- Creating Environments Conducive to Social Interaction
- Thinking Ethically: A Framework for Moral Decision Making
- Developing a Positive Climate with Trust and Respect
- Developing Self-Esteem, Confidence, Resiliency, and Mindset
- Developing Ability to Consider Different Perspectives
- Developing Tools and Techniques Useful in Social Problem-Solving
- Leadership Problem-Solving Model
- A Problem-Solving Model for Improving Student Achievement

Six-Step Problem-Solving Model
- Hurson’s Productive Thinking Model: Solving Problems Creatively
- The Power of Storytelling and Play
- Creative Documentation & Assessment
- Materials for Use in Creating “Third Party” Solution Scenarios
- Resources for Connecting Schools to Communities
- Resources for Enabling Students
weblink: http://www.yale.edu/bestpractices/resources/docs/problemsolvingmodel.pdf
This six-step model is designed for the workplace, but is easily adaptable to other settings such as schools and families. It emphasizes the cyclical , continuous nature of the problem-solving process . The model describes in detail the following steps:
Step One: Define the Problem
Step Two: Determine the Root Cause(s) of the Problem
Step Three: Develop Alternative Solutions
Step Four: Select a Solution
Step Five: Implement the Solution
Step Six: Evaluate the Outcome
ChatableApps
Mastering the Six Step Problem Solving Model – A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Solutions
Introduction.
Problem-solving skills are essential in both personal and professional settings. The ability to identify and resolve issues efficiently can lead to improved productivity, increased innovation, and overall success. One popular model commonly used for problem-solving is the Six Step Problem Solving Model. This model provides a structured approach to analyzing and addressing challenges, ensuring that comprehensive solutions are found. In this blog post, we will delve into each of the steps involved in the Six Step Problem Solving Model, along with some useful tips for mastering this process.
Understanding the Six Step Problem Solving Model
Step 1: identify the problem.
The first step in the Six Step Problem Solving Model is to identify the problem at hand. This involves clearly defining the issue and gathering relevant information. By clearly understanding the problem, you set the foundation for finding an effective solution. Take the time to analyze the situation and collect as much data as possible to gain insights into the problem’s nature and scope.
Defining the problem
It is crucial to clearly define the problem to ensure all stakeholders have a clear understanding of what needs to be solved. A well-defined problem statement includes specific details such as who is affected, when it occurs, and its impact on the overall operation or goal.
Gathering information
Once the problem is defined, it’s time to gather relevant information related to the issue. This may involve conducting research, collecting data, or consulting subject matter experts. The more information you have, the better you can understand the problem and make informed decisions.
Step 2: Analyze the problem
After identifying the problem, the next step is to analyze it thoroughly. This involves breaking down the problem into smaller components, identifying patterns or trends, and getting to the root causes. By dissecting the problem, you can better understand its complexities and identify potential solutions.
Breaking down the problem into smaller components
Complex problems are often composed of smaller components. Break down the main problem into manageable parts to tackle them individually. This approach allows for a more systematic and focused problem-solving process.
Identifying patterns or trends
In some cases, there may be trends or patterns that contribute to the problem. Identifying these recurring factors can help in understanding how and why the problem occurs. Look for commonalities and trends to gain insights into potential solutions.
Identifying root causes
At the heart of every problem are root causes that need to be addressed. By identifying the underlying factors contributing to the problem, you can develop more targeted and effective solutions. Dig deep to uncover the root causes and work towards resolving them.
Step 3: Generate potential solutions
Once the problem is thoroughly understood, it’s time to brainstorm and generate potential solutions. This step requires creativity, open-mindedness, and a willingness to explore various options.
Brainstorming techniques
Brainstorming is a powerful technique to generate a wide range of potential solutions. Encourage team collaboration and create a safe environment for sharing ideas. Write down all suggestions without judgment and explore each one thoroughly.
Considering different perspectives
When generating potential solutions, it’s important to consider different perspectives. Each person brings a unique viewpoint, and incorporating diverse ideas can lead to more well-rounded and innovative solutions. Encourage team members to share their thoughts and actively listen to their input.
Evaluating pros and cons
After generating a list of potential solutions, it’s time to evaluate the pros and cons of each option. Consider factors such as feasibility, cost, time, and potential risks. Assess each solution objectively to determine which ones are most viable.
Step 4: Evaluate and select the best solution
With potential solutions in hand, it’s important to evaluate each one to determine the best course of action. This step involves assessing the feasibility, potential outcomes, and resource availability of each solution.
Assessing the feasibility of each solution
Various solutions may be feasible, but it’s essential to evaluate whether they are practical and realistic. Consider factors such as available resources, time constraints, and potential obstacles. Eliminate options that are not feasible given the current circumstances.
Weighing the potential outcomes
Consider the potential outcomes that each solution can achieve. Look at both short-term and long-term impacts on stakeholders, productivity, and overall success. Choose solutions that offer the most significant positive impact.
