You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

How to Teach Creative Writing | 7 Steps to Get Students Wordsmithing

“I don’t have any ideas!”
“I can’t think of anything!”
While we see creative writing as a world of limitless imagination, our students often see an overwhelming desert of “no idea.”
But when you teach creative writing effectively, you’ll notice that every student is brimming over with ideas that just have to get out.
So what does teaching creative writing effectively look like?
We’ve outlined a seven-step method that will scaffold your students through each phase of the creative process from idea generation through to final edits.
7. Create inspiring and original prompts
Use the following formats to generate prompts that get students inspired:
- personal memories (“Write about a person who taught you an important lesson”)
- imaginative scenarios
- prompts based on a familiar mentor text (e.g. “Write an alternative ending to your favorite book”). These are especially useful for giving struggling students an easy starting point.
- lead-in sentences (“I looked in the mirror and I couldn’t believe my eyes. Somehow overnight I…”).
- fascinating or thought-provoking images with a directive (“Who do you think lives in this mountain cabin? Tell their story”).

Don’t have the time or stuck for ideas? Check out our list of 100 student writing prompts
6. unpack the prompts together.
Explicitly teach your students how to dig deeper into the prompt for engaging and original ideas.
Probing questions are an effective strategy for digging into a prompt. Take this one for example:
“I looked in the mirror and I couldn’t believe my eyes. Somehow overnight I…”
Ask “What questions need answering here?” The first thing students will want to know is:
What happened overnight?
No doubt they’ll be able to come up with plenty of zany answers to that question, but there’s another one they could ask to make things much more interesting:
Who might “I” be?
In this way, you subtly push students to go beyond the obvious and into more original and thoughtful territory. It’s even more useful with a deep prompt:
“Write a story where the main character starts to question something they’ve always believed.”
Here students could ask:
- What sorts of beliefs do people take for granted?
- What might make us question those beliefs?
- What happens when we question something we’ve always thought is true?
- How do we feel when we discover that something isn’t true?
Try splitting students into groups, having each group come up with probing questions for a prompt, and then discussing potential “answers” to these questions as a class.
The most important lesson at this point should be that good ideas take time to generate. So don’t rush this step!
5. Warm-up for writing
A quick warm-up activity will:
- allow students to see what their discussed ideas look like on paper
- help fix the “I don’t know how to start” problem
- warm up writing muscles quite literally (especially important for young learners who are still developing handwriting and fine motor skills).
Freewriting is a particularly effective warm-up. Give students 5–10 minutes to “dump” all their ideas for a prompt onto the page for without worrying about structure, spelling, or grammar.
After about five minutes you’ll notice them starting to get into the groove, and when you call time, they’ll have a better idea of what captures their interest.
Did you know? The Story Factory in Reading Eggs allows your students to write and publish their own storybooks using an easy step-by-step guide.

4. Start planning
Now it’s time for students to piece all these raw ideas together and generate a plan. This will synthesize disjointed ideas and give them a roadmap for the writing process.
Note: at this stage your strong writers might be more than ready to get started on a creative piece. If so, let them go for it – use planning for students who are still puzzling things out.
Here are four ideas for planning:
Graphic organisers
A graphic organiser will allow your students to plan out the overall structure of their writing. They’re also particularly useful in “chunking” the writing process, so students don’t see it as one big wall of text.
Storyboards and illustrations
These will engage your artistically-minded students and give greater depth to settings and characters. Just make sure that drawing doesn’t overshadow the writing process.
Voice recordings
If you have students who are hesitant to commit words to paper, tell them to think out loud and record it on their device. Often they’ll be surprised at how well their spoken words translate to the page.
Write a blurb
This takes a bit more explicit teaching, but it gets students to concisely summarize all their main ideas (without giving away spoilers). Look at some blurbs on the back of published books before getting them to write their own. Afterward they could test it out on a friend – based on the blurb, would they borrow it from the library?
3. Produce rough drafts
Warmed up and with a plan at the ready, your students are now ready to start wordsmithing. But before they start on a draft, remind them of what a draft is supposed to be:
- a work in progress.
Remind them that if they wait for the perfect words to come, they’ll end up with blank pages .
Instead, it’s time to take some writing risks and get messy. Encourage this by:
- demonstrating the writing process to students yourself
- taking the focus off spelling and grammar (during the drafting stage)
- providing meaningful and in-depth feedback (using words, not ticks!).

Reading Eggs also gives you access to an ever-expanding collection of over 3,500 online books!
2. share drafts for peer feedback.
Don’t saddle yourself with 30 drafts for marking. Peer assessment is a better (and less exhausting) way to ensure everyone receives the feedback they need.
Why? Because for something as personal as creative writing, feedback often translates better when it’s in the familiar and friendly language that only a peer can produce. Looking at each other’s work will also give students more ideas about how they can improve their own.
Scaffold peer feedback to ensure it’s constructive. The following methods work well:
Student rubrics
A simple rubric allows students to deliver more in-depth feedback than “It was pretty good.” The criteria will depend on what you are ultimately looking for, but students could assess each other’s:
- use of language.
Whatever you opt for, just make sure the language you use in the rubric is student-friendly.
Two positives and a focus area
Have students identify two things their peer did well, and one area that they could focus on further, then turn this into written feedback. Model the process for creating specific comments so you get something more constructive than “It was pretty good.” It helps to use stems such as:
I really liked this character because…
I found this idea interesting because it made me think…
I was a bit confused by…
I wonder why you… Maybe you could… instead.
1. The editing stage
Now that students have a draft and feedback, here’s where we teachers often tell them to “go over it” or “give it some final touches.”
But our students don’t always know how to edit.
Scaffold the process with questions that encourage students to think critically about their writing, such as:
- Are there any parts that would be confusing if I wasn’t there to explain them?
- Are there any parts that seem irrelevant to the rest?
- Which parts am I most uncertain about?
- Does the whole thing flow together, or are there parts that seem out of place?
- Are there places where I could have used a better word?
- Are there any grammatical or spelling errors I notice?
Key to this process is getting students to read their creative writing from start to finish .
Important note: if your students are using a word processor, show them where the spell-check is and how to use it. Sounds obvious, but in the age of autocorrect, many students simply don’t know.
A final word on teaching creative writing
Remember that the best writers write regularly.
Incorporate them into your lessons as often as possible, and soon enough, you’ll have just as much fun marking your students’ creative writing as they do producing it.
Need more help supporting your students’ writing?
Read up on how to get reluctant writers writing , strategies for supporting struggling secondary writers , or check out our huge list of writing prompts for kids .

Watch your students get excited about writing and publishing their own storybooks in the Story Factory
You might like....
Creative Writing for Kids: A Step-By-Step Guide to Writing a Story

Creative writing can be a real positive force for children’s lives and development, but how does a child get started with creative writing? There are many ways, but it can often be helpful to have a structure to work from, so we’ve outlined some simple steps on how your child can write a story and enjoy themselves in the process! As they brainstorm, a lot of ideas will come to mind, so we recommend they take notes throughout the process.
What is creative writing?
Creative writing is an expressive form of writing that allows children to explore their thoughts, ideas, and emotions in an imaginative way. Unlike academic or factual writing , creative writing encourages children to use their imagination to invent characters , settings , and plots , fostering a love for storytelling and self-expression.
In creative writing, children have the freedom to write stories , poems , letters , and even scripts for their own movies. It's an opportunity for them to unleash their creativity, experiment with language, and develop their unique voice as writers. Through creative writing, children learn to think critically, problem-solve, and communicate effectively, all while having fun and exploring their creativity.
Encouraging creative writing at home or as part of homeschooling not only helps children develop their writing skills but also nurtures their imagination and confidence.
Getting started

Your child may not be quite ready to start, and that’s normal - writing can be challenging!
Instead of jumping straight in, ease your child into it with activities like free writing. This will allow them to explore any topic without pressure, acting as a way to boost your child’s imagination before they start writing stories .
If your child is a reluctant writer, you can try different methods that don’t actively require them to put pen to paper, but are linked to creativity and storytelling. These include drawing , picking out new children’s books from the local library, telling stories out loud, or dedicating time to read your child’s favorite books as a family. Generally, reading lays the foundation for your child to be able to create their own stories, improving their narrative writing skills by exposing them to different techniques, genres, and styles.
When all else fails, encourage your child to read more. The more that your child reads, the easier it will be for them to start writing.
Step 1: Character development
Creating a character is a great starting point for your child to write their own story.
This character can be whatever your child wants them to be. They can be a human, an animal, a mystical creature, or something completely made-up! Once they have a general idea of what they want this character to be, they can brainstorm different plot points, which will further inform the characters traits, behaviours, and role in the story.
Here are some questions your child should be able to answer about their character:
- What is going on in this character’s life?
- Do they have a problem that they need to fix?
- Who are they interacting with in this story?
- How do they feel about other characters, and about the issue at hand?
A story normally relies on one character to be the hero, and on another to be the villain. The villain is typically portrayed as a negative character who introduces a problem (the antagonist), and the hero is a positive character who solves the problems (the protagonist). Once your child creates their main character, they should establish their role within the story. Are they writing from the perspective of the hero, or would they prefer to give the villain of the story a voice?
From there, they can create side characters! These are typically parents, siblings, and friends of the main character, but can also be total strangers. If your child is stuck on how to build their first character, they can use writing prompts to make it a little easier. Try this prompt:
Prompt: Create a character that is half dog, and half elephant and call it a Doggophant! What does a Doggophant like to eat?
Step 2: Setting and genre
The next step in your child’s creative writing process is to choose where it takes place . They should also decide the genre of their story, as some settings won’t work for some specific genres (for example, a sunny beach wouldn’t pair well with a moody mystery).
This story’s setting could be a real location, such as London, Paris, or New York, or a fictional location, like an enchanted forest or an underwater kingdom.
A helpful way to start brainstorming is to ask your child about places they’ve been to, seen on TV, or read about in stories. This is a chance for them to imagine how their story would look like in different settings, and will help them decide on the genre they’d like to go for too.
Prompt (continued): Where does a Doggophant usually live? Is it a magical Night Zoo?
Step 3: Structure and plot

Before starting to plan the plot, your child should understand the basic structure of a story . All good stories have a beginning, a middle, and an end.
The beginning serves as a way to introduce characters, set the scene, and show the "calm before the storm”. This happens before a conflict is introduced.
The middle of a story is where most of the action takes place. This is where your child should introduce the main problem, and the main character’s journey of trying to solve it.
Finally, the ending or conclusion of the story is where, normally, the conflict is resolved. This can change depending on how your child wants to end their story!
Prompt (continued): Doggophants love when people visit the Night Zoo, but a new character named Lord Nulth is trying to steal all of the creativity in the Zoo! Does Lord Nulth sound like a nice person? Why would he want to steal creativity? How will Doggophant and other animals stop him?
Step 4: Begin Writing
Now that all the planning is done, let’s get writing!
As your child starts to write, they’ll probably make changes and come up with new story ideas— this is normal and an integral part of the creative process.
It’s important that you offer your support throughout this process, especially if your child is a reluctant writer. While giving them space to concentrate, you can check-in every once in a while, offering help if they encounter any hurdles. Your role mirrors that of a writing prompt, providing your child with initial ideas and nudging them to develop their story further. This collaborative approach ensures their story unfolds organically, making the blank page a canvas for unlimited story possibilities!
Step 5: Keep Going!

One of the best things about creative writing is that it enables children to express themselves and grow in confidence with every story they craft. It pushes children to believe in the phrase "I can", as they embark on different writing exercises without the fear of failing or being held by the “what if’s”. As your child starts their journey through the exciting world of writing, it’s important to guide them in the right direction. Encourage them to not overthink and just write whatever comes to mind at first.
To keep the momentum, you can even set different goals, like writing different descriptions, drawing their main character, or brainstorming different story endings before writing the full story. For reluctant writers, setting small, attainable targets can make the process less overwhelming and more exciting. Avoid setting strict word counts or time limits, as these can add pressure and take the fun out of the writing experience.
It’s important to remember that progress isn’t linear, and that every child is unique. If they need to, you can allow your child to build their story gradually, creating a more fluid project that enables them to work when inspiration strikes. Once they finish their first story, you’ll probably see a change in their attitude, and a new motivation to write a different piece.
Creative writing can be a rewarding experience for you and your child. Make sure you give them positive encouragement, and to soak in the experience of reading the story once it has been completed. They’ll have created something one-of-a-kind, and it will give you an exciting look into their imagination!
Step 6: Try Night Zookeeper

Still having trouble getting your child motivated to write? You should try Night Zookeeper !
Our writing program for kids makes writing fantastically fun by turning different writing activities into games, keeping children engaged, entertained, and excited to learn!
We cover all styles of writing, and boost children’s writing skills using an array of different activities, including writing lessons, short story prompts, and challenges.
More creative writing activities
- 25 Creative Writing Prompts For Kids
- Writing Activities For Kids
- Story Writing Resources
Got any questions? Reach out to us via email at [email protected] . Follow us on social media:

Make Reading & Writing Fantastically Fun!
- Award-winning reading & writing program for kids
- Improves spelling, grammar, punctuation & vocabulary
- Over 1,000 different learning games and activities

“My Child Hates Writing.” What do I do?

How To Get Your Child To Love Writing

8 Fantastically Fun Writing Games For Kids

Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
The world of creative writing is as vast as it is rewarding. It’s a form of expression that allows the writer to explore different worlds, characters, and narratives – all within the power of their pen.
But what exactly is creative writing and why is it important? Let’s explore the value of creative writing and how to inspire young (or old!) minds to embark on the curious and exciting journey of writing creatively – it’s easier than you think!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing, in its simplest form, is writing that goes beyond the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature.
It’s characterized by its emphasis on:
- narrative craft
- character development
- the use of literary devices
From poetry to plays, scripts to sonnets, creative writing covers a wide range of genres . It’s about painting pictures with words, invoking emotions, and bringing ideas to life . It’s about crafting stories that are compelling, engaging, and thought-provoking.
Whether you’re penning a novel or jotting down a journal entry, creative writing encourages you to unleash your imagination and express your thoughts in a unique, artistic way. For a deeper dive into the realm of creative writing, you can visit our article on what is creative writing .
Benefits of Developing Creative Writing Skills
The benefits of creative writing extend beyond the page.
It’s not just about creating captivating stories or crafting beautiful prose. The skills developed through creative writing are invaluable in many aspects of life and work.
1. Creative writing fosters creativity and imagination.
It encourages you to think outside the box, broaden your perspective, and explore new ideas. It also enhances your ability to communicate effectively, as it involves conveying thoughts, emotions, and narratives in a clear and compelling manner.
2. Creative writing aids in improving critical thinking skills.
It prompts you to analyze characters, plotlines, and themes, and make connections between different ideas. This process activates different parts of the mind, drawing on personal experiences, the imagination, logical plot development, and emotional intelligence.
3. Creative writing is also a valuable tool for self-expression and personal growth.
It allows you to explore your feelings, experiences, and observations, providing an outlet for self-reflection and introspection. By both reading and writing about different characters in different situations, readers develop empathy in a gentle but effective way.
4. Creative writing skills can open up a host of career opportunities.
From authors and editors to content creators and copywriters, the demand for creative writers is vast and varied. You can learn more about potential career paths in our article on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
In essence, creative writing is more than just an art—it’s a skill, a craft, and a powerful tool for communication and self-expression. Whether you’re teaching creative writing or learning it, understanding its value is the first step towards mastering the art.
The 3 Roles of a Creative Writing Teacher
Amongst the many facets of a creative writing teacher’s role, three vital aspects stand out: inspiring creativity , nurturing talent , and providing constructive criticism . These elements play a significant role in shaping budding writers and fostering their passion for the craft.
1. Inspiring Creativity
The primary function of a creative writing teacher is to inspire creativity.
They must foster an environment that encourages students to think outside the box and explore new possibilities . This includes presenting students with creative writing prompts that challenge their thinking, promoting lively discussions around various topics, and providing opportunities for students to engage in creative writing activities for kids .
Teachers should also expose students to a range of literary genres , styles, and techniques to broaden their understanding and appreciation of the craft. This exposure not only enhances their knowledge but also stimulates their creativity, encouraging them to experiment with different writing styles .
2. Nurturing Talent
Nurturing talent involves recognizing the unique abilities of each student and providing the necessary support and guidance to help them develop these skills. A creative writing teacher needs to identify the strengths and weaknesses of each student and tailor their approach accordingly.
This means:
- offering personalized feedback
- setting realistic yet challenging goals
- providing opportunities for students to showcase their work
Encouraging students to participate in writing competitions or to publish their work can give them a confidence boost and motivate them to improve. Furthermore, teachers should educate students about various creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree . This knowledge can inspire students to pursue their passion for writing and explore career opportunities in the field.
3. Providing Constructive Criticism
Providing constructive criticism is a critical aspect of teaching creative writing. It involves assessing students’ work objectively and providing feedback that helps them improve .
Teachers should:
- highlight the strengths of the work
- address the areas that need improvement
- suggest ways to make the piece better
Constructive criticism should be specific, actionable, and encouraging . It’s important to remember that the goal is to help the student improve, not to discourage them. Therefore, teachers need to communicate their feedback in a respectful and supportive manner.
In essence, a teacher’s role in teaching creative writing extends beyond mere instruction. They are mentors who inspire, nurture, and shape the minds of budding writers. By fostering a supportive and stimulating environment, they can help students unlock their creative potential and develop a lifelong love for writing.
3 Techniques for Teaching Creative Writing
When it comes to understanding how to teach creative writing, there are several effective techniques that can help inspire students and foster their writing skills.
1. Encouraging Free Writing Exercises
Free writing is a technique that encourages students to write continuously for a set amount of time without worrying about grammar, punctuation, or topic. This type of exercise can help unleash creativity, as it allows students to freely express their thoughts and ideas without judgment or constraint.
As a teacher, you can set a specific theme or provide creative writing prompts to guide the writing session. Alternatively, you can allow students to write about any topic that comes to mind. The key is to create an environment that encourages creative exploration and expression.
2. Exploring Different Genres
Another effective technique is to expose students to a wide range of writing genres. This can include fiction, non-fiction, poetry, drama, fantasy, mystery, and more. By exploring different genres, students can discover their unique writing styles and interests. This variety also offers the chance to expand their writing skills and apply them to various writing formats.
To facilitate this exploration, you can assign writing projects in different genres, conduct genre-specific writing workshops, or invite guest speakers who specialize in different genres. You can also encourage students to critically analyze how different authors approach their work.
3. Analyzing Published Works
Analyzing published works is a powerful way to teach creative writing. This technique allows students to learn from established authors by studying their:
- writing styles
- narrative structures
- use of language.
It also provides a practical context for understanding writing concepts and techniques.
As a teacher, you can select diverse pieces of literature for analysis , ranging from classic novels to contemporary short stories. Encourage students to identify elements they admire in these works and discuss how they can incorporate similar techniques into their own writing.
These techniques for teaching creative writing are effective ways to inspire creativity, encourage self-expression, and develop writing skills. As a teacher, your role is crucial in guiding students through their creative journey and helping them realize their potential as writers.
Creative Writing Workshops and Exercises
One effective method on how to teach creative writing is through the use of targeted workshops and exercises. These interactive sessions can stimulate creativity, foster character development , and help in understanding story structures .
Idea Generation Workshops
Idea generation is a crucial aspect of creative writing. It is the starting point that provides a springboard for writers to explore and develop their narratives. Idea generation workshops can be an interactive and fun way to help writers come up with fresh ideas.
Workshops can include brainstorming sessions , where writers are encouraged to think freely and note down all ideas, no matter how unconventional they may seem. Another method is the use of writing prompts , which can serve as a creative spark.
A prompt could be:
- even an image
Editor’s Note : Encourage children to create a big scribble on a scrap piece of paper and then look for an image in it (like looking for pictures in the clouds). This can be a great creative writing prompt and students will love sharing their writing with each other! Expect lots of giggles and fun!
Character Development Exercises
Characters are the heart of any story. They drive the narrative and engage the readers. Character development exercises can help writers create well-rounded and relatable characters.
Such exercises can include character questionnaires , where writers answer a series of questions about their characters to gain a deeper understanding of their personalities, backgrounds, and motivations. Role-playing activities can also be useful, allowing writers to step into their characters’ shoes and explore their reactions in different scenarios.
Story Structure Workshops
Understanding story structure is vital for creating a compelling narrative. Story structure workshops can guide writers on how to effectively structure their stories to engage readers from start to finish .
These workshops can cover essential elements of story structures like:
- rising action
- falling action
In addition to understanding the basics, writers should be encouraged to experiment with different story structures to find what works best for their narrative style. An understanding of story structure can also help in analyzing and learning from published works .
Providing writers with the right tools and techniques, through workshops and exercises, can significantly improve their creative writing skills. It’s important to remember that creativity flourishes with practice and patience .
As a teacher, nurturing this process is one of the most rewarding aspects of teaching creative writing. For more insights and tips on teaching creative writing, continue exploring our articles on creative writing .
Tips to Enhance Creative Writing Skills
The process of teaching creative writing is as much about honing one’s own skills as it is about imparting knowledge to others. Here are some key strategies that can help in enhancing your creative writing abilities and make your teaching methods more effective.
Regular Practice
Like any other skill, creative writing requires regular practice . Foster the habit of writing daily, even if it’s just a few lines. This will help you stay in touch with your creative side and continually improve your writing skills. Encourage your students to do the same.
Introduce them to various creative writing prompts to stimulate their imagination and make their writing practice more engaging.
Reading Widely
Reading is an essential part of becoming a better writer. By reading widely, you expose yourself to a variety of styles, tones, and genres . This not only broadens your literary horizons but also provides a wealth of ideas for your own writing.
Encourage your students to read extensively as well. Analyzing and discussing different works can be an excellent learning exercise and can spark creative ideas .
Exploring Various Writing Styles
The beauty of creative writing lies in its diversity. From poetic verses to gripping narratives, there’s a wide range of styles to explore. Encourage your students to try their hand at different forms of writing. This not only enhances their versatility but also helps them discover their unique voice as a writer.
To help them get started, you can introduce a variety of creative writing activities for kids . These tasks can be tailored to suit different age groups and proficiency levels. Remember, the goal is to foster a love for writing, so keep the activities fun and engaging .
Have Fun Teaching Creative Writing!
Enhancing creative writing skills is a continuous journey. It requires persistence, curiosity, and a willingness to step out of your comfort zone. As a teacher, your role is to guide your students on this journey, providing them with the tools and encouragement they need to flourish as writers – and most of all – enjoy the process!
For more insights on creative writing, be sure to explore our articles on what is creative writing and creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Enriching Creative Writing Activities for Kids
You may also like, the art of dreaming: how rem sleep stimulates creativity.
Stream of Consciousness Journaling: A Beginner’s Guide
Diary vs journal: whats the difference and when to use each, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Writing Techniques
How to Teach Creative Writing
Last Updated: March 13, 2024 References
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 117,367 times.
Creative writing is one of the most enjoyable types of writing for students. Not only does it allow students to explore their imaginations, but it helps them to structure their ideas and produce writing that they can be proud of. However, creative writing is a relatively difficult type of writing to teach and offers challenges to both new and seasoned teachers alike. Fortunately, though, with some work of their own, teachers can better develop their own abilities to teach creative writing.
Providing Students with the Fundamentals

