- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Mathematics
- Multiplication and Division

How to Multiply
Last Updated: March 29, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was reviewed by Grace Imson, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD . Grace Imson is a math teacher with over 40 years of teaching experience. Grace is currently a math instructor at the City College of San Francisco and was previously in the Math Department at Saint Louis University. She has taught math at the elementary, middle, high school, and college levels. She has an MA in Education, specializing in Administration and Supervision from Saint Louis University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 832,025 times.
Multiplication is one of the four basic operations in arithmetic, along with addition, subtraction, and division. Multiplication can actually be considered repeated addition , and you can solve simple multiplication problems by adding repeatedly. For larger numbers, you'll want to do long multiplication, which breaks the process down into repeated simple multiplication and addition problems. You can also try a shortcut version of long multiplication by splitting the smaller number in the problem into tens and ones, but this works best when the smaller number is between 10 and 19.
Multiplying by Repeated Addition

- For an even quicker method for multiplying smaller numbers, practice your multiplication tables (or times tables ).
Joseph Meyer
Multiplication enables you to "add" numbers in a faster way. Consider buying 7 boxes, each containing 51 crayons. Instead of adding 51 seven times, multiplication (7 x 51) allows you to determine the total number of crayons quickly. Use it to solve problems efficiently rather than just memorizing facts.
Using Long Multiplication

- Place the 4 from the number 34 below the line under the 8, next to the number 8 that you wrote down in the previous step.
- Carry the 3 from the number 34 over the 1 in the number 187.

- Note that if the top number had 4 or more digits, you would just repeat the process until you multiplied the number in the ones place of the bottom number with all of the digits in the top number, continuing to move from right to left.

- Write down the 5 from 35 to the left of the zero (on the second row below the drawn line), and carry the 3 from the 35 above the 8 in the top number (187).

- Write down the 3 from 43 to the left of the 5 (giving you 350 on the bottom row), and carry the 4 from the 43 above the 1 in the top number.

Splitting 2-Digit Numbers into Tens and Ones

- This shortcut method works best when the smaller number is between 10 and 19. If the smaller number is between 20 and 99, you'll have to do some extra work to figure out the tens component. As a result, you'll probably find it easier to just do traditional long multiplication.
- You can also use this method with a 3-digit smaller number as well—in that case, you'll need to break it up into hundreds, tens, and ones. For example, 162 would become 100, 60, and 2. Once again, though, doing standard long multiplication will likely be easier.

Multiplication Worksheet and Problems

Community Q&A
- Remember anything multiplied by zero is zero! [17] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- To multiply by 10, add a zero to the end. Thanks Helpful 11 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.aaamath.com/pro39_x2.htm
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/numbers/multiplication-long.html
- ↑ https://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/math/longmultiplication.php
- ↑ http://mathworld.wolfram.com/LongMultiplication.html
- ↑ https://www.ducksters.com/kidsmath/long_multiplication.php
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/math/arithmetic/arith-review-multiply-divide/arith-review-multi-digit-mult/v/multiplication-6-multiple-digit-numbers
- ↑ https://www.cut-the-knot.org/Curriculum/Arithmetic/LongMultiplication.shtml
- ↑ https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/long-multiplication/
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/numbers/multiply-by-zero.html
About This Article

If you want to learn to multiply, first keep in mind that multiplication is an advanced form of addition. For example, for 5 × 3, add 5 three times: 5 + 5 + 5 =15. To multiply bigger numbers, place the larger number on top of the smaller number. Then, multiply the last digit in the bottom number by each individual digit in the top number. If your answer is a two digit number, use the digit in the one's place as your answer, and carry the digit in the 10's place to the next digit in the top number. Write each answer below the line under the problem, and if you carried a number over, add it to the corresponding answer. Then, if there's another digit in the bottom number, add a zero under your answer from the first digit and repeat the process with the next digit over. With each new digit in the bottom number, add an extra zero under the answer. Keep doing this until you've multiplied all of the bottom digits by all of the top digits. Then, add all of your answers below the line together to find your final answer. If you want to learn how to do simple multiplication equations with addition, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 17, 2019
Did this article help you?

Angela Holywell
Apr 11, 2016
Aug 26, 2017
Jul 11, 2016
Diana Martinez
Apr 11, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
How to multiply
Multiplication is one of the four basic arithmetic operations, with the other three being subtraction , addition , and division . Learning how to multiply is a necessary aspect of studying mathematics. For whole numbers, it can be thought of as repeated addition . Learning how to multiply largely involves memorizing a multiplication chart , also referred to as a times table or multiplication table. For larger values, a multiplication algorithm, sometimes referred to as "long multiplication," can be used.
Multiplication symbols
Multiplication is an operation that, unlike addition and subtraction, can be indicated in a number of ways. The following are all multiplication symbols: ×, *, ·. Furthermore, multiplication can also be indicated using parenthesis; if there is no operator separating two numerals in parenthesis, the assumed operation is multiplication.
2 × 2 = 4
2 · 2 = 4
Using parenthesis to indicate multiplication can be particularly helpful for negative values:
(-2)(-2) = 4
The above example makes it clear that the -2's are being multiplied. Otherwise, something like -2 · -2 could be mistaken for a subtraction problem.
Multiplication as repeated addition
Multiplying whole numbers can be thought of as performing repeated addition , which is simply adding equal groups of objects together a given number of times. For example, the multiplication problem
can be read as "two groups of four," meaning that we would add a set of 4 objects twice to find the result. It is also equivalent to four groups of two.
4 × 2 = 4 + 4 = 8
2 × 4 = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8
In both cases, we can perform the multiplication problem by repeatedly adding. For larger values, or when multiplying decimals, we can use long multiplication.
Long multiplication
Long multiplication is a multiplication algorithm we can use to multiply larger numbers or decimal numbers once we've memorized the multiplication chart . Use the following steps along with the example below to understand the process.
- Write the numerals being multiplied, aligning their ones places , with the largest numeral on top. Draw a line below the numerals being multiplied.
- Multiply the digit in the ones place in the bottom numeral by the digit in the ones place of the top numeral. Write the result below the line. If the product of the column is greater than 9, write the ones-place digit of the result below the line in the same column, and the tens-place digit above the top of the following column.
- Continue the process, multiplying the digit in the ones place in the bottom numeral with the digit in each column of the top numeral, moving from right to left; if there is a digit above the column, add it after multiplying the appropriate digits. The product of the last 2 digits, even if greater than 9, is simply written below the line in the appropriate result row.
- If the bottom numeral in the multiplication problem has more than one digit, continue the same process above for each digit, aligning the ones place of the result with the tens place of the previous result (shift the result one place value to the left).
- Once each digit in the top and bottom numerals have been multiplied, add the results of each row vertically. Refer to the addition algorithm if necessary.
Multiply 1437 × 28:
The problem above is separated just to make multiplication of the rows, as well as the carried digits, clearer. On top, shown in blue, is the first row of the result, obtained by multiplying 8 by each digit in the top numeral, and following the steps detailed above.
The bottom half shows the same process to multiply the digits shown in green.
The last line in black is the result of adding the blue and green rows, and is the solution. Therefore:
1437 × 28 = 40,236
How to multiply fractions
Multiplying fractions is similar to multiplying whole numbers, except that we need to pay attention to which digits we multiply. When multiplying fractions, multiply the numerators of all the fractions involved. Then multiply the denominators of all the fractions involved. The solution is the product of the numerators over the product of the denominators.
In the above example, we simplified the problem as we multiplied. Otherwise, we would've had to simplify the fraction after finding the solution.
Multiplication
In these lessons, we will look at some examples of the multiplication of whole numbers.
Related Pages Multiplication Using Fact Families Multiplication Word Problems More Lessons for Arithmetic Math Worksheets
For more practice in multiplication, you could go to our Interactive Math Zone where you can learn the multiplication tables and generate multiplication worksheets according to your needs and get them marked online.
The first number in the multiplication is called the multiplicand, the second number is called the multiplier and the answer is called the product.
The following diagram shows the parts of a multiplication: multiplicand, multiplier and product. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on multiplication.
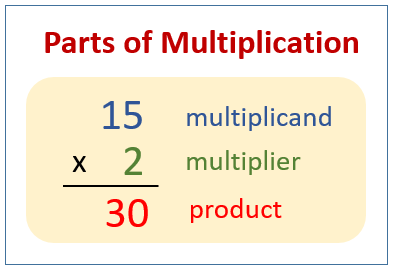
Remember : Any number multiplied by 0 becomes 0.
Example: 1,343,244,654 × 0 = 0.
Multiplication of 2 numbers a and b , written as a × b , is actually a repeated addition of the number a over b times.
Example: 6 × 4 = 6 times of 4 = 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 24
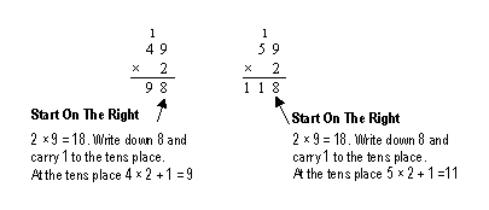
To multiply numbers with more than one digit correctly, all digits must be placed in the correct position starting from the right.
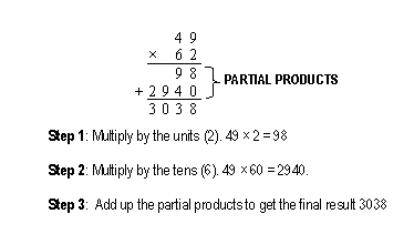
If the multiplier has 2 or more digits then it is necessary to calculate the partial products first and then add them to get the final product.
Avoid the following common mistakes in multiplication .
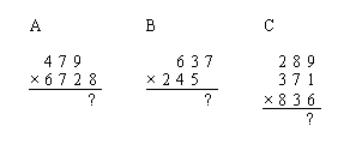
Examples A and B have numbers in the wrong positions – wrong place values.
Example C – it is confusing to multiply more than 2 numbers at one time. Multiply the first 2 numbers and then use the result to multiply with the third number to get the final answer.
Multi-Digit Multiplication Single digit multiplier
2-digit Multiplier

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

Multiplication
Ai generator.
Multiplication is a fundamental mathematical operation, representing the process of adding a number to itself a certain number of times. It’s not just a building block for math education but a critical tool in daily life and advanced science. Multiplication stands as one of the primary mathematical operations, sharing this core status with addition, subtraction , and division .This guide unveils its intricacies, applications, and tips for mastery, making multiplication accessible to learners at all levels
What is Multiplication?
Multiplication stands as one of the primary mathematical operations, sharing this core status with addition, subtraction, and division. Essentially, to multiply means to add together equal-sized groups repeatedly. This operation serves as a fundamental building block in mathematics, facilitating the calculation of numerous equal parts or quantities in a streamlined manner.
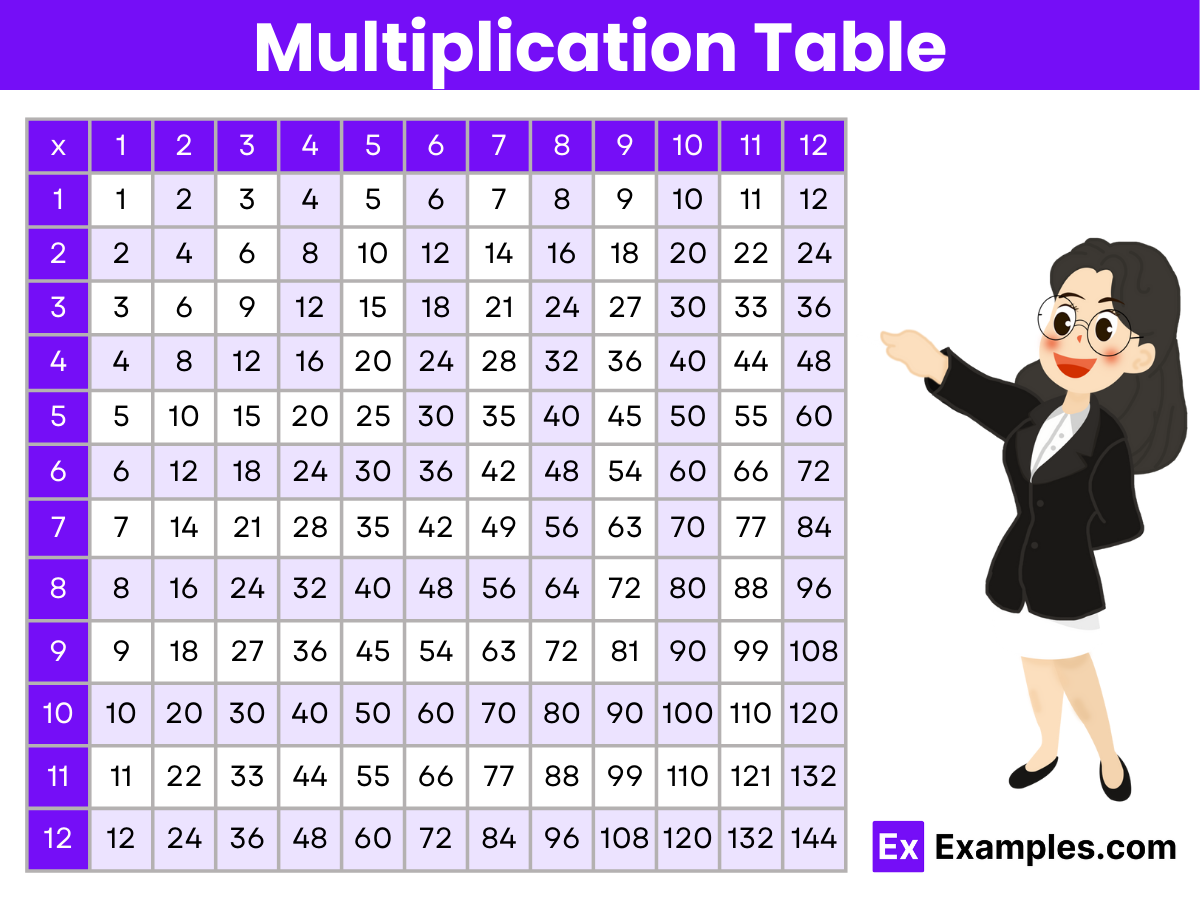
Multiplication Table Chart
Multiplication Symbol (×)
The multiplication symbol, denoted as “×,” serves as the mathematical operator indicating multiplication between two numbers or expressions. It is a cross-shaped sign that signifies the operation of taking one number and adding it to itself a certain number of times, as determined by the second number. For example, in the expression “4 × 3,” the “×” symbol instructs us to multiply 4 by 3, resulting in 12. This symbol is universally recognized in mathematics to represent the concept of multiplication.
Multiplication Formula
The formula for multiplication is straightforward, involving two numbers or variables that are multiplied together to find their product. Represented symbolically, it is:
Product = a × b
Product = Multiplicand × Multiplier
- a and b are the multiplicands, or the numbers being multiplied.
- The symbol × denotes the multiplication operation.
- The result of multiplying a by b is called the product.
8(multiplicand) × 5 (multiplier) = 40 (product)
How to Solve Multiplication Problems?
Basic multiplication:.
- Understand the Terms : Identify the numbers (factors) you need to multiply.
- Apply the Multiplication Formula : Use the formula a × b = product , where a and b are your factors.
- Calculate : Multiply the numbers to find the product.
Long Multiplication (For Larger Numbers):
- Write Down the Numbers : Place the larger number above the smaller number, aligning them by their rightmost digits.
- Multiply Each Digit of the Bottom Number by the Top Number : Start from the rightmost digit of the bottom number. Multiply it by each digit of the top number, carrying over any values as necessary.
- Add the Results : If you’re multiplying a number by a multi-digit number, write down each result under the numbers being multiplied, shifting one place to the left each time you move to the next digit of the bottom number. Then, add these results together to find the total product.
Multiplication Without Regrouping
Identify the Numbers : Choose the two numbers you want to multiply. This method is easiest with single-digit numbers, but it can also apply to specific cases of larger numbers.
Multiply Each Pair of Digits : If you’re dealing with single-digit numbers, simply multiply them together. For example, 3 × 4 = 12 . If your numbers are larger but carefully chosen (or the circumstances work out such that) no single multiplication step results in a number greater than 9, you can apply the same principle.
Write the Product : Since there’s no need to regroup (or carry), you can directly write down the answer obtained from your multiplication.
Example 1: Simple Multiplication Without Regrouping
- Problem : Multiply 4×2 4 × 2 .
- Solution : The product is 8 8 . Since both numbers are single-digit and their product is less than 10, regrouping is not necessary.
Example 2: Larger Numbers Without Regrouping
- Problem : Multiply 123 by 5.
- Multiply the ones place: 5 × 3 = 15 , write down 5, carry over 1 (note: in this case, because it’s the last digit, you’d typically write down the entire 15).
- Multiply the tens place: 5 × 2 = 10 , write down 0, carry over 1.
- Multiply the hundreds place: 5 × 1 = 5 , then add the carried over 1 for a total of 6, write down 615 as the product.
Multiplication With Regrouping
- Write the Numbers : Place the numbers you are multiplying vertically, aligning them by their right-hand digits.
- Multiply the Units First : Start with the rightmost digit (units) of the bottom number. Multiply it by the top number. If the product is 10 or more, write down the unit digit of the product and carry over the tens digit to the next column on the left.
- Move to the Next Digit : Move to the left to the next digit of the bottom number. Multiply it by the top number, add any carried number, and write down the result. If the product plus the carry is 10 or more, write down the unit and carry the tens digit again.
- Repeat for All Digits : Continue this process for each digit of the bottom number, moving from right to left, until all digits have been multiplied.
- Add the Products : If you’re multiplying a number by a multi-digit number, you’ll end up with multiples rows of products. Add these together to get the final answer.
Example: Multiplying 23 by 4
- Step 1 : Write 23 above 4.
- Step 2 : Multiply the rightmost digit of 23 (3) by 4. 3 × 4 = 12 . Write down 2 and carry over 1.
- Step 3 : Multiply the next digit of 23 (2) by 4. 2 × 4 = 8 , then add the carried over 1. 8 + 1 = 9 . Write down 9.
- Step 4 : Your final answer is 92
Multiplication Using Number Line
Multiplication using a number line is a visual method that helps illustrate the concept of multiplication as repeated addition . This technique is especially useful for teaching young learners or those new to the concept of multiplication. Here’s how to perform multiplication using a number line:
Steps for Multiplication Using a Number Line:
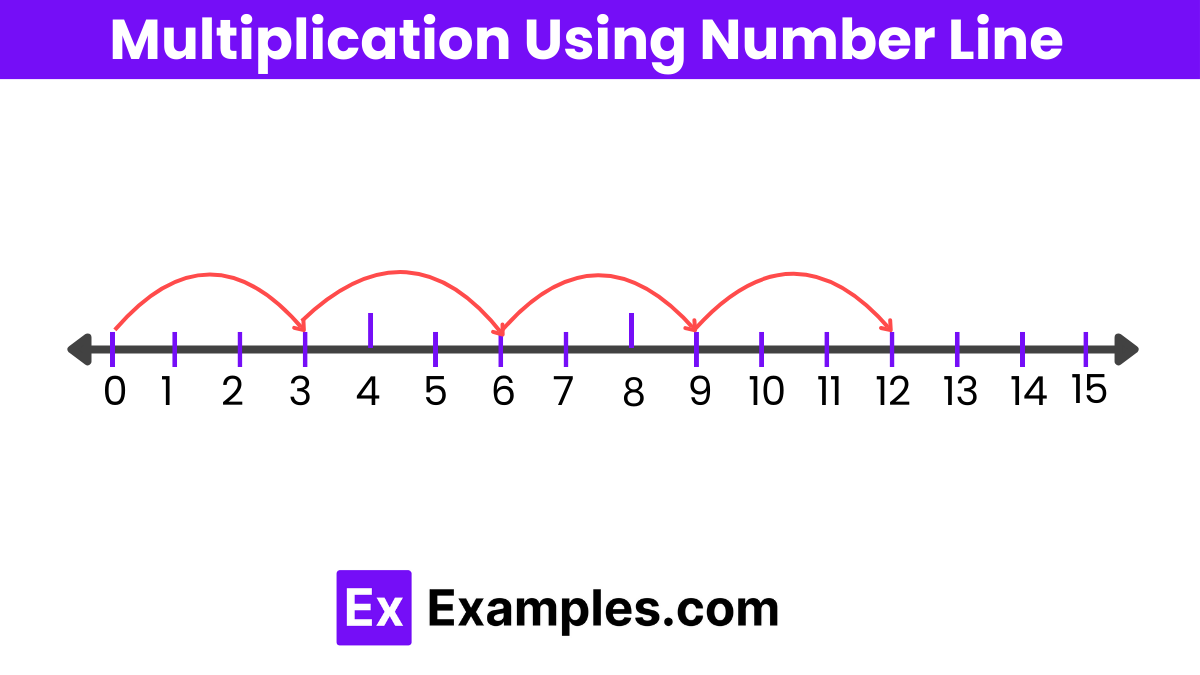
- Draw a Number Line : Begin by drawing a horizontal line and mark evenly spaced intervals or “hops” on it. Label the starting point as zero.
- Identify the Multiplier and Multiplicand : Determine which number will be repeated (multiplicand) and how many times it will be repeated (multiplier). For example, if you are multiplying 3 by 4, you will make 4 hops of 3 units each.
Make Hops on the Number Line : Start at zero. For each multiplication operation, make hops equal to the value of the multiplicand. Each hop should span a number of spaces on the number line equal to the multiplicand.
- Hop 3 spaces to the right from 0, landing on 3.
- Make a second hop of 3 spaces, landing on 6.
- Hop another 3 spaces, landing on 9.
- Make a final hop of 3 spaces, landing on 12.
- Mark Each Stop : As you make each hop, mark the stopping point on the number line . This point represents the cumulative total of the multiplication so far.
- Result : The point at which the final hop ends is the product of the multiplication. In the example of 3 by 4, the final hop ends at 12, so 3×4=12
Checking Multiplication
Multiplication Word Problems
Question : A landscaper plants 8 rows of flowers in a garden. Each row contains 9 flowers. How many flowers are there in total?
Answer : To find the total number of flowers, multiply the number of flowers per row by the number of rows: 8 rows×9 flowers/row=72 flowers Total Flowers : 72
Question : A factory produces 250 car parts each day. How many car parts are produced in 20 days?
Answer : Multiply the number of car parts produced each day by the number of days: 250 parts/day × 20 days = 5000 parts Total Parts Produced : 5000
Question : Each box of tea bags contains 15 tea bags. If a store sells 36 boxes, how many tea bags were sold?
Answer : Multiply the number of tea bags per box by the number of boxes sold: 15 tea bags/box × 36 boxes = 540 tea bags Total Tea Bags Sold : 540
Question : A parking lot has 45 spaces. On a particular day, if 32 cars are parked in each space, how many cars are in the parking lot?
Answer : Multiply the number of spaces by the number of cars per space: 45 spaces × 32 cars/space = 1440 cars Total Cars Parked : 1440
Question : A concert hall has 24 rows of seats. Each row has 42 seats. How many seats are in the concert hall?
Answer : Multiply the number of rows by the number of seats per row: 24 rows × 42 seats/row = 1008 seats Total Seats in Concert Hall : 1008
Question : A school cafeteria serves lunch to 18 classes each day. If each class has 26 students, how many students in total are served lunch?
Answer : Multiply the number of classes by the number of students per class: 18 classes × 26 students/class = 468 students Total Students Served : 468
FAQ’s
What is the multiplicand * multiplier.
The terms multiplicand and multiplier are factors in a multiplication equation. The multiplicand is the number being multiplied, while the multiplier is the quantity by which the multiplicand is multiplied. For instance, in 4 × 3 , 4 is the multiplicand, and 3 is the multiplier, yielding a product of 12.
How Do You Explain Multiplication to a Child?
To explain multiplication to a child, describe it as repeated addition. For example, if you have 3 groups of 4 apples, multiplication tells you the total number of apples. You simply add the number in each group together: 4 + 4 + 4 = 12 apples. This shows that 3 × 4 = 12 .
What Does Multiply Mean for Kids?
For kids, “multiply” means combining equal groups to find out how many items there are altogether. It is like adding the same number several times. For example, if you have 5 groups of 2 cookies, multiplying 5×2 5 × 2 tells you that there are 10 cookies in total.
How to Do Multiplier Math?
Multiplier math involves using one number (the multiplier) to increase another number (the multiplicand) repeatedly. The process is simple: multiply the multiplicand by the multiplier to get the product. For instance, multiplying 6 (multiplicand) by 4 (multiplier) means adding 6 to itself 4 times, resulting in 24.
What is Multiplication for Grade 2?
In Grade 2, multiplication is introduced as a method for quick addition of equal groups. Students learn to interpret multiplication as repeated addition, such as seeing 5×3 5 × 3 as adding three 5s (5+5+5). This foundational concept helps them understand how multiplication facilitates efficient counting and problem-solving.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

