Solving Problems Involving Distance, Rate, and Time
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Math Tutorials
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
In math, distance, rate, and time are three important concepts you can use to solve many problems if you know the formula. Distance is the length of space traveled by a moving object or the length measured between two points. It is usually denoted by d in math problems .
The rate is the speed at which an object or person travels. It is usually denoted by r in equations . Time is the measured or measurable period during which an action, process, or condition exists or continues. In distance, rate, and time problems, time is measured as the fraction in which a particular distance is traveled. Time is usually denoted by t in equations.

Solving for Distance, Rate, or Time
When you are solving problems for distance, rate, and time, you will find it helpful to use diagrams or charts to organize the information and help you solve the problem. You will also apply the formula that solves distance, rate, and time, which is distance = rate x tim e. It is abbreviated as:
There are many examples where you might use this formula in real life. For example, if you know the time and rate a person is traveling on a train, you can quickly calculate how far he traveled. And if you know the time and distance a passenger traveled on a plane, you could quickly figure the distance she traveled simply by reconfiguring the formula.
Distance, Rate, and Time Example
You'll usually encounter a distance, rate, and time question as a word problem in mathematics. Once you read the problem, simply plug the numbers into the formula.
For example, suppose a train leaves Deb's house and travels at 50 mph. Two hours later, another train leaves from Deb's house on the track beside or parallel to the first train but it travels at 100 mph. How far away from Deb's house will the faster train pass the other train?
To solve the problem, remember that d represents the distance in miles from Deb's house and t represents the time that the slower train has been traveling. You may wish to draw a diagram to show what is happening. Organize the information you have in a chart format if you haven't solved these types of problems before. Remember the formula:
distance = rate x time
When identifying the parts of the word problem, distance is typically given in units of miles, meters, kilometers, or inches. Time is in units of seconds, minutes, hours, or years. Rate is distance per time, so its units could be mph, meters per second, or inches per year.
Now you can solve the system of equations:
50t = 100(t - 2) (Multiply both values inside the parentheses by 100.) 50t = 100t - 200 200 = 50t (Divide 200 by 50 to solve for t.) t = 4
Substitute t = 4 into train No. 1
d = 50t = 50(4) = 200
Now you can write your statement. "The faster train will pass the slower train 200 miles from Deb's house."
Sample Problems
Try solving similar problems. Remember to use the formula that supports what you're looking for—distance, rate, or time.
d = rt (multiply) r = d/t (divide) t = d/r (divide)
Practice Question 1
A train left Chicago and traveled toward Dallas. Five hours later another train left for Dallas traveling at 40 mph with a goal of catching up with the first train bound for Dallas. The second train finally caught up with the first train after traveling for three hours. How fast was the train that left first going?
Remember to use a diagram to arrange your information. Then write two equations to solve your problem. Start with the second train, since you know the time and rate it traveled:
Second train t x r = d 3 x 40 = 120 miles First train t x r = d 8 hours x r = 120 miles Divide each side by 8 hours to solve for r. 8 hours/8 hours x r = 120 miles/8 hours r = 15 mph
Practice Question 2
One train left the station and traveled toward its destination at 65 mph. Later, another train left the station traveling in the opposite direction of the first train at 75 mph. After the first train had traveled for 14 hours, it was 1,960 miles apart from the second train. How long did the second train travel? First, consider what you know:
First train r = 65 mph, t = 14 hours, d = 65 x 14 miles Second train r = 75 mph, t = x hours, d = 75x miles
Then use the d = rt formula as follows:
d (of train 1) + d (of train 2) = 1,960 miles 75x + 910 = 1,960 75x = 1,050 x = 14 hours (the time the second train traveled)
- Distance, Rate, and Time Worksheets
- The Distance Between Degrees of Latitude and Longitude
- Popular Math Terms and Definitions
- Converting Cubic Meters to Liters
- What Is Velocity in Physics?
- Realistic Math Problems Help 6th-graders Solve Real-Life Questions
- 4th-Grade Math Word Problems
- Circumference of a Circle
- What Speed Actually Means in Physics
- Understanding the Distance Formula
- Help Kids Calculate the Area and Circumference of Circles
- How to Calculate Commissions Using Percents
- How to Derive the Formula for Combinations
- Rate of Change Worksheet with Solutions
- How to Determine the Geometry of a Circle
- Dimensional Analysis: Know Your Units
DISTANCE = RATE X TIME
Explore the formula d = rt by starting with unit conversion problems. Mathletes will solve for distance, rate and time by paying attention to the units given in the problem and using the appropriate equivalent version of the formula: d = rt , r = d / t or t = d / r .
Download Mathlete handout.
Download coach version with solutions.
Download The Problems PowerPoint.
- Pre-algebra lessons
- Pre-algebra word problems
- Algebra lessons
- Algebra word problems
- Algebra proofs
- Advanced algebra
- Geometry lessons
- Geometry word problems
- Geometry proofs
- Trigonometry lessons
- Consumer math
- Baseball math
- Math for nurses
- Statistics made easy
- High school physics
- Basic mathematics store
- SAT Math Prep
- Math skills by grade level
- Ask an expert
- Other websites
- K-12 worksheets
- Worksheets generator
- Algebra worksheets
- Geometry worksheets
- Free math problem solver
- Pre-algebra calculators
- Algebra Calculators
- Geometry Calculators
- Math puzzles
- Math tricks
- Member login
Distance rate time problems
Distance rate time problems involve object moving at a constant rate and this is called uniform motion. The formula d = r × t is the formula to use to solve problems related to distance, rate, and time.