- Theme. The theme of a story is its message or the main idea behind it.
- Setting. The setting of a story is the location or time it takes place in.
- Plot. The plot is the overall story, narrative, or sequence of events.
- Characterization. Characterization is how a character or person in a story is explained or presented to the reader.
- Conflict and dramatic action. Conflict and dramatic action are the main events of focus in the story. These events are often tense or exciting and are used to lure the reader in. [1] X Research source

- Explain how your students, as writers, can appeal to the humanity of their readers. One great way to do this is to ask them to explore character development. By developing the characters in their story, readers will become invested in the story.
- Discuss the triggers that engage readers in an effective story. Most great stories start with a problem, which is solved with the resolution, or conclusion of the story. Encourage students to create an engaging problem that will hook the readers in the first few pages of a short story or novel. [2] X Research source

- By setting the tone and atmosphere of a story, the author will establish his or her attitude to the subject and the feel of the story.
- Tone can be positive, neutral, or negative. [3] X Research source
- Atmosphere can be dark, happy, or neither.
- Descriptive words like “darkness” or “sunshine” can help set both the tone and atmosphere. [4] X Research source

- Active verbs are used to show action in the story.
- Active verbs are very often a better alternative to passive voice, as it keeps your writing clear and concise for your readers. [5] X Research source
- For example, instead of writing “The cat was chased by the dog” your student can write “The dog chased the cat.”
Guiding Students through the Process

- Tell your students to brainstorm about ideas they are truly interested in.
- If you must restrict the general topic, make sure that your students have a good amount of wiggle room within the broad topic of the assignment.
- Never assign specific topics and force students to write. This will undermine the entire process. [6] X Research source

- Letting your students know that the outline is non-binding. They don’t have to follow it in later steps of the writing process.
- Telling your students that the parts of their outline should be written very generally.
- Recommending that your students create several outlines, or outlines that go in different directions (in terms of plot and other elements of storytelling). The more avenues your students explore, the better. [7] X Research source

- Tell students that there is no “right” way to write a story.
- Let students know that their imaginations should guide their way.
- Show students examples of famous writing that breaks normal patterns, like the works of E.E. Cummings, William Faulkner, Charles Dickens, and William Shakespeare.
- Ask students to forget about any expectations they think you have for how a story should be written. [8] X Research source

- Gather the first drafts and comment on the student's work. For first drafts, you want to check on the overall structure of the draft, proper word use, punctuation, spelling, and overall cohesion of the piece. [9] X Research source
- Remind them that great writers usually wrote several drafts before they were happy with their stories.
- Avoid grading drafts for anything other than completion.

- Let students pair off to edit each others' papers.
- Have your students join groups of 3 or 4 and ask them to go edit and provide feedback on each member’s story.
- Provide guidance so students contribute constructively to the group discussion. [10] X Research source

- Reward your students if they are innovative or do something unique and truly creative.
- Avoid evaluating your students based on a formula.
- Assess and review your own standards as often as you can. Remember that the point is to encourage your students' creativity. [11] X Research source
Spurring Creativity

- Teach your students about a variety of writers and genres.
- Have your students read examples of different genres.
- Promote a discussion within your class of the importance of studying literature.
- Ask students to consider the many ways literature improves the world and asks individuals to think about their own lives. [12] X Research source

- Make sure your room is stocked with a wide variety of fiction stories.
- Make sure your room is stocked with plenty of paper for your students to write on.
- Line up other writing teachers or bring in writers from the community to talk to and encourage your students.

- Cut out pictures and photographs from magazines, comic books, and newspapers.
- Have your students cut out photographs and pictures and contribute them to your bank.
- Consider having your students randomly draw a given number of photos and pictures and writing a short story based on what they draw.
- This technique can help students overcome writer's block and inspire students who think that they're "not creative." [13] X Research source

- Pair your students with students from another grade in your school.
- Allow your students to write stories that younger students in your school would like to read.
- Pair your students with another student in the class and have them evaluate each others' work. [14] X Research source

- If you just have a typical classroom to work with, make sure to put inspirational posters or other pictures on the walls.
- Open any curtains so students can see outside.
- If you have the luxury of having an extra classroom or subdividing your own classroom, create a comfortable space with a lot of inspirational visuals.
- Writing spaces can help break writer's block and inspire students who think that they're "not creative." [15] X Research source

- Involve students in the printing process.
- Publication does not have to be expensive or glossy.
- Copies can be made in the school workroom if possible or each student might provide a copy for the others in the group.
- A collection of the stories can be bound with a simple stapler or brads.
- Seek out other opportunities for your students to publish their stories.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.writersonlineworkshops.com/courses/creative-writing-101
- ↑ https://kobowritinglife.com/2012/10/14/six-tips-for-engaging-readers-within-two-seconds-the-hook-in-fiction-and-memoir/
- ↑ https://www.dailywritingtips.com/in-writing-tone-is-the-author%E2%80%99s-attitude/
- ↑ http://ourenglishclass.net/class-notes/writing/the-writing-process/craft/tone-and-mood/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/539/02/
- ↑ http://www.alfiekohn.org/article/choices-children/
- ↑ https://www.writersdigest.com/write-better-fiction/7-steps-to-creating-a-flexible-outline-for-any-story
- ↑ http://thewritepractice.com/the-formula-to-write-a-novel/
- ↑ https://student.unsw.edu.au/editing-your-essay
- ↑ http://orelt.col.org/module/unit/5-promoting-creative-writing
- ↑ http://education.seattlepi.com/grade-creative-writing-paper-3698.html
- ↑ http://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2016/04/educating-teenagers-emotions-through-literature/476790/
- ↑ http://www.wrightingwords.com/for-teachers/5-tips-for-teaching-creative-writing/
About This Article

To teach creative writing, start by introducing your students to the core elements of storytelling, like theme, setting, and plot, while reminding them that there’s no formula for combining these elements to create a story. Additionally, explain how important it is to use tone and atmosphere, along with active verbs, to write compelling stories that come alive. When your students have chosen their topics, have them create story outlines before they begin writing. Then, read their rough drafts and provide feedback to keep them on the right path to storytelling success. For tips from our English reviewer on how to spur creativity in your students, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Yunzhe Yang
Mar 27, 2017
Did this article help you?
Daniel Hesse
Dec 5, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Create new account
- Reset your password
Register and get FREE resources and activities
Ready to unlock all our resources?
Creative writing techniques for kids: a step-by-step guide to writing a story

The way literacy is taught in primary schools has changed radically in the last couple of decades; when I was at school in the 80s we copied from blackboards, had whole hours of handwriting practice and sweated over spellings without any formal teaching of phonics whatsoever. While I think the more structured approach to literacy teaching we see in classrooms today makes learning more fun and accessible, my one worry is that there’s little time left for writing creatively.
When I was at school I adored writing stories – even stories with chapters and illustrations. I know my author brother did too – we found some of his old stories a few years back, and I felt so pleased he’d had the time to write these endless pages of action, adventure, characterisation and twisting plotlines.
As a primary teacher I ensured I would have a week each term when, during literacy sessions, we would focus solely on creating stories. I wasn’t deviating from the curriculum – far from it. During this week children would be consolidating their learning of phonics and be ‘writing for purpose’, considering carefully the aspects of story and who their audience might be.
It may very well be that your children write stories at home regardless of whether they’re required to for school, because most children have a seemingly natural urge to want to do so from time to time. This is just a little guidance on how you can support them and encourage a more structured approach to their story writing.
Plot planning
Firstly, ask your child where the story is going to take place . It could be somewhere fictional or real, it could be a planet, a country, a town or a house – anywhere!
Then, ask when the story is taking place – now? In the future? In the past?
Finally ask what they think is going to happen . Remember that this doesn’t have to be accurate and they don’t have to stick to what they say; many of the best writers say that their plots develop organically as they write. If they do have a firm idea of where they want to go with the plot, though, they can create an outline by completing a story planner, which could look something like this:
- And finally….
Download a FREE Creative Writing toolkit!
- KS1 & KS2 workbooks
- Bursting with fill-in prompt sheets and inspiring ideas
- Story structure tips, style guides and editing suggestions
Characterisation
Ask your child who is going to be in the story. How do they want their readers to feel about each character? Again, they may want to jot some ideas down. You could make a table for them to help them organise their thoughts, with these headings:
- Name of character
- Relationship to other characters
- What he/she looks like
Story language
Ask your child to think of some fabulous words to use in their story writing . They might be long words or simple ones, or they might be great descriptive words or words that help create pace and tension. Encourage them to jot these down and refer to the list as they write their story.
Story starters
All writers know that you’ve got to capture the attention of your readers right from the start; you want to make them desperate to read on. Ask your child to think of some good story openers that’ll entice people to find out more. Here are a few examples:
First sentences that are mysterious… Molly had no sense of the day that lay ahead.
Story starters that use language tricks like alliteration… It was damp, dark and dreadfully dusty when Molly entered the house.
Story openers that create tension… Molly could hear her heart beating faster than ever before. Could this really be happening?
Stories that go straight into dialogue… “But I don’t want to go to school, Mummy,” groaned Molly.
Encourage your child to look at some of the books they like to read and see how they begin in order to offer inspiration.
Get writing!
Once they’ve got all of these ideas in place, they can start writing. They could do a draft in the first instance and then a neat, polished version later. They may wish to write in short chapters, use illustrations, or make their own book to write in – let them use their imagination and creativity when it comes to presentation, and make sure you show how much you value the end product by keeping it to read again with the other books in your house.
If your child finds writing a story a little daunting, start with something small from our list of 9 fun writing projects to do with your children .
We also recommend the free art and creative writing challenges on the Night Zookeeper website ; your child will be contributing to a co-created animated television show.
You could also try a great story-making app and get your child writing fiction on their tablet!
Plus, find out how to support storytelling skills for children in EYFS , KS1 , KS2 and KS3 to get them thinking about story elements, plot and character development.

Give your child a headstart
- FREE articles & expert information
- FREE resources & activities
- FREE homework help
More like this

How to Effectively Teach Creative Writing in Elementary
Today let’s discuss how to effectively teach creative writing at the elementary level. Creative writing is such an important writing skill to teach students from a young age. Young writers need to understand the concept of creative writing as using their imagination to express themselves freely through words.
It’s not just about proper grammar and spelling (though those are important too!) , but rather about sparking their creativity , allowing them to dream up unique characters , exciting adventures, and incredible worlds. By nurturing their storytelling abilities early on, we’re not just helping them become better writers, but also fostering their confidence, encouraging self-expression, and igniting a lifelong love for writing. So, let’s dive into some strategies and tips to make your creative writing lesson plans a hit in your elementary classroom!

What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is essentially writing in which the author uses his or her imagination to create a story. Creative writing in simple terms refers to the process of expressing thoughts, ideas and stories in a unique and imaginative way.
It’s about letting children’s minds wander freely, encouraging them to use their imagination to create characters, settings, and plots. Creative writing isn’t just about grammar and spelling; it’s about fostering a love for storytelling, allowing kids to explore their creativity, and helping them find their voice through words on paper. It’s a journey that encourages self-expression, builds confidence, and nurtures a lifelong appreciation for writing. The whole purpose of creative writing is to think outside the box and stray from traditional structures and norms.
Creative writing falls under one of the 5 categories of writing but it also combines a lot of these styles together:
- Narrative Writing
- Descriptive Writing
- Persuasive Writing
- Expository Writing
- Creative Writing
Creative Writing Lesson Plans Don’t Have to Be Difficult
Finding creative ways for students to write using their imaginations doesn’t have to be difficult. No matter the grade level, creative writing lessons should offer plenty of opportunities for students to tell their point of view on a subject. Don’t let creating lesson plans for creative writing be a headache! It’s all about giving kids the chance to let loose and share their thoughts in their own special way.
Whether they’re in 2nd grade, 3rd grade, or 5th grade, the key is to let their imagination run wild. Get them talking about what interests them, throw in some fun prompts, and watch the magic happen! Mix things up with different writing styles – stories, poems, even real-life tales. Make it a safe space where they feel free to jot down whatever comes to mind. By balancing a bit of structure with loads of creative freedom, teaching creative writing becomes a blast for both the teachers and the students!

Here’s How to Teach a Creative Writing Activity to Elementary Students:
1. start with creative writing prompts.
One of the first activities you can try is using writing prompts with students. Writing prompts are a great tool to get students’ brain juices flowing, no matter if they are elementary, middle school, or high school students! Coming up with writing topics for younger students can be especially challenging sometimes.
Inside the How to Write a Paragraph Year-Long Bundle there are specific writing prompts that are scaffolded and differentiated to meet all learner’s needs. You will find everything you need inside this resource to help your students who struggle with writing understand how to write a paragraph all YEAR LONG … trust us! It allows for easy planning for your writing lessons because it’s got different seasonal writing resources and prompts inside no matter what time of year it is. These are the perfect place to start to get your students writing based on themes.
Once they are comfortable in this category, then it’s time to actually get them to come up with some of their own ideas to write about now (after all that is the ENTIRE point of a creative writing lesson!)
Try with these juicy writing prompts below to help get your student’s creativity flowing if they need help coming up with a topic to write about :
- Personal memories: “Tell about someone who taught you something really important.”
- Imaginative scenarios: “Let’s create a wild story set in a world where anything goes!”
- Prompts based on a familiar mentor text: “What if your favorite book ended differently? Give it a new twist!”
- Lead-in sentences: “I saw myself in the mirror and couldn’t believe what I saw. Overnight, I…”
- Fascinating or thought-provoking images with a directive: “Who do you think calls this log cabin home? Tell us their story and what they’re up to!”
2. Break Down the Prompts Together
Do NOT rush this next step! We need to make sure our students are coming up with unique and creative writing ideas. During this first week’s lesson plan, you want to make sure students know exactly what they are getting themselves into with the creative writing process. Make it known that these prompts above are to help guide them and their imagination. Help to break down what each prompt is asking/ looking for:
For example, if the prompt says “I saw myself in the mirror and couldn’t believe what I saw. Overnight, I…,” then what questions should the students be asking?
Hopefully, they will tell you they want to know what they look like in the mirror right now.
Then you can have students think of 5 possible situations for what happened and how they look.
3. Do a 5 Minute “Free Write Brain Dump”
During the next step of a creative writing lesson plan, encourage students to do a brain dump in their writing journals on all of their prior knowledge on the subject that they will be writing about. This lets you know a couple of things as the teacher: Do they have their own experience on this topic and enough background knowledge? Does the subject areas that they are free-writing about make sense for the creative writing topic? This should only take about 5 minutes and you are NOT worried about spelling or grammar during this step.
For example: if they are planning to write about the solar system but they don’t have much to say during this free write brain dump, this is where you may want to incorporate a mini lesson or guided conference with you to make sure they are picking a topic that they have a lot of background knowledge about or can at least figure out where to find the answers they might need for their writing.
The “free write brain dump” is helpful for students to see a couple of things- okay I know enough information about this topic and am ready to organize my thoughts OR I had a hard time just coming up with random thoughts to write about…maybe I need a need a new topic. It will truly help decide their confidence factor for this assignment.

4. Start Your Planning Process
The next step in your creative writing unit should be having students take their decided-upon creative writing topic and organize their thoughts and ideas. This step is super important because you want the information to be in the students’ own writing but you also want to make sure they have a plan for how to get their point across. Your stronger writers may be ready to go but some may need a bit more structure set up to help them.
There are a couple of different ways they can organize their ideas:
Use Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers are the perfect thing to use if students want to stick with a paragraph-type writing structure. For your lower writers, this might be the way to go because graphic organizers make planning a lot easier and the structure makes it super easy to follow. Graphic organizers also help break down the writing process into chunks so it doesn’t feel like such a difficult task to students who may struggle more with their writing skills or for ESL students.
Character Development Worksheets
Provide worksheets that prompt students to describe the characters in detail that they want in their story. Include sections for physical appearance, personality traits, motivations, and character arcs. This helps students develop well-rounded characters before they start writing.
Peer Brainstorming
Organize small group brainstorming sessions where students can share their ideas and receive feedback from their peers. This way can totally help students polish up their ideas and come up with fresh new ones for their creative writing.

