

150+ Engaging STEM Projects for Kids and Students
STEM projects, which encompass science, technology, engineering, and math, are the perfect way to ignite curiosity, develop problem-solving skills, and have a blast while learning.
Are you looking for exciting and educational activities for your kids, students, or even the whole family? Look no further! STEM projects, which encompass science, technology, engineering, and math, are the perfect way to ignite curiosity, develop problem-solving skills, and have a blast while learning. In this blog post, you’ll discover over 150 engaging STEM projects for young learners, elementary school students, middle school students, high school students, and even projects the whole family can enjoy together. Let’s dive in and explore the exciting world of STEM!
Key Takeaways
- Introduce young learners to STEM concepts with fun and easy projects!
- Encourage kids to explore technology, renewable energy, and water filtration through engaging projects.
- Inspire the whole family to learn about rocketry principles, meteorology & astronomy by creating DIY telescopes & backyard weather stations!
Fun and Easy STEM Projects for Young Learners
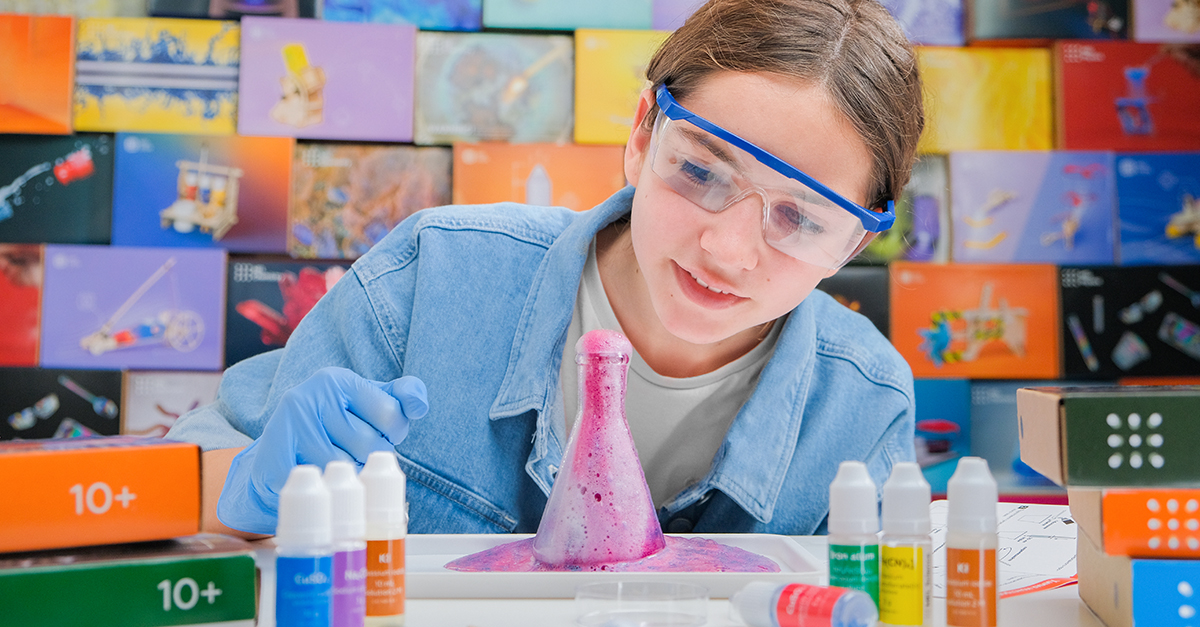

Young minds are naturally curious and eager to explore the world around them. Fun and easy STEM activities for kids, like creating homemade slime, building LEGO towers, and conducting homemade volcano experiments, are perfect for introducing young children to STEM concepts while keeping them engaged and entertained. These projects not only teach kids about science, technology, engineering, and math, but also help them develop critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Starting with basic supplies, most activities can be completed in just 15 to 30 minutes, making them perfect for classroom or home use. The hands-on nature of these projects allows kids to learn by doing, which is often the most effective way to teach and engage young learners. Now, here are some thrilling STEM projects that young learners can immediately embark on!
Creating Homemade Slime
A classic and fun STEM activity for kids is creating homemade slime. This gooey, slimy concoction not only provides hours of entertainment, but also teaches kids about chemical reactions and properties of matter. As they mix ingredients like glue, baking soda, and contact lens solution, they’ll observe how the combination results in a fascinating new substance with unique properties.
To get creative with slime, kids can:
- Experiment with different colors, textures, and even add-ins like glitter or small toys
- Follow instructions and ideas from online resources like Slime Design/Science Buddies and STEAM-Powered Family
- Make slime in various ways, with the range of choices being infinite
This promises endless fun with the egg drop challenge!
Building a LEGO Tower
LEGO bricks have been a popular toy for generations, and they’re also fantastic STEM resources for kids to develop their creativity, problem-solving skills, and engineering abilities. Building a LEGO tower is an exciting engineering challenge that encourages kids to think critically and strategically about how to construct the tallest tower possible.
This activity can be done individually or in groups, making it perfect for both classroom and home settings. Kids can experiment with different building techniques, materials, and styles, and even compete with their friends to see who can build the tallest tower. With this captivating STEM challenge blending enjoyment and education, there are no limits when it comes to stem stands!
Homemade Volcano Experiment
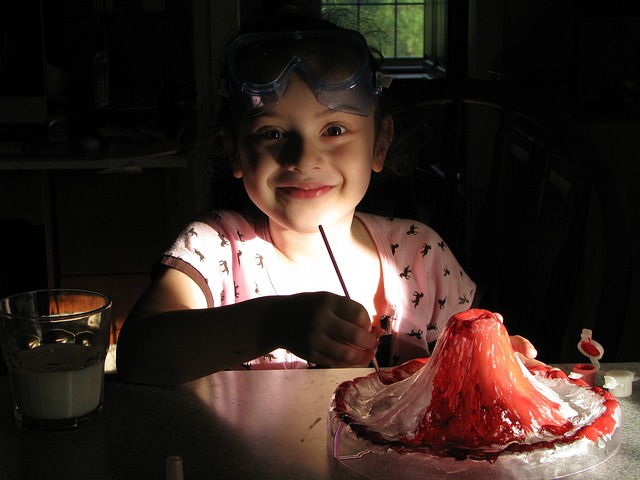
Who doesn’t love a good volcano eruption? The homemade volcano experiment is a classic science activity that introduces kids to chemical reactions and geology in a fun and exciting way. Using simple materials like baking soda, vinegar, and some food coloring, kids can create their very own volcanic eruption right in their own kitchen or backyard.
This hands-on science experiment not only provides a thrilling experience for young learners, but also helps them develop a deeper understanding of how chemical reactions work and the geological processes that occur within our Earth. This enjoyable activity ignites curiosity, motivating kids to delve into the intriguing world of science.
STEM Projects for Elementary School Students

Elementary school students, especially younger kids, are ready to take on more challenging STEM projects that help them develop their problem-solving skills, critical thinking, creativity, and engineering skills. Activities like simple machine construction, solar-powered car design, and building water filtration systems are perfect stem ideas for engaging young minds and teaching them valuable STEM concepts.
By participating in these hands-on projects, elementary school students will not only develop a strong foundation in science, technology, engineering, and math, but also gain a sense of accomplishment and pride in their creations. Let’s delve into some thrilling STEM projects suitable for elementary school students.
Simple Machine Construction

Simple machines are the building blocks of many complex devices we use in our daily lives. They make tasks easier by allowing us to use a single force to do work. Some examples of simple machines include:
- Inclined planes
- Wheels and axles
By understanding how these simple machines work, we can better understand and appreciate the technology that surrounds us.
By constructing their own simple machines, kids can gain a hands-on understanding of how these essential tools work and apply them to various tasks. To build a simple machine, kids will need to choose the type of machine they’d like to create, gather the required materials, and assemble the machine. This activity fosters creativity and problem-solving skills, while enhancing appreciation for the ease that simple machines bring to our lives.
Solar-Powered Car Design
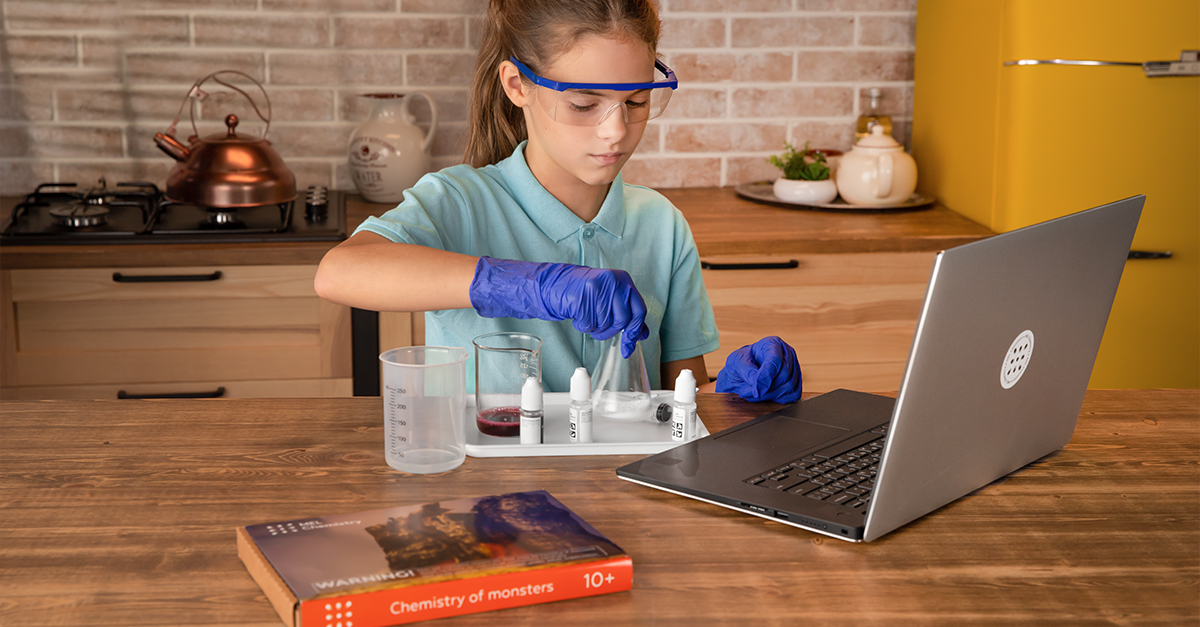

Designing and building a solar-powered car is an exciting and rewarding STEM project for elementary school students. This activity combines engineering, design, and environmental awareness as kids learn about the power of renewable energy and create their own solar-powered vehicles.
To gather materials such as a small solar panel, a motor, wheels, and a lightweight body made from recycled materials, you can create an alternative energy vehicle, like a balloon powered car.
Kids can design, build, and test their cars to see how well they perform in various conditions. This project not only imparts essential STEM concepts, but also cultivates an understanding of the importance of sustainable living and energy efficiency.
Water Filtration System
Clean water is essential for life, and understanding the science behind water filtration can help kids appreciate this vital resource. In this project, kids will create their own water filters using simple materials like:
- Plastic bottles
- Activated charcoal
By building their own water filtration system, kids will learn about the importance of clean water, the process of water filtration, and the effects of pollution on water sources. This practical activity not only imparts crucial STEM concepts, but also encourages kids to consider their actions’ environmental impact and the value of conservation.
Engaging STEM Projects for Middle School Students

Middle school students are ready to tackle more advanced STEM projects that challenge their critical thinking skills and creativity. Activities like coding challenges, bridge engineering, and circuit experiments provide the perfect opportunity for students to delve deeper into the world of STEM and apply their newfound knowledge to real-world problems.
These projects not only help students develop a strong foundation in STEM concepts, but also instill a sense of curiosity, determination, and resilience as they work through challenges and find innovative solutions. Let’s discover some intriguing STEM projects that middle school students can confidently undertake.
Coding Challenges
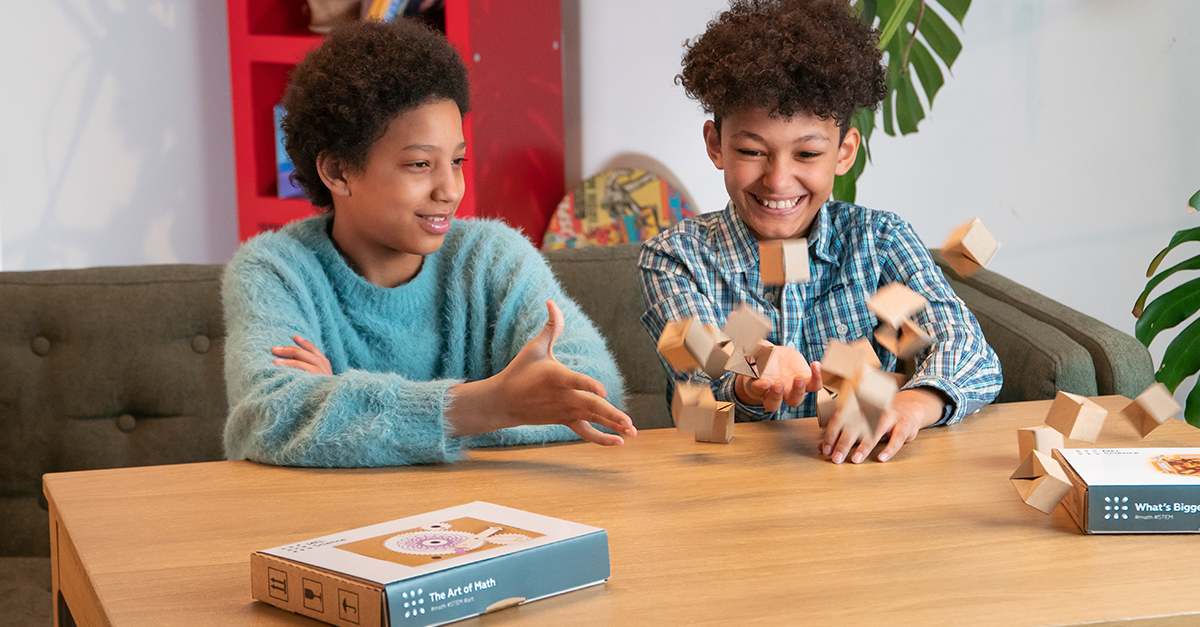

In today’s increasingly digital world, coding is a valuable skill that can open doors to exciting career opportunities. Introducing middle school students to computer programming through coding challenges and activities is a fantastic way to ignite their interest in this essential skill.
Platforms like Scratch and Code.org offer intuitive interfaces and engaging activities that make learning to code fun and accessible for students of all skill levels. Participation in coding challenges allows students to enhance their problem-solving skills, refine their logical thinking, and deepen their understanding of computer programming.
Bridge Engineering
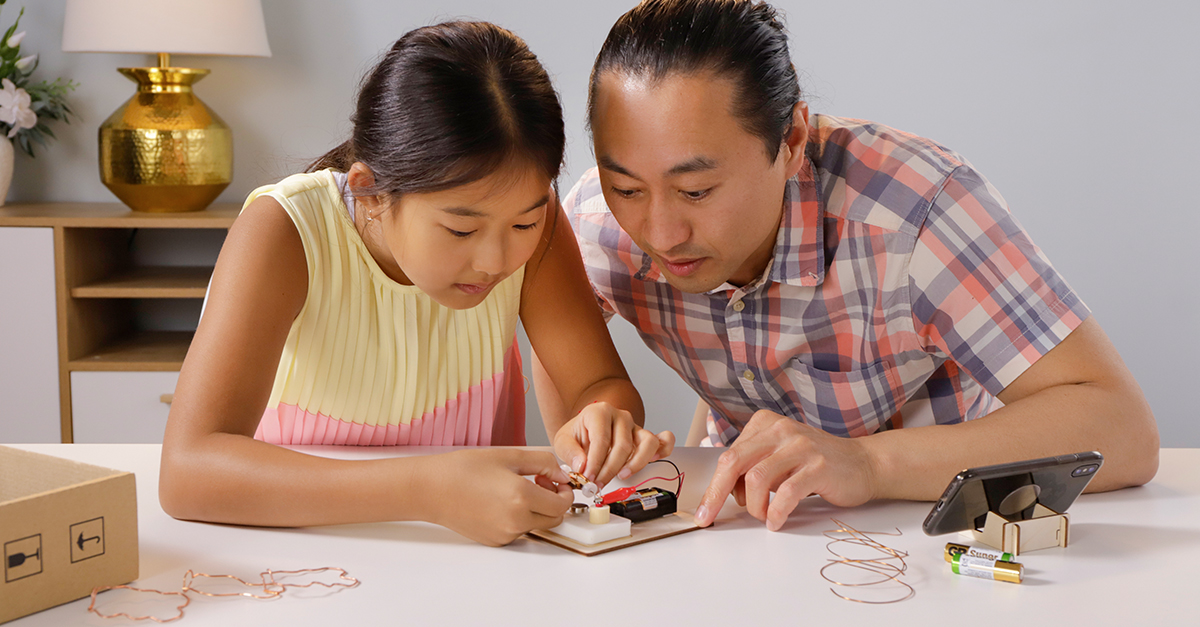

Bridge engineering is an exciting STEM project that teaches students about engineering principles, materials, and construction techniques. By designing and building their own bridges, students can develop an understanding of the forces at play in bridge construction and the importance of strong, stable structures.
Using materials like toothpicks, popsicle sticks, or even newspaper, students can experiment with different building techniques and styles to create bridges that can support weight and span distances. This practical activity not only imparts essential STEM concepts, but also instills a sense of achievement and pride in their creations.
Circuit Experiments
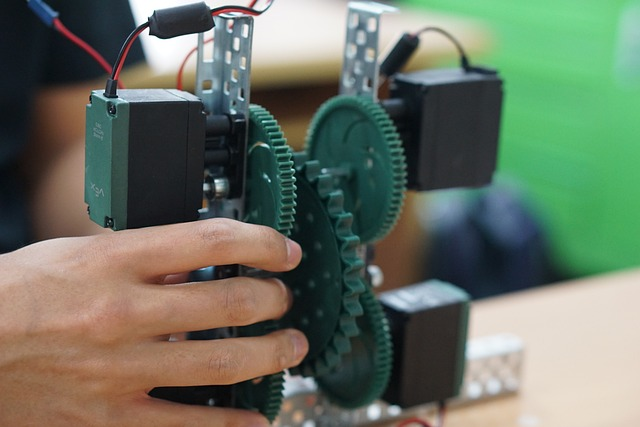
Electricity is a fundamental part of our daily lives, and understanding how circuits work is essential for students to grasp the principles of electrical engineering. Circuit experiments are a great way for middle school students to learn about electricity, components, and circuit design by building their own circuits using simple materials like batteries, wires, and light bulbs.
By creating and testing their own circuits, students can develop a hands-on understanding of how electrical components work together and the role of electricity in powering our devices. This captivating project not only imparts essential STEM concepts, but also ignites curiosity, encouraging students to delve into the intriguing world of electrical engineering.
Advanced STEM Projects for High School Students
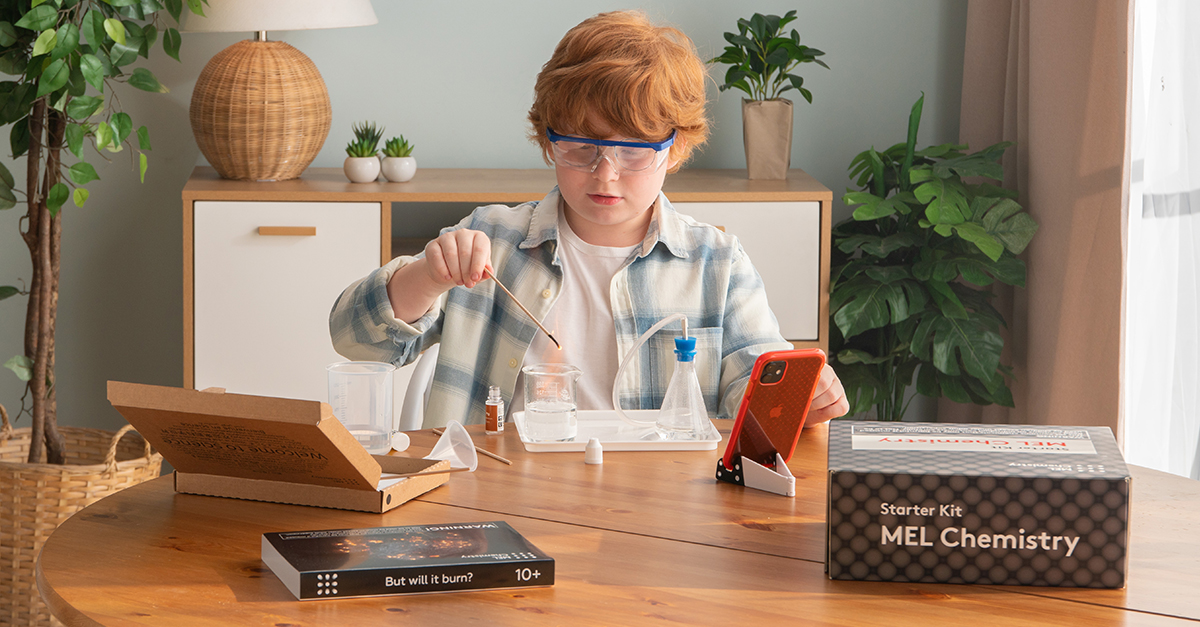

High school students are ready to tackle advanced STEM projects that challenge their knowledge, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Activities like robot building, energy-efficient home design, and chemistry experiments provide the perfect opportunity for students to delve deeper into the world of STEM and apply their skills to real-world problems.
These projects not only help students develop a strong foundation in STEM concepts, but also instill a sense of curiosity, determination, and resilience as they work through challenges and find innovative solutions.
Let’s explore STEM projects that high school students can confidently undertake and discover captivating ideas through a fun stem challenge.
Robot Building
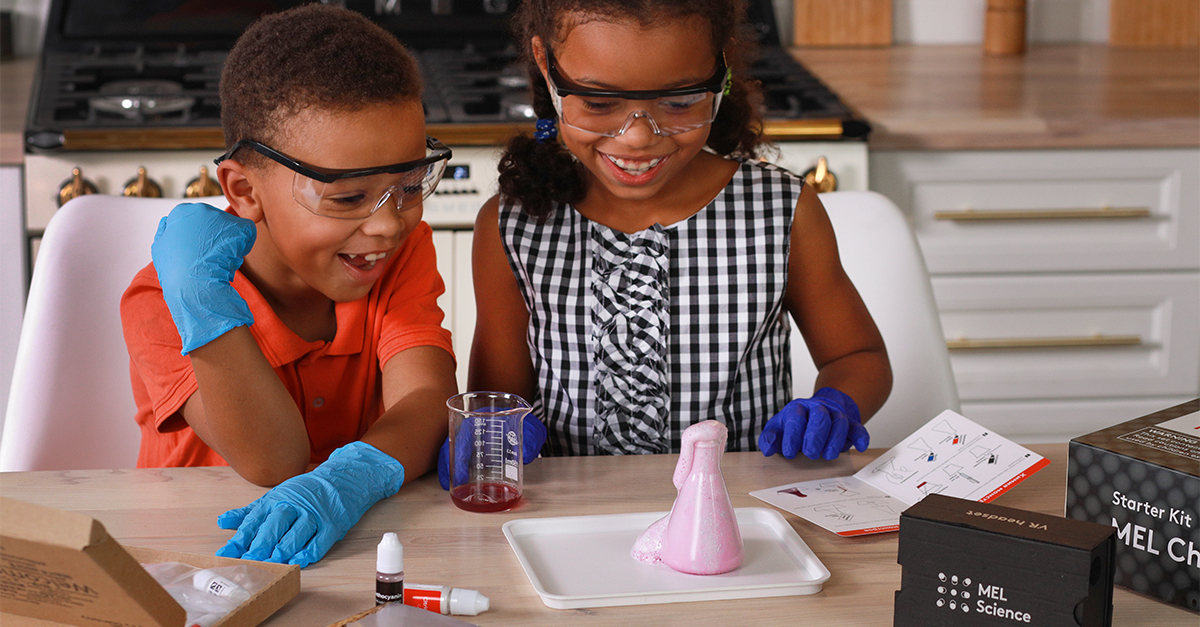

