

Fix network connection issues in Windows
Try these things to troubleshoot network connection issues in Windows 11.
Make sure Wi-Fi is on. Select Start > Settings > Network & internet , then turn on Wi-Fi . Next, select More options ( > ) next to Wi-Fi, then select Show available networks . If a network you expect to see appears in the list, select it, then select Connect . Open Wi-Fi settings
See if you can use the Wi-Fi network to get to websites from a different device. If you can’t, restart your modem, router, and device, and re-connect to the Wi-Fi.
Try turning Wi-Fi on and off. This can solve issues by restarting your connection.
If your Surface still isn't connecting, try the steps on Surface can't find my wireless network .
Get more help fixing network connection issues
Try these things to troubleshoot network connection issues in Windows 10.
Use the Network troubleshooter. Select Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Under Change your network settings , select Network troubleshooter . Open Status settings
Make sure Wi-Fi is on. Select Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . Next, select Show available networks , and if a network you expect to see appears in the list, select it, then select Connect . Open Wi-Fi settings
See if you can use the Wi-Fi to get to websites from a different device. If you can’t, restart your modem, router, and device, and re-connect to the Wi-Fi.

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
How to Troubleshoot Windows Network Connections
Get your Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection up and running.

Without a working Internet connection, most Windows devices really can’t work the way they should, nor allow users to function completely or well. That makes fixing network issues extremely important. Here’s how to get that done.
Arguably, Windows without a working network connection isn’t really worth much. That’s because access to email, social media, the Web – and even Windows updates and apps – doesn’t work without network (and Internet) access. That’s probably why Microsoft has put a lot of time and effort into making networking issues easy to recognize, diagnose and fix as part and parcel of how Windows works.
Getting Network Troubleshooting Started
The views from the more recent Windows 11 and Windows 10 builds appear in Figures 1 and 2 following. What they show is that by right-clicking on the network symbol in the notification area of the Task Bar (right-hand side, by default) you can jump straight into troubleshooting your Windows network connection.
Figure 1: Right-click on the Wi-Fi (or Ethernet) symbol (bottom center) and “Diagnose network problems” pops right up in Windows 11 Insider Preview
Figure 2: In all current Windows 10 versions, right-click on the active network symbol to get “Troubleshoot problems” instead.
Either way, it’s a one-click maneuver to start the network troubleshooting process in Windows 10 and in Windows 11 recent builds. Older Windows 11 versions aren’t quite as accommodating, as shown in Figure 3.
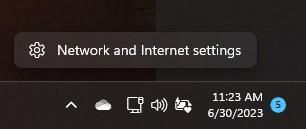
In older versions of Windows 11, however, network troubleshooting is never too far away. Click on Start 🡪 Settings, then enter “Trouble” into the Settings search box. As you can see in Figure 4, a number of options pop up in response, click the “Troubleshoot Other problems” item to continue.
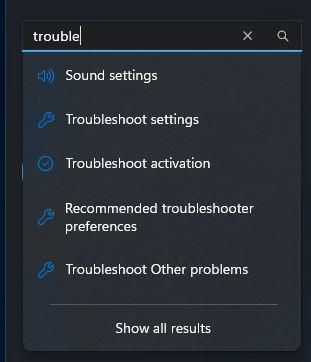
When you follow that “Other problems” entry, the “Network and Internet” item finally appears. That’s what you want (and that’s where the other Windows versions take you more directly). Click the “Run” button at the right to proceed from here.
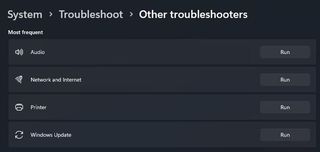
This approach works for all Windows 10 and 11 versions, actually (with some minor differences in Windows 10 for wording, but the pathway is pretty much identical).
Stay On the Cutting Edge: Get the Tom's Hardware Newsletter
Join the experts who read Tom's Hardware for the inside track on enthusiast PC tech news — and have for over 25 years. We'll send breaking news and in-depth reviews of CPUs, GPUs, AI, maker hardware and more straight to your inbox.
The Windows Network Troubleshooters
Because Windows networking mostly revolves around two kinds of networks, there are two kinds of troubleshooters to match: one for wired Ethernet, the other for wireless Wi-Fi, in all its many forms. Figure 6 shows the results of running the Wired Ethernet troubleshooter, with all options expanded in a “no trouble” situation:
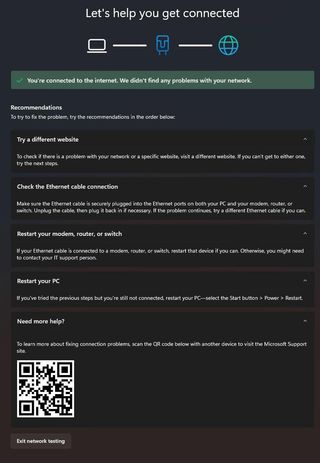
Figure 7 shows the same troubleshooter when run on a Wi-Fi attached system instead. Iconography and minor terminology changes aside, it’s identical to the version shown in Figure 6.
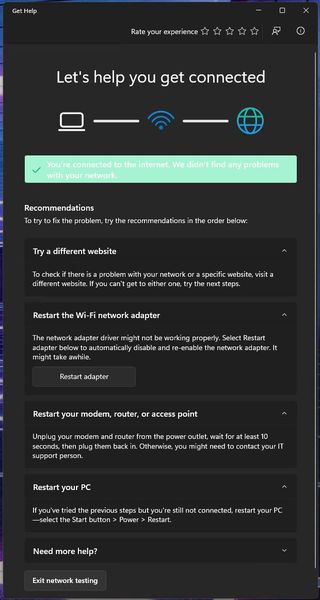
The various actions suggested in the troubleshooters cover a wide array of possible problem sources. Let’s walk through those items to discuss what the troubleshooters look for, what they might find, and related fixes.
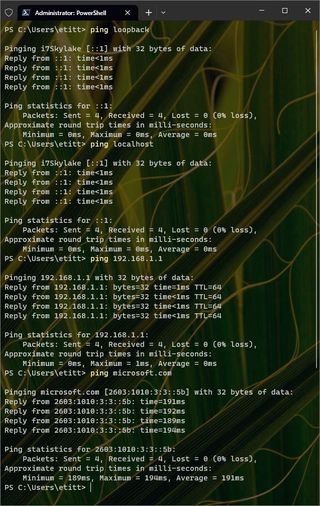
Try a different website : Any given website is, of course, somewhere on the Internet. But because websites go down, too, changing to a different one helps determine if the “other end” of the attempted connection is itself having problems. In the background, the troubleshooter checks local network access, Internet gateway access and then actual Internet access through a series of “reachability checks.” You can do the same thing at the command line using the PING command as follows:
1. Ping loopback (this checks that TCP/IP is working, and looks for a response from a synthetic address that’s always available).
2. Ping localhost (this checks that the current network interface device is up and running)
3. Ping the nearest router or gateway (Use ipconfig to look up the IP address for the “Default Gateway” – on my network it’s at 192.168.1.1, so that means ping 192.168.1.1 is the command to use)
4. Ping a known working Internet address ; for whatever reason MS often uses ping Microsoft.com as its check). See this sequence in Figure 8.
Restart the network adapte r (Wi-Fi or wired Ethernet, depending…): this basically turns off the network interface and then turns it back on. In some situations, signaling or traffic issues can cause the network interface to stop working temporarily. Turning it off, then back on, will usually clear such temporary glitches. Notice the button that reads “Restart adapter.” This performs the same actions you could do yourself in Device Manager by disabling the adapter, then re-enabling it after a short wait (usually 30 seconds or so).
Restart your modem, router, or access point (all three apply to Wi-Fi, and the first two to wired Ethernet). Anyone who uses a device at their network boundary to get off the LAN and onto an ISP’s network will see issues present at this device occasionally. I’ve seen power glitches, signaling issues, and even service outages show up as a boundary device issue. In many cases (except when a service outage persists) restarting the boundary device will set things back to rights. This is often signaled at the device itself (my Arris SAC2V1A has a status light that changes from blue to red to signal a connection problem, for example).
Restart your PC: In the DOS and early Windows days this was sometimes called the “three-fingered salute” and worked if the key combination CTRL-ALT-DEL was entered. Nowadays, if you use that same key combo, you’ll get the logout screen, from which you can indeed get to the restart button. But sometimes, Windows gets itself into a state where some things don’t work – including networking, in this context. But a restart will often clear whatever’s causing problems, so this is always worth a try if the network troubleshooter can’t fix what’s ailing your Windows network connection.
Other Sources of Network Difficulty
There are three basic ways in which networking can go wrong. This applies equally to Windows PCs and other devices, but the details will differ. First, the hardware that lets information come and go from the device might have issues (these span a wide range of possibilities including outright failure, shorts, partial or intermittent malfunctions, incorrect set-up or configuration, or incompatibility with local network capabilities and connections).
Second, the TCP/IP networking protocol (and wireless support, where applicable) may have issues with the software, or the addresses and services used to make it work – such as DHCP for local addresses, DNS for name resolution, and so forth. Third come all the various protocols used to support email, web, file transfer, and all the other Internet services that let users do things with networks they wish to access and use, along with the applications that support them (Outlook for email, Chrome or Firefox for Web access, and on and on).
The Windows network troubleshooter does a pretty thorough job of checking all of these things as it runs through its various tests. But if you find your PC still disconnected from the network (and/or the Internet) after it’s put through its paces, you can – and probably should – check on some (or all) of the following issues:
1. Make sure ipconfig shows a valid network address scheme and configuration.You can check this by entering “ipconfig” at the command line. One sure sign of IP troubles is PCs that present Microsoft Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) addresses. These IPv4 addresses fall in the range from 169.254.0.1 – 169.254.255.254 (basically the tail end of the 169.254 Class B address. They show up automatically when other sources of addressing aren’t working. This usually indicates some kind of trouble with local DHCP services (not working or unavailable). Fixing this often requires restarting (or sometimes, replacing) the local router, gateway or wireless access point.
2. Make sure that DNS is working and points to the correct DNS server . Improper name resolution can cause all kinds of Internet access problems (and may indicate security is compromised). Run ipconfig /all and check DNS information for the network adapter in active use. On my network, for example, the default address comes from Spectrum my ISP and shows up as 1.0.0.1. It’s tied to CloudFlare, which is a well-known, well-respected, and highly secure DNS provider. See LifeWire’s Best Free and Public DNS Servers (June 2023) for a list of reliable public DNS providers.
3. Keep an extra network interface handy. I always have one or two extra hardware devices around, so I can try a different network interface if the one on any particular PC appears to be acting up. On the wired (GbE) Ethernet side, I’ve got an USB 3.0 to GbE adapter ( US$20 -35 ): it plugs into any USB 3.0 (or better) port and provides an RJ-45 from which I can cable into my nearest switch. On the Wi-Fi side, I’ve got a USB 3.0 to 802.11ax adapter ( US$20-60 ). If a PC’s existing adapter stops working, or has trouble, I simply need to plug one or the other in. That’s usually all it takes to get networking back (with an RJ-45 cable into the switch for GbE as well). In a pinch, in fact, I’ve used the USB-to-Wi-Fi device with my iPhone as a hotspot to keep working on the Internet even during ISP outages, some extended for days.
Bottom Line
Should one (or all) of your Windows PCs run into networking difficulty, turn to the Windows Network and Internet Troubleshoot as your first point of action in attempting to diagnose and fix whatever’s wrong. In the vast majority of cases – over 90% in my personal experience – it will also be the last tool you need to use to help figure out what’s wrong and get started on a fix. Indeed, except for situations that require hardware changes, or working with ISP boundary devices, or similar third-party issues, this will probably also be the last tool you need to use to get networking and Internet access working again.

Ed Tittel is a long-time IT writer, researcher and consultant, and occasional contributor to Tom’s Hardware. A Windows Insider MVP since 2018, he likes to cover OS-related driver, troubleshooting, and security topics.
Microsoft is switching RAM speed units in Task Manager — finally moving to the more technically correct MT/s
Windows 11 24H2 will enable BitLocker encryption for everyone — happens on both clean installs and reinstalls
How to remote control your Raspberry Pi from a browser with Raspberry Pi Connect
Most Popular

8 Easy-to-Do Ways to Troubleshoot Network Connection
You'll be up and running in no time
A faulty Wi-Fi connection doesn’t have to ruin your day. There are plenty of ways you can restore a lost internet connection. Follow these network troubleshooting tips and you’ll be up and running in no time.
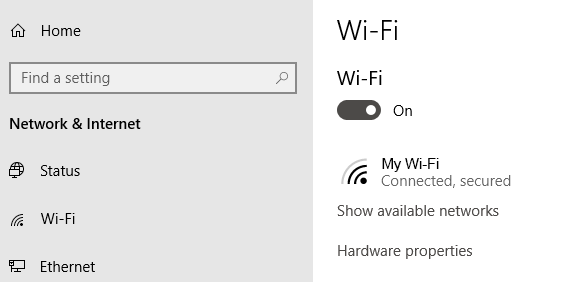
1. Check Your Settings
First, check your Wi-Fi settings. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . Switch Wi-Fi to the On position.
Phones and tablets also have settings that turn Wi-Fi on and off. Make sure that it is turned on so you can connect to the network.
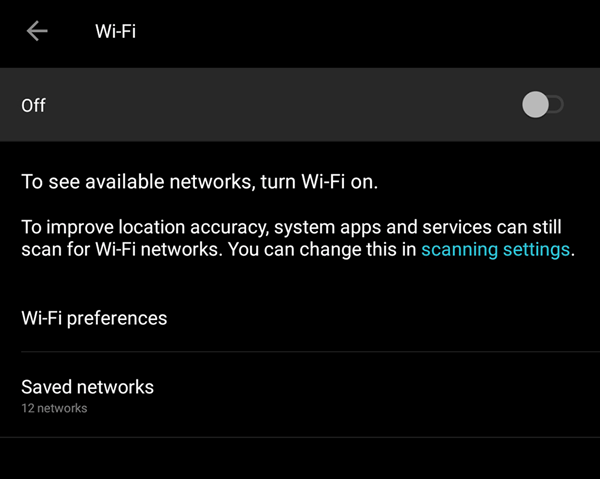
You also want to check if Airplane Mode is turned on.
2. Check Your Access Points
Check your WAN (wide area network) and LAN (local area network) connections. In layman’s terms, these are the Ethernet cables that go to and from your router.

If you suspect that the cables are the culprit, try swapping them out with new ones.
3. Go Around Obstacles
Walls, furniture, and other obstructions can be the reason why you’re unable to go online. Moving closer to the router can re-establish the connection. If moving closer to the router does not solve the issue, then at least we can remove it from the list of suspects.
4. Restart the Router
Sometimes restarting the router can help fix connectivity issues. This is even truer in cases where the router has not been turned off in a while. A quick restart can jolt the router back into working like it used to.
If that doesn’t work, you might also consider resetting the router. But only do so if you’re okay with it being restored to its factory settings. You will have to reconfigure everything including the SSID and password.
5. Check the Wi-Fi Name and Password
Check the network name (otherwise known as SSID) and password of the network connection. If you’re used to connecting automatically when in range of a router but are no longer able to, changes may have been made to the network while you’re away.
It could be as simple as administrators updating the password or the SSID could have been changed to a different one.
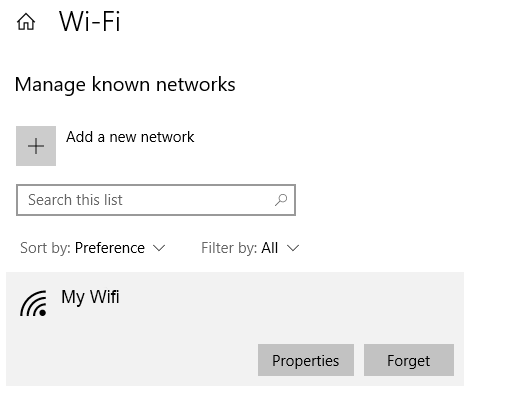
6. Check DHCP Settings
Routers are usually set up as DHCP servers. This setting lets computers join a network automatically. With DHCP turned on, users will no longer have to mess with IP Address and DNS Server settings manually.
To edit your DHCP settings, go to Windows Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . Under Wi-Fi , click Manage Known Networks . Select a network and click Properties .
Under IP Settings , click Edit . From the drop-down menu, select Automatic (DHCP) .
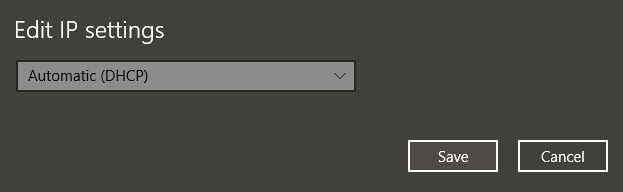
Note: Selecting Manual will let you set your DNS Server Address and IP Address settings manually.
7. Update Windows
Your network problems could be caused by your system. If that is the case, Windows could have possibly released a fix. Try updating your Windows machine to the latest release.
Go to Windows Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update . Click Check for Updates . If there are updates available, Windows will download and install them.
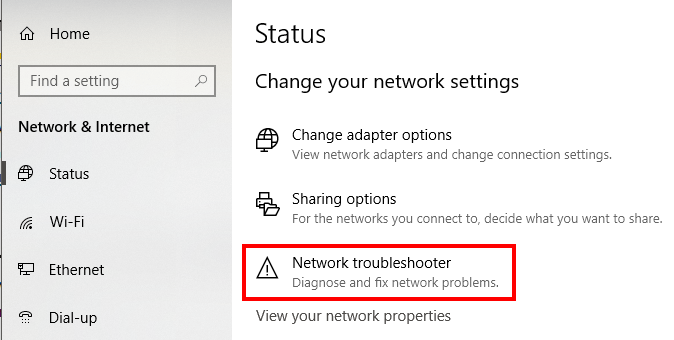
8. Open Windows Network Diagnostics
Windows has a tool called Windows Network Diagnostics that lets users troubleshoot connection issues.
Go to Windows Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Under Change Your Network Settings , click Network Troubleshooter .
Windows Network Diagnostics will run a couple of tests to see what’s possibly causing your Wi-Fi issues.
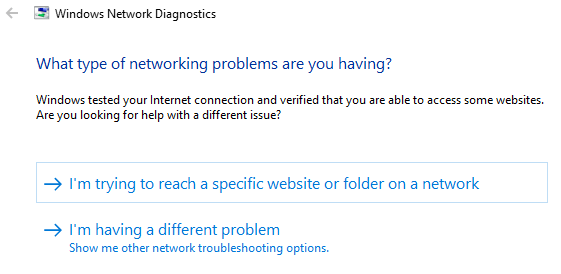
Windows will let you know if it does not find any issue. Otherwise, you will be given a list of possible actions to take to resolve the problem.
This tool, or a version of it, should be available in Windows 7 to Windows 10.
Christopher Jan Benitez is a freelance writer for hire who provides actionable and useful web content to small businesses and startups. In his spare time, he religiously watches professional wrestling and finds solace in listening to '80s speed metal. Read Christopher's Full Bio
Read More Posts:

