variety of topics including money , health, sports, cars, adventure, politics, and so on. Men’s magazines use masculinity as a marketing tool.
A literary magazine devoted to literature, usually publishes short stories, poetry, essays, literary criticism, book reviews, biographical profiles of authors, interviews, and any content related to literature.
Its aim is to promote literature, encompass an overall sense of the word, preserve indigenous literature and provide a platform for creative writers through its articles.
FAQs About Writing for Magazine
What is the difference between newspaper and magazine.
These are the following points of difference between newspapers and magazines: 1. Size and Appearance 2. Content 3. Style 4. Design and Layout 5. Target Audience 6. Readability 7. Display Ads 8. Visual Strength 9. Shelf Life.
What are the basics of magazine writing?
The following are the magazine writing styles: 1. Narrative Writing 2. Serialized Narrative Writing 3. Descriptive Writing 4. Persuasive Writing 5. Imaginative Writing 6. Visual Writing 7. Multiple Inverted Pyramid.
What are the types of magazines?
The following are the types of magazines: 1. General Interest Magazines 2. Special Interest Magazines 3. Farm Magazines 4. Sports Magazines 5. Business Magazines 6. Environmental Magazines 7. Entertainment Magazines 8. Automobile Magazines 9. Children’s Magazines 10. Women’s Magazines 11. Men’s Magazines 12. Literary Magazines.
Related posts:
- Mass Media and Society: Types, Characteristics, Functions
Written Communication: Definitions, Principal, Types, Advantages and Disadvantages, Ways to Improve
Oral communication: definitions, importance, methods, types, advantages, and disadvantages, mass communication: definitions, functions, characteristics, types, importance, and process.
- Downward Communication: Definitions, Types, Purposes, Objectives
Advantages and Disadvantages of Oral Communication
- 7 Types of Barriers of Communication
- 17 Ways to Overcome Barriers to Communication
8 Functions of Mass communication
- 8 Elements of Mass Communication
10 Characteristics of Mass Communication
- Scope of Business Communication
- Human Communication: Meaning, Origins, Stages, and Types
- Types of Folk Media
Impact of Digital Media
You might also like.

Upward Communication: Definitions, Importance, Methods. and Important Media

History of Advertising in India: Effects, Areas, Purpose of Advertising

Business Communication: Definition, Types, Importance, 7 Cs, Purpose, Barriers

Informal Communication: Types, Characteristics, Advantages, and Limitations
Media of communication: definitions, types and examples.

Nonverbal Communication: Principles, Functions, Types, and How to improve

Interpersonal Communication: Elements, Importance, Principles

Verbal Communication: Advantages and Disadvantages, Functions, and Types

Classification of Advertising Based on Area Coverage, Audience, Media, Functions

Role of Advertising: Characteristics, Advantages, Disadvantages, Negative Effects of Advertising

Organizational Communication: Types, Directions, Importance

Principles of Communication: 7 Cs of Communication
10 functions of communication.

- Entrepreneurship
- Organizational Behavior
- Financial Management
- Communication
- Human Resource Management
- Sales Management
- Marketing Management