Examples showing how to solve distance rate time problems
It may be obvious that for this type of problem, the distance is the same since you left the same place (your house) and are going to the same location.
Suppose that you went to no other places, the distance then to go back to your house is again the same.
Therefore, when solving distance rate time problems involving opposite direction travel, you can add the distances to get the total distance.
Study also the distance rate time problem in the figure below carefully
Mixture word problems
Recent Articles
How to divide any number by 5 in 2 seconds.
Feb 28, 24 11:07 AM
Math Trick to Square Numbers from 50 to 59
Feb 23, 24 04:46 AM
Sum of Consecutive Odd Numbers
Feb 22, 24 10:07 AM
100 Tough Algebra Word Problems. If you can solve these problems with no help, you must be a genius!

Recommended
About me :: Privacy policy :: Disclaimer :: Donate Careers in mathematics
Copyright © 2008-2021. Basic-mathematics.com. All right reserved
Module 9: Multi-Step Linear Equations
Using the distance, rate, and time formula, learning outcomes.
- Use the problem-solving method to solve problems using the distance, rate, and time formula
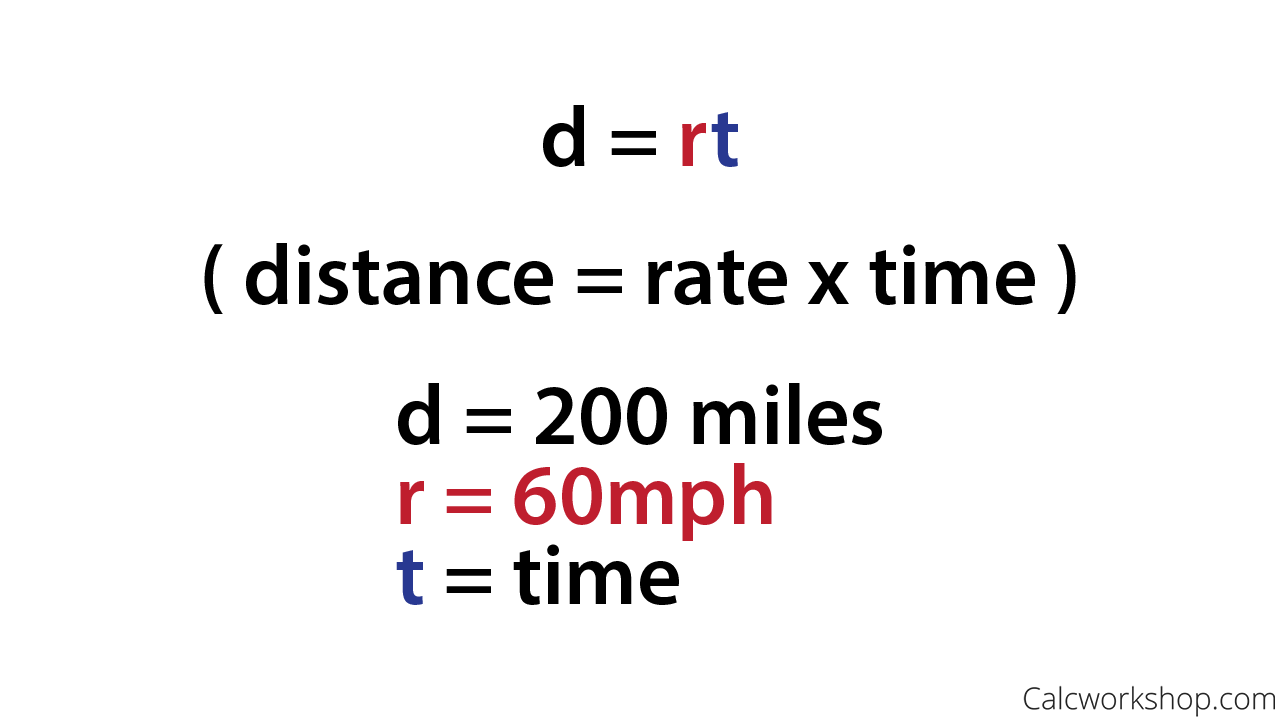
One formula you’ll use often in algebra and in everyday life is the formula for distance traveled by an object moving at a constant speed. The basic idea is probably already familiar to you. Do you know what distance you traveled if you drove at a steady rate of [latex]60[/latex] miles per hour for [latex]2[/latex] hours? (This might happen if you use your car’s cruise control while driving on the Interstate.) If you said [latex]120[/latex] miles, you already know how to use this formula!
The math to calculate the distance might look like this:
[latex]\begin{array}{}\\ \text{distance}=\left(\Large\frac{60\text{ miles}}{1\text{ hour}}\normalsize\right)\left(2\text{ hours}\right)\hfill \\ \text{distance}=120\text{ miles}\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
In general, the formula relating distance, rate, and time is
[latex]\text{distance}\text{=}\text{rate}\cdot \text{time}[/latex]
Distance, Rate, and Time
For an object moving at a uniform (constant) rate, the distance traveled, the elapsed time, and the rate are related by the formula
[latex]d=rt[/latex]
where [latex]d=[/latex] distance, [latex]r=[/latex] rate, and [latex]t=[/latex] time.