5 Common Network Errors & How to Fix Them
Network issues can be frustrating as they prevent you from connecting to the internet. Fortunately, you can fix most network errors within minutes.
We've all dealt with network issues before, sometimes to the point of total frustration. A vast range of network errors may pop up on our screen or even remain meddling in the background, which can interfere with our internet connection.
So, what are some of the most common network errors out there, and how can you fix them? Let's take a look.
1. Problems With Your DNS
A DNS, or Domain Name System, is a server that translates domain names to IP addresses, allowing your browser to load a page. DNS servers play a huge role in online networks, and you simply wouldn't be able to use the internet without them. Unfortunately, DNS issues are pretty common and can affect your network connection in several ways.
The most common DNS issue occurs when the DNS records aren't configured correctly. This can happen with computer updates when the DNS doesn't register certain records or when there is a failure to enter the correct IP addresses of your records. In short, it can happen easily, but you can fix it within minutes.
Related: How to Fix the 'DNS Server Not Responding' Error to Get Back Online
Firstly, you can try temporarily disabling your antivirus and firewall software. Don't worry about putting your device at risk, as you're only disabling it temporarily for a short duration. If you notice that the DNS issue has resolved itself after you try using your browser without your antivirus software, then the software itself may be the issue. So consider trying a different software if this is the case.
Alternatively, consider switching to a different browser if you don't have time to fix the problem directly. This may allow you to use the internet while the issue persists. Updating your current browser could also be a quick and convenient solution. Another quick fix could be simply restarting your router by unplugging it from its power source and then reconnecting it a few seconds later
2. VPN Connection Issues
VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, are now very popular pieces of software. A VPN is responsible for encrypting your data traffic while you're on the internet and therefore disguises your IP address. They essentially make it much safer to be online, protecting you against IP theft and various other external threats.
However, a VPN can significantly slow down your network connection speed. This is because your data traffic needs to be encrypted via a secure VPN for you to use the internet. Therefore, this little middle-man diversion can add a few seconds onto each loading page or video. However, you can do a few simple things to minimize this slowdown.
Related: Can ISPs Block Your VPN and What Can You Do About It?
Firstly, try changing from a wireless to a wired connection. This can be a little inconvenient, as you need an ethernet output and cable to do this. But, you can significantly improve your internet connection by doing so. Secondly, try changing your connected server via your VPN software. For example, if you connect to a VPN in France while living in New York, you'll significantly throttle your internet speeds purely due to the distance. Try connecting to a server that's closest to your geographical location.
You can also restart your router by unplugging and re-plugging it into its power source or restarting your device. The old on-and-off-again trick works sometimes!
3. Conflict of IP Address
An IP conflict occurs when two devices on the same network have the same IP address. An IP address is a line of numbers that makes your device identifiable for communication. Your device's IP address should always be unique within a network, and so things can start to go wrong when this isn't the case. Fortunately, you can fix this easily.
Start off simple by restarting your router. This could allow for a reassignment of IP addresses and resolve the conflict issue automatically. Secondly, try removing the static IP address from your device. A static IP address is usually entered manually onto the device. Switching to an automatic or dynamic IP will change your address and make it unique again.
The process of doing this differs depending on the device you're using. Hence, it's best to look up how to remove a static IP for the specific device model you have.
Related: How to Easily Fix the "Server IP Address Could Not Be Found" Google Chrome Error
4. Unplugged Network Cables
This one may seem like a no-brainer, but it's surprisingly common for cables to become loose in their ports and get unplugged while shifting a device. Hence, it's always important to check your network cables on either your device or router before anything else. Coaxial cables, specifically, can sometimes be a little tricky to correctly connect to your router, given that they need to be carefully screwed into the port. So, take time to ensure you've inserted them correctly.
Related: How to Fix a Faulty Ethernet Connection in Windows 10
If you're using a hardwired ethernet connection, make sure the port is correctly connected to both the wall output and your device, and make sure all ethernet cables stemming from your router are also plugged into their ports correctly. It may also be worth checking the ports themselves to ensure that dust and other debris don't affect the connection quality.
5. High Bandwidth Usage
If your router simultaneously connects multiple devices to the internet, you may be at risk of dealing with high bandwidth usage. This happens when one or more devices use up a large proportion of the network's bandwidth. When a device is downloading a significant amount of content from the internet, or when multiple devices are performing actions that require a considerable amount of the network's bandwidth, like streaming or gaming, you'll run into high bandwidth usage.
To solve this issue, first, try disconnecting and reconnecting your router. If this doesn't help, try updating your router's software. To do this, you'll need to connect your router to your device using an ethernet cable and then download the relevant firmware update from the website of your router's manufacturer. You can then use this software to update your router. Make sure you restart your router, or the upgrade won't be successful.
If neither of these methods works, you may need a router to support higher bandwidth usage. It will probably be pricier than your current router, but it will allow you to access better connection speeds without significantly reducing the overall bandwidth usage.
Fix Your Network Issues Within Minutes
Although it may feel like certain network errors are just impossible to get around, there's almost always a relatively quick solution available that can successfully fix the issue at hand. Usually, a couple of clicks or some simple reboots are the answer. Who would've thought?
- Documentation
- Screenshots
- Try for Free
The Monitoring Agent
4 types of Agents to help you measure network and application performance.
Network Device Monitoring
Monitor the health of devices like Firewalls, Routers, Switches, Wifi APs and more.
- Network Performance Monitoring
Monitor network performance to find and fix issues before they affect users.
Public Monitoring Agents Directory
Proactively Monitor network performance with these service providers.
16 Most Common Network Problems: How to Find & Fix Them
Table of contents.
Intermittent network problems frustrate users, affect productivity levels, overwhelm your IT team, and are a pain for network administrators to solve. There are many problems that can affect network performance, and some of them are very complex to identify and understand.
To address these challenges, we've tailored this article specifically towards business networks, focusing on the most common issues that can plague them. Our aim is to help you proactively identify network problems, allowing you to take prompt action to resolve them. By equipping you with valuable insights and troubleshooting techniques, we intend to minimize network downtime and improve overall network performance.
In addition to our comprehensive guide on network problem identification, we understand the significance of real-time monitoring in maintaining a healthy network. With the combined knowledge of identifying network problems proactively and implementing efficient monitoring measures, you'll be empowered to create a robust and reliable network infrastructure.
To help you proactively identify network problems that may be plaguing your network, we’re running you through some of the most common network problems, including how to monitor and troubleshoot them!
What are Network Problems
Laggy video calls, slow application or network speed , buffering downloads, choppy VoIP Quality , and no Internet connection are examples of network problem symptoms. If you're struggling to perform everyday tasks over the Internet, or unable to use important apps, there's a good chance your network is to blame.
Network problems impact things like, VoIP calls, ERP applications (Netsuite or SAP performance issues ), files downloads, and more. Anytime a bad network disconnection or network connection issues prevents you from accessing something outside your computer, you're likely dealing with a network problem.
There are many different network problems that can affect network performance.
Some network problems can arise from faulty hardware, such as routers, switches, firewalls, and even from unexpected usage patterns, like network bandwidth spikes, changes in app configuration, or security breaches.
Network problems are frustrating, and left unattended, they can have disastrous consequences for your business network. That’s why it’s important to understand what can go wrong with your network and to continuously monitor network performance to quickly identify and fix network problems even before they affect your end-users.

Why Network Problems Are Inevitable For Businesses
Modern technology and the increasing use of hosted services has brought major changes to network and application infrastructures. While these changes have equipped users with more functionality than ever before, they have also greatly increased our dependence on a high functioning network to help us ensure the maintenance of these critical applications.
This means that when a network problem or network error occurs, it can be even more disastrous and difficult to solve.Despite our best efforts, these pesky issues tend to sneak their way in and wreak havoc on our connectivity. Here are some of the main reasons why network problems are bound to happen:
- Complexity : Business networks are intricate beasts, with numerous devices, servers, and software working in tandem. The more complex the network, the higher the likelihood of something going awry. Managing all these interconnected components can be challenging, and even the tiniest misconfiguration can lead to network hiccups.
- Human Error : We're all human, and mistakes happen. Whether it's a misconfiguration, a typo in a command, or accidental unplugging of cables, human error is a significant factor behind network problems. No matter how skilled and experienced the IT team is, the occasional oopsie is part of being human.
- Constant Changes : Business networks are dynamic environments, constantly evolving to accommodate new devices, software updates, and expanding user needs. Each change introduces the potential for compatibility issues, security vulnerabilities, and other problems that need to be addressed.
- External Factors : The network's performance can be impacted by external factors like internet service provider (ISP) outages, weather-related disruptions, or even cyberattacks. These external influences are often beyond the control of the business and can cause unexpected network troubles. Increased Network Traffic: As a business grows and gains more users, the network faces increased traffic demands. This surge in activity can strain the network infrastructure , leading to slowdowns and bottlenecks.
- Aging Hardware : Network equipment, like any technology, has a finite lifespan. As hardware ages, it becomes more prone to failures and performance issues. Regular maintenance and upgrades can help mitigate this, but eventually, replacement is inevitable.
- Security Threats : Cyberattacks and security breaches pose a constant threat to business networks. From malware infiltrations to DDoS attacks, these security issues can disrupt network operations and cause considerable downtime.
While network problems are inevitable, they are not insurmountable. With proactive and active network monitoring , regular maintenance, and a skilled IT team, businesses can minimize the impact of these issues and keep their networks running smoothly most of the time.
And knowing which network problems can affect your network the most can help you understand how to identify network issues fast.

How to Identify the Most Common Network Problems With Network Monitoring
When it comes to identifying and troubleshoot the most common network problems bound to pop up in your business' network - you're not alone! The best tool at your disposal is a Network Monitoring software.
A Network Monitoring tool (or Network Performance Monitoring) monitors end-to-end network performance to identify network issues affecting your end-users, whether the problems occur in your local network infrastructure, over the Internet, or even in a service provider's network.
We recommend a software like Obkio Network Performance Monitoring Software because it does the work for you.
Here's a quick overview about how to Use Obkio to identify and troubleshoot the network problems in this article:
Step 1: Set Up Network Monitoring
Obkio Network Monitoring is a simple SaaS solution that allows users to monitor and troubleshoot end-to-end network and application performance to identify network issues, collect network performance data, and improve the end-user experience.Obkio is built to monitor and troubleshoot network problems related to connectivity, performance, VoIP, UC, Internet, network devices and more - for all network types!
Obkio leverages Network Monitoring Agents and synthetic traffic to continuously identify the causes of intermittent VoIP, video, and applications slowdown in seconds - and identify the data you need to troubleshoot and ultimately improve the end-user experience.
Put It to the Test: Trying Is the Ultimate Way to Learn!
Networks may be complex. But Obkio makes network monitoring easy. Monitor, measure, pinpoint, troubleshoot, and solve network problems.
- 14-day free trial of all premium features
- Deploy in just 10 minutes
- Monitor performance in all key network locations
- Measure real-time network metrics
- Identify and troubleshoot live network problems

1.1. Troubleshooting Network Problems for Businesses or Personal Users

Are you a network admin or IT pro looking to troubleshoot network problems for your business, or a personal user trying to solve network issues for your remote work? Whether you need to monitor large networks or single-user workstations, Obkio's network monitoring tool offers plans tailored for you. Find the right plan to help you troubleshoot your network problems and ensure smooth operations.

Step 2: Monitor All Network Locations
Obkio identifies network problems using Monitoring Agents , which are deployed at key network locations and continuously exchange synthetic traffic for synthetic testing . Install Obkio's agents on strategic points within your network, such as routers, switches, or end-user devices. These agents will collect data on various network metrics like latency, packet loss, and bandwidth.
The Agents are deployed in locations like head offices, branch offices, and data centers for end-user experience monitoring , Internet performance, VoIP applications, UC apps, and more. They can also be installed in the Cloud for Cloud Network Monitoring (this can include Microsoft network monitoring , Zoom monitoring , AWS network monitoring , etc.).
Step 3: Measure Network Metrics:
Install Obkio's agents on strategic points within your network, such as routers, switches, or end-user devices. These agents will continuously measure and collect data on various network metrics like latency , packet loss , bandwidth usage , DNS response times, and other crucial performance indicators.
Step 4: Establish Baselines:
Monitor your network's performance under normal conditions to establish baseline metrics. This data will serve as a reference point for identifying deviations from normal behavior.
Step 5: Configure Alerts
Define specific thresholds for each metric, and set up alerts to notify you when a metric exceeds its defined limit. This will enable you to detect anomalies and potential issues in real-time.
Step 6: Investigate Alerts
When an alert is triggered, investigate the issue promptly. Use Obkio's real-time data and historical analysis to pinpoint the problematic area or device.
Step 7: Path Analysis
Utilize Obkio's path analysis feature to assess the performance of different routes taken by network traffic. This helps you identify congested paths and optimize routing.
Step 8: Trend Analysis
Regularly review historical data and performance trends to spot patterns or recurring problems. This analysis can reveal issues that might not be immediately apparent from real-time network monitoring .
Step 9: Collaborate and Resolve
Involve your IT team in the troubleshooting process, using Obkio's visualizations and data to facilitate collaboration. Work together to resolve network problems efficiently.

The Most Common Network Problems
Now let’s run through some of the most common network problems (or network errors) that have left many users and network administrators pulling out their hair!
But worry not, brave troubleshooters, we're not leaving you to wrestle with these issues alone. In addition to discussing each type of network problem, we'll equip you with valuable tips and techniques to identify and troubleshoot them like seasoned network warriors. So for each network problem we'll discuss:
- What the network problem is
- The consequences of that network problem
- The causes of the network problem
- How to identify & troubleshoot the network problem
Network Problem #1. Intermittent Network Problems
Intermittent network problems are a frustrating and common network issue characterized by sporadic disruptions in network connectivity and performance . Unlike consistent or continuous problems, intermittent issues occur irregularly, making them challenging to diagnose and troubleshoot.
These problems can manifest in various ways, including intermittent connection drops, slow data transfer, or periods of complete network unavailability.
I. The Consequences of Intermittent Network Problems:
- Unpredictable Performance : Intermittent issues make network performance unpredictable, leading to inconsistent user experiences.
- Unreliable Connectivity : Users may experience unreliable connectivity, with connections dropping unexpectedly or becoming temporarily unresponsive.
- Productivity Loss : Intermittent network problems can disrupt workflow and lead to productivity losses.
- Difficult Troubleshooting : Diagnosing intermittent issues can be challenging and time-consuming, delaying the resolution process.
This can also lead to network brownouts or Internet brownouts .
II. The Causes of Intermittent Network Problems
- Loose or Damaged Cables : Interference from loose, damaged, or improperly connected network cables can result in intermittent connectivity issues.
- Wireless Interference : Radio frequency interference or signal blockage can lead to intermittent disruptions in Wi-Fi networks.
- Hardware Malfunctions : Intermittent network issues may arise from faulty network devices , such as routers, switches, or network interface cards (NICs).
- Software Conflicts : Software conflicts, outdated drivers, or firmware bugs can cause intermittent disruptions in network communication.
- Overheating : Network devices can experience intermittent issues when they overheat due to inadequate cooling or poor ventilation.
- IP Address Conflicts : Conflicting IP addresses assigned to devices can lead to intermittent connectivity problems.
III. How to Identify and Troubleshoot Intermittent Network Problems
- Network Monitoring : Utilize network monitoring tools like Obkio to continuously track network performance, diagnose network issues , identify patterns of intermittent issues and monitor metrics like network error rate .
- Log Analysis : Examine network device logs to identify any recurring error messages or patterns during periods of intermittent disruptions.
- Cable and Connection Checks : Physically inspect network cables and connections to ensure they are secure and undamaged.
- Device Testing : Test network performance and network devices under different conditions to identify any intermittent hardware malfunctions.
- Software Updates : Ensure that network devices have the latest firmware, drivers, and software updates to fix known bugs and compatibility issues.
- Environmental Assessment : Evaluate the environmental conditions of network devices and ensure they are adequately cooled and placed in suitable locations.
- IP Address Management: Implement IP address management practices to prevent conflicts and ensure proper assignment of IP addresses.
By diligently identifying and addressing intermittent network problems, businesses can create a more stable and reliable network environment, minimizing disruptions and ensuring a consistent user experience. Network monitoring and thorough troubleshooting play a crucial role in detecting and resolving intermittent issues promptly.
Learn how to detect intermittent network problems to troubleshoot performance issues that are hard to catch with Obkio Network Monitoring software.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Intermittent Network Problems
Intermittent network problems can be frustrating and challenging to troubleshoot because they occur sporadically and may not be immediately apparent. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with intermittent network problems:
- Loose or Damaged Cables : Physical issues with network cables, such as loose connections or damaged cables, can lead to intermittent connectivity problems. Inspect cables and connectors for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Wireless Interference : In a wireless network, interference from other wireless devices, neighboring networks, or electronic devices can cause intermittent connectivity issues. Conduct a wireless site survey and identify potential sources of interference.
- DHCP Issues : Problems with the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server can result in intermittent IP address assignment, leading to connectivity problems. Check DHCP logs and ensure the DHCP server is properly configured and responsive.
- DNS Problems : DNS (Domain Name System) issues can cause intermittent access to websites and services. Verify DNS settings and check for any DNS-related errors in the logs.
- Misconfigured Firewall or Security Software : Overly aggressive firewall rules or misconfigured security software can block legitimate traffic and cause intermittent connectivity problems. Review firewall and security software settings for potential issues.
- Bandwidth Saturation : Periodic spikes in network traffic can saturate the available bandwidth and cause intermittent connectivity problems. Monitor network traffic patterns to identify potential bandwidth saturation points.
- Network Device Overheating : Overheating of network devices, such as routers or switches, can lead to intermittent network outages or services outages (ex. Microsoft Teams outages ). Ensure that network equipment is properly ventilated and not subjected to excessive heat.
- Firmware or Software Bugs : Firmware or software bugs in network devices can cause intermittent problems. Check for firmware updates and apply the latest patches from the manufacturer.
- Duplicate IP Addresses : Duplicate IP addresses on the network can result in intermittent connectivity issues. Use network scanning tools to check for duplicate IP addresses.
- Routing Issues : Incorrect or unstable routing configurations can lead to intermittent connectivity problems. Review routing tables and ensure they are correctly configured.
- Power Fluctuations : Power fluctuations or intermittent power supply issues can cause network devices to reboot or lose connectivity. Use uninterrupted power supply (UPS) units to provide stable power to critical network equipment.
- Network Congestion : During periods of high network usage , congestion can cause intermittent performance issues. Monitor network traffic during peak hours and consider implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies.
- Malware or Security Breaches : Malware infections or security breaches can cause intermittent network disruptions. Regularly scan for malware and implement robust security measures.
Network Problem #2. High Bandwidth Usage
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data transmitted over an Internet connection in a given amount of time.
It refers to a network’s capacity to transfer data between devices or the Internet within a given span of time. Bandwidth is often mistaken for Internet speed when it's actually the volume of information that can be sent over a connection in a measured amount of time – calculated in megabits per second (Mbps).
Higher bandwidth allows data to be transferred across your network at a faster rate and can sustain a larger number of connected devices all at once - but it can significantly impact network performance and user experience.
It occurs when a considerable amount of data is being transmitted over the network, leading to increased congestion and potential bottlenecks . When someone or something, like a large application, on your network is monopolizing your bandwidth by downloading gigabytes worth of data, it creates a congestion in your network.
This excessive data transfer can result from various factors, both legitimate and non-legitimate, and it's essential to identify and address the root cause to maintain a smoothly functioning network.