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

23 Popular Magazines That Need Freelance Writers
Here are some magazines that may occasionally accept both writing and artwork/photography submissions. Some of these are very well known, while others are fairly small.
You'll need above-average writing and photography skills to get your work accepted, and there might be a lot of waiting.
With this kind of work, you will spend a lot of time sending query letters to editors to see if they're even interested in an article before you write it, then more months to see if your article is up to their standards.
You might even need a decent portfolio of previous work to prove your professionalism before they'll even take you seriously.
BUT if you're willing to wade through all the upfront difficulty, the pay rates are fantastic, and getting articles published with these magazines can help your career in a big way!
Read on for a list of magazines that are currently accepting submissions.
Popular Magazines Looking For Freelance Article Submissions
Animals – pets.
- Animal Wellness Magazine – Welcoming unsolicited articles and story outlines. Articles may range in length from 500 to 1,500 words.
- Reptile Magazine – A monthly publication that caters to reptile and amphibian hobbyists. Pays about $200 for 2,000 to 2,500 words.
- The Bark – About life with dogs. Pays upon publication. On their contact page, choose “write for us” from the dropdown to send them a pitch.
- The Horse – A monthly magazine devoted to horse care. They prefer “how to” and technical topics.
- Tropical Fish Hobbyist – They accept both articles and photos. Guidelines listed on site.
Business – Career
- Family Business Magazine – Family Business Magazine publishes only five times a year — thus, the opportunities we offer are few and far between. We accept very few of the dozens of writer queries we receive every day.
- Working Money – About investing. Flat rate payment made upon publication, about $180.
Children – Young Adult
- ADDitude Magazine – This publication is for parents raising children who suffer from Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. They pay up to $200.00 per article.
- Fun for Kidz – They are looking for lively writing that involves an activity that is both wholesome and unusual. We are looking for articles around 500 words as well as puzzles, poems, cooking, carpentry projects, jokes, riddles, crafts, and other activities that complement the theme. They pay five cents a word for both fiction and non-fiction.
- Girl's Life – Girl's Life magazine will pay for your freelance articles, but pay amount is not listed.
- High Five – High Five (affiliated with Highlights for Children) will be accepting freelance submissions from May 15th to June 30th, 2024. They are most interested in stories and non-fiction.
- Pockets Magazine – For kids aged 6-12, Christian magazine offering fiction, scripture, puzzles, games, etc. Pays 25 cents a word for stories and $25 and up for other types of submissions.
- American Craft Magazine – They work primarily with experienced arts journalists who are able to write with depth and nuance, and value freelancers who can write for a general creative audience with clarity and insight. They pay $.50–$1.00/word, depending on the assignment.
- Threads Magazine – Bi-monthly, how-to magazine. Interested in articles about construction and embellishment techniques, materials, tools, and design. They claim to accept submissions from inexperienced writers and say that submissions do not have to be perfect. It is your know-how they are most interested in. Pay is not mentioned, but that doesn't mean they don't offer payment if they publish your work.
- Teacher Magazine – Teacher magazine may take your commentary submissions, but amount of pay is not listed.
- Family Fun – This publication is looking for articles about games and fun outdoor activities that families can enjoy. According their submission guidelines, they pay $1.25 per word. They require 850 to 3,000 words.
General Interest
- Reader's Digest – You can submit jokes to Reader's Digest. They pay $25 for any joke, gag, or funny quote, and $100 for any true funny story they publish.
- Cosmopolitan – This is one of the big-time women's magazines, with a long and prestigious history. You can submit articles through email, and will usually hear back from them within a month. Submitted articles for the print version earn $200.00 to $400.00. They also accept submissions for their online magazine, but they only pay $100.00 per article.
- Good Housekeeping – This well known publication allows for unsolicited submissions, but they're only looking for articles in certain very limited categories. Check their submissions page to see what they're accepting at any given time. The pay rate is reportedly around $1.50 per word.
Sci-Fi/Fantasy
- Analog Science-Fiction – Analog pays 8-10 cents per word for short fiction (up to approximately 20,000 words), 6 cents per word for serials (40,000-80,000 words), 9 cents per word for fact articles, and $1 per line for poetry.
Literary Fiction
- VQR – This is a high end literary journal. They publish poetry, short fiction, and certain kinds of non-fiction, including book reviews. They pay $200.00 each for poems. Over $1000.00 for short fiction, and around $500.00 for reviews.
- One Story – They publish short stories, strictly literary fiction. They won't accept anything that's been published elsewhere, and stories need to be between 3000 and 8000 words. Other than that, their only guideline is that the story must be very good. They pay $500.00 per story.
Rural Life/Homesteading
- GRIT Magazine – DO NOT try to write for GRIT if you know nothing about rural life, gardening or urban farming. They intend to be an authoritative and sometimes playful voice for rural lifestyle farmers and country or small-town dwellers.
If you have an interest in jumping into the higher end freelance writing market, the above links should give you a good set of starting points.
Looking For More Freelance Writing Gigs?
I have a big list of sites that list freelance writing leads here that you should check out.
FlexJobs is another great option. They post hundreds of remote job leads five days per week, all carefully screened and legit. And there are NO ads on the site! You can access their listings for $2.95 for 14 days.
Go here to check out FlexJobs .
Photo by Jess Bailey Designs: https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-eyeglasses-on-top-of-magazines-1007027/