Robotics is an exciting and rapidly growing field, and introducing high school students to robot building is a fantastic way to ignite their interest in this cutting-edge discipline. Building robots not only teaches valuable engineering and programming skills, but also encourages creativity and innovation as students design their own robots using kits or DIY materials.
By constructing and programming their own robots, students can gain a hands-on understanding of how robotics technology works and the potential applications of robots in various industries. This captivating project not only imparts essential STEM concepts, but also ignites curiosity, encouraging students to delve into the intriguing world of robotics.
Energy-Efficient Home Design
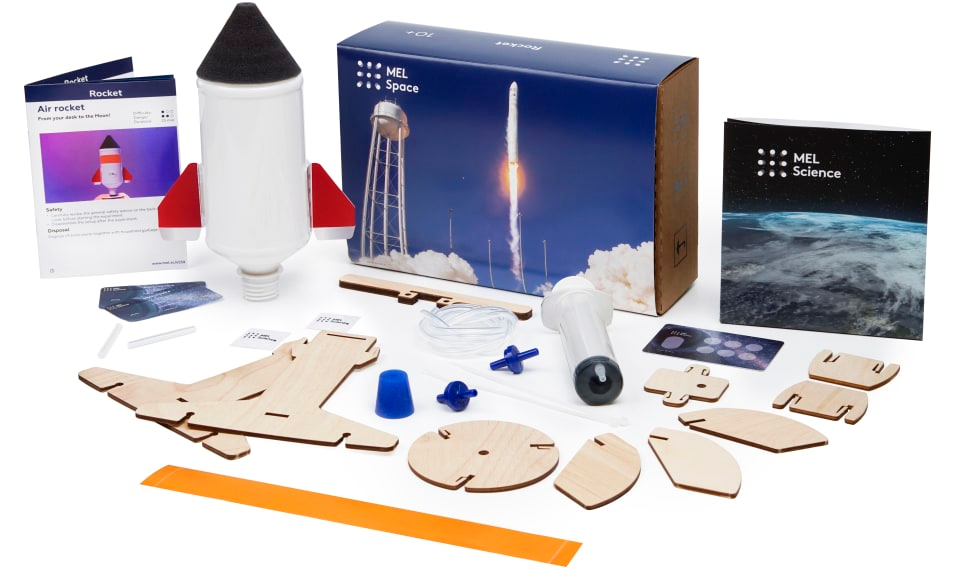

With growing concerns about climate change and the need for sustainable living, understanding energy-efficient home design is more important than ever. This project challenges high school students to design and build a model of an energy-efficient home, incorporating elements such as insulation, energy-efficient windows and doors, and renewable energy sources like solar panels.
By designing and constructing their own energy-efficient homes, students can develop an understanding of the importance of sustainable living and the role of energy efficiency in reducing our environmental impact. This practical activity not only imparts essential STEM concepts, but also fosters a sense of responsibility and awareness of the importance of conservation.
Chemistry Experiment

Chemistry experiments are an exciting way for high school students to explore the world of chemical reactions, properties of elements, and more. Hands-on experiments allow students to develop an understanding of the principles of chemistry and the role of chemical reactions in our daily lives.
By conducting their own chemistry experiments, students can gain a deeper understanding of the scientific method, develop critical thinking skills, and ignite their curiosity about the fascinating world of chemistry. This captivating project not only imparts essential STEM concepts but also encourages students to explore the marvels of science through engaging science experiments.
STEM Projects for the Whole Family
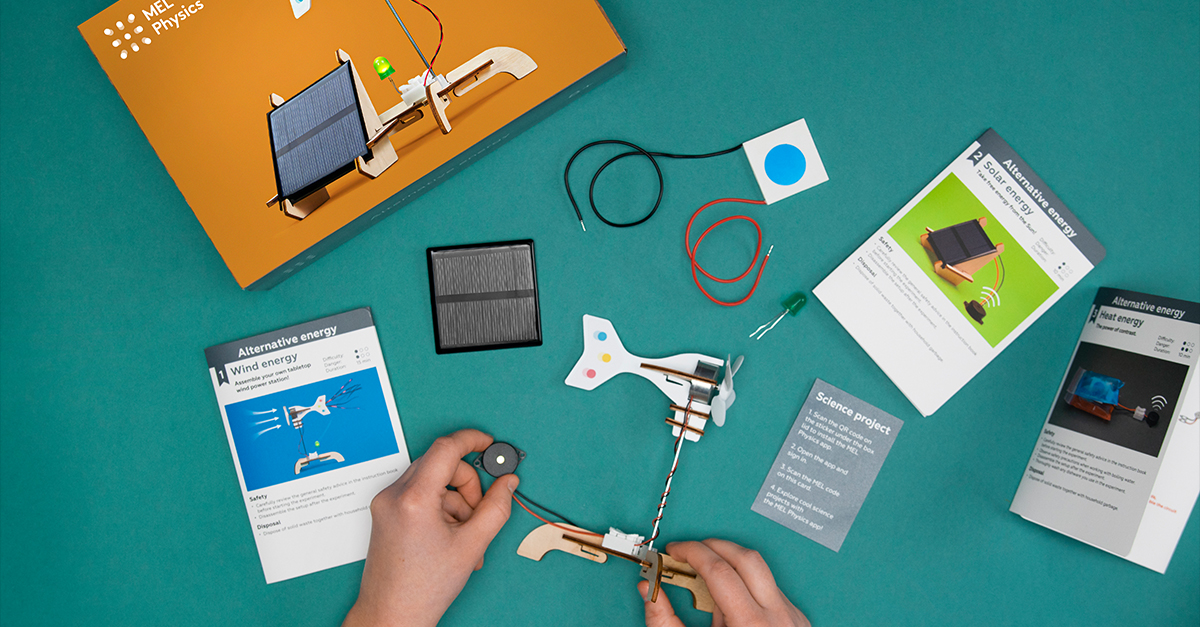

STEM projects aren’t just for kids! Engaging in STEM activities as a family is a fantastic way to bond, learn, and have fun together. Projects like homemade rocket launches, DIY telescope construction, and backyard weather stations are perfect for bringing the whole family together and sparking curiosity and creativity in everyone, regardless of age.
By participating in these family-friendly STEM projects, you’ll not only create lasting memories, but also instill a love for STEM in your children, setting them up for success in their future endeavors. So, gather the family and embark on some thrilling STEM projects that everyone can relish!
Homemade Rocket Launch
Launching homemade rockets is a thrilling and educational activity that’s perfect for the whole family. By building and launching rockets using simple materials like plastic bottles, baking soda, and vinegar, kids can learn about physics, aerodynamics, and the science behind rocket propulsion.
This practical activity not only offers a thrilling experience for the whole family, but also aids kids in developing a more profound understanding of rocketry principles and science’s role in powering our world. So, gather the family and prepare for lift-off with this enjoyable and educational project!
DIY Telescope Construction
Astronomy has fascinated humans for centuries, and building your own telescope is an exciting way for the whole family to explore the wonders of the night sky. Using simple materials like PVC pipes, lenses, and mirrors, kids can construct their own telescopes and learn about the principles of optics, astronomy, and the vast universe.
This practical activity not only offers an engaging learning experience for the whole family, but also fosters a sense of curiosity and awe about the universe. So gather your materials and set off on a starry journey with this DIY telescope project!
Backyard Weather Station
Understanding the weather is essential for everyday life, and building a backyard weather station is a fantastic way for the whole family to learn about meteorology and weather patterns. Using simple tools and materials, kids can create their own weather station that measures:
- Temperature
This practical activity not only imparts essential STEM concepts, but also encourages kids to develop an appreciation for the environment and the natural world. So, assemble the family and begin weather tracking with your very own backyard weather station!
In conclusion, STEM projects offer a world of exciting and educational opportunities for kids, students, and families alike. From fun and easy projects for young learners to engaging activities for middle and high school students, there’s a STEM project out there for everyone. By participating in these hands-on activities, we can foster a love for science, technology, engineering, and math, setting our children up for success in their future endeavors. So, whether you’re a parent, teacher, or student, dive into the exciting world of STEM and unleash your creativity, curiosity, and problem-solving skills!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good stem project.
The Egg Drop Challenge, DIY kite-building, solar oven-making, landmark building, and bridge-building are all great STEM projects for learning and fun.
Unleash your creativity to build something amazing!
What does STEM project mean?
STEM stands for science, technology, engineering and mathematics and is a learning approach that integrates these fields. It allows students to develop problem solving, creative, and critical analysis skills, making it an important priority for U.S. job markets.
STEM education is becoming increasingly important in the modern world, as it prepares students for the jobs of the future. It encourages students to think critically and develop skills that are essential for success in life.
What is STEM project in high school?
STEM projects in high school give students the opportunity to develop their skills in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics in a fun and engaging way.
These projects can help students gain a better understanding of the concepts they are learning in the classroom, as well as giving them the chance to apply their knowledge in a practical setting. They can also help to develop problem-solving skills.
What are some cool STEM projects?
Explore the exciting world of STEM with these 10 simple and fun activities for kids - from building volcanoes to constructing paper circuits!
Unlock your child’s creativity and develop their science, engineering, and technology skills today.
What age group is most suitable for the STEM projects listed?
The STEM projects listed are best suited for elementary, middle, and high school students, as well as for the whole family.
Sign up for more like this.

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, stem projects that tackle real-world problems.

STEM learning is largely about designing creative solutions for real-world problems. When students learn within the context of authentic, problem-based STEM design, they can more clearly see the genuine impact of their learning. That kind of authenticity builds engagement, taking students from groans of “When will I ever use this?” to a genuine connection between skills and application.
Using STEM to promote critical thinking and innovation
“Educational outcomes in traditional settings focus on how many answers a student knows. We want students to learn how to develop a critical stance with their work: inquiring, editing, thinking flexibly, and learning from another person’s perspective,” says Arthur L. Costa in his book Learning and Leading with Habits of Mind . “The critical attribute of intelligent human beings is not only having information but also knowing how to act on it.”
Invention and problem-solving aren’t just for laboratory thinkers hunkered down away from the classroom. Students from elementary to high school can wonder, design, and invent a real product that solves real problems. “ Problem-solving involves finding answers to questions and solutions for undesired effects. STEM lessons revolve around the engineering design process (EDP) — an organized, open-ended approach to investigation that promotes creativity, invention, and prototype design, along with testing and analysis,” says Ann Jolly in her book STEM by Design . “These iterative steps will involve your students in asking critical questions about the problem, and guide them through creating and testing actual prototypes to solve that problem.”
STEM projects that use real-world problems
Here are some engaging projects that get your students thinking about how to solve real-world problems.
Preventing soil erosion
In this project, meant for sixth – 12th grade, students learn to build a seawall to protest a coastline from erosion, calculating wave energy to determine the best materials for the job. See the project.
Growing food during a flood
A natural disaster that often devastates communities, floods can make it difficult to grow food. In this project, students explore “a problem faced by farmers in Bangladesh and how to grow food even when the land floods.” See the project .
Solving a city’s design needs
Get your middle or high school students involved in some urban planning. Students can identify a city’s issues, relating to things like transportation, the environment, or overcrowding — and design solutions. See the project here or this Lego version for younger learners.
Creating clean water
Too many areas of the world — including cities in our own country — do not have access to clean water. In this STEM project, teens will learn how to build and test their own water filtration systems. See the project here .
Improving the lives of those with disabilities
How can someone with crutches or a wheelchair carry what they need? Through some crafty designs! This project encourages middle school students to think creatively and to participate in civic engagement. See the project here .
Cleaning up an oil spill
We’ve all seen images of beaches and wildlife covered in oil after a disastrous spill. This project gets elementary to middle school students designing and testing oil spill clean-up kits. See the project here .
Building earthquake-resistant structures
With the ever-increasing amount of devastating earthquakes around the world, this project solves some major problems. Elementary students can learn to create earthquake resistant structures in their classroom. See the project here .
Constructing solar ovens
In remote places or impoverished areas, it’s possible to make solar ovens to safely cook food. In this project, elementary students construct solar ovens to learn all about how they work and their environmental and societal impact. See the project here .
Stopping apple oxidization
Stop those apples from turning brown with this oxidation-based project. Perfect for younger learners, students can predict, label, count, and experiment! See the project here .
Advancing as a STEAM educator
The push for STEM has evolved into the STEAM movement, adding the arts for further enrichment and engagement. There are so many ways to embed STEM or STEAM lessons in your curriculum, but doing it well requires foundational knowledge and professional development. Imagine what type of impact you could have on your students and your community if you were supported by a theoretical framework, a variety of strategies, and a wealth of ideas and resources.
You may also like to read
- Teaching STEM: Challenging Students to Think Through Tough Problems
- Professional Development Resources for STEM Teachers
- What is the Washington State STEM Lighthouse Program?
- Characteristics of a Great STEAM Program
- Building a Partnership Between Your School and a STEAM Organization
- The Art of Inquiry in STEAM Education
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Art , Educational Technology , Engaging Activities , Math and Science , Science , STEAM
- Online & Campus Master's in Elementary Educat...
- 2020 Civics Engagement & Resilience: Tools fo...
- Online & Campus Master's in Curriculum Develo...

21 Quick STEM Activities that Will Bring Out the Genius in Every Child
Categories STEM Activities
STEM activities (activities with elements of science, technology, engineering, and math) help children see that science and math can have a creative element, too. Try these quick STEM activities when you don’t have tons of time to plan!
In today’s world, technology seeps into everything we do, and children can be taught to approach all of their learning through the lens of scientific exploration.
However, we don’t always have time for involved STEM activities for kids that take weeks to complete (although those are beneficial as well!).

But if you’re simply looking for a few easy and quick STEM activities for your kiddos, you’ll appreciate the quick STEM lessons you’ll find in this post.
Today, I am sharing 21 quick STEM projects that are simple to set up and quick to do.
You’ll love how quickly you can set up these projects and get them completed, even if you have just a few minutes to do them in!
Perfect for easy STEM activities in the classroom or at home. Teach science in minutes, rather than hours.
What are Quick STEM Activities?

Integrating learning across Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics, there are quick and easy STEM challenges suitable for children of all ages on the list, and many of these activities can be easily scaled up or down through questioning to suit the age of your child.
In this case, a quick STEM challenge is one that takes 30 minutes or less to complete- or one class period!
The hardest thing might just be choosing which quick and easy STEM activity to try first!
21 Fast STEM Activities for Kids
Kids will love these hands-on STEM activities, and teachers and parents will love how quickly you can use these lessons to illustrate science lessons and teach STEM thinking skills to kids.
Why Do Quick STEM Activities with Kids?
A STEM activity is more than just a hands-on project that includes elements of science, technology, engineering, and math.
STEM activities are whole-brain exercises, that kids can use to explore disciplined subjects in a creative and exploratory way.
One of the best things about quick STEM activities is that there are no right or wrong answers.
In a true STEM experiment, children learn to think of solutions to problems on their own, with no particular planned outcome, just like in the real world.
STEM activities are one of the best ways to prepare children for problem solving and learning in the real world, and they give kids a taste of what sort of decision processes adults go through every day.
With the openness of STEM activities guiding children, there is no fear of failure and children who typically look for the “right” answer are encouraged to explore a topic, rather than just memorizing an answer.
Kids who regularly engage in quick STEM activities are better able to solve problems, think outside the box, go through a logical process to come up with an answer, and can tell you why they chose a certain solution clearly.
What Kids Learn Doing Quick STEM Activities
Quick STEM activities help illustrate the concepts of science, technology, engineering, and math in a fast, easy-to-see way that is ideal for quick science and STEM lessons, such as for early elementary science class, kindergarten lessons, STEM and science centers, preschool, STEM summer camp, and more!
The quick demonstrations work well when time crunches are an issue, and for many of these activities, kids can do them alone, making them perfect for self-guided play and exploration.
Check out more fun STEM themes, including our list of easy science experiments for kid s and creative STEM activities .

You don’t have to take a long time to teach a STEM lesson. Kids can learn the basic elements of science, technology, engineering, and math in these hands-on STEM projects for kids.
Use these lessons when you need to teach a scientific topic, but don’t have time to spend weeks on the project.
Quick STEM activities can be used to help keep morale up in the STEM classroom between bigger projects, as they often give fun, quick, and visually appealing results.
You can also use these quick STEM activities at home to make learning fun there!
How to Set Up Quick STEM Challenges for Kids

When possible, it’s best to mix several elements of STEM together, using elements of science, technology, engineering, and math all at once.
You’ll maximize the learning of children and help them understand how all the elements of STEM activities work together.
More STEM Activities for Kids
50+ LEGO STEM Challenges- Free Printable STEM Activities
20+ Carnival Themed STEM Activities for Kids
20+Spectacular and Fun Circus STEM Activities
Toy Making STEM Activities
Quick STEM Activities that Take 30 Minutes or Less
Follow along with these activities to find a bunch of fun science, technology, engineering, and math activities that can be done in less than a single class period.
And best of all, they are super fun, too!
Quick Science Experiments for Kids
These fast science experiments are a breeze! Learn about liquid density, surface tension, non-Newtonian fluids, slime, light refraction, and more!

Paper Towel Strength Test Science Experiment
With just paper towels and pennies, students can conduct a simple penny paper towel experiment to determine whether wet or dry paper towels can hold more weight. Students will learn how adding a variable to an experiment can drastically change the outcome even when no other changes are made.

Amazing Bending Pencil Experiment That's Just Like Magic!
Use light to break a pencil. How is it done? You'll have to try it to find out!

Flip a Rainbow Light Refraction Experiment
You can magically flip a rainbow with light! How? The science is complicated, but the project is a whole lot of fun!

How to Make Fluffy Rainbow Slime (without the mess)
Did you know that slime uses a lot of scientific chemistry principles? Apply them and learn all about polymer chains and molecular bonds when you make this fluffy slime.

Fortnite Slurp Drink Water Density Experiment
Fortnite is a lot of fun for kids. This Fortnite slurp drink density tower uses science to keep the colors apart!

How to Do the Hot and Cold Water Density Experiment
You can learn about color mixing and how temperature has different densities in this super fun and quick science experiment.

Sugar Rainbow Density Tower Experiment
Nothing is more fun than sweet science! Learn about density and viscosity in this quick experiment.

Super Fast Milk Surface Tension Science Experiment!
Surface tension is hard to describe, but with this experiment, its easy to see!
Quick Technology Activities for Kids
Fast technology challenges you can do in minutes! Learn about circuits, coding, binary, and more!

How to Make Binary Coding Bracelets with Secret Messages
Teach kids the basics of binary with these coding bracelets.

Fun Ways for Kids to Learn Computer Coding
Here are some super fun ways to teach coding to kids and learn how to make technology fun for them.

Rainbow Salt Circuit Engineering Activity
Learn how circuits work with this fun glow in the dark circuit activity!

How to Use Squishy Circuits for Electrical Engineering
Learn all about electricity and electrical engineering with Squishy Circuits!

Painting Brush Bot
With a motor and a brush, you can create a robot painting system!

How to Make a Unicorn Rainbow Scribble Bot
Learn how to put together a working motor and create a robot that can draw for you!

Map Skills for Kids: Planning a Route
Learning how to use a map is an essential skill for kids! Technology makes it easier.

The Best Coding Apps for Kids
These coding apps will teach kids the basics of coding and more!

Build a Minecraft Chessboard
There is a lot of tech behind Minecraft! In this simple activity, challenge your kiddos with how to make a chess board!
Quick Engineering Activities for Kids
Rome might have taken more than a day to complete, but these engineering projects won't! You can knock these quick engineering challenges out in just minutes!

Cotton Swab Bridge Building Engineering Challenge Lesson Plan
Learn how to teach this q tip bridge engineering challenge with the students in your classroom. It's a fun twist on other bridge building engineering challenges and students will have a blast coming up with their unique designs.

How to Build a Simple LEGO Flower
Building a LEGO flower is easy and fast and teaches kids the basics of design and engineering.

How to Build an Easy LEGO Car
Follow along with this simple guide to create a LEGO car in minutes!

Spaghetti Engineering Project
This Spaghetti Engineering Challenge is so easy, but kids can learn a lot!

How to Design a Paper Airplane Engineering Challenge
If you love building and designing and testing, then the Paper airplane Engineering Challenge is for you!

How to Make a LEGO Rainbow with Classic LEGO Bricks
Making a LEGORainbow sounds like it would be easy, but it's actually surprisingly difficult!

EASY! 3 Steps to the Perfect Leak Proof Bag Science Experiment
The leakproof bag science experiment teaches kids about polymer chains in less than five minutes!
Quick Math Activities for Kids
Quick math challenges for on-the-fly learning. You don't have to take forever to do math activities!

Design a Coin Activity for Kids
Design coins and learn all about coin values and how to use money in this super quick math activity!

Uno Math Game
Kids will love this fun math variation on the classic UNO game!

Multiplication Dice Game
Play the multiplication dice game when you have a few minutes to work some additional math practice in.

Hands-On Geometry Challenge: Building 3D Shapes
Build geometry shapes using geometry bricks for some fast geometry math practice.

Math Fraction Art Project
Learn about fractions and turn them into fun art pieces in this fast math activity!

Printable Lemon Fraction Clip Cards for Elementary Kids
Learning fractions is way less of a bother when you use these cheery lemon fraction clip cards !

Soup Can Printable PEMDAS Worksheet for Teaching Order of Operations
Grab this fun soup-themed printable PEMDAS worksheet .
Share this project with a friend!