I. The Consequences of High Bandwidth Usage:
- Network Congestion : Network congestion caused by high bandwidth usage, also runs the risk of leaving insufficient amounts of bandwidth for other parts of your network that need it. When this happens, you may start experiencing problems like slow download speed over the Internet.
- Slow Network Performance : High bandwidth consumption can lead to slower network speeds , causing delays in accessing resources and data.
- Latency and Packet Loss : As network resources become saturated, latency (delay) and packet loss may increase, affecting real-time applications like VoIP or video conferencing.
- Reduced Productivity : Sluggish network performance can hamper productivity, as users may experience delays in performing critical tasks.
- Increased Costs : Excessive bandwidth usage can lead to overage charges from internet service providers (ISPs) if they exceed the Internet SLA , or the need to upgrade to higher-tier plans, resulting in higher operational costs. Network Downtime: In extreme cases, high bandwidth usage can lead to network outages if the infrastructure is not equipped to handle the traffic load.
II. The Causes of High Bandwidth
- Large Downloads : Downloads consisting of large files that are being placed on your computer's harddrive from the Internet, like file transfers or backups, can drastically increase bandwidth usage. The more bytes the file contains, the higher your bandwidth usage.
- Latency : Latency refers to the time it takes for a data packet to reach its destination in a network, can. Consistent delays or odd spikes in delay time are signs of major performance issues and can affect bandwidth time.
- Packet Loss : Packet Loss occurs when a data packet is dropped during its journey across a network and never makes it to its final destination and back. It can cause a great deal of problems depending on how much of the packet does not go through and how often it occurs.
- Video Streaming : Streaming videos from the Internet is a more common cause of high bandwidth usage. Streaming video in 7k can take up to 200 times more bandwidth than audio streaming.
- Large Applications : Different applications have different requirements. Applications that require Internet connection, like programs for web development, email, computer games, etc. require a lot of bandwidth to function and can therefore increase your bandwidth usage.
- File Sharing : There are programs that allow users to share files from computer-to-computer connection over the Internet. These programs can result in high bandwidth usage as they require you to download and transfer large files, with large amounts of data, over the Internet.
- Legitimate Traffic : Legitimate high-bandwidth activities, such as large file transfers, video conferencing, cloud backups, and software updates, can consume significant network resources. While these activities are essential for business operations, they can lead to congestion during peak usage times.
- Malware and Unauthorized Activities : Malicious software or unauthorized users can exploit network resources, leading to unanticipated spikes in bandwidth usage. Botnets, malware downloads, or unauthorized file sharing can cause significant disruptions.
- Background Updates : Automatic updates for operating systems, applications, and antivirus software can utilize bandwidth without user intervention. These updates can coincide and cause temporary surges in bandwidth usage.
- P2P File Sharing : Peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing applications can lead to high bandwidth usage as users upload and download files directly from each other.
How to measure bandwidth, identify issues & optimize network performance. Use Obkio's Network Performance Monitoring tool for easy bandwidth monitoring.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot High Bandwidth Usage
- Network Monitoring : Use a network monitoring tool like Obkio to measure bandwidth and track bandwidth usage in real-time. Observe usage patterns and identify any unusual spikes or sustained high traffic.
- Application Analysis : Analyze the bandwidth consumption of various applications to identify resource-intensive processes. This will help you pinpoint which applications are contributing the most to high usage.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Policies : Implement QoS policies to prioritize critical applications and services over less important ones. This ensures that essential operations receive sufficient bandwidth even during peak usage.
- Bandwidth Optimization : Utilize bandwidth optimization techniques such as compression, caching, or content filtering to reduce overall data transfer.
- Traffic Shaping : Employ traffic shaping mechanisms to control and limit bandwidth usage for specific applications or users.
- Identify Malware or Unauthorized Activity : Regularly scan for malware and unauthorized users on the network, and implement security measures to prevent exploitation.
By proactively identifying and addressing high bandwidth usage, businesses can maintain a responsive and efficient network, enhancing overall productivity and user satisfaction.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for High Bandwidth Usage
High bandwidth usage can lead to various network performance issues and can be caused by several factors. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to investigate when experiencing high bandwidth usage:
- Malware or Botnet Activity : Malware-infected devices or botnet activity can consume significant bandwidth as they may be involved in malicious activities such as sending spam emails or participating in Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Use network monitoring tools to identify suspicious traffic patterns and isolate infected devices.
- Streaming and Video Content : High-quality video streaming or large file downloads can consume substantial bandwidth. Check for excessive video streaming or downloads that might be impacting the network, especially during peak hours.
- Cloud Services or Backups : Cloud services and data backups can utilize substantial bandwidth, especially if they are scheduled to occur during business hours. Check the bandwidth consumption of cloud services (with Microsoft Cloud Monitoring for example) and backup applications to see if adjustments can be made to their schedules.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) File Sharing : P2P file sharing applications can consume a significant amount of bandwidth, especially if multiple users are involved. Identify and control P2P traffic on the network.
- Software Updates : Automatic software updates from operating systems and applications can lead to sudden spikes in bandwidth usage. Ensure that updates are scheduled during off-peak hours.
- Network Misconfiguration : Misconfigured network devices, such as routers or switches, can lead to unnecessary broadcast/multicast traffic or loops that cause high bandwidth usage. Verify the network configuration for any issues.
- Bandwidth-Intensive Applications : Some applications inherently consume more bandwidth than others. Identify and analyze bandwidth usage by specific applications and determine if any optimization or restriction is required.
- Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) : Improperly configured VLANs can lead to unnecessary traffic and high bandwidth usage. Review VLAN configurations to ensure they are set up correctly.
- Wireless Network Interference : In a wireless network, interference from other devices, neighboring networks, or non-Wi-Fi devices operating in the same frequency range can cause high bandwidth utilization. Perform a wireless site survey and optimize Wi-Fi settings.
- Data Backups and Replication : Data backup and replication processes between geographically dispersed sites can consume significant bandwidth. Review backup and replication schedules and consider using deduplication and compression techniques.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks : DoS attacks can overwhelm a network with an excessive amount of traffic, leading to high bandwidth usage. Implement DoS protection mechanisms and analyze traffic patterns for signs of an ongoing attack.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices : The proliferation of IoT devices can contribute to increased bandwidth consumption if they are transmitting large amounts of data. Monitor IoT device traffic and assess their impact on overall bandwidth.
To troubleshoot high bandwidth usage, it is essential to use network monitoring tools that provide insights into traffic patterns, application usage, and device behaviour, like we mentioned in the last point. With this information, you can identify the root cause of the problem and take appropriate measures to optimize network performance.
Network Problem #3. High CPU Usage
CPU, or “ Central Processing Unit ”, is the primary component of a computer that receives and processes instructions for operating systems and applications.
High CPU usage is another common network problem that can significantly impact the performance and stability of a network. It occurs when the central processing unit (CPU) of a network device, such as a router, switch, firewall, or server, is operating at or near its maximum capacity . This can lead to various issues that affect the overall network functionality and user experience.
With such a big job on its shoulders, the signs of high CPU usage on a network device are a very troubling sign for many of us. As your network devices continue to work harder to perform an increasing amount of tasks, it increases the chance that things can go wrong.

I. The Consequences of High CPU Usage
- Sluggish Network Performance : High CPU usage can lead to delays in processing network traffic, causing slow response times and increased latency.
- Packet Loss : When the CPU is overloaded, it may drop packets, resulting in packet loss, which can degrade the quality of real-time applications like VoIP or video conferencing.
- Network Downtime : In extreme cases, when the CPU is overwhelmed, the device may become unresponsive, leading to network outages and disruptions.
- Security Vulnerabilities : High CPU usage can leave network devices more vulnerable to security threats as their ability to handle security tasks is compromised.
II. The Causes of High CPU Usage
The most common reason for high CPU usage occurs when your network becomes bogged down by enormous amounts of traffic. CPU usage can increase drastically when processes require more time to execute or when a larger number of network packets are sent and received throughout your network.
There are a number of network devices such as switches that have hardware components (ASICs or NPUs) that take charge and process packets super quickly. For this equipment, the CPU usage is not linked to the amount of traffic.
For equipment that analyzes or manipulates traffic, like firewalls, that's a whole different story. Depending on the features that you’ve enabled on your devices, the CPU may be in the critical path of packet routing or forwarding. If overused, network metrics like latency , jitter , and packet loss will increase, which will lead to significant levels of network performance degradation.
In summary, some common causes include:
- Network Traffic Overload : A sudden surge in network traffic or sustained high levels of data transfer can overwhelm the CPU, especially on devices handling routing, switching, or security tasks.
- Network Security Operations : CPU usage may spike during security-related activities such as deep packet inspection, intrusion detection, or denial-of-service attack mitigation.
- Resource-Intensive Applications : CPU usage can be driven up by resource-intensive applications running on servers or other network devices.
- Firmware/Software Bugs : Firmware or software bugs can cause abnormal CPU usage, leading to unexpected behavior and degraded performance.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot High CPU Usage
It can sometimes be difficult to gather the right information about the actual use of CPU. Several monitoring tools such as those included in the equipment's GUI or a poorly configured monitoring tool can report an average value on the use of 8 cores or over too long periods, such as every 5, 15 or 60 minutes. Which isn't enough - so to identify and troubleshoot - you need to go further!
- Network Monitoring : Employ a network monitoring tool like Obkio to track CPU utilization on network devices. Monitor CPU usage in real-time and set up alerts for abnormally high CPU levels.
- Identify Resource-Intensive Processes : Use monitoring tools and device logs to identify resource-intensive processes or applications causing high CPU usage.
- Adjust Network Traffic : Implement traffic shaping or quality of service (QoS) policies to prioritize critical traffic and prevent CPU overload during periods of heavy network usage.
- Software/Firmware Updates : Regularly update device firmware and software to patch bugs and optimize performance.
- Optimize Applications : Consider optimizing resource-intensive applications or distributing their load across multiple devices to reduce CPU burden.
- Security Measures : Ensure that security policies and mechanisms are properly configured to manage security-related CPU tasks effectively.
- Device Upgrades : If network devices are consistently experiencing high CPU usage, consider upgrading to more powerful hardware that can better handle the network load.
By promptly identifying and resolving high CPU usage issues, businesses can maintain a stable and responsive network environment, ensuring smooth operations and enhanced user satisfaction.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for High CPU Usage
High CPU usage in a network can impact the performance of network devices, leading to sluggish response times, increased latency, and potential service disruptions. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with high CPU usage on network devices:
- Traffic Spikes : Monitor network traffic patterns to identify if there are sudden spikes in data volume that could be causing high CPU usage. Investigate the source of the increased traffic and determine if it is legitimate or if it indicates a potential DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack.
- Packet Storms or Broadcast Storms : Excessive packet storms or broadcast storms can overload the CPU of network devices. Use packet capture tools to analyze the traffic and identify any sources of storms.
- Malware or Botnet Activity : Malware infections on network devices can cause high CPU utilization as they might be involved in malicious activities. Use security monitoring tools to detect and remove malware from affected devices.
- Routing or Switching Loops : Misconfigured or redundant routing or switching paths can cause loops, leading to a significant increase in CPU usage. Review the device configurations to ensure there are no loop-causing issues.
- Software Bugs or Memory Leaks : Software bugs or memory leaks within the operating system or network device firmware can cause CPU usage to spike over time. Ensure that the network devices have the latest firmware updates and patches.
- Network Device Overloading : If a network device is overloaded with traffic due to the number of connected devices or the volume of data being processed, the CPU usage can increase. Consider load balancing or upgrading the device to handle higher traffic volumes.
- Large Scale Routing Updates : In networks with dynamic routing protocols, large-scale routing updates can cause CPU spikes on routers. Analyze routing update events and fine-tune the routing protocols to minimize the impact.
- Monitoring or Debugging Tools : Certain monitoring or debugging tools running on network devices might consume a significant amount of CPU resources. Evaluate the impact of such tools and adjust their configurations if necessary.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Misconfiguration : Improperly configured QoS policies can lead to unnecessary CPU usage as the devices attempt to classify and prioritize traffic. Review and optimize QoS policies.
- Hardware Issues : Faulty hardware components, such as failing CPUs or inadequate cooling systems, can lead to high CPU usage. Perform hardware diagnostics and replace any faulty components.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) : IDS/IPS systems can be CPU-intensive, especially when handling a large number of network packets. Fine-tune the IDS/IPS settings and consider distributing the load across multiple devices if applicable.
- Virtualization Overhead : In virtualized environments, the hypervisor's CPU overhead can impact network device performance. Adjust virtualization settings and resource allocations as needed.
Uncover the secrets of measuring CPU usage in networking. Navigate high seas of performance with insights. Optimize with Obkio's Monitoring tool.
Network Problem #4. Physical Connectivity Issues
It may seem obvious, but some network issues may occur with the hardware outside of the network.
When the time comes to troubleshoot network issues , our instinct is often to think about the most complex situations, when sometimes the problem is actually very simple and right in front of us.
Hardware problems like defective cables or connectors can generate network errors on the network equipment to which it is connected . You may think that this problem is due to a network outage or network failure , or Internet connection problem, but it’s actually because you have a broken or malfunctioning cable.
This can also occur outside of the LAN network . If a copper cable, or fiber-optic cable is damaged, it will likely reduce the amount of data that can go through it without any packet loss.
I. The Consequences of Physical Connectivity Issues
Physical connectivity problems can manifest in various ways, leading to network outages, slow data transfer, or intermittent connectivity.
- Network Outages : A complete loss of physical connectivity can lead to network outages, preventing users from accessing network resources.
- Intermittent Connectivity : Loose or damaged cables may cause intermittent connectivity issues, resulting in unreliable network access.
- Slow Data Transfer : Poor physical connections can lead to data transmission errors and retransmissions, slowing down data transfer rates.
- Increased Downtime* : The time spent identifying and resolving physical connectivity issues can lead to increased network downtime and reduced productivity.
II. The Causes of Physical Connectivity Issues
- Loose or Damaged Cables : Loose, damaged, or improperly connected cables can lead to signal loss and intermittent connectivity. Cables that are bent, frayed, or crushed may not transmit data effectively.
- Faulty Connectors : Connectors that are not securely attached or have bent pins can result in poor connections between devices, leading to data transmission issues.
- Cable Length : Using cables that exceed their maximum recommended length can lead to signal degradation and data loss.
- Poorly Crimped or Terminated Cables : Improperly crimped or terminated cables may cause signal interference and connectivity problems.
- Network Device Issues : Faulty network interface cards (NICs) or malfunctioning ports on switches or routers can cause physical connectivity problems.
- Environmental Factors : External factors such as water damage, extreme temperatures, or physical disturbances can impact network cables and connectors.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Physical Connectivity Issues
- Network Monitoring : Checking every cable one by one can be repetitive, and can take a large amount of time out of your day. A simple way to monitor cables on a defective connector is to have a network performance monitoring software , like Obkio, that will measure network errors on all network interfaces and warn you if any problems arise.
- Visual Inspection : Perform a physical inspection of cables, connectors, and network devices to identify any visible signs of damage or loose connections.
- Cable Testing : Use cable testers to check for continuity and proper termination of network cables. Swap Cables and Connectors: If possible, try replacing suspect cables and connectors with known-good ones to determine if the issue persists.
- Check Device Indicators : Examine network device indicators, such as LED lights, to see if they indicate any connectivity or link issues.
- Environmental Assessment : Ensure that network equipment is kept in suitable environmental conditions, free from water damage, extreme temperatures, and physical obstructions.
- Label and Organize Cables : Properly label and organize network cables to prevent accidental disconnections and make troubleshooting easier.
- Update Firmware and Drivers : Ensure that network devices have up-to-date firmware and drivers to minimize the risk of hardware-related issues.
Learn how to troubleshoot network issues by identifying where, what, why network problems occur with Network Troubleshooting tools.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Physical Connectivity Issues
Physical connectivity issues can disrupt network communication and lead to various network problems. Troubleshooting physical connectivity issues requires a systematic approach and attention to detail. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with physical connectivity issues:
- Check Physical Connections : Verify that all network cables, connectors, and ports are properly connected and securely seated. Ensure that Ethernet cables are not damaged and have all pins intact.
- Swap Cables and Ports : If possible, swap suspect cables with known-working ones and test different network ports on the devices to rule out faulty cables or ports.
- Check Link Lights : Observe the link lights on network devices (routers, switches, and network interface cards) to determine if the devices are detecting link signals. If link lights are not active, it could indicate a physical connectivity problem.
- Inspect Patch Panels and Wall Outlets : In structured cabling systems, examine patch panels and wall outlets to ensure cables are correctly terminated and properly labeled.
- Use Cable Testers : Cable testers can help identify faulty cables, open circuits, or short circuits. Use a cable tester to check the integrity of network cables.
- Check Power Over Ethernet (PoE) : For PoE devices, ensure that power is being supplied correctly over the Ethernet cables.
- Verify Power Status : Check the power status of network devices to ensure they are powered on and functioning correctly.
- Check Physical Damage or Environmental Factors : Look for physical damage to network cables caused by bending, crushing, or exposure to environmental elements. Address any environmental factors that might be affecting the cables, such as excessive heat or moisture.
- Review Network Topology : Review the network topology to ensure that cables are appropriately connected between devices and network segments.
- Test Connectivity with Known Devices : Test connectivity with known working devices to isolate the issue to specific network segments or components.
- Check Wiring Standards : Ensure that network cabling adheres to appropriate wiring standards (e.g., TIA/EIA 568) and that cables are of the correct category (e.g., Cat 5e, Cat 6, etc.) for the required network speeds .
- Check Cable Lengths : Verify that the cable lengths do not exceed the maximum allowed length for the chosen cable category and network technology (e.g., Ethernet has specific cable length limits).
- Inspect Network Devices' LEDs : Network devices like switches and routers often have LEDs that indicate port activity and speed. Observe these LEDs to identify any abnormal behavior.
- Check Physical Security : Ensure that physical access to network devices and cables is restricted to authorized personnel to prevent accidental or intentional disconnections.
- Consider EMI/RFI Interference : Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) or Radio-Frequency Interference (RFI) from nearby electrical devices can affect network connectivity . Isolate network devices from potential sources of interference.
- Inspect Fiber Optic Connections : If your network uses fiber optic cables, check the connectors and fiber ends for any dirt, damage, or misalignment.
Network Problem #5. Malfunctioning Devices or Equipment
Sometimes, network issues occur within network equipment or devices like Firewalls, Routers, Switches, Wifi APs.
Malfunctioning devices or equipment are a common network problem that can disrupt network operations and lead to various connectivity issues. This category encompasses hardware failures or malfunctions within network devices, such as routers, switches, firewalls, servers, or network interface cards (NICs) . When devices malfunction, they may experience performance degradation or cease to function altogether, impacting the overall network performance and user experience.
You need to ensure that all the devices on your network are configured correctly in order for your network to work properly. Whenever you install or reconfigure a device, or upgrade equipment firmware on your network, you need to test that device to ensure that it’s been configured correctly.
Many network performance issues are caused by device misconfigurations that can affect different parts of your network and turn into major problems down the line. That’s why you need to pay attention to all the switches and devices on your network to ensure that they’re always working as they should be, and react quickly if they aren’t.
I. The Consequences of Malfunctioning Devices or Equipment
- Network Downtime : When crucial network devices fail, it can result in network outages and disrupt communication and data transfer.
- Slow Performance : Malfunctioning devices may struggle to process network traffic efficiently, leading to slow data transfer and increased latency.
- Data Loss : Hardware failures can cause data loss, especially if the malfunctioning device is responsible for data storage or backups.
- Reduced Reliability : Frequent device malfunctions erode the network's reliability, causing frustration for users and hindering business operations.
II. The Causes of Malfunctioning Devices or Equipment
- Hardware Failure : Components within network devices can fail due to wear and tear, manufacturing defects, or age. Common hardware failures include power supply issues, memory failures, or fan malfunctions.
- Overheating : Network devices that are not adequately cooled or positioned in poorly ventilated areas can overheat, leading to malfunctions and performance degradation.
- Software Bugs : Firmware or software bugs within network devices can cause erratic behavior or crashes, impacting their ability to function correctly.
- Power Surges or Electrical Issues : Power surges or electrical problems can damage network devices and render them inoperable.
- Environmental Factors : Adverse environmental conditions, such as exposure to moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures, can contribute to device malfunction.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Malfunctioning Devices or Equipment
- Network Device Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio to track device performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and temperature readings. Abnormal values may indicate potential device malfunctions. Obkio’s network device monitoring solution is a simple and easy solution that offers advanced polling for SNMP Monitoring for all SNMP-enabled devices along your network to ensure they’re all performing as they should be.
- Device Logs : Review device logs and error messages to identify any hardware or software-related issues reported by the device.
- Hardware Diagnostics : Many network devices come with built-in diagnostic tools that can identify hardware failures or malfunctions.
- Hardware Replacement : If a device is suspected to be malfunctioning, consider replacing it with a known-working spare or a new device to confirm if the issue is resolved.
- Firmware/Software Updates : Ensure that devices have the latest firmware and software updates to fix known bugs and optimize performance.
- Temperature Management : Check the environmental conditions of network devices and ensure they are adequately cooled and placed in suitable locations.
- Power Protection : Implement surge protectors and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems to safeguard devices against electrical issues.
By proactively identifying and addressing malfunctioning devices or equipment, businesses can reduce network downtime, maintain reliable operations, and ensure an efficient and responsive network infrastructure.
Learn how to identify network issues by looking at common problems, causes, consequences and solutions.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Malfunctioning Devices or Equipment
When dealing with malfunctioning network devices or equipment, prompt troubleshooting is essential to identify and resolve the issues efficiently. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when facing malfunctioning devices or equipment:
- Device Power Status : Check if the malfunctioning device is powered on and receiving adequate power. Verify power connections and consider testing the device with a different power source or power cable.
- Device Reset or Reboot : Perform a controlled restart or reboot of the malfunctioning device. Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve temporary issues.
- Check Device Status Lights : Observe the status lights or LEDs on the malfunctioning device to identify any error codes or abnormal behavior. Refer to the device's documentation for guidance.
- Verify Firmware/Software Versions : Ensure that the device's firmware or software is up to date. If available, apply the latest firmware updates or patches from the manufacturer's website.
- Inspect Device Logs : Review the device logs to identify any error messages or alerts that might indicate the cause of the malfunction.
- Device Configuration : Verify the device configuration to ensure it aligns with the network's requirements and network monitoring best practices . Look for misconfigurations or conflicting settings.
- Isolate Device from the Network : Temporarily disconnect the malfunctioning device from the network to determine if it is the cause of broader network issues.
- Test Connectivity and Cable : Check the connectivity of the malfunctioning device by testing it with a known-working cable and connecting it to a different network port.
- Temperature and Ventilation : Overheating can cause devices to malfunction. Ensure that the device has adequate ventilation and is not exposed to excessive heat.
- Test with Different Ports : If the device has multiple ports, test with different ports to check for faulty hardware on specific interfaces.
- Check for Hardware Faults : Examine the device's physical components for any signs of damage or hardware faults.
- Reinstall or Reset Device : If appropriate, consider reinstalling or performing a factory reset on the malfunctioning device to rule out software-related issues.
- Device Interoperability : Verify if the malfunctioning device is compatible with other devices on the network. Ensure that it supports required protocols and standards.
- Replace or Repair Faulty Components : If hardware components are found to be faulty, consider replacing or repairing them.
- Check for Environmental Factors : Determine if the malfunction could be caused by environmental factors such as electromagnetic interference or power fluctuations.
- Update Drivers : For network interface cards and other peripheral devices, update drivers to the latest versions to address potential compatibility issues.
- Verify Network Connectivity : Confirm that the malfunctioning device is connected to the correct network and VLAN (if applicable).
- Seek Vendor Support : If the issue persists or is beyond your troubleshooting capabilities, contact the vendor's technical support for further assistance.
Always document the troubleshooting steps and any changes made to the device or network during the process. Thorough documentation helps in future reference and sharing information with others who might be assisting with the troubleshooting process.
Network Problem #6. DNS Issues
DNS or Domain Name System, controls how visitors find your website over the Internet.
It is essentially a directory for the Internet (and every Internet-connected device) that matches domain names with IP addresses. Every single website has its own IP address on the web, and computers can connect to other computers via the Internet and look up websites using their IP address. When you type in a domain name in your Internet browser, DNS works to find the information connected to that domain.
DNS issues are very common network problems that many people tend to overlook. DNS issues occur when you are unable to connect to an IP address, signalling that you may have lost network or Internet access . For example, your site can simultaneously appear online for you, but looks to be offline to your visitors.
When DNS issues arise, users may experience difficulties accessing websites, sending emails, or connecting to network resources.
I. The Consequences of DNS Issues
The inability to access the Internet or particular sites can have a very immediate and negative impact on your business - especially if it means that users cannot access your site. Just a few hours offline can cost your company in more ways than one, which is why it’s important to find and fix DNS problems as soon as possible.
- Website Inaccessibility : Users may be unable to access websites or services due to failed DNS resolutions.
- Email Delivery Issues : DNS problems can affect email delivery, causing delays or preventing emails from being sent or received.
- Slow Internet Browsing : DNS lookup delays can result in sluggish website loading times and overall slow internet browsing experiences.
- Security Risks : DNS hijacking or cache poisoning can lead to security vulnerabilities, exposing users to phishing attacks or other malicious activities
II. The Causes of DNS Issues
- Bad Configurations: You may experience issues due to improper configuration of DNS records .
- High DNS Latency: High Latency, which is the measure of time it takes for data to reach its destination across a network, can cause slow and abnormally long loading times.
- High TTL Values: High “time to live” values on your records, will lead to high propagation wait times. Traceroute tools, like Obkio’s Live Traceroutes feature and Obkio Vision Visual Traceroue tool , actually track and monitor TTL values.
- Hardware/Network Failures: DNS problems can be caused by hardware failures on the host machine or network failures. Troubleshoot network/ hardware configuration settings using a network performance monitoring tool to identify the source of the problem.
- DNS Server Outages : If the DNS server responsible for resolving domain names becomes unavailable or experiences downtime, users will be unable to access websites or services.
- Misconfigured DNS Settings : Incorrectly configured DNS settings on network devices or client systems can lead to failed DNS lookups.
- DNS Cache Poisoning : Malicious actors can compromise DNS caches, leading to incorrect or spoofed DNS records being served, redirecting users to malicious websites.
- Network Connectivity Issues : Internet connectivity issues or problems or routing can prevent DNS queries from reaching DNS servers or receiving responses and lead to network connectivity issues
- DNS Propagation Delays : After making changes to DNS records, it can take time for the changes to propagate across the internet. During this period, users may experience inconsistent DNS resolution.
- DNS Hijacking : Cyber attackers may hijack DNS queries to redirect users to fraudulent websites or phishing pages.

