| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |

What Is A KPI? Definition & Examples

Published: Apr 24, 2023, 2:00pm

Table of Contents
What is a key performance indicator (kpi), kpi vs. metrics, common types of kpis, how to set kpis, kpi best practices, kpi benefits, frequently asked questions (faqs).
All businesses, from startup coffee roasters to billion-dollar e-commerce companies, are vested in tracking their progress, figuring out what works and fixing what doesn’t. That’s where Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) come in. Once you’ve determined what your strategic goals are, using KPIs to measure those goals regularly allows you to make informed decisions and improve outcomes. Keep reading to learn more about KPIs, how to choose your indicators and the best practices for using them.
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measurable target that indicates how individuals or businesses are performing in terms of meeting their goals. Reviewing and evaluating KPIs helps organizations determine whether or not they are on track for hitting their desired objectives.
By looking at several key indicators, which may include categories such as profits, sales numbers, employee turnover and average annual expenses, businesses can identify successes, as well as what is not working. Analyzing KPIs on a regular basis provides a solid overview of how well a business is performing, which allows the folks in charge to decide if current operations should be continued, or if a change of strategy is needed.
Although they are both designed to measure performance, KPIs and metrics have different characteristics and are used by businesses in different ways. Metrics are measures used to track progress and evaluate success, while KPIs are metrics tied to specific goals during a certain period of time.
KPIs are designed to align with business goals and targets, while metrics evaluate the performance of particular processes. Metrics are usually specific to a particular person or team, and frequently align with industry standards or best practices.
What Makes a Good KPI?
The best plans use between five and seven KPIs to track and manage progress. The best structured KPI plans include each element of what is called “SMART” criteria:
- Specific: define what each KPI is intended to measure, and why it is important
- Measurable: KPIs should include standards for measurement
- Achievable: the KPI should be a realistic, achievable goal
- Relevant: KPIs are intended to move a business forward, so they need to be relevant to improving outcomes
- Time-bound: it’s important to set a realistic time frame based on past performance, and make sure that the team sticks to the agreed-upon deadlines
Learn more about S.M.A.R.T. goals .
You’ll find KPIs across nearly every industry and category, including sales, marketing, customer service, IT, human resources and finance. Since these indicators are often responsible for driving performance goals and results, it’s important to choose the correct ones for your business. Opting for a smaller number of manageable KPIs per goal allows companies to make the necessary assessments and keep their workforce aligned.
These are some examples of commonly used KPIs:
Example of Sales KPIs:
- Monthly sales growth
- Monthly customers per sales rep
- Quarterly sales bookings
- Number of engaged leads in sales funnel
- Average conversion time
Example of Marketing KPIs:
- Monthly website traffic
- Page likes and comments
- Social media engagement rates
- Number of new monthly leads
- Click-through rate percentage
Example of Human Resources KPIs:
- Monthly overtime hours
- Quarterly training costs
- Cost per new hire
- Employee productivity
- Monthly absenteeism rate
Example of Customer Service KPIs:
- Customer satisfaction score
- Customer retention rate
- Monthly support ticket submissions
- Average resolution time
- Cost per resolution
You can’t begin using KPIs until you have clearly defined strategic goals; these are what will serve as the jumping-off point for deciding which indicators will be the most useful to your organization. Once your objectives are in place, the next step is to select the appropriate analytical and reporting tools, which are typically software programs designed specifically for your type of business.
Once you begin implementing KPIs, you will have a clearer picture of which indicators are useful and which ones may need to be adjusted. If the KPI you are using is not providing enough information, or the right type of information, it’s likely time to swap it for a different approach.
This will also be true as a business changes or grows, with the KPIs needing to provide different insights. The most effective KPIs are the ones that boost performance, demonstrate the success of a business and help move you closer to your goals.
Steps to Setting a KPI
KPIs should be set strategically, with defined objectives that correspond to a business’s desired outcomes and strategic goals. Remember to make KPIs measurable, specific and include a time frame. Here are the steps to setting up a KPI:
- Determine Key Objectives: Start by defining what the key objectives are, taking into account that KPIs should align teams with an organization’s goals.
- Define Intended Results: Once the objectives have been determined, define what the results need to be in order to achieve success.
- Utilize Lagging and Leading Indicators: Lagging indicators look at past performance variables, such as revenue and profit, to show the outcome of past performance. Leading indicators define what actions are needed to achieve goals and meet overall objectives.
- Set Targets and Thresholds: Setting targets and thresholds provides a way for teams to see exactly where they are and where they are going on a KPI objective time frame.
- Assess Progress and Readjust: KPIs will likely need to be adjusted as a project evolves, so assessing progress regularly illustrates any hiccups and helps keep the objective on track.
Using the wrong KPIs can lead to something as simple as wasted time, or as significant as an outcome that affects your bottom line. For example, if you manage a donut shop and want to know how many dozen are sold each day with an intended goal of reducing food waste, tracking a KPI such as average customer wait time won’t provide the measurements you need to meet your objective.
When choosing the KPIs to implement in your business, keep the following in mind:
- Choose indicators that are directly related to your objectives
- Think about lagging versus leading indicators
- Opt for realistic measurements that are attainable
- Pick a few, specific indicators instead of too many
There are many benefits associated with using KPIs, as they allow the proper resources to be allocated and channeled, ultimately improving performance. Some of the benefits include:
Real-time monitoring
Since KPIs are ongoing, managers are able to monitor team performance and progress in real time as a project unfolds. This allows adjustments to be made and necessary resources to be allocated in order to maximize productivity.
Help avoid delays
Using the KPI framework, teams can quickly view where each task stands on the timeline, allowing them to see what is on track and what might be stalled. This helps avoid delays since adjustments can be made as needed, helping to ensure completion of the objectives.
Easy to formulate
KPIs have the ability to be both simple and straightforward, making them easy to formulate. Because establishing KPIs is not a complicated process, it can be done by any type and size of business once they determine their goals.
Ensure equity and clarity
Using KPIs also means sharing objectives and providing transparency, which often leads to more invested team members. Empowering employees with the autonomy that KPIs provide means that everyone is aware of what is going on, who is responsible for what and that there is equity in success.
Bottom Line
KPIs are an important tool businesses use to evaluate achievements, analyze issues and solve problems. Performed regularly, these measurements illustrate trends and patterns that are essential to making the most informed decisions possible. When the right types and amounts of KPIs are used, these indicators provide the data that will help benefit the overall health of an organization.
What is a KPI?
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a way to measure performance or progress based on specific business goals and objectives. These show organizations how well they are performing and meeting objectives, as well as the areas that need improvement.
Are KPIs and metrics the same thing?
KPIs are different from metrics, in that they measure performance based on calculated business goals instead of specific business activities. Metrics tend to be more operational, while KPIs are strategic.
What are the most common KPIs?
The KPIs a business chooses to use are based on its individual goals and objectives. Some of the most common measurements are financial, customer service, performance, marketing and staffing.
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Construction Project Management Software
- Best Project Portfolio Management Software
- Best Gantt Chart Software
- Best Task Management Software
- Free Project Management Software
- Best Enterprise Project Management Software
- Best Kanban Software
- Best Scrum Software
- Asana Review
- Trello Review
- monday.com Review
- Smartsheet Review
- Wrike Review
- Todoist Review
- Basecamp Review
- Confluence Review
- Airtable Review
- ClickUp Review
- Monday vs. Asana
- Clickup vs. Asana
- Asana vs. Trello
- Asana vs. Jira
- Trello vs. Jira
- Monday vs. Trello
- Clickup vs. Trello
- Asana vs. Wrike
- What Is Project Management
- Project Management Methodologies
- 10 Essential Project Management Skills
- SMART Goals: Ultimate Guide
- What is a Gantt Chart?
- What is a Kanban Board?
- What is a RACI Chart?
- What is Gap Analysis?
- Work Breakdown Structure Guide
- Agile vs. Waterfall Methodology
- What is a Stakeholder Analysis
- What Is An OKR?
Next Up In Business
- Top Asana Alternatives
- Best Scheduling Apps
- monday.com Review: Features, Pros & Cons
- Asana Review: Features, Pricing & More
- Trello Review: Features, Pricing & More

How To Start A Print On Demand Business In 2024
HR For Small Businesses: The Ultimate Guide
How One Company Is Using AI To Transform Manufacturing
Not-For-Profit Vs. Nonprofit: What’s The Difference?
How To Develop an SEO Strategy in 2024
How To Make Money On Social Media in 2024
Laura is a freelance writer specializing in small business, ecommerce and lifestyle content. As a small business owner, she is passionate about supporting other entrepreneurs and sharing information that will help them thrive. Her work has been featured on Angi, Scary Mommy and Cubby.

2000 Regency Parkway Suite 420

(919) 460-8180 | [email protected]
HOW TO DEVELOP KPIS / PERFORMANCE MEASURES
The Balanced Scorecard Institute’s (BSI) Measure-Perform-Review-Adapt (MPRA) framework is a disciplined, practical, and tested approach for developing and implementing a KPI system. It gives organizations a way to systematically articulate a shared vision of what you are trying to achieve, set practical goals, develop meaningful indicators that can be managed and used for decision-making, and establish long-term discipline around getting things done.
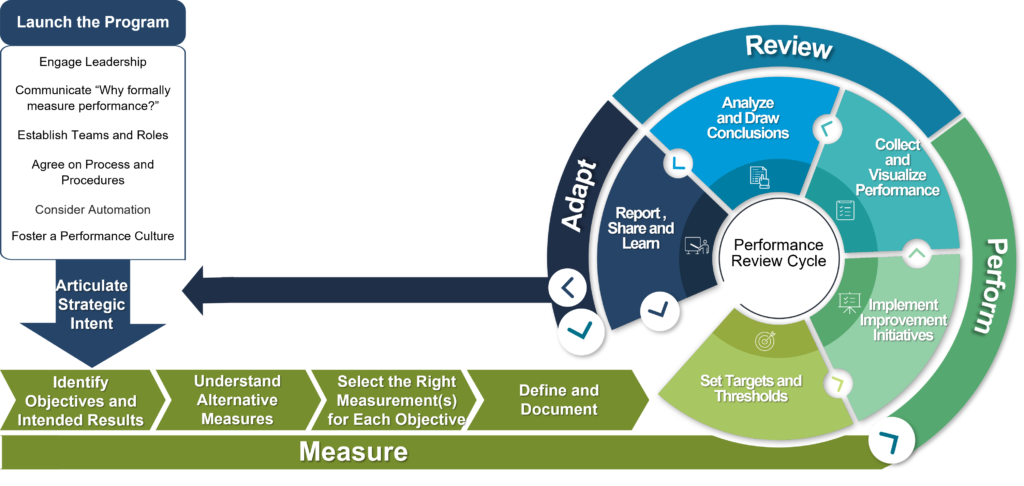
These practical step-by-step methodologies and tools were designed to help organizations:
- Select and design performance measures that are far more meaningful than simple brainstorming or benchmarking can produce
- Get buy-in from staff and stakeholders to enthusiastically own performance measurement and improvement
- Bring measures to life in a consistent way, using the right data and with the right ownership
- Design insightful and actionable reports and dashboards that focus discussion on improvement
- Convincingly hit performance targets, and make measurement about transformation
Measurement development is only the starting point for the improvement process. Once measures have been established, the Perform-Review-Adapt cycle gives the organization a chance to take improvement actions, assess impact, and adapt. Adaptation can take the form of incremental reforecasting for the next quarter or more dramatic changes in strategic intent. Rather than “setting and forgetting” their KPIs, teams use this review cycle as the discipline needed to keep their teams on track and adjust to changes in their strategic environment. It borrows the key principle from the agile world that assumes that we cannot possibly know everything about our strategic intentions at the beginning of the process and so need a disciplined learning process.
Always begin by articulating your strategy properly. Use one of the many popular frameworks for strategy or goal setting (Balanced Scorecard, SMART, MBO, OKRs, WIGs, or other) to set objectives/goals and determine your strategy for achieving them. If you don’t know what you are trying to accomplish, it is too early for KPIs!
Pre-Measurement
Launch the program.
The program is launched by project champion(s) and key stakeholders. Existing measurement materials and results are examined, a performance management good practice gap analysis is completed, key stakeholders are interviewed, and other assessment activities are completed to customize workshops to incorporate work done to date. Key activities covered during the program launch include:
- Engaging Leadership
- Communicating “Why formally measure performance?”
- Establishing Teams and Roles
- Agreeing on Process and Procedures
- Considering Automation
- Fostering a Performance Culture
Articulate Strategic Intent
Before discussing measures of success, first one must understand what you are trying to accomplish. Even the most narrowly focused operational activities can be more efficient by better communicating intent. We recommend using one of the many popular frameworks for strategy or goal setting (e.g., Balanced Scorecard, SMART, MBO, OKRs, WIGs, or other) to structure the conversations around goals and your strategy for achieving them. If you don’t know what you are trying to accomplish, it is too early for KPIs!
There are four process components within the measurement development phase of the MPRA framework:
- Identify objectives and intended result(s)
- Understand alternative measures
- Select the right measurement(s) for each objective
- Define and document selected performance measures
Identify Objectives and Intended Results
The development of meaningful measures starts with Objectives. The building blocks of strategic intent, Objectives are the linchpins of a successful KPI system, whether it is focused on strategy or operations. Objectives are qualitative, continuous improvement actions (outcomes) critical to strategy success. Once the objective is identified, unambiguous intended result(s) of the objective are defined. Once agreement is reached on the 0bjective and intended result, it’s easier to explicitly define what to measure.
Understand Alternative Measures
Once the objective and intended result are clear, alternative measures can be identified. The first option includes any direct measure of the intended result. If the intended result cannot be measured directly, more indirect measures will be identified, usually by analyzing measurable components of the objective based on a hypothesis around correlation or contribution to the result. The logic model, cause-effect analysis and/or process flow analysis are three popular tools that can be used to better understand measurable components before selecting indirect measurements.
Select the Right Measure(s) for Each Objective
Narrow down the potential measures identified in the previous steps and select final measures using a disciplined system that scores options based on their relative strength and data availability. Choose metrics that have meaning and relevance, and:
- Answer key user questions about the organization’s performance towards strategic objectives
- Provide information needed to make better strategic decisions
- Are valid and verified, measuring what is intended
- Encourage desirable employee behaviors
- Avoid an undue data collection burden or unintended consequences
Define and Document Selected Performance Measures
The Performance Measure Data Definition Table is used to document the essential information comprising every performance measure on a scorecard. This is a critical step for transitioning from performance management system development to implementation and use. It is important to document the details of the measure so that the measure is consistently calculated and presented from reporting period to reporting period, allowing for more meaningful performance analysis and conclusions.
The performance review cycle follows a regular pattern (usually quarterly) organized around a simple pattern: set targets, implement improvement actions, track performance, and learn from the results. In the Perform phase employees organize their activities around two process components:
Set Targets and Thresholds
Implement improvement initiatives.
Describing desired performance levels and determining how data is interpreted is as important as selecting the measure. Performance is based on targets, the desired level of performance for a specific reporting period, and thresholds, the upper and lower limits of desired performance around a target value. Thresholds create the exact points where an indicator displays green for good performance, yellow for satisfactory or red for poor.
The team will generally not achieve objectives and hit performance targets without taking action. Actions or improvement initiatives are developed, prioritized, and implemented to achieve objectives. Rather than create a long list of potential actions and projects, the organization focuses on a short list of experiments designed to make the biggest difference in desired outcomes.
In the Review phase of the process, data is transformed into evidence-based knowledge and understanding. The Review phase is organized around two process component steps:
Collect and Visualize Performance
Analyze and draw conclusions.
Gathering and tracking data on the historic levels and current trends in performance encompasses more than just counting things and capturing data. Creating meaningful visual comparisons enables deeper interpretation and better decisions. Visualizing performance over time identifies trends that show data direction and development and provide context for the underlying story relative to strategic intent.
Effective analysis helps people make better decisions that will drive improved strategic outcomes. The key is to evaluate the effect of each improvement action on an ongoing basis using the same principles and methods deployed in the earlier steps, monitor performance data for the desired signals relative targets and thresholds, enable dialog around conclusions, and maintain a continuous process improvement focus.
The Adapt phase of the process explores whether improvement strategies were effective and correctly executed, and if assumptions turned out to be valid. It includes an assessment of quarterly performance results, which can lead to a reforecasting of performance targets, a new set of actions or initiatives, or a complete recalibration of strategy, as needed. Sometimes the Adapt phase leads to the continuation of current activities and sometimes it means refocusing Strategic Intent based on a changing strategic environment. This phase focuses on identifying what worked well and what didn’t, taking corrective action and becoming a high-performance organization.
Report, Share, and Learn
Reporting and sharing information are the first steps toward making better decisions and acting on the information in a way that improves overall performance. Review meetings are held to review, interpret, and discuss performance information. These meetings are organized around desired results and highlight progress toward the intended results, as well as towards actions designed to improve gaps in performance. This gives the team an ongoing indication of whether actions taken are effective. The information and knowledge from this process should continuously feed the strategic planning cycle.
What Is KPI Reporting? KPI Report Examples, Tips, and Best Practices
Table of contents

To see what Databox can do for you, including how it helps you track and visualize your performance data in real-time, check out our home page. Click here .
We’re constantly bombarded by data points and it takes real effort to make sense of them. While having a lot of information is a good thing, it’s easy to get overwhelmed and miss what’s really important. Businesses especially need to be able to sort the wheat from the chaff and assess their data accurately.
But, how do you go about this exactly?
A recent Databox’s research proved that it’s not an easy task – in fact, more than half of the surveyed companies are not sure they are tracking the right KPIs.
It all starts from businesses understanding their audience, collating the relevant information, analyzing it, and then leveraging it all in order to make strategic decisions that will lead to success.
This is where tracking KPIs and ensuring that information is presented in a digestible format comes in. And using KPI reporting tools will streamline the whole process.
We’ll explain what KPIs are, explore KPI reporting in depth, and cover a variety of useful reports as well as give you some of the best practices for creating a KPI report.
- What is a KPI?
- What is a KPI Report?
- What is the Difference Between a KPI Report and a KPI Dashboard?
- How Do I Prepare a KPI Report?
- How to Distribute a KPI Report?
- KPI Reporting Examples and Templates
- KPI Examples
KPI Reporting Best Practices
Build more insightful kpi reports with databox.

What Is a KPI?
Let’s start with the basics. A key performance indicator (KPI) is a way to measure the performance of a project or a business in achieving a specific goal. The best way to think of them is as milestones that can be used to gauge progress and provide insight that will help you make better decisions. KPIs are applicable in any business sphere and used in every industry. Businesses of all sizes track KPIs and use them to measure success and plan future endeavors. While this may sound like simple metrics tracking , KPIs are more strategic and have the greatest impact on business planning. While all KPIs are metrics, not all metrics are KPIs. Non-KPI metrics support KPIs and aren’t as crucial in and of themselves.
Related : KPIs vs. Metrics: What’s the Difference & How Do You Measure Both?
KPIs can provide you with a realistic look at how your business is doing, providing information about everything from risk factors and opportunities to financial indicators. As such they can keep the whole organization moving in the same direction and allow you to course-correct as necessary.
What Is a KPI Report?
A KPI report is a performance tracking tool that allows you to quickly analyze key performance indicators and understand how your organization is doing with respect to specific goals. They include data visualization, consisting of charts, tables, and graphs. Modern KPI reports are interactive, and all the underlying data can be accessed quickly. In addition, they allow you to reorganize displayed information which allows for a quick change of focus.
Related : Business Report: What is it & How to Write a Great One? (With Examples)
Why Are KPI Reports Important?
KPIs are more than just numbers or even metrics. They make it possible to understand how your business is performing, allowing you to make adjustments in your procedures and achieve your long-term goals. Identifying the right KPIs and measuring them will help you achieve results more quickly, and you’ll have a better insight into how well you did.
A well-made KPI report with an organized dashboard provides important insights in an easy-to-understand format, allowing everyone to understand the overall situation. That way, even non-technical personnel can recognize relationships between data points and identify trends. This means that relevant people will be able to correctly set business objectives and chart a course for achieving them.
PRO TIP: How Are Users Engaging on My Site? Which Content Drives the Most Online Activity?
If you want to discover how visitors engage with your website, and which content drives the most engagement and conversions, there are several on-page events and metrics you can track from Google Analytics 4 that will get you started:
- Sessions by channel. Which channels are driving the most traffic to your website?
- Average session duration. How long do visitors spend on your website on average?
- Pageviews and pageviews by page . Which pages on your website are viewed the most?
- Total number of users . How many users engaged with your website?
- Engagement rate . Which percentage of your website visitors have interacted with a piece of content and spent a significant amount of time on the site?
- Sessions conversion rate . How many of your website visitors have completed the desired or expected action(s) and what percentage of them completed the goals you’ve set in Google Analytics 4?
And more…
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics 4 experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template showing the most important KPIs for monitoring visitor engagement on your website. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!

You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your Google Analytics account with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
What Is the Difference Between a KPI Report and a KPI Dashboard?
While an interactive KPI report you can use to navigate through different metrics and perform data exploration and analysis is fairly similar to modern KPI dashboards , they’re not necessarily the same thing. Traditional KPI reports are static documents distributed to shareholders, while interactive dashboards allow for much easier access to different layers of information.
KPI reports focus on the analytical interpretation of underlying metrics , mostly via tables and graphs that make decision-making easier. On the other hand, dashboards are visualization tools that can support KPI reports — they employ various visual formats like graphs and charts that give real-time insight into KPI and metric performance.
Today, the line between the two is very much blurred. Modern Dashboards are robust enough to take on the role of a full-fledged report, or they can be integrated into the report. Additionally, nothing is stopping you from feeding information from a KPI Report into a dashboard in order to create a pleasing and impactful presentation.
How Do I Prepare a KPI Report?
In order to prepare a good KPI report, you need to gather data and answer some questions. It’s best to present all important metrics. Ideally, you want to present performance over a period of time and showcase recent growth, decreases, and outliers.
In essence, no two KPI reports are the same. They need to be tailored to the user, industry, business, audience, and so on. You can and should customize your reports in order to match your requirements, and fortunately, modern reporting tools and dashboards can make the whole thing a breeze.
So, here’s what you should think about when you’re preparing a KPI report.
Consider your goals
Choose the right kpis, check your data, ensure you know who’ll use the report, consider the visualization.
First, you need to decide what your desired business result is. Set out your long-term goals and consider the steps you need to take to achieve them. The goals need to be feasible and paired with measurable results. Don’t forget to add milestones and expected changes in the numbers or percentages.
Related : Goals Based Reporting: Everything You Need to Know
Second, select the KPIs you want to use to measure your progress. In order to create a useful KPI, you need to determine how you intend to reach the goals defined in the previous step. Set down what key activities will bring your business closer to reaching each of these goals and make sure they’re quantifiable.
Third, take a look at your data sources . Thanks to modern dashboards, you can consolidate all the data you need. The process can be made even easier with reporting software and its integrations that allow you to automatically import information from other sources. Dashboards can crunch numbers for you and present insights based on your KPIs. However, in order to do that, they need access to good data.
That’s why you need to audit your data sources and make sure they align with your business objectives. Exclude chaff information that will only clutter up the dashboard, a KPI report needs to be trim, relevant, and actionable. If you do this, you’ll streamline the whole process and ensure that you only see information that needs to be analyzed.
Fourth, plan for the target audience. Consider who’s going to see and use the KPI report. If no one is interested in tracking a specific KPI, then there’s no real point in adding it to the dashboard. If the metric reflects a downward trend, then ensure that there’s a plan to correct this or that there’s someone ready to make that plan. In addition, keep in mind that not all people viewing the report may have permission to see the data reflected in the KPIs. Some information is confidential or just not relevant to some people so it may be worth it to create different versions of KPI reports for different audiences.
Fifth, take into account the visualization itself. How will the metrics be displayed? Will you use bar charts, graphs, pie charts, line charts, or something else to present a KPI and supporting metrics? You can place similar metrics close to each other to create a natural flow of information. This makes it easy to find all the relevant information.
By visualizing data properly, you can tell a story about how the business is performing. If you emphasize what truly matters in an easy-to-understand format, you’ll be able to share critical information even with people who aren’t too familiar with the subject matter.
How to Distribute a KPI Report
Of course, creating a successful KPI reporting strategy requires more than building informative and actionable reports. Without people to review them and implement the strategies suggested, the reports aren’t worth much. So distributing them to people who can use the information is vital.
Managers, project stakeholders, and other staff are there “in the trenches” and can see the effects of their actions directly. This is why distributing the reports at the project management level is vital. These people will be able to act on the reports and inform their coworkers about the progress towards the objectives that have been set up.
You can distribute them either through static reports (usually at scheduled meetings) or through live reports. Unfortunately, static reports often contain outdated information as collection, collation, and distribution are done manually, which comes with an inevitable time delay. Live reports can be distributed either as KPI dashboards that show trends and graphs or traditional reports with tables that display numeric data.
While they can be “distributed” by sending people emails or chat messages with links towards reports, they always exist and can be accessed anytime and anywhere. This real-time accessibility allows the recipients to have data at their fingertips and to make decisions in a timely fashion instead of waiting for the report to be compiled and then distributed. It makes the whole process much more streamlined and minimizes the chance of errors.
KPI Reporting Examples & Templates
Of course, there are countless possible reports you can make, all depending on what you’re trying to achieve, the type of organization, and the target audience. Here are templates and examples of some of the most common KPI reports you might need to make.
SEO report template
Employee performance dashboard, social media report template, financial kpi reporting template.
- Project management KPI report template
Sales performance KPI dashboard
- Customer support KPI dashboard
SaaS executive dashboard
Software development dashboard, ecommerce report example.
This SEO report template will help you track organic search performance in Google by showing you how your site is performing in organic search results. You’ll also see the changes in that performance by noting high-performing pages, keywords, and queries, as well as your average ranking.
An SEO report will help you identify which queries you should focus on, and you’ll be able to optimize search snippets to improve your CTR from search results. The key metrics are impressions, clicks, costs, clicks by queries, pages by clicks, position, and crawl errors.

