Teach Starter, part of Tes Teach Starter, part of Tes
Search everything in all resources

Natural Disasters – Instructional Slide Deck
Updated: 26 Oct 2023
Investigate rapid changes to Earth's surface and other natural disasters such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides with this instructional slide deck.
Editable: Google Slides
Pages: 1 Page
- Curriculum Curriculum: TEKS
Grades: 3 - 5
- Google Slides Sign up to Plus
Get inspired!
Tag #TeachStarter on Instagram for a chance to be featured!

Natural Disasters for Kids
Are you starting to teach your students about natural disasters ? If you are looking for a ready-to-go slide deck that covers this science material with integrated check-for-understanding points, you have come to the right place!
This instructional slide deck is an engaging and interactive way to help your students learn how the Earth can change quickly. Over a series of 27 slides, students will examine images and informational text and participate in activities to understand different natural disasters. The natural disasters covered in this presentation are:
- Earthquakes
Learn About Rapid Changes’ to Earth’s Surface
Use this instructional slide deck to help your third and fourth-graders understand the different types of natural disasters. Students will learn about
- How the surface changes
- What causes each natural disaster
- Where they take place
- And other fun facts!
Tips for Differentiation + Scaffolding
A team of dedicated, experienced educators created this resource to support your science lessons.
If you have a mixture of above and below-level learners, check out these suggestions for keeping students on track with the concepts:
🆘 Support Struggling Students
Help students who need help understanding the concepts by
- Complete the instructional slides in short, 10-15 minute “chunks” to allow for processing.
- Provide students with a printout of the slides to refer to during the lesson.
Easily Prepare This Resource for Your Students
Use the download button to download the editable Google Slides resource.
This resource was created by Kaylyn Chupp, a teacher in Florida and Teach Starter Collaborator.
Teach Starter Publishing
We create premium quality, downloadable teaching resources for primary/elementary school teachers that make classrooms buzz!
Write a review to help other teachers and parents like yourself. If you'd like to request a change to this resource, or report an error, select the corresponding tab above.
Suggest a Change
Would you like something changed or customised on this resource? While our team makes every effort to complete change suggestions, we can't guarantee that every change will be completed.
Report an Error
Did you spot an error on this resource? Please let us know and we will fix it shortly.
Are you having trouble downloading or viewing this resource? Please try the following steps:
- Check that you are logged in to your account
- For premium resources, check that you have a paid subscription
- Check that you have installed Adobe Reader ( download here )
If you are still having difficulty, please visit the Teach Starter Help Desk or contact us .
You may also like
- Earth and Space Science →
- Teaching Slides →
- Earth Science →
- Natural Disasters →
- 3rd Grade →
- 4th Grade →
- 5th Grade →
- Google Slide →

Water Conservation Foldable
Display different ways to save water with this water conservation foldable.

Water Overuse – Infographic Poster and Worksheet
Explore the overuse of water and its effects on the world’s population with this eye-opening infographic poster and accompanying comprehension worksheet.

Natural and Built Environments Sort Activity
A natural and built environments sort activity.
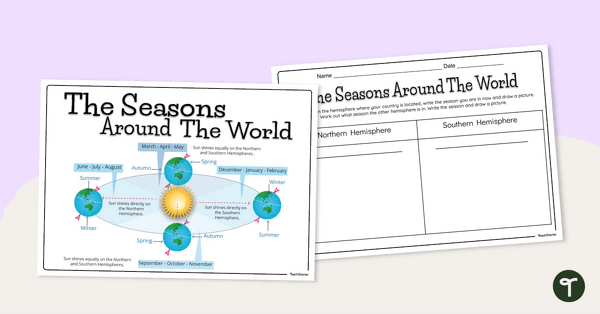
The Seasons Around the World Posters and Worksheet
A diagram showing the Earth's rotation around the sun and the corresponding seasons in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
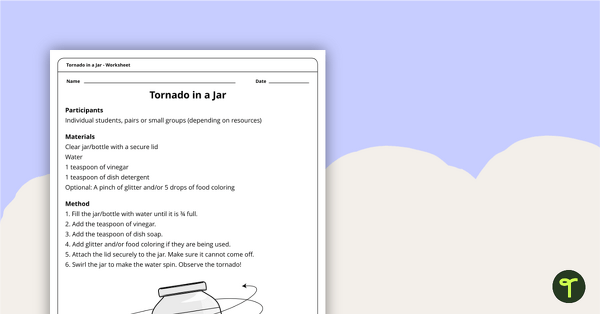
Tornado in a Jar Worksheet
A science activity that demonstrates some properties and effects of motion.

Ways to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint - Poster
Display this poster when learning about sustainability.

Four Seasons Spinner Activity - Northern Hemisphere
Spinner resource to consolidate your students' knowledge of the different seasons.

Seasons Sorting Activity
Teach students in K-2 the proper clothing, activities, and objects for different types of weather with this four seasons activity.

My Ecological Footprint - Worksheet
A worksheet for students to evaluate their family's ecological footprint and compare it with the class.
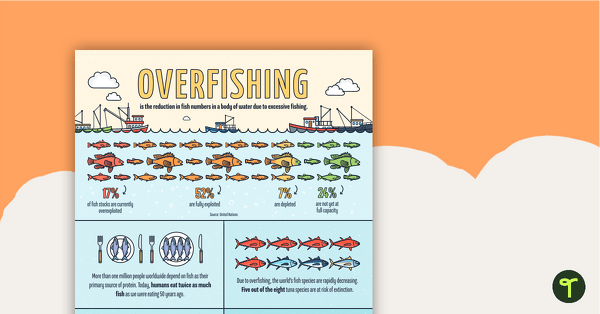
Overfishing – Infographic Poster and Worksheet
Explore overfishing and its effects on marine environments with this eye-opening infographic poster and accompanying comprehension worksheet.

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Natural disasters presentation
Published by Eustacia Bishop Modified over 7 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Natural disasters presentation"— Presentation transcript:

Calhoun County Schools – Technology Integration Project 2005

What are Natural Disasters?

Catastrophic Event. An event that results from Earth processes and that can cause damage and endanger human life Weather Geologic –tornadoearthquake –hurricane.

