
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Simple Random Sampling
Published by Sudirman Cahyadi Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Simple Random Sampling"— Presentation transcript:

Section 7.3 Confidence intervals for a population proportion

Unit 1 Section 1.3 – Day : Sampling Techniques Sample – a part of a population used in statistical studies. An unbiased sample is one where.

POPULATION- the entire group of individuals that we want information about SAMPLE- the part of the population that we actually examine in order to gather.

Section 5.1 What is Probability? 5.1 / 1. Probability Probability is a numerical measurement of likelihood of an event. The probability of any event is.

Chapter 2: Sampling and Surveys Section 2.1: Samples, Good and Bad.

1-3 Data Collection and Sampling Techniques Surveys are the most common method of collecting data. Three methods of surveying are: 1) Telephone surveys.

If you have your Parent Letter signed, please return the bottom portion. Scissors are on my desk. Grab the handout at the front. Complete the front. Wait.

Chapter 5 Section 1 – Part 2. Samples: Good & Bad What makes a sample bad? What type of “bad” sampling did we discuss previously?

Confidence Interval Estimation for a Population Proportion Lecture 31 Section 9.4 Wed, Nov 17, 2004.

A simple random sample of n measurements from a population is one selected in such a manner that 1. every sample of size n from the population has equal.

Investigation 1- IB2 Random sampling and Quadrats (G.1.3)

Testing Hypotheses about a Population Proportion Lecture 30 Sections 9.3 Wed, Oct 24, 2007.

Continuous Random Variables Lecture 25 Section Mon, Feb 28, 2005.

Continuous Random Variables Lecture 24 Section Tue, Mar 7, 2006.

Confidence Interval Estimation for a Population Proportion Lecture 33 Section 9.4 Mon, Nov 6, 2006.

Continuous Random Variables Lecture 22 Section Mon, Feb 25, 2008.

Section 5.1. Three ways to answer this question: 1. Actually carry out an experiment 2. Develop a probability model 3. Start with a model, and then.

Systematic Sampling Lecture 9 – Part 1 Sections 2.8 Wed, Jan 30, 2008.

Copyright © 2013, 2010 and 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Data Collection 1.

Copyright © 2016 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. B ASIC C ONCEPTS IN P ROBABILITY Section 5.1.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive
Simple Random Sampling: Definition & Examples
By Jim Frost Leave a Comment
What is Simple Random Sampling?
Simple random sampling (SRS) is a probability sampling method where researchers randomly choose participants from a population . All population members have an equal probability of being selected. This method tends to produce representative, unbiased samples.
For example, if you randomly select 1000 people from a town with a population of 100,000 residents, each person has a 1000/100000 = 0.01 probability. That’s a simple calculation requiring no additional knowledge about the population’s composition. Hence, simple random sampling.
Simple random sampling is a probability sampling method that helps ensure the sample mirrors the population. The process proportionately samples from larger subpopulations more frequently than smaller subpopulations.
Suppose the town contains subpopulation A with 40,000 people and subpopulation B with 10,000. Using SRS with a probability of 0.01, the process will tend to enlist 400 from subpopulation A and 100 from B. Hence, the process tends to produce a proportionate representation in the sample that reflects the entire population. You don’t need to know the details about the subpopulations for this process to work!
Learn more about Types of Sampling Methods in Research .
How to Use Simple Random Sampling
Performing simple random sampling requires that you have a sampling frame that contains a complete list of all population members and the ability to contact and involve them in your study. Learn more about Sampling Frames: Definition, Examples & Uses .

