- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides

MLA Citation Generator
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, the complete guide to mla & citations, what you’ll find in this guide.
This page provides an in-depth overview of MLA format. It includes information related to MLA citations, plagiarism, proper formatting for in-text and regular citations, and examples of citations for many different types of sources.
Looking for APA? Check out the Citation Machine’s guide on APA format . We also have resources for Chicago citation style as well.
How to be a responsible researcher or scholar
Putting together a research project involves searching for information, disseminating and analyzing information, collecting information, and repurposing information. Being a responsible researcher requires keeping track of the sources that were used to help develop your research project, sharing the information you borrowed in an ethical way, and giving credit to the authors of the sources you used. Doing all of these things prevents plagiarism.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the act of using others’ information without giving credit or acknowledging them. There are many examples of plagiarism. Completely copying another individual’s work without providing credit to the original author is a very blatant example of plagiarism. Plagiarism also occurs when another individual’s idea or concept is passed off as your own. Changing or modifying quotes, text, or any work of another individual is also plagiarism. Believe it or not, you can even plagiarize yourself! Reusing a project or paper from another class or time and saying that it’s new is plagiarism. One way to prevent plagiarism is to add citations in your project where appropriate.
What is a Citation?
A citation shows the reader of your project where you found your information. Citations are included in the body of a project when you add a quote to your project. Citations are also included in the body when you’re paraphrasing another individual’s information. These citations in the body of a research paper are called in-text citations. They are found directly next to the information that was borrowed and are very brief to avoid causing distraction while reading a project. These brief citations include the last name of the author and a page number. Scroll down for an in-depth explanation and examples of MLA in-text citations.
In-text citations provide us with a brief idea as to where you found your information, though they usually don't include the title and other components. Look on the last page of a research project to find complete citations.
Complete citations are found on what MLA calls a works-cited list, which is sometimes called an MLA bibliography. All sources that were used to develop a research project are found on the works-cited list. Complete citations are also created for any quotes or paraphrased information used in the text. Complete citations include the author’s name, the title, publisher, year published, page numbers, URLs, and a few other pieces of information.
Looking to create your citations in just a few clicks? Need an MLA format website or book citation? Visit Citation Machine.net! Our Citation Machine MLA generator, which is an MLA citation website, will create all of your citations in just a few clicks. Click here to see more styles .
Why Does it Matter?
Citing your sources is an extremely important component of your research project. It shows that you’re a responsible researcher and that you located appropriate and reputable sources that support your thesis or claim. In addition, if your work ends up being posted online or in print, there is a chance that others will use your research project in their own work!
Scroll down to find directions on how to create citations.
How the Modern Language Association Helps You Become a Responsible Researcher
What is mla format.
The Modern Language Association is an organization that was created to develop guidelines on everything language and literature related. They have guidelines on proper grammar usage and research paper layouts. In addition, they have English and foreign language committees, numerous books and journal publications, and an annual conference. They are not connected with this guide, but the information here reflects the association’s rules for formatting papers and citations.
What are citations?
The Modern Language Association is responsible for creating standards and guidelines on how to properly cite sources to prevent plagiarism. Their style is most often used when writing papers and citing sources in the liberal arts and humanities fields. “Liberal arts” is a broad term used to describe a range of subjects including the humanities, formal sciences such as mathematics and statistics, natural sciences such as biology and astronomy, and social sciences such as geography, economics, history, and others. The humanities focuses specifically on subjects related to languages, art, philosophy, religion, music, theater, literature, and ethics.
Believe it or not, there are thousands of other types of citation styles. While this citation style is most often used for the liberal arts and humanities fields, many other subjects, professors, and schools prefer citations and papers to be styled in MLA format.
What’s the difference between a bibliography and a works-cited list?
Great question. The two terms cause a lot of confusion and are consistently misused not only by students but educators as well! Let’s start with what the two words mean.
A bibliography displays the sources the writer used to gain background knowledge on the topic and also research it in-depth. Before starting a research project, you might read up on the topic in websites, books, and other sources. You might even dive a bit deeper to find more information elsewhere. All of these sources you used to help you learn about the topic would go in an MLA format bibliography. You might even include other sources that relate to the topic.
A works-cited list displays all of the sources that were mentioned in the writing of the actual paper or project. If a quote was taken from a source and placed into a research paper, then the full citation goes on the works-cited list.
Both the works-cited list and bibliography go at the end of a paper. Most teachers do not expect students to hand in both a bibliography AND a works-cited list. Teachers generally expect to see a works-cited list, but sometimes erroneously call it a bibliography. If you’re not sure what your teacher expects, a page in MLA bibliography format, a works-cited list, or both, ask for guidance.
Why do we use this MLA style?
These specific guidelines and standards for creating citations were developed for numerous reasons. When scholars and researchers in literature, language, and numerous other fields all cite their sources in the same manner, it makes it easier for readers to look at a citation and understand the different components of a source. By looking at an MLA citation, we can see who the author is, the title of the source, when it was published, and other identifiable pieces of information.
Imagine how difficult it would be to understand the various components of a source if we didn’t all follow the same guidelines! Not only would it make it difficult to understand the source that was used, but it would also make it difficult for readers to locate it themselves. This streamlined process aides us in understanding a researcher’s sources.
How is the new version different than previous versions?
This citation style has changed dramatically over the past couple of years. The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition.
The new version expands upon standards previously set in the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook, including the core elements. The structure of citations remains the same, but some formatting guidance and terminology have changed.
- DOI numbers are now formatted as https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx
- Seasons in publishing daters are lowercased: spring 2020
- The term “optional elements” is now “supplemental elements”
- “Narrative in-text citations” are called “citations in prose”
In addition, new information was added on the following:
- Hundreds of works-cited-list entries
- MLA formatting for papers
- Punctuation, spelling, and other mechanics of prose
- Chapter on inclusive language
- Notes (bibliographic and content)
For more information on MLA 9, click here .
A Deeper Look at Citations
What do they look like.
There are two types of citations. The first is a full, or complete, citation. These are found at the end of research projects. These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves.
Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a DOI, URL, or page range).
There are times when additional information is added into the full citation.
Not sure how to transfer the information from your source into your citation? Confused about the term, “containers”? See below for information and complete explanations of each citation component.
The second type of citation, called an “in-text citation,” is included in the main part, or body, of a project when a researcher uses a quote or paraphrases information from another source. See the next section to find out how to create in-text citations.
What are in-text citations?
As stated above, in-text citations are included in the main part of a project when using a quote or paraphrasing a piece of information from another source. We include these types of citations in the body of a project for readers to quickly gain an idea as to where we found the information.
These in-text citations are found directly next to the quote or paraphrased information. They contain a small tidbit of the information found in the regular MLA citation. The regular, or complete, citation is located at the end of a project, on the works-cited list.
Here’s what a typical in-text citation looks like:
In the book The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements…. Too much fire and you have a bad temper...too little wood and you bent too quickly...too much water and you flowed in too many directions” (Tan 31).
This specific in text citation, (Tan 31), is called an MLA parenthetical citation because the author’s name is in parentheses. It’s included so the reader sees that we are quoting something from page 31 in Tan’s book. The complete, regular citation isn’t included in the main part of the project because it would be too distracting for the reader. We want the reader to focus on our work and research, not get caught up on our sources.
Here’s another way to cite in the text:
In Tan’s novel The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements... Too much fire and you have a bad temper... too little wood and you bent too quickly... too much water and you flowed in too many directions" (31).
If the reader would like to see the source’s full information, and possibly locate the source themselves, they can refer to the last part of the project to find the regular citation.
The regular citation, at the end of the project looks like this:
%%Tan, Amy. The Joy Luck Club. Penguin, 1989, p. 31.
Notice that the first word in the full citation (Tan) matches the “Tan” used in the body of the project. It’s important to have the first word of the full citation match the term used in the text. Why? It allows readers to easily find the full citation on the works-cited list.
If your direct quote or paraphrase comes from a source that does not have page numbers, it is acceptable to place a line number (use line or lines), paragraph number (use the abbreviation par. or pars.), sections (sec. or secs.), or chapters (ch. or chs.). Only use these other terms if they are actually labeled on the source. If it specifically says on the source, “Section 1,” for example, then it is acceptable to use “sec. 1” in the in-text citation.
If there are no numbers to help readers locate the exact point in the source, only include the author’s last name.
To determine how to create in-text citations for more than one author, no authors, or corporate authors, refer to the “Authors” section below.
More about quotations and how to cite a quote:
- Use quotes from outside sources to help illustrate and expand on your own points. The majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas.
- Include the quote exactly as you found it. It is okay to use only certain words or phrases from the quote, but keep the words (spelling and capitalization) and punctuation the same.
- It is acceptable to break up a direct quote with your own writing.
Example from a movie:
Dorothy stated, "Toto," then looked up and took in her surroundings, "I’ve a feeling we’re not in Kansas anymore" ( Wizard of Oz ).
- The entire paper should be double-spaced, including quotes.
- If the quote is longer than four lines, it is necessary to make a block quote. Block quotes show the reader that they are about to read a lengthy amount of text from another source.
- Start the quote on the next line, half an inch from the left margin.
- Do not use any indents at the beginning of the block quote.
- Only use quotation marks if there are quotation marks present in the source.
- If there is more than one paragraph in the block quote, indent the beginning of the paragraphs after the first one an additional half an inch from the left margin.
- Add your in-text citation after the final period of the block quote. Do not add an additional period after the parenthetical citation.
While his parents sat there in surprise, Colton went onto say:
“Cause I could see you,” Colon said matter-of-factly. “I went up and out of my body and I was looking down and I could see the doctor working on my body. And I saw you and Mommy. You were in a little room by yourself, praying; and Mommy was in a different room, and she was praying and talking on the phone.” (Burpo xxi)
How to create a paraphrase:
As stated above, the majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas. It’s acceptable to include quotes, but they shouldn’t crowd your paper. If you’re finding that you’re using too many quotes in your paper, consider adding paraphrases. When you reiterate a piece of information from an outside source in your own words, you create a paraphrase.
Here’s an example:
Readers discover in the very first sentence of Peter Pan that he doesn’t grow up (Barrie 1).
What paraphrases are:
- Recycled information in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.
- They’re still references! Include an in-text citation next to the paraphrased information.
What paraphrases are not:
- A copy and pasted sentence with a few words substituted for synonyms.
Confused about whether footnotes and endnotes should be used?
Footnotes and endnotes are completely acceptable to use in this style. Use a footnote or endnote if:
- Adding additional information will help the reader understand the content. This is called a content note .
- You need to cite numerous sources in one small section of your writing. Instead of clogging up a small paragraph with in-text citations (which could cause confusion for the reader), include a footnote or endnote. This is called a bibliographic note .
Keep in mind that whether you choose to include in-text citations or footnotes/endnotes, you need to also include a full reference on the MLA format works-cited list.
Content note example:
Even Maurice Sendak’s work (the mastermind behind Where the Wild Things Are and numerous other popular children’s picture books) can be found on the banned books list. It seems as though nobody is granted immunity. 1
- In the Night Kitchen ’s main character is nude on numerous pages. Problematic for most is not the nudity of the behind, but the frontal nudity.
Work Cited:
%%Sendak, Maurice. In The Night Kitchen. Harper Collins, 1996.
Bibliographic note example:
Dahl had a difficult childhood. Both his father and sister passed away when he was a toddler. He was then sent away by his mother to boarding school (de Castella). 1
- Numerous books, such as Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG, all feature characters with absent or difficult parents.
MLA Works Cited:
Include 4 full citations for: de Castella’s article, Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG .
Don’t forget to create full, or regular citations, and place them at the end of your project.
If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net can help. Our MLA citation generator is simple and easy to use!
Common Knowledge: What Is It and How Will It Affect My Writing?
Footnotes, endnotes, references, proper structuring. We know it’s a lot. Thankfully, you don’t have to include a reference for EVERY piece of information you add to your paper. You can forget about including a reference when you share a piece of common knowledge.
Common knowledge is information that most people know. For example, these are a few facts that are considered common knowledge:
- The Statue of Liberty is located in New York City
- Tokyo is the capital of Japan
- Romeo and Juliet is a play written by William Shakespeare
- English is the language most people speak in England
- An elephant is an animal
We could go on and on. When you include common knowledge in your paper, omit a reference. One less thing to worry about, right?
Before you start adding tons of common knowledge occurrences to your paper to ease the burden of creating references, we need to stop you right there. Remember, the goal of a research paper is to develop new information or knowledge. You’re expected to seek out information from outside sources and analyze and distribute the information from those sources to form new ideas. Using only common knowledge facts in your writing involves absolutely zero research. It’s okay to include some common knowledge facts here and there, but do not make it the core of your paper.
If you’re unsure if the fact you’re including is common knowledge or not, it doesn’t hurt to include a reference. There is no such thing as being overly responsible when it comes to writing and citing.
Wikipedia - Yay or Nay?
If you’re wondering whether it’s okay to use Wikipedia in your project, the answer is, it depends.
If Wikipedia is your go-to source for quick information on a topic, you’re not alone. Chances are, it’s one of the first websites to appear on your results page. It’s used by tons of people, it’s easily accessible, and it contains millions of concise articles. So, you’re probably wondering, “What’s the problem?”
The issue with Wikipedia is that it’s a user-generated site, meaning information is constantly added and modified by registered users. Who these users are and their expertise is somewhat of a mystery. The truth is anyone can register on the site and make changes to articles.
Knowing this makes some cringe, especially educators and librarians, since the validity of the information is questionable. However, some people argue that because Wikipedia is a user-generated site, the community of registered users serve as “watchdogs,” ensuring that information is valid. In addition, references are included at the bottom of each article and serve as proof of credibility. Furthermore, Wikipedia lets readers know when there’s a problem with an article. Warnings such as “this article needs clarification,” or “this article needs references to prove its validity” are shared with the reader, thus promoting transparency.
If you choose to reference a Wikipedia article in your research project, and your teacher or professor says it’s okay, then you must reference it in your project. You would treat it just as you would with any other web source.
However, you may want to instead consider locating the original source of the information. This should be fairly easy to do thanks to the references at the bottom of each article.
Specific Components of a Citation
This section explains each individual component of the citation, with examples for each section for full citations and in-text citations.
Name of the author
The author’s name is usually the first item listed in the MLA citation. Author names start with the last name, then a comma is added, and then the author’s first name (and middle name if applicable) is at the end. A period closes this information.
Here are two examples of how an author’s name can be listed in a full citation:
Twain, Mark.
Poe, Edgar Allan.
For in-text:
(Author’s Last name page number) or Author’s Last name... (page).
Wondering how to format the author’s name when there are two authors working jointly on a source? When there are two authors that work together on a source, the author names are placed in the order in which they appear on the source. Place their names in this format:
Author 1’s Last Name, First name, and Author 2’s First Name Last Name.
Here are two examples of how to cite two authors:
Clifton, Mark, and Frank Riley.
Paxton, Roberta J., and Michael Jacob Fox.
(Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name page number) or Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name... (page).
There are many times when three or more authors work together on a source. This often happens with journal articles, edited books, and textbooks.
To cite a source with three or more authors, place the information in this format:
Author 1’s Last name, First name, et al.
As you can see, only include the first author’s name. The other authors are accounted for by using “et al.” In Latin, et al. is translated to “and others.” If using the Citation Machine citation generator, this abbreviation is automatically added for you.
Here’s an example of a citation for three or more authors:
%%Warner, Ralph, et al. How to Buy a House in California. Edited by Alayna Schroeder, 12th ed., Nolo, 2009.
(Author 1’s Last name et al. page number)
Is there no author listed on your source? If so, exclude the author’s information from the citation and begin the citation with the title of the source.
For in-text: Use the title of the source in parentheses. Place the title in italics if the source stands alone. Books and films stand alone. If it’s part of a larger whole, such as a chapter in an edited book or an article on a website, place the title in quotation marks without italics.
( Back to the Future )
(“Citing And Writing”)
Other in-text structures:
Authors with the same last name in your paper? MLA essay format requires the use of first initials in-text in this scenario.
Ex: (J. Silver 45)
Are you citing more than one source by the same author? For example, two books by Ernest Hemingway? Include the title in-text.
Example: (Hemingway, For Whom The Bell Tolls 12).
Are you citing a film or song? Include a timestamp in the format of hours:minutes:seconds. ( Back to the Future 00:23:86)
Was the source found on social media, such as a tweet, Reddit, or Instagram post? If this is the case, in an MLA format paper, you are allowed to start the citation with the author’s handle, username, or screen name.
Here is an example of how to cite a tweet:
%%@CarlaHayden. “I’m so honored to talk about digital access at @UMBCHumanities. We want to share the @libraryofcongress collection.” Twitter , 13 Apr. 2017, 6:04 p.m., twitter.com/LibnOfCongress/status/852643691802091521.
While most citations begin with the name of the author, they do not necessarily have to. Quite often, sources are compiled by editors. Or, your source may be done by a performer or composer. If your project focuses on someone other than the author, it is acceptable to place that person’s name first in the citation. If you’re using the MLA works cited generator at Citation Machine.net, you can choose the individual’s role from a drop-down box.
For example, let’s say that in your research project, you focus on Leonardo DiCaprio’s performances as an actor. You’re quoting a line from the movie Titanic in your project, and you’re creating a complete citation for it in the works-cited list.
It is acceptable to show the reader that you’re focusing on Leonardo DiCaprio’s work by citing it like this in the MLA works-cited list:
%%DiCaprio, Leonardo, performer. Titanic . Directed by James Cameron. Paramount, 1997.
Notice that when citing an individual other than the author, place the individual’s role after their name. In this case, Leonardo DiCaprio is the performer.
This is often done with edited books, too. Place the editor’s name first (in reverse order), add a comma, and then add the word editor.
If you’re still confused about how to place the authors together in a citation, the tools at CitationMachine.net can help! Our website is easy to use and will create your citations in just a few clicks!
Titles and containers
The titles are written as they are found on the source and in title form, meaning the important words start with a capital.
Here’s an example of a properly written title:
Practical Digital Libraries: Books, Bytes, and Bucks.
Wondering whether to place your title in italics or quotation marks? It depends on whether the source sits by itself or not. If the source stands alone, meaning that it is an independent source, place the title in italics. If the title is part of a larger whole, place the title of the source in quotation marks and the source it is from in italics.
When citing full books, movies, websites, or albums in their entirety, these titles are written in italics.
However, when citing part of a source, such as an article on a website, a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a scholarly journal, the part is written with quotation marks and then the titles of the sources that they are found in are written in italics.
Here are some examples to help you understand how to format titles and their containers.
To cite Pink Floyd’s entire album, The Wall , cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. The Wall. Columbia, 1979.
To cite one of the songs on Pink Floyd’s album in MLA formatting, cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. “Another Brick in the Wall (Part I).” The Wall, Columbia, 1979, track 3.
To cite a fairy tale book in its entirety, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. The Land of Stories. Little Brown, 2016.
To cite a specific story or chapter in the book, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. “Little Red Riding Hood.” The Land of Stories, Little Brown, 2016, pp. 58-65.
More about containers
From the section above, you can see that titles can stand alone, or they can sit in a container. Many times, sources can sit in more than one container. Wondering how? When citing an article in a scholarly journal, the first container is the journal. The second container? It’s the database that the scholarly journal is found in. It is important to account for all containers, so readers are able to locate the exact source themselves.
When citing a television episode, the first container is the name of the show and the second container is the name of the service that it could be streaming on, such as Netflix .
If your source sits in more than one container, the information about the second container is found at the end of the citation.
Use the following format to cite your source with multiple containers :
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
If the source has more than two containers, add on another full section at the end for each container.
Not all of the fields in the citation format above need to be included in your citation. In fact, many of these fields will most likely be omitted from your citations. Only include the elements that will help your readers locate the source themselves.
Here is an example of a citation for a scholarly journal article found in a database. This source has two containers: the journal itself is one container, and the site it sits on is the other.
%%Zanetti, Francois. “Curing with Machine: Medical Electricity in Eighteenth-Century Paris.” Technology and Culture, vol. 54, no. 3, July 2013, pp. 503-530. Project Muse, muse.jhu.edu/article/520280.
If you’re still confused about containers, the Citation Machine MLA cite generator can help! MLA citing is easier when using the tools at CitationMachine.net.
Other contributors
Many sources have people besides the author who contribute to the source. If your research project focuses on an additional individual besides the author, or you feel as though including other contributors will help the reader locate the source themselves, include their names in the citation.
To include another individual in the citation, after the title, place the role of the individual, the word “by,” and then their name in standard order.
If the name of the contributor comes after a period, capitalize the first letter in the role of the individual. If it comes after a comma, the first letter in the role of the individual is lowercased.
Here’s an example of a citation for a children’s book with the name of the illustrator included:
%%Rubin, Adam. Dragons Love Tacos. Illustrated by Daniel Salmieri, Penguin, 2012.
The names of editors, directors, performers, translators, illustrators, and narrators can often be found in this part of the citation.
If the source that you’re citing states that it is a specific version or edition, this information is placed in the “versions” section of the citation.
When including a numbered edition, do not type out the number, use the numeral. Also, abbreviate the word “edition” to “ed.”
Here is an example of a citation with a specific edition:
%%Koger, Gregory. “Filibustering and Parties in the Modern State.” Congress Reconsidered, edited by Lawrence C. Dodd and Bruce I. Oppenheimer, 10th ed., CQ Press, 2013, pp. 221-236. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=b7gkLlSEeqwC&lpg=PP1&dq=10th%20edition&pg=PR6#v=onepage&q=10th%20edition&f=false.
Many sources have numbers associated with them. If you see a number different than the date, page numbers, or editions, include this information in the “numbers” section of the citation. For MLA citing, this includes volume and/or issue numbers (use the abbreviations vol. and no.), episode numbers, track numbers, or any other numbers that will help readers identify the specific source that you used. Do not include ISBN (International Standard Book Numbers) in the citation.
It is important to include the name of the publisher (the organization that created or published the source), so that readers can locate the exact source themselves.
Include publishers for all sources except periodicals. Also, for websites, exclude this information when the name of the publisher matches the name of the website. Furthermore, the name of the publisher is often excluded from the citation for second containers, since the publisher of the second container is not necessarily responsible for the creation or production of the source’s content.
Publication dates
Publication dates are extremely important to include in citations. They allow the reader to understand when sources were published. They are also used when readers are attempting to locate the source themselves.
Dates can be written in MLA in one of two ways. Researchers can write dates as:
Day Mo. Year
Mo. Day, Year
Whichever format you decide to use, use the same format for all of your citations. If using the Citation Machine citation generator, the date will be formatted in the same way for each citation.
While it isn’t necessary to include the full date for all source citations, use the amount of information that makes the most sense to help your readers understand and locate the source themselves.
Wondering what to do when your source has more than one date? Use the date that is most applicable to your research.
The location generally refers to the place where the readers can find the source. This includes page ranges, URLs, DOI numbers, track numbers, disc numbers, or even cities and towns.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx .
For page numbers, when citing a source found on only one page, use p.
Example: p. 6.
When citing a source that has a page range, use pp. and then add the page numbers.
Example: pp. 24-38.
Since the location is the final piece of the citation, place a period at the end. When it comes to URLs, many students wonder if the links in citations should be live or not. If the paper is being shared electronically with a teacher and other readers, it may be helpful to include live links. If you’re not sure whether to include live links or not, ask your teacher or professor for guidance.
Looking for an online tool to do the work for you? Citation Machine citing tools could help! Our site is simple (and fun!) to use.
Need some more help? There is further good information here .
Common Citation Examples
ALL sources use this format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). *Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
*If the source does not have a second container, omit this last part of the citation.
Remember, the Citation Machine MLA formatter can help you save time and energy when creating your citations. Check out our MLA Citation Machine pages to learn more.
- Journal Articles
How to Format a Paper
When it comes to formatting your paper or essay for academic purposes, there are specific MLA paper format guidelines to follow.
- Use paper that is 8½-by-11 inch in size. This is the standard size for copier and printer paper.
- Use high quality paper.
- Your research paper or essay should have a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the paper.
- While most word processors automatically format your paper to have one-inch margins, you can check or modify the margins of your paper by going to the “Page setup” section of your word processor.
Which font is acceptable to use?
- Use an easily readable font, specifically one that allows readers to see the difference between regular and italicized letters.
- Times New Roman, Arial, and Helvetica are recommended options.
- Use 12-point size font.
Should I double-space the paper, including citations?
- Double-space the entire paper.
- There should be a double space between each piece of information in the heading.
- Place a double space between the heading and the title.
- Place a double space between the title and the beginning of the essay.
- The works-cited list should be double-spaced as well. All citations are double-spaced.
Justification & Punctuation
- Text should be left-justified, meaning that the text is aligned, or flush, against the left margin.
- Indents signal to the reader that a new concept or idea is about to begin.
- Use the “tab” button on your keyboard to create an indent.
- Add one space after all punctuation marks.
Heading & Title
- Include a proper heading and title
- The heading should include the following, on separate lines, starting one inch from the top and left margins:
- Your full name
- Your teacher or professor’s name
- The course number
- Dates in the heading and the body of your essay should be consistent. Use the same format, either Day Month Year or Month Day, Year throughout the entire paper
- Examples: 27 July 2017 or July 27, 2017
- The title should be underneath the heading, centered in the middle of the page, without bold, underlined, italicized, or all capital letters.
Page numbers
- Number all pages, including the very first page and the works-cited list.
- Place page numbers in the top right corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin.
- Include your last name to the left of the page number. Example: Jacobson 4
Here’s an example to provide you with a visual:

If you need help with sentence structure or grammar, check out our paper checker. The paper checker will help to check every noun , verb , and adjective . If there are words that are misspelled or out of place, the paper checker will suggest edits and provide recommendations.
- If a citation flows onto the second line, indent it in half an inch from the left margin (called a “hanging indent”).
- For more information on the works-cited list, refer to “How to Make a Works Cited Page,” which is found below.
How to Create a Title Page
According to the Modern Language Association’s official guidelines for formatting a research paper, it is unnecessary to create or include an individual title page, or MLA cover page, at the beginning of a research project. Instead, follow the directions above, under “Heading & Title,” to create a proper heading. This heading is featured at the top of the first page of the research paper or research assignment.
If your instructor or professor does in fact require or ask for an MLA title page, follow the directions that you are given. They should provide you with the information needed to create a separate, individual title page. If they do not provide you with instructions, and you are left to create it at your own discretion, use the header information above to help you develop your research paper title page. You may want to include other information, such as the name of your school or university.
How to Make a Works Cited Page
The MLA Works Cited page is generally found at the end of a research paper or project. It contains a list of all the citations of sources used for the research project. Follow these directions to format the works-cited list to match the Modern Language Association’s guidelines.
- The “Works Cited” page has its own page at the end of a research project.
- Include the same running head as the rest of the project (Your last name and then the page number). The “Works Cited” page has the final page number for the project.
- Name the page “Works Cited,” unless your list only includes one citation. In that case, title it in MLA “Work Cited.”
- The title of the page (either “Works Cited” or “Work Cited”) is placed one inch from the top of the page, centered in the middle of the document.
- Double space the entire document, even between the title of the page and the first citation.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the citation (usually the last name of the author or the first word in the title if the citation does not include the author’s name. Ignore “A,” “An,” and “The” if the title begins with these words.)
- If there are multiple citations by the same author, place them in chronological order by the date published.
- Also, instead of writing the author’s name twice in both citations, use three hyphens.
%%Angelou, Maya. I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings. Random House, 2009.
%%---. Gather Together in My Name. Random House, 1974.
- All citations begin flush against the left margin. If the citation is long and rolls onto a second or third line, indent the lines below the first line half an inch from the left margin. This is called a “hanging indent.” The purpose of a hanging indent is to make the citations easier to read. If you’re using our MLA citation machine, we’ll format each of your references with a hanging indent for you.
%%Wai-Chung, Ho. “Political Influences on Curriculum Content and Musical Meaning: Hong Kong Secondary Music Education, 1949-1997.” Journal of Historical Research in Music Education, vol. 22, no. 1, 1 Oct. 2000, pp. 5-25. Periodicals Index Online, search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/pio/docview/1297849364/citation/6B70D633F50C4EA0PQ/78?accountid=35635.
- MLA “Works Cited” pages can be longer than one page. Use as many pages as necessary. If you have only one source to cite, do not place the one citation below the text of your paper. In MLA, a “Work Cited” page is still created for that individual citation.
Here’s a sample paper to give you an idea of what an MLA paper could look like. Included at the end is an MLA “Works Cited” page example.

