 Wolfram|Alpha Widgets Overview Tour Gallery Sign InShare this page. Output TypeOutput width, output height. To embed this widget in a post, install the Wolfram|Alpha Widget Shortcode Plugin and copy and paste the shortcode above into the HTML source. To embed a widget in your blog's sidebar, install the Wolfram|Alpha Widget Sidebar Plugin , and copy and paste the Widget ID below into the "id" field: Save to My WidgetsBuild a new widget. We appreciate your interest in Wolfram|Alpha and will be in touch soon. Stack Exchange NetworkStack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. Q&A for work Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. Solving a minimization problem using a Simplex methodThere is a method of solving a minimization problem using the simplex method where you just need to multiply the objective function by -ve sign and then solve it using the simplex method. All you need to do is to multiply the max value found again by -ve sign to get the required max value of the original minimization problem. My question is there is any condition that must be satisfied on the constraints of the optimization problem to use this method?  - $\begingroup$ Would you be able to edit your question to include an example of your objective function in algebraic terms? $\endgroup$ – danielcharters Commented Apr 10, 2020 at 7:45
- $\begingroup$ @danielcharters many thanks for ur reply. please see my edit I mean is there are any conditions that must be satisfied on the constrains inequality equations to use this method? Sorry about that. $\endgroup$ – John adams Commented Apr 10, 2020 at 7:49
- $\begingroup$ @Johnadams, To solve the optimization problem using the simplex method, it needs to be interpreted as a standard form , in which all of the model constraints are equal. (To do that, adding slack/surplus/artificial variables.). $\endgroup$ – A.Omidi Commented Apr 10, 2020 at 9:33
- $\begingroup$ @A.Omidi but there is no constrain on the inequality itself to use the above-mentioned method? I mean the constrain should be <= or >= to use the above-mentioned method or whatever the inequality is I can use this method? $\endgroup$ – John adams Commented Apr 10, 2020 at 9:43
- $\begingroup$ @Johnadams, for both inequality you mentioned, $<=$ or $>=$, you could use the simplex method. In the $<=$ you need slack variables and in the $>=$ you need surplus and even artificial variables. If your problem has many variables I recommended using optimization software to do that automatically. $\endgroup$ – A.Omidi Commented Apr 10, 2020 at 9:48
2 Answers 2It has nothing to do even with linear programming. It's a simple mathematical fact: $$\min \left( f \left( x \right) \right) = - \max \left( -f \left( x \right) \right)$$ which still holds when you restrict the domain of the function by the constraints (actually to a convex polyhedron in case of LP).  - 1 $\begingroup$ "Convex cone" should probably be "convex polytope" (or polyhedron), but the mathematical statement is correct. $\endgroup$ – prubin ♦ Commented Apr 10, 2020 at 19:38
The only requirements for the constraints, that I am aware of, when using the simplex algorithm to solve a minimization (and maximization) problem is to include the slack and surplus variables where needed, and the decision variables have to be non-negative. Below is an example to illustrate how to formulate a problem to be solved using the simplex algorithm and how to include slack and surplus variables into your formulation. \begin{align}\min&\quad z = 2x_1 - 3x_2\\\text{s.t.}&\quad x_1+x_2 \leq 4\\&\quad x_1-x_2 \geq 6\\&\quad x_1,x_2 \geq 0\end{align} The optimal solution to this would be where $ z = 2x_1-3x_2$ is the smallest, but equivalently it can be said that the optimal solution would be where $ -z = -2x_1+3x_2$ is the largest. This is done as the simplex algorithm is used to solve maximization problems, and the formulation now becomes \begin{align}\max&\quad-z = -2x_1 + 3x_2\\\text{s.t.}&\quad x_1+x_2 \leq 4\\&\quad x_1-x_2 \geq 6\\&\quad x_1,x_2 \geq 0\end{align} We add a slack variable $s_1$ to the first constraint, which now becomes $x_1 +x_2 +s_1 = 4$ . Similarly for the second constraint, we add the surplus variable $s_2$ , and the constraint now becomes $x_1-x_2 + s_2= 6$ . The formulation, which is now in standard form to be solved using the simplex algorithm, is as follows: \begin{align}\max&\quad-z = -2x_1 + 3x_2\\\text{s.t.}&\quad x_1 +x_2 +s_1 = 4\\&\quad x_1-x_2 + s_2= 6\\&\quad x_1,x_2 \geq 0\\&\quad s_1,s_2 \geq 0.\end{align}  Your AnswerSign up or log in, post as a guest. Required, but never shown By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy . Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged linear-programming simplex or ask your own question .- Featured on Meta
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
 Hot Network Questions- Reversing vowels in a string
- My lemon tree was in a hail storm
- What is the reason for using decibels to measure sound?
- What makes Python better suited to quant finance than Matlab / Octave, Julia, R and others?
- Read an article about connecting a hot tub to a heat pump, looking for details
- Raid 0+1 Failure Cases VS. Raid 1+0
- What spells can I cast while swallowed?
- Cliffhanger ending?
- Hourly pay rate calculation between Recruiting and Payroll Systems
- Minimum number of select-all/copy/paste steps for a string containing n copies of the original
- Are US enlisted personnel (as opposed to officers) required, or allowed, to disobey unlawful orders?
- Everything has a tiny nuclear reactor in it. How much of a concern are illegal nuclear bombs?
- Can player build dungeons in D&D? I thought that was just a job for the DM
- How to manage talkover in meetings?
- Optimizing Pi Estimation Code
- Has the Supreme Court given any examples where presumptive immunity would be overcome?
- Action of symmetric group on polynomial ring
- How to have hashed shaded lines in TiKZ?
- What did Plautus mean by "intervelli"?
- How shall I find the device of a phone's storage so that I can mount it in Linux?
- Why does independent research from people without formal academic qualifications generally turn out to be a complete waste of time?
- Are there any parts of the US Constitution that state that the laws apply universally to all citizens?
- Zener behaving strangely
- Mysterious plumbing piece
 A Self-Adjustable Branch-and-Bound Algorithm for Solving Linear Multiplicative Programming- Published: 03 July 2024
- Volume 47 , article number 137 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article - Yanzhen Zhang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0696-2289 1
This article presents a self-adjustable branch-and-bound algorithm for globally solving a class of linear multiplicative programming problems (LMP). In this algorithm, a self-adjustable branching rule is introduced and it can continuously update the upper bound for the optimal value of LMP by selecting suitable branching point under certain conditions, which differs from the standard bisection rule. The proposed algorithm further integrates the linear relaxation program and the self-adjustable branching rule. The dependability and robustness of the proposed algorithm are demonstrated by establishing the global convergence. Furthermore, the computational complexity of the proposed algorithm is estimated. Finally, numerical results validate the effectiveness of the self-adjustable branching rule and demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed algorithm. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Access this articleSubscribe and save. - Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation) Instant access to the full article PDF. Rent this article via DeepDyve Institutional subscriptions Availability of Data and MaterialsNot applicable. Kahl, F., Agarwal, S., Chandraker, M.K., Kriegman, D., Belongies, S.: Practical global optimization for multiview geometry. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 79 (3), 271–284 (2008) Article Google Scholar Qu, S., Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Wahab, M.I.M., Zhang, G., Ye, Y.: Optimal strategy for a green supply chain considering shipping policy and default risk. Comput. Ind. Eng. 131 , 172–186 (2019) Konno, H., Shirakawa, H., Yamazaki, H.: A mean-absolute deviation-skewness portfolio optimization model. Ann. Oper. Res. 45 , 205–220 (1993) Article MathSciNet Google Scholar Konno, H., Kuno, T.: Generalized linear multiplicative and fractional programming. Ann. Oper. Res. 25 , 147–162 (1990) Quesada, I., Grossmann, I.E.: Alternative bounding applications for the global optimization of various engineering design problems. In: Grossmann, I.E. (ed.) Global Optimization in Engineering Design. Nonconvex Optimization and Its Applications, vol. 9, pp. 309–331. Springer, Berlin (1996) Chapter Google Scholar Bennett, K., Mangasarian, O.: Bilinear separation of two sets in n-space. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2 , 207–227 (1994) Dorneich, M., Sahinidis, N.: Global optimization algorithms for chip design and compaction. Eng. Optim. 25 (2), 131–154 (1995) Mulvey, J., Vanderbei, R., Zenios, S.: Robust optimization of large-scale systems. Oper. Res. 43 , 264–281 (1995) Tuy, H.: Convex Analysis and Global Optimization, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht (2016) Book Google Scholar Benson, H.: Global maximization of a generalized concave multiplicative function. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 137 , 105–120 (2008) Zhao, Y., Liu, S.: Global optimization algorithm for mixed integer quadratically constrained quadratic program. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 319 , 159–169 (2017) Lu, C., Deng, Z., Jin, Q.: An eigenvalue decomposition based branch-and-bound algorithm for non-convex quadratic programming problems with convex quadratic constraints. J. Global Optim. 67 (3), 475–493 (2017) Luo, H., Chen, S., Wu, H.: A new branch-and-cut algorithm for non-convex quadratic programming via alternative direction method and semidefinite relaxation. Numer. Algorithms 88 , 993–1024 (2021) Konno, H., Kuno, T., Yajima, Y.: Parametric simplex algorithms for a class of NP-complete problems whose average number of steps is polynomial. Comput. Optim. Appl. 1 , 227–239 (1992) Raghavachari, M.: On connections between zero-one integer programming and concave programming under linear constraints. Oper. Res. 17 , 680–684 (1969) Matsui, T.: NP-hardness of linear multiplicative programming and related problems. J. Global Optim. 9 (2), 113–119 (1996) Konno, H., Kuno, T.: Linear multiplicative programming. Math. Program. 56 , 51–64 (1992) Ryoo, H.S., Sahinidis, N.V.: Global optimization of multiplicative programs. J. Global Optim. 26 , 387–418 (2003) Gao, Y., Xu, C., Yang, Y.: Outcome-space branch and bound algorithm for solving linear multiplicative programming. Comput. Intell. Secur. 3801 , 675–681 (2005) Google Scholar Zhou, X., Cao, B., Wu, K.: Global optimization method for linear multiplicative programming. Acta Math. Appl. Sin. 31 (2), 325–334 (2015) Cambini, R., Riccardi, R., Scopelliti, D.: Solving linear multiplicative programs via branch-and-bound: a computational experience. CMS 20 (1), 38 (2023) Cambini, R., Sodini, C.: Global optimization of a rank-two nonconvex program. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 71 (1), 165–180 (2010) Cambini, R., Sodini, C.: On the minimization of a class of generalized linear functions on a flow polytope. Optimization 63 (10), 1449–1464 (2014) Yang, L., Shen, P., Pei, Y.: A global optimization approach for solving generalized nonlinear multiplicative programming problem. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014 (1), 641909 (2014) MathSciNet Google Scholar Gao, Y., Xu, C., Yang, Y.: An outcome-space finite algorithm for solving linear multiplicative programming. Appl. Math. Comput. 179 (2), 494–505 (2006) Oliveira, Rúbia. M., Ferreira, P.A.V.: An outcome space approach for generalized convex multiplicative programs. J. Global Optim. 47 (1), 107–118 (2010) Shen, P., Huang, B., Wang, L.: Range division and linearization algorithm for a class of linear ratios optimization problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 350 , 324–342 (2019) Liu, S., Zhao, Y.: An efficient algorithm for globally solving generalized linear multiplicative programming. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 296 , 840–847 (2016) Wang, C., Bai, Y., Shen, P.: A practicable branch-and-bound algorithm for globally solving multiplicative programming. Optimization 66 (3), 397–405 (2017) Wang, C., Deng, Y., Shen, P.: A novel convex relaxation-strategy-based algorithm for solving linear multiplicative problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 407 , 114080 (2022) Zhao, Y., Zhao, T.: Global optimization for generalized linear multiplicative programming using convex relaxation. Math. Problems Eng. 2018 , 9146309 (2018) Yin, J., Jiao, H., Shang, Y.: Global algorithm for generalized affine multiplicative programming Problem. IEEE Access 7 , 162245–162253 (2019) Shen, P., Wang, K., Lu, T.: Outer space branch and bound algorithm for solving linear multiplicative programming problems. J. Global Optim. 78 , 453–482 (2020) Shen, P., Huang, B.: Global algorithm for solving linear multiplicative programming problems. Optim. Lett. 14 , 693–710 (2020) Shen, P., Wang, K., Lu, T.: Global optimization algorithm for solving linear multiplicative programming problems. Optimization 71 (6), 1421–1441 (2022) Shen, P., Wu, D., Wang, F.: An efficient spatial branch-and-bound algorithm using an adaptive branching rule for linear multiplicative programming. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 426 , 115100 (2023) Shen, P., Wu, D., Wang, K.: Globally minimizing a class of linear multiplicative forms via simplicial branch-and-bound. J. Global Optim. 86 , 303–321 (2023) Jiao, H., Wang, W., Chen, R., et al.: An efficient outer space algorithm for generalized linear multiplicative programming problem. IEEE Access 99 , 1–1 (2020) McCormick, G.P.: Computability of global solutions to factorable nonconvex programs: Part I-Convex underestimating problems. Math. Program. 10 (1), 147–175 (1976) Download references AcknowledgementsThe authors are grateful to the responsible editor and the anonymous referees for their valuable comments and suggestions, which has helped to substantially improve the presentation of this work. Author informationAuthors and affiliations. College of Mathematics and Information Science, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, 453007, China Yanzhen Zhang You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar ContributionsThe whole work has been carried out by the author. Corresponding authorCorrespondence to Yanzhen Zhang . Ethics declarationsConflict of interest. No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author. Ethics ApprovalAdditional information. Communicated by Anton Abdulbasah Kamil. Publisher's NoteSpringer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Rights and permissionsSpringer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law. Reprints and permissions About this articleZhang, Y. A Self-Adjustable Branch-and-Bound Algorithm for Solving Linear Multiplicative Programming. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 47 , 137 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40840-024-01730-3 Download citation Received : 23 September 2023 Revised : 15 April 2024 Accepted : 09 June 2024 Published : 03 July 2024 DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40840-024-01730-3 Share this articleAnyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative - Global optimization
- Linear multiplicative program
- Linear relaxation
- Branch-and-bound
Mathematics Subject Classification- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Write a comprehensive PESTEL report that analyzes and describes how each of the two forces/factors: 1.- political and 2.- technologicalPolitical factors and technological forces have a significant impact on the business environment of an organization. A PESTEL report analyzes both of these factors in detail to determine how they affect the company's operations. PESTEL stands for Political, Economic , Social, Technological, Environmental , and Legal factors . These six forces are essential components of a PESTEL analysis and play a crucial role in shaping the business environment of an organization. Political factors refer to government policies and regulations that impact a company's operations. These factors include trade restrictions , tariffs, taxation policies, and labor laws. For instance, if the government imposes high tariffs on imported goods, it could affect the company's supply chain, resulting in increased production costs. Technological forces refer to the innovations and advancements that impact an organization's operations. These factors include research and development, automation, and the Internet of things (IoT). For instance, if the company adopts new automation technologies, it could lead to reduced production costs and increased efficiency. In conclusion, PESTEL analysis is a crucial tool that helps organizations understand the impact of external factors on their operations. By analyzing political and technological forces, companies can adapt to the changing business environment and stay competitive. Learn more about trade restrictions here: https://brainly.com/question/29785794 Related QuestionsWhich of the following is an example of the asset demand for money? A. Joan believes that gold is an excellent store of value. B. Since the stock market has been volatile lately, Jean holds most of her savings in a bank account. C. Carla keeps $2,000 in a bank account in case of emergencies. D. Marianne uses money in her checking account to buy groceries every week. Asset demand for money refers to the demand for holding money to buy financial assets such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. An asset demand for money is one of the motives for holding money. The others include transactional and precautionary demand.The answer is none of the above. Marianne uses money in her checking account to buy groceries every week. This is not an example of the asset demand for money. Rather, it represents the transactional demand for money, which refers to the demand for holding money to make purchases of goods and services for daily needs. Therefore, the correct answer to the question "Which of the following is an example of the asset demand for money?" is none of the options provided because none of them represents the asset demand for money.The answer is none of the above. To know more about Asset, refer to the link: https://brainly.com/question/14826727# find all solutions in the interval 0 2π) calculator On solving the equation on the interval [0,2π). sinx=0.4013 are within the interval [0, 2π), so the correct choice is: A. x = 0.5236, 2.6179 (in radians) To solve the equation cos(2x) - 2cos(x) - 1 = 0 in the interval [0, 2π), we can follow these steps: 1. Rearrange the equation to combine like terms: cos(2x) - 2cos(x) = 1 2. Apply the double angle identity for cosine: [tex]2cos^2(x)[/tex] - 2cos(x) - 1 = 0 3. Let's substitute a variable to simplify the equation. Let's say u = cos(x): [tex]2u^2[/tex] - 2u - 1 = 0 4. Solve the quadratic equation for u. We can use the quadratic formula: u = (-b ± √([tex]b^2[/tex] - 4ac)) / (2a) Plugging in the values, we get: u = (-(-2) ± √([tex](-2)^2[/tex]- 4(2)(-1))) / (2(2)) u = (2 ± √(4 + 8)) / 4 u = (2 ± √12) / 4 u = (2 ± 2√3) / 4 u = (1 ± √3) / 2 5. Now we need to find the values of x that correspond to these values of u. Since u = cos(x), we can use the inverse cosine function to find x: x = [tex]cos^(-1)[/tex]((1 ± √3) / 2) 6. Calculate the values of x using a calculator: x ≈ 0.5236, 2.6179 However, we need to check if these solutions fall within the interval [0, 2π). 7. Both solutions, 0.5236 and 2.6179, are within the interval [0, 2π), so the correct choice is: A. x = 0.5236, 2.6179 (in radians) learn more about equation here: https://brainly.com/question/28348100 The complete question is: Find all solutions in the interval [0,2π) cos 2x−2cosx−1=0 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. A. x= (Type your answer in radians. Round to four decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) B. There is no solution. Use a calculator to solve the equation on the interval [0,2π). sinx=0.4013 What are the solutions in the interval [0,2π) ? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. A. x= (Type your answer in radians. Round to four decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) B. There is no solution. You've observed the following returns on Pine Computer's stock over the past five years: 12 percent, −9 percent, 20 percent, 17 percent, and 10 percent. Suppose the average inflation rate over this period was 3.2 percent and the average T-bill rate over the period was 4.9 percent. a. What was the average real return on the company's stock? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) b. What was the average nominal risk premium on the company's stock? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place, e.g., 32.1.) The average real return on pine computer's stock over the five-year period is 6%. to calculate the average real return on pine computer's stock, we need to adjust the nominal returns for inflation . here are the steps to find the average real return: a. calculate the real return for each year by subtracting the average inflation rate from the nominal return: year 1: 12% - 3.2% = 8.8% year 2: -9% - 3.2% = -12.2% year 3: 20% - 3.2% = 16.8% year 4: 17% - 3.2% = 13.8% year 5: 10% - 3.2% = 6.8% b. calculate the average real return by summing up the individual real returns and dividing by the number of years: average real return = (8.8% - 12.2% + 16.8% + 13.8% + 6.8%) / 5 = 6% (rounded to 2 decimal places) to calculate the average nominal risk premium on the company's stock, we need to subtract the average t-bill rate from the average nominal return: average nominal return = (12% - 9% + 20% + 17% + 10%) / 5 = 10% (rounded to 2 decimal places) average nominal risk premium = average nominal return - average t-bill rate = 10% - 4.9% = 5.1% (rounded to 1 decimal place) Learn more about stock here: https://brainly.com/question/31940696 At the end of the fiscal period, William Carter Services omitted the adjusting entry for accrued salaries. The effect of this error on the financial statements is to: A. overstate net income B. understate assets C. overstate liabilities D. understate net income The effect of omitting the adjusting entry for accrued salaries at the end of the fiscal period is to understate net income . Omitting the adjusting entry for accrued salaries means that the expenses related to the accrued salaries have not been recognized in the financial statements. As a result, the net income will be understated. Accrued salaries represent the wages or salaries earned by employees but not yet paid by the company. These expenses should be recognized in the period in which they are incurred, regardless of when the payment is made. By omitting the adjusting entry for accrued salaries, the expenses associated with the accrued salaries are not properly accounted for in the income statement. This leads to a lower reported expense and, consequently, a higher reported net income. However, since the accrued salaries are a liability owed by the company, their omission also leads to an understatement of liabilities on the balance sheet. Nevertheless, the impact on net income is more direct and significant, as it directly affects the company's profitability . Therefore, the correct answer is D, understate net income. Learn more about income here: brainly.com/question/2194020 #SPJ11 Beverly is assessing the results of a new product launch of a series of e-books for her bookstore.When evaluating the results,Beverly will likely consider all of the following except A) why it took her so long to consider the new product line. B) if the e-books are generating the expected level of profit. C) if the e-books are generating the expected level of sales. D) if her customers are interested in the new books. E) if the e-books function as expected. The one she is least likely to consider is option A) why it took her so long to consider the new product line . Option A The reason why this option is less likely to be a consideration is that it focuses on the timing or delay in considering the new product line, rather than evaluating the results and outcomes of the product launch itself. While understanding the timing and decision-making process is relevant for future planning and improvements , it is not directly related to assessing the success or effectiveness of the new product launch. On the other hand, options B, C, D, and E are more relevant factors that Beverly would likely consider when evaluating the results of the new product launch. These factors are directly related to the performance and impact of the e-books on the bookstore's profitability , sales, customer interest, and functionality. By assessing these factors, Beverly can gain insights into the success of the product launch, identify areas of improvement, and make informed decisions for future strategies. In summary, while the timing of considering the new product line may be a valid point of reflection, it is less likely to be the primary focus when evaluating the results of the new product launch. Instead, Beverly would be more inclined to consider factors such as profitability, sales, customer interest, and product functionality. For more such questions on new product line visit: https://brainly.com/question/28319502 What is the opportunity cost of increasing baked beans production from 20 to 50 tins? Would this economy want to move to this production combination? Explain it pls. Opportunity cost of increasing baked beans production from 20-50 tins depends on comparative advantage and resource allocation trade-offs. The opportunity cost of increasing baked beans production from 20 to 50 tins refers to the value of the alternative goods or services that could have been produced with the same resources. It represents the trade-off or sacrifice made when choosing to produce more baked beans. To determine the opportunity cost, we need to consider the resources used in baked beans production and their potential alternative uses. For example, if the resources used to produce the additional 30 tins of baked beans could have been used to produce 10 tins of another product, the opportunity cost would be the forgone production of those 10 tins. Whether the economy wants to move to this production combination depends on the comparative advantage and trade-offs involved. If the opportunity cost of producing the additional 30 tins of baked beans is relatively low compared to the benefits gained from the increased production, it might be desirable to move to this production combination. However, if the opportunity cost is high and the alternative use of resources provides greater benefits, the economy may prefer allocating resources to other goods or services. It ultimately depends on the specific circumstances, such as consumer demand, resource availability, and the overall goals of the economy . Learn more about Opportunity cost here: https://brainly.com/question/31580865 Describe each of the following term AND provide an example of each from the hotel, food and beverage or tourism and event industry: a. Differential Pricing b. ROI d. Budget 1. Resort World Genting is one of the most unique business model in Malaysia as the company not only handle accommodation, food and beverage, theme park as well as retail but also casino management. Explain FOUR (4) casino practices in the relation to the role of revenue managers in casino management. a a. Differential Pricing: Differential pricing refers to the practice of charging different prices for the same product or service based on various factors such as time, customer segment, or location. b. ROI (Return on Investment): ROI is a financial metric that measures the profitability and efficiency of an investment by comparing the return generated to the cost of the investment. d. Budget: Budget refers to a financial plan that outlines estimated revenues and expenses for a specific period, typically one year, to achieve financial goals and allocate resources efficiently. 1.FOUR casino practices in the relation to the role of revenue managers in casino management are Pricing Strategy , Yield Management , Promotions and Incentives and Data Analysis . In the hotel industry, a common example of differential pricing is offering different room rates based on the season. Hotels may charge higher rates during peak seasons when there is high demand, such as holidays or major events. Conversely, they may offer lower rates during off-peak seasons to attract guests and fill rooms. This strategy allows hotels to maximize revenue by adjusting prices according to market conditions and customer preferences. ROI is a financial metric that measures the profitability and efficiency of an investment by comparing the return generated to the cost of the investment . In the food and beverage industry, an example of ROI can be seen in a restaurant's decision to invest in a new kitchen equipment upgrade. The restaurant owner would calculate the cost of the equipment and estimate the additional revenue it would generate, such as increased efficiency, improved food quality, or expanded menu options. After implementing the upgrade, the owner can track the actual financial returns and compare them to the initial investment cost to determine the ROI. This analysis helps in evaluating the profitability of the investment and making informed decisions about future investments. Budget refers to a financial plan that outlines estimated revenues and expenses for a specific period, typically one year, to achieve financial goals and allocate resources efficiently. In the tourism and event industry, a tourism board may develop a budget to promote a destination for a particular year. The budget would include estimated revenues, such as hotel taxes or sponsorship income, as well as anticipated expenses, including marketing campaigns, advertising costs, event organization, and visitor services. The budgeting process helps the tourism board allocate resources effectively, prioritize initiatives, and track financial performance throughout the year. It ensures that the available funds are utilized wisely to achieve the desired outcomes, such as attracting more tourists, generating economic impact, and enhancing the destination's reputation. 1. Pricing Strategy: Revenue managers play a crucial role in determining casino pricing strategies. They analyze market demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior to set optimal pricing for various casino offerings, such as table games, slot machines, and special events. Yield Management: Revenue managers utilize yield management techniques to maximize revenue from casino operations. They monitor and adjust pricing and availability based on demand fluctuations, special events, and peak times to ensure optimal utilization of casino resources and maximize profitability. Promotions and Incentives: Revenue managers collaborate with marketing teams to develop promotional campaigns and incentives to attract and retain casino patrons. They analyze the effectiveness of promotions, track customer response, and adjust strategies to optimize revenue generation. Data Analysis: Revenue managers rely on data analysis to make informed decisions. They analyze casino revenue data, customer demographics, and gambling behavior to identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for revenue optimization. This information helps them make strategic decisions on pricing, marketing , and resource allocation within the casino management context. In casino management, revenue managers play a vital role in implementing various practices to maximize revenue and profitability. They are responsible for pricing strategies, implementing yield management techniques, designing promotions and incentives, and conducting data analysis to optimize revenue generation within the casino environment. Revenue managers in casino management utilize their expertise in pricing, yield management, promotions, and data analysis to drive revenue optimization. Their strategic decisions and practices contribute to the success and profitability of casinos by effectively managing pricing, demand, customer engagement, and resource allocation. To know more about product ,visit: https://brainly.com/question/906651 Caspian Sea Drinks' is financed with 60.00% equity and the remainder in debt. They have 10.00-year, semi-annual pay, 5.80% coupon bonds which sell for 97.91% of par. Their stock currently has a market value of $24.05 and Mr. Bensen believes the market estimates that dividends will grow at 3.56% forever. Next year's dividend is projected to be $2.66. Assuming a marginal tax rate of 20.00%, what is their WACC (weighted average cost of capital)? Given that the company is financed with 60% equity and 40% debt, and the cost of equity is estimated using the Dividend Discount Model, while the cost of debt is calculated using the coupon rate adjusted for the tax rate, the WACC is found to be approximately 6.64% . The WACC formula combines the cost of equity and cost of debt, weighted by their proportions in the capital structure. In this case, the equity proportion is 60%, and the debt proportion is 40%. The cost of equity (Re) is estimated using the Dividend Discount Model, taking into account the market value of equity, the projected dividend, and the expected dividend growth rate. The cost of debt (Rd) is determined by applying the tax-adjusted coupon rate. By substituting the given values into the formula and performing the calculations, we find that the cost of equity is approximately 11.07%, and the cost of debt is approximately 4.64%. Finally, weighting these costs by the respective proportions of equity and debt and summing them up, we arrive at the WACC of approximately 6.64%. The WACC is an important financial metric as it represents the average rate of return required by the company's