III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot DNS Issues
- DNS Monitoring : Utilize network monitoring tools like Obkio to track DNS queries and response times. Monitor DNS servers' performance and ensure they are resolving queries promptly.
- DNS Testing Tools : Use DNS testing tools to check the network response time and accuracy of DNS queries from different locations.
- Flush DNS Cache : On client systems, flush the DNS cache to clear any outdated or corrupted entries that may be causing issues.
- Check DNS Server Status : Verify the status of DNS servers to ensure they are operational and responsive.
- Review DNS Settings : Check DNS settings on network devices, routers, and client systems for any misconfigurations.
- DNSSEC Implementation : Consider implementing DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) to prevent DNS cache poisoning and improve DNS security.
- Monitor DNS Logs : Review DNS server logs for any unusual activities or error messages that may indicate issues.
- Update DNS Records : Ensure that DNS records are correctly updated and propagated across authoritative DNS servers.
By proactively identifying and resolving DNS issues, businesses can ensure smooth and reliable access to online resources, improve internet browsing experiences, and enhance overall network security.
Learn how to troubleshoot intermittent Internet connection issues with Network Monitoring. Find & fix the cause of intermittent Internet issues.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for DNS Issues
DNS (Domain Name System) issues can cause various network problems, including the inability to access websites, email services, or other network resources. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with DNS issues:
- Ping and Traceroute : Use the ping and traceroute commands to verify DNS resolution. If you can ping IP addresses but not domain names, it indicates a DNS resolution problem.
- Check DNS Server Settings : Verify that the DNS server settings on the client devices are correct. Ensure that they are pointing to the appropriate DNS servers, such as those provided by the ISP or internal DNS servers.
- DNS Server Reachability : Check if the DNS servers are reachable from the client devices. Use ping to confirm if the DNS servers respond to requests.
- Flush DNS Cache : Clear the DNS cache on the client devices to ensure they fetch fresh DNS records from the DNS servers.
- DNS Server Logs : Analyze the DNS server logs for errors or issues. Look for failed DNS requests or unusual patterns.
- DNS Forwarding and Recursion : Ensure that DNS servers are properly configured for forwarding and recursion. Misconfigured forwarding can lead to failed DNS resolution.
- DNSSEC Validation : If DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) is enabled, check for DNSSEC validation issues that might prevent resolution for some domains.
- Check DNS Records : Verify the DNS records for the domain in question (A, CNAME, MX, etc.) to ensure they are correctly configured.
- Firewall and Filtering : Review firewall rules and content filtering settings that might block DNS traffic or DNS resolution.
- ISP DNS Issues : Contact the Internet Service Provider (ISP) to check if there are any DNS issues or outages in their DNS infrastructure.
- DNS Load Balancing : If using DNS-based load balancing, ensure that it is working correctly and directing traffic to the appropriate servers.
- DNS Round Robin : If DNS round-robin is used, verify that all the IP addresses in the DNS response are functional.
- Reverse DNS Lookup : Check reverse DNS lookup (PTR) records to ensure they match the corresponding forward (A) records.
- DNS Timeouts : Monitor for DNS timeouts in application logs or network captures, which may indicate DNS server unresponsiveness.
- DNS Hijacking or Spoofing : Investigate for any signs of DNS hijacking or spoofing, which could redirect users to malicious websites.
- DNS Over HTTPS (DoH) or DNS Over TLS (DoT) : If DoH or DoT is implemented, verify the configuration and connectivity to the chosen secure DNS resolver.
- IPv6 DNS Configuration : Ensure that DNS resolution works correctly for both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
- Third-Party DNS Services : If using third-party DNS services, verify their service status and reachability.
- DNS Health Check Tools : Utilize DNS health check tools or online DNS diagnostics to assess DNS configuration and performance.
By systematically troubleshooting DNS issues, you can identify and resolve the root cause of the problem, ensuring smooth DNS resolution and proper network connectivity. If the issue persists or is beyond your expertise, don't hesitate to seek assistance from qualified network administrators or DNS experts.
Network Problem #7. Interference in the Wireless Network
WiFi problems are one of the most common complaints surrounding modern day connectivity.
Interference in the wireless network is a common and frustrating network problem that can significantly impact Wi-Fi performance and reliability. Wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi, rely on radio frequencies to transmit data between devices. Interference occurs when other devices or signals disrupt this communication, leading to slow or unreliable wireless connections .
Several factors contribute to wireless interference, and identifying and mitigating these issues is crucial for maintaining a stable wireless network.
Signs of wireless interference include:
- Low signal strength even when close to a WiFi broadcast device
- Slower Internet connection when using connected over WiFi
- Slow file transfers between computers over WiFi
- Inability to pair WiFi or Bluetooth devices even when in proximity to the receiver
- Intermittently dropping of WiFi connection
I. The Consequences of Interference in the Wireless Network
- Slow Data Transfer : Interference can lead to a variety of Internet problems like slow data transfer rates and reduced Internet speeds, affecting productivity and user experience.
- Connection Drops : Wireless interference can cause frequent disconnections or dropped connections, disrupting ongoing tasks and communication.
- Unreliable Connectivity : Users may experience intermittent connectivity issues, making it challenging to access network resources consistently.
- Reduced Coverage : Interference can result in reduced Wi-Fi coverage, creating dead spots where wireless signals are weak or nonexistent.
II. The Causes of Interference in the Wireless Network
Very common household items, like microwave ovens or cordless phones, can slow down your home Wi-Fi network performance. If you live in a densely populated area, your neighbors’ Wi-Fi networks could actually be interfering with your own. This is particularly true if you’re using a 2.4GHz wireless router.
Seeing as a failure can occur at any time, the first challenge for network administrators is to quickly identify what can cause interference as well as the precise time they occurred.
- Overlapping Wi-Fi Channels : In environments with multiple Wi-Fi networks, overlapping channels can lead to interference as signals interfere with each other.
- Physical Obstructions : Physical obstacles like walls, floors, and large objects can attenuate Wi-Fi signals, reducing signal strength and causing interference.
- Electronic Devices : Other electronic devices operating on similar frequencies, such as cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and microwaves, can cause interference.
- Nearby Access Points : When multiple access points are in close proximity, they can interfere with each other's signals, especially if they are on the same or overlapping channels.
- Signal Reflection and Refraction : Wi-Fi signals can reflect off surfaces or refract through materials, creating signal interference and dead zones.
III. How to Identify and Troubleshoot Interference in the Wireless Network
While users are usually quick enough to report problems, it’s ideal to identify and solve the problem before it affects users.
- Real-Time Network Monitoring : Utilize network monitoring tool, like Obkio for real-time network monitoring to track Wi-Fi performance in real-time and detect sudden drops in signal strength or connectivity issues that may indicate interference.
- Wi-Fi Site Surveys : Conduct site surveys using Wi-Fi analysis tools within the network monitoring platform to identify signal strength, coverage areas, and potential interference sources.
- Channel Analysis : Utilize network monitoring tools to analyze Wi-Fi channel utilization and identify crowded or overlapping channels that may be contributing to interference.
- Signal Strength Testing : Measure Wi-Fi signal strength across different areas of the workspace using network monitoring tools to identify weak or strong signal zones.
- Device Interference Check : Identify and isolate devices or equipment that may be causing wireless interference, using network monitoring to detect their presence and impact on Wi-Fi performance.
- Automated Alerts : Set up automated network monitoring alerts within the network monitoring tool to be notified immediately when Wi-Fi interference is detected, allowing for quick investigation and resolution.
- Historical Analysis : Utilize historical data provided by the network monitoring platform to identify patterns of interference and assess the effectiveness of previous troubleshooting efforts.
- Network Topology Mapping : Use network monitoring tools or network observability tools to create visual representations of the network topology, helping identify potential physical obstructions or sources of interference.
By leveraging network monitoring alongside these troubleshooting approaches, businesses can proactively identify and address wireless interference, ensuring a more reliable and efficient Wi-Fi network. Network monitoring provides real-time insights, historical data, and automated alerts, empowering IT teams to promptly resolve interference issues and optimize wireless performance for enhanced user satisfaction.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Interference in the Wireless Network
Interference in a wireless network can cause signal degradation, reduced throughput, and disconnections. Troubleshooting wireless interference requires careful analysis and mitigation strategies. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with interference in a wireless network:
- Physical Obstructions: Identify and remove or reposition physical obstructions such as walls, furniture, metal objects, or large appliances that may block or attenuate the Wi-Fi signal.
- Neighboring Wi-Fi Networks : Use a Wi-Fi analyzer tool to identify nearby Wi-Fi networks and the channels they are operating on. Choose a less congested channel for your wireless network to reduce interference.
- Microwave Ovens and Cordless Phones : Microwave ovens and some cordless phones operate in the same frequency range as Wi-Fi networks (2.4 GHz). Keep Wi-Fi access points away from these devices to minimize interference.
- Bluetooth Devices : Bluetooth devices can cause interference with Wi-Fi networks, especially in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Separate Bluetooth devices from Wi-Fi access points or use Wi-Fi channels that are far from Bluetooth frequencies.
- Electronic Devices : Identify and relocate electronic devices that emit electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio-frequency interference (RFI), such as baby monitors, wireless cameras, or wireless speakers.
- Dual-Band Wi-Fi Devices : If possible, use dual-band Wi-Fi devices that can operate in both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. The 5 GHz band is typically less congested and offers better performance.
- Wi-Fi Signal Strength : Check the Wi-Fi signal strength at different locations within the coverage area to identify areas with weak signals that might be susceptible to interference.
- Wi-Fi Access Point Placement : Optimize the placement of Wi-Fi access points to achieve better coverage and reduce dead zones. Consider using Wi-Fi range extenders or mesh systems for larger areas.
- Wi-Fi Signal Overlapping : Avoid overlapping Wi-Fi signal coverage from multiple access points, as it can lead to interference. Adjust access point transmit power or channel settings to minimize overlap.
- Rogue Wi-Fi Devices : Look for rogue Wi-Fi access points or devices that might be interfering with your network. Use wireless intrusion detection systems (WIDS) to identify unauthorized devices.
- DFS Channels (5 GHz) : In the 5 GHz band, some channels require Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) due to radar detection requirements. Ensure your devices support DFS and are using appropriate DFS channels.
- WLAN Optimization : Use Wi-Fi optimization techniques such as band steering and airtime fairness to balance client connections and reduce interference.
- Wireless Site Survey : Perform a wireless site survey to assess the overall wireless environment and identify potential sources of interference.
- Quality of Service (QoS) : Implement QoS policies to prioritize critical Wi-Fi traffic and minimize the impact of non-essential traffic on network performance.
- Regular Monitoring : Continuously monitor Wi-Fi performance, interference levels, and client connectivity to detect and address issues proactively.
- Firmware Updates : Keep Wi-Fi access points and wireless devices' firmware up to date to take advantage of performance improvements and bug fixes.
By systematically troubleshooting wireless interference, you can optimize your Wi-Fi network's performance and deliver a more reliable wireless experience to users. Use appropriate network monitoring and diagnostic tools, like we mentioned in the section above, to analyze Wi-Fi performance and make informed decisions during the troubleshooting process.
Network Problem #8. Network Congestion
Network congestion is a prevalent network problem that occurs when there is an excessive amount of data traffic on the network, leading to congestion or bottlenecking . It can happen at various points in the network, such as routers, switches, or network links, where the capacity to handle data becomes overwhelmed by the volume of incoming traffic.
Network congestion can result from increased data demands, inefficient network configurations, or inadequate bandwidth allocation, and it can significantly impact the overall network performance and user experience.

I. The Consequences of Network Congestion
Network congestion can have severe ramifications on network performance and user experience. Let's go over the impact of congestion, including:
- Slow Data Transfer : Network congestion can result in slower data transfer rates, leading to delays in accessing resources and data.
- Latency and Packet Loss : Congestion can cause increased latency (delays) and packet loss, affecting real-time applications such as video conferencing or online gaming.
- Dropped Connections : Congestion can cause connections to drop or time out, resulting in failed file transfers or disrupted communication.
- Reduced Productivity : Sluggish network performance can hinder productivity, as users may experience delays in performing critical tasks.
- User Frustration : Network congestion can lead to frustration among users due to the inability to access resources or slow response times.
II. The Causes of Network Congestion
Understanding the root causes of network congestion is vital for devising appropriate solutions. Let’s go over the most common causes of network congestion in more detail:
- Increased Data Traffic : As the number of connected devices and users on the network grows, the demand for data transfer increases, leading to congestion.
- Bandwidth Limitations : Insufficient available bandwidth can cause congestion, especially in networks with limited capacity or where data-intensive applications dominate.
- Network Misconfigurations : Inefficient network configurations, such as incorrect Quality of Service (QoS) settings or improper routing, can lead to inefficient data flow and congestion.
- DDoS Attacks : Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks involve overwhelming a network with an enormous amount of traffic, causing congestion and rendering services unavailable.
- Software and Firmware Bugs : Network devices with software or firmware bugs can behave unpredictably, potentially contributing to network congestion.
III. How to Identify and Address Network Congestion
To mitigate network congestion, early detection and appropriate measures are essential.
- Network Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio to track network performance metrics, including bandwidth utilization and traffic patterns. Identify periods of high traffic and potential congestion.
- Traffic Analysis : Analyze the type of data traffic and its volume to identify bandwidth-intensive applications or devices causing congestion.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Implementation : Implement QoS policies to prioritize critical applications and services over less essential ones during periods of congestion.
- Bandwidth Upgrades : Consider upgrading network bandwidth to accommodate increasing data demands and alleviate congestion.
- Load Balancing : Utilize network load balancing techniques to distribute network traffic across multiple routes or devices, preventing bottlenecks in specific areas.
- Traffic Shaping : Implement traffic shaping to control the flow of data, ensuring fair distribution of bandwidth among different applications or users.
- Network Optimization : Regularly review network configurations and performance to identify areas for network optimization and improvement.
By proactively identifying and addressing network congestion, businesses can ensure a smoother and more responsive network, enhancing productivity and user satisfaction. Network congestion management plays a crucial role in maintaining a reliable and efficient network infrastructure that meets the growing demands of modern businesses.
Learn how to detect network congestion & perform a network congestion test inside & outside your network with Network Monitoring & Network Device Monitoring.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Network Congestion
Network congestion occurs when the network experiences high levels of traffic, causing slow data transmission, increased latency, and potential service disruptions. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with network congestion:
- Identify Peak Usage Hours : Monitor network traffic to identify peak usage hours when congestion is most likely to occur. Plan for additional resources during these periods.
- Bandwidth Monitoring : Use bandwidth monitoring tools or network monitoring tools with SNMP Network Monitoring to track bandwidth usage and identify which applications or devices are consuming the most bandwidth.
- Quality of Service (QoS) : Implement QoS policies to prioritize critical traffic, such as VoIP or video conferencing, over non-essential traffic during periods of congestion. Qos for VoIP is essential for mitigation congestion.
- Malware or Botnet Activity : Malware-infected devices or botnet activity can cause excessive traffic and contribute to network congestion. Use security tools to detect and isolate infected devices.
- Cloud Services and Backups : Cloud services and data backups can consume significant bandwidth. Schedule backups during off-peak hours to avoid congestion.
- Check Network Switches and Routers : Check network devices for errors or signs of packet drops. Upgrade hardware if required to handle increased traffic.
- Analyze Network Topology : Review the network topology to identify potential bottlenecks or areas of contention.
- Segment Network Traffic : Separate different types of traffic, such as voice, data, and video, into separate VLANs to reduce contention.
- Update Firmware and Drivers : Keep network devices' firmware and drivers up to date to ensure optimal performance.
- Optimize Protocols : Fine-tune network protocols to reduce overhead and improve efficiency.
- Load Balancing : Distribute traffic across multiple links or paths using load balancing techniques.
- Consider Network Upgrades : If congestion is chronic and impacting productivity, consider upgrading network infrastructure, such as increasing bandwidth or using faster network technologies.
- Monitor Network Flow : Use flow analysis tools to understand traffic patterns and identify potential sources of congestion.
- Implement Caching : Use caching solutions for frequently accessed content to reduce the need for repetitive data transfers.
- Throttle Bandwidth-Intensive Applications : Limit the bandwidth usage of certain applications or devices that are causing congestion.
- Review ISP Performance : If the congestion is beyond your local network, contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to assess the overall network performance.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Traffic Control : Implement policies to control and prioritize P2P traffic, which can consume a significant amount of bandwidth.
- Educate Users : Educate users about responsible internet usage and the impact of excessive data consumption on network performance.
By thoroughly troubleshooting network congestion, you can identify the root causes and implement appropriate solutions to improve overall network performance and user experience. Regular monitoring and analysis of network traffic patterns will help you proactively address congestion issues before they become significant problems.
Network Problem #9. Packet Loss
Packet loss is a prevalent network problem characterized by the failure of data packets to reach their intended destination within a network . It occurs when one or more packets of data are lost or discarded during transmission, leading to incomplete or corrupted data delivery.
Packet loss can happen due to various factors, such as network congestion, hardware issues, or data transmission errors, and it can significantly impact network performance and user experience.

