Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help

YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
Steps in the literature review process.
- What is a literature review?
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus
- Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy
- Finalize your research question
- Think about relevant dates, geographies (and languages), methods, and conflicting points of view
- Conduct searches in the published literature via the identified databases
- Check to see if this topic has been covered in other discipline's databases
- Examine the citations of on-point articles for keywords, authors, and previous research (via references) and cited reference searching.
- Save your search results in a citation management tool (such as Zotero, Mendeley or EndNote)
- De-duplicate your search results
- Make sure that you've found the seminal pieces -- they have been cited many times, and their work is considered foundational
- Check with your professor or a librarian to make sure your search has been comprehensive
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of individual sources and evaluate for bias, methodologies, and thoroughness
- Group your results in to an organizational structure that will support why your research needs to be done, or that provides the answer to your research question
- Develop your conclusions
- Are there gaps in the literature?
- Where has significant research taken place, and who has done it?
- Is there consensus or debate on this topic?
- Which methodological approaches work best?
- For example: Background, Current Practices, Critics and Proponents, Where/How this study will fit in
- Organize your citations and focus on your research question and pertinent studies
- Compile your bibliography
Note: The first four steps are the best points at which to contact a librarian. Your librarian can help you determine the best databases to use for your topic, assess scope, and formulate a search strategy.
Videos Tutorials about Literature Reviews
This 4.5 minute video from Academic Education Materials has a Creative Commons License and a British narrator.
Recommended Reading
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Conduct a literature review
What is a literature review.
A literature review is a summary of the published work in a field of study. This can be a section of a larger paper or article, or can be the focus of an entire paper. Literature reviews show that you have examined the breadth of knowledge and can justify your thesis or research questions. They are also valuable tools for other researchers who need to find a summary of that field of knowledge.
Unlike an annotated bibliography, which is a list of sources with short descriptions, a literature review synthesizes sources into a summary that has a thesis or statement of purpose—stated or implied—at its core.
How do I write a literature review?
Step 1: define your research scope.
- What is the specific research question that your literature review helps to define?
- Are there a maximum or minimum number of sources that your review should include?
Ask us if you have questions about refining your topic, search methods, writing tips, or citation management.
Step 2: Identify the literature
Start by searching broadly. Literature for your review will typically be acquired through scholarly books, journal articles, and/or dissertations. Develop an understanding of what is out there, what terms are accurate and helpful, etc., and keep track of all of it with citation management tools . If you need help figuring out key terms and where to search, ask us .
Use citation searching to track how scholars interact with, and build upon, previous research:
- Mine the references cited section of each relevant source for additional key sources
- Use Google Scholar or Scopus to find other sources that have cited a particular work
Step 3: Critically analyze the literature
Key to your literature review is a critical analysis of the literature collected around your topic. The analysis will explore relationships, major themes, and any critical gaps in the research expressed in the work. Read and summarize each source with an eye toward analyzing authority, currency, coverage, methodology, and relationship to other works. The University of Toronto's Writing Center provides a comprehensive list of questions you can use to analyze your sources.
Step 4: Categorize your resources
Divide the available resources that pertain to your research into categories reflecting their roles in addressing your research question. Possible ways to categorize resources include organization by:
- methodology
- theoretical/philosophical approach
Regardless of the division, each category should be accompanied by thorough discussions and explanations of strengths and weaknesses, value to the overall survey, and comparisons with similar sources. You may have enough resources when:
- You've used multiple databases and other resources (web portals, repositories, etc.) to get a variety of perspectives on the research topic.
- The same citations are showing up in a variety of databases.
Additional resources
Undergraduate student resources.
- Literature Review Handout (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill)
- Learn how to write a review of literature (University of Wisconsin-Madison)
Graduate student and faculty resources
- Information Research Strategies (University of Arizona)
- Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students (NC State University)
- Oliver, P. (2012). Succeeding with Your Literature Review: A Handbook for Students [ebook]
- Machi, L. A. & McEvoy, B. T. (2016). The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success
- Graustein, J. S. (2012). How to Write an Exceptional Thesis or Dissertation: A Step-by-Step Guide from Proposal to Successful Defense [ebook]
- Thomas, R. M. & Brubaker, D. L. (2008). Theses and Dissertations: A Guide to Planning, Research, and Writing
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Brazil’s plummeting graduate enrolments hint at declining interest in academic science careers
Career News 21 MAY 24

How religious scientists balance work and faith
Career Feature 20 MAY 24

How to set up your new lab space
Career Column 20 MAY 24

Pay researchers to spot errors in published papers
World View 21 MAY 24

US halts funding to controversial virus-hunting group: what researchers think
News 16 MAY 24

Egypt is building a $1-billion mega-museum. Will it bring Egyptology home?
News Feature 22 MAY 24

Harassment of scientists is surging — institutions aren’t sure how to help
News Feature 21 MAY 24
Editor (Structural biology, experimental and/or computational biophysics)
We are looking for an Editor to join Nature Communications, the leading multidisciplinary OA journal, publishing high-quality scientific research.
London or New York - hybrid working model.
Springer Nature Ltd
Wissenschaftliche/r Mitarbeiter/in - Quantencomputing mit gespeicherten Ionen
Wissenschaftliche/r Mitarbeiter/in - Quantencomputing mit gespeicherten Ionen Bereich: Fakultät IV - Naturwissenschaftlich-Technische Fakultät | St...
Siegen, Nordrhein-Westfalen (DE)
Universität Siegen
Wissenschaftliche/r Mitarbeiter/in (PostDoc) - Quantencomputing mit gespeicherten Ionen
Wissenschaftliche/r Mitarbeiter/in (PostDoc) - Quantencomputing mit gespeicherten Ionen Bereich: Fakultät IV - Naturwissenschaftlich-Technische Fak...
Professor Helminthology
Excellent track record on the biology and immunobiology of zoonotic helminths and co-infections, with a strong scientific network.
Antwerp, New York
Institute of Tropical Medicine
Assistant Professor in Plant Biology
The Plant Science Program in the Biological and Environmental Science and Engineering (BESE) Division at King Abdullah University of Science and Te...
Saudi Arabia (SA)
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
2. decide on the scope of your review., 3. select the databases you will use to conduct your searches., 4. conduct your searches and find the literature. keep track of your searches, 5. review the literature..
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
- Sample Literature Reviews
Disclaimer!!
Conducting a literature review is usually recursive, meaning that somewhere along the way, you'll find yourself repeating steps out-of-order.
That is actually a good sign.
Reviewing the research should lead to more research questions and those questions will likely lead you to either revise your initial research question or go back and find more literature related to a more specific aspect of your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by a central research question. Remember, it is not a collection of loosely related studies in a field but instead represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor.
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
Tip: This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
Make a list of the databases you will search. Remember to include comprehensive databases such as WorldCat and Dissertations & Theses, if you need to.
Where to find databases:
- Find Databases by Subject UWF Databases categorized by discipline
- Find Databases via Research Guides Librarians create research guides for all of the disciplines on campus! Take advantage of their expertise and see what discipline-specific search strategies they recommend!
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Write down the searches you conduct in each database so that you may duplicate them if you need to later (or avoid dead-end searches that you'd forgotten you'd already tried).
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Ask your professor or a scholar in the field if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Use RefWorks to keep track of your research citations. See the RefWorks Tutorial if you need help.
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions. Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited?; if so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Again, review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Finding "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: why do a literature review, why do a literature review.
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed.
You identify:
- core research in the field
- experts in the subject area
- methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
- gaps in knowledge -- or where your research would fit in
It Also Helps You:
- Publish and share your findings
- Justify requests for grants and other funding
- Identify best practices to inform practice
- Set wider context for a program evaluation
- Compile information to support community organizing
Great brief overview, from NCSU
Want To Know More?
- Next: How To Find "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.

c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students.

- Become Involved |
- Give to the Library |
- Staff Directory |
- UNF Library
- Thomas G. Carpenter Library
Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review, original research vs. survey of the literature.
- Benefits of Conducting a Literature Review
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Summary of the Process
- Additional Resources
Chat With Us Text Us (904) 507-4122 Email Us Schedule a Research Consultation
Visit us on social media!
Student Engagement Librarian

The literature review is an integral part of any research project and is undertaken as a means of surveying what research has been conducted previously on a particular topic.
There are many reasons for conducting a literature review, but one of the primary reasons is to establish a base line of what is already known on a topic before exploring the topic any further. The review typically involves a search of any previously published or presented materials that might have relevance to a prospective new study.
If the point of a research project is solely to review what has already been written on a topic, the resulting article is termed a "survey of the literature" or a "literature survey" or even a "literature review." In this case, the article is complete in itself and does not delve into anything new regarding the topic. A literature survey might end with a discussion of what work is still needed to further develop knowledge of a particular topic, but it does not, itself, flesh out any of those ideas. Articles of this type can be highly beneficial to someone seeking to launch an original study; literature surveys have already laid some of the groundwork for a prospective researcher's own literature review.
When the survey serves as the initial step that precedes a further investigation of an idea or ideas about a topic, then that review of the literature sets the stage for the presentation of original research. Original research usually involves the selection of a methodology for examining a topic and may include the gathering of data that can be further analyzed to arrive at assumptions about the topic. Data may be derived from the examination of human subjects, from conducting surveys or assessments, from the study of particular species of plants or animals, from the systematic scientific measurement of any physical phenomena, from nearly anything that can be documented and analyzed. Again, the whole point of launching an original study is to learn something new about a topic. Research typically begins with what is known (the literature review) and progresses into analyzing, through the observation and analysis of data, what is yet to be known through further study.
Both the literature survey and the original study are considered academic articles, as opposed to popular articles. Both involve research in order to come to a better understanding of a topic.
- Literature Review Tutorial by American University Library
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It by University of Toronto
- Write a Literature Review by UC Santa Cruz University Library
- Next: Benefits of Conducting a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2022 8:54 AM
- URL: https://libguides.unf.edu/litreview
How to Conduct a Literature Review: A Guide for Graduate Students
- Let's Get Started!
- Traditional or Narrative Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Typology of Reviews
- Literature Review Resources
- Developing a Search Strategy
- What Literature to Search
- Where to Search: Indexes and Databases
- Finding articles: Libkey Nomad
- Finding Dissertations and Theses
- Extending Your Searching with Citation Chains
- Forward Citation Chains - Cited Reference Searching
- Keeping up with the Literature
- Managing Your References
- Need More Information?
Bookmark This Guide!
https://instr.iastate.libguides.com/gradlitrev
Where to Get Help
Librarians at ISU are subject experts who can help with your research and course needs. There are experts available for every discipline at ISU who are ready to assist you with your information needs!
What we do:
- Answer questions via phone, chat and in-person
- Consult with student and faculty researchers on request
- Purchase materials for the collection
- Teach instruction session for ISU courses
- Support faculty getting ready for promotion & tenure reviews
- Help with data management plans
Find Your Librarian
“Google can bring you back 100,000 answers. A librarian can bring you back the right one.” - Neil Gaiman
The literature review is an important part of your thesis or dissertation. It is a survey of existing literature that provides context for your research contribution, and demonstrates your subject knowledge. It is also the way to tell the story of how your research extends knowledge in your field.
The first step to writing a successful literature review is knowing how to find and evaluate literature in your field. This guide is designed to introduce you to tools and give you skills you can use to effectively find the resources needed for your literature review.
Before getting started, familiarize yourself with some essential resources provided by the Graduate College:
- Dissertation and Thesis Information
- Center for Communication Excellence
- Graduate College Handbook
Below are some questions that you can discuss with your advisor as you begin your research:
Questions to ask as you think about your literature review:
What is my research question.
Choosing a valid research question is something you will need to discuss with your academic advisor and/or POS committee. Ideas for your topic may come from your coursework, lab rotations, or work as a research assistant. Having a specific research topic allows you to focus your research on a project that is manageable. Beginning work on your literature review can help narrow your topic.
What kind of literature review is appropriate for my research question?
Depending on your area of research, the type of literature review you do for your thesis will vary. Consult with your advisor about the requirements for your discipline. You can view theses and dissertations from your field in the library's Digital Repository can give you ideas about how your literature review should be structured.
What kind of literature should I use?
The kind of literature you use for your thesis will depend on your discipline. The Library has developed a list of Guides by Subject with discipline-specific resources. For a given subject area, look for the guide titles "[Discipline] Research Guide." You may also consult our liaison librarians for information about the literature available your research area.
How will I make sure that I find all the appropriate information that informs my research?
Consulting multiple sources of information is the best way to insure that you have done a comprehensive search of the literature in your area. The What Literature to Search tab has information about the types of resources you may need to search. You may also consult our liaison librarians for assistance with identifying resources..
How will I evaluate the literature to include trustworthy information and eliminate unnecessary or untrustworthy information?
While you are searching for relevant information about your topic you will need to think about the accuracy of the information, whether the information is from a reputable source, whether it is objective and current. Our guides about Evaluating Scholarly Books and Articles and Evaluating Websites will give you criteria to use when evaluating resources.
How should I organize my literature? What citation management program is best for me?
Citation management software can help you organize your references in folders and/or with tags. You can also annotate and highlight the PDFs within the software and usually the notes are searchable. To choose a good citation management software, you need to consider which one can be streamlined with your literature search and writing process. Here is a guide page comparing EndNote, Mendeley & Zotero. The Library also has guides for three of the major citation management tools:
- EndNote & EndNote Web Guide
- Mendeley Guide
- Getting Started with Zotero
What steps should I take to ensure academic integrity?
The best way to ensure academic integrity is to familiarize yourself with different types of intentional and unintentional plagiarism and learn about the University's standards for academic integrity. Start with this guide . The Library also has a guide about your rights and responsibilities regarding copyrighted images and figures that you include in your thesis.
Where can I find writing and editing help?
Writing and editing help is available at the Graduate College's Center for Communication Excellence . The CCE offers individual consultations, peer writing groups, workshops and seminars to help you improve your writing.
Where can I find I find formatting standards? Technical support?
The Graduate College has a Dissertation/ Thesis website with extensive examples and videos about formatting theses and dissertations. The site also has templates and formatting instructions for Word and LaTex .
What citation style should I use?
The Graduate College thesis guidelines require that you "use a consistent, current academic style for your discipline." The Library has a Citation Style Guides resource you can use for guidance on specific citation styles. If you are not sure, please consult your advisor or liaison librarians for help.
Adapted from The Literature Review: For Dissertations, by the University of Michigan Library. Available: https://guides.lib.umich.edu/dissertationlitreview
Center for Communication Excellence/ Library Workshop Slides
Slides from the CCE/ Library Workshop "A Citation Here...A Citation There...Pretty Soon You'll Have a Lit Review" held on February 21, 2024 are below:
- CCE Workshop February 21, 2024
- Next: Types of Literature Reviews >>
The library's collections and services are available to all ISU students, faculty, and staff and Parks Library is open to the public .
- Last Updated: Mar 14, 2024 12:15 PM
- URL: https://instr.iastate.libguides.com/gradlitrev
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Literature Reviews
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Getting started
- Types of reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
Introduction to AI
Research rabbit, copilot (powered by chatgpt4).
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
Generative AI tools have been receiving a lot of attention lately because they can create content like text, images, and music. These tools employ machine learning algorithms that can produce unique and sometimes unexpected results. Generative AI has opened up exciting possibilities in different fields, such as language models like GPT and image generators.
However, students need to approach these tools with awareness and responsibility. Here are some key points to consider:
Novelty and Creativity : Generative AI tools can produce content that is both innovative and unexpected. They allow users to explore new ideas, generate unique artworks, and even compose original music. This novelty is one of their most exciting aspects.
Ethical Considerations : While generative AI offers creative potential, it also raises ethical questions. Students should be aware of potential biases, unintended consequences, and the impact of their generated content. Responsible use involves considering the broader implications.
Academic Integrity : When using generative AI tools for academic purposes, students should consult their instructors. Policies regarding the use of AI-generated content may vary across institutions. Always seek guidance to ensure compliance with academic integrity standards.
In summary, generative AI tools are powerful and fascinating, but students should approach them thoughtfully, seek guidance, and adhere to institutional policies. Please refer to the Duke Community Standard for questions related to ethical AI use.
Looking for a tool that isn't listed here? Let us know about it!