Weather Emergencies and Natural Disasters In this lesson, you will Learn About… Different types of weather emergencies and natural disasters. Safety measures.

Weather Extreme Weather. Summary Thunderstorms Tornadoes Floods Droughts Hurricanes, Typhoons & Tropical Cyclones Blizzards.

NATURAL DISASTERS & Other Things You Need to Take Notes On.

Research Class notes Cause and Effect of Catastrophes.

Fast Changes Foldable Earth Science.

Natural Disasters around the world. What is a natural disaster? A natural disaster is the effect of a natural hazard. There are many different types,

Unit 4 Lesson 4 Severe Weather and Weather Safety

JH-KEADLE Catastrophic Events.

Volcanoes A volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock below the surface of the earth. When pressure builds up, eruptions occur.

Severe Weather. Thunderstorms Small intense systems that can produce strong winds, rain, lightning and thunder. Need 2 conditions –Air near surface needs.

Hurricanes Hurricanes form in the water. From space they look like a huge cloud with an eye in the middle. Only a few hurricanes made it to land, when.

Intro to WeatherIntro to Weather Clip Week 4 GLEs 6, 10, 17.

The Earth’s Atmosphere: Weather Related Phenomena SOL 6.6 Part 6.

Weather Joey Reitebach. Weather Weather is the day to day conditions of a place. Weather is the day to day conditions of a place.

COS: Identify ways to prepare for natural disasters in the United States. Examples: preparing for earthquakes by identifying structural needs of homes.

Unit 11 Lesson 4 Severe Weather and Weather Safety Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Natural Disasters
Mar 11, 2019
700 likes | 977 Views
Natural Disasters. Natural disasters by far account for the greatest loss of life and the greatest amount of property damage than any other type of event.
Share Presentation
- flash flood
- flood warnings
- flood warning
- flash flood watch
- special flood hazard area