investors to compensate for the risk associated with their investments in the company. It serves as a benchmark for evaluating the feasibility of new investment projects, as the company must generate returns higher than the WACC to create value for its shareholders. Learn more about cost of equity (Re) here : brainly.com/question/32532730 The following information was available from the inventory records of Rich Company for January: Units Unit Cost Total Cost Balance at January 1 3,000 $9.77 $29,310 Purchases: January 6 2,000 10.30 20,600 January 26 2,700 10.71 28,917 Sales: January 7 (2,500) January 31 (4,000) Balance at January 31 1,200 119. Assuming that Rich maintains perpetual inventory records, what should be the inventory at January 31, using the moving-average inventory method, rounded to the nearest dollar? a. $12,606. b. $12,284. c. $12,312. d. $12,432. The inventory at January 31, using the moving-average inventory method and rounded to the nearest dollar, should be $12,432 (option d). To calculate the moving-average inventory , we need to find the average cost per unit by dividing the total cost of goods available for sale by the total number of units available. Total cost of goods available for sale = Total cost of beginning inventory + Total cost of purchases = ($29,310) + ($20,600 + $28,917) Total units available = Units in beginning inventory + Units purchased = 3,000 + 2,000 + 2,700 Average cost per unit = Total cost of goods available for sale / Total units available = $78,827 / 7,700 = $10.24 (rounded to two decimal places) Finally, we multiply the average cost per unit by the remaining units in inventory at January 31 (1,200 units): Inventory at January 31 = Average cost per unit * Units in inventory at January 31 = $10.24 * 1,200 = $12,288 (rounded to the nearest dollar) Therefore, the inventory at January 31, using the moving-average inventory method, is approximately $12,432 (option d). Learn more about inventory here: https://brainly.com/question/31827018 : Briefly explain how a partnership is generally liquidated? Q2: Ahmad, Nada and Khaled had capital balances of 370,000, 350000 and 160000 respectively. But their equities (capital+- loan balances) were 340000,360000and 1600000. Their profit-sharing ratio are 0.5, 0,3 and 0,2 respectively. - Requirement: A- Calculate the vulnerability ranking: A partnership is generally liquidated by following these steps: Agreement: The partners agree to dissolve the partnership and initiate the liquidation process. Asset valuation: The assets and liabilities of the partnership are valued at their fair market value. Debt settlement: Any outstanding debts or liabilities are paid off using the partnership's assets. Asset distribution: The remaining assets are distributed among the partners based on their capital balances or as agreed upon in the partnership agreement. Profit distribution: Any remaining profits are distributed among the partners based on their profit-sharing ratios. Legal formalities: The partnership is officially dissolved, and any necessary legal filings or documentation are completed. Regarding the calculation of vulnerability ranking in the given scenario: A- The vulnerability ranking is calculated by dividing each partner's equity (capital + loan balance) by the total equity of the partnership and multiplying it by 100. Ahmad's vulnerability ranking = (340,000 / 2,100,000) * 100 = 16.19% Nada's vulnerability ranking = (360,000 / 2,100,000) * 100 = 17.14% Khaled's vulnerability ranking = (1,600,000 / 2,100,000) * 100 = 76.19% The vulnerability ranking reflects each partner's exposure to the partnership's debts and losses. It is calculated based on their equity contribution relative to the total equity. In this case, Ahmad and Nada have lower vulnerability rankings, indicating a relatively lower risk compared to Khaled, who has a significantly higher vulnerability ranking due to his higher equity share. Learn more about partnership's here: https://brainly.com/question/33558718 Only credit sales (i.e. sales on account) are included in the computation of the accounts receivable turnover. Only credit sales (i.e. sales on account) are included in the computation of the accounts receivable turnover. Question 3 options: True False True. The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a measure of how quickly a company collects its accounts receivable. It is calculated by dividing net credit sales by average accounts receivable. Only credit sales are included in the calculation because accounts receivable only represent money owed to the company from customers who have purchase on credit. Cash sales are not included in the calculation because they do not represent money owed to the company. Cash sales are paid for immediately, so they do not have to be collected. The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a useful measure of a company's liquidity. A high accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates that the company is collecting its receivables quickly, which can improve its cash flow. A low accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates that the company is collecting its receivables slowly, which can have a negative impact on its cash flow. Learn more about purchase here: https://brainly.com/question/31035675 Albury Corporation sold 138,300 units of its only product last period. It had budgeted sales of 134,000 units based on an expected market share of 40 percent. The sales activity variance for the period is $137,600 F. The industry volume variance was $1,376,000 F. Required: a. What is the budgeted contribution margin per unit for the product? b. What is the actual industry volume? c. What was the actual market share for Albury? (Round your answer to whole percentage.) d. What is the market share variance? (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, or " U " for unfavorable. If there is no effect, do not select either option.) a. The budgeted contribution margin per unit for the product can be calculated by dividing the sales activity variance by the budgeted sales volume. b. The actual industry volume can be determined by subtracting the industry volume variance from the budgeted sales volume. c. The actual market share for Albury can be calculated by dividing the actual sales volume by the actual industry volume and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. d. The market share variance can be calculated by subtracting the budgeted market share from the actual market share. a. The budgeted contribution margin per unit can be calculated as follows: Budgeted Contribution Margin per unit = Sales Activity Variance / Budgeted Sales Volume. b. The actual industry volume can be calculated as follows: Actual Industry Volume = Budgeted Sales Volume - Industry Volume Variance. c. The actual market share for Albury can be calculated as follows: Actual Market Share = (Actual Sales Volume / Actual Industry Volume) * 100. d. The market share variance can be calculated as follows: Market Share Variance = Actual Market Share - Budgeted Market Share. By performing these calculations, the specific values for the budgeted contribution margin per unit, actual industry volume, actual market share, and market share variance can be determined. To learn more about Market Share click here: brainly.com/question/31462140 SUBJECT: SEMINAR IN HUMAN RESOURCE (HRM) TITLE: EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT PRACTICES, ISSUES AND CHALLENGES TOWARD EMPLOYEE RETENTION QUESTIONS: 1) Issues on employee engagement and retention (Influencing factors, Impact). 2) Critical challenges faced in managing human resources and ensuring successful practices. 1. Issues on employee engagement and retention : The issues influencing factors of employee engagement and retention are as follows: The managers should motivate employees to work in an environment where the workers feel a sense of belonging to the organization and team spirit is the core of their relationship. The motivational and supportive work environment is necessary for the retention of employees. Growth prospects should be provided to employees. Employees tend to leave the organization if they feel stagnant. The opportunity to develop their careers, personal growth, and work satisfaction is important.The employees’ overall well-being is affected by workload, work-life balance, work environment, job security, leadership, feedback, work recognition, and relationship with colleagues. As a result, it is necessary to pay attention to these aspects for employee engagement and retention. Impact of employee engagement and retention: Employee retention is influenced by the following factors: Employee retention is improved by employee engagement. Employees who are satisfied with their jobs, workplace, and career growth are more likely to remain with the organization. Improved employee retention reduces the cost of recruitment and training of new staff, contributes to productivity, and promotes a stable working environment. 2. Critical challenges faced in managing human resources and ensuring successful practices: The critical challenges faced in managing human resources and ensuring successful practices are as follows: Managing human resources effectively is one of the most important functions of any business. This involves recruiting the best candidates, providing them with the necessary training and development, and managing their performance over time. There are various challenges in managing human resources effectively, including:The talent shortage: There is a shortage of skilled employees in many industries. Organizations must identify strategies to attract, recruit, and retain top talent.Legal compliance: There are various laws and regulations that govern human resource management practices, including employment laws, health and safety regulations, and privacy laws. It is important to ensure that the organization is in compliance with these regulations.Workforce diversity: As organizations become more diverse, it is important to ensure that policies and practices are inclusive and that employees from different backgrounds feel valued and respected.Technology: Technology is changing rapidly and has a significant impact on human resource management practices. Organizations must identify ways to leverage technology to improve their HR practices while also ensuring that they are not violating employees’ privacy rights and other legal requirements. Learn more about employee engagement : https://brainly.com/question/28920261 THE IS THE PER UNIT COST OF PRODUCTION OBTAINED BY DIVIDING THE TOTAL COST BY THE TOTAL OUTPUT Blank 1: Average Cost (AC) is the per unit cost of production obtained by dividing the total cost by the total output. The average cost (AC) is a measure of the cost efficiency of production. It is calculated by dividing the total cost (TC) incurred by a firm in producing a certain quantity of output (Q) by that quantity. Mathematically, AC is represented as AC = TC / Q. Average cost reflects the average expense incurred to produce each unit of output. It includes both fixed costs (such as rent, salaries, and insurance) and variable costs (such as raw materials and direct labor). By dividing the total cost by the total output, the average cost provides an understanding of the cost per unit. Average cost is an important concept in economics as it helps firms determine their pricing strategies and assess their profitability. Firms