In the same family of network issues, you may also encounter:
- Packet Reordering : When network packets arrive at their destination out of sequence
- Packet Duplication : The unintended replication of data packets during transmission. When packets are duplicated, multiple identical copies of the same packet are delivered to the destination.
I. The Consequences of Packet Loss
- Data Corruption : Packet loss can lead to incomplete or corrupted data transmissions, affecting the accuracy and integrity of transmitted information.
- Slow Data Transfer : Retransmitting lost packets can slow down data transfer rates, leading to increased latency.
- Degraded Voice and Video Quality : In real-time communication applications like VoIP and video conferencing, packet loss can result in choppy audio or pixelated video.
- Reduced Throughput : The loss of packets in data streams can reduce the overall throughput and efficiency of data delivery.
- Impact on Applications : Packet loss can negatively affect the performance of applications, leading to slower response times and disrupted services.
II. The Causes of Packet Loss
- Network Congestion : High levels of data traffic or network congestion can result in packets being dropped to alleviate the strain on the network.
- Network Jitter : Variations in packet delay, known as jitter, can lead to packet loss when packets arrive out of order or too late to be processed.
- Buffer Overflow : When network devices' buffers become overwhelmed due to high data rates, excess packets can be discarded.
- Data Transmission Errors : Errors during data transmission can cause packets to be corrupted or lost, especially in unreliable transmission mediums.
- Wireless Interference : Interference from other wireless signals or physical obstacles can lead to packet loss in Wi-Fi networks.
- Network Hardware Issues : Faulty network switches, routers, or other hardware can cause packet loss as packets fail to traverse the network correctly.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Packet Loss
- Network Monitoring : Utilize network monitoring tools like Obkio to measure packet loss and track packet loss rates and identify periods of increased packet loss.
- Packet Analysis : Conduct packet analysis to identify the root causes of packet loss and determine the affected network segments.
- Bandwidth Optimization : Optimize bandwidth allocation and implement Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize critical traffic and reduce packet loss.
- Jitter Control : Minimize network jitter through QoS and traffic shaping to prevent packet loss due to variations in packet delay.
- Network Hardware Inspection : Inspect network hardware to identify and replace faulty devices contributing to packet loss.
- Wireless Signal Optimization : Optimize Wi-Fi signals to reduce wireless interference and decrease packet loss in wireless networks.
By proactively identifying and addressing packet loss, businesses can improve network performance , maintain data integrity, and enhance the overall user experience. Network monitoring, packet analysis, and appropriate network optimization techniques play a vital role in detecting and mitigating packet loss issues effectively.
How to measure packet loss with Obkio’s Network & Packet Loss Monitoring tool. Check for packet loss in your network & read packet loss measurements.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Packet Loss
Packet loss can degrade network performance and cause disruptions in data transmission. Troubleshooting packet loss requires identifying the underlying causes and implementing appropriate solutions. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with packet loss:
- Ping and Traceroute : Use ping and traceroute commands to identify packet loss and latency issues between devices. This can help pinpoint the location and severity of packet loss.
- Check Network Cables : Inspect network cables and connectors for damage, loose connections, or faulty wiring that could lead to packet loss.
- Verify Network Interface Cards (NICs) : Test and update network interface card drivers to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Physical Layer Troubleshooting : Examine physical network components, such as switches and routers, for signs of hardware issues or congestion.
- Bandwidth Saturation : Monitor network traffic to see if bandwidth saturation is causing packet loss. Consider implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize critical traffic.
- Check for Network Congestion : Analyze network traffic patterns to identify areas of congestion that may be causing packet loss.
- Wireless Interference : In wireless networks, interference from neighboring Wi-Fi networks or other devices can lead to packet loss. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer to identify potential sources of interference.
- Reduce MTU Size : If you are experiencing fragmentation-related packet loss, reduce the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size to prevent fragmentation.
- Jitter and Buffering : Examine network devices for excessive jitter or inadequate buffering that can contribute to packet loss.
- Routing Issues : Verify routing configurations to ensure packets are being routed correctly without any loops or misconfigurations.
- Firewall Settings : Check firewall rules to ensure they are not blocking legitimate traffic and causing packet loss.
- Malware and DDoS Attacks : Monitor for signs of malware infections or Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, as they can cause packet loss.
- ISP Issues : If the packet loss is beyond your local network, contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to investigate potential problems with their network.
- Buffer Bloat : Address buffer bloat issues by configuring QoS and traffic shaping to manage buffer size and prevent excessive queuing delay.
- Ping Flood or DDoS Testing : If you suspect malicious activities, investigate for possible ping flood or DDoS testing targeting your network.
- Update Firmware and Software : Keep network devices' firmware and software up to date to prevent known issues causing packet loss.
- Trunk Port Errors : For VLANs and trunk ports, check for misconfigurations or errors that might cause packet loss.
- Segment and Isolate Network Traffic : Use VLANs and subnetting to isolate different types of network traffic and prevent congestion-related packet loss.
By methodically troubleshooting packet loss, you can identify the root causes and apply appropriate solutions to improve network performance and reliability.
Network Problem #10. Jitter
Jitter is a common network problem that refers to the variation in packet delay experienced during data transmission over a network. It occurs when data packets encounter fluctuations in the time it takes to traverse the network from the source to the destination .
Jitter is particularly relevant in real-time communication applications, such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) calls and video conferencing (like Zoom ), where timing precision is crucial for smooth and seamless communication.

I. The Consequences of Jitter
- Voice and Video Quality Issues : In real-time communication applications like VoIP and video conferencing, excessive jitter, especially VoIP jitter , can cause choppy audio or video, affecting the overall call quality.
- Delayed Data Transmission : Jitter can lead to variations in data transmission delays, impacting the responsiveness of applications and services.
- Synchronization Problems: For time-sensitive applications, jitter can cause synchronization issues between data packets, leading to data corruption or loss.
- Interference with Real-Time Applications : Jitter can disrupt the flow of real-time data, making it challenging to maintain a smooth user experience.
II. The Causes of Jitter
- Network Congestion : High levels of data traffic or network congestion can lead to varying packet queuing times and result in jitter.
- Packet Routing : Different paths and routing delays taken by packets can cause varying arrival times at the destination.
- Network Jitter : Variations in network jitter itself can compound the issue, leading to additional packet timing discrepancies.
- Network Interference : Physical obstacles, wireless interference, or other external factors can introduce varying transmission delays.
- Buffering : Buffering in network devices can introduce variations in packet arrival times due to the varying lengths of packets.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Jitter
- Network Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio to measure jitter levels and identify periods of increased jitter. Obbkio will also help you identify the cause, source and time of jitter spikes in you network so you where where and how to direct your troubleshooting efforts.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Implementation : Implement QoS policies to prioritize real-time traffic, reducing the impact of jitter on critical applications.
- Buffer Management : Optimize buffer settings in network devices to minimize the effects of buffering-induced jitter.
- Traffic Shaping : Use traffic shaping techniques to regulate the flow of data and manage jitter more effectively.
- Path Optimization : Optimize network paths to minimize variations in packet routing and reduce jitter.
- Wireless Signal Optimization : In wireless networks, optimize Wi-Fi signals to reduce interference and decrease jitter.
By proactively identifying and addressing jitter, businesses can improve the performance of real-time communication applications, ensuring smooth voice and video calls, and enhancing the overall user experience. Network monitoring, QoS implementation, and network optimization play a crucial role in detecting and mitigating jitter effectively.
Learn how to measure network jitter using Obkio’s Network Monitoring software to identify network problems & collect data to troubleshoot.

IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Jitter
Jitter is the variation in the delay of packet delivery in a network, which can lead to inconsistent and unpredictable performance. Troubleshooting jitter involves identifying the causes of delay variations and implementing measures to mitigate its impact. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with jitter:
- Ping and Traceroute : Use ping and traceroute commands to measure latency and identify potential variations in packet delivery times.
- Check Network Utilization : High network utilization can contribute to jitter. Monitor network traffic to identify congestion points and take appropriate actions to alleviate it.
- Quality of Service (QoS) : Implement QoS policies to prioritize real-time traffic, such as VoIP and video conferencing, over non-time-sensitive traffic to reduce jitter.
- Buffer Bloat : Buffer bloat occurs when excessively large buffers cause delays in packet delivery. Adjust buffer sizes on routers and switches to manage latency.
- Packet Loss : Packet loss can exacerbate jitter. Address any packet loss issues, as it may lead to increased jitter levels.
- Wireless Interference : In wireless networks, interference from other devices or neighboring networks can cause jitter. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer to identify sources of interference.
- Network Congestion : Congestion on the network can lead to increased jitter. Identify and resolve congestion points to minimize its impact.
- Physical Layer Issues : Inspect network cables and connectors for damage or faults that may cause delays in packet delivery.
- Network Switches and Routers : Verify the performance of network switches and routers, as hardware issues can contribute to jitter.
- Jitter Buffer : For real-time applications, such as VoIP, ensure that jitter buffer settings are appropriately configured to compensate for jitter.
- Traffic Shaping : Use traffic shaping techniques to control the flow of traffic and prevent sudden bursts of data that may cause jitter.
- Power Management : Disable power-saving features on network devices that may introduce latency variations.
- Proper Synchronization : Ensure that clocks are synchronized across network devices to prevent timing discrepancies that contribute to jitter.
- VoIP Codecs : For VoIP systems, consider using different codecs that are less sensitive to network jitter.
- Update Firmware and Software : Keep network devices' firmware and software up to date to address known issues related to jitter.
- ISP Performance : If jitter is beyond your local network, contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to assess and address potential issues on their network.
- Monitor Network Performance : Continuously monitor network performance to identify patterns of jitter and take proactive measures to improve and check network stability .
- Use Network Diagnostic Tools : Employ network diagnostic tools to analyze jitter levels and identify sources of delay variations.
By systematically troubleshooting jitter, you can identify the underlying causes and apply appropriate solutions to improve network performance and deliver a smoother experience for real-time applications.
Network Problem #11. Routing Problems
Routing problems are a common network issue that occurs w hen data packets are unable to reach their intended destination due to incorrect or inefficient routing decisions . Routing is the process of determining the best path for data to travel from the source to the destination across a network.
When routing problems arise, data packets may take suboptimal paths, experience delays, or even get lost, leading to disruptions in network communication and performance.
I. The Consequences of Routing Problems
- Slow Data Transfer : Routing problems can lead to longer data transmission times, causing delays in accessing resources and services.
- Packet Loss : Incorrect routing decisions can cause packets to be lost or dropped during transmission, affecting data integrity.
- Network Inefficiency : Routing problems can lead to inefficient use of network resources, increasing network latency and reducing overall performance.
- Disruptions in Communication : Critical services and applications may become unavailable or experience disruptions due to routing problems.
II. The Causes of Routing Problems
- Misconfigurations : Incorrect configuration of routing protocols or routing tables can lead to suboptimal or incorrect routing decisions.
- Network Congestion : High levels of network congestion can cause routers to make suboptimal routing choices, leading to delays and packet loss.
- Link Failures : When a link between network devices fails, routers may need to reroute traffic, and if this process is not seamless, routing problems can occur.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Issues : In large-scale networks, BGP misconfigurations or route flapping can cause routing problems and instability.
- Inadequate Bandwidth : Insufficient bandwidth on certain links can cause congestion and result in suboptimal routing decisions.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Routing Problems
- Network Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio to track routing metrics and identify anomalies or fluctuations in routing behavior.
- Routing Protocol Analysis : Analyze the configuration of routing protocols and routing tables to identify misconfigurations or inconsistencies.
- Route Flap Damping : In BGP environments, enable route flap damping to mitigate the impact of unstable routes.
- Bandwidth Upgrades : Consider upgrading network links with inadequate bandwidth to alleviate congestion and improve routing efficiency.
- Link Redundancy : Implement link redundancy and dynamic routing protocols to ensure seamless failover in case of link failures.
- Regular Audits : Conduct regular audits of network configurations and routing tables to identify and rectify potential issues.
By proactively identifying and addressing routing problems, businesses can maintain a more efficient and reliable network infrastructure. Network monitoring, analysis of routing protocols, and proper network configuration play a vital role in detecting and resolving routing problems promptly. This ensures smooth and seamless data transmission, optimizing network performance and user experience.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Routing Problems
Routing problems can lead to communication issues between network devices and services. Troubleshooting routing problems requires careful analysis of the routing configuration and associated network components. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with routing problems:
- Ping and Traceroute : Use ping and traceroute commands to verify connectivity between devices and identify potential routing issues.
- Routing Table Verification : Check the routing tables on routers and switches to ensure they are correctly configured and have the appropriate routes.
- Routing Protocol Issues : If dynamic routing protocols are used, verify the protocol configurations and adjacencies between neighboring routers.
- Default Gateway : Confirm that devices have the correct default gateway configured, which is critical for forwarding traffic to external networks.
- Routing Loops : Check for routing loops in the network, which can cause packets to circulate indefinitely. Correct any misconfigurations causing loops.
- Routing Redistribution : If multiple routing protocols are in use, check for proper redistribution to ensure that routes are distributed correctly.
- Static Routes : Verify that any static routes are accurate and up-to-date, especially if they are used to override dynamic routing protocols.
- Routing Metrics : Review routing metrics to ensure they are set appropriately, as improper metrics can lead to suboptimal routing decisions.
- Routing Blackholes : Look for cases where routing paths unexpectedly drop packets (routing blackholes) and investigate the cause.
- Network Topology Changes : If recent network topology changes have occurred, verify that routing configurations were updated accordingly.
- Routing Protocol Authentication : Check if routing protocol authentication is enabled and configured correctly to prevent unauthorized routing updates.
- Split Horizon : For networks using split horizon, ensure that the split horizon rule is properly applied to prevent routing information loops.
- Routing Protocol Timers : Examine routing protocol timers to ensure they are set appropriately for the network environment.
- Network Segmentation : Confirm that network segmentation is accurate and logical, and routes are correctly configured between segments.
- Router Interface Status : Verify that router interfaces are operational and have the correct IP addressing and subnet masks.
- Physical Connectivity : Check for physical connectivity issues that may prevent proper routing information exchange.
- Backup Routes : If using backup or redundant routes, validate their configurations and failover mechanisms.
- Update Firmware and Software : Keep router and switch firmware/software up to date to address known issues related to routing.
- Monitor Routing Changes : Continuously monitor routing tables and log any changes to quickly identify and address unexpected alterations.
By methodically troubleshooting routing problems, you can identify and resolve issues that may be disrupting communication in the network. Regular network monitoring, like we mentioned in the previous section, thorough analysis of routing configurations, and prompt resolution of routing-related errors will help ensure smooth and reliable network operation. If the issue persists or is beyond your expertise, seek assistance from qualified network administrators or engage with vendor support.
Network Problem #12. VoIP Call Quality Issues
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) call quality issues are a common network problem that affects the clarity and reliability of voice communications over the Internet .
VoIP enables real-time voice communication using the internet as the transport medium. However, various factors within the network environment can lead to degraded call quality, causing disruptions, echoes, or delays in voice conversations.

I. The Consequences of VoIP Call Quality Issues
- Poor Call Clarity : VoIP call quality issues can result in poor audio quality, making it challenging to understand and communicate effectively.
- Dropped Calls : Frequent call dropouts or disconnects due to packet loss or network issues can hinder communication.
- Communication Delays : High latency can lead to noticeable delays in conversations, causing awkward pauses and communication difficulties. This is especially true for VoIP latency .
- Unreliable Communication : Call quality problems can lead to unreliable communication experiences, affecting business operations and customer service.
II. The Causes of VoIP Call Quality Issues:
- Network Congestion : High data traffic and network congestion can lead to delayed or lost VoIP packets, resulting in poor call quality.
- Jitter : Variations in packet delay, known as jitter, can cause voice packets to arrive out of order, resulting in choppy or distorted audio during calls.
- Packet Loss : Packet loss occurs when VoIP packets fail to reach their destination, leading to gaps or dropouts in the conversation.
- Latency : Latency, the delay between sending and receiving data, can lead to noticeable delays and interruptions in VoIP calls.
- Insufficient Bandwidth : Inadequate bandwidth can restrict the amount of data that can be transmitted, leading to reduced call quality.
- Network Interference : Interference from other devices or signals can impact VoIP calls, especially in wireless environments.
How to Identify & Troubleshoot VoIP Call Quality Issues
- Network Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio to measure VoIP quality metrics, such as MOS score, jitter, packet loss, and latency and identify issues affecting VoIP Quality right on the VoIP Quality graph.
- QoS Implementation : Implement Quality of Service (QoS) ) policies to prioritize VoIP traffic and minimize the impact of other data traffic on call quality.
- Bandwidth Allocation : Ensure sufficient bandwidth is allocated to VoIP traffic to avoid congestion and call quality issues.
- Traffic Shaping : Utilize traffic shaping techniques to regulate data flow and prioritize VoIP packets.
- Jitter Buffer Optimization : Optimize jitter buffer settings to compensate for jitter and ensure smoother audio playback.
- Network Upgrades : Consider upgrading network infrastructure to handle increased VoIP traffic and improve call quality.
By proactively identifying and addressing VoIP call quality issues, businesses can ensure clear and reliable voice communication, improving collaboration and customer interactions. Network monitoring, QoS implementation, and network optimization are essential in detecting and mitigating VoIP call quality issues, enhancing overall communication experiences within the organization.
Learn how to measure VoIP Quality using MOS Score (Mean Opinion Score) & Obkio’s VoIP monitoring solution to identify poor VoIP Quality issues & dropped calls.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for VoIP Call Quality Issues
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) call quality issues can negatively impact communication and user experience. Troubleshooting VoIP call quality issues requires identifying and resolving factors that affect voice transmission over the network. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with VoIP call quality issues:
- Check Bandwidth and Network Utilization : Insufficient bandwidth or high network utilization can lead to call quality degradation. Monitor network traffic and ensure sufficient bandwidth is available for VoIP traffic.
- Quality of Service (QoS) : Implement QoS policies to prioritize VoIP traffic over other types of data to ensure smooth transmission and reduced latency.
- Ping and Jitter : Measure ping and jitter between endpoints to identify potential latency and jitter issues affecting call quality.
- Packet Loss : Monitor for packet loss, which can significantly impact call quality. Address any packet loss issues on the network.
- Buffer Bloat : Buffer bloat can introduce latency in the network. Optimize buffer sizes to prevent excessive delays in packet transmission.
- Codecs : Check the codecs used for VoIP calls. Some codecs may prioritize bandwidth savings over call quality. Consider using codecs that offer better voice quality.
- Network Congestion : Analyze network congestion points and address them to reduce the impact on VoIP call quality.
- Network Equipment : Verify the performance of network switches and routers, as hardware issues can contribute to call quality problems.
- Wireless Interference : In wireless networks, interference from neighboring Wi-Fi networks or other devices can affect VoIP call quality. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer to identify sources of interference.
- Check for Dropped Packets : Identify and address any dropped packets affecting call quality.
- VoIP Gateway Configuration : Verify the configuration of VoIP gateways and devices to ensure they are set correctly for the network environment.
- Codec Mismatch : Ensure that both ends of the call are using compatible codecs. A codec mismatch can lead to poor call quality.
- Router Configuration : Review router configurations for issues that may affect VoIP call quality, such as Access Control Lists (ACLs) or firewall settings.
- Router Firmware Updates : Keep router firmware up to date to address known issues related to VoIP call quality.
- SIP Trunk and Provider Issues : If using SIP trunks or a VoIP service provider , check for any issues with their service that may be affecting call quality.
- Jitter Buffer Settings : Adjust jitter buffer settings to optimize the handling of packet variations and reduce jitter-related issues.
- Network Monitoring : Continuously monitor network performance to detect any patterns of call quality degradation and identify the causes. Network monitoring tools with VoIP monitoring , like Obkio, are especially important for identifying VoIP Quality issues.
- Network Latency : Address any latency issues in the network that may affect VoIP call quality.
- ISP Performance : If VoIP call quality issues persist, contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to assess and address potential network problems.
By methodically troubleshooting VoIP call quality issues, you can identify and resolve factors impacting call quality, leading to improved voice communication over the network. Regular network monitoring and analysis will help you proactively detect and address VoIP call quality issues as they arise.
Network Problem #13. Network Device Failures
Network device failures are a common and potentially disruptive network problem that occurs when essential network devices, such as routers, switches, firewalls, or access points, stop functioning correctly .
Network devices play a crucial role in data transmission, routing, and security within a network infrastructure. When one of these devices fails, it can lead to service disruptions, connectivity issues, and downtime.