- Define the population.
- Create a list of all population members.
- Assign random numbers to each member.
- Use a random number generator to select participants until you reach your target sample size.
Alternatively, if the population is not too large, you can use a lottery system for drawing the sample. Place all the names in a hat and randomly draw your sample. For large populations, researchers typically use computers to select participants randomly from a database.
Example of Simple Random Sampling
Imagine we are studying the town with 100,000 residents. We want to perform simple random sampling to obtain a sample size of 1000. We first need to define the population. We’ll define it as residents of the town who pay township taxes and are at least 18 years old.
Next, we need to create a complete list of residents who meet those criteria. Perhaps we’ll work with the township tax office to make the list. We’ll add all eligible residents to our list.
Finally, we need to select participants randomly from the list. We can use a computer program to do that. Alternatively, we can print out names on slips of paper and draw them from a basket. We keep drawing from the list until we have 1000 names.
Benefits of Simple Random Sampling
Many statisticians consider simple random sampling to be the gold standard for producing representative samples. Because it is entirely random, it minimizes the potential for researchers biasing the results, even if unintentionally. As you’ll read, there are alternative sampling methods that provide concessions to real-world sampling difficulties. Unfortunately, the alternatives can unwittingly produce a biased sample. Learn more about representative samples .
Procedurally, SRS is the simplest method for obtaining an unbiased sample. While the researchers need a list of the entire population, they don’t need other information about that population, its subpopulations, and its features.
Conversely, other more complex forms of sampling require researchers to understand the population’s characteristics. Then, using that knowledge and a lot of preplanning, they divide the population into strata or clusters and perform other procedures before sampling. With SRS, you just randomly draw from the list until you have enough subjects.
Because simple random sampling tends to produce unbiased samples that mirror the population, it’s excellent for analysts who need to use a sample to infer the properties of a population (i.e., inferential statistics ). In a study, having a representative sample improves both its internal and external validity . After simple random sampling, you can use statistical hypothesis tests to use the sample to draw conclusions about the population.
For more information about inferential statistics, read my articles about Populations, Parameters, and Samples in Inferential Statistics and Descriptive versus Inferential Statistics .
Drawbacks of Simple Random Sampling
Even though there are great benefits to using this method, simple random sampling has some significant drawbacks.
Population List
First and foremost, this method can be quite cumbersome and require ample resources for large populations. You’ll need a list of all population members, which can be a tremendous hurdle by itself. If that list doesn’t exist, you might need to expend considerable resources to create it. An incomplete list can bias your results. Only a complete list allows the researchers to have an equal probability of selecting all population members.
Attempting to perform SRS with an incomplete population list causes undercoverage bias and a nonrepresentative sample.
Learn more about Undercoverage Bias: Definition & Examples .
Then you’ll need to contact and interact with everyone you randomly select. Depending on the nature of your study, that process can be pretty expensive and time-consuming if your participants span a wide geographic range, particularly when you need a large sample size.
Insufficient Representation of Subpopulations
Despite being entirely random, simple random sampling can miss important subpopulations and features in the population. For example, in our town with 100,000 residents, imagine that we’re particularly interested in surveying those who are at least 90 years old. You plan to obtain a sample size of 1000, which is 1 out of 100 residents. However, there are only 50 people in town who are older than 90. Your sample might not include anyone in this vital group! If it does, it’ll be a tiny number that doesn’t provide a clear picture of this subgroup.
Simple random sampling can fail to provide precise data about particular subgroups and differences between subgroups. Other sampling methods can ensure sufficient numbers from small subgroups that produce a clear picture and increase the ability to compare subgroups.
Simple Random Sampling vs. Other Methods
Because you need a list of the entire population, simple random sampling is most feasible when working with a relatively small population that is already defined. For example, if you’re surveying a company and can easily obtain a list of employees from Human Resources, SRS isn’t too difficult. Large populations can require extensive amounts of time and resources just to create the complete list. Simple random sampling is a great option when you don’t know much about your population other than its membership.
However, other sampling methods can be more efficient when creating the population list is difficult, your population is large and dispersed, or you need to guarantee sufficient data for specific subpopulations. Alternative methods can reduce the need for a complete list and reduce the logistical headaches of a geographically extensive study.
For example, a national opinion poll company might consider an alternative method to assess differences between subpopulations, such as gender, race, and age.
These other methods frequently require you to have a greater understanding of your population than SRS requires. Consider the following alternatives to simple random sampling that can also obtain representative samples:
- Systematic sampling : Uses a random starting point but then samples at a fixed interval. Does not require a complete population list.
- Stratified sampling: Divides the population into dissimilar strata. Ensures that the sample includes specific subpopulations and facilitates comparisons between them.
- Cluster sampling : Divides the population into clusters that mirror the entire population. Then you randomly select from a subset of clusters. Reduces the need for a complete list of the population and eases logistics issues.
For a contrast to representative sampling methods, learn about convenience sampling , which tends to produce biased samples.
Learn about the specialized random sampling process that Political Polls use, allowing a relatively small sample to predict an election.
Sampling in Developmental Science: Situations, Shortcomings, Solutions, and Standards (nih.gov)
Share this:

Reader Interactions
Comments and questions cancel reply.
Research Methods for Business
Definition…
Sampling is the process
of selecting a small number of elements
from a larger defined target group (Population)
of elements such that
the information gathered
from the small group will allow judgments
to be made about the larger groups .
Sampling is the act, process, or technique of selecting a suitable sample , or a representative part of a population for the purpose of determining parameters or characteristics of the whole population .
Purpose Of Sampling …
To draw conclusions about populations from samples, which enables us to determine a population`s characteristics by directly observing only a portion (or sample) of the population. We obtain a sample rather than a complete enumeration (a census ) of the population for many reasons.
6 MAIN REASONS FOR SAMPLING…
- . Timeliness
- . The large size of many populations
- . Inaccessibility of some of the population
- . Destructiveness of the observation
REASONS FOR SAMPLING…
- Economy - taking a sample requires fewer resources than a census.
- Time factor - a sample may provide you with needed information quickly.
- The very large populations - many populations about which inferences must be made are quite large
- The partly accessible populations- There are some populations that are so difficult to get access to that only a sample can be used.
- The destructive nature of the observation- sometimes the very act of observing the desired characteristic of a unit of the population destroys it for the intended use.
- Accuracy and sampling- A sample may be more accurate than a census. A sloppily conducted census can provide less reliable information than a carefully obtained sample.
Important terminologies...
- . Population
- . Sampling Unit
The population refers to the entire group of people, events or things of interest that the researcher wishes to investigate.
- If an organizational consultant is interested in studying the effects of a four-day work week on the white-coller workers in a telephone company in Ireland. Then all white-coller workers in that company will make up the population .
- If regulators wants to know how patients in nursing homes run by a company in France, then all the patients in all the nursing homes run by them will form the population. If however, the regulators are interested only in one particular nursing home run by that company, then only the patients in that particular nursing home will make the population.
An element is the
single member of the population.
- If 1000 blue-coller workers in a particular organization are working and an researcher is interested to know the satisfaction level of these workers then each member (blue-coller) of the particular organization will be considered as element.
- Census is a count of all elements in the human population .
A sample is a subset of the population. it comprises some members from it.
- . If 200 members are drawn/selected from a population of 1000 blue-coller workers to
study the desire outcome, then 200 members form the sample for the study .
- . If there are 145 patients in a hospital and 40 of them are to be surveyed by the hospital administrator to assess there level of satisfaction with the treatment received, then these 40 members will be called the sample .
A sample is thus a subgroup or subset of the population. By studying the sample, the researcher should be able to draw conclusions that are generalizable to the population of interest.
Sampling Unit
The sample unit is the element or the set of elements that is available for selection in some stage of the sampling process.
Example of sampling units in a multi stage sample are city blocks, house hold, and individuals with in the households.
A subject is a single member of the sample just as an element is a single member of the population.
- . If 200 members from the total population of 1000 blue-coller workers form the sample for the study. Then each blue-coller worker in the sample is a subject.
- . If there are 145 patients in a hospital and 40 of them are to be surveyed by the hospital administrator to assess there level of satisfaction with the treatment received, then each member from sample of 40 will be called the subject.
Representative of Sampling...�
- Choosing the right sample cannot be overemphasized.
- If we choose the sample in a scientific way, we can be reasonably sure that sample statistics (Mean, Standard Deviation, (S) Variation in the sample ) and population parameters (Mean (u), Standard Deviation, Variation in the sample ) are close to each others. �
Acknowledgments to Uma Sekaran
What is a Good Sample?
- . Accurate: absence of bias
- . Precise estimate: sampling error
Sampling error is any type of bias
that is attributable to mistakes
in either drawing a sample or
determining the sample size.
Sampling Process…
Define the Population
Determine the Sampling Frame
Select Sampling Technique(s)
Determine the Sample Size
Execute the Sampling Process
Defining Population of Interest…
Population of interest is entirely dependent on Management Problem, Research Problems, and Research Design.
Some Bases for Defining Population:
- . Geographic Area (Pakistan, Punjab, Banking sector, Our Institute etc.)
- . Demographics (Gender, Age, Color, Height etc.)
- . Usage/Lifestyle
- . Awareness
Sampling Frame …
A list of population elements (people, companies, houses, cities, etc.) from which units to be sampled can be selected.
- Difficult to get an accurate list.
- Sample frame error occurs when certain elements of the population are accidentally omitted or not included on the list.
Sampling Methods/Techniques
Probability
Nonprobability
Sampling Methods/Techniques/Types
Sampling Techniques
Convenience
Other Sampling
Simple Random
Probability Sampling Designs
A probability sample is one that gives every member of the population a known chance of being selected .
All are selected randomly.
- Simple random sampling - anyone
- Systematic sampling
- Stratified sampling - different groups (ages)
- Proportionate
- Cluster sampling - different areas (cities)
Simple Random Sampling
Simple random sampling is a method of probability sampling in which every unit has an equal nonzero
chance of being selected
- Each element in the population has a known and equal probability of selection.
- This implies that every element is selected independently of every other element.
Systematic Sampling
Systematic Random Sampling is a method of probability sampling in which the defined target population is ordered and the sample is selected according to position using a skip interval.
- The sample is chosen by selecting a random starting point and then picking every i th element in succession from the sampling frame.
- The sampling interval, i, is determined by dividing the population size N by the sample size n and rounding to the nearest integer.
- For example, there are 100,000 elements in the population and a sample of 1,000 is desired. In this case the sampling interval, i, is 100. A random number between 1 and 100 is selected. If, for example, this number is 23, the sample consists of elements 23, 123, 223, 323, 423, 523, and so on.
Stratified Sampling
Stratified Random Sampling is a method of probability sampling in which the population is divided into different subgroups and samples are selected from each
- A two-step process in which the population is partitioned into subpopulations.
- Divide the target population into homogeneous subgroups or strata
- Draw random samples fro each stratum
- Combine the samples from each stratum into a single sample of the target population
- A major objective of stratified sampling is to increase precision without increasing cost.
Cluster Sampling
- The target population is first divided into mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive subpopulations, or clusters.
- Then a random sample of clusters is selected, based on a probability sampling technique.
- For each selected cluster, either all the elements are included in the sample (one-stage) or a sample of elements is drawn probabilistically (two-stage).
- Elements within a cluster should be as heterogeneous as possible, but clusters themselves should be as homogeneous as possible. Ideally, each cluster should be a small-scale representation of the population.
- In probability proportionate to size sampling, the clusters are sampled with probability proportional to size. In the second stage, the probability of selecting a sampling unit in a selected cluster varies inversely with the size of the cluster.
Nonprobability Sampling
… Nonprobability sample is an arbitrary grouping that limits the use of some statistical tests. It is not selected randomly.
Classifications of Nonprobability Sampling
Convenience Sampling
- Judgment Sampling
Quota Sampling
Snowball Sampling
Convenience sampling attempts to obtain a sample of convenient elements. Often, respondents are selected because they happen to be in the right place at the right time.
- Use of students, and members of social organizations
- Mail intercept interviews without qualifying the
respondents.
- “people on the street” interviews
Judgmental Sampling
Judgmental sampling is a form of convenience sampling in which the population elements are selected based on the judgment of the researcher.
- Test markets
- Engineers selected in industrial marketing research
- Expert witnesses used in court
Quota sampling may be viewed as two-stage restricted judgmental sampling.
- The first stage consists of developing control categories, or quotas, of population elements.
- In the second stage, sample elements are selected based on convenience or judgment.
Population Sample� composition composition� Control �Characteristic Percentage Percentage Number� Sex� Male 48 48 480� Female 52 52 520� ____ ____ ____� 100 100 1000
In Snowball Sampling , an initial group of respondents is selected, usually at random.
- After being interviewed, these respondents are asked to identify others who belong to the target population of interest.
- Subsequent respondents are selected based on the referrals.
Factors to Consider in Sample Design
Research objectives
Degree of accuracy
Knowledge of
target population
Research scope
Determining Sample Size
- How many completed questionnaires do we need to have a representative sample?
- Generally the larger the better, but that takes more time and money.
- Answer depends on :
- How different or dispersed the population is.
- Desired level of confidence.
- Desired degree of accuracy.
In conclusion, it can be said that using a sample in research saves mainly on money and time, if a suitable sampling strategy is used, appropriate sample size selected and necessary precautions taken to reduce on sampling and measurement errors, then a sample should yield valid and reliable information .
Newly Launched - World's Most Advanced AI Powered Platform to Generate Stunning Presentations that are Editable in PowerPoint

- Random Sampling
- Popular Categories
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Powerpoint Templates and Google slides for Random Sampling
Save your time and attract your audience with our fully editable ppt templates and slides..