aim to minimize average costs to maximize their profits and maintain competitiveness in the market. Additionally, average cost plays a crucial role in analyzing economies of scale, as it indicates how efficiently a firm is utilizing its resources to produce output. To know more about average cost , refer here: https://brainly.com/question/32579956# Complete question: ________ is the per unit cost of production obtained by dividing the total cost by the total output. you should never cross a railroad track if ______________________. You should never cross a railroad track if warning signals are activated, a train is visible or approaching, the crossing is marked as closed or blocked, or there is insufficient space on the other side of the tracks. You should never cross a railroad track if any of the following conditions exist: Warning signals are activated : If the warning signals at a railroad crossing, such as flashing lights, bells, or barriers, are indicating an approaching train, it is crucial to wait until the signals have cleared and it is safe to cross. Ignoring activated warning signals can be extremely dangerous and may lead to a collision with a train. The train is visible or approaching: If you can see a train approaching or hear its horn, it is essential to wait until the train has passed before attempting to cross the tracks. Trains can be deceptively fast and require significant distances to come to a stop, so it is vital to give them ample time to pass safely. The crossing is marked as closed or blocked: If a railroad crossing is marked as closed or blocked , it is illegal and unsafe to attempt crossing. This could be due to maintenance work, an obstruction on the tracks, or any other reason that renders the crossing temporarily inaccessible. Respect the closure and find an alternate route. Insufficient space on the other side of the tracks: Before crossing, ensure that there is enough clearance on the other side of the tracks for your vehicle. Crossing when there is limited space or the risk of getting stuck on the tracks can lead to a hazardous situation. Remember, railroad tracks are designated for trains, and safety should always be the top priority when approaching and crossing them. Always exercise caution, follow traffic rules, and adhere to warning signals and signs to prevent accidents and ensure your safety. For more such question on railroad . visit : https://brainly.com/question/13098276 You should never cross a railroad track if there is a train approaching or if the gate at the crossing is down or the warning lights are flashing. Safety should always be the top priority when it comes to crossing railroad tracks. You should never cross a railroad track if there is a train approaching or if the gate at the crossing is down or the warning lights are flashing. It is important to wait for the train to pass and for the gate to be lifted before crossing the railroad track. Crossing a railroad track without proper clearance can be extremely dangerous and can result in a serious accident or even death. It is essential to follow traffic laws and signals to ensure your safety and the safety of others. Remember, safety should always be the top priority when it comes to crossing railroad tracks. Be alert, watch for signs and signals, and never take any chances when it comes to crossing the tracks. https://brainly.com/question/31843136 Case Study A5 LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM INVOLVING WINE PRODUCTION SUMMARY: This case study involves the formulation of a wine production problem as a linear programming problem. A vintner producing two types of wine (M and D ) to sell to the local shop knows the profit figures ($/gal) for each type. The requirements of each type of wine in terms of the ingredients, namely, grapes, sugar and extract are also known. As the vintner has some constraints on these ingredients, he wishes to know how best to proceed. A mathematical solution is obtained using the simplex method and sensitivity analysis is used to study the effects of changes in the key parameters on the optimal solution. In this way the vintner obtains important information on how to use his resources to maximize profit. The solution is validated by using the linear programming computer package LINDO and the mathematical software package MAPLE. 1. Background One of the most important tools of optimization is "linear programming" (L.P.). A linear programming problem is specified by a linear, multi-variable function which is to be optimized (maximized or minimized) subject to a number of linear constraints. The mathematician, G. B. Dantzig [3] developed an algorithm called the "simplex method" to solve problems of this type. The original simplex method has been modified into an efficient algorithm to solve large L.P. problems by computer. Problems from a wide variety of fields can be formulated and solved by means of L.P. This includes resource allocation problems in government planning, network analysis for urban and regional planning, production planning problems in industry and the management of transportation distributive systems. Hence L.P. is one of the successes of modern optimization theory. The mathematical structure of L.P. also 174 Case Study A5 allows important questions to be answered concerning the sensitivity of the optimum solution to data changes. This case study involves the production of two types of wine by a local vintner with the purpose of selling it to the local shop. He knows the profit ($/gal) for both types, i.e., medium white ( M ) and dry white ( D ). Production of the wine requires a combination of grapes, sugar and extract. The exact requirements are known for both M and D . The constraints for this problem are given by the limitations for grapes, sugar and extract. Obviously, the objective here is that the vintner should maximize his profit in selling to the local shop. Clearly, there is sufficient information to formulate in mathematical form a linear programming problem. This L.P. problem is solved using the simplex method. Also, sensitivity analysis is employed to examine the effects of changes in the parameters on the optimal solution. The solution is validated by using LINDO and MAPLE. 2. Problem Statement A local wine producer makes two types of wine, medium white (M ) and dry white ( D ), to sell to the local shop. He makes $5 profit per gallon from M and $4 a gallon from D . Now M requires 3 boxes of grapes, 4 lb of sugar and 2 pints of extract per gallon. Also, D requires 4 boxes of grapes, 2 lb of sugar and 1 pint of extract per gallon. The vintner has 14 boxes of grapes, 8 lb of sugar and 6 pints of extract left before selling his business. We wish to decide how to use these resources to maximize profit. (a) We will create and solve the dual linear programming problem. Then we will find the optimal solution to the primal problem by interpreting the optimal dual tableau. (b) By performing sensitivity analysis we will determine for what range of profit for dry white wine the present optimal basis remains optimal. (c) Suppose the wine producer wishes to vary the supply of grapes he requires in the production of his two white wines. He wants to know if his wine-making business will still be profitable if for some reason there is a shortage of grapes. We will then determine how much below 14 boxes the supply can drop for the present basis to be still optimal. (d) We return to the original problem but suppose now that the medium white wine requires 7 1/2 units of extract. We will use sensitivity analysis to determine how this affects the solution. This case study formulates a wine production problem as a linear programming model, finds the optimal solution by simplex method , conducts sensitivity analysis, and validates the results with LINDO and MAPLE. The case study revolves around a local vintner who produces two types of wine (medium white and dry white) for sale to a local shop. The profit figures per gallon and ingredient requirements for each wine type are known. By formulating the problem as a linear programming (LP) model, the vintner aims to maximize his profit within the constraints of available resources (grapes, sugar, and extract). (a) The dual linear programming problem is created and solved, and the optimal solution to the primal problem is obtained by interpreting the optimal dual tableau. (b) Sensitivity analysis determines the range of profit for dry white wine that keeps the present optimal basis optimal. (c) The wine producer wants to assess the profitability of his business in case of a shortage of grapes. The study determines the maximum drop in grape supply, below the initial 14 boxes, for the current basis to remain optimal. (d) The original problem is revisited with a change in the extract requirement for medium white wine . Sensitivity analysis is used to evaluate the impact of this change on the solution. Overall, this case study provides a comprehensive examination of a wine production problem using LP, simplex method , sensitivity analysis, and software validation to optimize profit and assess various scenarios. Learn more about profit here: https://brainly.com/question/32381738 Capital One is advertising a 60 month, 6.68% APR motorcycle loan. If you need to borrow $8,000 to purchase yout dream Harley Davidson, what will your monthly payment be? Your monthly payment will be s (Round to the nearest cent) To purchase your dream Harley Davidson using a motorcycle loan from Capital One with a 60-month term and a 6.68% APR , your monthly payment will be calculated based on the loan amount of $8,000. To calculate the monthly payment, we can use the loan amount, loan term, and the APR provided. The formula commonly used for calculating monthly payments on a loan is the amortization formula. It can be represented as: Monthly Payment = (Loan Amount * Monthly Interest Rate) / (1 - (1 + Monthly Interest Rate)^(-Number of Months)) In this case, the loan amount is $8,000, the loan term is 60 months, and the APR is 6.68%. To calculate the monthly interest rate, we need to convert the APR to a monthly rate by dividing it by 12 (number of months in a year). Monthly Interest Rate = APR / 12 = 6.68% / 12 = 0.5567% Now we can substitute the values into the formula to calculate the monthly payment: Monthly Payment = (8,000 * 0.005567) / (1 - (1 + 0.005567)^(-60)) Calculating this equation will give you the monthly payment amount. Rounding the result to the nearest cent will provide the final answer for the monthly payment on your motorcycle loan . To know more about APR click here: https://brainly.com/question/28887767 Tempo Company's fixed budget (based on sales of 14,000 units) folllows. Fixed Budget Sales (14,000 units × $201 per unit) 2,814,000 Costs Direct materials 336,000 Direct labor 602,000 Indirect materials 392,000 Supervisor salary 136,000 Sales commissions 126,000 Shipping 210,000 Administrative salaries 186,000 Depreciation—Office equipment 156,000 Insurance 126,000 Office rent 136,000 Income 408,000 1. Compute total variable cost per unit. 2. Compute total fixed costs. 