Notice that the units we used above for the rate were miles per hour, which we can write as a ratio [latex]\Large\frac{miles}{hour}[/latex]. Then when we multiplied by the time, in hours, the common units “hour” divided out. The answer was in miles.
Jamal rides his bike at a uniform rate of [latex]12[/latex] miles per hour for [latex]3\Large\frac{1}{2}[/latex] hours. How much distance has he traveled?
| Step 1. the problem. You may want to create a mini-chart to summarize the | [latex]d=?[/latex] [latex]r=12\text{mph}[/latex] [latex]t=3 \Large\frac{1}{2}\normalsize\text{hours}[/latex] |
| Step 2. what you are looking for. | distance traveled |
| Step 3. Choose a variable to represent it. | let = distance |
| Step 4. Write the appropriate formula for the situation. Substitute in the given information. | [latex]d=rt[/latex] [latex]d=12\cdot 3\Large\frac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| Step 5. the equation. | [latex]d=42\text{ miles}[/latex] |
| Step 6. Does 42 miles make sense?
| |
| Step 7. the question with a complete sentence. | Jamal rode 42 miles. |
In the following video we provide another example of how to solve for distance given rate and time.
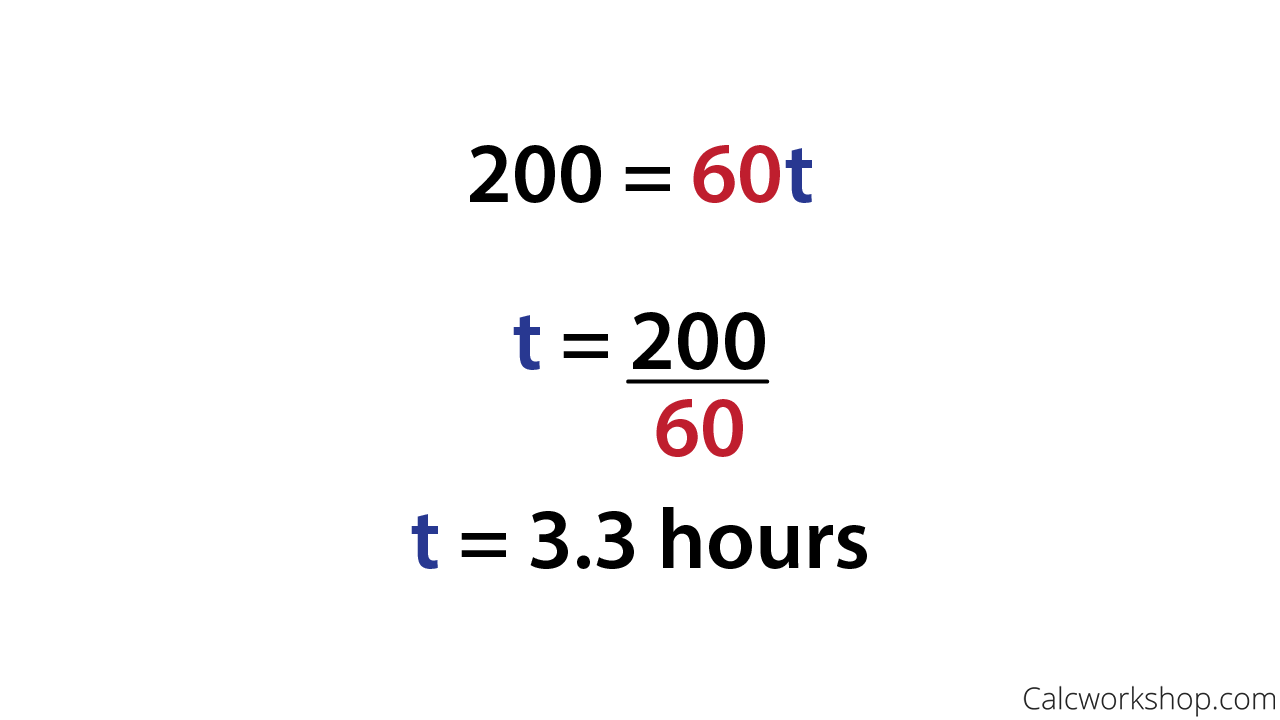
Rey is planning to drive from his house in San Diego to visit his grandmother in Sacramento, a distance of [latex]520[/latex] miles. If he can drive at a steady rate of [latex]65[/latex] miles per hour, how many hours will the trip take?
Show Solution
| Step 1. the problem. Summarize the information in the problem. | [latex]d=520[/latex] miles [latex]r=65[/latex] mph [latex]t=?[/latex] |
| Step 2. what you are looking for. | how many hours (time) |
| Step 3. Choose a variable to represent it. | let [latex]t[/latex] = time |
| Step 4. Write the appropriate formula. Substitute in the given information. | [latex]d=rt[/latex] [latex]520=65t[/latex] |
| Step 5. the equation. | [latex]t=8[/latex] |
| Step 6. Substitute the numbers into the formula and make sure [latex]d=rt[/latex] [latex]520\stackrel{?}{=}65\cdot 8[/latex] [latex]520=520\quad\checkmark [/latex] | |
| Step 7. the question with a complete sentence. We know the units of time will be hours because | Rey’s trip will take [latex]8[/latex] hours. |
In the following video we show another example of how to find rate given distance and time.