Presentation Transcript
Natural Disasters • Natural disasters by far account for the greatest loss of life and the greatest amount of property damage than any other type of event. • The United States is becoming more vulnerable to natural hazards mostly because of changes in population and national wealth density--more people and infrastructure have become concentrated in disaster-prone areas.
Worst Earthquake • July 28, 1976 - The world's most devastating quake of the 20th century (magnitude 7.8) hit the sleeping city of Tangshan, in northeast China. • The official death toll was 242,000. • Some unofficial estimates put the actual number of dead as high as 655,000.
Worst Volcano • May 8, 1902 - Mt. Pelee erupted on the Caribbean island of Martinique, destroying the capital city of St. Pierre. Up to 40,000 were killed.
Worst Flood • July-August 1931 - Massive flooding of China's Yangtze River led to more than three million deaths from drowning, disease and starvation.
Worst Pandemic • 1918-1919 - An epidemic of "Spanish Flu" spread around the world. At least 20 million died, although some estimates put the final toll at 50 million. • It is estimated that between 20 per cent and 40 per cent of the entire world's population got sick.
Worst US Flood • 1889 • May 31, Johnstown, Pa.: collapse of South Fork Dam left more than 2,200 dead.
Worst US Hurricane • 1900 • Sept. 8, Galveston, Tex.: an estimated 6,000–8,000 dead, mostly from devastation due to tidal surge.
Worst US Tornado • 1925 • March 18, Mo., Ill., and Ind.: great “Tri-State Tornado”; 689 dead; over 2,000 injured. Property damage estimated at $16.5 million.
Worst US Earthquake • 1906 • April 18, San Francisco: earthquake accompanied by fire razed more than 4 sq mi; estimates range from 700 to 3,000 dead or missing.
Natural Disasters • Natural hazards are more predictable than any other hazard. • Although may not know exactly when a natural disaster will occur, precisely where they will strike, or how severe they will be, past experience can be used to identify areas that are most vulnerable to certain types of natural disasters.
Natural Disasters • The largest single category of repetitive threats results from weather or geological events that can affect any area of the country. • Their impact can be localized or widespread, predictable or unpredictable; resulting damage can range from minimal to major.
Natural Disasters • Depending on the severity of the incident, they can have a long-term impact on the infrastructure (roads, bridges, and utilities) of any given location. • Threats involving landslide, tornado, tsunami, volcano, wildlife, thunderstorm, and winter storm.
Natural Disaster Planning • Specifically, the following steps are involved in the process: • Writing a management policy • Organizing a planning committee • Identifying perils or threats and assessing vulnerability to these hazards • Assessing the availability and capabilities of public emergency services, company personnel, and equipment resources • Deciding the level of response capability based upon local needs and regulatory requirements • Organizing the emergency response team • Writing the plan • Training personnel • Testing the plan
Earthquakes • An earthquake is a wave-like movement of the earth's surface. • The earth's crust and upper part of the mantle are consistently pushing and moving against one another along what are known as fault lines. • When rock masses slip along a fault, the energy of an earthquake is released in seismic waves. • An earthquake also can be produced by volcanic eruptions. Earthquakes can be extremely violent.
Interstate highway collapse in 1989 San Francisco Earthquake where 41 motorists were killed.
Richter Scale • Richter scale, invented by Charles F. Richter in 1934. • The damage caused by an earthquake depends on its severity or intensity. • The most widely known indicator of severity, the Richter scale, measures the energy released • A change of one full point in the Richter scale represents a difference factor of about 30 in energy released. • Thus, an earthquake of magnitude 7 is roughly 30 times as powerful – in terms of energy released – as one of magnitude 6.
Richter Scale
Modified Mercalli (MM) Intensity scale • Another scale is the Mercalli scale. • Invented by Giuseppe Mercalli in 1902 • Today, geologists use what is known as the Modified Mercalli (MM) Intensity scale to measure the intensity of ground shaking at a particular site.
Signs and Warnings • Earthquakes usually occur without warning. • Earthquake monitoring is conducted by the U.S. Geological Survey, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and universities throughout the United States. • However, the exact time and place an earthquake will occur still cannot be precisely.
Earthquake Risk Maps • Though quakes usually strike without warning, scientists have produced risk maps that show areas where an earthquake is likely to occur. • Other clues to the probability of a quake come from studying faults, measuring the tilt of the earth's crust, watching changes in the water levels of wells, and even observing the behavior of animals.
Immediate Dangers • The actual movement of the ground is seldom the direct cause of death or injury. • Earthquake-related casualties are commonly caused by: • partial or total building collapse, including toppling chimneys or walls, falling ceiling plaster, light fixtures, and pictures; • flying glass from broken windows and skylights (this danger may be greater from windows in high-rise structures): • overturned bookcases, fixtures, and other large furniture and appliances; • fires from broken chimneys and broken gas lines: • fallen power lines; and • an inappropriate or drastic human reaction caused by fear.
Secondary Emergencies • Fires caused by earthquakes are particularly dangerous. • Water mains may be broken and fire-fighting equipment may be unable to reach the fire. • Broken gas lines often are a major cause of earthquake-related fires. Damage to buildings, utility lines, bridges, or dams. • Water supplies can become contaminated by seepage around broken water mains. • Damage to roadways and to other means of transportation may create food and other resource shortages if transportation is interrupted.
Advanced National Seismic System Network • The Advanced National Seismic System Network will be a nationwide network of at least 7000 shaking measurement systems, both on the ground and in buildings.
Advanced National Seismic System Network • Provide emergency response personnel with real-time earthquake information. • Provide engineers with information about building and site response. • Provide scientists with high-quality data to understand earthquakeprocesses and solid earth structure and dynamics.
Seismic Probability MapsU.S. Geological Survey • Hazard maps are available from the US Geological Survey • http://earthquake.usgs.gov/research/hazmaps/products_data/images/nshm_us02.gif
Floods • Floods can be slow or fast rising. • They are sometimes seasonal, as when winter or spring rains and melting snow fill river basins with too much water too quickly. • Flash floods are usually the result of extremely heavy rain or snow and are sudden.
1993 Mississippi Flood • The 1993 midwest flood was one of the most significant and damaging natural disasters ever to hit the United States. • Damages totaled $15 billion, 50 people died, hundreds of levees failed, and thousands of people were evacuated, some for months.
Comparison Photos of the Mississippi, 1993
Mississippi and Missouri River Basin, 1993
Flood Experiences • On the average, each year more than 300,000 people are driven from their homes by floods, 200 flood-related fatalities occur, and $2 billion in total flood damages are sustained. • The worst recorded flood in terms of loss of lives was the 1889 flood in Johnstown, Pennsylvania, which resulted in the loss of more than 2,200 lives.
FEMA Map Services • Special flood hazard areas for some 18,000 communities are identified on a Flood Hazard Boundary Map or a Flood Insurance Rate Map issued by FEMA. • Many maps provide base flood elevations.
Floodways • FEMA also provides many communities with data to help them designate floodways. • The floodway is that part of the stream channel, plus any adjacent floodplain land, that must be reserved in order to allow the discharge of the base flood ("100-year flood") without increasing flood heights.
National Flood Insurance Program • Every community participating in the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) is required to maintain a repository for their flood maps. • The NFIP is a Federal program enabling property owners to purchase flood insurance. • FEMA administers the NFIP in communities throughout the United States. • Communities in the NFIP must require new buildings in the special flood hazard area to be constructed so that the lowest floor will be located at or above the base flood elevation.
Signs and Warnings • A flood may be build in areas near streams and rivers • Monitor radio for flood forecasts • Flash floods occur swiftly. • Flood warnings are issued by the National Weather Service. • Local police, the sheriff, the highway patrol, the county flood control district office, and other local agencies may also supply flood warnings.
Signs and Warnings • A flash flood watch is issued when flash flooding is possible within the designated watch area: be alert • A flash flood warning is issued when a flash flood has been reported or is imminent: take necessary precautions • A flood warning is issued as an advance notice that a flood is imminent or is in progress at a certain location or in a certain river basin.
Immediate Dangers • The immediate danger from flash floods is from the strength of the water current as it surges through an area, carrying debris and causing injuries and drowning • Floods can interrupt power, disable fuel sources, and make roads impassable. People may be stranded in their homes, or be unable to reach their homes.
Long Term Dangers • Long-term dangers include the outbreak of disease, widespread animal death, broken sewage lines and widespread water supply pollution broken gas lines, downed power lines, and fires. • Large-scale flooding can disrupt a community for a long time while utilities are restored, debris is cleared, and property is repaired.
Preparedness • Stockpile emergency building materials such as sandbags, plywood, plastic sheeting, and lumber. • Develop an evacuation and preparedness plan. • If in a flash flood area, have several alternate routes to ensure rapid evacuation. • Maintain emergency supplies such as a first aid kit, portable radio, • Store drinking water in jugs and bottles.
Prevention • Avoid building in a floodplains • Implement flood prevention strategies into building designs and equipment designs
Mitigation • FEMA'S The Mitigation Division manages the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) and a range of programs designed to reduce future losses to homes, businesses, schools, public buildings and critical facilities from floods, earthquakes, tornadoes and other natural disasters. • Mitigation includes such activities as: • Complying with or exceeding NFIP floodplain management regulations. • Adopting zoning ordinances that steer development away from areas subject to flooding, storm surge or coastal erosion.
Response • As flood waters rise, take these key precautions: • Secure all outdoor items or store them inside on upper levels • Move all valuable household possessions to upper levels away from rising floods. • Move cars, machinery, and all livestock to higher ground • Check emergency food and water supplies – keep them high and dry. • Listen to radio announcements from emergency officials. If you are told to evacuate, do so immediately. • Do not attempt to drive over a flooded road • In a flash flood warning, move immediately to high ground. • Because of the speed with which a flash flood travels, there is no time to save any possessions or implement any precautionary measures.
Recovery • Have all drinking water tested by local health authorities before using. • Before entering a building, check for structural damage; make sure it is not in danger of collapsing. • Check utilities • Report broken utility lines to appropriate authorities • Keep in mind that floods can cause landslides, mudflows, and power outages
Tornadoes • Tornados are relatively short-lived local storms. • They are composed of violently rotating columns of air that descend in the familiar funnel shape from thunderstorm cloud systems. • The weather conditions that tend to generate tornados are unseasonably warm and humid earth surface air, cold air at middle atmospheric levels, and strong upper-level jet stream winds. • Tornados can occur anywhere in the United States during any month of the year. • The destruction path of a tornado averages about 250 yards in width and 15 miles in length. • However, in extreme conditions, a tornado may travel more than 300 miles and leave a path of total destruction more than a mile wide. • Tornados will travel up to sixty miles per hour, with wind speeds approaching 400 miles per hour within the tornado's center.
SKYWARN Spotters Network • To obtain critical weather information, the National Weather Service of the U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and cooperating organizations, have established SKYWARN Spotter Networks
Greensburg, KS, June 4, 2007 • At 9:45 p.m. CDT on May 4, 2007, Greensburg was hit by an EF5 tornado. • The tornado was estimated to be 1.7 miles in width and traveled for nearly 22 miles. • Ninety-five percent of the city was confirmed to be destroyed, with the other five percent being severely damaged. • The National Weather Service estimated winds of the tornado to reach 205 mph. • Twelve fatalities were attributed to the tornado, ten of them residents of Greensburg. • Tornado sirens sounded in the city twenty minutes before the tornado struck, and a tornado emergency was issued, which undoubtedly saved many lives.
Greensburg, KS, June 4, 2007
Tornado Myths • MYTH: Areas near rivers, lakes, and mountains are safe from tornadoes. FACT: No place is safe from tornadoes. In the late 1980's, a tornado swept through Yellowstone National Park leaving a path of destruction up and down a 10,000 ft. mountain. • MYTH: The low pressure with a tornado causes buildings to "explode" as the tornado passes overhead.FACT: Violent winds and debris slamming into buildings cause most structural damage. • MYTH: Windows should be opened before a tornado approaches to equalize pressure and minimize damage.FACT: Opening windows allows damaging winds to enter the structure. Leave the windows alone; instead, immediately go to a safe place.
Signs and Warnings • Tornados develop during severe thunderstorms and hurricanes. • While not all thunderstorms and hurricanes create tornados, the potential is there.
- More by User

