- + ACCUPLACER Mathematics
- + ACT Mathematics
- + AFOQT Mathematics
- + ALEKS Tests
- + ASVAB Mathematics
- + ATI TEAS Math Tests
- + Common Core Math
- + DAT Math Tests
- + FSA Tests
- + FTCE Math
- + GED Mathematics
- + Georgia Milestones Assessment
- + GRE Quantitative Reasoning
- + HiSET Math Exam
- + HSPT Math
- + ISEE Mathematics
- + PARCC Tests
- + Praxis Math
- + PSAT Math Tests
- + PSSA Tests
- + SAT Math Tests
- + SBAC Tests
- + SIFT Math
- + SSAT Math Tests
- + STAAR Tests
- + TABE Tests
- + TASC Math
- + TSI Mathematics
- + ACT Math Worksheets
- + Accuplacer Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Worksheets
- + ALEKS Math Worksheets
- + ASVAB Math Worksheets
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Worksheets
- + FTCE General Math Worksheets
- + GED Math Worksheets
- + 3rd Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 4th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 5th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 8th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 9th Grade Math Worksheets
- + HiSET Math Worksheets
- + HSPT Math Worksheets
- + ISEE Middle-Level Math Worksheets
- + PERT Math Worksheets
- + Praxis Math Worksheets
- + PSAT Math Worksheets
- + SAT Math Worksheets
- + SIFT Math Worksheets
- + SSAT Middle Level Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + THEA Math Worksheets
- + TABE Math Worksheets
- + TASC Math Worksheets
- + TSI Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Course
- + ALEKS Math Course
- + ASVAB Math Course
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Course
- + CHSPE Math Course
- + FTCE General Knowledge Course
- + GED Math Course
- + HiSET Math Course
- + HSPT Math Course
- + ISEE Upper Level Math Course
- + SHSAT Math Course
- + SSAT Upper-Level Math Course
- + PERT Math Course
- + Praxis Core Math Course
- + SIFT Math Course
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Course
- + TABE Math Course
- + TASC Math Course
- + TSI Math Course
- + Number Properties Puzzles
- + Algebra Puzzles
- + Geometry Puzzles
- + Intelligent Math Puzzles
- + Ratio, Proportion & Percentages Puzzles
- + Other Math Puzzles

How to Solve Percent Problems? (+FREE Worksheet!)
Learn how to calculate and solve percent problems using the percent formula.
Related Topics
- How to Find Percent of Increase and Decrease
- How to Find Discount, Tax, and Tip
- How to Do Percentage Calculations
- How to Solve Simple Interest Problems
Step by step guide to solve percent problems
- In each percent problem, we are looking for the base, or part or the percent.
- Use the following equations to find each missing section. Base \(= \color{black}{Part} \ ÷ \ \color{blue}{Percent}\) \(\color{ black }{Part} = \color{blue}{Percent} \ ×\) Base \(\color{blue}{Percent} = \color{ black }{Part} \ ÷\) Base
Percent Problems – Example 1:
\(2.5\) is what percent of \(20\)?
In this problem, we are looking for the percent. Use the following equation: \(\color{blue}{Percent} = \color{ black }{Part} \ ÷\) Base \(→\) Percent \(=2.5 \ ÷ \ 20=0.125=12.5\%\)
The Absolute Best Books to Ace Pre-Algebra to Algebra II
The Ultimate Algebra Bundle From Pre-Algebra to Algebra II
Percent problems – example 2:.
\(40\) is \(10\%\) of what number?
Use the following formula: Base \(= \color{ black }{Part} \ ÷ \ \color{blue}{Percent}\) \(→\) Base \(=40 \ ÷ \ 0.10=400\) \(40\) is \(10\%\) of \(400\).
Percent Problems – Example 3:
\(1.2\) is what percent of \(24\)?
In this problem, we are looking for the percent. Use the following equation: \(\color{blue}{Percent} = \color{ black }{Part} \ ÷\) Base \(→\) Percent \(=1.2÷24=0.05=5\%\)
The Best Book to Help You Ace Pre-Algebra
Pre-Algebra for Beginners The Ultimate Step by Step Guide to Preparing for the Pre-Algebra Test
Percent problems – example 4:.
\(20\) is \(5\%\) of what number?
Use the following formula: Base \(= \color{black}{Part} \ ÷ \ \color{blue}{Percent}\) \(→\) Base \(=20÷0.05=400\) \( 20\) is \(5\%\) of \(400\).
Exercises for Calculating Percent Problems
Solve each problem..
- \(51\) is \(340\%\) of what?
- \(93\%\) of what number is \(97\)?
- \(27\%\) of \(142\) is what number?
- What percent of \(125\) is \(29.3\)?
- \(60\) is what percent of \(126\)?
- \(67\) is \(67\%\) of what?
Download Percent Problems Worksheet
- \(\color{blue}{15}\)
- \(\color{blue}{104.3}\)
- \(\color{blue}{38.34}\)
- \(\color{blue}{23.44\%}\)
- \(\color{blue}{47.6\%}\)
- \(\color{blue}{100}\)
The Greatest Books for Students to Ace the Algebra
Pre-Algebra Exercise Book A Comprehensive Workbook + PreAlgebra Practice Tests
Pre-algebra in 10 days the most effective pre-algebra crash course, college algebra practice workbook the most comprehensive review of college algebra, high school algebra i a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to mastering high school algebra 1, 10 full length clep college algebra practice tests the practice you need to ace the clep college algebra test.
by: Effortless Math Team about 4 years ago (category: Articles , Free Math Worksheets )
Effortless Math Team
Related to this article, more math articles.
- ParaPro Math Practice Test Questions
- Top 10 Tips to Create a TASC Math Study Plan
- Distinguishing Angles: Acute, Right, Obtuse, and Straight
- The Ultimate Praxis Core Math Formula Cheat Sheet
- Mastering the Metrics of Chance: A Complete Guide to Understanding Random Variables
- 5th Grade TNReady Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- What Are the Applications of Polar Coordinates?
- Growth Result As A Function of Time
- 8th Grade AZMerit Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- 4 Perfect Tablets for Note-Taking in 2024
What people say about "How to Solve Percent Problems? (+FREE Worksheet!) - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Pre-Algebra Practice Workbook The Most Comprehensive Review of Pre-Algebra
Algebra i practice workbook the most comprehensive review of algebra 1, algebra ii practice workbook the most comprehensive review of algebra 2, algebra i for beginners the ultimate step by step guide to acing algebra i, algebra ii for beginners the ultimate step by step guide to acing algebra ii, pre-algebra tutor everything you need to help achieve an excellent score.
- ATI TEAS 6 Math
- ISEE Upper Level Math
- SSAT Upper-Level Math
- Praxis Core Math
- 8th Grade STAAR Math
Limited time only!
Save Over 45 %
It was $89.99 now it is $49.99
Login and use all of our services.
Effortless Math services are waiting for you. login faster!
Register Fast!
Password will be generated automatically and sent to your email.
After registration you can change your password if you want.
- Math Worksheets
- Math Courses
- Math Topics
- Math Puzzles
- Math eBooks
- GED Math Books
- HiSET Math Books
- ACT Math Books
- ISEE Math Books
- ACCUPLACER Books
- Premium Membership
- Youtube Videos
Effortless Math provides unofficial test prep products for a variety of tests and exams. All trademarks are property of their respective trademark owners.
- Bulk Orders
- Refund Policy
Finding the Base Number in a Percent Problem Worksheet
Related Topics & Worksheets: Reverse Percentage Percentage Worksheet
Objective: I can find the base number in a percent problem.
Example: 8 is 32% of what number?
Answer: 25