- Question ID 145550, 145553,145619,145620. Authored by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Ex: Find the Rate Given Distance and Time. Authored by : James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com). Located at : https://youtu.be/3rYh32ErDaE . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Example: Solve a Problem using Distance = Rate x Time. Authored by : James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com). Located at : https://youtu.be/lMO1L_CvH4Y . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by : OpenStax. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]

Calcworkshop
How to Solve d=rt Word Problems? 5 Amazing Examples!
// Last Updated: January 20, 2020 - Watch Video //
An object is said to be in uniform motion when it moves without changing its speed.

Jenn, Founder Calcworkshop ® , 15+ Years Experience (Licensed & Certified Teacher)
All this means is that we can find the distance an object travels as long as we know the object is moving at a constant (fixed) speed or pace or at an average rate or speed.
In fact, whenever we encounter this type of scenario we can utilize a very powerful formula:
Distance-Rate-Time Example
- d represents distance
- r is an object’s rate (speed)
- t is the time the object takes to travel
The type of questions we will be investigating in this lesson involve:
Solving Distance Rate Time Example
And all three of these questions can be answered using the Distance formula listed above.
Yes, it is simple, but there is a warning.
Units of measure matter!
As Purple Math so accurately points out, we must always check our units to ensure they agree with one another.
Many questions will try to trick you by using miss-matched units, so always check and if necessary, convert to the correct unit before simplifying.
Together we will look at five examples in detail for how to solve Distance-Rate-Time word problems.
Distance Rate Time (How-To) – Video
Get access to all the courses and over 450 HD videos with your subscription
Monthly and Yearly Plans Available
Get My Subscription Now
Still wondering if CalcWorkshop is right for you? Take a Tour and find out how a membership can take the struggle out of learning math.


Rate, Time, Distance Problems

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

- HW Guidelines
- Study Skills Quiz
- Find Local Tutors
- Demo MathHelp.com
- Join MathHelp.com
Select a Course Below
- ACCUPLACER Math
- Math Placement Test
- PRAXIS Math
- + more tests
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- Pre-Algebra
- College Pre-Algebra
- Introductory Algebra
- Intermediate Algebra
- College Algebra
"Distance" Word Problems
Explanation More Examples
What is a "distance" word problem?
"Distance" word problems, often also called "uniform rate" problems, involve something travelling at some fixed and steady ("uniform") pace ("rate", "velocity", or "speed"), or else you are told to regard to object as moving at some average speed.
Content Continues Below

MathHelp.com
Distance Word Problems
Whenever you read a problem that involves "how fast", "how far", or "for how long", you should think of the distance equation, d = rt , where d stands for distance, r stands for the (constant or average) rate of speed, and t stands for time.
Make sure that the units for time and distance agree with the units for the rate. For instance, if they give you a rate of feet per second, then your time must be in seconds and your distance must be in feet. Sometimes they try to trick you by using mis-matched units, and you have to catch this and convert to the correct units.
In case you're wondering, this type of exercise requires that the rate be fixed and steady (that is, unchanging) for the d = rt formula to work. The only way you can deal with a speed that might be changing over time is to take the average speed over the time or distance in question. Working directly with changing speeds will be something you'll encounter in calculus, as it requires calculus-based (or more advanced) methods.
What is the difference between a fixed speed and an average speed?
A fixed-speed exercise is one in which the car, say, is always going exactly sixty miles an hour; in three hours, the car, on cruise-control, will have gone 180 miles. An average-speed exercise is one in which the car, say, averaged forty miles an hour, but this average includes the different speeds related to stop lights, highways, and back roads; in three hours the car went 120 miles, though the car's speed was not constant. Most of the exercises you'll see will be fixed-speed exercises, but obviously they're not very "real world". It's a simplification they do in order to make the situation feasible using only algebraic methods.
What is an example of a "distance" word problem?
- A 555 -mile, 5 -hour plane trip was flown at two speeds. For the first part of the trip, the average speed was 105 mph. Then the tailwind picked up, and the remainder of the trip was flown at an average speed of 115 mph. For how long did the plane fly at each speed?
There is a method for setting up and solving these exercises that I first encountered well after I'd actually been doing them while taking a class as an undergraduate. But, as soon as I was introduced to the method, I switched over, because it is *so* way easier.