I. The Consequences of Network Device Failures
- Network Downtime : When critical network devices fail, it can lead to network downtime and service interruptions.
- Connectivity Issues : Failures in routers, switches, or access points can disrupt network connectivity, affecting communication and data transfer.
- Security Vulnerabilities : Failed security devices like firewalls can expose the network to potential security breaches and unauthorized access. 8 Data Loss : Network device failures can lead to data loss, especially if devices were responsible for data storage or backup.
II. The Causes of Network Device Failures
- Hardware Malfunctions : Network devices can experience hardware failures due to wear and tear, overheating, power surges, or manufacturing defects.
- Firmware or Software Errors : Faulty firmware or software updates can cause network devices to behave unpredictably or fail.
- Configuration Errors : Incorrect or misconfigured settings in network devices can lead to malfunctions or instability.
- Environmental Factors : Environmental conditions, such as exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or dust, can impact the reliability of network devices.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Network Device Failures
- Network Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio, along with Obkio’s Network Device Monitoring feature to continuously monitor the health and performance of core network devices to identify device availability, resource and performance issues.
- Device Health Checks : Perform regular health checks on network devices to identify early signs of potential failures or abnormalities.
- Firmware and Software Updates : Keep network device firmware and software up to date with the latest stable releases to minimize potential issues.
- Configuration Backups : Regularly back up the configuration settings of network devices to facilitate quick recovery in case of failures.
- Redundancy and Failover : Implement redundancy and network failover mechanisms to ensure network continuity in the event of device failures.
- Hardware Maintenance : Regularly inspect and maintain network devices to address any physical issues and ensure proper functioning.
By proactively monitoring and maintaining network devices, businesses can reduce the risk of network disruptions caused by device failures. Quick identification and timely resolution of network device failures play a crucial role in minimizing downtime, improving network reliability , and ensuring seamless communication and data transfer.
Learn about Network Device Monitoring to easily monitor performance of firewalls, routers & switches to identify problems like high CPU & bandwidth usage.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Network Device Failures
Network device failures can disrupt network communication and lead to service outages. Troubleshooting network device failures requires a systematic approach to identify the failing device and address the issue promptly. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with network device failures:
- Physical Inspection : Perform a physical inspection of the device to check for any visible signs of damage, loose connections, or hardware failures.
- Power Cycle : Power cycle the device by turning it off and then back on. Sometimes, a simple reboot can resolve temporary issues.
- Check Power and Power Supply : Verify that the device is receiving power and that the power supply is functioning correctly.
- Check Device LEDs : Observe the status lights or LEDs on the device to identify any error codes or abnormal behavior.
- Device Logs : Analyze the device logs for error messages or alerts that might indicate the cause of the failure.
- Test Connectivity : Test connectivity to and from the device to see if it is responsive or if it is completely unreachable.
- Replace Network Cables : If applicable, try replacing the network cables connecting the device to the network.
- Isolate the Failing Device : If possible, isolate the failing device from the network to prevent it from causing further disruptions.
- Swapping Redundant Components : If the device has redundant components (e.g., power supplies, interface cards), try swapping them with spare parts to see if it resolves the issue.
- Verify Firmware/Software Versions : Ensure that the device's firmware or software is up to date. Apply the latest firmware updates or patches from the manufacturer's website.
- Temperature and Ventilation : Overheating can cause devices to fail. Ensure that the device has adequate ventilation and is not exposed to excessive heat.
- Check for Environmental Factors : Determine if the device failure could be caused by environmental factors such as power fluctuations or temperature variations.
- Backup and Restore Configurations : If the device can be replaced, backup its configuration and restore it on the replacement device to minimize downtime.
- RMA or Warranty : If the device is under warranty or support contract, contact the vendor for a possible replacement or repair.
- Identify the Impact : Assess the impact of the failed device on the network and affected services.
- Redundancy and Failover : Review the network design to ensure proper redundancy and failover mechanisms are in place to handle device failures.
- Replacement and Spare Parts : Keep spare devices or critical components on hand to quickly replace failed devices when needed.
- Document the Failure : Document all the troubleshooting steps, actions taken, and the resolution for future reference.
By following a systematic troubleshooting approach, you can quickly identify the failing device and take appropriate steps to address the issue, minimizing network downtime and ensuring smooth network operation. If the issue is beyond your expertise, seek assistance from qualified network technicians or engage with vendor support for further assistance.
Network Problem #14. VPN Connectivity Problems
VPN (Virtual Private Network) connectivity issues are a common network problem that can hinder remote workers or branch offices from securely accessing the corporate network. VPNs create encrypted tunnels over the public internet, allowing users to access internal resources and services as if they were directly connected to the corporate network.
However, various factors can lead to connectivity problems, preventing users from establishing or maintaining a stable VPN connection .
I. The Consequences of VPN Connectivity Issues
- Limited Remote Access : VPN connectivity issues can restrict remote workers' access to critical resources and data.
- Reduced Productivity : Users may experience delays or interruptions in their work due to VPN connection failures.
- Security Risks : VPN connectivity problems can prompt users to seek alternative and potentially insecure ways to access corporate resources.
II. The Causes of VPN Connectivity Issues
- Network Congestion : High levels of data traffic or network congestion can impact VPN performance and lead to connectivity problems.
- Firewall or Security Settings : Misconfigured firewalls or security settings can block VPN traffic, preventing successful connections.
- VPN Server Overload : An overloaded VPN server can struggle to handle incoming connection requests, leading to connection failures.
- Client Software Conflicts : Interference from other software or settings on the client device can cause VPN connectivity issues.
- Internet Connection Instability : Unstable or unreliable internet connections can disrupt VPN connections.
- VPN Protocol Issues : Compatibility issues between VPN protocols and devices can lead to connection problems.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot VPN Connectivity Issues
- Network Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio to track VPN connectivity metrics and identify potential issues. Obkio has remote network monitoring features, which is especially important for monitoring remote workers connectivity towards VPNs.
- Firewall and Security Configuration : Review and adjust firewall settings to ensure VPN traffic is permitted and secure.
- VPN Server Load Balancing : Implement load balancing for VPN servers to distribute connection requests evenly and avoid network overload .
- VPN Client Troubleshooting : Troubleshoot VPN client software on user devices to identify and resolve conflicts or configuration issues.
- Internet Connection Stability : Address internet connection problems on user devices to ensure a stable VPN connection.
- VPN Protocol Selection : Choose appropriate VPN protocols based on device compatibility and network requirements.
By proactively monitoring and troubleshooting VPN connectivity issues, businesses can ensure remote workers have reliable access to corporate resources. Network monitoring, VPN server optimization, and client device maintenance play a vital role in identifying and resolving VPN connectivity issues, enhancing productivity, and maintaining a secure remote work environment.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for VPN Connectivity Issues
VPN (Virtual Private Network) connectivity issues can prevent users from securely accessing resources on a remote network. Troubleshooting VPN connectivity problems requires a careful examination of both client-side and server-side configurations. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with VPN connectivity issues:
- Check Client Credentials : Verify that the VPN client has the correct username, password, and any necessary authentication tokens or certificates.
- VPN Client Software : Ensure that the VPN client software is installed correctly and up to date.
- VPN Server Status : Check the VPN server's status to ensure it is operational and accepting connections.
- Firewall and Security Software : Temporarily disable any third-party firewalls or security software that might be blocking VPN connections.
- Check VPN Server Logs : Review the VPN server logs for any error messages or connection attempts from the problematic client.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) : If the VPN server is behind a NAT device, ensure that proper NAT traversal (like NAT-T) is configured.
- VPN Protocol : Verify that both the client and server are using the same VPN protocol (e.g., OpenVPN, PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, IKEv2).
- Firewall Rules : Check firewall rules on the VPN server to ensure that incoming VPN traffic is allowed.
- Verify VPN Server and Client IP Addressing : Ensure that there are no IP address conflicts between the client and server networks.
- Internet Connectivity : Verify that both the client and server have a stable internet connection.
- ISP Blocking : Check if the internet service provider (ISP) is blocking VPN traffic. Try connecting from a different ISP to test.
- MTU Settings : Test different Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) settings on the client and server to avoid potential fragmentation issues.
- VPN Split Tunneling : Confirm that VPN split tunneling is not causing conflicts with local or remote network access.
- Restart VPN Services : Try restarting the VPN server and services.
- VPN Routing : Ensure that VPN routing is correctly configured to allow traffic to flow between client and server.
- VPN Server Certificates : Verify that server-side certificates (if used) are valid and not expired.
- Check VPN Encryption Settings : Ensure that both the client and server agree on encryption and authentication settings.
- Temporary Bypass VPN : Temporarily bypass the VPN and test regular internet connectivity to verify the issue is VPN-specific.
- NAT Traversal : If the VPN client is behind a NAT device, ensure that NAT traversal methods are enabled on both client and server.
- Update VPN Client and Server Software : Keep both the VPN client and server software up to date to address any known issues.
- Client and Server Time Sync : Verify that the client and server clocks are synchronized, as time differences can cause authentication problems.
By systematically troubleshooting VPN connectivity issues, you can identify and resolve the root causes, allowing users to securely access remote resources over the VPN. Documenting the troubleshooting steps and actions taken will aid in future reference and assist others in resolving similar issues. If the issue persists or requires expertise beyond your capabilities, don't hesitate to seek assistance from qualified network administrators or VPN specialists.
Network Problem #15. Load Balancing Configuration Errors
Load balancing configuration errors are a common network problem that occurs when the distribution of network traffic across multiple servers or links is not optimized or balanced correctly .
Load balancing is a technique used to evenly distribute incoming network requests or data traffic among multiple resources, ensuring optimal utilization of resources and preventing overload on individual components. However, misconfigurations or errors in load balancing setups can lead to uneven distribution, causing performance issues and potential service disruptions.
I. Consequences of Load Balancing Configuration Errors
- Overloaded Servers : Misconfigurations can lead to uneven distribution of traffic, overburdening certain servers while leaving others underutilized.
- Service Degradation : Load balancing errors can cause performance issues, leading to slow response times and reduced service availability.
- User Experience Issues : Users may experience inconsistent service quality or disruptions due to load balancing problems.
- Increased Downtime Risk : Load balancing configuration errors can increase the risk of service outages or downtime during peak traffic periods.
II. Causes of Load Balancing Configuration Errors
- Incorrect Weighting : Assigning improper weights to servers or links in the load balancing setup can result in disproportionate traffic distribution.
- Inadequate Health Checks : Inaccurate or inadequate health checks on servers can lead to the inclusion of faulty or overloaded servers in the load balancing pool.
- Session Persistence Misconfiguration : Misconfiguring session persistence can cause users to lose their session data when redirected to different servers.
- Improper Load Balancer Placement : Placing the load balancer in an inefficient location within the network can lead to suboptimal traffic routing.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Load Balancing Configuration Errors
- Network Monitoring : Utilize network monitoring tools like Obkio to track server performance and identify any imbalanced traffic patterns.
- Load Balancer Configuration Review : Regularly review load balancer settings and verify proper weightings and health checks.
- Testing and Validation : Conduct network load testing and validation to ensure load balancing configurations work as intended under different traffic conditions.
- Session Persistence Testing : Verify session persistence settings to ensure smooth user experience during server changes.
- Load Balancer Placement : Review the placement of load balancers in the network to optimize traffic routing.
By proactively identifying and addressing load balancing configuration errors, businesses can ensure efficient resource utilization, enhance service performance, and reduce the risk of downtime. Network monitoring, load balancer configuration reviews, and rigorous testing play a crucial role in detecting and resolving load balancing configuration errors, improving the overall reliability and network availability of network services.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Load Balancing Configuration Errors
Load balancing configuration errors can lead to uneven distribution of traffic, service disruptions, and degraded performance. Troubleshooting load balancing issues requires careful analysis of the load balancer's configuration and associated network components. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with load balancing configuration errors:
- Check Load Balancer Configuration : Review the load balancer's configuration to ensure it is set up correctly, including virtual server settings, server pools, and load balancing algorithms.
- Monitor Server Health : Monitor the health and status of the backend servers to ensure they are properly configured and responsive to requests.
- Verify Server Pool Membership : Check that all the intended backend servers are added to the appropriate server pools and that no servers are mistakenly excluded.
- Check Load Balancer Status : Verify that the load balancer is operational and not experiencing any issues.
- Load Balancer Firmware and Software Updates : Keep the load balancer's firmware and software up to date to address known issues and security vulnerabilities.
- Algorithm Selection : Ensure the appropriate load balancing algorithm (e.g., round-robin, least connections, weighted) is selected based on the specific application and server requirements.
- Monitor Traffic Distribution : Observe the traffic distribution among backend servers to identify any imbalances.
- Session Persistence : Check session persistence settings to ensure that client requests are directed to the same backend server for the duration of a session, if required.
- Health Checks and Monitors : Review health check settings to ensure they accurately monitor backend server availability and health.
- Virtual IP Address and Network Configuration : Verify that the virtual IP address and network configuration are properly set up and accessible.
- Firewall Rules and Security Groups : Check that firewall rules or security groups are not blocking the load balancer's traffic.
- Service Ports and Protocols : Confirm that the load balancer is configured to forward traffic to the correct service ports and protocols on the backend servers.
- Log Analysis : Analyze load balancer logs for any error messages or indications of misconfiguration.
- Service Check : Use network monitoring tools to perform service checks on the backend servers to identify any issues.
- Load Test and Simulation : Conduct load testing or simulate traffic to observe how the load balancer handles various loads and conditions.
- SSL Certificates : If using SSL termination, verify that the SSL certificates on the load balancer are valid and not expired.
- Application-Specific Configuration : For certain applications, ensure that any application-specific configurations or settings are correctly configured in the load balancer.
- Backup and Restore Configurations : Keep backups of load balancer configurations and restore them in case of accidental changes or misconfigurations.
- Rollback Changes : If you recently made changes to the load balancer configuration, consider rolling back the changes to a known working state.
By systematically troubleshooting load balancing configuration errors, you can identify and resolve issues that affect traffic distribution and optimize the performance and reliability of the load balancer. Regular monitoring and analysis of traffic patterns will help you proactively detect and address load balancing issues as they arise. If the issue persists or is beyond your expertise, seek assistance from qualified network administrators or load balancing specialists.
Network Problem #16. Link Flapping
Link flapping is a common network problem characterized by the frequent and rapid oscillation of a network link between the up and down states .
When a link flaps, it continuously alternates between being connected (up) and disconnected (down). This rapid and inconsistent behavior can disrupt network communication, cause service interruptions, and lead to instability within the network infrastructure.
I. The Consequences of Link Flapping
- Network Instability : Frequent link flapping can destabilize the network, leading to poor performance and service disruptions.
- Packet Loss : During link flapping, data packets may be lost or delayed, affecting data integrity and delivery.
- Connectivity Issues : Devices connected to the flapping link may experience intermittent connectivity or disconnections.
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Recalculation Delays : STP recalculations during link flapping can result in temporary network outages or increased convergence times.
II. The Causes of Link Flapping
- Physical Connectivity Issues : Loose or damaged cables, connectors, or network ports can cause link flapping when there are intermittent connections.
- Network Device Errors : Malfunctioning network switches, routers, or network interface cards (NICs) can lead to unstable link states.
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Misconfigurations: Incorrect STP configurations can create network loops, resulting in link flapping as STP tries to block or unblock redundant paths.
- Ethernet Auto-Negotiation Problems : Inconsistent auto-negotiation settings between devices can cause link flapping due to mismatched speeds or duplex modes.
III. How to Identify & Troubleshoot Link Flapping
- Network Monitoring : Use network monitoring tools like Obkio to track link status and identify instances of link flapping.
- Physical Inspection : Physically inspect network cables and connectors to ensure they are properly connected and not damaged.
- Interface Errors : Check for interface errors or error counters on network devices to identify potential issues.
- STP Configuration Review : Review and verify STP configurations to prevent network loops and link flapping.
- Speed and Duplex Settings : Ensure consistent speed and duplex settings between connected devices to avoid negotiation issues.
- Link Redundancy : Evaluate link redundancy and adjust configurations to avoid unintended loops.
By proactively identifying and addressing link flapping, businesses can maintain a stable and reliable network infrastructure. Network monitoring, physical inspections, and STP configuration reviews are essential in detecting and mitigating link flapping issues, ensuring smooth communication and data transfer within the network.
IV. Network Troubleshooting Scenarios for Link Flapping
Link flapping occurs when a network link experiences frequent up and down transitions, causing instability and disruptions in communication. Troubleshooting link flapping requires identifying the underlying causes and implementing solutions to stabilize the link. Here are some network troubleshooting scenarios to consider when dealing with link flapping:
- Physical Inspection : Inspect the physical connections of the link for loose cables, damaged connectors, or faulty network equipment.
- Cable Quality : Check the quality of the network cables. Use certified and properly shielded cables to reduce interference.
- Link Speed and Duplex Settings : Verify that both ends of the link are set to the same speed and duplex settings (e.g., 1 Gbps, full duplex) to avoid negotiation issues.
- Auto-Negotiation : Test the link with auto-negotiation enabled and disabled to see if it stabilizes the connection.
- Check Network Equipment : Review the logs and statistics of the network switches or routers connected to the link for any errors or alerts related to the flapping link.
- Firmware and Software Updates : Ensure that the firmware and software of network devices are up to date to address known issues.
- STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) Issues : Check if the link is part of a spanning tree loop or blocked by Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) due to redundancy misconfigurations.
- STP PortFast and BPDU Guard : If using STP, ensure that PortFast and BPDU Guard are configured correctly to prevent accidental loops.
- Link Aggregation (EtherChannel/LACP) : If the link is part of a link aggregation group, verify the configuration of the aggregation protocol (e.g., EtherChannel, LACP).
- Power Fluctuations : Verify that the devices connected to the link have stable power sources to prevent link flapping due to power issues.
- Update NIC Drivers : Keep network interface card (NIC) drivers up to date on connected devices to prevent compatibility issues.
- Interference : Check for sources of electromagnetic interference or signal degradation that might affect the link stability.
- Port Statistics : Monitor port statistics to check for excessive error counters, collisions, or other anomalies.
- MTU Size : Test different Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) sizes to avoid potential fragmentation issues.
- Bypass Network Equipment : Temporarily bypass any intermediate network equipment (e.g., switches, routers) to determine if the issue is specific to a particular device.
- Check Other Network Links : Investigate if any other links or devices in the network are causing network congestion or instability.
- Isolate Devices : Isolate devices connected to the link to test if the problem lies with one of the connected devices.
- Network Capture : Use network capture tools to analyze network traffic and look for patterns or events leading to link flapping.
By systematically troubleshooting link flapping, you can identify the root causes and implement appropriate solutions to stabilize the link and ensure reliable network communication. Regular monitoring and analysis of network performance will help you proactively detect and address link flapping issues as they arise. If the issue persists or requires expertise beyond your capabilities, seek assistance from qualified network administrators or network equipment vendors.
How to Troubleshoot the Most Common Network Problems: Steps & Tips
Now that we've gone over some of the most common network problems that businesses encounter in enterprise networks , it's essential to equip ourselves with effective troubleshooting steps. When network issues arise, swift and systematic troubleshooting is crucial to minimize downtime, ensure smooth operations, and maintain a reliable network infrastructure.
Identifying network issues is the first step to solving them - and it all comes down to pinpointing who , what , where , and when .
Step 1: Network Assessment
The first step when it comes to identifying network problems, with your Network Monitoring tool in hand, is performing a network assessment to collect some key information about your network. Obkio's Network Monitoring tool , which we helped you deploy earlier in this blog post, plays a vital role in this process.
By conducting a thorough network assessment , you can gain valuable insights into your network's health, performance, and potential bottlenecks. This information serves as a solid foundation for efficient troubleshooting and enables you to pinpoint the root causes of network issues more effectively. Now, let's delve into the general troubleshooting steps to address common network problems and make the most out of your network monitoring capabilities
- What actions to take: After you’ve collected all the information you need to identify the network issue, can then start network troubleshooting . That could include reaching out to your ISP or MSP, or bringing the problem to your network administrator to fix it internally.
For all the details about identifying network issues, check out our article on how to identify network issues!
Troubleshooting common network problems involves identifying the "what" issue is occurring, determining "where" the problem is located in the network, understanding "when" the issue is happening, identifying "who" is affected, and then taking appropriate actions to resolve the problem. Here are some steps to help troubleshoot common network problems:
Step 2: Identify the Issue (What)
To know how to solve these problems, you need to actually understand what they are. A network performance monitoring software will measure network metrics and report back if it finds any issues, with details about what the issue is, and what caused it.
- Gather information from users or monitoring tools to determine the symptoms and specific problem experienced.
- Clearly define the issue, such as slow internet speed, intermittent connectivity, or VoIP call quality problems.
Step 3: Locate the Problem (Where)
It’s important to identify where exactly in your network an issue has occurred. Using Monitoring Agents , Obkio allows you to deploy Agents in key network locations for end-to-end visibility over your network to provide you with details about where problems have occurred. This end-to-end network monitoring approach gives you visiblity of every end of your network, from your LAN to your WAN .
- Determine which part of the network is affected, such as a specific network segment, device, or service.
- Use network monitoring tools and analysis to identify potential network bottlenecks , high utilization areas, or devices showing errors.
Step 4: Determine the Timeframe (When)
Identifying the specific timeframe in which a network problem occurs is essential for effective troubleshooting. Pinpointing when the issue started and its recurrence patterns using historical data from Obkio's NPM tool can help correlate the problem with network changes or events, streamlining the resolution process.
- Find out when the problem started occurring to correlate with any changes in the network or configurations.
- Analyze network logs and timestamps to pinpoint when the issue typically happens, if it's intermittent.
Step 5. Identify Affected Users (Who)
Understanding which users or devices are experiencing network issues is crucial in troubleshooting. By pinpointing the affected users, network administrators can focus their efforts, assess the scope of the problem, and provide targeted support, ensuring a prompt resolution and improved user experience."
- Determine which users or devices are experiencing the problem to understand the scope of the issue.
- If the problem is widespread, identify common factors among affected users.
Step 6. Who is Responsible For the Network Segment
Once you know where a network problem is located, and what exactly it is, you can then easily decide who in your business is responsible for that network segment.
- Identifying the responsible party helps streamline communication and coordination, ensuring a more effective and targeted approach to resolving the issue.
- By involving the right stakeholders, you can facilitate a faster resolution and prevent delays in troubleshooting efforts.
Step 7. Take Initial Actions (What Actions to Take)
When network issues arise, it's essential to swiftly address the problem with initial actions. This step focuses on quick checks and basic troubleshooting to resolve common issues that might be causing the network problem. By taking these immediate actions, you can potentially resolve the problem right away or narrow down the root cause, setting the stage for further targeted troubleshooting.
- Perform basic checks, such as verifying cable connections, power cycling affected devices, or checking for software updates.
- Review network configuration changes or recent updates that might have contributed to the problem.
Step 8. Isolate the Issue
To efficiently troubleshoot network problems, isolating the issue is crucial. This step involves narrowing down the problematic area or component in the network. By systematically eliminating potential causes, you can pinpoint the specific source of the problem, leading to a more precise and effective resolution.
- Monitor network devices , like switches or routers, using Obkio's Network Device Monitoring feature, to identify if they are causing the problem or experiencing resource issues.
- Divide the network into segments and test each segment independently to narrow down the location of the problem.
- Use Visual Traceroutes to determine if the problem is in your local network or ISP network .
Step 9. Implement Solutions
After identifying the root cause of the network problem, it's time to implement targeted solutions. This step focuses on making necessary adjustments, configurations, or replacements to address the issue directly. By applying the appropriate solutions, you can effectively restore network functionality and prevent the problem from recurring
- Based on the gathered information, apply appropriate solutions, such as adjusting configurations, updating firmware, or replacing faulty hardware.
- If the network problem is beyond your organization's control and is related to the Internet Service Provider (ISP) or Managed Service Provider ( MSP network ) infrastructure, promptly reach out to them for assistance.
- Collaborating with your ISP or MSP can expedite the resolution process for issues that lie outside your network's scope.
- Document the changes made during troubleshooting for future reference.
Step 10. Test, Verify & Continuously Monitor Network Performance
Culminating the troubleshooting process, this section outlines the essential steps to verify the effectiveness of the implemented solutions and ensure a stable network environment. From thorough network testing to continuous monitoring, these practices ensure that network issues are promptly resolved and potential future problems are proactively addressed.
- After implementing solutions, thoroughly test and continuously monitor network performance with your Network Monitoring tool to ensure the problem is resolved.
- Verify that the network is functioning as expected and the previously identified issues are no longer present. Monitor the network post-resolution to verify the stability and effectiveness of the applied changes.
- Continuously monitor network performance using tools like Obkio to ensure the problem does not reoccur and to detect any new issues that may arise.
- By ongoing monitoring, you can proactively address potential problems before they impact the network's stability and user experience.