Presenting our Random Sample Statistics In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Random Sample Statistics. This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting Simple Random Sampling In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb. slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Simple Random Sampling. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Simple Random Sampling Example In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Simple Random Sampling Example This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.
Presenting Example Random Sampling In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Example Random Sampling. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting our Simple Random Sampling Method In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Simple Random Sampling Method This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting Systematic Random Sample Pros Cons Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Layouts Graphic Images Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Systematic Random Sample Pros Cons. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Method Chance Selection Random Sampling Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Infographics Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase six stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Method Chance Selection Random Sampling. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Systematic Random Sample Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Summary Inspiration Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Systematic Random Sample. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.
Presenting our Stratified Random Sampling Example Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Show Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Stratified Random Sampling Example. This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting our Stratified Random Sampling Example Situation In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases five stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Stratified Random Sampling Example Situation. This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting our Types Non Random Sampling In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases five stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Types Non Random Sampling This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting our Four Types Random Sampling In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Four Types Random Sampling This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.
Presenting Stratified Random Sample In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Stratified Random Sample. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting this set of slides with name Gather And Track Data Random Sample Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Portfolio. This is a six stage process. The stages in this process are Population, Sampling Variability, Random Sample, Census, Idea Bulb. This is a completely editable PowerPoint presentation and is available for immediate download. Download now and impress your audience.
Presenting this set of slides with name Random Sampling Vs Random Assignment Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Gallery Show. This is an editable Powerpoint five stages graphic that deals with topics like Random Sampling Vs Random Assignment to help convey your message better graphically. This product is a premium product available for immediate download, and is 100 percent editable in Powerpoint. Download this now and use it in your presentations to impress your audience.

Presenting our Stratified Random Sampling Vs Cluster Sampling Examples Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases six stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Stratified Random Sampling Vs Cluster Sampling Examples This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting our Random Sampling Technique Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Pictures Themes Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Random Sampling Technique This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting Random Stratified Sampling Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Professional Graphics Pictures Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Random Stratified Sampling. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Random Sampling Advantages Disadvantages Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Pictures Show Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase six stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Random Sampling Advantages Disadvantages. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.
Presenting our Random Sampling Pros Cons Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Portfolio Picture Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Random Sampling Pros Cons This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting our Systematic Random Sampling Ppt Powerpoint Presentation File Images Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases five stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Systematic Random Sampling This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting our Perform Simple Random Sampling Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Slides Templates Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Perform Simple Random Sampling This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.
Presenting Random Sampling Techniques In Statistics Ppt Powerpoint Presentation File Sample Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase five stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Random Sampling Techniques In Statistics. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.
Presenting Simple Random Sample Vs Random Sample Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Icon Objects Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Simple Random Sample Vs Random Sample. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

- Social Science
- Experimental Psychology
Random Sampling Powerpoint
Related documents.

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
- Preferences

SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING
Random - each unit in the population has the same ... south east quad. 800 students. bias due to nonresponse. 3,116 total population(nc peach growers) ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- PSYCHOLOGY MAJORS
- A separate sample is randomly selected from each stratum (or layer) of the population.
- CMU Residence Hall Students
- Divide population based on meaningful geographic areas.
- 3,116 Total Population(NC peach growers)
- Mean Trees for each group (M329)
- Mail Surveys
- Mail more than one questionnaire
- Call nonrespondents
- Use special delivery or hand stamped
- Make questionnaires clear, easy to read, and attractive layout
- Phone Survey
- Send advanced letter
- Pilot testing
- Call on weekend and/or evenings
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

- Python »
- 3.12.4 Documentation »
- The Python Standard Library »
- Numeric and Mathematical Modules »
- random — Generate pseudo-random numbers
- Theme Auto Light Dark |
random — Generate pseudo-random numbers ¶
Source code: Lib/random.py
This module implements pseudo-random number generators for various distributions.
For integers, there is uniform selection from a range. For sequences, there is uniform selection of a random element, a function to generate a random permutation of a list in-place, and a function for random sampling without replacement.
On the real line, there are functions to compute uniform, normal (Gaussian), lognormal, negative exponential, gamma, and beta distributions. For generating distributions of angles, the von Mises distribution is available.
Almost all module functions depend on the basic function random() , which generates a random float uniformly in the half-open range 0.0 <= X < 1.0 . Python uses the Mersenne Twister as the core generator. It produces 53-bit precision floats and has a period of 2**19937-1. The underlying implementation in C is both fast and threadsafe. The Mersenne Twister is one of the most extensively tested random number generators in existence. However, being completely deterministic, it is not suitable for all purposes, and is completely unsuitable for cryptographic purposes.
The functions supplied by this module are actually bound methods of a hidden instance of the random.Random class. You can instantiate your own instances of Random to get generators that don’t share state.
Class Random can also be subclassed if you want to use a different basic generator of your own devising: see the documentation on that class for more details.
The random module also provides the SystemRandom class which uses the system function os.urandom() to generate random numbers from sources provided by the operating system.
The pseudo-random generators of this module should not be used for security purposes. For security or cryptographic uses, see the secrets module.
M. Matsumoto and T. Nishimura, “Mersenne Twister: A 623-dimensionally equidistributed uniform pseudorandom number generator”, ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation Vol. 8, No. 1, January pp.3–30 1998.
Complementary-Multiply-with-Carry recipe for a compatible alternative random number generator with a long period and comparatively simple update operations.