Research Rabbit is a literature mapping tool that takes one paper and performs backward- and forward citation searching in addition to recommending "similar work." It scans the Web for publicly available content to build its "database" of work.
Best suited for...
Disciplines whose literature is primarily published in academic journals.
Considerations
- Integrates with Zotero
- Works mostly with just journal articles
- Potential for bias in citation searching/mapping
» researchrabbit.ai «

What is it?
Elicit is a tool that semi-automates time-intensive research processes, such as summarizing papers , extracting data , and synthesizing information . Elicit pulls academic literature from Semantic Scholar , an academic search engine that also uses machine learning to summarize information.
Empirical research (i.g., the sciences, especially biomedicine).
- Both free and paid versions
- Doesn't work well in identifying facts or in theoretical/non-empirical research (e.g., the humanities)
- Potential biases in the natural language processing (NLP) algorithms
- Summarized information and extracted data will still need to be critically analyzed and verified for accuracy by the user
» elicit.com «

Think of Consensus as ChatGPT for research! Consensus is "an AI-powered search engine designed to take in research questions, find relevant insights within research papers, and synthesize the results using the power of large language models" ( Consensus.app ). Consensus runs its language model over its entire body of scientific literature (which is sourced from Semantic Scholar ) and extracts the “key takeaway” from every paper.
The social sciences and sciences (non-theoretical disciplines).
- Free and paid versions
- Similar to Elicit, Consensus should not be used to ask questions about basic facts
- Consensus recommends that you ask questions related to research that has already been conducted by scientists
- Potential for biases in the input data from participants
» consensus.app «

Dubbed the "AI-powered Swiss Army Knife for information discovery," Perplexity is used for answering questions (including basic facts, a function that many other AI tools are not adept at doing), exploring topics in depth utilizing Microsoft's Copilot, organizing your research into a library, and interacting with your data (including asking questions about your files).
Perplexity has wide-reaching applications and could be useful across disciplines.
- Free and paid pro versions (the pro version utilizes Microsoft's Copilot AI tool)
- Available in desktop, iOS, and Android apps
- See Perplexity's blog for more info
- Your personal information and data on how you use the tool are stored for analytical purposes (however, this feature can be turned off in settings)
- Features a browser plug-in, Perplexity Companion , that is essentially a blend of Google and ChatGPT
» perplexity.ai «
Did you know that as Duke faculty, staff, and students, we have free access to ChatGPT4 via Microsoft Copilot ?
Log in with your Duke credentials to start using it today.

The OG of generative AI tools, ChatGPT-4 is the latest iteration of the popular chatbot, answering questions and generating text that sounds like it was written by a human. While not a replacement for conducting research, it can be helpful when it comes to brainstorming topics or research questions and also as a writing tool (rewriting or paraphrasing content, assessing tone, etc.).
All users across all disciplines.
- ChatGPT-3.5 is the default version of free and paid-tier chat users.
- Since it can't verify its sources, be wary of hallucinations (or made-up citations) that can look very real.
- It is not 100% accurate ! While ChatGPT-4 is touted as being 40% more accurate than its predecessor, users are still expected to verify the information generated by it.
- There is always the potential for bias since ChatGPT was trained on a massive dataset of websites, articles, books, etc. (much of which is inherently biased since it was created by humans).
For ChatGPT-4 (access provided by Duke and requires login) » copilot.microsoft.com «
For ChatGPT-3.5 (free) » chat.openai.com «
- << Previous: 6. Write the review
- Next: Thompson Writing Studio >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