Story Boarding
Encourage students to create a visual storyboard for their story. They can draw a series of pictures or scenes that outline the plot, helping them visualize the sequence of events in their narrative. We really love this idea for planning for students who are learning English as a second language and students who have more difficulties communicating their thoughts out loud.
Voice Recording
Finally, one last idea: If your students are feeling unsure about writing things down, suggest they talk it out and record their thoughts on a device such as a classroom iPad.
They might be amazed at how easily their spoken words turn into great written stuff on the page! This is another favorite of ours for those students who struggle with getting their thoughts on paper or are learning English as a second language.
During the planning phase , it is a good time to take the opportunity to do any mini lessons you feel needed with students on any of the skills above.
5. Write the Rough Draft
Next is taking the creative narrative and putting it into a rough draft version using their planning method. It’s time for them to start coming up with their own creative short story. Do they have a main character? Is there a problem and solution? Does the writing make sense? After the rough draft, it can be super beneficial to meet with students individually or in small groups to give feedback before they move forward on the final copy.
Word of advice: Don’t worry about spelling or grammar too much in the rough draft phase! Just help students get their thoughts out onto paper!
6. Time To Write the Final Draft
As the creative writing journey nears its conclusion, it’s time to guide your students toward the crucial phase of crafting their final drafts. This stage marks a shift towards independent work, where students take ownership of refining their narratives. Encourage them to enrich their stories with vibrant sensory details to help bring the writing to life.
This isn’t just about polishing; it’s about infusing their words with emotions and imagination. The final draft represents all of their hard work! Make sure you help them reach their fullest potential with their creative writing and storytelling skills!
A Final Word on Teaching Creative Writing to Elementary Students
When planning your creative writing lesson plans for the school year, it’s best to think about the overall entire writing process. For students that you KNOW creative writing will be a challenge for, take some time during English language arts sessions and work with them on the simple structures of writing to help build their confidence. If they struggle with the mechanics and confidence to write, they honestly may not be ready for the creative writing process just yet. Use the resource below to help them refine their writing skills so that all of your students can be a confident and creative writer!

How do you feel about creative writing lesson plans?
You might also like:.
FREE Differentiated Creative Writing Prompts for Fall
Excuse our digital dust! We’re busy renovating this website to make it even more fabulous. Stay tuned!
- Read more about: Writing
You might also like...

What is the RACE Writing Strategy?

The Best Paragraph Writing Worksheets for 5th Grade

4 Steps to Teach Students When Summarizing Nonfiction Text

The Best Writing Activities and Tips for ESL Students
Teach smarter, not harder join the newsletter.
Transform your teaching with our teaching tips, resources, and freebies delivered straight to your inbox!

The Goodies
© GRASPhopper Learning • Website by KristenDoyle.co

How to teach writing to Grade 1 kids: New strategies for teachers and parents
Associate Dean (Research), Faculty of Education, Western University
Disclosure statement
Perry Douglas Klein receives funding from The Social Sciences and Humanties Research Council of Canada
Western University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
Western University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA.
View all partners
Writing is a craft that is vital for both communicating and learning . However, many children struggle to learn to write. For most, their difficulties persist throughout elementary school unless they get help. As recently as 2018, there was very little research on how to teach Grade 1s effectively .
However, recent research shows how teachers can help Grade 1s make a strong start on writing. Parents have a vital role to play in laying a foundation for early writing success.
Many parents have likely heard children say, “I don’t know what to write.” Teaching children strategies for writing tackles this problem head-on.
Breaking writing down into steps
In 2019, a team of Spanish and British researchers published one of the first experiments on teaching writing strategies in Grade 1 . They explored how a child can learn to write a story by asking themselves a series of questions: When did it happen? Where did it happen? Who is the story about? What did they do? What happened? How did it end? These questions help the child to generate and organize their ideas.
To help children remember this writing strategy, teachers in the study used a picture of a mountain with a path that led past six houses — one for each question. The teachers discussed the strategy, modelled how to use it and wrote together with the class. After instruction, the children wrote stories that were higher in quality, longer and more coherent.
Strategies work
The value of teaching writing strategies in Grade 1 has been confirmed by additional studies that examine teaching specific kinds of writing: Procedural writing (instructions for someone on how to do something) , and opinion writing (short essays meant to persuade someone of something) . In this writing research, teachers combined strategy instruction with discussions, picture books and dramatization.
And in our own recent research, we found that strategy instruction is effective for Grade 1 students across the range of writing achievement levels: low, medium and high . These Grade 1 studies join over 100 previous studies with students in higher grades in showing that teaching writing strategies works .

Printing, handwriting, spelling
Recent research also provides renewed support for the seemingly old-fashioned skill of printing. Grade 1s who can print accurately and quickly are able to create better and longer stories and reports . Teaching printing helps students to create better stories . Despite over 70 previous studies on the benefits of teaching printing and cursive writing , systematic teaching and assessment of these skills has declined in some curricula.
Read more: Writing and reading starts with children's hands-on play
Spelling is another traditional skill, the importance of which has been confirmed by recent research. Better spellers create better and longer stories, while poor spellers struggle with composing , and Grade 1 spelling affects the development of composition in later years.
Spelling education works best if it is formal, including, for example, lessons and practice activities . Additionally, teaching writing strategies combined with spelling and printing is more effective than teaching each of these skills alone .
Parents can help children practice spelling at home. Teachers and parents can also show children the “invented spelling” strategy of saying a word slowly, stretching out the sounds, and printing a letter (or letter combinations, such as “th”) for each sound. This will lead to some errors, but in kindergarten and Grade 1, invented spelling is an important driver of spelling development .
New understanding of Grade 1
This new understanding of the importance of Grade 1 is beginning to change writing education . In the past, many schools in Canada and the United States waited for struggling readers and writers to reach the middle elementary grades . Then, they were assessed by a school psychologist. If they were diagnosed with a learning disability, they were placed in a special education class.
However, in a new approach, response to intervention, teachers use evidence-based methods (like strategy instruction) to teach the whole class. They assess students regularly based on their daily writing, and if a child is below grade level, they receive help in a small group .
This approach is not yet common. However, it is almost certainly coming to some provinces in reading education . Reading education and writing education are intertwined, so we can expect the same approach to follow in writing.
Laying the foundations
The foundation for writing success is ideally being supported at home before children start kindergarten.
Parents can ask children to tell them stories, print the stories for them, then read them aloud for the child. They can teach children simple skills like forming letters and printing their name.
Parents can also practice printing with children at home; this is especially valuable for struggling writers . They can help children to write things that are important to them, like birthday cards for family members .
Read more: To help children learn how to read in the pandemic, encourage writing messages as part of play
Parents can also encourage children to read and write independently . Once children begin to write, parents can be their best audience, praising their efforts and the good qualities of their writing, and making suggestions to help with ideas, printing, and spelling .
When children begin school, and into Grade 1, parents can watch for red flags in their child’s writing development. During Grade 1, the average student learns to print the letters of the alphabet legibly and fluently, spell one syllable words the way that they sound (cat, game) and spell common short words that are not spelled the way that they sound (you, they). They also learn to write a story a few sentences in length about a personal experience .
If your child is missing these basic skills, don’t wait and see — talk with your child’s teacher and make a plan to help them succeed.
- Handwriting

Research Fellow

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Encouraging Your Child’s Creativity: How to Write a Short Story with Khanmigo
posted on September 20, 2023
By Stephanie Yamkovenko , group manager of Khan Academy’s Digital Marketing Team.

Storytelling is an essential part of a child’s development. It allows them to explore their imagination, develop language skills, and improve their understanding of the world around them. However, not every parent has the confidence to write a story with their child. That’s where Khanmigo , an AI tutor from Khan Academy, comes in. In this blog post, we will look at the importance of story writing for children and how parents can use AI to write short stories with their children. We will also provide step-by-step instructions on how to use Khanmigo to piece together a short story using Khanmigo’s AI prompts as well as offer examples of stories created using Khanmigo.
Why Story Writing is Important for Children
Storytelling is an ancient form of communication, and it has always been an essential part of human culture. It is not just a leisure activity but has a significant impact on children’s growth and development ( Bietti, 2019) . Writing stories can be an exciting and fun way for kids to explore their creativity, develop their language abilities, expand their vocabulary, practice critical thinking, and build their communication skills (National Research Council, 2015) . Not only does writing stories improve a child’s writing skills, but it can also boost their reading comprehension, critical thinking, and self-expression. Check out some of the benefits children gain from learning how to write short stories, backed by research:
- Enhanced cognitive development: According to a study from Sook-Yi Kim (2014) , storytelling can enhance children’s cognitive development, particularly in areas such as memory and sequencing events.
- Improved language skills: Reports from the National Literacy Trust suggest that storytelling helps children develop a wider vocabulary and a better understanding of language structure.
- Boosted creativity: Per research in the Journal of Creative Behavior , storytelling allows children to explore different narratives and perspectives, thereby fostering creativity.
- Developed emotional intelligence: A study published in Reading & Writing Quarterly indicates that through storytelling, children can explore diverse emotions and situations, helping them better understand and express their feelings.
Prompts to Use for a Short Story with ChatGPT
To write a story using ChatGPT, follow these prompts:
- Start with a question: Think of an intriguing question that can capture the reader’s attention and lead them to the story’s plot. For example, “What would happen if gravity suddenly stopped working?”
- (optional) Choose a setting (e.g., Mars, an elementary school, or a grocery store).
- (optional) Choose a conflict (e.g., a misunderstanding, a lost object, or a personal fear that holds back the protagonist).
- Create your characters: Develop a protagonist, an antagonist, and secondary characters. Give the characters personalities, traits, and quirks that will make them stand out.
- Make a plot: Craft an exciting and engaging storyline that includes a beginning, a middle, and an end. Use the question and topic as a starting point. Decide how your protagonist will overcome their conflict, and develop the story from there.
- Review and edit: After finishing the story, review and edit it to make sure it flows smoothly and makes sense.
Using Khanmigo for Story Writing
Khanmigo can do all of this for you via a question-and-answer format that will walk your child through the entire process of writing a story. Khan Academy released a new feature in 2023 called Khanmigo—an AI-powered tutor that assists children in their learning journey. Khanmigo offers a wide range of interactive student-focused activities that can encourage creativity and support writing development, such as creative writing prompts.
Khanmigo’s AI tutor can provide invaluable assistance to parents who want to encourage their child’s writing development. When children use Khanmigo for story writing, they receive personalized guidance and suggestions that help them improve their writing skills.
Khanmigo will ask your child questions about the story they are writing together to draw out ideas for plot, characters, conflict, and more. Even if these concepts are unfamiliar to your child, Khanmigo will help explain each step along the way. For example, “Now, let’s start with the setting. Where does our mystery take place? A spooky old mansion? A bustling city? A quiet little town? Or somewhere else entirely? And what’s the weather like? Remember, the setting can add so much to the mood of our story!”
Khanmigo can serve as a writing partner, providing feedback and support throughout the writing journey. Children using Khanmigo will be able to practice their writing skills while developing their creativity, imagination, and critical thinking abilities.
Parents can use Khanmigo to monitor their children’s progress, provide feedback, and make sure that children are effectively developing their writing skills and creativity. Through Khanmigo, parents can keep track of their child’s writing progress, view their work, and set weekly writing goals.
Start writing stories with your child
We promise, you’ll have an adventure…
How to Start Creating a Story with Khanmigo
Here is an example of how you may start an interaction to create a story with Khanmigo.
Khanmigo: “Would you like to write an awesome story together? Let’s do it.
- You can choose a topic from the list, or suggest another idea.
- If I use new words like ‘theme’ or ‘plot,’ just ask me to explain.
- At any point, you can ask me to show you what we have so far.
- Once we’re done, you can chat with some of the characters and admire the world we’ve built!”

…we don’t want to ruin the end of the story, but we hope this gives you a sense of the journey your child will go on while co-creating with Khanmigo.
Raising Confident Story Tellers
Encouraging your child to write stories is an excellent way to foster their creativity and imagination. By providing them with engaging prompts, you can help them develop their critical thinking and language skills while also having fun.
With Khanmigo, parents can take their child’s creativity and writing to a whole new level. By leveraging Khan Academy’s AI tutor, parents can help their children practice their writing skills, expand their vocabulary, and develop their communication skills. Give your child a tool that will help shape their writing and help them grow into confident story writers.
Bietti LM, Lucas M., Tilston O, 1 and Bangerter A, “Storytelling as Adaptive Collective Sensemaking” Top Cogn Sci. 2019 Oct; 11(4): 710–732.
National Research Council; Institute of Medicine ; Board on Children, Youth, and Families ; Committee on the Science of Children Birth to Age 8: Deepening and Broadening the Foundation for Success ; LaRue Allen and Bridget B. Kelly, Editors, “Transforming the Workforce for Children Birth Through Age 8: A Unifying Foundation”, 2015
Kim, Sook-Yi, “The effects of storytelling and pretend play on cognitive processes, short-term and longterm narrative recall.” (1996). Doctoral Dissertations 1896 – February 2014. 5243. https://scholarworks.umass.edu/dissertations_1/5243
Best. E, “Playful storytelling: The role of interactive audio in building children’s literacy skills and engagement”, National Literacy Trust, June 2021
Angus Fletcher, Patricia Enciso, Mike Benveniste, Narrative creativity training: A new method for increasing resilience in elementary students, Journal of Creativity, Volume 33, Issue 3 , December 2023, 100061
Catherine Z. Wright & Sandra Dunsmuir (2019) The Effect of Storytelling at School on Children’s Oral and Written Language Abilities and Self-Perception, Reading & Writing Quarterly, 35:2, 137-153, DOI: 10.1080/10573569.2018.1521757
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents
It's Lit Teaching
High School English and TPT Seller Resources
- Creative Writing
- Teachers Pay Teachers Tips
- Shop My Teaching Resources!
- Sell on TPT
How to Teach Creative Writing to High School Students

Creative Writing was forced onto my schedule; I didn’t ask for it. But it ended up becoming my favorite class period of the day. While academic English courses can feel high-stakes and always short on time, Creative Writing can be a refreshingly relaxed elective class. In many districts with loose curriculums, Creative Writing is what you make of it. In this post, I outline six steps to show you how to teach creative writing to high school students.
Why Teach Creative Writing
Before we get into the how , let’s first address the why . Why bother teaching Creative Writing in the first place? Students’ basic skills are lower than ever; is now really the time to encourage them to break the rules?
If you want to get really deep into why you should teach Creative Writing, I have a whole post about it here.
But think about why you love reading. Is it because you were made to annotate or close read a bunch of classic novels? Probably not. You probably fell in love with reading while you were reading something that was fun. And because it was fun, you read more, and your skills as a reader grew.
The same principle applies to writing. If we can make it fun for our students, perhaps we can foster a love for it. And passion is what leads, eventually, to mastery.
Giving our students the opportunity to fall in love with writing is a gift that might help them grow in their academic writing later.

Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #1: Decide on Your Standards or Goals
Your school or district may have a mandated syllabus or curriculum. Mine did not.
Whether you’re given student goals or have to create them, you must have an overall vision for what your Creative Writing class will accomplish.
Is this a laid-back, engaging course designed to help students discover the fun in writing? Or is it a supplement to rigorous academics for college-bound high school students?
If you know your school’s student population well, I encourage you to think about their needs. Some students just need to write more–more of anything, but lots more. Some students are high achieving and ready to write their first novels! If possible, design your course around the needs and interests of the general student population in your school or district.
Regardless of how rigorous your Creative Writing course will be, deciding on these goals first will help you in backwards planning.

Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #2: Choose Your Final Assessments and Big Projects
Before we can start planning our lessons, we have to decide what skills or knowledge our students will need. And to know what they need, we have to decide on their summative assessments.

Will your final assessment be a short story? A collection of poetry? Are you required to offer a final exam?
Once you know what students will need to do, you can make a list of the skill they’ll need. This list will become a list of lessons you’ll need to teach.
Fairy Tale Retelling Project
My Fairy Tale Retelling Project is a great Creative Writing assessment. For this project, students had to first choose a fairy tale. Then, they rewrote the story from the perspective of the villain.
This project works really well because students have structure. They can pick any fairy tale they want, but they can’t write about just anything.

Secondly, students already know the story, so they don’t have to worry about a beginning, middle, and end. The open-endedness of writing a story completely from scratch has paralyzed my students before. Structure allows students lots of creative freedom without the excuse of “I don’t know what to write.”
Author Study Project
If you’d like your Creative Writing class to help beginner writers have fun and just get some practice with fiction writing, a Fairy Tale Retelling Project would probably be perfect for your class.
Another project I’ve done with my students is an Author Study . In this project, students choose one author to study in-depth. Then, they attempt to replicate that author’s style in an original work.

If you’d like your class to also include lots of exposure to other writers or classic literature, then this might be a great assessment for your class.
Learn more about doing an author study in this step-by-step post.
Test or Final Exam
I also gave my students a final exam focused on literary terms.
This Literary Terms Test allowed me to test students on the academic knowledge they gained throughout class instead of their writing ability. This test also helped me fulfill my district’s requirement of having a final exam at the end of each course.
Once you’ve decided on your class’s major projects and assessments, you can begin designing the rest of your class.
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #3: Backwards Plan
Now that you know what your students will need to do at the end of this class, you can list out everything you need to teach them in order for them to be successful.
For example, if you opt for an author study as a final project, you know what you will need to cover. You will need to teach students some literary terms so that they can describe an author’s style. You’ll need to show them how to analyze a poem.
During the course of your class, you’ll also want to expose students to a variety of authors and mentor texts. Students will need to practice basic writing techniques in order to replicate those of their chosen authors.
If you need some inspiration for what kinds of lessons to teach, check out this post on essential Creative Writing lessons.
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #4: Decide on Your Class Structure
Once you’ve decided on the end goals for your Creative Writing class, you can use them to help create day-to-day plans.
What will your class look like? Will it be full of lots of quiet and independent work time? Will it be full of frenetic energy with students working in collaborative groups? Are students writing in notebooks or on laptops?

Of course, a successful class will most likely include a mixture of all of the above. But it’s up to you to decide on your ratio.
Again, I encourage you to think about your school’s population. If you’re on ninety-minute blocks, is it realistic for students to be quietly writing that whole time? If you have high-achieving students, might they benefit from working independently at home and then getting and giving peer feedback during class time?
Use your goals to help decide on a general class structure.
Warm-ups for Creative Writing
You’ll need a consistent way to begin each class.
When I initially began teaching Creative Writing, I just wanted to provide my students with more time to write. We began every class period with free writing. I gave students a couple of prompts to choose from each day, and then we’d write for about ten minutes.
( Those journal prompts are right here . Every day includes two prompts plus a third option of freewriting.)
Students were given the option to share part of their writing if they wanted to. Every couple of weeks I’d flip through their notebooks to make sure they were keeping up, but I only read the entries they starred for me in advance.

Later, I wanted to add some rigor to my Creative Writing class and leverage more mentor texts. I created a Poem of the Week activity for each week of the course.
This gave students the opportunity to study professional writing before using it as a mentor text for a new, original piece.
(You can read more about using these Poem of the Week activities here.)
As my goals for the class and my students change, so did the way we began class.
How can you begin your class in a way that supports the end goals or teaches the desired standards? How often will peers work together?
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #5: Focus on Engagement Strategies
Now you can actually start planning lessons and projects!
But as you do so, focus on creating engaging ones–especially if your class is meant to be a fun elective.
Need more tips? Check out this post full of Creative Writing teaching tips!
Use Mentor Texts and Lots of Examples
Have you ever tried putting a puzzle together without knowing what the image was going to look like? It would be pretty difficult! Similarly, students need lots of examples of strong writing to aspire to.
Without clear models or mentor texts , students will happily turn in unread drafts. They’ll choose the first word that comes to their mind instead of searching for a better one.
But if you surround students with great writing, highlight strong technique when discussing the writing of others, and challenge them to notice the details in their own writing, they’ll naturally become better at self-editing.
I don’t believe that you can provide students with too many mentor texts or examples of strong writing. As you teach Creative Writing, keep or take pictures of strong writing samples from students to use as examples later.
Nearly all of my lessons and projects include an example along with instruction.
Model and Create with Your Students
You can even use your own writing as an example. When I had students free write to creative writing prompts, I always wrote with them. Sometimes I would then put my notebook under the document camera and model reading my own work.
I would cross out words and replace them or underline phrases I thought were strong enough to keep. Model for students not just great writing, but the process of strengthening writing.
And then give them plenty of time to edit theirs. This is when having students engage in peer feedback is a game-changer.
Without great writing to aspire to, however, students easily become lazy and turn in work that is “good enough” in their eyes. Don’t let them get lazy in their writing. Keep throwing greater and greater work in front of them and challenge them to push themselves.
(This is another reason I love using Poem of the Week warm-ups –they expose students to a new writer every week!)
Set Clear Expectations
Creative writing causes a lot of students anxiety. There’s no “right” answer, so how will they know if they creatively wrote “correctly?”
Help them out by setting clear expectations. Offering a rubric for every project is great for this. If you can, give them specifics to include. “At least 500 words” or “three or more similes” are nice, concrete guidelines that students can follow.
Give Students Choice
Offering students choice always boosts engagement. It lets students take charge of their learning and pursue something that interests them.
For example, when I teach odes , students are given the opportunity to write about something they love.
With an author study , students can study a writer whose style and work they admire.

Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #6: Use Clear and Structured Expectations
While showing students excellent prose or perfect poetry should help inspire students, your writers will still need some hard parameters to follow.
Academic writing is often easier for students than creative writing. Usually, academic writing follows a structure or certain formula. The rubric dictates exactly how many quotes need to be included or how long an essay needs to be. MLA or APA formats tell students how to punctuate quotes and citations.
These rules don’t apply to creative writing. And while that’s exactly what makes creative writing awesome, it’s often overwhelming.
So do your students a favor and give them some clear expectations (without, of course, entirely dictating what they need to write about).
The project also includes a rubric, so young writers know what should be included in their stories.
Don’t give your students so much creative freedom that it paralyzes them! Your writers are still students; give them the same level of structure and organization that you would in any other class.

Engage your students in more creative writing!
Sign up and get five FREE Creative Writing journal prompts to use with your students!
Opt in to receive news and updates.
Keep an eye on your inbox for your FREE journal prompts!
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #7: Give Students Choices
So how do you give students frameworks, requirements, and uphold high expectations without stifling their creativity?
Give students choices. You can write about A, B, or C, as long as you meet requirements 1, 2, and 3.
Offering choices works with small one-day assignments or lessons as well as bigger, longer-term projects.

The previously mentioned Fairy Tale Retelling Project is a great example of offering a narrow selection of choices that uphold expectations without dictating what students write.
Another one of my favorite examples of offering students choices is my “Show. Don’t Tell” Mini-lesson . This lesson touches on everything students need to successfully learn creative writing.
First I teach them the concept of showing vs. telling in writing through direct instruction. I show them lots of examples of expanding a “telling sentence” into a “showing paragraph.”
Then I model for students how I would write a paragraph that shows crucial information, rather than telling it.
Lastly, I have students pick a strip of paper from a hat or a bag. Each strip of paper contains a “telling sentence” that they must then write as a “showing paragraph.” Students are limited by the sentences I provide, but they still have complete freedom over how they achieve that detailed paragraph.
If you wanted to give students even more freedom, you could let them pick their sentences or trade with a peer rather than blindly choosing.
Any time you can give students a choice, you give them permission to use their creativity and allow them to take some of the initiative in their own learning.
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #8: Encourage Peer Collaboration and Feedback
We can tell students something a hundred times, but they won’t listen until a peer says the same thing. Us educators know the value of positive peer interaction, so don’t limit it in a creative writing class!
There are a ton of ways to implement peer interaction in a creative writing class. I often do this on the first day of class with a writing game. You’ve probably heard of it: everyone writes a sentence on a piece of paper, then everyone passes the paper and adds a sentence, and so on.
I highly encourage you to use peer feedback throughout the class. I usually start having students share their work from day one with my free “I Am” Poem Lesson so that they can start getting used to having their work read by others immediately.

Make getting feedback so routine in your room that students don’t even question it.
It’s really tempting to let students get away without sharing their work. We don’t want to make shy or anxious students uncomfortable. I mean, what better way to completely ruin creative writing for a student than to make them feel embarrassed all the time, right?
But keep trying to encourage shy students to share. Even if that means you share it anonymously or read it aloud for them.
I recommend including some kind of peer feedback with every writing assignment . Yes, even short practice assignments. This will work as a kind of “immersion therapy” for receiving feedback on more involved work.
After some time, you might find that your students even begin to share their work without your prompting!
I like to organize the desks in my Creative Writing class so that students are in little groups. I’ve found that at least half of my classes will begin talking and sharing with one another in their little groups while working on projects.
They’ll ask each other questions or to remind them of a word. They’ll read sentences aloud and ask if they sound right. Personally, I would much rather hear this kind of chatter in my class than have a dead silent room of boring writers!
However you decide to allow students to work together, be sure to provide the opportunity. Reading and getting feedback from peers could possibly teach students more about writing than any of your instruction (sorry!).

One of the truly great things about teaching creative writing to high school students is that there often isn’t a rigid curriculum. Of course, this is also sometimes one of the worst things about teaching creative writing to high school students!
You have total freedom over the assignments you give, the standards you teach, and how you organize and structure your classroom. After a few years of teaching Creative Writing, however, I’ve found that sticking to these six steps is a great way to have a successful semester.
If you’re excited about teaching your Creative Writing class, but are running low on prep time, check out my complete 9-week Creative Writing course ! Included are two different types of warm-ups, poetry analysis activities from well-known authors, mini-lesson, projects, and more!


- Math for Kids
- Parenting Resources
- ELA for Kids
- Teaching Resources

15 Famous Mathematicians in History That Kids Should Know
11 Best Multiplication Apps for Kids
How to Teach Number Formation in 5 Easy Steps
13 Best Resources for Math Videos for Kids: Math Made Fun
How to Teach Skip Counting to Kids in 9 Easy Steps
6 Best Alternatives to Public Schooling: A Guide for Parents
How to Cope With Test Anxiety in 12 Easy Ways
Developmental Milestones for 4 Year Olds: The Ultimate Guide
Simple & Stress-Free After School Schedule for Kids of All Ages
When Do Kids Start Preschool: Age & Readiness Skills
How to Improve Reading Comprehension: Strategies & Tips
40 Best Summer Writing Prompts for Kids of All Ages
12 Best Ways to Teach Rhyming Words to Kids
How to Teach Letter Sound in 6 Easy Steps
How to Teach Letter Formation to Kids in 9 Easy Steps
12 Best Tips for Substitute Teachers
30 best classroom reward ideas for elementary students.
12 Best Websites for English Teachers
10 Best Game-Based Learning Platforms for Kids
60 Fun Animal Facts for Kids

How to Teach Kids to Write in 9 Easy Steps
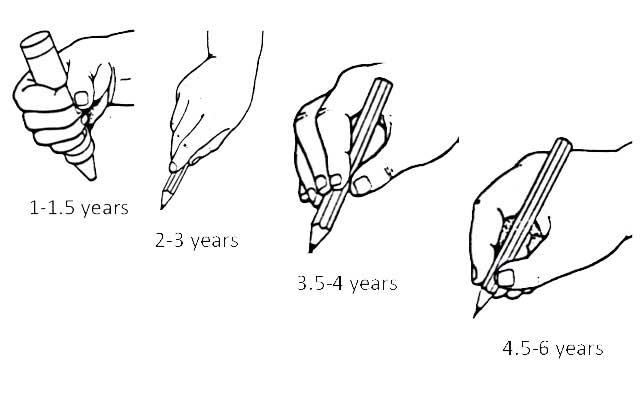
Step 1: Develop Fine Motor Skills
Step 2: introduce prewriting skills, step 3: teach letter recognition, step 4: practice writing letters, step 5: connect letters to sounds, step 6: encourage writing words, step 7: introduce writing instruments, step 8: expand writing contexts, step 9: encourage reading.
Ever felt a mix of joy and worry watching a kid clutch a crayon for the first time? If you’re nodding, you’re not alone. Figuring out how to teach kids to write is a common puzzle for many of us. It’s that first big step from messy lines to meaningful words.
SplashLearn: Most Comprehensive Learning Program for PreK-5

SplashLearn inspires lifelong curiosity with its game-based PreK-5 learning program loved by over 40 million children. With over 4,000 fun games and activities, it’s the perfect balance of learning and play for your little one.
Surprisingly, teaching kids to write doesn’t have to be a head-scratcher. With some simple steps and fun activities, it can become an exciting journey for you and your little one.
In the following sections, we’ll dive into a detailed step-by-step guide on how to teach kids to write. Each step is crafted to build upon the last, ensuring a solid foundation is laid for your child’s writing skills. By the end of these strategies, your kids will be equipped with the tools to express their thoughts and ideas clearly and creatively.
9 Easy Steps to Teach Kids to Write
Fine motor skills are the foundation of learning to write. They involve using small muscles in the hands and fingers to perform tasks like holding a pencil, turning pages, and eventually writing letters and words. Developing these skills is crucial for teaching kids to write because it directly impacts their ability to control writing instruments and make the precise movements required.
When to Start:
The journey to develop writing skills begins long before a child ever picks up a pencil to write. It starts as early as toddlerhood. Children can begin engaging in activities to enhance their fine motor skills from as young as 18 months old. Starting early is important to ensure they have a strong foundation to build upon as they grow.
How to Do It:
- Engage your child in activities that encourage using their hands and fingers. Play with clay, finger painting, and threading beads are excellent ways to strengthen these muscles. Using safety scissors for cutting simple shapes out of paper is another beneficial activity.
- Incorporate fine motor skills development into daily tasks. Encourage your child to help with buttoning clothes, zipping up bags, or using child-safe utensils during meal times.
- Provide toys and tools that promote fine motor development. Puzzles , building blocks, and age-appropriate art supplies or online fine motor skills games are great choices.
Here are some fun fine motor skills games to get started:

Key Milestones:
- Initially, focus on your child’s ability to grasp and hold objects. This is the first step towards holding a pencil correctly.
- Children should be able to manipulate objects more precisely as their skills advance, such as turning pages or unscrewing lids.
Prewriting skills are the early writing skills children need before they can form letters and words. These skills include drawing lines, shapes and eventually combining these to make letters. Introducing prewriting skills is critical in teaching kids how to write because it helps children understand the basic strokes involved in letter formation.
Children are ready to start developing prewriting skills around the age of 3. This is when they typically have enough control over their hand and finger movements to begin drawing basic shapes and lines.
- Begin with simple shapes like circles, straight lines, and curves. These shapes are the building blocks of letters.
- Use tracing worksheets or apps that allow children to trace lines and shapes. This helps them understand the motion of writing and builds their confidence.
Here are some fun shapes worksheets to get started:

- Being able to draw circles, lines, and crosses is a sign they’re developing the necessary control for writing.
- Successfully tracing over dotted lines or shapes shows they’re ready to start forming more complex figures, like letters.
Letter recognition is the ability to recognize and name all the letters of the alphabet. It’s a fundamental aspect of learning how to teach kids to write because recognizing letters is the first step towards understanding that letters represent sounds, which combine to form words.
Letter recognition can begin as early as age 2 or 3, alongside or shortly after introducing prewriting skills. At this stage, children are usually curious about letters and eager to learn more about them.
- Using alphabet books is a great way to familiarize children with letters. Read together and point out each letter, discussing its shape and sound.
- Engage children with games that involve finding and naming letters. This could be as simple as a letter hunt around the house or structured games like alphabet puzzles.
Begin with these letter games:

- Naming each letter, both uppercase and lowercase, is a key milestone in letter recognition.
- Recognizing letters not just in books or games but also in the world around them, like on signs or in their favorite storybooks .
Practicing writing letters is a crucial step in teaching a preschooler to write. It’s where the physical act of writing starts to take shape, moving from recognizing and drawing shapes to forming actual letters. This stage is essential for children to learn how to express themselves through writing.
Once children are comfortable with prewriting shapes and have a good grasp of letter recognition, usually around ages 3 to 4, they’re ready to start practicing writing letters.
- Motivating children by teaching them to write their names first is a powerful tool. It makes the learning process personal and engaging, giving them a sense of pride in their writing.
- Providing worksheets for tracing and writing letters helps children understand the form and structure of each letter. Start with uppercase letters, which are generally easier to write, and then move to lowercase letters.
Begin with these letter tracing games :

- Being able to write their own name is a significant milestone for preschoolers.
- Moving from tracing to independently writing letters shows progress in their writing skills.
By introducing letter sounds, children begin to understand that letters are not just shapes but symbols that represent sounds. This understanding is crucial for developing reading skills and is a fun way to teach writing as it makes the process more interactive and meaningful.
This step can begin concurrently with practicing writing letters, typically around ages 4 to 5, as children’s understanding of the alphabet solidifies.
- Introducing letter sounds with phonics games and flashcards makes learning dynamic and engaging. Phonics activities help children make the connection between letters and sounds, a critical step in learning to read and write.
Start with these letter sound games:

- Start forming simple words to emphasize the connection between writing and reading. This can be as straightforward as writing C-A-T and sounding it out together. It reinforces the idea that combining letters creates words with meaning.
- Being able to associate specific sounds with their corresponding letters.
- The ability to write and sound out simple words marks a significant advancement in their writing and reading journey.
Encouraging writing words is a pivotal step in how to teach kids to write. It transitions them from understanding individual letters and sounds to recognizing and forming whole words. This stage boosts their confidence and demonstrates the practical use of writing in communication.
After children are comfortable with letters and simple phonics, usually around the age of 5 or when they show interest in creating words, it’s time to introduce this step.
- Teaching common sight words for recognition and writing is essential. Sight words are frequently used words children are encouraged to recognize on sight. Start with a small, manageable list and gradually expand as they become more confident.
Begin here:

- Encouraging the formation of simple sentences helps children see how words come together to express ideas. Begin with sentences that are relevant to them, like “I like my cat” or “The sun is hot.”
- Being able to write and recognize common sight words .
- The ability to string words together to form basic sentences.

Introducing a variety of writing instruments is crucial for children to explore and find what they are most comfortable using. It’s also an opportunity to teach the proper grip, which is essential for writing efficiently and avoiding hand fatigue. This step is about refining their physical skills for writing and offering writing tips for kids to enhance their writing experience.
This can be introduced as soon as children start showing interest in drawing or writing, and should be continuously adapted as they grow and their skills develop.
- Allow children to experiment with different writing tools such as pencils, crayons, markers, and chalk. Each tool offers a different grip, resistance, and experience on paper, helping them develop a versatile skill set.
- Teaching the correct way to hold a pencil is fundamental. Show them the “tripod grip,” which is holding the pencil with the thumb, index, and middle finger. This grip controls the pencil, making writing easier and more comfortable.
- Experimenting with Different Tools: Children should feel comfortable trying out various writing instruments and expressing a preference.
- Mastering the Tripod Grip: Successfully using the tripod grip when writing or drawing is a sign of developing fine motor control and readiness for more advanced writing tasks.
Expanding writing contexts is about broadening a child’s understanding and application of writing across different genres. This step is crucial to improve writing skills as it exposes children to a variety of writing forms, structures, and purposes. It encourages them to think creatively and apply their writing skills in diverse ways.
This can be introduced once children are comfortable writing sentences and simple paragraphs, typically around ages 6 to 8.
- Introduce various writing forms such as stories , letters, poems , and reports. Discuss the structure and purpose of each genre. This variety keeps writing exciting and shows its practical uses in real life.
- Use prompts to inspire creativity and interest in different topics. Prompts can be questions, pictures, or scenarios that spark ideas for writing. This is one of the effective ways to improve writing skills for students by making them think and write creatively.
- Successfully writing a simple story, letter, or poem.
- Being able to create a coherent piece of writing in response to a given prompt.

A strong reading habit is foundational to writing well. Reading regularly exposes children to a wide range of vocabulary , sentence structures , and styles, enhancing their language skills and understanding. This, in turn, significantly improves writing skills as children learn to emulate the structures and styles they encounter in their reading.
Encouraging a love for reading should start as early as possible, even before a child begins to write, and continue throughout their education.
- Foster a love for reading by sharing books together, visiting libraries, and discussing stories. Encourage children to explore books on topics that interest them, which will keep them engaged and motivated to read more.
- Talk about the books they are reading. Discussing characters, plots, and what they enjoyed helps deepen their understanding and appreciation of writing.
- Establishing a routine where reading is a daily activity.
- Being able to talk about what they read, including story elements and what they liked or didn’t like.
How SplashLearn Can Encourage Children to Write
Math & ela | prek to grade 5, kids see fun ., you see real learning outcomes ..
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.

SplashLearn is a fun and interactive platform designed to make learning an exciting adventure for children. When it comes to writing, SplashLearn offers a variety of resources and activities that can significantly encourage and improve children’s writing skills. Here’s how SplashLearn can be a valuable tool in your child’s writing journey:
- Interactive Writing Games: SplashLearn includes a range of writing games that are not only engaging but also educational. These games are designed to teach children the basics of writing, from letter recognition to word formation, in a fun and interactive way.
- Personalized Learning Paths: One of the key features of SplashLearn is its ability to adapt to each child’s learning pace and style. This personalized approach ensures that children are not overwhelmed or bored but are constantly challenged in a way that’s just right for them. This tailored learning experience can help children progress in their writing skills more effectively.
- Rewards and Motivation: SplashLearn uses a system of rewards and achievements to motivate children. As they complete writing tasks and games, they earn points or badges, which can motivate young learners. This positive reinforcement encourages children to keep practicing their writing, helping them improve over time.
- Parental Involvement: SplashLearn also provides tools and reports for parents to track their child’s progress. This feature allows parents to see how their child is advancing in their writing skills and identify areas where they might need extra help. It also offers suggestions for activities outside the app that encourage writing practice.
- Educational Resources: Beyond games , SplashLearn offers a wealth of worksheets to support writing learning at home. These resources can be used alongside interactive games to provide children with a comprehensive writing learning experience.
5 Benefits of Teaching Kids How to Write Effectively
- Writing is a fundamental form of communication. Teaching kids how to write effectively helps them express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions clearly and confidently in academic settings and their personal lives.
- Good writing skills are crucial for success in school. From completing homework assignments to writing essays and taking notes, the ability to write well can significantly impact a child’s academic achievement and future educational opportunities.
- Writing offers children a unique outlet to explore their creativity and imagination. By learning to write stories, poems, or even journal entries, kids can develop their creative talents and discover new ways of seeing the world.
- The process of writing involves complex thinking skills such as planning, organizing, and problem-solving. Teaching kids to write effectively helps enhance these cognitive abilities, contributing to overall intellectual growth.
Conclusion
Learning how to teach kids to write is a journey filled with opportunities to enhance their communication, creativity, and cognitive development. By embracing this journey, we can help our children build a strong foundation in writing, setting them up for success in school and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best age to teach a child to write.
The best age to start teaching a child to write is around 3 to 4 years old, beginning with basic prewriting skills and gradually moving to more structured writing tasks.
How should a 4 year old be writing?
A 4-year-old should be practicing prewriting skills such as drawing lines, shapes, and beginning to recognize and attempt writing letters, especially those in their name.
Should a 3 year old be able to write their name?
While some 3-year-olds may start showing interest in writing their names, it’s more common for them to recognize and trace letters rather than write their names independently.
- Pre-Kindergarten
- Kindergarten
Most Popular

15 Best Report Card Comments Samples

117 Best Riddles for Kids (With Answers)

40 Best Good Vibes Quotes to Brighten Your Day
Recent posts.

50 Best Father’s Day Quotes: Celebrate with Laughter & Love
Math & ela | prek to grade 5, kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
- Games for Kids
- Worksheets for Kids
- Math Worksheets
- ELA Worksheets
- Math Vocabulary
- Number Games
- Addition Games
- Subtraction Games
- Multiplication Games
- Division Games
- Addition Worksheets
- Subtraction Worksheets
- Multiplication Worksheets
- Division Worksheets
- Times Tables Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Writing Games
- Phonics Games
- Sight Words Games
- Letter Tracing Games
- Reading Worksheets
- Writing Worksheets
- Phonics Worksheets
- Sight Words Worksheets
- Letter Tracing Worksheets
- Prime Number
- Order of Operations
- Long multiplication
- Place value
- Parallelogram
- SplashLearn Success Stories
- SplashLearn Apps
- [email protected]
© Copyright - SplashLearn