Natural Disasters Part One: Pathophysiology Part Two: Environmental Physiology Part One - Pathophysiology Definition : The functional changes associated with or resulting from disease or injury; the study of such changes (distinguished from s structural defect)
1.45k views • 39 slides

Natural Disasters. By: Patrick L. Abbott. Chapter 9. Climate Change. Overview. Climate Early Earth Climate - A Runaway Greenhouse Climate History of the Earth: Time Scale in Millions of Years Glacial Advance and Retreat: Time Scale in Thousands of Years. Overview (cont.).
967 views • 14 slides

Natural Disasters. The Earthquake and an explanation on Mountains. Jacinta 8D. Earthquakes are terrible! Especially if you get caught in one. Through this special presentation I will guide you through as I explain about our topic; landforms .
595 views • 16 slides

NATURAL DISASTERS
NATURAL DISASTERS. Chandon Covington-Staton November 1, 2012 Ms. Robles. TSUNAMIS. A tsunami is a giant wave or series of waves created by an undersea earthquake, volcanic eruption or landslide .
503 views • 6 slides

Natural Disasters. BY: Jasmine Bess. Tsunami.
290 views • 11 slides

Natural Disasters. In the water. Hurricanes. In the Northern hemisphere, hurricanes spin counter clockwise, but the move clockwise. (In the Southern Hemisphere, it’s the opposite!) The center of the hurricane is the eye. The eye is the most calm area of the hurricane.
352 views • 11 slides

Natural Disasters . A disaster caused by natural forces. Earthquake. A shaking of the ground caused by moving underground plates . Hurricane.
853 views • 15 slides

Natural Disasters. Natural disasters happen all across the globe at different periods of time such as : Volcanoes,Tsunami’s,Huricanes,Forest fires and typhoons. Ice Storms . Ice storms happen usually in mostly America, Oklahoma it is basically rain that falls through freezing air.
400 views • 5 slides

Natural Disasters. Tintinalli Chap. 7. Impact. 3,197 events worldwide between 1995-2004 1500-2.5 million deaths per event Burden likely to rise Increasing population in high-risk areas Expanding technology Loss of resources is uniformly present Economic, social, health.
358 views • 17 slides

Natural Disasters. By: Seth Hunter. Tsunami.
263 views • 6 slides

natural disasters
natural disasters. Natural disaster - a natural phenomenon of an extraordinary nature and leads to disruption of the normal population, the loss of life, damage and destruction of property. recently happened terrible catastrophe (flood) in Brazil, it took the lives of over 500 people.
1.08k views • 8 slides

Natural Disasters. By: Grayson . Where does your disaster happen. Volcanoes typically happen/erupt on fault lines like the Ring of Fire A fault line is where a plate in the Earth cracks. How often does your disaster happen.
256 views • 11 slides

Natural Disasters. Subject: English Teacher: A.Petkoska Students: Ana Todoroska , Ivona Ilijevska , Simona Petroska.
260 views • 9 slides

Natural Disasters. 5Ws and H about the disaster. 6 th - Student/Disaster. Monica – Hurricane Katrina Angeles – Haiti Earthquake Ibrahim – Cyclone Nargis Salvador – Hurricane Katrina Nasser – The Black Death Thomas – Haiyuan Earthquake. 7 th – Student/Disaster. Pakistan Earthquake
412 views • 6 slides

Natural Disasters. By: Raymon Hughes Joselyn Barron Enrique Rodriguez. They Poured fire on us from the sky.
225 views • 10 slides

Natural Disasters. The Effects of an Earthquake. http://cse.ssl.berkeley.edu/img/earthquakes/Railroad.gif. http://tasmania.globat.com/~archibase.net/dl/articles/kobe/4.jpg. http://www.geography.learnontheinternet.co.uk/images/nathaz/sanfran.jpg. The Effects of a Volcano.
300 views • 8 slides

Natural Disasters. Hurricanes. Hurricanes. Massive tropical storms Occur over oceans near the equator. Characteristics. Rotational winds Circular motion High-speed winds. Characteristics. Energy 12X that of other storms Eye Area of low pressure Clear skies No rainfall. Causes.
231 views • 8 slides