The Linkage Between Digital Transformation and Organizational Culture: Novel Machine Learning Literature Review Based on Latent Dirichlet Allocation
- Open access
- Published: 21 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Tobias Reisberger ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0003-0190-7368 1 ,
- Philip Reisberger ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0004-4678-4151 1 ,
- Lukáš Copuš ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9502-830X 1 ,
- Peter Madzík ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1655-6500 1 &
- Lukáš Falát ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2597-7059 2
Organizational culture is a crucial component of innovation in company success, particularly in the setting of the information economy. The purpose of this research is to conduct a bibliometric analysis in order to identify dominant research topics, their potential shifts, and recent developments in the fields of organizational culture and digital transformation. It demonstrates a machine learning–supported method for identifying and segmenting the current state of this research field. The literature was identified from the Scopus database through a search query. The analyzed amount of papers (3065) was published in 1619 sources (journals, proceedings, books, etc.) with various research impacts. Identifying the dominant research topics resulted in eight topics: Social Media Connectivity; Digital Innovation Ecosystems; Socio-economic Sustainability; Digital Workforce Transformation; Digital Competence and Cultural Transformation; Knowledge, Culture, and Innovation; Data and Resource Management; and Digital Transformation Maturity. The results showed a shift in the research field on organizational culture related to digital transformation towards the subject area of business, management, and accounting, with increasing research interest and impact for the Digital Workforce Transformation as well as for the Knowledge, Culture, and Innovation topics.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
In recent years, the world has gone through many events that have changed how we live, relax, work, or communicate. These changes are still resonating in the business environment, for example, in the transition to partial or complete work from home and bring several challenges that organizations have to deal with (Yang et al., 2023 ). One of the crucial areas is the socialization of employees and the formation and maintenance of organizational values expressed by the organizational culture (Noto et al., 2023 ).
Organizational culture has been well-researched since the early 1980s (O’Reilly et al., 1991 ; Schein, 1985 ). The focus originated in American-based qualitative studies and shifted over time towards a more international perspective (Cameron & Quinn, 1999 ; Denison & Mishra, 1995 ; Hofstede, 1998 ), as well as adopting a more quantitative viewpoint with many published papers (O’Reilly et al., 2014 ). Several different areas of organizational culture have already been analyzed, including performance, motivation, leadership, and innovation, among many others (Affes & Affes, 2022 ; Aasi & Rusu, 2017 ; Abu Bakar et al., 2021 ). One of the up-to-date research areas is the topic of digitalization.
The advent of automation and digitalization and the resulting digital transformation in recent history have significantly impacted many markets and organizations and influenced the behaviors and expectations of customers. Digital transformation is driven by several external factors, including the rapid growth and adoption of new technologies that foster e-commerce, big data, a changing competitive landscape, and altered consumption behavior, driven by better-informed, connected, and more empowered customers (Verhoef et al., 2021 ). It provides many challenges and opportunities, including relevant impacts on organizational culture (Alloghani et al., 2022 ). In recent years, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant influence on organizational culture (Daum & Maraist, 2021 ; Spicer, 2020 ).
Even before the pandemic, the fast development of digital technologies, including automation, smart technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and robots, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is radically altering the nature of work and of organizations (Nimawat & Gidwani, 2021 ). The combination of technological advancements was coined as the Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0 by Klaus Schwab in late 2015 (Schwab, 2015 ). The speed and scope of current technological changes are prompting concerns about the extent to which new technologies will fundamentally alter organizational cultures, workplaces, or completely replace workers (Acemoglu & Autor, 2011 ; Brynjolfsson & McAfee, 2014 ; Frey & Osborne, 2017 ).
These Industry 4.0 developments and an agile workforce are all components of a global digital transformation that changed the workplace dynamics and led to significant changes in organizations and employee behavior. Due to the unexpected interruption brought on by the coronavirus pandemic, working from anywhere has become the new standard for millions of people worldwide (Özkazanç-Pan & Pullen, 2020 ).
The combination of these two driving forces will have a lasting effect on the formation and effectiveness of organizational culture in the future (Kniffin et al., 2021 ; Trenerry et al., 2021 ). However, the number and range of publications in recent years on organizational culture, digital transformation, Industry 4.0, and COVID-19 make it necessary to provide a structured overview of the published literature.
Firstly, this paper shall give an overview of the research being conducted on organizational culture and digital transformation and identify the main research areas, authors and journals. The methods utilized are outlined, along with the applied bibliometric tools. Secondly, this paper aims to provide an overview of the status quo of research by identifying the different research clusters with its critical analysis.
Literature Review
Research on organizational culture and digital transformation.
Over time, the concept of organizational culture has been the center of attention for many researchers. It has been the main focus of study of several scientific works, especially in management and business (Mohelska & Sokolova, 2018 ; Streimikiene et al., 2021 ; Vallejo, 2011 ).
The concept of organizational culture has been studied from different angles, with researchers exploring the role that organizational culture can play and which factors impact organizational culture (Guzal-Dec, 2016 ; Polyanska et al., 2019 ; Zeng & Luo, 2013 ).
A high number of researchers agree with Schein’s ( 1985 ) model, which asserts that there are three levels at which an organizational culture may be conceptualized: fundamental presumptions and beliefs, norms and values, and cultural artifacts (Chatman & O’Reilly, 2016 ). From the perspective of the organization and its working environment, organizational culture emerges from behavior in which basic assumptions and beliefs are shared and seen as given by organizational members (Schein, 1985 ).
Academics primarily focused on organizational culture’s definition, connotation, structural components and type categorization in the 1980s; most of this research was qualitative (Cui et al., 2018 ). Even though there was no universal agreement on the meanings of organizational culture at the time, Schein’s framework (Schein, 1992 ) was somewhat representational in the academic world. Research on organizational culture then evolved from mainly qualitative research to quantitative studies in the 1990s (Cameron & Quinn, 1999 ; Denison & Mishra, 1995 ; Hofstede, 1998 , 2001 ; O’Reilly et al., 2014 ). According to Cui et al. ( 2018 ), contemporary views of organizational culture are seen as a key factor for success, promoting organizational effectiveness and performance (Gregory et al., 2009 ), organizational innovation (Hogan & Coote, 2014 ), and organizational identity (Ravasi & Schultz, 2006 ). Organizational culture is now considered a key component of innovation in company success, particularly in the setting of the information economy (Büschgens et al., 2013 ). Cartwright identifies nine relevant factors that drive the cultural transformation in organizations that enable successful business practices (Cartwright, 1999 ).
Organizational culture has two basic academic foundations: sociology (organizations have culture) and anthropology (organizations are cultures). The sociological position has become dominant in recent years (Cameron & Quinn, 1999 ). Based on this, there are two opposing viewpoints regarding the possibility of managing organizational culture — the functionalist and symbolist view (Schueber, 2009 ). The functionalist perspective regards culture as an organizational variable (Alvesson, 1993 ), and it can be determined by management (Meek, 1988 ; Silverzweig & Allen, 1976 ). According to the functionalist perspective, culture is seen as something that the organization possesses and can be controlled (Barley et al., 1988 ; Smircich, 1983 ). The symbolist viewpoint regards culture as a representation of what an organization is rather than anything it has . This implies major challenges in controlling or managing organizational culture (Morgan, 1986 ; Smircich, 1983 ). Functionalists would argue that the culture should be changed to fit the strategy, whereas symbolists would propose that the strategy should be adjusted to the organization’s culture (Ogbonna, 1992 ; Senior, 1997 ). In this paper, the functionalist view is supported by implications of the results.
Digitalization is defined as “the transformation of business models as a result of fundamental changes to core internal processes, customer interfaces, products and services, as well as the use of information and communications technologies” (Isensee et al., 2020 ). However, digitalization and digital transformation are quite different. A company may embark on several digitalization initiatives, from automating procedures to retraining staff members to utilize computers. On the other hand, businesses cannot conduct digital transformation as projects. Instead, this more general phrase refers to a client-centered strategic business transformation that calls for adopting digital technology and organizational changes across all departments (Verhoef et al., 2021 ).
An executive’s view that does not distinguish between digitalization and digital transformation could lead to an insufficient strategic focus (Li & Shao, 2023 ). Digital transformation efforts will often involve several digitalization projects, which require management sponsorship and the willingness to change existing structures and practices. Various papers have studied the challenges that may arise from organizational culture when adopting new technologies and structures, e.g., agile practices (Anwar et al., 2016 ; Ghimire et al., 2020 ; Raharjo & Purwandari, 2020 ), technology adoption (Melitski et al., 2010 ), or even Green Supply Chain Management (El Baz & Iddik, 2021 ). As the business becomes primarily customer-driven, digital transformation necessitates improving how well the organization manages change (Anghel, 2019 ).
Industry 4.0 began in the twenty-first century with the development of cyber-physical systems (CPS), the Internet of Things (IoT), the Internet of Services, smart factories, and cloud computing. It continues today (Hermann et al., 2016 ; Kagermann et al., 2013 ; Liao et al., 2017 ; Xu et al., 2018 ). It is characterized as a combination of CPS and IoT in the manufacturing industry, which can have repercussions for value creation, company growth, work organization, and downstream businesses (Kagermann et al., 2013 ; Kiel et al., 2017 ). The advent of Industry 4.0 involves significant changes for organizations and societies and has various effects on nations, businesses, industries, and society (Schwab, 2015 ). Industry 4.0 implementation is a complicated process involving horizontal, vertical and seamless integration and will rely on the synergies between the business and stakeholders from many functional domains (Müller, 2019a , 2019b ; Wang et al., 2016 ). In particular, many organizations fail to capture their Industry 4.0 vision and strategy throughout the change process (Schumacher et al., 2016a ). Other important factors that hinder the application of a successful digital transformation towards a functional Industry 4.0 concept are fear of uncertainty and wrong expectation of requirements (Balasingham, 2016 ). Willingness to adopt this technology is another reason to fail (Adebanjo et al., 2021 ). Organizations aiming to incorporate and adopt digital transformation into their operational procedures must recognize and assess important critical factors (Nimawat & Gidwani, 2021 ).
Organizational communication and collaboration styles have changed due to globalization, advancements in information and communication technologies (ICTs), an increase in hybrid work models and the rise of computer-mediated groups (Sharma et al., 2022 ). With the knowledge economy, digital culture, and recent technological innovations, new working styles have quietly emerged in organizations (Powell et al., 2004 ). Then, the spreading of the coronavirus and the required shift in transition to remote working acted as a catalyst for how organizations operate and employees engage. The drastic changes in the workplace naturally affected employees and spurred changes in their behavior and attitudes (Caligiuri et al., 2020 ). The corresponding research topic of COVID-19-related impacts and the implications on digital transformation in the context of organizational culture is relatively new. Many partial aspects that have gained new relevance during the corona pandemic have already received attention in the research community over the past 20 years.
Therefore, this study aims to conduct a bibliometric analysis in order to identify dominant research topics, their potential shifts, and recent developments in the fields of organizational culture and digital transformation. The most significant research articles or authors and their related relationships can be found using the scientific computer-aided review process known as bibliometric analysis. It can help to forecast the possible direction of such identified fields and is widely applied in academic research (Diem & Wolter, 2013 ). This method aids in providing a thorough overview of the subject as well as visually summarizing its patterns and trends (Baker et al., 2020 ; Zhou et al., 2020 ).
Overview of Bibliometric Reviews
The topic of organizational culture has had a large number of contributors in the past decades. Several articles were published on organizational culture as bibliometric studies (Cicea et al., 2022 ). Only a few reviews were conducted on digital transformation in organizations related to organizational culture (e.g., as digitalization). Table 1 lists a few publications on these topics.
Overview of Systematic Reviews
Apart from bibliometric literature reviews, many authors have conducted systematic literature reviews on various research areas relating to organizational culture and digital transformation. As seen in the following non-conclusive overview in Table 2 and Table 3 , researchers have focused their attention on heterogeneous study fields like performance-orientation, entrepreneurship, Industry 4.0, agile practices, work-from-anywhere, SMEs, and many others. This broad overview indicates that the topic of organizational culture plays a very relevant role in recent research, especially in the context of digital transformation.
The provided overview on digital transformation research mainly focuses on functional areas and its application. The center of research is the implementation, readiness, adoption, as well as barriers, opportunities, and challenges. Additionally, research fields like examining potential directions (Belinski et al., 2020 ; Kamble et al., 2018 ; Pagliosa et al., 2019 ; Piccarozzi et al., 2018 ; Schneider, 2018 ; Sony & Naik, 2020 ); implementation, readiness and adoption (Çınar et al., 2021 ; Pacchini et al., 2019 ; Sung & Kim, 2021 ); barriers, opportunities, and challenges to the adoption and implementation of Industry 4.0 (Bajic et al., 2021 ; Raj et al., 2020 ); and sustainability (de Sousa Jabbour et al., 2018 ; Luthra & Mangla, 2018 ) are analyzed.
The main focus areas, among many others, which are influenced by digital transformation are agile and collaborative teamwork and management (Kerber & Buono, 2004 ; Huang et al., 2003 ; Sheppard, 2020 ; Parry & Battista, 2019 ; Singer-Velush et al. 2020 ; Hamouche, 2020 ), adaptive business culture in dynamic , supportive , environments , with focus on employee well-being , work design , open innovation , workforce effectiveness (Am et al., 2020 ; Ngoc Su et al., 2021 ; Baker et al., 2006 ; Žižek et al., 2021 ; Parry & Battista, 2019 ; Bélanger et al., 2013 ; Carnevale & Hatak, 2020 ), and recent technological developments (Ågerfalk et al., 2020 ; Bloom et al., 2015 ; Bondarouk & Ruël, 2009 ; Johnson et al., 2020 ; Spreitzer et al., 2017 ; Wiggins et al., 2020 ).
Research Gap
The research mentioned in the aforementioned literature review sought to examine several factors of organizational culture and digital transformation. However, reviews of literature based solely on a systematic or bibliometric methodology have significant drawbacks. Studies of systematic literature reviews are frequently in-depth and typically handle only a small number of documents. As a result, the findings are more constrained (Moher et al., 2015 ; Page et al., 2021 ). Contrarily, bibliometric reviews are concentrated on a wider range of the studied areas. They mostly reveal major trends as an outcome (Cobo et al., 2011 ; van Eck & Waltman, 2010 ). Using machine learning to find latent patterns in textual data is one of the most popular study methods in the field of bibliometric review (Han, 2020 ; Mariani & Baggio, 2022 ). Automated processing is used to analyze the scientific publications for our study. It employs an advanced machine learning–based methodology to extract topics from the scientific literature. This paper contributes to the existing literature by answering the following research questions:
Research Question 1 (RQ1) . How has the organizational culture — digital transformation relationship evolved over time?
The number of publications on digital transformation is growing, and organizational culture is a well-established research area with years of academic work. Consequently, a bibliometric analysis of the growth of the top journals, articles, and most cited publications may be able to provide relevant insights.
Research Question 2 (RQ2) . What are the dominant research topics on organizational culture and digital transformation?
The total number of publications on the subject of this study is rapidly increasing. Therefore, we may apply machine learning to extract particular study ideas from a large body of published scientific literature.
Research Methodology
This paper aims to establish the trends of research papers in the field of organizational culture research with a focus on digital transformation. The authors conducted the review of the literature using bibliometric analysis and a machine learning method.
Researchers often undertake bibliometric analysis with the main goal to determine the body of knowledge on a certain subject, to provide an assessment of the research already conducted, and to develop networking structures for the scientific community. Five steps ( study design , data collection , data analysis , data visualization , and interpretation of results ) represent the workflow of science mapping and were used to apply the bibliometric approach and network analysis (Aria & Cuccurullo, 2017 ).
The review usually starts by determining the database that contains the input data. The only source for this paper are the bibliographic records from the Scopus database as data collection input. This source has been considered reliable in prior works. Scopus, developed by Elsevier B.V., is the largest database of scientific peer-review literature hosting more than 27,950 journal published articles (Elsevier, 2023 ). It was chosen for this study as it is the largest and most relevant scientific database in the world, covering most of the publications available. This includes consistent repositories of documents as well as additional information such as country of all the authors, citations per document, and further information that is relevant in terms of quality and quantity for the study.