If you need to make a more specific SEO KPI report, you can browse our library of SEO dashboard templates .
If you want to track custom metrics from Jira, this employee performance dashboard is exactly what you need. This is especially true if you use Agile principles.
By tracking key metrics like hours tracked, billable hours, and billing amounts, you’ll be able to visualize the data from Harvest in the way you want. The template will allow you to split tracked time by project, team, task, or client. It makes it easy to see how many hours have been tracked on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis.

You can also browse all of our employee performance dashboards and customize them according to your needs.
Social media report templates can give you insights into how your social media campaign is progressing by tracking metrics like impressions, reach, followers, and more. If you want to track the performance of your business Instagram account, you’ll be able to see what posts have been popular with your followers, see the impact of your activity, and communicate how social media strategy is impacting the overall ROI.

All Databox’s social media dashboard templates come pre-built with the most commonly tracked metrics and are fully customizable. You can browse our library of social media dashboards and pick the right one for your purposes.
A well-made financial reporting dashboard will give you insight into your business’ bank accounts, cash flows, sales, expenses, etc. Databox’s financial reporting dashboards like this Quickbooks financial report can be integrated with accounting and streamline the whole reporting process with just a few clicks.
You can use them to track your company’s financial transactions, open and unpaid invoices, debits and credits, and many more metrics. They can even visualize cash flow projections and allow you to sort all the data by any category you wish.

Browse the full selection of our financial dashboards , and you’re guaranteed to find something you need.
Project Management KPI report template
Project management KPIs are possibly the most important for the long-term health of any organization. If you connect a dashboard to your work management software, you’ll be able to keep your workflow organized and track your team’s progress very easily.
With a project management report , you’ll be able to monitor relevant metrics related to task organization like assigned tasks, overdue, completed, and assigned tasks, time spent on tasks, team performance and productivity, and many more. These, in turn, can be turned into indicators of the health of the organization. An increasing number of overdue tasks could be a sign that there are workflow issues that need to be addressed.

You can browse all project management dashboards and find the one that works for your organization.
This type of KPI report dashboard is a visual snapshot of the sales team’s performance. You can use sales performance KPI dashboards to track sales performance and productivity KPIs, sales leaderboards, and progress towards achieving goals. You’ll be able to understand the sales pipeline better and compare team results with revenue goals.

Databox has a large selection of sales dashboards you can browse.
Customer support KPI dashboard template
This customer support report template that pulls data from Intercom is easy-to-use and allows you to assess your overall Help Desk performance and efficiency of individual customer service agents. You can integrate it with Intercom or any other CRM software and pull up a variety of metrics from leads and conversations to average handle time and customer satisfaction. You can use these data points and collate them into useful and actionable KPIs for your KPI report.

If you need a different dashboard, you can browse our library of customer support dashboards .
Executive dashboards include an array of important SaaS metrics like Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and churn rate. By using it you’ll learn how much did you make on any given day, the number of current customers, the percentage of customers churned in a specific time period, how much revenue was lost due to customer churn, etc. This can be built using an executive dashboard software .

You can also browse the full list of our SaaS dashboards and pick whatever suits your business.
Software development reports can help you track new features and bug fixes across your digital portfolio. They’re powerful collaboration tools that will enable your software team to execute projects quickly and efficiently. You’ll learn how many changes were made to the projects over a period of time, the number of branches, commits, and forks in the selected repository, the number of open issues that you can sort by kind, and so on.

All of our dashboards are fully customizable, and if you’d like a wider selection, you can browse our library of software development dashboards .
Ecommerce reports allow you to get full insights into your online sales statistics, product performance, conversion rate, and many more metrics. If you integrate it with Google Analytics, Facebook Ads, or Shopify, you’ll have access to a variety of data points you’ll be able to use to put together actionable KPIs and build useful KPI reports.

Check out our full selection of ecommerce dashboard templates and pick the one that suits your needs.
KPI Examples
As we mentioned, metrics need to be selected with the target audience in mind. There’s no single list of best KPIs that are suitable for every report and every circumstance. However, there are some that tend to be more broadly applicable and can be used by various departments to measure performance.
Financial KPIs
Customer support kpis, marketing kpis, project management kpis.
These are particularly important to C-suite and the accounting department. After all, revenue information is perhaps the clearest measure of a business’ profitability.
Here are some common and useful financial KPIs :
- Gross Profit Margin
- Net Profit margin
- Current Ratio
- Return on Equity
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio
- Inventory Turnover
Important for any business that wants to maintain a good relationship with their customers. They’re useful for managers, executives, and agents in companies that deal with customers on a daily basis.
The effective use of these metrics can improve productivity and create efficient processes.
Here are some very useful customer support KPIs :
- Average Response Time
- Customer Churn
- Number of Issues
- Customer Retention
- First Call Resolution
- Top Support Agents
These metrics provide insight into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and are invaluable to not only marketing agencies but also to any business that relies on advertising (which is probably every business, at this point).
Marketers should keep track of the following KPIs:
- Return on Investment
- Return on Ad Spend
- Conversion Rate
- Customer Acquisition Cost
- Lifetime Value of a Customer
- SEO Keyword Ranking
Sales performance information needs to cover both completed work and the effectiveness of existing processes. Sales teams are the natural audience for these metrics, as are their managers and some executives.
Here are important sales KPIs :
- Sales Revenue
- Sales Growth
- Product Performance
- Sales Target
- Average Purchase Target
- Quote to Close Ratio
Looking for an effective tool to help you track your sales KPIs? Check out this sales dashboard software .
KPIs for project management cover a team’s ability to achieve goals. Project managers and their supervisors can make the best use of this data to ensure better team cohesion and improved performance in the future. They cover quality, timeliness, budget, and effectiveness.
Here are some important project management KPIs :
- Cost Performance Index
- Employee Churn Rate
- Number of Project Milestones
- Customer Complaints
Focusing on the right metrics is important. You don’t want to waste resources on measuring and monitoring KPIs that don’t matter. Poorly constructed KPI report with poorly chosen metrics can easily send you on the wrong path and waste opportunities or even cause irreparable damage to your business.
To help you with that, we’ve put together a list of best practices for KPI reporting.
Keep it simple
Set clear objectives, ensure the data is consistent and accurate, understand the relationship between kpis, embrace digital accessibility, coordinate across the organization, perform regular reviews.
It’s easy to get overwhelmed by the sheer number of data points available. The best idea is to focus on a small number of KPIs (key is the operative word in key performance indicators) and measure only the metrics that align with your business objectives. The most common KPIs aren’t necessarily the most important, and you should tailor your report to include only what’s truly relevant.
This is an extension of the previous point but avoid the temptation to add more information to the report without a clear reason to do so. Make a plan and stick to it. You want the report to be clear and concise and not bury the target audience under a mountain of data.
The computing maxim “garbage in, garbage out” applies to all data analysis applications. You simply cannot trust the result if the data isn’t up to par. Spend some time testing data sets and double-checking inputs before deciding to use them.
Metrics don’t exist in isolation. They impact each other, and sometimes it isn’t clear what caused a change (or what will cause the change) until you dig deeper and examine their relationships.
This is important when developing KPIs because just wanting to increase certain metrics without understanding underlying causes can cause them to stagnate until you identify exact ways to improve them.
Using cloud-level solutions can make the whole process much simpler and even faster. Having immediate central access to a variety of data points is simply a must in today’s fast-paced world if you want your KPI reports to be useful by the time you’re done with them.
If you have something that’s not digitized, digitize it, and ensure that all metric sources are integrated with the right reporting dashboards.
The best reports require input from multiple people. Invite coworkers or stakeholders who will have to act on the information in the report to provide input about the required metrics. If you can, organize brainstorming sessions with relevant personnel before building KPIs and create dashboards and data visualizations that will make the communications and planning simpler.
Objectives change with time. Old ones are achieved, the market shifts or the company decides to pivot in a new direction. It’s important to regularly review existing KPIs and ensure they’re still relevant. This will ensure you’re tracking metrics that matter and that your business will continue to benefit from them.
As you can see, writing a KPI report can be a complex task. You need to be able to analyze a lot of information and identify important data points that will be useful to your business. These reports then need to be kept up to date, variables need to be monitored, and relevant people need to be in the loop.
However, it doesn’t have to be that time-consuming or complex.
With Databox, you can build more insightful KPI reports in less time, and it only takes a few clicks to get started. Stop wasting time on time-consuming busy work. Connect the relevant data sources, customize one of our existing dashboard templates or build your own, and visualize the data in one spot. You’ll be able to create lean and actionable KPI reports that will make sure your business is on the right track.
Sounds good? Feel free to try it out. Just sign up for a free trial and make KPI reporting easier than you thought possible.
Davor is an English literature graduate and an avid reader with a passion for languages. Working as a translator, editor, and writer has allowed him to learn about a wide range of topics — making him something of a jack-of-all-trades when it comes to content. In his spare time, he reads, plays video games and boardgames, and runs/plays tabletop RPGs.
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

How to Write an Executive Summary for a Report: Step By Step Guide with Examples

Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- Implementing an Outcomes-Led Strategy (w/ Alli Blum, Hypothesis Department) June 8, 2024
- Marketing and Sales in Uncertain Times: Strategies & Spending Impact (2024) June 5, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation

How To Write KPIs In 4 Steps + Free KPI Template

What Does KPI Stand For?
KPI stands for Key Performance Indicator, a measurable value that shows the organization's progress toward achieving key business objectives. Organizations can use KPIs as a way to track whether their key business objectives are on track, behind, ahead, or have been achieved.
KPIs are typically used to assess performance against a benchmark (target) or industry standard. They can be applied to various business areas, such as marketing, sales, customer service, and operations, and are often used to guide decision-making and drive continuous improvement.
Check out our KPI Meaning & KPI examples article with 84 examples from different industries!

4 Reasons Why KPIs Are Important
Like the famous Peter Drucker once said: "You can't improve what you don't measure."
So, running a business without KPIs is like driving a car with your eyes closed. You don't really know where you're going, and the chances are it won't have a happy ending.
Now that we've established how fundamental KPIs are for a company's success, let's look into why they are so important and what benefits they provide to organizations:
Act as a scorecard for company health
KPIs provide a snapshot of how well a company is performing. By tracking metrics that are aligned with business goals, KPIs can help managers and leaders quickly assess company health and identify areas that need improvement. KPIs can also provide an easy way to communicate performance to stakeholders, such as investors, partners, or employees.
Measure progress through the tracking of metrics
KPIs allow organizations to track progress toward specific goals and objectives. By measuring and analyzing data on a regular basis, organizations can gain insights into what is working well and what needs improvement. This information can be used to make data-driven decisions, adjust strategies, and optimize processes for better outcomes.
Help identify when to make adjustments
KPIs can help organizations identify when to make adjustments to strategies or operations. By tracking performance against established benchmarks, KPIs can reveal trends and patterns that may indicate areas of concern or opportunities for improvement. This information can be used to make informed decisions about when and how to make adjustments to optimize performance.
Recognize and analyze patterns
KPIs provide valuable insights into patterns and trends in performance over time. By analyzing KPI data, organizations can identify patterns and trends that may indicate underlying causes of performance issues or opportunities for improvement. This information can be used to guide strategic decision-making and inform ongoing efforts to optimize performance.
Quick Overview Of Writing KPIs In 4 Steps:
- Determine strategic objectives
- Define success
- Decide on measurement
- Write your SMART KPIs
✋🏼But before we zoom into each step, let us give you an important tip: don't copy your KPIs straight from someone else's list!
While there's a wealth of KPI examples available online - scrolling through industry lists, picking out a KPI and attempting to force it into your strategy won't do you any favors.
Well, KPIs should be developed to contribute to achieving a specific strategic objective. If they're not developed with a specific strategic objective in mind, they run the risk of stealing attention, time, and money from KPIs that actually help to achieve strategic objectives.
The best KPIs for YOUR business are designed by starting with YOUR specific business objectives. Now, this is not to say all the content available on KPI examples is useless, because it's definitely not - it's actually an important resource. But, looking through KPI examples shouldn't begin till AFTER you have determined your own key strategic objectives.
Ok, let's get into it! 👇🏻
How To Write KPIs In 4 Steps
Your organization's business model, industry, and even the department in which you operate will have an impact on the type of KPI you need.
Luckily, we've devised a best practice process for how to write KPIs that will allow you to create the perfect KPIs every time.
Step 1 - Determine the key strategic objectives
Before writing KPIs, you'll first need to determine which of your organization's strategic objectives you're trying to gauge.
If you've been following along our mini-series "How To Write A Strategic Plan: The Cascade Model' then you will have already defined some strategic objectives for your organization, and you're ready to create some KPIs.
If you haven't defined any strategic objectives (or goals) for your organization yet, check out this article first and then jump back over here to create your KPIs.
E.g. Strategic Objective: Increase the flow of the marketing pipeline by 2022.
Step 2 - Define success
Now that you've identified your strategic objectives, you'll need to begin thinking about what the success of each objective looks like.
Sticking with the same example used in Step 1, if my objective is to increase the flow of the marketing pipeline, the success of this objective means increasing the number of contacts that enter the pipeline, and increasing the number of contacts that pass through the end of the pipeline and get handed over to Sales.
By first defining what success looks like, deciding how you will measure the success of your objective becomes a lot easier.
When defining the success of your KPI, you will usually find there are multiple parts to the definition of the success of your objectives. In the example used above, we found there were two parts to achieving the success of our objective -
- Increasing the number of contacts that enter the pipeline.
- Increasing the number of contacts that pass through the end of the pipeline and get handed over to Sales.
As mentioned earlier, this is the time when it might be useful to look through a few KPI examples to help get some inspiration for how you can define the success of your key business objectives.
Again, you should avoid copying KPIs straight from a list, as, chances are, they won't perfectly fit your strategic objectives. Instead, use the KPI examples as a way to ideate how you can measure the success of your own strategic objectives.
We've collated a whole bunch of KPI examples already and grouped them by the department to help give you a little inspiration:
- Operational KPIs
- Marketing KPIs
- Financial KPIs
- Customer Service KPIs
- Health & Safety KPIs
- Change Management KPIs
- Product Management KPIs
Looking for specific industry KPIs? We also have some of those:
- Retail KPIs
- Healthcare KPIs
- Higher Education KPIs
- Manufacturing KPIs
Step 3 - Decide on measurement
Next, you'll need to decide how you will actually measure success. Going back to our example once again, we've identified that the success of our objective means increasing the number of contacts that enter our pipeline AND increasing the number of contacts that pass through the end of our pipeline
Let's start with the first part of this - Increasing the number of contacts that enter our pipeline. Contacts enter our marketing pipeline when they subscribe to our mailing list or exchange their details for content for the first time.
When contacts engage in either activity, they automatically get added to our marketing automation platform as a subscriber. Using the number of new subscribers added to our marketing automation platform over a time period is an easy way for us to measure the number of contacts entering our marketing pipeline.
Now let's look at the second part - Increasing the number of contacts that pass through the end of our marketing pipeline. Contacts pass through the end of the marketing pipeline when they're ready to be handed over to our Sales Team.
We use the term "SQL" (Sales Qualified Lead) to define a lead that has moved through the end of our marketing pipeline and is ready for our Sales Team to pick up. Our marketing automation platform adds a tag on each contact profile to identify which life-cycle stage they are in based on a certain activity.
Again, through our marketing automation software, we can use the number of contacts who become a SQL in a given time period to measure our success.
This is where it might be wise to start considering dashboard software to track and display your KPIs.
You'll likely use various platforms and tools across your business to measure your KPIs, but having a central location to track and view all your departmental and organizational KPIs will ensure you have a clear view of your success.
Cascade's Dashboard tool is extremely powerful and allows you to pull data from all around your business, so you can display your most important information, real-time, to whoever in your organization needs it.
📚 Recommended read: 10 Popular KPI Software Tools To Connect & Visualize Your Data (2023 Guide)
Step 4 - Write your KPIs
Finally, it's time to begin actually writing your KPIs. KPIs should follow the SMART format (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound), to ensure your KPIs meet this criterion, we've devised a formula that you can follow to ensure you end up with SMART KPIs every time.
The main advice here is to keep things simple. KPIs should be understood by everyone within the organization . That means no jargon (if possible), and keeping them to one sentence long.
We suggest a structure as follows:
Action Detail Value Unit Deadline
Putting it all together, our KPI example may look something like this:
Writing KPIs Example 1
Increase new HubSpot lead profiles to 40,000 people by 31st December 2019
Writing KPIs Example 2
Increase new SQL profiles to 20,000 people by 31st December 2019
Starting off with a verb forces you to be specific about what you’re trying to do. A metric and unit ensure your KPI is measurable and a deadline will do wonders for staying timely on your progress.
How Are KPIs Used In An Organization?
Key performance indicators are a communication tool for organizations. They inform business leaders of their organization's progress towards reaching key business objectives.
KPIs are able to provide this information because they actually track the most important performance measures, which can be taken together to represent how successful you are in achieving an objective.
This information channel is extremely valuable as, in a well-designed strategy, an organization's key business objectives should have a direct impact on the organization's overall performance.
Therefore, KPIs will communicate whether your activities are achieving, for example, business growth at the rate expected or not, and how much growth you've actually achieved.
KPIs also assist in identifying issues with organizational processes. If the progress on an objective falls behind, the key performance indicator associated with it will communicate this to business leaders as soon as the trend begins to show itself ( assuming you have leading & lagging KPIs ).
The organization will know that something has gone wrong and an investigation is required. A strategy to mitigate the issue can then be created and implemented before it has far-reaching effects on the organization's performance.
How Many Key Performance Indicators Do You Need?
The question of how many key performance indicators you need will vary with every company. However, we do have a framework that you can apply to help you assess how many KPIs you'll need to implement for your organization.
The number you need will depend on how many key business objectives you have in your organization. As a rule, we generally say you should have 2-3 KPIs per objective, to ensure a variety of measures without overwhelming the picture.
The reason we use a minimum of 2 KPIs as a rule, is because we believe each business objective should have at least 1 leading indicator and 1 lagging indicator.
This allows you to predict future performance as well as record the actual performance and compare these to the direction of your business objective.
Alternative vs Value-Based Decision-Making
To get a better understanding of why you should always start the KPI process by having first defined strategic objectives, consider the two potential ways of deriving your KPIs:
- Alternative-based decision-making
- Value-based decision-making
Alternative-based decision-making relies on choosing your preferred option from the alternatives offered.
Decision maker: I would like a coffee
Waiter: Sure, what milk would you like?
Decision maker: What do you have?
Waiter: We have full cream, skim, or soy milk?
Decision maker: I'll take the full cream milk.
Value-based decision-making relies on assessing what matters most to you and then making a decision that meets your needs.
Decision maker: (Considers objectives: I like a good tasting coffee, but also want to keep the fat content down because I'm watching my weight) I'll take soy milk with one serve of artificial sweetener.
Waiter: No problem.
As you can see, the decision-maker in the first example listened to the alternatives presented and then selected their preference based on the options given.
However, the decision-maker in the second example examined their objectives and what they really wanted from a cup of coffee first and then made a decision that met their needs.
When writing KPIs, using the alternative-based approach and scrolling through industry KPI lists will leave you with your preferred KPI from that list, but achieving that KPI won't necessarily mean you've achieved your strategic objectives.
On the other hand, using the value-based approach and considering your key strategic objectives first will ensure you end up with KPIs that once achieved, will mean you've also achieved your strategic objectives.
What Are Leading And Lagging KPIs?
Leading and lagging KPIs are often mentioned when it comes to strategy, but what is the difference between the two? A leading KPI indicator is a measurable factor that changes before the company starts to follow a particular pattern or trend.
Leading KPIs are used to predict changes in the company and future performance, but as predictors, they cannot always accurately forecast the future. On the other hand, a lagging KPI is a measurable fact that records the actual performance of an organization.
Leading key performance indicators are often easier to influence than lagging KPIs, however, generally measuring them can prove more difficult.
Lagging KPIs , on the other hand, are usually easier to measure, though much harder to influence. If you'd like to learn more about Leading and Lagging KPIs, check out this post .
KPI Reporting
Creating relevant, measurable, and time-bound key performance indicators is great, but it's only half the job done. The other half (which can often go overlooked) comes down to figuring out how to actually track and report on them appropriately and accurately.
While it can be tough setting up this kind of tracking and reporting, if you don't create an easy way to view and stay on top of progress, the KPIs aren't going to be of much use. A KPI report is a presentation that displays and communicates the current performance of an organization compared to its business objectives.
It's a tool used by management in order to analyze performance and identify issues. These reports can take many formats, including formal written reports, spreadsheets, powerpoint slides, or dashboards.
KPI Dashboards
Creating a KPI dashboard is a great way to provide at-a-glance views of key performance indicators relevant to a specific business objective, department, or the whole organization.
Now, before your eyes glaze over with boredom as another business term is introduced, dashboards are just another name for a progress report. However, what makes dashboards more powerful than your typical business report is that they're usually hooked up to business systems so the data is automatically updated.
The benefit of this is it ensures the data is always relevant, as it doesn't rely on someone in the organization continuously updating numbers. This is just one of the many benefits of using dashboard software for your strategy report.
Dashboards also give you total visibility of your business performance instantly, display KPI progress in a visual presentation to keep reporting engaging, and save time when compared to the hours poured into creating regular reports.
👉Here’s how Cascade can help you:
With Cascade , you can track the progress of your strategic objectives in real time by assigning a measure (or KPI) to that objective very easily:
- Select the objective you want to track and add the KPI - give it a name that specifies how you want the objective to be assessed
- Set a Start date and End date, which will set a timeline for your KPI.
- Set the initial and target value for your KPI - and don't forget to clarify the unit you'll be using to measure the result
You can also give your KPI a description to provide more context and add collaborators that will also be working on achieving that KPI.
🚀 Want to take it a step further? Instead of updating the progress of your KPI manually, you can automate this process by integrating Cascade with tools like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets.
After your KPIs are set in place, you can use Cascade's Report & Dashboard functionalities that allow you to visually see the progress of your KPIs in real-time:
Want to see Cascade in action? Get started for free or book a 1:1 demo with Cascade’s in-house strategy expert.
📚Editor’s note:
This article was originally part of our ‘How to Write a Strategy’ series. You can find the individual articles here:
- How To Write A Strategic Plan: The Cascade Model
- How to Write a Good Vision Statement
- How To Create Company Values
- Creating Strategic Focus Areas
- How To Write Strategic Objectives
- How To Create Effective Projects
- How To Write KPIs (This Article)
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment

How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)

The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.


KPIs: Best Practices to Set Up, Measure, and Track Them Effectively

Implement best practices for setting up, measuring, and tracking KPIs to achieve your business goals & objectives. Contact us for more information!
Key Performance Indicators, or KPIs, are a much talked-about but frequently underutilized business tool; few companies implement them with the level of rigor required to produce good results. Choosing the right KPIs and implementing a KPI tracking process requires dedication and commitment on everyone’s part.
We put together this guide to help organizations like yours get more out of their KPIs. Here you’ll learn the best ways to create and track them and understand how to gauge their relevance over time. By following the guidance presented here, you can rest assured you’re measuring and tracking the right things for your business—and doing it in the most efficient way possible.
What Are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)? A Definition
You’ve heard it before: “What gets measured gets managed.” Nowadays, companies can (and do) measure almost everything in an effort to somehow manage it all. But most are so inundated with data about their business activities and performance that they fail to see the forest for the trees.
In fact, all data points tell the story of your business, but only a few are crucial for understanding performance. Those few are the ones to concentrate on—they are the key performance indicators, or KPIs, that relate to your strategic business goals.
Here’s how we define KPIs :
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the subset of performance indicators most critical to your business at the highest level of your organization. You use them to help measure your progress toward achieving your strategic goals.
ClearPoint Strategy provides a platform where key performance indicators can be customized and closely monitored to reflect the health and direction of your business.
See ClearPoint Strategy in action! Click here to watch a quick DEMO on the software
What distinguishes a kpi from other traditional business metrics.
You can gather data on just about any aspect of your business, but not everything you measure qualifies as a key performance indicator. KPIs have several important characteristics that differentiate them from other metrics:
- They show if the organization is accomplishing its objectives. KPIs track measures that reflect your organization’s performance, specifically as it relates to a strategic goal. Not all measures drive business performance.
- They are tied to specific business objectives. The main point of using KPIs is to ensure your organization reaches its highest-level objectives; therefore, you should link KPIs directly to strategic goals.
Some metrics are just that— metrics . Think of them as supporting characters in a play. They may measure progress in a certain area—for example, your product return rate. Those metrics impart useful information, and improvement in that area may help you achieve a larger objective. But metrics alone don’t drive performance as a company.
Though they are different, KPIs and metrics are interrelated. Think of a KPI as a kind of early-warning signal for your business. If you’re not meeting a key performance indicator target, it’s a sign there’s either a strategic or operational problem that will prevent you from reaching your goal. To investigate the problem, dig deeper into other related metrics to diagnose the problem and see where you might need a course correction.
Download your FREE eBook on 68 effective financial KPIs you should use for better strategic insights
Kpis vs. metrics example.
For an example, consider X Company that sells cybersecurity software. One of the company’s strategic objectives is to educate its target audience via its website about cybersecurity threats and approaches to protecting their business systems.
In this case, here’s what its KPI and associated metrics might look like:."
KPI: Website traffic
KPI target: 50,000 visitors per month
Method for measuring: Track the number of website visits
Metrics that support the KPI:
- Time on site
- Bounce rate
- Exit rate
If X Company doesn’t meet the KPI target, it is not attracting people to its site and will have difficulty achieving its goal. To understand why this problem is occurring, the company could dig into the associated metrics for clues.
Done right, KPIs can be an incredibly useful tool for measuring performance. If you’re not seeing any value from them, it may be because the metrics you’ve chosen are not relevant to business performance, or they aren’t clearly linked to your strategy. The fact that there’s so much data available these days makes it more difficult to choose the right KPIs.
It may take some experimentation, but as you continue working with KPIs, keep these two points in mind:
#1: If you find you’re not using a particular KPI to make decisions, scrap it and look for something better. KPIs should provide insights that become the basis of strategy meeting discussions. If that’s not the case, you may not be measuring the right thing.
#2: For each of your KPIs, make sure you know what’s making them move either positively or negatively and that you have control over those levers. You may be doing multiple things that affect the KPI; you need to know which actions will have an impact.
Now that you know the definition of a KPI, let’s move on to the process of creating key performance indicators that align with your business objectives.