Looking to add a relevant image, figure, table, or musical score to your paper? Here’s the easy way to do it, while following guidelines set forth by the Modern Language Association:
- Place the image, figure, table, or music close to where it’s mentioned in the text.
- Provide source information and any additional notes directly below the image, figure, table, or music.
For tables:
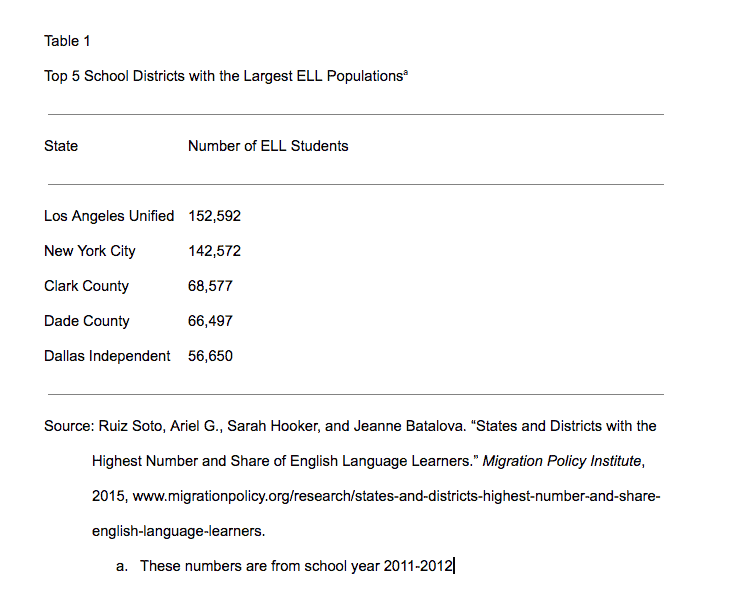
- Label the table as “Table” followed by an arabic numeral such as “1.” Table 1 is the table closest to the beginning of the paper. The next table mentioned in the text would be Table 2, and so on.
- Create a title for the table and place it below the label. Capitalize all important words.
- The label (Table 1) and the title should be flush against the left margin.
- Double-space everything.
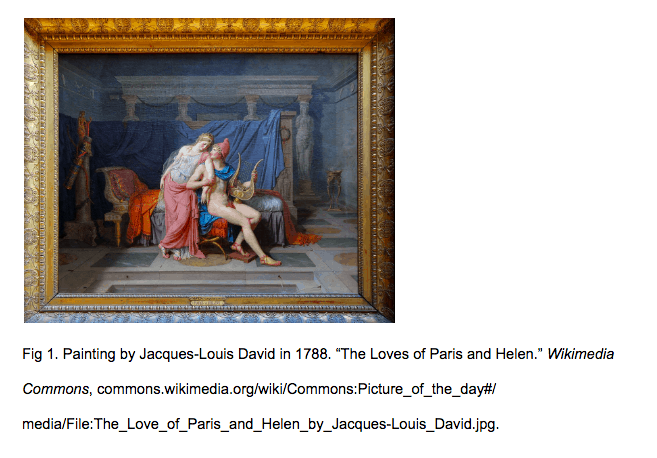
- A figure can be a map, photograph, painting, pie chart, or any other type of image.
- Create a label and place it below the figure. The figure first mentioned in the text of the project is either “Figure 1” or “Fig 1.” Though figures are usually abbreviated to “Fig.” Choose one style and use it consistently. The next mentioned figure is “Figure 2” or “Fig. 2.”, and so on.
- Place a caption next to the label. If all of the source information is included in the caption, there isn’t a need to replicate that information in the works-cited list.
MLA Final Checklist
Think you’re through? We know this guide covered a LOT of information, so before you hand in that assignment, here’s a checklist to help you determine if you have everything you need:
_ Are both in-text and full citations included in the project? Remember, for every piece of outside information included in the text, there should be a corresponding in-text citation next to it. Include the full citation at the end, on the “Works Cited” page.
_ Are all citations, both in-text and full, properly formatted in MLA style? If you’re unsure, try out our citation generator!
_ Is your paper double-spaced in its entirety with one inch margins?
_ Do you have a running header on each page? (Your last name followed by the page number)
_ Did you use a font that is easy to read?
_ Are all citations on the MLA format works-cited list in alphabetical order?
Our plagiarism checker scans for any accidental instances of plagiarism. It scans for grammar and spelling errors, too. If you have an adverb , preposition , or conjunction that needs a slight adjustment, we may be able to suggest an edit.
Common Ways Students Accidentally Plagiarize
We spoke a bit about plagiarism at the beginning of this guide. Since you’re a responsible researcher, we’re sure you didn’t purposely plagiarize any portions of your paper. Did you know students and scholars sometimes accidentally plagiarize? Unfortunately, it happens more often than you probably realize. Luckily, there are ways to prevent accidental plagiarism and even some online tools to help!
Here are some common ways students accidentally plagiarize in their research papers and assignments:
1. Poor Paraphrasing
In the “How to create a paraphrase” section towards the top of this page, we share that paraphrases are “recycled information, in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.” If you attempt to paraphrase a few lines of text and it ends up looking and sounding too close to the original author’s words, it’s a poor paraphrase and considered plagiarism.
2. Incorrect Citations
If you cite something incorrectly, even if it’s done accidentally, it’s plagiarism. Any incorrect information in a reference, such as the wrong author name or the incorrect title, results in plagiarism.
3. Forgetting to include quotation marks
When you include a quote in your paper, you must place quotation marks around it. Failing to do so results in plagiarism.
If you’re worried about accidental plagiarism, try our Citation Machine Plus essay tool. It scans for grammar, but it also checks for any instances of accidental plagiarism. It’s simple and user-friendly, making it a great choice for stress-free paper editing and publishing.
Updated June 15, 2021
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Wendy Ikemoto. Michele Kirschenbaum has been an awesome school librarian since 2006 and is an expert in citing sources. Wendy Ikemoto has a master’s degree in library and information science and has been working for Citation Machine since 2012.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
- powered by chegg, all of our writing tools, none of the ads, your ultimate mla format guide & generator, what is mla.
MLA stands for the Modern Language Association , an organization that focuses on language and literature.
Depending on which subject area your class or research focuses on, your professor may ask you to cite your sources in MLA style. This is a specific way to cite, following the Modern Language Association's guidelines. There are other styles, such as APA format and Chicago citation style , but MLA format is often used for literature, language, liberal arts, and other humanities subjects. This guide extensively covers this format but is not associated with the organization.
What is MLA Citing?
The Modern Language Association Handbook is in its 9th edition and standardizes the way scholars document their sources and format their papers. When everyone documents their sources and papers in the same way, it is simple to recognize and understand the types of sources used for a project. Readers of your work will look at your citations not only to understand them but possibly to explore them as well.
When you're borrowing information from a source and placing it in your research or assignment, it’s important to give credit to the original author. This is done by creating an MLA citation. Depending on the type of information you're including in your work, you may place citations in the body of your project and in a works-cited list at the end of your project.
The handbook explains how to create MLA citations. This page summarizes the information in the handbook’s 9th edition.
There is also a section below on a recommended way to create an MLA header. These headers appear at the top of your assignment’s pages. Check with your instructor on whether they prefer a certain MLA format for the header.
What is MLA Format?
The 9th edition is the most recent and updated version for MLA citations. Released in April 2021, the citation format differs slightly from previous versions. This update follows the 2016 update for the 8th edition that contained many significant changes from previous editions.
For the 8th edition, the biggest difference and most exciting update was the use of one standard format for all source types. In previous versions, scholars were required to locate the citation format for the specific source that they used. There were different formats for books, websites, periodicals, and so on. After 2016, using one universal MLA citation format allowed scholars to spend less time trying to locate the proper format to document their sources and focus more on their research .
Other updates included the addition of “containers.” A container provides details on a work contained within a larger work. For example, books contain chapters, albums contain songs, and journals contain journal articles. The source is the larger work, such as a website, while the container is a smaller work within that source, such as a short story on the website.
MLA now encourages you to add DOIs or URLs to citations. Use a DOI instead of a URL when it’s available. According to the MLA 9th edition, you can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx).
Social media pseudonyms and usernames can replace the real name of the author. Volume and issue numbers are now abbreviated as “vol.” and “no.” Cities of publication and the source’s medium (such as print or web) are no longer included in citations. For academic presses/publishers, with the words “university” or “press,” shorten “university” to “U”, and “press” to “P” (Cambridge UP). Lowercase seasons when using them in the date field of a citation (spring 2021 not Spring 2021).
Bibliography vs. Works Cited - What's the Difference?
You may have heard the two terms, "Bibliography" and "Works Cited" thrown around interchangeably. The truth is that they are two different words with two completely different meanings.
A bibliography is a list of sources that the writer recommends for further reading. A works-cited list is a list of sources that were included in the author's writing.
Want to suggest some books and websites to your reader? Create an MLA format bibliography by creating a list of full citations and label the page as "Bibliography."
Did you use any quotes or place any paraphrases in your writing? Create in-text citations and place them in the body of your work. Then, create a list of full citations and place them at the end of the project. Label the page as "Works Cited."
The good news is that references in MLA bibliography format and regular works-cited lists are structured the exact same way.
Citing Basics
When adding information to your project from another source, you are required to add an MLA citation. There are two types of MLA format citations: in-text citations and full citations.
Full Citation Basics:
All sources used for a project are found on the MLA format “Works Cited” page, which is generally the last portion of a project.
MLA citing format often includes the following pieces of information, in this order:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Source." Title of Container , Other contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication Date, Location.
For more information about each individual element and for proper formatting rules, see the sections below on author names, titles, containers, names of other contributors, source versions, numbers, publishers, publication dates, and locations.
Find more in-depth rules regarding the works-cited list in MLA format on the page down below, along with a sample page.
Don't forget, our BibMe MLA citation generator is an MLA formatter that helps you create your citations quickly and easily!
Citation Components
The author's name is generally the first item in a citation (unless the source does not have an author). The author's name is followed by a period.
If the source has one author , place the last name first, add a comma, and then the first name.
MLA format:
Lee, Harper.
Fitzgerald, F. Scott.
If your source has two authors , place them in the same order they're shown on the source. The first author is in reverse order, add a comma and the word "and", then place the second author in standard form. Follow their names with a period.
Monsen, Avery, and Jory John.
For three or more authors , only include the first listed author's name. Place the first author's name in reverse order (Last name, First name) place a comma afterwards, and then add the Latin phrase "et al."
Borokhovic, Kenneth A., et al.
For social media posts, it's acceptable to use a screen name or username in place of the author's name. Start the citation with the user's handle.
@TheOnion. "Experts Warn Number of Retirees Will Completely Overwhelm Scenic Railway Industry by 2030." Twitter , 9 Oct. 2017, 9:50 a.m., twitter.com/TheOnion/status/917386689500340225.
No author listed? If there isn't an author, start the citation with the title and skip the author section completely.
Citations do not need to always start with the name of the author. When your research focuses on a specific individual that is someone other than the author, it is appropriate for readers to see that individual's name at the beginning of the citation. Directors, actors, translators, editors, and illustrators are common individuals to list at the beginning. Again, only include their name in place of the author if your research focuses on that specific individual.
To include someone other than the author at the beginning of the citation, place their name in reverse order, add a comma afterwards, and then the role of that individual followed by a period.
Fimmel, Travis, performer. Vikings . Created by Michael Hirst, History Channel, 2013-2016.
Gage, John T., editor. The Promise of Reason: Studies in the New Rhetoric . SIU Press, 2011.
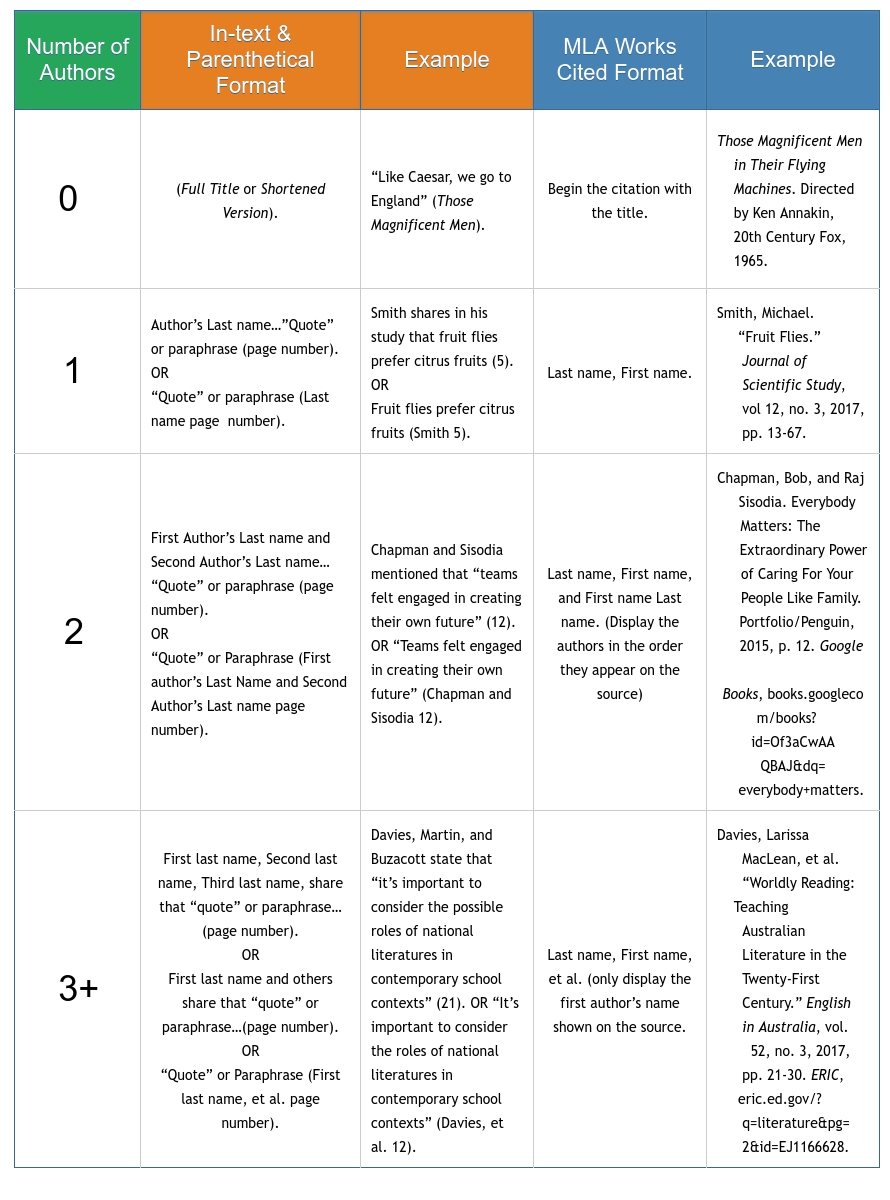
Here's a helpful table to refer to when structuring author names:
Titles and Containers:
Titles follow the name of the author and are written in title capitalization form.
If you're citing a source in its entirety, such as a full book, a movie, or a music album, then place the title in italics.
Franzen, Jonathan. The Corrections . Farrar, Straus, and Giroux, 2001.
Rufus Du Sol. Bloom . Sweat It Out! 2016.
If you're citing a source, such as a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a journal or website, then place the title of the piece in quotations and add a period afterwards. Follow it with the title of the full source, in italics, and then add a comma. This second portion is called the container . Containers house smaller works, such as songs, in larger comprehensive works, such as albums.
Examples with containers:
| Song | Album | "Song." , | Beyonce. "Single Ladies (Put a Ring on It)." , Sony, 2008, track 2. |
| Chapter | Book | "Chapter." , | Aku, Hanjat. "I'm Drifting." , edited by Burton Raffel, State University of New York Albany, 1964. |
| Article | Website or Periodical | "Article Title." , | Vance, Erik, and Erika Larsen. "Mind Over Matter." , Dec. 2016, pp. 30-55. |
| Web page | Website | "Web page." | Becker, Mikkel. "6 Common Dog Behavior Myths Get Busted." , 19 July 2016, www.vetstreet.com/our-pet-experts/6-common-dog-behavior-myths-get-busted. |
Wondering what to do with subtitles? Place a colon in between the title and subtitle. Write both parts in title capitalization form.
Nasar, Sylvia. A Beautiful Mind: The Life of Mathematical Genius and Nobel Laureate John Nash . Simon and Schuster, 2001.
If the source does not have a title , give a brief description and do not use quotation marks or italics.
Israel, Aaron. Brooklyn rooftop acrylic painting. 2012, 12 W 9th Street, New York City.
For a tweet , the full text of the tweet is placed where the title sits.
@LOCMaps. "#DYK the first public zoo to open in the US was the #Philadelphia Zoo? #50States." Twitter , 9 Feb. 2017, 3:14 p.m., twitter.com/LOCMaps/status/829785441549185024.
For email messages, the subject of the email is the title. Place this information in quotation marks.
Rabe, Leor. "Fwd: Japan Itinerary." Received by Raphael Rabe, 11 Feb 2017.
Citations with Two Containers:
It is possible for a source to sit in a second or larger container. A journal article sits in its first container, which is the journal itself, but it can also sit in a larger container, such as a database. A song can sit in its first container, which is the album it's found on. Then it can sit in its next container, which could be Spotify or iTunes.
It is important to include the second container because the content on one container may differ from content from another container.
MLA citing with two containers should be formatted like this:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Source." Title of Container , Other Contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication Date, Location. Title of Second Container , Other Contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication Date, Location.
In most cases, for the second container, only the title of the second container and the location is needed. Why? For readers to locate the source themselves, they'll most likely use the majority of the information found in the first part of the citation.
Examples of Citations with 2 Containers:
Sallis, James, et al. "Physical Education's Role in Public Health: Steps Forward and Backward Over 20 Years and Hope for the Future." Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport , vol. 83, no. 2, Jun. 2012, pp. 125-135. ProQuest , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=http://search.proquest.com/docview/1023317255?accountid=35635.
Baker, Martha. "Fashion: Isaac in Wonderland." New York Magazine , vol. 24, no. 3, 21 Jan. 1991, pp. 50-54. Google Books , books.google.com/books?id=PukCAAAAMBAJ&lpg=PP1&dq=magazine&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=magazine&f=false.
Remember, BibMe has an MLA works-cited generator that creates citations for you quickly and easily!
Format for Other Contributors:
In MLA citing, when there are other individuals (besides the author) who play a significant role in your research, include them in this section of the citation. Other contributors can also be added to help individuals locate the source themselves. You can add as many other contributors as you like.
Start this part of the citation with the individual's role, followed by the word "by". Notice that when adding other contributors after a period, you capitalize the first letter of the individual's role. When adding other contributors after a comma, you lowercase the first letter of the individual’s role.
Gaitskill, Mary. "Twilight of the Superheroes." The Scribner Anthology of Contemporary Short Fiction: 50 North American Stories Since 1970, edited by Lex Williford and Michael Martone, Simon and Schuster, 2012, pp. 228-238.
The Incredibles . Directed by Brad Bird, produced by John Walker, Pixar, 2004.
Gospodinov, Georgi. The Physics of Sorrow . Translated by Angela Rodel, Open Letter, 2015.
Format for Versions:
Sources can come in different versions. There are numerous bible versions; books can come in versions (such as numbered editions), and even movies and songs can have special versions.
When a source indicates that it is different than other versions, include this information in the citation. This will help readers locate the exact source that you used for your project.
The Bible . Lexham English Version, Logos, 2011, lexhamenglishbible.com.
Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion . 2nd ed., Clarendon, 1979.
Afrojack. "Take Over Control." Beatport , performance by Eva Simons, extended version, 2011, www.beatport.com/track/take-over-control-feat-eva-simons-extended/1621534.
Format for Numbers:
Any numbers related to a source that isn't the publication date, page range, or version number should be placed in the numbers position of the citation. This includes volume and issue numbers for journal articles, volume or series numbers for books, comic book numbers, and television episode numbers, to name a few.
When including volume and issue numbers, use the abbreviation “vol.” for volume and “no.” for number.
Zhai, Xiaojuan, and Jingjing Wang. "Improving Relations Between Users and Libraries: A Survey of Chinese Academic Libraries." The Electronic Library , vol. 34, no. 4, 2016, pp. 597-616. ProQuest Research Library , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=http://search.proquest.com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/1841764839?accountid=35635.
"Chestnut." Westworld , directed by Richard J. Lewis, season 1, episode 2, Warner Bros., 2016.
Publishers:
The publisher produces the source. In the citation, place the publisher before the date of publication. Include the publisher for any source type except websites when the name of the publisher is the same as the name of the website. Also, it’s not necessary to include the name of publishers for newspapers, magazines, or journal articles, since the name of the publisher is generally insignificant.
When sources have more than one publisher that share responsibility for the production of the source, place a slash between the names of the publishers.
Use the abbreviation “UP” when the name of the publisher includes the words “University Press.”
Cambridge UP
Publication Dates:
When including the date that the source was published, display the amount of information that is found on the source, whether it's the full date, the month and year, or just the year.
If the date includes a season rather than a month, make sure to lowercase the season (spring 2021 not Spring 2021). Do not capitalize the season.
2 Nov. 2016 or Nov. 2, 2016
When multiple dates are shown on the source, include the date that is most relevant to your work and research.
Abbreviate months longer than 4 letters.
The location refers to the place where the source can be found. This can be in the form of a URL, page number, disc number, or physical place.
When citing websites in MLA, include DOIs or URLs. Copy the DOI or URL directly from the address bar or link in your browser window. If a DOI number is present, use it in place of a URL. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx.
For page numbers, use the abbreviation “p.” when referring to only one page, and “pp.” for a range of pages.
In-Text & Parenthetical Citation Basics:
When using a direct quote or paraphrasing information from a source, add an in-text or parenthetical citation into the body of your work. Direct quotes are word-for-word quotes pulled from a source and added to your project. A paraphrase is when you take a section of information from a source and put it in your own words. Both direct quotes and paraphrases require an in-text or parenthetical citation to follow it.
Format your parenthetical or in-text citation in MLA as follows:
"Direct quote" or paraphrase (Author's last name and page number).
Author's last name said that "Direct Quote" or paraphrase (page number).
*See the comprehensive section below on MLA in-text citations for further clarification and instructions.
MLA In-Text and Parenthetical Citations
What is an in-text citation or parenthetical citation.
You used information from websites, articles, books, and other sources for your paper, right? Hopefully, you did, because the best research and writing projects validate claims using information from other sources.
The purpose of an in-text citation is to give the reader a brief idea about where you found the information used in your writing.
When you place a line of text, word for word (called a direct quote), or an idea (called a paraphrase) from another source into your writing, you, the writer, must display:
- who created that information (the original author's name)
- the page number you found it on
Check out this example:
"A main clause has to have a finite verb " (Cameron 94).
No author? No problem! Include the title, and if it's lengthy, shorten it.
The major thing to keep in mind is that whichever information you include in the in-text or parenthetical citation, whether it's the author's name or the title, it needs to match the first word in the full citation. The full citation is found on the “Works Cited” page in MLA.
Format your parenthetical and MLA in-text citation as follows:
"Direct quote" or Paraphrase (Author's last name and page number). This is an MLA parenthetical citation as the author's name is in parentheses.
Author's Last Name states, "Direct Quote" or paraphrase (page number). This is an MLA citation in prose as the author's name is in the prose of your sentence.
"Jim never got back with a bucket of water under an hour—and even then somebody generally had to go after him" (Twain 8).
Twain went on to say, “Jim never got back with a bucket of water under an hour—and even then somebody generally had to go after him” (8).
Other things to keep in mind:
If your in-text citation comes from a website or another source that does not have page numbers, use the following abbreviations:
- If the source has designated paragraph numbers, use par. or pars.
- If the source has designated sections, use sec. or secs.
- If the source has designated chapters, use ch. or chs.
- If the source has designated lines, use line or lines.
Example in MLA formatting:
Gregor's sister is quite persuasive, especially when she states to her parents, "It'll be the death of both of you, I can see it coming. We can't all work as hard as we have to and then come home to be tortured like this, we can't endure it" (Kafka, ch. 3).
- If there aren't page, paragraph, section, or chapter numbers, only include the author's name in the in-text or parenthetical citation.
- If the original source is an audio or video recording, after the author's name or title, place a timestamp.
The girl's affection towards Marley is clear when she blushes upon his arrival and shares that she would like to accompany him to the theater ( Tales of Times Ago 12:45).
- Two authors : place both names in the reference.
Malcolm and Knowles state... (12).
The smaller the class size, the more attention a student receives, which greatly impacts learning (Malcolm and Knowles 12).
- Three or more authors : place all three names in the in-text citation. It's also acceptable to use the phrase, "and others," or another cohesive term. For parenthetical citations, use the abbreviation et al.
Smith, Baker, and Klein share that.... (78). OR Smith and others share that.... (78).
Many lizards, including the Carolina anole, only eat when they're hungry. They'll ignore food until their body sends a signal to eat (Smith et al. 78).
- Authors with the same last name : Include the first initial of the author’s first name in the in-text or parenthetical citation.
One study shows that the average time spent on homework is 52 minutes (R. Brown 17). However, a more recent study, released in 2018, found that the average student spends 42 minutes completing homework (S. Brown 966).
- Quoted text : Share in the text that the quote comes from another individual.
Lawrence shares his insight by stating that “instructions need to be shared, not assumed” (Young 55).
Common Examples:
Citations for books:.
The basic entry for a book consists of the author's name, the book title, the publisher, and the year published.
Author's Last name, First name. Book Title . Publisher, Year Published.
MLA book citation example:
Shelley, Mary. Frankenstein . Lackington, Hughes, Harding, Mavor & Jones, 1818.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears on the title page.
For a book written by two authors:
- List them in order as they appear on the cover or title page.
- Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the second author's name is written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the second author's name.
Smith, John, and Bob Anderson. The Sample Book . Books For Us, 2017.
- For books with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by a comma and the abbreviation "et al."
Campbell, Megan, et al. The Best Noun Book . Books For Us, 2017.
The full title of the book, including any subtitles, should be italicized and followed by a period. If the book has a subtitle, the main title should be followed by a colon (unless the main title ends with a question mark or exclamation point).
The Best Books for Kids: A Complete Anthology.
Publication information can generally be found on the title page of a book. If it is not available there, it may also be found on the copyright page. State the name of the publisher.
If you are citing a specific page range from the book, include the page(s) at the end of the citation.
Smith, John, and Bob Anderson. The Sample Book . Books For Us, 2017, pp. 5-12.
When a book has no edition number/name present, it is generally a first edition. If you have to cite a specific edition of a book later than the first, see the section below on citing edited books.
Citations for Translated Books:
If the translation is the focus of your project, include the translator's name at the beginning of the citation, like this:
Translator's Last name, First name, translator. Title . By Original Author's First name Last name, Publisher, Year published.
If it's not the actual translation that is the focus, but the text itself, include the translator's name in the "other contributors" position, like this:
Original Author's Last name, First name. Title . Translated by First Name Last name. Publisher, Year published.
Citations for E-Books:
E-books are formatted differently than print books. Why? Some e-books have different, or extra, information than print books. In addition, e-book pages are often numbered differently. Since the content and format may differ from print books, e-book citations are structured differently. When citing an e-book from a website, format the e-book citation with the website title and URL. When citing an e-book in a digital book format, which lacks a URL or that requires software on an e-reader device, include “e-book ed.” for the Version element of the citation. If you know that the e-book file format (EPUB, MOBI, etc.) varies depending on the e-book publication, you may also include the file format as a supplemental element at the end of the entry.
Format for an e-book found on the Internet:
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-Book . Publisher, Year Published. Title of Website , URL.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . Duke UP, 2010. Google Books , books.google.com/books?id=syqTarqO5XEC&lpg=PP1&dq=electronic%20music&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=electronic%20music&f=false.
Format for an e-book found on an e-reader:
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-book. . E-Book ed., Publisher, Year Published.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . E-book ed., Duke UP, 2010. EPUB.
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-book. E-Book ed., Publisher, Year Published. File Format.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . E-Book ed., Duke UP, 2010. EPUB.
Citations for Chapters in Books:
Individual chapters are cited when a writer uses a book filled with many chapters, each written by different authors. When citing a specific chapter in a book or an anthology, structure the citation like this:
Last name, First name of Chapter's Author. "Title of Chapter." Title of Book , Other Contributors and their roles, Version (if there's a specific edition), Publisher, Year Published, Page or Page Range.
Levi-Strauss, Claude. "The Structural Study of Myth." Literary Adverb Theory: An Anthology , edited by Julie Rivkin and Michael Ryan, 3rd ed., Wiley Blackwell, 2017, pp. 178-195.
Citations for Edited Books:
If your book is not a first edition, you should note this in the citation. If the book is a revised edition or an edition that includes substantial new content, include the number, name, or year of the edition and the abbreviation "ed." after the book title. "Revised edition" should be abbreviated as "Revised ed." and "Abridged edition" should be "Abridged ed." The edition can usually be found on the title page, as well the copyright page, along with the edition's date.
Author's Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book . Numbered ed., Publisher, Year Published.
Ferraro, Gary, and Susan Andreatta, editors. Cultural Anthropology: An Applied Perspective . 10th ed., Cengage Learning, 2014.
Smith, John. The MLA Sample Paper Book . Revised ed., Books For Us, 2017.
If your edited book has more than one author, refer to the directions above under the heading "Authors."
Also, BibMe.org helps you create your citations with more than one author quickly and easily! Try our MLA formatter!
Citations for Websites:
Wondering how to cite a website in MLA? The most basic entry for an MLA website citation consists of the author name(s), page title, website title, sponsoring institution/publisher, date published, and the DOI or URL.
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Individual Web Page." Title of Website , Publisher, Date, DOI or URL.
Fosslien, Liz, and Mollie West. "3 Ways to Hack Your Environment to Help You Create." Huffpost Preposition Endeavor , Huffington Post, Dec. 7, 2016, www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/3-ways-to-hack-your-environment-to-help-you-create us 580f758be4b02444efa569bc.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears on the website.
For a page with two or more authors, list them in the order they appear on the website. Only the first author's name should be reversed, with the others written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the last author's name. For pages with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by the abbreviation "et al."
If no author is available, begin the citation with the page title.
The page title should be placed within quotation marks. Place a period after the page title within the quotation marks. The page title is followed by the name of the website, which is italicized, followed by a comma.
After the website title, include the sponsoring institution or publisher followed by a comma. The sponsoring institution/publisher can usually be found at the bottom of the website, in the footer. If the name of the publisher is the same as the name as the website, do not include the publisher information in your citation. In MLA format, it is not recommended to include duplicate information for a website.
Next, state the publication date of the page.In some cases, a specific date might not be available, and the date published may only be specific to a month or even a year. Provide whatever date information is available.
End the citation with the URL. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. End the entire citation with a period.
Looking for an MLA formatter to create your website citations quickly and easily? Check out the BibMe MLA citation machine! Our MLA format website creates your citations in just a few clicks.
Citations for Online Journal Articles:
The most basic entry for a journal consists of the author name(s), article title, journal name, volume number, issue number, year published, page numbers, name of website or database where the article was found, and URL or Direct Object Identifier (DOI).
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Journal Article." Title of Journal , vol. number, issue no., Date, Page Range. Database or Website Name , URL or DOI.
Snyder, Vivian. "The Effect Course-Based Reading Strategy Training on the Reading Comprehension Skills of Developmental College Students." Research and Teaching in Developmental Education , vol. 18, no. 2, spring 2002, pp. 37-41. *JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/42802532.
*According to MLA 9th edition, lowercase seasons (spring 2002 not Spring 2002). Do not capitalize seasons.
Most online journal articles have two containers. The first is the journal that the article is in, and the second is the website or database the journal is in.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears in the journal.
For an article written by two authors, list them in the order they appear in the journal. Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the second is written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the second author's name.
Krispeth, Klein, and Stewart Jacobs.
For articles with three or more authors, include the name of the first author in the citation, followed by a comma and the abbreviation "et al."
Jones, Langston, et al.
The article title should be placed within quotation marks. Place a period after the article title within the quotation marks, unless the article title ends with a question mark or exclamation mark. The article title is followed by the name of the journal, which is italicized.
Include the volume number of the journal, but use the abbreviation "vol." You may also need to include the issue number, depending on the journal. Use the abbreviation "no." before the journal's issue number.
Jones, Robert, et al. "Librarianship in the Future." Libraries Today , vol. 5, no. 2, Mar. 2017, pp. 89-103. Database Life , www.dbl.com/6854.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. If the article has a DOI, use the DOI instead of the URL.
Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs)
Simply put, a Digital Object Identifier (usually abbreviated as “DOI”) is an identification number or source link for a document or file. It’s a system that is widely used by journals today. The DOI is comprised of symbols, numbers, and letters.
Example: https://doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1805-z.
This unique number system is very beneficial to readers and authors since it can be used to immediately locate an exact document, even if a host web page or database has altered an article’s URL.
How do I find an article’s DOI?
In print or PDF form, the first place to check is the front page of the article. If it is an online article, look for the DOI near the top of the article, at the very end of the article, or wherever citation information is located. Here are a few examples:
Here is an example from The New England Journal of Medicine:

Here is an example from the bottom of a Nature article:
Where in a citation is the DOI included?
If a DOI for an article exists, place it at the end of the citation. Here’s an example for the New England Journal of Medicine article previously shown:
Thomas, Cristina, et al. “Facing Uncertainty.” New England Journal of Medicine , vol. 381, no. 23, 2019, pp. 2253–2259, https://doi:10.1056/nejmcps1906037.
Citations for Blogs:
Blogs can be good sources to use for research papers and projects since many are regularly updated and written by influencers and experts.
Blogs can belong to a single individual, a group of people, or a company. Most entries for a blog include a title for that day’s entry, the date it was posted, and the information.
To cite a blog, you’ll need the following pieces of information: * The author’s name(s) or the name of the company who posted the blog * The title of the individual blog post * The title of the blog * The name of the publisher (if it differs from the name of the author(s) or title of the blog) * The date the blog post was posted * The website address (URL) for the blog post
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Blog Post.” Title of Blog , Publisher, Date Published, URL.
BibMe. “How to Spell in English: British vs. American.” BibMe Blog, www.bibme.org/blog/writing-tips/how-to-spell-in-english-british-vs-american/.
Notice in the above example, the date is missing. If there is no date shown on the blog post, omit it from the full citation.
Williams, Lindsay. “How to Get the Most from Your Online Language Lessons with a Tutor.” Lindsay Does Languages , 2019 Feb. 12, www.lindsaydoeslanguages.com/how-to-get-the-most-from-your-online-language-lessons-with-a-tutor/.
Cite a blog post in the text of the paper using this format:
(Author’s Last name) OR Author’s Last name...
Since there isn’t a page number, only use the author’s last name.
Citations for Newspapers:
The most basic entry for a newspaper consists of the author name(s), article title, newspaper name, publication date, page numbers, and sometimes a URL if found online. Omit volume numbers, issue numbers, and the names of publishers from newspaper citations.
Format if found on a website:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Article." Title of Newspaper's Website , Publication Date, URL.
Format if found on a database:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Article." Title of Newspaper , Publication Date, Page or Page Range (if available). Title of Database , URL.
MLA format example:
This example is for a print newspaper:
Hageman, William. "Program Brings Together Veterans, Neglected Dogs." Chicago Tribune , 4 Jan. 2015, p. 10.
The full article title should be placed within quotations. Next, state the name of the newspaper in italics.
Towards the end of the citation, include the page numbers on which the article appears with a period. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
Don't forget, the BibMe citation generator in MLA creates citations for you quickly and easily! Also, check out BibMe Plus paper checker, which scans your paper for correct usage of language elements. Have a determiner out of place in your writing? A pronoun spelled incorrectly? An overused adjective ? No worries, BibMe Plus has you covered!
Citations for Photographs:
The most basic entry for a photograph consists of the photographer's name, the title of the photograph, the title of the book, website, or collection where the photograph can be located, the publisher of the photograph or publication where the image was located, the date the photograph was posted or taken, and the page number, location of the museum (such as a city and state), or URL if found online.
Photographer's Last name, First name. "Title of the Photograph." Title of the Book, Website, Collection, or other type of publication where the photograph was found , Date photograph was taken, Page Number (if applicable), Location (such as a city and state if necessary) where the photograph can be found, or URL.
Begin with the name of the photographer or main contributor (if available). This person's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (and any middle name).
For a photograph taken from a publication or website, include the title of the photograph in quotation marks followed by a period. If the photograph does not have a formal title, create a description. If you make your own description, only include a capital at the beginning of the description and at the beginning of any proper nouns. Do not place the description in italics or quotation marks.
Place the title of the publication in italics immediately following the description, followed by a comma.
Digital Image/Photograph found online:
Photograph of the Hudson Area Public Library. JMS Collective , 19 Apr. 2016, www.jmscollective.com/hudson-ny-3/historic-hudson-armory-now-public-\ library/.
*Note that the above photograph does not have a formal title, so the photograph citation contains a description instead.
Photograph or Image viewed in a museum:
Vishniac, Roman. "Red Spotted Purple." Roman Vishniac's Science Work , early 1950s - late 1960s, International Center of Photography at Mana, New Jersey.
Photograph or Image found in a book:
Barnard, Edwin. Photograph of Murray Street, Hobart. Exiled: The Port Arthur Convict Photographs , National Library of Australia, 2010, p. 20.
Citing Social Media in MLA Format:
It's not uncommon to see social media posts included in research projects and papers. Most social media citations use the following structure:
@Username (First name Last name, if known, and differs from handle). "Text of post." Social Media Platform , Date posted, URL.
If the post is a photo or image instead of text, include a description of the image. Only capitalize the first letter in the description and the first letter for any proper nouns. Do not place the description in quotation marks.
If the post is long or includes emojis or links, it is acceptable to include only the beginning of the tweet with an ellipsis at the end of the included portion.
Citing a Twee:
@BibMe. "Need help with MLA essay format? Here are 6 steps to getting it done..." Twitter , 3 Dec. 2018, twitter.com/bibme/status/1069682724716204032.
Citing a Facebook Post:
DeGeneres, Ellen. "Holiday party goals..." Facebook , 21 Dec. 2018, www.facebook.com/ellentv/photos/a.182755292239/10157188088077240/?type=3&theater.
Citing an Instagram Post:
@dualipa. "A lil Hollywood glam brunch! Thank you @variety for by Breakthrough Artist of the Year award and thank you for your continuous support...." Instagram , 2 Dec. 2018, www.instagram.com/p/Bq33SC2BAsr/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link.
Citations for Music:
Citing a Song from the Internet:
To cite this type of source, structure the reference as follows:
Singer's Last Name, First name OR Band Name. "Title of Song." Title of Website or Service , Other Contributors and their roles (if applicable), Version, Date Published, URL.
Lopez, Jennifer. "Us." Spotify , 2 Feb. 2018, open.spotify.com/track/2MMvonKGALz6YOJwaKDO3q.
Citing a song from an album or downloaded:
Singer's Last name, First name OR Band Name. "Title of Song." Title of Album , Other Contributors and their roles (if applicable), Version, Publisher, Date Published or Released.
Lopez, Jennifer. "On the Floor." LOVE? , performance by Pitbull, Island, 2011.
Citations for Films:
The most basic entry for a film consists of the title, director, publisher, and year of release. You may also choose to include the names of the writer(s), performer(s), and the producer(s), depending on who your research focuses on. You can also include certain individuals to help readers locate the exact source themselves.
Example of a common way to cite a film:
Film Title . Directed by First name Last name, performance by First Name Last Name, Publisher, Year.
BibMe: The Movie . Directed by John Smith, performance by Jane Doe, New York Stories, 2017.
If your research focuses on a specific individual, you can begin the citation with that individual's name (in reverse order) and their role. Format it the same way as you would an author's name.
Doe, Jane, performer. BibMe: The Movie . Directed by John Smith, New York Stories, 2017.
If the film is dubbed in English or does not have an English title, use the foreign language title in the citation, followed by a square bracket that includes the translated title.
Citas gobiernan el mundo [ Citations Rule the World ]. Directed by Sara Paul, Showcase Films, 2017.
If the film was found online, such as YouTube or another site, include the name of the website and the URL.
Last name, First name of Individual who posted the video OR Account name. "Film Title." Website Title , other individuals and their roles (if applicable), Publisher, Year Published, URL.
The New York Public Library. "2018 National Book Awards Finalists at NYPL." YouTube , 15 Nov. 2018, youtu.be/edJqg3NuF2Q.
*Note that the New York Public Library was not listed as the publisher of the video. Adding "The New York Public Library" in the citation twice is not necessary.
Since the citation has two titles included (the title of the film and the title of the website), the title of the film is placed in quotation marks and the title of the website is in italics.
Citations for TV/Radio:
The most basic MLA format citation for a radio/TV program consists of the individuals responsible for the creation of the episode (if they're important to your research), the episode title, program/series name, broadcasting network or publisher, the original broadcast date, and the URL.
"The Highlights of 100." Seinfeld , NBC, 2 Feb. 1995.
If your research focuses on a specific individual from a TV or radio broadcast, include their name at the beginning of the citation in the author position.
If relevant, you may also choose to include the names of personnel involved with the program. Depending if the personnel are relevant to the specific episode or the series as a whole, place the personnel names after the program/series name. You may cite narrator(s) preceded by "narrated by", writer(s) preceded by "written by", directors preceded by "directed by", performer(s) preceded by "performance by", and/or producer(s) preceded by "produced by" and then the individual names. Include as many individuals as you like. Write these personnel names in normal order --- do not reverse the first and last names.
"The Highlights of 100." Seinfeld , directed by Andy Ackerman, written by Peter Mehlman, NBC, 2 Feb. 1995.
Also include the name of the network on which the program was broadcasted, followed by a comma.
State the date on which your program was originally broadcasted, followed by a period. When including the URL, follow the date with a comma and place the URL at the end, followed by a period to end the citation. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them.
Citations for Lectures:
The most basic entry for a lecture consists of the speaker's name, presentation title, date conducted, and the name and location of the venue.
Speaker's Last name, First name. Title of Lecture . Date Conducted, Venue, Location.
Pausch, Randy. Really Achieving Your Childhood Dreams . 18 Sept. 2007, McConomy Auditorium, Pittsburgh.
Begin the citation with the name of the speaker. This person's name should be reversed. If the lecture has a title, place it in the citation in italics, followed by a period. State the date on which the lecture was conducted, followed by a comma. Conclude your citation with the location/venue name and the city in which it occurred, separated by a comma.
Citations for Encyclopedias
The most basic entry for an encyclopedia consists of the author name(s), article title, encyclopedia name, publisher, and year published.
Last Name, First Name. "Article Title." Encyclopedia Name , Publisher, Year Published.
Smith, John. "Internet." Encyclopedia Britannica , 2012.
Notice that the name of the publisher was not included in the example above. Only include the name of the publisher if it differs from the name of the encyclopedia. Encyclopedia Britannica is the name of the encyclopedia AND the name of the publisher. It is not necessary to include Encyclopedia Britannica twice in the citation.
If there are no authors for the article, begin the citation with the article title instead.
"Media." World Book Encyclopedia , 2010.
If the encyclopedia arranges articles alphabetically, do not cite the page number(s) or number of volumes. If articles are not arranged alphabetically, you may want to include page number(s) and/or volume number, which is preceded by the abbreviation "vol." The volume should be cited after the encyclopedia name (or any edition), and before any publication information. After the publication year, include the page numbers on which the article appears, along with a period. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
Saunders, Bill. "Treasure." Encyclopedia Britannica , vol. 18, 2012, p. 56.
If the encyclopedia entry is found on a website, use the following structure:
Last name, First name. "Encyclopedia Entry." Title of Encyclopedia Website , Publisher, Year published, URL.
Citations for Magazines:
The most basic entry for a magazine consists of the author name(s), article title, magazine name, the volume and issue numbers (if available), publication date, page numbers, and URL if found online.
Last name, First name. "Article Title." Magazine Name , vol. number, issue no., Publication Date, Page Numbers or URL.
Print example:
Pratt, Sybil. "A Feast of Tradition." BookPage , Oct. 2017, p. 8.
Online example:
Geagan, Kate. "Sweeter Swaps: How to Choose Sustainable Sweeteners." Clean Eating , no. 83, Nov./Dec. 2018, pp. 36-37. Flipster , cleaneating.eoncontent.ebscohost.com/1927216#&pageSet=19.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears in the magazine.
For an article written by two or more authors, list them in the order as they appear on the title page. Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the others are written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the last author's name. For articles with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by the abbreviation "et al."
The full article title should be placed within quotations. Unless there is punctuation that ends the article title, place a period after the title within the quotations. Next, state the name of the magazine in italics.
If volume and issue numbers are available, include them in the citation. Use the abbreviations “vol.” and “no.” before the volume number and issue number.
Example: vol. 6, no. 1
The date the magazine was published comes directly after the volume and issue number. Use whichever date the magazine includes, whether it's a complete date, a period spanning two months, a season (lowercased), or just a month and year. Follow this information with a comma.
Include the page number(s) on which the article appears. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
If the magazine article was found online, include the DOI or URL. Use a DOI instead of a URL when it is available. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. End the citation with a period.
Citations for Interviews:
Begin your citation with the name of the person interviewed. This person's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name).
For an interview that has been broadcast or published, if there is a title, include it after the name of the person interviewed.
Jolie, Angelina. "Being a Mother." Interview conducted by Steve Kroft, 60 Minutes , CBS, 3 Feb. 2009.
If there is no title, use the word "Interview" in place of a title and do not use quotation marks or italics. If the interviewer's name is known, add it, preceded by "Conducted by", after the word "Interview". Do not reverse the interviewer's name.
Jenkins, Lila. Interview. Conducted by Jessica Grossman. 5 Mar. 2017.
For published interviews found online, include the title of the website after the title of the interview. In addition, add the URL at the end of the citation.
Michaels, Jamye. "Fighting to Survive." Women's Magazine of Life , 2 Nov. 2016, www.womensmagazine.com/fightingtosurvive.com.
Citations for Dissertations and Theses:
In order to obtain a degree, most colleges and universities require students to submit a dissertation or thesis towards the end of their academic track. Dissertations and theses are lengthy essays or in-depth research projects that relate to the scope of the student’s learning.
For example, if a student is close to obtaining their Master’s in Library Science, the student could study and write about the Internet searching habits of elderly individuals, or perhaps focus on the research skills of economically disadvantaged adults.
Upon completion, this individual assignment is often presented to the main directors, committee members, or professors at the school for approval.
A dissertation is generally assigned to students who are completing their doctorate degree, and many graduate schools require students to hand in a thesis to obtain a master’s degree.
Since so much research and work went into these scholarly projects, and new ideas and conclusions are often produced, many colleges and universities publish the completed papers. You can find these projects on many school websites and databases.
Here’s one way you can reference a dissertation or thesis:
Author’s Last Name, First name. Title of Dissertation or Thesis . Year Completed. University or College, Degree Abbr. Database , DOI or URL.
Kim, Kee Han. Development of an Improved Methodology for Analyzing Existing Single-Family Residential Energy Use . 2014. Texas A & M U, PhD. ProQuest , https://ezproxy.nypl.org/socabs/docview/1665251619/abstract/E9D36166E31040AEPQ/1?accountid=35635.
Fletcher, Marissa. Influences of Nutrition and Pathogenicity from a Microbial Diet on Immunity and Longevity in Caenorhabditis Elegans . 2012. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, PhD. DSpace@MIT , https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/120633.
Using Visuals
Including a visual in your project is a great way to make information come to life, as visuals can complement written work and enhance understanding.
Photographs, maps, charts, graphs, line drawings, musical scores, and tables are images that can be included in a project.
Follow these directions to add an image to your research paper:
- Images should be placed close to where they’re mentioned in the text.
- Provide a brief explanation about the image in the written portion of the paper, but do not write out all data shown in the image. Doing so would make the image unnecessary. (See the visual “Table example” at the end of this section.)
Correct example: Table 1 shows commonly used words in Shakespeare’s plays and their English translation.
Incorrect example: Table 1 shows commonly used words in Shakespeare’s plays and their English translation. Brave translates to handsome , character means a letter or word , egal means equal , fancy is a term for desire , and honest translates to pure .
- Tables are titled Table X, figures are Fig. X, and examples are Ex. X.
- Any type of image that includes an illustration is considered a “Figure”.
- Musical scores or sheet music are considered “Examples”.
- If the information below the image contains all of the source information, a full reference on the “Works Cited” page is not necessary.
- Double space everything.
- The image should have the same 1-inch margins as the rest of the paper.
Check out the examples below to see how tables, figures, and musical scores are arranged.
Table Example:
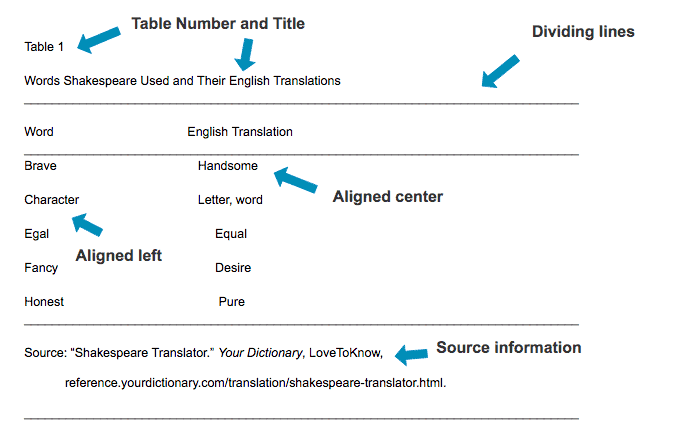
Figure Example:
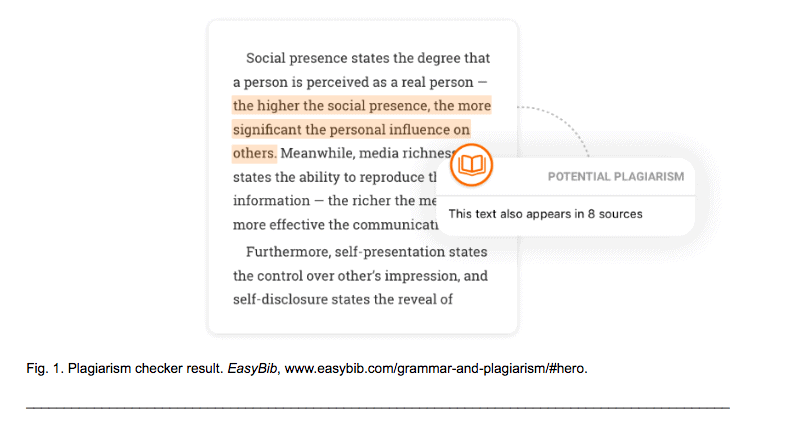
Musical score example:
Your “Works Cited” Page
An MLA "Works Cited" or MLA "Work Cited" page contains all of the citations for a project.
- This page sits on its own and is found at the end of a project.
- If there is only one citation on the page, title the page: Work Cited. While it might seem silly to have a full page dedicated to one citation, a “Work Cited” page in MLA is still necessary. If there are multiple citations on the page, title the page: Works Cited.
- Double space the entire list of works cited.
- Include the writer's last name and the page number, at the top right corner of the page.
- Every in-text or parenthetical citation in the body of the project should correspond with its full citation listed on the MLA “Works Cited” or “Work Cited” page.
- All full citations in MLA formatting have a hanging indent. This means that the first line of the citation sits flush against the left margin. The second line, and any subsequent lines, are indented in another half inch. If you need a visual, all full citations on this page have a hanging indent.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first letter found in the citation.
- If there are multiple sources by the same author, only include the author's name in the first citation. For each citation afterwards, MLA formatting requires you to include three dashes and a period. Organize the citations by the title.
Example of a Works-Cited List with Multiple Works by Same Author:
Riggs, Ransom. Miss Peregrine's Home for Peculiar Children . Quirk, 2011.
---. Tales of the Peculiar . Dutton, 2016.
- When alphabetizing by titles, ignore “A,” “An,” and “The,” and use the next part of the title.
- If the title starts with a number, place the title where it would belong if the number was spelled out.
MLA formatting example:
1492: The Year Our World Began would be alphabetized under F (for fourteen)
Sample Works Cited:

Formatting Your Header:
The first page of your MLA format paper should include a header. An MLA cover page, or MLA title page, that sits on its own isn't necessary or recommended.
MLA heading format includes the following pieces of information, styled like this, in this order:
Your professor or teacher's name
The class and/or course number
Date of submission
- Double space everything on the page.
- In the top right corner, include your last name and the page number.
- The title should be centered in the middle of the page.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read for the entire paper.
- MLA paper format requires 12-point font, or another size close to it.
Sample MLA Header:

Using BibMe.org to Create Citations for your MLA Works Cited Page or MLA Bibliography
Wondering how to use MLA format? The BibMe automatic MLA format generator formats your citations for you. Enter a title, web address, ISBN number, or other identifying information into the MLA format template to automatically cite your sources. If you need help with BibMe.org or our citation machine in MLA, click here on more styles .
Try This Out:
The BibMe service is an extremely helpful resource that helps you create your citations for your project, but there's more. The BibMe service also has a feature that will help to proofread your entire MLA format essay. The BibMe Plus paper checker scans for proper spelling, punctuation, language elements, and syntax. It will tell you if a language element, such as a preposition , conjunction , or interjection , is a bit off. It also has a built-in plagiarism checker , which scans papers for instances of accidental plagiarism. Try it out now!
More Information:
Here's more information on the previous handbooks. There's further good information here , including MLA format examples and examples of MLA in-text citations.
Background Information and History:
The Modern Language Association was developed in 1883 and was created to strengthen the study and teaching of languages and literature. With over 25,000 current members worldwide, the Modern Language Association continuously strives to keep its members up-to-date on the best practices, methods, and trends related to language and literature. The Modern Language Association boasts an annual conference, journal, an online communication platform, numerous area-focused committees, and one of its most popular publications, the MLA Handbook, now in its 9th edition.
Updated June 25, 2021
Edited and written by Elise Barbeau and Michele Kirschenbaum. Elise is a citation expert and has her master’s degree in public history/library science. She has experience in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing. Michele is a certified library media specialist who loves citations and teaching. She’s been writing about citing sources since 2014.
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

Generate formatted bibliographies, citations, and works cited automatically
What is mybib.
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers.
If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically for books, journals, websites, and videos just by searching for a title or identifier (such as a URL or ISBN).
Plus, we're using the same citation formatting engine as professional-grade reference managers such as Zotero and Mendeley, so you can be sure our bibliographies are perfectly accurate in over 9,000 styles -- including APA 6 & 7, Chicago, Harvard, and MLA 7 & 8.
Quick features:
| ⚙️ Styles | APA, MLA, Harvard |
|---|---|
| 📚 Sources | Websites, books, journals, newspapers |
| 🔎 Autocite | Yes |
| 📥 Download to | Microsoft Word, Google Docs |
Works-Cited-List Entries
Citations by format.
Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements —facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you’re citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on the template.
The examples below show you how to cite five basic source types. Click on an entry to get more information, as well as links to posts with more examples. For hundreds of sample entries by format, check out the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Book by One Author
Mantel, Hilary. Wolf Hall . Picador, 2010.
Book by an Unknown Author
Beowulf . Translated by Alan Sullivan and Timothy Murphy, edited by Sarah Anderson, Pearson, 2004.
An Edited Book
Sánchez Prado, Ignacio M., editor. Mexican Literature in Theory . Bloomsbury, 2018.
Online Works
Article on a website.
Deresiewicz, William. “The Death of the Artist—and the Birth of the Creative Entrepreneur.” The Atlantic , 28 Dec. 2014, theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2015/01/ the-death-of-the-artist-and-the-birth-of-thecreative-entrepreneur/383497/.
Book on a website
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Masque of the Red Death.” The Complete Works of Edgar Allan Poe , edited by James A. Harrison, vol. 4, Thomas Y. Crowell, 1902, pp. 250-58. HathiTrust Digital Library , hdl.handle.net/2027/coo.31924079574368.
Journal Article in a Database
Goldman, Anne. “Questions of Transport: Reading Primo Levi Reading Dante.” The Georgia Review , vol. 64, no. 1, spring 2010, pp. 69-88. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/41403188.
Songs, Recordings, and Performances
Song from an album.
Snail Mail. “Thinning.” Habit , Sister Polygon Records, 2016. Vinyl EP.
Song on a website
Snail Mail. “Thinning.” Bandcamp , snailmailbaltimore.bandcamp.com.
Concert Attended in Person
Beyoncé. The “Formation” World Tour. 14 May 2016, Rose Bowl, Los Angeles.
Movies, Videos, and Television Shows
A movie viewed in person.
Opening Night. Directed by John Cassavetes, Faces Distribution, 1977.
A Movie Viewed Online
Richardson, Tony, director. Sanctuary . Screenplay by James Poe, Twentieth Century Fox, 1961. YouTube , uploaded by LostCinemaChannel, 17 July 2014, www.youtube.com/watch?v=IMnzFM_Sq8s .
A Television Show Viewed on Physical Media
“Hush.” 1999. Buffy the Vampire Slayer: The Complete Fourth Seaso n, created by Joss Whedon, episode 10, Mutant Enemy / Twentieth Century Fox, 2003, disc 3. DVD.
A Photograph Viewed in Person
Cameron, Julia Margaret. Alfred, Lord Tennyson . 1866, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City.
A Painting Viewed Online
Bearden, Romare. The Train . 1975. MOMA , www.moma.org/collection/works/65232?locale=en.
An Untitled Image from a Print Magazine
Karasik, Paul. Cartoon. The New Yorker , 14 Apr. 2008, p. 49.
MLA Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What is Cite This For Me’s Citation Generator?
Are you looking for an easy and reliable way to cite your sources in the MLA format? Look no further because Cite This For Me’s MLA citation generator is designed to remove the hassle of citing. You can use it to save valuable time by auto-generating all of your citations.
The Cite This For Me citation machine accesses information from across the web, assembling all of the relevant material into a fully-formatted works cited MLA format page that clearly maps out all of the sources that have contributed to your paper. Using a generator simplifies the frustrating citing process, allowing you to focus on what’s important: completing your assignment to the best of your ability.
Have you encountered an unusual source, such as a microfiche or a handwritten manuscript, and are unsure how to accurately cite this in the MLA format? Or are you struggling with the dozens of different ways to cite a book? If you need a helping hand with creating your citations, Cite This For Me’s accurate and powerful generator and handy MLA format template for each source type will help to get you one step closer to the finishing line.
Continue reading our handy style guide to learn how to cite like a pro. Find out exactly what a citation generator is, how to implement the MLA style in your writing, and how to organize and present your work according to the guidelines.
Popular MLA Citation Examples
- Archive material
- Book Chapter
- Dictionary entry
- E-book or PDF
- Image online or video
- Presentation or lecture
- Video, film, or DVD
Why Do I Need To Cite?
Whenever you use someone else’s ideas or words in your own work, even if you have paraphrased or completely reworded the information, you must give credit where credit is due to avoid charges of plagiarism. There are many reasons why.
First, using information from a credible source lends credibility to your own thesis or argument. Your writing will be more convincing if you can connect it to information that has been well-researched or written by a credible author. For example, you could argue that “dogs are smart“ based on your own experiences, but it would be more convincing if you could cite scientific research that tested the intelligence of dogs.
Second, you should cite sources because it demonstrates that you are capable of writing on an academic or professional level. Citations show that your writing was thoughtfully researched and composed, something that you would not find in more casual writing.
Lastly, and most importantly, citing is the ethical thing to do. Imagine that you spent months of your life on a paper: researching it, writing it, and revising it. It came out great and you received many compliments on your thesis and ideas. How would you feel if someone took those ideas (or even the whole paper) and turned them in as their own work without citations? You’d probably feel terrible.
All of the source material that has contributed to your work must be acknowledged with an MLA in-text citation (also known as a parenthetical citation ) and be featured in your works cited list as full references.
Create citations, whether manually or by using the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator, to maintain accuracy and consistency throughout your project.
Do I Have to Cite Everything?
When writing a research paper, any information used from another source needs to be cited. The only exceptions to this rule are everyday phrases (e.g., all the world’s a stage) and common knowledge (e.g., President Kennedy was killed in 1963).
Also, your own work does not need to be cited. That includes your opinions, ideas, and visuals (e.g., graphs, photos, etc.) you created. However, you do need to cite your own work if you have previously published it or used it in another assignment. Otherwise it’s considered self plagiarism . For example, submitting a paper that you wrote and already turned in for another class is still plagiarism, even though it is your own work.
If you have any doubts about whether or not something you’ve written requires a citation, it’s always better to cite the source. While it may be a tedious process without an MLA citation machine, attributing your research is essential in validating the statements and conclusions you make in your work. What’s more, drawing on numerous sources elevates your understanding of the topic, and accurately citing these sources reflects the impressive research journey that you have embarked on.
Consequences of Not Citing
The importance of crediting your sources goes far beyond ensuring that you don’t lose points on your assignment for citing incorrectly. Plagiarism, even when done unintentionally, can be a serious offense in both the academic and professional world.
If you’re a student, possible consequences include a failing assignment or class grade, loss of scholarship, academic probation, or even expulsion. If you plagiarize while writing professionally, you may suffer legal ramifications as well, such as fines, penalties, or lawsuits.
The consequences of plagiarism extend beyond just the person who plagiarized: it can result in the spread of misinformation. When work is copied and/or improperly cited, the facts and information presented can get misinterpreted, misconstrued, and mis-paraphrased. It can also be more difficult or impossible for readers and peers to check the information and original sources, making your work less credible.
What is the MLA Format?
The MLA format was developed by the Modern Language Association as a consistent way of documenting sources used in academic writing. It is a concise style predominantly used in the liberal arts and humanities, first and foremost in research focused on languages, literature, and culture. The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook has the most current format guidelines. It was updated to reflect the expanding digital world and how researchers and writers cite more online sources. You can find out more here .
It is important to present your work consistently, regardless of the style you are using. Accurately and coherently crediting your source material both demonstrates your attention to detail and enhances the credibility of your written work. The MLA format provides a uniform framework for consistency across a scholarly document, and caters to a large variety of sources. So, whether you are citing a website, an article, or even a podcast, the style guide outlines everything you need to know to correctly format all of your MLA citations.* The style also provides specific guidelines for formatting your research paper, and useful tips on the use of the English language in your writing.
Cite This For Me’s style guide is based on (but not associated with) the 9th edition of the Modern Language Association Handbook for Writers of Research Papers. Our MLA generator also uses the 9th edition – allowing you to shift focus from the formatting of your citations to what’s important – how each source contributes to your work.
MLA has been widely adopted by scholars, professors, journal publishers, and both academic and commercial presses across the world. However, many academic institutions and disciplines prefer a specific style of referencing (or have even developed their own unique format) so be sure to check which style you should be using with your professor. Cite This For Me supports citing in thousands of styles, so the odds are good that we have tools for the citation style you need. Whichever style you’re using, be consistent!
So, if you’re battling to get your citations finished in time, you’ve come to the right MLA citation website. The generator above will can cite any source in 7,000+ styles. So, whether your discipline uses the APA citation style, or your institution requires you to cite in the Chicago style citation , simply go to Cite This For Me’s website to find generators and style guides for ASA , IEEE , AMA and many more.
*You may need to cite a source type that is not covered by the format manual – for these instances we have developed additional guidance and MLA format examples, which we believe stick as closely as possible to the spirit of the style. It is clearly indicated where examples are not covered in the official handbook.
How Do I Create and Format MLA In-text Citations?
The MLA format is generally simpler than other referencing styles as it was developed to emphasize brevity and clarity. The style uses a straightforward two-part documentation system for citing sources: parenthetical citations in the author-page format that are keyed to an alphabetically ordered works cited page. This means that the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text as a parenthetical citation, and a complete corresponding reference should appear in your works cited list.
Keep your MLA in-text citations brief, clear and accurate by only including the information needed to identify the sources. Furthermore, each parenthetical citation should be placed close to the idea or quote being cited, where a natural pause occurs – which is usually at the end of the sentence. Essentially you should be aiming to position your parenthetical citations where they minimize interruption to the reading flow, which is particularly important in an extensive piece of written work.
Check out the examples below…
Citation Examples
Parenthetical citation examples:
- Page specified, author mentioned in text:
If the author’s name already appears in the sentence itself then it does not need to appear in the parentheses. Only the page number appears in the citation. Here’s an MLA format example:
Sontag has theorized that collecting photographs is a way “to collect the world” (3).
- Page specified, author not mentioned in text:
Include the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken in a parenthetical citation after the quote. This way of citing foregrounds the information being cited.
“To collect photographs is to collect the world” (Sontag 3).
When the author is referred to more than once in the same paragraph, you may use a single MLA in-text citation at the end of the paragraph (as long as the work cannot be confused with others cited).
On Photography posits that “to collect photographs is to collect the world.” It intensifies that sentiment by saying photography “means putting oneself into a certain relation to the world that feels like knowledge—and, therefore, like power.” (Sontag 3, 4)
- Page specified, same author, different works:
If you are citing two works by the same author, you should put a comma after the author’s surname and add a shortened title to distinguish between them. Italicize book titles, put article titles within quotation marks. As with the above examples, if you mention the author in the text, they don’t need to be included in the parenthetical MLA citation.
In the line “Ask Benjy ef I did. I aint stud’in dat winder” ( The Sound 276), Faulkner employs spelling and diction to communicate the character background of Dilsey. He’s also seen doing this in other books. For example, “He kilt her.” ( As I Lay 54).
- Page specified, two authors, same last name:
In MLA citing, if there are two authors with the same surname, be sure to include their first initial in your citation to avoid confusion.
- Page specified, two authors, same work:
Each author’s name will be included in both the parenthetical and the full source reference in your MLA bibliography.
Crowley is in fact, the snake who convinced Eve to eat the apple in the Garden of Eden (Prattchett and Gaiman 4).
- Page specified, more than two authors, same work:
For any work with three authors or more, you’ll include the last name of the first author listed and the abbreviation “et al.” which is Latin for “and others.”
“The skills required to master high-stakes interactions are quite easy to spot and moderately easy to learn” (Patterson et al. 28).
- Websites and other online sources:
The MLA formatting examples below above are for information or quotes that have specified pages, usually from a book. If you are using information from a website or online source, the author rules below still apply but a page number is not needed. Instead, just include the first bit of identifiable information that will be shown in the source’s full reference (e.g., author name, video title, website name, etc.).
“Scientists speculate that this might be due to a large chunk of nickel and iron embedded beneath the crater – perhaps the remnants of the asteroid that created it” (Ravilious).
“There’s a flag on the flag; it’s bad design” (“In Defense of Bad Flags”)
Full citations/references MLA website citation:
One of the most common sources cited are websites, so it’s useful to know how to cite a website in MLA.
Ravilious, Kate. “Terrawatch: The Mysteries of the Moon’s Largest Crater.” The Guardian , 1 Oct 2019, www.theguardian.com/science/2019/oct/01/terrawatch-the-mysteries-of-the-moons-largest-crater.
Format for books:
Franke, Damon. Modernist Heresies: British Literary History, 1883-1924 . Ohio State UP, 2008.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography . Penguin, 2008.
MLA citation format for journal articles:
Stanton, Elizabeth Cady. “Progress of the American Woman.” The North American Review , vol. 171, no. 529, 1900, pp. 904–907. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/25105100.
Format for online videos:
“In Defense of Bad Flags.” YouTube , uploaded by Vlogbrothers, 4 Oct. 2019, www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkpAe3_qmq0.
Works cited / bibliography example:
Unlike an MLA in-text citation, you must include all of the publication information in your works cited entries.
Franke, Damon. Modernist Heresies: British Literary History, 1883-1924. Ohio State UP, 2008.
There’s a lot of formatting needed when you cite. Luckily for you, we know where the commas go, and our MLA citation maker will help you put them there.
If citing is giving you a headache, use Cite This For Me’s free, accurate and intuitive MLA citation generator to add all of your source material to your works cited page with just a click.
How Do I Format My MLA Works Cited Page?
A works cited page is a comprehensive list of all the sources that directly contributed to your work – each entry links to the brief parenthetical citations in the main body of your work. An in-text citation MLA only contains enough information to enable readers to find the source in the works cited list, so you’ll need to include the complete publication information for the source in your works cited entries.
Your works cited page in MLA should appear at the end of the main body of text on a separate page. Each entry should start at the left margin and be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name (note that if there is no author, you can alphabetize by title). For entries that run for more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) – this format is called a ‘hanging indentation.’
The title of the page should be neither italicized nor bold – it is simply center-aligned. Like the rest of your MLA format paper the list should be double-spaced, both between and within entries.
Sometimes your professor will ask you to also list the works that you have read throughout your research process, but didn’t directly cite in your paper. This list should be called ‘Work Cited and Consulted,’ and is an excellent opportunity to demonstrate the full extent of the research you have carried out.
As long as you clearly indicate all of your sources via both parenthetical citations and an MLA format works cited list, it is very unlikely that you will lose points for citing incorrectly.
Works cited examples:
Anderson, Benedict. Imagined Communities. Verso, 1983.
Fox, Claire F. The Fence and the River: Culture and Politics at the U.S.-Mexico Border. U of Minnesota P, 1999.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography. Penguin, 2008.

