Want Better Math Grades?
✅ Unlimited Solutions
✅ Step-by-Step Answers
✅ Available 24/7
➕ Free Bonuses ($1085 value!)
On this page
- Search IntMath
- Math interactives
- About (site info)
- Uses of Trignometry
- ASCIIMath input, KaTeX output
- ASCIIMath input, LaTeX and KaTeX output
- Send Math in emails
- Syntax for ASCIIMathML
- Math Display Experiments
- Scientific Notebook

Math Problem Solver
Related Sections
Math Tutoring
Need help? Chat with a tutor anytime, 24/7.

This tool combines the power of mathematical computation engine that excels at solving mathematical formulas with the power of artificial intelligence large language models to parse and generate natural language answers. This creates a math problem solver that's more accurate than ChatGPT, more flexible than a math calculator, and provides answers faster than a human tutor.
Sign up for free here .
Problem Solver Subjects
Our math problem solver that lets you input a wide variety of math math problems and it will provide a step by step answer. This math solver excels at math word problems as well as a wide range of math subjects.
- Math Word Problems
- Pre-Algebra
- Geometry Graphing
- Trigonometry
- Precalculus
- Finite Math
- Linear Algebra
Here are example math problems within each subject that can be input into the calculator and solved. This list is constanstly growing as functionality is added to the calculator.
Basic Math Solutions
Below are examples of basic math problems that can be solved.
- Long Arithmetic
- Rational Numbers
- Operations with Fractions
- Ratios, Proportions, Percents
- Measurement, Area, and Volume
- Factors, Fractions, and Exponents
- Unit Conversions
- Data Measurement and Statistics
- Points and Line Segments
Math Word Problem Solutions
Math word problems require interpreting what is being asked and simplifying that into a basic math equation. Once you have the equation you can then enter that into the problem solver as a basic math or algebra question to be correctly solved. Below are math word problem examples and their simplified forms.
Word Problem: Rachel has 17 apples. She gives some to Sarah. Sarah now has 8 apples. How many apples did Rachel give her?
Simplified Equation: 17 - x = 8
Word Problem: Rhonda has 12 marbles more than Douglas. Douglas has 6 marbles more than Bertha. Rhonda has twice as many marbles as Bertha has. How many marbles does Douglas have?
Variables: Rhonda's marbles is represented by (r), Douglas' marbles is represented by (d) and Bertha's marbles is represented by (b)
Simplified Equation: {r = d + 12, d = b + 6, r = 2 �� b}
Word Problem: if there are 40 cookies all together and Angela takes 10 and Brett takes 5 how many are left?
Simplified: 40 - 10 - 5
Pre-Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Pre-Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Variables, Expressions, and Integers
- Simplifying and Evaluating Expressions
- Solving Equations
- Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities
- Ratios, Proportions, and Percents
- Linear Equations and Inequalities
Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Concepts and Expressions
- Points, Lines, and Line Segments
- Simplifying Polynomials
- Factoring Polynomials
- Linear Equations
- Absolute Value Expressions and Equations
- Radical Expressions and Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Inequalities
- Complex Numbers and Vector Analysis
- Logarithmic Expressions and Equations
- Exponential Expressions and Equations
- Conic Sections
- Vector Spaces
- 3d Coordinate System
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Linear Transformations
- Number Sets
- Analytic Geometry
Trigonometry Solutions
Below are examples of Trigonometry math problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Concepts and Expressions Review
- Right Triangle Trigonometry
- Radian Measure and Circular Functions
- Graphing Trigonometric Functions
- Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions
- Verifying Trigonometric Identities
- Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Complex Numbers
- Analytic Geometry in Polar Coordinates
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Vector Arithmetic
Precalculus Solutions
Below are examples of Precalculus math problems that can be solved.