Considering resource availability
Resource availability is a critical factor when selecting the best solution. Assess the resources required for each solution and compare them with the resources available. Opt for solutions that utilize resources optimally and effectively.
Step 5: Implement the chosen solution
After selecting the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. This involves formulating an action plan, assigning responsibilities, and setting timelines and milestones.
Formulating an action plan
Create a detailed action plan that outlines the steps required to implement the solution. Break down the plan into manageable tasks, assign responsibilities, and establish deadlines. A well-crafted plan ensures a smooth and organized implementation process.
Assigning responsibilities
All stakeholders need to know their roles and responsibilities in implementing the solution. Clearly define and communicate these assignments to ensure everyone is aware of their contribution. Collaboration and coordination are vital for successful implementation.
Setting timelines and milestones
Establish clear timelines and milestones to track progress throughout the implementation process. Define specific dates or deadlines for achieving key milestones. Regularly review and adjust these timelines as needed to accommodate changes or unforeseen circumstances.
Step 6: Evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
Implementing the chosen solution is not the end of the problem-solving process. It’s important to continuously monitor the effectiveness of the solution, collect feedback, and make necessary adjustments.
Monitoring progress
Closely monitor the progress of the solution implementation. Regularly review and evaluate whether the solution is achieving the desired outcomes. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge progress and make data-driven decisions.
Collecting feedback
Seek feedback from stakeholders involved in the problem-solving process. Gather their insights, opinions, and suggestions for improvement. This feedback can provide valuable information to refine the solution and enhance its effectiveness.
Making necessary adjustments
Based on the feedback and data collected, make any necessary adjustments to the solution. Identify areas that require improvement or modification and implement changes accordingly. Continuous improvement is a key aspect of effective problem-solving.
Tips for Mastering the Six Step Problem Solving Model
Mastering the Six Step Problem Solving Model requires practice and the development of certain skills. Here are some useful tips to help you become proficient in this problem-solving approach:
Practice critical thinking and analytical skills
Critical thinking and analytical skills are fundamental for effective problem-solving. Continuously develop these skills through practice and by seeking opportunities to analyze and evaluate various situations. This will enhance your ability to identify problems and find optimal solutions.
Foster a collaborative problem-solving environment
Encourage collaboration and teamwork when solving problems. Foster an environment where individuals feel comfortable brainstorming ideas and sharing their perspectives. Collaboration often leads to more creative solutions and promotes a sense of ownership among team members.
Develop effective communication skills
Effective communication is crucial throughout the problem-solving process. Practice active listening, asking clarifying questions, and conveying your ideas clearly. Strong communication skills facilitate effective collaboration and alignment with stakeholders.
Learn from past experiences and mistakes
Past experiences and mistakes can be valuable learning opportunities. Reflect on previous problem-solving efforts, analyze what worked well and what didn’t, and apply those learnings to future challenges. Embrace a growth mindset and view mistakes as opportunities for growth.
Seek feedback and continuous improvement
Regularly seek feedback from stakeholders and those affected by the problem and its solution. Actively listen to their suggestions and criticisms, and use them to refine and improve your problem-solving skills. Continuous improvement is essential to becoming a master problem solver.
Mastering the Six Step Problem Solving Model is a valuable skill that can be applied to various aspects of life and work. By following a structured problem-solving process, you can ensure comprehensive and effective solutions. Remember to diligently identify the problem, analyze it thoroughly, generate potential solutions, evaluate and select the best one, implement it with careful planning, and continuously evaluate its effectiveness. With practice and the adoption of the tips provided, you can become a proficient problem solver capable of overcoming any challenge that comes your way.
So, start applying the Six Step Problem Solving Model today and unlock your problem-solving potential!
Related articles:
- Unlocking the Secrets of World-Class Service – Exploring the Essence of Six Star Service
- Exploring the Top Product Management Models – A Comprehensive Guide
- Decoding the Rice Score Model – Unraveling Its Impact on Risk Assessment and decision-making
- Diving Into the David Rest Model – Understanding its Benefits and Features
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Tuesday, May 15, 2012
- The Six-Step Problem-Solving Process

- Select the problem to be analyzed
- Clearly define the problem and establish aprecise problem statement
- Set a measurable goal for the problem solving effort
- Establish a process for coordinating with and gaining approval of leadership
- Identify the processes that impact the problem and select one
- List the steps in the process as it currently exists
- Map the Process
- Validate the map of the process
- Identify potential cause of the problem
- Collect and analyze data related to the problem
- Verify or revise the original problem statement
- Identify root causes of the problem
- Collect additional data if needed to verify root causes
- Establish criteria for selecting a solution
- Generate potential solutions that will address the root causes of the problem
- Select a solution
- Gain approval and supporter the chosen solution
- Plan the solution
- Implement the chosen solution on a trial or pilot basis
- If the Problem Solving Process is being used in conjunction with the Continuous Improvement Process, return to Step 6 of the Continuous Improvement Process
- If the Problem Solving Process is being used as a standalone, continue to Step 5
- Gather data on the solution
- Analyze the data on the solution
- Achive the desired results?