Natural Disasters. What are natural disasters? Ms. Gleason 9 th Grade. Definition. A natural disaster is the effect of a natural hazard that affects the environment, and leads to financial, environmental and/or human losses. TYPES OF DISASTERS. F lood T ornado H urricane
543 views • 6 slides

Natural Disasters. Tornadoes. A tornado is a violent, rotating column of air which is in contact with both the ground and a cloud. Tornadoes. Tornadoes are most common during the spring and early summer. Tornado alley.
251 views • 8 slides

Natural Disasters. John Gyakum (AOS) John Stix (EPS). What are we talking about ?. DISASTER: dis - unfavourable astro - stars To the ancients, disasters were precipitated by the stars. Our role as scientists.
524 views • 40 slides
Home Collections Nature Natural Disasters Types Of Natural Disasters Powerpoint
Types Of Natural Disasters PPT Template & Google Slides

Types Of Natural Disasters
Features of the template:.
- 100% customizable slides and easy-to-download
- The slides contain 16:9 and 4:3 formats.
- Easy to change the slide colors quickly.
- It is a well-crafted template with an instant download facility.
- We designed this slide with a stunning design.
- You can use this in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
- Natural Disasters
- Types of Natual Disaster
- Natural Disaster Infographics

25+ Templates

267+ Templates

128+ Templates

Agriculture
61+ Templates

53+ Templates

13+ Templates


Renewable Energy
67+ Templates

70+ Templates

56+ Templates

31+ Templates
You May Also Like These PowerPoint Templates


- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
Frequency and disaster patterns
Damage and deaths, disaster warning systems.

- Can people cause avalanches?
- What causes a landslide?
- How can the hazards of landslides to humans be mitigated?
- What is a tsunami?
- What have been some of the worst tsunamis in history?

natural disaster
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies - What is a disaster?
- U.S. Department of Homeland Security - Natural Disasters
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - PubMed Central - Natural Disasters
- NeoK12 - Educational Videos and Games for School Kids - Natural Disaster
- Table Of Contents

Recent News
natural disaster , any calamitous occurrence generated by the effects of natural, rather than human-driven, phenomena that produces great loss of human life or destruction of the natural environment , private property, or public infrastructure . A natural disaster may be caused by weather and climate events or by earthquakes , landslides , and other occurrences that originate at Earth ’s surface or within the planet itself. No spot on Earth is immune from a natural disaster; however, certain types of disasters are often limited to or occur more frequently in specific geographic regions.

Weather- and climate-driven natural disasters include flooding caused by heavy rains associated with hurricanes and typhoons ( tropical cyclones ) and other intense storms; drought , famine , and wildfires brought on by heat waves and shifts in precipitation patterns; wind -generated devastation caused by tropical cyclones, tornadoes , derechos , and other windstorms ; and damage and loss of life caused by blizzards and heavy snowfalls. Earth-driven natural disasters include large volcanic eruptions (which produce lava flows, explosions, toxic gas clouds, ash falls, and pyroclastic flows that damage populated areas) and strong earthquakes (which result from the sudden fracturing of Earth’s crust ) powerful enough to damage or destroy built-up areas near their origin points.

Some phenomena that produce natural disasters may be caused by a combination of several different forces. For example, landslides (the movement of large masses of rock , debris, and soil downslope) may be caused by rains that saturate the soil on an unstable slope, or they may be triggered by earthquakes. In a similar manner, the buildup of snow on mountain slopes increases the risks of localized avalanches . Tsunamis , catastrophic ocean waves that can rise as high as 30 metres (about 100 feet) above normal sea level , are produced by submarine earthquakes, underwater or coastal landslides, volcanic eruptions, or meteor or comet impacts. The largest tsunamis are fast-moving waves that can travel across oceans to wreak havoc in coastal areas separated thousands of kilometres from one another.

Certain types of natural disasters are more likely to occur in specific geographic regions, and in some places these events occur with seasonal regularity, as in the spring tornado season in the United States or the summer-and-fall hurricane season in the Atlantic Ocean , Caribbean Sea , and the Gulf of Mexico . Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are most frequent near tectonic plate boundaries, and an especially active boundary exists between the Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates.
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO)—a United Nations (UN) agency that monitors Earth’s land, water , and atmosphere —reported in 2021 that the number of natural disasters per decade showed a fivefold increase from 1979 to 2019, and data collected in the EM-DAT, an international disaster database maintained by the Center for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters, Brussels, indicate that more than 300 disasters have been tallied each year since 1998. Though many natural disasters are neither preventable nor largely predictable, the WMO report notes that global warming —an increasingly human-driven phenomenon generated by the emission of greenhouse gases , specifically those released by the combustion of fossil fuels —is increasing the frequency of weather- and climate-related natural disasters, such as droughts, heat waves, increasingly intense hurricanes, and flooding due to sea-level rise. Warmer temperatures are causing more extreme weather events by delivering more precipitation to some areas—which may be unused to receiving heavy rains and snows, increasing flooding risk—while delivering less to other areas that rely on it, increasing drought risk. In addition, reliable sources of rainfall, such as the South Asian monsoon , on which agriculture of the Indian subcontinent has long depended, are becoming less predictable, and rain events have become more violent and dangerous, damaging crops and producing more intense flooding. This change has subjected some areas under the monsoon’s influence to extended drought conditions, whereas other areas receive too much rainfall, a pattern that scientists predict will worsen in the 21st century.