- Operations on Functions
- Rational Expressions and Equations
- Polynomial and Rational Functions
- Analytic Trigonometry
- Sequences and Series
- Analytic Geometry in Rectangular Coordinates
- Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
Calculus Solutions
Below are examples of Calculus math problems that can be solved.
- Evaluating Limits
- Derivatives
- Applications of Differentiation
- Applications of Integration
- Techniques of Integration
- Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
- Differential Equations
Statistics Solutions
Below are examples of Statistics problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Review
- Average Descriptive Statistics
- Dispersion Statistics
- Probability
- Probability Distributions
- Frequency Distribution
- Normal Distributions
- t-Distributions
- Hypothesis Testing
- Estimation and Sample Size
- Correlation and Regression
Finite Math Solutions
Below are examples of Finite Math problems that can be solved.
- Polynomials and Expressions
- Equations and Inequalities
- Linear Functions and Points
- Systems of Linear Equations
- Mathematics of Finance
- Statistical Distributions
Linear Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Linear Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Introduction to Matrices
- Linear Independence and Combinations
Chemistry Solutions
Below are examples of Chemistry problems that can be solved.
- Unit Conversion
- Atomic Structure
- Molecules and Compounds
- Chemical Equations and Reactions
- Behavior of Gases
- Solutions and Concentrations
Physics Solutions
Below are examples of Physics math problems that can be solved.
- Static Equilibrium
- Dynamic Equilibrium
- Kinematics Equations
- Electricity
- Thermodymanics
Geometry Graphing Solutions
Below are examples of Geometry and graphing math problems that can be solved.
- Step By Step Graphing
- Linear Equations and Functions
- Polar Equations
Looking for the old Mathway Calculator? We've moved it to here .
Tips, tricks, lessons, and tutoring to help reduce test anxiety and move to the top of the class.
Email Address Sign Up

- Math Forum/Help
- Problem Solver
- College Math
- Word Problems
Math Word Problems and Solutions - Distance, Speed, Time
Problem 1 A salesman sold twice as much pears in the afternoon than in the morning. If he sold 360 kilograms of pears that day, how many kilograms did he sell in the morning and how many in the afternoon? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the number of kilograms he sold in the morning.Then in the afternoon he sold $2x$ kilograms. So, the total is $x + 2x = 3x$. This must be equal to 360. $3x = 360$ $x = \frac{360}{3}$ $x = 120$ Therefore, the salesman sold 120 kg in the morning and $2\cdot 120 = 240$ kg in the afternoon.
Problem 2 Mary, Peter, and Lucy were picking chestnuts. Mary picked twice as much chestnuts than Peter. Lucy picked 2 kg more than Peter. Together the three of them picked 26 kg of chestnuts. How many kilograms did each of them pick? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the amount Peter picked. Then Mary and Lucy picked $2x$ and $x+2$, respectively. So $x+2x+x+2=26$ $4x=24$ $x=6$ Therefore, Peter, Mary, and Lucy picked 6, 12, and 8 kg, respectively.
Problem 3 Sophia finished $\frac{2}{3}$ of a book. She calculated that she finished 90 more pages than she has yet to read. How long is her book? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the total number of pages in the book, then she finished $\frac{2}{3}\cdot x$ pages. Then she has $x-\frac{2}{3}\cdot x=\frac{1}{3}\cdot x$ pages left. $\frac{2}{3}\cdot x-\frac{1}{3}\cdot x=90$ $\frac{1}{3}\cdot x=90$ $x=270$ So the book is 270 pages long.
Problem 4 A farming field can be ploughed by 6 tractors in 4 days. When 6 tractors work together, each of them ploughs 120 hectares a day. If two of the tractors were moved to another field, then the remaining 4 tractors could plough the same field in 5 days. How many hectares a day would one tractor plough then? Click to see solution Solution: If each of $6$ tractors ploughed $120$ hectares a day and they finished the work in $4$ days, then the whole field is: $120\cdot 6 \cdot 4 = 720 \cdot 4 = 2880$ hectares. Let's suppose that each of the four tractors ploughed $x$ hectares a day. Therefore in 5 days they ploughed $5 \cdot 4 \cdot x = 20 \cdot x$ hectares, which equals the area of the whole field, 2880 hectares. So, we get $20x = 2880$ $ x = \frac{2880}{20} = 144$. Hence, each of the four tractors would plough 144 hectares a day.