Make learning a game for your students
Unlock endless learning fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Teachers, Use for Free
A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Narrative Writing
July 29, 2018
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Listen to this post as a podcast:
Sponsored by Peergrade and Microsoft Class Notebook
This post contains Amazon Affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, Cult of Pedagogy gets a small percentage of the sale at no extra cost to you.
“Those who tell the stories rule the world.” This proverb, attributed to the Hopi Indians, is one I wish I’d known a long time ago, because I would have used it when teaching my students the craft of storytelling. With a well-told story we can help a person see things in an entirely new way. We can forge new relationships and strengthen the ones we already have. We can change a law, inspire a movement, make people care fiercely about things they’d never given a passing thought.
But when we study storytelling with our students, we forget all that. Or at least I did. When my students asked why we read novels and stories, and why we wrote personal narratives and fiction, my defense was pretty lame: I probably said something about the importance of having a shared body of knowledge, or about the enjoyment of losing yourself in a book, or about the benefits of having writing skills in general.
I forgot to talk about the power of story. I didn’t bother to tell them that the ability to tell a captivating story is one of the things that makes human beings extraordinary. It’s how we connect to each other. It’s something to celebrate, to study, to perfect. If we’re going to talk about how to teach students to write stories, we should start by thinking about why we tell stories at all . If we can pass that on to our students, then we will be going beyond a school assignment; we will be doing something transcendent.
Now. How do we get them to write those stories? I’m going to share the process I used for teaching narrative writing. I used this process with middle school students, but it would work with most age groups.
A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?
When teaching narrative writing, many teachers separate personal narratives from short stories. In my own classroom, I tended to avoid having my students write short stories because personal narratives were more accessible. I could usually get students to write about something that really happened, while it was more challenging to get them to make something up from scratch.
In the “real” world of writers, though, the main thing that separates memoir from fiction is labeling: A writer might base a novel heavily on personal experiences, but write it all in third person and change the names of characters to protect the identities of people in real life. Another writer might create a short story in first person that reads like a personal narrative, but is entirely fictional. Just last weekend my husband and I watched the movie Lion and were glued to the screen the whole time, knowing it was based on a true story. James Frey’s book A Million Little Pieces sold millions of copies as a memoir but was later found to contain more than a little bit of fiction. Then there are unique books like Curtis Sittenfeld’s brilliant novel American Wife , based heavily on the early life of Laura Bush but written in first person, with fictional names and settings, and labeled as a work of fiction. The line between fact and fiction has always been really, really blurry, but the common thread running through all of it is good storytelling.
With that in mind, the process for teaching narrative writing can be exactly the same for writing personal narratives or short stories; it’s the same skill set. So if you think your students can handle the freedom, you might decide to let them choose personal narrative or fiction for a narrative writing assignment, or simply tell them that whether the story is true doesn’t matter, as long as they are telling a good story and they are not trying to pass off a fictional story as fact.
Here are some examples of what that kind of flexibility could allow:
- A student might tell a true story from their own experience, but write it as if it were a fiction piece, with fictional characters, in third person.
- A student might create a completely fictional story, but tell it in first person, which would give it the same feel as a personal narrative.
- A student might tell a true story that happened to someone else, but write it in first person, as if they were that person. For example, I could write about my grandmother’s experience of getting lost as a child, but I might write it in her voice.
If we aren’t too restrictive about what we call these pieces, and we talk about different possibilities with our students, we can end up with lots of interesting outcomes. Meanwhile, we’re still teaching students the craft of narrative writing.
A Note About Process: Write With Your Students
One of the most powerful techniques I used as a writing teacher was to do my students’ writing assignments with them. I would start my own draft at the same time as they did, composing “live” on the classroom projector, and doing a lot of thinking out loud so they could see all the decisions a writer has to make.
The most helpful parts for them to observe were the early drafting stage, where I just scratched out whatever came to me in messy, run-on sentences, and the revision stage, where I crossed things out, rearranged, and made tons of notes on my writing. I have seen over and over again how witnessing that process can really help to unlock a student’s understanding of how writing actually gets made.
A Narrative Writing Unit Plan
Before I get into these steps, I should note that there is no one right way to teach narrative writing, and plenty of accomplished teachers are doing it differently and getting great results. This just happens to be a process that has worked for me.
Step 1: Show Students That Stories Are Everywhere
Getting our students to tell stories should be easy. They hear and tell stories all the time. But when they actually have to put words on paper, they forget their storytelling abilities: They can’t think of a topic. They omit relevant details, but go on and on about irrelevant ones. Their dialogue is bland. They can’t figure out how to start. They can’t figure out how to end.
So the first step in getting good narrative writing from students is to help them see that they are already telling stories every day . They gather at lockers to talk about that thing that happened over the weekend. They sit at lunch and describe an argument they had with a sibling. Without even thinking about it, they begin sentences with “This one time…” and launch into stories about their earlier childhood experiences. Students are natural storytellers; learning how to do it well on paper is simply a matter of studying good models, then imitating what those writers do.
So start off the unit by getting students to tell their stories. In journal quick-writes, think-pair-shares, or by playing a game like Concentric Circles , prompt them to tell some of their own brief stories: A time they were embarrassed. A time they lost something. A time they didn’t get to do something they really wanted to do. By telling their own short anecdotes, they will grow more comfortable and confident in their storytelling abilities. They will also be generating a list of topic ideas. And by listening to the stories of their classmates, they will be adding onto that list and remembering more of their own stories.
And remember to tell some of your own. Besides being a good way to bond with students, sharing your stories will help them see more possibilities for the ones they can tell.
Step 2: Study the Structure of a Story
Now that students have a good library of their own personal stories pulled into short-term memory, shift your focus to a more formal study of what a story looks like.
Use a diagram to show students a typical story arc like the one below. Then, using a simple story (try a video like The Present or Room ), fill out the story arc with the components from that story. Once students have seen this story mapped out, have them try it with another one, like a story you’ve read in class, a whole novel, or another short video.
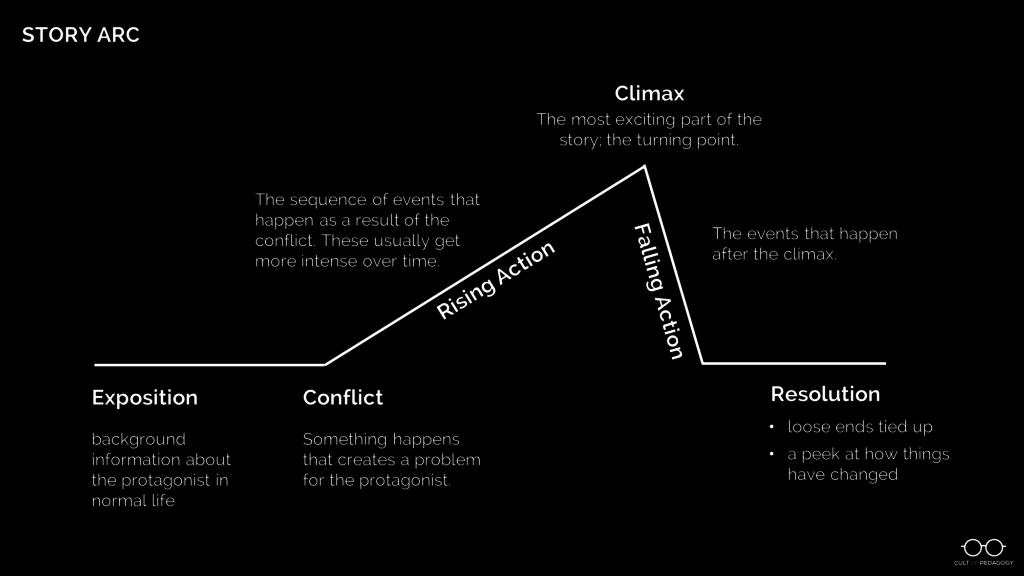
Step 3: Introduce the Assignment
Up to this point, students have been immersed in storytelling. Now give them specific instructions for what they are going to do. Share your assignment rubric so they understand the criteria that will be used to evaluate them; it should be ready and transparent right from the beginning of the unit. As always, I recommend using a single point rubric for this.
Step 4: Read Models
Once the parameters of the assignment have been explained, have students read at least one model story, a mentor text that exemplifies the qualities you’re looking for. This should be a story on a topic your students can kind of relate to, something they could see themselves writing. For my narrative writing unit (see the end of this post), I wrote a story called “Frog” about a 13-year-old girl who finally gets to stay home alone, then finds a frog in her house and gets completely freaked out, which basically ruins the fun she was planning for the night.
They will be reading this model as writers, looking at how the author shaped the text for a purpose, so that they can use those same strategies in their own writing. Have them look at your rubric and find places in the model that illustrate the qualities listed in the rubric. Then have them complete a story arc for the model so they can see the underlying structure.
Ideally, your students will have already read lots of different stories to look to as models. If that isn’t the case, this list of narrative texts recommended by Cult of Pedagogy followers on Twitter would be a good place to browse for titles that might be right for your students. Keep in mind that we have not read most of these stories, so be sure to read them first before adopting them for classroom use.
Step 5: Story Mapping
At this point, students will need to decide what they are going to write about. If they are stuck for a topic, have them just pick something they can write about, even if it’s not the most captivating story in the world. A skilled writer could tell a great story about deciding what to have for lunch. If they are using the skills of narrative writing, the topic isn’t as important as the execution.
Have students complete a basic story arc for their chosen topic using a diagram like the one below. This will help them make sure that they actually have a story to tell, with an identifiable problem, a sequence of events that build to a climax, and some kind of resolution, where something is different by the end. Again, if you are writing with your students, this would be an important step to model for them with your own story-in-progress.
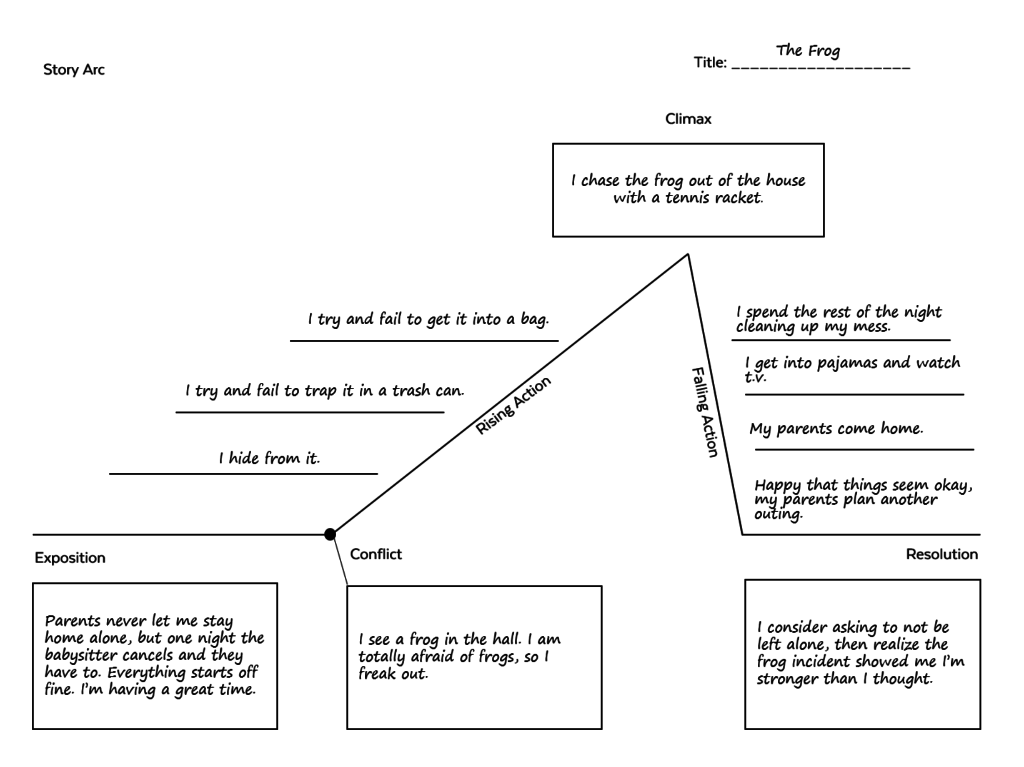
Step 6: Quick Drafts
Now, have students get their chosen story down on paper as quickly as possible: This could be basically a long paragraph that would read almost like a summary, but it would contain all the major parts of the story. Model this step with your own story, so they can see that you are not shooting for perfection in any way. What you want is a working draft, a starting point, something to build on for later, rather than a blank page (or screen) to stare at.
Step 7: Plan the Pacing
Now that the story has been born in raw form, students can begin to shape it. This would be a good time for a lesson on pacing, where students look at how writers expand some moments to create drama and shrink other moments so that the story doesn’t drag. Creating a diagram like the one below forces a writer to decide how much space to devote to all of the events in the story.

Step 8: Long Drafts
With a good plan in hand, students can now slow down and write a proper draft, expanding the sections of their story that they plan to really draw out and adding in more of the details that they left out in the quick draft.
Step 9: Workshop
Once students have a decent rough draft—something that has a basic beginning, middle, and end, with some discernible rising action, a climax of some kind, and a resolution, you’re ready to shift into full-on workshop mode. I would do this for at least a week: Start class with a short mini-lesson on some aspect of narrative writing craft, then give students the rest of the period to write, conference with you, and collaborate with their peers. During that time, they should focus some of their attention on applying the skill they learned in the mini-lesson to their drafts, so they will improve a little bit every day.
Topics for mini-lessons can include:
- How to weave exposition into your story so you don’t give readers an “information dump”
- How to carefully select dialogue to create good scenes, rather than quoting everything in a conversation
- How to punctuate and format dialogue so that it imitates the natural flow of a conversation
- How to describe things using sensory details and figurative language; also, what to describe…students too often give lots of irrelevant detail
- How to choose precise nouns and vivid verbs, use a variety of sentence lengths and structures, and add transitional words, phrases, and features to help the reader follow along
- How to start, end, and title a story
Step 10: Final Revisions and Edits
As the unit nears its end, students should be shifting away from revision , in which they alter the content of a piece, toward editing , where they make smaller changes to the mechanics of the writing. Make sure students understand the difference between the two: They should not be correcting each other’s spelling and punctuation in the early stages of this process, when the focus should be on shaping a better story.
One of the most effective strategies for revision and editing is to have students read their stories out loud. In the early stages, this will reveal places where information is missing or things get confusing. Later, more read-alouds will help them immediately find missing words, unintentional repetitions, and sentences that just “sound weird.” So get your students to read their work out loud frequently. It also helps to print stories on paper: For some reason, seeing the words in print helps us notice things we didn’t see on the screen.
To get the most from peer review, where students read and comment on each other’s work, more modeling from you is essential: Pull up a sample piece of writing and show students how to give specific feedback that helps, rather than simply writing “good detail” or “needs more detail,” the two comments I saw exchanged most often on students’ peer-reviewed papers.
Step 11: Final Copies and Publication
Once revision and peer review are done, students will hand in their final copies. If you don’t want to get stuck with 100-plus papers to grade, consider using Catlin Tucker’s station rotation model , which keeps all the grading in class. And when you do return stories with your own feedback, try using Kristy Louden’s delayed grade strategy , where students don’t see their final grade until they have read your written feedback.
Beyond the standard hand-in-for-a-grade, consider other ways to have students publish their stories. Here are some options:
- Stories could be published as individual pages on a collaborative website or blog.
- Students could create illustrated e-books out of their stories.
- Students could create a slideshow to accompany their stories and record them as digital storytelling videos. This could be done with a tool like Screencastify or Screencast-O-Matic .
So this is what worked for me. If you’ve struggled to get good stories from your students, try some or all of these techniques next time. I think you’ll find that all of your students have some pretty interesting stories to tell. Helping them tell their stories well is a gift that will serve them for many years after they leave your classroom. ♦
Want this unit ready-made?
If you’re a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you’d like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including slideshow mini-lessons on 14 areas of narrative craft, a sample narrative piece, editable rubrics, and other supplemental materials to guide students through every stage of the process, take a look at my Narrative Writing unit . Just click on the image below and you’ll be taken to a page where you can read more and see a detailed preview of what’s included.