Anna Thurman is a work at home blogger and mom of two. She has been researching and reviewing remote jobs for over 13 years. Her findings are published weekly here at Real Ways to Earn.
- Israel-Hamas War
My Writing Students Were Arrested at Columbia. Their Voices Have Never Been More Essential
O n April 30, 56 years after Columbia sent the police in to arrest student protesters who had taken over Hamilton Hall in protest of the Vietnam War—protests the school loves to promote—I was walking my 12-year-old daughter home after her choir performance. We had gone an extra stop on the subway because the stop at 116th, Columbia’s stop, was closed. Instead, we had to walk back to our apartment from the 125th stop. When we got within sight of Columbia, a line of dozens of police blocked our path. I asked them to let us through; I pointed to our apartment building and said we lived there. As a Columbia professor, I live in Columbia housing.
“I have my orders,” the cop in charge said.
“I live right there,” I said. “It’s my daughter’s bedtime.”
“I have my orders,” he said again.
“I’m just trying to get home,” I said.
We were forced to walk back the way we came from and circle around from another block. Luckily, our building has an entrance through the bodega in the basement. This is how I took my daughter up to her room and sent her to bed.
Read More: Columbia's Relationship With Student Protesters Has Long Been Fraught
A week earlier, I had brought some food for the students camping out on Columbia’s West Lawn and had met with similar resistance. Security guards asked whether I was really faculty; I had already swiped my faculty badge that should have confirmed my identity. They asked to take my badge, then they said I hadn’t swiped it, which I had, two seconds earlier, as they watched. They said their professors had never brought food to them before. I didn’t know what to say to this—“I’m sorry that your professors never brought you food?” They called someone and told them the number on my badge. Finally, they were forced to let me through. They said again that their professors had never brought them food. “OK,” I said, and walked into campus. I reported their behavior and never received a reply.
On April 30, after I had got my daughter to bed, my partner and I took the dog down to pee. We watched the protesters call, “Shame!” as the police went in and out of the blockade that stretched 10 blocks around campus. Earlier that day, we had seen police collecting barricades—it seemed like there would be a bit of peace. As soon as it got dark, they must have used those barricades and more to block off the 10 blocks. There were reports on campus that journalists were not allowed out of Pulitzer Hall, including Columbia’s own student journalists and the dean of the School of Journalism, under threat of arrest. Faculty and students who did not live on campus had been forbidden access to campus in the morning. There was no one around to witness. My partner and I had to use social media to see the hundreds of police in full riot gear, guns out, infiltrate Columbia’s Hamilton Hall, where protesters had holed up , mirroring the 1968 protests that had occupied the same building.
In the next few days, I was in meeting after meeting. Internally, we were told that the arrests had been peaceful and careful, with no student injuries. The same thing was repeated by Mayor Adams and CNN . Meanwhile, president Minouche Shafik had violated faculty governance and the university bylaws that she consult the executive committee before calling police onto campus. (The committee voted unanimously against police intervention .)
Read More: Columbia Cancels Main Commencement Following Weeks of Pro-Palestinian Protests
Then, Saturday morning, I got an email from a couple of writing students that they had been released from jail. I hadn’t heard that any of our students had been involved. They told me they hadn’t gotten food or water, or even their meds, for 24 hours. They had watched their friends bleed, kicked in the face by police. They said they had been careful not to damage university property. At least one cop busted into a locked office and fired a gun , threatened by what my students called “unarmed students in pajamas.”
In the mainstream media, the story was very different. The vandalism was blamed on students. Police showed off one of Oxford Press’s Terrorism: A Very Short Introduction . (This series of books offers scholarly introductions that help students prepare for classes, not how-to pamphlets teaching them to do terrorism.)
“I feel like I’m being gaslit,” one of my students said.
I teach creative writing, and I am the author of a book about teaching creative writing and the origins of creative-writing programs in the early 20th century. The oldest MFA program in the country, the Iowa Writers’ Workshop, was funded by special-interest groups like the Rockefeller Foundation and, famously, the CIA, and was explicitly described by director Paul Engle as a tool to spread American values.
Read More: 'Why Are Police in Riot Gear?' Inside Columbia and City College's Darkest Night
The way we teach creative writing is essential because it shapes what kinds of narratives will be seen as valuable, pleasurable, and convincing. Today’s writing students will record how our current events become history. One of the strategies Columbia took with its police invasion was to block access of faculty, students, and press to the truth. It didn’t want any witnesses. It wanted to control the story.
For weeks, Columbia administration and the mainstream media has painted student protesters as violent and disruptive—and though there have been incidents of antisemitism, racism, and anti-Muslim hatred, including a chemical attack on pro-Palestine protesters , I visited the encampment multiple times and saw a place of joy, love, and community that included explicit teach-ins on antisemitism and explicit rules against any hateful language and action. Students of different faiths protected each other’s right to prayer. Meanwhile, wary of surveillance and the potential use of facial recognition to identify them, they covered their faces. Faculty have become afraid to use university email addresses to discuss ways to protect their students. At one point, the administration circulated documents they wanted students to sign, agreeing to self-identify their involvement and leave the encampment by a 2 p.m. deadline or face suspension or worse. In the end, student radio WKCR reported that even students who did leave the encampment were suspended.
In a recent statement in the Guardian and an oral history in New York Magazine , and through the remarkable coverage of WKCR, Columbia students have sought to take back the narrative. They have detailed the widespread support on campus for student protesters; the peaceful nature of the demonstrations; widespread student wishes to divest financially from Israel, cancel the Tel Aviv Global Center, and end Columbia’s dual-degree program with Tel Aviv University; and the administration’s lack of good faith in negotiations. As part of the Guardian statement, the student body says that multiple news outlets refused to print it. They emphasize their desire to tell their own story.
In a time of mass misinformation, writers who tell the truth and who are there to witness the truth firsthand are essential and must be protected. My students in Columbia’s writing program who have been arrested and face expulsion for wanting the university to disclose and divest, and the many other student protesters, represent the remarkable energy and skepticism of the younger generation who are committed not only to witnessing but participating in the making of a better world. Truth has power, but only if there are people around to tell the truth. We must protect their right to do so, whether or not the truth serves our beliefs. It is the next generation of writers who understand this best and are fighting for both their right and ours to be heard.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- What Student Photojournalists Saw at the Campus Protests
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Why Maternity Care Is Underpaid
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Rita, Anita, My Mother and Me