- If YES, go to Step 6.
- If NO, go back to Step 1.
- Identify systemic changes and training needs for full implementation
- Adopt the solution
- Plan ongoing monitoring of the solution
- Continue to look for incremental improvements to refine the solution
- Look for another improvement opportunity
4 comments:
Tim, This is a good guideline for any practitioner to follow. I wish I had this a few weeks ago. A client liked a training deck I prepared but didn't want to confuse anyone with terms like Deming Cycle and such. The final version of PDCA was a 6 step process improvement method that's very similar to yours. Thanks for sharing. Cheers, Chris
Thank you for you brief and easy to understand on each step problem solving above.
Wonderful. Well Explained. Thank you for sharing
I mapped this to PDCA and observed that the first 3 steps correspond to P, the next 3 to D, C and A respectively. This Show that indeed planning is the most important step in PDCA.
Search A Lean Journey
Twitter updates.
- Facebook Updates
- Advertising
Subscribe Now

Get new posts by email:
A Lean Journey LinkedIn Group
Recent comments, search this blog, top 10 posts.
- Celebrating my 500th Blog Post
- Visual Management Board
- Guest Post: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle...
- What Do We Mean By True North?
- Five Lean Games Every Company Can Benefit From
- 10 Characteristics of a Good Measure and 7 Pitfalls to Avoid
- DOWNTIME and the Eight Wastes
- The 8 Common Wastes in an Office That Cause Downtime
- Lean Leadership: Lessons from Abe Lincoln
Blog Archive
- ► May (10)
- ► April (13)
- ► March (13)
- ► February (12)
- ► January (14)
- ► December (11)
- ► November (13)
- ► October (12)
- ► September (13)
- ► August (13)
- ► July (8)
- ► June (13)
- ► May (14)
- ► April (12)
- ► February (13)
- ► January (13)
- ► December (12)
- ► October (13)
- ► August (14)
- ► July (13)
- ► May (13)
- ► August (10)
- ► March (14)
- ► July (14)
- ► December (10)
- ► June (12)
- ► April (9)
- ► December (13)
- ► October (14)
- ► September (12)
- ► May (12)
- ► January (12)
- ► October (15)
- ► December (14)
- ► November (12)
- ► January (15)
- ► August (17)
- ► July (19)
- ► June (16)
- ► May (19)
- ► April (18)
- ► March (17)
- ► February (16)
- ► January (18)
- ► December (19)
- ► November (18)
- ► October (20)
- ► September (18)
- ► August (22)
- ► July (23)
- ► June (21)
- Lean Roundup #36 – May, 2012
- Meet-up: Beyond Lean's Matt Wrye
- Meet-up: 6 Questions to Learn of Those in Our Comm...
- Memorial Day is a Time for Remembrance
- Lean Quote: Change Leaders Create Constancy of Pur...
- Celebrating A Lean Journey's Third Year With Some ...
- Quality Improvement in Government?
- Webinar: Checking Your Lean Progress
- Lean Quote: Ability, Motivation, Attitude
- Daily Lean Tips Edition #31
- Leveraging Quality to Achieve Your Business Goals
- Lean Quote: Continuous Improvement is About Findin...
- Management Improvement Blog Carnival #166
- Top 3 “Old School” Apps for Lean
- Creating A Quality Focused Culture
- Lean Quote: Opportunity is Dressed as Hard Work
- Kanban Flow - A Free, Fast, & Flexible Kanban Tool
- Demonstrating Commitment Is A Combination of Suppo...
- ► April (17)
- ► February (18)
- ► January (20)
- ► December (18)
- ► November (19)
- ► October (17)
- ► September (22)
- ► July (20)
- ► June (20)
- ► May (21)
- ► April (19)
- ► March (20)
- ► February (17)
- ► January (17)
- ► December (20)
- ► November (15)
- ► August (18)
- ► July (17)
- ► April (14)
- ► November (17)
- ► July (15)
- ► June (9)
- ► May (5)
- A Lean Journey (80)
- A Year Ago (8)
- ASQ's Influential Voices (40)
- Book Review (64)
- Change Management (53)
- Communication (13)
- Conference (10)
- Culture (38)
- Customer Focus (2)
- Daily Management (1)
- Development/Training (13)
- Empowerment (19)
- Engagement (37)
- Exercises/Games (8)
- Facilitation (2)
- Feedback (3)
- Guest Post (167)
- In the News (69)
- Innovation (2)
- L.A.M.E. (5)
- Leadership (218)
- Lean and Green (12)
- Lean Basics (109)
- Lean Definition (24)
- Lean Fun (10)
- Lean in Practice (55)
- Lean Management (152)
- Lean Office (14)
- Lean Products (4)
- Lean Quote (725)
- Lean Resources (44)
- Lean Roundup (198)
- Lean Thinking (5)
- Lean Tips (233)
- Meet-up (29)
- Podcast (5)
- Problem Solving (21)
- Product Review (2)
- Project Management (6)
- Quality (48)
- Respect For People (57)
- Sharing Best Practices (129)
- Soft Skills (3)
- Strategy (6)
- Supply Chain (1)
- Talking Lean (1)
- Teamwork (42)
- Visual Factory (31)
- Webinar (23)
Lean Blogs I Like
- 2 Lean Principles
- 5S Supply Blog
- Avoiding The Corporate Death Spiral
- Be More Careful!