We hope that the free math worksheets have been helpful. We encourage parents and teachers to select the topics according to the needs of the child. For more difficult questions, the child may be encouraged to work out the problem on a piece of paper before entering the solution. We hope that the kids will also love the fun stuff and puzzles.
We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
A free service from Mattecentrum
Solving problems with percentages
- Price difference I
- Price difference II
- How many students?
To solve problems with percent we use the percent proportion shown in "Proportions and percent".
$$\frac{a}{b}=\frac{x}{100}$$
$$\frac{a}{{\color{red} {b}}}\cdot {\color{red} {b}}=\frac{x}{100}\cdot b$$
$$a=\frac{x}{100}\cdot b$$
x/100 is called the rate.
$$a=r\cdot b\Rightarrow Percent=Rate\cdot Base$$
Where the base is the original value and the percentage is the new value.
47% of the students in a class of 34 students has glasses or contacts. How many students in the class have either glasses or contacts?
$$a=r\cdot b$$
$$47\%=0.47a$$
$$=0.47\cdot 34$$
$$a=15.98\approx 16$$
16 of the students wear either glasses or contacts.
We often get reports about how much something has increased or decreased as a percent of change. The percent of change tells us how much something has changed in comparison to the original number. There are two different methods that we can use to find the percent of change.
The Mathplanet school has increased its student body from 150 students to 240 from last year. How big is the increase in percent?
We begin by subtracting the smaller number (the old value) from the greater number (the new value) to find the amount of change.
$$240-150=90$$
Then we find out how many percent this change corresponds to when compared to the original number of students
$$90=r\cdot 150$$
$$\frac{90}{150}=r$$
$$0.6=r= 60\%$$
We begin by finding the ratio between the old value (the original value) and the new value
$$percent\:of\:change=\frac{new\:value}{old\:value}=\frac{240}{150}=1.6$$
As you might remember 100% = 1. Since we have a percent of change that is bigger than 1 we know that we have an increase. To find out how big of an increase we've got we subtract 1 from 1.6.
$$1.6-1=0.6$$
$$0.6=60\%$$
As you can see both methods gave us the same answer which is that the student body has increased by 60%
Video lessons
A skirt cost $35 regulary in a shop. At a sale the price of the skirtreduces with 30%. How much will the skirt cost after the discount?
Solve "54 is 25% of what number?"
- Pre-Algebra
- The mean, the median and the mode
- Stem-and-Leaf Plots and Box-and-Whiskers Plot
- Calculating the outcome
- Combinations and permutations
- Finding the odds
- Probability of events
- Geometry – fundamental statements
- Circle graphs
- Angles and parallel lines
- Quadrilaterals, polygons and transformations
- Measure areas
- Pyramids, prisms, cylinders and cones
- Square roots and real numbers
- The Pythagorean Theorem
- Trigonometry
- Algebra 1 Overview
- Algebra 2 Overview
- Geometry Overview
- SAT Overview
- ACT Overview
Percent , Rate , Base
Understanding percent , rate , and base is essential in various mathematical and real-life contexts. In this study guide, we will cover the basics of percent , rate , and base , and provide examples to help you grasp these concepts.
Percent means "per hundred" and is denoted by the symbol "%". It is used to express a number as a fraction of 100. For example, 25% is equivalent to the fraction 25/100 or the decimal 0.25.
A rate is a special ratio in which the two terms are in different units . For example, miles per hour (mph) is a rate . It compares the distance traveled to the time taken. Rates are often expressed using the word "per" or the symbol "/", such as 60 miles per hour or 60 mph.
The base is the original value in a percent problem. It is the whole or the original amount before a percentage is calculated. For example, if you're calculating 20% of 80, then 80 is the base .
Key Formulas
The following formulas are essential when dealing with percent , rate , and base :
Percent = (Part / Whole) * 100
Rate = (Part / Base )
Base = (Part / Rate )
Let's work through a few examples to illustrate these concepts:
Example 1: Calculating Percent
If you scored 35 out of 50 on a test, what is your score as a percentage?
Percent = (35 / 50) * 100 = 70%
Example 2: Calculating Rate
If a car travels 300 miles in 5 hours , what is its speed in miles per hour ?
Rate = 300 miles / 5 hours = 60 mph
Example 3: Finding the Base
If 15 is 20% of a number, what is the original number?
Base = 15 / 0.20 = 75
When studying percent , rate , and base , it's helpful to practice converting between fractions , decimals , and percentages . Additionally, working through real-life problems involving discounts, taxes, and tips can improve your understanding of these concepts.
Remember to use the key formulas and units to guide your problem-solving process. Understanding the relationship between percent , rate , and base will also make it easier to solve problems in various scenarios.
By mastering percent , rate , and base , you'll develop a valuable skill set for handling a wide range of mathematical and practical situations.
Good luck with your studies!
[Percent, Rate, Base] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
- Applying Percents Mathematics • Seventh Grade
Read More...
◂ Math Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Percent, Rate, Base

The resources above cover the following skills:
- Download and Print thousands of standards-based ELA, Social Study, Science and Math Worksheets and Study Guides!
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Membership Benefits
- Completing Worksheets Online
- Share to Google Classroom
- NewPathLearning
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: 6th grade > Unit 3
- Percent word problem: recycling cans
Percent word problems
- Rates and percentages FAQ
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
Percent Maths Problems
Helping with Math
Applying Percentage, Base, and Rate 6th Grade Math Worksheets
Download applying percentage, base, and rate worksheets.
Click the button below to get instant access to these premium worksheets for use in the classroom or at a home.
Download this Worksheet
This download is exclusively for Helping With Math Premium members!
To download this worksheet collection, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start the download!
Edit this Worksheet
Editing worksheet collections is available exclusively for Helping With Math Premium members.
To edit this worksheet collection, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start editing!
This worksheet can be edited by Premium members using the free Google Slides online software. Click the Edit button above to get started.
Download free sample
Not ready to purchase a subscription yet? Click here to download a FREE sample of this worksheet pack.
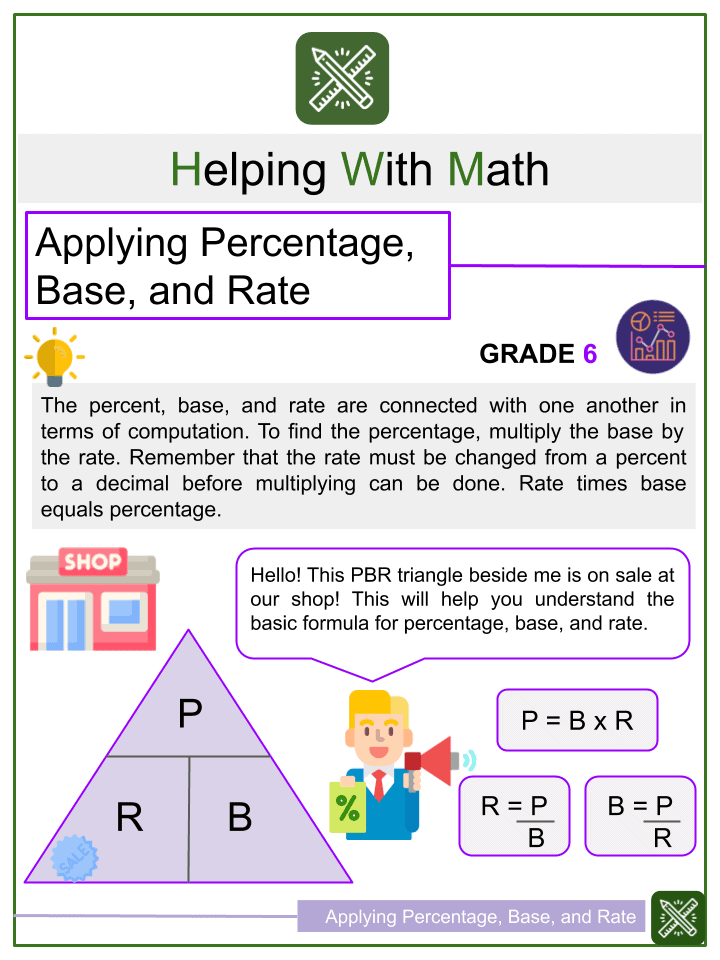
Definition:
The percent, base, and rate are connected with one another in terms of computation. To find the percentage , multiply the base by the rate. Remember that the rate must be changed from a percent to a decimal before multiplying can be done. Rate times base equals percentage.
PERCENTAGE (P=BxR) – The result obtained when a number is multiplied by a percent.
BASE (B=P/R) – The whole in a problem. The amount you are taking a percent of.
RATE (R=P/B) – The ratio of amount to the base. It is written as a percent.
Applying Percentage, Base, and Rate Worksheets
This is a fantastic bundle which includes everything you need to know about Applying Percentage, Base, and Rate across 15+ in-depth pages. These are ready-to-use Common core aligned Grade 6 Math worksheets. Each ready to use worksheet collection includes 10 activities and an answer guide. Not teaching common core standards ? Don’t worry! All our worksheets are completely editable so can be tailored for your curriculum and target audience.
Resource Examples
Click any of the example images below to view a larger version.
Even More Math Worksheets
- Understanding Exponents 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Constructing Geometry Nets 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Multiplying and Dividing Fractions 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Examining Shapes of Distribution 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Polygons in the Coordinate Plane 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Distance Formula of Two Points 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Solving Measures of Variability 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Writing and Evaluating Algebraic Expressions 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- The Distributive Property and Algebraic Expressions 6th Grade Math Worksheets
Lifetime Membership Offer
Exclusive, limited time offer! One payment, lifetime access.
While we continue to grow our extensive math worksheet library, you can get all editable worksheets available now and in the future. We add 100+ K-8, common core aligned worksheets every month.
To find out more and sign up for a very low one-time payment , click now!
Similar Worksheets
The worksheets listed below are suitable for the same age and grades as Applying Percentage, Base, and Rate 6th Grade Math.
Counting Numbers 1 – 100 (by tens) Kindergarten Math Worksheets