Problem 5 A student chose a number, multiplied it by 2, then subtracted 138 from the result and got 102. What was the number he chose? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the number he chose, then $2\cdot x - 138 = 102$ $2x = 240$ $x = 120$
Problem 6 I chose a number and divide it by 5. Then I subtracted 154 from the result and got 6. What was the number I chose? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the number I chose, then $\frac{x}{5}-154=6$ $\frac{x}{5}=160$ $x=800$
| V (km/hr) | t (hr) | S (km) | |
| Car | x + 5 | 4 | 4(x +5) |
| Truck | X | 4 | 4x |
Problem 8 One side of a rectangle is 3 cm shorter than the other side. If we increase the length of each side by 1 cm, then the area of the rectangle will increase by 18 cm 2 . Find the lengths of all sides. Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the length of the longer side $x \gt 3$, then the other side's length is $x-3$ cm. Then the area is S 1 = x(x - 3) cm 2 . After we increase the lengths of the sides they will become $(x +1)$ and $(x - 3 + 1) = (x - 2)$ cm long. Hence the area of the new rectangle will be $A_2 = (x + 1)\cdot(x - 2)$ cm 2 , which is 18 cm 2 more than the first area. Therefore $A_1 +18 = A_2$ $x(x - 3) + 18 = (x + 1)(x - 2)$ $x^2 - 3x + 18 = x^2 + x - 2x - 2$ $2x = 20$ $x = 10$. So, the sides of the rectangle are $10$ cm and $(10 - 3) = 7$ cm long.
Problem 9 The first year, two cows produced 8100 litres of milk. The second year their production increased by 15% and 10% respectively, and the total amount of milk increased to 9100 litres a year. How many litres were milked from each cow each year? Click to see solution Solution: Let x be the amount of milk the first cow produced during the first year. Then the second cow produced $(8100 - x)$ litres of milk that year. The second year, each cow produced the same amount of milk as they did the first year plus the increase of $15\%$ or $10\%$. So $8100 + \frac{15}{100}\cdot x + \frac{10}{100} \cdot (8100 - x) = 9100$ Therefore $8100 + \frac{3}{20}x + \frac{1}{10}(8100 - x) = 9100$ $\frac{1}{20}x = 190$ $x = 3800$ Therefore, the cows produced 3800 and 4300 litres of milk the first year, and $4370$ and $4730$ litres of milk the second year, respectively.
Problem 10 The distance between stations A and B is 148 km. An express train left station A towards station B with the speed of 80 km/hr. At the same time, a freight train left station B towards station A with the speed of 36 km/hr. They met at station C at 12 pm, and by that time the express train stopped at at intermediate station for 10 min and the freight train stopped for 5 min. Find: a) The distance between stations C and B. b) The time when the freight train left station B. Click to see solution Solution a) Let x be the distance between stations B and C. Then the distance from station C to station A is $(148 - x)$ km. By the time of the meeting at station C, the express train travelled for $\frac{148-x}{80}+\frac{10}{60}$ hours and the freight train travelled for $\frac{x}{36}+\frac{5}{60}$ hours. The trains left at the same time, so: $\frac{148 - x}{80} + \frac{1}{6} = \frac{x}{36} + \frac{1}{12}$. The common denominator for 6, 12, 36, 80 is 720. Then $9(148 - x) +120 = 20x +60$ $1332 - 9x + 120 = 20x + 60$ $29x = 1392$ $x = 48$. Therefore the distance between stations B and C is 48 km. b) By the time of the meeting at station C the freight train rode for $\frac{48}{36} + \frac{5}{60}$ hours, i.e. $1$ hour and $25$ min. Therefore it left station B at $12 - (1 + \frac{25}{60}) = 10 + \frac{35}{60}$ hours, i.e. at 10:35 am.