How To Successfully Set Up Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Follow the steps below to create KPIs that will provide clear signals about whether your performance is improving or not.
1. First, define your business objectives
Creating KPIs is an important part of the strategic planning process, which includes defining the organization’s goals and objectives. But you can’t create meaningful performance measures if you don’t know what you’re trying to accomplish. So first things first— determine a concrete set of objectives that express the goals your company wants to achieve in the future.
2. Ask: Do we know which activity will help us reach this goal?
This step attacks the main problem most organizations have, which is how to define key performance indicators. To start, ask yourself the question above.
If the answer is no , select a lagging indicator. Lagging indicators aren’t predictors of what is going to happen, but they do tell you what did happen. So if your goal is to increase sales but you don’t know which activity will make that happen, then simply measure “sales.” This KPI will tell you what happened for that goal over the last quarter or the last year by examining your outputs and outcomes. In the meantime, you’ll want to try different activities to see what actually does make an impact on sales.
If the answer is yes , select a leading indicator . When you do find out which activity will drive better results, select that activity as your KPI. For example, if you know sales increase when your sales team makes more outbound calls, choose “# of outbound calls” as your KPI. You’ll know that if you hit or exceed your target for outbound calls, your sales numbers will also increase. You could have more than one KPI if both are strong leading indicators.
Example: Leading Vs. Lagging Indicators In KPI Selection
Let’s continue with our X Company example, whose goal is to educate the public about cybersecurity issues via content on its website.
- If the company doesn't know which activity will increase the number of website visits, it would simply track "website visits." While tracking this KPI, the company would also experiment with ways to increase visits to see what works.
- If the company already knows that appearing on page 1 for various Google search results leads to more website visits, it could start to measure keyword page 1 rankings. In this case, the company might still track website visits as a measure but not as a key performance measure.
Leading indicator KPIs help you see progress (or setbacks) sooner, so you can act accordingly without having to wait for outcomes.
3. Make sure each KPI meets the SMART framework
Identifying the activities that have an impact on your objectives gets you closer to determining your KPIs, but an effective KPI should also be SMART:
- Specific: It should be clearly defined and not too broad.
- Measurable: It should be easily quantifiable.
- Attainable: It should be realistic to obtain.
- Realistic: It should be practical and pragmatic.
- Timely: It should be measurable on a regular—and fairly frequent—basis, for example, monthly or quarterly as opposed to annually.
Other metrics don’t have to be SMART, but KPIs should be. These criteria help you further define your KPIs, producing a more effective measure of performance.
4. Clearly define all aspects of each KPI
You have a good KPI in mind—that’s great! Before you can start using it, you need to clarify the essential information outlined below. Doing so will help you introduce and explain each KPI to the relevant parties; it will also help with tracking. We recommend using a template like the one shown below so you know you’ve covered everything.
1. Description: Write a brief description of the measure and what it should reveal.
2. Formula: Is there a calculation required to report the measure? If so, record it clearly.
3. Reporting frequency: Decide how often to report the KPI—monthly, quarterly, etc.
4. Owner: Who is the person or department that will report on the measure and performance? Accountability is crucial for follow-through.
5. Target: Note the level of performance you are trying to achieve. It should be a numerical (quantitative) target.
-%20The%20Ultimate%20Guide%20(4).webp)
5. Get feedback from your team about each KPI
We’ve seen it happen too often: When presented with KPI data in strategy meetings , attendees spend too much time trying to figure out what the data means and why they’re collecting it, instead of making decisions based on the data. What could have been a productive strategy meeting turns into an information session on KPIs.
All it takes is a little bit of planning to prevent this scenario. Talk to your team about each KPI ahead of time. Find out what questions people have about the data and include the answers in the KPI descriptions. If a formula is involved, write it out in a way that’s easy to understand. Incorporate any suggestions they have into the defining list when appropriate. Then, at the meeting, you can talk about strategy instead.
Think you’ve developed some meaningful measures? Great! Now it’s time to find out how well your organization—and your KPIs—are performing.
Setting up effective KPIs involves defining clear business objectives, which ClearPoint Strategy facilitates through its strategic planning capabilities. Our software allows you to:
- Define and align KPIs directly with strategic goals.
- Automate data collection and reporting to streamline the process.
- Evaluate KPI performance using real-time dashboards that provide insights into your organization's operational efficiency.
Get your FREE 48 Human Capital KPI library for effective HR strategy
Key performance indicators (kpis) measurement & tracking.
The KPI process doesn’t end once you’ve set the measures; next, you need to gauge their performance. That requires tracking them effectively and knowing when it’s time to replace them.
Tracking KPIs The Right Way
It’s necessary to continually review and track your KPIs and their performance on a monthly, quarterly, or other predefined reporting frequency. Regular monitoring makes it easy to see the time frame in which something may have underperformed or overperformed, as well as what may have happened within this period to cause the change.
Here are the steps involved in setting up a reporting system:
- Identify your data source(s). Where is the data for the KPI coming from? For X Company’s website example, it might be Google Analytics and/or HubSpot. For customer data, it might be Salesforce. For revenue data, it’s your company accounting software. The source will be key to the KPI tracking workflow.
- Define your reporting frequency. Decide how often you should track your KPI. It depends on the availability of the data and how frequently it becomes available. It’s also useful to consider how the data helps you make decisions.
For example, X Company may want to track website visits monthly so it knows if enough people are coming to the site for the sales team to source leads from. If the KPI target is falling short, the company will need to find another way to provide leads to the sales team that month. On the other hand, it may want to track the KPI quarterly because the number of website visitors can be extremely volatile depending on the month. As long as the KPI goes up quarter by quarter, there’s probably no need for a strategy change.
- Create your calculations. Build out your calculations in the system you’ll be using to track KPIs. Some organizations use spreadsheets to track KPIs; others use strategy reporting software to ease the burden of reporting and help them gain better insights from the data.
- Decide on your evaluations. You need a way to quickly and expertly evaluate whether you’re meeting your goals, which is where evaluation status signals are useful. RAG—or red, amber, green—statuses act as a KPI traffic light: Red is an alert; amber signals caution, and green means you’re on track. Consider the target levels you want for your KPIs. One example scenario: If a KPI is within 20% of your target, it might be considered yellow; below 20%, it's red; above that, it’s green. Regardless of what you decide, you also need to think about whether your target will change from one quarter to the next or if it will stay the same.
- Build your chart. Charts are useful for visualizing data, making it easy to see trends, progression over time, target vs. actual performance, industry benchmarks, etc. Figure out the appropriate visualization for your data and how to construct it to highlight the information you want to convey.
With ClearPoint Strategy , you can visualize data through customized dashboards that help elucidate trends and pinpoint areas requiring attention. Our software supports decision-making by providing actionable insights and timely data.
See ClearPoint Strategy in action! Click here to watch our quick 6-minute demo
How strategy reporting software like clearpoint strategy simplifies kpi tracking.
For KPI and strategy reporting, consider leveraging an advanced performance management software like ClearPoint Strategy . While the time you'll save in tracking and reporting alone is well worth the investment (some of our customers reduced the time they spent gathering and reporting data by 89%!), another extremely useful feature of our software is its ability to link KPIs to organizational objectives. Ultimately, that makes it easier to evaluate whether you're using the right KPIs.
Before switching to ClearPoint, one healthcare organization was tracking KPIs in Excel. Keeping track of the key measures for each department and physician required manually copying and pasting data from various systems into +400 Excel spreadsheets that included complex calculations to produce a total "score". The organization found it difficult to get a handle on its overall performance–and challenging to gain any insights from the spreadsheet alone.
Now that they're using ClearPoint, leaders can easily see ho the organization is tracking on a set of standar measures, and compare the performance or physicians and departments. Different departments upload data monthly, and LPI dashboards are shared on the intranet for all employees to see. Individual physicials receive their own scorecards every month. And strategy meetings are now simpler and more focused because it has replaced the Excel spreadsheets with easy-to-read briefing books summarizing the most important information leaders need to know. That's the power of ClearPoint Strategy KPI tracking!
Claim your FREE 108 healthcare KPI library to improve your organizational performance
Kpi tracking: using dashboards.
A KPI dashboard consolidates all your KPIs in one place for easy viewing and decision-making. With a KPI dashboard, you can quickly identify which metrics have fallen below target and which ones are trending upwards. It provides a holistic view of all your metrics, so you can move forward with the quantitative information you need to decide what's next. In ClearPoint, KPI dashboards automatically update as you update the data sources, saving you time and effort.
You can create any type of KPI dashboard that suits your needs; below are three examples of KPI dashboards that are especially useful.
Red Measures Dashboard
A red measures dashboard focuses on poorly performing metrics, making it easy to identify and address lagging KPIs.
-%20The%20Ultimate%20Guide%20(7).webp)
KPI Dashboard Template
A KPI dashboard template visualizes the performance of an organization's metrics over time. These dashboards typically include indicators to specify the red, yellow, or green status of each measure; adding qualitative fields to your KPI dashboards is a great way to add more context alongside these indicators.
-%20The%20Ultimate%20Guide%20(8).webp)
Trend Dashboard Template
Trend dashboard templates visually display trends in metrics over time, making it easy to identify problematic periods and dig deeper to address their potential causes.
-%20The%20Ultimate%20Guide%20(9).webp)
Conducting Your First Strategy Review Meeting
The most important part of the KPI process is actually using them in the way they were intended—to help drive business decisions. The strategy meeting is when your team will analyze these key performance indicators to determine how well your company is meeting goals. To conduct a productive strategy meeting that encourages discussion around KPI progress:
- Have your team add qualitative analysis to all your KPIs. Numerical data can be hard to interpret when presented on its own. Present qualitative data as well to provide additional context. Ideas, explanations, and hypotheses help readers get an in-depth understanding of the factors that may be influencing the data.
- Send a report with KPIs in advance so your team can review them. If everyone comes to the meeting prepared, it will allow for a more efficient use of time.
- If people have questions about the KPI, update the definition and formula so they are clear to everyone. This will help prevent the same questions from popping up again in the next meeting.
- Update the chart to show the information you need. Make sure it highlights the information attendees need to know and includes the most current data available.
- Ask: Do these KPIs help us determine if we’re making progress on our goals? Use your meeting to reassess your performance measures. Which measures are working well and should be kept? Which ones should you drop or replace because they aren’t really telling you how the objective is doing? If the KPI doesn’t seem to be a good indicator after all, it may be time to go back to the drawing board.
Get your FREE eBook on 142 important KPIs for local governments here
When is it time to retire/change a kpi.
Because the goals and circumstances of your business are always changing, your KPIs should change as well. How do you know when it’s time to make a change? Things that should trigger a reevaluation of your KPIs include:
- When you’ve completed an objective
- When you have another KPI for your objective that helps you better make decisions
- When your KPI doesn’t lead to decisions
- When your initiatives change (and therefore the way you track progress toward your objective should change)
3 Key Performance Indicator (KPI) Best Practices
Organizations that are serious about using KPIs to reach their strategic goals tend to be high-performers. If you’re hoping to become part of that group, remember these three best practices as you design and deploy your own KPI framework:
1. Choose the minimum number of KPIs necessary to achieve your objectives
Few metrics actually have the potential to make a major difference in performance, but it’s easy to get carried away by the overabundance of data. In one MIT study, executives were asked how many of the KPIs they oversee required most of their attention; a majority of respondents said just two or three. Many organizations choose too many KPIs and then waste resources trying to keep up with them. Be stingy and stick to the best measures—the ones that directly contribute to your objectives. We recommend only tracking a few—one to two KPIs per objective.
You can (and should) track other data, but separate those measures from your KPIs. That data will be helpful if you need to dive into the underlying components that make up a KPI.
2. Use a tool that does most of the work for you
Today, there’s simply no need to spend time cutting and pasting data from various sources into Excel or spending a full week per month generating KPI reports in PowerPoint. When companies have to expend that much effort to track KPIs, they eventually abandon the effort altogether. Technology has made it easier to manage KPIs every step of the way, from data-gathering to analysis to presentation. As one of the leading strategy reporting platforms, ClearPoint has automated 70% of the reporting process. Not only does automation save time, but it also makes your reports more accurate, and useful for your audience.
3. Create a culture of KPI monitoring & improvement
If you want to embrace the idea of KPI monitoring, reporting, and improvement, your people will have to embrace it, too. There’s no “right” way to get people on board, but if you’re transparent about your actions and maintain open lines of communication, your efforts are more likely to succeed. Include your team in the KPI process by asking for their feedback and answering their questions. Create clear accountability for specific data points, including how data is acquired, how it’s reported, and who can speak to what occurred during that reporting period. Also, make sure the levers that drive each KPI are fully controllable by your team, or there will be little motivation to improve.
Claim your FREE eBook on 53 important customer KPIs for enhanced customer satisfaction
Make the most of your kpis.
There’s no question that KPIs can have a positive impact on your organization, but it does take time and dedication to use them effectively. And while we’ve emphasized the importance of choosing the “right” KPIs, keep in mind that, no matter how long you’ve been doing it, this is something of an experimental process. With experience and practice, you’ll start to gain better visibility into performance and more easily make the strategic decisions that will take your business in the right direction.
ClearPoint Strategy simplifies this integration, ensuring that KPIs contribute effectively to strategic discussions and decision-making processes.
If you have more questions about how to use KPIs, or about how ClearPoint might work for your organization, please reach out—we’re here to help!
Discover the Power of Effective KPI Management with ClearPoint Strategy Software
Take the first step towards mastering your business performance metrics with ClearPoint Strategy. Our software simplifies the creation, tracking, and analysis of KPIs, ensuring your strategic goals are met with precision and ease. Don't miss out on the opportunity to see ClearPoint Strategy in action— book a demo today!
Book your FREE 1-on-1 DEMO with ClearPoint Strategy
.webp)
Ted Jackson
Ted is a Founder and Managing Partner of ClearPoint Strategy and leads the sales and marketing teams.
Table of Contents
Latest posts.

Strategic VS. Operational Planning: The 7 Main Differences
.webp)
Baldrige Excellence Framework: A Success Story by The City of Germantown, TN
.webp)
3 Reasons To Pursue Local Government Digital Transformation in 2024
- Common Leadership Styles
- People Management Skills
- Life Skills to Build
- Managing Time Effectively
- Self-Management Skills
- Skills of Successful Entrepreneurs
- Best Leadership Quotes
- What is a KPI?
- What is OKR?
- What are SMART Goals?
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Best Business Objectives
- Goal Setting Statistics
- Best Goals Quotes
- Boost Cross Team Collaboration
- Leading And Managing Remote Teams
- Apps For Managing Remote Teams
- Virtual Team-building Activities
- Effective Team Meeting Agenda
- Manage a Software Development Team
- Team Communication Quotes
- Teamwork Quotes
- Accountability Quotes
- Powerful Boss Quotes
- Emotional Intelligence Quotes
- Hard Work Quotes
- Perseverance Quotes
- Achievement Quotes
- Positive Attitude Quotes
- Networking Quotes
- Project Management Basics
- Principles of Total Quality Management
- Elements of Total Quality Management
- Key Elements of Strategic Management
- 5 Elements of Management Process
What is a KPI? Definition, Best-Practices, and Examples
You have heard about KPI, right? The key performance index tool that organizations use to measure how effective they are in achieving their business goals.
There is no doubt that KPI is a common performance-related term in the business world. Almost every large company in the business world uses them.
The standard protocol in a well-structured company is for different departments in the company to have their own unique KPIs based on specific goals and objectives . HR departments, sales teams, marketing departments, and finance departments need KPIs.
As a small business owner, you are probably wondering what the fuss about KPIs is?
If you are looking to understand what a KPI is and how to use it in your daily business, then you stumbled on the right article.
After reading this article, you will have more than enough information about KPI to start implementing KPI best-practices in your small business.
Let’s start with the basics.
Key Performance Indicator: A Short Definition
KPI is an acronym for Key Performance Indicator. A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measurable or analytical tool used by businesses to track how companies or/and individual departments are effectively meeting up with the outlined business objectives.
What are the various dictionaries saying about KPI? How do they define it? Let’s check them out.
“A KPI is a performance metric for a specific business activity.” “Key performance indicators (KPIs) provide managers with advanced warning signals that there may be problems ahead.” – Online Cambridge English Dictionary .
“Key Performance Indicator: A way of measuring the effectiveness of an organization and its progress towards goals.” – Online MacMillian English Dictionary .
“A measure of achievement that can be attributed to an individual, team, or department. KPIs should be constructed using the SMART principles of objective-setting, and are normally developed as part of a performance management system.” – Oxford Reference .
There are two forms of KPIs: the high-level KPIs and the low-level KPIs . The high-level KPIs deal with the overall business performance, while low-level KPIs measure the performances of the several units that make up the business or company.
No KPI form is more important than the other. Companies use both to get a clearer and more accurate picture of their overall performance.
Major Types of KPIs
There are different types of KPIs available, numbering as many as eighteen or more. However, not all KPIs are relevant for every business or industry.

Before selecting a KPI type to use to evaluate the performance of your business, find out if it is relevant to your industry or department. An organization can use different KPIs to track the performance of different departments.
Some of the major types of KPIs include:
1. Marketing KPIs
Marketing KPIs refer to the various measurable metrics used by marketing teams to analyze their performance in light of the set objectives.
This KPI type covers digital marketing metrics, SEO marketing metrics, social media marketing metrics, and email marketing metrics. With marketing KPI in place, sales and marketing teams can effectively reach their set objectives.
When setting up a marketing KPI, ensure it has all the top metrics needed to track your marketing goals. These metrics include funnel conversion rates, brand awareness, customer engagement, customer acquisition cost (CAC), return on marketing investment, and customer retention.

2. Sales KPIs
Sales KPIs refer to the various metrics that sales teams use to evaluate their sales campaign performances. In every organization, the sales teams are the most important force behind the success or failure of the organization.
They are directly responsible for selling the organization’s productions and services and generating revenue. Little wonder the sales teams’ performances are measured by their sales numbers.
Thanks to Sales KPIs, organizations can measure every aspect of their sales team’s performance. Sales KPIs provide more customization than what is attainable with many sales funnel tools .

There are a lot of top-rated sales metrics used to evaluate the performance of sales teams. They include monthly sales growth, average profit margin, sales per rep, sales target, sales by contact method, retention and churn rates, customer lifetime value, and more.
3. Email Marketing KPIs
Email Marketing KPIs refer to the various metrics used by marketing teams to evaluate their email marketing campaigns.
Email newsletters remain one of the top avenues for businesses to nurture their leads, promote their products, and generate revenue. There are several email newsletter software that helps businesses create, automate and analyze their email marketing campaigns.
Tracking email marketing campaigns will help businesses improve their email marketing results.
There are key email marketing metrics every business should use to evaluate their email marketing campaigns. They include open rate, click-through rate, forward, unsubscribes, and engagement scores .

4. eCommerce KPIs
The eCommerce industry is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world. According to Statista , retail eCommerce sales will reach $6.5 trillion in 2023.

eCommerce platforms such as Shopify and BigCommerce help small businesses track their eCommerce performance.
Businesses with online stores need to use the right eCommerce KPIs and metrics to track their overall performance. They include shopping cart conversion rate, sessions, and abandonment, coupon conversion, revenue per visitor, cost per order, revenue for new visitors, returning customers, unique online buyers , and more.
What Makes a KPI Effective?
Many organizations are doing KPIs wrongly. The Key Performance Index (KPI), contrary to what many business owners believe, is not a standardized formula for improving the performance of their businesses.
There are a lot of nuances that every organization has to take into consideration about their values before structuring their unique KPIs.
Blindly adopting a KPI because it is working for an organization may end up being counterproductive, even if it is an industry-recognized KPI. Every business and organization has its unique structure. For a KPI to work, it must be a suitable fit for that business’ needs.
One aspect that tends to get overlooked in the KPI discussion is the idea of KPI being a communication tool . On its own, KPI cannot boost performance, it needs to be backed by valuable actions.
What KPI does is to communicate the performance of your business or aspects of it to its readers. Because KPI is a communication tool, it has to stick to the basic rules and best-practices of communication for it to be effective.
One of such best-practices is that it must be clearly expressed in a form that the user can easily understand. Also, the information the KPI produces must be relevant to the needs of your business.
When developing KPIs for your organization or individual departments in your business, consider the following best-practices:
- Identify and make clear the objectives of the organization or the department to your teams.
- Set up a plan on how to achieve your objectives.
- Define the roles that different departments or individuals will play in actualizing the set objectives.
This process may involve some back-and-forth meetings with your team, but it is well worth it. During the process, it will become evident the KPIs your business need and what part of your business or process needs such attention.
In summary, effective communication is what makes a KPI effective.
How to Define a KPI
We briefly defined KPI at the surface level as:
“A measurable or analytical tool used by businesses to track how companies or/and individual departments are effectively meeting up with the outlined business objectives.”
Now, it is time for the more practical test. How do businesses define what key performance indicators are the best fit for them? Defining the suitable KPIs can be a tricky task.
Many businesses bundle the whole idea of KPIs by putting it in the same bracket as business metrics. You will be shocked to know how many businesses do not differentiate KPIs from business metrics.
At its core, KPI refers to all the “key” metrics that are relevant to the organization’s result. While KPIs can be grouped as business metrics, organizations need to differentiate both terms to get the best results.
KPIs are super-targeted metrics that help businesses measure their performance in light of their set business objectives . Business metrics refer to all the possible statistics, criteria, and measurements about the business (important or unimportant).
Once you understand that KPI’s sole function is strictly related to the business objectives, defining it will be a lot easier. Here are some key questions that will help you define the appropriate KPI for any industry or business type.
- What is the desired result?
- Why do you want to achieve it?
- What can you use to measure or track your progress or journey?
- Who are the key players that can influence the result?
- Who is in charge of the project?
- What is the expected timeframe for its completion?
- How will you know when you reach your objective?
- What are your plans for reviewing the progress made towards achieving the desired result?
Let’s take an example that clearly shows how to define a KPI to meet your desired result. This example is the eCommerce Growth KPI.
- The desired result is to increase revenue from our eCommerce store by 25%
- Reaching this goal will help our business make a profit
- We will track and measure our progress by using monthly earning targets
- Our eCommerce sales and marketing teams are responsible for this goal
- Our online sales manager is in charge of the project
- We expect to reach our milestone by December 21, 2021
- When our eCommerce sales revenue for the year reaches $350,000
- We will review progress monthly.
Best Tips for Managing Your Business Using KPIs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are super-specific signals that reveal the performance of your business. It tells you if it is performing, overperforming or underperforming.
KPIs are an important evaluation tool to track business performance. Although it is critical for you to track your business performance for optimal results, doing it wrongly can harm your business.
A round-hole KPI in a square-hole business will cost the business valuable time and money. It will also cause the business to make a series of bad decisions based on misleading data . If you do not properly optimize your KPI, even if it is the right fit, it can lead to the same disastrous outcomes.
KPIs are not metrics you set and forget about it. You need to monitor it regularly to get the most out of it for your business.
In a data-driven world, businesses that use KPIs have the advantage of arriving at more informed business decisions than those who don't. Here are some of the best tips for managing your business using KPIs.
1. Select KPIs that Match Your Key Business Objectives
Key Performance Indicators should match your business goals and objectives. Picking KPIs that align with your business objectives will move you a step forward towards its actualization.
Selecting the right KPIs can be a difficult task. Some businesses' complex structure allows for confusion in the selection process.
Some companies have several key objectives, worsened by their use of short, medium, and long-term goals. Companies have different approaches to measuring performance, making it hard to use a one-size-fits-all approach.
Here are some tips that will help you select the right KPIs even amid organizational complexities.
#1 Use Different KPIs for Different Department or Managerial Needs
In an organization, individuals have their separate roles and objectives. For example, the executive class focuses more on medium to long-term objectives. The management class focuses on short to mid-term objectives. The rest of the workforce focuses on short-term objectives.
Choosing one-size-fits-all KPIs that have general implications for all groups is not the most effective approach . Instead, use unique KPIs that match the objectives and focus of the group. Every group (executive, management, and workforce) should have different KPIs.
#2 KPIs Should be Linked to Business Success
The most effective KPIs are the ones that combine your business success with your customer success. A good example is the Customer Referral Rate . This KPI shows you how your team members are performing, and how your customers are responding to your products.