First I set up a grid, with the columns being labelled with the variables from the "distance" formula, and the rows being labelled with the "parts" involved:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
first part |
|
|
|
second part |
|
|
|
total |
|
|
|
In the first part, the plane covered some distance. I don't know how much, so I'll need a variable to stand for this unknown value. I'll use the variable they give me in the distance equation:
They gave me the speed, or rate, for this part, so I'll add this to my table:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
first part |
| 105 |
|
second part |
|
|
|
total |
|
|
|
The plane flew for some amount of time during this first part, but I don't know how long that was. So I need a variable to stand for this unknown value; I'll use the variable from the distance equation:
For the second part, the plane travelled the rest of the total distance. I don't know the exact distance that was flown during this second part, but I do know that it was "however much was left of the 555 miles, after the first d miles were flown in the first part. "How much was left after [some amount] was taken out" is expressed with subtraction: I take the amount that has been taken care of already, and subtract this from whatever was the total. Adding this to my table, I get:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
first part |
| 105 |
|
second part | 555 − |
|
|
total |
|
|
|
They've given me the speed, or rate, for the second part, and I can use the same "How much is left?" construction for whatever was the time for this second part. So now my table looks like this:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
first part |
| 105 |
|
second part | 555 − | 115 | 5 − |
total |
|
|
|
For the "total" row, I add down (or take info from the exercise statement):
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
first part |
| 105 |
|
second part | 555 − | 115 | 5 − |
total | 555 | --- | 5 |
Advertisement
Why did I not add down in the "rate" column? Because I cannot add rates! In this exercise, adding the rates would have said that the average rate for the entire trip was 105 + 115 = 220 miles per hour. But obviously this makes no sense.
The genius of this table-based method of set-up is that I can now create equations from the rows and columns. In this exercise, there is more than one way to proceed. I'll work with the "distance" equation to create expressions for the distances covered in each part.
Multiplying across, the first row tells me that the distance covered in the first part of the flight was:
1st part distance: 105 t
Again multiplying across, the second row tells me that the distance covered in the second part of the flight was:
2nd part distance: 115(5 − t )
I can add these two partial-distance expressions, and set them equal to the known total distance:
105 t + 115(5 − t ) = 555
This is an equation in one variable, which I can solve:
105 t + 115(5 − t ) = 555 105 t + 575 − 115 t = 555 575 − 10 t = 555 20 = 10 t 2 = t
Looking back at my table, I see the I had defined t to be the time that the plane spent in the air on the first part of its journey. Looking back at the original exercise, I see that they want to know the times that the plane spent at each of the two speeds.
I now have the time for the first part of the flight; the time was two hours. The exercise said that the entire trip was five hours, so the second part must have taken three hours (found by subtracting the first-part time from the total time). They haven't asked for the partial distances, so I now have all the information I need; no further computations are necessary. My answer is:
first part: 2 hours second part: 3 hours
When I was setting up my equation, I mentioned that there was more than one way to proceed. What was the other way? I could have used the table to create an expression for each of the two partial times, added, set the result equal to the given total, and solved for the variable d . Since the distance equation is d = rt , then the expressions for the partial times would be created by solving the equation for t = . My work would have looked like this:
first part: d /105
second part: (555 − d )/115
adding: d /105 + (555 − d )/115 = 5 23 d + 11,655 − 21 d = 12,075 2 d = 420 d = 210
Looking back at my table, I would have seen that this gives me the distance covered in the first half of the flight. Looking back at the exercise, I would have seeing that they are wanting times, not distances. So I would have back-solved for the time for the first part, and then done the subtraction to find the time for the second part. My work would have had more steps, but my answer would have been the same.
There are three things that I hope you take from the above example:
- Using a table or grid to keep track of what you're doing can be incredibly helpful.
- It is important to clearly define your variables, so you know (by the end) what you'd meant (back in the beginning), so you can apply your results correctly.
- You should always check the original exercise, so you can be sure that you're answering the question that they'd actually asked.
(My value for the distance, found above, is correct, but was not what they'd asked for.) But even more important to understand is this:
NEVER TRY TO ADD RATES! Think about it: If you drive 20 mph on one street, and 40 mph on another street, does that mean you averaged 60 mph? Of course not.
Can I even average the rates? If I drove at 20 mph for one hour, and then drove 60 mph for two hours, then I would have travelled 140 miles in three hours, or a little under 47 mph. But 47 is not the average of 20 and 60 .
As you can see, the actual math involved in solving this type of exercise is often quite simple. It's the set-up that's the hard part. So what follows are some more examples, but with just the set-up displayed. Try your hand at solving, and click on the links to get pop-ups from which to check your equations and solutions.
- An executive drove from home at an average speed of 30 mph to an airport where a helicopter was waiting. The executive boarded the helicopter and flew to the corporate offices at an average speed of 60 mph. The entire distance was 150 miles; the entire trip took three hours. Find the distance from the airport to the corporate offices.
I will start in the usual way, by setting up my table:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
driving |
|
|
|
flying |
|
|
|
total |
|
|
|
I have labelled my rows so it's clear how they relate to the exercise. Now I need to fill in the rows. As before, I don't know the distance or the time for the part where the executive was driving, so I'll use variables for these unknowns, along with the given rate.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
driving |
| 30 |
|
flying |
|
|
|
total |
|
|
|
For the flying portion of the trip, I'll use the "how much is left" construction, along with the given rate, to fill in my second row. I'll also fill in the totals.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
driving |
| 30 |
| flying | 150 − | 60 | 3 − |
total | 150 | --- | 3 |
The first row gives me the equation d = 30 t . The second row is messier, giving me the equation:
150 − d = 60(3 − t )
There are various ways I can go from here; I think I'll solve this second equation for the variable d , and then set the results equal to each other.