Understanding Measurements Length and Width of an Object Kindergarten Math Worksheets

Properties of Shapes Kindergarten Math Worksheets

Decomposition of Numbers within 10 Kindergarten Math Worksheets

Pie Chart (Space Day Themed) Math Worksheets

Understanding the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations of 2D figures 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Solving Linear Equations in One Variable Integral Coefficients and Rational Coefficients 8th Grade Math Worksheets


Interpreting linear functions in a form of y=mx+b and its graph 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Performing Operations using Scientific Notation 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Understanding Irrational Numbers 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Solving Percent Problems

Percent is a great mathematical tool to express quantities and is used extensively in different things – from interest rates, discounts, and taxes to surveys, censuses, etc.
This article is your guide to percent and solving percent problems frequently appearing in major national examinations.
Click below to go to the main reviewers:
Ultimate UPCAT Reviewer
Ultimate NMAT Reviewer
Ultimate Civil Service Exam Reviewer
Ultimate PMA Entrance Exam Reviewer
Ultimate PNP Entrance Exam Reviewer
Ultimate LET Reviewer
Table of Contents
What does percent mean.
The word “percent” originated from the Latin phrase per centum, meaning “by hundred.” When we say “percent,” we refer to “parts per 100”. This means that a percent is a fraction with 100 as the denominator. The symbol % is used to indicate a percent.
For example, 3% means three parts per 100 or 3⁄100; 45% means 45⁄100; and 92% means 92⁄100.
Illustrating Percent
Suppose a vendor has 100 biscuits. If 10% of those biscuits are ube-flavored, 10⁄100 or 10 out of 100 biscuits are ube-flavored.

On the other hand, suppose there are 100 students in a school auditorium. If 42% of those students are honor students, 42⁄100 students, or 42 out of 100 students, are honor students.
Expressing Percent as Fraction and Decimal
Since percent means a fraction with 100 as the denominator, we can express a percent as a fraction or a decimal number .
Drop the percent sign and put 100 as the denominator to transform a percent into a fraction. For instance, 25% is simply 25⁄100.
Note that when 25⁄100 is reduced to its lowest terms, you will obtain ¼. This means that 25% is also equivalent to ¼.

Furthermore, note that when you transform ¼ into its decimal form using the steps we have discussed in the previous reviewer , you will obtain 0.25. Hence, 25% is also equal to 0.25.
There is an easier way to transform percent into decimals . Drop the percent sign and move the decimal point two places to the left of the given number.

For example, 54% is equivalent to 0.54
Example: Transform 3% to decimal form.

Suppose that your mom prepared ten pieces of your favorite cookies. You are excited to taste those cookies, but you realize that your brother ate 20% of the cookies that your mom prepared. What exactly is the number of cookies eaten by your brother?
To determine the answer to your question above, you must determine 20% of 10. This case involves the application of percentages.
The percentage is the result when you multiply a number by a percent. Returning to your problem about the number of cookies your brother ate, 20% of 10 can be determined if you multiply ten by 20%. The result after you multiply the numbers is called the percentage.
How To Find the Percentage
Follow these steps if you want to find the percentage:
Step 1: Convert the given percent (the one with the % sign) into decimals .

Again, to convert percent into its decimal form, we drop the percent sign and then move the decimal point two places to the left. Thus, 20% = 0.20
Step 2 : Multiply the decimal you have obtained from Step 1 to the given number. The result is the percentage.

To multiply 0.20 by 10, we ignored the decimal point for a while and multiplied the given decimals like whole numbers. We have obtained 0200. Since 0.20 has two decimal places while 10 has none, the final answer should have two decimal places. We count two digits from the right of 0200 and put the decimal point there. Hence, the answer is 02.00, which is equivalent to 2.
Hence, 20% of 10 is 2. This means that out of 10 cookies your mother prepared, 2 of those were eaten by your brother.
Let us have another example.
Example: What is 50% of 120?
Step 1 : Convert the given percent (the one with the % sign) into decimals.
We drop the % sign of 50% and move the decimal point two places to the left.

Thus, 50% = 0.50
Step 2: Multiply the decimal you have obtained from Step 1 to the given number. The result is the percentage.