Bookkeeping functions ¶
Initialize the random number generator.
If a is omitted or None , the current system time is used. If randomness sources are provided by the operating system, they are used instead of the system time (see the os.urandom() function for details on availability).
If a is an int, it is used directly.
With version 2 (the default), a str , bytes , or bytearray object gets converted to an int and all of its bits are used.
With version 1 (provided for reproducing random sequences from older versions of Python), the algorithm for str and bytes generates a narrower range of seeds.
Changed in version 3.2: Moved to the version 2 scheme which uses all of the bits in a string seed.
Changed in version 3.11: The seed must be one of the following types: None , int , float , str , bytes , or bytearray .
Return an object capturing the current internal state of the generator. This object can be passed to setstate() to restore the state.
state should have been obtained from a previous call to getstate() , and setstate() restores the internal state of the generator to what it was at the time getstate() was called.
Functions for bytes ¶
Generate n random bytes.
This method should not be used for generating security tokens. Use secrets.token_bytes() instead.
Added in version 3.9.
Functions for integers ¶
Return a randomly selected element from range(start, stop, step) .
This is roughly equivalent to choice(range(start, stop, step)) but supports arbitrarily large ranges and is optimized for common cases.
The positional argument pattern matches the range() function.
Keyword arguments should not be used because they can be interpreted in unexpected ways. For example randrange(start=100) is interpreted as randrange(0, 100, 1) .
Changed in version 3.2: randrange() is more sophisticated about producing equally distributed values. Formerly it used a style like int(random()*n) which could produce slightly uneven distributions.
Changed in version 3.12: Automatic conversion of non-integer types is no longer supported. Calls such as randrange(10.0) and randrange(Fraction(10, 1)) now raise a TypeError .
Return a random integer N such that a <= N <= b . Alias for randrange(a, b+1) .
Returns a non-negative Python integer with k random bits. This method is supplied with the Mersenne Twister generator and some other generators may also provide it as an optional part of the API. When available, getrandbits() enables randrange() to handle arbitrarily large ranges.
Changed in version 3.9: This method now accepts zero for k .
Functions for sequences ¶
Return a random element from the non-empty sequence seq . If seq is empty, raises IndexError .
Return a k sized list of elements chosen from the population with replacement. If the population is empty, raises IndexError .
If a weights sequence is specified, selections are made according to the relative weights. Alternatively, if a cum_weights sequence is given, the selections are made according to the cumulative weights (perhaps computed using itertools.accumulate() ). For example, the relative weights [10, 5, 30, 5] are equivalent to the cumulative weights [10, 15, 45, 50] . Internally, the relative weights are converted to cumulative weights before making selections, so supplying the cumulative weights saves work.
If neither weights nor cum_weights are specified, selections are made with equal probability. If a weights sequence is supplied, it must be the same length as the population sequence. It is a TypeError to specify both weights and cum_weights .
The weights or cum_weights can use any numeric type that interoperates with the float values returned by random() (that includes integers, floats, and fractions but excludes decimals). Weights are assumed to be non-negative and finite. A ValueError is raised if all weights are zero.
For a given seed, the choices() function with equal weighting typically produces a different sequence than repeated calls to choice() . The algorithm used by choices() uses floating point arithmetic for internal consistency and speed. The algorithm used by choice() defaults to integer arithmetic with repeated selections to avoid small biases from round-off error.
Added in version 3.6.
Changed in version 3.9: Raises a ValueError if all weights are zero.
Shuffle the sequence x in place.
To shuffle an immutable sequence and return a new shuffled list, use sample(x, k=len(x)) instead.
Note that even for small len(x) , the total number of permutations of x can quickly grow larger than the period of most random number generators. This implies that most permutations of a long sequence can never be generated. For example, a sequence of length 2080 is the largest that can fit within the period of the Mersenne Twister random number generator.
Changed in version 3.11: Removed the optional parameter random .
Return a k length list of unique elements chosen from the population sequence. Used for random sampling without replacement.
Returns a new list containing elements from the population while leaving the original population unchanged. The resulting list is in selection order so that all sub-slices will also be valid random samples. This allows raffle winners (the sample) to be partitioned into grand prize and second place winners (the subslices).
Members of the population need not be hashable or unique. If the population contains repeats, then each occurrence is a possible selection in the sample.
Repeated elements can be specified one at a time or with the optional keyword-only counts parameter. For example, sample(['red', 'blue'], counts=[4, 2], k=5) is equivalent to sample(['red', 'red', 'red', 'red', 'blue', 'blue'], k=5) .
To choose a sample from a range of integers, use a range() object as an argument. This is especially fast and space efficient for sampling from a large population: sample(range(10000000), k=60) .
If the sample size is larger than the population size, a ValueError is raised.
Changed in version 3.9: Added the counts parameter.
Changed in version 3.11: The population must be a sequence. Automatic conversion of sets to lists is no longer supported.
Discrete distributions ¶
The following function generates a discrete distribution.
Binomial distribution . Return the number of successes for n independent trials with the probability of success in each trial being p :
Mathematically equivalent to:
The number of trials n should be a non-negative integer. The probability of success p should be between 0.0 <= p <= 1.0 . The result is an integer in the range 0 <= X <= n .
Added in version 3.12.
Real-valued distributions ¶
The following functions generate specific real-valued distributions. Function parameters are named after the corresponding variables in the distribution’s equation, as used in common mathematical practice; most of these equations can be found in any statistics text.
Return the next random floating point number in the range 0.0 <= X < 1.0
Return a random floating point number N such that a <= N <= b for a <= b and b <= N <= a for b < a .
The end-point value b may or may not be included in the range depending on floating-point rounding in the expression a + (b-a) * random() .
Return a random floating point number N such that low <= N <= high and with the specified mode between those bounds. The low and high bounds default to zero and one. The mode argument defaults to the midpoint between the bounds, giving a symmetric distribution.
Beta distribution. Conditions on the parameters are alpha > 0 and beta > 0 . Returned values range between 0 and 1.
Exponential distribution. lambd is 1.0 divided by the desired mean. It should be nonzero. (The parameter would be called “lambda”, but that is a reserved word in Python.) Returned values range from 0 to positive infinity if lambd is positive, and from negative infinity to 0 if lambd is negative.
Changed in version 3.12: Added the default value for lambd .
Gamma distribution. ( Not the gamma function!) The shape and scale parameters, alpha and beta , must have positive values. (Calling conventions vary and some sources define ‘beta’ as the inverse of the scale).
The probability distribution function is:
Normal distribution, also called the Gaussian distribution. mu is the mean, and sigma is the standard deviation. This is slightly faster than the normalvariate() function defined below.
Multithreading note: When two threads call this function simultaneously, it is possible that they will receive the same return value. This can be avoided in three ways. 1) Have each thread use a different instance of the random number generator. 2) Put locks around all calls. 3) Use the slower, but thread-safe normalvariate() function instead.
Changed in version 3.11: mu and sigma now have default arguments.
Log normal distribution. If you take the natural logarithm of this distribution, you’ll get a normal distribution with mean mu and standard deviation sigma . mu can have any value, and sigma must be greater than zero.
Normal distribution. mu is the mean, and sigma is the standard deviation.
mu is the mean angle, expressed in radians between 0 and 2* pi , and kappa is the concentration parameter, which must be greater than or equal to zero. If kappa is equal to zero, this distribution reduces to a uniform random angle over the range 0 to 2* pi .
Pareto distribution. alpha is the shape parameter.
Weibull distribution. alpha is the scale parameter and beta is the shape parameter.
Alternative Generator ¶
Class that implements the default pseudo-random number generator used by the random module.
Changed in version 3.11: Formerly the seed could be any hashable object. Now it is limited to: None , int , float , str , bytes , or bytearray .
Subclasses of Random should override the following methods if they wish to make use of a different basic generator:
Override this method in subclasses to customise the seed() behaviour of Random instances.
Override this method in subclasses to customise the getstate() behaviour of Random instances.
Override this method in subclasses to customise the setstate() behaviour of Random instances.
Override this method in subclasses to customise the random() behaviour of Random instances.
Optionally, a custom generator subclass can also supply the following method:
Override this method in subclasses to customise the getrandbits() behaviour of Random instances.
Class that uses the os.urandom() function for generating random numbers from sources provided by the operating system. Not available on all systems. Does not rely on software state, and sequences are not reproducible. Accordingly, the seed() method has no effect and is ignored. The getstate() and setstate() methods raise NotImplementedError if called.
Notes on Reproducibility ¶
Sometimes it is useful to be able to reproduce the sequences given by a pseudo-random number generator. By reusing a seed value, the same sequence should be reproducible from run to run as long as multiple threads are not running.
Most of the random module’s algorithms and seeding functions are subject to change across Python versions, but two aspects are guaranteed not to change:
If a new seeding method is added, then a backward compatible seeder will be offered.
The generator’s random() method will continue to produce the same sequence when the compatible seeder is given the same seed.
Basic examples:
Simulations:
Example of statistical bootstrapping using resampling with replacement to estimate a confidence interval for the mean of a sample:
Example of a resampling permutation test to determine the statistical significance or p-value of an observed difference between the effects of a drug versus a placebo:
Simulation of arrival times and service deliveries for a multiserver queue:
Statistics for Hackers a video tutorial by Jake Vanderplas on statistical analysis using just a few fundamental concepts including simulation, sampling, shuffling, and cross-validation.
Economics Simulation a simulation of a marketplace by Peter Norvig that shows effective use of many of the tools and distributions provided by this module (gauss, uniform, sample, betavariate, choice, triangular, and randrange).
A Concrete Introduction to Probability (using Python) a tutorial by Peter Norvig covering the basics of probability theory, how to write simulations, and how to perform data analysis using Python.
These recipes show how to efficiently make random selections from the combinatoric iterators in the itertools module:
The default random() returns multiples of 2⁻⁵³ in the range 0.0 ≤ x < 1.0 . All such numbers are evenly spaced and are exactly representable as Python floats. However, many other representable floats in that interval are not possible selections. For example, 0.05954861408025609 isn’t an integer multiple of 2⁻⁵³.
The following recipe takes a different approach. All floats in the interval are possible selections. The mantissa comes from a uniform distribution of integers in the range 2⁵² ≤ mantissa < 2⁵³ . The exponent comes from a geometric distribution where exponents smaller than -53 occur half as often as the next larger exponent.
All real valued distributions in the class will use the new method:
The recipe is conceptually equivalent to an algorithm that chooses from all the multiples of 2⁻¹⁰⁷⁴ in the range 0.0 ≤ x < 1.0 . All such numbers are evenly spaced, but most have to be rounded down to the nearest representable Python float. (The value 2⁻¹⁰⁷⁴ is the smallest positive unnormalized float and is equal to math.ulp(0.0) .)
Generating Pseudo-random Floating-Point Values a paper by Allen B. Downey describing ways to generate more fine-grained floats than normally generated by random() .
Table of Contents
- Bookkeeping functions
- Functions for bytes
- Functions for integers
- Functions for sequences
- Discrete distributions
- Real-valued distributions
- Alternative Generator
- Notes on Reproducibility
Previous topic
fractions — Rational numbers
statistics — Mathematical statistics functions
- Report a Bug
- Show Source
Types of Sampling
Jan 05, 2020
120 likes | 174 Views
Types of Sampling. Simple Random Cluster Stratified Systematic (every kth element is sampled). Assumptions. Members of the Population can be numbered from 1 to N where N is the population size
Share Presentation
- population element
- random sample
- simple random
- cluster sample
- 7th element sample