By Deborah Paredez
Professor Paredez is the chair of the writing program at Columbia and the author of the forthcoming “American Diva.”
Some Latina mothers teach their daughters how to spoon masa or plátano onto a corn husk or banana leaf when making tamales or pasteles.
My Latina mother taught me to love musicals.
Or, more precisely, how to worship the diva at the center of a musical, the woman pulling at the seams of its tidy romance plot, unraveling in her wake a trail of delight and mayhem. Some days it was Barbra Streisand as Fanny Brice in her mink hat and muff insisting that no one rain on her parade. Or Diana Ross easing on down the road. But most times it was Rita Moreno as Anita dancing her way beyond the borders of “Ameríca” in “West Side Story.”
In the decades since its opening night on Broadway in 1957, “West Side Story” has been the story, the persistent white fantasy of “Latinness,” that Latinas like my mom and I have had to reckon with. And yet my mom and I kept watching. Perhaps it’s because, like all musicals, “West Side Story” is a complex form of representation that revels in both its messiness and its marvelousness. My mother taught me to see in “West Side Story” not just the problems of brown-face makeup, but also the choreography of another Latina who could dance her way out of any script that sought to confine her or relegate her to a supporting role. My mother was showing me a diva who could move across these imposed limits. And who did it in a fabulous dress and heels.
It is not without a measure of sheepishness that I admit this now, long after the public and private conversations Latinos have engaged in about our vexed relationship to “West Side Story.” No doubt, it presents damaging stereotypes of “Latin” culture in America. Many of us have cataloged and condemned the musical’s depictions of criminal youth and blatantly sexual women all speaking in exaggerated accents.
Musical divas like Ms. Moreno helped my mother and me forge our bond as we made our own way in America from our working-class neighborhood in San Antonio, Texas, a city that has long had a Latino majority. “West Side Story” endures as a paradoxical — and often pleasurable — cultural text by which many Latinos have come to know ourselves and one another. Artists and thinkers like Lin-Manuel Miranda , Justice Sonia Sotomayor of the Supreme Court and Jennifer Lopez , to name a few, have turned to the musical as a means of understanding themselves or as a jumping-off point into a new narrative.
According to my mom, the first time we watched the 1961 film adaptation of “West Side Story” together was when NBC aired it over two successive nights in March 1972. I was a little more than a year old. In those days, she and I were sharing a bed in the front room of my grandparents’ house on San Antonio’s south side. My father was fighting in Vietnam. I spent countless nights in the years that followed curled up in bed with my mother singing along to “West Side Story.”
We learned every line, every lyric. We scoffed at the brown-cake makeup. Rolled our eyes at the accents. We believed that, yes, a boy like that could kill your brother. We cried every time Bernardo died. We cursed. We crooned. We held our breaths when Anita’s purple petticoat flared, her leg kicked up and stretching to forever, to the smattering of stars above, to some beyond somewhere far from here.
In “West Side Story,” Rita Moreno doesn’t just master the notoriously exacting rigors of Jerome Robbins’s choreography. She expresses undisciplined delight in her body’s movement beyond it. In Ms. Moreno’s mauve-blurred movements as Anita there is both a sense of well-rehearsed control and improvisatory curve, a sense of what my mother would call “movidas,” of finding a way when there seems to be no way, of creating space where none is ceded. Movidas are not just ways of making do but making do with Latina flair, of hustling so smoothly it becomes dancing.
Rita-as-Anita refuses to move in a straight line — and why should she when the playing field is so full of obstacles? Latinos know there are few straightforward paths toward securing a place for ourselves; the only constant is the well-rehearsed control and improvisatory curve and sartorial flair and audacious joy we perform in our movidas. We recognize in Anita’s movements the choreographies of our own refusals and striving for self-possession.
Again and again I saw in the film how Anita tends fiercely to Maria, the teenager left in her charge. Just as I joined my mother in bed to watch and cry and sing along, Anita joins Maria on her bed to sing the duet “A Boy Like That/I Have a Love.” It’s a pivotal moment when Anita, despite her own reservations, romantic attachments and aspirations, sacrifices herself to help Maria try to achieve what she wants. Anita and Maria are the only couple central to the narrative who survive.
My mother taught me to memorize the steps and the songs in a musical diva’s repertoire. Together, we studied the ways Rita-as-Anita moves across the battered gymnasium floor, across the rooftop, across the boundaries of turf and tribe. She showed me how to follow the diva who shows Latinas how to move and move and keep on moving, how to move until the skirts of our dresses achieve lift off, how to move past the violence done to our bodies and our boyfriends, how to move closer to one another across the borders that seek to keep us apart.
Deborah Paredez is the chair of the writing program at Columbia and the author of the forthcoming critical memoir “American Diva .”
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Book News & Features
Ai is contentious among authors. so why are some feeding it their own writing.