To multiply 0.50 by 120, we ignored the decimal point for a while and multiplied the given decimals like whole numbers. Through this process, we have obtained 06000. Since 0.50 has two decimal places while 120 has none, the final answer should have two decimal places. We count two digits from the right of 06000 and put the decimal point there. Hence, the answer is 060.00, which is equivalent to 60.
Hence, 50% of 120 is 60.
Simple Tricks in Computing Percentages
We always want to make our computations in mathematics faster and more accurate. For this reason, I will share two tricks you can use when computing percentages.
Trick #1: You can compute some percentages using only mental computation.
If you want to determine the 25%, 50%, 75%, or 100% of a number, you can do so without the help of pen and paper.
- 25% is equivalent to 25⁄100 or ¼. Hence, to find the 25% of a number, divide the given number by 4. Example: 25% of 40 is just 40 ÷ 4 = 10.
- 50% is equivalent to 50⁄100 or ½. Thus, to find the 50% of a number, divide the given number by 2. This means 50% of a number is just half the given number. Example: 50% of 40 is just 40 ÷ 2 = 20.
- 75% is equivalent to 75⁄100 or ¾. Thus, to find the 75% of a number, multiply the given number by three and then divide the result by 4. Example: 75% of 40 is just 40 x 3 = 120 ÷ 4 = 30.
- 100% is equivalent to 100⁄100 or 1. Thus, 100% of a number is the number itself . Example: 100% of 40 is just 40 itself.
Trick #2: X% of a number Y is equal to Y% of number X
This trick means we can transfer the % sign to the other number, and the result will be the same.
Example : What is 40% of 25?
Using trick #2, we can transfer the % sign from 40% to 25. Thus, we have 25%. This means 40% of 25 is the same as 25% of 40.
Thus, applying our first trick on finding the 25% of a number, 40 ÷ 4 = 10; hence, 40% of 25 is 10.
Example : What is 92% of 50?
92% of 50 is the same as 50% of 92. Hence, we can just divide 92 by 2 to obtain the answer, 92 ÷ 2 = 46
Therefore, 92% of 50 is 46.
Base and Rate
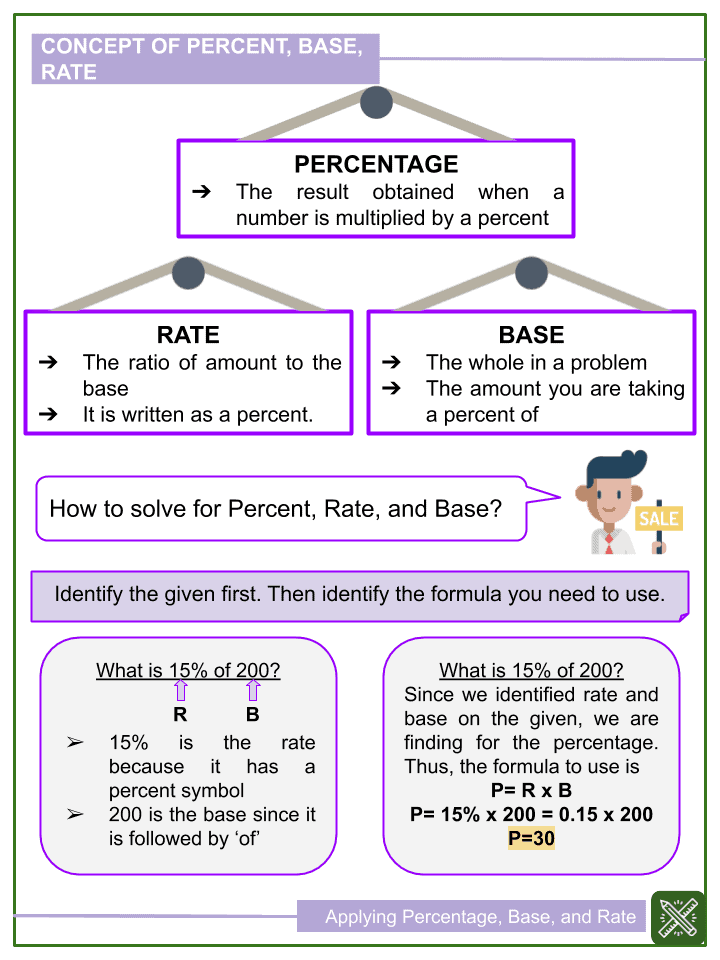
The base is the amount you are taking a percent of. Meanwhile, the rate is the percent you are calculating.

For example, if there are 50 students in a classroom and 20% of those students are honor students, it follows that ten students are honor students. 50 is the base since it is the amount we take a percent of. Meanwhile, 20% is the rate since we calculate the percentage. Lastly, 10 is the percentage.
The product of the base and the rate is the percentage .
Percentage = Base × Rate
Example: Determine the percentage, base, and rate if 20% of 90 is 18.
Since 90 x 20% = 90 x 0.20 = 18, 90 is the base, 20% is the rate, and 18 is the percentage.
Calculating Percentage, Base, and Rate
Formula to find the percentage.
The formula to find the percentage, as we have stated, is:
We can manipulate the mathematical equation above to obtain the formulas for computing the base and the rate:
Formula to Find the Base
Base = Percentage ÷ Rate
Formula to Find the Rate
Rate = Percentage ÷ Base
Example 1: If 10% of a number is 90, what is the number?
We can interpret this question as 10% of ______ = 90. Since “of” is a signal word for multiplication, it also implies 10% x ______ = 90
This means that 10% is the rate while 90 is the percentage. The unknown number is the base. Thus, we need to compute the base.
Using the formula to find the base:
Base = Percentage ÷ Rate
Base = 90 ÷ 10%
Convert the given percent into decimal:
Base = 90 ÷ 0.10
Now that you have already transformed the rate into decimal form, you may divide 90 by 0.10 to obtain the answer.
To perform division with decimal numbers , we need to transform the divisor (0.10) into a whole number by moving two decimal places to the right. Thus, the new divisor is 10. We also move two decimal places for the dividend (90). Thus, the new dividend is 9000.

We now perform long division with our new dividend and divisor:

To find the base, we compute 90 ÷ 0.10 = 900
Hence, the base is 900.
Example 2: What percent of 720 is 90?
We can translate the question above in this form: _____% of 720 is 90 or _____% x 720 = 90. Therefore, 720 is the base, while 90 is the percentage. The missing number is the rate.
We will now use the formula for finding the rate.
Again, based on the given problem, the percentage is 90 while the base is 720
Rate = 90 ÷ 720
Notice that the dividend (the first number) is smaller than the divisor (the second number). In this case, you may apply the same steps in transforming fractions into decimal form because 90 ÷ 720 is a proper fraction (i.e., 90⁄720).
Let us divide 90 by 720 using the steps in transforming fractions into decimal form .
We add some zeros and decimal points to proceed with the division process.

We can now divide 900 by 720.

Note that every time the remainder becomes smaller than the divisor, we add zeros to 900 and the remainder to continue the division process.
The quotient we obtained is 0.125. Thus, 0.125 is our rate.
However, the rate must always be expressed with a percent sign. To do this, we multiply 0.125 by 100 or move two decimal places to the right of it and put a percent sign. Thus, 0.125 is equal to 12.5%.

Therefore, the rate is 12.5%
The Percentage, Base, and Rate Triangle
What if you forgot the formula to determine the percentage, base, or rate in a particular problem? Don’t worry because there is a fun way to derive these formulas.
Shown below is the Percentage, Base, and Rate Triangle . It is a triangle divided into three portions where P (for percentage) is written on the upper portion, and B (for base) and R (for rate) are written on the lower portions. There are also division signs in the triangle’s outer left and outer right parts and a multiplication sign below it.

How To Use the Percentage, Base, and Rate Triangle
Suppose you are looking for the base. You have to cover the B in the triangle and look at the remaining letters and the operation between them. Notice that if you cover B, the remaining letters are P and R, with a division sign between them. This means that to find the base, you must divide P by R.

Next topic: Ratio and Proportion
Previous topic : Fundamental Operations on Fractions and Decimals
Return to the main article: The Ultimate Basic Math Reviewer
Download Printable Summary/Review Notes
Download printable flashcards, test yourself, 1. practice questions [free pdf download], 2. answer key [free pdf download], 3. math mock exam + answer key.
Written by Jewel Kyle Fabula
in Civil Service Exam , College Entrance Exam , LET , NAPOLCOM Exam , NMAT , PMA Entrance Exam , Reviewers , UPCAT
Jewel Kyle Fabula
Jewel Kyle Fabula is a Bachelor of Science in Economics student at the University of the Philippines Diliman. His passion for learning mathematics developed as he competed in some mathematics competitions during his Junior High School years. He loves cats, playing video games, and listening to music.
Browse all articles written by Jewel Kyle Fabula
Copyright Notice
All materials contained on this site are protected by the Republic of the Philippines copyright law and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, displayed, published, or broadcast without the prior written permission of filipiknow.net or in the case of third party materials, the owner of that content. You may not alter or remove any trademark, copyright, or other notice from copies of the content. Be warned that we have already reported and helped terminate several websites and YouTube channels for blatantly stealing our content. If you wish to use filipiknow.net content for commercial purposes, such as for content syndication, etc., please contact us at legal(at)filipiknow(dot)net

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

18.4: Solving Percentage Problems
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 39948
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Let's solve more percentage problems.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\): Number Talk: Multiplication with Decimals
Find the products mentally.
\(6\cdot (0.8)\cdot 2\)
\((4.5)\cdot (0.6)\cdot 4\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\): Coupons
Han and Clare go shopping, and they each have a coupon. Answer each question and show your reasoning.
- Han buys an item with a normal price of $15, and uses a 10% off coupon. How much does he save by using the coupon?