- Publications
- Conferences & Events
- Professional Learning
- Science Standards
- Awards & Competitions
- Instructional Materials
- Free Resources
- American Rescue Plan
- For Preservice Teachers
- NCCSTS Case Collection
- Partner Jobs in Education
- Interactive eBooks+
- Digital Catalog
- Regional Product Representatives
- e-Newsletters
- Bestselling Books
- Latest Books
- Popular Book Series
- Prospective Authors
- Web Seminars
- Exhibits & Sponsorship
- Conference Reviewers
- National Conference • Denver 24
- Leaders Institute 2024
- National Conference • New Orleans 24
- Submit a Proposal
- Latest Resources
- Professional Learning Units & Courses
- For Districts
- Online Course Providers
- Schools & Districts
- College Professors & Students
- The Standards
- Teachers and Admin
- eCYBERMISSION
- Toshiba/NSTA ExploraVision
- Junior Science & Humanities Symposium
- Teaching Awards
- Climate Change
- Earth & Space Science
- New Science Teachers
- Early Childhood
- Middle School
- High School
- Postsecondary
- Informal Education
- Journal Articles
- Lesson Plans
- e-newsletters
- Science & Children
- Science Scope
- The Science Teacher
- Journal of College Sci. Teaching
- Connected Science Learning
- NSTA Reports
- Next-Gen Navigator
- Science Update
- Teacher Tip Tuesday
- Trans. Sci. Learning
MyNSTA Community
- My Collections
A Problem-Solving Experiment
Using Beer’s Law to Find the Concentration of Tartrazine
The Science Teacher—January/February 2022 (Volume 89, Issue 3)
By Kevin Mason, Steve Schieffer, Tara Rose, and Greg Matthias
Share Start a Discussion
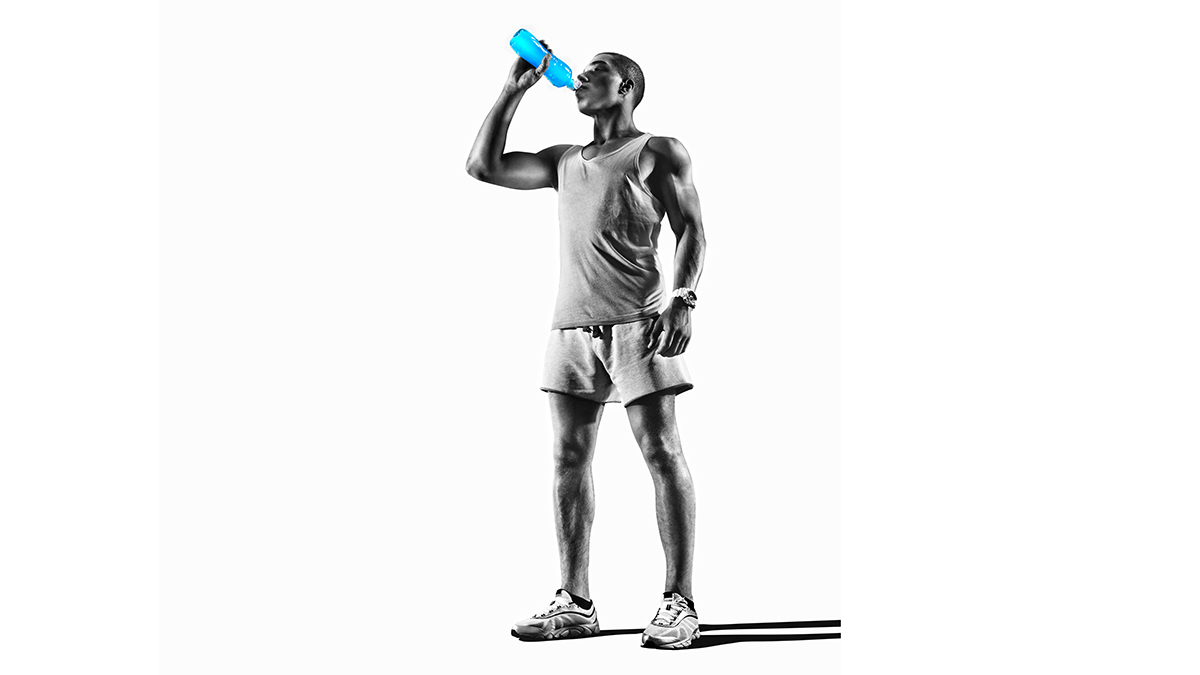

A problem-solving experiment is a learning activity that uses experimental design to solve an authentic problem. It combines two evidence-based teaching strategies: problem-based learning and inquiry-based learning. The use of problem-based learning and scientific inquiry as an effective pedagogical tool in the science classroom has been well established and strongly supported by research ( Akinoglu and Tandogan 2007 ; Areepattamannil 2012 ; Furtak, Seidel, and Iverson 2012 ; Inel and Balim 2010 ; Merritt et al. 2017 ; Panasan and Nuangchalerm 2010 ; Wilson, Taylor, and Kowalski 2010 ).
Floyd James Rutherford, the founder of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Project 2061 once stated, “To separate conceptually scientific content from scientific inquiry,” he underscored, “is to make it highly probable that the student will properly understand neither” (1964, p. 84). A more recent study using randomized control trials showed that teachers that used an inquiry and problem-based pedagogy for seven months improved student performance in math and science ( Bando, Nashlund-Hadley, and Gertler 2019 ). A problem-solving experiment uses problem-based learning by posing an authentic or meaningful problem for students to solve and inquiry-based learning by requiring students to design an experiment to collect and analyze data to solve the problem.
In the problem-solving experiment described in this article, students used Beer’s Law to collect and analyze data to determine if a person consumed a hazardous amount of tartrazine (Yellow Dye #5) for their body weight. The students used their knowledge of solutions, molarity, dilutions, and Beer’s Law to design their own experiment and calculate the amount of tartrazine in a yellow sports drink (or citrus-flavored soda).
According to the Next Generation Science Standards, energy is defined as “a quantitative property of a system that depends on the motion and interactions of matter and radiation with that system” ( NGSS Lead States 2013 ). Interactions of matter and radiation can be some of the most challenging for students to observe, investigate, and conceptually understand. As a result, students need opportunities to observe and investigate the interactions of matter and radiation. Light is one example of radiation that interacts with matter.
Light is electromagnetic radiation that is detectable to the human eye and exhibits properties of both a wave and a particle. When light interacts with matter, light can be reflected at the surface, absorbed by the matter, or transmitted through the matter ( Figure 1 ). When a single beam of light enters a substance at a perpendicularly (at a 90 ° angle to the surface), the amount of reflection is minimal. Therefore, the light will either be absorbed by the substance or be transmitted through the substance. When a given wavelength of light shines into a solution, the amount of light that is absorbed will depend on the identity of the substance, the thickness of the container, and the concentration of the solution.
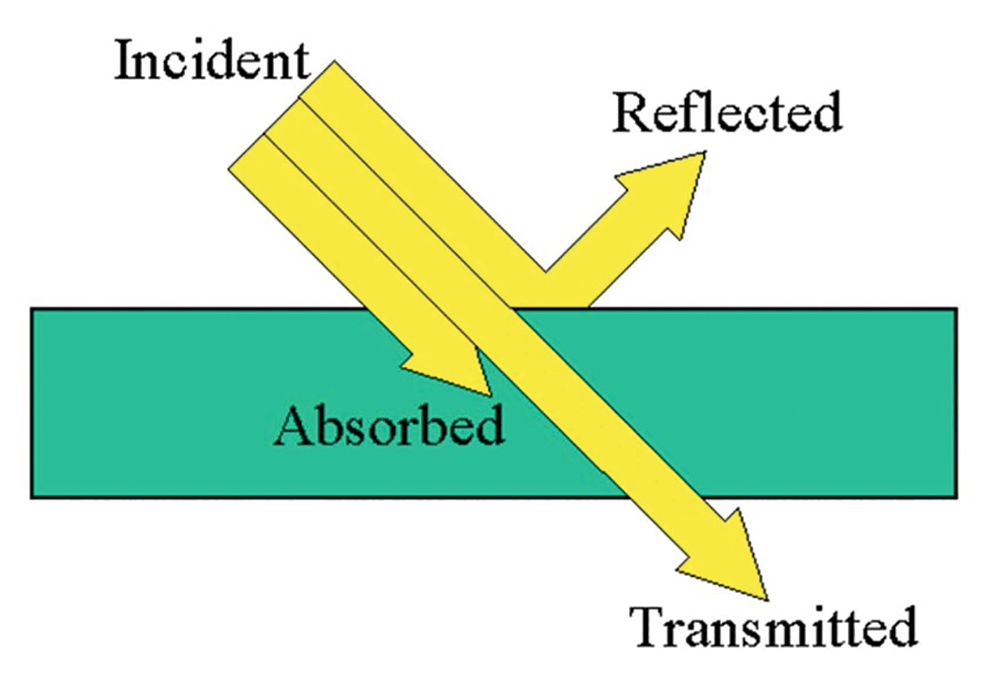
Light interacting with matter.
(Retrieved from https://etorgerson.files.wordpress.com/2011/05/light-reflect-refract-absorb-label.jpg ).
Beer’s Law states the amount of light absorbed is directly proportional to the thickness and concentration of a solution. Beer’s Law is also sometimes known as the Beer-Lambert Law. A solution of a higher concentration will absorb more light and transmit less light ( Figure 2 ). Similarly, if the solution is placed in a thicker container that requires the light to pass through a greater distance, then the solution will absorb more light and transmit less light.
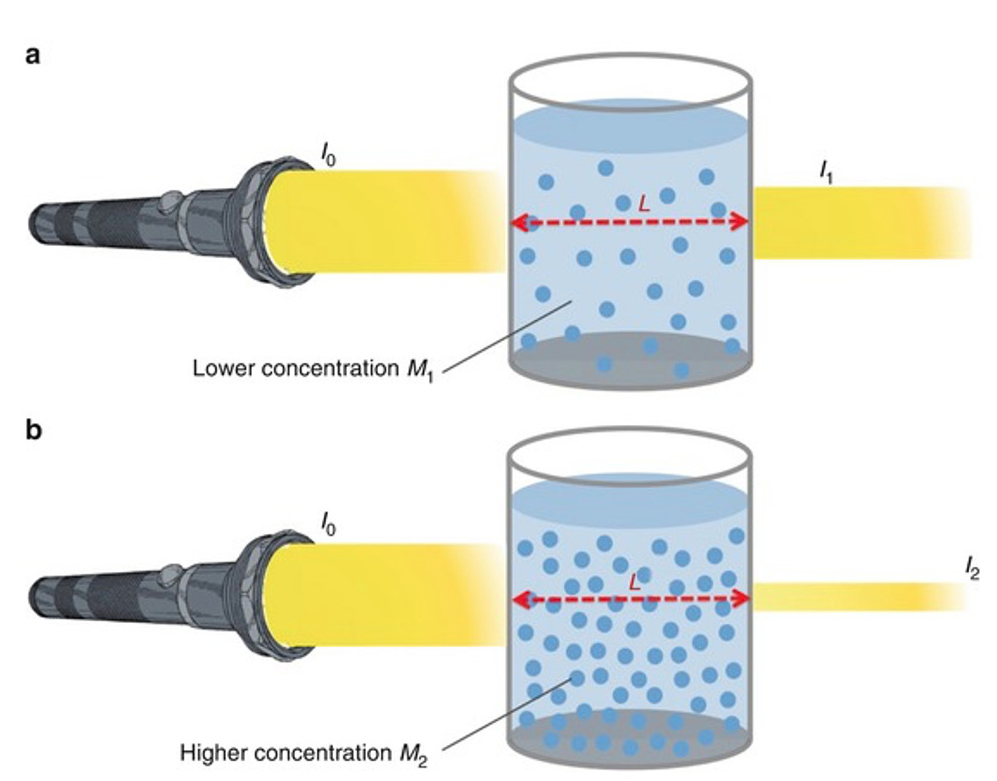
Light transmitted through a solution.
(Retrieved from https://media.springernature.com/original/springer-static/image/chp%3A10.1007%2F978-3-319-57330-4_13/MediaObjects/432946_1_En_13_Fig4_HTML.jpg ).
Definitions of key terms.
Absorbance (A) – the process of light energy being captured by a substance
Beer’s Law (Beer-Lambert Law) – the absorbance (A) of light is directly proportional to the molar absorptivity (ε), thickness (b), and concentration (C) of the solution (A = εbC)
Concentration (C) – the amount of solute dissolved per amount of solution
Cuvette – a container used to hold a sample to be tested in a spectrophotometer
Energy (E) – a quantitative property of a system that depends on motion and interactions of matter and radiation with that system (NGSS Lead States 2013).
Intensity (I) – the amount or brightness of light
Light – electromagnetic radiation that is detectable to the human eye and exhibits properties of both a wave and a particle
Molar Absorptivity (ε) – a property that represents the amount of light absorbed by a given substance per molarity of the solution and per centimeter of thickness (M-1 cm-1)
Molarity (M) – the number of moles of solute per liters of solution (Mol/L)
Reflection – the process of light energy bouncing off the surface of a substance
Spectrophotometer – a device used to measure the absorbance of light by a substance
Tartrazine – widely used food and liquid dye
Transmittance (T) – the process of light energy passing through a substance
The amount of light absorbed by a solution can be measured using a spectrophotometer. The solution of a given concentration is placed in a small container called a cuvette. The cuvette has a known thickness that can be held constant during the experiment. It is also possible to obtain cuvettes of different thicknesses to study the effect of thickness on the absorption of light. The key definitions of the terms related to Beer’s Law and the learning activity presented in this article are provided in Figure 3 .
Overview of the problem-solving experiment
In the problem presented to students, a 140-pound athlete drinks two bottles of yellow sports drink every day ( Figure 4 ; see Online Connections). When she starts to notice a rash on her skin, she reads the label of the sports drink and notices that it contains a yellow dye known as tartrazine. While tartrazine is safe to drink, it may produce some potential side effects in large amounts, including rashes, hives, or swelling. The students must design an experiment to determine the concentration of tartrazine in the yellow sports drink and the number of milligrams of tartrazine in two bottles of the sports drink.
While a sports drink may have many ingredients, the vast majority of ingredients—such as sugar or electrolytes—are colorless when dissolved in water solution. The dyes added to the sports drink are responsible for the color of the sports drink. Food manufacturers may use different dyes to color sports drinks to the desired color. Red dye #40 (allura red), blue dye #1 (brilliant blue), yellow dye #5 (tartrazine), and yellow dye #6 (sunset yellow) are the four most common dyes or colorants in sports drinks and many other commercial food products ( Stevens et al. 2015 ). The concentration of the dye in the sports drink affects the amount of light absorbed.
In this problem-solving experiment, the students used the previously studied concept of Beer’s Law—using serial dilutions and absorbance—to find the concentration (molarity) of tartrazine in the sports drink. Based on the evidence, the students then determined if the person had exceeded the maximum recommended daily allowance of tartrazine, given in mg/kg of body mass. The learning targets for this problem-solving experiment are shown in Figure 5 (see Online Connections).
Pre-laboratory experiences
A problem-solving experiment is a form of guided inquiry, which will generally require some prerequisite knowledge and experience. In this activity, the students needed prior knowledge and experience with Beer’s Law and the techniques in using Beer’s Law to determine an unknown concentration. Prior to the activity, students learned how Beer’s Law is used to relate absorbance to concentration as well as how to use the equation M 1 V 1 = M 2 V 2 to determine concentrations of dilutions. The students had a general understanding of molarity and using dimensional analysis to change units in measurements.
The techniques for using Beer’s Law were introduced in part through a laboratory experiment using various concentrations of copper sulfate. A known concentration of copper sulfate was provided and the students followed a procedure to prepare dilutions. Students learned the technique for choosing the wavelength that provided the maximum absorbance for the solution to be tested ( λ max ), which is important for Beer’s Law to create a linear relationship between absorbance and solution concentration. Students graphed the absorbance of each concentration in a spreadsheet as a scatterplot and added a linear trend line. Through class discussion, the teacher checked for understanding in using the equation of the line to determine the concentration of an unknown copper sulfate solution.
After the students graphed the data, they discussed how the R2 value related to the data set used to construct the graph. After completing this experiment, the students were comfortable making dilutions from a stock solution, calculating concentrations, and using the spectrophotometer to use Beer’s Law to determine an unknown concentration.
Introducing the problem
After the initial experiment on Beer’s Law, the problem-solving experiment was introduced. The problem presented to students is shown in Figure 4 (see Online Connections). A problem-solving experiment provides students with a valuable opportunity to collaborate with other students in designing an experiment and solving a problem. For this activity, the students were assigned to heterogeneous or mixed-ability laboratory groups. Groups should be diversified based on gender; research has shown that gender diversity among groups improves academic performance, while racial diversity has no significant effect ( Hansen, Owan, and Pan 2015 ). It is also important to support students with special needs when assigning groups. The mixed-ability groups were assigned intentionally to place students with special needs with a peer who has the academic ability and disposition to provide support. In addition, some students may need additional accommodations or modifications for this learning activity, such as an outlined lab report, a shortened lab report format, or extended time to complete the analysis. All students were required to wear chemical-splash goggles and gloves, and use caution when handling solutions and glass apparatuses.
Designing the experiment
During this activity, students worked in lab groups to design their own experiment to solve a problem. The teacher used small-group and whole-class discussions to help students understand the problem. Students discussed what information was provided and what they need to know and do to solve the problem. In planning the experiment, the teacher did not provide a procedure and intentionally provided only minimal support to the students as needed. The students designed their own experimental procedure, which encouraged critical thinking and problem solving. The students needed to be allowed to struggle to some extent. The teacher provided some direction and guidance by posing questions for students to consider and answer for themselves. Students were also frequently reminded to review their notes and the previous experiment on Beer’s Law to help them better use their resources to solve the problem. The use of heterogeneous or mixed-ability groups also helped each group be more self-sufficient and successful in designing and conducting the experiment.
Students created a procedure for their experiment with the teacher providing suggestions or posing questions to enhance the experimental design, if needed. Safety was addressed during this consultation to correct safety concerns in the experimental design or provide safety precautions for the experiment. Students needed to wear splash-proof goggles and gloves throughout the experiment. In a few cases, students realized some opportunities to improve their experimental design during the experiment. This was allowed with the teacher’s approval, and the changes to the procedure were documented for the final lab report.
Conducting the experiment
A sample of the sports drink and a stock solution of 0.01 M stock solution of tartrazine were provided to the students. There are many choices of sports drinks available, but it is recommended that the ingredients are checked to verify that tartrazine (yellow dye #5) is the only colorant added. This will prevent other colorants from affecting the spectroscopy results in the experiment. A citrus-flavored soda could also be used as an alternative because many sodas have tartrazine added as well. It is important to note that tartrazine is considered safe to drink, but it may produce some potential side effects in large amounts, including rashes, hives, or swelling. A list of the materials needed for this problem-solving experiment is shown in Figure 6 (see Online Connections).
This problem-solving experiment required students to create dilutions of known concentrations of tartrazine as a reference to determine the unknown concentration of tartrazine in a sports drink. To create the dilutions, the students were provided with a 0.01 M stock solution of tartrazine. The teacher purchased powdered tartrazine, available from numerous vendors, to create the stock solution. The 0.01 M stock solution was prepared by weighing 0.534 g of tartrazine and dissolving it in enough distilled water to make a 100 ml solution. Yellow food coloring could be used as an alternative, but it would take some research to determine its concentration. Since students have previously explored the experimental techniques, they should know to prepare dilutions that are somewhat darker and somewhat lighter in color than the yellow sports drink sample. Students should use five dilutions for best results.
Typically, a good range for the yellow sports drink is standard dilutions ranging from 1 × 10-3 M to 1 × 10-5 M. The teacher may need to caution the students that if a dilution is too dark, it will not yield good results and lower the R2 value. Students that used very dark dilutions often realized that eliminating that data point created a better linear trendline, as long as it didn’t reduce the number of data points to fewer than four data points. Some students even tried to use the 0.01 M stock solution without any dilution. This was much too dark. The students needed to do substantial dilutions to get the solutions in the range of the sports drink.
After the dilutions are created, the absorbance of each dilution was measured using a spectrophotometer. A Vernier SpectroVis (~$400) spectrophotometer was used to measure the absorbance of the prepared dilutions with known concentrations. The students adjusted the spectrophotometer to use different wavelengths of light and selected the wavelength with the highest absorbance reading. The same wavelength was then used for each measurement of absorbance. A wavelength of 650 nanometers (nm) provided an accurate measurement and good linear relationship. After measuring the absorbance of the dilutions of known concentrations, the students measured the absorbance of the sports drink with an unknown concentration of tartrazine using the spectrophotometer at the same wavelength. If a spectrophotometer is not available, a color comparison can be used as a low-cost alternative for completing this problem-solving experiment ( Figure 7 ; see Online Connections).
Analyzing the results
After completing the experiment, the students graphed the absorbance and known tartrazine concentrations of the dilutions on a scatter-plot to create a linear trendline. In this experiment, absorbance was the dependent variable, which should be graphed on the y -axis. Some students mistakenly reversed the axes on the scatter-plot. Next, the students used the graph to find the equation for the line. Then, the students solve for the unknown concentration (molarity) of tartrazine in the sports drink given the linear equation and the absorbance of the sports drink measured experimentally.
To answer the question posed in the problem, the students also calculated the maximum amount of tartrazine that could be safely consumed by a 140 lb. person, using the information given in the problem. A common error in solving the problem was not converting the units of volume given in the problem from ounces to liters. With the molarity and volume in liters, the students then calculated the mass of tartrazine consumed per day in milligrams. A sample of the graph and calculations from one student group are shown in Figure 8 . Finally, based on their calculations, the students answered the question posed in the original problem and determined if the person’s daily consumption of tartrazine exceeded the threshold for safe consumption. In this case, the students concluded that the person did NOT consume more than the allowable daily limit of tartrazine.
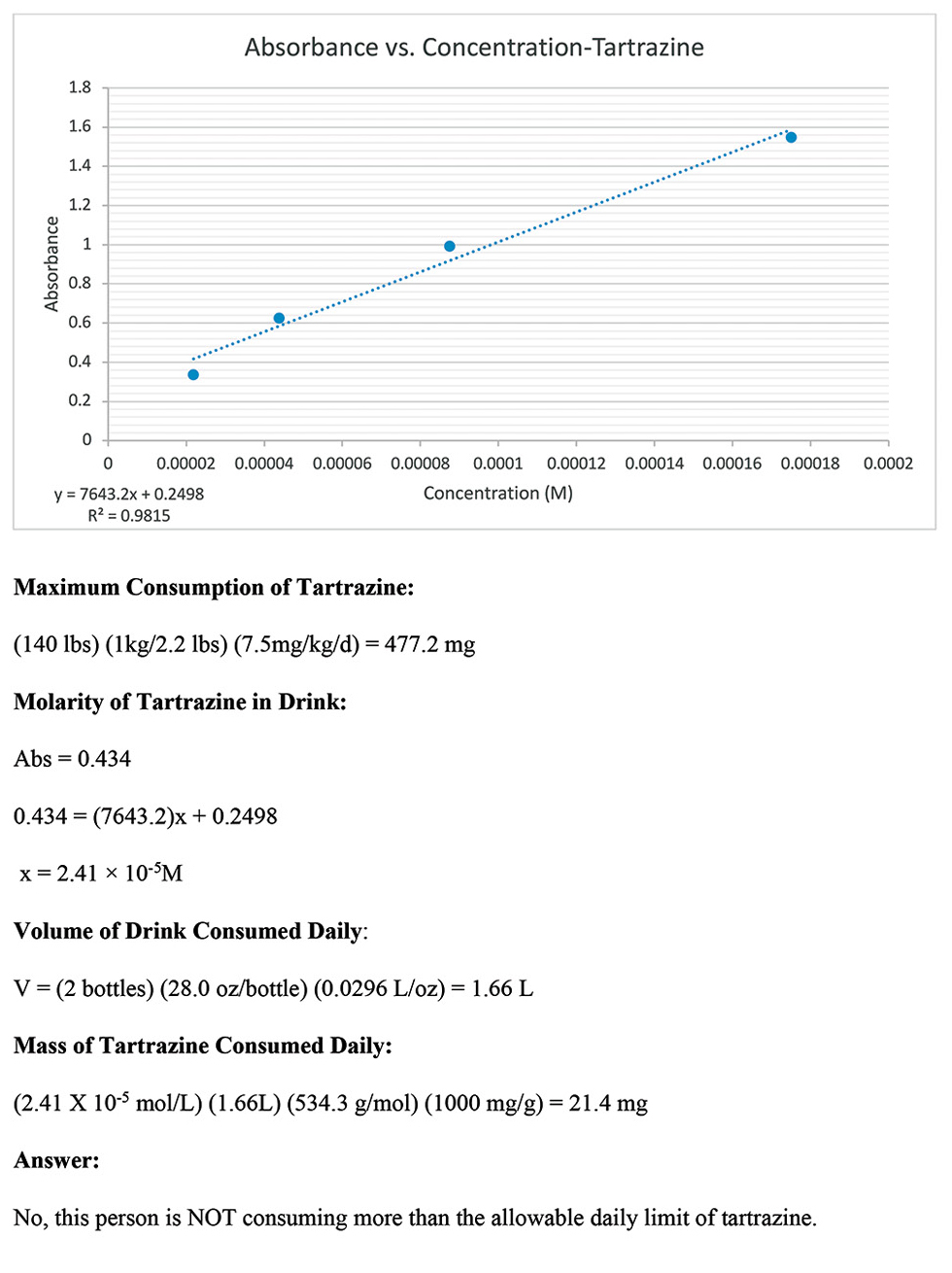
Sample graph and calculations from a student group.
Communicating the results
After conducting the experiment, students reported their results in a written laboratory report that included the following sections: title, purpose, introduction, hypothesis, materials and methods, data and calculations, conclusion, and discussion. The laboratory report was assessed using the scoring rubric shown in Figure 9 (see Online Connections). In general, the students did very well on this problem-solving experiment. Students typically scored a three or higher on each criteria of the rubric. Throughout the activity, the students successfully demonstrated their ability to design an experiment, collect data, perform calculations, solve a problem, and effectively communicate those results.
This activity is authentic problem-based learning in science as the true concentration of tartrazine in the sports drink was not provided by the teacher or known by the students. The students were generally somewhat biased as they assumed the experiment would result in exceeding the recommended maximum consumption of tartrazine. Some students struggled with reporting that the recommended limit was far higher than the two sports drinks consumed by the person each day. This allows for a great discussion about the use of scientific methods and evidence to provide unbiased answers to meaningful questions and problems.
The most common errors in this problem-solving experiment were calculation errors, with the most common being calculating the concentrations of the dilutions (perhaps due to the use of very small concentrations). There were also several common errors in communicating the results in the laboratory report. In some cases, students did not provide enough background information in the introduction of the report. When the students communicated the results, some students also failed to reference specific data from the experiment. Finally, in the discussion section, some students expressed concern or doubts in the results, not because there was an obvious error, but because they did not believe the level consumed could be so much less than the recommended consumption limit of tartrazine.
The scientific study and investigation of energy and matter are salient topics addressed in the Next Generation Science Standards ( Figure 10 ; see Online Connections). In a chemistry classroom, students should have multiple opportunities to observe and investigate the interaction of energy and matter. In this problem-solving experiment students used Beer’s Law to collect and analyze data to determine if a person consumed an amount of tartrazine that exceeded the maximum recommended daily allowance. The students correctly concluded that the person in the problem did not consume more than the recommended daily amount of tartrazine for their body weight.
In this activity students learned to work collaboratively to design an experiment, collect and analyze data, and solve a problem. These skills extend beyond any one science subject or class. Through this activity, students had the opportunity to do real-world science to solve a problem without a previously known result. The process of designing an experiment may be difficult for some students that are often accustomed to being given an experimental procedure in their previous science classroom experiences. However, because students sometimes struggled to design their own experiment and perform the calculations, students also learned to persevere in collecting and analyzing data to solve a problem, which is a valuable life lesson for all students. ■
Online Connections
The Beer-Lambert Law at Chemistry LibreTexts: https://bit.ly/3lNpPEi
Beer’s Law – Theoretical Principles: https://teaching.shu.ac.uk/hwb/chemistry/tutorials/molspec/beers1.htm
Beer’s Law at Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry: http://www.chem.ucla.edu/~harding/IGOC/B/beers_law.html
Beer Lambert Law at Edinburgh Instruments: https://www.edinst.com/blog/the-beer-lambert-law/
Beer’s Law Lab at PhET Interactive Simulations: https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/beers-law-lab
Figure 4. Problem-solving experiment problem statement: https://bit.ly/3pAYHtj
Figure 5. Learning targets: https://bit.ly/307BHtb
Figure 6. Materials list: https://bit.ly/308a57h
Figure 7. The use of color comparison as a low-cost alternative: https://bit.ly/3du1uyO
Figure 9. Summative performance-based assessment rubric: https://bit.ly/31KoZRj
Figure 10. Connecting to the Next Generation Science Standards : https://bit.ly/3GlJnY0
Kevin Mason ( [email protected] ) is Professor of Education at the University of Wisconsin–Stout, Menomonie, WI; Steve Schieffer is a chemistry teacher at Amery High School, Amery, WI; Tara Rose is a chemistry teacher at Amery High School, Amery, WI; and Greg Matthias is Assistant Professor of Education at the University of Wisconsin–Stout, Menomonie, WI.
Akinoglu, O., and R. Tandogan. 2007. The effects of problem-based active learning in science education on students’ academic achievement, attitude and concept learning. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science, and Technology Education 3 (1): 77–81.
Areepattamannil, S. 2012. Effects of inquiry-based science instruction on science achievement and interest in science: Evidence from Qatar. The Journal of Educational Research 105 (2): 134–146.
Bando R., E. Nashlund-Hadley, and P. Gertler. 2019. Effect of inquiry and problem-based pedagogy on learning: Evidence from 10 field experiments in four countries. The National Bureau of Economic Research 26280.
Furtak, E., T. Seidel, and H. Iverson. 2012. Experimental and quasi-experimental studies of inquiry-based science teaching: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research 82 (3): 300–329.
Hansen, Z., H. Owan, and J. Pan. 2015. The impact of group diversity on class performance. Education Economics 23 (2): 238–258.
Inel, D., and A. Balim. 2010. The effects of using problem-based learning in science and technology teaching upon students’ academic achievement and levels of structuring concepts. Pacific Forum on Science Learning and Teaching 11 (2): 1–23.
Merritt, J., M. Lee, P. Rillero, and B. Kinach. 2017. Problem-based learning in K–8 mathematics and science education: A literature review. The Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning 11 (2).
NGSS Lead States. 2013. Next Generation Science Standards: For states, by states. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Panasan, M., and P. Nuangchalerm. 2010. Learning outcomes of project-based and inquiry-based learning activities. Journal of Social Sciences 6 (2): 252–255.
Rutherford, F.J. 1964. The role of inquiry in science teaching. Journal of Research in Science Teaching 2 (2): 80–84.
Stevens, L.J., J.R. Burgess, M.A. Stochelski, and T. Kuczek. 2015. Amounts of artificial food dyes and added sugars in foods and sweets commonly consumed by children. Clinical Pediatrics 54 (4): 309–321.
Wilson, C., J. Taylor, and S. Kowalski. 2010. The relative effects and equity of inquiry-based and commonplace science teaching on students’ knowledge, reasoning, and argumentation. Journal of Research in Science Teaching 47 (3): 276–301.
Chemistry Crosscutting Concepts Curriculum Disciplinary Core Ideas General Science Inquiry Instructional Materials Labs Lesson Plans Mathematics NGSS Pedagogy Science and Engineering Practices STEM Teaching Strategies Technology Three-Dimensional Learning High School
You may also like
Web Seminar
Join us on Tuesday, June 4, 2024, from 7:00 PM to 8:30 PM ET, to learn about the free lesson plans and storyline units designed for high school s...
Reports Article
Join us on Thursday, October 24, 2024, from 7:00 PM to 8:00 PM ET, to learn about all NSTA Teacher Awards available and how to apply.Did you come up w...