Problem 11 Susan drives from city A to city B. After two hours of driving she noticed that she covered 80 km and calculated that, if she continued driving at the same speed, she would end up been 15 minutes late. So she increased her speed by 10 km/hr and she arrived at city B 36 minutes earlier than she planned. Find the distance between cities A and B. Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the distance between A and B. Since Susan covered 80 km in 2 hours, her speed was $V = \frac{80}{2} = 40$ km/hr. If she continued at the same speed she would be $15$ minutes late, i.e. the planned time on the road is $\frac{x}{40} - \frac{15}{60}$ hr. The rest of the distance is $(x - 80)$ km. $V = 40 + 10 = 50$ km/hr. So, she covered the distance between A and B in $2 +\frac{x - 80}{50}$ hr, and it was 36 min less than planned. Therefore, the planned time was $2 + \frac{x -80}{50} + \frac{36}{60}$. When we equalize the expressions for the scheduled time, we get the equation: $\frac{x}{40} - \frac{15}{60} = 2 + \frac{x -80}{50} + \frac{36}{60}$ $\frac{x - 10}{40} = \frac{100 + x - 80 + 30}{50}$ $\frac{x - 10}{4} = \frac{x +50}{5}$ $5x - 50 = 4x + 200$ $x = 250$ So, the distance between cities A and B is 250 km.
Problem 12 To deliver an order on time, a company has to make 25 parts a day. After making 25 parts per day for 3 days, the company started to produce 5 more parts per day, and by the last day of work 100 more parts than planned were produced. Find how many parts the company made and how many days this took. Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the number of days the company worked. Then 25x is the number of parts they planned to make. At the new production rate they made: $3\cdot 25 + (x - 3)\cdot 30 = 75 + 30(x - 3)$ Therefore: $25 x = 75 + 30(x -3) - 100$ $25x = 75 +30x -90 - 100$ $190 -75 = 30x -25$ $115 = 5x$ $x = 23$ So the company worked 23 days and they made $23\cdot 25+100 = 675$ pieces.
Problem 13 There are 24 students in a seventh grade class. They decided to plant birches and roses at the school's backyard. While each girl planted 3 roses, every three boys planted 1 birch. By the end of the day they planted $24$ plants. How many birches and roses were planted? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the number of roses. Then the number of birches is $24 - x$, and the number of boys is $3\times (24-x)$. If each girl planted 3 roses, there are $\frac{x}{3}$ girls in the class. We know that there are 24 students in the class. Therefore $\frac{x}{3} + 3(24 - x) = 24$ $x + 9(24 - x) = 3\cdot 24$ $x +216 - 9x = 72$ $216 - 72 = 8x$ $\frac{144}{8} = x$ $x = 18$ So, students planted 18 roses and 24 - x = 24 - 18 = 6 birches.