- Clare buys an item with a normal price of $24, but saves $6 by using a coupon. For what percentage off is this coupon?
Are you ready for more?
Clare paid full price for an item. Han bought the same item for 80% of the full price. Clare said, “I can’t believe I paid 125% of what you paid, Han!” Is what she said true? Explain.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\): Info Gap: Music Devices
Your teacher will give you either a problem card or a data card . Do not show or read your card to your partner.
If your teacher gives you the problem card :
- Silently read your card and think about what information you need to be able to answer the question.
- Ask your partner for the specific information that you need.
- Explain how you are using the information to solve the problem. Continue to ask questions until you have enough information to solve the problem.
- Share the problem card and solve the problem independently.
- Read the data card and discuss your reasoning.
If your teacher gives you the data card :
- Silently read your card.
- Ask your partner “What specific information do you need?” and wait for them to ask for information. If your partner asks for information that is not on the card, do not do the calculations for them. Tell them you don’t have that information.
- Before sharing the information, ask “ Why do you need that information? ” Listen to your partner’s reasoning and ask clarifying questions.
- Read the problem card and solve the problem independently.
- Share the data card and discuss your reasoning.
A pot can hold 36 liters of water. What percentage of the pot is filled when it contains 9 liters of water?
Here are two different ways to solve this problem:
- Using a double number line:

We can divide the distance between 0 and 36 into four equal intervals, so 9 is \(\frac{1}{4}\) of 36, or 9 is 25% of 36.
- Using a table:

Glossary Entries
Definition: Percent
The word percent means “for each 100.” The symbol for percent is %.
For example, a quarter is worth 25 cents, and a dollar is worth 100 cents. We can say that a quarter is worth 25% of a dollar.

Definition: Percentage
A percentage is a rate per 100.
For example, a fish tank can hold 36 liters. Right now there is 27 liters of water in the tank. The percentage of the tank that is full is 75%.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
For each problem, explain or show your reasoning.
- 160 is what percentage of 40?
- 40 is 160% of what number?
- What number is 40% of 160?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5}\)
A store is having a 20%-off sale on all merchandise. If Mai buys one item and saves $13, what was the original price of her purchase? Explain or show your reasoning.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6}\)
The original price of a scarf was $16. During a store-closing sale, a shopper saved $12 on the scarf. What percentage discount did she receive? Explain or show your reasoning.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\)
Select all the expressions whose value is larger than 100.
- 120% of 100
- 500% of 400
- 1% of 1,000
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8}\)
An ant travels at a constant rate of 30 cm every 2 minutes.
- At what pace does the ant travel per centimeter?
- At what speed does the ant travel per minute?
(From Unit 3.3.4)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Is \(3\frac{1}{2}\) cups more or less than 1 liter? Explain or show your reasoning. (Note: 1 cup \(\approx\) 236.6 milliliters)
(From Unit 3.2.3)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{10}\)
Name a unit of measurement that is about the same size as each object.
- The distance of a doorknob from the floor is about 1 _____________.
- The thickness of a fingernail is about 1 _____________.
- The volume of a drop of honey is about 1 _____________.
- The weight or mass of a pineapple is about 1 _____________.
- The thickness of a picture book is about 1 _____________.
- The weight or mass of a buffalo is about 1 _____________.
- The volume of a flower vase is about 1 _____________.
- The weight or mass of 20 staples is about 1 _____________.
- The volume of a melon is about 1 _____________.
- The length of a piece of printer paper is about 1 _____________.
(From Unit 3.2.1)
Grade 6 Mathematics Module: Finding the Percentage, Base and Rate in a Given Problem
This Self-Learning Module (SLM) is prepared so that you, our dear learners, can continue your studies and learn while at home. Activities, questions, directions, exercises, and discussions are carefully stated for you to understand each lesson.
Each SLM is composed of different parts. Each part shall guide you step-by-step as you discover and understand the lesson prepared for you.
Pre-tests are provided to measure your prior knowledge on lessons in each SLM. This will tell you if you need to proceed on completing this module or if you need to ask your facilitator or your teacher’s assistance for better understanding of the lesson. At the end of each module, you need to answer the post-test to self-check your learning. Answer keys are provided for each activity and test. We trust that you will be honest in using these.
Please use this module with care. Do not put unnecessary marks on any part of this SLM. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises and tests. And read the instructions carefully before performing each task.
If you have any questions in using this SLM or any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator.
This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you master the lessons on Finding the Percentage, Base and Rate or Percent in given problems. The scope of this module permits it to be used in many different learning situations. The language used recognizes your diverse vocabulary level. The lessons are arranged to follow the standard sequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be changed to correspond with the textbook you are now using.
The module is divided into three lessons, namely:
- Lesson 1 – Finding the Percentage in a Given Problem
- Lesson 2 – Finding the Rate in a Given Problem
- Lesson 3 – Finding the Base in a Given Problem
After going through this module, you are expected to:
1. identify the percentage, rate and base in a given problem;
2. find the base, percentage or rate or percent in a given problem; and
3. solve routine and non-routine problems involving the percentage, rate and base using appropriate strategies and tools.
Grade 6 Mathematics Quarter 2 Self-Learning Module: Finding the Percentage, Base and Rate in a Given Problem
Can't find what you're looking for.
We are here to help - please use the search box below.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Determining Percentage, Base, & Rate
Loading ad...
Cathy Gonzaga
This serves as additional worksheet to develop skill in identifying and solving for the percentage, base or rate in a given situation
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF

Watch CBS News
Teens come up with trigonometry proof for Pythagorean Theorem, a problem that stumped math world for centuries
By Bill Whitaker
May 5, 2024 / 7:00 PM EDT / CBS News
As the school year ends, many students will be only too happy to see math classes in their rearview mirrors. It may seem to some of us non-mathematicians that geometry and trigonometry were created by the Greeks as a form of torture, so imagine our amazement when we heard two high school seniors had proved a mathematical puzzle that was thought to be impossible for 2,000 years.
We met Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson at their all-girls Catholic high school in New Orleans. We expected to find two mathematical prodigies.
Instead, we found at St. Mary's Academy , all students are told their possibilities are boundless.
Come Mardi Gras season, New Orleans is alive with colorful parades, replete with floats, and beads, and high school marching bands.
In a city where uniqueness is celebrated, St. Mary's stands out – with young African American women playing trombones and tubas, twirling batons and dancing - doing it all, which defines St. Mary's, students told us.
Junior Christina Blazio says the school instills in them they have the ability to accomplish anything.
Christina Blazio: That is kinda a standard here. So we aim very high - like, our aim is excellence for all students.
The private Catholic elementary and high school sits behind the Sisters of the Holy Family Convent in New Orleans East. The academy was started by an African American nun for young Black women just after the Civil War. The church still supports the school with the help of alumni.
In December 2022, seniors Ne'Kiya Jackson and Calcea Johnson were working on a school-wide math contest that came with a cash prize.

Ne'Kiya Jackson: I was motivated because there was a monetary incentive.
Calcea Johnson: 'Cause I was like, "$500 is a lot of money. So I-- I would like to at least try."
Both were staring down the thorny bonus question.
Bill Whitaker: So tell me, what was this bonus question?
Calcea Johnson: It was to create a new proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. And it kind of gave you a few guidelines on how would you start a proof.
The seniors were familiar with the Pythagorean Theorem, a fundamental principle of geometry. You may remember it from high school: a² + b² = c². In plain English, when you know the length of two sides of a right triangle, you can figure out the length of the third.
Both had studied geometry and some trigonometry, and both told us math was not easy. What no one told them was there had been more than 300 documented proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem using algebra and geometry, but for 2,000 years a proof using trigonometry was thought to be impossible, … and that was the bonus question facing them.
Bill Whitaker: When you looked at the question did you think, "Boy, this is hard"?
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Yeah.
Bill Whitaker: What motivated you to say, "Well, I'm going to try this"?
Calcea Johnson: I think I was like, "I started something. I need to finish it."
Bill Whitaker: So you just kept on going.
Calcea Johnson: Yeah.
For two months that winter, they spent almost all their free time working on the proof.
CeCe Johnson: She was like, "Mom, this is a little bit too much."
CeCe and Cal Johnson are Calcea's parents.
CeCe Johnson: So then I started looking at what she really was doing. And it was pages and pages and pages of, like, over 20 or 30 pages for this one problem.
Cal Johnson: Yeah, the garbage can was full of papers, which she would, you know, work out the problems and-- if that didn't work she would ball it up, throw it in the trash.
Bill Whitaker: Did you look at the problem?
Neliska Jackson is Ne'Kiya's mother.
Neliska Jackson: Personally I did not. 'Cause most of the time I don't understand what she's doing (laughter).
Michelle Blouin Williams: What if we did this, what if I write this? Does this help? ax² plus ….
Their math teacher, Michelle Blouin Williams, initiated the math contest.