Why Should Businesses Find & Fix Network Problems Anyways?
In this section, we'll delve into why finding and troubleshooting network problems is a critical mission for businesses. From bolstering productivity and enhancing customer experience to safeguarding data and gaining a competitive edge, we'll explore the myriad reasons why proactive network monitoring is an indispensable investment.
- Maintaining Productivity : A smooth and reliable network is the backbone of business productivity. When network problems occur, they disrupt communication, data access, and collaborative efforts, leading to downtime and decreased efficiency. By identifying and resolving these issues promptly, businesses can minimize disruptions and keep productivity levels at their peak.
- Enhancing Customer Experience : In a digitally interconnected world, customer satisfaction hinges on swift and seamless interactions. Network problems can affect customer-facing services, leading to slow response times, website downtime, and impaired online transactions. By proactively addressing network issues, businesses can provide a positive customer experience, which can bolster loyalty and brand reputation.
- Cost Savings : Network problems can be costly in terms of both time and resources. Extended downtime can result in revenue losses, missed opportunities, and increased operational expenses as IT teams rush to troubleshoot and fix issues. By resolving problems swiftly, businesses can mitigate these financial impacts and avoid potential long-term consequences.
- Security and Data Protection : Network problems, especially those related to security breaches, can expose sensitive data and compromise the overall integrity of the business. Troubleshooting network vulnerabilities and promptly addressing security threats is essential for safeguarding valuable information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
- IT Team Efficiency : Persistent network issues can place an immense burden on IT teams, overwhelming them with repetitive troubleshooting tasks. By proactively identifying and resolving problems, IT teams can focus on strategic initiatives and improvements, ultimately making the best use of their expertise and time.
- Business Continuity : In today's digital-dependent landscape, uninterrupted business operations are crucial for survival and growth. Network problems, if left unchecked, can lead to extended outages and interruptions, threatening business continuity. By troubleshooting and resolving issues, businesses can ensure a more robust and resilient infrastructure.
- Competitive Advantage : In a competitive market, businesses must deliver a seamless user experience to stand out from their rivals. A well-maintained and efficient network allows companies to differentiate themselves by providing reliable services and smooth interactions, ultimately gaining a competitive edge.
- Employee Satisfaction : A functional network translates to a smoother work experience for employees. When network problems are addressed promptly, employees can focus on their tasks without the frustration and stress caused by technology-related hurdles.
In conclusion, finding and troubleshooting network problems is crucial for businesses to maintain productivity, enhance customer experience, save costs, protect data, streamline IT operations, ensure business continuity, gain a competitive advantage, and foster employee satisfaction. It's an essential investment in the overall success and growth of any modern business.
In Conclusion
There are a variety of network problems that could take over your network at any given moment. With the growing complexity and size of modern network infrastructures, network problems can be more frustrating than ever.
Businesses can’t afford to waste time and money dealing with network problems that effect:
- Productivity
- IT resources
Knowing about some of the most common network problems helps you prepare for what your network may encounter in the future.
Network performance monitoring using a network performance monitor tool is your key to identifying network problems, because it pinpoints intermittent network slowness issues that are difficult to troubleshoot otherwise! A distributed network monitoring solution like Obkio's offers visibility that traditional systems are unable to offer.
Obkio is a simple Network Performance Monitoring SaaS solution for IT pros to help you continuously monitor the health of their network and core business applications to improve the end-user experience!
You can rest assured that we're not like those pushy Sellsy people - there's no catch here. We firmly believe in the excellence of our product, but if it's not the right fit for you, we understand and want what's best for you.
Monitor mutliple network types, apps and services with features for:
- Network Audits
- Cloud Network Monitoring
- VoIP Monitoring
- Remote Network Monitoring
- UC Monitoring
- SD-WAN Monitoring
- SD-WAN Migration Monitoring
- MPLS Network Monitoring
- Internet Monitoring
- Firewall Monitoring
- SASE Monitoring
- Dual-WAN Monitoring
- Internet Multihoming
- SASE Networks
These might interest you
Don't let network issues slow you down - learn how obkio can help, see how obkio finds & fixes network problems - watch now, say goodbye to network headaches..
Get a live demo of Obkio now!
Did you know?


How to Fix Network Connection Issues in Windows 11
The ultimate guide to fixing any and all network connection issues on your Windows 11 computer with perfectly outlined steps.

The Internet has traveled the journey from being a utility to becoming a necessity. In today’s age, a computer without the Internet is almost as good as a paperweight. From communication and work to entertainment, everything requires an Internet connection.
In a constantly connected world, experiencing network connection issues is nothing short of a nightmare. Fortunately, the issue is well documented and there are several methods listed in this guide that you can try to fix the issues.
Before moving on to the fixes though, double-check that Wi-Fi is on.
1. Restart the System
While the fix may come across as elementary, restarts can fix process deadlocks, a bug that is interfering with the network service and even finish the driver installation process, which are all reasons why you could be facing network connection issues.
Head to the Start Menu and click on the ‘Power’ button icon and then click on the ‘Restart’ option. After the restart, check if the issue has been resolved.

2. Restart the Router
If you are connected to the network but the access seems to be limited or not at all, there is a high chance the problem is not your computer. Moreover, if you’re also facing issues on other devices, the router must be the one responsible for the mayhem. Hence, before you tinker with your system, turn off the router/modem and switch it back on after a couple of minutes.
Usually, the button to power off is located at the back of the router alongside all the LAN ports. In case you are not able to find it, you can also pull the plug on it. Once you have restarted the router, try connecting to the Internet again.
ISP outage could also be a reason behind limited network access. A router uses LEDs to display the current status of power, internet, and LAN ports. If you realize the LED for ‘Internet’ is either turned off or emitting a different color than regular, your ISP is likely facing some issues; better to call and check with them.
3. Toggle Airplane Mode on your Computer
In case restarting the computer and router did not resolve the issue for you, turning on airplane mode and turning it back off might help.
From the taskbar, click on the ‘Wi-Fi’ icon. Then, click on the ‘Airplane Mode’ icon from the overlay menu. Wait for a couple of minutes and then click it again to turn it off. Then, check if the problem persists.

4. Update Windows
If you are running on an older version of Windows, that can also be the reason you’re facing connectivity issues.
First, head to the Start Menu and click on the ‘Settings’ tile to proceed.

After that, ensure you have selected the ‘Windows Update’ tab from the left sidebar.

Then, from the right pane, click on the ‘Download & install/ Restart now’ to install pending updates.

Once the updates are installed, check if the issue has been resolved.
5. Update your Network Drivers
Updating your drivers is pretty elementary, however, if they haven’t been updated lately, there’s a pretty good chance you will be able to fix the solution just by doing this simple step.
First, head to the Start Menu and type Device Manager to perform a search. Then, from the search results, click on the ‘Device Manager’ tile.

Afterward, locate and double-click on the ‘Network adapters’ option. Once the category expands, find the Wi-Fi component and double-click on it. This will open a separate ‘Properties’ window on your screen.

Then, click on the ‘Driver’ tab present on the WiFi properties window. After that, locate and click on the ‘Update Driver’ button to continue. This will again open a separate window on your screen.

Now, click on the ‘Automatically update drivers’ if you desire to let Windows find a driver for the installed component. Otherwise, if you already have a package downloaded, click on the ‘Browse my computer for drivers’ option.

6. Run Internet Connection and Network Adapter Troubleshooter
If updating your network drivers did not fix the issue, running the troubleshooter for Internet connections and network adapters might help you rectify the improper configuration or any other issues along the same lines.
First, open the Start Menu and click on the ‘Settings’ tile to proceed.

Then, click on the ‘System’ tab from the left sidebar to continue.

Next, from the right section, click on the ‘Troubleshoot’ tile.

Afterward, click on the ‘Other troubleshooters’ tile.

On the next screen, click on the ‘Run’ button following the ‘Internet Connections’ tile.

From the troubleshooter window, click on the ‘Troubleshoot my connection to the Internet’ option. Windows will then check for the issues and report back on the same if it finds any.

If the ‘Internet Connection’ troubleshooter is not able to resolve the issue, you can also run the ‘Network Adapter troubleshooter’.
To run the Network Adapter troubleshooter, click on the ‘Run’ button present on the ‘Network Adapter’ tile.

After that, select the network medium you are facing a problem with. Once selected, click on the ‘Next’ button.

Windows will now check for errors in the network adapter and report back with anomalies along with the suggested steps to resolve the issue.
7. Change Power Management Settings
If you are using a laptop computer, your ‘Power Management’ settings can also disable your Wi-Fi network card to save battery. Though useful when you don’t need the Internet, it is not ideal if it disrupts the workflow.
To change the settings, head to the Start Menu and type Control to perform a search. Then, from the search results, click on the ‘Control Panel’ tile to proceed.

Then, click on the ‘Power Options’ from the Control Panel window.

On the next screen, click on the ‘Change plan settings’ option for the currently selected plan.

Then, click on the ‘Change advanced power settings’ option. This will open a separate window on your screen.

After that, from the ‘Power Options’ window, locate the ‘Wireless adapter settings’ and double-click on the option to expand the section.

Now, expand the ‘Power Saving Mode’ section and then click on the dropdown menu for the ‘On battery’ option. Next, select the ‘Maximum performance’ option.

Then, repeat the step for the ‘Plugged in’ option as well.

8. Disable IPv6
If IPv6 has been turned on in the adapter settings, that could also create network connection issues and it doesn’t hurt to check.
First, head to the Start Menu and click on the ‘Settings’ tile.

After that, click on the ‘Network & internet’ option from the left sidebar.

Next, from the right section of the window, click on the ‘Advanced network settings’ tile to continue.

After that, click on the ‘More network adapter options’ tile to proceed. This will open a separate window.

Now, right-click on the medium of connection and click on the ‘Properties’ option.

Then, on the ‘Properties’ window, uncheck the ‘Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)’ option and click on the ‘OK’ button.

9. Reset Network Components
Resetting all network components like Firewall settings, TCP/IP settings, renewing IP configuration lease, Windows socket, and flushing the DNS will eliminate all and any issues of improper configuration.
First, head to the Start Menu and type Terminal to perform a search. Then, from the search results, right-click on the ‘Terminal’ tile and click on the ‘Run as administrator’ option.

Now, an UAC (User Account Control) window will appear on your screen. If you are not logged in with an admin account, enter the credentials for one. Otherwise, click on the ‘Yes’ button.

Then, click on the chevron (downward arrow) and select the ‘Command Prompt’ option.

After that type or copy+paste the below-mentioned command and hit Enter to execute.

Similarly, type or copy+paste the below-mentioned commands one by one and hit Enter after entering each of them to execute them individually.

After executing all of the commands, restart your PC and check if the issue has been resolved.
10. Reinstall All Network Adapters
If no fix seems to be working for you, you can completely uninstall and reinstall all network adapters on your device. However, be aware that by doing this, all your saved network credentials will be reset.

Next, from the left sidebar present on the ‘Settings’ window, click on the ‘Network & internet’ tab.

Now, from the right section, click on the ‘Advanced network settings’ tile to proceed.

On the next screen, click on the ‘Network reset’ tile.

Afterward, click on the ‘Reset now’ button. This will restart your PC.
Note: This will completely uninstall and reinstall all the network adapters on your device. It will also uninstall any VPN software and virtual switches you might have installed on your system.

Once the PC has been restarted, try connecting to the Internet using your preferred medium and check if the problem is resolved.
11. Roll Back to a System Restore Point
In case nothing from the above methods seems to be working for you, it is time to bring out the big guns. If you created a system restore point before you started facing network problems on your PC, you can roll back to the restore point and you should be rid of the problem. However, do remember that any apps or data from after the restore point will be lost.
Head to the Start Menu and type Control to perform a search. Then, from the search results, click on the ‘Control Panel’ tile to proceed.

After that, locate and click on the ‘Recovery’ tile from the grid of icons.

Next, click on the ‘Open System Restore’ option from the list. This will open a separate window on your screen.

From the separately opened window, click on the ‘Next’ button.

All created system restore points will be listed on the screen. Click to select the desired one and then click on the ‘Next’ button to initiate the rolling back process.

Next, a list of drives that will be impacted by the rollback will be displayed along with the timestamp of the restore point created. You can also check the programs that will be affected; click on the ‘Scan for the affected programs’ button. A new window will appear on the screen.

On the new window, you can view the programs that will be deleted and the ones that will be restored. Click on the ‘Close’ button to navigate to the previous window.

Finally, click on the ‘Finish’ button to initiate the rollback process.

Experiencing network connection issues sucks, thankfully they can be easily resolved using the above-mentioned methods.

How to Use Gemini Code Assist in VS Code

How to Code Using AI

Microsoft Copilot Pro Review: There is a lot of Unrealized Potential
Get all the latest posts delivered straight to your inbox., member discussion.