150 − d = 60(3 − t ) 150 − 60(3 − t ) = d
Setting equal these two expressions for d , I get:
30 t = 150 − 60(3 − t )
Solve for t ; interpret the value; state the final answer.

- A car and a bus set out at 2 p.m. from the same point, headed in the same direction. The average speed of the car is 30 mph slower than twice the speed of the bus. In two hours, the car is 20 miles ahead of the bus. Find the rate of the car.
Both vehicles travelled for the same amount of time.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
car |
|
| 2 |
bus |
|
| 2 |
total |
| --- |
|
The car's values are expressed in terms of the bus' values, so I'll use variables for the bus' unknowns, and then define the car in terms of the bus' variables. This gives me:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
car | + 20 | 2 − 30 | 2 |
bus |
|
| 2 |
total | --- | --- | --- |
(As it turns out, I won't need the "total" row this time.) The car's row gives me:
d + 20 = 2(2 r − 30)
This is not terribly helpful. The second row gives me:
I'll use the second equation to simplify the first equation by substituting " 2 r " from the second equation in for the " d " in the first equation. Then I'll solve the equation for the value of " r ". Finally, I'll need to interpret this value within the context of the exercise, and then I'll state the final answer.
(Remember that the expression for the car's speed, from the table, was 2 r − 30 , so all you need to do is find the numerical value of this expression. Just evaluate; don't try to solve — again — for the value of r .)
URL: https://www.purplemath.com/modules/distance.htm
Page 1 Page 2
Standardized Test Prep
College math, homeschool math, share this page.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy / Cookies
- About Purplemath
- About the Author
- Tutoring from PM
- Advertising
- Linking to PM
- Site licencing
Visit Our Profiles

How to use the formula for distance, rate (speed), and time to solve problems
Equations with fractions — video lesson
Math Mammoth Grade 7 curriculum (pre-algebra)
Back to pre-algebra videos index
Back to the index of all videos
© 2006-2024 MathMammoth.com

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
- + ACCUPLACER Mathematics
- + ACT Mathematics
- + AFOQT Mathematics
- + ALEKS Tests
- + ASVAB Mathematics
- + ATI TEAS Math Tests
- + Common Core Math
- + DAT Math Tests
- + FSA Tests
- + FTCE Math
- + GED Mathematics
- + Georgia Milestones Assessment
- + GRE Quantitative Reasoning
- + HiSET Math Exam
- + HSPT Math
- + ISEE Mathematics
- + PARCC Tests
- + Praxis Math
- + PSAT Math Tests
- + PSSA Tests
- + SAT Math Tests
- + SBAC Tests
- + SIFT Math
- + SSAT Math Tests
- + STAAR Tests
- + TABE Tests
- + TASC Math
- + TSI Mathematics
- + ACT Math Worksheets
- + Accuplacer Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Worksheets
- + ALEKS Math Worksheets
- + ASVAB Math Worksheets
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Worksheets
- + FTCE General Math Worksheets
- + GED Math Worksheets
- + 3rd Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 4th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 5th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 8th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 9th Grade Math Worksheets
- + HiSET Math Worksheets
- + HSPT Math Worksheets
- + ISEE Middle-Level Math Worksheets
- + PERT Math Worksheets
- + Praxis Math Worksheets
- + PSAT Math Worksheets
- + SAT Math Worksheets
- + SIFT Math Worksheets
- + SSAT Middle Level Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + THEA Math Worksheets
- + TABE Math Worksheets
- + TASC Math Worksheets
- + TSI Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Course
- + ALEKS Math Course
- + ASVAB Math Course
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Course
- + CHSPE Math Course
- + FTCE General Knowledge Course
- + GED Math Course
- + HiSET Math Course
- + HSPT Math Course
- + ISEE Upper Level Math Course
- + SHSAT Math Course
- + SSAT Upper-Level Math Course
- + PERT Math Course
- + Praxis Core Math Course
- + SIFT Math Course
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Course
- + TABE Math Course
- + TASC Math Course
- + TSI Math Course
- + Number Properties Puzzles
- + Algebra Puzzles
- + Geometry Puzzles
- + Intelligent Math Puzzles
- + Ratio, Proportion & Percentages Puzzles
- + Other Math Puzzles
How to Master Motion: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Distance Formula in Real-World Problems
Understanding motion and work problems, especially those involving the formula \(d=rt\) (where \(d\) stands for distance, \(r\) for rate, and \(t\) for time), can be simplified through a step-by-step guide:

A step-by-step guide to Master Motion
Step 1: understanding the formula.
- Formula : \(d=rt\).
- Distance (\(d\)) : This represents the total distance traveled.
- Rate (\(r\)) : This is the speed or velocity at which an object moves. It’s expressed as a distance per unit of time (like miles per hour or kilometers per hour).
- Time (\(t\)) : The duration for which the object has been moving.
Step 2: Consistency in Units
- Importance of Consistent Units : It’s crucial to ensure that the units of rate and time match. For example, if the rate is in miles per hour, time should be in hours, not minutes.
- Converting Units : If units do not match, convert them. For instance, if time is given in minutes and rate in hours, convert time to hours by dividing by \(60\).
Step 3: Solving for Any Variable
- Solving for Distance (\(d\)) : If rate and time are known, multiply them to find the distance.
- Solving for Rate (\(r\)) : If distance and time are known, divide the distance by time to find the rate.