- Curious Cat
- Daily Kaizen
- Evolving Excellence
- Gemba Panta Rei
- Gemba Tales
- Got Boondoggle?
- Gotta Go Lean Blog
- Improve With Me
- Jamie Flinchbaugh
- Kaizen Notebook
- Lean Builder
- Lean Communications
- Lean For Everyone
- Lean Healthcare Exchange
- Lean Homebuilding
- Lean Insider
- Lean Is Good
- Lean Leadership
- Lean Pathways
- Lean Printing
- Lean Reflections
- Lean Simulations
- Lean Six Sigma Academy
- LeanCor Blog
- Learn Lean Manufacturing
- Learning About Lean
- Old Lean Dude Blog
- The A3 Post
- The Lean Edge
- The Lean Library
- The Lean Logistics Blog
- The Lean Thinker
- The Lean Way Consulting
- TimeBack Blog
- To The Gemba
- Training Within Industry
- Visual Management Blog
Other Sites I like
- AME's Target Magazine
- AnythingLean.com
- Art of Lean
- Bosch Rexroth Lean Production
- CIRAS - Theory of Constraints
- Chasing The Rabbit
- Corporate Event Management
- Creative Safety Supply
- Creative Safety Supply 5S Resource Page
- Fuss & O'Neill SPL
- Gemba Academy
- Grassroots Innovation
- IndustryWeek
- Lean Enterprise Institute
- Leanovations
- Learn More McGraw-Hill
- MEP University
- Manufacturers BlogNotions
- Manufacturing Business Technology
- Manufacturing Pulse
- Modern Machine Shop
- Running A Hospital
- Superfactory
- The 5S Store
- Unclutterer
- Visual Workplace
- Xtreme Lean Consulting
- catalyst for change
- freeleansite.com
wibiya widget
A lean journey blog - copyright © 2009-2024 tim mcmahon - all rights reserved.

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.

Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Problem Solving Overview SIX-STEP PROBLEM SOLVING MODEL

Related Papers
The Leadership Quarterly
Min Basadur
Siti S. Salim
Diabetes Spectrum
Felicia Hill-Briggs, PhD
Jurnal Pendidikan IPA Indonesia
Muhammad Syukri
This study aimed to determine the impact of the integration of engineering design process (asking, imagining, planning, creating and improving) in an electrical & magnetism module to improve problem-solving skills in physics among secondary school students in Aceh, Indonesia. The quasi-experimental study was carried out with 82 form three (age 15 years old) students of a secondary school in Aceh Besar, Indonesia. The first author had randomly chosen two classes as the experimental group and two other classes as the control group. Independent samples t-test analysis was conducted to determine the difference between the physics teaching and learning module which integrated the five steps of engineering design process and the existing commonly used science " Pudak " teaching and learning module. The results of the independent samples t-test analysis showed that the use of the physics teaching and learning module which integrated the five steps of engineering design process was more effective compared to the use of the existing " Pudak " module in increasing the students' skills in solving physics problems. The findings of the study suggest that the science learning approach is appropriate to be applied in the teaching and learning of science to enhance science problem-solving skills among secondary school students. In addition, it can be used as a guide for teachers on how to implement the integration of the five steps of engineering design process in science teaching and learning practices.
IOSR Journals
Education and Training in Autism and Developmental Disabilities
Mark Doggett
Despite the availability of a wide range of problem solving methods, individuals continue to struggle with problems. Scientists attempt to address recurring economic, social, political, and organizational problems through the expansion of knowledge and theory. ... Cause-effect relationships advance logical explanations, predict future events,and forecast consequences. Theories and thinking based on cause-effect findings become recognized science (Goldratt, 1990) and move the field of inquiry from "art" to that of disciplined examination. In problem solving, the root cause of the problem produces an undesirable effect. Any pursuit that does not seek the root cause leads only to the symptom of the problem and, by definition, solving a symptom will not solve a problem. Problem solvers identify root causes of problems to be able to predict future cause and effect relationships. The purposeful application of an analysis method can address complex problems using a structured app...