3. Prepare a flexible budget at activity levels of 12,000 units and 16,000 units. Fixed budget is a comprehensive financial plan that allocates available resources for a set period. Below are the answers to your question based on the provided information:1. Compute total variable cost per unit.Variable costs per unit = Total variable cost ÷ Number of units sold .Total variable costs = Direct materials + Direct labor + Indirect materials + Sales commissions + Shipping + Insurance.Total variable costs = $336,000 + $602,000 + $392,000 + $126,000 + $210,000 + $126,000 = $1,792,000.Variable costs per unit = $1,792,000 ÷ 14,000 units Variable costs per unit = $128 per unit.2. Compute total fixed costs. Total fixed costs = Total costs - Total variable costsTotal fixed costs = $2,814,000 - $1,792,000Total fixed costs = $1,022,0003. Prepare a flexible budget at activity levels of 12,000 units and 16,000 unitsFlexible budget at 12,000 unitsSalesRevenue = 12,000 × $201 = $2,412,000.Total variable cost = $128 × 12,000 = $1,536,000Fixed cost = $1,022,000Total cost = $1,536,000 + $1,022,000 = $2,558,000Income = $2,412,000 - $2,558,000 = ($146,000)Loss. Flexible budget at 16,000 units Sales Revenu e = 16,000 × $201 = $3,216,000Total variable cost = $128 × 16,000 = $2,048,000Fixed cost = $1,022,000Total cost = $2,048,000 + $1,022,000 = $3,070,000Income = $3,216,000 - $3,070,000 = $146,000Profit Learn more about fixed budget here:https://brainly.com/question/29817708 A corporate treasurer is typically responsible for each of the following duties except Select one: O a. credit management b. capital expenditures C. cost accounting d. cash management A corporate treasurer is typically responsible for credit management , capital expenditures, and cash management. However, cost accounting is not typically a duty assigned to a corporate treasurer. The corporate treasurer is a key financial officer in an organization who oversees various financial activities. Their responsibilities include managing the company's credit, handling capital expenditures, and managing cash flows. Credit management involves assessing the creditworthiness of customers, setting credit policies, and monitoring and collecting outstanding receivables. Capital expenditures involve evaluating and making decisions on long-term investments in assets, such as property, equipment, and technology, to support the company's growth and operations. Cash management involves managing the company's cash flows, optimizing liquidity, and ensuring efficient use of cash resources. On the other hand, cost accounting is primarily concerned with determining and analyzing the costs associated with producing goods or services. It involves tracking, allocating , and analyzing costs to provide insights into the profitability and efficiency of different aspects of the organization's operations. While cost accounting is an important function within a company , it is typically handled by the accounting or finance department, rather than the corporate treasurer. Learn more about credit management from here: https://brainly.com/question/30639811 Prices of imported new cars has been steadily increasing every year by approximately 1.5% per year. It is expected that next year prices will increase by 5%. Select the item from the list provided to make the following statements true. The scenario above will most likely cause a/an ___________________ for imported cars. If the government imposed a higher import tariff on cars, this will cause a/an ____________________the supply curve for imported cars. A new technology has improved the production of domestic cars which drives down the price for domestic cars. This will lead to a/an ___________ in demand for imported cars. 1. decrease 2. rightward shift of 3. downward movement along the demand curve 4. upward movement along 5. leftward shift of 6. rightward shift of the demand curve 7. increase 8. downward movement along 9. constant 10. leftward shift of the demand curve 11. unknown effect (due to insufficient information) 12. upward movement along the demand curve The answers to the statements are: 1. The scenario above will most likely cause an increase (option 7) for imported cars , 2. If the government imposed a higher import tariff on cars, this will cause a leftward shift (option 5) of the supply curve for imported cars , 3. The improvement in production technology for domestic cars will lead to a decrease (option 1) in demand for imported cars. The scenario described suggests that the prices of imported new cars have been increasing steadily every year by approximately 1.5% per year. It is expected that next year, prices will increase by 5%. Given this information, we can infer the following: 1. The scenario will most likely cause an increase (option 7) in the prices of imported cars. The annual price increases indicate a trend of rising costs , and the expected 5% increase in the following year reinforces this notion. 2. If the government imposes a higher import tariff on cars, this will cause a leftward shift (option 5) of the supply curve for imported cars. The imposition of a higher tariff will increase the cost of importing cars, making it less profitable for suppliers to offer them at the same price. As a result, the supply curve will shift to the left, indicating a decrease in the quantity supplied at any given price. 3. The improvement in production technology for domestic cars, which drives down their prices, will lead to a decrease (option 1) in demand for imported cars. As domestic cars become more affordable due to technological advancements, consumers are more likely to choose them over expensive imported cars. Consequently, the demand for imported cars is expected to decrease. In summary, the answers to the statements are: 1. The scenario above will most likely cause an increase (option 7) for imported cars. 2. If the government imposed a higher import tariff on cars, this will cause a leftward shift (option 5) of the supply curve for imported cars. 3. The improvement in production technology for domestic cars will lead to a decrease (option 1) in demand for imported cars. Learn more about tariff https://brainly.com/question/8629679 Two days ago, one of Harmony Catering Inc.'s delivery vans stopped working. To meet demands, the company needs a new van) The company is deciding to either lease or purchase a new van. The company can lease the van from Leaselt Lid. under a 5 year contract. The lease cost would be $10,500 per year. On the other hand, Harmony can purchase a van from Buyt Ltd. for $49,400. Assume Harmony has a required rate of return of 8%. Do not enter dollar signs or commas in the input boxes. Use the present value tables found in the textbook appendix. Round your answer to the nearest whole number. Use the NPV method to determine which altemative the company should accept. Lease Cost: 1 Purchase Costs 5 Therefore, Harmony should: The NPV(Purchase ) value is higher than NPV(Lease), which means the purchase option has a higher NPV. Therefore, Harmony should choose to purchase the van from Buyt Ltd. to determine whether harmony should lease or purchase the van, we will compare the net present value (npv) of each alternative. here's the calculation : lease cost: the lease cost is $10,500 per year for 5 years. purchase costs: the purchase cost of the van is $49,400. required rate of return: harmony has a required rate of return of 8%. to calculate the npv for the lease , we need to calculate the present value of the lease payments: pv(lease) = lease cost * pvifa(rate, years) pv(lease) = $10,500 * pvifa(8%, 5) to calculate the npv for the purchase , we need to calculate the present value of the purchase cost: pv(purchase) = purchase cost now, let's calculate the npv for each : npv(lease) = pv(lease) - initial investment (which is $0 for the lease ) npv(purchase) = pv(purchase) - initial investment (which is the purchase cost) compare the npv values and choose the with the higher npv. if npv is positive, it indicates that the investment generates a positive return, and if npv is negative, it indicates a negative return. based on the calculations, if the npv(lease) is higher than npv(purchase), harmony should choose the lease . if npv(purchase) is higher than npv(lease), harmony should choose the purchase . Suppose Surfers Paradise bank holds a short position in a portfolio of annual coupon bonds valued at $51,000. The modified duration of the bond portfolio, i.e., duration/ (1+yield), is 10 years. Based on the past 2-year daily data, the bank's risk management team estimates the following statistics for the daily yield changes: • The daily yield changes have a mean = -0.2% and standard deviation = 0.1%. • The DEAR of the portfolio is $300. There is a 5% chance that the bond portfolio value will increase by at least 1.2% or decrease by at least 10% over the next 10 days. Assume the daily yield changes follow a normal distribution but are NOT independently distributed across days, what is the 10-day VaR of the portfolio? (Please only provide the magnitude of VaR, i.e. without a minus sign, and round your answer Rounding the VaR to the nearest whole number, the magnitude of the 10-day VaR of the portfolio is 11.12%. To calculate the 10-day Value at Risk (VaR) of the portfolio, we need to consider the mean, standard deviation, and modified duration of the bond portfolio, as well as the given statistics for daily yield changes. Given that the daily yield changes are not independently distributed, we need to account for the correlation between the changes. However, the information provided does not specify the correlation, so we'll assume no correlation for simplicity. The formula to calculate the 10-day VaR is: VaR = (portfolio value) × (modified duration) × (daily yield change mean) × (square root of number of days) + (portfolio value) × (daily yield change standard deviation) × (square root of number of days) × (Z-score) Using the given data: Portfolio value = $51,000 Modified duration = 10 years Daily yield change mean = -0.2% (or -0.002 in decimal form) Daily yield change standard deviation = 0.1% (or 0.001 in decimal form) Number of days = 10 Z-score for a 5% chance is approximately 1.645 ( corresponding to the 95% confidence level) Plugging the values into the formula: VaR = ($51,000) × (10) × (-0.002) × (√10) + ($51,000) × (0.001) × (√10) × (1.645) = $57,536.97 Learn more about bond here: https://brainly.com/question/31994049 Assuming ASPE, indicate for each of the fosowing what should be disclosed on a staternent of cash fows (indirect method) a) For 2020 , net income was $650,000. (1 marks) b) Amortization of bond premlum, $1,100, ( 1 marks) The balance in Retained Earnings was $485,000 at December 31,2019 and $728,000 at December 31 . c) 2020. A stock dividend was declared and distributed which increased common shares by $280,000. (Show calculation of the cash didend and indicate how it and the stock dividend would be shown). (2 makk) d) Equipment, which cost $115,000 with sccumulated deproclotion of $53,000, was sold for $67,000. (2 maris) e) The deferred tax fiability increasod $18,000. ( 1 marks) f) Issued 2,000 preferred shares with a fair value of $130 per shere for a parcel of land. (1 mark) For 2020, the net income of $650,000 would be disclosed in the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows. A) The amortization of bond premium of $1,100 would not be separately disclosed in the statement of cash flows. It is considered a non-cash expense and is already reflected in the net income figure. B) The stock dividend declared and distributed, which increased common shares by $280,000, would not be shown as a cash dividend in the statement of cash flows. Stock dividends do not involve the outflow of cash. Instead, it would be disclosed in the financing