The costs of individual natural disasters frequently reach the tens of billions of dollars. Such costs may be associated with damage to crops, buildings, and infrastructure that occurs annually in areas prone to tropical cyclone activity or heavy seasonal rains, with some events, such as the Pakistan floods of 2022 and Hurricane Katrina (which struck the southern United States in 2005), costing more than $30 billion and $186 billion, respectively. Similarly, costs associated with earthquakes, which occur less regularly, can be high (such as China ’s Sichuan earthquake of 2008 and Japan ’s Kōbe earthquake of 1995 , which incurred costs estimated at more than $86 billion and more than $100 billion, respectively).
The number of deaths from natural disasters also varies by location and the intensity of the event; however, the overall trend points to a decline from several hundreds of thousands of deaths annually during the first half of the 20th century to roughly 45,000 deaths globally each year. The number of deaths also varies widely from year to year, with smaller natural disasters (or natural disasters occurring in areas far from human settlement) killing few and shockingly large disasters producing truly massive losses of life. Some of the most notable catastrophic disasters in history include the Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004 (which killed more than 225,000 people), the Tangshan earthquake of 1976 (which resulted in more than 242,000 deaths), the 2010 Haiti earthquake (which by some estimates may have killed at least 300,000 people), and China’s Shaanxi province earthquake of 1556 (which killed more than 800,000 people).
Although deaths from natural disasters have decreased overall, people in lower-income countries often suffer disproportionately, because these locations have fewer resources and thus greater vulnerability to the elements and to food insecurity . In contrast, highly developed countries have better infrastructure (for communications, evacuation procedures, the movement of resources, and the delivery of medical services). In addition, high-income countries can implement policies that limit construction in flood-prone areas or mandate the construction of more earthquake-resistant homes, office buildings, and other structures, thereby reducing the risk of crushing injury and death stemming from building collapses. Consequently, relatively few people die from earthquakes in California , a location well-known for its strong building codes with respect to withstanding earthquakes, compared with places such as Iran and Pakistan, where building codes are either less stringent or whose codes frequently go unenforced.

Advances in weather forecasting and advances in land-based seismic sensors and sensors placed aboard satellites , aircraft, and stationary buoys floating in the world’s oceans have led to the development of various kinds of early warning systems. In some cases, these systems are capable of predicting or accurately classifying the strength of the physical forces that generate natural disasters before they cause damage. The perhaps most widespread and best known of these systems are those used by national weather bureaus that classify, track, and predict various weather events and issue bulletins about storms and other weather and climate phenomena affecting their land areas and sea zones. National weather bureaus are often made up of a network of numerous local offices spread across a country that gauge local weather conditions several times per day. Data collected by these offices can be used to develop weather models that help to predict the strength of a storm , as well as its location, days in advance of its arrival in a local area.
In addition, specialized units within national governments—such as the China Earthquake Administration, the Japan Meteorological Agency, the United Kingdom’s Met Office, India’s National Center of Seismology, the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , and the U.S. Geological Survey—monitor specific physical forces capable of causing the most damaging and deadly natural disasters (that is, earthquakes, tsunamis, droughts , flooding, and winds driven by tornadoes and tropical cyclones). Many of these organizations within specific countries cooperate with their counterparts in others or assist international organizations, such as the WMO and the International Tsunami Information Center, to issue warnings, develop international safety standards, and assess the risks associated with forces that affect several countries or the planet as a whole. Some early warning systems even look beyond Earth’s atmosphere; the near-Earth objects system operated by the European Space Agency and the Scout and Sentry impact hazard systems run by NASA in the United States are a few of several systems designed to detect, track, and predict the risk associated with asteroids , comets, and other extraterrestrial objects capable of striking Earth.
NTRS - NASA Technical Reports Server
Available downloads, related records.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

education technology
252 templates

meet the teacher
30 templates
19 templates

63 templates

cybersecurity
6 templates

public health
39 templates
Natural Disaster Mitigation Plan
It seems that you like this template, natural disaster mitigation plan presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Natural disasters can be devastating and cause immense damage to human lives, infrastructure, and the environment. This is why it is essential to have a plan in place to mitigate these disasters to the best of our abilities. With the help of this amazing minimalist template, creating a plan to mitigate natural disasters has never been easier. The dark background and faded images of natural disasters create the perfect mood for the topic. It provides the structure and guidance necessary to create a comprehensive plan that will minimize the impact of these disasters
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