Lecture Notes in Computer Science
Myriam Lewkowicz
Juan Sebastián Betancourt Tabares
Lauren E Rudd
Solving problems is a necessary life skill and design is a problem solving process. This study investigated whether learning to design affected college students’ awareness and perception of their problem solving ability, and whether that ability correlated to academic success. Pretest-posttest scores of The Problem Solving Inventory were compared from a design fundamentals class. Results showed significant improvement in self-appraisal of problem solving ability subsequent to learning design. Student awareness of problem solving skills development was identified through student opinions involving solving problems for design and real life. Students indicated broader thinking, simplified solution development, and improved confidence. The study clearly shows correlations between learning to design and problem solving skills, and between problem solving skills and real-life problem solving.
RELATED PAPERS
Cornelius Holtorf
หนังสือรวมบทความครบรอบ 60 ปี ศ.ดร.สุรพล นิติไกรพจน์
Piyabutr Saengkanokkul
Recherches féministes
isabelle Fortier
Journal of Group Theory
Cheryl Praeger
Debra Lipson
Martine Le Besnerais
Journal of Cultural and Religious Studies
aboneh ashagrie
Information Technology Journal
Syahanim Mohd Salleh
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology
Molecular Plant Pathology
Maggie Levy
A vida fora da Matéria
Roberto Freire
La Ode Muhammad Erif
SSRN Electronic Journal
Isabel Ortiz
13th International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications
Sergio R.F. Díaz
Proceedings of the Nigerian Academy of Science
Nneka Angela Okoli
SAR and QSAR in Environmental Research
indira ghosh
LUM ABIENWI AMBE
Francis Kabubo
Frontiers in Psychiatry
Archives of Disease in Childhood
Leonid Pankratov
Head & Neck
Floortje Mols
The Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal
Ana greys Castro mercado
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Business & Money
- Human Resources

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Follow the author

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Strategies: A Practical Guide (Management) Hardcover – September 28, 2021
Purchase options and add-ons.
- Book 4 of 10 Management
- Print length 236 pages
- Language English
- Publication date September 28, 2021
- Dimensions 6 x 0.73 x 9 inches
- ISBN-13 979-8485855529
- See all details

Product details
- ASIN : B09HFWZF6Z
- Publisher : Independently published (September 28, 2021)
- Language : English
- Hardcover : 236 pages
- ISBN-13 : 979-8485855529
- Item Weight : 14.7 ounces
- Dimensions : 6 x 0.73 x 9 inches
About the author
Sorin dumitrascu.
Sorin developed and delivered on management, project management, computer literacy, human resources, career development, soft skills for employees and even corrections incidents management.
Currently working as a prison service consultant, he is a certified trainer and project manager, holding a master degree in International Relations and Policy Making and a bachelor degree in Law and Public Administration.
Sorin coordinated during the last 15 years projects in the areas of rule of law, regional development and human resources.
He has more than 15 years of middle/senior managerial experience within the civil service (justice, corrections, internal affairs, training), private sector (project management, consultancy, training) and NGO (industrial relations, rural development).
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top review from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 4 min read
The Problem-Solving Process
Looking at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself.
We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity. Some, such as the resolution of a serious complaint, require a significant amount of time, thought and investigation. Others, such as a printer running out of paper, are so quickly resolved they barely register as a problem at all.

Despite the everyday occurrence of problems, many people lack confidence when it comes to solving them, and as a result may chose to stay with the status quo rather than tackle the issue. Broken down into steps, however, the problem-solving process is very simple. While there are many tools and techniques available to help us solve problems, the outline process remains the same.
The main stages of problem-solving are outlined below, though not all are required for every problem that needs to be solved.
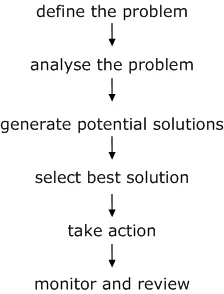
1. Define the Problem
Clarify the problem before trying to solve it. A common mistake with problem-solving is to react to what the problem appears to be, rather than what it actually is. Write down a simple statement of the problem, and then underline the key words. Be certain there are no hidden assumptions in the key words you have underlined. One way of doing this is to use a synonym to replace the key words. For example, ‘We need to encourage higher productivity ’ might become ‘We need to promote superior output ’ which has a different meaning.
2. Analyze the Problem
Ask yourself, and others, the following questions.
- Where is the problem occurring?
- When is it occurring?
- Why is it happening?
Be careful not to jump to ‘who is causing the problem?’. When stressed and faced with a problem it is all too easy to assign blame. This, however, can cause negative feeling and does not help to solve the problem. As an example, if an employee is underperforming, the root of the problem might lie in a number of areas, such as lack of training, workplace bullying or management style. To assign immediate blame to the employee would not therefore resolve the underlying issue.
Once the answers to the where, when and why have been determined, the following questions should also be asked:
- Where can further information be found?
- Is this information correct, up-to-date and unbiased?
- What does this information mean in terms of the available options?