The Customer Referral Rate is one of those evergreen KPIs that cut across the three levels of workers in the organization: executive, managers, and workers.
At the worker level, it speaks about the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns. At the manager level, it speaks of their effectiveness in converting referrals into paying and dedicated consumers. At the highest peak (the executive), it speaks of the ability to meet set objectives.
#3 Avoid Using Irrelevant KPIs
If a KPI does not relate to your business objectives, no matter how fancy and data-driven it is, avoid giving it a central focus. Every business objective is unique , which explains why there are so many types of KPIs available.
Select only meaningful and relevant KPIs that can take you to your destination, your business objectives.
2. Select KPIs That Are Within Reach
Many business owners choose KPIs for their business out of preference rather than necessity. If you choose a KPI for your business that is not the perfect fit, the KPI is as good as useless.
Avoid picking KPIs that your business does not have the data needed to operate. Stay off KPIs where the cost of operation is costlier than what your budget permits.
Choosing the right KPIs for your business ultimately comes down to two variables: cost and benefit. Here are some questions you can use to ensure you pick KPIs that are within reach.
- What data do I need to use for the KPI?
- What are the processes and tools I need to use?
- How often do I need to add data to the KPI?
- What platforms or systems do I use to share the KPI with relevant stakeholders?
- What is the overall cost of the KPI?
- What are its potential returns?
3. Limit The Number of KPIs Used
There is no standard limit of KPIs for any business or industry. However, no business can realistically integrate all the available forms of KPIs into its systems.
Apart from its cost, it will distract you from concentrating on the data you truly need to measure your business performance.
Evaluate your business objectives and the processes it needs to achieve them. Consider all the KPIs you have in mind to use, and remove the ones that do not add much value.
Keep your KPIs to a number that your business can handle . By restricting it to a few super-relevant choices, you improve your business chances of success instantly.
Here are the reasons why limiting your KPIs is the hack you need to better manage your business.
- It forces you to narrow down KPIs to a shortlist that includes only key metrics for accurately measuring your business performance.
- Fewer KPIs mean more time and energy to review performance results.
- It saves you the cost required for monitoring and optimizing a wealth of KPIs.
4. Review Your KPIs
Avoid the trap of getting too familiar with a set of KPIs and putting them on autopilot for a long time. Your business is not static and can outgrow the need for a particular KPI overtime.
Spend time to evaluate your KPIs to find out if they remain the best solutions available for your business.
If your business experienced growth, organizational or structural changes recently, a KPI review is required.
Here are some questions you can use to review your KPIs.
- Is the reason why you picked this KPI still relevant today?
- Has your business outgrown the KPI?
- Can you adjust the KPI for better results?
How to Use KPIs as Part of Your Performance Management Appraisals
There are lots of similarities in the function of KPIs and performance management appraisals. KPI refers to the key performance metrics used by businesses to evaluate their performance.
Performance management appraisals are the process by which relevant stakeholders in an organization work together to review the business objectives of an organization.
It is the continuous process of accessing the progress made, communicating, and training workers to ensure that the business objectives are met.
KPI is a type of performance management indicator that is relevant for businesses. When preparing your performance management appraisals, you can use KPIs. Here is how to do it.
1. Align Your Business Strategy
Businesses or startups today lookout for that single metric that they can use to evaluate their performances. This fascination with a single metric solution requires businesses to thoroughly understand what the business is about, and how to use it for performance appraisals.
For many businesses, sales is that single metric solution they rely on to evaluate their business performance. In many cases, sales are the key performance indicators that everyone by default wants to use.
The challenge is not about sales being the single most important metric for businesses. Rather, it is about the challenge of quantifying the outcome.
How do you drive sales? Take time out to figure out the answer, and ensure it aligns with your overall business strategy.
2. Cover Your Tracks
As a business owner, you are familiar with the concept of having to choose between two items of equal value. Now and then, you face these painful choices. Why can’t you just have both?
With KPIs and performance management appraisals, you can navigate these scenarios by using an established framework.
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is the framework that helps you navigate such tight situations. It does this by breaking down your business into key smaller parts for effective monitoring.

Balanced Scorecard has four key parts: the financial perspective, customer relationship perspectives, internal processes perspectives, and education and growth perspectives.
For effective performance management appraisals, all these four key parts must be aligned. They overlap each other. Isolating one from the others will not produce full reporting details.
If there is a slight unbalance in the Balanced Scorecard, for example, one part is affected, it will also impact the others.
3. Activate Your BSC Strategy with OKRs
BSC Strategy is an acronym for Balanced Scorecard (BSC) strategy while OKR is an acronym for Objectives and Key Results.
The BSC strategy is all about developing KPIs, objectives, goals, and actions for each perspective you have as a business. Many businesses use this framework to integrate KPIs as part of their performance management appraisals.
There is a newer but not necessarily a better framework that is gaining popularity among businesses today. It is the OKR framework that became popular because of its use by the internet giant, Google.

OKR is an objective and key result framework that helps businesses define and track their objectives to produce the desired outcome. It is a strategy that serves as a middle ground between the KPI strategy and the BSC framework.

OKRs is a simple framework used by businesses to track their business performance. The tool helps to set objectives, communicate them, and track their implementation simply and clearly so that everyone can focus on the same direction.
When you implement the OKR framework properly for your business, it can boost your business productivity. If you struggle with setting clear work objectives and identifying the desired key results, OKR can help you solve your problems with three framework questions:
- Objectives – Where do I need to go?
- Key Results – How do I know I am getting there?
- Initiatives – What will I do to get there?
What makes OKR attractive for many businesses is its simple framework. It is easily a middle-ground solution that features parts of KPI features and parts of the performance management appraisal features.
OKR is a practical framework for defining, tracking, and measuring business key objectives. It covers what we can quantify (measurable values) and what we cannot measure (aspirations).
4. Use a KPI Dashboard for Your Performance Management Appraisals
A KPI dashboard is a data-driven tool that provides real-time business performance results. Setting up a KPI framework for your organization is ineffective if you do not use a KPI dashboard.
Businesses use KPI dashboards as part of their performance management appraisals. These dashboards provide a comprehensive analysis of the performance of the organization.
A KPI dashboard consists of the following terms:
- Key Risk Indicator (KRI) – for measuring the risk of an activity
- Critical Success Factor (CSF) – for measuring the critical factors needed for an organization to achieve its objectives.
- Performance Metrics – for measuring the organization’s performance
Good KPI Examples
There are tons of KPI examples available for businesses to use in their overall KPI strategy. What determines if a KPI example is ideal for your business or not is primarily your business objectives.
Before selecting a KPI example, define the goals and objectives you want to achieve. Next, determine how best you can measure your progress towards the attainment of your desired results (goals and objectives).
KPIs are designed to show you how much progress you are making towards the attainment of your goals and objectives.
We will divide KPIs into four popular categories that cut across organizations to list the best KPI examples under each category. These categories include sales, financial, project management, and marketing.
1. Sales Growth
Sales growth is directly related to your business growth. By tracking your sales growth, you are indirectly getting a full picture of your business performance. It involves the tracking of your sales representative’s performances.
2. Sales Target
What are your sales targets? Measuring sales targets should be a priority for every business . It is not just enough to set it, tracking it is equally as important as reaching your sales milestone.
Tracking your sales target is a crucial sales KPI that helps you know if you are on track or not.
3. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
This sales KPI helps you identify how much you can expect to earn from each of your customers. It helps you keep track of your core business objectives, which is to make revenue.
Financial KPI
1. current ratio.
This financial KPI measures the ability of your business to meet up its financial goals within one year.
2. Net Profit Margin
How well is your company performing after subtracting all expenses including operation cost and taxes from your revenue? The net profit margin is one of the top financial KPIs used by businesses and organizations.
3. Working Capital
This financial KPI measures the financial health of your business by tracking all its available assets. It helps businesses identify if they are in positive financial health or a negative one.
The working capacity is simply a function of the value left after subtracting total liabilities from your total assets.
Project Management KPI
1. cycle time.
This refers to the time needed to accomplish a task or activity. Tracking the cycle time for your projects is one of the best ways to effectively track their performance. Setting up a cycle time KPI is a valuable metric for repeated tasks or projects.
2. Cost Performance Index
This project management KPI measures the efficiency of your project performance. It divides the actual amount of time spent doing the project by the actual budgeted costs.

3. Customer Satisfaction
Measuring customer satisfaction or loyalty will help your business determine if it is performing well or not.
A larger number of customers turning into repeat customers, or simply expressing satisfaction about your services means your business performance is top-notch.
Marketing KPI
1. return on marketing investment (roi).
This marketing KPI is one of the most important when tracking the performance of your marketing campaigns. With this KPI, you can track the revenue generated from your campaigns .
2. Incremental Sales
This KPI tracks your sales revenue from your marketing campaigns. It shows you if your campaigns are effective (leading to increased sales revenue) or ineffective (reduced sales revenue).
3. Social Traffic and Conversions
This marketing KPI is valuable for businesses running social media campaigns. With this KPI, you can track the effectiveness of your social media campaigns at meeting your conversion goals.
How to Use KPIs in Your Daily Business
You can use KPIs to monitor, track and evaluate your business daily. For example, if your objective is to sell 100 packs of organic milk in a day, set up KPIs that can track your progress towards your set objective.
The process for setting up KPIs is similar for different organizations and business needs. You first have to set your business objectives and then select the appropriate KPIs to help you attain them.
Using KPIs in your daily business can best be accomplished by using KPI reports and KPI dashboard solutions.
1. KPI Reports
A KPI report is a visual management tool that facilitates the management of the various key performance indicators. Businesses use these KPI reports to track their progress and performance and compare it with their targets.
KPI reports are the visual, mathematical sides of the KPI. They often involve the use of a mixture of graphs, charts, and tables.

These reports help businesses to define or achieve their objectives, identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Any business, whether small to medium businesses or large companies can use KPI reports in their data and routine activities. The enormous amount of data that businesses generate daily can be converted into KPI reports , through which businesses can track their performances.
Not every data that a business generates makes it into the KPI reports. As the name suggests, only key data that are relevant for evaluating the business are tracked.
KPIs make tracking your business performance easy by comparing it directly to your set objectives. With KPI reports, you get a detailed summary of your performance. It allows you to track your progress, holds you accountable, and keeps you on the path to attaining your objectives.
2. KPI Dashboard Solutions
KPI dashboards are a valuable tool for any business executive or manager. These dashboards provide an overview of the business performance. They help business managers identify the areas where their businesses are underperforming, performing, and overperforming.
Decision-making at businesses or organizations becomes clearer and more effective with KPI dashboards. Businesses can make better judgments and track short-term, mid-term, and long-term goals in real-time.
There are a rich array of KIP dashboard solutions in the market. Some offer simple KPI tracking tools for small businesses, while others use advanced business intelligence solutions suitable for large organizations.
Here are four of the best KPI dashboard solutions for businesses.
Easy-To-Use KPI Dashboard Solution
Scoro KPI dashboard software is a cloud-based business tracking and monitoring tool for small to medium-sized businesses . The platform allows you to oversee all parts of your business from one central point.
Its dashboards are customizable and user-friendly. If you have an existing software you use to track and monitor your data, you can integrate it with Scoro.
#2 Geckoboard
Best KPI Dashboard Solution with Multiple Integrations

Geckoboard is a KPI dashboard solution that helps businesses collect, track, visualize and share information in real-time . The platform presents a clear overview that is easy to understand for all.
There are over 80 integrations available on the software for businesses to use. You can find custom KPI templates to use on the platform.
Best Visually-Appealing KPI Dashboard Solution

Sisense is a KPI dashboard solution that converts complex data into understandable insights. The business intelligence platform uses an interactive online dashboard that provides businesses with multiple visualization templates to choose from .
The software integrates with platforms such as SalesForce, Adwords, and Google Analytics.
Best KPI Dashboard Solution for Sales-Driven Data

Tableau is a KPI dashboard solution for data discovery and visualization. The platform supports the use of different data sources such as Salesforce, Oracle, MS Excel, Google Analytics, and MS SQL.
KPIs and Metrics FAQ
KPI is an abbreviation, which spells out in full as the Key Performance Index. It is a measurable value that businesses use to evaluate their performance towards achieving their primary business objectives.
KPI is a tool used to collect, track and evaluate business performance in comparison to the business set objectives. Companies use the data-driven process to effectively track their business performance. When set up properly, KPI is a dependable metric for evaluating if your business is on the right track to prosperity or not. It helps keep you on track, by showing you when you are falling short of your set business target. KPI can be used to boost areas of your business that are falling short of the expected projections. The KPI framework is more than a normal business metric , it consists of key performance indicators that can improve any business. Small businesses and even financial leaders in large organizations use KPI to measure their business results and performance. They leverage the information provided by KPI to drive their business performance.
Anyone can determine KPIs. In large companies, it is the executives such as CEOs and executive teams that are responsible for constructing KPIs for the companies. These KPIs cut across all departments in the company, and other department KPIs are tailored to match it. Small business owners can determine the KPIs that they want to use to track the business performance. In large companies, with several departments, department heads are responsible for determining KPIs. Apart from setting the KPIs for their various departments, they are responsible for ensuring that their teams work according to the KPIs.
Choosing the right Key Performance Indicators (KPI) depends on your business goals. When searching for KPIs to use, restrict your search to only those KPIs that directly relate to the business goals and objectives you set . The purpose of KPIs is to gauge and evaluate your business performance relative to some objective. For example, if your business goal is to increase your revenue, then the KPIs used should revolve around sales, marketing, and finances. If your goal is related to project management, consider project management KPIs such as Planned Value (PV) project KPI, Actual Cost (AC) project KPI, Earned Value (EV) project KPI, and Cost Performance Index (CPI).
There is no best time to use a KPI. Ideally, you want to use a KPI before you start a business goal or objective. If you launch a KPI midway into the project timeframe, it may not prove useful because of missed timeframes. Use a KPI any time you need to track your business objectives . Also, note that you may need to change KPIs for some of your objectives as they change. Business objectives are dynamic and ever-changing. Once you reach an objective, another one replaces it. If you use an old KPI for the new project, it may not be relevant for it.
Reviewing your KPIs regularly is essential for your business growth. KPIs help you collect, monitor, track, and evaluate your business performance . It refers to the key metrics that you use to track how much progress you are making towards your business objectives. KPIs provide key information about your business. Reviewing your KPIs will help you take advantage of this information for your business prosperity . Also, your business objectives are not stagnant and change as you accomplish them. A KPI used to achieve a goal may not work for the next. It is essential to review your KPIs from time to time to stay on top of recent changes and trends. KPI strengthens employees’ morale. By tracking KPIs to assess an employee’s performance, the employee feels his or her work has better value to the company. Employees will feel extra motivated to perform since the company knows who is performing and rewarding accordingly.
The best time to review your KPIs is weekly or monthly . However, based on unique situations, you can adjust the timeframe for review to best suit your business goals and objectives. Whatever time you choose, ensure that there is enough data collected in that duration to make an informed decision. Many businesses review their KPIs monthly.
Both small-scale companies and large-scale companies can use KPIs to evaluate their business performances. Organizations of all kinds use KPI to track their performances for better results.
KPI dashboard provides a real-time visual overview of the business performance . They are valuable tools for any business executive or manager. When used properly, they help business managers identify the areas where their businesses are underperforming, performing, and overperforming. The best KPI dashboards are easy to use and customizable . You can change the fonts, colors, and views of your dashboards. KPI dashboards make decision-making at businesses or organizations clearer.
A good KPI should be simple, straightforward, and easy to use . It should be able to convert complex data into simple forms that anyone can understand at a glance. A good KPI is one that prompts action and not results in more confusion. Good KPI is data-driven and helps businesses track their performance , pointing them to areas where they can improve, and areas where they are performing well. The right KPI communicates valuable data, one that is easily understandable by your employees.
Many KPI tools in the market offer excellent KPI services for businesses. Here are four of the best KPI tools. All four KPI tools are simple to use, have attractive KPI views, and several goof integrations. #1 Scoro The software is a business tracking and monitoring dashboard solution for businesses . The platform allows you to oversee all parts of your business from one central point. Scoro dashboards are user-friendly and customizable. Data security is assured with its cloud-based data protection system. #2 Geckoboard Geckoboard is a KPI dashboard solution that collects, tracks, monitors, and shares KPI statistics. The software provides clear insights that are easy to understand for all. There are over 80 integrations available on the software for businesses to use. You can find custom KPI templates to use on the platform. #3 Sisense Sisense is a KPI dashboard solution that converts complex data into understandable insights. The business intelligence platform uses an interactive online dashboard that provides businesses with multiple visualization templates to choose from . The software integrates with platforms such as SalesForce, Adwords, and Google Analytics. #4 Tableau Tableau is a KPI dashboard solution for data discovery and visualization. The platform supports the use of different database software such as Salesforce, Oracle, MS Excel, Google Analytics, and MS SQL.
KPI management refers to the process of setting, collecting, tracking, and analyzing key performance indicators (or KPIs) to boost a company's chances of achieving its set objectives.
Next Step: Become A More Data-Driven Company
Today’s world places more emphasis on data than in any time in human history. With every business aspect now available in quantifiable data, businesses have little choice but to embrace a more-data driven culture.
However, not all business metrics are important for businesses. Only key performance indicators are relevant.
You can become a more data-driven and effective company through the use of KPIs (Key Performance Indicators). While implementing KPIs, only use those that are directly related to your business goals.
Make the KPI process easier with KPI dashboard solutions. Scoro is an easy-to-use KPI dashboard solution for small to medium-sized businesses.
Geckoboard offers real-time KPI statistics with over 80 integrations. Sisense is the best visually-appealing KPI dashboard solution.
Tableau is the best for businesses focusing on sales-driven KPIs.
Use KPIs the right way and watch how easily your company performance increases and your company objectives are met.
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
KPI Reporting in 2024: Best Practices, Templates & Examples
You can't improve what you don't measure. KPIs or Key Performance Indicators are a superb way to stay on top of your work and its progress. Here is what KPIs are and how to track them effectively.

Dec 30 2019 ● 9 min read

Table of Contents
What are kpis (key performance indicators), what is a kpi report, metrics vs kpi: differences, what is the difference between an sla and a kpi, what is the difference between kra and kpi, the benefits of kpi reporting, 1. measure results, 2. set concrete business goals, 3. refine your business strategy, 4. align efforts throughout all departments, 5. empower employees, kpi report best practices: 4 steps to setting up your report, examples of key performance indicators, financial kpis, digital marketing kpis, customer support and customer satisfaction kpis, what are kpi dashboards, examples of kpi reporting dashboards and templates, kpi report template from whatagraph, kpi dashboard example for google ads, final thoughts.
Following the correct Key Performance Indicators for your business, agency, or clients with clear KPI dashboards and KPI reports will answer how to make your strategies increasingly successful.
Making sure your business thrives can account for a lot of sleepless nights, especially if you’re not too confident in the growth plan and performance indicators and benchmarks you’ve set up.
Agencies use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure and analyze the progress and growth of their marketing and sales team efforts, as well as identify the areas that can be improved.
This makes it crucial to follow the correct data and constantly improve your KPI process.
Clear KPIs and KPI reports have the power of delivering important insights into how your business (or your client’s company) can thrive, as well as be used as progress goals for your entire team (from financial departments to marketing and sales).
In fact, individuals are 42% more likely to achieve goals when they are physically recorded, according to Inc . So let’s start recording those KPIs!
A Key Performance Indicator is a value (measurable through different metrics) that offers information on how effective is a business at reaching its targets and objectives, as well as which areas need improvement.
KPI analytics such as revenue growth leads by sales platform, net sales, customer retention, turnover, etc., hold a lot of information about your business’ strengths and weaknesses.
They also show how you sell, where you sell, how much you sell, and why you sell.
While high-level indicators reveal the overall performance of a company, lower-lever KPIs analyze processes across all departments: financial, sales, marketing, support, etc. In short, there are different types of KPIs and choosing the right ones makes all the difference.
A KPI report is a system, tool, or file that helps you keep track of and analyze the evolution of your key performance indicators on a monthly, quarterly, or yearly basis. Reporting offers insights into a business’ trajectory in a simple and concise manner.
A report should be easy to follow, but still include all the KPI metrics that help identify strengths, weaknesses, and trends in your business model across all departments, as well as one-on-one comparisons with data points from previous marketing reports.
Use interactive metrics dashboards, charts, and graphs to complement the information and make it easier to understand.
There’s a common misconception that metrics and KPIs are the same things. In reality, metrics are tools that help measure KPI. In other words, current values, target values, and different metrics are used to create key performance indicators.
To set your KPI, find the key areas of interest for your business, then measure important metrics that will indicate the performance in those key areas.
Here are some questions to help you create effective KPIs, and examples of metrics that will offer answers:
- How big is the growth of your revenue?
If your KPI is revenue growth, you can follow net or gross sales, and also look at data such as call center KPIs , website sales, mobile app KPIs, sales by country, return on equity, etc.
- What is your most effective sales method?
In other words, how do your customers prefer to buy from you? The metrics you need to look for have to do with customer care, call center leads to sales ratio, website leads to sales ratio, social media leads, ad leads, etc.
- What is your target audience?
To better understand the core audience that is truly interested in your product or service and is more likely to buy, you need to follow audience stats like country, age range, sex, purchase method (website vs. call center), etc.
SLA , short for Service Level Agreement , is a progress measurement system and is often confused with KPIs. Here’s how they are different:
SLAs are expectations established between a service provider and the customers.
KPIs are generally used to measure how well a company, business metrics, or team is doing against its strategic goals.
Sometimes, a KPI is a part of the service level agreement. You set requirements from Service Level Agreements to create the metrics and define the key performance indicators. Therefore, the KPI measurement will show how well you are achieving your goals.
KRA stands for Key Result Area and highlights the areas of business processes that require a high-level performance to achieve the desired results.
Key Performance Indicator is used to measure the achievement of an objective – these objectives are defined using KRAs. KRAs identify the areas that need top-notch performance, while KPI gauges how well these business objects are getting achieved.

As the main solution to measuring a business’ evolution towards its goals, key performance reports also come with a series of extra benefits for your business at both a macro and micro level.
Here’s what you can do through KPI tracking :
The obvious first benefit is that this is the best method to measure through clear values how different aspects of a company’s efforts are evolving.
The best part is that the insights you obtain through KPI reports are actionable, enabling you to make better decisions going forward.
While every business sets off with a few general goals in mind, the data you obtain through reports gives you the option to elaborate on those goals and make informed decisions for improvement.
Clear KPIs can also break down complex situations and help uncover alternative goals you might have neglected initially.
This amount of data explicitly showcases which parts of your strategy are working seamlessly and which parts need to be re-evaluated. You’ll be able to find all of the strategic issues, start fixing them and improve business performance.
It will challenge your strategic thinking but improve your decision-making skills, and you’ll only have to gain from it.
Sometimes the main concern within a certain department may not be in line with the efforts of their colleagues from different departments.
While the sales department is preoccupied with…well, sales, marketing may tend to focus on their campaigns. So how do you bring everyone on the same page?
It may not be as easy as it sounds, since 40% of managers cite failure to align as the single greatest challenge to executing company strategy, shows Harvard Business Review .
Setting clear goals that absolutely everyone within the company works to achieve will surely focus the energy on the most important tasks and drive better results.
Everybody likes to know they’re good at their jobs, right? Measurable positive results are the best way to show employees that they’re doing a great job, which will further incentivize them to perform even better. One of the ways to find those results is to use a 90 day review and keep the pattern.
In fact, you can also use KPIs to send out bonuses to the top-performing employees, just as an extra ‘ thank you ’.
The key to creating a relevant indicator is finding out what are the main objectives of your data-driven company. You should also figure out how these indicators are going to help achieve business goals, and offer confidence to any stakeholders that might get to read the report.
The conventional metrics used in KPI reporting may include informative and actionable parts such as Charts, Graphs, and Tables.
However, following industry-recognized KPIs without understanding your own business and objectives will not get you far. To see actual results, you need to set simple, easy-to-understand keys that are adjusted to your business exclusively.
Here are 4 steps that will help your process:
Measuring is an important part of KPI reporting: it’s the primary key that informs you about the success or failure of your work.
You need to measure the progress made towards the achievement of your target. That could be increasing the number of sales or the number of new customers.
Pick a target audience you aim to reach during a set timeframe. Think of your ideal customer.
You can set more than one target group, or even secondary audiences, and create different KPIs for each one.
This way, you’ll be measuring your progress step-by-step and you’ll have more detailed information about your ideal customers and their expectations.
Your KPI data source is just as important as any of the above steps. Good reporting tools like Whatagraph have a large number of integrations with platforms such as AdWords, ecommerce platforms, social media networks and more.
There is no shortage of software that offers data analysis. Moreover, finding the right tool for your needs may prove difficult. Make sure to find out what functionality you can benefit from the most and use that as your starting point.
Choosing a few well-trusted sources that offer features and data that are relevant to your objectives will make work easier.
Once you’ve found your ideal software for KPI reports, you can start evaluating whether you’re achieving your goals by seeing what methods are working or what needs to be changed.
Another important step is deciding on how often you want to review your plans and report your progress.
For this purpose, there are two categories of KPIs you need to know:
Leading KPIs
A leading key performance indicator measures the change and predicts the immediate progress of a company's performance in advance.
Leading KPIs are easier to improve but not as easy to measure.
Lagging KPIs
A lagging KPI defines the performance of an organization. In other words, it shows the achieved results.
Lagging KPIs are easier to measure but harder to improve.
Therefore, a lagging indicator shows the outcome, and a leading indicator is set in advance to improve the outcome. Monitoring the leading KPIs can improve the lagging KPI. Hence, both are essential parts of KPI reporting.
Organizations choose different types of indicators depending on their needs. A good report includes quite a number of KPIs, without going overboard. Bernie Smith , Founder of Made to Measure KPIs, recommends adding between 2 and 4 KPIs per goal.
Now that you have an idea of how to create the KPI report, it's time to select the indicators you want to include in your report.