A new disaster assistance organization helping Claremore residents after tornado damage
by CJ Maclin
CLAREMORE, OKLA. (KTUL) — A new organization is helping Claremore residents in the wake of the tornado that struck their town three weeks ago.
It's called the Claremore and Rogers County disaster assistance.
When NewsChannel 8 arrived at the interview, there was an older gentleman outside putting the pieces of his home back together with a sling on.
This organization explained its process to him and assisted him without any hesitation.
- SEE ALSO: Cleanup and recovery ramp up in Claremore after devastating weekend tornado
The same thing they are doing for the City of Claremore.
“For us specifically, me and my wife, we lost our camper. Everything was completely destroyed. Gone. There wasn’t anything left but the toilet and the frame. And both of our vehicles were also totaled,” said Andrew Klauditz, a Claremore resident affected by the tornado.
Andrew is just one of many Claremore residents who have been helped by the Rogers County Disaster Assistance Organization after the Memorial Day tornado.
Residents are continuing to pick up the pieces from what's left of their homes three weeks later.
Some lost their homes in this disaster and others are trying to hold the city of Claremore together.
One of those organizations is CRCDA who are providing shelter for people after they received a generous amount of aid from one local bank.
“I only see the need in helping out a fellow citizen and getting back to their normalcy that they rightfully deserve. No one asked for a tornado to come and rip apart their life. They didn’t do anything to cause it, but we can do something to fix it. And we need the donations and funds to help that,” said team member of Claremore & Rogers disaster assistance, Kacey Alchammat.
Andrew said that this organization helped his family find a new place to live on a campsite and they didn’t charge his family a dime.
“It was a relief. That’s something a lot of people have been asking me. You must be ecstatic, you must be excited? No, I can breathe. That’s the most important part for me at least. Is that now I can breathe.”
This organization started two days after the tornado struck Claremore.
They set a goal of $500,000.
- SEE ALSO: "Thankful to be alive" - Claremore residents after tornado
Right now, they’ve reached 20% of that goal while receiving nearly 400 applications.
The funds they receive are donor funds.
On Friday, they will be presenting checks to households to start the re-building process.
“It’s a blessing to help anyone in need. When you come out here and you just see the depravity and destruction of what’s happened; and the way that people are having to live currently, said Alchammat. They're living with water leaking in their roof, people needing medical attention that can’t afford it can’t provide it.”
You can donate to the Claremore & Rogers County disaster assistance organization here .
SIGN UP FOR THE CHANNEL 8 NEWSLETTER
Watch CBS News
Keller: Disastrous performance by Biden in first 2024 presidential debate with Trump
By Jon Keller
Updated on: June 28, 2024 / 5:39 AM EDT / CBS Boston
The opinions expressed below are Jon Keller's, not those of WBZ, CBS News or Paramount Global.
BOSTON - President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump each had an obvious goal coming into Thursday night's debate , their first presidential debate of 2024.
For Trump, it was to avoid the clownish behavior and constant interruptions that backfired on him so badly four years ago. And while the fact-checkers will have a field day with his usual parade of boasts and whoppers, for the most part he accomplished his mission. Trump's delivery was crisp and forceful, however dubious the rhetoric.
For President Biden, job number one was to dispel the persistent doubts about his age and cogency. But from the get-go his presentation was halting, his voice raspy . He seemed tired and over-programmed. (During the debate his people told reporters he had a cold. Must have been a bad one.) And Biden provided his enemies with an ample supply of faltering sound bites, including one where he completely lost the thread and declared he had "beat Medicaid."
Biden debate hole
It was a disastrous performance by the incumbent, but will it make a shambles of his candidacy?
The good news for Biden - if you can call it that - is that this debacle occurred more than four months before election day, ample time for events to overtake what happened. But there's no sugar-coating the fact that if the Biden campaign was in a hole before last night, that hole is even deeper now.
And keep in mind, this election still seems likely to be determined by the undecideds, that small group of voters who tend to be uninterested in politics, not following the news closely, and supremely skeptical about partisan politics when they do pay attention.
Uninspired presidential debate
For those who tuned in, neither man offered much inspiration, Biden in the role of the elderly neighbor who isn't making much sense anymore, Trump acting the part of the self-aggrandizing boor at the end of the bar.
Will these unappetizing options keep voters home in November, or cause them to ignore their mail-in ballot? If so, it makes the race a get-out-the-vote contest, with each party trying to whip up their partisans into a "he-must-be-stopped" frenzy. It's the kind of hate-fueled petri-dish that domestic and foreign trolls thrive in and promises to deliver the ugliest four months in U.S. political history. Not to mention what comes after.
Let's hope that come next Thursday, July 4th, the weather is fine, the burgers cook up perfectly, and the fireworks displays are choice. That, at least, will give us something to celebrate.
- Keller @ Large
- Donald Trump

Jon Keller is Political Analyst for WBZ-TV News, and his "Keller @ Large" reports on a wide range of topics are regularly featured during WBZ-TV News at 5 and 6 p.m. Keller's commentaries are also seen weekday mornings at 5:30 a.m. on WBZ This Morning.
Featured Local Savings
More from cbs news.

Mass. Secretary of State concerned over public distrust in election process

These Massachusetts beaches are closed to swimming due to bacteria levels

Biker-runner raises money for Boston hospital treating Declan Lyons

Risk of severe weather in Mass. on Sunday. Map shows timing and path of storm
Opinion | After Biden’s debate disaster: The president’s…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
Daily News e-Edition
Evening e-Edition
- Bramhall’s World: Editorial cartoons
SUBSCRIBER ONLY
Opinion | after biden’s debate disaster: the president’s tough choice about quitting or continuing.

The American economy is the envy of the world. Abortion rights are under threat due to Trump’s appointments to the Supreme Court. The sitting president is on the right side of public opinion on gun rights, health care and much more — immigration remains a very real vulnerability — yet he was less persuasive than a reasonably well-educated man on the street, offering an all-you-can-eat word salad bar in stumbling answer after mumbling answer .
None of this came as a surprise . Even Joe Biden’s strongest supporters have known for months that he is rusty when unscripted in public. That doesn’t mean he is an ineffective president; by all accounts, he understands complex questions and makes intelligent decisions. He has a strong team around him, both in the White House and in federal agencies.
But an election is a binary contest: A candidate either wins or loses, and that win or loss is based not on some elevated intellectual analysis of the quality of the job he does. The political impressions we sometimes dismiss as mere “optics” are, for millions of swing and low-information voters, decisive. A candidate with massive political liabilities and insufficient political strengths does no favors to his cause, however just.
This was not about a stumble or two . The consistent and holistic impression of the night from Biden was of a man who couldn’t make a coherent argument for himself, his party or his ideals. A man who at 81 is well past his prime is now asking the public to reelect him to serve until he is the age of 86.
Biden has some real accomplishments achieved and he feels that he has been a better president than Trump and would be a better president than Trump even at that advanced age. That is not the question, however. The question is whether he can beat Trump in November.
In the 1960s and earlier, both national parties were strong organizations led by bosses with the power to step in and tell a candidate to step aside. No longer: The president is the head of the party; his power comes straight from the voters. Biden ran essentially unopposed in the primaries and at this late date will be the nominee in November unless he himself makes the affirmative choice to bow out.
It would indeed be a big gamble for Biden to step aside. An open convention would be messy, and whoever was hastily chosen — Vice President Kamala Harris or someone else from a plenty-talented field of governors and senators — would have to scramble to rally the Democratic coalition, much less win over independents and any persuadable Republicans.
But after Thursday night’s debate, it’s equally apparent to those who fear a second Trump term that keeping Biden is also a big gamble.
The choice is Biden’s. The moment to search his soul is now. He must make a decision motivated not by pride, but by digging deep and honestly answering a difficult question: Is he the Democrats’ best option to put up a fight against Donald Trump?
More in Opinion