Problem 14 A car left town A towards town B driving at a speed of V = 32 km/hr. After 3 hours on the road the driver stopped for 15 min in town C. Because of a closed road he had to change his route, making the trip 28 km longer. He increased his speed to V = 40 km/hr but still he was 30 min late. Find: a) The distance the car has covered. b) The time that took it to get from C to B. Click to see solution Solution: From the statement of the problem we don't know if the 15 min stop in town C was planned or it was unexpected. So we have to consider both cases. A The stop was planned. Let us consider only the trip from C to B, and let $x$ be the number of hours the driver spent on this trip. Then the distance from C to B is $S = 40\cdot x$ km. If the driver could use the initial route, it would take him $x - \frac{30}{60} = x - \frac{1}{2}$ hours to drive from C to B. The distance from C to B according to the initially itinerary was $(x - \frac{1}{2})\cdot 32$ km, and this distance is $28$ km shorter than $40\cdot x$ km. Then we have the equation $(x - 1/2)\cdot 32 + 28 = 40x$ $32x -16 +28 = 40x$ $-8x = -12$ $8x = 12$ $x = \frac{12}{8}$ $x = 1 \frac{4}{8} = 1 \frac{1}{2} = 1 \frac{30}{60} =$ 1 hr 30 min. So, the car covered the distance between C and B in 1 hour and 30 min. The distance from A to B is $3\cdot 32 + \frac{12}{8}\cdot 40 = 96 + 60 = 156$ km. B Suppose it took $x$ hours for him to get from C to B. Then the distance is $S = 40\cdot x$ km. The driver did not plan the stop at C. Let we accept that he stopped because he had to change the route. It took $x - \frac{30}{60} + \frac{15}{60} = x - \frac{15}{60} = x - \frac{1}{4}$ h to drive from C to B. The distance from C to B is $32(x - \frac{1}{4})$ km, which is $28$ km shorter than $40\cdot x$, i.e. $32(x - \frac{1}{4}) + 28 = 40x$ $32x - 8 +28 = 40x$ $20= 8x$ $x = \frac{20}{8} = \frac{5}{2} = 2 \text{hr } 30 \text{min}.$ The distance covered equals $ 40 \times 2.5 = 100 km$.
Problem 15 If a farmer wants to plough a farm field on time, he must plough 120 hectares a day. For technical reasons he ploughed only 85 hectares a day, hence he had to plough 2 more days than he planned and he still has 40 hectares left. What is the area of the farm field and how many days the farmer planned to work initially? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the number of days in the initial plan. Therefore, the whole field is $120\cdot x$ hectares. The farmer had to work for $x + 2$ days, and he ploughed $85(x + 2)$ hectares, leaving $40$ hectares unploughed. Then we have the equation: $120x = 85(x + 2) + 40$ $35x = 210$ $x = 6$ So the farmer planned to have the work done in 6 days, and the area of the farm field is $120\cdot 6 = 720$ hectares.
Problem 16 A woodworker normally makes a certain number of parts in 24 days. But he was able to increase his productivity by 5 parts per day, and so he not only finished the job in only 22 days but also he made 80 extra parts. How many parts does the woodworker normally makes per day and how many pieces does he make in 24 days? Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the number of parts the woodworker normally makes daily. In 24 days he makes $24\cdot x$ pieces. His new daily production rate is $x + 5$ pieces and in $22$ days he made $22 \cdot (x + 5)$ parts. This is 80 more than $24\cdot x$. Therefore the equation is: $24\cdot x + 80 = 22(x +5)$ $30 = 2x$ $x = 15$ Normally he makes 15 parts a day and in 24 days he makes $15 \cdot 24 = 360$ parts.
Problem 17 A biker covered half the distance between two towns in 2 hr 30 min. After that he increased his speed by 2 km/hr. He covered the second half of the distance in 2 hr 20 min. Find the distance between the two towns and the initial speed of the biker. Click to see solution Solution: Let x km/hr be the initial speed of the biker, then his speed during the second part of the trip is x + 2 km/hr. Half the distance between two cities equals $2\frac{30}{60} \cdot x$ km and $2\frac{20}{60} \cdot (x + 2)$ km. From the equation: $2\frac{30}{60} \cdot x = 2\frac{20}{60} \cdot (x+2)$ we get $x = 28$ km/hr. The intial speed of the biker is 28 km/h. Half the distance between the two towns is $2 h 30 min \times 28 = 2.5 \times 28 = 70$. So the distance is $2 \times 70 = 140$ km.