50+ Genius STEM Activities for Kids
With a name like The STEM Laboratory, it’s no surprise that we’re obsessed with science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) activities for kids.
These 50+ STEM projects are sure to keep little scientists engaged, learning and well-prepared for their STEM-filled future.
Get inspired below and then sign up for our 5 Day STEM Challenge!
Not only will you learn exactly how to plan and teach STEM like a pro – but we’ll show you how to do it using supplies you already have in your storage closet. Score!
It’s never been simpler (or faster!) to get everything in place. Hop over and join right here!
This post contains Amazon affiliate links.

Science Projects
There are countless science experiments for kids but these 14 projects are our hands-down favorites!
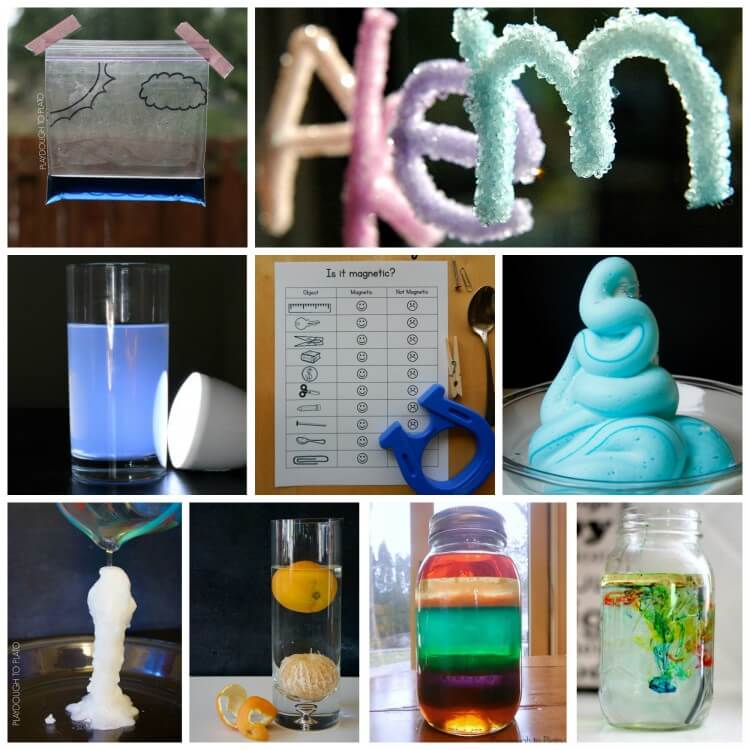

Make a mini model of the water cycle with just a Ziploc bag!
Turn your name into crystals!
Find out why the sky is blue. // Rookie Parenting
Test whether objects are magnetic . // The Measured Mom
Whip up some frothy, foamy toothpaste .
Pour ice that is warm to the touch but freezes.
Make one orange sink and another one float!
Pour a rainbow into a jar.
Capture fireworks in a jar using just a few common household supplies. // I Can Teach My Child
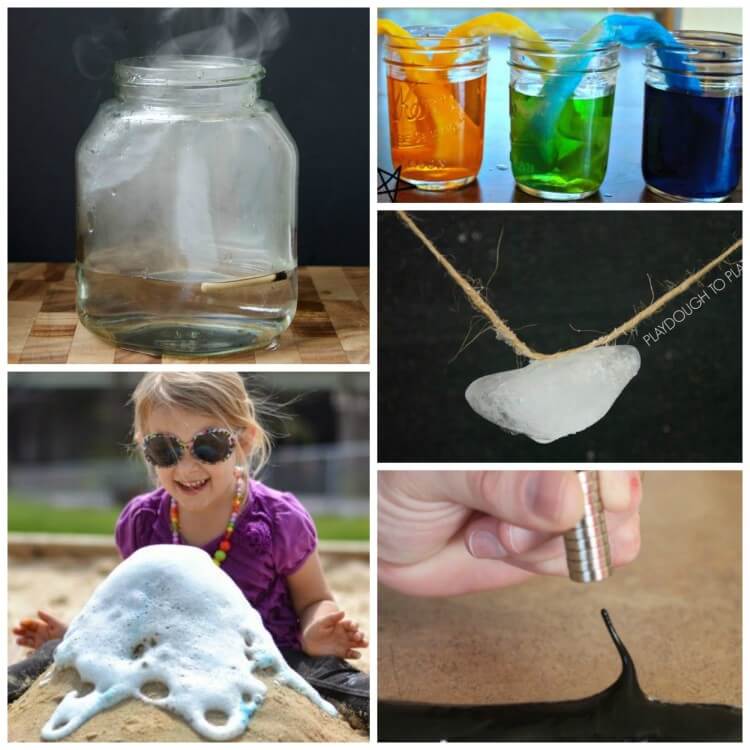

Go fishing for ice.
Learn about color mixing when you make water walk! // Parenting Chaos
Catch a cloud in a jar.
Build a sand volcano that really erupts. // Growing a Jeweled Rose
Play with Magnetic Slime . // Frugal Fun 4 Boys
Technology Activities
Build robots that really walk, talk and “think”. // Amazon
Teach kids about coding !
Let kids have a little screen time playing 20 teacher-approved apps.
Program a set of kid-friendly robot friends: Dash and Dot . // Amazon
Or build a Kano computer! // Amazon
Engineering Projects
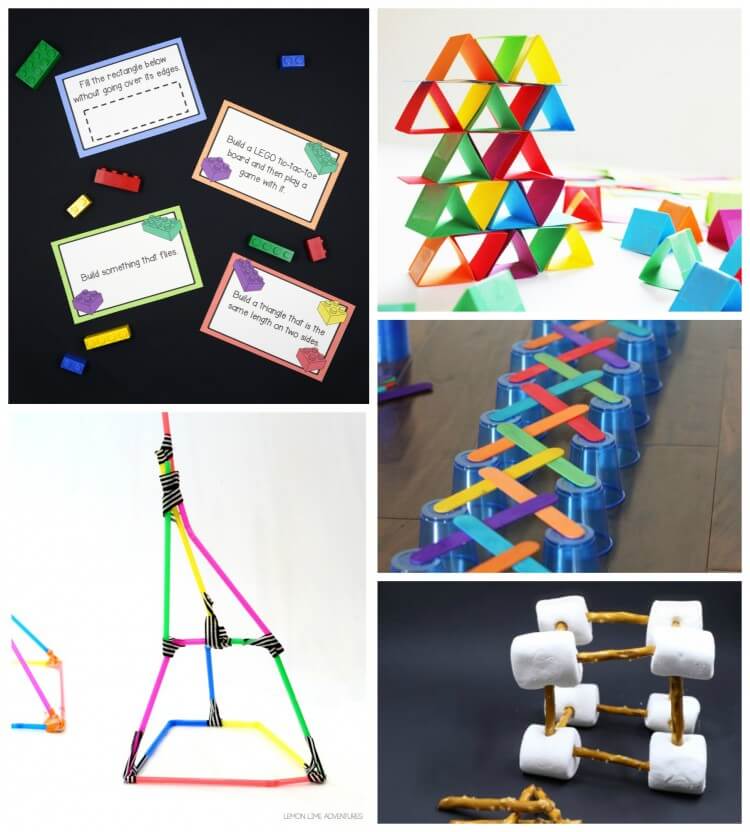

Solve a batch of LEGO challenge cards.
Fold paper into building blocks that really stack. // Babble Dabble Do
Use plastic cups and craft sticks to create four brilliant challenges . // Frugal Fun 4 Boys
Build with straws and tape. // Lemon Lime Adventures
Build structures with marshmallows and pretzels.
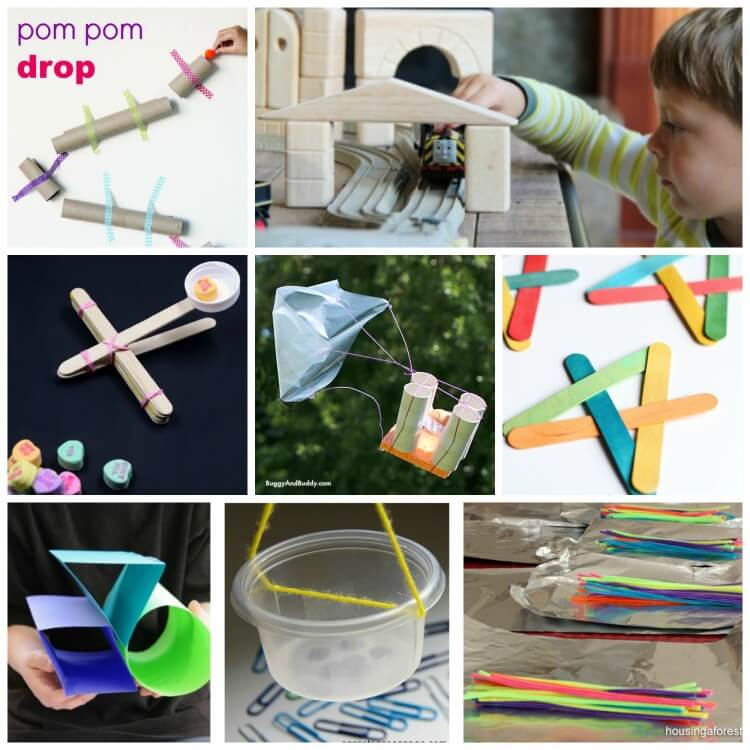

Design a pom pom drop that guides the pom pom from one paper towel roll to the next. // Coffee Cups and Crayons
Learn about bridges and then build your own. // Carrots are Orange
Make a craft stick catapult that really launches!
Try a classic! Organize an egg drop challenge . Can you build a structure that will keep the egg from breaking?! // Buggy and Buddy
Build a batch of exploding boomerangs . // I Can Teach My Child
Test the strength of a piece of paper . // Creekside Learning
Make a moveable pulley! // Carrots Are Orange
Work as a team to build with pipe cleaners and aluminum foil. // Housing a Forest
Math Activities

Practice counting with some truck playdough mats . // Pre Kinders
Or add googly eyes to monsters!
Teach kids about odd and even numbers with some hands-on activity sheets.
Clip 2-dimensional shapes. // The Measured Mom
Solve a batch of shape puzzles.
Use a Ziploc bag to solve addition problems on a number line. // Source unknown
Make a set of little math books. // Liz’s Early Learning Spot
Solve hands-on addition problems with LEGOS!
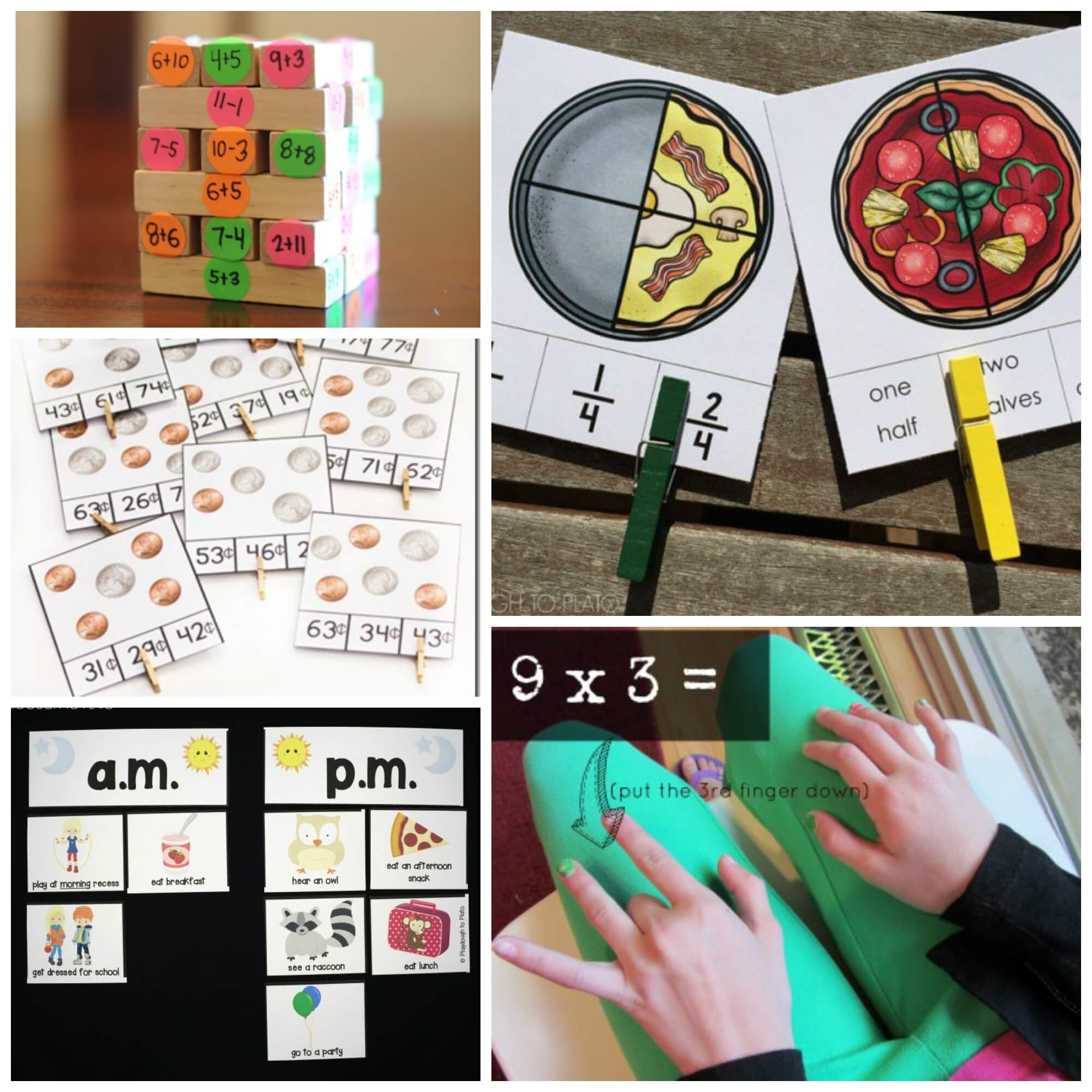

Play a round of math fact Jenga.
Learn about fractions with some handy pizza clip cards.
Practice adding together a handful of coins.
Teach kids about AM and PM.
Learn about the multiplication rule of nine. // Shelley Gray Teaching
Now Let’s Take Your STEM Centers to the Next Level
If you’re ready to give your STEM centers a MAJOR boost, hop over and take our 5 Day Challenge!
Not only will you learn exactly how to plan and teach STEM like a pro – but how to do it using supplies you already have in your storage closet.
It’s never been simpler (or faster!) to get everything in place.
Hop over and join right here!
Similar Posts

Ocean Write and Wipe Addition Cards

Addition Flower Puzzles

Dancing Cranberries

Robot Subtraction Cards

Roll and Cover Pattern Block Mats
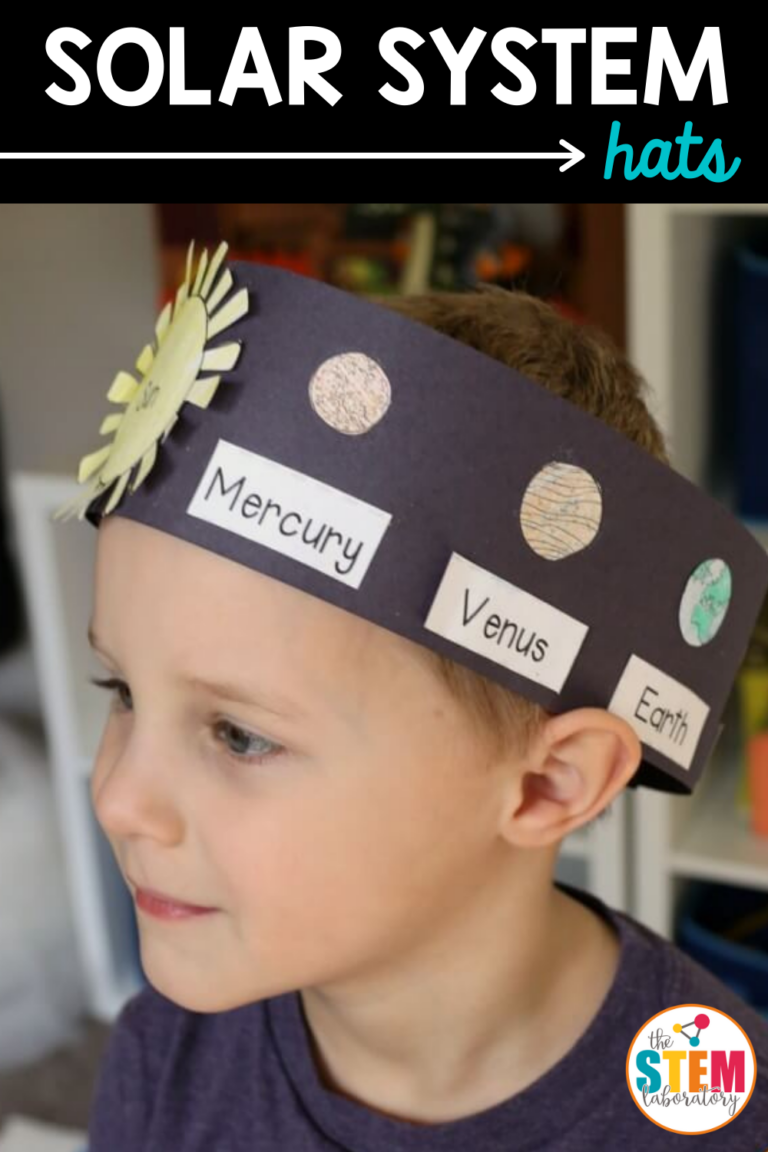

Solar System Hats
How do i buy the 50 genius stem activities for kids? i did not see that in the shop thank you
All of the STEM activities are linked to free blog posts. Just click on the activity you’d like to try and you’ll automatically be taken to the page with all the details. 🙂
- Pingback: How the Young Aviators Area helps with STEM learning | Aviation Heritage Museum
- Pingback: Straw Bridges - The Stem Laboratory - keiseronlineuniversity.com
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

7 Science Fair Projects that Solve Problems
- August 5, 2023
Share this post:

Science fair projects that solve problems are a great way for students to test their interest and aptitude for a career in STEM (science-technology-engineering-math). But they shouldn’t choose just any old topic. To make the most of the opportunity, try to focus on projects with real-world applications. This will give them hands-on experience directly related to a good-paying job field, like engineering .
With planning and hard work, the right science fair project might bump up a student’s chances for a scholarship or a trip to one of the science competitions sponsored by the Society for Science .
Do your students need help sketching the experimental set-up for a science fair presentation? Check out these resources:
- No-Prep Worksheets – How to Draw like an Engineer and Isometric Drawing
- 3D Isometric Drawing and Design for Middle School
- My Engineering Draw & Write Journal for Kids : 48 Fun Drawing and Writing Prompts to Learn about the Engineering Design Process.
Don’t get me wrong — creating foaming volcanoes or diagramming the human circulatory system are fun and classic ideas for a science fair project. But unless your student plans to go to med school or major in geology, these typical projects won’t do much to advance his or her future career. Far more practical engineering jobs will be available in the 21st century.
In this post you’ll find seven problem-solving science fair projects gleaned from the Education.com website. They provide simple, but realistic, introductions to real-world careers in electronics, robotics & automation, and construction engineering.
For more help with choosing a science fair topic, setting up your experiment, collecting and analyzing the data, and presenting your results, visit NASA’s video page on How to do a Science Fair Project .
Solving problems in Smart Technology
Consider the hottest topic in industry today – Smart Manufacturing, or Industry 4.0, sometimes called the Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT). Industry 4.0 is just one facet of the global push towards Smart Cities, Smart Homes, and Smart Agriculture.
All these concepts center on wireless connectivity between machines using cellular networks. So, for Smart Homes, this means your utilities, fridge, lights, security, HVAC, and other systems would be connected through an app on your smartphone. From there you can track and control these systems to keep your home safe and comfortable, while reducing water and energy use.
[Click here to join the STEM-Inspirations mailing list ]
For Industry 4.0, companies are connecting the machines used in their manufacturing and power generation plants at different locations around the world. On top of that, they are creating “digital twins” of each machine, which are 3D animated computer models of the machines.
The idea is to collect real-time data from each machine and then use that data, along with artificial intelligence (AI), machine vision, and even virtual reality simulations, to:
- Design new products
- Predict when a machine will need maintenance BEFORE something goes wrong
- Optimize the output of the machines and harmonize them to work together
Solving problems in Robotics
Another major topic in industry is robotics and automation . Automation means that machines are programmed to perform tasks without human help. Some robots are standalone, “service” robots, like the Roomba. Others, like robotic arms in factories and warehouses, pick and place items to be processed.
The more human-friendly “collaborative” robots can improve human capacity and are safe to work around. Put together, these technologies allow some manufacturing plants to run “lights out,” without any human input for days.