Presentation Transcript
Types of Sampling • Simple Random • Cluster • Stratified • Systematic (every kth element is sampled)
Assumptions • Members of the Population can be numbered from 1 to N where N is the population size • You have a mechanism for randomly picking n numbers (usually without replacement) from the collection of numbers 1,2,3,…,N • If number k is selected, the population element with that number is in the sample
Simple Random Sample 1 12 17 10 6 9 • Population above right • In a Simple Random Sample each population member is equally likely to be selected • Click to sample 2 13 8 18 16 20 3 14 4 15 19 7 11 21 5
1 2 13 14 12 4 17 3 5 18 15 16 8 24 7 22 9 21 6 19 23 20 11 10 Cluster Sampling • The Population (right) can be divided into strata • A stratum consists of population elements that are similar in some way • All of one or more strata are randomly selected and used in the sample—see next slide
24 22 21 19 23 20 Population Above—Click to take a Cluster Sample 1 2 13 14 12 4 17 3 5 18 15 16 8 7 9 6 11 10
1 2 13 14 12 4 17 3 5 18 15 16 8 24 7 22 9 21 6 19 23 20 11 10 Stratified Sampling • The Population (right) can be divided into strata • A stratum consists of population elements that are similar in some way • A random sample from each stratum is randomly selected and used in the sample—see next slide
Population Above—Click to take a Stratified Sample 1 2 13 14 12 4 17 3 5 18 15 16 8 24 7 22 9 21 6 19 23 20 11 10
Systematic (every kth) • A starting number is randomly chosen • The population element corresponding to the starting number and every kth population element after that are selected for the sample • ‘Circular’ counting is used
Every 7th Element Sample 1 12 17 10 6 9 • Population above right • Click once to get a random starting element • Click again to get every 7th element after that 2 13 8 18 16 20 3 14 4 15 19 7 11 21 5
- More by User