KPI examples include customer satisfaction, employee retention, revenue growth, and cost reduction. Key performance indicators should always be measurable, attainable, and relevant to the company’s objectives. The best way to measure KPIs is through dashboards or monthly, quarterly, or annual reports.
Below you’ll find some examples of KPIs for various organizations. You can use them as a guide, but you should still set your own objectives keeping the specific needs of your organization in mind.
Per period:
- New Contracts
- Sale growth
- New qualified leads
- Resources spent
- Conversion rate
- Growth in Revenue
- Net and growth
- Profit Margin OPC (operational Cash Flow)
- Current Account receivables and existing accounts payable
- Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, & Amortization
- Current expense ratio
- Inventory Turnover
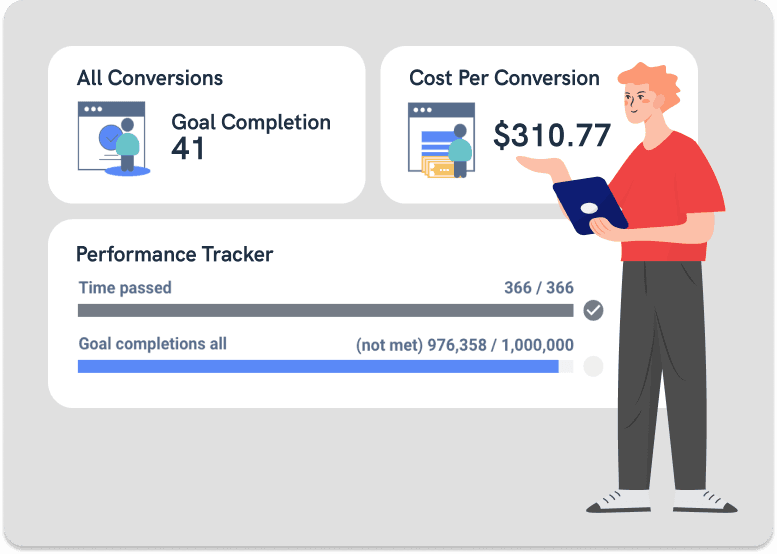
- New and qualified leads
- The average rate of conversion and retention
- SEO ranking
- Website traffic
- Blog published
- Social Media Metrics
- Content quality improvement
- Number of eBooks published
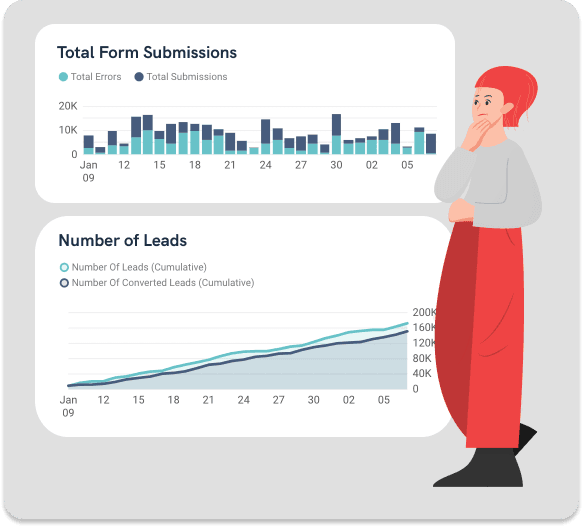
- The average number of support tickets
- The average number of complaint resolution
- Customers retained
- Customers satisfaction
- Average wait time for callers
- Support agent ratings
- Call center productivity , measured by the number of calls handled per support agent per day
KPI dashboards are marketing tools that offer a glance into how your KPIs are performing, as a means to getting some situational awareness without creating an entire report.
They’re graphical snapshots of your stats, goals, and the progress you’ve made. It also shows what else you need to do to make progress towards reaching your high-level goals.
In short, KPI dashboards make it easier to visualize, compare the data and see trends.
One of the easiest ways to create a visual representation of your performance is to use Whatagraph. It’s a reporting tool designed for marketing agencies to collect data from multiple channels and build reports in just a few minutes.
To create the perfect KPI reporting dashboard for your agency or your clients, you’ll first need to zoom in to some of your top goals and metrics you need to follow on a regular basis.
Here are a few KPI examples:
Leads (number of leads, the evolution of the number of leads, etc.)
Website traffic and sessions
Top-performing post (engagement, clicks, cost per click)
Cost per click or cost per acquisitions
Conversions (percentage of conversions, cost per conversion, etc.)
Goal completions
Of course, there are many other metrics and KPIs you might want to add to your dashboard and reports. In addition to KPI Dashboards, admin templates can also be helpful. Using admin templates will save you a lot of time as they offer ready-to-use, pre-built components. Continue reading to find out some of our choices and examples↓
To better understand all of the above information, here is an example of a report created using Whatagraph for an ad campaign.
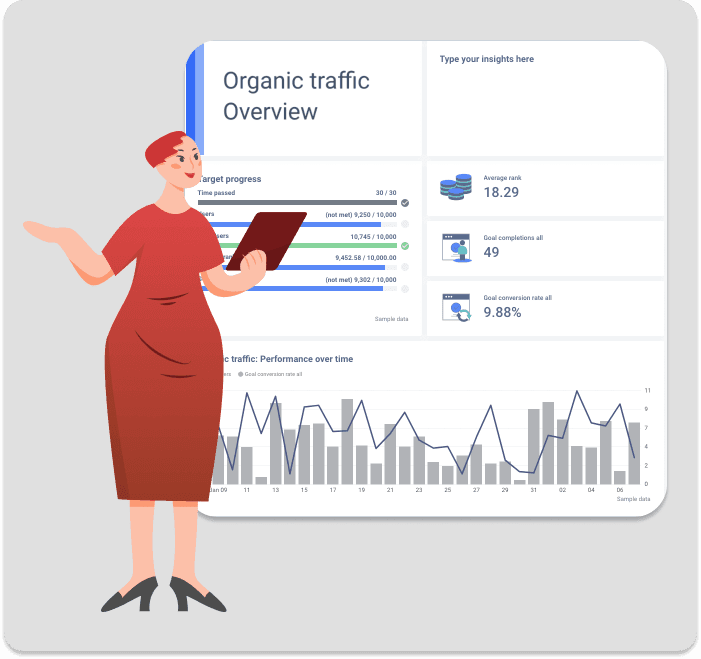
At the top, you’ll see a day-by-day breakdown of the top-performing devices, followed by a funnel of clicks, users, and leads and some of the main KPIs: total spend, cost per link click, and cost per lead.
Below, you’ll find info on the best performing post and its stats, as well as a breakdown of your audience by age and location
Get our KPI report template for PPC campaigns.
Additionally, dashboard software of your metrics shows you how your KPIs are performing, while KPI reports are excellent for more in-depth knowledge.
As mentioned, the dashboard’s role is to show a quick glimpse of your stats in real-time. Below is an example of a KPI dashboard for Google ads.
On the left, you can see the time range for the analysis and the goals: time passed, conversions, clicks, speed.
On the right, you have a more detailed account of the primary KPIs: conversions, clicks, CPC (cost per click), CTR (click-through rate), as well as a correlation between conversions and cost per conversion.
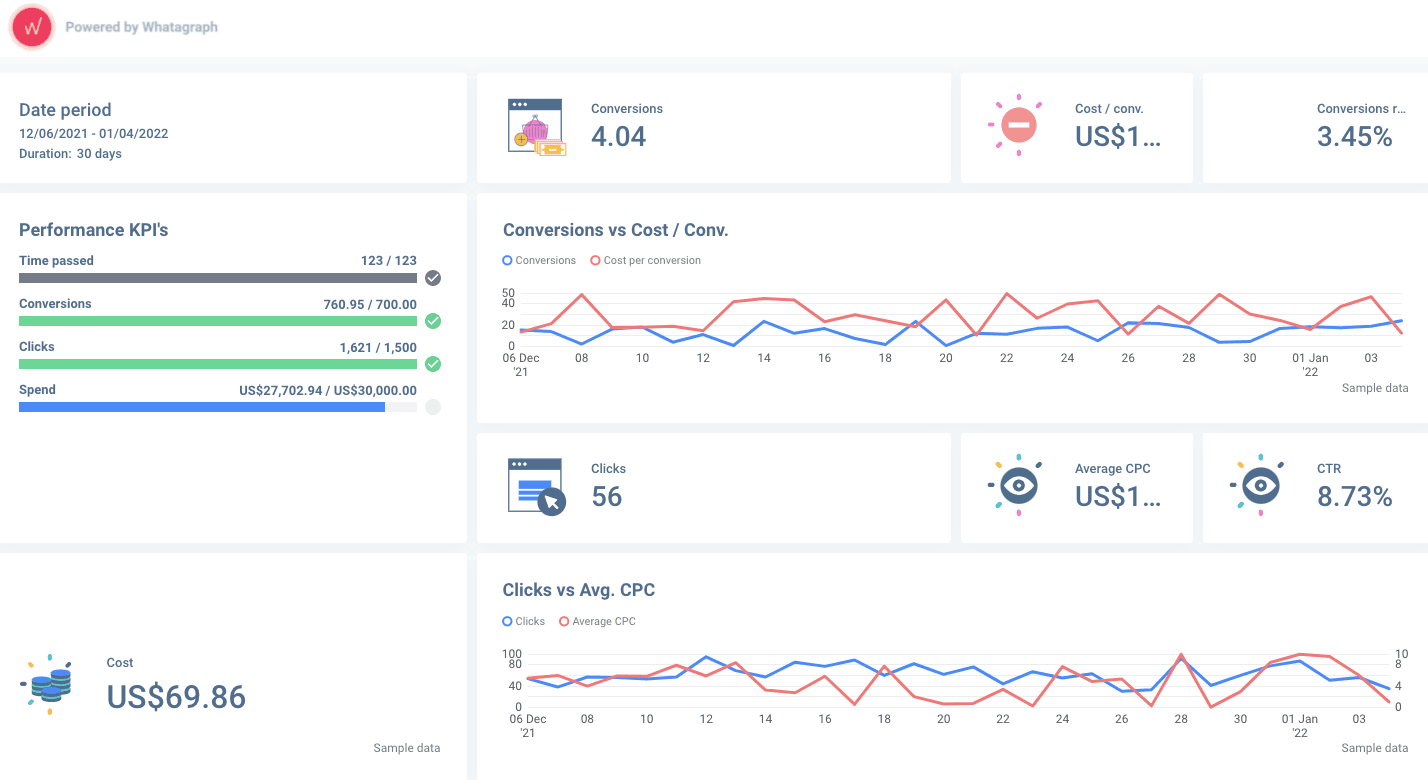
Get our Google Analytics report template!
KPIs talk about the core goals of your organization. They require an understanding of your business objectives and the ability to turn those objectives into measurable goals.
The easiest way to create a visual KPI report is to use Whatagraph. Our tool allows selecting relevant KPIs, measuring your performance based on them, and sharing it with your company so that everyone keeps track. With proper data visualization, your clients will able to see what's working and what's not.
So, what are you waiting for? Sign up for your free tria l of Whatagraph today!

Published on Dec 30 2019
Dominyka is a copywriter at Whatagraph with a background in product marketing and customer success. Her degree in Mass Communications/Media Studies helps her to use simple words to explain complex ideas. In addition to adding value to our landing pages, you can find her name behind numerous product releases, in-app notifications, and guides in our help center.
Related articles

Marketing analytics & reporting · 10 mins
Best Marketing Analytics Tools and Software in 2024

Agency guides · 5 mins
Building Trust with Clients: Tips for Marketing Agencies

Agency guides · 7 mins
How to Exceed Client Expectations as Marketing Agency

Agency guides · 10 mins
Agency Client Retention: Common Mistakes & Expert Tips

Marketing analytics & reporting · 8 mins
Social Media Analytics Report: Best Practises, Tools & Reporting Templates