Chloe Veltman

The vast majority of authors don't use artificial intelligence as part of their creative process — or at least won't admit to it.
Yet according to a recent poll from the writers' advocacy nonprofit The Authors Guild, 13% said they do use AI, for activities like brainstorming character ideas and creating outlines.
The technology is a vexed topic in the literary world. Many authors are concerned about the use of their copyrighted material in generative AI models. At the same time, some are actively using these technologies — even attempting to train AI models on their own works.
These experiments, though limited, are teaching their authors new things about creativity.
Best known as the author of technology and business-oriented non-fiction books like The Long Tail, lately Chris Anderson has been trying his hand at fiction. Anderson is working on his second novel, about drone warfare.
He says he wants to put generative AI technology to the test.
"I wanted to see whether in fact AI can do more than just help me organize my thoughts, but actually start injecting new thoughts," Anderson says.
Anderson says he fed parts of his first novel into an AI writing platform to help him write this new one. The system surprised him by moving his opening scene from a corporate meeting room to a karaoke bar.
Authors push back on the growing number of AI 'scam' books on Amazon
"And I was like, you know? That could work!" Anderson says. "I ended up writing the scene myself. But the idea was the AI's."
Anderson says he didn't use a single actual word the AI platform generated. The sentences were grammatically correct, he says, but fell way short in terms of replicating his writing style. Although he admits to being disappointed, Anderson says ultimately he's OK with having to do some of the heavy lifting himself: "Maybe that's just the universe telling me that writing actually involves the act of writing."
Training an AI model to imitate style
It's very hard for off-the-shelf AI models like GPT and Claude to emulate contemporary literary authors' styles.
The authors NPR talked with say that's because these models are predominantly trained on content scraped from the Internet like news articles, Wikipedia entries and how-to manuals — standard, non-literary prose.
But some authors, like Sasha Stiles , say they have been able to make these systems suit their stylistic needs.
"There are moments where I do ask my machine collaborator to write something and then I use what's come out verbatim," Stiles says.
The poet and AI researcher says she wanted to make the off-the-shelf AI models she'd been experimenting with for years more responsive to her own poetic voice.
So she started customizing them by inputting her finished poems, drafts, and research notes.
"All with the intention to sort of mentor a bespoke poetic alter ego," Stiles says.
She has collaborated with this bespoke poetic alter ego on a variety of projects, including Technelegy (2021), a volume of poetry published by Black Spring Press; and " Repetae: Again, Again ," a multimedia poem created last year for luxury fashion brand Gucci.
Stiles says working with her AI persona has led her to ask questions about whether what she's doing is in fact poetic, and where the line falls between the human and the machine.
read it again… pic.twitter.com/sAs2xhdufD — Sasha Stiles | AI alter ego Technelegy ✍️🤖 (@sashastiles) November 28, 2023
"It's been really a provocative thing to be able to use these tools to create poetry," she says.
Potential issues come with these experiments
These types of experiments are also provocative in another way. Authors Guild CEO Mary Rasenberger says she's not opposed to authors training AI models on their own writing.
"If you're using AI to create derivative works of your own work, that is completely acceptable," Rasenberger says.