Sampling Sampling plays back samples of the original tone. For simple decaying tones (e.g., piano, harp, marimba, guitar, plucked strings), playing back the samples from start to finish works well: [iv:73] sample of piano Bb3 tone, 9.33 seconds Sampling (Soundin) soundin:
627 views • 22 slides

Sampling. MICS3 Regional Workshop “Survey Design”. MICS Sample Design. MICS is a complex survey (Multi-stage stratified). MICS is a worldwide program, consistence & comparability are important issues. We will discuss only a few of the highlights including: Sample size determination
740 views • 30 slides

Sources of sampling error Correct and incorrect sampling Estimation of sampling uncertainty Optimization of sampling pro
1.29k views • 50 slides

Sampling. Outline FT of comb function Sampling • Nyquist Condition sinc interpolation • Truncation • Aliasing. Sampling.
991 views • 43 slides

Sampling. Terms . Sample Population Population element Census. Why use a sample?. Cost Speed Accuracy Destruction of test units. Steps. Definition of target population Selection of a sampling frame (list) Probability or Nonprobability sampling Sampling Unit Error
733 views • 35 slides

Overview of Sampling
Overview of Sampling. There are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics – Benjamin Disraeli. Audit Sampling.
1.78k views • 109 slides
Sampling Types Techniques
Discussion Problem. Natalie surveys randomly from her on-line youth book club members as well as the lists of youth card holders at the two nearest community libraries.She returns to school and suggests to her friend on students' council that the school should host a read-a-thon to raise money for
424 views • 14 slides

Sampling and Sampling Distributions
Sampling and Sampling Distributions. Aims of Sampling Probability Distributions Sampling Distributions The Central Limit Theorem Types of Samples. Aims of sampling. Reduces cost of research (e.g. political polls)
1k views • 33 slides

SAMPLING. Sampling. Sampling is the process that a researcher uses to select people, places, things, signals or any other item of interest to study. We will look at ways to select a sample, and consider whether it is expected to be representative. The Population.
405 views • 19 slides
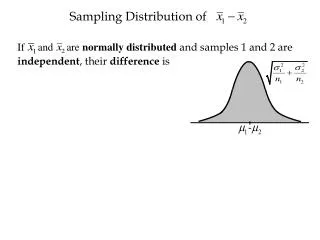
Sampling Distribution of
Sampling Distribution of . If and are normally distributed and samples 1 and 2 are independent , their difference is. Sampling Distribution of . If and are normally distributed and samples 1 and 2 are
396 views • 28 slides

Sampling. W&W, Chapter 6. Rules for Expectation. Examples Mean: E(X) = xp(x) Variance: E(X-) 2 = (x- ) 2 p(x) Covariance: E(X- x )(Y- y ) = (x- x )(y- y )p(x,y). Rules for Expectation. E(X + Y) = E(X) + E(Y) E(aX + bY) = aE(X) + bE(Y) E(R) where R=10+X+Y =
545 views • 32 slides

Sampling. 12/6/2012. Readings. Chapter 8 Correlation and Linear Regression (Pollock) ( pp 199- 206) Chapter 6 Foundations of Statistical Inference (Pollock) ( pp 122-135). Final Exam. SEC 1 December 12 th (Wednesday) 1:30 pm - 3:30 pm SEC 2 December 11 th (Tuesday)
434 views • 35 slides
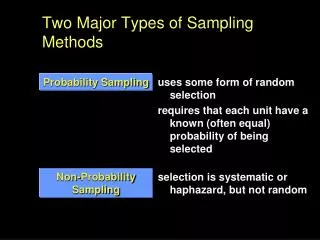
Two Major Types of Sampling Methods
Two Major Types of Sampling Methods. uses some form of random selection requires that each unit have a known (often equal) probability of being selected selection is systematic or haphazard, but not random. Probability Sampling. Non-Probability Sampling. Sampling and representativeness.
1.11k views • 70 slides

Sampling Designs Systematic Sampling Cluster Sampling Multistage Sampling
Sampling Designs Systematic Sampling Cluster Sampling Multistage Sampling. Pg 1.2 Name this sampling method. Page 1.3 Name this sampling method. Page 1.4 Name this sampling method. Systematic Sample start with a list of elements. Choose a random starting point.
1.38k views • 22 slides

Sampling and Sampling Distributions. 2013/12/02. Sampling methods. Random sampling : Choose the elements for the sample one at a time in such a way that, at each step, each of the events remaining in the population has the same probability of being selected.
412 views • 8 slides

Recap of sampling…
Recap of sampling…. Sampling example….
159 views • 6 slides

Sampling dan Distribusi Sampling()
Sampling dan Distribusi Sampling(). Why Use..?. Why Use..?. Method. Method. Method. Method. Method. Method. Method. Method. Method. Distribusi Sampling. Distribusi Sampling. Distribusi Sampling. Distribusi Sampling. Distribusi Sampling.
716 views • 37 slides
Std MCC9-12.S.ID4 Types of sampling methods
Std MCC9-12.S.ID4 Types of sampling methods. The mean score of the ACT test takers at OLA High is 1450 and the standard deviation is 20. Carl scored 1.34 Standard deviations below the mean. a) What is his z score? What is his actual ACT score ?
201 views • 11 slides