3. Generate Potential Solutions
When generating potential solutions it can be a good idea to have a mixture of ‘right brain’ and ‘left brain’ thinkers. In other words, some people who think laterally and some who think logically. This provides a balance in terms of generating the widest possible variety of solutions while also being realistic about what can be achieved. There are many tools and techniques which can help produce solutions, including thinking about the problem from a number of different perspectives, and brainstorming, where a team or individual write as many possibilities as they can think of to encourage lateral thinking and generate a broad range of potential solutions.
4. Select Best Solution
When selecting the best solution, consider:
- Is this a long-term solution, or a ‘quick fix’?
- Is the solution achievable in terms of available resources and time?
- Are there any risks associated with the chosen solution?
- Could the solution, in itself, lead to other problems?
This stage in particular demonstrates why problem-solving and decision-making are so closely related.
5. Take Action
In order to implement the chosen solution effectively, consider the following:
- What will the situation look like when the problem is resolved?
- What needs to be done to implement the solution? Are there systems or processes that need to be adjusted?
- What will be the success indicators?
- What are the timescales for the implementation? Does the scale of the problem/implementation require a project plan?
- Who is responsible?
Once the answers to all the above questions are written down, they can form the basis of an action plan.
6. Monitor and Review
One of the most important factors in successful problem-solving is continual observation and feedback. Use the success indicators in the action plan to monitor progress on a regular basis. Is everything as expected? Is everything on schedule? Keep an eye on priorities and timelines to prevent them from slipping.
If the indicators are not being met, or if timescales are slipping, consider what can be done. Was the plan realistic? If so, are sufficient resources being made available? Are these resources targeting the correct part of the plan? Or does the plan need to be amended? Regular review and discussion of the action plan is important so small adjustments can be made on a regular basis to help keep everything on track.
Once all the indicators have been met and the problem has been resolved, consider what steps can now be taken to prevent this type of problem recurring? It may be that the chosen solution already prevents a recurrence, however if an interim or partial solution has been chosen it is important not to lose momentum.
Problems, by their very nature, will not always fit neatly into a structured problem-solving process. This process, therefore, is designed as a framework which can be adapted to individual needs and nature.
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and take advantage of our 30% offer, available until May 31st .
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Working for Yourself

4-Step Action Plans Infographic
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Successful strategy execution.
With Andrew MacLennan
Expert Interviews
Managing Arrogant People
Developing Team Players
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
The action priority matrix.
Making the Most of Your Opportunities
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Join Mind Tools

Hurson's Productive Thinking Model
Solving problems creatively.
© iStockphoto Rawpixel
A creative framework for problem solving.
Creativity is incredibly important in problem solving. If you're not creative, you'll struggle to understand the issues surrounding a problem, and you'll find it hard to identify the best solutions. Worse still, you might fail to solve the problem altogether!
So, what's a good way to be more creative in your problem solving, and come up with the best ideas to move forward with? Hurson's Productive Thinking Model could be just the thing to help you. This framework encourages you to use creativity and critical thinking at each stage of the problem-solving process. This means that you get a better understanding of the problems you face, and you come up with better ideas and solutions as a result.
About the Model
The Productive Thinking Model was developed by author and creativity theorist, Tim Hurson, and was published in his 2007 book, " Think Better ."
The model presents a structured framework for solving problems creatively. You can use it on your own or in a group.
The model consists of six steps, as follows:
- Ask "What is going on?"
- Ask "What is success?"
- Ask "What is the question?"
- Generate answers.
- Forge the solution.
- Align resources.
From " Think Better: An Innovator's Guide to Productive Thinking " by Tim Hurson. © 2008. Reproduced with permission from The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
The advantage of this model over other problem-solving approaches (like Simplex or Plan-Do-Check-Act ) is that it encourages you to use creative and critical thinking skills at each stage of the problem-solving process. This means that you can take a well-rounded look at a problem, and come up with better potential solutions.
Let's look at each step in further detail, and explore how you can apply the model.
Step 1: Ask "What Is Going On?"
First, you need to get a good understanding of the problem that you want to deal with. This is often the most involved part of the process.
To do this, explore the following four questions:
What Is the Problem?
First, brainstorm all of the problems and issues that you have – a tool such as CATWOE will help here. As you do this, think about the following questions:
- What's bugging you? And what annoys your customers?
- What's out of balance?
- What could work better? What could you improve?
- What are your customers or users complaining about?
- What challenges do you have?
- What's making you take action?
List as many issues as possible, even if you already have a good idea of what your main problem is. These don't have to be well defined or even justified. All that you're doing is generating a good list of possibilities, so don't worry about being right or wrong.
Then, use an Affinity Diagram to organize the issues that you've identified into common themes, and identify the most important problem or group of problems to deal with. If this isn't obvious, use techniques like Pareto Analysis or Paired Comparison Analysis to decide.
What Is the Impact?
Next, brainstorm how the problem impacts you and your organization, and how it affects other stakeholders such as customers, suppliers and competitors.
Make a list of all of your stakeholders, and identify the positive and negative impact that the problem has on each of them.
To help with this, ask questions such as:
- Who does this problem affect, directly and indirectly?