activities section as an increase in common shares . To calculate the cash dividend associated with the stock dividend, we need to multiply the number of common shares issued as a stock dividend by the fair value per share. However, since the question does not provide the number of common shares issued as a stock dividend, it is not possible to calculate the cash dividend . Learn more about stock link: https://brainly.com/question/14649952 which business form has the advantage of limited liability? The business form that has the advantage of limited liability is the corporation. A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners, known as shareholders. One of the main advantages of a corporation is that it provides limited liability protection to its shareholders. Limited liability means that the shareholders' personal assets are generally protected from the debts and liabilities of the corporation. In the event of financial loss , creditors can only seek repayment from the assets of the corporation and not the personal assets of the shareholders. This feature provides a significant advantage as it helps to safeguard the personal wealth and assets of the shareholders. The limited liability protection offered by a corporation encourages investment and entrepreneurship as it reduces the financial risk for shareholders. It allows individuals or other entities to invest in the corporation without being personally responsible for its debts or legal obligations. Limited liability is particularly beneficial for large-scale businesses with substantial financial risks, as it provides a shield for individual shareholders from excessive personal liability . This legal protection can also make it easier for corporations to raise capital by attracting investors who are willing to invest in the business without risking their personal assets. In summary, the business form that offers the advantage of limited liability is the corporation. Limited liability protection provides shareholders with a level of security by separating their personal assets from the financial obligations and liabilities of the corporation. This protection encourages investment and facilitates capital raising for the corporation, making it an attractive option for businesses with significant financial risks. Learn more about liabilities here : brainly.com/question/15006644 A clothing merchant purchases a shipment of clothes for $36,000.00 with discounts of 10.00% and 5.00%. He sells it to a customer at a price which includes 19.00% profit on selling price and overhead expenses of 23.00% on selling price. a. How much did it cost him to purchase the container of clothes?Round to the nearest cent b. What was the selling price of the container of clothes? Round to the nearest cent The cost of purchasing the container of clothes for the clothing merchant can be calculated by subtracting the discounts from the original purchase price of $36,000.00.The selling price of the container of clothes can be determined by adding the profit percentage and overhead expenses percentage to the cost of purchase. To calculate the cost of purchasing the container of clothes, we first subtract the discount percentages from the original purchase price of $36,000.00. The first discount of 10.00% is calculated as 10.00% of $36,000.00, which equals $3,600.00. Subtracting this discount from the original purchase price gives us $36,000.00 - $3,600.00 = $32,400.00. Then, we apply the second discount of 5.00% to $32,400.00, which is calculated as 5.00% of $32,400.00, resulting in a discount of $1,620.00. Subtracting this second discount gives us the final cost of purchase, which is $32,400.00 - $1,620.00 = $30,780.00 (rounded to the nearest cent). To calculate the selling price of the container of clothes, we need to add the profit percentage and overhead expenses percentage to the cost of purchase. The profit percentage of 19.00% is calculated as 19.00% of the cost of purchase ($30,780.00), which equals $5,848.20. Adding this profit to the cost of purchase gives us $30,780.00 + $5,848.20 = $36,628.20. Similarly, the overhead expenses percentage of 23.00% is calculated as 23.00% of the cost of purchase ($30,780.00), which equals $7,084.40. Adding this amount to the selling price gives us the final selling price of the container of clothes, which is $36,628.20 + $7,084.40 = $43,712.60 (rounded to the nearest cent). To know more about Profit percentage : brainly.com/question/30168821 common stock that pays cash dividends can be viewed as Common stock that pays cash dividends can be viewed as a source of income for investors , providing regular payments from a company's profits. Common stock that pays cash dividends can be viewed as a source of income for investors who own these stocks. When a company pays cash dividends to its shareholders, it distributes a portion of its profits to its owners, which can provide a regular income stream. Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership in a corporation. When you purchase common stock, you become a shareholder in the company . This gives you the right to vote on important company matters, such as electing members of the board of directors and making decisions about mergers and acquisitions. The value of common stock is subject to market fluctuations, which means that the price can go up or down depending on various factors, such as economic conditions, industry trends, and company performance. When you own common stock, you have the potential to make money if the stock price goes up, but you also run the risk of losing money if the stock price goes down. Cash dividends: Cash dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholders. When a company has profits left over after it has paid its expenses and taxes, it can choose to distribute these profits to its owners in the form of cash dividends. The amount of the dividend is usually a fixed amount per share, which means that the more shares you own, the more money you will receive in dividends. Cash dividends can be a source of income for investors who own common stock that pays them. If you rely on this income, it is important to consider the stability of the company and its ability to continue paying dividends in the future. Learn more about dividends here: https://brainly.com/question/2960815 Calculate deadweight loss given below information: A price floor of \$12 has been set by the government, how much is deadweight loss (in \( \$ \) thousande) comparing to market equilibrium? To calculate the deadweight loss caused by a price floor, we need more information about the market equilibrium and the demand and supply curves. It is not possible to calculate the specific deadweight loss in thousands of dollars. The deadweight loss occurs when the quantity supplied and demanded at the price floor is lower than the quantity that would be exchanged in a free market equilibrium. It represents the loss of consumer and producer surplus due to the inefficient allocation of resources caused by the price floor. To learn more about market equilibrium , visit here https://brainly.com/question/31104772 2. Suppose the following data for an economy; a consumption function of C = 600 + 0.6(Y - T), Investment spending is fixed at 300, Government purchases are 400, and net taxes are 100. 1. What is the MPC, MPS, and the value of the tax multiplier? 10 pts. 2. Calculate the equilibrium level of income (Y) and graph AE? 20pts. 3. Suppose taxes decrease by 100, use the multiplier to calculate the new equilibrium level of income. 15 pts. The MPC is 0.6, MPS is 0.4 and the value of the tax multiplier is -1.5. The point where the AE curve intersects the 45-degree line represents the equilibrium level of income. The new equilibrium level of income is 2150. 1. The MPC (Marginal Propensity to Consume) is 0.6, indicating that for every one-unit increase in income, consumption increases by 0.6 units. The MPS (Marginal Propensity to Save) is 0.4, representing the portion of income saved rather than consumed. The value of the tax multiplier is -1.5, which means that a change in taxes will have a 1.5 times larger impact on equilibrium income. 2. To calculate the equilibrium level of income (Y), we need to set aggregate expenditure (AE) equal to income. AE consists of consumption (C), investment (I), government purchases (G), and net exports (NX). Assuming net exports are zero, we can calculate AE as AE = C + I + G. Substituting the given values, AE = (600 + 0.6(Y - T)) + 300 + 400. Solving for Y, we find the equilibrium level of income to be Y = 2000. Graphically, we plot the AE curve and the 45-degree line to identify the intersection as the equilibrium level. 3. If taxes decrease by 100, we can use the tax multiplier to calculate the change in equilibrium income. The change in taxes (ΔT) is -100, and multiplying it by the tax multiplier (-1.5), we find the change in income (ΔY) to be 150. Adding this change to the initial equilibrium income of 2000, we determine the new equilibrium level of income to be 2150. To know more about MPC , click here, https://brainly.com/question/32276464 Ohio Quarry Inc. has $13 million in assets. Its expected operating income (EBIT) is $2 million and its income tax rate is 40 percent. If Ohio Quarry finances 20 percent of its total assets with debt capital, the pretax cost of funds is 10 percent. If the company finances 40 percent of its total assets with debt capital, the pretax cost of funds is 15 percent. Round your answers to the questions below to two decimal places. Determine the rate of return on equity (ROE) under the three different capital structures (0, 20, and 40% debt ratios). 0% debt ratio: % 20% debt ratio: % 40% debt ratio: % The Rate of Return on Equity ( ROE ) under the three different capital structures (0, 20, and 40% debt ratios ) are as follows:0% debt ratio: 9.23%20% debt ratio: 8.46%40% debt ratio: 6.67% Given Data: Total Assets (TA) = $13 million Expected EBIT = $2 million Income Tax Rate = 40%Debt Capital for 20% Debt Ratio (D20) = TA × 20% = 0.20 × $13 million = $2.6 million Debt Capital for 40% Debt Ratio (D40) = TA × 40% = 0.40 × $13 million = $5.2 million Pretax Cost of Funds with 20% Debt Ratio = 10%Pretax Cost of Funds with 40% Debt Ratio = 15%Rate of Return on Equity (ROE) with 0% Debt Ratio: ROE = (Net Income / Equity) × 100%Since the company has zero debt in this scenario, the net income will be the same as the EBIT. Net Income = EBIT - (EBIT × Income Tax Rate) = $2 million - ($2 million × 40%) = $1.2 million Equity = TA - D = $13 million - $0 = $13 millionROE = (Net Income / Equity) × 100% = ($1.2 million / $13 million) × 100% = 9.23%ROE with 20% Debt Ratio: ROE = [(Net Income - Interest) / Equity] × 100% Interest = D20 × Pretax Cost of Debt = $2.6 million × 10% = $260,000 Net Income = EBIT - Interest - (EBIT × Income Tax Rate) = $2 million - $260,000 - ($2 million × 40%) = $880,000 Equity = TA - D20 = $13 million - $2.6 million = $10.4 million ROE = [(Net Income - Interest) / Equity] × 100% = ($880,000 / $10.4 million) × 100% = 8.46% ROE with 40% Debt Ratio: Interest = D40 × Pretax Cost of Debt = $5.2 million × 15% = $780,000 Net Income = EBIT - Interest - (EBIT × Income Tax Rate) = $2 million - $780,000 - ($2 million × 40%) = $520,000 Equity = TA - D40 = $13 million - $5.2 million = $7.8 million ROE = [(Net Income - Interest) / Equity] × 100% = ($520,000 / $7.8 million) × 100% = 6.67%. To know more about ROE