Bill Whitaker: And did you think anyone would solve it?
Michelle Blouin Williams: Well, I wasn't necessarily looking for a solve. So, no, I didn't—
Bill Whitaker: What were you looking for?
Michelle Blouin Williams: I was just looking for some ingenuity, you know—
Calcea and Ne'Kiya delivered on that! They tried to explain their groundbreaking work to 60 Minutes. Calcea's proof is appropriately titled the Waffle Cone.
Calcea Johnson: So to start the proof, we start with just a regular right triangle where the angle in the corner is 90°. And the two angles are alpha and beta.
Bill Whitaker: Uh-huh
Calcea Johnson: So then what we do next is we draw a second congruent, which means they're equal in size. But then we start creating similar but smaller right triangles going in a pattern like this. And then it continues for infinity. And eventually it creates this larger waffle cone shape.
Calcea Johnson: Am I going a little too—
Bill Whitaker: You've been beyond me since the beginning. (laughter)
Bill Whitaker: So how did you figure out the proof?
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Okay. So you have a right triangle, 90° angle, alpha and beta.
Bill Whitaker: Then what did you do?

Ne'Kiya Jackson: Okay, I have a right triangle inside of the circle. And I have a perpendicular bisector at OP to divide the triangle to make that small right triangle. And that's basically what I used for the proof. That's the proof.
Bill Whitaker: That's what I call amazing.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Well, thank you.
There had been one other documented proof of the theorem using trigonometry by mathematician Jason Zimba in 2009 – one in 2,000 years. Now it seems Ne'Kiya and Calcea have joined perhaps the most exclusive club in mathematics.
Bill Whitaker: So you both independently came up with proof that only used trigonometry.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Yes.
Bill Whitaker: So are you math geniuses?
Calcea Johnson: I think that's a stretch.
Bill Whitaker: If not genius, you're really smart at math.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Not at all. (laugh)
To document Calcea and Ne'Kiya's work, math teachers at St. Mary's submitted their proofs to an American Mathematical Society conference in Atlanta in March 2023.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Well, our teacher approached us and was like, "Hey, you might be able to actually present this," I was like, "Are you joking?" But she wasn't. So we went. I got up there. We presented and it went well, and it blew up.
Bill Whitaker: It blew up.
Calcea Johnson: Yeah.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: It blew up.
Bill Whitaker: Yeah. What was the blowup like?
Calcea Johnson: Insane, unexpected, crazy, honestly.
It took millenia to prove, but just a minute for word of their accomplishment to go around the world. They got a write-up in South Korea and a shout-out from former first lady Michelle Obama, a commendation from the governor and keys to the city of New Orleans.
Bill Whitaker: Why do you think so many people found what you did to be so impressive?
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Probably because we're African American, one. And we're also women. So I think-- oh, and our age. Of course our ages probably played a big part.
Bill Whitaker: So you think people were surprised that young African American women, could do such a thing?
Calcea Johnson: Yeah, definitely.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: I'd like to actually be celebrated for what it is. Like, it's a great mathematical achievement.
Achievement, that's a word you hear often around St. Mary's academy. Calcea and Ne'Kiya follow a long line of barrier-breaking graduates.
The late queen of Creole cooking, Leah Chase , was an alum. so was the first African-American female New Orleans police chief, Michelle Woodfork …
And judge for the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals, Dana Douglas. Math teacher Michelle Blouin Williams told us Calcea and Ne'Kiya are typical St. Mary's students.
Bill Whitaker: They're not unicorns.
Michelle Blouin Williams: Oh, no no. If they are unicorns, then every single lady that has matriculated through this school is a beautiful, Black unicorn.
Pamela Rogers: You're good?
Pamela Rogers, St. Mary's president and interim principal, told us the students hear that message from the moment they walk in the door.

Pamela Rogers: We believe all students can succeed, all students can learn. It does not matter the environment that you live in.
Bill Whitaker: So when word went out that two of your students had solved this almost impossible math problem, were they universally applauded?
Pamela Rogers: In this community, they were greatly applauded. Across the country, there were many naysayers.
Bill Whitaker: What were they saying?
Pamela Rogers: They were saying, "Oh, they could not have done it. African Americans don't have the brains to do it." Of course, we sheltered our girls from that. But we absolutely did not expect it to come in the volume that it came.
Bill Whitaker: And after such a wonderful achievement.
Pamela Rogers: People-- have a vision of who can be successful. And-- to some people, it is not always an African American female. And to us, it's always an African American female.
Gloria Ladson-Billings: What we know is when teachers lay out some expectations that say, "You can do this," kids will work as hard as they can to do it.
Gloria Ladson-Billings, professor emeritus at the University of Wisconsin, has studied how best to teach African American students. She told us an encouraging teacher can change a life.
Bill Whitaker: And what's the difference, say, between having a teacher like that and a whole school dedicated to the excellence of these students?
Gloria Ladson-Billings: So a whole school is almost like being in Heaven.
Bill Whitaker: What do you mean by that?

Gloria Ladson-Billings: Many of our young people have their ceilings lowered, that somewhere around fourth or fifth grade, their thoughts are, "I'm not going to be anything special." What I think is probably happening at St. Mary's is young women come in as, perhaps, ninth graders and are told, "Here's what we expect to happen. And here's how we're going to help you get there."
At St. Mary's, half the students get scholarships, subsidized by fundraising to defray the $8,000 a year tuition. Here, there's no test to get in, but expectations are high and rules are strict: no cellphones, modest skirts, hair must be its natural color.
Students Rayah Siddiq, Summer Forde, Carissa Washington, Tatum Williams and Christina Blazio told us they appreciate the rules and rigor.
Rayah Siddiq: Especially the standards that they set for us. They're very high. And I don't think that's ever going to change.
Bill Whitaker: So is there a heart, a philosophy, an essence to St. Mary's?
Summer Forde: The sisterhood—
Carissa Washington: Sisterhood.
Tatum Williams: Sisterhood.
Bill Whitaker: The sisterhood?
Voices: Yes.
Bill Whitaker: And you don't mean the nuns. You mean-- (laughter)
Christina Blazio: I mean, yeah. The community—
Bill Whitaker: So when you're here, there's just no question that you're going to go on to college.
Rayah Siddiq: College is all they talk about. (laughter)
Pamela Rogers: … and Arizona State University (Cheering)
Principal Rogers announces to her 615 students the colleges where every senior has been accepted.
Bill Whitaker: So for 17 years, you've had a 100% graduation rate—
Pamela Rogers: Yes.
Bill Whitaker: --and a 100% college acceptance rate?
Pamela Rogers: That's correct.
Last year when Ne'Kiya and Calcea graduated, all their classmates went to college and got scholarships. Ne'Kiya got a full ride to the pharmacy school at Xavier University in New Orleans. Calcea, the class valedictorian, is studying environmental engineering at Louisiana State University.
Bill Whitaker: So wait a minute. Neither one of you is going to pursue a career in math?
Both: No. (laugh)
Calcea Johnson: I may take up a minor in math. But I don't want that to be my job job.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Yeah. People might expect too much out of me if (laugh) I become a mathematician. (laugh)
But math is not completely in their rear-view mirrors. This spring they submitted their high school proofs for final peer review and publication … and are still working on further proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem. Since their first two …
Calcea Johnson: We found five. And then we found a general format that could potentially produce at least five additional proofs.
Bill Whitaker: And you're not math geniuses?
Bill Whitaker: I'm not buying it. (laughs)
Produced by Sara Kuzmarov. Associate producer, Mariah B. Campbell. Edited by Daniel J. Glucksman.