- Solving for Time (\(t\)) : If distance and rate are known, divide the distance by rate to find the time.
Step 4: Application in Problems
- Problem Analysis : Identify what is being asked, what is given, and what is unknown.
- Assign Variables : Assign the given values to their respective variables in the formula.
- Solve : Perform the necessary calculations to find the unknown value.
Step 5: Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not Converting Units : One of the most common mistakes is not converting units to ensure they are consistent.
- Ignoring Decimal Places : Be precise with calculations, especially when dealing with decimals.
- Misreading the Problem : Carefully read what is asked to correctly identify the known and unknown variables.
Step 6: Practice and Application
- Practice Problems : Regularly solve different types of motion problems to get a better grasp of the concept.
- Real-Life Application : Apply these concepts to everyday situations like calculating travel time for a trip or the speed of a vehicle.
By following these steps and practicing regularly, understanding motion and work problems, especially those related to the distance formula \(d=rt\), becomes more manageable and intuitive.
Example 1 :
A car travels at a speed of \(50\) miles per hour. How far will it travel in \(3\) hours?
\(Distance = Rate × Time = 50 \ \frac{miles}{hour} × 3 \ hours = 150 \ miles\).
Example 2 :
A cyclist covers a distance of \(90\) kilometers in \(3\) hours. What is the cyclist’s average speed?
\(Speed = Distance ÷ Time = 90 \ km ÷ 3 \ hours = 30 \frac{km}{hour}\).
by: Effortless Math Team about 7 months ago (category: Articles )
Effortless Math Team
Related to this article, more math articles.
- How to Unlock the Secrets of Success: “ISEE Upper Level Math for Beginners” Solution Guide
- How to Master Work Problems: A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide
- Calculus: Navigating the Pathways of Particles
- How to Solve Systems of Equations Word Problems? (+FREE Worksheet!)
- 4th Grade WY-TOPP Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- The Ultimate 6th Grade MCAS Math Course (+FREE Worksheets)
- 10 Most Common 7th Grade SBAC Math Questions
- How to Solve Problems Using Venn Diagrams
- Top 10 ISEE Middle-Level Math Practice Questions
- How to Learn Properties of Logarithms
What people say about "How to Master Motion: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Distance Formula in Real-World Problems - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Mastering Grade 6 Math Word Problems The Ultimate Guide to Tackling 6th Grade Math Word Problems
Mastering grade 5 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 5th grade math word problems, mastering grade 7 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 7th grade math word problems, mastering grade 2 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 2nd grade math word problems, mastering grade 8 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 8th grade math word problems, mastering grade 4 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 4th grade math word problems, mastering grade 3 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 3rd grade math word problems, algebra i study guide a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for algebra i, oar math study guide 2020 – 2021 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the oar math, act math study guide 2020 – 2021 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the act math, pre-algebra study guide 2020 – 2021 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the pre-algebra, tsi math study guide 2020 – 2021 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the tsi math, tabe 11 & 12 math study guide 2020 – 2021 for level d a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the tabe math, ftce math study guide 2020 – 2021 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the ftce general knowledge math, ged math study guide 2020 – 2021 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the ged math.
- ATI TEAS 6 Math
- ISEE Upper Level Math
- SSAT Upper-Level Math
- Praxis Core Math
- 8th Grade STAAR Math
Limited time only!
Save Over 45 %
It was $89.99 now it is $49.99
Login and use all of our services.
Effortless Math services are waiting for you. login faster!
Number Line
- solve\:for\:t,\:2t-s=p
- solve\:for\:x,\:\frac{x}{a}+b=c
- solve\:for\:y,\:ax+by=c
- solve\:for\:a,\:\frac{3}{a}+\frac{a}{b}=4b
- solve\:for\:t,\:\frac{2t}{k-3}=\frac{8}{k-2t}
solve-for-equation-calculator
solve for r, d=rt
- High School Math Solutions – Quadratic Equations Calculator, Part 1 A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial having the general form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.

Game Central
Inequalities, absolute value and rounding, related concepts.
Precalculus Examples
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Before you can use the distance, rate, and time formula, D=RT, you need to make sure that your units for the distance and time are the same units as your rate. If they aren't, you'll need to change them so you're working with the same units.
Algebra. Solve for r d=rt. d = rt d = r t. Rewrite the equation as rt = d r t = d. rt = d r t = d. Divide each term in rt = d r t = d by t t and simplify. Tap for more steps... r = d t r = d t. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just ...
D. Russell. Print the PDF: Distance, Rate, and Time Worksheet No. 2. If students are struggling, explain that to solve these problems, they will apply the formula that solves distance, rate, and time, which is distance = rate x time. It is abbreviated as: d = rt The formula can also be rearranged as: r = d/t or t = d/r
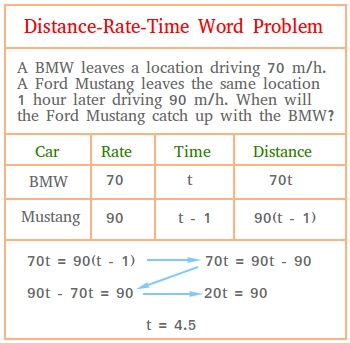
Rate is distance per time, so its units could be mph, meters per second, or inches per year. Now you can solve the system of equations: 50t = 100 (t - 2) (Multiply both values inside the parentheses by 100.) 50t = 100t - 200. 200 = 50t (Divide 200 by 50 to solve for t.) t = 4. Substitute t = 4 into train No. 1.