https://brainly.com/question/30404824 The current state in the economy are as follows; Autonomous Consumption: 10000, Marginal Propensity to Consume: 0.3, Investment: 15000, Government Spending: 35000, Net Exports: -1000, Income Tax rate: 30%. The government wishes to conduct an injection into the economy to achieve a 40000 increase in national income. When providing answers to the questions below, please provide answers by 2 decimal places, unless stated otherwise. Calculated the current equilibrium income in the economy The government increases spending by 30000. Does this achieve the desired increase of 40000? If the answer to be does not achieve the desired increase of 40000 in national income, how much should the government increase its spending to achieve the 40000 increase in national income (to the nearest whole number)? (Hint: consider the what the multiplier in this economy is) The current equilibrium income in the economy is $85,714.29. Yes it achieve desired increase of 40000 the increase in national income from the government's increase in spending is $42,857.14. To calculate the current equilibrium income in the economy, we use the formula: Y = C + I + G + NX Where Y is national income, C is consumption, I is investment, G is government spending, and NX is net exports. Plugging in the given values, we get: Y = 10000 + 0.3Y + 15000 + 35000 - 1000 Y = 60000 + 0.3Y 0.7Y = 60000 Y = 85714.29 Therefore, the current equilibrium income in the economy is $85,714.29. Next, we can calculate the new equilibrium income after the government increases spending by $30,000. We use the formula: ∆Y = ∆G × (1 / (1 - MPC)) Where ∆Y is the change in national income, ∆G is the change in government spending, and MPC is the marginal propensity to consume . ∆Y = 30000 × (1 / (1 - 0.3)) ∆Y = 42857.14 Therefore, the increase in national income from the government's increase in spending is $42,857.14, which is greater than the desired increase of $40,000. So, the government's increase in spending by $30,000 achieves the desired increase in national income. Therefore, there is no need to calculate how much the government should increase its spending to achieve the desired increase in national income, as the increase of $30,000 is sufficient to achieve the desired increase of $40,000. To know more about equilibrium income here https://brainly.com/question/33454309  | 

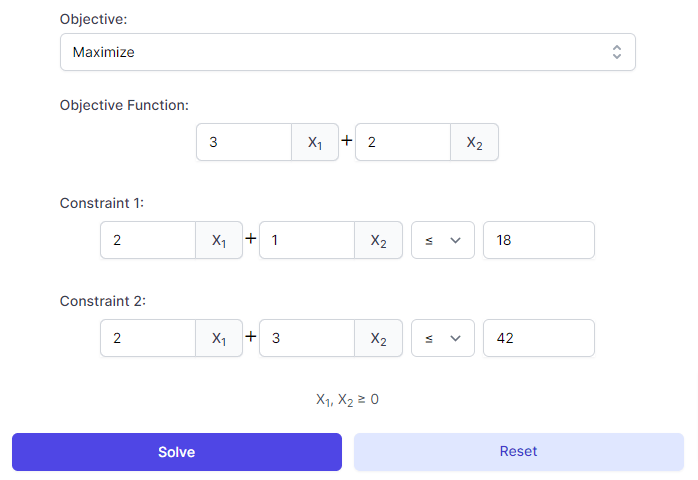
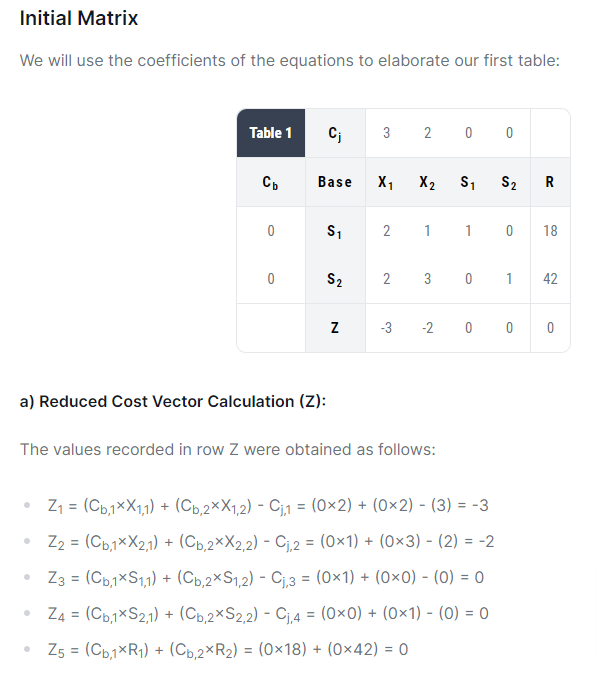
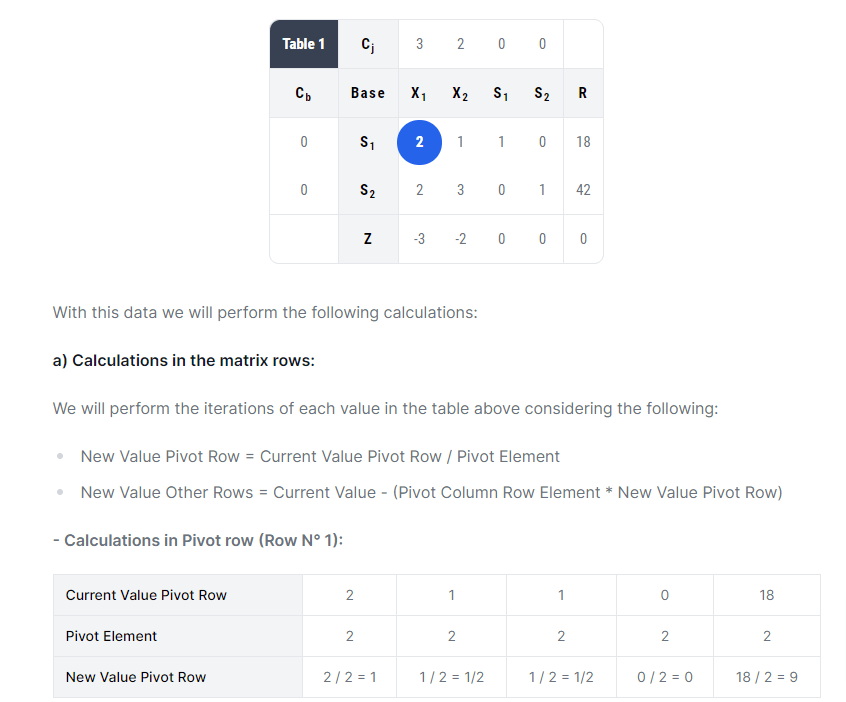
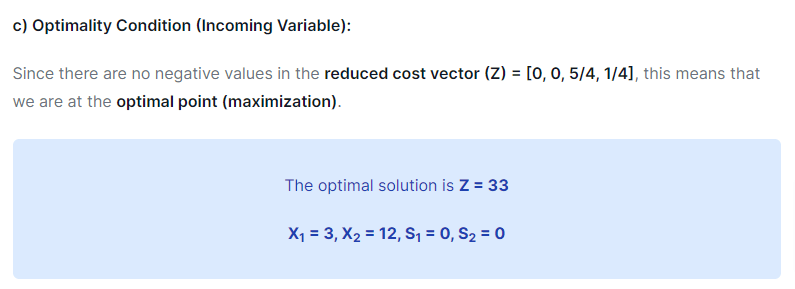


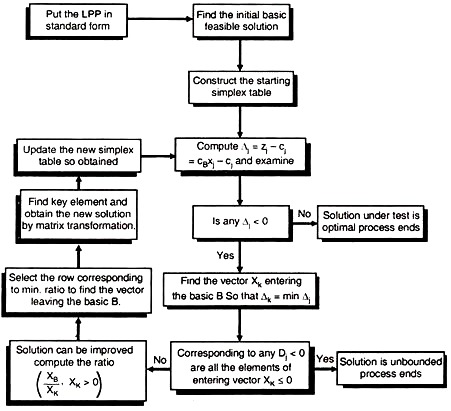


COMMENTS
In this section, we will solve the standard linear programming minimization problems using the simplex method. Once again, we remind the reader that in the standard minimization problems all constraints are of the form \(ax + by ≥ c\). The procedure to solve these problems was developed by Dr. John Von Neuman.
STEP 1. Set up the problem. Write the objective function and the constraints. Since the simplex method is used for problems that consist of many variables, it is not practical to use the variables x x, y y, z z etc. We use symbols x1 x 1, x2 x 2, x3 x 3, and so on. Let.
Simplex method is an approach to solving linear programming models by hand using slack variables, tableaus, and pivot variables as a means to finding the optimal solution of an optimization problem.
4.2.1: Maximization By The Simplex Method (Exercises) 4.3: Minimization By The Simplex Method In this section, we will solve the standard linear programming minimization problems using the simplex method. The procedure to solve these problems involves solving an associated problem called the dual problem.
2. The simplex method (with equations) The problem of the previous section can be summarized as follows. Maximize the function xˆ = 5x 1 +4x2 subject to the constraints: x 1 +3x2 18 x 1 + x2 8 2x 1 + x2 14 where we also assume that x 1, x2 0. Linear algebra provides powerful tools for simplifying linear equations. The first step
A systematic procedure for solving linear programs - the simplex method. Proceeds by moving from one feasible solution to another, at each step improving the value of the objective function. Terminates after a finite number of such transitions. Two important characteristics of the simplex method: The method is robust.
Chapter 6: The Simplex Method 1 Minimization Problem (§6.5) We can solve minimization problems by transforming it into a maximization problem. Another way is to change the selection rule for entering variable. Since we want to minimize z, we would now choose a reduced cost c¯ k that is negative, so that increasing the nonbasic variable x
A linear programming problem with a bounded set always has an optimal solution. This means that a bounded set has a maximum value as well as a minimum value. Example 1: Given the objective function P = 10 x − 3 y and the following feasible set, Find the maximum value and the point where the maximum occurs.
Examples and standard form Fundamental theorem Simplex algorithm Simplex method I Simplex method is first proposed by G.B. Dantzig in 1947. I Simply searching for all of the basic solution is not applicable because the whole number is Cm n. I Basic idea of simplex: Give a rule to transfer from one extreme point to another such that the objective function is decreased.
The following system can be solved by using the simplex method: Objective Function: P = 2x + 3y + z Subject to Constraints: 3x + 2y ≤ 5 2x + y - z ≤ 13 z ≤ 4 x,y,z≥0 Standard Maximization Problem Mathematically speaking, in order to use the simplex method to solve a linear programming problem, we need the standard maximization problem:
1 The basic steps of the simplex algorithm Step 1: Write the linear programming problem in standard form Linear programming (the name is historical, a more descriptive term would be linear optimization) refers to the problem of optimizing a linear objective function of several variables subject to a set of linear equality or inequality constraints.
Solving Linear Programs2In this chapter, we present a systematic procedure fo. solving linear programs. This procedure, called the simplex method, proceeds by moving from one feasible solution to another, at each step improving the value. f the objective function. Moreover, the method terminates after a finite n.
How to use the simplex method online calculator. To use our tool you must perform the following steps: Enter the number of variables and constraints of the problem. Select the type of problem: maximize or minimize. Enter the coefficients in the objective function and the constraints. You can enter negative numbers, fractions, and decimals (with ...
SECTION 4.2 PROBLEM SET: MAXIMIZATION BY THE SIMPLEX METHOD. Solve the following linear programming problems using the simplex method. 4) A factory manufactures chairs, tables and bookcases each requiring the use of three operations: Cutting, Assembly, and Finishing. The first operation can be used at most 600 hours; the second at most 500 ...
The simplex method provides an algorithm which is based on the fundamental theorem of linear programming. This states that "the optimal solution to a linear programming problem if it exists, always occurs at one of the corner points of the feasible solution space.". The simplex method provides a systematic algorithm which consist of moving from one basic feasible solution to another in a ...
Simplex method calculator - Solve the Linear programming problem using Simplex method, step-by-step online We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. By browsing this website, you agree to our use of cookies.
The simplex method is the most common way to solve large LP problems. Simplex is a mathematical term. In one dimension, a simplex is a line segment connecting two points. In two dimen-sions, a simplex is a triangle formed by joining the points. A three-dimensional simplex is a four-sided pyramid having four corners.
Linear Programming. Linear programming solver with up to 9 variables. New constraints could be added by using commas to separate them. Get the free "Linear Programming Solver" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. Find more Mathematics widgets in Wolfram|Alpha.
There is a method of solving a minimization problem using the simplex method where you just need to multiply the objective function by -ve sign and then solve it using the simplex method. All you need to do is to multiply the max value found again by -ve sign to get the required max value of the original minimization problem.
This video explains how to maximize or minimize an objective function using the simplex method of linear programming with the help of an example.Hope everyon...
general, be solved with the simplex method. The problem has a simplex- method solution (with unrestricted basis entry) only if c, are nonpositive (nonnegative for minimizing problems). CONSIDER the problem maximize z= cj(xj/,subject to Ax=b. (1) Parts of the literature imply that the standard simplex method can be used to solve this problem.
SECTION 4.3 PROBLEM SET: MINIMIZATION BY THE SIMPLEX METHOD. In problems 1-2, convert each minimization problem into a maximization problem, the dual, and then solve by the simplex method.
3. (12 pts.) Solve the following linear programming problem graphically (NOT using the simplex method. Identify the coordinates of all corner points of the feasible region. Show all work! State your final conclusion clearly and correctly. Maximize € Ζ=6x+12y Subject to € x−y≥−3 € 2x−y≤4 € x+2y≤12 € x,y≥0 y x 4. (8 pts.)
Question: Use simplex method to solve the maximization linear programming problem Use simplex method to solve the maximization linear programming problem This question hasn't been solved yet!
This article presents a self-adjustable branch-and-bound algorithm for globally solving a class of linear multiplicative programming problems (LMP). In this algorithm, a self-adjustable branching rule is introduced and it can continuously update the upper bound for the optimal value of LMP by selecting suitable branching point under certain conditions, which differs from the standard bisection ...
linear programming problem is specified by a linear, multi-variable function which is to be optimized (maximized or minimized) subject to a number of linear constraints. The mathematician, G. B. Dantzig [3] developed an algorithm called the "simplex method" to solve problems of this type. The original simplex method has been modified into an ...
Solving the Linear Programming Problem by Using the Initial Tableau. We will present the algorithm for solving, however, note that it is not entirely intuitive. 1. Select a pivot column We first select a pivot column, which will be the column that contains the largest negative coefficient in the row containing the objective function.
2) Gurobi : We use the Gurobi solver [12] to solve the pricing problem to optimality and add the optimal column to start the next iteration of CG. Note that Gurobi is a state-of-the-art mixed-integer programming solver; 3) Gurobi : In this setting, we use Gurobi to solve a pricing problem to optimality and add multiple columns
In this section, we will solve the standard linear programming minimization problems using the simplex method. Once again, we remind the reader that in the standard minimization problems all constraints are of the form \(ax + by ≥ c\). The procedure to solve these problems was developed by Dr. John Von Neuman.