- Why is this problem important to them? What concerns do you have about it?
- Who'll benefit if you don't deal with the problem? And who'll benefit when you solve it?
Rolestorming is also useful here, as it helps you to look at problems from other people's perspectives.
What Is the Information?
Now, gather information about the problem. What do you know about it? What don't you know? Has someone else tried to fix this or a similar problem before? If so, what happened, and what can you learn? Make sure that you have evidence that the problem really does exist.
Finding This Article Useful?
You can learn another 44 problem-solving skills, like this, by joining the Mind Tools Club.

Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Receive new career skills every week, plus get our latest offers and a free downloadable Personal Development Plan workbook.
This is where it helps to use tools such as Cause and Effect Analysis , Root Cause Analysis , and Interrelationship Diagrams to identify the actual causes of your problem. You'll need to deal with these root causes to solve the problem fully.
What Is the Vision?
Finally in this step, identify your vision for the future once you've solved the problem – what Hurson calls the "target future."
Begin by writing down as many target futures as possible, and then narrow these down to something that's achievable and important to you.
If you're finding this difficult, use starter phrases such as "I wish...," "If only we could...," or "It would be great if...." For example, you might say, "I wish that the majority of our customers were happy with how we process returns," or, "It would be great if we could cut waste by 20 percent."
Step 2: Ask "What Is Success?"
In this step, you're going to develop your target future by defining what success is once you've implemented a solution to your problem.
A good way to do this is to use the "DRIVE" acronym. This stands for:
- Do – What do you want the solution to do?
- Restrictions – What must the solution not do?
- Investment – What resources are available? What are you able to invest in a solution? How much time do you have?
- Values – What values must this solution respect?
- Essential outcomes – What defines success? How will you measure this?
Step 3: Ask "What Is the Question?"
The aim in this step is to generate a list of questions that, if answered well, will solve your problem.
To do this, look at all of the information that you gathered in the first two steps. Then brainstorm the questions that you'll need to answer to achieve your target future. Use phrases such as "How can I…?" and "How will we…?" to begin.
For instance, imagine that your target future is to have a bigger departmental budget. One question might be, "How can I get a bigger budget?" Then you could brainstorm related questions, such as, "How can we spend less on routine work, so that we can do more with our existing budget?" or, "How would we operate if we had no budget?"
If you generate a long list of questions, narrow these down to the questions that are most relevant for solving your problem.
Step 4: Generate Answers
In this step, you generate solutions to your problem by coming up with answers to the questions that you developed in the previous step.
Again, brainstorm as many possible solutions as possible, and don't criticize – just concentrate on coming up with lots of ideas. If you're struggling to come up with solutions, techniques like Reverse Brainstorming , Random Input , and Provocation will help to jump-start your creativity.
Step 5: Forge the Solution
You're now going to develop your ideas into a fully formed solution.
First, evaluate the most promising ideas by comparing them with the success criteria that you identified in step 2. Pick the solution that best meets those criteria. ( Decision Matrix Analysis is helpful here.)
Then develop your best idea further. What else could make this idea better? How could you refine the solution to fit your success criteria better?
If you're working on a complex problem or project, don't underestimate the effort needed to develop and refine your solution.
Step 6: Align Resources
In this last step, you identify the people and other resources that you need in order to implement your solution.
For small projects, Action Plans are useful for this. However, if you're implementing a large-scale project, you'll need to use a more formal project management approach .
At this point, you may still decide not to move ahead with your solution. See our article on Go/No-Go Decision-Making for more on this.
Tim Hurson developed the Productive Thinking Model and published it in his 2007 book, "Think Better." The model provides a structured approach for solving problems creatively. You can use it on your own and in a group.
There are six steps in the model:
The advantage of the model is that it encourages you to use creative and critical thinking skills at each step of the problem-solving process. This means that you can take a well-rounded look at a problem, and come up with better solutions.
This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter , or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!
Rate this resource
The Mind Tools Club gives you exclusive tips and tools to boost your career - plus a friendly community and support from our career coaches!

Comments (3)
- Over a month ago Midgie wrote Hi tsuhaimin, Thanks for the feedback. Hope you enjoy more of our article to help further improve your skills and knowledge. Midgie Mind Tools Team
- Over a month ago tsuhaimin wrote A Superb Article on Problem Solving!
- Over a month ago Midgie wrote This is a great new model for problem solving because it provides a framework and questions for each stage of the process. Not only do you tap into your creativity for generating ideas, you then put on your analytical hat to evaluate it. It also taps into different problem solving models that many of us already know so it feels more familiar! It will definitely be put into my tool kit for future reference! Has anyone used this model and what was their experience? Midgie
Please wait...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Six Step Problem Solving Model provides a shared, collaborative, and systematic approach to problem solving. • Each step must be completed before moving on to the next step. However, the steps are repeatable. At any point the group can return to an earlier step, and proceed from there. •
The Six Step Problem Solving Model isn't just a method; it's a mindset. A mindset that ensures problems are tackled systematically and collaboratively, driving teams towards effective ...