A sampling of the types of law
A legal education can open up new and interesting career opportunities. Law schools offer a wide variety of degrees or certificates to match your interests, your goals, and your schedule. http://ccbstcollege.com
91 views • 7 slides

Sampling of Coal
Sampling of Coal. Dr kalyan sen Director, Central Fuel Research Institute, Dhanbad, 2003. Quality Monitoring (QM) of Coal is an essential requirement for process control, plant performance or for any commercial transaction between Consumer and Producer.
579 views • 37 slides

Sampling. Why Sample? Some Issues:. Time, cost, accuracy accuracy/ representativeness Link to interesting general introduction of sampling for public Link to website advertising services of market research firm. What is a sample? Key Ideas & Basic Terminology.
507 views • 39 slides

233 views • 18 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Simple random sampling involves selecting a sample that gives each individual an equal chance of being selected by identifying the population, determining sample size, listing all population members, assigning them numbers, selecting numbers at random from a table, and including individuals in the sample if their number is selected.
It begins by defining simple random sampling as selecting a sample from a population where each individual has an equal probability of being selected at each stage of sampling. It then discusses two common methods for obtaining a simple random sample: the lottery method and using a random number table. The document also explains the difference ...
Presentation Transcript. Simple Random Sampling Module 3 Session 5. Session Objectives • Define simple random sampling • To demonstrate how a Simple random sample is selected in practice. Simple Random Sampling • Simplest sampling design • In simple random sampling each element has an equal chance of being selected • The procedure for ...
In order to obtain the sample we use the simple random method selecting from each subgroup. Examples. 1. Separate cookies by type for a contest and select the top 5 in each group. image taken from google images. In the example, when you separate cookie entries by type (drop, filled, cutout, and bar) and then selecting the top 5 in each group.
Simple Random Sampling. Basic ideas 1. "Random" refers to the method. of selecting a sample rather than to the. particular sample selected. It refers the. process rather the outcome of the process. 2. The random selection process determines the.
Presentation Transcript. Simple Random Sample • Simple Random Sample of size n - A sample of size n chosen in such a way that all possible samples of size n have the same chance of being selected. Selecting a Simple Random Sample • Given a population of size N, number the members from 1 to N. • Then use a random number generator (such ...
3 Selecting a Simple Random Sample Given a population of size N, Number the members from 1 to N. Use a random number generator (such as on a calculator) to generate n random integers from 1 to N. The sampling may be done with or without replacement. If the sampling is done without replacement, then repetitions should be discarded.
Key Definitions Pertaining to Sampling (cont.) • (Simple) sampling frame:a list of every unit in the population or • more generally, a setup that allows a random sample to be drawn • Random (or Probability) Sample:a sample such that each unit in the population has a calculable, i.e., precise and known in advance, chance of appearing in ...
Simple random sampling (SRS) is a probability sampling method where researchers randomly choose participants from a population. All population members have an equal probability of being selected. This method tends to produce representative, unbiased samples. For example, if you randomly select 1000 people from a town with a population of ...
Systematic Random Sampling is a method of probability sampling in which the defined target population is ordered and the sample is selected according to position using a skip interval.. The sample is chosen by selecting a random starting point and then picking every i th element in succession from the sampling frame.; The sampling interval, i, is determined by dividing the population size N by ...
Presenting Simple Random Sample Vs Random Sample Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Icon Objects Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout ...
A simple random sample of a certain size is drawn. from each strata. Often, the size is chosen by using the actual percentage. of occurrence in the overall population. Example: Divide class into males and females and. randomly select from each gender in the proportion. that they occur in the population (class).
2.1 Simple Random Sampling. Variable In statistics, a variable is a characteristic of the individuals to be measured or observed. The data that we observe for a variable are called observations. Definition. Example: Identifying Individuals, Variables, and Observations The five movies with the largest worldwide gross receipts of all time are shown in the table.
Simple random sampling. Jul 14, 2014 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 5 likes • 1,383 views. S. suncil0071. Data & Analytics. 1 of 7. Download now. Simple random sampling - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Illustrate Random Sampling - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The document discusses random sampling techniques used in statistics including simple random sampling, systematic random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling. It provides examples of each technique and how they are ...
more generally, a setup that allows a random. sample to be drawn. Random (or Probability) Sample a sample such. that each unit in the population has a. calculable, i.e., precise and known in advance, chance of appearing in the (drawn) sample, e.g., selected by lottery, i.e., use random mechanism to pick units out of. the sampling frame.
SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING. Description: Random - Each unit in the population has the same ... South East Quad. 800 students. Bias due to Nonresponse. 3,116 Total Population (NC peach growers) ... - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views: 3289. Avg rating:3.0/5.0. Slides: 8.
Simple Random Sampling. Simple Random Sampling. Lecture 7 Section 2.5 Tue, Jan 27, 2004. Simple Random Sample. Simple Random Sample of size n - A sample of size n chosen in such a way that all possible samples of size n have the same chance of being selected. Selecting a Simple Random Sample. 638 views • 13 slides
random. shuffle (x) ¶ Shuffle the sequence x in place.. To shuffle an immutable sequence and return a new shuffled list, use sample(x, k=len(x)) instead. Note that even for small len(x), the total number of permutations of x can quickly grow larger than the period of most random number generators. This implies that most permutations of a long sequence can never be generated.
Presentation Transcript. Types of Sampling • Simple Random • Cluster • Stratified • Systematic (every kth element is sampled) Assumptions • Members of the Population can be numbered from 1 to N where N is the population size • You have a mechanism for randomly picking n numbers (usually without replacement) from the collection of ...