What to Read Next

Categories: Instruction , Podcast
Tags: English language arts , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , teaching strategies
52 Comments
Wow, this is a wonderful guide! If my English teachers had taught this way, I’m sure I would have enjoyed narrative writing instead of dreading it. I’ll be able to use many of these suggestions when writing my blog! BrP
Lst year I was so discouraged because the short stories looked like the quick drafts described in this article. I thought I had totally failed until I read this and realized I did not fai,l I just needed to complete the process. Thank you!
I feel like you jumped in my head and connected my thoughts. I appreciate the time you took to stop and look closely at form. I really believe that student-writers should see all dimensions of narrative writing and be able to live in whichever style and voice they want for their work.
Can’t thank you enough for this. So well curated that one can just follow it blindly and ace at teaching it. Thanks again!
Great post! I especially liked your comments about reminding kids about the power of storytelling. My favourite podcasts and posts from you are always about how to do things in the classroom and I appreciate the research you do.
On a side note, the ice breakers are really handy. My kids know each other really well (rural community), and can tune out pretty quickly if there is nothing new to learn about their peers, but they like the games (and can remember where we stopped last time weeks later). I’ve started changing them up with ‘life questions’, so the editable version is great!
I love writing with my students and loved this podcast! A fun extension to this narrative is to challenge students to write another story about the same event, but use the perspective of another “character” from the story. Books like Wonder (R.J. Palacio) and Wanderer (Sharon Creech) can model the concept for students.
Thank you for your great efforts to reveal the practical writing strategies in layered details. As English is not my first language, I need listen to your podcast and read the text repeatedly so to fully understand. It’s worthy of the time for some great post like yours. I love sharing so I send the link to my English practice group that it can benefit more. I hope I could be able to give you some feedback later on.
Thank you for helping me get to know better especially the techniques in writing narrative text. Im an English teacher for 5years but have little knowledge on writing. I hope you could feature techniques in writing news and fearute story. God bless and more power!
Thank you for this! I am very interested in teaching a unit on personal narrative and this was an extremely helpful breakdown. As a current student teacher I am still unsure how to approach breaking down the structures of different genres of writing in a way that is helpful for me students but not too restrictive. The story mapping tools you provided really allowed me to think about this in a new way. Writing is such a powerful way to experience the world and more than anything I want my students to realize its power. Stories are how we make sense of the world and as an English teacher I feel obligated to give my students access to this particular skill.
The power of story is unfathomable. There’s this NGO in India doing some great work in harnessing the power of storytelling and plots to brighten children’s lives and enlighten them with true knowledge. Check out Katha India here: http://bit.ly/KathaIndia
Thank you so much for this. I did not go to college to become a writing professor, but due to restructuring in my department, I indeed am! This is a wonderful guide that I will use when teaching the narrative essay. I wonder if you have a similar guide for other modes such as descriptive, process, argument, etc.?
Hey Melanie, Jenn does have another guide on writing! Check out A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Argumentative Writing .
Hi, I am also wondering if there is a similar guide for descriptive writing in particular?
Hey Melanie, unfortunately Jenn doesn’t currently have a guide for descriptive writing. She’s always working on projects though, so she may get around to writing a unit like this in the future. You can always check her Teachers Pay Teachers page for an up-to-date list of materials she has available. Thanks!
I want to write about the new character in my area
That’s great! Let us know if you need any supports during your writing process!
I absolutely adore this unit plan. I teach freshmen English at a low-income high school and wanted to find something to help my students find their voice. It is not often that I borrow material, but I borrowed and adapted all of it in the order that it is presented! It is cohesive, understandable, and fun. Thank you!!
So glad to hear this, Nicole!
Thanks sharing this post. My students often get confused between personal narratives and short stories. Whenever I ask them to write a short story, she share their own experiences and add a bit of fiction in it to make it interesting.
Thank you! My students have loved this so far. I do have a question as to where the “Frog” story mentioned in Step 4 is. I could really use it! Thanks again.
This is great to hear, Emily! In Step 4, Jenn mentions that she wrote the “Frog” story for her narrative writing unit . Just scroll down the bottom of the post and you’ll see a link to the unit.
I also cannot find the link to the short story “Frog”– any chance someone can send it or we can repost it?
This story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. You can find a link to this unit in Step 4 or at the bottom of the article. Hope this helps.
I cannot find the frog story mentioned. Could you please send the link.? Thank you
Hi Michelle,
The Frog story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. There’s a link to this unit in Step 4 and at the bottom of the article.
Debbie- thanks for you reply… but there is no link to the story in step 4 or at the bottom of the page….
Hey Shawn, the frog story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link Debbie is referring to at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit and you would have to purchase that to gain access to the frog story. I hope this clears things up.
Thank you so much for this resource! I’m a high school English teacher, and am currently teaching creative writing for the first time. I really do value your blog, podcast, and other resources, so I’m excited to use this unit. I’m a cyber school teacher, so clear, organized layout is important; and I spend a lot of time making sure my content is visually accessible for my students to process. Thanks for creating resources that are easy for us teachers to process and use.
Do you have a lesson for Informative writing?
Hey Cari, Jenn has another unit on argumentative writing , but doesn’t have one yet on informative writing. She may develop one in the future so check back in sometime.
I had the same question. Informational writing is so difficult to have a good strong unit in when you have so many different text structures to meet and need text-dependent writing tasks.
Creating an informational writing unit is still on Jenn’s long list of projects to get to, but in the meantime, if you haven’t already, check out When We All Teach Text Structures, Everyone Wins . It might help you out!
This is a great lesson! It would be helpful to see a finished draft of the frog narrative arc. Students’ greatest challenge is transferring their ideas from the planner to a full draft. To see a full sample of how this arc was transformed into a complete narrative draft would be a powerful learning tool.
Hi Stacey! Jenn goes into more depth with the “Frog” lesson in her narrative writing unit – this is where you can find a sample of what a completed story arc might look. Also included is a draft of the narrative. If interested in checking out the unit and seeing a preview, just scroll down to the bottom of the post and click on the image. Hope this helps!
Helped me learn for an entrance exam thanks very much
Is the narrative writing lesson you talk about in https://www.cultofpedagogy.com/narrative-writing/
Also doable for elementary students you think, and if to what levels?
Love your work, Sincerely, Zanyar
Hey Zanyar,
It’s possible the unit would work with 4th and 5th graders, but Jenn definitely wouldn’t recommend going any younger. The main reason for this is that some of the mini-lessons in the unit could be challenging for students who are still concrete thinkers. You’d likely need to do some adjusting and scaffolding which could extend the unit beyond the 3 weeks. Having said that, I taught 1st grade and found the steps of the writing process, as described in the post, to be very similar. Of course learning targets/standards were different, but the process itself can be applied to any grade level (modeling writing, using mentor texts to study how stories work, planning the structure of the story, drafting, elaborating, etc.) Hope this helps!
This has made my life so much easier. After teaching in different schools systems, from the American, to British to IB, one needs to identify the anchor standards and concepts, that are common between all these systems, to build well balanced thematic units. Just reading these steps gave me the guidance I needed to satisfy both the conceptual framework the schools ask for and the standards-based practice. Thank you Thank you.
Would this work for teaching a first grader about narrative writing? I am also looking for a great book to use as a model for narrative writing. Veggie Monster is being used by his teacher and he isn’t connecting with this book in the least bit, so it isn’t having a positive impact. My fear is he will associate this with writing and I don’t want a negative association connected to such a beautiful process and experience. Any suggestions would be helpful.
Thank you for any information you can provide!
Although I think the materials in the actual narrative writing unit are really too advanced for a first grader, the general process that’s described in the blog post can still work really well.
I’m sorry your child isn’t connecting with The Night of the Veggie Monster. Try to keep in mind that the main reason this is used as a mentor text is because it models how a small moment story can be told in a big way. It’s filled with all kinds of wonderful text features that impact the meaning of the story – dialogue, description, bold text, speech bubbles, changes in text size, ellipses, zoomed in images, text placement, text shape, etc. All of these things will become mini-lessons throughout the unit. But there are lots of other wonderful mentor texts that your child might enjoy. My suggestion for an early writer, is to look for a small moment text, similar in structure, that zooms in on a problem that a first grader can relate to. In addition to the mentor texts that I found in this article , you might also want to check out Knuffle Bunny, Kitten’s First Full Moon, When Sophie Gets Angry Really Really Angry, and Whistle for Willie. Hope this helps!
I saw this on Pinterest the other day while searching for examples of narritives units/lessons. I clicked on it because I always click on C.o.P stuff 🙂 And I wasn’t disapointed. I was intrigued by the connection of narratives to humanity–even if a student doesn’t identify as a writer, he/she certainly is human, right? I really liked this. THIS clicked with me.
A few days after I read the P.o.C post, I ventured on to YouTube for more ideas to help guide me with my 8th graders’ narrative writing this coming spring. And there was a TEDx video titled, “The Power of Personal Narrative” by J. Christan Jensen. I immediately remembered the line from the article above that associated storytelling with “power” and how it sets humans apart and if introduced and taught as such, it can be “extraordinary.”
I watched the video and to the suprise of my expectations, it was FANTASTIC. Between Jennifer’s post and the TEDx video ignited within me some major motivation and excitement to begin this unit.
Thanks for sharing this with us! So glad that Jenn’s post paired with another text gave you some motivation and excitement. I’ll be sure to pass this on to Jenn!
Thank you very much for this really helpful post! I really love the idea of helping our students understand that storytelling is powerful and then go on to teach them how to harness that power. That is the essence of teaching literature or writing at any level. However, I’m a little worried about telling students that whether a piece of writing is fact or fiction does not matter. It in fact matters a lot precisely because storytelling is powerful. Narratives can shape people’s views and get their emotions involved which would, in turn, motivate them to act on a certain matter, whether for good or for bad. A fictional narrative that is passed as factual could cause a lot of damage in the real world. I believe we should. I can see how helping students focus on writing the story rather than the truth of it all could help refine the needed skills without distractions. Nevertheless, would it not be prudent to teach our students to not just harness the power of storytelling but refrain from misusing it by pushing false narratives as factual? It is true that in reality, memoirs pass as factual while novels do as fictional while the opposite may be true for both cases. I am not too worried about novels passing as fictional. On the other hand, fictional narratives masquerading as factual are disconcerting and part of a phenomenon that needs to be fought against, not enhanced or condoned in education. This is especially true because memoirs are often used by powerful people to write/re-write history. I would really like to hear your opinion on this. Thanks a lot for a great post and a lot of helpful resources!
Thank you so much for this. Jenn and I had a chance to chat and we can see where you’re coming from. Jenn never meant to suggest that a person should pass off a piece of fictional writing as a true story. Good stories can be true, completely fictional, or based on a true story that’s mixed with some fiction – that part doesn’t really matter. However, what does matter is how a student labels their story. We think that could have been stated more clearly in the post , so Jenn decided to add a bit about this at the end of the 3rd paragraph in the section “A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?” Thanks again for bringing this to our attention!
You have no idea how much your page has helped me in so many ways. I am currently in my teaching credential program and there are times that I feel lost due to a lack of experience in the classroom. I’m so glad I came across your page! Thank you for sharing!
Thanks so much for letting us know-this means a whole lot!
No, we’re sorry. Jenn actually gets this question fairly often. It’s something she considered doing at one point, but because she has so many other projects she’s working on, she’s just not gotten to it.
I couldn’t find the story
Hi, Duraiya. The “Frog” story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit, which you can purchase to gain access to the story. I hope this helps!
I am using this step-by-step plan to help me teach personal narrative story writing. I wanted to show the Coca-Cola story, but the link says the video is not available. Do you have a new link or can you tell me the name of the story so I can find it?
Thank you for putting this together.
Hi Corri, sorry about that. The Coca-Cola commercial disappeared, so Jenn just updated the post with links to two videos with good stories. Hope this helps!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.
Creative Composing: A Lesson Plan for Students, Teachers, and Teacher-Writers

Peitho Volume 26 Issue 1, Fall 2023
Author(s): Meg Scott-Copses
Meg Scott-Copses specializes in creative writing, composition, and an embodied pedagogy that fuses the two. She earned her Ph.D. in poetry from Florida State with a dissertation on service learning in at-risk environments such as prisons and youth shelters. At her home institution, the College of Charleston, she specializes in composition and writing studies, and is the Director of the First-Year Writing program. In 2020, she won the University’s Distinguished Teaching Award, in part based on her research into experiential and embodied teaching practices. She challenges students to explore the intuitive connection between experiential observation and analysis, and between creative and critical thinking.

Introduction
This lesson plan focuses specifically on Wendy Bishop’s chapter “When All Writing is Creative and Student Writing is Literature,” from The Subject is Writing , 2nd edition. Like so much of Bishop’s work, her style and structure serve as direct evidence for her primary argument. She “creatively composes” this chapter, demonstrating the natural overlap between creative and academic pursuits and between student writing and the literature we teach. While Bishop’s work predates the subject we now call rhetorical feminism, she offers a clear example of its key tenets—inclusivity, community, and equity. She privileges dialogue over monologue, inviting students to draw on their own experiences as they develop an empowered and growth-oriented writing practice.
It was long after my graduate training at Florida State that I found language for the re-orientation that Wendy instilled in me. In reading Carolyn Shrewsbury’s “What is Feminist Pedagogy?” and later Cheryl Glenn’s “Remapping Rhetorical Territory,” I came to recognize that my teaching practice moved in these same directions and that I had been guided by Wendy to radically alter the power dynamics and the communication opportunities in my writing classroom. In Shrewsbury’s words, I had created, somewhat unconsciously, a “liberatory environment,” which she describes as:
A classroom characterized as persons connected in a net of relationships…in which we, teacher-student and student-teacher, act as subjects, not objects. Feminist pedagogy is engaged teaching/learning—engaged with self in continuing reflective process; engaged actively with the material being studied; engaged with others in a struggle to get beyond destructive hatreds and to work together to enhance our knowledge; engaged with the community and with movements for social change (166).
Reading any of Wendy’s work reveals these same values as she challenges us to re-orient our understanding of what an academic article is and does. Her chapter “When All Writing is Literature and Student Writing is Creative” offers a clear example of what we might call a “flipped article” (again Wendy’s pedagogy and scholarship was well before the term flipped classroom came into popularity). Readers are immediately inside the experience of her pedagogy, as she places her students’ writing alongside her own. She fuses pedagogical research with lived experience, insisting on a more embodied approach. As for methodology in both creative writing and composition classrooms, she suggests:
Writing always involves the study of exemplary or expert writing in the forms you hope to learn. But you also need the opportunity to write against and experiment with those forms. You have to try it to do it (Bishop 197).
The following lesson plan grows out of this “Try-It” spirit, both for students and for teachers. Recently a colleague asked me about building rapport; he lamented that the buzzwords all sound good in theory—“experiential” “embodied” “hands-on,” “active.” His question: but how do you actually do it? My answer: Not unlike writing, teaching is also about trying it. You have to try it to do it.
Background and Audience
This lesson is appropriate for any of the following courses: Introduction to Academic Writing, First-Year Seminar, Freshman Composition I or II, Introduction to Creative Writing, Introduction to Literary or English Studies, Advanced Composition, Theories of Teaching Writing, Graduate Teaching in English or English Education. Students should come to class having read the article “When All Writing is Creative and Student Writing is Literature,” but even if they haven’t prepared as thoroughly as we’d like, this assignment is designed to experientially teach the key findings of the article and to generate helpful discussions about thinking and writing.
- To understand existing distinctions between disciplinary fields of creative writing, literature, and composition.
- To generate new, experience-based definitions of creative writing, analytical writing, professional writing, and academic writing
- To consider what separates student writing from literature
- To study our own writing preferences, beliefs, and practices
- To discuss helpful teaching and learning strategies for writing
Discussion and Mapping 10-15 minutes
Create binaries on a whiteboard, smartboard, or overhead using the terms Creative Writing vs. Academic Writing and Student Writing vs. Literature. Ask the class to generate key words and associations that typically fall under each heading, as seen below:
Creative Writing /Academic Writing Student Writing / Literature
Discuss areas of overlap between these divisions. For example, both student writing and literature might be published. Both creative writing and academic writing may involve research. Consider what Bishop’s article adds to this discussion. For example, both creative and academic writing are process-based. Both student writing and literature involve an understanding of generic conventions. In Bishop’s view, risk-taking and engagement apply equally to creative and critical thinking.
Two Writing Prompts 20-25 minutes
Divide the class into two groups, A and B, and assign two different quotations (below), both of which are lines from Bishop’s article. Students should begin with this line. Note: students aren’t quoting Bishop (or Bishop’s students); they are acting as though this is their own opening line.
- Group A opening line: Is creative writing stuff that you do for fun and composition stuff that your teacher makes you do? That’s how it felt in elementary school.
- Group B opening line: Creativity involves risk taking. It’s likely that in your past, you were not praised for taking risks.
Subdivide these two groups further so that:
- Group A-Academic will use opening line A to write an academic/analytical piece .
- Group A-Creative will use opening line A to write a creative piece .
- Group B-Academic will use opening line B to write an academic/analytical piece.
- Group B-Creative will use opening line B to write a creative piece.
Allow 7-10 minutes for this first writing prompt. Make sure students understand that this is an exercise, a first try, and that they may not be finished when time is called. The purpose is to see what we know intuitively about these genres and to notice our own thinking and writing process as we try it out.
After time is called for Prompt 1, explain that students will now use the same opening line, but this time to write in the other genre. For example, students who first worked on a creative piece will now use the same line to write something more academic or analytically driven. Allow 7-10 minutes for the other genre.
Partner Work and Class Discussion 20 minutes
Pair students with a partner to discuss this experiment. Ideally, a student from A-Academic should pair with a student from B-Creative. This will offer students a chance to learn more about the opening line they weren’t assigned. It will also control for variables such as which genre they worked on first or second. Students should trade their writing or read what they’ve written aloud, then discuss their process. Which piece felt more successful? Which one surprised you the most? Students might also identify new ideas or emerging definitions for the thinking processes used in each. It’s unlikely that this discussion will need much prompting. In my experience, this portion of class is extremely lively.
Finish class by returning to the charts made at the beginning. What new ideas have developed as a result of this experiential lesson? Assign a reflective follow-up to be completed as homework. Students may post to an online discussion board or bring their reflections to the next class.
Teacher Reflection and Follow-Up Instructions:
As I hinted above, this lesson was a big hit. I knew it would be interactive and hoped it would help students grasp the article, but it far exceeded these expectations. Students were completely engaged in what Bishop describes as the “messy, generative, exciting process of writing” (194). For whatever reason, this particular line has stayed with me years beyond graduate school. I’ve even used this quote on syllabi and assignments, and it came to me again—almost in a chill-bumps way—while watching my students so completely immersed in the act of discovery. The messy, generative, exciting process of writing . Yes!
As good as I felt about the class, I was even more impressed with students’ follow-up posts, which they submitted a few days later. Reflecting on this distilled experience proved to be as important for them as the experience itself. I will insert, here, the prompt I used. In keeping with my earlier theft of Wendy’s lines, please feel free to steal:
- In Thursday’s class, we used the same prompt to write two entries—one creative, one analytical. What did you discover about your own writing through this experience? What takeaways did you glean from your partner in follow-up discussion? Describe your relative comfort with one style over (or in tandem with) another and consider Bishop’s claim that “all writing is creative.”
- After processing your experience, think about what these ideas mean in the context of teaching writing. What’s the role of “the creative” in composition classes? What’s the benefit of considering “student writing” alongside “literature?”
Student Writing
It seems only fitting to focus now on student responses as valuable testimonials and direct evidence for Wendy Bishop’s vision. More than anything else I learned from her, it’s that teaching writing really means writing alongside your students , reading them, letting them read you, learning from them as equally as they learn from you. When I think about recent discussions I’ve had with colleagues and students about the advent of ChatGPT, I take comfort in writing that feels authentic, metacognitive, collaborative, and instructive.
Below, I’ve excerpted passages from students (used with permission) that have given me plenty to think about. These students will be delighted to learn that their writing—not unlike literature—was published, and that their words are worthy of study.
From the unlikely English major:
Bishop’s article discusses the problem of students believing that they aren’t worthy to be named a “writer,” that what they write is so much less than “literature.” The constraints students often face when interacting with academic writing, such as research papers and essays, disregard writing as a creative process. This resonated personally with me as I would’ve never guessed in a million years I would be an English major. Growing up, I enjoyed reading and writing, but never excelled in school. I wasn’t a great essay writer, and I never did anything that deserved praise. I accepted my place outside of the discipline. But I finally had a teacher who encouraged us to take risks and encouraged us to lean into the discomfort we felt and do some exploring. He treated us as if we were all equably capable of producing publishable work. I started reading more, writing more, and caring more, and here I am. —Eliza
From a self-professed analytical writer:
In Thursday’s class, I came to the realization that I really need to get out of my comfort zone when it comes to writing. I naturally gravitate towards writing in a manner that seems academically correct—always. I was assigned to write creatively first, which I really struggled with. Without realizing, I wrote the creative prompt in a more analytical manner. Honestly, I don’t think I wrote creatively at all. And then afterward, when writing analytically, I just used more professional verbiage and somehow making things even more structured than before. Am I really this boring? When discussing with my partner, I noticed that she took a more anecdotal approach, which I think made her text seem less analytical and created a distinction between the two styles. Her writing was fun, personable, and relatable. I noticed that my writing seemed to only answer the prompt. I learned a lot about potential areas for growth. —Chelsea
From an unabashed creative writer:
Reading my creative piece and then moving to my analysis is a bit funny, honestly. It’s like I turned around, put a suit and tie on, slicked my hair back, and turned back to face the audience, ready to lay out some facts and cite some quotes. Lewie and I had a blast conversing and focused mostly on how similar we are in our inability to hush our creativity, humor, and emotion under any circumstances. We never actually read our analyses to each other because we were too busy laughing about how we both wrote intensely dramatic, poetic pieces about risk-taking and creative writing itself. Needless to say, we were both fully immersed —Luca
From students who cultivate the merging of these styles, or who use one genre to think strategically about the other:
From Thursday’s class I learned that I have become a better analytical writer than a creative writer. It was kind of sad to realize this, since I fell in love with writing through the creative writing I did in elementary school. In middle and high school, I still loved creating stories and new approaches with the prompts I was given, and I realize now that this made me a better analytical writer because I would look at these boring papers and still try finding a way to be creative! I think that if students at any level were allowed to release some sort of inner creativity, or allowed their own spin, that both their creative and analytical writing would improve. —Elizabeth
This exercise got me thinking that creative writing and academic writing have a systematic relationship, not a hierarchical one. When we colloquially talk of creative versus academic, we are more speaking about the Inspirational Process versus the Mechanical Process of writing, both in the actual crafting of language and in the crafting of ideas: the fundamental systems employed by the writer. The Inspirational/Mechanical Processes are more akin to energy sources than anything else, and the writer bounces between them whether writing a post, a school essay, a poem, or a novel. The writer uses the Mechanical Process while integrating quotes but may draw on the Inspirational Process when their integration becomes ineffective or repetitive: they dive into the creative energy to find a new, more unexpected way to craft the language and ideas surrounding this quote. When the movement between these two processes is unconscious and fluid, we feel in the zone. When it’s not fluid, we become conscious of the discrepancy and may feel writer’s block. —Jacob
The exercise we did in Thursday’s class was a surprising challenge. I noticed that writing in separate styles forced me to look at the same topic from more than one angle and with different audiences in mind. In talking to Hailey about this experience, we agreed that it was difficult to mentally switch between the analyzing and creative parts of our minds. I can see that this is a skill writers need to practice in order to weave the two aspects together in a singular piece of writing. This experience showed me that academic writing and creative writing really shouldn’t be taught as completely separate entities. It would be a disservice to student writers to not be allowed to start experimenting with the mixture of analysis and creativity before they get to the college level. It would be like parents who don’t let their children cook or try out spicing their own food and exploring flavors. They wonder why kids end up only cooking bland dishes once they move out of the house. Bishop mentions that “creativity involves risk-taking.” What better place for student writers to take risks and try new things with their writing than the classroom? What is a teacher really doing for their students if they don’t foster a safe environment for that? How can a student confidently mix ingredients in new ways if their work keeps coming back to them covered in scolding remarks about criteria and convention errors? —Vaccarella
From students who plan to teach:
I want to be a teacher who praises/encourages students to take risks! I remember what it felt like once when a teacher told me I clearly didn’t get it, and that I should “try something easier.” I had an idea, and though it wasn’t perfect, all ideas deserve attention in a writing class, even if you end up throwing it out because that is part of the writing process too. —Sarah
Rather than thinking of the two as separate categories, Bishop believes one should come before the other: “If you are creative before you are careful, you will be more likely to gain an understanding of the writing process of professionals.” I think this shows the importance of maintaining “the creative” in composition when teaching writing to students. When students are taught to write in a strict, rubric-driven way, they’re being shielded from taking the risks that could make them really grow as writers and invest in the process itself, which most of them come to dread. This activity felt empowering, and I was energized by knowing that it was up to me to feel what was working. I want my future students to use their own instincts. —Ariel
So in teaching writing, maybe teachers should stop giving out super in-depth rubrics and prompts. Let the student read the prompt and use their writing to give the prompt some shape and depth. That way, the teacher may get a new insight instead of receiving what they already know, what they expect, the answers teachers are looking for. —Kennedy
From a rule-breaker:
Ummm…through my experience with responding to the same prompt creatively and analytically, I discovered I need to read prompts more closely. But no matter my oversight, I discovered that I will make any writing prompt my own. Even when I realized I was supposed to be writing something analytical and then something creative, both of my responses took the same form. They failed to be either specifically creative or specifically analytical and became instead what I wanted to write. I even struggled to stay on the topic of creativity, instead finding myself connecting the prompt to some recent experiences. Neither struck me as easier, considering I found it impossible to meet the criteria of both! The other day I saw a TikTok about how at 5 years old 98% of children met the requirements of being a “creative genius.” By age 10, only about 30% did and by adulthood it was less than 5% (or something.) I think the role of creativity in teaching writing should be fostered. There are also many reasons to consider student writing as literature beyond the fact that they are far more similar than they are different. The most compelling to me is building the confidence of students. Regardless of what a teacher may say to their students, their underlying beliefs come through, and if it’s clear that a teacher doesn’t take their students’ writing seriously, students won’t take their own writing seriously either. —Mo
From a student with big questions about academic voice:
It was easier to get into a state of flow when writing creatively. I got nearly three times more words out in the first write-up compared to the second (which I would attribute to the need I felt to incorporate evidence in the academic writing style). It’s interesting that I naturally associate academic writing with evidence-based style and creative writing with a more intuitive style. If I dig further, I realize that the academic voice that I attempted is neither natural or captivating, and it is certainly not a voice that I ever see myself utilizing outside of academia. Why do I use it? Who has shaped my understanding of this academic style… one that I think is both boring and impractical? If you take another step, one must wonder: why do we teach students to write with this voice? I don’t even think this is done intentionally, but I also think this is a bigger question than it appears to be on the surface.—Ryan
Even if you only browsed a few of these student samples, it’s easy to detect their level of engagement. These writers are asking interesting questions and courageously posing solutions for themselves, as well as for the educational systems they are a part of. It’s worth noting that these Discussion Posts are entirely credit-based; students receive a 100 for completion if they meet a 250-word count. All students easily wrote much more than this, not simply checking a box to receive a grade. They continued to mention the impact of this assignment all semester long, even referencing it in final projects and on course-instructor evaluations.
Thank you, Ryan, Mo, Kennedy, Ariel, Sarah, Vaccarella, Jacob, Sarah, Elizabeth, Chelsea, Eliza, Luca, and Mo for giving us new ideas about Wendy Bishop’s work and the larger practice of engaged teaching and writing.
Works Cited
Bishop, Wendy. “When All Writing is Creative and Student Writing is Literature.” The Subject Is Writing , 2nd ed. Edited by Wendy Bishop, Heinemann Educational Books, 1999, pp.192-201.
Glenn, Cheryl. “Remapping Rhetorical Territory.” Rhetoric Review , vol. 13, no. 2, 1995, pp. 287–303.
Shrewsbury, Carolyn M. “What Is Feminist Pedagogy?” Women’s Studies Quarterly , vol. 15, no. 3/4, 1987, pp. 6–14.
Share this Article