Robots are boosting agriculture, both in planting and harvesting fields and in packaging food. With Smart Agriculture technology, farmers collect data in their fields with mobile apps applying artificial intelligence (AI) software to reduce fertilizer needs and optimize water use.
Help students sketch their experimental set-up for science fair presentations with these resources: No-Prep Worksheets – How to Draw like an Engineer and Isometric Drawing 3D Isometric Drawing and Design for Middle School My Engineering Draw & Write Journal for Kids : 48 Fun Drawing and Writing Prompts to Learn about the Engineering Design Process.
Solving Engineering Problems
Most science fair projects on the internet seem to focus on the basic sciences, like biology and chemistry. But in light of the skills gap we are now experiencing between the available job force and manufacturing industry requirements, I believe engineering-focused science fair projects that solve problems in Industry 4.0, robotics, automation, and construction may be better choices for building up tomorrow’s workforce.
Here are 7 science fair project ideas that focus on solving problems:
1. cell phone dead zones science fair project.
https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/cell-phone-dead-zones/
Students learn how wireless networks work, find dead zones where wireless signals are lost, and determine ways to reduce these zones – important preparation for students who hope to work on Smart Homes, Smart Factories, Smart Cities, or Smart Agriculture.
2. App development science fair project
https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/iphone-application-design/
An app on a phone or tablet can be an interactive game, a navigational device, a business software package, or just about anything else you can imagine. This project allows you to get a head start in the growing app design field by designing your own app for popular smartphones.
3. Smoke detector science fair project
https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/smoke-detectors-working/?source=related_materials&order=2
Sensors of all kinds solve problems for smart technologies and robotics engineering. Sensors can detect motion, gases, light, heat, and other changes in the environment to allow robots to avoid collisions or Smart Homes to detect a fire, for example. This project compares the effectiveness of two types of sensors in a smoke detector.
4. Faraday’s experiment science fair project
https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/faraday-experiment-current-generated-magnet/
Electric currents create their own magnetic fields, and the movement of magnets induces , or creates, current in a wire. Motors and generators use magnetic movement to create current and send electricity to do useful work to power machines. In this lab, you will recreate Michael Faraday’s famous experiment by building a solenoid (a coil of wire) and experiment with moving magnets to produce current.
5 & 6. EMFs science fair projects
https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/smart-card-electromagnetic-fields/
https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/EMF-affect-us/
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is an electronic technology used in credit cards, ID Cards, and theft prevention systems, as well as in manufacturing, warehousing and shipping products. The first project measures the electromagnetic fields (EMFs) given off by various RFID transmitters, which may have harmful effects on people. The second project looks directly at how EMFs can affect us physically.
7. Rust prevention science fair project
https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/bust-that-rust/
Metals rust, and that can be a big problem when it comes to bridges, buildings, cars, and any object exposed to air and water. This project examines the process of oxidation (not just rust) that ultimately breaks down every physical object and looks at ways to prevent that from happening.
For more problem-solving science fair project ideas, follow the STEM-Inspirations Science Fair Projects board on Pinterest.
Copyright © 2017-2021 by Holly B. Martin
Click here to join the STEM-Inspirations mailing list .

Hi, I'm Holly!
I help you educate and inspire students to pursue careers in STEM/STEAM!
Click here to learn more about me and how I can help you .
Let's Connect!

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Free printable Mother's Day questionnaire 💐!
50 STEM Activities for Kids of All Ages and Interests
Inspire the innovators of tomorrow.

These days, STEM learning is more important than ever. Science, technology, engineering, and math are the keys to many modern careers, so a good grounding in them from an early age is a must. The best STEM activities for kids are hands-on, leading students to cool innovations and real-world applications . Here are some of our favorites, with challenges and experiments that will really get kids thinking about how STEM plays a part in their everyday lives.
Want some quick challenges to try with elementary students? Get free printable stem challenge cards for grades K-5:
- Kindergarten STEM Challenges
- First Grade STEM Challenges
- Second Grade STEM Challenges
- Third Grade STEM Challenges
- Fourth Grade STEM Challenges
- Fifth Grade STEM Challenges
For more STEM activities for kids across a range of subjects, take a look at these ideas.
1. Add STEM bins to your classroom

STEM Focus: Science, Technology, Engineering, Math
Prepare for a wide variety of STEM activities for kids with these cool bins. Incorporate them into literacy centers, create a makerspace, and offer early finishers fun enrichment ideas. Learn how to create and use STEM bins.
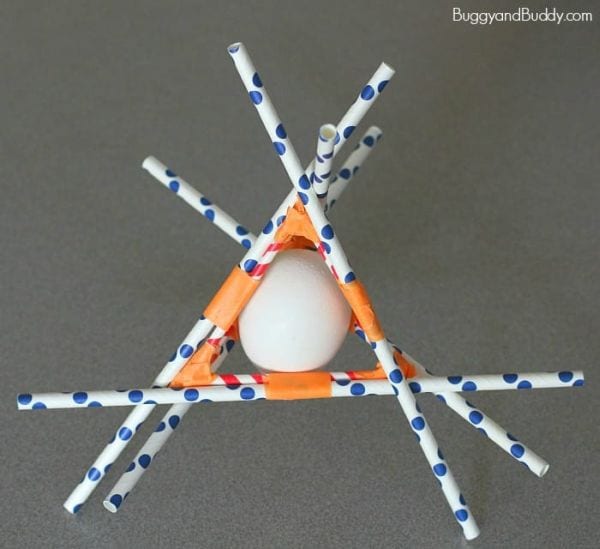
2. Conduct an egg drop

STEM Focus: Engineering
This is one of those classic STEM activities every kid should try at least once. Kids can do it at any age, with different materials and heights to mix it up.
Learn more: Egg Drop at Buggy and Buddy
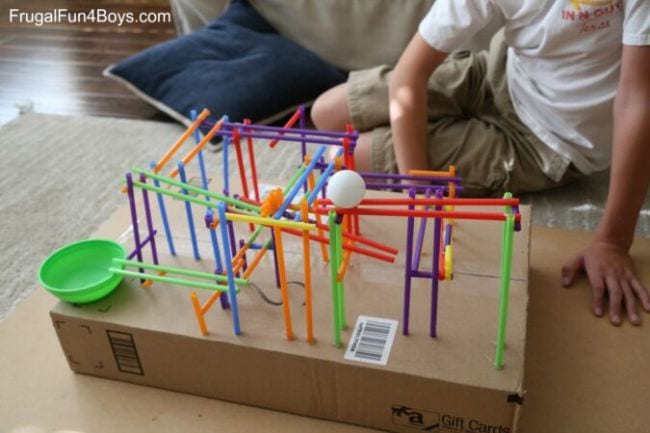
3. Engineer a drinking straw roller coaster

This is such a fun way to encourage engineering skills! All you need are basic supplies like drinking straws, tape, and scissors.
Learn more: Straw Roller Coaster at Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls
4. Find ways to slow soil erosion

STEM Focus: Science (Ecology), Engineering
Compare the effects of “rain” on hills of bare soil vs. those covered with grass. Have your 3rd grade science students predict which they think will stand up to erosion better and then test their hypotheses.
Learn more: Erosion Experiment at Third Grade Thinkers
5. Simulate an earthquake
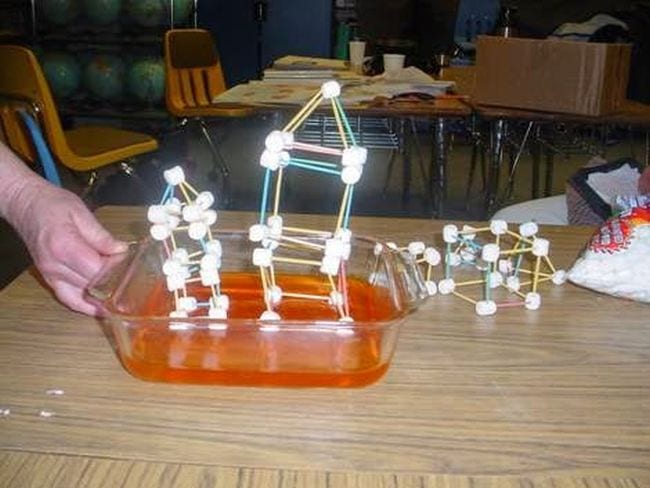

The ground under our feet may feel solid, but an earthquake changes that pretty quickly. Use Jell-O to simulate the earth’s crust, then see if you can build an earthquake-proof structure.
Learn more: Earthquake Science at Teaching Science
6. Stand up to a hurricane

In a hurricane zone, houses must be able to stand up to strong winds and possible flooding. Can your students design houses that make it safer to live in these dangerous areas?
Learn more: Hurricane Houses at Carly and Adam
7. Create a new plant or animal

STEM Focus: Science (Biology)
Kids will really get into this project, indulging their creativity as they invent a plant or animal that’s never been seen before. They’ll need to be able to explain the biology behind it all, though, making this an in-depth project you can tailor to any class.
Learn more: Create a Creature at I Love 2 Teach
8. Design a helping hand
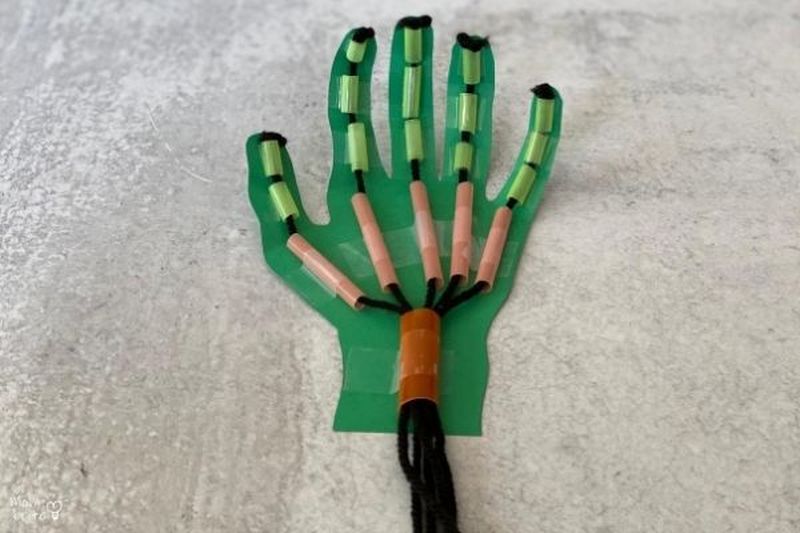

STEM Focus: Technology, Engineering
This is a great group science project. Students hone their design and engineering skills to make a working model of a hand. For a more advanced activity, challenge students to build a robotic hand that can be controlled remotely.
Learn more : Model Hand at Mombrite
9. Understand the impact of non-renewable resources

STEM Focus: Science (Environmental Science)
Discuss the differences between renewable and non-renewable resources, then have your class form “companies” to “mine” non-renewable resources. As they compete, they’ll see how quickly the resources are used. It’s a great tie-in to energy conservation discussions.
Learn more: Energy Resources at The Owl Teacher
10. Devise an amazing marble maze

Marble mazes are one of students’ favorite STEM activities! You can provide supplies like straws and paper plates for their project. Or let them use their imaginations and create marble mazes from any materials they can think of.
Learn more: Marble Maze on Raising Lifelong Learners
11. Fly clothespin airplanes

STEM: Engineering
Ask students what they think the airplane of the future might look like. Then, provide them with clothespins and wood craft sticks, and challenge them to build a new kind of airplane. Bonus points if it can actually fly!
Learn more: Clothespin Airplane at STEAMsational
12. Launch a catapult cannon
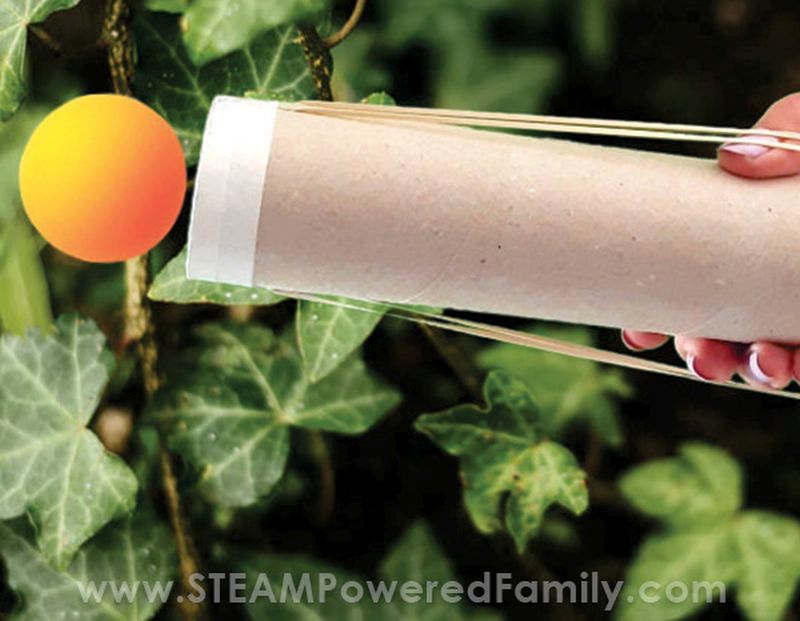

Catapult STEM challenges are always fun, but this one adds a new twist that allows kids to launch objects much farther than the usual wood craft stick version!
Learn more: Catapult Cannon and STEAM Powered Family
13. Bounce on a trampoline
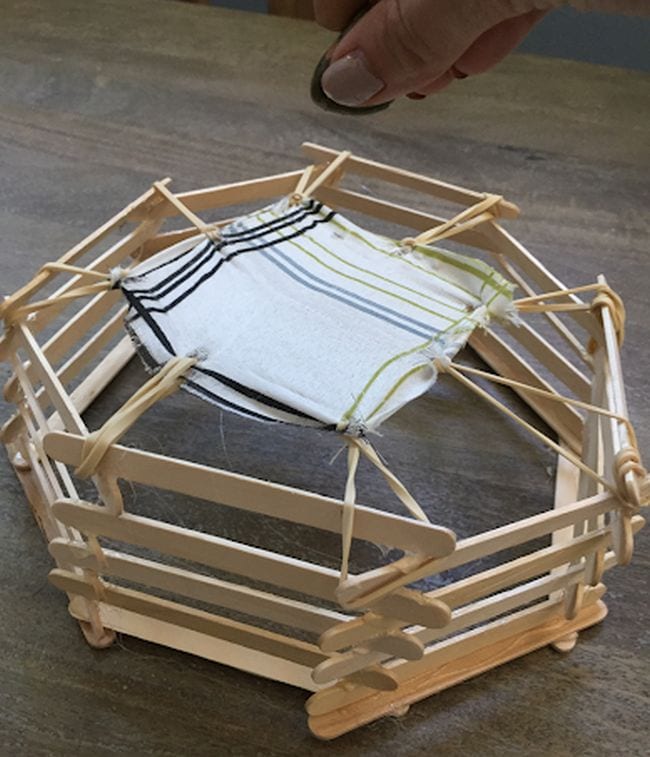

Kids love bouncing on trampolines, but can they build one themselves? Find out with this totally fun STEM challenge.
Learn more: Trampoline Challenge at Student Savvy
14. Build a solar oven
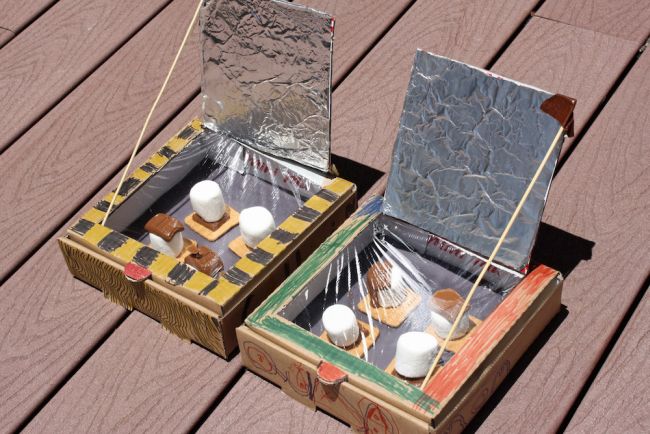

STEM Focus: Science, Engineering
Learn about the value of solar energy by building an oven that cooks food without electricity. Enjoy your tasty treats while discussing ways we can harness the energy of the sun and why alternative energy sources are important.
Learn more: Solar Oven at Desert Chica
15. Build a snack machine

Incorporate everything students learn about simple machines into one project when you challenge them to build a snack machine. Using basic supplies, they’ll need to design and construct a machine that delivers snacks from one location to another.
Learn more: Snack Machine at Left Brain Craft Brain
16. Recycle newspaper into an engineering challenge

It’s amazing how a stack of newspapers can spark such creative engineering. Challenge students to build the tallest tower, support a book, or even build a chair using only newspaper and tape.
Learn more: Newspaper STEM Challenges at STEM Activities for Kids
17. Design a biosphere

This project really brings out kids’ creativity and helps them understand that everything in a biosphere is really part of one big whole. You’ll be overwhelmed by what they come up with!
Learn more: Biosphere Project at Laney Lee
18. See the effects of an oil spill
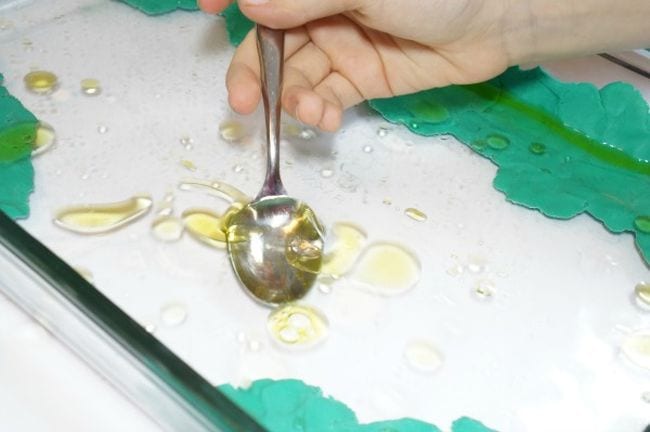

Learn why an oil spill is so devastating for wildlife and the ecosystem with this hands-on activity. Kids experiment to find the best way to clean up oil floating on water and rescue the animals affected by the spill.
Learn more: Oil Spill Cleanup at Kitchen Counter Chronicle
19. Assemble a steady-hand game

STEM Focus: Engineering, Technology
This is such a fun way to learn about circuits. It also brings in a bit of creativity, adding the “A” for STEAM.
Learn more: Steady Hand Game at Left Brain Craft Brain
20. Use cabbage to test pH

STEM Focus: Science (Chemistry)
Teach kids about acids and bases without needing pH test strips! Simply boil some red cabbage and use the resulting water to test various substances—acids turn red and bases turn green.
Learn more: Cabbage pH at Education Possible
21. Engineer a craft stick bridge
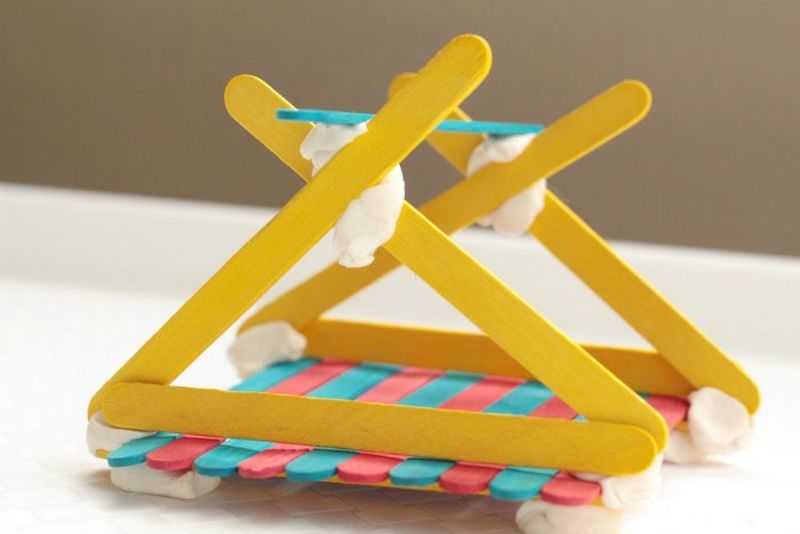

Here’s another one of those classic STEM activities that really challenge kids to use their skills. Build a bridge with Popsicle sticks and other materials, then compete to see which can bear the most weight.
Learn more: Bridge Challenge at Mommy Evolution
22. Forage and build a bird nest

STEM Focus: Science (Biology), Engineering
Birds build incredibly intricate nests from materials they find in the wild. Take a nature walk to gather materials, then see if you can build a sturdy, comfy nest of your own!
Learn more: Build a Bird Nest at Kids Craft Room
23. Drop parachutes to test air resistance

Use the scientific method to test different types of material and see which makes the most effective parachute. Your students also learn more about the physics behind air resistance.
Learn more: Parachute Challenge at Education.com
24. Find the most waterproof roof

Calling all future engineers! Build a house from LEGO, then experiment to see what type of roof prevents water from leaking inside.
Learn more: Waterproof Roof at Science Sparks
25. Build a better umbrella
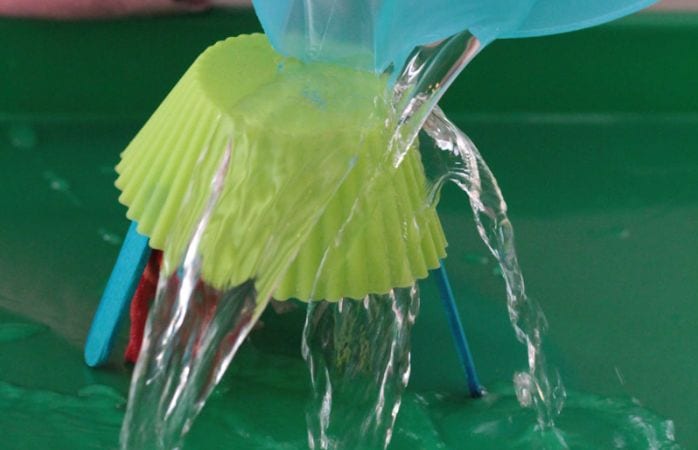