The search query was developed after identifying the research area. This was done by splitting the topic into three fields of research. The first set was organization with the corresponding synonyms followed by culture (second set). The third was digital transformation and its phases digitization and digitalization following Verhoef et al. ( 2021 ) and its synonyms including Industry 4.0 . The database was queried using additional synonyms and alternative spellings to increase the study’s coverage.
To collect these articles, the combination of the following keywords was selected:
Digital transformation , digitalization , digitalisation , digitization , digitisation combined with Industry 4.0 search terms fourth industrial revolution , 4IR , 4-IR , industry 4.0 and the organizational culture related keyword organisation *, organization *, firm , company , corporate , enterprise , business and culture .
The search criteria were then determined. The authors used the title , abstract and keywords from the articles provided by the Scopus database (TITLE-ABS-KEY). This resulted in 3077 identified papers. The search query and result are shown in Table 4 . The search was conducted on March 30, 2023.
After collecting the data, all documents with no abstracts were removed. The authors also removed all documents with abstracts defined as: “[No abstract available]”. After this removal, the dataset consisted of 3065 documents. The applied dataset was made up of the following eight variables: authors, title, year, source, cited by, abstract, authors keywords, index keywords. A total of 139 documents were tagged as Review . In addition, to answer the research question RQ1, we joined our dataset with a dataset that defined individual subject areas for each journal. Thanks to such an expanded dataset, we were able to better structure the results.
Topic Modelling
In order to be able to answer research question RQ2, we needed to perform an analysis of the sentific field. There are several ways to conduct a literature review. Instead of the standard literature review process, we decided to carry out the literature review based on machine learning. This way of analyzing the scientific field allowed us to assess a much larger number of documents and thus make the literature review more relevant. Our review based on machine learning analyzed 3065 document abstracts in total.
Before the actual process of identifying individual research topics in the selected area, it was necessary to perform text preprocessing and then divide the analyzed documents into individual topics. Data preprocessing included several steps which are common in text analytics. After removing some special characters, we removed punctuation, further removed numbers and stopwords defined in the tm package in R. In addition, we defined other custom stopwords that were removed from the corpus of abstracts. Then we then removed the extra spaces and stemmed the words in the document. The last step was to delete custom stopwords Footnote 1 specific to our area of interest. In this case, these were words that were irrelevant to our field of research and, in our opinion, did not add value to the resulting analysis. We defined these words based on the frequency analysis of stemmed words from the corpus of analyzed abstracts. The mentioned procedures were performed in the R programming language using the tm and SnowballC packages. After removing the specific stopwords, we finally removed the extra spaces. Subsequently, a document-term matrix (dtm) was created, which contained the frequencies of all individual words in every document. Since the dtm itself also contained low-frequency words, we removed words that appeared in less than 0.5% of the abstracts in the resulting matrix. The resulting dtm contained 1108 words.
After preprocessing the text of the abstracts, we proceeded to structure the abstracts into research topics. We implemented the mentioned process, also called topic modeling, using the Latent Dirichlet Allocation method, also known as LDA (Blei et al., 2003 ). LDA is a probabilistic generative process, the result of which is a set of topics that represent the composition of the entire space into individual parts. Based on the words in individual documents, the so-called latent topical structure is created, while latent topics are a mixture of several documents. Based on the posterior estimates of the hidden variables, we can estimate the structure of the latent topics. Hidden variables in our case represent latent topical structure (Blei & Lafferty, 2009 ).
Topic modeling using LDA was implemented in the R programming language using the topicmodels library. Topic modeling itself assumes the number of topics into which the entire space needs to be divided. There are several approaches for finding the number of topics. Since the approach based on the evaluation of statistical criteria resulted in a large number of topics, we decided to prefer an expert approach. This approach consisted in manually assessing the interpretability of the most frequent words in individual alternatives. As part of the testing itself for a suitable number of topics, we gradually manually evaluated solutions with the number of topics k = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}.
To quantify the parameters of the LDA model, we used Gibbs sampling (Gelfand, 2000 ; Griffiths & Steyvers, 2004 ; Grün & Hornik, 2011 ). For parameter quantification, we used 2000 iterations, taking into account only every 200th observation for a higher degree of independence between. For each k, we repeated the process five times, always recording only the best solution. Based on the results of the expert analysis, we chose a solution with the number of topics k = 8. Finally, we realized the visualization of topics, which was performed using the ldavis package (Sievert & Shirley, 2014 ).
Development of Related Research Papers
The direct or indirect role of organizational culture in various processes of digital transformation has been the subject of a lot of research. The studies that formed the basis for our analysis were identified from the Scopus bibliometric database through a search query, which is presented in the “ Research Methodology ” section. The data was collected on March 30, 2023, while on this date, 3065 valid documents were registered in the mentioned database. A significant increase in the number of studies has only been noticeable since 2018. Still, it must be said that studies investigating the links between organizational culture and digitalization appeared sporadically even before that. Figure 1 shows an overview of the annual development of published papers and the number of citations related to the given papers. We can notice that in the last 5 years, research has an exponential character (measured through the number of published papers per year), but at the same time, this research area is interesting for academics (measured through the absolute number of citations).
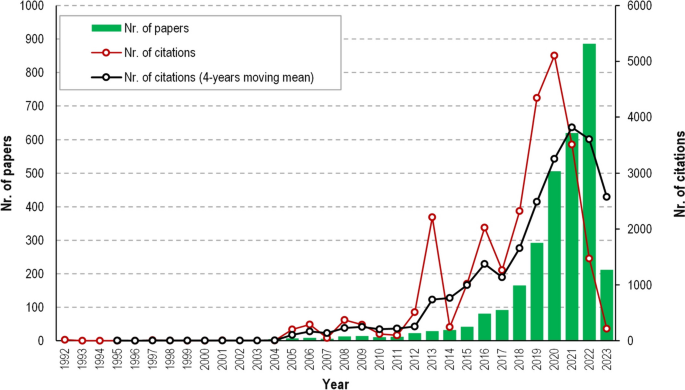
Development of published papers related to organizational culture and digital transformation
The analyzed amount of papers were published in 1619 sources (journals, proceedings, books, etc.) with various research impacts. Table 5 shows the ranking of the sources that had the greatest impact on research on organizational culture and digital transformation in terms of the total number of citations. The research impact is primarily dominated by journals that directly or indirectly deal with the business environment, which is natural considering the nature of the papers. Of the ten listed top influential papers, as many as seven are from the last 5 years, which indicates that since 2018, research interest and the research impact of the given topic have grown dramatically.
Each analyzed document in our dataset was assigned to one of the 28 subject areas used by the Scopus database for their classification. Such an assignment took place based on pairing information about the journal in which the given article is located with the categorization of the journal according to the subject areas of the Scopus database. Figure 2 shows an overview of research interest and research impact for the individual subject areas.
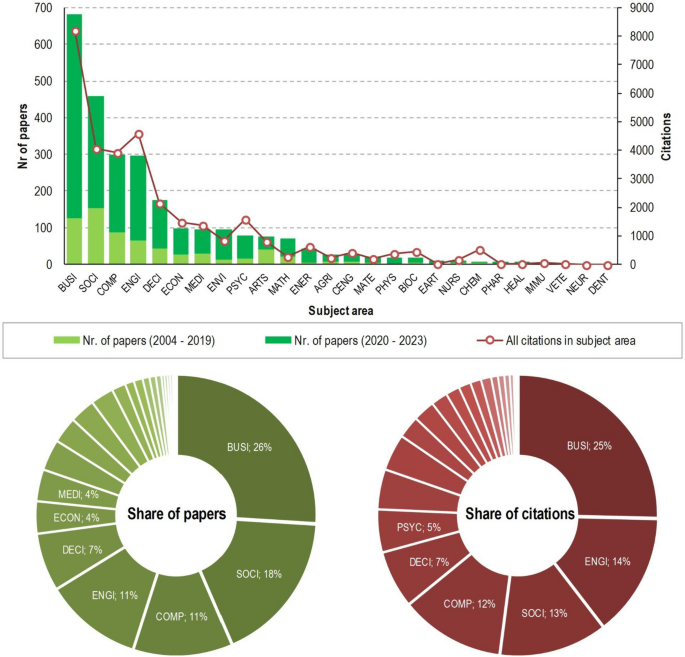
Overview of research impact and research interest of subject areas
Until 2019, ENGI (engineering) was the most frequent category, while a dramatic increase in papers in the BUSI (business, management, and accounting) group can be seen in the last four years. This increase has caused BUSI to be the subject area with the most outstanding research impact and research interest. No such significant changes were recorded in the other subject areas. Possible reasons for the increased interest of researchers in the field of BUSI in the topic of organizational culture and digital transformation are indirectly indicated by some current studies. For example, the study by Priyanto et al. ( 2023 ) emphasizes the importance of proactively modernizing a business to maintain a competitive edge. The need to increase the competitive edge was also pointed out in the study by Troise et al. ( 2022 ), in which the authors examined the relationships between SMEs’ agility (measured by digital technologies capability, relational capability, and innovation capability) and the effects of agility on three outcomes (financial performance, product and process innovation). These studies and many others (Alomari, 2021 ; Carvalho et al., 2020 ; Chaurasia et al., 2020 ; Tessarini Junior & Saltorato, 2021 ) emphasize the managerial aspect of digitalization, which could explain the dramatic increase in research interest and research impact that we have seen over the last 4 years.
These results are also confirmed by a more detailed analysis of the development of the annual number in the five most numerous subject areas (Fig. 3 ). In the left part, we can see the absolute number of articles in the given subject areas, while the dominance of BUSI is visible mainly in the last three years. However, comparing the share of papers in particular subject areas is very interesting (right part of Fig. 3 ). We see that the increase in the BUSI subject area is continuous, while the share of SOCI (social sciences) and COMP (computer science) is decreasing in the long term. Areas such as ENGI and DECI (decision science) maintain a relatively constant share. According to the long-term trend, it can be assumed that the share of the BUSI subject area will grow in research on topics related to organizational culture and digital transformation in the coming years.
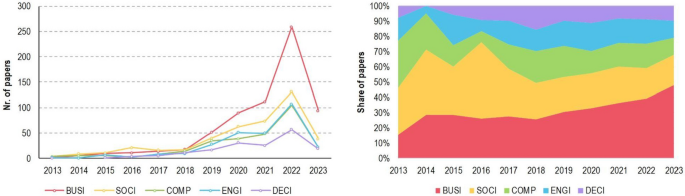
Development of papers in top 5 subject areas — absolute numbers (left) and share (right)
Topics Identification and Their Development
By analyzing the abstracts of the individual papers, it was possible to categorize documents into thematically related clusters using LDA. Such clusters contain papers with the occurrence of the same terms and are called topics. The individual steps of extracting topics from the analyzed dataset are listed in the “ Topic Modelling ” section. To choose the number of topics, several experiments were carried out with the aim of identifying such a constellation in which the individual topics would be well interpretable and, at the same time, sufficiently distinguishable from each other. The number of topics k = 8 was selected by expert assessment according to these criteria. The results and a brief description of the topics via the top-5 most frequent terms can be found in Fig. 4 as an intertopic distance map between two principal components (PC).
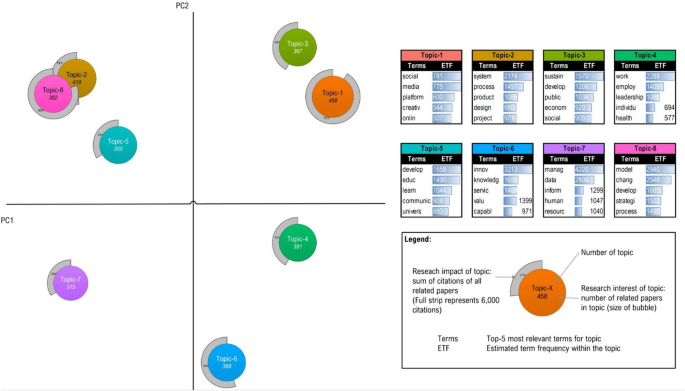
Intertopic distance map
Eight identified topics were analyzed with regard to the most frequented words, and at the same time, the most cited articles in the given topic were also used for their better characterization. This allowed these topics to be named and briefly characterized:
Social Media Connectivity (Topic-1)
This topic includes various aspects of digital and social media, as well as online platforms and the cultural impacts of digital technologies. The Social Media Connectivity topic focuses on main areas like the rise of social media (Munar, 2012 ; van Dijck, 2013 ), its platforms (Mikos, 2016 ; Morris, 2015 ), as well as structural change (Kim, 2020 ; Peukert, 2019 ). The articles of topic-1 explore a wide range of subjects in particular such as social media strategies, digital engagement with heritage, digital storytelling, cultural globalization, and the transformative effects of digital technological change. There are many different inter-organizational subcultures present within organizations that are dealing with convergence and cooperation across media platforms. According to Erdal ( 2009 ), cooperation between those cultures is frequently linked to competition. It is the topic with the most significant research interest (measured through the number of papers), and at the same time, it is the topic with the highest research impact (measured through the number of citations). There are 458 related papers in this topic with a sum of all citations of 91% (based on a 6000 citation strip).
Digital Innovation Ecosystems (Topic-2)
This topic captures the overarching theme of digital transformation across various domains. It emphasizes the integration of digital technologies, innovation processes and the development of ecosystems to drive transformative change in industries and organizations with regard to culture. Regarding the function of organizational culture throughout this transformation process, two alternative viewpoints may be seen. When individuals are empowered to use their problem-solving skills, their capacity for learning and their sense of responsibility, a culture may result in a workforce that is people-centered and engaged driving the integration of digital technologies. On the other hand, there is a culture that focuses primarily on promoting this technology for the purpose of managing or substituting processes neglecting the input and use of people (Rossini et al., 2021 ). The main subjects of this topic include healthcare (Jacob et al., 2020 ), manufacturing (Reinhardt et al., 2020 ), and a digital transformation focus of information systems and organizational practices (Ulas, 2019 ). Additionally, the challenges for the organization and management in rapidly changing environments are analyzed (Granlund & Taipaleenmäki, 2005 ). This topic has a relatively considerable research interest with 419 papers published, but its research impact is average with 51%.
Socio-economic Sustainability (Topic-3)
The Socio-economic Sustainability topic captures the intersection of digital transformation, sustainability and socio-economic considerations across a wide variety of domains such as urban development (Anttiroiko, 2016 ), corporate responsibility and sustainability (Etter et al., 2019 ; Lăzăroiu et al., 2020 ), technology management (Tasleem et al., 2019 ), and organizational practices with regard to culture, among others. In the case of sustainable performance, all forms of organizational culture — based on the types defined by Quinn and Spreitzer ( 1991 ) — have a positive effect on sustainable performance (Gebril Taha & Espino-Rodríguez, 2020 ). There is also a strong correlation between organizational culture and eco-innovation (Reyes-Santiago et al., 2017 ). Furthermore, the sharing economy and its cultural effects towards consumption and ownership are analyzed (Dabbous & Tarhini, 2021 ). The third topic has an average research interest, counting 367 papers and a slightly below-average research impact of 42% compared to the other topics.
Digital Workforce Transformation (Topic-4)
Digital Workforce Transformation highlights the themes of digital transformation with the focus of organizational resilience, leadership, and the impact of technology on work culture and employee well-being. The main focus is on the employee-work relationship, including subjects like leadership (Cortellazzo et al., 2019 ; Guzmán et al., 2020 ), employee well-being (Coldwell, 2019 ; Theurer et al., 2018 ), and resilience (McFadden et al., 2015 ). In particular, the implications on cultural organizational characteristics, operations, digital transformation, and financial planning of COVID-19 for work, workers, and organizations are analyzed (Kniffin et al., 2021 ; Obrenovic et al., 2020 ). As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, many organizations have changed their mode of operation. They adopted a pure work from home model or make use of a hybrid mode of operation. Establishing a communicative work from home culture will result in increased employee satisfaction (Fay & Kline, 2011 ; Mandal et al., 2023 ). Organizations have to educate their employees concerning these new processes and technologies. Individuals dislike change, so organizations must coordinate training and awareness programs to demonstrate the advantages of new digital platforms and related technologies (Mandal et al., 2023 ). Regarding research interest, this topic is average with 381 papers, and its research impact is slightly below average with 42%.
Digital Competence and Cultural Transformation (Topic-5)
This topic refers to the concepts of competence in the digital era, cultural transformation, innovation, and sustainability. These articles explore different aspects of digital transformation (Suárez-Guerrero et al., 2016 ), the impact of digital competence on various sectors (Konttila et al., 2019 ), cultural factors in innovation and enterprise, and the intersection of technology and culture (Mohelska & Sokolova, 2018 ). The role of leadership in the transformation of organizational culture is also a focus of analysis (Sá & Serpa, 2020 ). From the point of view of research interest, this is a minor topic (355 papers) that simultaneously has a relatively small research impact (33%).
Knowledge, Culture and Innovation (Topic-6)
Knowledge, Culture, and Innovation captures the common themes of knowledge management (Gandini, 2016 ; Yeh et al., 2006 ), organizational culture (Dubey et al., 2019 ), innovation, and the transformative effects (Ungerman et al., 2018 ) of digitalization across various sectors. Digital innovation is linked to organizational culture by the digital capabilities of an organization (Zhen et al., 2021 ). The capabilities required by management in dynamic environments are examined in particular (Karimi & Walter, 2015 ). Research interest, counting 388 papers, as well as research impact, with 56%, of this topic are both average.
Data and Resource Management (Topic-7)
The Data and Resource Management topic encompasses the concepts of digitalization, Industry 4.0, data management, quality management, organizational culture and the impact of technology on various industries (Durana et al., 2019 ; Gunasekaran et al., 2019 ; Sony et al., 2020 ). These titles explore different aspects of implementing Industry 4.0, including the utilization of big data (Chiang et al., 2017 ), improving organizational performance through digital transformation (Ananyin et al., 2018 ) and the role of data-driven decision-making in different sectors. A number of relevant factors for Industry 4.0 implementation like the development of Industry 4.0-specific know-how, securing financial resources, integration of employees into the implementation process, and the establishment of an open-minded and flexible corporate culture are analyzed. (Veile et al., 2020 ). The research interest of this topic is the smallest of all with only 315 papers, and its research impact is also relatively small with 34%.
Digital Transformation Maturity (Topic-8)
This topic covers the concepts of digital transformation, Industry 4.0, maturity models, organizational culture, and the impact of technology on business strategies and performance (Gajsek et al., 2019 ; Teichert, 2019 ). These titles explore various aspects of digitalization, technology implementation, strategic management, organizational resilience, and the adoption factors of Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing industry (Kohnová et al., 2019 ). The analysis shows that factors like organizational identity, dematerialization, and collaboration play a key role in the digital transformation (Tronvoll et al., 2020 ). The size of research interest of this topic is average (382 papers), but its research impact is among the largest (of 80%).