How to Solve a Multiplication Problem
Do you want to know how to solve a multiplication problem? Have you already learned how to multiply? Did you know that solving problems is the best way to learn multiplication?
That’s why we are going to look at the different steps that we need to follow in order to solve a multiplication problem.
Let’s get to it and look at a multiplication problem:

The witch Malitch made 10 bottles of potion to take to the annual Witches of the World convention. At this convention, all of the witches present new magic potions and the best one wins the Flying Broom Prize. To make each potion, she used 3 boxes of magic herbs that were 5 pounds each. How many pounds of magic herbs did she use in total?
1) The first thing we need to do is to read the problem carefully . In order to make sure that we understand it, we can ask ourselves questions about the problem, for example:
- What did the witch Malitch make? She made 10 bottles of potion.
- Why did she make them? S he made them for a magic potion contest.
2) Once we understand what the problem said, we continue reading the question and analyze it by asking ourselves more questions:
- What is the question asking me? The question is asking me how many pounds of magic herbs Malitch used in total, in all of the potions.
- Do I need to do a math operation in order to solve the problem? Yes, because I only know how many pounds of magic herbs that each box had.
- Ok, so what information do I need to use? ( T his last question is extremely important. You won’t always use all of the information that is given to you in a problem). I need to use the number of pounds that each box had (5), the number of boxes that she used for each potion (3) and lastly, the number of bottles of potions that she made (10).
3) Now, we can move on to think about the operation that we need to carry out:
We want to know how many pounds she used in total. We know that she used 3 boxes for each potion and that each box weighed 5 pound s, so:
For each potion she used 5 + 5 + 5 pounds . Or, expressed in a different way: 3 x 5 = 15 pounds.
Now we know that she used 15 pounds of magic herbs for each potion and we know that she made 10 bottles of potion, so:
In total, to make all of the potions, she used 15 x 10 = 150 pounds of magic herbs.
4) This last step is very important. We’ve gotten an answer, but now we need to critically reflect on the number that we got:
Finally, does it make sense that the answer (150) is greater than the numbers given in the problem (10, 3, 5)? Yes, it makes sense because these numbers referred to each potion or each box. The answer refers to the total amount of potions and the total amount of boxes.
Let’s solve the problem mentally using approximations: does it make sense that the number we got is 150? Yes. For example, it wouldn’t make sense if we got an answer of 30 because it’s too small of a number to be the answer of 10 x 3 x 5. It wouldn’t make sense either if we got 150,000 because it’s too big of a number.
So we have the final answer:
The witch Malitch used 150 pounds of magic herbs in total.
See? In order to solve a multiplication problem correctly, it’s not enough to just multiply all of the numbers, rather, we need to understand, analyze and reflect on what the problem says before we go ahead with the operation. We also need to check the answer.
Remember this for the next time that you have to solve a multiplication problem or any other problem for that matter!
Meanwhile, you can learn more about multiplication by clicking on the following links:
- Multiplication tables
- Singapore Model for Multiplication
- How to Multiply 2 and 3 Digit Numbers
Did you like this post? If it helped you understand how to solve a multiplication problem, share it with your friends.
Learn More:
- How to Apply the Associative Property in a Problem
- Learn How to Solve 1-Digit Division Problems
- Compound Rule of 3: When to Use It and Some Problems
- Using the LCM (Least Common Multiple) to Solve Problems
- Mathematical Problems and Their Semantic Categories
- 15 fun minutes a day
- Adapts to your child’s level
- Millions of students since 2009

- Recent Posts
- Educational Technology: The Christodoulou Test - 05/06/2024
- Multiplication Activities in Smartick - 04/09/2024
- Pythagorean Theorem: Definition, Proofs and an Example of Practical Application - 02/29/2024
Add a new public comment to the blog: Cancel reply
The comments that you write here are moderated and can be seen by other users. For private inquiries please write to [email protected]
Your personal details will not be shown publicly.
I have read and accepted the Privacy and Cookies Policy
Multiplication Methods & Types
Emily Oxford has taught students from Kindergarten through 10th Grade for over 11 years. She has two Master's degree in Curriculum and Instruction and Elementary Education from Western Governors University, and studied behavioral science as an undergraduate. She also has advanced training and research experience in elementary math pedagogy. Emily has served as an educator and curriculum specialist in the US and abroad at American international schools.
Cori has degrees in Elementary Education and Early Childhood Education and has taught lower elementary.
What is the easiest way to multiply?
Using a calculator is the easiest way to multiply. However, when the calculation must be done manually, choose the method that you understand most and makes the most sense for the problem.
Which method is best for multiplication?
No one method is best for multiplication. The best strategy is the one that makes the most sense to you and helps you efficiently and accurately solve problems.
How many methods of multiplication are there?
There are many methods for multiplication. Here are four of those methods: repeated addition, long multiplication (traditional algorithm), grid method, and drawing lines.
Table of Contents
Multiplication methods, types of multiplication, lesson summary.
How do you multiply? Multiplication is a shortcut for adding a number to itself multiple times. Multiplication can be thought of as 'groups of'. For example, 5 x 3 simply means 5 groups of 3. The numbers being multiplied are called factors and the answer is called the product . There are many strategies for multiplying. Read to find out four different ways to multiply.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account

An error occurred trying to load this video.
Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support.
You must c C reate an account to continue watching
Register to view this lesson.
As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed.
Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons.
Already registered? Log in here for access
Resources created by teachers for teachers.
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
You're on a roll. Keep up the good work!
Just checking in. are you still watching.
- 0:00 The Different Ways to Multiply
- 0:17 The Addition Method
- 0:42 The Grid Method
- 1:37 The Long Multiplication Method
- 2:22 The Drawing Lines Method
- 3:15 Lesson Summary
There are many strategies for multiplying. In school, teachers may require certain methods to be practiced and used but it is important for each person to find the multiplication method that works well for them. All methods of multiplication can be used to accurately solve any multiplication problem, though some methods are better suited to certain types of problems. Keep reading to learn about four types of multiplication: addition method , long multiplication , grid method , and drawing lines . Some other strategies for multiplication include partial products, area model, and lattice.
Addition Method
The addition method for multiplying is simply repeatedly adding the same number to itself. For example, to solve 20 x 5, 20 would be added to itself 5 times.
20 + 20 + 20 + 20 + 20 = 100
This is a good strategy for small numbers or just a few groups of a large number. It also works well for multiples of ten because it is relatively easy to add those mentally. Using this strategy for multiplying large numbers becomes cumbersome and is prone to errors. Imagine trying to solve 473 x 75 by adding 473 to itself 75 times. This would be very inefficient and there is a high chance of making a mistake.
The addition method works because multiplication is simply a shortcut for adding equal groups.
Long Multiplication Method
Long multiplication is also known as the traditional algorithm. This is the method most commonly taught in the United States and is usually accepted as the best method. However, this method is prone to mistakes when students do not fully understand the steps.
Look at the example of 364 x 32. Read the steps and try to match the steps to the example.
- Write the factors vertically, one above the other. Make sure the place values are lined up. The product with the most digits should go on top.
- Draw a horizontal line under the equation.
- Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom factor by the digit in the ones place of the top factor. In this case it is 2 x 4. The product goes in the ones place below the line.
- Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom factor by the digit in the tens place of the top factor. In this case it is 2 x 6 to get a product of 12. Since 12 is a two-digit number, the 1 must be 'carried' to the hundreds place.
- Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom factor by the digit in the hundreds place of the top factor. In this case it is 2 x 3 to get 6. Since the 1 was 'carried' to the hundred place, this must be added to get 7.
- Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom factor by the remaining digits in the top factor in order (thousands, ten thousands, etc.). If a product has two digits, the first digit should be 'carried' to the top of the next place. Now the first factor has been multiplied completely by the digit in the ones place of the second factor. In this case, 364 x 2 = 728.
- The same steps are repeated using the digit in the tens place of the second factor. The only difference is that since we are working in the tens place now, the product will begin in the tens place. Usually, a 0 is written as a placeholder in the ones place of the second product.
- Write the product of 364 x 30 under the first product.
- Add the two products together: 728 + 10,920 = 11,648.
As with the addition method, this strategy will work for any multiplication problem. There are fewer errors to be made using the long multiplication method than with repeated addition. However, this method is not fool-proof. The most common error is to start recording the second product in the ones place. Another common error is to forget to add any carried digits to the product.
The long multiplication method, or traditional algorithm, works because of the distributive property. Each place value of the second factor is multiplied by the first factor. Then the products are added together to get a total product.
Grid Method
The grid method of multiplication relies on place value and the distributive property. The grid method is also known as the area model for multiplication. To avoid mistakes and locate errors, it is helpful to understand the distributive property of multiplication. To use the grid method, each factor is broken up into its place value and each part of the factor is multiplied by each part of the other factor.
Look at the example of 23 x 74. Read the steps and try to match the steps to the example.
| x | 70 | 4 |
| 20 | 1400 | 80 |
| 3 | 210 | 12 |
- Split each factor into its place values. The factor 23 is split into 20 and 3 while 74 is broken into 70 and 4.
- Arrange the factor parts in the top row and left column of a grid.
- Multiply each part of one factor by each part of the other factor. In this case, it is 20 x 70 and 20 x 4 then 3 x 70 and 3 x 4.
- Add each product together to get the final product.
This method has fewer places for errors than repeated addition or the long multiplication method. A tip is to match the number of products to the number of digits in the original problem. In the example, there are 4 digits in 23 x 74, so there will be 4 products to be added together.
The grid method, and area model, works because of the distributive property. In this case, all factors are broken up into their place values and multiplied by all the parts of the other factor.
Method of Drawing Lines
The drawing lines methods of multiplication originated in Japan and is now sometimes taught in the United States. This method relies on place value. To find any mistakes after using this method, it is helpful to think about place value.
Look at the example of 12 x 24. Read the steps and try to match the steps to the example.
- Set up the problem by drawing diagonal lines that match the value of each digit in the factors.
- For the first factor, 12, draw 1 diagonal line for the 1 (yellow), leave a space, and draw 2 diagonal lines for the 2 (blue). All the lines should be parallel.
- For the second factor, draw the lines perpendicular to the first sets of lines. For 24, draw 2 diagonal lines for the 2 (red) and 4 diagonal lines for the 4 (green). All lines should be parallel to each other and perpendicular to the lines for the factor 12.
- Separate the intersections into 3 sections: left, center, and right.
- Count the number of times the lines in each section intersect and record them in order.
- In the example, there are 2 intersections in the left section, 8 in the center, and 8 in the right. So the product is 288.
The drawing lines method is a fun trick for multiplication. However, it is difficult to use when multiplying large multi-digit numbers. To prevent errors when using the lines method, think about the long multiplication method. In the lines method, each digit of the first factor is multiplied by each digit of the second factor.
This method relies on place value and understanding what to do when any section results in 2 digits. This method can lead to mistakes without a solid understanding of the process of multiplication.
There are many ways to multiply. Multiplication is the process of adding many equal groups together. Any multiplication method can be used for any problem. Choose the method that is most efficient and least likely to have errors for the given problem. Four multiplication methods are: addition method , long multiplication , grid method , and drawing lines . Each of these methods will result in the same correct product .
Video Transcript
The different ways to multiply.
This lesson will cover four different ways to multiply numbers: addition, memorizing the grid method, long multiplication, and drawing lines. Learning about each of them will help you decide which method works best for you.
The Addition Method
One of the most basic ways to multiply is to add. When we multiply two numbers, we're simply adding one number to itself a certain number of times. For example, if the problem says to multiply 20 x 5, you're adding the number 20 to itself five times. So:
20 x 5 = 100
The Grid Method
When using grid multiplication , you separate your numbers into boxes. The problem in this grid is asking you to multiply 23 x 74. In the top row, the number '23' appears as '20' and '3'. In the first column on the left, the number '74' appears as '70' and '4'.
Multiply the first number in the top row by the first number in the first column:
20 x 70 = 1,400
Then multiply the next number in the top row by 70:
3 x 70 = 210
Next, multiply the first number in the top row by the second number in the first column:
20 x 4 = 80
Finally, multiply 3 x 4 = 12.
Now, add the answers together:
1,400 + 210 + 80 + 12 = 1,702
The Long Multiplication Method
Long multiplication is a way to multiply two multiple-digit numbers. For instance, let's say that a multiplication problem asks you to multiply 364 x 32. Begin by writing the problem on a piece of paper. Then multiply the top number (364) by the bottom right number (2), shown in red, and write that below the line. Now, multiply the top number (364) by the bottom left number (3), shown in blue. When you write your answer down, leave a space for a zero. Then add the two answers together to obtain your final answer:
728 + 10,920 = 11,648
Drawing Lines
Drawing lines is one of the newer methods of multiplication in the United States. It is a method that has been used by the Japanese. Let's take the problem 12 x 24. To solve the problem, you would first draw lines to represent the numbers given.
These lines are color coordinated with the numbers they represent. The first number in the problem, '1,' and the lines representing it are yellow. The second number, '2,' and the lines representing it are blue. The other numbers, '2' and '4,' are shown in red and green.
After the diagonal lines are drawn, curved lines are drawn to separate the contact points between the lines into sections. Count each contact point in each section, and that will give you the answer to your problem. Section 1 had two contact points (2). Sections 2 and 3 each had eight contact points (8); so the answer to this problem is 288.
There are several ways to solve multiplication problems. Whether you prefer to use addition , since when we multiply we're simply adding one number to itself a certain number of times; long multiplication , or a way to multiply two multiple-digit numbers; grid multiplication , or when you separate your numbers into boxes; or drawing lines , a newer method they use in Japan that involves drawing lines that represent the given numbers, being familiar with each of the different ways can help you decide which method works best for you.
Unlock Your Education
See for yourself why 30 million people use study.com, become a study.com member and start learning now..
Already a member? Log In
Recommended Lessons and Courses for You
Related lessons, related courses, recommended lessons for you.