Data analytics · 7 mins
Data Blending: Clear Insights for Data-Driven Marketing
Get marketing insights direct to your inbox.
By submitting this form, you agree to our privacy policy
A Step By Step Guide to Set KPIs for Team Members
An organization without key performance indicators (KPIs) is like a journey without a map. When your journey doesn’t have a map, there is no way for you to determine how far you have come since you started. You keep on driving towards a destination without any knowledge of what is in your way. In an organization, having clear KPIs that are linked to your company’s ultimate goals help derive the progress you have made within a set time frame. It helps understand the contributions of team members and what needs to improve.
Scroll down to learn:
What is a KPI?
Why are kpis important, how do kpis fit into an organizational structure, kpis in project management, kpis for teams and individuals, kpis and employee performance, how to set kpis.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) allows you to obtain quantifiable measurements over time to accomplish a specific goal (or objective). KPIs drive teams towards achieving targets, provide metrics to measure the progress of targets, and ultimately offer valuable insights to make informed decisions on operations management or business processes. The KPI process helps every aspect of a business – be it finance, HR, customer service or marketing – to be efficient and effective in fulfilling its responsibilities.
As mentioned above, KPIs are essential to identify the contributions of your team members towards overall business goals. Here are some notable reasons why you should implement a KPI process in your organization.
To ensure your teams are accountable and aligned towards goals. This is especially important when monitoring the progress of a particular project. A clearly defined KPI process ensures that team members acknowledge their responsibilities and are making collective efforts towards fulfilling them.
To keep track of the company’s health score. Key performance indicators undoubtedly provide valuable insights into an organization’s operations. While they offer a comprehensive understanding of prevalent financial performance, they also shed light on potential risk factors such as shortages in the capital, new competitors, or knowledge gaps.
To monitor progress over time. KPIs allow you to set goals at the beginning of the financial year and utilize monthly or quarterly reports to measure the progress made by tracking key criteria such as revenue, cost per transaction, customer satisfaction rate and so on. Since KPIs are aligned with organizational targets, this will also assist to track the progress towards a company’s long term goals and strategies.
To make improvements when and where necessary. Once KPI results are analyzed, they allow you to concentrate on which areas of the business need improvement and whether any adjustments should be made to the current course of action. This will save you from making the wrong decisions and predict future scenarios. Since KPIs are measurable, you can directly influence the factors that determine their results and take preventative actions to ensure that you are on track to achieve your goals.
KPIs are an important part of an organizational structure, especially in aligning individual and team goals with the organization’s overall strategy and objectives. KPIs provide a framework for measuring progress, monitoring performance, and identifying areas for improvement across different levels of the organization. They help to ensure that the department and individual goals are aligned with the organization’s overall strategy. Furthermore, KPIs can be used to manage performance and drive continuous improvement.
The below image shows how the KPIs fit into the organizational flow or structure. The company can first decide its vision or what it considers to be its ‘north start’. Once the vision is determined, the organization can list what it hopes to accomplish (goals) and how the product or service can help achieve them. The KPIs are then the indicators that signal successful outcomes. Coupled with the KPIs, the organization must look at the critical success factors required.
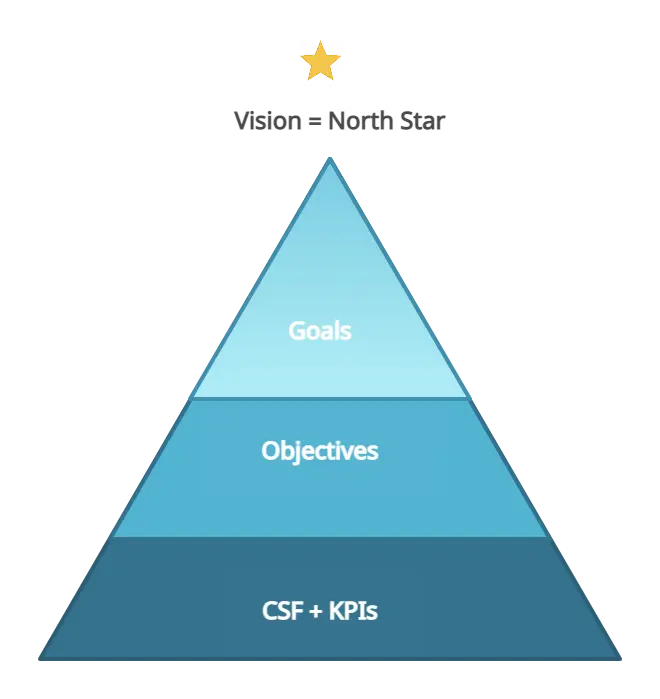
KPIs are used as metrics in project management to measure progress toward achieving project goals and objectives. KPIs in project management are used to monitor the performance of the project team, identify potential risks or issues, and make data-driven decisions to keep the project on track.
KPIs in project management can be broadly categorized into the following areas.
- Time: Time-related KPIs measure progress against the project timeline, including project duration, completion dates, and critical path analysis.
- Cost: Cost-related KPIs track project expenses against the budget and include metrics such as planned versus actual project costs, earned value, and cost variance.
- Quality: Quality-related KPIs measure project deliverable quality, including defect density, error rate, and customer satisfaction.
- Scope: Scope-related KPIs measure project work and include metrics such as scope creep, change requests, and requirements volatility.
Team KPIs can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a team’s performance. Team KPIs can help to identify areas for improvement and facilitate data-driven decision-making. By setting clear performance metrics and tracking progress over time, team leaders can motivate team members to work towards common goals and achieve better outcomes.
Teams can use KPIs may vary depending on the nature of the team’s work. Some common examples of team KPIs include:
- Team productivity: measures the team’s output over a given period of time, such as the number of tasks completed, projects delivered, or products manufactured.
- Customer satisfaction: measures the team’s ability to meet customer needs and expectations, as reflected in customer feedback or surveys.
- Quality of work: measures the team’s ability to produce high-quality work, which can be seen through the number of errors in the team’s output.
- Collaboration: measures the team’s ability to work together effectively. Communication frequency, problem-solving skills, or teamwork assessments can be used to assess this KPI.
- Time management: measures the team’s ability to manage their time effectively. Are they achieving meeting deadlines or completing tasks within a given timeframe?
- Employee engagement: measures the team’s engagement and satisfaction with their work. This looks into employee turnover, job satisfaction surveys, or employee feedback.
Individual KPIs
Individual KPIs, also known as personal performance metrics or individual performance goals, focus on setting up specific, measurable targets used to evaluate an individual employee’s performance within an organization. They help managers and employees to set clear expectations, monitor progress, and provide feedback for performance improvement. Employees can understand how their contributions impact the organization’s success by aligning individual KPIs with the organization’s overall goals and objectives.
Here are a few examples of individual KPIs.
- Sales targets: measures an individual’s ability to meet or exceed sales targets within a given period of time, such as monthly or quarterly sales goals.
- Customer satisfaction: measures an individual’s ability to meet customer needs and expectations.
- Quality of work: measures an individual’s ability to produce high-quality work.
- Timeliness: measures an individual’s ability to complete tasks or projects within a given timeframe.
- Attendance: measures an individual’s attendance and punctuality.
- Professional development: measures an individual’s commitment to their professional development.
Employee performance is at the heart of organizational success. Whether an organization’s journey is successful or not, depends on how driven its employees are in reaching its milestones. In order to achieve organizational goals, we first need to set targets at individual and team levels so that they can be linked to that of the company.
Employees are the greatest asset of a company. They need to be encouraged, empowered, and assessed in view of accomplishing business goals. It is vital to pay attention to an employee’s positive and negative behaviours, discuss and give feedback to create an enabling environment for them to learn and improve. This will also align them to work towards team and organizational goals.
How do you measure performance? What quantifiable data can you present as proof of your team’s hard work? Are all team members working on the right goals? And does their work contribute to achieving the ultimate company objectives ?
This is where KPIs come into the limelight. KPIs are a form of quantifiable targets that help you to track the progress of your business goals. They will help you to comprehend how the performance of your team members contributes to it. Moreover, KPIs will also support in identifying knowledge gaps and allow you to implement qualitative training plans accordingly.
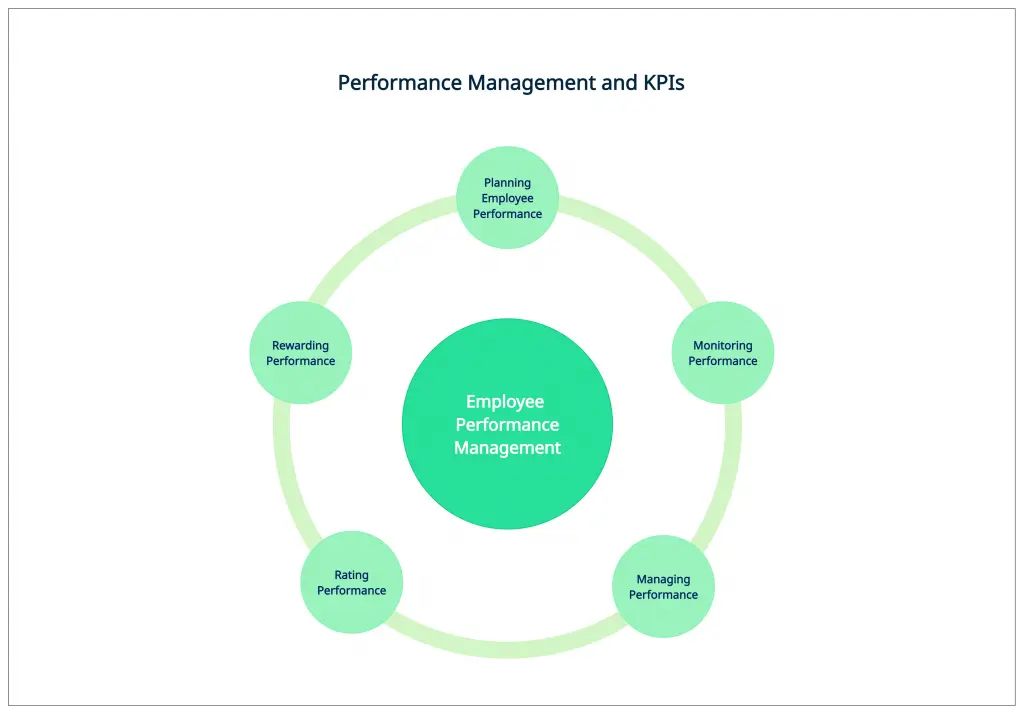
How Can KPIs be Used for Recognition and Appraisal
KPIs can be used for recognition and appraisal by linking individual or team performance against specific, measurable targets or goals. Organizations can ensure that employees are on board with the business’s overall strategy and collaborate to achieve shared objectives by creating clear expectations and tracking success against these benchmarks. Here are some ways in which KPIs can be used for recognition and appraisal:
- KPIs provide regular feedback on performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement and keeping employees motivated and engaged.
- KPIs are used for performance appraisals, providing objective data to assess progress against targets and identifying areas where support or development is needed.
- KPIs can be used for recognition and rewards, linking bonuses or promotions to specific performance targets or goals, motivating employees, and acknowledging their contributions.
- KPIs can identify areas for career development and growth, helping managers create development plans that focus on building skills and knowledge in alignment with organizational goals.
Step 01 – Determine how KPIs will be used
The first step in setting KPIs is to understand how these performance indicators will be used to monitor progress. Before setting KPIs for teams, gather the members and discuss what criteria should be used to determine their KPIs and how these will impact their performance.
KPIs are simply a form of communication, and like any communication framework, KPIs too should be clearly understood by the people they are assigned to so that they can be acted upon. Make sure your team members are data literate and equipped with the right knowledge, tools and skills to make the right decisions based on the data they work with.
Step 02 – Link KPIs to organizational goals
Companies often make the mistake of adopting vague KPIs that don’t reflect their business processes and thus fail to see any substantial impact. Your KPIs should be linked to organizational goals so that you know that the company is on the right track. For instance, companies may define their development strategies under the perspectives of finance, internal business processes, learning and growth, and customer. Accordingly, the KPIs that you set too should fall under these categories.
For instance, company ABC may set a goal under the learning and growth aspect to provide soft skills training to its employees within a budget of 6 million. Here, the Human Resources Manager and his/her team would be chief custodians of achieving this target. Hence, to align with this goal, they could have a KPI to conduct six soft skills training workshops per quarter (24 workshops per year) while maintaining their expenses under the set budget.
Another key aspect of the KPI process is to ensure that your team understands the ultimate goals of the organization and the plan of action that should be followed to achieve them. This will empower your workforce with a purpose to fulfil their responsibilities.
Step 03 – Are your KPIs SMART?
Use the SMART formula to determine how effective your KPIs are.
S pecific – The KPI you set should be focused on a specific aspect of your business that can be measurable, and determine why it is important.
M easurable – As mentioned above, it should be measurable and benchmarked against a defined standard.
A chievable – The KPI should be deliverable.
R elevant – It should be relevant to a business process within the company while being linked to the organization’s strategic objectives.
T ime-Bound – The KPI should be achievable in a set time frame.
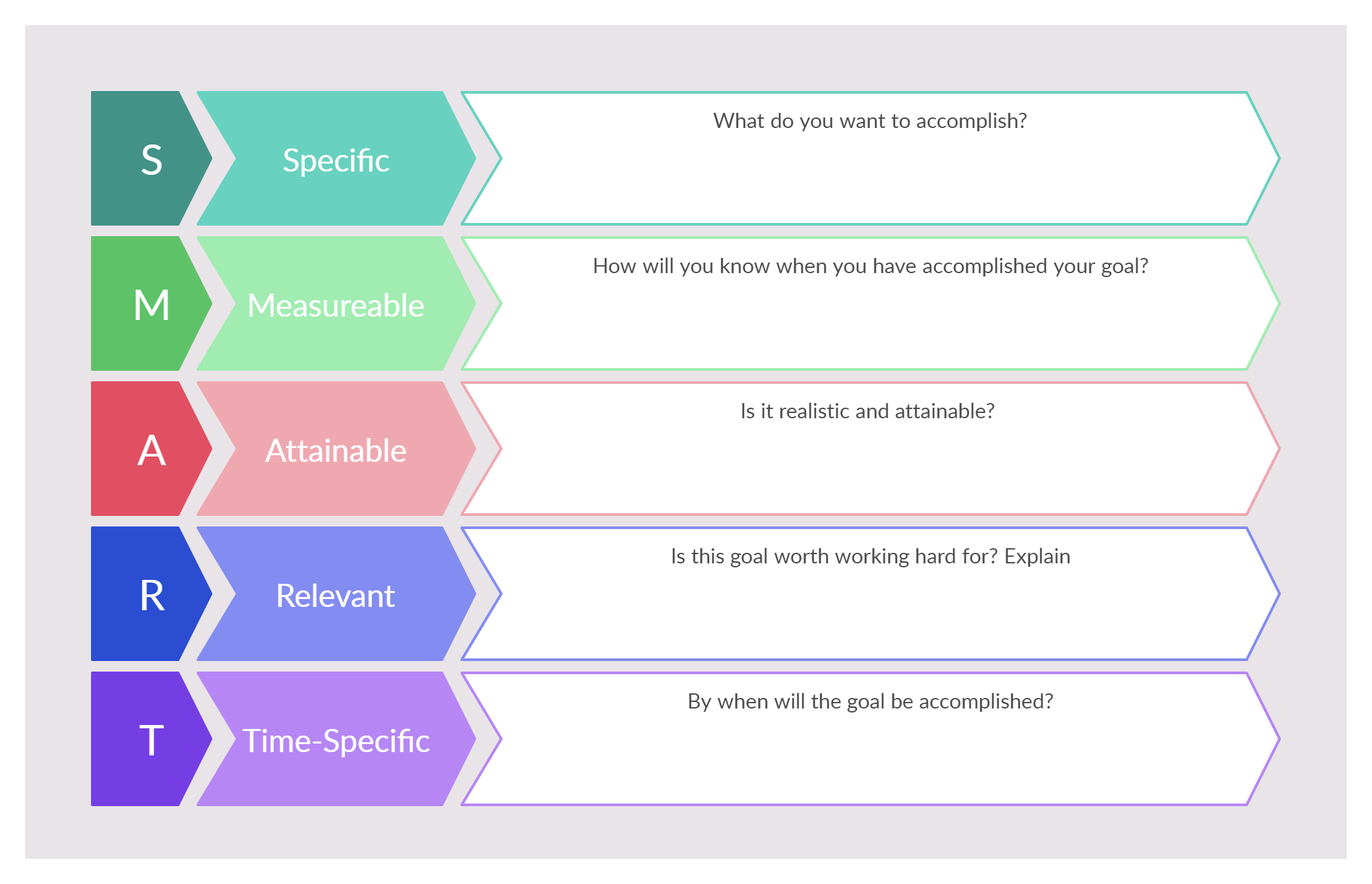
Step 04 – Audit KPIs when necessary and make changes
Businesses diversify or change their existing processes depending on market conditions. When this happens you may need to revise the previously set KPIs and establish new indicators which would align with the new goals. Hence, it is important to audit KPIs annually and make changes where necessary – so you are certain that KPIs are aligned with changed directives of the business. Use the below template to audit your KPIs.
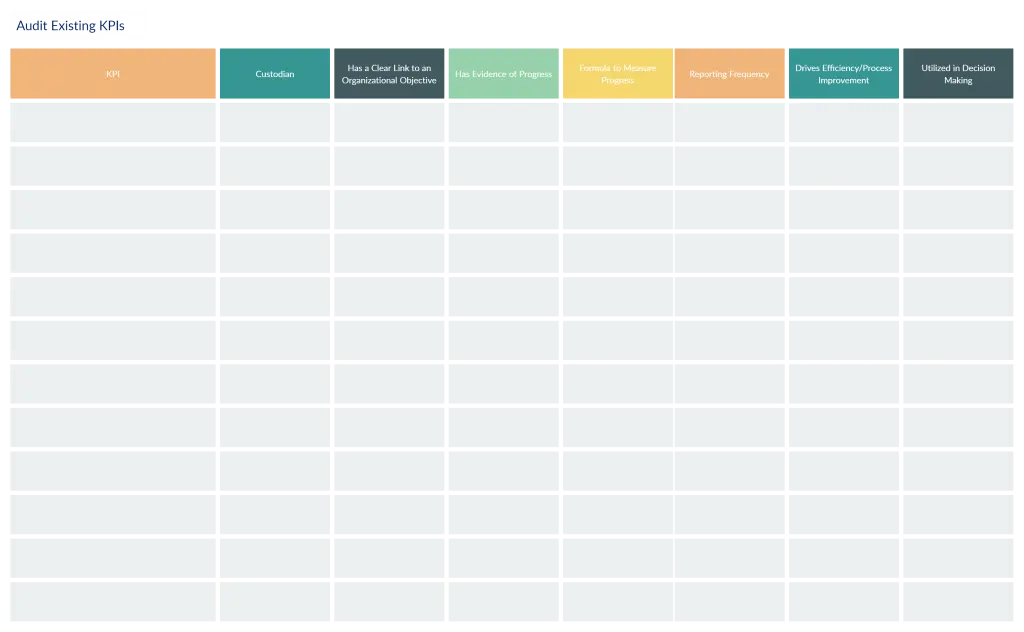
Let KPIs Guide You Towards Success
Key performance indicators significantly contribute to driving a business to achieve its goals. In today’s competitive and complex business environment, it is becoming increasingly important to have defined business goals and a clear plan of action on how to achieve them. As such, KPIs can be your guiding light to determine the direction of your journey and your progress.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About KPIs
- Setting too many KPIs
- Setting KPIs that are not relevant to the team’s work
- Setting unrealistic targets
- Failing to involve team members in the KPI-setting process
More Related Articles
Hansani has a background in journalism and marketing communications. She loves reading and writing about tech innovations. She enjoys writing poetry, travelling and photography.
A Step-by-Step Guide: How to Develop Key Performance Indicators?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial tools for measuring and tracking the progress of your business objectives.
Whether you’re aiming to increase revenue, improve customer satisfaction, or enhance operational efficiency, well-developed KPIs provide valuable insights into the health and performance of your organization.
However, developing effective KPIs requires careful consideration and strategic alignment with your business goals.
This blog post is about how to develop key performance indicators that drive success.
From understanding the purpose of KPIs to selecting the right metrics, designing measurement systems, and analyzing data, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to create meaningful KPIs and unlock valuable business insights.
So, let’s dive in and discover the key to measuring and achieving your desired outcomes with precision.
What are Key Performance Indicators?
Key Performance Indicators or KPIs, are quantifiable metrics used to measure and evaluate the performance of an organization, team, or individual in achieving specific business objectives.
These indicators are carefully selected to provide actionable insights into critical areas of performance, allowing businesses to monitor progress, identify strengths and weaknesses, and make informed decisions.
The primary purpose of KPIs is to align strategic goals with measurable outcomes. They serve as a means to track performance and assess whether targets are being met.
Why are Key Performance Indicators Important?
Using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) offers numerous benefits to organizations. Here are some of the key advantages of implementing KPIs in your business:
- Goal Alignment: KPIs ensure that all levels of the organization are aligned with strategic goals. By clearly defining and measuring progress towards these objectives, KPIs help create a unified focus and direction for the entire organization.
- Performance Measurement: KPIs provide a quantifiable way to measure performance and progress. They offer a clear view of how well specific goals and targets are being achieved, allowing for accurate assessment and comparison of performance over time.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: KPIs enable data-driven decision making by providing objective and relevant information. They help identify trends, patterns, and areas of improvement, allowing leaders to make informed decisions based on reliable metrics rather than subjective assessments.
- Focus and Prioritization: KPIs help organizations prioritize their efforts by identifying key areas of focus. By highlighting the most critical metrics, KPIs ensure that resources, time, and energy are directed towards activities that have the greatest impact on achieving strategic objectives.
- Performance Monitoring and Early Warning: KPIs serve as a monitoring tool, enabling organizations to proactively identify potential issues and take corrective action before they escalate. By setting thresholds or benchmarks for KPIs, businesses can receive early warnings of performance deviations and make timely adjustments.
- Accountability and Transparency: KPIs promote accountability within the organization. When individuals and teams have clear performance targets, they are more likely to take ownership of their responsibilities and be accountable for their results. KPIs also foster transparency by providing a shared set of metrics that can be easily communicated across the organization.
- Continuous Improvement: KPIs support a culture of continuous improvement by highlighting areas for enhancement. They help identify gaps, inefficiencies, and bottlenecks, prompting organizations to seek innovative solutions and refine processes to drive better performance.
- Performance Recognition and Incentives: KPIs can be used to recognize and reward high performance. By linking KPI achievements to performance-based incentives and recognition programs, organizations can motivate employees and teams to strive for excellence and align their efforts with strategic objectives.
Key characteristics of effective KPIs
Effective Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) possess several key characteristics that contribute to their usefulness and impact. When developing KPIs for your organization, consider the following characteristics to ensure their effectiveness:
- Relevance: Effective KPIs are directly aligned with the strategic objectives of the organization. They measure aspects of performance that are critical to achieving desired outcomes and provide insights into areas that significantly impact the success of the business.
- Measurability: KPIs should be measurable and quantifiable. They should be based on data that can be objectively collected, analyzed, and tracked over time. This allows for accurate and consistent measurement of performance and enables meaningful comparisons and analysis.
- Specificity: Well-defined KPIs are specific and clearly articulated. They should focus on a particular aspect of performance and provide a clear understanding of what is being measured. Vague or ambiguous KPIs can lead to confusion and hinder effective tracking and improvement efforts.
- Actionability: Effective KPIs drive action and provide insights that can be acted upon. They should highlight areas where improvement is needed and offer actionable information to guide decision-making and performance improvement efforts. Actionable KPIs empower individuals and teams to take targeted steps to enhance performance.
- Time-bound: KPIs should be time-bound, meaning they have a specific timeframe within which they are measured. This allows for tracking progress and assessing performance over a defined period. Time-bound KPIs also provide a sense of urgency and help establish clear deadlines for achieving targets.
- Alignment with benchmarks or targets: Effective KPIs are often set in relation to benchmarks or targets. They provide a reference point against which performance can be compared. Comparing actual performance to predetermined benchmarks or targets helps evaluate progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Reliable and Accessible Data: KPIs rely on accurate and reliable data to provide meaningful insights. It is important to ensure that the data used for KPI measurement is trustworthy, regularly updated, and easily accessible. Reliable data sources and robust data management systems contribute to the credibility and effectiveness of KPIs.
- Balance: A set of effective KPIs maintains a balance between different aspects of performance. They consider multiple dimensions such as financial, operational, customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and other relevant areas. A well-balanced set of KPIs provides a holistic view of performance and enables comprehensive evaluation.
Different types of Key Performance Indicators
There are various types of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), each focusing on different aspects of organizational performance. Here are some common types of KPIs that span different areas of business:
- Financial KPIs: These KPIs measure financial performance and help assess the organization’s profitability, revenue generation, cost management, and financial stability. Examples include revenue growth rate, gross profit margin, return on investment (ROI), and cash flow.
- Operational KPIs: Operational KPIs evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations. They focus on key processes, productivity, quality, and resource utilization. Examples include production cycle time, order fulfillment rate, customer complaints resolved, and inventory turnover.
- Customer KPIs: Customer-centric KPIs assess various aspects of customer satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement. They provide insights into customer behavior, preferences, and the overall customer experience. Examples include customer satisfaction score (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rate, and average order value.
- Sales and Marketing KPIs: These KPIs measure the effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts in generating leads, acquiring customers, and driving revenue. Examples include conversion rate, lead-to-opportunity ratio, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and marketing return on investment (ROI).
- Employee KPIs: Employee-focused KPIs evaluate individual and team performance, employee engagement, and development. They can include metrics such as employee satisfaction, training and development hours, employee turnover rate, and productivity per employee.
- Quality and Service KPIs: These KPIs assess the quality of products or services delivered by the organization. They measure aspects such as defect rate, service response time, customer complaints, and adherence to quality standards.
- Sustainability and Environmental KPIs: These KPIs focus on environmental and sustainability efforts within the organization. They evaluate metrics such as energy consumption, waste reduction, carbon footprint, and adherence to sustainability goals.
- Health and Safety KPIs: Health and safety KPIs monitor the organization’s commitment to maintaining a safe work environment. They can include metrics like accident frequency rate, near-miss incidents, compliance with safety regulations, and employee training hours on safety protocols.
Steps in Developing Key Performance Indicators
Here are seven essential steps that lead you to develop robust KPIs that drive performance, inform decision-making, and contribute to the achievement of your organizational objectives.
Step 1: Identify and Prioritize Strategic Goals
Begin by identifying the key strategic goals that will drive your organization’s success. These goals should be specific to your business and reflect what you aim to achieve within a defined timeframe. For example, increasing market share, expanding into new markets, improving customer satisfaction, or enhancing operational efficiency.
Ensure that your objectives align with your organization’s mission and vision statements. These statements define the purpose and long-term aspirations of your business. Aligning your objectives with them creates a sense of purpose and direction, ensuring that your KPIs contribute to the overall strategic direction of the organization.
Step 2: Selecting the Right KPIs
Once you have defined your business objectives, the next step is to identify the relevant metrics that will help measure progress and performance in relation to those objectives.
Break down each business objective into specific components or key focus areas. For example, if your objective is to increase customer satisfaction, relevant focus areas may include response time, complaint resolution rate, or customer retention.
Brainstorm a list of potential metrics that align with each focus area. Consider both quantitative and qualitative measures that provide insights into the specific aspect of performance you want to track.
For instance, if response time is a focus area, a relevant metric could be average response time to customer inquiries.
Step 3: Linking KPIs to strategic goals
Once you have identified the relevant metrics, the next step is to link them to your strategic goals. This linkage ensures that your KPIs directly contribute to the achievement of your overall strategic objectives.
Determine how each KPI directly relates to a specific strategic goal. Articulate how achieving the KPI will impact the progress towards the strategic objective. This connection helps create a clear line of sight between your KPIs and your broader business goals.
Ensure that each KPI aligns with only one or a few strategic goals. Avoid selecting KPIs that overlap or dilute the focus of your objectives. Each KPI should have a clear and direct relationship to a specific strategic goal, allowing for targeted measurement and improvement efforts.
Step 4: Establishing a data collection and management system
To effectively measure and track your KPIs, it’s important to establish a robust data collection and management system.
Identify the sources of data needed to measure each KPI. This may include internal systems, databases, surveys, customer feedback, or external sources. Ensure that the data sources are reliable and provide the necessary information for accurate measurement.
Define the processes and procedures for collecting data. Determine how and when data will be collected, who is responsible for data collection, and any necessary tools or technology required. Implement quality control measures to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Step 5: Defining measurement methods and frequency
Determine the most appropriate methods for measuring each KPI. This could involve quantitative analysis, surveys, qualitative assessments, or a combination of methods. Consider the nature of the KPI and the available data when selecting measurement methods.
Identify the specific metrics and formulas used to calculate quantitative KPIs. Determine the units of measurement and any necessary calculations or aggregations.
For KPIs that involve subjective or qualitative data, define the assessment criteria and rating scales. Establish guidelines to ensure consistency and objectivity in the assessment process.
Determine how often each KPI will be measured and reported. The frequency may vary depending on the nature of the KPI and the need for real-time or periodic tracking. Consider the availability of data and the desired level of granularity when determining measurement frequency.
Assign clear responsibilities for data collection, analysis, and reporting. Identify the individuals or teams responsible for collecting the data, analyzing the results, and ensuring data integrity. Foster collaboration and communication among the responsible parties to facilitate effective KPI management.
Step 6: Creating a KPI reporting framework
Develop a reporting framework that outlines the structure and content of your KPI reports. Consider the following elements:
Determine the format of your KPI reports, such as dashboards, visualizations, or written summaries. Choose a format that effectively communicates the key information and insights.
Define the structure of the report, including the KPIs to be included, supporting metrics, targets or benchmarks, and any contextual information or analysis. Ensure that the report provides a clear and concise overview of performance.
Step 7: Visualization techniques for effective communication
Utilize visualization techniques to enhance the communication of KPI data. Visualizations such as charts, graphs, and infographics can make complex data more understandable and engaging. Choose visualizations that best represent the data and highlight trends, patterns, and performance gaps.
Choose visualizations that effectively represent the KPI data and highlight the key insights. Consider bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, or heatmaps, depending on the nature of the data and the message you want to convey.
Ensure that the visualizations are easy to interpret and understand. Use clear labels, appropriate color schemes, and appropriate scaling to enhance clarity and readability.
Final Words
Knowing how to develop key performance indicators is important skill because KPIs are crucial to measure progress and success in organizations. By following the essential steps of defining business objectives, identifying relevant metrics, and linking KPIs to strategic goals, you can ensure that your KPIs are aligned with your organization’s mission and vision.
Remember, the journey of developing and implementing KPIs is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Regularly review and refine your KPIs to ensure their relevance and alignment with your evolving business needs. By leveraging the power of KPIs, you can gain valuable insights, track progress, make data-driven decisions, and foster a culture of continuous improvement, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and success for your organization
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

Nudge Theory in Change Management

How to Develop Change Management Strategy

7 Rs of Change Management

Insights from Engagedly’s State of AI in HRM, 2nd Edition Survey.
- Engagedly Blog
Performance Management
How to build a kpi system for performance reviews.

The People Strategy Leaders Podcast

Measuring employee’s performance is an inevitable part of assessing business health. Since employees are a business’ most valuable asset, it is imperative to ensure that individuals and teams achieve their full potential with adequate support and development opportunities. It is the key performance indicators (KPIs) that work as useful metrics to benchmark the progress. Put in the best KPIs in the business evaluation system to check employees’ effectiveness and level of productivity.
KPIs make everyone accountable for their performance. The KPI system helps employees measure their impact on business work, daily activities and how they affect the foundation of the role. Such a program contributes to the long-term success of the organization. KPI for performance evaluation would set the team and individual on the right track.
What do you understand about the Key Performance Indicator (KPI) and how to use it for reviews?
KPI is a way to quantify employee performance in an organization. The metrics are used to track employee productivity and to manage the team based on the requirements at work. It is critical to monitor and assess performance in a timely manner, but finding details about one’s duties proves to be a challenge.
This demands the use of the latest methods for developing KPIs for employees . Successful leaders should plan and adopt effective evaluation techniques for suitable results. Therefore, a lot of companies deploy KPI systems for performance reviews based on valuable insights. If you measure the value of employees with profit margins, it will give inaccurate and ambiguous results on productivity and performance.
Performance evaluation includes both qualitative and quantitative elements to get an appropriate outcome and includes more than just one’s past performance . However, one can get qualified data only by using KPIs to motivate a team. Once you find a person’s potency, you can assign tasks accordingly for the most effective results. The performance review will help in better understanding what motivates an employee and identifying weak points.
Using performance evaluation, pricing policy, project management, team management, and other elements allows identification of problems early on. However, KPIs help evaluate payroll operations when salaries of employees reflect the performance potential of an individual.
What metrics help measure employee performance?
KPIs alone cannot be used to evaluate an individual’s performance. Performance appraisals are based on both qualitative and quantitative feedback from managers, which is more than just productivity. An employee’s worth cannot be solely determined based on KPIs, and it extends beyond that.
Employee KPIs are high-level markers that show the level of employee productivity. It allows businesses to identify their potential and assign tasks to individuals or groups. This would help one focus on operational issues, having smooth workflow and resource availability.
1. Review the participation rate
Performance reviews are difficult to maintain regularly and take a lot of time. One of the primary benefits of deploying a people enabled platform is its flexibility and focus on user experience. Some of these are:
- Edit reviews for sick or absent employees
- Users can access and complete it on their own using its web version or app
- It saves drafts, allowing one to pick where they left
With better user experience, you have to encourage clients to set goals for work completion. Analyze how organizations can benefit from this performance management program.
2. Efficiency of HR process
Switching from the traditional paper-based review method to the latest user-enabled platform saves time for HR to process and report results. Meanwhile, managers and employees can participate in the review and use the platform easily. As a result, long-term goals can be achieved and in a timely fashion.
3. Quantity of feedback exchanged
As managers share real-time feedback with their employees or teams, it helps clarify expectations, share advice and celebrate achievements. Not all employees manage to get feedback once a week, though real-time feedback can help them improve at a greater scale.
It is not just a manager feedback that boosts engagement. Managers can help teams develop new habits. Management should set a feedback goal for better results. If giving continuous feedback is new to your company, set a goal to share feedback with at least one member of the team and slowly improve it. With this, track how often you give feedback and how it affects individuals and motivates the entire team.
4. Quality of feedback
A performance management tool can facilitate the feedback experience. It helps management learn how to give feedback to achieve the most effective results. Measure the effectiveness of feedback, and include surveys on how employees found it valuable and helpful. Set a goal and work to improve the quality of feedback based on the positive response.
5. Check on employee net promoter score (NPS)
If you wish to enhance employee engagement, focus on measuring feedback and plan for quarterly surveys. Prepare a set of questions and invite both positive and negative responses. Use the survey data to make the company a better place to work and help employees perform better.
Choosing and tracking KPIs
Are you unsure whether the company has deployed the appropriate KPI? Being a team leader, it is a common instinct to find out how the team is performing. Here, a positive KPI is enough as an indicator to show that you are sailing in the right direction. To pick the right KPIs to track performance and goals, you need to make sure they are related to the performance metrics.
- Is the goal quantifiable?
The performance metrics should be easy to evaluate and quantify. If you tell someone, ‘to be more positive’, it can be difficult to quantify. Instead, try setting goals based on KPIs that can be easily measured and objectively.
- Is the goal aligned with business objectives?
One should be careful when deciding on KPIs, as they should align with business objectives. If an objective is to offer customer satisfaction, KPI should also measure how much time it takes to resolve a problem raised by a customer.
- Can employees get a realistic impact from KPI measured?
The level of realistic impact for measuring KPIs mostly depends on the way a service is offered at the employee’s end. The solution depends on several factors, including how a problem can be resolved by a single person or whether it requires several steps.
- Is KPI relevant to a person’s role?
Not every employee should have the same metrics to measure the KPI, as it differs from one employee to another. When deciding on KPI for a team, it should be aligned with the role of each employee of the team.
To build an efficient KPI system, change the way of tracking elements and improve them. Try to create quarterly reports to track employees’ progress towards goals. It helps understand whether performance is declining, improved, or stabilized. Employees experiencing stagnant performance should seek new challenges and contribute effectively to business growth.
How to set organizational KPIs to assess performance?
Organizations should carefully choose KPIs to measure activity in the critical business areas. A satisfactory KPI for performance review should be built on customer surveys using the right data. The satisfaction score will help you decide how much to contribute to achieve the benchmark. No matter what the nature of KPIs are, they should be measurable, achievable, specific, relevant and time bound so that they give correct results. Measure metrics that are aligned with a business’ strategy and vision and help it reach its goals.
Use KPIs for development and recognition
If you want meaningful KPIs for performance reviews, keep the team motivated with the help of incentives and training. It is important to measure employee recognition and rewards based on KPIs.
For instance, if your goal is to attract new customers, KPI should be set to measure how many new customers you gain in a week. Based on this, build a performance system to reward employees effectively.
If you are using formal performance measures for managing performance, it should be accompanied by tips on effective leadership and inspiration for a team. Thus, KPIs can be used to measure any area of performance and should align with the strategic direction of the company.
KPI and performance management
Besides performance, managers must set objectives and targets that can be achieved by each individual and team. But how to measure performance and understand how much effort one puts into achieving goals? This is where performance management can help and understand who is working harder and who is not. Does the work to achieve the level that the organization requires maintaining? Key performance indicators help measure these by quantifying the performance level of an individual and a team. Check the goals and based the evaluation on the KPIs to get effective answers on each and work on the weak organizational areas.
What are the elements included in the KPI process?
The key elements of employee measurement for business success are:
- Describe the intended outcome
- Understand the alternative options to be taken
- Select the right measure for objectives
- Define the complex indices as required for business functions
- Set targets and path to achieve them smoothly
- Define and list the effective performance measures
How to develop KPIs for employee performance reviews?
No matter which industry you work in, managers look for competency in the right places. This is when managers will look at whether employees can meet goals, effectively contribute their part in a team, and apply critical thinking to ensure successful business operations. Although there are many key indicators, critical business operations should be the primary focus.
Colleagues who are working in a team actively participate and brainstorm ideas for the group. Taking part in different team projects, sharing ideas among team members and deciding on approaches often contribute to the success of the project.
Communication
An employee should know appropriate, accurate and professional communication in business and one should communicate, keeping in mind:
- Have the habit of concise and clear verbal communication
- One should be responsive to managers and colleagues
- Do timely follow-up via mail or for customer enquiry
- Try to articulate concepts and feedback accurately
Customer Service
No matter what your role is, you directly or indirectly help customers and, in any critical situation, employers will reach out to you for answers. Here, one should ensure they can handle the problem and not delay it, give timely responses to the customer, and offer adequate solutions to customers as required.
Track performance metrics, set goals, reduce turnover, and try to improve performance. By establishing these, it helps the team clearly understand where they stand and what it will take to reach the goals. Having clearly defined business goals will help set KPIs for thorough employee performance reviews.
Want to know how Engagedly can help you manage your employees better? Request a live demo from our experts!
Request A Demo
Srikant Chellappa is the Co-Founder and CEO at Engagedly and is a passionate entrepreneur and people leader. He is an author, producer/director of 6 feature films, a music album with his band Manchester Underground, and is the host of The People Strategy Leaders Podcast . He is currently working on his next book, Ikigai at the Workplace, which is slated for release in the fall of 2024.

How To Manage Your Non-Inclusive Manager?