Challenge students to engineer the best possible umbrella from various household supplies. Encourage them to plan, draw blueprints, and test their creations using the scientific method.
Learn more: Better Umbrella at Raising Lifelong Learners
26. Go green with recycled paper

STEM Focus: Science (Ecology)
We talk a lot about recycling and sustainability these days, so show kids how it’s done! Recycle old worksheets or other papers using screen and picture frames. Then, ask kids to brainstorm ways to use the recycled paper.
Learn more: Recycled Paper at Undercover Classroom
27. Brew up your own slime
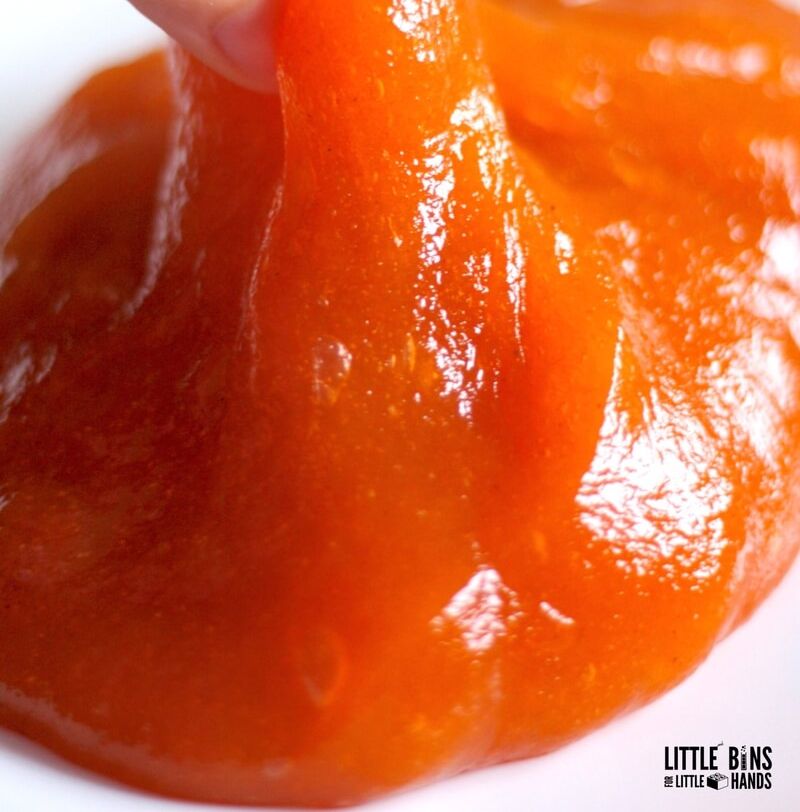

Chances are good your students already love making and playing with slime. Turn the fun into an experiment by changing the ingredients to create slime with a variety of properties—from magnetic to glow-in-the-dark!
Learn more: Slime Experiments at Little Bins for Little Hands
28. Create a taxonomy system

Students can step into Linnaeus’ shoes by creating their own system of taxonomy using a handful of different dried beans. This is a fun science project to do in groups, so students can see the differences between each group’s system.
Learn more: Classification Systems at Our Journey Westward
29. Find out which liquid is best for growing seeds

As you learn about the life cycle of plants , explore how water supports plants’ growth. Plant seeds and water them with a variety of liquids to see which sprout first and grow best.
Learn more: Plants and Liquids at Lessons for Little Ones
30. Create giant bubbles

It’s easy to mix your own soap bubble solution with just a few ingredients. Let kids experiment to find the best proportion of ingredients to create giant bubbles, long-lasting bubbles, and other variations.
Learn more: Giant Soap Bubbles at Make and Takes
31. Make compost in a cup

This is an easy science activity, and you can turn it into a science fair project by experimenting with different mixtures, layering, and conditions for your compost cups.
Learn more: Compost Cups at The Happy Housewife
32. Help monarch butterflies
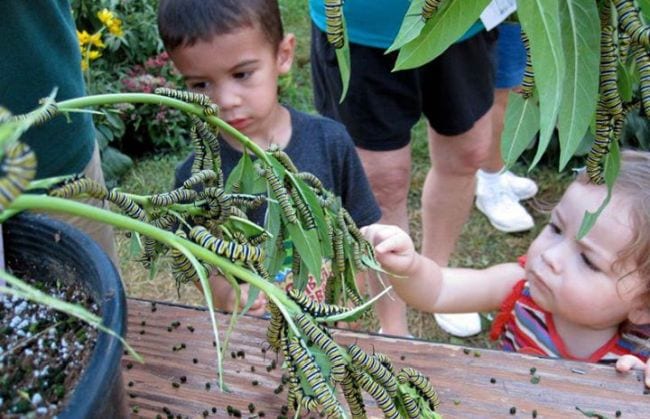

You may have heard that monarch butterflies are struggling to keep their population alive. Join the fight to save these beautiful bugs by planting your own butterfly garden, monitoring monarch populations, and more. Get all the info you need at the link.
Learn more: Monarch Education at Monarch Watch
33. See water pollution in action

STEM Focus: Science (Environmental Science, Chemistry, Biology)
Learn about the challenges of cleaning up polluted water sources like rivers and lakes with this interesting outdoor science activity. Pair it with a visit to a local water treatment plant to expand the lesson.
Learn more: Water Pollution at JDaniel4’s Mom
34. Test your local water quality
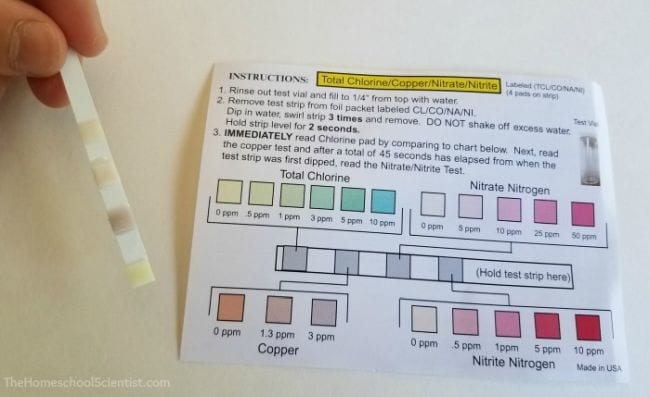
STEM Focus: Science (Chemistry, Environmental Science)
Once you’ve “cleaned up” your water, try testing it to see how clean it really is! Then head out to test other types of water. Kids will be fascinated to discover what’s in the water in their local streams, ponds, and puddles. Student water-testing kits are readily available online.
Learn more: Water Quality Experiment at The Homeschool Scientist
35. Explore with an edible Mars Rover

STEM Focus: Science (Space), Engineering
Learn about the conditions on Mars and the tasks the Mars Rover will need to complete. Then, give kids supplies to build their own. (Add to the challenge by making them “buy” the supplies and stick to a budget, just like NASA!)
Learn more: Edible Mars Rover at Library Makers

36. Bake the best potato

STEM Focus: Science (Physics)
This edible science project is a nutritious way to explore the scientific method in action. Experiment with a variety of methods for baking potatoes—microwaving, using a traditional oven, wrapping them in foil, using baking pins, etc.—testing hypotheses to discover which works best.
Learn more: Potato Science at Left Brain Craft Brain
37. Waterproof a boot

Ask kids to select various materials and tape them over the free boot printable. Then, test their hypotheses to see which ones work best.
Learn more: Waterproof a Boot at Science Sparks
38. Determine the best way to melt ice

Conventional wisdom says we sprinkle salt on ice to melt it faster. But why? Is that really the best method? Try this science experiment and find out.
Learn more: Melting Ice at The Chaos and the Clutter
39. Don’t melt the ice

We spend a lot of time in winter trying to get rid of ice, but what about when you don’t want the ice to melt? Experiment with different forms of insulation to see which keeps ice frozen the longest.
Learn more: Ice Insulation at Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls
40. Build a straw house

Grab a box of straws and a package of pipe cleaners. Then task kids with designing and building their dream house, using only those two items.
Learn more: Building a Straw House at Deceptively Educational
41. Design a balloon-powered car
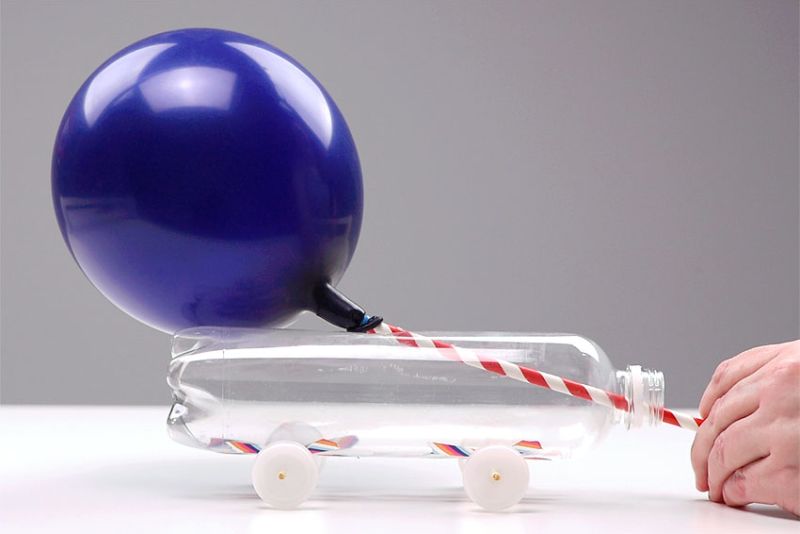

Explore the laws of motion and encourage creativity when you challenge students to design, build, and test their own balloon-powered cars. Bonus: Use only recycled materials to make this project green!
Learn more: Balloon-Powered Car at One Little Project
42. Learn map skills by designing an amusement park
STEM Focus: Science (Physics), Technology, Engineering, Math
For this cross-curricular activity, students investigate the parts of a map by creating an amusement park. After they create their map, they do a detailed drawing and write about one of their ride designs. Then they design an all-access park pass. So many STEM activities in one! Find out more about it here.
43. Reach for the ceiling
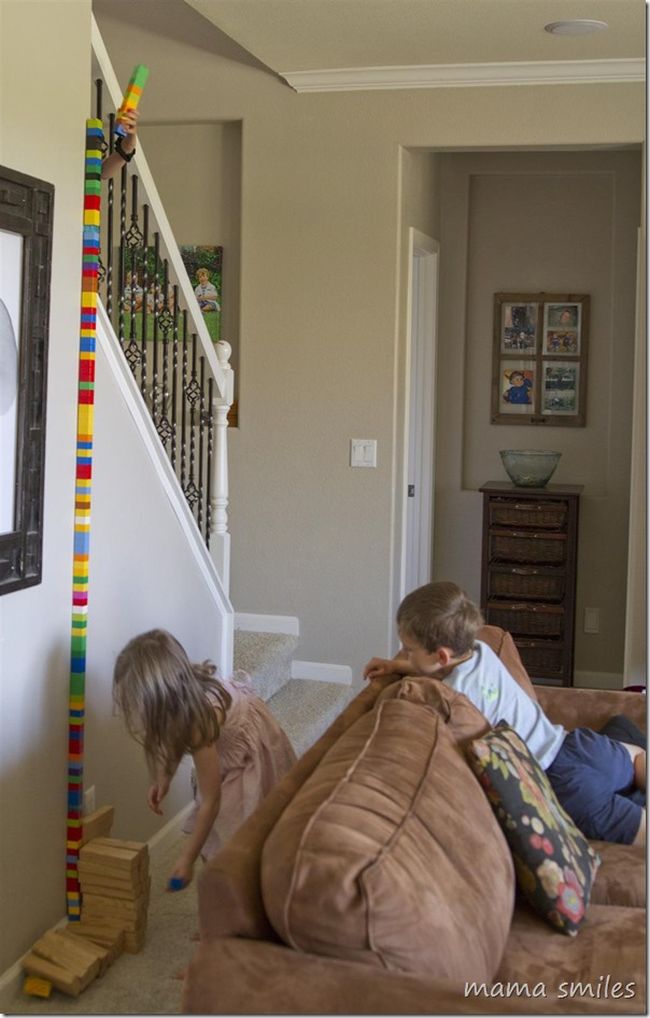

Round up all your building blocks and try this whole-class project. What will students need to do to be able to construct a tower that reaches all the way to the ceiling?
Learn more: Block Tower at Mama Smiles
44. Cast a tall shadow

STEM Challenge: Science (Physics)
Here’s another tower-building challenge, but this one’s all about shadows! Kids will experiment with the height of their tower and the angle of their flashlight to see how tall of a shadow they’re able to cast.
Learn more: Shadow Towers at No Time for Flash Cards
45. Devise a recycled toy bot

These adorable toy bots are made from pool noodles and recycled electric toothbrushes. So clever! Kids will have fun designing their own, plus they can tweak this idea to make other fun wiggling toys.
Learn more: Recycled Toy Bot at Artsy Momma
46. Link up the longest paper chain

This incredibly simple STEM activity really gets kids thinking. The challenge? Create the longest-possible paper chain using a single piece of paper. So simple and so effective.
Learn more: Paper Chain Challenge at Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls
47. Find out what you can make from a plastic bag

STEM Focus: Science (Environmental Science), Engineering
Plastic bags are one of the most ubiquitous items on the planet these days, and they’re difficult to recycle. Give each student a plastic bag and ask them to create something new and useful. ( These ideas from Artsy Craftsy Mom offer some inspiration. )
48. Start a school robotics team

STEM Focus: Technology
Coding is one of the most valuable STEM activities you can include in your classroom plans. Set up a school robotics club and inspire kids to embrace their newfound skills! Learn how to set up your own club here.
49. Embrace the Hour of Code
The Hour of Code program was designed as a way to get all teachers to try just one hour of teaching and learning coding with their students. Originally, the Hour of Code event was held in December, but you can organize yours any time . Then, continue to learn using the huge amount of resources on Hour of Code’s website .
50. Give kids a Maker Cart and a pile of cardboard

You don’t need a whole lot of fancy supplies to create a STEM Cart or makerspace. Scissors, tape, glue, wood craft sticks, straws—basic items like these combined with a stack of cardboard can inspire kids to create all sorts of amazing projects! See how these STEM activities work here.
What are your favorite STEM activities for kids? Come share in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, get 20+ free stem posters for your classroom .

You Might Also Like

25 Kindergarten STEM Challenges That Little Ones Will Love
They're never too young to create and explore! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Coffee Cups and Crayons
Simple play ideas, learning activities, kids crafts and party ideas, plus acts of kindness for kids!
Science Experiments for Kids
Do you love science experiments for kids ? We totally do and want to help you love them too!
Doing simple science experiments at home or in your classroom is the easiest way to teach kids to be problem solvers and critical thinkers and help them develop a curiosity about the world around them. These skills empower kids to be confident in their ability to handle life’s challenges which is a life skill that cannot be overrated!
Plus they are a ton of fun to do and a great way to make memories with your family. Ready to get started? Here are some of our most popular and very favorite science experiments for kids to do!

If you are a long time reader of Coffee Cups and Crayons (high five!) then you already know that we strongly believe in simple fun and learning. You probably already have most of the supplies needed for these experiments in your kitchen cupboards right now. Which is important because it doesn’t matter how cool the science experiment is, if it’s not do-able it will just end up being an image that sits on your Pinterest board forever.
Speaking of Pinterest, you’ll want to make sure to pin this page to your favorite board . There’s a ton of experiments on here that you can keep coming back to when you’re looking for a new idea. We’ll also continue to add to this list as we post new ones to make this the best list of science experiments ever!
Kitchen Science Experiments
These are the ones you can set up in minutes with items you have in your kitchen. They also make great boredom busters for kids and are perfect for a rainy day!
- Make an Egg Float
- Celery Transpiration Experiment
- Make a Rubber Egg
- Dancing Raisins
- Liquid Layers Density Experiment
- Apple Acid and Base Experiment
- Making Rock Candy
- Skittles or M&M Experiment (try both on the same day!)
- Mad Scientist Baking Soda and Vinegar Art
- Walking Water Science
- Salt Crystal Painting STEAM Activity
- Flying Tea Bag Experiment for Kids
- Magic Pepper and Soap Experiment
- Milk Rainbow Science Experiment
- Climbing Rainbow Science Experiment
Nature and Weather Experiments
Kids are naturally curious about the world around them. Capitalize on this by doing fun weather and nature themed experiments to help them understand abstract concepts.
- How Wind Works
- Tornado in a Jar
- How to Make a Lava Lamp
- Cloud in a Bottle Experiment
- Classic Volcano Experiment
- Rain Cloud in a Jar
- Flower Pigment Experiment
Candy Science Experiments
What can be more fun than experimenting with candy? Not much. Many of the candies (not all) in the experiments below can be swapped for whatever you may have on hand so feel free to do some experimenting of your own!
- Diet Coke and Mentos Experiment
- M&M Experiment
- Take the S of a Skittle Experiment
- Peeps Science Experiments
- Candy Corn Experiments
- Conversation Heart Experiments
- Marshmallow Engineering
Explosions and Chemistry Experiments
Pop! Fizz! Bubble! Explosions and reactions get kids excited about chemistry and these experiments all pack a big bang.
- Diet Coke and Mentos Geyser
- Make a Volcano
- Make Silly Putty
- Does It Dissolve Experiment
- Mad Scientist Art
- Exploding Baggie
- How to Make Slime
- Make Super Bouncy Snowballs
Engineering and Physical Science Experiments
Turn your kids into problem solving engineers with these cool STEM experiments. They can explore how things work and test out some properties of physics while tinkering and experimenting.
- Lemon Battery
- Pom Pom Drop Experiment
- DIY Catapults
- Sun Melted Crayon Experiment
- Walking Water Science Experiment
- Simple Heat Experiment
- Marshmallow Engineering Experiment
- How to Build a Paddleboat
- DIY Marble Mazes for Preschool Kids
Holiday and Seasonal Science Experiments
Get kids in the holiday spirit with science! These experiments make use of the seasonal candy and products and are a great way to add a little learning into the fun of the holidays.
- Insta Snow Science Experiments
- Peeps Experiments
- Super Cool Rainbow Science Experiments
- Apple Experiments
- Pumpkin Investigations
- Candy Corn Science Experiments
- Dissolving Candy Cane Science

Get Your ALL ACCESS Shop Pass here →

45 Outdoor STEM Activities For Kids
Welcome to our list of amazing outdoor STEM activities to keep your kids busy outside! Get kids outdoors to enjoy the natural world while developing problem-solving, creativity, observation, engineering skills, and more. We love easy and doable STEM projects for kids!

What Is Outdoor STEM?
These outdoor STEM activities can be used for home, school, or camp. Get kids outside and get kids interested in STEM! Take STEM outdoors, on the road, camping, or to the beach, wherever you go, but take it outside this year!
So you might ask, what does STEM stand for? STEM stands for science, technology, engineering, and math. Additionally, you might hear about STEAM , which includes an “A” for art!
We love STEM for kids because of its value and importance for the future. The world needs critical thinkers, doers, and problem solvers. STEM activities help kids better understand science, adapt to the latest technology, and engineer new solutions to solve problems of all sizes. Try our Real World STEM challenge !
Outdoor STEM is one of the best ways to get kids involved and keep them engaged. Below you will find nature STEM activities, outdoor science activities, and ideas for STEM camping activities. We even include some cool outdoor science experiments!
Helpful STEM Resources To Get You Started
Here are a few resources to help you introduce STEM more effectively to your kiddos or students and feel confident when presenting materials. You’ll find helpful free printables throughout.
- Engineering Design Process Explained
- What Is An Engineer
- Engineering Words
- Questions for Reflection (get them talking about it!)
- BEST STEM Books for Kids
- 14 Engineering Books for Kids
- Jr. Engineer Challenge Calendar (Free)
- Must Have STEM Supplies List
Click below to get your free printable STEM challenges!
You’ll find fantastic Nature STEM challenge cards that are meant to be done outdoors!

Outdoor STEM Activities
These outdoor STEM activities provide new ways to incorporate favorite electronics, get dirty, look at nature differently, and explore and experiment. Don’t spend too much time sitting indoors when the weather is beautiful outdoors!
Click on the links below to learn more about each activity.
Outdoor Science Experiments
- Love fizzing and exploding experiments? YES!! All you need are Mentos and coke .
- Or here is another way to do it with diet coke and mentos .
- Take this baking soda and vinegar volcano outdoors.
- Bursting Bags is a great outdoor science experiment.
- Simple outdoor science and a cool chemical reaction with an easy DIY Alka Seltzer rocket !
- Explore surface tension while you blow geometric bubbles !
- Try this color-changing slime outdoors and watch what happens!
- Set up a leakproof bag science experiment .
- Make a bottle rocket and blast off!
- Blow bubble snakes and learn about surface tension.

Nature STEM Activities
- Build an insect hotel .
- Make a cloud viewer and determine if the clouds you can see will bring rain.
- Set up a bird feeder , grab a book, and identify the birds around your house or classroom.
- Start a rock collection and learn about the rocks you find.
- Build your own mason bee house for a few simple supplies and help the pollinators in the garden.

Outdoor Engineering Projects
- Explore physics through play with this homemade Toy Zip Line .
- Design a homemade pulley system and learn about simple machines.
- Make a paper helicopter and see if it flies.
- Craft a paddle boat and watch it move!
- Test the wind with a DIY Anemometer.
- Make a wind vane .
- Set up a DIY rain gauge .

- Develop those design and planning skills when you build a stick fort .
- Build a solar oven and even try s’mores on it.
- Design and build a water wall .
- Explore forces as you fly a kite .
- Alternatively, track the time with a DIY sundial .

More Outdoor STEM Activities
Set up an outdoor STEM camp, explore nature-inspired STEAM, learn about the weather, or study plants.
- Want to set up a STEM camp? Check out these summer science camp ideas !
- Love science? Check out all our summer science experiments .
- Find all our nature activities and plant activities .
- Here’s our list of things to do outside for easy outdoor activities for kids.
- Get creative with these outdoor art activities .
- Design and craft a DIY kaleidoscope for kids or try this spectroscope .
- Record the moon’s phases for the month, or track the weather !
Printable Engineering Projects Pack
Get started with STEM and engineering projects today with this fantastic resource that includes all the information you need to complete more than 50 activities that encourage STEM skills!

Do you have instructions for the Stem challenges please? Particularly catapults.
- Pingback: Principle 3: Putting Some Meaning Back Into Buzzwords: Resilience, Confidence, Independent and Creative – Creative Curriculums Ontario
- Pingback: Spring STEM Activities and Plant Science Activities for Kids
- Pingback: Water Science Activities for Kids STEM
- Pingback: Simple Ways To Take STEAM Outdoors This Summer
Comments are closed.
~ Projects to Try Now! ~

The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Reasons You Should Study Geography: Everything You Need to Know
The vtoman jump 1800 portable power station: the best of the best, key roles of a school superintendent: everything you need to know, why learners cheat: everything you need to know, top issues in education: everything you need to know, duties of a school principal: everything you need to know, private vs. public education: everything you need to know, choosing the perfect college: everything you need to know, common college freshmen fears: how to overcome them, how to fix it when brightness is not changing on windows 10, 14 project-based learning activities for the science classroom.