Multiplication Methods & Types Related Study Materials
- Related Topics
Browse by Courses
- High School Trigonometry Textbook
- College Calculus Textbook
- High School Geometry: Homeschool Curriculum
- Geometry: Credit Recovery
- Fundamental Geometry
- ELM: CSU Math Study Guide
- High School Algebra II: Homework Help Resource
- High School Algebra II: Help and Review
- High School Algebra II: Tutoring Solution
- Study.com PSAT Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide
- Study.com ACT® Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide
- Study.com SAT Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide
- Algebra II: High School
- Algebra I: High School
- Trigonometry: High School
Browse by Lessons
- How to Multiply Three or More Numbers
- 100 x 1000: How-To & Steps
- Reducing Fractions | Steps & Examples
- Concave in Geometry | Definition, Shapes & Functions
- Operations with Fractions | Steps & Examples
- Solving Polynomial Equations in the Complex Field
- How to Model & Solve Problems Using Nonlinear Functions
- Waiting-Line Problems: Where They Occur & Their Effect on Business
- The Business Economics of Waiting Lines
- The Importance of Extreme Points in Problem Solving
- Interpreting Computer Solutions of Linear Programming Models
- Marketing Applications of Linear Programs for Media Selection & Marketing Research
- LSAT Prep & Test Strategies
- Sample LSAT Reading Comprehension Questions & Explanations
- Strategies for Reading Comprehension Passages on the LSAT
Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Create an account
Explore our library of over 88,000 lessons
- Foreign Language
- Social Science
- See All College Courses
- Common Core
- High School
- See All High School Courses
- College & Career Guidance Courses
- College Placement Exams
- Entrance Exams
- General Test Prep
- K-8 Courses
- Skills Courses
- Teacher Certification Exams
- See All Other Courses
- Create a Goal
- Create custom courses
- Get your questions answered

How to do long multiplication
Multiplying large numbers is easy when breaking down the problem into parts!

Author Amber Watkins
Published November 14, 2023

Published Nov 14, 2023
- Key takeaways
- Long multiplication makes multiplying large numbers easy by breaking them down into parts
- Mastering long multiplication takes practice, but it’s a very important skill that will help with maths more widely
Table of contents
What is long multiplication?
- Practice questions
Are you encountering large numbers in maths? They can seem a bit scary at first! But luckily, there’s a silly saying that can help: ‘How to eat an elephant? One bite at a time!’. It teaches us that if you have a large task, the best way to do it is in parts.
The same can be true with multiplication. When we are given large numbers to multiply, instead of trying to do the problem all at once in our heads, we can multiply those numbers in parts.
When we multiply large numbers in parts, then add those parts together, it’s called long multiplication.
Long multiplication is the steps you follow to multiply larger numbers in an easy way. Long multiplication allows you to find partial answers and add them together to find the final product.
For example, instead of multiplying the numbers 64 x 32 as they are, you can break up the number 32 into two parts: 30 and 2, then multiply those parts by 64. It would look like this:
(64 x 2) + (64 x 30) 128 + 1,920 You would get a total of 2,048. Multiplying in parts, and then adding the products together, makes multiplying large numbers easy!
Unlock unlimited maths questions
Put your learning into practice with fun exercises + games that are proven to boost ability!
How to set up a long multiplication problem
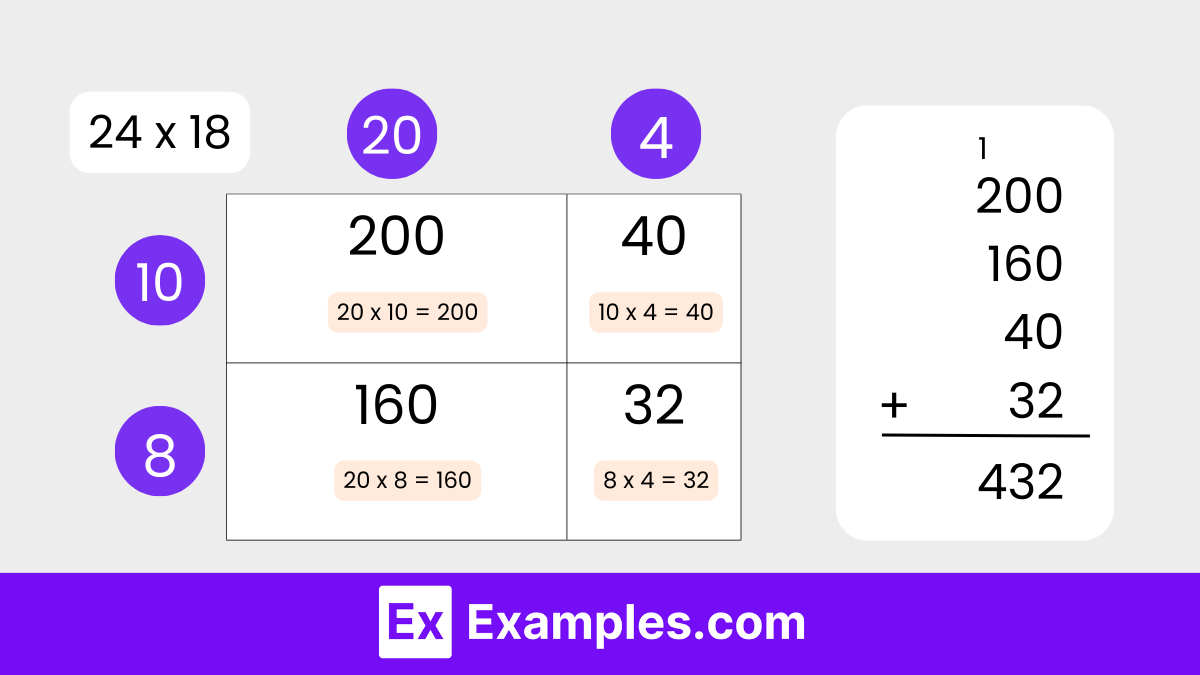
When doing long multiplication problems in a column method, you first line up the numbers you’re multiplying in columns.
For example, would we set up the problem 64 x 32 using the column method?
- The number 62 would be written above the number 32. The equal sign will be represented with a line underneath
- You will also have two or more rows beneath. This is where you write the partial products. The first partial product is written in the first row, the second partial product is written in the second row, and so on.
Let’s keep this in mind when reviewing the steps for how to do long multiplication .
Try DoodleMaths for free!
Select a year group
- Early Years
Shape, space and measure
Number and place value, addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, operations (asmd), shape/geometry, ratio and proportion, probability, sample questions, long multiplication methods: column method.
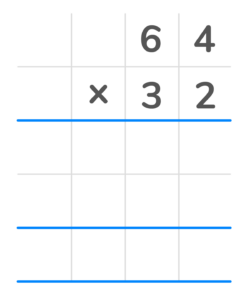
Let’s learn the use what’s known as the column method to solve the following problem:
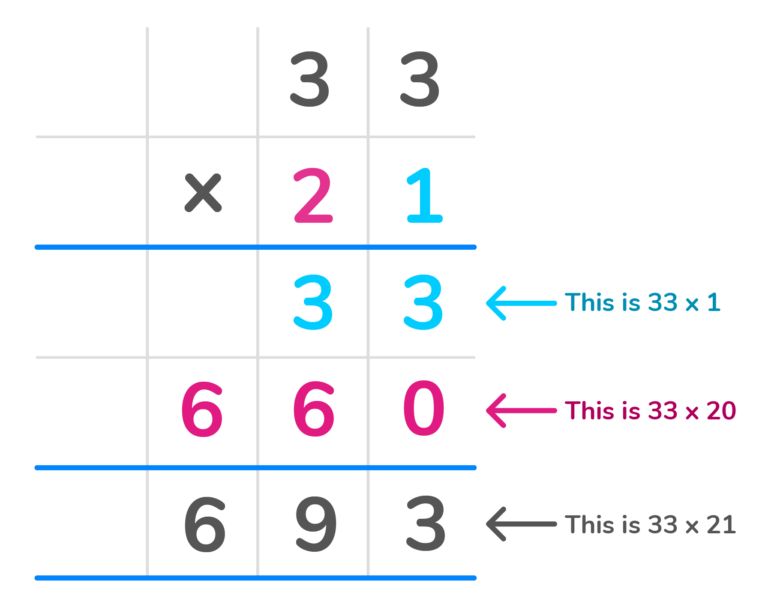
What is 33 x 21?
1. Line up the numbers in a column format.
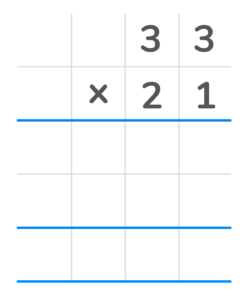
2. Multiply each top digit by the last digit in the bottom number. Place each answer in the first row from right to left. You should have the number 33 in the first product row.
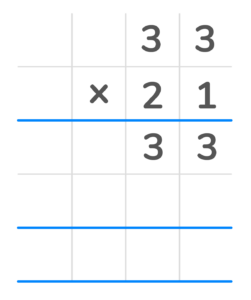
3. Once each of the top digits is multiplied by that number, cross it off. 4. Next add a zero as a place value holder in the second row to represent already multiplying by the digit in that place value.
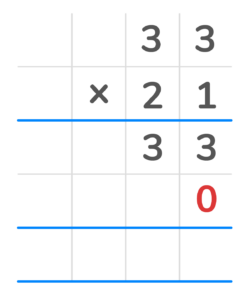
5. Multiply each top digit by the first digit in the bottom number. You will have the number 660 in the second partial product row.
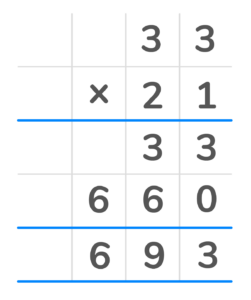
6. Finally add the two products 31 and 660 to get the final answer of 693.
Explore long multiplication with DoodleMaths
DoodleMaths is an award-winning app that’s filled with thousands of questions and games exploring multiplication, division and more!
Designed by teachers, it creates each child a unique work programme tailored to their needs, doubling their progression with just 10 minutes of use a day. Try it for free !

Carry-over rule while doing long multiplication
If you multiply two digits and the answer is in the double digits, the carry-over rule says you must write the second digit in the partial product line, and the first digit above the next number you will need to multiply. That way it carries over.
Let’s see how these long multiplication steps and the carry-over rule work
Long multiplication method: horizontal method
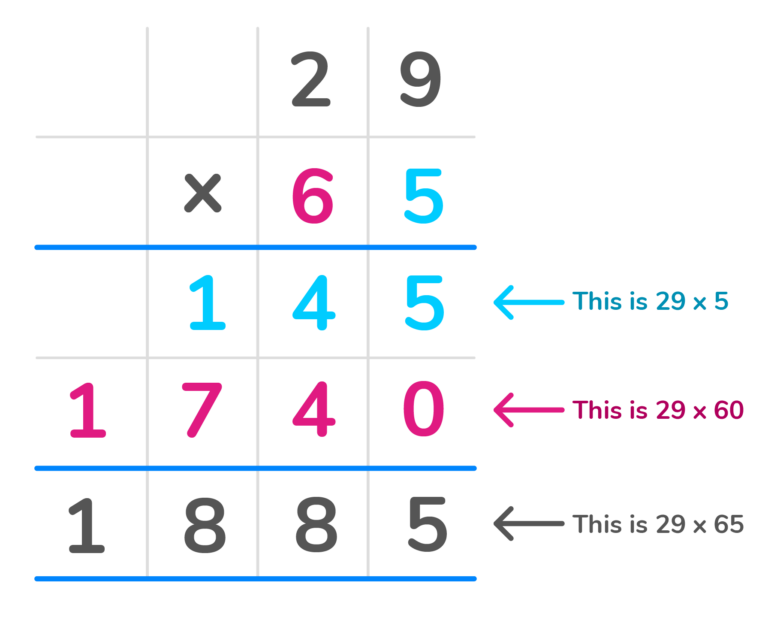
There’s also another way to do long multiplication – the horizontal method. The horizontal method allows us to break up the second number in parts and multiply those parts by the first number. Let’s learn how to do long multiplication with the horizontal method. Let’s look at this example.
Multiply 43 x 65 using the horizontal method 1. Write the second number 65 in Expanded form. Those two numbers will be the parts we multiply the first number 43 by. 65 in Expanded form is 60 + 5. 2. Begin by multiplying 43 by the first part, 60. This can be done by multiplying 43 x 6, then adding a zero to the answer.
43 x 6 is 258.
Then add a zero, so it would be 258 0 . 3. Next we will multiply 43 by the second part 5.
43 x 5 is 215. 4. Finally, we add the two partial products together to get the final answer.
2580 + 215 is 2,795.
Long multiplication practice questions
Click on the boxes below to see the answers!
- Write 72 and 24 in columns.
- Multiply 2 x 4 and 7 x 4 and write the answers in the first row.
- Cross off the 4 and add a zero placeholder in the second row.
- Multiply 2 x 2 and 7 x 2 and write the answers in the second row.
- Add both columns together to get 1,728 .
- Write 48 and 62 in columns.
- Multiply 8 x 2 and 4 x 2 and write the answers in the first row.
- Cross off the 2 and add a zero placeholder in the second row.
- Multiply 8 x 6 and 4 x 6 and write the answers in the second row.
- Add both columns together to get 2,976
- Write the second number 54 in expanded form: 50 + 4.
- Multiply 98 times the first part 50. Multiply 98 x 5 and add a zero to the answer: 4,900.
- Next multiply 98 times the second part 4: 392.
- Finally, add those two partial products together: 4,900 + 392 = 5,292
FAQs about long multiplication
You do long multiplication by multiplying numbers in parts. You multiply each digit in the top number, by each digit in the bottom number. Finally, you add the partial products to get the final answer.
Long multiplication helps make multiplication with large numbers easy. The more you practice long multiplication, the easier these problems will be.
The long multiplication method is often called the column method. This is because the numbers you multiply are written above and below one another in columns.
You begin learning long multiplication in Year 5 and learn to multiply even larger numbers in Year 6.

Lesson credits

Amber Watkins
Amber is an education specialist with a degree in Early Childhood Education. She has over 12 years of experience teaching and tutoring. "Knowing that my work in math education makes such an impact leaves me with an indescribable feeling of pride and joy!"
Amber is an education specialist with a degree in Early Childhood Education. She has over 12 years of experience teaching and tutoring . "Knowing that my work in math education makes such an impact leaves me with an indescribable feeling of pride and joy!"
Related posts
How to multiply fractions

Take your learning further by exploring how to multiply fractions
Easy ways to learn times tables

Take a look at our tips for learning the 1-12 times tables off by heart
The best order to learn times tables
We outline the best (and easiest!) order to learn the 1-12 multiplications in
What we offer
Quick links
All rights reserved.

Are you a parent, teacher or student?
Get started for free!
Maths information pack
We ask for your contact info so we can send our info pack directly to your inbox for your convenience, exam prep information pack, case studies information pack.
Book a chat with our team

I’m new to Doodle

My school is already using Doodle

Information pack
We ask for your contact info so that our education consultants can get in touch with you and let you know a bit more about doodle., student login, which programme would you like to use.
DoodleMaths
DoodleTables
DoodleEnglish
DoodleSpell
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here:

Long Multiplication: Definition with Examples
What is long multiplication, how to multiply using long multiplication, long multiplication column method, solved examples on long multiplication, practice problems on long multiplication, frequently asked questions on long multiplication.
Long multiplication is a method of multiplying large numbers easily. It simplifies the process of multiplication of two numbers that are not otherwise easy to multiply.
For example, we can easily find the product of $55 \times 20$ by multiplying 55 by 2 and then adding a 0 at the rightmost place of the answer.
$55 \times 2 = 110$ and $55 \times 20 = 1100$
However, sometimes, finding the product is not this easy. In such cases, we use the method of long multiplication. It is often termed as the long hand multiplication (long multiplication by hand).
Long Multiplication: Definition
Long multiplication is a method of multiplication using which multiplying two large numbers that have two or more digits becomes easier.
But how to multiply large numbers? Many times, finding the product is not this easy. In such cases, we use the long method of multiplication.
For example: $47 \times 63 =$ ?
We can find the answer in simple steps using long multiplication. Let’s discuss the method in detail in the next section.