How to Develop a Successful Communication Plan for Performance Management
The Culture Code: How Core Values Shape Thriving Workplaces
Privacy preference center, privacy preferences.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Are Your KPIs Really Measuring?
- Graham Kenny

Performance is about more than just numbers.
Management teams often switch off when reviewing KPIs. This may be because they’re overwhelmed by the slicing and dicing of the measures. They need to remind themselves that KPIs are about stakeholder relationships, how what you do affects what the other does to you, and that the metrics will not always be the same.
No CEO doubts the importance of measuring their company’s performance properly. Yet the executive teams I’ve assisted over more than 25 years generally struggle to engage with the challenge. As one CEO put it to me, “when we get to corporate KPIs their eyes glaze over.” Or, as another said “they [the managers] start looking for the exits.”
- Graham Kenny is the CEO of Strategic Factors and author of Strategy Discovery . He is a recognized expert in strategy and performance measurement who helps managers, executives, and boards create successful organizations in the private, public, and not-for-profit sectors. He has been a professor of management in universities in the U.S. and Canada.
Partner Center
Key performance indicators
Table of Contents
What is a kpi.
KPI stands for key performance indicators. This is a quantifiable measurement of performance over time for a specific activity that is tied to a company objective.
A key performance indicator can help you better understand your business’ financial and operational achievements, so you can see where you’re at and make improvements to your strategy.
Picture Robin Hood aiming for his archery target. Without the target, Robin Hood wouldn’t know where to aim his bow. But, with the target, he can measure exactly how far off he is from his goal, so he can adjust his aim, strength, or his bow.
The same is true for the KPIs in your business. They give you a clear marker of how you’re performing so you can understand if you’re in the right direction, or if you need to make strategic adjustments along the way.
A KPI provides your business with a target to shoot for, milestones to track your performance over time, and insights to help your organization's leaders make better decisions. From marketing to sales to finance and even HR, key performance indicators can help improve productivity, progress, and achievement across every area of your business.
What is KPI reporting?
KPI reporting is the business management practice of measuring, organizing, and analyzing a business’ most important key performance indicators.
KPI reports help business leaders identify strengths and weaknesses, optimize company performance, improve engagement, and reach strategic goals. Managers also use KPI reporting to analyze trends in specific departments or in the business as a whole to improve decision-making.
KPI reporting is typically presented visually in the form of an interactive dashboard. KPI dashboards give managers a quick overview of the essential data points associated with your specific key performance indicators.
KPI dashboards present your KPIs in an easily digestible format so managers can quickly analyze and extract the most crucial information to help them optimize their overall strategy.
How to measure KPI
If you’re going to be successful in your KPI tracking, then you need to build a proper KPI measurement framework, or use a KPI Tree Template . Here are six steps to setting a framework for your KPI measurement:
1. Determine your main goal(s)
The first step to measuring your KPIs is to first identify which KPIs you'll be tracking. To figure out your KPIs, you need to first determine the goal you and your team are working towards. For instance, the goal of a specific marketing campaign could be to generate $50,000 in revenue or bring in 50 leads. No matter what your goal is, we’ll use it to establish KPIs.
2. Establish primary KPIs
Now that you have your overall goal, it’s time to establish your primary KPIs. These are significant KPIs designed to measure the overall results of your campaign and whether it was a success or not. Some primary KPI examples include the amount of revenue generated by specific channels like email marketing or Facebook ads. Or, if your goal is brand awareness, it could be your overall reach or impressions on different social platforms.
3. Establish secondary KPIs
Next up, it’s time to establish secondary key performance indicators to further understand the success of your campaign. These could be three to five additional metrics that are important to your campaign but not necessarily your primary KPI. For instance, if your primary KPI is email revenue generated, secondary KPIs could include average order value or return customer rate.
4. Choose health metrics
Next, we’ll establish metrics that'll help you understand the overall health of your campaign, rather than whether or not you've reached your primary goal. Following our email marketing KPIs, health metrics could include metrics like open rate, click rate, and total email opens.
5. Establish specific KPI targets
Now that you’ve chosen the KPIs that you’ll track, it’s time to determine the exact numerical target for each KPI. The numbers you establish should be realistic and measurable numbers to help you stay on track. Simply stating you want to earn more revenue from email marketing isn’t enough. Get specific. State that you want to generate $50,000 from the campaign, with $20,000 of that coming from email. If your average order value (AOV) is $50, set a goal for your AOV to be $60. Aim for a 40% email open rate if you usually get 35%.
By setting specific, measurable KPIs, you’re much more likely to achieve them or at least come close.
6. Set up benchmarks
Finally, you need to set up benchmarks. Remember to look at past campaign performance to better understand what a typical benchmark for KPIs is. But, don’t stop there. Look at competitors. Look at others in your industry or similar businesses in other industries. By understanding where you’re at relative to your competitors or your own past performance, it'll help you determine whether you’re on the right track or not.
Benefits of tracking KPIs
KPIs are a critical part of any business strategy to ensure you’re staying on track and improving performance. Here are a few reasons why you should be tracking KPIs.
Measure performance
First off, KPIs help you measure your performance. If you’re just “winging it” when you’re working on a project or a campaign, how will you know whether or not you’re a success?
Without KPIs, you’ll be driving blind, not knowing what’s improving or worse yet — harming — your organization.
Tracking KPIs can help you measure your progress — or lack thereof — toward crucial business goals.
Improve employee morale and engagement
A business is nothing without people, and a business is almost as good as nothing if people aren’t engaged. One key path to improving engagement at work is by establishing KPIs.
You may think that pressuring your team to hit certain targets will make them dislike their job. But, the opposite is true. People crave growth. Establishing KPIs for individuals and different departments is a great way to get your team engaged.
Remember to align your KPIs with organizational goals and goals for your department. The better you can tie your KPIs to a deeper, purposeful goal, the more engaged your employees will be and the greater company morale will be overall.
Improve decision-making
KPIs provide leaders with key insights into their organization and department. They offer more than just numbers on a page or a screen. They offer valuable information that can help you understand what specific points of action are improving your business and what ones are hurting it.
Instead of just making decisions based on gut feelings, you can use KPIs to make data-informed decisions that will improve your odds of success.
Examples of KPIs
Curious to know what the most commonly tracked KPIs are?
Here are a few examples of KPIs, broken down by different departments that you can use as a baseline to establish your own key performance indicators:
Revenue by channel
Customer satisfaction
Conversion rates
Marketing qualified leads (MQLs)
Return on investment (ROI)
Return on advertising spend (ROAS)
Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
Total sales generated
Sales volume by location
Sales qualified leads (SQLs)
New inbound leads
New qualified opportunities
Total pipeline value
Average order value
Operating profit margin
Gross profit margin
Net profit margin
Operating expense ratio
Working capital ratio
Return on investment
Customer Service
Average response time
First contact resolution rate
Cost per conversation
Customer effort score
Most active support agents
What makes for an effective KPI?
Now that you know a few different types of KPIs you can track broken down by department, it’s time to figure out what makes for an effective KPI so you know how you can craft yours the right way.
First and foremost, the KPIs you track should be relevant to your role, team, department, and business. It should be connected with your team and organization’s overall business goals and mission.
For example, let’s say your company is aiming to increase annual recurring revenue (ARR) by 30% at the end of the year. If you’re on the marketing team, you might consider tracking conversion rates as this directly aligns with revenue.
KPIs need to be measurable. If you don’t know how to measure it, then you need to change it or throw it out. When you set up KPIs, ask yourself, ‘What am I trying to achieve? What is my desired end result?’
You need to make sure you don’t just set a number, but also a date. By setting a deadline, you will have a clear yes or no on whether you hit your KPI goals or not.
Your KPIs can’t be vague, and they can’t be passive. You need to set KPIs that can be achieved by taking specific actions. Once you have your KPI, it should be relatively straightforward to make an action plan broken down into smaller goals to achieve success.
Finally, your KPIs need to be simple. Don’t get too complicated, and don’t track too many. You don’t need to track every single possible KPI. Depending on your overall goals, you should only stick to a few primary KPIs and potentially some secondary ones.
What’s the difference between KPIs and OKRs?
So, how are KPIs different from OKRs? Are they the same? Do you choose one or the other?
Simply put, OKRs and KPIs work together. However, they serve different purposes.
While key performance indicators measure performance against specific targets, you can create OKRs, or objectives and key results, to achieve goals within a specific period of time that align with an organization's vision.
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs)
Objectives and key results are broken down into two parts.
Think of objectives as where you want to go. For example, an organization may decide they want to evolve their brand image from cheap to premium. This is an objective.
Key results are how you’re going to achieve your strategic objectives. These are measurable metrics to track your progress. For instance, if you’re trying to become a more premium brand, one key result may be increasing your average product price from $60 to $100. Another one may be upgrading the materials used to make your products from a $10 manufacturing cost per product to higher quality manufacturing for $20 per product.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The way KPIs fit into an OKR strategy is one step lower. Think of Objectives as the bird’s eye view. Key results are skyscraper buildings. Key performance indicators are the foundation on which key results lay.
For instance, a key performance indicator aligned with the objective to become a premium brand and increase your average product price might be to track your average order value (AOV). In this example, if you raise your price point, you’ll want to track if the AOV is aligning with it and by how much. Perhaps the average order value isn’t rising even though you’ve raised your prices.
Another KPI you could track is your conversion rate. Since you have started raising your prices, are your conversion rates dropping? They’re likely going to dip down to some degree. If it’s too much, perhaps you moved the price up too high too quickly.
Collaboratively set and track your KPIs
With Miro, teams can collaboratively define, visualize, and monitor KPIs in real-time. Whether you need to track sales targets, project milestones, or customer satisfaction metrics, Miro makes it easy to document your KPIs in one shared space, fostering transparency and accountability. Sign up for free to get started!
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.

How to Set Key Performance Indicators for Employees (+7 Examples)
- Performance
Types of KPIs
4 steps to setting kpis for employees, identifying the right kpis for your employees (+7 examples), marketing and sales, human resources, tracking and measuring performance, effectively manage performance with omni.
Measurement is an important tool for management as it allows you to assess the effectiveness of your (and your team’s) work, showcase the value of that work, efficiently manage resources, and focus on improving performance. Setting key performance indicators for employees provides a framework to easily track, measure, and report on their performance.
Here, we’ll explore how to identify, set, and measure key performance indicators for employees.
Defining KPIs and Their Benefits
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are a type of measure that is used to evaluate the performance of an organization against its strategic objectives. Key performance indicators for employees, much like performance review SMART goals , help every area of your business move forward at the strategic level by providing goals and targets for your team to work towards. They are also milestones to measure progress, and insights that help employees across an organization to make smarter decisions.
In sum, KPIs can help employees to stay focused, motivated, and engaged while providing clear direction for their professional growth and development.
KPIs and SMART goals are often used as interchangeable terms which can cause confusion and misguide managers. It’s important to understand the difference between the two to effectively implement them into your management efforts.

Key performance indicators for employees come in many forms. While some are used to measure monthly progress against a goal, others have a longer-term focus. Regardless of their differences, all KPIs have one thing in common: they’re tied to strategic goals. Here’s an overview of some of the most common types of KPIs.
- Strategic: Think of these as “big-picture” key performance indicators for employees. Overall, strategic KPIs monitor organizational goals and can include things like return on investment, revenue, and market share. These are the KPIs that executives typically look to determine how the organization is doing at any given time.
- Operational: These KPIs typically measure performance in a shorter time frame, and are focused on organizational processes and efficiencies such as customer response time, average monthly transportation costs or cost per acquisition.
- Leading vs Lagging: Leading KPIs can help predict outcomes whereas lagging KPIs track what has already happened. Organizations use a mix of both to ensure they’re tracking what’s most important.
One of the most important steps in setting key performance indicators for employees is to ensure you’re only measuring what will help you reach your business goals. To help determine what KPIs are right for your employees, keep in mind the components that make up effective KPIs.

Setting key performance indicators for employees can be achieved by following these 4 steps:
- Determine goals: Talk to your employees to understand and align on the goals they’d like to achieve, and discuss how you can use KPIs to measure their progress
- Tie them to strategic objectives: Consider the objectives of the employees department as well as the company as a whole. Every key performance indicator should tie directly back to your overall business goals.
- Write SMART KPIs: The most effective KPIs follow the SMART goal format . Make sure they’re Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Time-Bound.
- Plan to iterate: As your business and customers change, you may need to revise your key performance indicators. Perhaps certain ones are no longer relevant, or you need to adjust based on performance. Be sure you have a plan in place to evaluate and make changes to key performance indicators when necessary.
Omni Tip: Starting a KPI with a verb tells you what needs to be done. Assigning a value ensures your KPI is measurable, and a timeline will do wonders for staying timely on your progress.
Now that you know what makes a good KPI, it’s important to understand how to choose the right key performance indicators for employees. KPIs will vary employee to employee depending on their department, position, and overall goals.
First, let’s assess the steps to identifying the right key performance indicators for employees:
- Define Business Goals: Start by defining the business goals you want to achieve. This will help you identify the KPIs that are most relevant and valuable for measuring progress towards those goals.
- Determine Critical Success Factors: Identify the critical success factors that are necessary for achieving those goals. For example, if your goal is to increase revenue, a critical success factor might be to increase customer acquisition rates.
- Brainstorm: Once you have identified critical success factors, brainstorm potential KPIs that could be used to measure progress towards those factors. Consider both quantitative and qualitative metrics.
- Prioritize: Evaluate and prioritize the KPIs based on their relevance, importance, and ability to drive progress towards the critical success factors.
- Communicate: Communicate the KPIs clearly to employees, providing guidance on how they will be measured and how they relate to business goals. Encourage employees to take ownership of their performance and track their progress towards achieving the KPIs.
By following these steps, you can identify the right KPIs for your employees, which can help drive performance, improve productivity, and achieve business objectives.
Now, let’s look at some KPIs as they apply to different areas of a business. Here are 7 examples of key performance indicators for employees that cover financials, marketing and sales, and HR.
Gross and net profit margin
Setting profit KPIs helps you keep your business on track financially, and allows you to course correct early on to save money and manage your financial goals. The key difference in measuring profit margins is between ‘gross’ and ‘net’ profits.
- Gross profit margins calculate the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting only the cost of goods sold (COGS). It is calculated by subtracting COGS from total revenue and then dividing the result by total revenue.
Example KPI: Keep gross profit margins at 40% for the year.
- Net profit margins calculate the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after deducting all expenses, including COGS, operating expenses, and taxes. It is calculated by dividing net income by total revenue.
Example KPI: Keep net profit margins at 20% for the year.
Inventory turnover
Inventory turnover measures how quickly your company sells and replaces its inventory during a specific period. A higher your inventory turnover ratio, the more efficient you are at managing inventory by selling your products quickly and replacing them with new inventory. Inventory turnover is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory value.
Example KPI: Maintain an inventory turnover ratio of 4 during the next production cycle.
Lead conversion rate
Measuring lead conversion rates allows you to assess the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. Let’s look at how to calculate your website lead conversion rate, the percentage of website visitors who become leads by filling out a form or contacting your company. It is calculated by dividing the number of leads generated by the number of website visitors and multiplying the result by 100.
Example KPI: Maintain a website lead conversion rate of 5% until the new website launch.
Customer lifetime value
Your average customer lifetime value (CLV) measures the average revenue you can expect to generate from a single customer over the course of your relationship. It is calculated by multiplying the average purchase value by the average purchase frequency rate and multiplying the result by the average customer lifespan. A high average CLV indicates you company have loyal customers who are likely to continue making purchases in the future.
For example, if the average purchase value is S$100, the average purchase frequency rate is twice per year, and the average customer lifespan is 5 years, the average CLV would be S$1,000.
Example KPI: Maintain an average CLV of S$1,000 each month.
Employee satisfaction There are many ways to determine employee satisfaction. One easy indicator is by employee turnover rate, the rate at which employees leave your company. It is calculated by dividing the number of employees who leave by the total number of employees and multiplying the result by 100. A low employee turnover rate indicates that employees are satisfied with their work and are less likely to leave the organization.
Example KPI: Maintain an employee turnover rate of 10% or less each quarter.
Employee engagement
Employee engagement scores help HR teams measure the level at which your employees are engaged with their work and the overall company. Typically, this is measured through data gathered from employee surveys. Once this data is collected, the score is calculated by averaging the responses among participants. A high score indicates your employees are emotionally invested and likely to excel at their job responsibilities.
Example KPI: Achieve and maintain an employee engagement score of 3.5 out of 5 until the next employee performance review cycle .

KPI tracking, the monitoring of changes in KPI trends over a specific time period to understand how your business is performing, helps you keep track of the health and success of your business.
To track and measure key performance indicators for employees performance, capture the necessary data for each KPI and convert it into useful metrics, then follow up with those elements by tracking and monitoring them over time.
Effectively tracking and measuring the performance of KPIs also allows you to measure the overall progress of your teams, provides opportunities to make real-time adjustments to stay on track, and consistently analyzes trends.
Setting key performance indicators for employees requires strategic input and consideration from managers, however the tracking and gathering of data can become yet another time-consuming administrative task. Omni helps you track, analyze and gain actionable insights from performance data through an automated and digitized platform. Easily and quickly gather the data you need so you can spend more time on the strategic planning necessary to drive business outcomes.
To learn more about how Omni can automate and improve your performance tracking practices, schedule a demo with our team today.

- Global HR Insights
- 10 min read

Get started today!
More Like this
Kpi meaning + 27 examples of key performance indicators.
As your organization begins to sketch out what your strategic plan might look like, it’s likely to come to your attention that you’ll need to gain consensus around what your key performance indicators will be and how they will impact your organization. If you haven’t thought much about your KPIs yet, that’s okay. We can help!
We’ve compiled a complete guide that includes an overview of what makes a good KPI, the benefits of good key performance indicators, and a list of KPI examples [organized by department and industry] for your reference as you run your strategic planning process to build your organization’s strategic plan and goals.

Video Transcript – How to Write KPIs
Hi, my name is Erica Olsen. Today’s whiteboard video is on key performance indicators, or KPIs for short. These are those things that are associated with either goals or objectives, whatever you’re calling them, those elements of your plan that are the expressions of what you want to achieve by when those quantifiable outcome-based statements.
So KPI’s answer the quantifiable piece of your goals and objectives. They come in three different flavors. So we’ll talk about that in just a minute. But before we do, putting great measures together and making sure they work well for you, you need to have these four attributes. And before I talk about those four attributes, so I just want to say the reason they need to work well for you is because KPIs are the heartbeat of your performance management process. They tell you whether you’re making progress, and ultimately, we want to make progress against our strategy. So KPIs are the thing that do that for us. So you’re going to live with them a lot. So let’s make sure they’re really good.
Okay, so the four things you need to have in order to make sure your these measures work for you.
Our number one is your measure. So the measure is the verbal expression very simply, in words, what are we measuring, which is fairly straightforward. The tricky thing is, is we need to be as expressive as we possibly can with our measures. So number of new customers, that’s fine. There’s nothing wrong with that. But a little bit advanced or a little bit more expressive, would be number of new customers this year, or number of new customers for a certain product or a certain service. So what is it is it? Yeah, so it is, so be really clear. And when it comes to measuring it on a monthly basis, you’re gonna want to be as clear as possible. So number of new customers, let’s say this year,
Number two, is our target, or target is the numeric value that we want to achieve. So a couple of things that are important about this is, the target needs to be apples to apples with when the goal date is set, or the due date is set. So we want to achieve 1000 new customers by the end of the year. This is your time frame. So the due date in the target works hand in hand. The other thing is the measure and the target need to work hand in hand. So it’s a number. So this is a number, this is a percentage, this is a percentage, you get the idea.
Third thing, we actually run a report on this data. So where is it coming from? Be clear about what the source is. Most organizations have all sorts of data sources, fragmented systems. So making sure you identify where this data is coming from will save you a lot of time.
And then frequency. So how often are you going to be reporting on this KPI, ideally, you’re running monthly strategy reviews to report on the progress of your plan, at least monthly, in which case we’d like to see monthly KPIs. So you got to be able to pull the data monthly in order to make that happen. That’s not always possible. But let’s try to get there. Certainly some organizations are weekly and others are daily, monthly is a good place to start. So frequency. Great.
So now we know the components that we need to have in place in order to have our KPIs. Here are some different types of KPIs that you might think about as you’re putting your plan together.
So there are just straight up raw numbers, I call these widget counting, there’s nothing wrong with widget counting, they don’t necessarily tell a story. And I’ll talk about how to make this tell a story in a minute. But this is just simply widget counting number of things.
The second thing is progress. So this is really often used, it’s great. We use this, which is expressed as percent complete percent complete of the goal, percent completed a project, whatever it might be, it’s a project type measure. It’s a good measure, if if you don’t have quantifiable measures, or you can’t get the data, and you just want to track the performance of the goal as it relates to action items being completed under it.
The third type of indicator is a Change Type Indicator, like percent increase in sales, making this better would be percent increase in sales compared to last year. And the idea is 22%. So you can see how that starts to be more expressive, and work with the target. So this serves to tell a little bit more of a story than this one does, right? And if you want to actually make your widget counting measures tell more of a story like this one does, you might change something like this to read percentage of new customers acquired compared to same time last year. So that’s an example.
Okay, so now we know what we have to have in place and kind of different types of measures to get our ideas flowing. Let’s talk about one thing that you might take your measure writing to the next level and that is think about the fact that there are leading and lagging measures so are leading and lagging indicators. So percent increase in sales or sales is a lagging indicator it occurred as an outcome. If you want to make sure that you’re on track ACC, you might have a KPI in place, which is telling us whether we’re going to hit that increase such as your pipeline, maybe number of leads, or the size of your pipeline. So we don’t want to over rotate on this necessarily, but we do want to make sure we have a combination of leading and lagging measures when we’re looking at our performance on a monthly basis.
So with that, that’s all we have for today. Hopefully you have what you need to write great KPIs for your organization. Happy strategizing. And don’t forget, subscribe to our channel.
What is a Key Performance Indicator KPI — KPI Definition
Key performance indicators, also called KPIs, are the elements of your organization’s plan that express the quantitative outcomes you seek and how you will measure success. In other words, they tell you what you want to achieve and by when.
They are the qualitative, quantifiable, outcome-based statements you’ll use to measure progress and determine if you’re on track to meet your goals or objectives. Good plans use 5-7 KPIs to manage and track their progress against goals.

DOWNLOAD THE FREE KPI GUIDE
KPI Meaning, and Why Do You Need Them?
Key performance indicators are intended to create a holistic picture of how your organization is performing against its intended targets, organizational goals, business goals, or objectives. A great key performance indicator should accomplish all the following:
- Outline and measure your organization’s most important set of outputs.
- Work as the heartbeat of your performance management process and confirm whether progress is being made against your strategy.
- Represent the key elements of your strategic plan that express what you want to achieve by when.
- Measure the quantifiable components of your goals and objectives.
- Measure the most important leading and lagging measures in your organization.
The Five Elements of a KPI
These are the heartbeat of your performance management process and must work well! Your plan’s strategic KPIs tell you whether you’re making progress or how far you are from reaching your goals. Ultimately, you want to make progress against your strategy. You’ll live with these KPIs for at least the quarter (preferably the year), so make sure they’re valuable!
Great strategies track the progress of core elements of the plan. Each key performance indicator needs to include the following elements:
- A Measure: Every KPI must have a measure. The best ones have more specific or expressive measures.
- A Target: Every KPI needs to have a target that matches your measure and the period of your goal. These are generally a numeric values you’re seeking to achieve.
- A Data Source: Each of these needs to have a clearly defined data source so there is no gray area in measuring and tracking each.
- Reporting Frequency: Different measures may have different reporting needs, but a good rule to follow is to report on them at least monthly.
- Owner: While this isn’t a mandatory aspect of your KPI statement, setting expectations of who will take care of tracking, reporting, and refining specific KPIs is helpful to your overall organizational plan.

Indicators vs. Key Performance Indicators
An indicator is a general term that describes a business’s performance metrics.
There can be several types of indicators a company may track, but not all indicators are KPIs, especially if they don’t tie into an organization’s overall strategic plan or objectives, which is a MUST!
Key Performance Indicators
On the other hand, a key performance indicator is a very specific indicator that measures an organization’s progress toward a specific company-wide goal or objective. We typically recommend you narrow down the KPIs your organization tracks to no more than 7. When you track too many goals, it can get daunting and confusing.
Pro Tip : You should only track the best and most valuable indicators that tie to your organization’s long-term strategic goals and direction.
Benefits of Good Key Performance Indicators
What benefits do key performance indicators have on your strategic plan, and on your organization as a whole? A lot of benefits, actually! They are extremely important to the success of your strategic plan as they help you track progress of your goals. Implementing them correctly is critical to success.
- Benefit #1: They provide clarity and focus to your strategic plan by measuring progress and aligning your team’s efforts to the organization’s objectives. They also show your measurable progress over time and create ways to track your organization’s continued improvement.
- Benefit #2: Key performance indicators create a way to communicate a shared understanding of success. They give your team a shared understanding of what’s important to achieve your long-term vision and create a shared language to express your progress.
- Benefit #3: They provide signposts and triggers to help you identify when to act. A good balance of leading and lagging key performance indicators allow you to see the early warning signs when things are going well, or when it’s time to act.