The Six Step Problem Solving Model provides individuals and teams with an effective framework for approaching and resolving problems. By defining the problem, analyzing it thoroughly, generating potential solutions, choosing the most suitable option, implementing it effectively, and continuously evaluating and adjusting strategies, you can ...
The Six-Step Problem Solving Model provides a systematic approach to addressing and resolving problems. By following these steps, individuals and teams can enhance their problem-solving skills and arrive at effective solutions. Remember to always start with a clear definition of the problem, analyze it thoroughly, generate potential solutions ...
Using a problem solving model enables a group to consider all possible causes of a problem and all possible solutions. A problem solving model uses a series of logical steps to help a group identify the most important causes and the best solution. Following the model not only helps the group arrive at a solution, it helps the group arrive at a
This six-step model is designed for the workplace, but is easily adaptable to other settings such as schools and families. It emphasizes the cyclical, continuous nature of the problem-solving process. The model describes in detail the following steps: Step One: Define the Problem. Step Two: Determine the Root Cause(s) of the Problem
This chapter introduces the three behaviours (curiosity, collaboration, evidence-based thinking) and provides an integrated model showing the problem solving steps, tools, and behaviours together. This chapter also provides a complete list of the tools, and discusses the importance of using the tools with other people. Problem solving is a team ...
This process makes group problem solving in projects and meetings agreeable, action-oriented, and productive. Without a process, it can become challenging for teams or groups to create the best solutions and establish a plan of action. Do tell us about the problem solving methods you use within your organization. We would love to
Mastering the Six Step Problem Solving Model is a valuable skill that can be applied to various aspects of life and work. By following a structured problem-solving process, you can ensure comprehensive and effective solutions. Remember to diligently identify the problem, analyze it thoroughly, generate potential solutions, evaluate and select ...
Terms in this set (6) Step One. Identify the Problem. Step Two. Identify the Resources. Step Three. Make Use of Your Resources. Step Four. Identify Possible Solutions.
Step 1: Identify The Problem. Select the problem to be analyzed. Clearly define the problem and establish aprecise problem statement. Set a measurable goal for the problem solving effort. Establish a process for coordinating with and gaining approval of leadership. Step 2: Analyze The Problem.
Step 5: Evaluate. Identify the pros and cons of each of your possible solutions. Choose the solution that seems to work best for you. Step 6: Create a plan of action. Determine a solution and create a plan. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Step 1: Identify the problem, Step 2: Identify your resources, Step 3 ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Lean Six Sigma is simply a process for solving a problem. It consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, & Control. This process is also known as DMAIC ("duh-may-ik"), its acronym. DMAIC is a five-step method for improving existing process problems with unknown causes.
Problem Solving Overview SIX-STEP PROBLEM SOLVING MODEL Problem solving models are used to address many issues that come up on a daily basis in the workplace. These problems may be technical or issue-based. While many of you have probably already engaged in solving problems, you have probably used many different approaches in order to achieve a ...
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Strategies: A Practical Guide (Management) Hardcover - September 28, 2021 . by Sorin Dumitrascu (Author) 4.3 4.3 out of 5 stars 34 ratings. Book 4 of 10: Management . See all formats and editions ... The book then proceeds to present a step-by-step approach to effective problem-solving, providing readers ...
Although problem-solving is something everyone does on a daily basis, many people lack confidence in their ability. Here we look at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track. Explore. input your search term How it works. Blog ...
Problem-solving model for the evaluation. My problem-solving model will consist of six steps. First, we will engage in defining the problem, which in our case, is the problem of overcrowding in prisons (Dumitrascu, 2021). Secondly, my model will attempt to establish the root cause of our problem. In this step, we will establish dig into the ...
The Productive Thinking Model was developed by author and creativity theorist, Tim Hurson, and was published in his 2007 book, " Think Better ." The model presents a structured framework for solving problems creatively. You can use it on your own or in a group.
The Six Step Problem Solving Model. Use the five steps for problem solving to answer the following question. Please show all of your work. Angle A and Angle B are complementary angles. If Angle A ...
The six-step problem-solving model provides these skills and guidelines on going about different problems on personal and professional levels. ... Dumitrascu S. (2020). The Six-Step Problem Solving Model. The Medium. Retrieved 4 June 2021 from - solving-model-7c457b6bf134 Frensch, P. A., & Funke, J. (Eds.). (1995).
Problem Solving Six-Step Problem-Solving Process.Use the five steps for problem solving to answer the following question. Please show all of your work. Angle A and Angle B are complementary angles ...
Access Entrepreneurship 6th Edition Chapter 1 Problem 1CP10 solution now. Our solutions are written by Chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality! ... Step-by-step solution. ... So, there is a model which is related to the problem solving of the entrepreneurs. Chapter 1, Problem 1CP10 is solved. View this answer View this answer ...