Let’s discuss the steps for multiplying a two-digit number by a two-digit number using the long multiplication method.
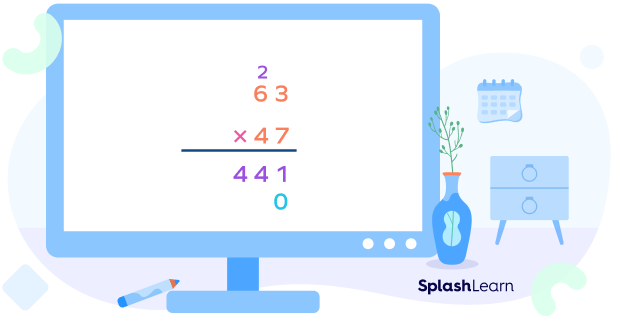
Let us multiply 47 by 63 using the long multiplication method .
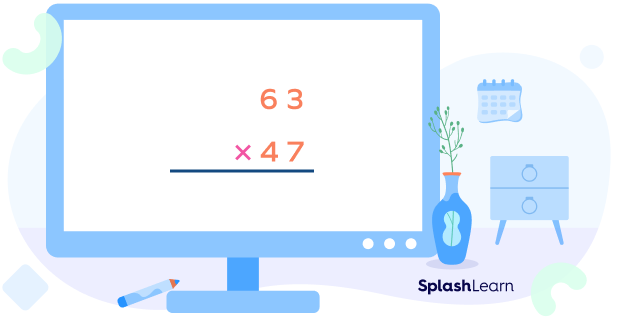
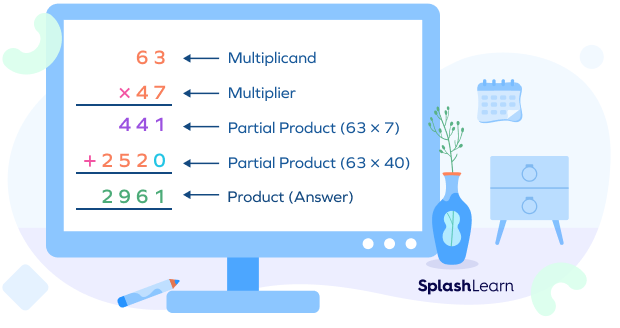
Step 1: First, write the two numbers, one below the other, such that their place values are aligned. We generally write the bigger number on top and a multiplication sign on the left and draw a line below the numbers as shown below.
Important Note:
- In the long multiplication method, the number on the top (63) is called the multiplicand . The number by which it is multiplied, that is, the number at the bottom (47), is called the multiplier .
- If you write the small number on the top and perform the multiplication, the answer will still be the same since the order does not matter while multiplying two numbers.
Step 2: Multiply the ones digit of the top number by the ones digit of the bottom number.
Write the product as shown in the image. Don’t forget the carryover that goes in the next place!
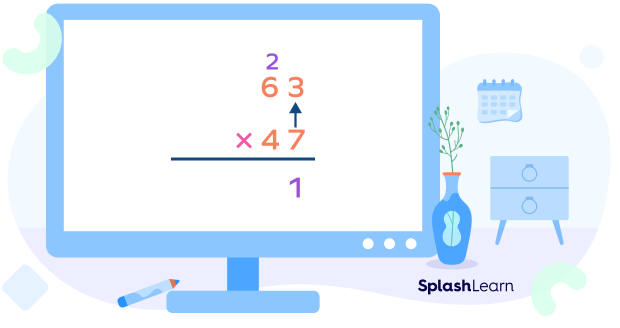
Step 3: Multiply the tens digit of the top number by the ones digit of the bottom number. Add the carryover.
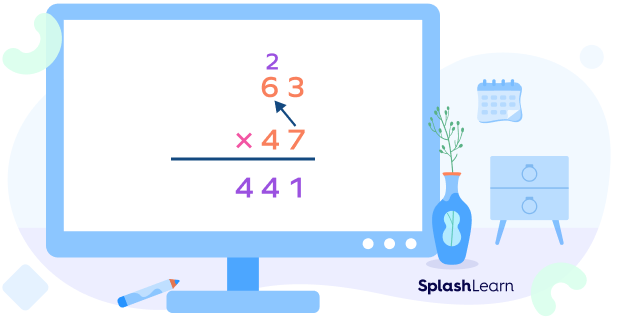
This is our first partial product which we got by multiplying the top number by the ones digit of the bottom number.
Step 4: Now, we place a 0 below the ones digit as shown. This is because we will now be multiplying the digits of the top number by the tens digit of the bottom number.
Step 5: Multiply the ones digit of the top number by the tens digit of the bottom number.
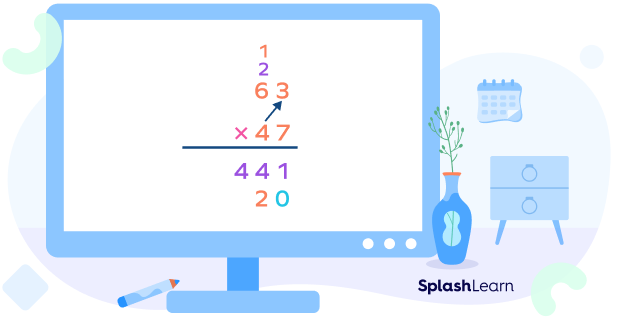
Step 6: Multiply the tens digit of the top number by the tens digit of the bottom number.
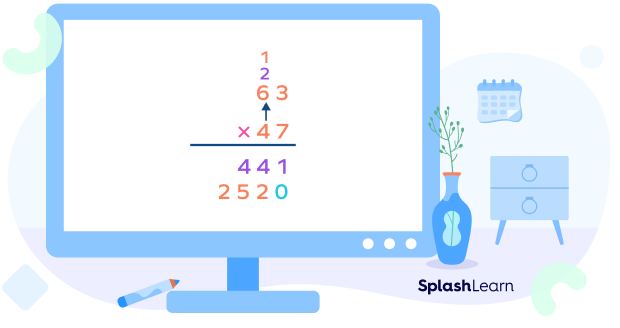
This is the second partial product obtained by multiplying the top number by the tens digit of the bottom number.
Step 7: Now, add the two partial products.
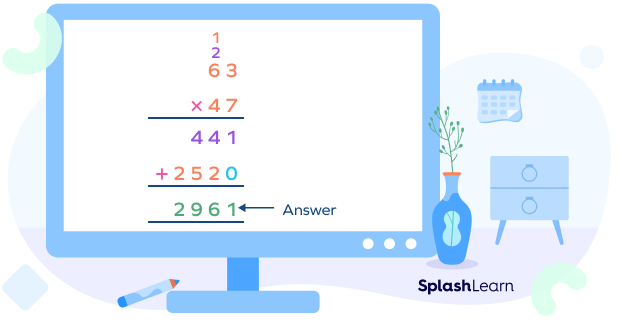
Let’s summarize.
We follow the above long multiplication steps only for multiplying numbers greater than two digits.
Related Worksheets

Long multiplication is also known as the column method of multiplication since we perform the multiplication vertically or column wise.
Let’s take another example to understand this better.
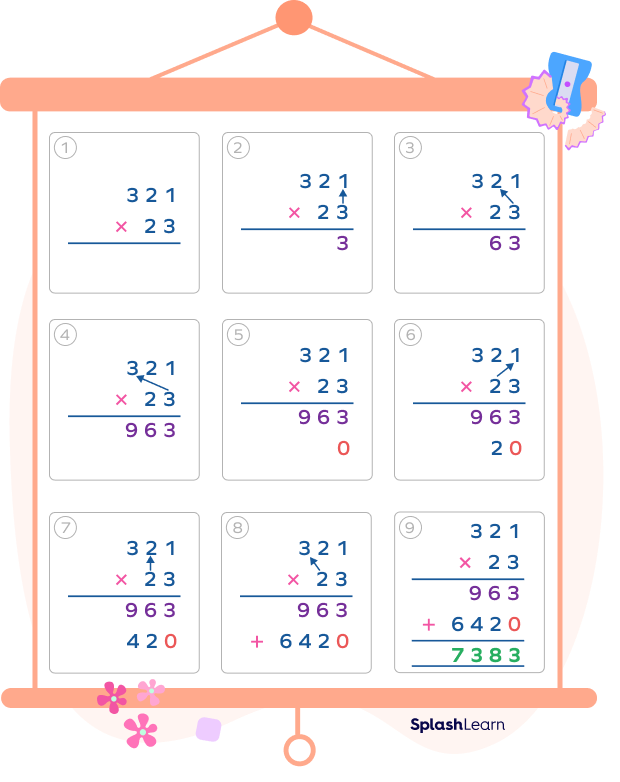
Multiply 321 by 23.
Take a look at the long multiplication chart that shows the long multiplication step by step. You can refer to it to avoid mistakes when solving long multiplication problems.
Multiplying Decimals Using Long Multiplication
Let’s understand how to multiply decimals with the help of the long multiplication method.
Example: Multiply $3.6 \times 5.5$
Step 1 : First, we place the smaller number out of the two on the right-hand side and change the decimal number to a fraction.
$5.5 \times 3.6 = \frac{55}{10} \times \frac{36}{10}$
Step 2 : Then, we multiply the numerators using the steps of the long multiplication method. We leave the denominator as it is for now.
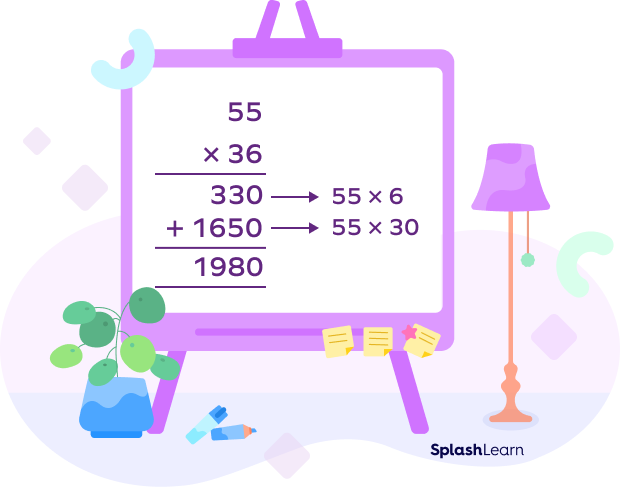
Step 3 : Now, we divide the answer (that we got in step 2) by the denominator to get the final answer.
$\frac{1980}{100} = 19.80$
Long Multiplication Using the Horizontal Method
Let’s now understand how to use the horizontal method with the help of a long multiplication example. As the name suggests, we multiply the numbers horizontally but follow the same steps as we discussed earlier.
Example: Multiply 48 by 24.
Step 1 : First, we write the numbers beside each other and place them horizontally.
$48 \times 24$
Step 2 : Now, we multiply the second number (number on the right side) with the ones digit of the first number.
Here, we multiply 24 with 8, since 8 is at the ones place in 48.
$24 \times 8 = 192$
Step 3 : Now, we multiply the second number with the tens digit of the first number.
Here, we multiply 24 with 40, since 4 is at the tens place in 48.
$24 \times 40 = 960$
Step 4 : Finally, we add the partial products obtained from steps 2 and 3 to get the final answer.

Thus, $48 \times 24 = 1152$
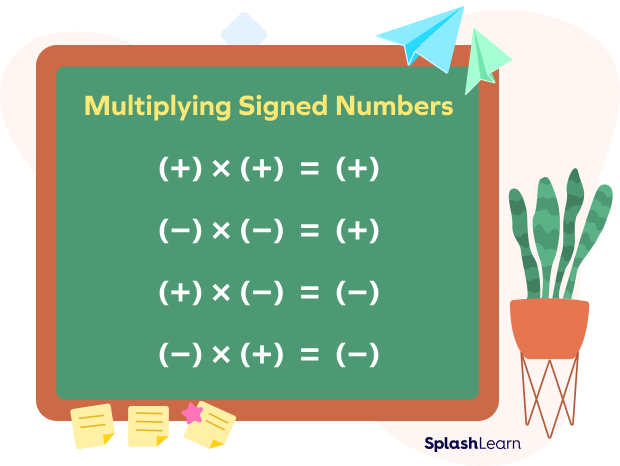
Long Multiplication with Negative Numbers
The multiplication of negative numbers using the method of long multiplication follows the same steps as mentioned above. However, we have to carefully consider the signs of the two numbers in order to decide the sign of the product.
For instance, when we multiply two negative numbers with each other, the sign of the result remains positive. On the other hand, it becomes negative when a negative number and a positive number are multiplied.
The figure below shows how the sign changes upon multiplication with negative numbers:
Fun Facts about Long Multiplication
- Long multiplication is also known as the column method of multiplication.
- Whenever any number is multiplied by zero, the answer is also zero.
- When the number 9 is multiplied by any other number, the sum of digits in the product is always 9.
For example, $9 \times 25 = 225$ and $2 + 2 + 5 = 9$;
$9 \times 9 = 81$ and $8 + 1 = 9$.
- Long multiplication can also be referred to as repeated addition because multiplying any number is just an alternative to adding it repeatedly.
- Whenever any even number from 0 to 9 is multiplied by 6, the product has the same even number in the ones digit.
For example, $6 \times 4 = 24,\; 6 \times 2 = 12$
- Whenever two large numbers (let’s say three-digit or four-digit numbers) are multiplied, the process of long multiplication remains the same. For example:

Long multiplication is a method that simplifies the multiplication of large numbers, including two-digit, three-digit numbers, etc., with each other. Let’s solve a few examples and practice problems based on long multiplication!
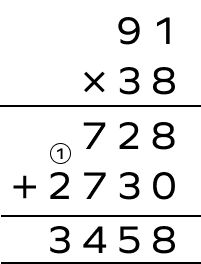
1. Multiply 38 by 91 using the column method.
Solution:
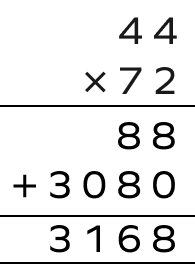
2. Multiply 72 by 44 using the column method.
Solution :
3. Multiply – 58 by 30.
The sign of the product when we calculate $(\;-\;58) \times (30)$ will be negative.
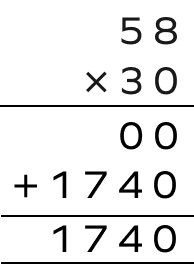
Since 58 has a negative sign, the final answer will be $ – 1740$.
$(\;-\;58) \times (30) = \;-\;1740$
4. Alia bought 42 notebooks, each worth $\$9.6$ . How much did she spend?
To find the amount Alia spent, multiply 9.6 by 42.
$9.6 \times 42 = \frac{96}{10} \times 42$
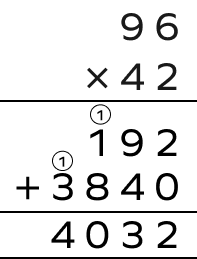
Now, we divide 4032 by 10 to get the final answer, which is $403.2$.
$9.6 \times 42 = 403.2$
Thus, Alia spent $403.2 on notebooks.
5. Multiply $-70$ and $-15$ .
Let’s find $(70) \times (15)$.
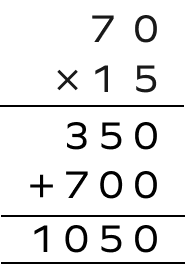
Since both the numbers are negative, the final answer will remain positive, $1050$.
$(70) \times (15) = 1050$
Attend this quiz & Test your knowledge.
Multiply 95 by 13 using the column method.
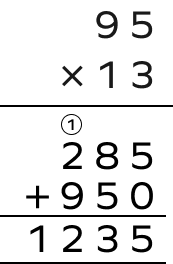
Multiply the decimals 1.2 and 6.7.
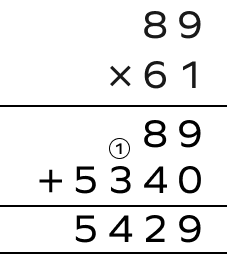
Multiply the negative numbers $(-\;89)$ and $(-\;61)$..
Multiply 45 by 21 using the horizontal method.
Multiply 530 by 22..
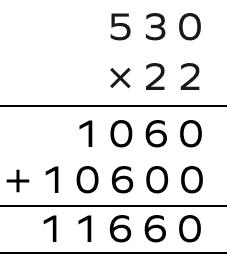
What are negative numbers?
Negative numbers are those whose value is less than zero and thus have a negative sign (-) before them.
What are positive numbers?
Positive numbers are those whose value is greater than zero.
What is a decimal?
A decimal number represents the number that separates a whole number from a fractional number. It is represented by a dot (.) sign.
What is the meaning of the horizontal method of multiplication?
The horizontal method refers to a method wherein numbers are arranged in a horizontal line from left to right.
What is the meaning of the column method of multiplication?
The column method refers to a method wherein numbers are placed one below the other from top to bottom.
What is short multiplication?
Short multiplication is the method of multiplication commonly used when multiplying a three-digit or larger number with a single-digit number.
RELATED POSTS
- Brackets in Math – Definition, Types, Examples
- Volume of a Pentagonal Prism – Definition, Formula, Examples, Facts
- Area in Math – Definition, Composite Figures, FAQs, Examples
- Multiplication Chart – Definition with Examples
- Slope of Parallel Line: Formula, Derivation, Example

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free
Try out your Multiplication Tables
Learn your Multiplication Table with these quizzes:
Multiplication Table Instructions
To use the times tables follow this guide:
- Select the times tables you want to try
- Use the drop down boxes and select the one you think is the correct answer
- Once you have completed all the questions press the OK Done button
- You then see your results!
- Then do more ( the test is always different! ), or come back here and choose another table
- Math Article
Multiplication Tricks