DISTANCE = RATE X TIME. Explore the formula d = rt by starting with unit conversion problems. Mathletes will solve for distance, rate and time by paying attention to the units given in the problem and using the appropriate equivalent version of the formula: d = rt, r = d / t or t = d / r. Download Mathlete handout. Download coach version with ...
30. t. 30 × t. The total distance you and your wife travel is 45t + 30t = 75t and this must be equal to 225. 75 × t = 225. Since 75 times 3 = 225, t = 3. Therefore, you will be 225 miles apart after 3 hours. The above are great examples of distance rate time problems. Try to do some now in your math textbook.
Distance, Rate, and Time. For an object moving at a uniform (constant) rate, the distance traveled, the elapsed time, and the rate are related by the formula. d= rt d = r t. where d = d = distance, r = r = rate, and t= t = time. Notice that the units we used above for the rate were miles per hour, which we can write as a ratio miles hour m i l ...
In fact, whenever we encounter this type of scenario we can utilize a very powerful formula: d = rt. Distance-Rate-Time Example. Where: d represents distance. r is an object's rate (speed) t is the time the object takes to travel. The type of questions we will be investigating in this lesson involve:
Distance - Rate - Time Word Problems Date_____ Period____ 1) An aircraft carrier made a trip to Guam and back. The trip there took three hours and the trip back took four hours. It averaged 6 km/h on the return trip. Find the average speed of the trip there. 2) A passenger plane made a trip to Las Vegas and back.
Solve problems from Pre Algebra to Calculus step-by-step step-by-step. d=rt , for r. en. Related Symbolab blog posts. Practice Makes Perfect. Learning math takes practice, lots of practice. Just like running, it takes practice and dedication. If you want... Enter a problem. Cooking Calculators.
In 3 hours, they are 81 miles apart. Find the rate of each cyclist. Rate-Time-Distance Problem 2. Solve this word problem using uniform motion rt = d formula. Example: A jogger started running at an average speed of 6 mph. Half an hour later, another runner started running after him starting from the same place at an average speed of 7 mph.
2nd part distance: 115 (5 − t) I can add these two partial-distance expressions, and set them equal to the known total distance: 105 t + 115 (5 − t) = 555. This is an equation in one variable, which I can solve: 105 t + 115 (5 − t) = 555. 105 t + 575 − 115 t = 555. 575 − 10 t = 555. 20 = 10 t.
How to use the formula for distance, rate (speed), and time to solve problems. This video lesson is an introduction to the formula for distance, constant speed, and time: d = vt (or d = rt if you use r as rate instead of v as velocity). First I explain an easy way to memorize this formula in the form v = d/t, comparing it to the common way to express the speed of cars, such as 55 miles per hour.
Step 1: Determine what information given in the word problem represents d, distance, r, rate, and t, time. Step 2: Plug d, r, and t into the equation d = r × t . Step 3: Solve for the unknown ...
Understanding motion and work problems, especially those involving the formula \(d=rt\) (where \(d\) stands for distance, \(r\) for rate, and \(t\) for time), can be simplified through a step-by-step guide: Effortless Math. X + eBooks ... Practice Problems: Regularly solve different types of motion problems to get a better grasp of the concept.
Differentiation. dxd (x − 5)(3x2 − 2) Integration. ∫ 01 xe−x2dx. Limits. x→−3lim x2 + 2x − 3x2 − 9. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. ... Enter a problem... Algebra Examples. Popular Problems. Algebra. Solve for r d=rt for r. for . Step 1. Rewrite the equation as . Step 2. Divide each term in by and simplify ...
Free equations calculator - solve linear, quadratic, polynomial, radical, exponential and logarithmic equations with all the steps. Type in any equation to get the solution, steps and graph.
Algebra questions and answers. Practice Problems 1. Solve d rt for r 2. Solve P=144p for p 3. Solve R.cs for C 4. Solve P-a+b+c for b 5. Solve T m-n for n 6. Solve A for b 7, Solve V = lvvh for w 8. Solve m=m for y2 9.
Free solve for a variable calculator - solve the equation for different variables step-by-step
Integration. ∫ 01 xe−x2dx. Limits. x→−3lim x2 + 2x − 3x2 − 9. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Solve for t D=rt. D = rt D = r t. Rewrite the equation as rt = D r t = D. rt = D r t = D. Divide each term in rt = D r t = D by r r and simplify. Tap for more steps... t = D r t = D r. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a ...
Polynomial. In mathematics, a polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of indeterminates and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate x is x² − 4x + 7. An example with three indeterminates ...
Algebra. Solve for r rt=d. rt = d r t = d. Divide each term in rt = d r t = d by t t. rt t = d t r t t = d t. Simplify the left side. Tap for more steps... r = d t r = d t. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. ... Solve for r d=r/(1+rt) Step 1. Rewrite the equation as . Step 2. Find the LCD of the terms in the equation. Tap for more steps... Step 2.1. Finding the LCD of a list of ...