These topics are sufficiently distinguishable from each other not only from an interpretive point of view but also within the position in the intertopic distance map (Fig. 4 ). In the coordinates of two principal components, almost all topics are relatively isolated, meaning they are sufficiently distinguishable from each other. In one case, however, a statistical similarity was identified, namely for topic-2 Digital Innovation Ecosystems and topic-8 Digital Transformation Maturity (Fig. 4 top left). This finding suggests that there is some interrelationship between the two topics. After a closer examination of the articles from both topics, it was found that topic-2 and topic-8 share a rather similar basis of content. The central point of investigation in these articles is the identification of various (success) factors and challenges that arise for organizations and their cultures during the phase of digital transformation (AlBar & Hoque, 2019 ; Cichosz et al., 2020 ; Shardeo et al., 2020 ). Topic-2 builds on this common foundation by focusing on systems and functional aspects. There, the organization’s implementation, integration, and management of tools and data (ERP, big data) is examined. Additionally, this topic focuses on the organization’s life cycle, evolution, business models, and processes like DevOps and Agile development (Gupta et al., 2019 ; Jacob et al., 2020 ; Nascimento et al., 2019 ). On the other hand, the majority of the articles in topic-8 focus on a perspective with regard to the organizational readiness of the organization towards changes related to Industry 4.0, including the impacts those changes will have on culture, the implications for strategy, and the general organization’s maturity through the examination of maturity models (Ganzarain & Errasti, 2016 ; Mittal et al., 2018 ; Santos & Martinho, 2020 ; Schumacher et al., 2016a , b ).
The eight topics identified are not static and their development may change over time. To capture such changes, we analyzed the share of papers (research interest) and the share of citations (research impact) of papers in the last 10 years. We did not analyze the absolute numbers but their relative share primarily to avoid the risk of distortion caused by the exponential increase in the number of articles and citations. The results can be found in Fig. 5 .
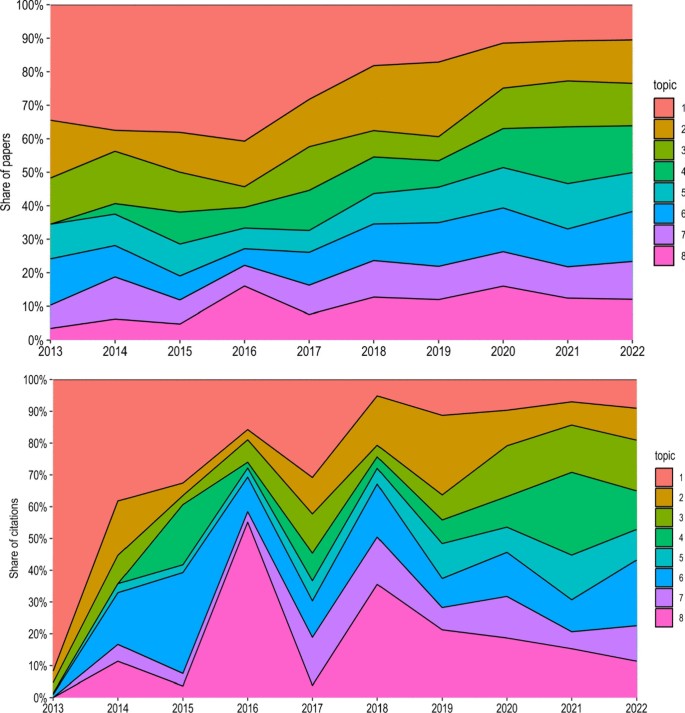
Development of research interest (top) and research impact (bottom) in last 10 years
Several findings can be seen in Fig. 5 . The first of them is a marked decrease in topic-1 both from the point of view of research interest and the point of view of research impact. As mentioned earlier, this topic is currently one of the most important. However, trend analysis shows that its importance is declining relatively quickly. It is gradually being replaced by topics with higher research interest (e.g., topic-4) or research impact (e.g., topic-6).
The downward trend of topic-1 Social Media Connectivity can be explained with the growing maturity of this research field. In the early start of the new millennium, the rise of social networks and communication platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Whatsapp, and other social media services and applications changed the way of communication and collaboration. As of 2023, this field of research is established and many papers have been published and cited already. Based on our search query, there were 458 papers identified with over 5400 citations in total from 1997 to 2023.
The second finding is the gradual emergence of new topics. These are topics that almost or did not exist 10 years ago. The most significant representative of such topics is topic-4, which almost did not exist in 2013, but is currently one of the most important topics. The upward trend of topic-4 Digital Workforce Transformation is strongly connected with the emergence of new working modes and cultural shifts within the organizational landscape due to COVID-19 pandemic related effects. The rise of topic-4 with a strong focus on the employee-work relationship and employee well-being is relatively new. This was triggered with the start of the worldwide pandemic (COVID-19). The worldwide pandemic had a significant impact on how people worked and communicated. This remote work model has many implications on a number of different fields like organizational culture, collaboration, employee motivation, and productivity, among many others. Thus, the requirement for employees and the organizations to adapt to this new work reality open up many new research fields. The growing topic-6 Knowledge, Culture, and Innovation combines knowledge management, organizational culture, and innovation in regard to the transformative effects of digitalization across various sectors. This topic recently gained special attention because the world economy is facing challenges during the pandemic caused by less international business and trade and increased costs (Amirul et al., 2023 ). Competitive advantages through knowledge management, knowledge sharing, and innovation are the key to deal with the (project) uncertainty many companies face (Borodako et al., 2023 ).
The third finding is that increasing research interest does not necessarily increase research impact. For example, we can mention topic-5 Digital Competence and Cultural Transformation , which is gradually gaining research interest, but its research impact is the smallest of all. However, it should be noted here that research impact is based on processing the number of citations, which can generally have a time delay.
A more detailed characterization of topics is also possible by comparing them to the analyzed subject areas. Figure 6 shows the decomposition of individual topics into subject areas. The basis for this decomposition was the papers themselves.
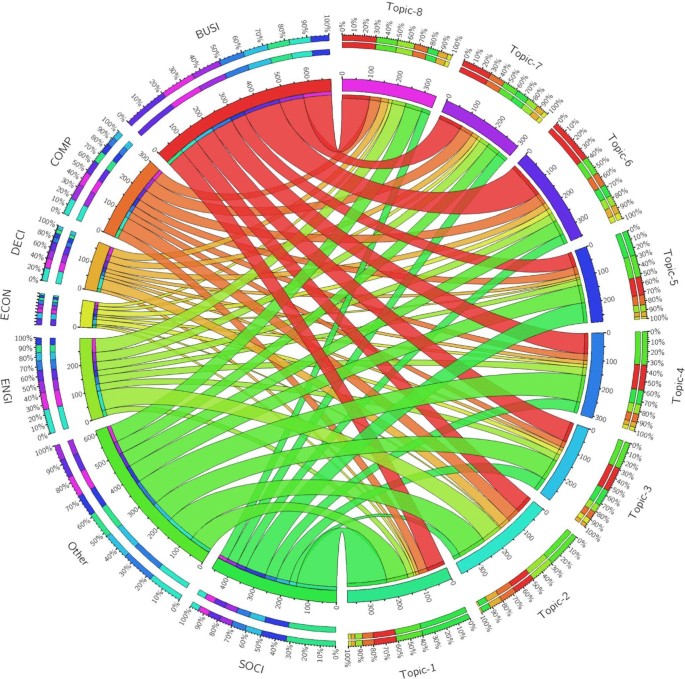
Decomposition of topics to subject areas
Several findings can be seen in Fig. 6 . Topic-1, which currently dominates research impact and research interest, but has a negative trend, is most associated with papers from the SOCI subject area. If we compare these results with the analysis of subject areas (Fig. 2 ), we can conclude that there are two parallel phenomena — a decrease in interest in both SOCI and topic-1. This topic played a key role in the past, but its outlook, as well as the outlook of organizational culture research in relation to digital transformation in the SOCI subject area, is negative. On the other hand, we can see that the BUSI subject area is most prominently represented in topic-6. By comparing the development of BUSI and the development of topic-6, we can also notice parallel phenomena — in this case, however, with a positive trend. Both topic-6 and the BUSI subject area have been growing in recent years, and it is assumed that this could be the case in the following years as well. In the past the focus of research has been on identification and introduction as well as adaptation of new technologies that drive the trend of digital transformation. With this established foundation, nowadays, the research shifts more towards the application and impacts of these technologies in organizations and its consequences on innovation-orientation, knowledge generation and sharing as well as cultural effects (Kronblad et al., 2023 ). This can be seen with the strengthening of topic-6. Other topics appear more heterogeneous from the point of view of subject areas, and the papers that fall into them are from different subject areas.
This article begins with a brief review of organizational culture research in relation to digital transformation. Later, an overview of the research area was presented based on the 3065 publications listed and identified in the Scopus database. To answer research question 1, we have identified the key journals, papers and authors and have shown the development of publications over time. Research interest and research impact of the given topic have grown dramatically since 2018. According to research areas, from 2004 until 2023, the share of papers (research impact) as well as the share of citations (research interest) is mainly contributed to the subject area of BUSI (with a share of more than 25%). The dominance of BUSI has been visible mainly in the last 3 years.
The identification of the dominant research topics (research question 2) resulted in eight topics: Social Media Connectivity , Digital Innovation Ecosystems , Socio-economic Sustainability , Digital Workforce Transformation , Digital Competence and Cultural Transformation , Knowledge, Culture and Innovation , Data and Resource Management , and Digital Transformation Maturity . The topic with the most significant research interest (measured by the number of papers) and the highest research impact (measured by the number of citations) is Social Media Connectivity (topic-1). This is because of the strong role of this topic in the past. The outlook is declining for this topic as well as the related subject area SOCI. Two rising topics were identified. In recent years Digital Workforce Transformation (topic-4) and Knowledge, Culture, and Innovation (topic-6) gained strong interest. Both are from the area of BUSI.
To fulfil the aims of the article, following the completion of the literature review, we were able to identify a number of research topics that are distinct due to the methodology that we have utilized. As a result of their development over time, some of these topics are also relatively new; for instance, as of 2013, topic-4 ( Digital Workforce Transformation ) did not exist at all. In light of the fact that the topics have developed over time, it is clear that the most important areas influencing culture have been transformed under the conditions brought about by digital transformation.
Implications
Firstly, this study demonstrated a machine learning–supported method for identifying and segmenting the current state of this research field. This method, as used in this paper, can be applied to other fields to obtain a systematic overview of research topics.
Secondly, organizational culture has been a field of research for many years and research on digital transformation is constantly growing. The interrelation of these two research areas is relatively new, and their findings will have a lasting effect on the formation and effectiveness of organizational culture in the future.
With the increased interest in Digital Workforce Transformation and Knowledge, Culture, and Innovation , we could identify a shift in the research field on organizational culture in relation to digital transformation towards the subject area of BUSI. Those two rising topics show a need to focus on the impact of technology on work culture and employee well-being, as well as on knowledge management and innovation in relation to organizational culture.
The long-term trend of the share development of the BUSI subject area indicates that this area will also grow continuously in the future. From 2019 onwards, the constant increase of papers published per year implies that additional distinct new topics will be established in this field of research. These and other future trends will help researchers to focus on relevant topics and areas for their work.
A possible explanation for this shift in research could derive from the impact technological changes have on businesses today. The work-related requirements during the COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst for many technological advancements due to the necessity to work instantly remote, changing many processes and all communication to digital. This growing importance of technology for every business could lead to an increased relevance and importance for management practice as well as for researchers. An additional cause for organizations to reevaluate matters related to knowledge and innovation is the pervasive integration and accessibility of AI technology in routine business operations. The alignment of current processes, particularly the innovation process within organizations, with this novel capability will be a subject of interest for managers and researchers as well.
Following the functionalist perspective on organizational culture, the management of organizations can attempt to control and change culture (Alvesson, 1993 ). The introduction of these two topics has significant implications for management practice. A strong organizational culture that is people-centered is essential for successful knowledge-driven organizational innovation. As a result, managers must pay special attention to the factors that influence work culture, address the challenges that arise during the transformation, and understand and improve their organization’s digital capabilities.
Managers can focus their efforts on a variety of areas to foster an adaptable, innovative, and supportive work culture while effectively leveraging technology for digital transformation. Enhanced emphasis is placed on the behavior and collaboration of the team and managers, while these recommendations also encompass measures pertaining to the structure and processes.
The delegation of decision-making authority and work ownership responsibility to employees by managers is a critical structural element. Utilizing data to facilitate well-informed decision-making can provide support for this. Establishing a work environment that offers adequate resources and support, including tools, training, and assistance in adjusting to digital transformations and fostering innovation, is an additional critical element (Veile et al., 2020 ). Furthermore, it is beneficial to measure and communicate progress by assessing the impact of digital transformation on work culture, employee well-being, knowledge management, and innovation on a regular basis. The manager should be willing to make the necessary cultural changes to align, adapt, and evolve organizational culture in the digital age (Cortellazzo et al., 2019 ).
During digital transformation, an open and productive organizational culture will be fostered through the promotion of a flexible and inclusive work environment that actively solicits employee feedback and input, with a focus on employee well-being (Coldwell, 2019 ). Managers who set a good example and encourage their employees’ continuous learning and skill development, as well as cross-functional collaboration, will be better able to promote an adaptive organizational culture in an increasingly digital and competitive landscape (Sá & Serpa, 2020 ). Creating a culture that values innovation and encourages employees to come up with new ideas and solutions, as well as celebrating successful innovations, can help managers create a people-oriented work culture that is essential for organizational innovation (Karimi & Walter, 2015 ). This can be seen in the increased interest in the area on Knowledge, Culture, and Innovation by organizations as well as by researchers.
Limitations and Future Research
This study has a number of limitations, which can be mainly attributed to the way the analysis was conducted. The focus of this study is on an automated bibliometric analysis of the literature. While the quantitative focus has many advantages, it also has some limitations. The main advantage includes the possibility to process and analyze a large number of papers via automation and machine learning techniques. A total of 3065 papers were analyzed. This approach — in comparison to a standard systematic literature review — does not analyze the papers manually. Therefore, some relevant documents could be missing, as well as some irrelevant ones might be included. The authors have selected a search query that yields highly relevant search results. Thus, it is assumed that the share of notable articles that are missing is very small and therefore neglectable and does not have a significant impact on the results.
The applied dataset covers most of the important publications, but all the data comes from just one database (Scopus). This is not comprehensive, and some relevant articles (or journals) could be excluded. In addition, some information may be missing because the source of analysis is not the full text of the articles. Another limitation comes from the fact that the primary focus in the topic modeling are the abstracts of the relevant papers and not the whole text. The analysis of the full text could potentially provide a more extensive understanding, but at the same time, it would take much longer.
We decided on the expert approach by determining the number of topics, as the statistical approach resulted in a large number of topics. This may be of a subjective nature, but it resulted in eight well interpretable and sufficiently distinguishable topics. The title, abstract, and keywords of each topic’s top-30 papers (based on citation count) were used to name each topic. This results in subjective topic names but helps to sum up each topic with a generalized distinct phrase.
This study suggests a number of possible future directions for additional research. It is recommended to extend the data sources to other databases than Scopus as well as the search query. This could result in capturing an increased number of relevant papers. In this research two developing, fast growing topics (topic-4 and topic-6) were identified. Further research should concentrate on examining this trend and focusing on those topics.
Future research could concentrate on finding various organizational culture types that reflect and favor those two emerging topics. Considering Quinn and Rohrbaugh’s CVF (Cameron & Quinn, 1999 ; Quinn & Rohrbaugh, 1983 ), the characteristics of the adhocracy culture type may align with the aspects connected to Digital Workforce Transformation and Knowledge, Culture and Innovation as this culture type values innovation and flexibility. This can be supported through the systematic research and cultural audits in organizations.
Data Availability
The data and code that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