Multiplication tricks are required to calculate long and difficult multiplication problems. For single digit, 2-digit and even for 3-digit numbers, it is easy to do the multiplication. But for larger numbers which have more digits such as 4, 5, 6, 7,etc., it takes a long time to solve it. Therefore, we will learn here some magic maths tricks for fast calculation. These tricks can also be used to prepare for competitive exams.
In Maths, there is a number of arithmetic calculations or operations which includes multiplication and division, addition, subtraction, differentiation, integration, etc. Each calculation has its own method to calculate the relation between the numbers based upon the operation performed on them. Along with the methods, it is always useful to learn some multiplication tricks to save time.
What are Multiplicand and Multiplier?
It is necessary to know, what are the numbers called when we apply multiplication operation in them.
- The multiplicand is the number which is being multiplied
- The multiplier is the number which is multiplying the first number.
For example : In this operation, 45 × 20, 45 is the multiplicand and 20 is the multiplier.
How to Multiply Fast?
Here are some tips and tricks with the help of which, you can easily solve multiplication problems. These tricks you can use in competitive exams as well. Students can by-heart multiplication tables to calculate fats. Let check the multiplication tricks for different numbers.
Multiplication by 2: It denotes to double a number.
For example; 5 × 2, here we have to double the number 5, so we can use addition method here, i.e.
Multiplication by 3: It denotes triple times of a number.
Example: 5 × 3 = 5 + 5 + 5 = 15
Multiplication by 4: It denotes double of a double number.
Example: 5 × 4: double of 5 is 10. Thus double of 10 is 20(10+10)
Multiplication by 5: If a number is multiplied by 5, then divide the number by 2 and multiply by 10.
Example: 8 × 5: 8 divide by 2 = 4, multiply 4 by 10, 4 × 10 = 40.
Multiplication by 8: Double → Again Double → Again Double
Example: 5 × 8: 5 + 5 = 10; 10 + 10 = 20; 20 + 20 = 40
Multiplication by 9: Add +1 to 9 and minus the number with itself, which is to be multiplied.
Example: 5 × 9: 9+1 × 5-5 = 10 × 5 – 5 = 50 -5 = 45
Multiplication Table
Multiplication method is basically designed to form tables of different numbers. It is always suggested for students to learn by heart the tables from 2 to 20 at least, which will help to solve multiplication problems very easily.
Let us create a table for multiplication of 2 to 10 numbers, which will help you to memorize the table.
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | |||||
| 6 | 10 | 14 | 18 | ||||||
| 3 | 6 | 9 | 15 | 21 | 27 | ||||
| 20 | 28 | 36 | |||||||
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 35 | 45 | |||
| 42 | 54 | ||||||||
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 49 | 63 | ||
| 72 | |||||||||
| 9 | 18 | 27 | 36 | 45 | 54 | 63 | 72 | 81 | |
With this table, you can see each number is appearing twice. There is a duplicate for each number inside the table. For example, 3 × 6 = 18 but also 6 × 3 = 18.
Learning from the table is the general trick of multiplication. Now let us learn about multiplying tricks of 4 digit numbers along with the general method and rounding up method.
Also, learn:
General Method for Multiplication
In this method, we apply the simple procedure of multiplication.
For example 6780
————–
So you can see there are only one digit multiplier and 4 digit multiplicand. Easily with the help of a table, you can solve such problems.
List of Important Multiplication Tricks
Case 1: Multiplication of the given number by 5 n . (5, 25, 125, …)
Step 1: Add as many zeroes at the end of the given number, as there is a power of 5
Step 2: Divide the resultant number by 2 (Po wer o f 5 ) , to get the result.
Multiply 94 by 125
Given: 94 × 125
Here 125 = 5 3 . The power of 5 is 3.
Step 1: Now, add 3 zeros at the end of 94, and hence it becomes 94000
Step: Now, divide 94000 by 2 3 . Hence, it becomes
Therefore, 94 × 125 is 11750
Case 2: In the multiplication of two numbers, if the sum of whose unit digit is 10, and the remaining digits are the same in both the numbers.
Step 1: Multiply the unit digits of the numbers
Step 2: Now multiply the digit (which are same) with its consecutive number
Step 3: Finally, append the result obtained in step 1 to the right of the result obtained in step 2.
Multiply 22 by 28
Given: 22 × 28
Here, the sum of the unit digit is 10 (2+8 = 10)
Step 1: Multiply unit digits: 2 × 8 = 16
Step 2: Multiply the digit 2 with its consecutive number 2 × (2+1) = 2 x 3 = 6
Step 3: Append 16 to the right side of 6. Hence, it becomes 616.
Therefore, 22 × 28 is 616.
Case 3: Multiplication of the given number by 9 n . (9, 81, 729)
Step 1: Identify the power of 9, such that step 2 has to be performed based on the power of 9.
Step 2: Multiply the given number by 10, and then subtract the given number from the result obtained.
Multiply 232 by 81.
Here the power of 9 is 2. (9 2 = 81)
Hence, step 2 has to be performed twice.
- (232 × 10) – 232 = 2088
- (2088 × 10) – 2088 = 18792
Therefore, the product of 232 and 81 is 18792.
Case 4: Multiplication of a number by a given number whose unit digit is 9
Step 1: Split the second number, such that it should be equal to the given number
Step 2: Now, apply distributive property of multiplication over addition or subtraction, as per the problem requirement
Step 3: Simplify the arithmetic operation
Example: Multiply 142 by 49
Step 1: Split the second number, and hence it becomes 142 × (50-1)
Step 2: Now, apply the distributive property of multiplication over subtraction.
= (142×50)-(142×1)
= 7100 -142
Therefore, 142 × 49 = 6958
Case 5: Multiplication of a number by a given number which contains all the digits a 9
Step 1: Split the given number (multiplier) in the form of (10 n – 1)
Step 2: Now, apply the distributive property of multiplication over subtraction
Step 3: Simplify the arithmetic operations
Multiply 436 by 999
Step 1: 999 can be written as (1000-1). Hence, the given problem is written as 436×(1000-1)
436×(1000-1) = (436×1000) – (436×1)
436×(1000-1) = 436000 – 436
436×(1000-1) = 435564
Therefore, the product of 436 and 999 is 435564.
Case 6: Multiplication of the given numbers which are close to the powers of 10. (10 1 , 10 2 , 10 3 , …)
Step 1: Write down the two numbers with the difference from the base number
Step 2: Now take the sum of two numbers, which are obtained in step 1 (Considering the sign also) along with either of the two diagonals. This should be the first part of the answer)
Step 3: Now, take the product of two numbers (numbers obtained from step 1), with the consideration of the symbols. This should be the second part of the answer.
Step 4: Combine the first part (result from step 2) and the second part (result from step 3) of the solution together to get the final solution.
Multiply 93 by 94
93 = (93 – 100) = -7
94 = (94 -100) = -6
Take the sum of two numbers along either of two diagonals (Consider the sign also)
Diagonal sum ⇒ 93 + (-6) = 94 +(-7) = 87
Therefore, the first part of the solution is 87
Step 3: Take the product of two numbers: -7 ×-6 = 42
Therefore, the second part of the solution is 42
Step 4: Combine the first and second part of the solution together, and hence it becomes 8742
Therefore, 93 × 94 = 8742.
Rounding Up Method for Multiplication
In this method, we round up the complex numbers in the simple form to make the multiplication easier. Let us explain to you with example problems.
Multiplication Tricks for a 2-digit number
Rounding the number 58 to 60,
Multiplying the rounded amount to itself;
Subtracting 120-4=116
So, 116 is the final answer.
If we right, 22 as 20+2 and then multiplying them separately,
26 × 20 and 26 × 2 and adding them.
—— ——
520 + 52 = 572
So the answer for 26 × 22 is 572.
In the same way, you can practice more of multiplication problems by using these simple multiplication tricks.
Frequently Asked Questions on Multiplication Tricks
Mention the multiplication tricks for 4.
While multiplying 4 with any number, use the double-up tricks twice. For example, 3 ×4 is the same 3+3 = 6, then 6+6 = 12. Hence the answer should be 12.
Mention the multiplication tricks for 5?
We know that 5 can be written as 10/2. If any number is multiplied by 5, first multiply the given number by 10, and then divide the resultant number by 2. For example, 12 × 5. To simplify this, multiply 12 by 10, hence the result becomes 120. Now, divide 120 by 2, we get 60. Therefore, 12 × 5 = 60.
Mention the multiplication tricks for 8?
The multiplication trick for 8 is double, double and double again. For example, 4×8. Now, double the number 4 = 4+4 = 8 Now, double the number 8 = 8+8 = 16 Now, double the number 16 = 16+16 = 32
Write down the multiplication tricks for 10
Add the zero at the end of the given number. For example, 5 × 10. Now add zero at the end of the number 5, hence, the answer becomes 5.
Mention the multiplication tricks for 12
Assume, we need to multiply 6 by 12 Step 1: Multiply the given number by 10. (6×10 = 60) Step 2: Multiply the given number by 2. (6 × 2 = 12) Step 3: Add the result obtained from step 1 and step 2 (60+12 = 72) Hence, 6 ×12 = 72

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Maths How To with Anita

7 simple Multiplication Strategies for Students of All Ages (The Why and How to)
Multiplication can be a daunting task for students of all ages. However, with the right multiplication strategies in place, it can become a fun and easy process.
In this article, we will discuss 7 multiplication strategies that will help students understand the why behind multiplication before learning how to do it.
With these strategies in place, students will be able to confidently approach multiplication problems and succeed before learning multiplication facts.
The importance of understanding the why before learning how to multiply
It can not be understated. multiplication is a fundamental building block for many mathematical concepts.
If students do not have a strong foundation in multiplication, they will likely struggle with more complex topics down the road.
Therefore, it is essential that students understand the why behind multiplication facts before moving on to learning how to do it.
What are the 7 strategies for multiplication?
In my 14+ years as a high school mathematics teacher, I have noticed that many students have gaps in their knowledge about multiplication strategies.
Once they are allowed to use a calculator they rely on this heavily and forget the mental math strategies they used in primary and middle school.
Knowing the times tables becomes assumed knowledge in high school to be able to readily apply them to algebra, measurement and other topics quickly. So these multiplication strategies are extremely useful to all students.
Commutative property
If you know that 4 x 7 = 28, then 7 x 4 also equals 28 because the commutative property of multiplication states that the order of numbers does not affect the product.
This is a key multiplication strategy for students to understand because it can help them save time and effort when multiplying large numbers.
It also means students only need to memorize half of the times tables.
x4 = Double double
If you know that doubling a number and then doubling the result is the same as multiplication by four, then you can use this strategy to solve multiplication problems quickly.
For example, if you need to calculate 28 x 4, you can first double 28 to get 56. Then, double 56 to get 112. Therefore, 28 x 4 = 112
Doubling and halving
This multiplication strategy is great when multiplication by a large even number is required.
For example, if you need to calculate 16 x 3, you can first halve 16 to get 8. Then, double 3 to get 6. Therefore, 16 x 3 = 8 x 6 = 48
This diagram shows two rectangles of dimensions 16 x 3 and 8 x 6.
You can see that they have the same area.
9 times tables on fingers
This multiplication strategy is one that students often learn in primary school.
To use this strategy, you hold up your hands and put down your finger that you are multiplying by 9.
For example, if you are finding 9 x 7, you put down your 7th finger like this.

This leaves 6 fingers to the left of the finger that was folded down and 3 fingers to the right.

So 9 x 7 = 63
Try it with your fingers and 9 x 8. Hold down your 8th finger and you should have 7 fingers to the left and 2 to the right, so 9 x 8 = 72
Repeated addition
This multiplication strategy is often used with young students who are just learning to multiply.
It is a helpful strategy for them to understand that multiplication is simply repeated addition.
For example 4 x 3, can be thought of as 4 + 4 + 4 = 12
Skip counting
Skip counting is a strategy that can be used with any number. It relies on multiplication facts that have already been learned to skip count by the number being multiplied.
For example, if you need to calculate 5 x 13, you can start by skip counting by 5’s like this:
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65
Skipping count by the number that you are multiplying to find the answer.
Equal groups
When we group objects into equal sets, we can add them up to find the total number of objects.
This is a strategy that is often used with young students who are just learning to multiply.
For example, 4 x 3 can be represented by equal groups of 3.
This can be represented with a diagram with 4 plates of cookies with 3 cookies on each plate. Then we can count the cookies.

So 4 x 3 = 12
Whole number multiplication can also be thought of as repeated addition with an array.
An array is a rectangular arrangement of objects. The number of rows in the array tells us how many times we need to add.
The number of columns tells us what number we are adding.
For example, this array has three rows and four columns
There are 12 dots altogether so 3 x 4 = 12
What order do you teach multiplication strategies?
There is no definitive answer to this question as different students will learn multiplication strategies at different rates. However, it is generally recommended that students learn repeated addition and skip counting first. Then the commutative property before moving on to more difficult strategies such as doubling and halving.
What is a multiplication fact strategy?
Using the commutative property is the simplest multiplication fact strategy.
The commutative property is when the order of the numbers being multiplied does not affect the answer.
So this means you only need to learn half of the multiplication facts since
5 x 4 = 4 x 5
The benefits of using multiplication strategies
There are many benefits to using multiplication strategies.
Some of these benefits include:
– Students will develop a deeper understanding of multiplication concepts.
– Students will be able to approach multiplication problems with confidence.
– Students will be better prepared to tackle more complex mathematical concepts in the future.
Final thoughts and my experience of using multiplication strategies in the classroom
These multiplication strategies are essential for students to understand the multiplication facts which are often rote learned. They can then be applied to any multiplication, even if it is for the multiplication of decimals or algebraic terms.
In my teaching experience, the students who were able to apply these different strategies had better success solving unfamiliar problems and were faster, allowing them more time to think about harder questions.
Related posts:

Multiplication Tables
A multiplication table is a list of multiples of a number and is also commonly referred to as the times table . We can obtain the times tables of a number by multiplying the given number with whole numbers. Multiplication is one of the basic mathematical operations which is taught to students at an early age. A simple approach to teaching students the concept of multiplication is through a multiplication table chart.
Maths tables can be extremely helpful in doing basic arithmetic calculations. These work as building blocks for doing higher maths like fractions, exponents, and many more. Free Printable times table charts and tables are provided to help you learn times tables effortlessly. These times tables charts help the students to memorize them faster if they frequently revise them.
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. | |
| 6. |

What is a Multiplication Chart?
A multiplication times tables chart is a table that shows the product of two numbers. Usually, one set of numbers is written on the left column and another set is written on the top-most row. Having a multiplication chart saves a considerable amount of time and energy in doing calculations.
Multiplication Chart 1 to 10
Times table chart 1 to 10 consists of the numbers written from 1 to 10 on the top-most row of the grid as well as on the left-most column of the grid. For all other rows and columns, each of the boxes represent numbers as the product of numbers, one from the top-most row and the other from the left column. A multiplication times tables chart is given below.

Printable Multiplication Chart
Here is the link for the multiplication table pdf which can be easily downloaded and printed, if needed.
☛ Download Printable Multiplication Chart PDF
This multiplication chart should be placed somewhere where it can be seen frequently. This helps a lot in memorizing these math tables and makes the students thorough with them.
Multiplication Tables from 1 to 20
Multiplication tables are building blocks for multi-digit calculations and solving problems based on fractions, percentages , and factoring. These times tables from 1 to 20 help a child in doing mental arithmetic and also enables them to skillfully tackle more complex calculations.
Times Tables Meaning
A multiplication table is a list of multiples of a particular number. It is a tool used to learn how to multiply two numbers. A times table helps us to calculate answers quickly and easily. Observe the following table which shows the times tables from 2 to 20.
Multiplication Tables 2 to 5
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 × 1 = 2 | 3 × 1 = 3 | 4 × 1 = 4 | 5 × 1 = 5 |
| 2 × 2 = 4 | 3 × 2 = 6 | 4 × 2 = 8 | 5 × 2 = 10 |
| 2 × 3 = 6 | 3 × 3 = 9 | 4 × 3 = 12 | 5 × 3 = 15 |
| 2 × 4 = 8 | 3 × 4 = 12 | 4 × 4 = 16 | 5 × 4 = 20 |
| 2 × 5 = 10 | 3 × 5 = 15 | 4 × 5 = 20 | 5 × 5 = 25 |
| 2 × 6 = 12 | 3 × 6 = 18 | 4 × 6 = 24 | 5 × 6 = 30 |
| 2 × 7 = 14 | 3 × 7 = 21 | 4 × 7 = 28 | 5 × 7 = 35 |
| 2 × 8 = 16 | 3 × 8 = 24 | 4 × 8 = 32 | 5 × 8 = 40 |
| 2 × 9 = 18 | 3 × 9 = 27 | 4 × 9 = 36 | 5 × 9 = 45 |
| 2 × 10 = 20 | 3 × 10 = 30 | 4 × 10 = 40 | 5 × 10 = 50 |
Maths Tables 6 to 10
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 × 1 = 6 | 7 × 1 = 7 | 8 × 1 = 8 | 9 × 1 = 9 | 10 × 1 = 10 |
| 6 × 2 = 12 | 7 × 2 = 14 | 8 × 2 = 16 | 9 × 2 = 18 | 10 × 2 = 20 |
| 6 × 3 = 18 | 7 × 3 = 21 | 8 × 3 = 24 | 9 × 3 = 27 | 10 × 3 = 30 |
| 6 × 4 = 24 | 7 × 4 = 28 | 8 × 4 = 32 | 9 × 4 = 36 | 10 × 4 = 40 |
| 6 × 5 = 30 | 7 × 5 = 35 | 8 × 5 = 40 | 9 × 5 = 45 | 10 × 5 = 50 |
| 6 × 6 = 36 | 7 × 6 = 42 | 8 × 6 = 48 | 9 × 6 = 54 | 10 × 6 = 60 |
| 6 × 7 = 42 | 7 × 7 = 49 | 8 × 7 = 56 | 9 × 7 = 63 | 10 × 7 = 70 |
| 6 × 8 = 48 | 7 × 8 = 56 | 8 × 8 = 64 | 9 × 8 = 72 | 10 × 8 = 80 |
| 6 × 9 = 54 | 7 × 9 = 63 | 8 × 9 = 72 | 9 × 9 = 81 | 10 × 9 = 90 |
| 6 × 10 = 60 | 7 × 10 = 70 | 8 × 10 = 80 | 9 × 10 = 90 | 10 × 10 = 100 |
Times Tables 11 to 15
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 × 1 = 11 | 12 × 1 = 12 | 13 × 1 = 13 | 14 × 1 = 14 | 15 × 1 = 15 |
| 11 × 2 = 22 | 12 × 2 = 24 | 13 × 2 = 26 | 14 × 2 = 28 | 15 × 2 = 30 |
| 11 × 3 = 33 | 12 × 3 = 36 | 13 × 3 = 39 | 14 × 3 = 42 | 15 × 3 = 45 |
| 11 × 4 = 44 | 12 × 4 = 48 | 13 × 4 = 52 | 14 × 4 = 56 | 15 × 4 = 60 |
| 11 × 5 = 55 | 12 × 5 = 60 | 13 × 5 = 65 | 14 × 5 = 70 | 15 × 5 = 75 |
| 11 × 6 = 66 | 12 × 6 = 72 | 13 × 6 = 78 | 14 × 6 = 84 | 15 × 6 = 90 |
| 11 × 7 = 77 | 12 × 7 = 84 | 13 × 7 = 91 | 14 × 7 = 98 | 15 × 7 = 105 |
| 11 × 8 = 88 | 12 × 8 = 96 | 13 × 8 = 104 | 14 × 8 = 112 | 15 × 8 = 120 |
| 11 × 9 = 99 | 12 × 9 = 108 | 13 × 9 = 117 | 14 × 9 = 126 | 15 × 9 = 135 |
| 11 × 10 = 110 | 12 × 10 = 120 | 13 × 10 = 130 | 14 × 10 = 140 | 15 × 10 = 150 |
Times Tables 16 to 20
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 × 1 = 16 | 17 × 1 = 17 | 18 × 1 = 18 | 19 × 1 = 19 | 20 × 1 = 20 |
| 16 × 2 = 32 | 17 × 2 = 34 | 18 × 2 = 36 | 19 × 2 = 38 | 20 × 2 = 40 |
| 16 × 3 = 48 | 17 × 3 = 51 | 18 × 3 = 54 | 19 × 3 = 57 | 20 × 3 = 60 |
| 16 × 4 = 64 | 17 × 4 = 68 | 18 × 4 = 72 | 19 × 4 = 76 | 20 × 4 = 80 |
| 16 × 5 = 80 | 17 × 5 = 85 | 18 × 5 = 90 | 19 × 5 = 95 | 20 × 5 = 100 |
| 16 × 6 = 96 | 17 × 6 = 102 | 18 × 6 = 108 | 19 × 6 = 114 | 20 × 6 = 120 |
| 16 × 7 = 112 | 17 × 7 = 119 | 18 × 7 = 126 | 19 × 7 = 133 | 20 × 7 = 140 |
| 16 × 8 = 128 | 17 × 8 = 136 | 18 × 8 = 144 | 19 × 8 = 152 | 20 × 8 = 160 |
| 16 × 9 = 144 | 17 × 9 = 153 | 18 × 9 = 162 | 19 × 9 = 171 | 20 × 9 = 180 |
| 16 × 10 = 160 | 17 × 10 = 170 | 18 × 10 = 180 | 19 × 10 = 190 | 20 × 10 = 200 |
Importance of Multiplication Tables for Students
Multiplication tables, also known as maths times tables , are the basic building blocks for arithmetic calculations. The memory of a child is much more powerful than an adult. The things which we learn at an early age have a strong impact on the brain and they are retained lifelong.
The math times tables are very useful and a few uses of these maths tables are given below:
- Maths tables support the mathematical learning of a student.
- Gives them a strong grasp of the facts associated with multiplication.
- Makes it easier for students to work out problems in mathematics.
- Students who have a strong grasp of math times tables, tend to be more self-assured when learning new math concepts.
- Multiplication Tables 1 to 10
Here are the links of the pages that have maths tables from 2 to 10.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Easy Way to Learn Maths Tables
Students typically struggle to memorize multiplication tables. Here are a few effective tips to help students in memorizing these math times tables.
- Practice Skip Counting: Start with a number and then keep adding that same number. For instance, if you start by 3, keep adding 3 every time to count. So, you will get the result as 3, 6, 9, 12...
- Recite the Multiplication Table in Order: For instance, you should say '2 ones are 2, 2 twos are 4, 2 threes are 6,' and so on. Make it a practice to recite this table once daily until you master the structure that it follows.
- Practice by Writing: If you are facing some difficulty in memorizing the multiplication table, you always have the option of writing and learning. Make it a daily routine to write the multiplication tables and then recite them once.
- Apply Multiplication to Real Life: Try to understand multiplication tables using real-life examples. You can also try practicing multiplication during various instances, if possible. For example, multiplying the price of one product by the number of products or multiplying the amount by the number of notes in a bundle.
- Identify Patterns: Every multiplication table has its own pattern. It is very important to identify this pattern. It will help you to memorize these math times tables faster.
Times Tables 11 to 20
Here are the links of the pages that have maths tables from 11 to 20.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cuemath is one of the world's leading math learning platforms that offers LIVE 1-to-1 online math classes for grades K-12 . Our mission is to transform the way children learn math, to help them excel in school and competitive exams. Our expert tutors conduct 2 or more live classes per week, at a pace that matches the child's learning needs.
Multiplication Tables Solved Examples
Example 1: Sam works for 5 hours a day and is paid $8 per hour. How much does Sam earn in a day?
Solution: Sam works for 5 hours and is paid $8 per hour. Therefore, let us use the multiplication tables to find the total amount that he earns in a day, that is, 5 × 8 = 40.
∴ Sam earns $40 in a day.
Example 2: Fill in the blanks using the maths times tables.
a.) 3 × 4 =
b.) 6 × 7 =
c.) 8 × 2 =
Solution: Using the maths tables, we can fill in the blanks:
a.) 3 × 4 = 12
b.) 6 × 7 = 42
c.) 8 × 2 = 16
Example 3: State true or false using the times tables.
a.) 4 × 7 = 28
b.) 9 × 8 = 98
c.) 3 × 6 = 18
Solution: Using the maths times tables, we can write true and false for the following.
a.) True, 4 × 7 = 28
b.) False, 9 × 8 = 72
c.) True, 3 × 6 = 18
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free trial Class
FAQs on Multiplication Tables and Charts
Is it important to memorize multiplication tables.
Yes, it is important to memorize multiplication tables. We cannot always do repeated addition in order to multiply numbers. There has to be a way to find the product in less time and effort. Multiplication helps in solving problems based on operations on fractions and integers . Multiplication tables act as powerful tools to deal with various arithmetic-related problems easily and also save time in complicated calculations. The students can download math times tables from 2 to 20 and make a regular routine to go through these multiplication tables. Check the following links which have multiplication tables of numbers.
- Multiplication Tables 1 to 100
- Multiplication Tables 1 to 30
- Multiplication Tables 13 to 20
- Multiplication Tables 1 to 15
What are Multiplication Tables used for?
The multiplication tables can be in the following ways.
- Multiplication tables are helpful in quick calculations.
- They help in understanding the patterns of multiples .
- They are used for calculating the bill while purchasing anything from a shop, for example, groceries, etc.
- For mathematical calculations related to any dimensional quantity like area, volume, etc for an object.