One of the most popular methods of facilitating deep learning in K-12 schools in problem-based learning. It starts, as the name suggests, with a problem. In this model, students are presented with an open-ended problem. Students must search through a variety of resources, called trigger material, to help them understand the problem from all angles. What would project-based learning look like in a subject like science? That’s what I plan to explore in this piece. Below you will find a list of 14 project-based learning activities for the K-12 science classroom.
- Student Farm. Students will learn lessons about science, social studies, math, and economics through planting their organic farm. They can begin by researching the crops they want, figure out what kind of care is needed, and then use a budget to determine what materials they must purchase. They can even sell food from their farm to contribute to a cause or fundraiser.
- Bridge Building. Students begin by studying the engineering of bridge building, comparing the construction of famous bridges such as the Golden Gate Bridge or Tower Bridge in London. Then they work in teams to construct bridges out of Popsicle sticks. The challenge is to get their bridge to hold five pounds (for younger students) or twenty pounds (for more advanced students).
- Shrinking Potato Chip Bags in the Microwave. Students can learn about polymers through hands-on activities using some of their favorite products, like shoes and sporting equipment. As a culminating activity, they can put a wrapper from their favorite chips or candy bar into the microwave for five seconds to learn about how polymers return to their natural state when exposed to the heat.
- Design an App. Students love using the newest apps and games, so take it to the next level by having them design their own! With Apple developer tools, kids can learn how to create an app or online game. They can learn about technology and problem-solving skills while engaged in what they love.
- Gummy Bear: Shrink or Grow? For a project-based lesson on osmosis and solubility, you will just need gummi bears and different liquids and solutions (water, salt water, vinegar, etc.). Children will place a gummi bear in each solution overnight and then measure the results.
- The Old Egg in a Bottle Trick . This old trick is an impressive PBL activity for kids to learn about the correlation between temperature and pressure,. Using just eggs, a wide mouth glass bottle, matches, and strips of paper, children will be able to make an egg “magically” fit through the bottle’s opening.
- Cabbage Acid-Base Indicator . Children will love this hands-on approach to learning how to identify an acid or a base just using purple cabbage and seeing colors change.
- Carnation Color Wonders . An uncomplicated way to teach the importance of the various parts of the flower, the carnation color experiment shows kids how stems provide nourishment to the whole plant.
- Polymers & Pampers . If your middle school scientist has a younger sibling at home in diapers, this is a great PBL activity to teach how polymers are essential for products like diapers.
- Make a Battery Using… Anytime a kid can turn produce into a battery, it is fun! So, why not compare a lemon battery to a potato battery to see which one works better?
- Helmet Drop Test . The helmet drop test is a practical PBL project to teach kids the importance of safety helmets. Simply gather different types of helmets and a several melons. Strap the helmets to the melons and drop each from the same height and measure the results.
- How Much Sugar is in that Soda? . Health-conscious parents will love this PBL activity because it teaches kids how much sugar is in their soft drinks. If you have soft drinks, sugar, and measuring cups, you can do this experiment in your kitchen.
- Ways to Clean a Penny . To teach children how acid reacts with salt works to remove the dullness of pennies, kids can do a simple PBL activity using salt and vinegar. They can also test other acids to compare results.
- Oranges: Float or Sink? . To teach kids about density, all you need are oranges and a bowl of water. You can add to this experiment by testing other fruits with peels.
Did we miss any. Please share your favorite project-based learning activities in the comments below.
How College Athletics Programs are Innovativating with ...
How teachers can use podcasts to promote ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

The Best Affordable Watches from Luxury Brands (2024)

Beximco Pharma on Forbes list of best companies in Asia

5 Best Ultrabooks With Dedicated Graphics Cards in 2024

Best Testosterone Booster Supplements: Top 10 Most Effective Testosterone Pills for Men

6 Best Sleeves and Cases for 16-inch MacBook Pro M3 in the UK

6 Best Clear Cases for Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra

Science Experiments for Kids: Making Learning Fun
by Marilyn Price-Mitchell, PhD
Resourcefulness
Ability to find and use available resources to achieve goals, problem-solve, and shape the future.
Conscientious
Decision-making, goal-orientedness, negotiating, problem-solving, risk-taking.

If you’re looking for creative science experiments for kids, we’ve got some great resources for you! Whether or not you have a budding ecologist, neuroscientist, or engineer, all children gain important abilities when parents support and encourage doing at-home, easy science experiments .
For kids of all ages, the benefits are enormous. Doing science projects helps develop a child’s resourcefulness , particularly their skills at goal-setting, planning, and problem-solving. It also nurtures intellectual curiosity , helping children acquire new ways of asking questions and understanding the world.
Scientific exploration is a great summertime activity for families or just plain old-fashioned fun during the school year. When accomplished in a non-competitive home or after-school environment, children are free to discover new interests that often lead to fascinating hobbies or educational pursuits.
How Parents Boost Kid’s Fun and Learning
To get the most out of science experiments, kids need to choose the activity and be involved in planning, decision-making, and executing the experiment. If you are inclined to browse the Internet for just the right science experiments, stop! Your kid’s brains will thank you later in life because you allowed them to feel what piques their own interests. Let them decide what’s cool!
Kids have more fun learning (and learn more!) when parents see themselves as mentors. Good mentors listen, ask questions, encourage, and support. As you begin to plan and evaluate science experiments, you may find the following guidelines useful:
- Discuss ideas with your children to determine their areas of interest.
- Take your children to a library or help them think through keywords for internet searches that will produce attention-grabbing results. (You can start with the ideas below, and then expand from there.)
- Let children read about and find the right materials for the project or experiment. If it means shopping for supplies, make sure your child accompanies you to the store and chooses wisely.
- Monitor your child’s safety and check that correct procedures are followed. If you notice an important missing task, ask a question! “Have you rechecked the directions?” “I’m a little confused…can you go through this procedure with me?”
- Fun science experiments for kids are often full of surprises! When stumbling blocks or surprising results occur, ask questions to help your child find answers. “What else could you try?” “Why do you think this result occurred?” “What will you do differently next time?”
- Following the experiment, invite your child to reflect on what happened and how. “What did you learn?” “What other projects or experiments would be fun to try?”
- Whether the experiment failed or succeeded, praise children for their hard work, perseverance, ability to follow directions, and other skills they used during the project. Remember, it’s the whole process of planning, organizing, and executing that engage kids in learning, not just the end result.
Choosing Science Experiments for Kids
The first and most important part of choosing a science experiment for kids is finding the right match between the project and the child. The websites below offer insights into the many science categories and topics that can pique children’s interests at a variety of ages, from pre-school onward. Have fun exploring them with your child!
For Kids with Specific Interests
Astronomy – Learn about planets, stars, moons, galaxies, asteroids, comets, telescopes and all kinds of astronomical objects.
Biology – Biology activities and lesson plans for classrooms that can also be done at home, from growing plants to learning about food.
Chemistry – You will be able to experiment with color-changing chemicals, test the nutrients of different food substances, grow crystals, make invisible ink, and much more.
Dinosaurs – Have fun learning about these mighty creatures that lived millions of years ago. Enjoy fossil projects, videos, and fun activities.
Energy and Electricity – Offers kid-friendly science facts, science experiments and tips on places to learn about science. The experiment supplies are a bit more technical for these.
Food – Spend some time in the kitchen exploring these 10 fun and easy food science experiments – some you can even eat!
Earth Science – Provides several easy, classic, and fun earth science experiments.
Physics – You will find fun experiments you can do with stuff you probably already have around the house.
Nature – Learn about animals, plants, oceans, recycling and all kinds of interesting nature topics.
Neuroscience – Sponsored by neuroscientist, Eric Chudler, Ph.D., there are neuroscience experiments for kids and all kinds of inside and outside activities and experiments related to neuroscience. For children of all ages.
Rocks and Minerals – provides innovative hands-on activities, demonstrations, and creative learning tools.
Weather – This site has numerous experiments your budding meteorologist can perform. Make thunder, lightning, and even a rainbow!
For Kids with Eclectic Interests
Bizarre Stuff – In their words, “This site is an ever-growing warehouse of the kinds of projects some of the more demented of us tried as young people, collecting in one place many of the classic, simple science projects that have become part of the collective lore of amateur science.”
Enchanted Learning – Educational website that has over 35,000 pages covering a wide range of topics. The site includes educational activities that emphasize creativity and the pure enjoyment of learning.
Kid Spot – Simple science experiments searchable by age and interest with easy-to-follow, step-by-step instructions.
Ology – The science website for kids from the American Museum of Natural History. From a long list, kids can choose which “ology” they would like to explore.
Reeko’s Mad Scientist Lab – Great site for science experiments and science news.
Science4Fun – Founded by an electrical engineering student, this site has a variety of experiments and articles for kids and teens on subjects that include animals, planets, electricity, renewable energy, and physics.
Science Buddies – A vast site that contains activities for all ages and interests. Also includes science fair project ideas.
Science Experiments for All Around your Home – Great suggestions for experiments in every room of your house!
Science Bob – “Science Bob” Pflugfelder is an award-winning science teacher whose science experiments for kids have been featured in many magazines.
Science is Fun – University of Wisconsin-Madison Chemistry Professor Bassam Z. Shakhashiri, shares the fun of science through home science activities.
School of Dragons – Contains fun and easy science experiments for kids, and includes printable experiment instruction sheets.
Weird Science Kids – Provides a large variety of easy and free science experiments and science demonstration videos that introduce children to the basic concepts of science and how it relates to the environment that surrounds them.
Wonderville – This award-winning site has a reputation for scientific accuracy and encourages exploration and curiosity in youth of all ages.
Very Cool Science Experiments for Kids of Different Ages
Especially for pre-schoolers: .
PBS Parents – A great site whose goal is to make your child’s first memories of science fun and meaningful. Contains science activities for preschool and kindergarten ages.
Science Sparks – Wonderful site full of fun science experiments – from making fizzy paint to discovering what makes the best pretend snow.
Especially for Elementary School Kids:
Funology – Introduces your kids to the world around them with fun and educational experiments.
Home Science Tools – Designed for preK through 4th grade, these hands-on activities and science experiments for kids focus on tactile subjects like bubbles, magnets, and ladybugs.
Science for Kids – Choose from chemistry experiments, physics games, biology lessons, animal videos, technology activities, space images, weather projects, plant diagrams, and much more.
Especially for Middle Schoolers:
Hunkin’s Experiments – Creative cartoons that will have you experimenting with food, light, sound, clothes, and a whole lot more. Hundreds of cartoon experiments from cartoonist, broadcaster and engineer Tim Hunkin.
Scientific American – Features a fun, new, science-related activity every week that parents and their middle schoolers can do together. Adults will find easy-to-follow instructions and simple materials lists, as well as additional background to help them explain key concepts.
Photo Credit: Andrey Kiselev
RELATED TOPICS:
Belief in self.
Published: June 23, 2015
Share Article:
About the author.

Marilyn Price-Mitchell, PhD, is founder of Roots of Action and author of Tomorrow's Change Makers: Reclaiming the Power of Citizenship for a New Generation . A developmental psychologist and researcher, she writes for Psychology Today and Edutopia on positive youth development, K-12 education, and family-school-community partnerships. Website // @DrPriceMitchell // Facebook
Recent Articles

Teach Students to Achieve Goals

Compass-Inspired
Best back-to-school articles for parents: 2023.

Skeptic or Cynic? How to Model Positive Skepticism to Children
15 Awesome Science Experiments For Older Kids
Its time for another Saturday Science ! This is one of my favorite days in the week. If you are a regular here, you know how much we love science. We love simple science and we also love approaching science like real scientists. On my Facebook page , many readers have started to ask for resources for older children and since Legoman (8) and Bones (6) are technically considered “older”, I thought it would be fun to gather up some science experiments that we want to try on our own.

Science can be loads of fun. From creating contraptions and models to learning about the inner-workings of life… there are so many science experiments that can be done at home. {Please note: Adult supervision is always suggested with any science experiment}.
Simple Science Experiments for Older Children
- Explore Static Electricity with balloons, bending water, and electrifying gelatin.
- Study Electricity and try making your own Electric Tootbrush
- Test your engineering abilities by making a straw and rubber band bridge .
- Learn more about physics with your very own Egg Drop Contraptions .
- Explore the basics of light and color with experiments like bending, scattering, and comparing light.
- Make a bottle rocket using recycled materials.
- Use problem solving and predictions in a Lego science experiment .
- Develop the young chemist in you by exploring unknown liquids.
- Make concoctions and test chemical reactions with 5 simple fizzing experiments .
- Take your chemistry to the next level by making a mentos soda dispenser .
- Make your own smores in your recycled solar oven .
- Learn about the rock cycle by making an edible rock cycle .
- Learn about your own DNA with ingredients from your kitchen.
- Discover how sound travels and is amplified by making your own balloon speakers.
- Compare and contrast the viscosity of various liquids and the effect they have in a simple 2 ingredient recipe for cloud dough.
More Science Ideas:
Which one will you try? Have you tried something that isn’t listed? I can’t wait to hear! Connect with me on Facebook , Twitter , Google+ , Pinterest , Instagram or subscribe by email . I can’t wait to hear your ideas.
Are You Ready for More Science Fun?
Time for saturday science blog hop, super simple science experiment: build a flying contraption from the usual mayhem, static electricity from suzy homeschooler, growing bean seeds in bags from p is for preschooler, milk color explosion from stir the wonder.
FREE DOWNLOAD
Discover how to get siblings to get along even when all they do is annoy each other with the Sibling “Get Along” Poster Pack!
8 thoughts on “15 Awesome Science Experiments For Older Kids”
Pingback: Milk Color Explosion | Stir The Wonder
I’m going to have to keep this in mind for when my daughter is a little older. I love that straw bridge!
I swear, I want to try ALL of these experiments! Thanks for sharing, Dayna.
Pingback: Saturday Science Blog Hop - The Joys of Boys
Pingback: Saturday Science: Static Electricity | Suzy Homeschooler
Thanks for featuring our bottle rocket!
Great round up. Thanks for including our backyard chemistry. I am featuring this post in After School Round Up.
I must thank you for the efforts you have put in penning thijs website. I really hope to see the sme high-grade content by you in the future as well. In truth, yur creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal website now 😉
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

CONNECT WITH ME

The Problem Solving Approach in Science Education

Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how science , with its vast array of facts and figures, becomes so deeply integrated into our understanding of the world? It isn’t just about memorizing data; it’s about engaging with problems and seeking solutions through a systematic approach. This is where the problem\-solving approach in science education takes the spotlight. It transforms passive listeners into active participants, nurturing the next generation of critical thinkers and innovators.
What is the Problem-Solving Approach?
At its core, the problem-solving approach is a student\-centered method that encourages learners to tackle scientific problems with curiosity and rigor. It isn’t just a teaching strategy; it’s a journey that begins with recognizing a problem and ends with reaching a conclusion through investigation and reasoning.
Step 1: Identifying the Problem
Every scientific journey begins with a question. In the classroom, this means fostering an environment where students are prompted to observe phenomena and articulate their curiosities in the form of clear, concise problems. This might look like a teacher demonstrating an unexpected result in an experiment and asking students to ponder why it occurred.
Step 2: Gathering Information
Once the problem is set, the next step is to gather relevant information. Here, students exercise their research skills, looking through textbooks, scientific journals, and credible internet sources to understand the context of their problem. They learn to differentiate between reliable and unreliable information—a skill with far-reaching implications.
Step 3: Formulating Hypotheses
Armed with information, students then formulate hypotheses. A hypothesis is an educated guess that can be tested through experiments. Encouraging learners to come up with their hypotheses promotes creativity and ownership of the learning process.
Step 4: Conducting Experiments
What sets science apart is its reliance on empirical evidence . In this step, students design and conduct experiments to test their hypotheses. They learn about controls, variables, and the importance of replicability. This hands-on experience is invaluable and often the most engaging part of the approach.
Step 5: Analyzing Data
After the experiment, comes the analysis. Students examine their results, often using statistical methods , to see if the data supports or refutes their hypotheses. This is where critical thinking is paramount, as they must interpret the data without bias.
Step 6: Drawing Conclusions
The final step in the process is drawing conclusions. Here, students evaluate the entirety of their work and determine the implications of their findings. Whether their hypotheses were supported or not, they gain insights into the scientific process and develop the ability to argue their conclusions based on evidence.
The Benefits of Problem Solving in Science Education
This methodology goes beyond knowledge acquisition; it’s about instilling a scientific mindset. Let’s explore how this approach benefits learners:
Develops Higher-Order Thinking Skills
By grappling with complex problems, students develop higher\-order thinking skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. These are not only vital in science but in everyday decision-making as well.
Encourages Active Learning
Active engagement in learning through problem-solving keeps students invested in their education. They’re not passive receivers of information but active participants in their learning journey.
Promotes Autonomy and Confidence
As students navigate through problems on their own, they build autonomy and confidence in their ability to tackle challenges. This self-assurance can translate to various aspects of their lives.
Fosters a Deeper Understanding of Scientific Principles
By connecting theoretical knowledge to practical problems, students develop a more nuanced understanding of scientific principles. It’s one thing to read about a concept; it’s another to see it in action.
Improves Collaboration Skills
Problem-solving often involves teamwork, allowing students to improve their collaborative skills . They learn to communicate ideas, share tasks, and respect different viewpoints.
Enhances Persistence and Resilience
Not every experiment will go as planned, and not every hypothesis will be correct. Navigating these challenges teaches learners persistence and resilience —qualities that are essential in science and in life.
Bringing Problem Solving Into the Classroom
Integrating the problem-solving approach into science education requires careful planning and a shift in mindset. Teachers become facilitators rather than lecturers, guiding students through the process and providing support when needed. Classrooms become active learning environments where mistakes are seen as learning opportunities.
The problem-solving approach in science education is more than a teaching strategy; it’s a blueprint for developing curious, independent, and analytical thinkers. By engaging learners in this manner, we’re not just teaching them science; we’re equipping them with the tools to solve the complex problems of tomorrow.
What do you think? How can we further encourage problem-solving skills in students from an early age? Do you believe that the problem-solving approach should be applied to other subjects beyond science? Share your thoughts and experiences with this dynamic educational strategy.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Pedagogy of Science
1 Science – Perspectives and Nature
- Understanding Science
- Myths about Nature of Science
- Understanding Nature of Science
- Domains of Science
2 Aims and Objectives of Science Teaching-Learning
- Aims of Science Education
- Objectives of Science Teaching-Learning
- Developing Learning Objectives
- Shift in Pedagogic Approach
3 Process Skills in Science
- Process Skills in Science
- Basic Process Skills in Science
- Developing Scientific Attitude and Scientific Temper
- Nurturing Aesthetic Sense and Curiosity
- Interdependence of Different Aspects of Nature of Science
4 Science in School Curriculum
- Historical Development of Science Education in India
- Teaching of Science as Recommended in National Curriculum Framework-2005
- Correlation of Science with Other Subjects/Disciplines
5 Organizing Teaching – Learning Experiences
- Linking Process Skills with Content
- Formulating Learning Objectives
- Unit Planning in Science
- Lesson Planning in Science
- Using Laboratory for Teaching-Learning
6 Approaches in Science Teaching – Learning
- Science as a Process of Construction of Knowledge
- Inquiry Approach
- Problem Solving Approach
- Cooperative Learning Approach
- Experiential Learning Approach
- Concept Mapping as an Approach for Planning and Transaction
- Adopting Critical Pedagogy in Science Teaching-Learning
7 Methods in Science Teaching – Learning
- Teacher Centric Methods
- Learner Centric Methods
- Cooperative Learning Methods
- Inclusion in Science Classroom
- Adopting Critical Pedagogy
8 Learning Resources in Science
- Identifying Appropriate Learning Resource
- Various Learning Resources
- Classroom Learning Resources
- ICT as Learning Resource
- Developing Learning Resource Centres
- Importance of Various Activities in Science Teaching-Learning
- Innovations in Science Laboratories
- Role of Innovation and Research in Science
- Professional Development of Science Teachers
9 Assessment in Science
- Nature of Assessment in Science
- Assessment Indicators in Science
- Tools and Techniques for Assessment
- Diagnostics Assessment in Science
- Schemes for Promoting Scientific Attitude
- Components of Food
- How to Get Higher Yields
- Animal Husbandry
11 Material
- Classification of Substances
- States of Material
- Mole Valency and Equivalence
- Types of Chemical Reactions
- Basic Metallurgical Processes
12 The Living World
- Diversity in Plants and Animals
- Nomenclature Scientific Names and Hierarchy
- Cell and Cell Organelles
- Life Processes
13 How Things Work
- Electric Current and Electric Circuit
- Electric Potential and Potential Difference
- Combination of Resistors — Series and Parallel
- Electric Power
- Heating Effects of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Electric Generator
- Domestic Electric Circuits
14 Moving Things, People and Ideas
- Newton’s Law of Motion
- Conservation of Momentum
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
15 Natural Phenomenon
- Light as a Natural Phenomenon
- Water Cycle
- Conservation of Water Bodies
- Natural Disasters
- Waste Management
16 Natural Resources
- Physical Resources and their Utilization
- Pollution and Role of Human Being
- Bio-Geo-Chemical Cycles in Nature
- Natural Resource Management
Share on Mastodon

Mind-Blowing Science Experiments to Do with Your Kids at Home
T eaching kids science at home can be incredibly useful for their educational development. It can also be a really great way to give kids a break from their screen time while allowing them to discover something new.
So, today, we are going to be discussing various science experiments that can be easily conducted at home.
Additionally, we will provide you with the details on all the necessary tools and resources to ensure a safe and enjoyable learning experience.
So let's get to it!
Photo Credit: Polina Tankilevich from corelens via Canva.com
*Post contains affiliate links. Full disclosure can be viewed here .
STEM Science Experiments
All of the following STEM experiments can be done using the STEM science kits found here .
Racecar with a Spring Engine
MEL Science Kits offers an exciting opportunity for kids to build their own racecar powered by a spring engine. This experiment not only teaches fundamental concepts of physics but also encourages creativity and problem-solving skills.
Hydraulic Lift
Another fascinating experiment with MEL Science Kits involves the construction of a hydraulic lift . By understanding the principles of hydraulics, children can explore the concepts of pressure and force while constructing this hands-on project. You can check out the hydraulic lift we built HERE !
Infinity Portal
The MEL Science project called the “Infinity Porta l, ” allows children to explore the wonderful world of mirror reflections. By creating their own infinite reflection tunnel, kids can discover and learn about the physical laws behind this fascinating phenomenon.
MEL Science offers a kit that enables children to assemble their own music box while exploring the principles of sound waves. This experiment is a perfect combination of science and creativity, fostering a deeper understanding of acoustics. Pro Tip: You can also use this experiment as part of a music lesson.
Earthquake-Resistant Buildings
Through the Earthquakes MEL Science Kit , kids can learn how to construct buildings capable of withstanding the force of an earthquake. This experiment provides a hands-on approach to comprehend engineering concepts and helps develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
Space Science Experiments
All of the following Space science experiments can be done using the Space science kits found here .
Rocket Launch
Encourage your child’s curiosity about space with the Rocket MEL Science Kit , which allows kids to launch their very own space rocket. This experiment introduces the basics of rocket propulsion and sparks an interest in aerospace exploration.
Water Recovery Systems
The Water Recovery Systems MEL Science Kit provides an opportunity for kids to learn about the challenges of water purification in space. By conducting various experiments, children can explore innovative techniques for cleaning water in a challenging environment.
Model of Jupiter
With the Gas Giants Science Kit from MEL Science, children can build a realistic model of Jupiter. This experiment not only teaches kids about the largest planet in our solar system but also introduces them to concepts like planetary composition and scale modeling.
Physics Science Experiments
All of the following Physics science experiments can be done using the Physics science kits found here .
Luminescence
Kids can make their own liquid nightlight with the Luminescence MEL Science Kit . This kit provides all the necessary materials and instructions for creating a unique and glowing nightlight using special luminescent substances.
Electric Motor
Another exciting experiment is building an electric motor with the “Electric Motor” set by MEL Science. Kids can learn about electromagnetic principles and construct a working motor using the provided components.
Glasses Vision Physics
For those interested in vision physics, the “Glasses” Vision Physics Set by MEL Science enables kids to build their own 3D goggles. This experiment explores how our eyes perceive depth and helps children understand the science behind 3D visuals.
Magnetic Levitation
This Magnetic Levitation Set offers an incredible experiment where kids can make a rod levitate using magnetic forces. This hands-on activity introduces concepts of magnetism and levitation in a captivating way.
Create Your Own Mic and Speaker
With the “Mic and Speaker” experiment , children can learn about sound waves and create their own speaker and microphone. This experiment allows kids to understand the basics of sound and how it can be amplified using simple components.
Chemistry Science Experiments
All of the following Chemistry science experiments can be done using the Chemistry science kits found here .
Set Hydrogen Foam on Fire
Using the But Will it Burn MEL Science Kit , kids can set hydrogen foam on fire and learn about combustion. This experiment demonstrates the flammability of hydrogen and the principles of a chemical reaction.
Set Fire Using Pure Oxygen
For older kids, this Oxygen Science Kit provides an experiment where they can set a fire using pure oxygen. This activity focuses on oxidizers and reducers and emphasizes the importance of oxygen in combustion.
Build Your Own Battery
The Zinc-carbon Battery Kit allows kids to build their own working battery. Through this experiment, children gain an understanding of the chemical reactions that occur within a battery and how electrical energy is produced.
Medicine Science Experiments
All of the following Medical science experiments can be done using the Medicine science kits found here .
Filling a Tooth
The Dentistry: Caries MEL Science Kit provides an opportunity for kids to practice removing the damaged part of a tooth using a dental burr and make dental fillings. This experiment introduces concepts of dentistry and allows children to learn about dental procedures in a safe and educational manner.
Make Your Own ECG
With the ECG MEL Science Kit, kids can learn how to take their own electrocardiogram (ECG). This experiment familiarizes children with the medical device used to measure heart activity and helps them understand the basics of the human cardiovascular system.
Practice Basic Surgical Skills
The Surgery MEL Science Kit offers an exciting opportunity for kids to learn basic surgical skills. They can make incisions in artificial skin and practice applying stitches, providing a hands-on understanding of surgical procedures and promoting dexterity.
Where to Find The Tools and Lesson Plans for These Experiments
All the necessary tools and lesson plans for these experiments can be found in the MEL Science Kits. To start your MEL Science subscription and gain access to a wide range of exciting experiments, visit their website and follow the instructions to subscribe.
Wrapping Up
MEL Science Kits offer so many fun ways for kids (and parents) to explore different scientific concepts. Additionally, these kits provide hands-on learning experiences, spark curiosity, and encourage critical thinking. By subscribing to MEL Science, children can explore various scientific concepts and conduct a wide variety of experiments in the comfort of their own homes.
You can also talk to the administration at your child's school to see if they'd be interested in bringing some of these MEL Science projects into the classroom!
Which one of the experiments above would be something you'd try at home with your kids? Feel free to share in the comments!
The post Mind-Blowing Science Experiments to Do with Your Kids at Home appeared first on Major League Mommy .