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Need a resource? Head over to the shop and save 15% off your first purchase! SHOP NOW
- Text Messaging
- Facebook Group
- Search this website
Proud to be Primary
Be inspired, motivate kids, and make a positive impact in your classroom.

9:00 am By Proud to be Primary Leave a Comment
Fun & Creative Summer Activity Sheets & Writing Prompts for Kids
Summer vacation is almost here. That means it’s time to start planning which summer activity sheets and writing prompts you’ll be sending home with students!

Summer Activity Sheets & Writing Prompts
Ah, summer – a season of endless blue skies, warm breezes, and the promise of adventures waiting to be had. For kids, it’s a time of boundless energy and imagination, just waiting to be unleashed.
As teachers, we encourage students to use this energy productively and still have meaningful learning experiences, even during the break from school.
That’s where summer activity sheets and writing prompts come into play—they’re not just tools to keep young minds engaged but also help with exploration, creativity, and fun-filled learning.
Why Summer Learning Matters
Summer is more than just a break from the routine; it’s an opportunity to keep young minds active and engaged. By providing stimulating activities and prompts, we can prevent the dreaded “summer slide” and ensure that students return to school ready to hit the ground running.
The Power of Writing Prompts & Activity Sheets
Writing prompts and activity sheets are like fuel for the imagination. They help with creativity, encourage self-expression, and foster a love for storytelling. Through these prompts, kids can explore many topics – from beach adventures to camping trips – while improving their writing skills.

Summer Writing Prompts
As teachers, we are not looking to give students hours of work during the summer. We want them to enjoy the long days as much as we do. But that doesn’t mean we can’t send home some work to keep their young minds active and engaged, even during the break from school. That’s where summer writing prompts come in.
Summer Writing Prompts:
- Describe your perfect summer day.
- Imagine a summer picnic with your favorite foods.
- Imagine you’re on a summer expedition.
- How do you celebrate the longest day of the year? Describe your summer solstice traditions.
- Write down all the fun activities you want to do before summer ends!
Beach Writing Prompts:
- Write a story about a day at the beach.
- Imagine you’re at the beach. Describe what you see, hear, and feel.
- Create a list of all the things you would bring to the beach for a fun day.
- Write a letter to a friend inviting them to join you for a day at the beach.
- Draw a picture of your favorite beach memory and write a few sentences about it.
Camping Writing Prompts:
- Tell a tale of camping under the stars.
- Share a spooky or adventurous story told around a summer campfire.
- Tell a story about a camping trip with your family or friends.
- Describe your dream camping spot.
- Write a list of essentials for a camping trip.
Back To School Prompts:
- Share your hopes and dreams for the upcoming school year.
- Write about your feelings on the first day of a new school year.
- Imagine you are the teacher on the first day of school.
- Describe your favorite thing about starting a new school year.
- Create a list of goals you want to achieve during the upcoming school year.

To introduce these prompts, consider setting the scene with a short discussion or a fun activity related to each topic. Encourage students to use their own experiences and let their imaginations soar!
Fun Summer Writing & Activity Sheets
Whether you’re a teacher, parent, or homeschooler, keeping students engaged during the break is essential. Summer writing prompts and activity sheets make great summer review activities and are the perfect way to blend learning with enjoyment, all while capturing the season’s spirit.
Writing Mats
These handy summer writing mats provide picture-word support and include a convention checklist to guide young writers in crafting their writing independently. Additionally, they come with a collection of vocabulary cards, ensuring that students have many words at their fingertips to boost their writing. Writing mats allow students to get creative while building essential writing skills, making them the perfect addition to any summer learning routine.

Story Idea Tear Strips
These special story idea strips are filled with different story prompts you can tear off and use to start writing your own stories. Each strip provides a new idea for a story so kids can let their imaginations run wild. These tear-off prompts help kids get creative and have fun with their writing.

BINGO Boards with Writing Ideas
Writing BINGO boards are filled with exciting writing prompts that make the writing process enjoyable and engaging. Each square on the board contains a different prompt, from describing a favorite summer memory to creating a character for a story.
With Bingo Boards, students can have fun while practicing their writing skills, turning what might feel like work into a playful activity. Plus, with the element of competition, they can challenge each other to complete lines or even entire boards, adding an extra layer of motivation.

“Write About It” Picture Prompts
These visual prompts are designed to ignite imagination and inspire storytelling. Kids create a story to match the picture shown. Each picture prompt invites them to dive into a world of their creation, making writing a fun experience. Then, they can color!

Summer Journal
Encourage a summer full of writing adventures with a Summer Journal! This journal is perfect for young writers looking to capture their summer memories and creative ideas. It can help inspire daily writing practice while inviting students to reflect on their summertime experiences. Grab a free summer journal h e re !
In addition, consider incorporating other activities, such as word searches, crossword puzzles, and more, to keep the learning experience varied and exciting.
How to Use Writing Prompts
To make the most of writing prompts, it is important to create a welcoming environment where kids feel comfortable expressing themselves. This means encouraging them to share their thoughts and ideas freely.
Once they’re ready to start writing, remind them to add many details to their stories. Encourage them to use descriptive words that paint a clear picture in the reader’s mind. Also, suggest that they draw pictures to accompany their writing. By doing these things, kids can bring their stories to life and have fun while they’re at it!

Ideas for Incorporating Summer Writing Activities
Incorporating summer writing activities into your summer school routine or practice at home offers many opportunities to engage writers and get them writing everyday .
Here are some ways to infuse creativity and excitement into summer writing sessions :
- Independent Writing Time : Dedicate a portion of each day to independent writing sessions where kids explore their interests and ideas. Provide a variety of writing prompts and materials to spark their imagination, allowing them the freedom to choose topics that resonate with them.
- Outdoor Writing Adventures: Take advantage of the summer weather by incorporating outdoor writing activities into your curriculum. Whether journaling in nature, conducting interviews with local wildlife, or writing poetry inspired by the sights and sounds of the outdoors, getting outside can inspire young writers.
- Themed Writing Days: Choose a different summer-related theme each week, such as “Beach Day,” “Outdoor Adventure Day,” “Ice Cream Day,” etc. On each themed day, provide writing prompts, activities, and materials related to the chosen theme. For example, on “Beach Day,” students can write about their favorite beach memories, create stories about imaginary beach adventures, or even write about why their favorite beach activity is the best.
Strategies to Help Young Writers
There are many ways of helping kid writers . Above all, celebrate efforts and achievements to create a love for writing. Provide constructive feedback and guidance and allow room for exploration and self-expression. You’re preparing kids for success in life and the next school year by instilling confidence and a passion for storytelling.
Incorporating these summer writing ideas into your summer activities can inspire creativity, promote literacy skills, and instill a lifelong love of writing in your students. Get creative, explore new ideas, and make the most of the summer season to cultivate a writing community in your classroom or at home.
Summer Writing Activity Resources
Free writing activities.
Try the writing mats in your classroom with this FREE Writing Activity Mats sample resource! Your students will be begging to take some home for summer break.
Click the image below to grab a copy.
Writing Activities That Are Perfect For Summer!
There are plenty of writing activities by Proud to Be Primary that are perfect for sending home with students during summer vacation or using in summer school!
- Summer Writing & Word Activities
- June Writing Mats
- June Writing Center
- Vocabulary Cards
- Writing Prompts
- Story Idea Tear Off Strips
- Writing Idea Spinners
More Summer Review Ideas

Summer Review Activities

Summer Reading Activities For Kids

End Of The Year Activities
PIN for Later

You may also enjoy these posts:

Reader Interactions
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Shop Our Site
- Social-Emotional learning
- Classroom Management
- Teaching Ideas
- Directed Drawing
- Best-Sellers
- Social-Emotional Learning
- Sight Words
- Non-Fiction
Join more than 100,000 proud primary teachers!
Sign up for exclusive access to teacher freebies & weekly emails filled with teacher tips, lesson ideas, and resource suggestions sent straight to your inbox!


100 Totally Free Printable Activities for Kids
P rintable activities for kids may seem a little old-school, but there's something to be said for good old pen-and-paper fun. While there are tons of great online resources for kids , it's important to take a break from screens sometimes.
We've rounded up 100 printables you can take with you just about anywhere. From printable coloring pages and paper dolls to craft instructions and STEM-inspired fun, these activities provide hours of entertainment. They also keep kids actively learning by developing fine-motor skills, working on critical thinking, and even inspiring some gross motor play workouts. And the best part is, they're completely free!
Bookmark this list of printable activities and come back to it anytime you hear the dreaded, "I'm bored!" You can also check out our guide to Boredom Busters for Kids for more ideas for screen-free fun.
Sign up for our FREE newsletters to get posts like this delivered to your inbox.
There are so many great printables that teach kids how to draw various pictures and patterns. Photo by Pixelshot, courtesy of Canva
Drawing Printables for Kids
1. Learn how to draw a cat .
2. Save the world when you design your own superhero .
3. These blank-face drawing prompts leave a lot to the imagination.
4. Be the star of your own comic with these blank comic-book strips .
5. Learn how to draw a box turtle with these easy step-by-step instructions .
6. Mandalas are a meditative activity that can take a long time to complete. Learn all about them with the Asian Art Museum's downloadable Mandala drawing activity .
7. Learn how to draw anything you can imagine with these instructional drawing guides .
8. Chill out with these creative doodle pattern tiles .
9. Build drawing skills with grid drawing puzzles .
Writing Printables for Kids
10. Use pictures to write your own story .
11. Print out your own envelope and write a letter to family and friends.
12. Print these fill-in-the-blank stories from Nickelodeon and exercise your funny bone.
13. These writing-practice printables are great for kids learning their letters.
14. Browse over 100 writing printables for early readers.
15. Put pen to paper with creative-writing templates .
16. Build penmanship (yes, that's still a thing) with amazing handwriting worksheets .
17. Flex those brain muscles with writing printables for preschoolers.
18. These writing worksheets work on skills like capitalization and punctuation.
RELATED: Water Games to Play All Summer Long
Printable activity pages can keep kids from saying the dreaded, "I'm bored!" Photo by Wave Break Media, courtesy of Canva
Printable Activity Pages for Kids
19. Download an activity pack from Puffin Books. These brightly colored and beautifully illustrated packs keep kids busy for hours.
20. Spend some time learning about yourself with this All About Me activity sheet .
21. Explore your home with this fun activity sheet .
22. SpongeBob fans will love Nickelodeon's Spongebob activity book .
23. These mind-bending mazes will keep your kids mesmerized.
24. This 10-page printable includes everything from a list of boredom busters to daily learning projects.
25. You don't need much to learn how to build a tent !
26. Make a time capsule with this printable time capsule activity pack .
27. Explore a variety of printable activities for preschoolers .
28. Look through tons of free themed printable activity packs .
Hidden-Picture Printables for Kids
29. These hidden-picture printables are perfect for long car rides.
30. Spruce Crafts has some beautiful seek-and-find printables .
31. These difficult hidden-picture printables are perfect for older kids.
32. Check out these simple hidden-picture printables .
33. These find-the-difference coloring pages are a two-in-one activity.
34. Enjoy these spot-the-difference puzzle printables .
35. Monthly themed hidden-image printables are perfect for holidays and classrooms.
36. Have double the fun with this hidden-image printable that doubles as a coloring page.
37. Try these animal-themed hidden-image worksheets .Scavenger Hunt Printables for Kids
38. Go on a scavenger hunt to find red objects.
39. Shiver me timbers! It's time to go on a pirate treasure hunt .
40. Take this printable to-go as you embark on a nature scavenger hunt.
41. Have fun inside and outside with these scavenger hunt printables .
42. These simple scavenger hunts are perfect for younger kids.
43. The pictures on these printable scavenger hunts make them perfect for early readers.
44. Browse over 50 free printable scavenger hunts .
RELATED: Free Coloring Pages for Kids to Download
No need to buy coloring books when you can print out free coloring pages. Photo by Ketut Subiyanto, courtesy of Pexels
Coloring-Page Printables for Kids
45. Color-by-numbers are a great way to recognize numbers and have a little fun.
46. These color-by-numbers printables are tons of fun for younger kids.
47. Crayola has oodles and oodles of free coloring pages to download.
48. Download and print this silly story you can color created by a licensed art therapist.
49. These color-by-numbers pages feature cute scenes and characters your kids will love.
50. Check out these free coloring pages for kids (and adults)!
51. With just a few markers or crayons, these color-by-numbers printables will turn into masterpieces.
52. These coloring pages are based on famous works of art.
53. Browse tons of coloring and color-by-number pages .
54. Color Me PhD has free science coloring books based on PhD-level scientific research. Don't worry, you don't need a degree to color inside the lines.
Printable Calendars for Kids
55. These adorable printable calendars have cute graphics themed for each month.
56. These printable calendars have fun themes like Star Wars , superheroes, Disney princesses, and more.
57. Print some blank calendars and fill in the dates. These will work every year.
58. This free printable calendar doubles as a coloring book.
59. Printable weekly planners might just be what you need to organize your life.
60. This weekly planner can break up your schedule into days or hours, and also has a section for goals and behavior tracking.
61. Look through a variety of printable calendars for kids .
RELATED: Crafts for Kids: 100 Awesome Art Projects
Put on a show with printable finger puppets. Photo courtesy of Easy Peasy Play
Printable Craft Instructions for Kids
62. Put on a show with printable finger puppets .
63. San Francisco's Museum of Craft and Design's MCD@Home program partnered with local artists to create a collection of fine-art projects to complete at home.
64. Enjoy soothing sounds when you learn how to make your own rain stick .
65. Browse beautiful themed printable crafts for kids .
66. Get crafty with these printer-friendly flower magnets .
67. Catch them all with these free Pokemon-inspired fidgets and bookmarks .
68. These adorable printable paper dolls are ready to be dressed in their printable outfits.
69. Learn to design your own paper dolls and doll clothes .
Printable Games for Kids
70. Make your own Blue's Clues guessing game .
71. Playing bingo is as easy as printing one of these game boards .
72. Design your own Snakes and Ladders game.
73. Toddlers love this Feed the Monkey board game.
74. Teach numbers with this Buggy Board Game .
75. Check out these cute printable games including Pin the Tail on the Donkey and Dots.
76. Try this flag matching game that will help your kids learn about countries across the world.
77. Learn early reading skills with this printable digraphs board game .
78. This rainbow unicorns game is great for practicing colors.
79. Arrange Magna-Tiles into an airplane, a duck, and other fun shapes with these magnetic-tile printables .
80. Take this printable License Plate Bingo game on your next road trip to battle boredom.
RELATED: 64 Easy Science Experiments for Kids to Do at Home
Kids can print out instructions to learn how to make their own slime. Photo courtesy of Liberty Science Center's Slime Time
Math and Science Printables for Kids
81. Learn the science of slime with Liberty Science Center's Slime Time .
82. Learn how to map and plan a vegetable garden with the New York Botanical Garden .
83. Brush up on math skills with Dad's Worksheets .
84. Learn all about monarch butterflies in this fully illustrated collection of butterfly activities .
85. School your kid on our planet's diverse habitats and ecosystems with the World Wildlife Fund's Biodiversity Toolkit .
86. Create a pollination station with Ranger Rick.
87. NASA's Climate Kids teaches children how to make a solar oven, a terrarium, a bird feeder, and more earth-friendly crafts!
88. Explore hundreds of free learning pages from Enchanted Learning .
89. Learn about 3D shapes with these printable activities for early learners.
90. Teach patterns using LEGO bricks with these printable LEGO pattern cards .
91. Kids can try their hand at Sudoku with these easy Sudoku puzzles .
92. This counting board game will help kids learn the numbers 6 through 10.
Printable Word Games for Kids
93. These themed word searches are sure to please.
94. Look through tons of printable crosswords for kids .
95. Browse a variety of printable word games including word scrambles.
96. Get searching with these word searches for each grade level .
97. These crossword puzzles for kids are themed around subjects like the solar system, verbs, and Minecraft.
98. Tree Valley Academy has adorable printable word searches with different themes.
99. Find a themed word scramble to match your interests.
100. Pick the perfect word puzzle printable for your picky kid.
This post was originally published in 2020 and has been updated with additional reporting by Amelia Eigerman


( Courtesy of Leslie Sherman and Conrad Useldinger; Realtor.com )
How Parents Are Helping Their Adult Children Buy Homes Today: ‘We Own 25%, Mom and Dad Own 75%’
Leslie Sherman was resigned to being a renter the rest of her life.
The 33-year-old couples therapist and her husband, Conrad Useldinger , 30, a dance academy director, live in San Jose, CA . Nestled in the heart of Silicon Valley, where Apple, Google, and Nvidia are based, it is the most expensive housing market in America, according to a Realtor.com analysis . There, the median home list price hovers around $1.46 million—and homebuyers need to earn at least $361,000.
“We didn’t have plans to buy a place because it was not going to be financially feasible for us,” she says. “So we were going to rent indefinitely.”
But, that’s when Mom and Dad stepped in.
“My husband and I started investing in Silicon Valley real estate in the early 1980s,” says Kathy Fitzgerald Sherman , a retired lawyer. “We benefited greatly from the explosion in real estate values, which also made it impossible for our kids to purchase real estate on their own. Our decision to help them was a ‘pay it forward’ kind of action.”
In February, Kathy and her husband, Michael Sherman , helped Leslie and her husband close on an $850,000 condo. All four of their names are on the deed: Leslie and her spouse own 25% of the property, while Kathy and Michael own 75%.
Here’s how this unusual deal came together, along with the pros, cons, and other considerations that homebuyers (and their parents) might want to know.