Why are Times Tables Important?
Learning the multiplication table is an essential skill for long multiplication and division because it helps in faster mental calculations and this helps the children enhance their confidence in the subject.
How do Multiplication Tables help Problem Solving Abilities?
Multiplication tables can improve problem-solving abilities by building the number sense and once the child starts calculating faster using these maths tables, he builds up confidence and gets more inclined towards the subject.
Why is a Multiplication Chart Helpful?
A multiplication times table chart shows all the math times tables clearly in one grid. It is a handy reference to memorize multiplication facts. Create a math multiplication tables chart, read it daily, or even utilize it for calculation purposes. This helps in faster mental calculations and helps in saving time.
- Multiplication Tables 11 to 20
- Multiplication Tables 20 to 30
- Multiplication Tables 12 to 20
- Multiplication Tables 41 to 50
What is an Easy way to Learn Times Tables?
The best way to learn multiplication tables is to recite each math table every day. Apart from this, the following tips help in learning maths tables faster.
- Write the multiplication tables at least two times to learn them.
- Try to recite them aloud as you write them because this helps in learning them faster.
- Place the sheet of the maths tables at some common place where it is always visible. This can be on the wall next to your study area, or anywhere where you can easily read them. This helps in saving time, and quickly memorizing them. Check out the following links for the multiplication tables of different numbers:
- Multiplication Tables 1 to 12
- Multiplication Tables 15 to 20
- Multiplication Tables 11 to 30
- Multiplication Tables 21 to 30
What is an Easy Way to Learn Tables from 1 to 20?
An easy way to learn tables from 1 to 20 is by using the following tips:
- Write the tables in the format as shown above on the page under the heading ' Multiplication Tables from 1 to 20' and practice writing them while reciting each row aloud. This helps in memorizing them faster.
- Another trick is to understand that all the multiplication tables follow a pattern. For example, if it is the maths table of 7, then it can be learned by adding 7 to each multiple to get the next multiple. This means there is a difference of 7 in each of its multiples. For example, 7 × 1 = 7, 7 × 2 = 14, 7 × 3 = 21, 7 × 4 = 28, and so on. This rule applies to all times tables, like, if it is the multiplication table of 6, then it can be obtained by adding 6 to each multiple to get the next multiple.
- Place the maths tables from 1 to 20 right in front of your study area so that you can frequently revise them whenever you happen to look at them. This is an easy way to learn tables from 2 to 9 also.
How to Memorize Multiplication Tables?
Multiplication tables can be memorized by using the following techniques:
- Check for the pattern of the particular times table because all the multiplication tables follow a pattern. If it is the table of 4, then it can be obtained by adding 4 to each multiple to get the next multiple. This means there is a difference of 4 in each of its multiples. For example, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, and so on. This rule is applicable to all maths tables.
- Practice writing the multiplication tables at least twice to learn them and revise them every day.
- Place the handwritten tables somewhere where they can be easily seen, may be, on the wall next to your study table. This will help you to look at them frequently whenever you pass by or you are free.

Bridge Builder X

Treasure Quest X

Math Racer Multiplication

Number Trails Multiplication

Factor Pairs

Monster Multiplication

Penguin Multiplication

Music Shop Multiplication

Multiplication Snake

Multiplication Blocks

Mach 10 Multiples

Puzzle Pics Multiplication

Math Surpass X

Grand Prix Multiplication

Factor Pair Up

Math Surpass Division

Puzzle Pics Division

Monster Division

Product Blocks

Just Divide

Dino Park Division

Demolition Division

Pony Pull Division

Monster Stroll Multiplication

Tug Team Multiplication

Meteor Multiplication

Division Derby

Missing Factors

Take the Cake X

Undercover X

Do/Undo Multiplication

Zogs and Monsters

Drag Race Division

Two Digit Multiplication

Dare to Share Fairly

Candy Challenge Pro

Math Surpass Remainders

Problem Solving

Candy Challenge Junior

Monster Mischief

Make a Number

All Aboard Multiplication

Venn Puzzle 2

Secret Code X

PEMDAS Exhibit

Missing Digits Multiplication

Missing Digits Division

One Product

Multiplying Integers

Intro to Multiplication

Multiplication with Three

Multiplication Vocabulary

Division Vocabulary

Division and Remainders

Long Division

Multiplication and Division

Commutative Property

Associative Property

Distributive Property

Thinking Blocks

Word Problem Practice

Undercover X Pro

Grid X Challenge

Function Machine

Function Machine Pro

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
NEW: Classroom Clean-Up/Set-Up Email Course! 🧽
50 Fun Hands-On Activities and Games To Teach Multiplication
Making it fun makes it stick!
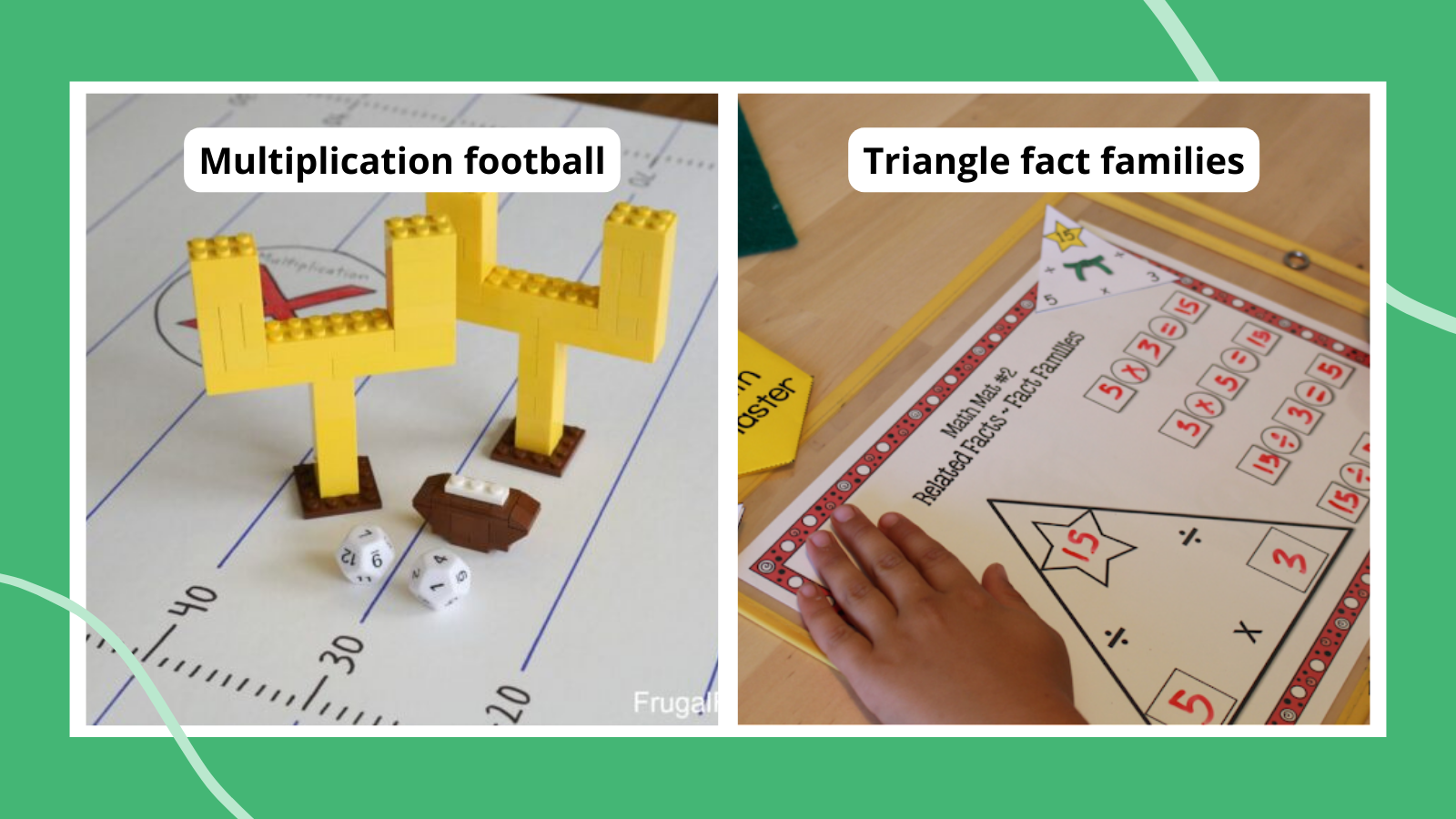
Multiplication is a basic skill students need to master before they can move on to more advanced math. Memorizing multiplication tables is one option, but it’s important for kids to understand exactly what it means to multiply. This list of fun and engaging ways to teach multiplication has so many options. You’re sure to find a way to resonate with every one of your students!
1. Play a game of Scoot

This is a fun way to break up the routine of worksheets. One at a time, you will post one of the multiplication task cards and your students will work to find the answer. After a set amount of time (up to you), say “Scoot.” Students will leave their answer sheet on their desk and move one seat to their left. Post another task card. Again, say “Scoot” and have students rotate.
2. Practice skip-counting with a song
For many of us, setting information to music helps us memorize it. This series of videos from HeavenSentHorse features common tunes that your students will quickly catch on to like Jingle Bells, This Old Man and more.
3. Solve multiplication puzzles

Puzzles are a great way to engage students and build their problem-solving skills. These puzzles help students put together the pieces to get the whole picture and really understand how to solve a multiplication problem.
4. Play Four in a Row

This fun game challenges kids to practice their math facts. Partners will take turns choosing a circle and solving the math fact. If they get it right, they place a marker over it (here, a penguin stamp). The first player to connect four wins.
5. Solve Mystery Pictures

Students will solve the one-digit multiplication problems, then use the key to color in the boxes and create the mystery picture.
6. Play multiplication tic-tac-toe

Playing with partners, each player chooses a multiplication problem to solve. If they get it right, they mark it with their dot marker. If not, it’s the next person’s turn. Play goes back and forth until someone gets three in a row.
7. Build multiplication skills with Minecraft

Your kids will flip for this fun version of Minecraft multiplication. Download the game and instructions for free!
8. Deal a hand of Spiral

Players take turns rolling the dice and moving around the game board with this fun multiplication card game.
9. Sweeten up multiplication practice

Write multiplication problems on the bottom of small cupcake paper liners. On the inside, write the product. Two players take turns picking a liner, finding the answer, and flipping it over to check.
10. Take a whirl at fidget spinner math

The object of the game is simple: Spin the spinner and complete as many problems as possible.
11. Make multiplication pool noodles
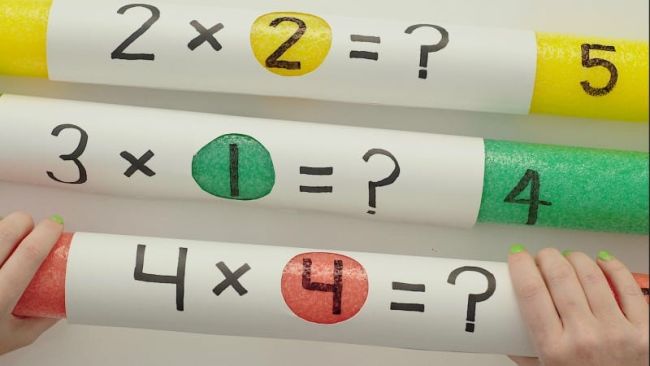
Pick up some pool noodles and use our easy tutorial to turn them into the ultimate multiplication manipulatives ! This is such a unique way for kids to practice their math facts.
12. Match wits at Array Capture
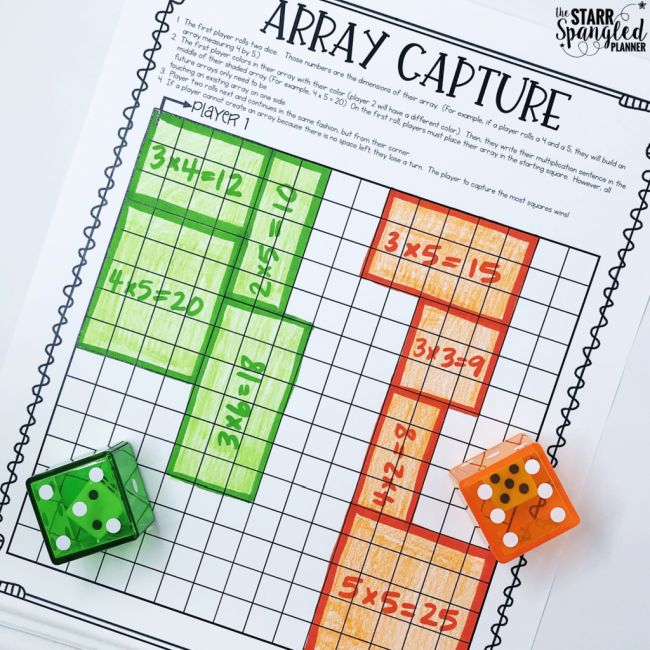

You can use dice-in-dice or just a regular pair of dice for this game. Players roll the dice and use the numbers to block off space on the grid, writing in the math sentence too. At the end of the game, the player with the most spaces colored in wins.
13. Punch holes to make arrays

Arrays introduce multiplication in a way that kids can easily understand. This activity is great for active learners who will love punching holes as they create multiplication arrays for basic facts.
14. Fold a multiplication cootie catcher

We love finding new and clever ways to practice math facts! Get these free printables , then let kids color and fold them up. Now they’ve got self-checking practice at their fingertips.
15. Visit the Multiplication Shop

How fun is this? Set up a “store” with small items for sale. Kids choose a number of items from each section to “buy” and write out the multiplication sentences as their receipt!
16. Ask a partner, “Do You Have …?”