How to Change User Folder Name on Windows 11

How to Change Fan Speed in Windows 11

How to Create a System Image in Windows 11

How to Factory Reset Windows 11 From Boot

How to Stop Computer From Sleeping on Windows 11
7 Common Network Issues and How to Resolve Them Fast

Networks are networks. Despite best efforts to keep things smooth all the time every day, things happen. Here's a look at some common network issues, some tips for quickly resolving them, and even better, how to prevent them from occurring again.
1. Duplicate IP Addresses
When two devices attempt to share a single IP, you see the dreaded "Address Already in Use" Kill — with no ability to access the network.
The Quick Fix: The blame for this often rests with your router's default DHCP configuration. DHCP is probably trying to assign your new device an address at the beginning of your subnet , and another device may already occupy these low-numbered addresses with static IPs. If you've just introduced a new device or server to your network, it may have its own DHCP server. Simply disable the DHCP server on that device to restore sanity to your network.
The Preventive Measure: You can take one simple step to avoid IP conflicts by modifying your router's configuration to begin assigning DHCP addresses near the top end of your subnet, leaving the lower addresses available for devices that require static IPs.
2. IP Address Exhaustion
To troubleshoot this issue, use the ipconfig command. If the workstation has assigned itself an IP address that begins with 169.x.x.x, it means that no IP address was available from the DHCP server.
The Quick Fix: Some users on cable internet might not have a local router, in which case IP addresses are assigned on a limited basis directly from your ISP. You have probably run out of allowed IP addresses from your ISP. The solution to this is to purchase either a standalone router or WiFi access point with an integrated router. This creates your own local pool of internal addresses, ensuring you won't run out.
If you already have a local router with DHCP, the default address pool might be too small for your network. By accessing the DHCP settings on the router, you can adjust the size of the address pool to meet your network's needs.
The Preventive Measure: It's important that any internet-connected network have a local router in operation with NAT and DHCP, both for security reasons and to prevent IP address exhaustion. The router needs to be the only device connected to the modem, with all other devices connecting through the router.
3. DNS Problems
Errors such as The Network Path Cannot Be Found, IP Address Could Not Be Found, or DNS Name Does Not Exist, can usually be traced to a DNS configuration issue . The command line utility nslookup can be used to quickly show a workstation's DNS settings.
The Quick Fix: Workstations and other network devices can be configured to use their own DNS servers, ignoring the server assigned by DHCP. Checking the 'Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IP)' settings for your adapter will show if an incorrect DNS server is specified, so just select "Obtain DNS server address automatically" instead.
The Prevention Measure: Your local router might be configured to operate as a DNS Server, creating a DNS pass-through to your ISPs servers. On busy networks, this may overload the capabilities of the router. Change your network's DHCP settings to directly access your DNS servers.
4. Single Workstation Unable to Connect to the Network
If only a single workstation is displaying the "No internet" message when opening a web browser, we can usually assume that the rest of the network is healthy and turn our attention to any hardware and software that is particular to this system.
The Quick Fix: To resolve this network issue, start by eliminating the obvious communication barriers such as a bad cable, poor WiFi signal , failing network card or incorrect drivers. Ensure that the workstation's network adapter is configured with the correct IP, subnet, and DNS servers.
If that doesn't solve the problem, check any firewall software on the device to ensure that necessary ports are open to the external network. Common ports include 80 and 443 for web traffic, plus 25, 587, 465, 110, and 995 for email.
The Preventive Measure: It's usually best to leave all workstation TCP/IP settings to "Automatically assigned." Use a DHCP server to hand out a uniform configuration to all devices on the network. If a static IP is needed on a particular workstation or server, most DHCP servers allow the ability to create static IP mappings.
5. Unable to Connect to Local File or Printer Shares
Sharing problems are among the most difficult network problems to solve, due to the number of components that need to be configured properly.
Most commonly, sharing problems arise due to conflicts between mixed security environments. Even different versions of the same operating system sometimes use slightly different security models, which can make interconnection of workstations difficult.
The Quick Fix: We can cure sharing problems most efficiently by drilling down through the possibilities in this order:
Ensure that the required services are running. On Windows systems, the server, TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper, workstation, and computer browser services all need to be running. On Linux machines, Samba is the primary component required to share with Windows systems.
Check your firewall(s) . It's very common for a workstation's firewall to be configured to block file and printer sharing traffic, especially if a new antivirus package is installed that introduces its own firewall. Firewall issues can also exist at the hardware level, so ensure that routers or managed switches are passing share traffic within the subnet. Speaking of subnet….
Ensure all workstations are on the same subnet. This problem typically only appears on complex networks, however, even simple networks sometimes have static-IP equipment with an improperly configured subnet. The result is that external traffic will move about just fine, while internal traffic will hit unexpected roadblocks.
All Windows network adapters will need File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks, Client for Microsoft Networks, and NetBIOS over TCP/IP enabled.
Once the above checks have passed, it's finally time to check the most likely culprit, permissions. There are multiple layers of access required, each with their own interface within the OS. Check for:
Systems configured with the wrong workgroup or domain.
Incorrectly configured HomeGroup.
Network type set to Public.
Incorrect NTFS permissions.
6. Local Network is Unable to Connect to the internet
This situation can either be intermittent or persistent. Often times, the most difficult aspect of dealing with any external network problem is finding the company responsible. And then tasking them to solve the issue, particularly with intermittent failures that are difficult to trace. It can sometimes be such a problem that organizations will have to switch internet providers in order to solve the issue.
The Quick Fix: A router and modem reboot is the first order of business. The tracert then utility can be used to identify communication breaks. It will clearly hiccup on the particular router hop that is causing the problem. Contact your ISP with your findings, providing screenshots as necessary.
The Preventive Measure: To avoid the finger-pointing that can prevent rapid resolution of external issues, do some research to ensure that you procure connectivity only from local Tier 1 providers. Other ISPs are more than happy to sell you service, however, they are simply piggybacking the Tier 1 connection, since they don't actually own the infrastructure in your area.
The goal is to remove as many middle-men as possible, so that when (not if) you experience a problem, one phone call is all that is required to identify the issue and get technicians to work on it.
7. Slow Internet Performance
Slow performance is typically due to congestion, or sometimes poor quality connections that have corroded or otherwise deteriorated. Congestion may not be directly related to bandwidth exhaustion, as a single overloaded port on a switch or router can diminish network performance.
This can be especially true on leased lines where dedicated bandwidth is to be expected, but speed tests indicate the network is not reaching it's rated potential.
The Quick Fix: Use speed test websites, conducting tests from geographically remote servers. This can pinpoint areas of congestion on the ISP's network. In the case of cable internet, the local network is shared amongst your neighbors, committing your ISP to a costly bandwidth upgrade when saturation occurs. Report your findings to your ISP so that they can take steps to resolve the issue.
DNS servers are an often overlooked aspect of internet performance . Using incorrect DNS servers can result in routing congestion or load balancing problems. While you should typically use your ISP's DNS settings whenever possible, they may actually be routing traffic through overloaded web caches. You can temporarily adjust your DNS settings to use OpenDNS instead.
The Preventive Measure: if internet performance is critical, you'll need to procure adequate connectivity. While cable internet may be inexpensive, you could be setting yourself up for frequent jeers from employees. A local DSL operator may offer improved reliability for a slightly higher cost, but for the most consistent performance, you may find that an expensive leased line is a requirement for your organization.
There's plenty of help out there — use it!
The good news is there are a plethora of resources for troubleshooting and solving network issues, and many of them are free and built into most operating systems. Ping, tracert, ipconfig, nslookup, and speedtest.net should be in the top drawer of every admin's toolkit .
More advanced utilities such as Wireshark provide a detailed analysis of your network's potential stumbling points, while wardriving tools can be called upon to identify WiFi performance or interference issues.
Armed with a deeper knowledge of how your network works, you can be prepared for the inevitable , and can even train end users to troubleshoot simple problems themselves. Your reputation as a network hero lives on!
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy .
Recommended Articles
I have read and understood the privacy policy and am able to consent to it.
- Product Product
- Browse training
- All courses
- Certification training
- New training
- Solutions Solutions
- Active Military
- All Solutions
- Resources Resources
- Learner stories
- Why e-learning?
- Customer reviews
- Study Plans
- Ultimate Cert Guides
- Company Company
- Become a Trainer
- Transparency in Coverage
- Support Support
- Help Center
Let's chat!
Dominick Fair
Chief Technology Officer
15 Common Network Problems & How To Solve Them

So, your network crashed. It’s a great day.
You just lost an entire morning’s work because your network quit on you- and this is not some college research paper, this is your business .
Life is crazy and busy enough already! You don’t need more network and IT stressors added to it.
The only thing you need is a business network that makes your job and your life fluid.
It doesn’t matter if you live in Frederick, Bethesda , Rockville, McLean or Alexandria- you live in the future tech-hub of the world. Amazon is moving in, and Google has already caught on. You need protected, reliable and progressive IT.
If your business network breaks down, we have you covered.
We know about the uncommon network problems on the backend. But, did you know there are common network problems that can sometimes be prevented with the services of a managed service provider?
Here’s some information that may help you take a positive step towards never having to deal with annoying network issues again:
1. Networking Issues
IT management companies can always help businesses with their networking issues. But not all IT companies which help you with network issues are created equal.
Some aren’t worth the time to call them. Some have great network solutions for issues but cost too much. What if we were to tell you about a company that can handle your networking issues at an affordable price?
Maybe you’re skeptical at this point, so we’ll go over 15 of the most common network problems. Then we will tell you why we’re the best IT company in your area.
Here are a few common network problems:
- Your network is too slow. You have rebooted your computer. You have deleted files and folders that take up a lot of memory. But you still have a slow network speed.
- The Wi-Fi signal is strong in some areas and weak in other areas of the office. It makes no sense. It continues, no matter how you rearrange the furniture.
- The IP addresses have snafus. Sometimes there may be duplicate IP addresses. Sometimes there can be IP address exhaustion.
- Network path cannot be found. This is also knowns as a DNS problem. If there is a network error message that drives most people to distraction, it is that one.
- Unable to connect to a printer or file on a network share program. That can put a group meeting in an indefinite hold pattern if not fixed as soon as possible.
We know how aggravating and stressful these network issues can be. As an IT management company with clients from Virginia to DC and Maryland, we also know how important our network solutions are.
They are the reasons our solutions need to work the first time, every time.
2. Network Problems
We are presenting you with common network issues and problems that affect all businesses from time to time. We also have solutions for these problems.
Here’s a small cheat sheet of brief solutions you may try for a couple of these ongoing network problems.
Here are more everyday common network problems;
- Cyber Security or hacking your network . Only about 14 percent of small businesses can mitigate cyber risks and their network’s vulnerability. Of the 14%, 60 percent of them go out of business within six months.
- Data Back-ups . You have a lot of data that needs to be backed up at the end of each workday. But sometimes that doesn’t happen right, or it doesn’t happen at all. It’s a nightmare to figure out what happened.
- The Cloud and those who don’t understand it, misuse it, keep incorrect data on it or cannot figure it out so they get rid of it on their computer.
- No IT plan at all? This is when we have our work cut out for us and we love every minute. Because it allows us to help a business develop an IT plan that grows and develops with them.
- Account Privilege Abuse. That’s when someone who shouldn’t be using company networks does. It can be a nightmare because 60% of all security breaches on your network are done from the inside. That means it is someone who works with or for you.
There are solutions to these network problems we work with every day. But the longer the problems go on, the more difficult it is to fix at every level. We get it done, but it is time-intensive.
3. Common Network Problems
The last five common network problems are some of our unique network problems. But that being said, they are still common enough to include on our the list. They are:
- Misconfigurations cause as much as 80% of all network problems. Setting parameters manually may be something you can do. But when it is done wrong, it can cause untold IT headaches.
- VLAN issues happen when a VLAN is not configured to the correct port, which supports its services.
- Wireless connections don’t work. There is nothing worse than going to use the wireless connection with your boatload of work only to realize that you cannot get access to the connection.
- Unable to establish a VPN connection. Many people may not know what or how the VPN connects so this can be a real stress-inducer IT problem.
- Ongoing network processes are using up all the memory. This one can be a puzzler without an IT management group which can help you walk through what is going on.
The value of an IT management company cannot be overstated. We say the heartbeat of your business is your network. There is no substitute you can put in the place of a network that crashed. Because it doesn’t exist.
Reliable networks are a necessity for businesses everywhere. If your network problems cause you to lose business, for a day or even an hour- it is going to make a huge difference in office flow and client relations on your end.
Managed IT can prevent these problems before they happen.
Common Network Problems & Solutions
Some answers to a few of the common network problems we mentioned above you may find surprising. Some will seem too easy to be true but sometimes it works out that way.
But there are other network problems that can take the average IT knowledgeable person, more days than they want to figure it all out. This is often because of all the moving parts in network systems and servers.
The good news is that there isn’t a single network problem or issue we haven’t seen already. When it comes to complicated and in-depth network problems, we know what to do and how to do it almost as soon as we make it.
Here are some short answers to what can be difficult network problems.
- When your network is too slow , it can be the router’s positioning causing wireless interference. We test in all positions when we need to.
- The WiFi signal is strong and weak throughout the building may be because of your network’s administrator interface. It needs to be set to optimum performance.
- Data Back-up issues can be caused by hardware and software problems so all need to be checked out. You can back up directly to an outside server or another outside source as a temporary measure.
- VLAN issues require you to check the cabling and the interface first before doing anything else.
- Continuous loss of memory because your network has a memory hog somewhere. Damaged hardware or a capacity bottleneck can cause this. Either can be fixed in a straight-forward manner.
Network Issues
There is no network issue you have which does not have a solution or answer. That’s what we will as truth in our industry. We give you the IT management services and answers to meet your network needs.
View pricing on our management plans that vary and are based on your particular needs. We have starter package plans for new businesses. We also have our obsidian package plan for established, larger businesses.
All of our packages can handle any of your current or potential network issues and provide your business with the answers and solutions to get you back on track. Our mission is to create fluidity in the workspace so that you and your business can get back to what it does best in its day-to-day operations.
All technology today evolves at the speed of a week-to-week and sometimes day to day basis. Problems in networking, cloud computing, and remote access are what we fix for our customers every day.
Your business should be able to hop online with the touch of a button and click of a mouse. Many of our calls come when people have tried to fix their network issues themselves but think they may have made things worse. We can fix those network issues too.
Our IT Service Management Plans
Our IT service management plans allow us to be there for you so you never have to worry about having network problems or issues.
We offer timely network solutions that give you peace of mind. Also, they get your business back up to speed as quickly as possible.
Wouldn’t it be great to know that your network protection is just around the corner with 24/7 support?
SADOS offers more than solutions to your network problems. We offer specialized architecture and deployment. SADOS does maintenance and LAN/WAN network monitoring in our managed service packages.
We’re only one call away . Reach out to us before you need us in a network emergency.
Try our FREE AI-powered help desk. No login required.
Need a quick fix?
Try our free ai-powered tech support.
Describe the problem you are facing. Be friendly, descriptive. Remember that AI can make mistakes. If you’re having an IT emergency, please contact us .
You may also like...

What Does a Content Delivery Network Do?
If you’re interested in optimizing your company’s website to improve page load speed, boost security, or lower your bandwidth cost, using a content delivery network will help.

6 Steps to Surviving an IT Emergency
When you operate your own business, your IT system is your lifeline. That’s why it’s important to be prepared for an IT emergency.

Is Your Business Protected with a Disaster Recovery Plan?
Disaster recovery plans are necessary to help businesses avoid unrecoverable loss. Here are some disaster recovery plans available.
News to your inbox
Keep tabs on what’s happening in the world of technology. We’ll send you new posts to your inbox
Ready to modernize your IT?
Service Status

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Select Start > Settings > Network & internet, then turn on Wi-Fi. Next, select More options ( >) next to Wi-Fi, then select Show available networks. If a network you expect to see appears in the list, select it, then select Connect . Open Wi-Fi settings. See if you can use the Wi-Fi network to get to websites from a different device.
Here are nine of the most common network issues to troubleshoot. 1. Slow network. Users complain the network is too slow. There can be many reasons why a network that provided adequate performance in the past is now frustrating its users. For instance, a new application, such as video conferencing or online training videos, may have been added.
2. Ping localhost (this checks that the current network interface device is up and running) 3. Ping the nearest router or gateway (Use ipconfig to look up the IP address for the "Default Gateway ...
Go to Windows Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update. Click Check for Updates. If there are updates available, Windows will download and install them. 8. Open Windows Network Diagnostics. Windows has a tool called Windows Network Diagnostics that lets users troubleshoot connection issues.
1. Identify the Problem. The first step in troubleshooting a network is to identify the problem. As a part of this step, you should do the following: Gather information about the current state of the network using the network troubleshooting tools that you have available to you. Duplicate the problem on a test piece of hardware or software, if ...
The troubleshooting steps to take to resolve such network connectivity issues include: Checking hardware Check all your devices to make sure everything is connected properly, has been switched on, and is working well. Make sure all switches are in the correct positions. Power cycling the device is a good idea.
3. Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter. Windows includes some built-in troubleshooters that can automatically find and fix issues. To run the troubleshooter for network problems, right-click the network icon in your System Tray and choose Troubleshoot Problems .
Updating your current browser could also be a quick and convenient solution. Another quick fix could be simply restarting your router by unplugging it from its power source and then reconnecting it a few seconds later. 2. VPN Connection Issues. VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, are now very popular pieces of software.
As you work through the steps to try to solve network issues, following these network troubleshooting best practices can help streamline the process and avoid unnecessary or redundant efforts. 1. Collect information. To best support your end users, you first need to make sure you're clear on what the problem is.
Check Your Cables. Try Restarting the Problem Device. Ensure That Network Hardware Is Working. Reboot Your Router. Check the Connection Status on Your Router/Modem. Try Another Device to Isolate the Issue. Finally: Contact Your Service Provider. It's useful to have a checklist of things to try when your internet is not working. Sometimes you ...
In Windows 10, in Cortana's search box on the taskbar, type the word troubleshooting and click or tap the search result with the same name. Windows, troubleshoot, network, internet, problems. In Windows 7, type the word troubleshooting in the Start Menu search box. Then, click the Troubleshooting search result.
2. Next, click on the " Additional troubleshooter " option. 3. Finally, click on "Internet Connections," and then click on "Run the troubleshooter.". It will detect the problem and will try to fix the issue automatically. 4. Also, scroll down and click on " Network Adapter ". After that, run the troubleshooter to fix most of the ...
Identifying network issues is the first step to solving them - and it all comes down to pinpointing who, what, where, and when. Step 1: Network Assessment . The first step when it comes to identifying network problems, with your Network Monitoring tool in hand, is performing a network assessment to collect some key information about your network.
First, head to the Start Menu and click on the 'Settings' tile. After that, click on the 'Network & internet' option from the left sidebar. Next, from the right section of the window, click on the 'Advanced network settings' tile to continue. After that, click on the 'More network adapter options' tile to proceed.
The Final Word: Best Tool to Fix Network Problems. All network issues can be (or become) complex, and it can be difficult to pinpoint the exact issue when there are so many different components, connections, and network configurations interacting at the same time. Generally, the easiest and best way to detect and solve network problems is to ...
Wait 5 minutes for it to fully boot back up. The lights on the modem or router should turn solid when it is connected to the internet. 7. Restart your internet-connected devices. Sometimes restarting your internet-connected devices can fix network problems with individual devices. 8.
Network Troubleshooting Definition. Network troubleshooting in the process of measuring, identifying, and resolving network-related issues. It's also defined as a logical process network engineers follow to improve the overall network operations. Troubleshooting is a repetitive, rigorous, and effective process that involves regular analysis ...
6. Local Network is Unable to Connect to the internet. This situation can either be intermittent or persistent. Often times, the most difficult aspect of dealing with any external network problem is finding the company responsible. And then tasking them to solve the issue, particularly with intermittent failures that are difficult to trace. It ...
The way you solve the problem depends on whether or not you control the failing part of the network. You can solve local network problems by yourself because you control the network. Outside network problems require help from whoever runs that network. Either way, this guide has the steps you need to move toward a solution.
Here are more everyday common network problems; Cyber Security or hacking your network. Only about 14 percent of small businesses can mitigate cyber risks and their network's vulnerability. Of the 14%, 60 percent of them go out of business within six months. Data Back-ups.
Here's our list of the best network diagnostic tools and troubleshooting software: Datadog Network Performance Monitoring EDITOR'S CHOICE A cloud-based network monitoring and management service that includes autodiscovery, topology mapping, performance alerts, and troubleshooting tools Start a 15-day free trial.
Using network simulation software is another useful method for solving complex network issues and server troubleshooting. Using tools such as Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3, you can simulate various scenarios to test configurations, diagnose issues, and evaluate potential solutions, observing network behavior without disrupting your production ...
Under Advanced network settings, click Network troubleshooter. Once clicked, the troubleshooter may ask which network you want to troubleshoot. Once you've selected a network, it will begin to detect issues with your connection. Once finished, it will give a diagnosis and potential fix. Sometimes, it will even be able to fix the problem for you.
Preparation is key to effective networking. Familiarize yourself with the event agenda and identify sessions and social functions where networking opportunities are likely to occur. Craft a ...
The New York Jets ' unwillingness to draft Georgia tight end Brock Bowers at No. 11 overall has arguably left a hole in their offense. Jets brass is apparently content with the team's tight ends ...
The Energy Network Association, the body that represents district network operators, says connection issues are rare for housing projects, but where they do occur operators are working to find ...
Xindi Hu, Jiaming Weng, Shengfeng Zhu. This research presents a novel method using an adversarial neural network to solve the eigenvalue topology optimization problems. The study focuses on optimizing the first eigenvalues of second-order elliptic and fourth-order biharmonic operators subject to geometry constraints.
Taking this a step further, it could use a forecast strong budget position to double the size of the HAFF to $20 billion, which would provide a down payment on homes that will still be required in ...
Chinese and Hong Kong students studying abroad are living in fear of intimidation, harassment and surveillance as Chinese authorities seek to prevent them from engaging with 'sensitive' or political issues while overseas, Amnesty International said in a new report published today. Students based in Europe and North America interviewed for the report, 'On my campus, […]