Problem 18 A train covered half of the distance between stations A and B at the speed of 48 km/hr, but then it had to stop for 15 min. To make up for the delay, it increased its speed by $\frac{5}{3}$ m/sec and it arrived to station B on time. Find the distance between the two stations and the speed of the train after the stop. Click to see solution Solution: First let us determine the speed of the train after the stop. The speed was increased by $\frac{5}{3}$ m/sec $= \frac{5\cdot 60\cdot 60}{\frac{3}{1000}}$ km/hr = $6$ km/hr. Therefore, the new speed is $48 + 6 = 54$ km/hr. If it took $x$ hours to cover the first half of the distance, then it took $x - \frac{15}{60} = x - 0.25$ hr to cover the second part. So the equation is: $48 \cdot x = 54 \cdot (x - 0.25)$ $48 \cdot x = 54 \cdot x - 54\cdot 0.25$ $48 \cdot x - 54 \cdot x = - 13.5$ $-6x = - 13.5$ $x = 2.25$ h. The whole distance is $2 \times 48 \times 2.25 = 216$ km.
Problem 19 Elizabeth can get a certain job done in 15 days, and Tony can finish only 75% of that job within the same time. Tony worked alone for several days and then Elizabeth joined him, so they finished the rest of the job in 6 days, working together. For how many days have each of them worked and what percentage of the job have each of them completed? Click to see solution Solution: First we will find the daily productivity of every worker. If we consider the whole job as unit (1), Elizabeth does $\frac{1}{15}$ of the job per day and Tony does $75\%$ of $\frac{1}{15}$, i.e. $\frac{75}{100}\cdot \frac{1}{15} = \frac{1}{20}$. Suppose that Tony worked alone for $x$ days. Then he finished $\frac{x}{20}$ of the total job alone. Working together for 6 days, the two workers finished $6\cdot (\frac{1}{15}+\frac{1}{20}) = 6\cdot \frac{7}{60} = \frac{7}{10}$ of the job. The sum of $\frac{x}{20}$ and $\frac{7}{10}$ gives us the whole job, i.e. $1$. So we get the equation: $\frac{x}{20}+\frac{7}{10}=1$ $\frac{x}{20} = \frac{3}{10}$ $x = 6$. Tony worked for 6 + 6 = 12 days and Elizabeth worked for $6$ days. The part of job done is $12\cdot \frac{1}{20} = \frac{60}{100} = 60\%$ for Tony, and $6\cdot \frac{1}{15} = \frac{40}{100} = 40\%$ for Elizabeth.
Problem 20 A farmer planned to plough a field by doing 120 hectares a day. After two days of work he increased his daily productivity by 25% and he finished the job two days ahead of schedule. a) What is the area of the field? b) In how many days did the farmer get the job done? c) In how many days did the farmer plan to get the job done? Click to see solution Solution: First of all we will find the new daily productivity of the farmer in hectares per day: 25% of 120 hectares is $\frac{25}{100} \cdot 120 = 30$ hectares, therefore $120 + 30 = 150$ hectares is the new daily productivity. Lets x be the planned number of days allotted for the job. Then the farm is $120\cdot x$ hectares. On the other hand, we get the same area if we add $120 \cdot 2$ hectares to $150(x -4)$ hectares. Then we get the equation $120x = 120\cdot 2 + 150(x -4)$ $x = 12$ So, the job was initially supposed to take 12 days, but actually the field was ploughed in 12 - 2 =10 days. The field's area is $120 \cdot 12 = 1440$ hectares.
Problem 21 To mow a grass field a team of mowers planned to cover 15 hectares a day. After 4 working days they increased the daily productivity by $33 \times \frac{1}{3}\%$, and finished the work 1 day earlier than it was planned. A) What is the area of the grass field? B) How many days did it take to mow the whole field? C) How many days were scheduled initially for this job? Hint : See problem 20 and solve by yourself. Answer: A) 120 hectares; B) 7 days; C) 8 days.