Got an old “Guess Who?” game lying around? Turn it into a multiplication game instead!
17. Pull out the base-10 blocks
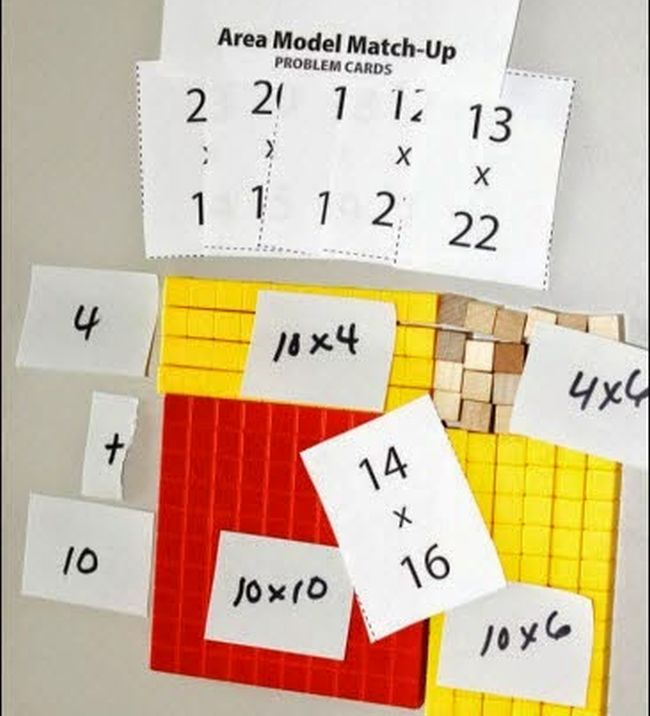
Base-10 blocks are one of our favorite manipulatives, and they’re a terrific tool to help you teach multiplication. Build arrays with them to let kids visualize the problems and their answers.
18. Color in Emoji Mystery pages

Here’s a twist on color-by-number. First, kids have to answer the multiplication problems in each square. Then they get to color! Get a free set of these pages at Artsy Fartsy Mama .
19. Multiply with dice-in-dice

Something about dice-in-dice just makes learning more fun! If you don’t have a set, you can use a pair of regular dice for this activity. Mix things up with polyhedral dice with higher numbers too.
20. Pick sticks to play Kaboom!

So easy and so fun! Write multiplication facts at the end of a variety of wood craft sticks. On a few, write “Kaboom!” instead. To play, kids draw sticks from a cup and answer the problem. If they get it right, they can keep pulling sticks. But if they get a Kaboom! stick, they have to put their whole collection back!
21. Match Multiplication memory cards
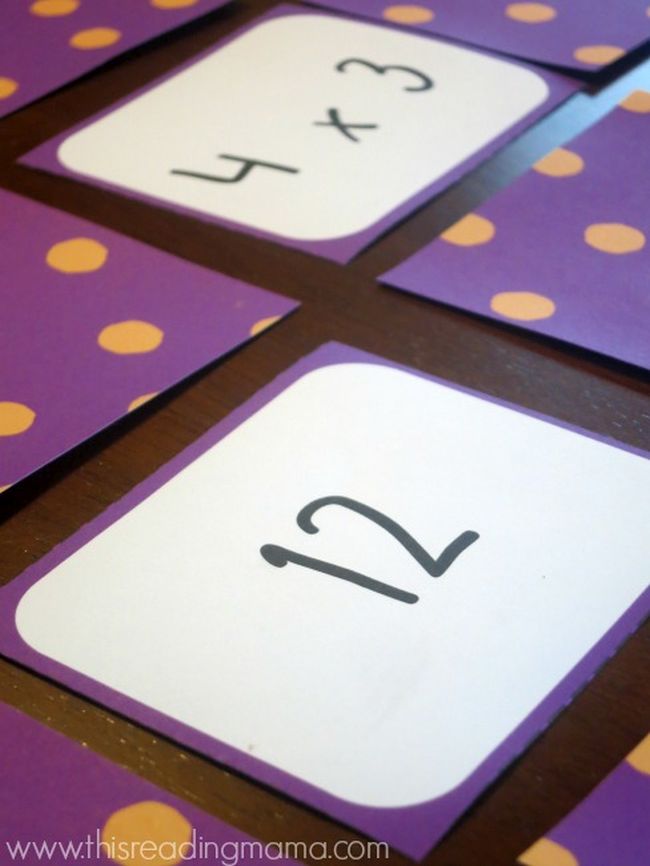

Practice facts with a memory game. Make your own cards by writing facts and answers, then lay them all face down. Turn over a card and try to find its matching answer or problem. Your turn continues as long as you’re able to make matches.
22. Find it first

Write a series of products on the whiteboard, and mix in a few random numbers too. Send two students up to the board and call out a multiplication problem. The first one to find and point to the correct answer wins a point.
23. Draw Waldorf multiplication flowers

This is a creative way to teach multiplication facts. Draw a flower with 12 petals and a circle in the center. In the circle, write the multiplicand; on the petals, the numbers 1 to 12. Now, draw larger petals outside, and fill in the product of each fact. Add some color to make fun classroom decorations!
24. Play multiplication war

All you need for this is a deck of cards, plus paper and a pencil for each player. Split the deck between the players. Each player flips two cards, then writes out the multiplication sentence and the answer. The player with the higher product takes all the cards. Play until the deck is gone. The player with the most cards wins!
25. Compete at multiplication bingo

Grab these free printable bingo cards at the link and provide one to each student along with some chips or beans to use as counters. Call out multiplication facts and have students cover the answers if they have them. When they get five in a row, it’s a bingo!
26. Put a twist on Rock, Paper, Scissors

Chances are your students already know how to play Rock, Paper, Scissors. This is similar, but instead, each player holds out a random number of fingers. The first one to correctly multiply them together and call out the answer wins a point. Play to 5, 10, or any number you choose.
27. Do some egg carton multiplication

Number the cups of an egg carton from 1 to 12. Drop in two marbles or beans, then close the carton and shake it up. Open it up and have students write out the multiplication number sentence based on where the marbles landed. This is an easy tool parents can make for kids at home too.
28. Try interactive flash cards
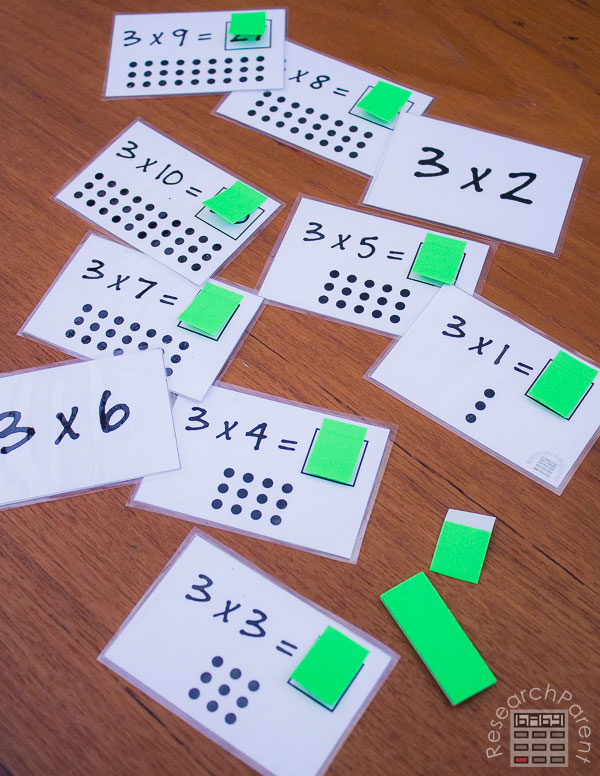
These aren’t your ordinary flash cards! These free printables are a cool way to teach multiplication since the answer side includes a dot array to help kids visualize the solution. You can use sticky-note flags to cover the answers while kids use the arrays for help too.
29. Teach multiplication facts with a paper plate wheel
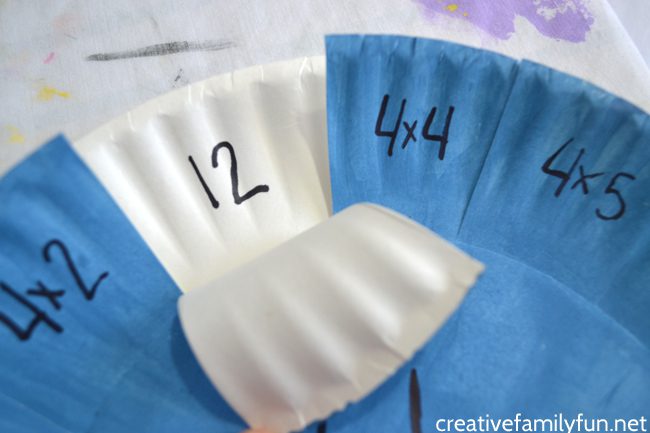

All it takes is paper plates, glue, and a marker to help your students learn their multiplication tables. Let kids have fun decorating their plates, and this doubles as a math craft!
30. Practice with fact family triangles

Tie together multiplication and division facts with triangle flash cards. Learn how to use them and buy a printable set at Primary Flourish . You can also have kids make their own.
31. Make LEGO arrays

LEGO bricks are one of our favorite ways to teach math! You can use multiple bricks to make arrays or just look at the bumps on the top of a single brick as an array in itself.
32. Try the finger trick

This cute craft also teaches kids a clever multiplication trick that can help them if they’re stuck with multiplication “times nine.” Learn the easy trick at 5-Minute Crafts .
33. Use the Force to teach multiplication

Sometimes learning multiplication facts just takes practice. Worksheets may not be very exciting, but adding a theme that kids are interested in may motivate your students. This free download from Royal Baloo features homework sheets and practice papers with graphs, mazes, puzzles, and more, all with a Star Wars theme.
34. Watch a multiplication video

From Schoolhouse Rock to Animaniacs and beyond, there are lots of fun videos to help you teach multiplication. Find our big list here.
35. Play multiplication checkers
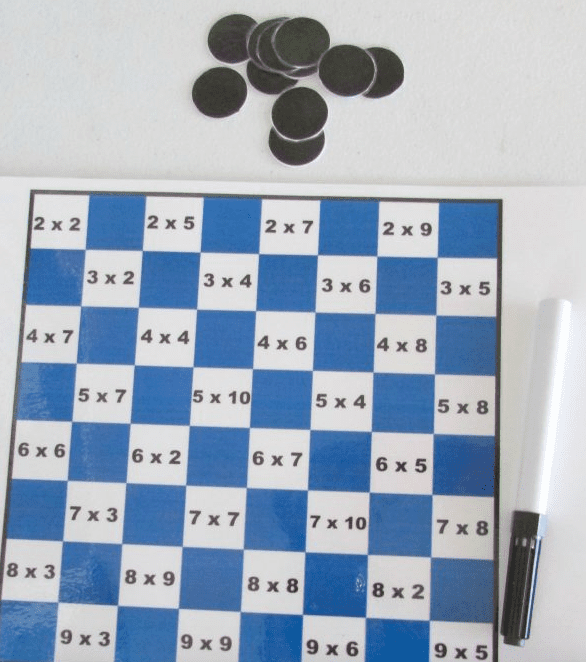
Turn a thrift store checkerboard into a multiplication game with some stickers and a marker. The play is similar to traditional checkers, but you have to solve the problem before you can leave your checker on a new space.
36. Toss a multiplication soccer ball

What better way to appeal to students than to combine math with one of their favorite activities? These fun balls can be used in so many ways to support learning.
37. Flip bottle caps
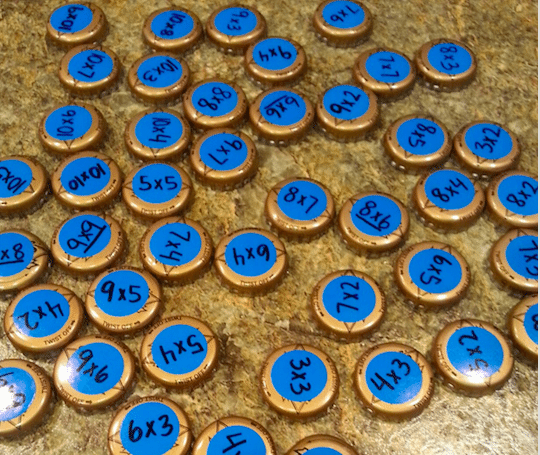
Here’s a cool alternative to flash cards. You can use metal bottle caps or plastic bottle lids, along with round stickers that fit the caps. It’s a great way to go green while you teach multiplication!
38. Batter up to learn multiplication

Sports-loving kids will love this one! Get the free printables and use them along with a 10-sided die to get some multiplication facts practice.
39. Line up dominoes
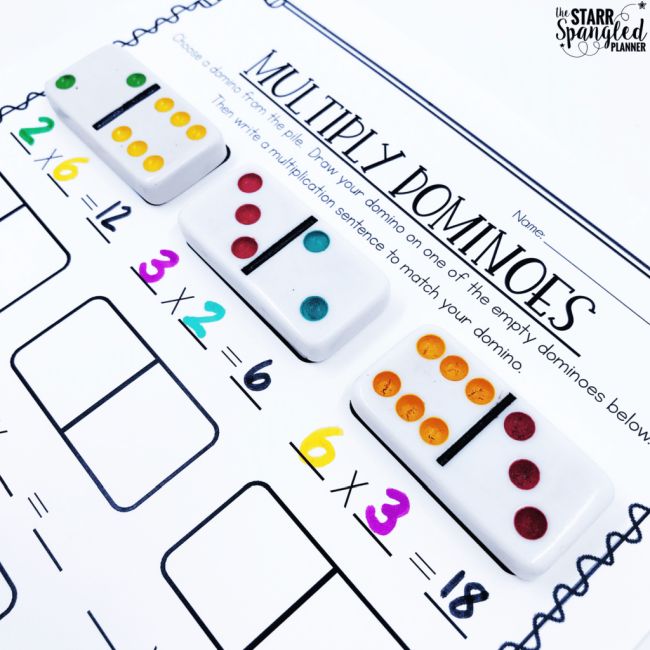
Single dominoes turned sideways become multiplication number sentences! Grab a handful and have kids write out the sentences and their answers.
40. Roll to win

This works a bit like Yahtzee. Roll a die, then choose a number from 1 to 6 to multiply it by. Each number can only be used once, so choose carefully to rack up the most points. If you have polyhedral dice, you can play with higher numbers too.
41. Sculpt play dough arrays
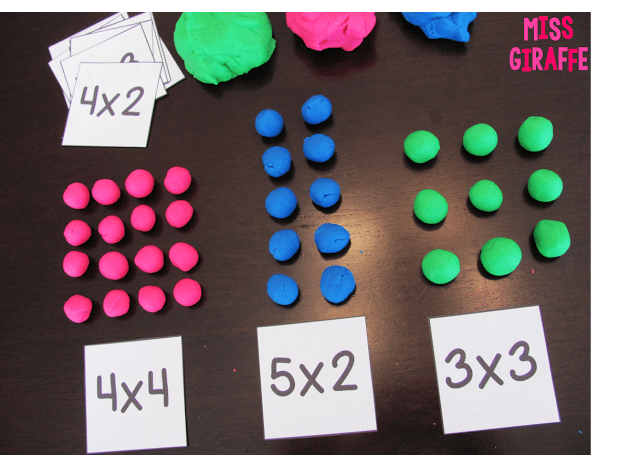
What kid doesn’t love the chance to play with play dough? Use this activity for math centers, and kids will really enjoy practicing their multiplication facts.
42. Connect the dots with Multiplication Squares
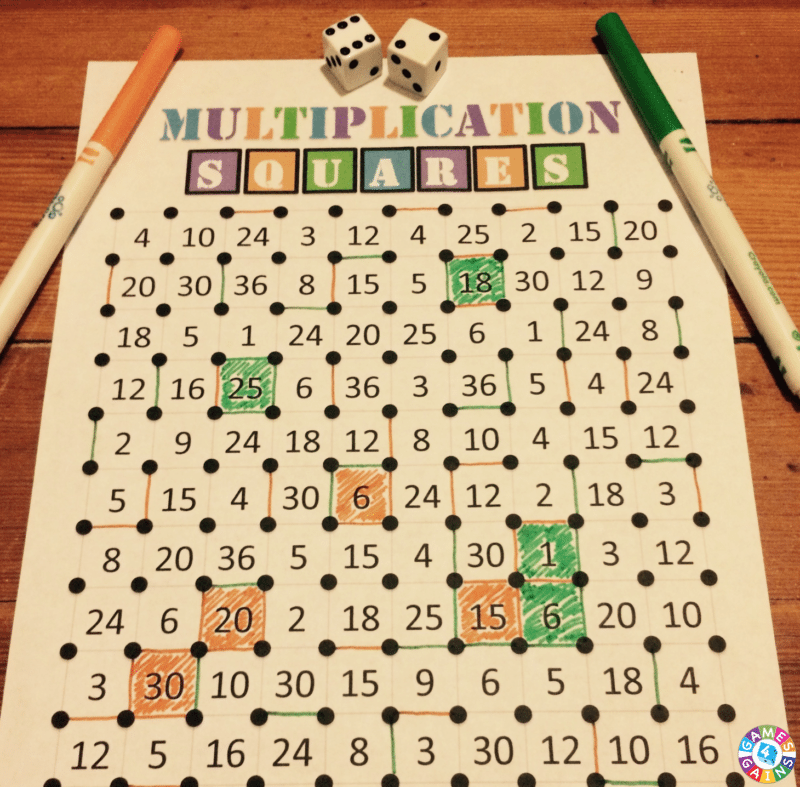

This is a math spin on the old Dots and Boxes game. Kids roll two dice and multiply the numbers together. Then they find the answer on the board and connect two dots next to it. The goal is to complete a box, coloring it in with your own color marker. When the board is full, count the squares to see who wins.
43. Cut out and assemble array cities

Here’s another colorful math craft: multiplication array cities. Most high-rises have their windows arranged to make perfect arrays. Have kids make their own city skylines with buildings showing various multiplication arrays.
44. Stack math power towers
There’s a universal appeal about making stacks of cups, so don’t be surprised if kids clamor to play this game over and over again. Pull a cup, answer correctly, and stack. See who can get a stack of 10 first, or who can build the highest tower in 2 minutes, and so on.
45. Change your students’ names (temporarily)

Grab some name tags and write multiplication equations on each. Give a tag to each of your students. For the remainder of the day, everyone will refer to each other by the answer to the equation on their tag (e.g., the student with the name tag that says 7 x 6 would be referred to as “42”).
46. Take multiplication to the gridiron
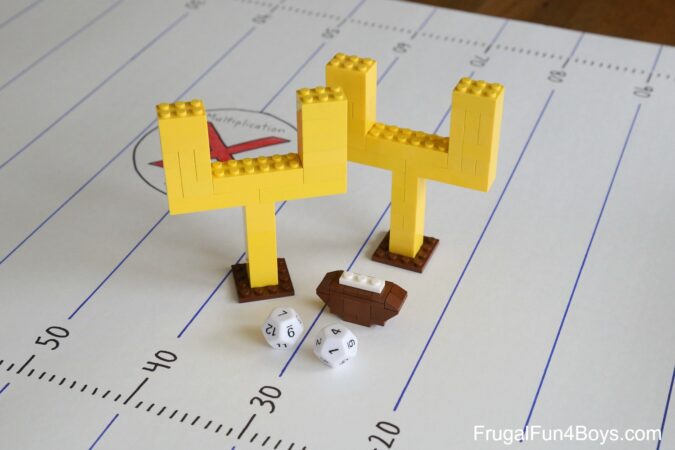

All you need is poster board, 12-sided dice, and a couple of game pieces to teach multiplication using football. Students move their game piece up the field by rolling the dice and multiplying the two numbers that face up. They get four chances to score a touchdown.
47. Roll and Bump!
Print the free game boards , each with a multiplier in the heading. Roll two dice, add them together, then multiply by the multiplier. Then place your game piece over that answer. If another player also comes up with the same product, they can “bump” your game piece off and replace it with their own. The player with the most markers on the board at the end of the game wins.
48. Weave multiplication patterns

Skip-counting provides an introduction to multiplication. We love this hands-on activity where kids skip-count and weave yarn into pretty patterns.
49. Challenge kids with Multiplication Jenga

Grab an old Jenga game at the thrift store (or pick up the generic version at the dollar store). Write multiplication problems on each block, then stack ’em up. Player one pulls a block and tries to answer the problem. If they get it right, they keep the block. If they miss, their partner gets a chance. But if no one can answer it, the block gets stacked up on top. Keep playing until the tower collapses!
50. Twist and learn

Your students will love this twisted version of an old favorite! The original Math Twister was designed for addition, but it works for multiplication too. Simply write products on sticky notes and add them to circles. Then call out math problems like “Left foot, 4 x 5!” The player must put their left foot on the number 20—if they can!
Looking for more activities to teach multiplication? Try these Teacher-Tested Tips and Activities for Teaching the Area Model Multiplication Method .
Plus, get all the latest teaching tips and ideas when you sign up for our free newsletters .