cultur, digit, studi, research, technolog, busi, industri, organ, organiz, use, transform, practic, compani, paper, result, factor, perform, effect, find, implement, author, analysi, provid, differ, organis, approach, base, adopt, identifi, impact, improv, literatur, support, relat, increas, focus, success, level, structur, present, purpos, aim, relationship, influenc, understand, method, enterpris, signific, firm, articl, includ, limit, publish, framework, context, contribut, corpor, show, requir, sector, case, review, futur, within, creat, examin, key, explor, right, current, propos, institut, collect, main, howev, reserv, natur, analyz, implic, discuss, consid, concept, mani, construct, investig, achiev, conduct, among, becom, toward, exist, respons, applic, enabl, theori, affect, issu, survey, assess, opportun, three, interview, adapt, indic, appli, perspect, area, suggest, critic, determin, specif, high, aspect, field, build, form, order, evalu, direct, establish, relev, offer, object, various, methodolog, address, problem, enhanc, addit, part, empir, initi, scienc, associ, analyt, reveal, term, theoret, test, springer, possibl, generat, complex, big, open, continu, switzerland, particip, academ, state, mediat, originalityvalu, designmethodologyapproach, across, solut,advanc, content, regard, characterist, highlight, analys, therefor, higher, interest, access, allow, emerald, advantag, face, make, better, year, insight, goal, select, trend, function, small, element, due, must, conceptu, view, systemat, action, chapter, combin, play, accord, question, describ, questionnair, sever, valid, larg, general, thus, â€, major, recent, type, technic, mean, concern, moder, topic, facilit,sampl, gap, respond, way, attent, outcom, stage, scientif, final, expect, repres, creation, report, still, variabl, especi, techniqu, ensur, compar, number, carri, practition, necessari, exampl, defin, second, copyright, document, compon, subject, common, obtain, demonstr, evid, drive, link, depend, exclus, principl, multipl, essenti, observ, quantit, format, revolut, effort, reflect, four, negat, recommend, made, idea, top, ltd, awar, five, regul, standard, rapid, previous, statist, take, strong, introduc, european, journal, foster, sinc, conclus, featur, basi, driver, equat, digitalis, special, best, comprehens, hand, help, forc, given, consist, align, uniqu, total, explain, overal, materi, refer, gain, furthermor, remain, taylor, whether, moreov, imag, conclud, origin, hypothes, consider, think, similar, russian, attribut, fundament, ieee, clear, bring, caus, around, encourag, period, live, shape, step, start, deploy, name, crisi, intent, contemporari, produc, particular, today, protect, satisfact, ident, accept, six, despit, progress, paradigm, theme, appropri, although, elsevi, argu, datadriven, attract, seek, complet, scholar, search, deal, china, maintain, act, respect, introduct, pattern, serv, less, acceler, indepth, predict, crucial, style, detail, procedur, extend, limitationsimpl, phase, emphas, togeth, greater, abl, central, via, confirm, novel, draw, correl, databas, rate, emot, primari, basic, wide, degre, give, machin, legal, domin, thing, map, basel, record, turn, interpret, south, transfer, cover, mdpi, along, leverag, pressur, move, hospit, decad, least, expand, evolv, fourth, holist, now, informa, rang, other, reliabl, solv, excel, site, uncertainti, henc, partial, littl, without, contain, balanc, prefer, real, cours, overcom, alreadi, india, prepar, sale, actor, instrument, valuabl, beyond, past, center, histori, fact, regress, prevent, preserv, assist, deliv, low, definit, mine, substanti, extens, answer, close, known, third, taken, contextu, popular, employees’, index, fit, deriv, locat, embrac, text, scenario, outlin, certain, ongo, desir, independ, transpar, avoid, proceed, realiz, illustr, visual, promis, inc, reach, usag, algorithm, identif, consult, feder, gather, whole, prioriti, russia, altern, constant, occur, shown, actual, proactiv, seem, europ, matter, resist, express, igi, appear, sociotechn, light, extent, germani, done, hybrid, upon, just, read, receiv, driven, german, cycl, suitabl, mainten, fulli, look, long, bodi, ground, attempt, broad, compris, varieti, indonesia, frame, african, rise, home, weak, proper, financ, keep, maker, dissemin, properti, senior, mitig, next, difficulti, captur, correspond, flow, begin, code, overview, stimul, squar, prove, volum, reduct, full, american, choic, malaysia, intend, llc, eight, tri, occup, diffus, vari, under, numer, extract, organization’, anoth, len, rule, indian, aid, know, joint, socioeconom, lower, summar, classifi, fast, experiment, exhibit, paramet, brought, widespread, understood, nowaday, mix, embed, africa, built, provis, sociolog, good, comparison, adjust, behind, quick, adequ, channel, instead, verifi, indirect, seven, primarili, soft, safe, company’, pose, handl, themat, routin, therebi, interconnect, reform, assumpt, either, constitut, utilis, believ, prior, john, separ, come, segment, item, assum, suffici, minim, whose, sem, plssem, outsid, seri, huge, restrict, wast, classif, updat, translat, obstacl, frequent, hold, version, interfac, discov, almost, represent, equal, wherea, hypothesi, presenc, simpl, robust, alway, categor, claim, score, like, print, interdisciplinari, ten, australia, note, italian, bibliometr, lie, america, underpin, synthesi, wiley, promin, alter, typic, stori, fuzzi, simultan, fulfil, estim, pursu, correct, return, manner, narrat, becam, besid, contrast, ration, inspir, replac, hinder, imper, detect, thought, son, faculti, convers, asia, profound, pilot, acknowledg, maxim, configur, urgent, argument, hard, sensit, gmbh, charact, larger, rich, wider, elabor, highest, shed, phenomena, deep, necess, mutual, mass, option, trigger, expans, poor, extant, domest, today’, concentr, demograph, reinforc, clarifi, anticip, eas, expos, deeper, most, editor, devot, middl, crosssect, usual, nine, ultim, manifest, scopus, calcul, vulner, andor, run, massiv, tension, ideal, old, retriev, first, singapor, ambigu, list, conscious, inher, insid, ministri, rethink, serious, compos, stay, modifi, per, encount, rare, attain, circumst, date, recognis, enter, near, spss, explicit, held, incent, unpreced, largest, stronger, insuffici, lack, nevertheless, word, longer, input, decreas, conting, accur, tendenc, preval, match, tackl, undertaken, sciencebusi, amongst, mention, easili, reader, chosen, prosper, elimin, coupl, hope, authors’, get, later, everyday, dedic, encompass, thrive, miss, acm, refin, interdepend, guarante, precis, except, random, accomplish, latest, easi, vast, prevail.
Aasi, P., & Rusu, L. (2017). Facing the digitalization challenge: Why organizational culture matters and how it influences IT governance performance. In N. Paspallis, M. Raspopoulos, C. Barry, M. Lang, H. Linger, & C. Schneider (Eds.), Information systems development: Advances in methods, tools and management (ISD2017 Proceedings). Larnaca.
Google Scholar
Abu Bakar, M. R., Mat Razali, N. A., Wook, M., Ismail, M. N., & Tengku Sembok, T. M. (2021). The mediating role of cloud computing and moderating influence of digital organizational culture towards enhancing SMEs performance. In H. Badioze Zaman, et al. (Eds.), Advances in visual informatics. IVIC 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (vol 13051, pp. 447–458). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90235-3_39
Acemoglu, D., & Autor, D. (2011). Skills, tasks and technologies: Implications for employment and earnings. Handbook of Labor Economics, 4 , 1043–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-7218(11)02410-5
Article Google Scholar
Adebanjo, D., Laosirihongthong, T., Samaranayake, P., & Teh, P.-L. (2021). Key enablers of Industry 4.0 development at firm level: Findings from an emerging economy. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 70 (2), 400–416. https://doi.org/10.1109/tem.2020.3046764
Affes, W., & Affes, H. (2022). Business model and firm performance in Tunisian firms: A mediated moderation analysis. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 13 (4), 2822–2839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00836-4
Ågerfalk, P. J., Conboy, K., & Myers, M. D. (2020). Information systems in the age of pandemics: COVID-19 and beyond. European Journal of Information Systems, 29 (3), 203–207. https://doi.org/10.1080/0960085x.2020.1771968
Alankarage, S., Chileshe, N., Rameezdeen, R., Edwards, D. J., & Samaraweera, A. (2021). Exploring BIM-triggered organisational and professional culture change: A systematic literature review. Construction Innovation, 23 (1), 229–247. https://doi.org/10.1108/ci-04-2021-0084
AlBar, A. M., & Hoque, Md. R. (2019). Factors affecting cloud ERP adoption in Saudi Arabia: An empirical study. Information Development, 35 (1), 150–164. https://doi.org/10.1177/0266666917735677
Alloghani, M., Thron, C., & Subair, S. (2022). Past achievements and future promises of digital transformation: A literature review. In M. Alloghani, C. Thron, & S. Subair. (Eds.), Artificial intelligence for data science in theory and practice. Studies in computational intelligence (vol 1006, pp. 27–39). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92245-0_2
Alomari, K. M. (2021). Identifying critical success factors in designing effective and efficient supply chain structures: A literature review. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 9 (2), 447–456. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2021.1.006
Alvesson, M. (1993). Cultural perspectives on organizations . Cambridge University Press.
Am, E. N., Affandi, A., Udobong, A., Sarwani, S., & Hernawan, H. (2020). Implementation of human resource management in the adaptation period for new habits. International Journal of Educational Administration, Management, and Leadership, 1 (1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.51629/ijeamal.v1i1.4
Amirul, S. R., Ahmad, S. N. B., & Nasip, S. (2023). Organisational culture and dynamic marketing capabilities in the digital age of pandemic crisis. In B. Alareeni, & A. Hamdan. (Eds.), Impact of artificial intelligence, and the fourth industrial revolution on business success. ICBT 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems (vol 485). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08093-7_21
Ananyin, V., Zimin, K., Lugachev, M., Gimranov, R., & Skripkin, K. (2018). Digital organization: Transformation into the new reality. Business Informatics, 2018 (2), 45–54. https://doi.org/10.17323/1998-0663.2018.2.45.54
Anghel, D. (2019). The ground rules for managers and leaders in the change management process of digitization. Quality - Access to Success, 20 (3), 37–42.
Anttiroiko, A.-V. (2016). City-as-a-platform: The rise of participatory innovation platforms in Finnish cities. Sustainability, 8 (9), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8090922
Anwar, A., Kamel, A. A., & Ahmed, E. (2016, May). Agile Adoption Case Study, Pains, Challenges & Benefits. AMECSE ‘16: Proceedings of the 2nd Africa and Middle East Conference on Software Engineering. Association for Computing Machinery, 60–65. https://doi.org/10.1145/2944165.2944175
Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11 (4), 959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Assoratgoon, W., & Kantabutra, S. (2023). Toward a sustainability organizational culture model. Journal of Cleaner Production, 400 , 136666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136666
Baek, P., Chang, J., & Kim, T. (2019). Organizational culture now and going forward. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 32 (6), 650–668. https://doi.org/10.1108/jocm-05-2018-0121
Bajic, B., Rikalovic, A., Suzic, N., & Piuri, V. (2021). Industry 4.0 implementation challenges and opportunities: A managerial perspective. IEEE Systems Journal, 15 (1), 546–559. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsyst.2020.3023041
Baker, E., Avery, G. C., & Crawford, J. (2006). Home alone: The role of technology in telecommuting. Information Resources Management Journal, 19 (4), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.4018/irmj.2006100101
Baker, H. K., Kumar, S., & Pandey, N. (2020). Thirty years of small business economics: A bibliometric overview. Small Business Economics, 56 , 487–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-020-00342-y
Balasingham, K. (2016). Industry 4.0: Securing the future for German manufacturing companies. Retrieved 12 April 2023, from http://essay.utwente.nl/70665/1/Balasingham_BA_MA.pdf
Barley, S. R., Meyer, G. C., & Gash, D. W. (1988). Cultures of culture: Academic, practitioners and the pragmatics of normative control. Administrative Science Quarterly, 33 , 24–60.
Bélanger, F., Watson-Manheim, M. B., & Swan, B. R. (2013). A multi-level socio-technical systems telecommuting framework. Behaviour & Information Technology, 32 (12), 1257–1279. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929x.2012.705894
Belinski, R., Peixe, A. M. M., Frederico, G. F., & Garza-Reyes, J. A. (2020). Organizational learning and Industry 4.0: Findings from a systematic literature review and research agenda. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 27 (8), 2435–2457. https://doi.org/10.1108/bij-04-2020-0158
Betto, F., Sardi, A., Garengo, P., & Sorano, E. (2022). The evolution of balanced scorecard in healthcare: A systematic review of its design, implementation, use, and review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19 (16), 10291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610291
Bibby, L., & Dehe, B. (2018). Defining and assessing Industry 4.0 maturity levels – Case of the defence sector. Production Planning & Control, 29 (12), 1030–1043. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2018.1503355
Blei, D. M., & Lafferty, J. D. (2009). Topic models. In A. N. Srivastava & M. Sahami (Eds.), Text mining: Classification, clustering, and applications (pp. 71–93). Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Blei, D. M., Ng, A. Y., & Jordan, M. I. (2003). Latent Dirichlet allocation. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3 , 993–1022.
Bloom, N., Liang, J., Roberts, J., & Ying, Z. J. (2015). Does working from home work? Evidence from a Chinese experiment. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 130 (1), 165–218. https://doi.org/10.3386/w18871
Bondarouk, T. V., & Ruël, H. J. M. (2009). Electronic human resource management: Challenges in the digital era. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 20 (3), 505–514. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585190802707235
Borodako, K., Berbeka, J., Rudnicki, M., & Łapczyński, M. (2023). The impact of innovation orientation and knowledge management on business services performance moderated by technological readiness. European Journal of Innovation Management, 26 (7), 674–695. https://doi.org/10.1108/ejim-09-2022-0523
Brynjolfsson, E., & McAfee, A. (2014). The second machine age: Work, progress, and prosperity in a time of brilliant technologies. W. W. Norton and Company.
Büschgens, T., Bausch, A., & Balkin, D. B. (2013). Organizational culture and innovation: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 30 (4), 763–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12021
Caligiuri, P., Cieri, H., Minbaeva, D., Verbeke, A., & Zimmermann, A. (2020). International HRM insights for navigating the COVID-19 pandemic: Implications for future research and practice. Journal of International Business Studies, 51 (5), 697–713. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41267-020-00335-9
Cameron, K. S., & Quinn, R. E. (1999). Diagnosing and changing organizational culture: Based on the competing values framework . Addison-Wesley Publishing.
Carnevale, J. B., & Hatak, I. (2020). Employee adjustment and well-being in the era of COVID-19: Implications for human resource management. Journal of Business Research, 116 , 183–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.05.037
Cartwright, J. (1999). Cultural transformation: Nine factors for continuous business improvement . Prentice Hall.
Carvalho, A. M., Sampaio, P., Rebentisch, E., Carvalho, J. Á., & Saraiva, P. (2020). The influence of operational excellence on the culture and agility of organizations: Evidence from industry. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 38 (7), 1520–1549. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijqrm-07-2020-0248
Chatman, J. A., & O’Reilly, C. A. (2016). Paradigm lost: Reinvigorating the study of organizational culture. Research in Organizational Behavior, 36 , 199–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riob.2016.11.004
Chaurasia, S. S., Kaul, N., Yadav, B., & Shukla, D. (2020). Open innovation for sustainability through creating shared value-role of knowledge management system, openness and organizational structure. Journal of Knowledge Management, 24 (10), 2491–2511. https://doi.org/10.1108/jkm-04-2020-0319
Chen, Y., Liu, L., Li, W., Xie, Z., & Wei, C. (2023). Microfoundations of dynamic capabilities: A systematic review and a multilevel framework. Management Decision, 61 (6), 1717–1753. https://doi.org/10.1108/md-05-2022-0615
Chiang, L., Lu, B., & Castillo, I. (2017). Big data analytics in chemical engineering. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 8 (1), 63–85. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-060816-101555
Chung, N., Lee, H., Lee, S. J., & Koo, C. (2015). The influence of tourism website on tourists’ behavior to determine destination selection: A case study of creative economy in Korea. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 96 , 130–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.03.004
Cicea, C., Țurlea, C., Marinescu, C., & Pintilie, N. (2022). Organizational culture: A concept captive between determinants and its own power of influence. Sustainability, 14 (4), 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042021
Cichosz, M., Wallenburg, C. M., & Knemeyer, A. M. (2020). Digital transformation at logistics service providers: Barriers, success factors and leading practices. The International Journal of Logistics Management, 31 (2), 209–238. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijlm-08-2019-0229
Çınar, Z. M., Zeeshan, Q., & Korhan, O. (2021). A framework for Industry 4.0 readiness and maturity of smart manufacturing enterprises: A case study. Sustainability, 13 (12), 6659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126659
Cobo, M. J., López-Herrera, A. G., Herrera-Viedma, E., & Herrera, F. (2011). Science mapping software tools: Review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 62 (7), 1382–1402. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21525
Coldwell, D. A. L. (2019). Negative influences of the 4th industrial revolution on the workplace: Towards a theoretical model of entropic citizen behavior in toxic organizations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16 (15), 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152670
Cortellazzo, L., Bruni, E., & Zampieri, R. (2019). The role of leadership in a digitalized world: A review. Frontiers in Psychology, 10 (1), 1938. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01938
Cui, Y., Liu, Y., & Mou, J. (2018). Bibliometric analysis of organisational culture using CiteSpace. South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences, 21 (1). https://doi.org/10.4102/sajems.v21i1.2030
Dabbous, A., & Tarhini, A. (2021). Does sharing economy promote sustainable economic development and energy efficiency? Evidence from OECD countries. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 6 (1), 58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2020.11.001
Daum, D. L., & Maraist, C. C. (2021). The importance of culture in the era of COVID-19. Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 14 (1–2), 160–162. https://doi.org/10.1017/iop.2021.40
de Sousa Jabbour, A. B. L., Jabbour, C. J. C., Foropon, C., & Godinho Filho, M. (2018). When titans meet – Can Industry 4.0 revolutionise the environmentally-sustainable manufacturing wave? The role of critical success factors. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 132 , 18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.01.017
Denison, D. R., & Mishra, A. K. (1995). Toward a theory of organizational culture and effectiveness. Organization Science, 6 (2), 204–223. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.6.2.204
Diem, A., & Wolter, S. C. (2013). The use of bibliometrics to measure research performance in education sciences. Research in Higher Education, 54 (1), 86–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-012-9264-5
Dubey, R., Gunasekaran, A., Childe, S. J., Roubaud, D., Fosso Wamba, S., Giannakis, M., & Foropon, C. (2019). Big data analytics and organizational culture as complements to swift trust and collaborative performance in the humanitarian supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 210 , 120–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.01.023
Durana, P., Kral, P., Stehel, V., Lazaroiu, G., & Sroka, W. (2019). Quality culture of manufacturing enterprises: A possible way to adaptation to Industry 4.0. Social Sciences, 8 (4), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci8040124
El Baz, J., & Iddik, S. (2021). Green supply chain management and organizational culture: A bibliometric analysis based on Scopus data (2001–2020). International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 30 , 156–179. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijoa-07-2020-2307
Elsevier. (2023). Scopus content coverage guide. Retrieved 10 June 2023, from https://www.elsevier.com/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/69451/ScopusContentCoverageGuideWEB.pdf
Erdal, I. J. (2009). Cross-media (re)production cultures. convergence. The International Journal of Research into New Media Technologies, 15 (2), 215–231. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354856508105231
Etter, M., Fieseler, C., & Whelan, G. (2019). Sharing economy, sharing responsibility? Corporate social responsibility in the digital age. Journal of Business Ethics, 159 (4), 935–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-019-04212-w
Fay, M. J., & Kline, S. L. (2011). Coworker relationships and informal communication in high-intensity telecommuting. Journal of Applied Communication Research, 39 (2), 144–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/00909882.2011.556136