Problem 22 A train travels from station A to station B. If the train leaves station A and makes 75 km/hr, it arrives at station B 48 minutes ahead of scheduled. If it made 50 km/hr, then by the scheduled time of arrival it would still have 40 km more to go to station B. Find: A) The distance between the two stations; B) The time it takes the train to travel from A to B according to the schedule; C) The speed of the train when it's on schedule. Click to see solution Solution: Let $x$ be the scheduled time for the trip from A to B. Then the distance between A and B can be found in two ways. On one hand, this distance equals $75(x - \frac{48}{60})$ km. On the other hand, it is $50x + 40$ km. So we get the equation: $75(x - \frac{48}{60}) = 50x + 40$ $x = 4$ hr is the scheduled travel time. The distance between the two stations is $50\cdot 4 +40 = 240$ km. Then the speed the train must keep to be on schedule is $\frac{240}{4} = 60$ km/hr.
Problem 23 The distance between towns A and B is 300 km. One train departs from town A and another train departs from town B, both leaving at the same moment of time and heading towards each other. We know that one of them is 10 km/hr faster than the other. Find the speeds of both trains if 2 hours after their departure the distance between them is 40 km. Click to see solution Solution: Let the speed of the slower train be $x$ km/hr. Then the speed of the faster train is $(x + 10)$ km/hr. In 2 hours they cover $2x$ km and $2(x +10)$km, respectively. Therefore if they didn't meet yet, the whole distance from A to B is $2x + 2(x +10) +40 = 4x +60$ km. However, if they already met and continued to move, the distance would be $2x + 2(x + 10) - 40 = 4x - 20$km. So we get the following equations: $4x + 60 = 300$ $4x = 240$ $x = 60$ or $4x - 20 = 300$ $4x = 320$ $x = 80$ Hence the speed of the slower train is $60$ km/hr or $80$ km/hr and the speed of the faster train is $70$ km/hr or $90$ km/hr.
Problem 24 A bus travels from town A to town B. If the bus's speed is 50 km/hr, it will arrive in town B 42 min later than scheduled. If the bus increases its speed by $\frac{50}{9}$ m/sec, it will arrive in town B 30 min earlier than scheduled. Find: A) The distance between the two towns; B) The bus's scheduled time of arrival in B; C) The speed of the bus when it's on schedule. Click to see solution Solution: First we will determine the speed of the bus following its increase. The speed is increased by $\frac{50}{9}$ m/sec $= \frac{50\cdot60\cdot60}{\frac{9}{1000}}$ km/hr $= 20$ km/hr. Therefore, the new speed is $V = 50 + 20 = 70$ km/hr. If $x$ is the number of hours according to the schedule, then at the speed of 50 km/hr the bus travels from A to B within $(x +\frac{42}{60})$ hr. When the speed of the bus is $V = 70$ km/hr, the travel time is $x - \frac{30}{60}$ hr. Then $50(x +\frac{42}{60}) = 70(x-\frac{30}{60})$ $5(x+\frac{7}{10}) = 7(x-\frac{1}{2})$ $\frac{7}{2} + \frac{7}{2} = 7x -5x$ $2x = 7$ $x = \frac{7}{2}$ hr. So, the bus is scheduled to make the trip in $3$ hr $30$ min. The distance between the two towns is $70(\frac{7}{2} - \frac{1}{2}) = 70\cdot 3 = 210$ km and the scheduled speed is $\frac{210}{\frac{7}{2}} = 60$ km/hr.
Word Problem Calculator
Get detailed solutions to your math problems with our word problem step-by-step calculator . practice your math skills and learn step by step with our math solver. check out all of our online calculators here ., example, solved problems, difficult problems, are you struggling with math.
Access detailed step by step solutions to thousands of problems, growing every day!
Popular problems
Most popular problems solved with this calculator:
Math Word Problems
Welcome to the math word problems worksheets page at Math-Drills.com! On this page, you will find Math word and story problems worksheets with single- and multi-step solutions on a variety of math topics including addition, multiplication, subtraction, division and other math topics. It is usually a good idea to ensure students already have a strategy or two in place to complete the math operations involved in a particular question. For example, students may need a way to figure out what 7 × 8 is or have previously memorized the answer before you give them a word problem that involves finding the answer to 7 × 8.