How to Develop KPIs
We’ve covered this extensively in our How to Identify Key Performance Indicators post. But, here’s a really quick recap:
Step 1: Identify Measures that Contribute Directly to Your Annual Organization-wide Objectives
Ensure you select measures that can be directly used to quantify your most important annual objectives.
PRO TIP: It doesn’t matter what plan structure you’re using – balanced scorecard, OKRs, or any other framework – the right KPIs for every objective will help you measure if you’re moving in the right direction.
Step 2: Evaluate the Quality of Your Core Performance Indicators
Select a balance of leading and lagging indicators (which we define later in the article) that are quantifiable and move your organization forward. Always ensure you have relevant KPIs. Having the right key performance indicators makes a world of difference!
Step 3: Assign Ownership
Every key performance indicator needs ownership! It’s just that simple.
Step 4: Monitor and Report with Consistency
Whatever you do, don’t just set and forget your goals. We see it occasionally that people will select measures and not track them, but what’s the point of that? Be consistent. We recommend selecting measures that can be reported upon at least monthly.
The 3 Common Types of KPIs to Reference as You Build Your Metrics
Key performance indicators answer the quantifiable piece of your goals and objectives . They come in three different flavors. Now that you know the components of great key performance indicators, here are some different ones that you might think about as you’re putting your plan together:
Broad Number Measures
The first type of KPI is what we like to call broad number measures. These are the ones that essentially count something. An example is counting the number of products sold or the number of visits to a webpage.
PRO TIP: There is nothing wrong with these, but they don’t tell a story. Great measures help you create a clear picture of what is going on in your organization. So, using only broad ones won’t help create a narrative.
Progress Measures
Progress key performance indicators are used to help measure the progress of outcomes . This is most commonly known as the “percent complete” KPI, which is helpful in measuring the progress of completing a goal or project. These are best when quantifiable outcomes are difficult to track, or you can’t get specific data.
PRO TIP: Progress KPIs are great, but your KPI stack needs to include some easily quantifiable measures. We recommend using a mixture of progress KPIs and other types that have clear targets and data sources.
Change Measures
The final type of KPI is a change indicator. These are used to measure the quantifiable change in a metric or measure. An example would be, “X% increase in sales.” It adds a change measure to a quantifiable target and is usually measured as a percentage increase in a given period of time.
The more specific change measures are, the easier they are to understand. A better iteration of the example above would be “22% increase in sales over last year, which represents an xyz lift in net-new business.” More expressive measures are better.
PRO TIP: Change measures are good for helping create a clear narrative . It helps explain where you’re going instead of just a simple target.
Leading KPIs vs Lagging KPIs
Part of creating a holistic picture of your organization’s progress is looking at different types of measures, like a combination of leading and lagging indicators. Using a mixture of both allows you to monitor progress and early warning signs closely when your plan is under or over-performing (leading indicator) and you have a good hold on how that performance will impact your business down the road (lagging indicator). Here’s a deep dive and best practices on using leading versus lagging indicators:
Leading Indicator
We often refer to these metrics as the measures that tell you how your business might/will perform in the future. They are the warning buoys you put out in the water to let you know when something is going well and when something isn’t.
For example, a leading KPI for an organization might be the cost to deliver a good/service. If the cost of labor increases, it will give you a leading indicator that you will see an impact on net profit or inventory cost.
Another example of a leading indicator might be how well your website is ranking or how well your advertising is performing. If your website is performing well, it might be a leading indicator that your sales team will have an increase in qualified leads and contracts signed.
Lagging Indicator
A lagging indicator refers to past developments and effects. This reflects the past outcomes of your measure. So, it lags behind the performance of your leading indicators.
An example of a lagging indicator is EBITA. It reflects your earnings for a past date. That lagging indicator may have been influenced by leading indicators like the cost of labor/materials.
Balancing Leading and Lagging Indicators
If you want to ensure that you’re on track, you might have a KPI in place telling you whether you will hit that increase, such as your lead pipeline. We don’t want to over-rotate on this, but as part of a holistic, agile plan, we recommend outlining 5-7 key performance metrics or indicators in your plan that show a mix of leading and lagging indicators. .
Having a mixture of both gives you both a look-back and a look-forward as you measure the success of your plan and business health. A balanced set of KPIs also gives you the data and business intelligence you need for making decision making and strategic focus. We also recommend identifying and committing to tracking and managing the same KPIs for about a year, with regular monthly or quarterly reporting cadence, to create consistency in data and reporting.

27 KPI Examples
Sales key performance indicators.
- Number of contracts signed per quarter
- Dollar value for new contracts signed per period
- Number of qualified leads per month
- Number of engaged qualified leads in the sales funnel
- Hours of resources spent on sales follow up
- Average time for conversion
- Net sales – dollar or percentage growth
- New sales revenue
- Growth rate
- Customer acquisition count
- Lead conversion rate
- Average sales cycle
Increase the number of contracts signed by 10% each quarter.
- Measure: Number of contracts signed per quarter
- Target: Increase number of new contracts signed by 10% each quarter
- Data Source: CRM system
- Reporting Frequency: Weekly
- *Owner: Sales Team
- Due Date: Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4
Increase the value of new contracts by $300,000 per quarter this year.
- Measure: Dollar value for new contracts signed per period
- Data Source: Hubspot Sales Funnel
- Reporting Frequency: Monthly
- *Owner: VP of Sales
Increase the close rate to 30% from 20% by the end of the year.
- Measure: Close rate – number of closed contracts/sales qualified leads
- Target: Increase close rate from 20% to 30%
- *Owner: Director of Sales
- Due Date: December 31, 2023
Increase the number of weekly engaged qualified leads in the sales from 50 to 75 by the end of FY23.
- Measure: Number of engaged qualified leads in sales funnel
- Target: 50 to 75 by end of FY2023
- Data Source: Marketing and Sales CRM
- *Owner: Head of Sales
Decrease time to conversion from 60 to 45 days by Q3 2023.
- Measure: Average time for conversion
- Target: 60 days to 45 days
- Due Date: Q3 2023
Increase number of closed contracts by 2 contracts/week in 2023.
- Measure: Number of closed contracts
- Target: Increase closed contracts a week from 4 to 6
- Data Source: Sales Pipeline
- *Owner: Sales and Marketing Team
Examples of KPIs for Financial
- Growth in revenue
- Net profit margin
- Gross profit margin
- Operational cash flow
- Current accounts receivables
- Operating expenses
- Average cost of goods or services
- Average account lifetime total value
Financial KPIs as SMART Annual Goals
Grow top-line revenue by 10% by the end of 2023.
- Measure: Revenue growth
- Target: 10% growt
- Data Source: Quickbooks
- *Owner: Finance and Operations Team
- Due Date: By the end 2023
Increase gross profit margin by 12% by the end of 2023.
- Measure: Percentage growth of net profit margin
- Target: 12% net profit margin increase
- Data Source: Financial statements
- *Owner: Accounting Department
Increase net profit margin from 32% to 40% by the end of 2023.
- Measure: Gross profit margin in percentage
- Target: Increase gross profit margin from 32% to 40% by the end of 2023
- Data Source: CRM and Quickbooks
- *Owner: CFO
Maintain $5M operating cash flow for FY2023.
- Measure: Dollar amount of operational cash flow
- Target: $5M average
- Data Source: P&L
- Due Date: By the end FY2023
Collect 95% of account receivables within 60 days in 2023.
- Measure: Accounts collected within 60 days
- Target: 95% in 2023
- Data Source: Finance
- Due Date: End of 2023
Examples of Customer Service KPIs
- Number of customers retained/customer retention
- Customer service response time
- Percentage of market share
- Net promotor score
Customer KPIs in a SMART Framework for Annual Goals
90% of current customer monthly subscriptions during FY2023.
- Measure: Number of customers retained
- Target: Retain 90% percent of monthly subscription customers in FY2023
- Data Source: CRM software
- *Owner: Director of Client Operations
Increase market share by 5% by the end of 2023.
- Measure: Percentage of market share
- Target: Increase market share from 25%-30% by the end of 2023
- Data Source: Market research reports
- Reporting Frequency: Quarterly
- *Owner: Head of Marketing
Increase NPS score by 9 points in 2023.
- Measure: Net Promoter Score
- Target: Achieve a 9-point NPS increase over FY2023
- Data Source: Customer surveys
- *Owner: COO
Achieve a weekly ticket close rate of 85% by the end of FY2023.
- Measure: Average ticket/support resolution time
- Target: Achieve a weekly ticket close rate of 85%
- Data Source: Customer support data
- *Owner: Customer Support Team
Examples of KPIs for Operations
- Order fulfillment time
- Time to market
- Employee satisfaction rating
- Employee churn rate
- Inventory turnover
- Total number of units produced or on-hand
- Resource utilization
Operational KPIs as SMART Annual Goals
Average 3 days maximum order fill time by the end of Q3 2023.
- Measure: Order fulfilment time
- Target: Average maximum of 3 days
- Data Source: Order management software
- *Owner: Shipping Manager
Achieve an average SaaS project time-to-market of 4 weeks per feature in 2023.
- Measure: Average time to market
- Target: 4 weeks per feature
- Data Source: Product development and launch data
- *Owner: Product Development Team
Earn a minimum score of 80% employee satisfaction survey over the next year.
- Measure: Employee satisfaction rating
- Target: Earn a minimum score of 80% employee
- Data Source: Employee satisfaction survey and feedback
Maintain a maximum of 10% employee churn rate over the next year.
- Measure: Employee churn rate
- Target: Maintain a maximum of 10% employee churn rate over the next year
- Data Source: Human resources and payroll data
- *Owner: Human Resources
Achieve a minimum ratio of 5-6 inventory turnover in 2023.
- Measure: Inventory turnover ratio
- Target: Minimum ratio of 5-6
- Data Source: Inventory management software
- *Owner: perations Department
Marketing KPIs
- Monthly website traffic
- Number of marketing qualified leads
- Conversion rate for call-to-action content
- Keywords in top 10 search engine results/organic search
- Blog articles published this month
- E-Books published this month
- Marketing campaign performance
- Customer acquisition cost
- Landing page conversion rate
Marketing KPIs as SMART Annual Goals
Achieve a minimum of 10% increase in monthly website traffic over the next year.
- Measure: Monthly website traffic
- Target: 10% increase in monthly website
- Data Source: Google analytics
- *Owner: Marketing Manager
Generate a minimum of 200 qualified leads per month in 2023.
- Measure: Number of marketing qualified leads
- Target: 200 qualified leads per month
- Data Source: Hubspot
Achieve a minimum of 10% conversion rate for on-page CTAs by end of Q3 2023.
- Measure: Conversion rate on service pages
- Target: 10%
- Due Date: End of Q3, 2023
Achieve a minimum of 20 high-intent keywords in the top 10 search engine results over the next year.
- Measure: Keywords in top 10 search engine results
- Target: 20 keywords
- Data Source: SEM Rush data
- *Owner: SEO Manager
Publish a minimum of 4 blog articles per month to earn new leads in 2023.
- Measure: Blog articles
- Target: 4 per month
- Data Source: CMS
- *Owner: Content Marketing Manager
- Due Date: December 2023
Publish at least 2 e-books per quarter in 2023 to create new marketing-qualified leads.
- Measure: E-Books published
- Target: 2 per quarter
- Data Source: Content management system
Bonus: +40 Extra KPI Examples
Supply chain example key performance indicators.
- Number of on-time deliveries
- Inventory carry rate
- Months of supply on hand
- Inventory-to-sales Ratio (ISR)
- Carrying cost of inventory
- Inventory turnover rate
- Perfect order rate
- Inventory accuracy
Healthcare Example Key Performance Indicators
- Bed or room turnover
- Average patient wait time
- Average treatment charge
- Average insurance claim cost
- Medical error rate
- Patient-to-staff ratio
- Medication errors
- Average emergency room wait times
- Average insurance processing time
- Billing code error rates
- Average hospital stay
- Patient satisfaction rate
Human Resource Example Key Performance Indicators
- Organization headcount
- Average number of job vacancies
- Applications received per job vacancy
- Job offer acceptance rate
- Cost per new hire
- Average salary
- Average employee satisfaction
- Employee turnover rate
- New hire training Effectiveness
- Employee engagement score
Social Media Example Key Performance Indicators
- Average engagement
- % Growth in following
- Traffic conversions
- Social interactions
- Website traffic from social media
- Number of post shares
- Social visitor conversion rates
- Issues resolved using social channel
- Social media engagement
Conclusion: Keeping a Pulse on Your Plan
With the foundational knowledge of the KPI anatomy and a few example starting points, it’s important you build out these metrics with detailed and specific data sources so you can truly evaluate if you’re achieving your goals. Remember, these will be the 5-7 core metrics you’ll live by for the next 12 months, so it’s crucial to develop effective KPIs that follow the SMART formula. They should support your business strategy, measure the performance of your strategic objectives, and help you make better decisions.
A combination of leading and lagging KPIs will paint a clear picture of your organization’s strategic performance and empower you to make agile decisions to impact your team’s success.
Need a Dedicated App to Track Your Strategic Plan with KPI Dashboards? We’ve got you covered.
The StrategyHub by OnStrategy is a purpose built tool to help you build and manage a strategic plan with KPIs. Run your strategy reviews with zero prep – get access to our full suite of KPI reports, dynamic dashboards for data visualization, access to your historical data, and reporting tools to stay connected to the performance of your plan. Get 14-day free access today!
Our Other KPI Resources
We have several other great resources to consider as you build your organization’s Key Performance Indicators! Check out these other helpful posts and guides:
- OKRs vs. KPIs: A Downloadable Guide to Explain the Difference
- How to Identify KPIs in 4 Steps
- KPIs vs Metrics: Tips and Tricks to Performance Measures
- Guide to Establishing Weekly Health Metrics
FAQs on Key Performance Indicators
KPI stands for Key Performance Indicators. KPIs are the elements of your organization’s business or strategic plan that express what outcomes you are seeking and how you will measure their success. They express what you need to achieve by when. KPIs are always quantifiable, outcome-based statements to measure if you’re on track to meet your goals and objectives.
The 4 elements of key performance indicators are:
- A Measure – The best KPIs have more expressive measures.
- A Target – Every KPI needs to have a target that matches your measure and the time period of your goal.
- A Data Source – Every KPI needs to have a clearly defined data source.
- Reporting Frequency – A defined reporting frequency.
No, KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are different from metrics. Metrics are quantitative measurements used to track and analyze various aspects of business performance, while KPIs are specific metrics chosen as indicators of success in achieving strategic goals.
16 Comments
HI Erica hope your are doing well, Sometime Strategy doesn’t cover all the activities through the company, like maintenance for example may be quality control …. sure they have a contribution in the overall goals achievement but there is no specific new requirement for them unless doing their job, do u think its better to develop a specific KPIs for these department? waiting your recommendation
Thanks for your strategic KPIs
Hello Erica, Could you please clarify how to set KPIs for the Strategic Planning team?
Hi Diana, check out the whitepaper above for more insight!
Hello Erica, Could you please clarify, how to set the KPIs for the Strategic PLanning team?
exampels of empowerment kpis
I found great information in this article. In any case, the characteristics that KPIs must have are: measurability, effectiveness, relevance, utility and feasibility
How to write methodology guidelines for strategy implementation / a company’s review and tracking (process and workflow) for all a company’s divisions
support on strategizing Learning & Development for Automobile dealership
Could you please to clarify how to write the KPIs for the Secretary.
Check out our guide to creating KPIs for more help here: https://onstrategyhq.com/kpi-guide-download/
That’s an amazing article.
Could you please to clarify how to write the KPIs for the office boy supervisor
Could you please clarify how to write KPIs for the editorial assistant in a start up publishing company.
Kindly advice how I would set a kpi for a mattress factory
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.

KPI Evaluation and Review - Key Performance Indicators Explained
The KPI Playbook: Strategies for Effective Evaluation and Review
KPI Evaluation and Review: A Comprehensive KPI Guide
- Tip 1 - Start with the Right Question
- Tip 2 - Less is More
- Tip 3 - Use Leading Indicators to Drive Results
- Tip 4 - Red, Yellow, Green
- Tip 5 - Maintain a Healthy Balance

What is a KPI?

Tracking KPIs is important for 2 reasons:
- They are a balanced scorecard for company health - you only need a handful of KPIs to monitor your company's vital signs. Only measure what you want to move so you can put energy where you want to effect change.
- They can be a Dashboard for specific business problems or opportunities - you can track what's happened in the past and the results you want to achieve with Lagging (Results) Indicators. Then, you can also measure Leading Indicators to ensure you are on track to achieve the desired results. Leading Indicators give you an execution advantage over your competition.
I have included below 5 tips to help you evaluate your current KPIs, create the right KPIs, and use them to drive results in your business.

KPI Evaluation and Review: Start With The Right Question.
The right question to start with is "What business results are we trying to impact?" or "What problems are we trying to solve?"
Follow these 4 steps to create KPIs that really matter:
- Select a business result or problem that needs to be improved.
- Determine what levers in your business influence the outcome and find a way to measure those levers.
- Set Red-Yellow-Green success criteria for each. ( Watch this 5 minute video to learn how )
- Determine specific actions required to achieve the Green success criteria and get to work.
Start with just one result or problem you want to work on, and set up KPIs that measure your progress on the activities that influence the result.
KPI Evaluation and Review Tip: Measure What Matters
Less Is More.
The purpose of having KPIs is to drive action that affects results. Many times we find that companies track, measure and report on a boatload of KPIs every week, but there are only a handful that ever cause anyone on the team to take action. This is a big waste of time for the executives responsible for collecting and reporting the data, and can easily cause a team to overlook the few that really do matter.
Remember that the secret to success is not in the KPI itself. The secret to success lies in the actions you take to impact the KPI. Don't measure everything that moves, Measure what you want to move . Focus on actions, get value, achieve success, and maintain momentum. Once you move into the phase of maintaining momentum, you're ready to tackle another area and develop a few more KPIs. You can keep the original KPIs on your dashboard for a period of time to ensure they stay on track, but eventually you may be able to remove them. Less is more!
If you start by developing and focusing on a couple of KPIs each quarter, before you know it, you will have a good, healthy dashboard with 10-12 KPIs that are action-oriented, driving positive results for your business.

KPI Evaluation and Review: Use Leading Indicators
KPIs come in two flavors: Results Indicators and Leading Indicators.
Results indicators report what you have achieved. These are the usual suspects, such as sales closed, products shipped, or net profit. Use results indicators to establish targets for effective annual and quarterly plans. Begin with the end in mind by setting targets and developing a plan to hit the targets.
Leading indicators, on the other hand, are predictive in nature. These measure how you are doing on the activities and levers that will move your outcome in a positive or negative way. Identifying and tracking leading indicators with frequency will help guide your day-to-day operations and decision-making, and can give you a glimpse into the future, allowing you to make adjustments mid-stream that will positively impact your results.
Starting at your result indicator will not get you there. Instead, push on your leading indicators to drive towards your results.
To find your leading indicators, ask yourself, "What results are we trying to achieve?" Once you understand what you need to achieve, start peeling back the onion layers by asking more questions to determine what causes that result. You may need to go several layers deep to get to the most important leading indicator. Once you have discovered your most important leading indicator KPI , track it frequently (weekly or daily).
KPI Evaluation and Review Tip: Clear Success Criteria
Red-Yellow-Green
Each KPI should be assigned an owner, have a clear success definition of what success looks like and be visible for all to see. In order not to be blindsided by the final result, it is important for the KPI to be tracked and discussed weekly if possible. This will give you an opportunity to recognize a potential problem, make adjustments and avoid disaster. It's a lot easier to prevent fires than fight them.
You should discuss, debate and agree as a team on what success looks like and what failure looks like. Red-Yellow-Green the success criteria for each KPI.
- Green is your goal. You will create your plan for the purpose of achieving your Green goal.
- Red is an unacceptable result. It is the definition of failure.
- Yellow is the warning zone between Green and Red. Here you still have time to make adjustments before it's too late.
- SuperGreen is the stretch goal and should signify a time to celebrate.
You will also want to think about actions you will take if at some point your results start falling into Yellow or Red. If you have KPIs that consistently fall into Yellow or Red, and there's no action or sense of urgency from the team, then it's likely you are measuring something that isn't important after all, or you have set the wrong success criteria. Remember, KPIs should drive action.
Watch Patrick Thean, CEO of Rhythm Systems, explain how to set SMART Red-Yellow-Green Success Criteria.
KPI Evaluation and Review Tip: Use a Balanced Scorecard of KPIs
Maintain A Healthy Balance
Finally, you want to make sure your KPIs indicate you are maintaining a good balance between People and Process. It is very easy to become so narrowly focused on solving one problem that you create new problems in other places. For example, if an efficiency measure in one area of your business has fallen behind, you may want to develop on or two KPIs designed to drive up productivity in this area. In doing this, you need to be aware of the possibility that you could push too hard on improving this KPI, burning out your people, and possibly doing permanent damage to your relationship with employees.
On the People side, make sure you have 1-2 KPIs to monitor the health of your relationships with:
- Shareholders
On the Process side, make sure you have 1-2 KPIs to monitor productivity in:
- Operations (how you make/buy/deliver)
- Record keeping (how you monitor your finances)
- List of manufacturing KPIs
- List of Balanced Scorecard KPIs
- Key Performance Indicators for employees
- Staffing KPIs
Taking the time to make sure you've identified the right KPIs, that you're using Leading Indicators to track your progress, that you have clearly identified what success looks like, and that you're taking a healthy, balanced approach to running your business can be one of the most important exercises you and your executive team can do together. Invest the time, commit to the process, assign ownership, and improve your company's results.
Take your KPIs to the next level.
Related kpi articles.
- 25 KPI Examples for Manufacturing Companies
- 33 KPI Examples to Measure Productivity & Prevent Organizational Drag
- Employee KPI Examples: How to Measure What (or Who) You Want to Move (Video)
- Comprehensive List of 183 KPI Examples for a Balanced Scorecard KPI Dashboard
- KPI Examples for Successful Sales Teams
- 10 Best Employee KPI Examples
- 27 Recruiting KPI Examples for the Staffing Industry
- Rhythm Systems - KPI Resource Center
Book your personalized demo

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Metrics are measures used to track progress and evaluate success, while KPIs are metrics tied to specific goals during a certain period of time. KPIs are designed to align with business goals and ...
Measure-Perform-Review-Adapt (MPRA) framework is a disciplined, practical, and tested approach for developing and implementing a KPI system. It gives organizations a way to systematically articulate a shared vision of what you are trying to achieve, set practical goals, develop meaningful indicators that can be managed and used for decision-making, and establish long-term discipline around ...
A KPI report is a performance tracking tool that allows you to quickly analyze key performance indicators and understand how your organization is doing with respect to specific goals. They include data visualization, consisting of charts, tables, and graphs. Modern KPI reports are interactive, and all the underlying data can be accessed quickly.
Here’s a quick explanation: KPIs are the key targets you should track to make the most impact on your strategic business outcomes. KPIs support your strategy and help your teams focus on what’s important. An example of a key performance indicator is, “targeted new customers per month”. Metrics measure the success of everyday business ...
Step 4 - Write your KPIs. Finally, it's time to begin actually writing your KPIs. KPIs should follow the SMART format (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound), to ensure your KPIs meet this criterion, we've devised a formula that you can follow to ensure you end up with SMART KPIs every time.
A KPI report is a critical business performance tool because they provide a clear and accurate picture of organizational performance, well-being, and potential for growth. These reports help authors communicate to specific audiences about how well parts of the business or initiatives are meeting objectives.
Organizations that are serious about using KPIs to reach their strategic goals tend to be high-performers. If you’re hoping to become part of that group, remember these three best practices as you design and deploy your own KPI framework: 1. Choose the minimum number of KPIs necessary to achieve your objectives.
KPI Reports. A KPI report is a visual management tool that facilitates the management of the various key performance indicators. Businesses use these KPI reports to track their progress and performance and compare it with their targets. KPI reports are the visual, mathematical sides of the KPI.
1. Measure Results. The obvious first benefit is that this is the best method to measure through clear values how different aspects of a company’s efforts are evolving. The best part is that the insights you obtain through KPI reports are actionable, enabling you to make better decisions going forward. 2.
Step 04 – Audit KPIs when necessary and make changes. Businesses diversify or change their existing processes depending on market conditions. When this happens you may need to revise the previously set KPIs and establish new indicators which would align with the new goals.
With that in mind, the KPI Review Process is a key ritual to check for progress, celebrate success, debug issues, and get back on track when needed. The first key here is “Plan, Actual, Variance.”. We want to be exceptionally clear about whether we’re on track, ahead of plan, or behind plan. If we’re ahead, this is a great opportunity ...
Step 2: Selecting the Right KPIs. Once you have defined your business objectives, the next step is to identify the relevant metrics that will help measure progress and performance in relation to those objectives. Break down each business objective into specific components or key focus areas.
Set a goal and work to improve the quality of feedback based on the positive response. 5. Check on employee net promoter score (NPS) If you wish to enhance employee engagement, focus on measuring feedback and plan for quarterly surveys. Prepare a set of questions and invite both positive and negative responses.
They need to remind themselves that KPIs are about stakeholder relationships, how what you do affects what the other does to you, and that the metrics will not always be the same. No CEO doubts ...
KPI reporting is the business management practice of measuring, organizing, and analyzing a business’ most important key performance indicators. KPI reports help business leaders identify strengths and weaknesses, optimize company performance, improve engagement, and reach strategic goals. Managers also use KPI reporting to analyze trends in ...
Setting key performance indicators for employees can be achieved by following these 4 steps: Tie them to strategic objectives: Consider the objectives of the employees department as well as the company as a whole. Every key performance indicator should tie directly back to your overall business goals.
The final type of KPI is a change indicator. These are used to measure the quantifiable change in a metric or measure. An example would be, “X% increase in sales.”. It adds a change measure to a quantifiable target and is usually measured as a percentage increase in a given period of time.
KPI Evaluation and Review: A Comprehensive KPI Guide. Tip 1 - Start with the Right Question. Tip 2 - Less is More. Tip 3 - Use Leading Indicators to Drive Results. Tip 4 - Red, Yellow, Green. Tip 5 - Maintain a Healthy Balance.