You Might Also Like

40 Creative Ways To Make Teaching Division Easier (and More Fun!)
It's time to divide and conquer! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Game Central
Inequalities, absolute value and rounding, related concepts.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What the data says about gun deaths in the U.S.
More Americans died of gun-related injuries in 2021 than in any other year on record, according to the latest available statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). That included record numbers of both gun murders and gun suicides. Despite the increase in such fatalities, the rate of gun deaths – a statistic that accounts for the nation’s growing population – remained below the levels of earlier decades.
Here’s a closer look at gun deaths in the United States, based on a Pew Research Center analysis of data from the CDC, the FBI and other sources. You can also read key public opinion findings about U.S. gun violence and gun policy .
This Pew Research Center analysis examines the changing number and rate of gun deaths in the United States. It is based primarily on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). The CDC’s statistics are based on information contained in official death certificates, while the FBI’s figures are based on information voluntarily submitted by thousands of police departments around the country.
For the number and rate of gun deaths over time, we relied on mortality statistics in the CDC’s WONDER database covering four distinct time periods: 1968 to 1978 , 1979 to 1998 , 1999 to 2020 , and 2021 . While these statistics are mostly comparable for the full 1968-2021 period, gun murders and suicides between 1968 and 1978 are classified by the CDC as involving firearms and explosives; those between 1979 and 2021 are classified as involving firearms only. Similarly, gun deaths involving law enforcement between 1968 and 1978 exclude those caused by “operations of war”; those between 1979 and 2021 include that category, which refers to gun deaths among military personnel or civilians due to war or civil insurrection in the U.S . All CDC gun death estimates in this analysis are adjusted to account for age differences over time and across states.
The FBI’s statistics about the types of firearms used in gun murders in 2020 come from the bureau’s Crime Data Explorer website . Specifically, they are drawn from the expanded homicide tables of the agency’s 2020 Crime in the United States report . The FBI’s statistics include murders and non-negligent manslaughters involving firearms.
How many people die from gun-related injuries in the U.S. each year?
In 2021, the most recent year for which complete data is available, 48,830 people died from gun-related injuries in the U.S., according to the CDC. That figure includes gun murders and gun suicides, along with three less common types of gun-related deaths tracked by the CDC: those that were accidental, those that involved law enforcement and those whose circumstances could not be determined. The total excludes deaths in which gunshot injuries played a contributing, but not principal, role. (CDC fatality statistics are based on information contained in official death certificates, which identify a single cause of death.)
What share of U.S. gun deaths are murders and what share are suicides?
Though they tend to get less public attention than gun-related murders, suicides have long accounted for the majority of U.S. gun deaths . In 2021, 54% of all gun-related deaths in the U.S. were suicides (26,328), while 43% were murders (20,958), according to the CDC. The remaining gun deaths that year were accidental (549), involved law enforcement (537) or had undetermined circumstances (458).
What share of all murders and suicides in the U.S. involve a gun?
About eight-in-ten U.S. murders in 2021 – 20,958 out of 26,031, or 81% – involved a firearm. That marked the highest percentage since at least 1968, the earliest year for which the CDC has online records. More than half of all suicides in 2021 – 26,328 out of 48,183, or 55% – also involved a gun, the highest percentage since 2001.
How has the number of U.S. gun deaths changed over time?
The record 48,830 total gun deaths in 2021 reflect a 23% increase since 2019, before the onset of the coronavirus pandemic .
Gun murders, in particular, have climbed sharply during the pandemic, increasing 45% between 2019 and 2021, while the number of gun suicides rose 10% during that span.
The overall increase in U.S. gun deaths since the beginning of the pandemic includes an especially stark rise in such fatalities among children and teens under the age of 18. Gun deaths among children and teens rose 50% in just two years , from 1,732 in 2019 to 2,590 in 2021.
How has the rate of U.S. gun deaths changed over time?
While 2021 saw the highest total number of gun deaths in the U.S., this statistic does not take into account the nation’s growing population. On a per capita basis, there were 14.6 gun deaths per 100,000 people in 2021 – the highest rate since the early 1990s, but still well below the peak of 16.3 gun deaths per 100,000 people in 1974.
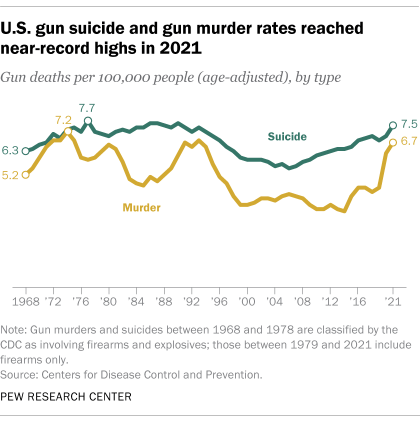
The gun murder rate in the U.S. remains below its peak level despite rising sharply during the pandemic. There were 6.7 gun murders per 100,000 people in 2021, below the 7.2 recorded in 1974.
The gun suicide rate, on the other hand, is now on par with its historical peak. There were 7.5 gun suicides per 100,000 people in 2021, statistically similar to the 7.7 measured in 1977. (One caveat when considering the 1970s figures: In the CDC’s database, gun murders and gun suicides between 1968 and 1978 are classified as those caused by firearms and explosives. In subsequent years, they are classified as deaths involving firearms only.)
Which states have the highest and lowest gun death rates in the U.S.?
The rate of gun fatalities varies widely from state to state. In 2021, the states with the highest total rates of gun-related deaths – counting murders, suicides and all other categories tracked by the CDC – included Mississippi (33.9 per 100,000 people), Louisiana (29.1), New Mexico (27.8), Alabama (26.4) and Wyoming (26.1). The states with the lowest total rates included Massachusetts (3.4), Hawaii (4.8), New Jersey (5.2), New York (5.4) and Rhode Island (5.6).

The results are somewhat different when looking at gun murder and gun suicide rates separately. The places with the highest gun murder rates in 2021 included the District of Columbia (22.3 per 100,000 people), Mississippi (21.2), Louisiana (18.4), Alabama (13.9) and New Mexico (11.7). Those with the lowest gun murder rates included Massachusetts (1.5), Idaho (1.5), Hawaii (1.6), Utah (2.1) and Iowa (2.2). Rate estimates are not available for Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont or Wyoming.
The states with the highest gun suicide rates in 2021 included Wyoming (22.8 per 100,000 people), Montana (21.1), Alaska (19.9), New Mexico (13.9) and Oklahoma (13.7). The states with the lowest gun suicide rates were Massachusetts (1.7), New Jersey (1.9), New York (2.0), Hawaii (2.8) and Connecticut (2.9). Rate estimates are not available for the District of Columbia.
How does the gun death rate in the U.S. compare with other countries?
The gun death rate in the U.S. is much higher than in most other nations, particularly developed nations. But it is still far below the rates in several Latin American countries, according to a 2018 study of 195 countries and territories by researchers at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington.
The U.S. gun death rate was 10.6 per 100,000 people in 2016, the most recent year in the study, which used a somewhat different methodology from the CDC. That was far higher than in countries such as Canada (2.1 per 100,000) and Australia (1.0), as well as European nations such as France (2.7), Germany (0.9) and Spain (0.6). But the rate in the U.S. was much lower than in El Salvador (39.2 per 100,000 people), Venezuela (38.7), Guatemala (32.3), Colombia (25.9) and Honduras (22.5), the study found. Overall, the U.S. ranked 20th in its gun fatality rate that year .
How many people are killed in mass shootings in the U.S. every year?
This is a difficult question to answer because there is no single, agreed-upon definition of the term “mass shooting.” Definitions can vary depending on factors including the number of victims and the circumstances of the shooting.
The FBI collects data on “active shooter incidents,” which it defines as “one or more individuals actively engaged in killing or attempting to kill people in a populated area.” Using the FBI’s definition, 103 people – excluding the shooters – died in such incidents in 2021 .
The Gun Violence Archive, an online database of gun violence incidents in the U.S., defines mass shootings as incidents in which four or more people are shot, even if no one was killed (again excluding the shooters). Using this definition, 706 people died in these incidents in 2021 .
Regardless of the definition being used, fatalities in mass shooting incidents in the U.S. account for a small fraction of all gun murders that occur nationwide each year.
How has the number of mass shootings in the U.S. changed over time?
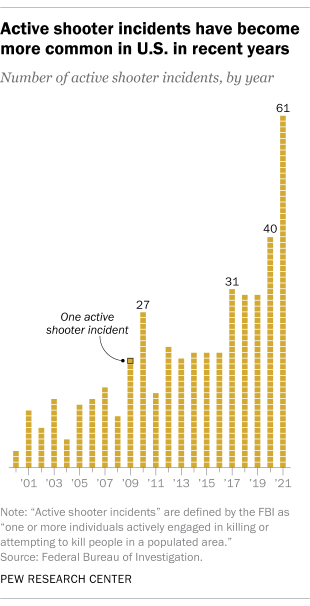
The same definitional issue that makes it challenging to calculate mass shooting fatalities comes into play when trying to determine the frequency of U.S. mass shootings over time. The unpredictability of these incidents also complicates matters: As Rand Corp. noted in a research brief , “Chance variability in the annual number of mass shooting incidents makes it challenging to discern a clear trend, and trend estimates will be sensitive to outliers and to the time frame chosen for analysis.”
The FBI found an increase in active shooter incidents between 2000 and 2021. There were three such incidents in 2000. By 2021, that figure had increased to 61.
Which types of firearms are most commonly used in gun murders in the U.S.?
In 2020, the most recent year for which the FBI has published data, handguns were involved in 59% of the 13,620 U.S. gun murders and non-negligent manslaughters for which data is available. Rifles – the category that includes guns sometimes referred to as “assault weapons” – were involved in 3% of firearm murders. Shotguns were involved in 1%. The remainder of gun homicides and non-negligent manslaughters (36%) involved other kinds of firearms or those classified as “type not stated.”
It’s important to note that the FBI’s statistics do not capture the details on all gun murders in the U.S. each year. The FBI’s data is based on information voluntarily submitted by police departments around the country, and not all agencies participate or provide complete information each year.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on Aug. 16, 2019.
- Partisanship & Issues
- Political Issues
- Politics & Policy

John Gramlich is an associate director at Pew Research Center .
Cultural Issues and the 2024 Election
About 1 in 4 u.s. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year, striking findings from 2023, key facts about americans and guns, for most u.s. gun owners, protection is the main reason they own a gun, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. Multiply the top and bottom numbers in the ones place. In other words, multiply the bottom number's far right digit by the top number's far right digit. If your answer is two digits long (for instance, 28), carry the first digit of your answer (e.g., 2) above the digit in the tenths place of the top number.
And if we did that we get 3 plus 3 is 6. 6 plus 3 is 9. 9 plus 3 is 12. And we learned up here, this part of the video, we learned that this same multiplication could also be interpreted as 3 times 4. You can switch the order and this is one of the useful and interesting actually, kind of properties of multiplication.
We can use multiplication to find out how many total treats you gave Tuffy. The symbol for multiplication is × . If we translate this symbol into words it means " groups of ." For this problem, we have 5 groups of 2 dog treats. We can use the × symbol to write the problem: 5 groups of 2 = 5 × 2.
Get ready for fun facts and tricks in this multiplication learning video for kids! Math doesn't have to be tricky! Learn how to do basic multiplication and l...
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/arithmetic-home/multiply-divide...
Use the following steps along with the example below to understand the process. Write the numerals being multiplied, aligning their ones places, with the largest numeral on top. Draw a line below the numerals being multiplied. Multiply the digit in the ones place in the bottom numeral by the digit in the ones place of the top numeral.
If we multiply by 3 we can cancel out the divide by 3 (because 3/3=1) So, let us try multiplying by 3 on both sides : x 3 ×3 = 5 ×3 A little arithmetic ( 1 3 × 3 = 1 and 5 × 3 = 15) becomes: 1x = 15
Commutative property of multiplication. Multiplication is like a shortcut for repeated addition. Instead of adding 2+2+2, you can multiply 2x3 and get the same answer! Whether you're using a number line, drawing groups of objects, or just crunching the numbers in your head, multiplication is a great way to take your math skills up a notch.
Example: 1,343,244,654 × 0 = 0. Multiplication of 2 numbers a and b, written as a × b, is actually a repeated addition of the number a over b times. Example: 6 × 4 = 6 times of 4 = 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 24. To multiply numbers with more than one digit correctly, all digits must be placed in the correct position starting from the right.
Welcome to Parts of a Multiplication Problem: Factors, Partial Products, & Product with Mr. J! Need help with multiplication vocabulary? You're in the right ...
1, 3, or 5 Minute Drill Multiplication Worksheets. A multiplication math drill is a worksheet with all of the single digit problems for multiplication on one page. A student should be able to work out the 100 problems correctly in 5 minutes, 60 problems in 3 minutes, or 20 problems in 1 minute. This multiplication math drill worksheet is ...
The formula for multiplication is straightforward, involving two numbers or variables that are multiplied together to find their product. Represented symbolically, it is: Product=a×b. Product = Multiplicand × Multiplier. Where: a and b are the multiplicands, or the numbers being multiplied. The symbol × denotes the multiplication operation.
For each potion she used 5 + 5 + 5 pounds. Or, expressed in a different way: 3 x 5 = 15 pounds. Now we know that she used 15 pounds of magic herbs for each potion and we know that she made 10 bottles of potion, so: In total, to make all of the potions, she used 15 x 10 = 150 pounds of magic herbs. 4) This last step is very important.
Let the two expressions be x m and x n. Here, the base is " x ". When the terms with the same base are multiplied, the powers gets added, i.e., x m x n = x ( m + n) For example: 3 2 3 5 = 3 2 + 5 = 3 7. When the base is different but the exponent is the same. Let the two expressions be x m and y m.
For instance, let's say that a multiplication problem asks you to multiply 364 x 32. Begin by writing the problem on a piece of paper. Then multiply the top number (364) by the bottom right number ...
1. Line up the numbers in a column format. 2. Multiply each top digit by the last digit in the bottom number. Place each answer in the first row from right to left. You should have the number 33 in the first product row. 3. Once each of the top digits is multiplied by that number, cross it off.
Step 1: First, we place the smaller number out of the two on the right-hand side and change the decimal number to a fraction. 5.5 × 3.6 = 55 10 × 36 10. Step 2: Then, we multiply the numerators using the steps of the long multiplication method. We leave the denominator as it is for now. Step 3: Now, we divide the answer (that we got in step 2 ...
Select the times tables you want to try. Use the drop down boxes and select the one you think is the correct answer. Once you have completed all the questions press the OK Done button. You then see your results! Then do more ( the test is always different! ), or come back here and choose another table. Multiplication Tables for Viewing or ...
Multiplication tricks are required to calculate long and difficult multiplication problems. For single digit, 2-digit and even for 3-digit numbers, it is easy to do the multiplication. But for larger numbers which have more digits such as 4, 5, 6, 7,etc., it takes a long time to solve it.
Multiplication can be a daunting task for students of all ages. However, with the right multiplication strategies in place, it can become a fun and easy process. In this article, we will discuss 7 multiplication strategies that will help students understand the why behind multiplication before learning how to do it.
Multiplication for KidsGo on a learning journey with J&A where you discover how to use grouping of objects to work out how to solve multiplication problems! ...
Multiplication tables are building blocks for multi-digit calculations and solving problems based on fractions, percentages, and factoring.These times tables from 1 to 20 help a child in doing mental arithmetic and also enables them to skillfully tackle more complex calculations.. Times Tables Meaning. A multiplication table is a list of multiples of a particular number.
Multiplication and division games, videos, word problems, manipulatives, and more at MathPlayground.com! Marvelous Multiplication Facts and Games Game Spotlight: Penguin Jump ... Do/Undo Multiplication. Zogs and Monsters. Drag Race Division. Two Digit Multiplication. Space Race.
1. Play a game of Scoot. Teaching With a Mountain View/Scoot via teachingwithamountainview.com. This is a fun way to break up the routine of worksheets. One at a time, you will post one of the multiplication task cards and your students will work to find the answer. After a set amount of time (up to you), say "Scoot.".
This math video tutorial provides a basic introduction into long multiplication. it explains how to multiply multi-digit numbers.Basic Addition: ...
You can solve multiplication and division during the same step in the math problem: after solving for parentheses, exponents and radicals and before adding and subtracting. Proceed from left to right for multiplication and division. Solve addition and subtraction last after parentheses, exponents, roots and multiplying/dividing.
Polynomial. In mathematics, a polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of indeterminates and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate x is x² − 4x + 7. An example with three indeterminates ...
About eight-in-ten U.S. murders in 2021 - 20,958 out of 26,031, or 81% - involved a firearm. That marked the highest percentage since at least 1968, the earliest year for which the CDC has online records. More than half of all suicides in 2021 - 26,328 out of 48,183, or 55% - also involved a gun, the highest percentage since 2001.