share this!
April 29, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Intervention based on science of reading and math boosts comprehension and word problem-solving skills
by University of Kansas
New research from the University of Kansas has found that an intervention based on the science of reading and math effectively helped English learners boost their comprehension, visualize and synthesize information, and make connections that significantly improved their math performance.
The intervention , performed for 30 minutes twice a week for 10 weeks with 66 third-grade English language learners who displayed math learning difficulties, improved students' performance when compared to students who received general instruction. This indicates that emphasizing cognitive concepts involved in the science of reading and math are key to helping students improve, according to researchers.
"Word problem-solving is influenced by both the science of reading and the science of math. Key components include number sense, decoding, language comprehension and working memory. Utilizing direct and explicit teaching methods enhances understanding and enables students to effectively connect these skills to solve math problems . This integrated approach ensures that students are equipped with necessary tools to navigate both the linguistic and numerical demands of word problems," said Michael Orosco, professor of educational psychology at KU and lead author of the study.
The intervention incorporates comprehension strategy instruction in both reading and math, focusing and decoding, phonological awareness, vocabulary development, inferential thinking, contextualized learning and numeracy.
"It is proving to be one of the most effective evidence-based practices available for this growing population," Orosco said.
The study, co-written with Deborah Reed of the University of Tennessee, was published in the journal Learning Disabilities Research and Practice .
For the research, trained tutors implemented the intervention, developed by Orosco and colleagues based on cognitive and culturally responsive research conducted over a span of 20 years. One example of an intervention session tested in the study included a script in which a tutor examined a word problem explaining that a person made a quesadilla for his friend Mario and gave him one-fourth of it, then asked students to determine how much remained.
The tutor first asked students if they remembered a class session in which they made quesadillas and what shape they were, and demonstrated concepts by drawing a circle on the board, dividing it into four equal pieces, having students repeat terms like numerator and denominator. The tutor explains that when a question asks how much is left, subtraction is required. The students also collaborated with peers to practice using important vocabulary in sentences. The approach both helps students learn and understand mathematical concepts while being culturally responsive.
"Word problems are complex because they require translating words into mathematical equations, and this involves integrating the science of reading and math through language concepts and differentiated instruction," Orosco said. "We have not extensively tested these approaches with this group of children. However, we are establishing an evidence-based framework that aids them in developing background knowledge and connecting it to their cultural contexts."
Orosco, director of KU's Center for Culturally Responsive Educational Neuroscience, emphasized the critical role of language in word problems, highlighting the importance of using culturally familiar terms. For instance, substituting "pastry" for "quesadilla" could significantly affect comprehension for students from diverse backgrounds. Failure to grasp the initial scenario could impede subsequent problem-solving efforts.
The study proved effective in improving students' problem-solving abilities, despite covariates including an individual's basic calculation skills, fluid intelligence and reading comprehension scores. That finding is key, as while ideally all students would begin on equal footing and there would be few variations in a classroom, in reality, covariates exist and are commonplace.
The study had trained tutors deliver the intervention, and its effectiveness should be further tested with working teachers, the authors wrote. Orosco said professional development to help teachers gain the skills is necessary, and it is vital for teacher preparation programs to train future teachers with such skills as well. And helping students at the elementary level is necessary to help ensure success in future higher-level math classes such as algebra.
The research builds on Orosco and colleagues' work in understanding and improving math instruction for English learners. Future work will continue to examine the role of cognitive functions such as working memory and brain science, as well as potential integration of artificial intelligence in teaching math.
"Comprehension strategy instruction helps students make connections, ask questions, visualize, synthesize and monitor their thinking about word problems," Orosco and Reed wrote. "Finally, applying comprehension strategy instruction supports ELs in integrating their reading, language and math cognition…. Focusing on relevant language in word problems and providing collaborative support significantly improved students' solution accuracy."
Provided by University of Kansas
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Solar storm puts on brilliant light show across the globe, but no serious problems reported
May 11, 2024
Study discovers cellular activity that hints recycling is in our DNA

Weaker ocean currents lead to decline in nutrients for North Atlantic ocean life during prehistoric climate change
Research explores ways to mitigate the environmental toxicity of ubiquitous silver nanoparticles

AI may be to blame for our failure to make contact with alien civilizations

Saturday Citations: Dietary habits of humans; dietary habits of supermassive black holes; saving endangered bilbies
Scientists unlock key to breeding 'carbon gobbling' plants with a major appetite
May 10, 2024

Clues from deep magma reservoirs could improve volcanic eruption forecasts

Study shows AI conversational agents can help reduce interethnic prejudice during online interactions

NASA's Chandra notices the galactic center is venting
Relevant physicsforums posts, plagiarism & chatgpt: is cheating with ai the new normal.
3 hours ago
Physics Instructor Minimum Education to Teach Community College
Studying "useful" vs. "useless" stuff in school.
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
Digital oscilloscope for high school use
Apr 25, 2024
Motivating high school Physics students with Popcorn Physics
Apr 3, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories
Study shows program improves teaching skills, students' word problem–solving
Jun 14, 2022
Study shows approach can help English learners improve at math word problems
Jun 19, 2018

Study examines role of working memory, cognitive functions in English learners learning to write
Oct 17, 2023

Cognitive study shows lack of bilingual education adversely affects English language learners' writing skills
Oct 14, 2021

How vocabulary breadth and depth influence bilingual reading comprehension
Aug 21, 2023

Study validates the simple view of reading for enhancing second and foreign language learners' experience
Aug 17, 2023
Recommended for you

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
For IEEE Members
Ieee spectrum, follow ieee spectrum, support ieee spectrum, enjoy more free content and benefits by creating an account, saving articles to read later requires an ieee spectrum account, the institute content is only available for members, downloading full pdf issues is exclusive for ieee members, downloading this e-book is exclusive for ieee members, access to spectrum 's digital edition is exclusive for ieee members, following topics is a feature exclusive for ieee members, adding your response to an article requires an ieee spectrum account, create an account to access more content and features on ieee spectrum , including the ability to save articles to read later, download spectrum collections, and participate in conversations with readers and editors. for more exclusive content and features, consider joining ieee ., join the world’s largest professional organization devoted to engineering and applied sciences and get access to all of spectrum’s articles, archives, pdf downloads, and other benefits. learn more →, join the world’s largest professional organization devoted to engineering and applied sciences and get access to this e-book plus all of ieee spectrum’s articles, archives, pdf downloads, and other benefits. learn more →, access thousands of articles — completely free, create an account and get exclusive content and features: save articles, download collections, and talk to tech insiders — all free for full access and benefits, join ieee as a paying member., ai copilots are changing how coding is taught, professors are shifting away from syntax and emphasizing higher-level skills.
Generative AI is transforming the software development industry. AI-powered coding tools are assisting programmers in their workflows, while jobs in AI continue to increase. But the shift is also evident in academia—one of the major avenues through which the next generation of software engineers learn how to code.
Computer science students are embracing the technology, using generative AI to help them understand complex concepts, summarize complicated research papers, brainstorm ways to solve a problem, come up with new research directions, and, of course, learn how to code.
“Students are early adopters and have been actively testing these tools,” says Johnny Chang , a teaching assistant at Stanford University pursuing a master’s degree in computer science. He also founded the AI x Education conference in 2023, a virtual gathering of students and educators to discuss the impact of AI on education.
So as not to be left behind, educators are also experimenting with generative AI. But they’re grappling with techniques to adopt the technology while still ensuring students learn the foundations of computer science.
“It’s a difficult balancing act,” says Ooi Wei Tsang , an associate professor in the School of Computing at the National University of Singapore . “Given that large language models are evolving rapidly, we are still learning how to do this.”
Less Emphasis on Syntax, More on Problem Solving
The fundamentals and skills themselves are evolving. Most introductory computer science courses focus on code syntax and getting programs to run, and while knowing how to read and write code is still essential, testing and debugging—which aren’t commonly part of the syllabus—now need to be taught more explicitly.
“We’re seeing a little upping of that skill, where students are getting code snippets from generative AI that they need to test for correctness,” says Jeanna Matthews , a professor of computer science at Clarkson University in Potsdam, N.Y.
Another vital expertise is problem decomposition. “This is a skill to know early on because you need to break a large problem into smaller pieces that an LLM can solve,” says Leo Porter , an associate teaching professor of computer science at the University of California, San Diego . “It’s hard to find where in the curriculum that’s taught—maybe in an algorithms or software engineering class, but those are advanced classes. Now, it becomes a priority in introductory classes.”
“Given that large language models are evolving rapidly, we are still learning how to do this.” —Ooi Wei Tsang, National University of Singapore
As a result, educators are modifying their teaching strategies. “I used to have this singular focus on students writing code that they submit, and then I run test cases on the code to determine what their grade is,” says Daniel Zingaro , an associate professor of computer science at the University of Toronto Mississauga . “This is such a narrow view of what it means to be a software engineer, and I just felt that with generative AI, I’ve managed to overcome that restrictive view.”
Zingaro, who coauthored a book on AI-assisted Python programming with Porter, now has his students work in groups and submit a video explaining how their code works. Through these walk-throughs, he gets a sense of how students use AI to generate code, what they struggle with, and how they approach design, testing, and teamwork.
“It’s an opportunity for me to assess their learning process of the whole software development [life cycle]—not just code,” Zingaro says. “And I feel like my courses have opened up more and they’re much broader than they used to be. I can make students work on larger and more advanced projects.”
Ooi echoes that sentiment, noting that generative AI tools “will free up time for us to teach higher-level thinking—for example, how to design software, what is the right problem to solve, and what are the solutions. Students can spend more time on optimization, ethical issues, and the user-friendliness of a system rather than focusing on the syntax of the code.”
Avoiding AI’s Coding Pitfalls
But educators are cautious given an LLM’s tendency to hallucinate . “We need to be teaching students to be skeptical of the results and take ownership of verifying and validating them,” says Matthews.
Matthews adds that generative AI “can short-circuit the learning process of students relying on it too much.” Chang agrees that this overreliance can be a pitfall and advises his fellow students to explore possible solutions to problems by themselves so they don’t lose out on that critical thinking or effective learning process. “We should be making AI a copilot—not the autopilot—for learning,” he says.
“We should be making AI a copilot—not the autopilot—for learning.” —Johnny Chang, Stanford University
Other drawbacks include copyright and bias. “I teach my students about the ethical constraints—that this is a model built off other people’s code and we’d recognize the ownership of that,” Porter says. “We also have to recognize that models are going to represent the bias that’s already in society.”
Adapting to the rise of generative AI involves students and educators working together and learning from each other. For her colleagues, Matthews’s advice is to “try to foster an environment where you encourage students to tell you when and how they’re using these tools. Ultimately, we are preparing our students for the real world, and the real world is shifting, so sticking with what you’ve always done may not be the recipe that best serves students in this transition.”
Porter is optimistic that the changes they’re applying now will serve students well in the future. “There’s this long history of a gap between what we teach in academia and what’s actually needed as skills when students arrive in the industry,” he says. “There’s hope on my part that we might help close the gap if we embrace LLMs.”
- How Coders Can Survive—and Thrive—in a ChatGPT World ›
- AI Coding Is Going From Copilot to Autopilot ›
- OpenAI Codex ›
Rina Diane Caballar is a writer covering tech and its intersections with science, society, and the environment. An IEEE Spectrum Contributing Editor, she's a former software engineer based in Wellington, New Zealand.
Yes! Great summary of how things are evolving with AI. I’m a retired coder (BS comp sci) and understand the fundamentals of developing systems. Learning the lastest systems is now the greatest challenge. I was intrigued by Ansible to help me manage my homelab cluster, but who wants to learn one more scripting language? Turns out ChatGPT4 knows the syntax, semantics, and work flow of Ansible and all I do is tell is to “install log2ram on all my proxmox servers” and I get a playbook that does just that. The same with Docker Compose scripts. Wow.
Disney's Robots Use Rockets to Stick the Landing
Video friday: robot bees, the new shadow hand can take a beating, related stories, ai spam threatens the internet—ai can also protect it, what is generative ai, generative ai has a visual plagiarism problem.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- May 13, 2024 • 27:46 How Biden Adopted Trump’s Trade War With China
- May 10, 2024 • 27:42 Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
- May 9, 2024 • 34:42 One Strongman, One Billion Voters, and the Future of India
- May 8, 2024 • 28:28 A Plan to Remake the Middle East
- May 7, 2024 • 27:43 How Changing Ocean Temperatures Could Upend Life on Earth
- May 6, 2024 • 29:23 R.F.K. Jr.’s Battle to Get on the Ballot
- May 3, 2024 • 25:33 The Protesters and the President
- May 2, 2024 • 29:13 Biden Loosens Up on Weed
- May 1, 2024 • 35:16 The New Abortion Fight Before the Supreme Court
- April 30, 2024 • 27:40 The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
- April 29, 2024 • 47:53 Trump 2.0: What a Second Trump Presidency Would Bring
- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
The porn star testified for eight hours at donald trump’s hush-money trial. this is how it went..
Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Jonah E. Bromwich
Produced by Olivia Natt and Michael Simon Johnson
Edited by Lexie Diao
With Paige Cowett
Original music by Will Reid and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
This episode contains descriptions of an alleged sexual liaison.
What happened when Stormy Daniels took the stand for eight hours in the first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump?
Jonah Bromwich, one of the lead reporters covering the trial for The Times, was in the room.
On today’s episode

Jonah E. Bromwich , who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times.

Background reading
In a second day of cross-examination, Stormy Daniels resisted the implication she had tried to shake down Donald J. Trump by selling her story of a sexual liaison.
Here are six takeaways from Ms. Daniels’s earlier testimony.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Jonah E. Bromwich covers criminal justice in New York, with a focus on the Manhattan district attorney’s office and state criminal courts in Manhattan. More about Jonah E. Bromwich
Advertisement
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computational Complexity
Title: solving quantified boolean formulas with few existential variables.
Abstract: The quantified Boolean formula (QBF) problem is an important decision problem generally viewed as the archetype for PSPACE-completeness. Many problems of central interest in AI are in general not included in NP, e.g., planning, model checking, and non-monotonic reasoning, and for such problems QBF has successfully been used as a modelling tool. However, solvers for QBF are not as advanced as state of the art SAT solvers, which has prevented QBF from becoming a universal modelling language for PSPACE-complete problems. A theoretical explanation is that QBF (as well as many other PSPACE-complete problems) lacks natural parameters} guaranteeing fixed-parameter tractability (FPT). In this paper we tackle this problem and consider a simple but overlooked parameter: the number of existentially quantified variables. This natural parameter is virtually unexplored in the literature which one might find surprising given the general scarcity of FPT algorithms for QBF. Via this parameterization we then develop a novel FPT algorithm applicable to QBF instances in conjunctive normal form (CNF) of bounded clause length. We complement this by a W[1]-hardness result for QBF in CNF of unbounded clause length as well as sharper lower bounds for the bounded arity case under the (strong) exponential-time hypothesis.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
STEM projects, which encompass science, technology, engineering, and math, are the perfect way to ignite curiosity, develop problem-solving skills, and have a blast while learning. In this blog post, you'll discover over 150 engaging STEM projects for young learners, elementary school students, middle school students, high school students ...
Here are some engaging projects that get your students thinking about how to solve real-world problems. Preventing soil erosion In this project, meant for sixth - 12th grade, students learn to build a seawall to protest a coastline from erosion, calculating wave energy to determine the best materials for the job.
43. "Flip" a drawing with water. Light refraction causes some really cool effects, and there are multiple easy science experiments you can do with it. This one uses refraction to "flip" a drawing; you can also try the famous "disappearing penny" trick. Learn more: Light Refraction With Water.
In a true STEM experiment, children learn to think of solutions to problems on their own, with no particular planned outcome, just like in the real world. STEM activities are one of the best ways to prepare children for problem solving and learning in the real world, and they give kids a taste of what sort of decision processes adults go ...
Science activities in preschool involve observation, exploration, and problem-solving. These activities prompt children to think critically, make connections between cause and effect, and develop reasoning skills. Fosters Creativity: Science is not just about facts and formulas; it also encourages creativity.
Over 50 fun science experiments for kids! Simple science activities you can do at home or in the classroom. ... These eight science and engineering practices are less structured and allow for a more free-flowing approach to problem-solving and finding answers to questions. These skills are critical to developing future engineers, inventors ...
A problem-solving experiment is a learning activity that uses experimental design to solve an authentic problem. It combines two evidence-based teaching strategies: problem-based learning and inquiry-based learning. The use of problem-based learning and scientific inquiry as an effective pedagogical tool in the science classroom has been well established and strongly supported by research ...
Our middle school projects are written and tested by scientists and are specifically created for use by students in the middle school grades. Students can choose to follow the science experiment as written or put their own spin on the project. For a personalized list of science projects, middle schoolers can use the Science Buddies Topic ...
Science Projects. There are countless science experiments for kids but these 14 projects are our hands-down favorites! Make a mini model of the water cycle with just a Ziploc bag! Turn your name into crystals! ... Who knew practicing symmetry, problem-solving, counting, geometry, and comparison skills could be so easy and fun? ...
STEM Activities for Kids. (481 results) Anytime can be the right time to explore STEM (science, technology, engineering and math). Explore our favorite experiments, engineering challenges and demonstrations with these fun hands-on STEM activities! Materials are easy to find, most activities take an hour or less, and the STEM learning is limitless.
Science fair projects that solve problems are a great way for students to test their interest and aptitude for a career in STEM (science-technology-engineering-math). But they shouldn't choose just any old topic. To make the most of the opportunity, try to focus on projects with real-world applications.
This edible science project is a nutritious way to explore the scientific method in action. Experiment with a variety of methods for baking potatoes—microwaving, using a traditional oven, wrapping them in foil, using baking pins, etc.—testing hypotheses to discover which works best. Learn more: Potato Science at Left Brain Craft Brain. 37.
You can discover the answer by conducting a science fair project to determine whether different types of cookie sheets result in noticeably different cookies. First you'll need to do some background research to figure out what kinds of baking sheets you can buy. For example, there are aluminum, steel, insulated, and….
Liquid Layers Density Experiment. Apple Acid and Base Experiment. Making Rock Candy. Skittles or M&M Experiment (try both on the same day!) Mad Scientist Baking Soda and Vinegar Art. Walking Water Science. Salt Crystal Painting STEAM Activity. Flying Tea Bag Experiment for Kids. Magic Pepper and Soap Experiment.
Get kids outdoors to enjoy the natural world while developing problem-solving, creativity, observation, engineering skills, and more. We love easy and doable STEM projects for kids! Pin. ... Bursting Bags is a great outdoor science experiment. Simple outdoor science and a cool chemical reaction with an easy DIY Alka Seltzer rocket!
aimed at solving one of three environmental problems. Suggested Materials Paper; pens; post it notes; rulers; internet/laptop/tablet as required. Published by European Space Agency (ESA) Resource Booklet ESERO-UK Resources Published by Design Club 50+ STEM activities for any secondary classroom 3 Ages 9 -14Ages 9-14 Ages 11 -14 Ages 11 -16 Ages ...
Science is an excellent way to teach these skills because it involves experimentation and discovery. Children can learn problem-solving skills by conducting experiments and observing the results. Science also encourages children to think critically and ask questions. There are many fun science experiments that you can do with your children to ...
Science Problem Solving Activities. Chris has a master's degree in history and teaches at the University of Northern Colorado. Problem solving is an essential skill for scientists, but thinking in ...
Below you will find a list of 14 project-based learning activities for the K-12 science classroom. Student Farm. Students will learn lessons about science, social studies, math, and economics through planting their organic farm. They can begin by researching the crops they want, figure out what kind of care is needed, and then use a budget to ...
Earth Science - Provides several easy, classic, and fun earth science experiments. Physics - You will find fun experiments you can do with stuff you probably already have around the house. Nature - Learn about animals, plants, oceans, recycling and all kinds of interesting nature topics. Neuroscience - Sponsored by neuroscientist, Eric ...
Explore the basics of light and color with experiments like bending, scattering, and comparing light. Make a bottle rocket using recycled materials. Use problem solving and predictions in a Lego science experiment. Develop the young chemist in you by exploring unknown liquids. Make concoctions and test chemical reactions with 5 simple fizzing ...
Step 1: Identifying the Problem. Every scientific journey begins with a question. In the classroom, this means fostering an environment where students are prompted to observe phenomena and articulate their curiosities in the form of clear, concise problems. This might look like a teacher demonstrating an unexpected result in an experiment and ...
The six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) communicating the results ...
This experiment provides a hands-on approach to comprehend engineering concepts and helps develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Space Science Experiments
"Word problem-solving is influenced by both the science of reading and the science of math. Key components include number sense, decoding, language comprehension and working memory.
Computer science students are embracing the technology, using generative AI to help them understand complex concepts, summarize complicated research papers, brainstorm ways to solve a problem ...
Computational thinking skill is a new framework that belongs to the hybrid modes of thinking. This study aims to explore the effect of the problem-solving laboratory and gender in practicing computational thinking skills. Learning media is pursued by designing experimental-based learning using smartphone sensors. A smartphone sensor was used to facilitate students to measure physical ...
On today's episode. Jonah E. Bromwich, who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times. Stormy Daniels leaving court on Thursday, after a second day of cross-examination in the ...
The quantified Boolean formula (QBF) problem is an important decision problem generally viewed as the archetype for PSPACE-completeness. Many problems of central interest in AI are in general not included in NP, e.g., planning, model checking, and non-monotonic reasoning, and for such problems QBF has successfully been used as a modelling tool. However, solvers for QBF are not as advanced as ...