Bill Whitaker is an award-winning journalist and 60 Minutes correspondent who has covered major news stories, domestically and across the globe, for more than four decades with CBS News.
More from CBS News

Israel preparing for Rafah invasion in Gaza amid increasing tension with U.S.

60 Minutes Archive: Coverage of North Korea

How much does it cost to file for bankruptcy?

As a Social Security cut looms, should seniors buy long-term care insurance now?
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- May 13, 2024 • 27:46 How Biden Adopted Trump’s Trade War With China
- May 10, 2024 • 27:42 Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
- May 9, 2024 • 34:42 One Strongman, One Billion Voters, and the Future of India
- May 8, 2024 • 28:28 A Plan to Remake the Middle East
- May 7, 2024 • 27:43 How Changing Ocean Temperatures Could Upend Life on Earth
- May 6, 2024 • 29:23 R.F.K. Jr.’s Battle to Get on the Ballot
- May 3, 2024 • 25:33 The Protesters and the President
- May 2, 2024 • 29:13 Biden Loosens Up on Weed
- May 1, 2024 • 35:16 The New Abortion Fight Before the Supreme Court
- April 30, 2024 • 27:40 The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
- April 29, 2024 • 47:53 Trump 2.0: What a Second Trump Presidency Would Bring
- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
The porn star testified for eight hours at donald trump’s hush-money trial. this is how it went..
Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Jonah E. Bromwich
Produced by Olivia Natt and Michael Simon Johnson
Edited by Lexie Diao
With Paige Cowett
Original music by Will Reid and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
This episode contains descriptions of an alleged sexual liaison.
What happened when Stormy Daniels took the stand for eight hours in the first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump?
Jonah Bromwich, one of the lead reporters covering the trial for The Times, was in the room.
On today’s episode

Jonah E. Bromwich , who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times.

Background reading
In a second day of cross-examination, Stormy Daniels resisted the implication she had tried to shake down Donald J. Trump by selling her story of a sexual liaison.
Here are six takeaways from Ms. Daniels’s earlier testimony.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Jonah E. Bromwich covers criminal justice in New York, with a focus on the Manhattan district attorney’s office and state criminal courts in Manhattan. More about Jonah E. Bromwich
Advertisement
Two-Stage Attention Model to Solve Large-Scale Traveling Salesman Problems
- Conference paper
- First Online: 15 November 2023
- Cite this conference paper