Thousands of authors urge AI companies to stop using work without permission
But building an AI system that responds fluently to user prompts requires vast amounts of training data. So the foundational AI models that underpin most of these investigations in literary style may contain copyrighted works.
Rasenberger pointed to the recent wave of lawsuits brought by authors alleging AI companies trained their models on unauthorized copies of articles and books.
"If the output does in fact contain other people's works, that creates real ethical concerns," she says. "Because that you should be getting permission for."
Circumventing ethical problems while being creative
Award-winning speculative fiction writer Ken Liu says he wanted to circumvent these ethical problems, while at the same time creating new aesthetic possibilities using AI.
So the former software engineer and lawyer attempted to train an AI model solely on his own output. He says he fed all of his short stories and novels into the system — and nothing else.
Liu says he knew this approach was doomed to fail.
That's because the entire life's work of any single writer simply doesn't contain enough words to produce a viable so-called large language model.
"I don't care how prolific you are," Liu says. "It's just not going to work."
Liu's AI system built only on his own writing produced predictable results.
"It barely generated any phrases, even," Liu says. "A lot of it was just gibberish."
Yet for Liu, that was the point. He put this gibberish to work in a short story. 50 Things Every AI Working With Humans Should Know , published in Uncanny Magazine in 2020, is a meditation on what it means to be human from the perspective of a machine.
"Dinoted concentration crusch the dead gods," is an example of one line in Liu's story generated by his custom-built AI model. "A man reached the torch for something darker perified it seemed the billboding," is another.
Liu continues to experiment with AI. He says the technology shows promise, but is still very limited. If anything, he says, his experiments have reaffirmed why human art matters.
"So what is the point of experimenting with AIs?" Liu says. "The point for me really is about pushing the boundaries of what is art."
Audio and digital stories edited by Meghan Collins Sullivan .
- large language model
- mary rasenberger
- chris anderson
- sasha stiles
- authors guild