MLA Style Research
When you are gathering sources in your research phase, be sure to make note of the following bibliographical items that will later make up your works cited MLA.
- Name of original source owner: author, editor, translator, illustrator, or director …
- Titles: article or newspaper title, title of publication, series title …
- Important dates: date of publication, date of composition, issue date, event date, date accessed …
- Publishing information: publisher name
- Identifying information: number of volumes, volume number, issue number, edition, chapter, pages, lines …
If you’re still in your research phase, why not try out Cite This For Me for Chrome? It’s an intuitive and easy-to-use browser extension that enables you to instantly create and edit a citation for any online source while you browse the web.
Racing against the clock? If your deadline has crept up on you and you’re running out of time, the Cite This For Me MLA citation maker will collect and add any source to your bibliography with just a click.
In today’s digital age, source material comes in all shapes and sizes. Thanks to the Cite This For Me citation generator, citing is no longer a chore. The citation generator will help you accurately and easily cite any type of source in a heartbeat, whether it be a musical score, a work of art, or even a comic strip. Cite This For Me helps to elevate a student’s research to the next level by enabling them to cite a wide range of sources.
MLA Citation Formatting Guidelines
Accurately citing sources for your assignment doesn’t just prevent the appearance of or accusations of plagiarism – presenting your source material in a clear and consistent way also ensures that your work is accessible to your reader. So, whether you’re following the MLA format citation guidelines or using the Cite This For Me citation generator, be sure to abide by the presentation rules on font type, margins, page headers, and line spacing.
For research papers, an MLA cover page or title page is not required. Still, some instructors request an MLA title page. In these cases, ask your instructor for an example of a title page so you know the format they want.
Instead of a cover page, headings are used on a paper’s first page to indicate details like the author’s name, instructor’s name, the class, and date written. Read on for more details.
General page and header formatting:
To format your research paper according to the MLA guidelines:
- Set the margins to 1 inch (or 2.5 cm) on all sides
- Choose an easily readable font, recommended Times New Roman
- Set font size to 12 point
- Set double space for your entire paper
- Indent every new paragraph by ½ inch – you can simply use your tab bar for this
- In the header section – on the top right corner of the pages – give your last name followed by the respective page number
For your headings (which replace the need for a cover page), do the following:
- On the first page, ensure that the text is left-aligned and then give your details: starting with your full name in line one, followed by the name of your teacher or professor, the course name and number, and the date in separate lines
- Center align your MLA format heading for the paper’s title – do not italicize, bold or underline, or use a period after the title
- The body of your text should start in the next line, left-aligned with an indentation

You’ll also need to include a running head on each page. It should include your last name and the page number. For example: Johnson 2. Place the running head in the upper right-hand corner of the paper, ½ inches from the top and 1 inch from the page’s right edge.

MLA Style 9th Edition - Changes From Previous Editions
It is worth bearing in mind that the MLA format is constantly evolving to meet the various challenges facing today’s researchers. Using the Cite This For Me citation generator will help you to stay ahead of the game without having to worry about the ways in which the style has changed.
Below is a list outlining the key ways in which MLA has developed since previous editions.
- Titles of independent works (such as books and periodicals) are now italicized rather than underlined .
- You are encouraged to include a source’s URL when citing a source from the internet, and you should no longer include “https://” at the beginning of the URL with the exception of DOIs.
- You are no longer required to include medium information at the end of your citation, i.e., Print, Web, etc.
- Including the city of publication is optional, and only encouraged if the version of the work changes based on location, or if it was published prior to 1900.
How Do I Cite My Sources With The Cite This For Me Citation Machine MLA?
If you’re frustrated by the time-consuming process of citing, the Cite This For Me multi-platform citation management tool will transform the way you conduct your research. Using this fast, accurate and accessible generator will give you more time to work on the content of your paper, so you can spend less time worrying about tedious references.
So if you’re having issues with accurately formatting your citations, sign up to Cite This For Me and let our MLA format generator do the grunt work for you.
To use the generator:
- Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g., website, book, journal & video)
- Enter the URL , DOI , ISBN , title, or other unique source information to locate your source
- Click the ‘Search’ button to begin looking for your source
- Look through the search results and click the ‘Cite’ button next to the correct source. Cite This For Me citation tool will automatically pull your sources data for you!
- Review the citation details and make sure that everything you need is included and accurate
- Click ‘Complete citation’
- Copy your fully-formatted citation into your MLA works cited list</li/>
- Repeat the same process for each source that has contributed to your work
As well as making use of the powerful generator, you can cite with our Chrome add-on or Word add-on.
Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool
Published October 1, 2015. Updated June 16, 2021.
There are many consequences for not providing a correct citation in MLA style. The biggest consequence is that without proper citations, your paper will lose marks for incorrect citations. In addition, your paper can also be considered plagiarism. The responsibility for using proper citations rests with the author of the paper. Failing to properly cite your sources implies that the information in the paper is solely yours when it is not.
While some instructors might be lenient about incorrect citations, others might not. Ultimately, this could land you in serious trouble with your school, organization, or institution. To avoid such issues, always ensure that you provide proper citations. If you are finding it difficult to provide proper citations, Chegg’s citation generator may help.
When citing multiple works by the same author, include the title (or a shortened version of the title) along with the author’s last name and page number in in-text citations.
You can include the author’s name and/or the title in the prose, or you can include all three pieces of information in the parenthetical citation.
(Last Name, Shortened Title page number)
(Sam, Notes to Live By 42)
(Sam, Pointers From a Friend 85)
If you’d like to shorten a title in parenthetical citations, the title can be condensed to the first noun phrase. In the examples above, the titles would be shortened to Notes and Pointers in the parenthetical citations.
When using MLA style to cite a source with two authors, the last names of both authors and the page number being referenced should be included in in-text citations. The names should be listed in the same order in which they appear on the works cited list and be separated by the word “and” in parenthetical citations. If mentioning the authors in the prose, be sure to use both authors’ first and last names on first reference.
Below are a template and example for how to create an in-text citation for a source with two authors in MLA style.
(Last Name 1 and Last Name 2 page number)
(Prusty and Patel 75)
When using MLA style to cite a source with more than two authors, include the last name of the first author listed on your works cited page along with “et. al” and the page number in your in-text citations.
You should only use “et. al” in your works cited list and parenthetical citations. If you include the authors’ names in your prose instead, you can list all the authors’ names or the name of the first author and a phrase like “and her co-authors,” “and others,” etc.
Below are a template and example for how to create an in-text citation for a source with more than two authors in MLA style.
(Author 1 Last Name et al. page number)
(Krishnaswamy et al. 75)
Sources may be cited for various reasons, including to provide credit to others’ ideas, to ensure that readers can find the right sources, and to improve a paper’s credibility. There are some situations when a citation might not be necessary. To avoid ambiguity, here are the situations in which you should include a citation in an MLA style paper:
- When you are directly quoting an expert or other source of information
- When you are paraphrasing a quotation, passage, or idea
- When you are summarizing another person’s ideas
- When you are specifically referencing a fact, phrase, or statistics found in another source
Things that may be considered common knowledge (like dates of historical events or widely known biographical facts) do not need to be cited. However, if you are unsure whether or not a source needs to be cited, it is always better to err on the side of caution and include a citation.
As per MLA standards, a title page is NOT required. In fact, MLA recommends using a header with all relevant information instead, including your name, instructor’s name, course name, date of submission, and title. However, when your instructor requires a title page or when you are authoring your paper as a group with other people, it is recommended to create a title page for your paper.
If you are creating a title page, you should include the below information:
- Name of the paper’s author(s)
- Names of the instructor(s)
- Course name and number
- Title of the paper
Since websites don’t usually have page numbers, include only the author’s last name within parentheses using the standard MLA format. If using a citation in prose, directly referring to the author’s name in the sentence, then there is no need to provide any additional parenthetical citation.
Plastics contribute to the single greatest pollutant source for oceans (Shimla).
Shimla states that plastics are the oceans’ greatest pollutant source. [No additional citation is needed since you include the author’s name in the citation in prose and there is no page number available.]
As per section 1.3 of the MLA 9 handbook, center the title of a paper and use double-spacing. Do NOT underline, italicize, bold, or use all capitals for the title. Instead, follow standard rules of capitalization. Any italicized words within the text (e.g., book titles or literary movements) would ALSO be italicized in the title. Don’t use a period after your paper’s title.
Usually, you nclude the paper title on your first page. Only when the instructor needs a specific title page or when the paper is a group paper necessitating a list of all authors should you provide a separate title page. Apart from these two situations, a title page is NOT required.
Below are some examples when you would need to italicize words in the title because they include names of books and/or literary movements.
Perspective Shift during the Baroque Period
Is Macbeth Relevant in 2022 and Beyond?
While the MLA handbook recommends using “an easily readable typeface” and a font size “between 11 and 13,” it also clarifies to follow a professor’s or instructor’s guidelines if they differ. The handbook advises using double-spacing and the same font and size throughout the paper.
Check with your instructor on their preferences, and in the absence of any such preference, use a decent and readable font, like Times New Roman, with font size 12, which is a good balance between readability and aesthetics. The most important thing is to use the same font and size consistently throughout your paper.
As per Sections 5 and 6 of the MLA 9 handbook, if you are referring multiple times to a single source in the same paragraph, you do not need to repeat the author’s name each time you make a reference. However, you must include the page number(s), or another applicable locator, if you are referring to different pages of the same source in the same paragraph. In the examples below, it is clear in the second sentence that you’re citing the same source, so you don’t need to include the author name again, only the page number you’re referring to.
However, if you quote or paraphrase a different source by a different author between mentions of a source by the same author in the same paragraph, you need to reintroduce the source and original author name to clarify who you’re citing.
Citation in Prose Example
According to Theodore Garner, “It is evident that Caucasian males have a proclivity toward thrift than their African counterparts” (352). This can be seen from the high saving levels over a decade (345).
Parenthetical Citation Example
“It is evident that Caucasian males have a proclivity toward thrift than their African counterparts” (Garner 352). This can be seen from the high saving levels over a decade (345).
If referring to different sources by the same author(s), include the source’s title in your in-text citation, so readers know which source you are referring to. You can style such citations in various ways, as shown below. The style remains the same for works with more than one author.
Example with the author’s name and the title in the citation in prose
Howitzer says it best when he talked about the Moonmakers in his poem (23). Howitzer does contradict himself at a later point in time in Sunchanters (46).
Example with the author’s name in prose and the title in a parenthetical citation
Shakespeare writes pessimistically about existence from Hamlet’s point of view (Hamlet 103) . In another work, Shakespeare writes, “Life is a tale told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing” ( Macbeth 55).
Example with the author’s name and the title in the parenthetical citation
A similar pessimism about existence is present in other works, for instance when Hamlet contemplates suicide (Shakespeare, Hamlet 103). Macbeth similarly claims, “Life is a tale told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing” (Shakespeare, Macbeth 55).
To format an MLA works-cited page, follow these fundamental steps:
Place the works-cited list at the end of the paper and after any endnotes, should they be used.
Set a one-inch margin all around (top, bottom, left, and right). Like the prose portion of the paper, use a left margin, not a justified margin.
Running head
Place a running head on the right side of the page in the one-inch header, one-half inch from the top of the page. The running head format includes Surname and page #. The page number continues from the last page of the prose portion of the paper.
Use an easily readable font in which the italics feature is clearly distinguishable. Use the same font as in the prose portion of the paper. Times New Roman and Helvetica are popular standard fonts. Use a font size between 11 and 13 points.
Title the heading “Works Cited”; do not use bold or italics. Align it to the center of the page. Then double-space to begin the first entry. Double-space throughout the page.
Begin the entries flush with the left margin. Indent the second and subsequent lines of each entry one-half inch from the left margin.
Arranging entries
Arrange the Works-cited-list entries alphabetically according to the name of the author, or title if there is no author. If there is more than one author, cite the author listed first on the title page of the work in the alphabetical entry.
A separate medium identification, such as “Print,” is no longer used; however, the medium usually can be identified by the information provided in the citation.
Gann, Ernest K. A Hostage to Fortune . Alfred A. Knopf, 1978.
Invest Answers [@InvestAnswers]. “Taking another run at $45,000.” Twitter , 2 Mar. 2022, twitter.com/invest_answers/status/1499033186734542850.
To include the URL in website citation in MLA style, copy the URL from the browser, but exclude the http:// or https:// unless it is used in a DOI. If the work has a DOI, it is used instead of the URL.
Woldermont, Slat. “Sharks Impacted by Great Atlantic Garbage.” The Atlantic Cleanup , 4 May 2020, www.theatlanticcleanup.com/updates/sharks-impacted-by-Great-Atlantic-Garbage.
Saunders, Judith P. “Philosophy and Fitness: Hemingway’s ‘A Clean, Well-Lighted Place’ and The Sun Also Rises .” American Classics: Evolutionary Perspectives , Academic Studies Press, 2018, pp. 204–25, https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv4v3226.15.
The 6 th , 7 th , 8 th , and 9 th editions of MLA style are available on the Cite This For Me citation generator . The default MLA edition is the 9 th edition, the most current edition.
For a webpage/website, journal article, or book, you’ll need 1-2 pieces of basic publication information. For example:
- Website : URL, page title, etc.
- Journal article : Article title, DOI number, author(s), etc.
- Book : Book title, author, date published, etc.
Using those pieces of information, you can search for the source in the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator and it will help you to create a citation.
Other source types (newspaper article, video, government document, etc.) will provide a form on which you provide all source information. Using that information, the citation generator will create a properly formatted MLA citation for you.
Omitting or making up sources are unethical actions that can lead to plagiarism. An MLA citation generator can help a writer create citations for their sources, which is an ethical step needed to avoid plagiarism.
An MLA citation generator can make it easier (and sometimes faster) for a writer to create citations versus manually making each citation. We recommend trying the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator and deciding for yourself.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- School access
MLA Citation Generator
- powered by chegg, all of our writing tools, none of the ads, consider your source's credibility. ask these questions:, contributor/author.
- Has the author written several articles on the topic, and do they have the credentials to be an expert in their field?
- Can you contact them? Do they have social media profiles?
- Have other credible individuals referenced this source or author?
- Book: What have reviews said about it?
- What do you know about the publisher/sponsor? Are they well-respected?
- Do they take responsibility for the content? Are they selective about what they publish?
- Take a look at their other content. Do these other articles generally appear credible?
- Does the author or the organization have a bias? Does bias make sense in relation to your argument?
- Is the purpose of the content to inform, entertain, or to spread an agenda? Is there commercial intent?
- Are there ads?
- When was the source published or updated? Is there a date shown?
- Does the publication date make sense in relation to the information presented to your argument?
- Does the source even have a date?
- Was it reproduced? If so, from where?
- If it was reproduced, was it done so with permission? Copyright/disclaimer included?
What You Need to Know About MLA Formatting
Writing a paper soon? If your assignment requires the use of Modern Language Association (MLA) style, then you're in luck! EasyBib® has tools to help you create citations for over 50 source types in this style, as well as a guide to show you how an MLA paper should be formatted. Review the guide to learn how to format a paper's title page, paragraphs, margins, quotations, abbreviations, numbers, tables, and more! There are even tips on editing, as well as on the type of paper you choose to print your paper on—yes, it's that comprehensive!
A Handy Guide for Using APA Format
Ever wonder how to cite a book with no author in APA style? Do you know how graphics should be formatted in a paper? Thanks to our EasyBib® guide on citing and formatting in American Psychological Association (APA) style, you don't have to guess anymore! We break down the guidelines for you into separate, digestible chunks of information that range from the ways to present headers, to use of abbreviations, to how to format titles for citations. There are also several helpful citation examples for you to review. Read up and start learning today!
Chicago Style Simplified
Jump start your knowledge of the Chicago Manual of Style (or Turabian style) with our structured EasyBib® guides. Each one will teach you the structure of a Chicago-style citation, followed by a real-life citation example for you to examine. Begin with our "“"Quick Guide" on citing common source types (books, magazines, newspapers, and websites). Then, discover why we have footnotes and how they work, or choose a "How to Cite" guide based on the source type you're using (e.g. photo, film, tweet, journal, blog, video on YouTube, conference paper, etc.). You're in charge of your own learning path!
Student & Teacher Blog for Better Papers
Keep your citing skills current and your writing skills fresh by reading our weekly EasyBib® Blog. You'll find articles about citing interesting source types (know how to cite a meme?), the latest updates to our tools and services, writing tips and tricks, and more! Aside from content that students (or any writer) could benefit from, we also feature posts written by educators, for educators! They discuss writing and information literacy pedagogy, present resource recommendation lists, and generally share their experience and knowledge.
Discover the EasyBib® Writing Center
Visit our writing center and explore our library of engaging guides, articles, videos, lesson plans, infographics, and other informative resources on citing, writing, and the research process. Best of all, it's free, and you can visit it anytime you need assistance. Need it now? Simply go to our homepage and input keywords based on your topic into the search bar. From there, any relevant guides will be listed with a brief description, allowing you to make an educated selection. Click on a result that fits your needs and begin reading! Easy peasy.
- EasyBib® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style Format
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

Serving the Community College of Vermont & Vermont State University
How To Do Research