- Feng Wang 12 &
- Jingge Song 13
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Computer Science ((LNCS,volume 14448))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Neural Information Processing
604 Accesses
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) widely exists in real-world scenarios. Various methods, such as exact methods, heuristic methods, and deep learning-based methods, can solve TSPs efficiently. However, as the size of the problems increases, these methods become increasingly time-consuming due to the high complexity of large-scale TSPs. This paper proposes a two-stage attention model (TSAM) that incorporates the divide-and-conquer strategy and attention model to solve large-scale TSPs efficiently. Experimental results demonstrate that TSAM can rapidly produce promising solutions for TSP instances ranging from 500 to 10,000 nodes.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Applegate, D., Bixby, R., Chvatal, V., Cook, W.: Concorde tsp solver (2006)
Google Scholar
Applegate, D.L., et al.: Certification of an optimal tsp tour through 85,900 cities. In: Operations Research Letters, pp. 11–15 (2009)
Helsgaun, K.: General k-opt submoves for the lin-kernighan tsp heuristic. Math. Program. Comput. 1 , 119–163 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12532-009-0004-6
Helsgaun, K.: An Extension of the lin-kernighan-helsgaun TSP Solver for Constrained Traveling Salesman and Vehicle Routing Problems, Roskilde University, Roskilde, pp. 1–60 (2017)
Kool, W., van Hoof, H., Welling, M.: Attention, learn to solve routing problems! In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, pp. 1–25 (2019)
Taillard, É. D., Helsgaun, K.: Popmusic for the travelling salesman problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 272 , 420–429 (2019)
Vinyals, O., Fortunato, M., Jaitly, N.: Pointer networks. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2692–2700 (2015)
Bello, I., Pham, H., Le, Q.V., Norouzi, M., Bengio, S.: Neural combinatorial optimization with reinforcement learning, arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.09940 (2016)
Mnih, V., et al.: Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1928–1937 (2016)
Deudon, Michel, Cournut, Pierre, Lacoste, Alexandre, Adulyasak, Yossiri, Rousseau, Louis-Martin.: Learning heuristics for the TSP by policy gradient. In: van Hoeve, Willem-Jan. (ed.) CPAIOR 2018. LNCS, vol. 10848, pp. 170–181. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93031-2_12
Chapter Google Scholar
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 6000–6010 (2017)
Kwon, Y.D., Choo, J., Kim, B., Yoon, I., Gwon, Y., Min, S.: Pomo: policy optimization with multiple optima for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 21 188–21 198 (2020)
Gidaris, S., Singh, P., Komodakis, N.: Unsupervised representation learning by predicting image rotations, arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.07728 (2018)
Kim, M., Park, J., Park, J.: Sym-NCO: leveraging symmetricity for neural combinatorial optimization. In: Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1936–1949 (2022)
Joshi, C.K., Laurent, T., Bresson, X.: An efficient graph convolutional network technique for the travelling salesman problem, arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.01227 (2019)
Wu, Y., Song, W., Cao, Z., Zhang, J., Lim, A.: Learning improvement heuristics for solving routing problems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33 (9), 5057–5069 (2021)
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
d O Costa, P.R., Rhuggenaath, J., Zhang, Y., Akcay, A.: Learning 2-opt heuristics for the traveling salesman problem via deep reinforcement learning. In: Asian Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 465–480 (2020)
Ma, Y., Li, J., Cao, Z., Song, W., Zhang, L., Chen, Z., Tang, J.: Learning to iteratively solve routing problems with dual-aspect collaborative transformer. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 11 096–11 107 (2021)
Chen, X., Tian, Y.: Learning to perform local rewriting for combinatorial optimization. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 6281–6292 (2019)
Gao, L., Chen, M., Chen, Q., Luo, G., Zhu, N., Liu, Z.: Learn to design the heuristics for vehicle routing problem, arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.08539 (2020)
Lu, H., Zhang, X., Yang, S.: A learning-based iterative method for solving vehicle routing problems. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, pp. 1–15 (2020)
Xin, L., Song, W., Cao, Z., Zhang, J.: Neurolkh: combining deep learning model with lin-kernighan-helsgaun heuristic for solving the traveling salesman problem. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 7472–7483 (2021)
Kool, W., van Hoof, H., Gromicho, J., Welling, M.: Deep policy dynamic programming for vehicle routing problems. In: Proceedings of Integration of Constraint Programming, Artificial Intelligence, and Operations Research: 19th International Conference, pp. 190–213 (2022)
Fu, Z.-H., Qiu, K.-B., Zha, H.: Generalize a small pre-trained model to arbitrarily large tsp instances. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 7474–7482 (2021)
Chaslot, G. M. J.-B. C.: Monte-carlo tree search (2010)
Veličković, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Liò, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, pp. 1–12 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 448–456 (2015)
Download references
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China [Grant Nos. 62173258, 61773296].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Computer Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Qi He & Feng Wang
Hongyi Honor College, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Jingge Song
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Feng Wang .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Central South University, Changsha, China
Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Zheng-Guang Wu
Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
UNSW Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper.
He, Q., Wang, F., Song, J. (2024). Two-Stage Attention Model to Solve Large-Scale Traveling Salesman Problems. In: Luo, B., Cheng, L., Wu, ZG., Li, H., Li, C. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14448. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8082-6_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8082-6_10
Published : 15 November 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-8081-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-8082-6
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Solution. 20 100 = amount base. The percent in this problem is 20%. Write this percent in fractional form, with 100 as the denominator. 20 100 = 30 n. The percent is written as the ratio 20 100, the amount is 30, and the base is unknown. 20 ⋅ n = 30 ⋅ 100 20 ⋅ n = 3, 000 n = 3, 000 ÷ 20 n = 150.
This math video tutorial explains how to solve percentage, base, and rate problems.Percentages Made Easy: https://www.youtube.com/watc...
Solving Percent Problems: Percent Decrease. Finding the percent decrease in a number is very similar. To find the percent of decrease: Subtract the two numbers to find the amount of decrease. Using this result as the amount and the original number as the base, find the unknown percent.
Now we can solve our equation for x. 10 = 80x Original equation. 10 80 = 80x 80 Divide both sides by 80. 1 8 = x Reduce: 10 / 80 = 1 / 8. 0.125 = x Divide: 1 / 8 = 0.125. But we must express our answer as a percent. To do this, move the decimal two places to the right and append a percent symbol.
Learn how to calculate and solve percent problems using the percent formula. Learn how to calculate and solve percent problems using the percent formula. ... {blue}{Percent} = \color{ black }{Part} \ ÷\) Base; Percent Problems Percent Problems - Example 1: \(2.5\) is what percent of \(20\)? Solution: In this problem, we are looking for the ...
This video will demonstrate how to solve problems about percentage, base and rate.Please like and follow our facebook page:https://www.facebook.com/MathTeach...
Identify the percent. Well, that looks like 25%, that's the percent. The amount and the base in this problem. And based on how they're wording it, I assume amount means when you take the 25% of the base, so they're saying that the amount-- as my best sense of it-- is that the amount is equal to the percent times the base. Let me do the base in ...
Problems involving percents have any three quantities to work with: the percent, the amount, and the base. The percent has the percent symbol (%) or the word "percent." In the problem above, 15% is the percent off the purchase price. The base is the whole amount. In the problem above, the whole price of the guitar is $220, which is the base.
Examples, solutions, and videos that will help GMAT students review how to solve percent word problems. The following diagram shows some examples of solving percent problems using the part, base, rate formula. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions of solving percent problems. Solving Percent Problems. Show Step-by-step Solutions.
So we have the percent times the base. We have the percent times the base is equal to some amount. And you could try to solve this in your head. This is essentially saying 25% of some number, 25% times some number is equal to 150. If it helps, we could rewrite this as 0.25, which is the same thing as 25%. 0.25 times some number is equal to 150.
Step 1: Identify the percent, amount, and base from the given problem. Step 2: Write an equation to represent the relationship between the percent, amount, and base. Step 3: Solve for the missing ...
Percentage Worksheet. Share this page to Google Classroom. Objective: I can find the base number in a percent problem. Example: 8 is 32% of what number? Solution: Answer: 25. Fill in all the gaps, then press "Check" to check your answers. Use the "Hint" button to get a free letter if an answer is giving you trouble.
To solve problems with percent we use the percent proportion shown in "Proportions and percent". a b = x 100 a b = x 100. a b ⋅b = x 100 ⋅ b a b ⋅ b = x 100 ⋅ b. a = x 100 ⋅ b a = x 100 ⋅ b. x/100 is called the rate. a = r ⋅ b ⇒ Percent = Rate ⋅ Base a = r ⋅ b ⇒ P e r c e n t = R a t e ⋅ B a s e. Where the base is the ...
This is the full video about percentage, rate, and base. It will help you understand how to find and solve for the percentage, rate, and base in a given prob...
The base is the original value in a percent problem. It is the whole or the original amount before a percentage is calculated. For example, if you're calculating 20% of 80, then 80 is the base. Key Formulas. The following formulas are essential when dealing with percent, rate, and base: Percent = (Part / Whole) * 100. Rate = (Part / Base) Base ...
Percent word problems. 2 % of the students at Hamilton Middle School have red hair. There are 700 students at Hamilton Middle School. How many students at Hamilton Middle School have red hair? Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more.
Problems that deal with percentage increase and decrease as well as problems of percent of quantities. ... y = 30 and solve for x which the original price. x - 0.22 x = 30 0.78 x = 30 x = $38.5 Check the solution to this problem by ... Solution to Problem 17 Total area of rectangle Ar = L * W Area of triangle At = (1/2) base * height = (1/2 ...
EXAMPLE 1: 15 is what percent of 120? To solve the problem, identify the given and unknown parts: Given: Base = 120 Unknown: Percent = x Amount = 15 Equation: 120 • x = 15 120• x 15 120 120 x 0.125 12.5% = == 0.125 120 15.000 Percent Proportion Problems involving the percent equation can also be solved with the proportion: Percent Amount (is)
BASE (B=P/R) - The whole in a problem. The amount you are taking a percent of. RATE (R=P/B) - The ratio of amount to the base. It is written as a percent. Applying Percentage, Base, and Rate Worksheets. This is a fantastic bundle which includes everything you need to know about Applying Percentage, Base, and Rate across 15+ in-depth pages.
We can translate the question above in this form: _____% of 720 is 90 or _____% x 720 = 90. Therefore, 720 is the base, while 90 is the percentage. The missing number is the rate. We will now use the formula for finding the rate. Rate = Percentage ÷ Base. Again, based on the given problem, the percentage is 90 while the base is 720
Here are two different ways to solve this problem: Using a double number line: Figure 18.4.2 18.4. 2. We can divide the distance between 0 and 36 into four equal intervals, so 9 is 14 1 4 of 36, or 9 is 25% of 36. Using a table: Figure 18.4.3 18.4. 3: A table with two columns. First column, volume in liters, 36, 9.
2. find the base, percentage or rate or percent in a given problem; and. 3. solve routine and non-routine problems involving the percentage, rate and base using appropriate strategies and tools. Grade 6 Mathematics Quarter 2 Self-Learning Module: Finding the Percentage, Base and Rate in a Given Problem Math-G6-Q2-Mod4-v2
PERCENTAGE, BASE AND RATEFollow me on my social media accounts:Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/MathTutorial...Tiktok:https://vt.tiktok.com/ZSdHt9Nt3/Youtub...
Language: English (en) ID: 660599. 24/01/2021. Country code: PH. Country: Philippines. School subject: Math (1061955) Main content: Percentage, Base, & Rate (1255408) From worksheet author: This serves as additional worksheet to develop skill in identifying and solving for the percentage, base or rate in a given situation.
A high school teacher didn't expect a solution when she set a 2,000-year-old Pythagorean Theorem problem in front of her students. Then Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson stepped up to the challenge.
Based on the results of data analysis, it is known that the indicator of problem-solving ability with the highest indicator is understanding the problem of 81.75% with a very high category and the lowest indicator of devising a plan is 48.41% with a moderate category. ... The average percentage of mastery of problem-solving skills is 66.27% in ...
This investigation stems from the observed low problem-solving skills among students as indicated in prior research. The primary objective is to evaluate the impact of employing case-based learning on students' problem-solving aptitude concerning buffer solutions. Carried out during April-May 2023, the study involved 11th-grade students at a public high school in Jakarta, Indonesia.
On today's episode. Jonah E. Bromwich, who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times. Stormy Daniels leaving court on Thursday, after a second day of cross-examination in the ...
This paper proposes a two-stage attention model (TSAM) that incorporates the divide-and-conquer strategy and attention model to solve large-scale TSPs efficiently. Experimental results demonstrate that TSAM can rapidly produce promising solutions for TSP instances ranging from 500 to 10,000 nodes. Download conference paper PDF.
Solving Percent Problems. Learning Objectives. Identify the amount, the base, and the percent in a percent problem. Find the unknown in a percent problem. Introduction. Percents are a ratio of a number and `100`, so they are easier to compare than fractions, as they always have the same denominator, `100`.