Frey, C. B., & Osborne, M. A. (2017). The future of employment: How susceptible are jobs to computerisation? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 114 (1), 254–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2016.08.019
Gajsek, B., Marolt, J., Rupnik, B., Lerher, T., & Sternad, M. (2019). Using maturity model and discrete-event simulation for Industry 4.0 implementation. International Journal of Simulation Modelling, 18 (3), 488–499. https://doi.org/10.2507/ijsimm18(3)489
Gandini, A. (2016). The reputation economy. Understanding knowledge work in digital society. Palgrave Macmillan . https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-56107-7
Ganzarain, J., & Errasti, N. (2016). Three stage maturity model in SME’s toward Industry 4.0. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, 9 (5), 1119–1128. https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.2073
Garro Abarca, V. M., Palos-Sanchez, P. R., & Rus-Arias, E. (2020). Working in virtual teams: A systematic literature review and a bibliometric analysis. IEEE Access, 8 , 168923–168940. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3023546
Gebril Taha, M., & Espino-Rodríguez, T. F. (2020). The impact of the organizational culture on hotel outsourcing and sustainable performance an empirical application in the Egyptian hotel sector. Sustainability, 12 (22), 9687. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12229687
Gelfand, A. E. (2000). Gibbs sampling. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 95 (452), 1300–1304. https://doi.org/10.2307/2669775
Ghimire, D., Charters, S., & Gibbs, S. (2020, January). Scaling Agile Software Development Approach in Government Organization in New Zealand. ICSIM ‘20: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Software Engineering and Information Management , 100–104. https://doi.org/10.1145/3378936.3378945
Granlund, M., & Taipaleenmäki, J. (2005). Management control and controllership in new economy firms - A life cycle perspective. Management Accounting Research, 16 (1), 21–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2004.09.003
Gregory, B. T., Harris, S. G., Armenakis, A. A., & Shook, C. L. (2009). Organizational culture and effectiveness: A study of values, attitudes, and organizational outcomes. Journal of Business Research, 62 (7), 673–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2008.05.021
Griffiths, T. L., & Steyvers, M. (2004). Finding scientific topics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101 (Supplement 1), 5228–5235. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0307752101
Grün, B., & Hornik, K. (2011). Topicmodels: An R package for fitting topic models. Journal of Statistical Software, 40 (13), 1–30. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v040.i13
Gunasekaran, A., Subramanian, N., & Ngai, W. T. E. (2019). Quality management in the 21st century enterprises: Research pathway towards Industry 4.0. International Journal of Production Economics, 207 (1), 125–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.09.005
Gupta, S., Qian, X., Bhushan, B., & Luo, Z. (2019). Role of cloud ERP and big data on firm performance: A dynamic capability view theory perspective. Management Decision, 57 (8), 1857–1882. https://doi.org/10.1108/md-06-2018-0633
Guzal-Dec, D. (2016). The role of local authorities in developing pro-ecological organizational culture of the communal offices located in areas of natural value (the example of Lubelskie Voivodeship). Economics and Environment, 57 (2), 235–248.
Guzmán, V. E., Muschard, B., Gerolamo, M., Kohl, H., & Rozenfeld, H. (2020). Characteristics and skills of leadership in the context of Industry 4.0. Procedia Manufacturing, 43 (1), 543–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.02.167
Hamouche, S. (2020). COVID-19 and employees’ mental health: Stressors, moderators and agenda for organizational actions. Emerald Open Research, 2 (15), 15. https://doi.org/10.35241/emeraldopenres.13550.1
Han, X. (2020). Evolution of research topics in LIS between 1996 and 2019: An analysis based on latent Dirichlet allocation topic model. Scientometrics, 125 (3), 2561–2595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03721-0
Hermann, M., Pentek, T., & Otto, B. (2016, January). Design principles for Industrie 4.0 scenarios. 2016 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS) , 3928–3937. https://doi.org/10.1109/hicss.2016.488
Hofstede, G. (1998). Identifying organizational subcultures: An empirical approach. Journal of Management Studies, 35 (1 January 1998), 0022–2380.
Hofstede, G. (2001). Culture consequences: Comparing values, behaviors, institutions and organisations across nations (2nd ed.). Sage Publication Inc.
Hogan, S. J., & Coote, L. V. (2014). Organizational culture, innovation, and performance: A test of Schein’s model. Journal of Business Research, 67 (8), 1609–1621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.09.007
Huang, W. W., Wei, K.-K., Watson, R. T., & Tan, B. C. Y. (2003). Supporting virtual team-building with a GSS: An empirical investigation. Decision Support Systems, 34 (4), 359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-9236(02)00009-x
Isensee, C., Teuteberg, F., Griese, K.-M., & Topi, C. (2020). The relationship between organizational culture, sustainability, and digitalization in SMEs: A systematic review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 275 (1), 122944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122944
Jacob, C., Sanchez-Vazquez, A., & Ivory, C. (2020). Social, organizational, and technological factors impacting clinicians’ adoption of mobile health tools: Systematic literature review. JMIR Mhealth and Uhealth, 8 (2), e15935. https://doi.org/10.2196/15935
Johnson, A., Dey, S., Nguyen, H., Groth, M., Joyce, S., Tan, L., Glozier, N., & Harvey, S. B. (2020). A review and agenda for examining how technology-driven changes at work will impact workplace mental health and employee well-being. Australian Journal of Management, 45 (3), 402–424. https://doi.org/10.1177/0312896220922292
Kagermann, H., Wahlster, W., & Helbig, J. (2013, April). Securing the future of German manufacturing industry: Recommendations for implementing the strategic initiative Industrie 4.0. Final report of the Industrie 4.0 Working Group. Retrieved March 29, 2023, from https://www.din.de/resource/blob/76902/e8cac883f42bf28536e7e8165993f1fd/recommendations-for-implementing-industry-4-0-data.pdf
Kamble, S. S., Gunasekaran, A., & Sharma, R. (2018). Analysis of the driving and dependence power of barriers to adopt Industry 4.0 in Indian manufacturing industry. Computers in Industry, 101 , 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2018.06.004
Kar, S., Yadav, M., & Panda, T. K. (2023). Inclusive organizational behaviour – The dynamic rules of building new workplaces. VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems . https://doi.org/10.1108/vjikms-05-2022-0155
Karimi, J., & Walter, Z. (2015). The Role of Dynamic Capabilities in Responding to Digital Disruption: A Factor-Based Study of the Newspaper Industry. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32 (1), 39–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2015.1029380
Kerber, K. W., & Buono, A. F. (2004). Leadership challenges in global virtual teams: Lessons from the field. SAM Advanced Management Journal, 69 (4), 4.
Kiel, D., Müller, J. M., Arnold, C., & Voigt, K.-I. (2017). Sustainable industrial value creation: Benefits and challenges of Industry 4.0. International Journal of Innovation Management, 21 (08), 1740015. https://doi.org/10.1142/s1363919617400151
Kim, R. Y. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on consumers: Preparing for digital sales. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 48 (3), 212–218. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMR.2020.2990115
Kitsios, F., Kamariotou, M., & Talias, M. A. (2020). Corporate sustainability strategies and decision support methods: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability, 12 (2), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020521
Kniffin, K. M., Narayanan, J., Anseel, F., Antonakis, J., Ashford, S. P., Bakker, A. B., Bamberger, P., Bapuji, H., Bhave, D. P., Choi, V. K., Creary, S. J., Demerouti, E., Flynn, F. J., Gelfand, M. J., Greer, L. L., Johns, G., Kesebir, S., Klein, P. G., Lee, S. Y., & Ozcelik, H. (2021). COVID-19 and the workplace: Implications, issues, and insights for future research and action. American Psychologist, 76 (1), 63–77. https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0000716
Kohnová, L., Papula, J., & Salajová, N. (2019). Internal factors supporting business and technological transformation in the context of Industry 4.0. Business: Theory and Practice, 20 , 137–145. https://doi.org/10.3846/btp.2019.13
Konttila, J., Siira, H., Kyngäs, H., Lahtinen, M., Elo, S., Kääriäinen, M., Kaakinen, P., Oikarinen, A., Yamakawa, M., Fukui, S., Utsumi, M., Higami, Y., Higuchi, A., & Mikkonen, K. (2019). Healthcare professionals’ competence in digitalisation: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 28 (5–6), 745–761. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.14710
Kronblad, C., Pregmark, J. E., & Berggren, R. (2023). Difficulties to digitalize: Ambidexterity challenges in law firms. Journal of Service Theory and Practice, 33 (2), 217–236. https://doi.org/10.1108/jstp-05-2022-0120
Lăzăroiu, G., Ionescu, L., Andronie, M., & Dijmărescu, I. (2020). Sustainability management and performance in the urban corporate economy: A systematic literature review. Sustainability, 12 (18), 7705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187705
Leyva-Duarte, J. E., Chávez Martínez, J. D. J., Pinedo-de-Anda, F. J., & Niebla-Zatarain, J. C. (2019). Bibliometric analysis of organizational culture in business economics of Web of Science, 1980–2018. Nova Scientia, 11 (22), 478–500. https://doi.org/10.21640/ns.v11i22.1810
Leyva-Duarte, J. E., De la Garza Carranza, M. T., Chávez Martínez, J. D. J., Pinedo-de-Anda, F. J., Niebla Zatarain, J. C., & González Farías, J. P. (2020). Organizational culture in the hospitality industry a bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review. Independent Journal of Management & Production, 11 (4), 1140–1162. https://doi.org/10.14807/ijmp.v11i4.1089
Li, G., & Shao, Y. (2023). How do top management team characteristics affect digital orientation? Exploring the internal driving forces of firm digitalization. Technology in Society, 74 , 102293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102293
Liao, Y., Deschamps, F., Loures, E. D. F. R., & Ramos, L. F. P. (2017). Past, present and future of Industry 4.0 - a systematic literature review and research agenda proposal. International Journal of Production Research, 55 (12), 3609–3629. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1308576
Luthra, S., & Mangla, S. K. (2018). Evaluating challenges to Industry 4.0 initiatives for supply chain sustainability in emerging economies. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 117 , 168–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.04.018
Mandal, S., Das, P., Menon, G. V., & Amritha, R. (2023). Enablers of work from home culture: an integrated empirical framework. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 30 (4), 1231–1258. https://doi.org/10.1108/bij-08-2021-0476
Mariani, M., & Baggio, R. (2022). Big data and analytics in hospitality and tourism: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 34 (1), 231–278. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijchm-03-2021-0301
McFadden, P., Campbell, A., & Taylor, B. (2015). Resilience and burnout in child protection social work: Individual and organisational themes from a systematic literature review. British Journal of Social Work, 45 (5), 1546–1563. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bct210
Meek, V. L. (1988). Organizational culture: Origins and weaknesses. Organization Studies, 9 (4), 453–473. https://doi.org/10.1177/017084068800900401
Melitski, J., Gavin, D., & Gavin, J. (2010). Technology adoption and organizational culture in public organizations. International Journal of Organization Theory & Behavior, 13 (4), 546–568. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijotb-13-04-2010-b005
Mikos, L. (2016). Digital media platforms and the use of TV content: Binge watching and video-on-demand in Germany. Media and Communication, 4 (3), 154–161. https://doi.org/10.17645/mac.v4i3.542
Mittal, S., Khan, M. A., Romero, D., & Wuest, T. (2018). A critical review of smart manufacturing & Industry 4.0 maturity models: Implications for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 49 , 194–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.10.005
Mkoba, E. S., & Marnewick, C. (2022). Organisational culture attributes influencing the adoption of agile practices: A systematic literature review. Journal of Information Systems Engineering and Management, 7 (1), 11690. https://doi.org/10.55267/iadt.07.11690
Mohelska, H., & Sokolova, M. (2018). Management approaches for Industry 4.0 - The organizational culture perspective. Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 24 (6), 2225–2240. https://doi.org/10.3846/tede.2018.6397
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., & Stewart, L. A. (2015). Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and meta-analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Systematic Reviews, 4 (1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Montini, P., de Araújo Pinho, C. M., de Oliveira, R. M., Costa, I., & Napolitano, D. M. (2020). Evaluation of the relationship between lean philosophy and organizational culture: A bibliometric review [Avaliação da relação da Filosofia Lean e a Cultura Organizacional: uma revisão bibliométrica]. Research, Society and Development, 9 (11), e059119386. https://doi.org/10.33448/rsd-v9i11.938
Morgan, G. (1986). Images of an organization. Sage Publications.
Morris, J. W. (2015). Curation by code: Infomediaries and the data mining of taste. European Journal of Cultural Studies, 18 (4–5), 446–463. https://doi.org/10.1177/1367549415577387
Müller, J. M. (2019a). Assessing the barriers to Industry 4.0 implementation from a workers’ perspective. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 52 (13), 2189–2194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.11.530
Müller, J. M. (2019b). Antecedents to digital platform usage in Industry 4.0 by established manufacturers. Sustainability, 11 (4), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041121
Munar, A. M. (2012). Social media strategies and destination management. Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 12 (2), 101–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/15022250.2012.679047
Nascimento, D. L. M., Alencastro, V., Quelhas, O. L. G., Caiado, R. G. G., Garza-Reyes, J. A., Rocha-Lona, L., & Tortorella, G. (2019). Exploring Industry 4.0 technologies to enable circular economy practices in a manufacturing context. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 30 (3), 607–627. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmtm-03-2018-0071
Ngoc, Su., & D., Luc Tra, D., Thi Huynh, H. M., Nguyen, H. H. T., & O’Mahony, B. (2021). Enhancing resilience in the Covid-19 crisis: Lessons from human resource management practices in Vietnam. Current Issues in Tourism, 24 (22), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2020.1863930
Nidhi, & Arti,. (2020). Impact of organisational culture on work-life balance a bibliometric analysis and growth in research. European Journal of Molecular & Clinical Medicine, 7 (8), 5308–5319.
Nimawat, D., & Gidwani, B. D. (2021). Identification of cause and effect relationships among barriers of Industry 4.0 using decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory method. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 28 (8), 2407–2431. https://doi.org/10.1108/bij-08-2020-0429
Noto, G., Marisca, C., & Barresi, G. (2023). Adapting management control to virtual teams: Evidence from a natural experiment. Qualitative Research in Accounting & Management . https://doi.org/10.1108/qram-04-2022-0066
Obrenovic, B., Du, J., Godinic, D., Tsoy, D., Khan, M. A. S., & Jakhongirov, I. (2020). Sustaining enterprise operations and productivity during the COVID-19 pandemic: “Enterprise effectiveness and sustainability model.” Sustainability, 12 (15), 5981. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12155981
Ogbonna, E. (1992). Managing organisational culture: Fantasy or reality? Human Resource Management Journal, 3 (2), 42–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-8583.1992.tb00309.x
O’Reilly, C. A., Chatman, J., & Caldwell, D. F. (1991). People and organizational culture: A profile comparison approach to assessing person-organization fit. Academy of Management Journal, 34 (3), 487–516. https://doi.org/10.2307/256404
O’Reilly, C. A., Caldwell, D. F., Chatman, J. A., & Doerr, B. (2014). The promise and problems of organizational culture. Group & Organization Management, 39 (6), 595–625. https://doi.org/10.1177/1059601114550713
Özkazanç-Pan, B., & Pullen, A. (2020). Gendered labour and work, even in pandemic times. Gender, Work & Organization, 27 (5), 675–676. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwao.12516
Pacchini, A. P. T., Lucato, W. C., Facchini, F., & Mummolo, G. (2019). The degree of readiness for the implementation of Industry 4.0. Computers in Industry, 113 , 103125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2019.103125
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., & McGuinness, L. A. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. British Medical Journal, 372 (71), n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Pagliosa, M., Tortorella, G., & Ferreira, J. C. E. (2019). Industry 4.0 and lean manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 32 (5), 543–569. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmtm-12-2018-0446
Parry, E., & Battista, V. (2019). The impact of emerging technologies on work: a review of the evidence and implications for the human resource function. Emerald Open Research, 1 , 5. https://doi.org/10.12688/emeraldopenres.12907.1
Peukert, C. (2019). The next wave of digital technological change and the cultural industries. Journal of Cultural Economics, 43 (2), 189–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10824-018-9336-2
Piccarozzi, M., Aquilani, B., & Gatti, C. (2018). Industry 4.0 in management studies: A systematic literature review. Sustainability, 10 (10), 1–24, 3821. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103821
Polyanska, A., Zapukhliak, I., & Diuk, O. (2019). Culture of organization in conditions of changes as an ability of efficient transformations: The case of gas transportation companies in Ukraine. Oeconomia Copernicana, 10 (3), 561–580. https://doi.org/10.24136/oc.2019.027
Powell, A., Piccoli, G., & Ives, B. (2004). Virtual teams: A review of current literature and directions for future research. ACM SIGMIS Database, 35 (1), 6–36. https://doi.org/10.1145/968464.968467
Priyanto, P., Murwaningsari, E., & Augustine, Y. (2023). Exploring the relationship between robotic process automation, digital business strategy and competitive advantage in banking industry. Journal of System and Management Sciences, 13 (3), 290–305. https://doi.org/10.33168/JSMS.2023.0320
Quinn, R. E., & Rohrbaugh, J. (1983). A spatial model of effectiveness criteria: Towards a competing values approach to organizational analysis. Management Science, 29 (3), 363–377. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.29.3.363
Quinn, R. E., & Spreitzer, G. M. (1991). The psychometrics of the competing values culture instrument and an analysis of the impact of organizational culture on quality of life. Research in Organizational Change and Development, 5 , 115–142.
Raharjo, T., & Purwandari, B. (2020). Agile project management challenges and mapping solutions. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Software Engineering and Information Management , 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1145/3378936.3378949
Raj, A., Dwivedi, G., Sharma, A., de Sousa, Lopes, Jabbour, A. B., & Rajak, S. (2020). Barriers to the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies in the manufacturing sector: An inter-country comparative perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 224 (1), 107546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.107546