MLA 9th Edition Citation Style
Pause or complete the video before closing. Otherwise it will keep playing.
MLA (Modern Language Association) format is most commonly used to cite sources in the humanities. The following examples use MLA 9th edition.
Parenthetical Citation
MLA format uses a parenthetical citation, which is a brief mention in the text of your paper that leads the reader to the complete information about that reference. It usually appears at the end of a sentence. A parenthetical citation involves placing relevant source information in parentheses after a quote or a paraphrase. The author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your works cited page.
Seed says of Dracula “in short, he is a combination of Gothic villain, Regency rake, and monster” (62).
Dracula, “…is a combination of Gothic villain, Regency rake, and monster” (Seed 62).
Seed believes that Dracula is a mix of scoundrel, ogre, and devilish man (62).
Reference List
Parenthetical citations will refer your reader to the full list of sources you used. This list is at the end of your paper.
- Works Cited : A list of sources that are directly quoted, summarized or paraphrased in the writing.
- Bibliography : A list of sources that were used in the background research, development of ideas, and any other research that contributed to the writing.
For both a works cited page and bibliography, references are listed in alphabetical order by author’s last name. Each reference citation is made up of the same elements that always appear in the same order. Leave out any that aren't available for or don't apply to a source.
- One author: Last Name, First Name.
- Two authors: Author 1 Last Name, First Name, and Author 2 First Name Last Name.
- Three or more authors: Author 1 Last Name, First Name, et al.
- Title: The title or description of the work.
- Title of container: The title or description of the larger work this source is part of, such as a journal, an anthology, or a podcast series.
- Other contributors : This can include editors, translators, and others. Include the contributor's role in addition to their name (for example, "Edited by Ana Jones").
- Version: The edition, revision, or other version of the work. Not included for first editions.
- Number: Where the work appears if it is part of a sequence, such as the volume, issue, or episode number.
- Publisher: Included unless the work is self-published, a journal, or a website whose site name and publisher are very similar.
- Publication date: If no formal publication date exists, provide the most exact date available.
- Location : Where the work appears within its container, such as the page range for a chapter in a book. For online works, this is the DOI or URL.
MLA Style | Reference List Citation Format Examples
- Generative AI
Electronic articles
Seed, David. "The Narrative Method of Dracula." Nineteenth-Century Fiction , vol. 41, no. 1, 1985, pp. 61-75. JSTOR , https://doi.org/10.2307/3044836.
Electronic articles with no DOI
Caesar, Terry Paul. “Slavery and Motherhood in Toni Morrison’s ‘Beloved.’” Revista de Letras , vol. 34, 1994, pp. 111–20. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/27666617.
Print articles
Smith, Jane. "Student Search Strategies." College Research Quarterly, vol. 79, no.23, 2010, pp. 42-49.
Hopkins, Lisa. Bram Stoker: A Literary Life. Palgrave Macmillan, 2007.
Books with no author
New Concise World Atlas . Oxford University Press, 2001.
eBooks in library databases
Collins, Wilkie, and Steve Farmer. Moonstone. Broadview Press, 1999. EBSCO eBook Collection , search.ebscohost.com.hrt-proxy.libraries.vsc.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,cookie&db=nlebk&AN=313817&site=eds-live&scope=site&profile=eds-ccv.
(If a DOI is present, use that instead of the URL.)
Kindle eBook
Rowley, Hazel. Franklin and Eleanor: An Extraordinary Marriage. Kindle ed., Farrar, 2010.
eBook from Google Books or an eBook website
Wallace, Mike. Greater Gotham: A History of New York City from 1898 to 1919. Oxford University Press, 2017, Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=AnUzDwAAQBAJ&lpg=PP1&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false.
Page from a Website
Gaiman, Neil. "The Neil Story (With Additional Footnote)." Neil Gaiman , May 17, 2017. journal.neilgaiman.com/2017/05/the-neil-story-with-additional-footnote.html.
Page from a Website with No Author
"Well-Being Concepts". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , May 31, 2016, www.cdc.gov/hrqol/wellbeing.htm. Accessed 11 Nov. 2022.
Note : Date of access is not required but is recommended, especially if access or the content is likely to change.
Video From a Library Database
I Am Not Your Negro: James Baldwin and Race in America . Directed by Raoul Peck, Kino Lorber, 2016. Kanopy , www.kanopy.com/en/castleton/video/542400.
If emphasizing a specific performer or director, you can list them as the author.
Sennott, Rachel, performer. Shiva Baby . Directed by Emma Seligman. Utopia, 2020. Kanopy , www.kanopy.com/en/castleton/video/11394284.
YouTube Video
MrsBoschert. “Hellenistic Art.” YouTube , 23 Feb. 2010, https://youtu.be/hvryEuuTtNY.
Online works of art, photographs, maps, or charts
Bearden, Romare. The Train . 1975. MOMA, www.moma.org/collection/works/65232?locale=en.
- << Previous: Citing Sources
- Next: APA Style >>
Additional Resources
- MLA Official Site The official site of the MLA Style Guide
- MLA Interactive Practice Template This template is a tool for teaching and learning MLA style, not a citation generator. To verify that your entry is correct, consult the MLA Handbook.
- MLA Format (OWL Purdue Univ.)
- MLA Sample Works Cited (OWL, Purdue Univ.)
- How do I cite generative AI in MLA style? - Ask the MLA
Printable Cheat Sheet
- MLA Cheat Sheet
- Tutorial: MLA 9th Edition Citation Style
- Last Updated: Jul 10, 2024 3:10 PM
- URL: https://libraries.vsc.edu/research
Researching Charleston History and News
- Research Local History
- Writing and Citing in MLA Format
Writing Help
- Tutor.com This link opens in a new window Real-Time Tutoring: 24 hours a day, seven days a week for English and Spanish speakers. Connect with a tutor on a variety of subjects, test prep assistance, or parent coaching. An account is not necessary to use this service. Tutorial for Tutor.com
- Tutoring/Academic Assistance This research guide gives you information on how to access Tutor.com.and other tutor support services.
Creating an Annotated Bibliography
- How to create an annotated bibliography
Online Citation Guides
- Research and Citation Resources (Purdue OWL) Purdue's Online Writing Lab provides tips on conducting research, using research, and APA / MLA style guides.
- MLA Format (Purdue OWL) An online guide to citing your sources and formatting your paper in MLA Format.
- MLA Work Cited Quick Guide
- MLA In-Text citations: The Basics (Purdue Owl) Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual.
Videos and Tutorials
- MLA Style Citations & Formatting (Scribbr) Series of YouTube videos from Scribbr that walk you through MLA Style: in-text citations, creating citations, formatting a paper.
Citation Tip!
Did you know that most of the library databases have a citation feature that will create a citation to your article, ebook or film - in APA or MLA format?
- Find an article in a library database
- Click Cite (or Citation)
- Choose the appropriate format (typically APA or MLA)
- Copy and paste the citation
- Always double check that it is correct
Quick Tutorial:
- Database Citation Features Use the database citation tools to get your citations.
Video Tutorials:
- Citing Articles in EBSCOhost (Video)
- Citing Court Cases in Westlaw (Video)
Free Online Citation Tools
- << Previous: Research Local History
- Next: Contact Us >>
- Last Updated: Jul 9, 2024 1:30 PM
- URL: https://libguides.tridenttech.edu/LocalHistory
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual . Both books provide extensive examples, so it's a good idea to consult them if you want to become even more familiar with MLA guidelines or if you have a particular reference question.
Basic in-text citation rules
In MLA Style, referring to the works of others in your text is done using parenthetical citations . This method involves providing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way to do this is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as the examples below will illustrate, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- The source information required in a parenthetical citation depends (1) upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD) and (2) upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page.
In-text citations: Author-page style
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
In-text citations for print sources by a corporate author
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
In-text citations for sources with non-standard labeling systems
If a source uses a labeling or numbering system other than page numbers, such as a script or poetry, precede the citation with said label. When citing a poem, for instance, the parenthetical would begin with the word “line”, and then the line number or range. For example, the examination of William Blake’s poem “The Tyger” would be cited as such:
The speaker makes an ardent call for the exploration of the connection between the violence of nature and the divinity of creation. “In what distant deeps or skies. / Burnt the fire of thine eyes," they ask in reference to the tiger as they attempt to reconcile their intimidation with their relationship to creationism (lines 5-6).
Longer labels, such as chapters (ch.) and scenes (sc.), should be abbreviated.
In-text citations for print sources with no known author
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article) or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
"The Impact of Global Warming in North America." Global Warming: Early Signs . 1999. www.climatehotmap.org/. Accessed 23 Mar. 2009.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Parenthetical citations and Works Cited pages, used in conjunction, allow readers to know which sources you consulted in writing your essay, so that they can either verify your interpretation of the sources or use them in their own scholarly work.
Author-page citation for classic and literary works with multiple editions
Page numbers are always required, but additional citation information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto . In such cases, give the page number of your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:
Author-page citation for works in an anthology, periodical, or collection
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
See also our page on documenting periodicals in the Works Cited .
Citing authors with same last names
Sometimes more information is necessary to identify the source from which a quotation is taken. For instance, if two or more authors have the same last name, provide both authors' first initials (or even the authors' full name if different authors share initials) in your citation. For example:
Citing a work by multiple authors
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
Corresponding Works Cited entry:
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR, doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al.
Franck, Caroline, et al. “Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic.” American Journal of Preventative Medicine , vol. 45, no. 3, Sept. 2013, pp. 327-333.
Citing multiple works by the same author
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author :
Citing two books by the same author :
Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
Citing multivolume works
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
Citing the Bible
In your first parenthetical citation, you want to make clear which Bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
If future references employ the same edition of the Bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
Citing indirect sources
Sometimes you may have to use an indirect source. An indirect source is a source cited within another source. For such indirect quotations, use "qtd. in" to indicate the source you actually consulted. For example:
Note that, in most cases, a responsible researcher will attempt to find the original source, rather than citing an indirect source.
Citing transcripts, plays, or screenplays
Sources that take the form of a dialogue involving two or more participants have special guidelines for their quotation and citation. Each line of dialogue should begin with the speaker's name written in all capitals and indented half an inch. A period follows the name (e.g., JAMES.) . After the period, write the dialogue. Each successive line after the first should receive an additional indentation. When another person begins speaking, start a new line with that person's name indented only half an inch. Repeat this pattern each time the speaker changes. You can include stage directions in the quote if they appear in the original source.
Conclude with a parenthetical that explains where to find the excerpt in the source. Usually, the author and title of the source can be given in a signal phrase before quoting the excerpt, so the concluding parenthetical will often just contain location information like page numbers or act/scene indicators.
Here is an example from O'Neill's The Iceman Cometh.
WILLIE. (Pleadingly) Give me a drink, Rocky. Harry said it was all right. God, I need a drink.
ROCKY. Den grab it. It's right under your nose.
WILLIE. (Avidly) Thanks. (He takes the bottle with both twitching hands and tilts it to his lips and gulps down the whiskey in big swallows.) (1.1)
Citing non-print or sources from the Internet
With more and more scholarly work published on the Internet, you may have to cite sources you found in digital environments. While many sources on the Internet should not be used for scholarly work (reference the OWL's Evaluating Sources of Information resource), some Web sources are perfectly acceptable for research. When creating in-text citations for electronic, film, or Internet sources, remember that your citation must reference the source on your Works Cited page.
Sometimes writers are confused with how to craft parenthetical citations for electronic sources because of the absence of page numbers. However, these sorts of entries often do not require a page number in the parenthetical citation. For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
Miscellaneous non-print sources
Two types of non-print sources you may encounter are films and lectures/presentations:
In the two examples above “Herzog” (a film’s director) and “Yates” (a presentor) lead the reader to the first item in each citation’s respective entry on the Works Cited page:
Herzog, Werner, dir. Fitzcarraldo . Perf. Klaus Kinski. Filmverlag der Autoren, 1982.
Yates, Jane. "Invention in Rhetoric and Composition." Gaps Addressed: Future Work in Rhetoric and Composition, CCCC, Palmer House Hilton, 2002. Address.
Electronic sources
Electronic sources may include web pages and online news or magazine articles:
In the first example (an online magazine article), the writer has chosen not to include the author name in-text; however, two entries from the same author appear in the Works Cited. Thus, the writer includes both the author’s last name and the article title in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader to the appropriate entry on the Works Cited page (see below).
In the second example (a web page), a parenthetical citation is not necessary because the page does not list an author, and the title of the article, “MLA Formatting and Style Guide,” is used as a signal phrase within the sentence. If the title of the article was not named in the sentence, an abbreviated version would appear in a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence. Both corresponding Works Cited entries are as follows:
Taylor, Rumsey. "Fitzcarraldo." Slant , 13 Jun. 2003, www.slantmagazine.com/film/review/fitzcarraldo/. Accessed 29 Sep. 2009.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL , 2 Aug. 2016, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Multiple citations
To cite multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the citations by a semi-colon:
Time-based media sources
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
When a citation is not needed
Common sense and ethics should determine your need for documenting sources. You do not need to give sources for familiar proverbs, well-known quotations, or common knowledge (For example, it is expected that U.S. citizens know that George Washington was the first President.). Remember that citing sources is a rhetorical task, and, as such, can vary based on your audience. If you’re writing for an expert audience of a scholarly journal, for example, you may need to deal with expectations of what constitutes “common knowledge” that differ from common norms.
Other Sources
The MLA Handbook describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the handbook does not describe, making the best way to proceed can be unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of MLA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard MLA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source. For example, Norquest College provides guidelines for citing Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers —an author category that does not appear in the MLA Handbook . In cases like this, however, it's a good idea to ask your instructor or supervisor whether using third-party citation guidelines might present problems.

ENGL 1101 Benning Summer 2024: MLA Citation Help
- Library Catalog
- MLA Citation Help
- Tutoring at Decatur
MLA In-Text Citation Basics
From OWL at Purdue -
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
Further Citation Resources
- GSU MLA Citation LibGuide
- MLA Style Center Citation Guide
- Purdue OWL (Online Writing Lab )
Citing Web Pages
Note: The examples here do not apply to articles retrieved from online library databases, such as JSTOR and MLA International Bibliography.
To cite an entire web site, include:
Author or compiler name (if available). Name of site . Name of institution or organization affiliated with the site
(sponsor or publisher), date of site creation (if available), URL, DOI, or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
For example:
Victorian Women Writers Project. Indiana University, https://webapp1.dlib.indiana.edu/ vwwp/welcome.do;jsessionid
=EF6E5C7368B07CAAAF93A4509B363499. Accessed 23 October 2020.
To cite a page on a web site, include:
Author (if available). "Name of page." Name of site , Date of page creation (if available), URL. Date of access
(if applicable).
For example:
"Mahogany L. Browne." Poets.org , https://poets.org/poet/mahogany-l-browne. Accessed 26 October 2020.
Citing Videos
Video and audio sources need to be documented using the same basic guidelines for citing print sources in MLA style. Include as much descriptive information as necessary to help readers understand the type and nature of the source you are citing. If the author’s name is the same as the uploader, only cite the author once. If the author is different from the uploader, cite the author’s name before the title.
McGonigal, Jane. “Gaming and Productivity.” YouTube , uploaded by Big Think, 3 July 2012, www.youtube.com/watch?v=mkdzy9bWW3E.
“8 Hot Dog Gadgets put to the Test.” YouTube, uploaded by Crazy Russian Hacker, 6 June 2016, www.youtube.com/watch?v=WBlpjSEtELs.
Citation information from the Purdue OWL
Citing Articles
Article citations consist of the basic form:
Author's last name, first name. "Title of the article." Publication information.
Publication information usually consists of the journal title in italics, the volume and issue number, the year of publication, the page numbers, and a period. If the article is retrieved online, the 8th edition of the MLA Style Manual dictates including the location from which the article was retrieved, followed by a period. For example:
Monk, Craig. "The Political F. Scott Fitzgerald: Liberal Illusion and Disillusion in This Side of Paradise and The Beautiful and Damned ." American Studies International , vol. 33, no. 2, 1995, pp. 60-70. EBSCOhost , https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,shib&db=mzh&AN=1997060111&site=ehost-live&scope=site&custid=gsu1.
Citing Books
Book citations consist of the basic form:
Author's last name, first name. Title of the book . Publication information.
The publication information typically includes the publisher name, and the year of publication. If the work is an e-book, the 8th edition of the MLA Style Manual dictates including the database from which the book was retrieved, followed by a period. For example:
Zauditu-Selassie, K. African Spiritual Traditions in the Novels of Toni Morrison . UP of Florida, 2009.
EBSCOHost, https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,shib&db=e000xna&AN=380225&site=ehost-live&scope=site&custid=gsu1.
Cite book chapters and essays in books as follows:
Careri, Elisabetta."Home, Streets, Nature: Esperanza's Itineraries in Sandra
Cisneros' The House on Mango Street." Landscapes of Writing in Chicano Literature , edited by Imelda Martín-Junquera, Palgrave Macmillan, 2013, pp. 13-22.
- << Previous: Databases
- Next: Tutoring at Decatur >>
- Last Updated: Jul 8, 2024 12:40 PM
- URL: https://research.library.gsu.edu/ENGL1101BenningSummer2024
Mastering MLA Annotated Bibliography Format
Let’s master the MLA annotated bibliography format. Learn how to craft an annotated bibliography, a crucial skill in many academic studies.
Knowing MLA annotated bibliography format is essential for researchers, students, and scholars alike. It serves not only to catalog sources used in a project but also to provide concise summaries and evaluations that offer insights into the relevance and quality of each source. Adhering to specific MLA style guidelines ensures consistency and clarity in formatting. This guide will navigate through the essential elements of crafting an MLA annotated bibliography format, helping you effectively organize and present your research sources.
Understanding the Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography is a structured list of sources used in research projects or academic papers, each accompanied by a brief descriptive and evaluative paragraph, known as the annotation. Unlike a standard bibliography that merely lists sources, an annotated bibliography provides a summary and critical assessment of each source’s content, relevance, and quality.
Definition and Purpose
An annotated bibliography is a detailed list of sources used in research or academia, each accompanied by a brief summary and evaluation of its content and relevance. Unlike a standard bibliography that simply lists references, an annotated bibliography provides additional information to the reader about each source’s significance and quality.
Primary Purposes
The primary purpose of an annotated bibliography is to provide readers with a comprehensive overview of the literature available on a particular topic. It serves several important functions:
- Informational : Annotations summarize the main arguments, methodologies, and findings of each source, allowing readers to quickly grasp the key points without reading the entire source.
- Evaluation : Annotations critically evaluate the credibility, reliability, and objectivity of each source. This helps researchers assess whether the source is suitable for their research needs.
- Contextualization : Annotations place each source within the broader scholarly conversation on the topic. They explain how the source contributes to understanding different perspectives or aspects of the research topic.
- Research Depth: By compiling and annotating a variety of sources, an annotated bibliography demonstrates the depth and breadth of research conducted on a topic. It highlights the diversity of sources consulted and the methodological approaches employed.
Components of an Annotation
- Summary of the Source: A concise overview of the source’s main arguments, methodology, and findings. It typically ranges from a few sentences to a short paragraph.
- Evaluation of the Source: A critical assessment of the source’s credibility, reliability of information, and objectivity. This section may also discuss the author’s authority and the publication’s reputation.
- Reflection on the Source’s Use: A reflection on how the source contributes to your research project. This includes discussing its relevance to your thesis or research question, as well as any biases or limitations.
MLA Formatting Overview
An annotated bibliography in MLA format not only lists the sources used for research but also includes annotations that summarize, evaluate, and reflect on each source. Here are the key formatting guidelines:
General Guidelines
- Font and Spacing Specifications: Use a legible font such as Times New Roman, 12-point size, and double-space the entire document, including annotations.
- Margins and Indentation Rules: Maintain one-inch margins on all sides of the page. Indent the second and subsequent lines of each citation by 0.5 inches (or one tab space).
- Order of Entries: Arrange citations alphabetically by the author’s last name. If there is no author, use the title of the work for alphabetization.
Citation Structure
- Author Details: Include the author’s full name (last name, first name) or the name of the organization responsible for the work.
- Title Conventions: Italicize book titles and titles of larger works (e.g., journals, websites). Use quotation marks for titles of shorter works (e.g., articles, chapters).
- Publication Information: Include the publisher’s name, publication date (year), and relevant page numbers (for articles or chapters).
Also read: A Writer’s Guide to MLA Format: How to Get It Right
Writing MLA Annotated Bibliography Format
Writing annotations in MLA style involves summarizing the content of each source, evaluating its credibility and relevance, and reflecting on its usefulness to your research. Here’s a detailed guide on how to write annotations in MLA style:
Summarizing the Source
- Key Points to Include: Summarize the main arguments, methodology, and conclusions of the source. Focus on the most relevant aspects to your research topic.
- Length of the Summary: Aim for 1-2 paragraphs summarizing the source’s content concisely. The length may vary depending on the complexity of the source.
Evaluating the Source
- Criteria for Assessing Credibility: Evaluate the author’s credentials, the accuracy of information presented, and the objectivity of the source.
- Discussing Relevance and Bias: Analyze how the source contributes to your understanding of the topic. Discuss any potential biases or limitations that may affect its reliability.
Reflecting on the Source
- Personal Engagement with the Material: Reflect on how the source has influenced your thinking or approach to the topic. Discuss any insights gained or challenges posed by the source.
- Usefulness in Your Research Context: Explain how the source contributes to your research goals, supports your thesis or arguments, or provides contrasting viewpoints.
Final Tips for Writing Annotations in MLA Style
- Stick to the word limit recommended for annotations (typically 100-200 words) and prioritize the most pertinent information about the source.
- Focus on summarizing the main arguments, methodologies, and findings without delving into unnecessary details.
Maintain Objectivity
- Provide a balanced evaluation of the source’s strengths and weaknesses. Avoid personal biases or opinions that are not supported by evidence.
- Critically assess the author’s credibility, the reliability of the information presented, and any potential biases in the source.
Link to Your Research
- Clearly articulate how each source contributes to your broader research objectives or thesis statement.
- Explain how the source supports your arguments, provides relevant data or theoretical frameworks, or offers contrasting viewpoints that enrich your analysis.
- Discuss any limitations or gaps in the source and how you plan to address them in your research.
Consider the Audience
- Tailor your annotations to the intended audience, ensuring that your summaries and evaluations are clear and accessible to readers who may not be familiar with the topic.
- Use language that is scholarly yet understandable, avoiding jargon or technical terms that may obscure the meaning for non-specialists.
Revise and Proofread
- After writing your annotations, revise them for clarity, coherence, and accuracy.
- Proofread carefully to correct any grammatical or typographical errors, as well as to ensure consistency in formatting according to MLA style guidelines.
Seek Feedback
- If possible, seek feedback from peers, instructors, or colleagues to get insights into the clarity and effectiveness of your annotations.
- Incorporate constructive feedback to strengthen your annotations and improve their overall quality.
Examples of MLA Annotated Bibliography Format
The examples below illustrate how to format and annotate sources in MLA style for an annotated bibliography. Each annotation provides a summary of the source’s content, an evaluation of its reliability and relevance, and a reflection on its contribution to the broader research topic. Adjustments can be made based on specific requirements or additional criteria for evaluation as needed.
Book Citation with Annotation
- Citation Example:
Smith, John. The Art of Writing . Oxford University Press, 2019.
- Annotation Example:
In this comprehensive guide to writing, Smith explores various techniques and strategies for improving writing skills. He emphasizes the importance of clarity and structure, making it an invaluable resource for aspiring writers. Smith’s practical examples and insightful advice help readers understand complex concepts in a straightforward manner. This book is particularly useful for students and professionals looking to enhance their writing proficiency across different genres and disciplines.
Journal Article Citation with Annotation
Brown, Sarah. “The Impact of Climate Change on Global Agriculture.” Environmental Studies Review , vol. 25, no. 2, 2020, pp. 45-60.
- Annotation Example:
Brown’s article examines the effects of climate change on global agriculture, highlighting challenges and potential solutions. Through a review of current literature and empirical data, Brown provides a nuanced perspective on this critical issue. The article discusses the impact of changing weather patterns on crop yields and explores adaptive strategies employed by agricultural communities worldwide. Brown’s research contributes significantly to the understanding of environmental sustainability and underscores the urgency of addressing climate-related threats to global food security.
Browse Through 75.000+ Scientifically Accurate Illustrations In 80+ Popular Fields
Mind the Graph is a platform that provides scientists with access to a vast library of over 75,000 scientifically accurate illustrations across 80+ fields. Researchers can create professional-quality visuals for their papers, presentations, and educational materials using customizable templates and designs. These visuals enhance research impact by simplifying complex information and improving audience comprehension. The platform also supports collaboration among researchers, making it easier to communicate complex scientific concepts effectively. Sign up for free and start creating amazing science figures in minutes.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags

Shopping Cart
No products in the cart.