(Leslie Sherman)
Why parents are pitching in to help their kids buy a home
While turning to Mom and Dad for help buying a home is an age-old practice, today’s high-priced housing market has made it a growing necessity.
Although San Jose’s million-plus list prices are at the high end of the spectrum, they aren’t all that unusual. The national median list price currently hovers at $424,900 , according to the latest Realtor.com data. Mortgage rates are high, too, passing the dreaded 7% threshold in April.
In a new study by Intuit and Credit Karma, 38% of Gen Z homeowners say they received financial assistance from their parents to buy a home. It also helps that boomers tend to be a wealthy generation, whereas their kids are often saddled with massive student debt, making it hard to enter the housing market.
“Even with zero-down payment programs, high home prices and interest rates can put buying a home out of reach without help,” says real estate agent and attorney Bruce Ailion , of Re/Max Town and Country in Alpharetta, GA.
The Shermans helped both of their kids purchase their first home, and see the money they’d invest as an advance on their inheritance. But in both cases, they did so carefully.

(Leslie Sherman and Conrad Useldinger)
The two generations sat down to craft a “shared equity” deal. (You’ll sometimes hear this called, humorously enough, a “rich uncle” arrangement.) Based on their income, they figured out how much the young couple could afford to pay monthly. Next, they worked backward to determine what size mortgage the young couple could handle. The parents stood ready to pay the rest.
Once they had an estimate of what price house they could afford, they were off to the house-hunting races, which they did as a team.
“Since we’d had experience buying several properties in the area, we went with them, pointing out plusses and minuses,” says Kathy. She admits that she didn’t give them carte blanche to choose just any place.
“But we were sensitive to their feelings and wanted them to love what they purchased,” she explains.
House hunting as a family
At first, they checked out houses in the Los Gatos Mountains, but the maintenance costs seemed too much.
“They were in our budget, but I absolutely hated them,” admits Leslie. “They all required some amount of work right out the gate, and I did not want my future to be filled with endless home improvement projects. That is just not the life I had envisioned for myself.”
Their attention then turned to condos , and they found one they really liked—and that her parents liked, too. It was a two-bedroom, two-bath with a spacious kitchen, office space in the primary bedroom, and in-unit laundry (at the top of Leslie’s wish list). Also part of the package were killer amenities, including a pool, hot tub, playground, and beautiful gym.
“We decided to make an offer the very next day, before others came in,” says Leslie.

(Realtor.com)

The deal this couple could offer was strong: With her parents’ backing, Leslie and her husband could offer all cash if needed, with no contingencies . They snagged the property for $850,000 ($5,000 below asking price).
At closing, her parents ponied up $650,000 in cash, leaving Leslie and Conrad with a $200,000 mortgage—$1,297 a month at a 6.75% interest rate. Leslie and Conrad also pay property taxes, homeowners association fees (currently $465 a month), and maintenance.
“We pay for all repairs,” notes Leslie. “But if there are ever any major upgrades, we could split the cost. Under their arrangement, it would be in the same 75% versus 25% proportion.”
Get it in writing
All of these details were written up in a rock-solid legal agreement, which is exactly how you want to do this to protect all involved—no casual “pinky swear” kind of deals allowed. Such arrangements need guardrails.
“The best way to make sure bad feelings don’t arise is to have a contract,” explains Kathy. “If there ever is a disagreement about how to handle something, we can just look in the agreement.”
There are infinite ways to structure investing in a home for a child, Ailion notes. For instance, when the property sells, the parents might get their money back plus interest. This interest could be similar to what their funds would have earned if they had been sitting in the bank. Or, if the child is making the interest payments and maintaining the home, they might want to negotiate a bigger cut of any gains in the property’s value.
For most families executing this kind of deal, a lawyer will be necessary. Because Kathy is a retired lawyer, she jumped in, buying a boilerplate equity-sharing agreement and modifying it to suit their needs.
“In theory, anyone can do this,” she notes. “Since I am an attorney, I was particularly comfortable doing that.”
But what about that old saying “Never do business with friends or relatives”—does it apply here? Can it all backfire? Not for the Sherman clan so far.
“We haven’t had any issues,” says Leslie. “My parents are not controlling, but that’s not the case with everyone’s parents. To avoid problems, you would definitely want the contract to spell out how decisions about changes to the home will be made. That’s especially important if there are disagreements.”
And the upside of doing this kind of deal right is tremendous.
“I know that without this arrangement, we wouldn’t be able to get into the housing market in this area,” says Leslie, “so we are really very lucky.”

Janet Siroto is a journalist, editor, and trend tracker. Her work has appeared in Cosmopolitan, Good Housekeeping, and other publications.
- Related Articles
Share this Article
Connect with an agent, a realtor.com coordinator will connect you with a local agent in minutes.
A local real estate agent can answer questions, give guidance, and schedule home tours.
By proceeding, you consent to receive calls and texts at the number you provided, including marketing by autodialer and prerecorded and artificial voice, and email, from Realtor.com and others Persons who may contact you include real estate professionals such as agents and brokers, mortgage professionals such as lenders and mortgage brokers, realtor.com and its affiliates, insurers or their agents, and those who may be assisting any of the foregoing. about your inquiry and other home-related matters, but not as a condition of any purchase. More You also agree to our Terms of Use, and to our Privacy Policy regarding the information relating to you. Msg/data rates may apply. This consent applies even if you are on a corporate, state or national Do Not Call list.

A Realtor.com coordinator will call you shortly
What’s next.
- A coordinator will ask a few questions about your home buying or selling needs.
- You’ll be introduced to an agent from our real estate professional network.
To connect right away, call (855) 650-5492

Rare photos of Sting's six ultra-creative children from his two marriages
Sting has two children with ex-wife frances tomelty and four kids with current spouse trudie styler.
Did you know that singer Sting is a dad of six children?
The Roxanne star shares four children with his film producer wife Trudie Styler and two kids from his first marriage to actress Frances Tomelty.
Sting – real name Gordon Sumner - married longtime girlfriend Trudie in 1992, in the local church near his beautiful Wiltshire house. Their children are: Mickey, 40, Jake, 38, Eliot, 33, and Giacomo, 28. His children with his ex-wife Frances are Fuchsia, 42, and Joe, 47.
Sting admitted in 2020 that he never intended to become a father, telling People : "I became a dad by accident six times — that's how smart I am," he said. "Yet they were the happiest accidents of my life because they're remarkable human beings."
He added: "I can't really take much credit for that, but they are, and they, too, have produced seven grandchildren at this point, who are also wonderful. So all of this has happened by accident. I didn't intend to be the patriarch of a tribe, but I am."
You may also like
Of his parenting style, he revealed: "My kids are fiercely independent."
"They're not sitting there waiting for a handout at all, and I wouldn't want to rob them of that adventure in life: to make your own living. It's a wonderful and difficult thing to do. So I haven't promised them anything. I'll obviously help them if they're in trouble, but they're not waiting for a handout. They're too independent."
Read on to learn about Sting's six children:

Joseph Sumner
Just like his famous father, Joe has a passion for music. Born in 1976, he is a singer-songwriter and a bassist for the rock band Fiction Plane. He also co-founded the video app Vyclone.
In his home life, Joe is married to Kate Finnerty and the couple have three daughters and one son.

Fuschia Kate Sumner
Fuschia has taken after her mother Frances and gone into acting and directing.
Born on 17 April 1982 in London, Fuschia is known for the movies Everything I Ever Wanted to Tell My Daughter About Men, Saving Mr. Banks and Being Michael Madsen.

Mickey Sumner
Born in 1984, Brigitte Michael Sumner was Sting and Trudie's first child together.
She started her career as a model but soon moved over to acting, starring in Frances Ha and the series Snowpiercer.
Mickey is married to entrepreneur Chris Kantrowitz and the pair share one child, a son named Akira Rogue Kantrowitz.

Jake Sumner
Jake is Sting and Trudie's second child, born in 1985, and like the rest of his family, is also involved in the arts.
Jake is a filmmaker, known for his documentaries such as I Was There When House Took Over The World . He's the creative director of production company AllDayEveryDay and has created videos for Bruno Mars, Google and Nike.

Eliot Sumner
Eliot has also got the creative gene like their mum and dad.
Born in 1990 in Pisa, Italy, Eliot was raised in Wiltshire with their five siblings, and from a young age, music was life for Eliot.
"I got my first guitar for my 4th or 5th birthday," Eliot told The Cut .
They are now known as a DJ under the alias Vaal, playing in dance clubs across Europe, as well as an actor with roles in Me Without You, Stardust , the 2020 James Bond film No Time to Die, Showtime's Ripley , and Infinite Storm .

Giacomo Sumner
The only one of Sting's children not to go into a career in entertainment, Giacomo is believed to have joined the police force in London.
"Becoming a police officer has been my dream since I was 13," he once posted on social media.
Giacomo previously studied criminal justice at California Lutheran University.
- Celebrity Dads
More Parenting

Travis Scott is a doting dad with daughter Stormi as they enjoy adorable date together

Gallery Ben Affleck and ex Jennifer Garner's three children Violet, Fin, and Samuel's cutest public appearances in photos
Angelina Jolie's daughter Vivienne is latest to distance from Brad Pitt as she drops dad's last name

Gwen Stefani and Gavin Rossdale come together to celebrate son Kingston's milestone 18th birthday — see sweet photos

Joanna Gaines reveals son Duke's bittersweet milestone in rare family video: 'Makes mama cry'

Chris Hemsworth's twin sons look just like their dad in emotional rare appearance

Jessica Biel and Justin Timberlake's son 'looks different' as she marvels over how much Silas, 9, has grown

Ant McPartlin makes rare family comment on first outing since baby Wilder's birth
Daniel radcliffe opens up about emotional and 'crazy' first year with baby son with erin darke, michael j. fox's wife tracy pollan celebrates with lookalike daughters schuyler and esmé in rare family snap, gallery tom cruise's rarest photos with his kids suri, bella, and connor cruise: meet his kids with exes nicole kidman and katie holmes, lionel richie hints at sofia richie's baby daughter's arrival: 'the baby is a diva'.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
This wholesome banger from a group of Irish kids is the spark you need

Anastasia Tsioulcas
Music fans, have we got a new, totally infectious bop for you: "The Spark," a song created by a group of kids in Cork, Ireland. "I searched for my spark and I found it," they exuberantly sing over a vibrant techno beat. They let their rhymes fly, too: "Making bangers at a young age," one girl raps, "My pen setting fire to the page."
As one listener enthused on X: "They had no business putting out something this deadly."

Interview: Billie Eilish finally remembers who she is
"The Spark" was created by Rhyme Island, a youth rap initiative in Cork. The kids worked with a local producer named GMCBeats and The Kabin Studio, a music and creativity-focused nonprofit in the Knocknaheeny suburb of Cork.
They made the song in advance of Cruinniú na nÓg, an annual "national free day of creativity for young people" in Ireland. It features over 1,000 free events for kids and teenagers across Ireland, sponsored by the Irish government and supported by the Irish public broadcaster RTE. This year's Cruinniú na nÓg activities take place on Saturday, June 15.
Rhyme Island's video for "The Spark" was released by Creative Ireland , the Irish government initiative behind Cruinniú na nÓg. The video is just as cheery and wholesome as the song: The band of kids bounce down the aisle of a school bus and zip along a Cork sidewalk, decked out in colorful bucket hats and shades.
While "The Spark" does not yet seem to be available on digital platforms, Rhyme Island has a playlist of their other work on SoundCloud .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We've outlined a seven-step method that will scaffold your students through each phase of the creative process from idea generation through to final edits. 7. Create inspiring and original prompts. Use the following formats to generate prompts that get students inspired: personal memories ("Write about a person who taught you an important ...
Step 2: Setting and genre. The next step in your child's creative writing process is to choose where it takes place. They should also decide the genre of their story, as some settings won't work for some specific genres (for example, a sunny beach wouldn't pair well with a moody mystery). This story's setting could be a real location ...
Whether you're teaching creative writing or learning it, understanding its value is the first step towards mastering the art. The 3 Roles of a Creative Writing Teacher. Amongst the many facets of a creative writing teacher's role, ... Encourage children to create a big scribble on a scrap piece of paper and then look for an image in it ...
Teaching Creative Writing. Creative writing plays an important role in a child's literacy development. This article makes suggestions for the instruction and evaluation of children's stories. Most children enter school with a natural interest in writing, an inherent need to express themselves in words (Graves, 1983).
6 Ways to Teach Writing reatively Teach your students the fun aspects of writing. Students of all ages write short stories and papers, from younger elementary-school writers through college-age students.
Download Article. 1. Allow students to pick their topic. The first step in guiding students through the writing process is to allow them to pick their topic. Picking their topic will allow your students to own their writing and to use their own creative energy to craft an engaging story.
Students should be encouraged to learn words they frequently misspell, as well as words they wish to include in their writing. Teachers also should help students acquire the skills they need to generate and check plausible spellings for words. 3. Teach students to construct sentences for fluency , meaning and style.
Story language. Ask your child to think of some fabulous words to use in their story writing. They might be long words or simple ones, or they might be great descriptive words or words that help create pace and tension. Encourage them to jot these down and refer to the list as they write their story.
Hopefully, they will tell you they want to know what they look like in the mirror right now. Then you can have students think of 5 possible situations for what happened and how they look. 3. Do a 5 Minute "Free Write Brain Dump". During the next step of a creative writing lesson plan, encourage students to do a brain dump in their writing ...
4. Writing practice for preschoolers and kindergarten kids. If your child is new to writing, start with beginner skills like pencil grip practice and tracing the letters of the alphabet. Show your child how to hold a pencil with three fingers, in a tripod grip. This will give them more control when they write.
Writing. Mary Amato's Tips for Parents: How to Encourage Creative Writing. Create a time and place for writing. Children will want to write if you make it a fun activity to do together. "Let's write a story!". Accept your child's ideas. Your child may create a character/story you don't like.
A parent asks, "How do we get kids to write? How do you teach creative writing in primary school ages? Kids are always running from writing." In this Ask Coz...
4. Help your child keep a dream journal. A dream journal is a great way to help your child record dreams and write them down before they forget. They can decorate and personalize their own dream journal and fill it with words and pictures. 5. Provide other tools for creative expression. Sometimes writing isn't the easiest option for your child ...
Do you struggle with getting your kids to write? This video is a step by step guideline on how to write creatively. 🌞Facebook https://www.facebook.com/group...
Teachers and parents can also show children the "invented spelling" strategy of saying a word slowly, stretching out the sounds, and printing a letter (or letter combinations, such as "th ...
Give the characters personalities, traits, and quirks that will make them stand out. Make a plot: Craft an exciting and engaging storyline that includes a beginning, a middle, and an end. Use the question and topic as a starting point. Decide how your protagonist will overcome their conflict, and develop the story from there.
This course is designed for teaching children creative writing in a heart-centred way. The principles of the classes can be applied to large groups, small groups or individual children. They contain age appropriate exercises - covering topics such as character, dialogue, journaling and nature writing. They also offer inspiring quotes and ...
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #6: Use Clear and Structured Expectations. While showing students excellent prose or perfect poetry should help inspire students, your writers will still need some hard parameters to follow. Academic writing is often easier for students than creative writing.
Create Story Prompts. A fun way to improve kids' creative writing skills is to have them write short stories. Cut out pictures from a magazine with different characters or locations, or write down different words. Place these in a container or glue them to cards to use as writing prompts for creating a unique story.
Use games. There are numerous games and puzzles that help children with spelling while increasing their vocabulary. Some of these may include crossword puzzles, word games, anagrams, and cryptograms designed especially for children. Flash cards are fun to use too, and they're easy to make at home. Turn your child's writing into books.
Writing offers children a unique outlet to explore their creativity and imagination. By learning to write stories, poems, or even journal entries, kids can develop their creative talents and discover new ways of seeing the world. The process of writing involves complex thinking skills such as planning, organizing, and problem-solving.
Step 2: Study the Structure of a Story. Now that students have a good library of their own personal stories pulled into short-term memory, shift your focus to a more formal study of what a story looks like. Use a diagram to show students a typical story arc like the one below.
Creative Composing: A Lesson Plan for Students, Teachers, and Teacher-Writers. Peitho Volume 26 Issue 1, Fall 2023. Author(s): Meg Scott-Copses Meg Scott-Copses specializes in creative writing, composition, and an embodied pedagogy that fuses the two. She earned her Ph.D. in poetry from Florida State with a dissertation on service learning in at-risk environments such as prisons and youth ...
Teaching and Supporting Students on the Autism Spectrum Creative writing tasks are often a trigger for heightened anxiety for those students on the autism spectrum. An abundant amount of skills are required, e g. social imagination, language skills, decision making, auditory and visual memory, the organisation of thoughts ...
Draw a picture of your favorite beach memory and write a few sentences about it. Camping Writing Prompts: Tell a tale of camping under the stars. Share a spooky or adventurous story told around a summer campfire. Tell a story about a camping trip with your family or friends. Describe your dream camping spot.
Encourage your kids to. write. stories, poems, or journals. Provide them with colorful notebooks and writing prompts to ignite their imagination. Reading together and exploring different literary ...
NASA's Climate Kids teaches children how to make a solar oven, a terrarium, a bird feeder, and more earth-friendly crafts! 88. Explore hundreds of free learning pages from Enchanted Learning .
How Parents Are Helping Their Adult Children Buy Homes Today: 'We Own 25%, Mom and Dad Own 75%'. Leslie Sherman was resigned to being a renter the rest of her life. The 33-year-old couples ...
The Roxanne star shares four children with his film producer wife Trudie Styler and two kids from his first marriage to actress Frances Tomelty. Sting - real name Gordon Sumner - married ...
Creative Ireland YouTube. Music fans, have we got a new, totally infectious bop for you: "The Spark," a song created by a group of kids in Cork, Ireland. "I searched for my spark and I found it ...