Opinion | Joe Biden has to learn a new trick

Opinion | Presidential elections have major consequences

Opinion | A shot at better health: Guns now an official public health threat

Opinion | Balancing the books: Timely budget season for everyone but Albany

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A. avy123. Disasters can be natural or man-made. Natural disasters include cyclones, earthquakes, tornados, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, floods, wildfires, droughts, avalanches, and landslides. Man-made disasters involve human elements like negligence, intent, or technological failures and include nuclear bombings, acts of terrorism, and oil ...
Download the Biology Subject for High School: Natural Disasters - Tropical Cyclone presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template's design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements ...
Natural disasters are major changes that can damage the earth's land and threaten human and animal lives. They include earthquakes caused by shifting tectonic plates that release shock waves, prolonged droughts like the one in Africa in 1968 that lasted 5 years, powerful cyclones with swirling winds that can destroy infrastructure, flooding from heavy rain or snowmelt that causes rivers to ...
Natural disasters' Impacts & Prevention. A natural disaster is a major event caused by natural hazards that affects the environment and leads to financial, environmental, and human losses. Common natural disasters include floods, tsunamis, tornadoes, hurricanes, cyclones, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, heatwaves, droughts, wildfires ...
Our natural disasters presentation templates category with ready-made slides will captivate your audience and create an impact. Here's what you'll find: Single slides or complete decks: Choose the perfect fit for your presentation, whether you need a single slide to illustrate a point or a full deck to guide you through the whole story. ...
A natural disaster is an extreme event resulting from natural processes of the Earth. Examples include floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis, and other geological processes. NATURAL DISASTERS. A natural disaster can cause loss of life or property damage. It typically leaves some economic damage in its wake ...
With a range of material to cover the different types of disasters, it alternates blocks of text with splash of color and images that bring the subject matter to life. Whether you're talking earthquakes, tornados, volcanic eruptions or any other natural catastrophe, you have everything you need to keep your students glued to your presentation.
These presentation templates with a disaster theme are suitable for presentations related to emergency management, natural disasters, crisis response, and risk assessment. They can be used by professionals in the fields of disaster management, government agencies, NGOs, and educational institutions.
Download the Natural Disasters: Wildfires presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic resources.
Our natural disasters presentation can help you educate your audience on the causes and effects of natural disasters. With customizable slides, you can tailor the content to fit your specific needs. Features of the template: 100% customizable slides and easy to download.
Natural disasters are changes which are so great they may cause damage to the shape of the land or to the lives of people and other living things. Great changes happen deep inside the Earth and on its surface. The changes on the outer part of the Earth happen because of different kinds of weather. 4 A tall column of air spinning round very fast ...
This comprehensive PowerPoint presentation addresses the following topics: the layers of the Earth. plate tectonics. geological natural disasters. meteorological natural disasters. hydrological natural disasters. other natural disasters. natural disaster effects and management. Activities for students are also included.
This instructional slide deck is an engaging and interactive way to help your students learn how the Earth can change quickly. Over a series of 27 slides, students will examine images and informational text and participate in activities to understand different natural disasters. The natural disasters covered in this presentation are:
Usually are once in a while incidents. 3 Examples of a Natural disaster. Earthquakes Floods Hurricanes Tornados Tsunamis Wild Fires. 4 Natural disasters across USA. 5 Earthquakes An earthquake is formed when enough stress builds up in a vault and the stress releases causing an earthquake. If you are in a car stay in and move from under a bridge ...
Natural disasters occur all around the world, from risky floods and tsunamis, to treacherous forest fires and volcanic eruptions. The ring of fire (Pacific Ocean) is the most common place for these catastrophic disasters for example: Tsunamis, earthquakes, hurricanes and much. Download Presentation. volcanic eruptions. tropical areas.
Presentation Transcript. Natural Disasters Natural disasters happen all across the globe at different periods of time such as : Volcanoes,Tsunami's,Huricanes,Forest fires and typhoons. Ice Storms • Ice storms happen usually in mostly America, Oklahoma it is basically rain that falls through freezing air.
Presentation on Natural Disaster - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document discusses different types of natural disasters including cyclones, earthquakes, tornados, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and floods. It provides details on the characteristics of each type of disaster and lists some of ...
Natural Disasters • Natural disasters by far account for the greatest loss of life and the greatest amount of property damage than any other type of event. • The United States is becoming more vulnerable to natural hazards mostly because of changes in population and national wealth density--more people and infrastructure have become concentrated in disaster-prone areas.
Types Of Natural Disasters. Natural disasters can strike anytime, anywhere. From floods and hurricanes to earthquakes and wildfires, the world is prone to a variety of calamities. Floods can submerge entire cities, hurricanes can ravage coastlines, earthquakes can shake entire regions, and wildfires can destroy vast swathes of forests.
natural disaster, any calamitous occurrence generated by the effects of natural, rather than human-driven, phenomena that produces great loss of human life or destruction of the natural environment, private property, or public infrastructure. A natural disaster may be caused by weather and climate events or by earthquakes, landslides, and other ...
Natural disasters can severely injure or kill people and cause immense property damage. In 2010, natural disasters killed 295,000 people and cost insurers $218 billion globally. The 2011 Tsunami and earthquake in Japan killed over 10,000 people, while Hurricane Katrina in 2005 alone caused $81 billion in property damage to New Orleans, flooding ...
These projects use the vantage point of space to address environmental issues across a broad set of themes, including agricultural monitoring, disaster risk and resilience planning, water resource and coastal management, wildfire cartography, health & air quality, and urban development.
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. Natural disasters can be devastating and cause immense damage to human lives, infrastructure, and the environment. This is why it is essential to have a plan in place to mitigate these disasters to the best of our abilities. With the help of this amazing minimalist ...
Presentation: National Disaster Medical System Pilot Program Addition of Ketamine to Tactical Combat Casualty Care Guidelines May 2021 Webinar ... Established in 2008, the National Center for Disaster Medicine and Public Health was established to advance the Nation's medical and public health readiness for disasters, and is a partnership ...
A new organization is helping Claremore residents in the wake of the tornado that struck their town three weeks ago.It's called the Claremore and Rogers County
But from the get-go his presentation was halting, his voice raspy. He seemed tired and over-programmed. He seemed tired and over-programmed. (During the debate his people told reporters he had a cold.
It was clear a political disaster was about to unfold as soon as the 81-year-old commander in chief stiffly shuffled on stage in Atlanta to stand eight feet from ex-President Donald Trump at what ...
Yes, it was that bad. A devious Donald Trump unleashed a torrent of lies, and all President Biden could offer was a pallid, halting presentation — failing to counter the former president's ...