Citation Management for Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews present unique citation management challenges. Andy Hickner and Kathryn Vanderboll, veterans of many systematic reviews, will show you how to select the right software for your review and successfully address the challenges.
Whether you are new to citation management software or have used or taught it to manage paper citations, systematic review citation management software will present you with unique challenges. Andy Hickner and Kathryn Vanderboll, multi-platform citation software users and collaborators on many reviews, will show you how to address the challenges of using the software on systematic reviews.
You’ll learn the pros and cons of a variety of free and subscription software and how to address common challenges, including:
- Managing large numbers of citations with many duplicates
- Using software with diverse teams
- Exporting database results
- Exporting to and from systematic review software
- Screening process considerations
- Locating full texts
- Documenting your process in order to satisfy PRISMA and other reporting requirements.
The workshop will include lecture, discussion questions, and self-assessment questions, and time for you to ask questions.
This course is required for Level I of the Systematic Review Services Specialization .
Audience
Medical librarians and other health information professionals who are involved in systematic reviews and other evidence syntheses. No experience with citation managers needed.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, participants will be able to:
- Critique commonly used citation management software on their usefulness for systematic reviews
- Explain citation management software organization and documentation strategies for systematic reviews
- Explain solutions to common problems when using citation management softwares for systematic reviews
MLA CE : 1.5

Andy Hickner is Education and Outreach Librarian at the Samuel J. Wood Library at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, New York. Andy has 13 years of experience teaching and using a range of citation management software, with particular expertise in EndNote, Zotero, and Sciwheel. He has collaborated on over 20 evidence synthesis projects, published in journals, including the Lancet , the Journal of the American Medical Association , and the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association .
Kathryn Vanderboll is an Informationist at the Taubman Health Sciences Library at the University of Michigan. She has 10 years of experience using and teaching citation management software for use in many academic disciplines, with a particular focus on Zotero and EndNote. She is a team member on a number of ongoing evidence synthesis projects.
Course Content

Course Includes
- Course Certificate
Email Address
Remember Me
Registration confirmation will be emailed to you.
Top of page
Article United States: Appeals Court Rules that Courts Cannot Require State Department to Issue Visas Past Deadline
Back to Search Results
On June 25, 2024, the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit held that district courts lacked the authority to order the U.S. Department of State to continue processing applications and issuing visas delayed by the COVID-19 pandemic after the statutory deadline had passed. ( Goodluck v. Biden , No. 21-5263 (DC Cir. 2024).)
Background to the Case
The diversity visa program , created by the Immigration and Nationality Act, 8 U.S.C. § 1153(c) , allows the State Department to issue up to 55,000 immigration visas for immigrants from countries with low rates of immigration to the U.S.. The State Department operates a lottery for individuals to apply for visas; the selected individuals must still submit an application, appear for an interview before a consular officer, satisfy all admissibility requirements, and receive the visa before the end of fiscal year. Once an individual receives the diversity visa, they are permitted to travel to the U.S. and have an immigration officer determine their eligibility to enter the country. ( Goodluck at 3-4.)
Between April 2020 and February 2021, Presidential Proclamation 10014 suspended immigration during the pandemic and no diversity visas were issued during that period. The pandemic caused a backlog in visa services and, in November 2020, the State Department issued guidance to its “consular posts to follow a four-tiered prioritization scheme for addressing the backlog, with diversity visas in the lowest-priority tier.” Four cases were filed in district courts by plaintiffs selected for the fiscal year 2020 and 2021 lotteries who argued that the State Department’s policies unlawfully prevented them from obtaining visas before the end-of-fiscal-year deadlines. The district courts ordered the State Department to process and issue visas beyond the end of the fiscal years. ( Goodluck at 5.)
The Courts’ Authority to Issue an Injunction
On appeal, the circuit court consolidated the four district court cases to consider whether the lower courts had the authority to order the State Department to process and issue visas past the deadlines. The circuit court held that the district courts lacked this authority, as the governing statutes controlled the deadline for the program and Congress gave the State Department administrative authority over the diversity visa program. ( Goodluck at 9-16.)
The circuit court emphasized that the district courts did not have statutory authority and there was no history or context to support a court ordering the State Department to consider visa applications beyond the statutory deadline. According to statute, lottery selectees only become “eligible” to receive visas through the end of the fiscal year; they are not entitled to a visa by the deadline. ( Goodluck at 9, citing 8 U.S.C. §§ 1153(e)(2) , 1154(a)(1)( I )(ii)(II) .) They also noted that immigration policy is typically governed by the executive and legislative branches; therefore, unless statutory authority is given to the judicial branch, judicial interference is generally inappropriate. ( Goodluck at 10-11.)
The circuit court also rejected the plaintiffs’ argument that the district courts could extend the deadline because they issued their orders prior to the statutory deadlines. According to the circuit court, it did not matter that the plaintiffs had submitted their documents, filed a lawsuit, and obtained preliminary relief before the end of the fiscal year, because “the deadline is keyed to the receipt of a visa.” ( Goodluck at 14.) The circuit court concluded that the injunction entered before the deadline “merely required the government to ‘undertake good-faith efforts’ to process diversity-visa applications ‘expeditiously’ and until the end of the fiscal year.” ( Goodluck at 16-17.) The plaintiffs failed to present evidence that the State Department did not meet its obligation to act in good faith without undue delay, so the district courts could not rely on that as justification for extending the deadline. ( Goodluck at 17.)
Because the circuit court held that the district courts lacked authority to extend the statutory deadline beyond the end of the fiscal year, it remanded the cases instructing the district courts to enter judgment for the government and reversed the orders extending the diversity-visa deadlines. ( Goodluck at 17.)
Sarah Friedman, Law Library of Congress July 9, 2024
Read more Global Legal Monitor articles .
About this Item
- United States: Appeals Court Rules that Courts Cannot Require State Department to Issue Visas Past Deadline
Online Format
- Global Legal Monitor (7,691)
- Law Library of Congress (422,825)
- Executive Agencies
- Immigration
- Judicial Powers
- Visas and Passports
Jurisdiction
- United States
Article Author
- Friedman, Sarah
Featured in
- About the Law Library | Law Library of Congress | Research Centers
Rights & Access
Publications of the Library of Congress are works of the United States Government as defined in the United States Code 17 U.S.C. §105 and therefore are not subject to copyright and are free to use and reuse. The Library of Congress has no objection to the international use and reuse of Library U.S. Government works on loc.gov . These works are also available for worldwide use and reuse under CC0 1.0 Universal.
More about Copyright and other Restrictions.
For guidance about compiling full citations consult Citing Primary Sources.
Credit Line: Law Library of Congress
Cite This Item
Citations are generated automatically from bibliographic data as a convenience, and may not be complete or accurate.
Chicago citation style:
Friedman, Sarah. United States: Appeals Court Rules that Courts Cannot Require State Department to Issue Visas Past Deadline . 2024. Web Page. https://www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2024-07-08/united-states-appeals-court-rules-that-courts-cannot-require-state-department-to-issue-visas-past-deadline/.
APA citation style:
Friedman, S. (2024) United States: Appeals Court Rules that Courts Cannot Require State Department to Issue Visas Past Deadline . [Web Page] Retrieved from the Library of Congress, https://www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2024-07-08/united-states-appeals-court-rules-that-courts-cannot-require-state-department-to-issue-visas-past-deadline/.
MLA citation style:
Friedman, Sarah. United States: Appeals Court Rules that Courts Cannot Require State Department to Issue Visas Past Deadline . 2024. Web Page. Retrieved from the Library of Congress, <www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2024-07-08/united-states-appeals-court-rules-that-courts-cannot-require-state-department-to-issue-visas-past-deadline/>.
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- How to cite a book in MLA
How to Cite a Book in MLA | Format & Examples
Published on June 28, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024.
An MLA book citation always includes the author(s) , title (italicized), publisher, and publication year in the Works Cited entry. If relevant, also include the names of any editors or translators, the edition, and the volume. “University Press” should be abbreviated to “UP” in a Works Cited entry.
The in-text citation gives the author’s last name and a page number in parentheses.
To automattically create MLA citations, try our free MLA Citation Generator .
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing a book chapter, editions of books, multi-volume books, translated books, e-books and online books, where to find information for a book citation, frequently asked questions about mla style.
Use this format if the book’s chapters are written by different authors, or if the book is a collection of self-contained works (such as stories , essays, poems or plays ). A similar format can be used to cite images from books or dictionary entries . If you cite several chapters from the same book, include a separate Works Cited entry for each one.
Start the Works Cited entry with the author and title of the chapter, followed by the book’s title, editor, publisher, and date , and end with the page range on which the chapter appears.
If there are two editors, give the full names of both. If there are more than two editors, follow the same rules as for citing multiple authors : name only the first editor followed by et al.
If you are citing a work from a book with no named editor (e.g. a collection of a single author’s poems or plays), use the same format, but leave out the editor element.
- Multiple editors
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. “Title of Chapter or Work.” , edited by Editor name, Publisher, Year, pp. Page range. |
| Smith, Ali. “The Universal Story.” y, edited by Philip Hensher, Penguin Books, 2018, pp. 99–107. | |
| (Smith 101) |
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. “Title of Chapter or Work.” , edited by Editor names, Publisher, Year, pp. Page range. |
| Le Guin, Ursula K. “Deep in Admiration.” , edited by Anna Tsing et al., U of Minnesota P, 2017, pp. 15–21. | |
| (Le Guin 17) |
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. “Title of Chapter or Work.” , Publisher, Year, pp. Page range. |
| Beckett, Samuel. “Catastrophe.” , Grove Press, 2010, pp. 293–300. | |
| (Beckett 299) |
Citing a whole collection or anthology
If you refer to a whole collection without citing a specific work within it, follow the standard book citation format. Include the editor(s) where the author would usually go, with a label to identify their role.
| MLA format | Editor last name, First name, editor. Publisher, Year. |
| Tsing, Anna, et al., editors. . U of Minnesota P, 2017. | |
| (Tsing et al. 3) |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If the book cover or title page specifies an edition, add the edition number or name, followed by the abbreviation “ed.”, after the title. Note that versions of the Bible are treated slightly differently.
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Edition ed., Publisher, Year. |
| Butler, Judith. . 2nd ed., Routledge, 1999. | |
| (Butler 23) |
Including the original publication date
Classic books are often published and republished many times. If the original publication date is relevant or necessary to put the source in context, you can also include this directly after the title.
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Original publication year. Edition ed., Publisher, Edition publication year. |
| Brontë, Emily. . 1847. Revised ed., Penguin Classics, 2002. | |
| (Brontë 31) |
If you cite only one volume of a multi-volume work, include the volume number in the Works Cited entry.
If you cite more than one volume of the book, cite them as a single work and specify the total number of volumes in your Works Cited entry. In this case, the in-text citations must include the volume number as well as the page number.
- Citing a single volume
- Citing multiple volumes
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Edition ed., vol. Volume number, Publisher, Year. |
| Rampersad, Arnold. . 2nd ed., vol. 2, Oxford UP, 2002. | |
| (Rampersad 64) |
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Edition ed., Publisher, Year. Number of volumes vols. |
| Rampersad, Arnold. . 2nd ed., Oxford UP, 2002. 2 vols. | |
| (Rampersad 1: 25) |
If the book is translated, include the translator’s name after the title.
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Translated by Translator name, Publisher, Year. |
| Camus, Albert. . Translated by Robin Buss, Penguin Books, 2013. | |
| (Camus 62) |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The citation format for an e-book depends on how you accessed it.
Books accessed online
If you accessed the book via a website or database, use the standard MLA book citation format, followed by the name of the website or database and a link to the book. Look for a DOI, stable URL or permalink. If the book was accessed as a PDF, you may note this in your reference .
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Publisher, Year. , DOI/URL. |
| Brown, Wendy. . Princeton UP, 1995. , hdl.handle.net/2027/heb.32981. | |
| (Brown 12) |
Downloaded e-books
If you downloaded the book onto an e-reader device or app, you only have to add “E-book ed.” after the title.
If the e-book does not have page numbers, use an alternate locator, such as a chapter or section heading, in your in-text citation. Do not use locators that are specific to the device (e.g. Kindle locations).
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Format, Publisher, Year. |
| Anderson, Benedict. . E-book ed., Verso, 2006. | |
| (Anderson, ch. 5) |
The title, author, publisher, and publication year are usually found on the book’s title page. You might have to check the copyright page for the publisher and publication year.
Note that the copyright date is not always the same as the publication date. If several different years appear on the copyright page, use the most recent one.
If the book has any editors or translators named on the cover page, include them in the citation after the book’s title.

In MLA style , book titles appear in italics, with all major words capitalized. If there is a subtitle, separate it from the main title with a colon and a space (even if no colon appears in the source). For example:
The format is the same in the Works Cited list and in the text itself. However, when you mention the book title in the text, you don’t have to include the subtitle.
The title of a part of a book—such as a chapter, or a short story or poem in a collection—is not italicized, but instead placed in quotation marks.
If a source has two authors, name both authors in your MLA in-text citation and Works Cited entry. If there are three or more authors, name only the first author, followed by et al.
| Number of authors | In-text citation | Works Cited entry |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | (Moore 37) | Moore, Jason W. |
| 2 authors | (Moore and Patel 37) | Moore, Jason W., and Raj Patel. |
| 3+ authors | (Moore et al. 37) | Moore, Jason W., et al. |
In MLA Style , you should cite a specific chapter or work within a book in two situations:
- When each of the book’s chapters is written by a different author.
- When the book is a collection of self-contained works (such as poems , plays , or short stories ), even if they are all written by the same author.
If you cite multiple chapters or works from the same book, include a separate Works Cited entry for each chapter.
Some source types, such as books and journal articles , may contain footnotes (or endnotes) with additional information. The following rules apply when citing information from a note in an MLA in-text citation :
- To cite information from a single numbered note, write “n” after the page number, and then write the note number, e.g. (Smith 105n2)
- To cite information from multiple numbered notes, write “nn” and include a range, e.g. (Smith 77nn1–2)
- To cite information from an unnumbered note, write “un” after the page number, with a space in between, e.g. (Jones 250 un)
You must include an MLA in-text citation every time you quote or paraphrase from a source (e.g. a book , movie , website , or article ).
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). How to Cite a Book in MLA | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/book-citation/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, a complete guide to mla in-text citations, how to format your mla works cited page, how to cite a play in mla, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An MLA bibliography is similar to the Works Cited list that you include at the end of your paper. The only difference between a Works Cited list and a bibliography is that for the former, you need to include the entries for only the sources you cited in the text, whereas for the latter you can also include the sources you consulted to write ...
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
This guide follows the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook, published by the Modern Language Association in 2021. To cite sources in MLA style, you need. In-text citations that give the author's last name and a page number. A list of Works Cited that gives full details of every source. Make sure your paper also adheres to MLA ...
MLA Citation Examples. MLA citing is easier when you have visuals and examples to take a peek at. That's why we've put together a list of the most common source types that students and scholars reference. If you're trying to reference a book, newspaper article, website, or tweet, you'll find the structures you need to get on the right ...
MLA Works Cited: Include 4 full citations for: de Castella's article, Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG. Don't forget to create full, or regular citations, and place them at the end of your project. If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net can help.
An MLA "Works Cited" or MLA "Work Cited" page contains all of the citations for a project. This page sits on its own and is found at the end of a project. If there is only one citation on the page, title the page: Work Cited. While it might seem silly to have a full page dedicated to one citation, a "Work Cited" page in MLA is still necessary.
Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text citations using Scribbr's APA Citation Generator, MLA Citation Generator, Harvard Referencing Generator, and Chicago Citation Generator. Plagiarism Checker: Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to ...
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers. If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically ...
This is the total package when it comes to MLA format. Our easy to read guides come complete with examples and step-by-step instructions to format your full and in-text citations, paper, and works cited in MLA style. There's even information on annotated bibliographies.
Citations by Format. Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements—facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you're citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on ...
MLA Citations: Works Cited Page. In-text citations are important, but so is your MLA works cited page. This is the MLA version of a bibliography. However, a works cited and a bibliography have a few key differences, like their titles, how they are set up, and what sources to include. Make sure to set up a works cited for your MLA paper.
The Cite This For Me citation machine accesses information from across the web, assembling all of the relevant material into a fully-formatted works cited MLA format page that clearly maps out all of the sources that have contributed to your paper. Using a generator simplifies the frustrating citing process, allowing you to focus on what's ...
MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) The MLA Handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any ...
Cite a book automatically in MLA. The 8 th edition of the MLA handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any ...
MLA format is a widely used citation style for academic papers. Learn how to format your title page, header, and Works Cited page with our free template and examples. Watch our 3-minute video to see how easy it is to apply MLA rules to your document.
EasyBib® has tools to help you create citations for over 50 source types in this style, as well as a guide to show you how an MLA paper should be formatted. Review the guide to learn how to format a paper's title page, paragraphs, margins, quotations, abbreviations, numbers, tables, and more! There are even tips on editing, as well as on the ...
Style selection. Format your bibliography using APA, MLA, Chicago / Turabian, Harvard, or any of the 10,000+ other CSL styles.. Copy Citation / Note. As you're writing, you can quickly generate parenthetical citations or footnotes /endnotes to paste into your document without typing names or dates by hand.
Parenthetical Citation. MLA format uses a parenthetical citation, which is a brief mention in the text of your paper that leads the reader to the complete information about that reference. It usually appears at the end of a sentence. A parenthetical citation involves placing relevant source information in parentheses after a quote or a paraphrase.
Click Cite (or Citation) Choose the appropriate format (typically APA or MLA) Copy and paste the citation ; Always double check that it is correct; Quick Tutorial: Database Citation Features. Use the database citation tools to get your citations. Video Tutorials: Citing Articles in EBSCOhost (Video)
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
Video and audio sources need to be documented using the same basic guidelines for citing print sources in MLA style. Include as much descriptive information as necessary to help readers understand the type and nature of the source you are citing. If the author's name is the same as the uploader, only cite the author once.
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead. If the publication date is unknown, or if the content is ...
Knowing MLA annotated bibliography format is essential for researchers, students, and scholars alike. It serves not only to catalog sources used in a project but also to provide concise summaries and evaluations that offer insights into the relevance and quality of each source. Adhering to specific MLA style guidelines ensures consistency and ...
Whether you are new to citation management software or have used or taught it to manage paper citations, systematic review citation management software will present you with unique challenges. Andy Hickner and Kathryn Vanderboll, multi-platform citation software users and collaborators on many reviews, will show you how to address the ...
An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range. If you want to cite multiple non ...
On June 25, 2024, the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit held that district courts lacked the authority to order the U.S. Department of State to continue processing applications and issuing visas delayed by the COVID-19 pandemic after the statutory deadline had passed. (Goodluck v. Biden, No. 21-5263 (DC Cir. … Continue reading "United States ...
The following rules apply when citing information from a note in an MLA in-text citation: To cite information from a single numbered note, write "n" after the page number, and then write the note number, e.g. (Smith 105n2) To cite information from multiple numbered notes, write "nn" and include a range, e.g. (Smith 77nn1-2)