COMMENTS
Magazine writing is a craft that stands apart from the kind of writing you might encounter in a newspaper, journal, essay, or full-length book. Even within the broader landscape of magazine writing, many subgenres demand different styles and skills—you'll approach a long feature article differently than you would a human interest story; tackling an investigative exposés requires a ...
Examples of round up articles are: " 12 Fiction Writing Tips From Authors and Editors " or "1,001 Types of Articles to Write for Magazines.". I enjoy writing round-ups because I can squeeze in lots of information in 1,000 words. 11. Research Shorts. Describe current scientific information.
Types of Magazine Articles News and Feature Stories. ... Fact-checking is a non-negotiable aspect of writing magazine articles, whether you're covering a news story, writing a feature, or even ...
Types of magazine articles include service pieces, profiles, investigative articles, and personal essays. ... Writing a magazine article requires a solid idea and research to craft a solid piece ...
Julia Clementson. Understanding the art of writing for magazines involves a multi-faceted approach. First, grasp the fundamental structure of a piece, then learn to engage your target audience with compelling content. The writing process includes thorough research, fact-checking, and crafting captivating headlines.
Step 1: Choose a magazine. If you're thinking about how to write an article for a magazine, you may already have titles in mind. That's great - go ahead and pitch them! It's also fine not to have a target publication in mind. Don't worry, they're out there!
1. Research your article idea using sources like books and published texts. One of the key elements of a good magazine article is good research. Take the time to locate good sources and read any necessary supplementary material to help you get a better sense of the article idea.
An effective writing style for a magazine article should be clear, concise, and engaging. It is essential to cater to the target audience by using language that resonates with them and addressing relevant topics. Keep sentences and paragraphs short and easily digestible, and avoid jargon unless the publication targets industry professionals. ...
1. Choose a subject you are an expert in. Keeping true to our earlier advice of specializing, when you start to write a magazine article, choose a topic you show certain expertise in. Publishers typically choose articles with an in-depth take on a subject, and that's where your level of experience will come into play.
Let's delve into some common magazine article types and unpack their unique structural nuances, offering illustrative examples for better understanding. Feature Articles. Structure: This is the crown jewel of magazine article writing, often diving deep into a topic, person, event, or trend. Feature articles typically start with a strong lead ...
About the Book This comprehensive, practical, how-to guide answers all of your questions about writing for magazines. In this all-new second edition of a best-selling classic, today's most successful freelance writers, including Robert Bly, Linda Formichelli, Kelly James-Enger, Jenna Glatzer, and others, provide up-to-date information on e-querying, writing for digital media, knowing your e ...
Photo by Patrick Tomasso on Unsplash 1. Find Your Inspiration. The journey of writing an article often begins with an idea. Finding inspiration can be as simple as observing the world around you ...
Since magazines aim to plan months in advance, time your pitch and query letter accordingly. 4. Draft a query letter. Write a short, formal letter to an editor that expresses your interest in writing for their magazine. If the publication has more than one editor, send it to the person who accepts pitches for the story's topic.
In magazine writing, the body text forms the backbone of the article, providing the substance and depth required to convey the author's message or argument effectively. Drawing inspiration from magazine editorial examples can help writers build a compelling narrative that keeps readers engaged and maintains their interest throughout the article.
Types of Magazine Articles to Impress Your Online Audience. The best types of magazine articles are the ones that you enjoy writing. So, try to look for an idea you'll enjoy the most. 1. Lists. People are always looking for something. They search for movies to watch, products to buy, games to play, companies to trust, and many more.
All of them pass a certain message across but the format is what differs. According to the specialists from izood, the different types of magazine articles include profiles, round-ups, 'how to' articles, and research shorts and are a great way to get your creative juices flowing as a freelance writer and to get as many different assignments ...
Here are some tips for writing with descriptive writing styles: Use literary devices such as metaphors and similes. Use well thought out adjectives and adverbs to describe nouns and verbs. Bring attention to small details. Use the 6 senses: sight, touch, taste, smell, sound, and feeling.
4. Make connections and meet people. Networking is important in any business, especially for freelance writers who want to make a jump to magazine writing. Editors regularly quit one magazine to work for another. Therefore, remember to know the people first and foremost than the magazine they work for. 5.
Descriptive: to describe things. Expository: to give facts. Narrative: to tell a story. Persuasive: to convince the reader of something. If you're struggling to figure out the writing style of a piece, ask yourself what its purpose is and why the author wants you to read it.
The types are: Hard News, First Person Article, Opinion Piece, Informational or Service Piece, How-To Article, Personality Profile, and Think Piece. Since most Hard News articles are assigned to full-time staff, we will skip this type of article. Let's examine the characteristics and differences of the remaining types of articles for ...
Target Audience. The main difference between a newspaper and a magazine is that newspapers are written for a general audience, while magazines are for specific types of audiences. A magazine attracts varied target audiences. A newspaper's target audience is determined by its geography and its focus is broad. Here, the editor determines what ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects.
Analog Science-Fiction - Analog pays 8-10 cents per word for short fiction (up to approximately 20,000 words), 6 cents per word for serials (40,000-80,000 words), 9 cents per word for fact articles, and $1 per line for poetry.; Literary Fiction. VQR- This is a high end literary journal.They publish poetry, short fiction, and certain kinds of non-fiction, including book reviews.
Hints to help you solve today's word-grouping NYT's Connections game—including the answers for all four categories for #334 on Friday, May 10, 2024.
O n April 30, 56 years after Columbia sent the police in to arrest student protesters who had taken over Hamilton Hall in protest of the Vietnam War—protests the school loves to promote—I was ...
All vaccines have at least occasional side effects. But people who say they were injured by Covid vaccines believe their cases have been ignored.
Some Latina mothers teach their daughters how to spoon masa or plátano onto a corn husk or banana leaf when making tamales or pasteles. My Latina mother taught me to love musicals.
The sentences were grammatically correct, he says, but fell way short in terms of replicating his writing style. Although he admits to being disappointed, Anderson says ultimately he's OK with ...