Ravasi, D., & Schultz, M. (2006). Responding to organizational identity threats: Exploring the role of organizational culture. Academy of Management Journal, 49 (3), 433–458. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2006.21794663
Reinhardt, I. C., Oliveira, D. J. C., & Ring, D. D. T. (2020). Current perspectives on the development of Industry 4.0 in the pharmaceutical sector. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 18 , 100131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2020.100131
Reis, N. R., Ferreira, M. P., Santos, J. C., & Serra, F. R. (2013). A bibliometric study of the cultural models in international business research [Um estudo bibliométrico dos modelos culturais na pesquisa em negócios internacionais]. BASE - Revista De Administração E Contabilidade Da Unisinos, 10 (4), 340–354. https://doi.org/10.4013/base.2013.104.04
Reyes-Santiago, M., & d. R., Sánchez-Medina, P. S., & Díaz-Pichardo, R. (2017). Eco-innovation and organizational culture in the hotel industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 65 , 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2017.06.001
Rossini, M., Cifone, F. D., Kassem, B., Costa, F., & Portioli-Staudacher, A. (2021). Being lean: How to shape digital transformation in the manufacturing sector. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 32 (9), 239–259. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmtm-12-2020-0467
Sá, M. J., & Serpa, S. (2020). The COVID-19 pandemic as an opportunity to foster the sustainable development of teaching in higher education. Sustainability, 12 (20), 1–16, 8525. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208525
Sahoo, P., Saraf, P. K., & Uchil, R. (2022). Identification of critical success factors for leveraging Industry 4.0 technology and research agenda: A systematic literature review using PRISMA protocol. Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration . https://doi.org/10.1108/apjba-03-2022-0105
Santos, R. C., & Martinho, J. L. (2020). An Industry 4.0 maturity model proposal. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 31 (5), 1023–1043. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmtm-09-2018-0284
Schein, E. H. (1985). Organizational Culture and Leadership. Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Schein, E. H. (1992). Organizational Culture and Leadership. Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Schneider, W. (2018). Psychosocial ramifications of digitalization [Psychosoziale Folgen der Digitalisierung]. Psychotherapeut, 63 (4), 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00278-017-0186-8
Schueber, M. (2009). Understanding organisational culture in a development NGO in Nepal by applying academic theory to witnessed organisational behaviour. Omertaa: Journal for Applied Anthropology. Retrieved April 4, 2023, from https://www.omertaa.org/archive/omertaa0050.pdf
Schumacher, A., Erol, S., & Sihn, W. (2016a). Strategic Guidance Towards Industry 4.0 - A Three-Stage Process Model. In D. Dimitrov & T. Oosthuizen (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Competitive Manufacturing - Resource Efficiency for Global Competitiveness (pp. 495–501).
Schumacher, A., Erol, S., & Sihn, W. (2016b). A maturity model for assessing Industry 4.0 readiness and maturity of manufacturing enterprises. Procedia CIRP, 52 (1), 161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.07.040
Schwab, K. (2015). The Fourth Industrial Revolution: What it means and how to respond. Retrieved 11 June 2023, from https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/2015-12-12/fourth-industrial-revolution
Senior, B. (1997). Organisational Change. Pitman Publishing.
Shardeo, V., Patil, A., & Madaan, J. (2020). Critical success factors for blockchain technology adoption in freight transportation using fuzzy ANP - modified TISM approach. International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making, 19 (6), 1549–1580. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219622020500376
Sharma, G. M., Pandiya, B., Anand, I.M., Oberai, H., & Chauhan, S. (2022). Virtual team leadership: A Bibliometric Analysis. Res Militaris , 12 (6). Retrieved March 14, 2023, from https://resmilitaris.net/index.php/resmilitaris/article/view/3184
Sheppard, B. (2020). A guide to thriving in the post-COVID-19 workplace. Retrieved 9 June 2023, from https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/05/workers-thrive-covid-19-skills
Sievert, C., & Shirley, K. (2014). LDAvis: A method for visualizing and interpreting topics. In J. Chuang, S. Green, M. Hearst, J. Heer, & P. Koehn (Eds.), Proceedings of the Workshop on Interactive Language Learning, Visualization, and Interfaces (pp. 63–70). Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/W14-3110
Silverzweig, S., & Allen, R. F. (1976). Changing the corporate culture. Sloan Management Review, 17 , 33–49.
Sindakis, S., Kitsios, F., Aggarwal, S., & Kamariotou, M. (2022). Entrepreneurial strategies and family firm culture in the Arab world: A systematic literature review. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 29 (7), 994–1016. https://doi.org/10.1108/jsbed-03-2022-0143
Singer-Velush, N., Sherman, K., & Anderson, E. (2020). Microsoft analyzed data on its newly remote workforce. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved June 3, 2023, from https://hbr.org/2020/07/microsoft-analyzeddata-on-its-newly-remote-workforce
Smircich, L. (1983). Concepts of culture and organizational analysis. Administrative Science Quarterly, 28 (3), 339–358.
Sony, M., Antony, J., & Douglas, J. A. (2020). Essential ingredients for the implementation of Quality 4.0. The TQM Journal, 32 (4), 779–793. https://doi.org/10.1108/tqm-12-2019-0275
Sony, M., & Naik, S. (2020). Industry 4.0 integration with socio-technical systems theory: A systematic review and proposed theoretical model. Technology in Society, 61 , 101248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101248
Spicer, A. (2020). Organizational culture and COVID-19. Journal of Management Studies, 57 (8), 1737–1740. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12625
Spreitzer, G. M., Cameron, L., & Garrett, L. (2017). Alternative work arrangements: Two images of the new world of work. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 4 (1), 473–499. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-032516-113332
Streimikiene, D., Mikalauskiene, A., Digriene, L., & Kyriakopoulos, G. (2021). Assessment of the role of a leader in shaping sustainable organizational culture. Amfiteatru Economic, 23 (57), 486–503. https://doi.org/10.24818/EA/2021/57/483
Suárez-Guerrero, C., Lloret-Catalá, C., & Mengual-Andrés, S. (2016). Teachers’ perceptions of the digital transformation of the classroom through the use of tablets: A study in Spain. Comunicar, 24 (49), 81–89. https://doi.org/10.3916/c49-2016-08
Sung, W., & Kim, C. (2021). A study on the effect of change management on organizational innovation: Focusing on the mediating effect of members’ innovative behavior. Sustainability, 13 (4), 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042079
Tasleem, M., Khan, N., & Nisar, A. (2019). Impact of technology management on corporate sustainability performance. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 36 (9), 1574–1599. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijqrm-01-2018-0017
Teichert, R. (2019). Digital transformation maturity: A systematic review of literature. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 67 (6), 1673–1687. https://doi.org/10.11118/actaun201967061673
Teravainen, V., Suominen, A., & Kahkonen, K. (2017). Positioning organizational culture studies between the construction industry and other industries. In M. Buser, G. Lindahl, & C. Räisänen (Eds.), 9th Nordic Conference on Construction Economics and Organization (pp. 428–441).
Tessarini Junior, G., & Saltorato, P. (2021). Workforce agility: A systematic literature review and a research agenda proposal. Innovar, 31 (81), 155–167. https://doi.org/10.15446/innovar.v31n81.95582
Theurer, C. P., Tumasjan, A., & Welpe, I. M. (2018). Contextual work design and employee innovative work behavior: When does autonomy matter? PLoS ONE, 13 (10), e0204089. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204089
Trenerry, B., Chng, S., Wang, Y., Suhaila, Z. S., Lim, S. S., Lu, H. Y., & Oh, P. H. (2021). Preparing workplaces for digital transformation: An integrative review and framework of multi-level factors. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.620766
Troise, C., Corvello, V., Ghobadian, A., & O’Regan, N. (2022). How can SMEs successfully navigate VUCA environment: The role of agility in the digital transformation era. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 174 , 121227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121227
Tronvoll, B., Sklyar, A., Sörhammar, D., & Kowalkowski, C. (2020). Transformational shifts through digital servitization. Industrial Marketing Management . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.02.005
Ulas, D. (2019). Digital transformation process and SMEs. Procedia Computer Science, 158 (1), 662–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.09.101
Ungerman, O., Dedkova, J., & Gurinova, K. (2018). The impact of marketing innovation on the competitiveness of enterprises in the context of Industry 4.0. Journal of Competitiveness, 10 (2), 132–148. https://doi.org/10.7441/joc.2018.02.09
Vallejo, M. C. (2011). A model to study the organizational culture of the family firm. Small Business Economics, 36 , 47–64.
van Dijck, J. (2013). The culture of connectivity. A critical history of social media. Oxford Academic . https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199970773.001.0001
van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84 (2), 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
van Nunen, K., Li, J., Reniers, G., & Ponnet, K. (2018). Bibliometric analysis of safety culture research. Safety Science, 108 , 248–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2017.08.011
Veile, J. W., Kiel, D., Müller, J. M., & Voigt, K.-I. (2020). Lessons learned from Industry 4.0 implementation in the German manufacturing industry. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 31 (5), 977–997. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmtm-08-2018-0270
Verhoef, P. C., Broekhuizen, T., Bart, Y., Bhattacharya, A., Qi Dong, J., Fabian, N., & Haenlein, M. (2021). Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 122 , 889–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.09.022
Wang, S., Wan, J., Li, D., & Zhang, C. (2016). Implementing smart factory of Industrie 4.0: An outlook. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 12 (1), 3159805. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3159805
Wiggins, M. W., Auton, J., Bayl-Smith, P., & Carrigan, A. (2020). Optimising the future of technology in organisations: A human factors perspective. Australian Journal of Management, 45 (3), 449–467. https://doi.org/10.1177/0312896220918915
Xu, L. D., Xu, E. L., & Li, L. (2018). Industry 4.0: State of the art and future trends. International Journal of Production Research, 56 (8), 2941–2962. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1444806
Yang, E., Kim, Y., & Hong, S. (2023). Does working from home work? Experience of working from home and the value of hybrid workplace post-COVID-19. Journal of Corporate Real Estate, 25 (1), 50–76. https://doi.org/10.1108/jcre-04-2021-0015
Yeh, Y., Lai, S., & Ho, C. (2006). Knowledge management enablers: A case study. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 106 (6), 793–810. https://doi.org/10.1108/02635570610671489
Yun, J. J., Zhao, X., Jung, K., & Yigitcanlar, T. (2020). The culture for open innovation dynamics. Sustainability, 12 (12), 5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125076
Zeng, K., & Luo, X. (2013). Impact of ownership type and firm size on organizational culture and on the organizational culture effectiveness linkage. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 14 (Supplement 1), 96–111. https://doi.org/10.3846/16111699.2012.754373
Zhen, Z., Yousaf, Z., Radulescu, M., & Yasir, M. (2021). Nexus of digital organizational culture, capabilities, organizational readiness, and innovation: Investigation of SMEs operating in the digital economy. Sustainability, 13 (2), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020720
Zhou, W., Luo, D., Fang, H., Gou, X., & Jin, C. (2020). Bibliometric overview and retrospective analysis of fund performance research between 1966 and 2019. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 33 (1), 1510–1537. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677x.2020.1755879
Žižek, S. Š, Mulej, M., & Potočnik, A. (2021). The sustainable socially responsible society: Well-Being Society 6.0. Sustainability, 13 (16), 9186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13169186
Download references
Open access funding provided by The Ministry of Education, Science, Research and Sport of the Slovak Republic in cooperation with Centre for Scientific and Technical Information of the Slovak Republic This paper was funded by Faculty of Management, Comenius University Bratislava, Slovakia, and supported by the project VEGA 1/0614/23 Preparedness of companies for the challenges associated with Industry 4.0 in terms of business processes and business process management.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Management, Comenius University Bratislava, Bratislava, Slovakia
Tobias Reisberger, Philip Reisberger, Lukáš Copuš & Peter Madzík
Faculty of Management Science and Informatics, University of Žilina, Žilina, Slovakia
Lukáš Falát
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Tobias Reisberger .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Reisberger, T., Reisberger, P., Copuš, L. et al. The Linkage Between Digital Transformation and Organizational Culture: Novel Machine Learning Literature Review Based on Latent Dirichlet Allocation. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-02027-3
Download citation
Received : 14 August 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 21 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-02027-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Organizational culture
- Digital transformation
- Industry 4.0
- Machine learning
- Latent Dirichlet allocation
- Literature review
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis).The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
The Literature Review by Diana Ridley The Literature Review is a step-by-step guide to conducting a literature search and writing up the literature review chapter in Masters dissertations and in Ph.D. and professional doctorate theses. The author provides strategies for reading, conducting searches, organizing information and writing the review.
Step 3: Critically analyze the literature. Key to your literature review is a critical analysis of the literature collected around your topic. The analysis will explore relationships, major themes, and any critical gaps in the research expressed in the work. Read and summarize each source with an eye toward analyzing authority, currency ...
A literature review I am currently working on, for example, explores barriers to higher education for undocumented students. Step Two: Search for the literature: Conduct a comprehensive bibliographic search of books and articles in your area.
As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it. University ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Conducting a literature review requires you to gather information on a subject or evidence to support a hypothesis in order to contextualise research data. These days, knowledge is at our fingertips and we can readily access online information via sophisticated search engines, such as Google, 2 without even having to enter a library.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review. 1. Choose a topic. Define your research question. 2. Decide on the scope of your review. 3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches. 4. Conduct your searches and find the literature. Keep track of your searches! 5. Review the literature. Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed. You identify: core research in the field. experts in the subject area. methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
Conducting Your Literature Review. 3. A. literature reviewis an overview of the available research for a specific scientific topic. Literature reviews summarize existing research to answer a review question, provide the context for new research, or identify important gaps in the existing body of literature. We now have access to lots of ...
Literature Review A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources that provides an overview of a particular topic. Literature reviews are a collection of the most relevant and significant publications regarding that topic in order to provide a comprehensive look at what has been said on the topic and by whom.
Conduct a Literature Review This chapter describes the steps taken to conduct a literature review. Although the following sections provide detail on these steps, this initial section presents an overview, or a road map, of this process. As shown in Figure 3.1, the first step in conducting a literature review is to
Conducting a literature review . Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It's important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1 . Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue . Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective ... (2012) Conducting systematic reviews in medical education: a stepwise approach. Med Educ 46: 943 ...
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
The literature review is an integral part of any research project and is undertaken as a means of surveying what research has been conducted previously on a particular topic. There are many reasons for conducting a literature review, but one of the primary reasons is to establish a base line of what is already known on a topic before exploring ...
Depending on your area of research, the type of literature review you do for your thesis will vary. Consult with your advisor about the requirements for your discipline. You can view theses and dissertations from your field in the library's Digital Repository can give you ideas about how your literature review should be structured.
After conducting the literature review and deciding on a final sample, it is important to consider how the articles will be used to conduct an appropriate analysis. That is, after selecting a final sample, a standardized means of abstracting appropriate information from each article should be used. Data abstracted can be in the form of ...
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour (vom Brocke et al., 2009). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and ...
An overview of conducting literature reviews in the social sciences and STEM fields. Getting started; Types of reviews; 1. Define your research question; 2. Plan your search; 3. Search the literature ... Tags: literature review, narrative review, rapid review, scoping review, systematic review. Contact Us. 411 Chapel Drive Durham, NC 27708 (919 ...
There are several ways to conduct a literature review. Instead of the standard literature review process, we decided to carry out the literature review based on machine learning. This way of analyzing the scientific field allowed us to assess a much larger number of documents and thus make the literature review more relevant. Our review based ...
This study aims to conduct a systematic literature review (SLR) of the GEO to synthesize empirical findings about how it is investigated in the literature during the period 2014-2024. The PRISMA method is used in this study to evaluate relevant GEO research, and SLR matrix utilized for analyzing the GEO literature in peer-reviewed English ...
This study aims to explore key aspects contributing to the successful applications of the SE concept across diverse industries by conducting a systematic literature review (SLR). Out of 4848 articles, 57 peer-reviewed articles in two databases published between 2013 and 2022 were subjected to descriptive and content analysis.