There are a number of strategies used in solving math word problems; if you don't have a favorite, try the Math-Drills.com problem-solving strategy:
- Question : Understand what the question is asking. What operation or operations do you need to use to solve this question? Ask for help to understand the question if you can't do it on your own.
- Estimate : Use an estimation strategy, so you can check your answer for reasonableness in the evaluate step. Try underestimating and overestimating, so you know what range the answer is supposed to be in. Be flexible in rounding numbers if it will make your estimate easier.
- Strategize : Choose a strategy to solve the problem. Will you use mental math, manipulatives, or pencil and paper? Use a strategy that works for you. Save the calculator until the evaluate stage.
- Calculate : Use your strategy to solve the problem.
- Evaluate : Compare your answer to your estimate. If you under and overestimated, is the answer in the correct range. If you rounded up or down, does the answer make sense (e.g. is it a little less or a little more than the estimate). Also check with a calculator.
Most Popular Math Word Problems this Week

Arithmetic Word Problems

- Addition Word Problems One-Step Addition Word Problems Using Single-Digit Numbers One-Step Addition Word Problems Using Two-Digit Numbers
- Subtraction Word Problems Subtraction Facts Word Problems With Differences from 5 to 12
- Multiplication Word Problems One-Step Multiplication Word Problems up to 10 × 10
- Division Word Problems Division Facts Word Problems with Quotients from 5 to 12
- Multi-Step Word Problems Easy Multi-Step Word Problems
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
Solving Word Questions
With LOTS of examples!
In Algebra we often have word questions like:
Example: Sam and Alex play tennis.
On the weekend Sam played 4 more games than Alex did, and together they played 12 games.
How many games did Alex play?
How do we solve them?
The trick is to break the solution into two parts:
Turn the English into Algebra.
Then use Algebra to solve.
Turning English into Algebra
To turn the English into Algebra it helps to:
- Read the whole thing first
- Do a sketch if possible
- Assign letters for the values
- Find or work out formulas
You should also write down what is actually being asked for , so you know where you are going and when you have arrived!
Also look for key words:
| When you see | Think | |
|---|---|---|
| add, total, sum, increase, more, combined, together, plus, more than | + | |
| minus, less, difference, fewer, decreased, reduced | − | |
| multiplied, times, of, product, factor | × | |
| divided, quotient, per, out of, ratio, percent, rate | ÷ | |
| maximize or minimize | geometry formulas | |
| rate, speed | distance formulas | |
| how long, days, hours, minutes, seconds | time |
Thinking Clearly
Some wording can be tricky, making it hard to think "the right way around", such as:
Example: Sam has 2 dollars less than Alex. How do we write this as an equation?
- Let S = dollars Sam has
- Let A = dollars Alex has
Now ... is that: S − 2 = A
or should it be: S = A − 2
or should it be: S = 2 − A
The correct answer is S = A − 2
( S − 2 = A is a common mistake, as the question is written "Sam ... 2 less ... Alex")
Example: on our street there are twice as many dogs as cats. How do we write this as an equation?
- Let D = number of dogs
- Let C = number of cats
Now ... is that: 2D = C
or should it be: D = 2C
Think carefully now!
The correct answer is D = 2C
( 2D = C is a common mistake, as the question is written "twice ... dogs ... cats")
Let's start with a really simple example so we see how it's done:
Example: A rectangular garden is 12m by 5m, what is its area ?
Turn the English into Algebra:
- Use w for width of rectangle: w = 12m
- Use h for height of rectangle: h = 5m
Formula for Area of a Rectangle : A = w × h
We are being asked for the Area.
A = w × h = 12 × 5 = 60 m 2
The area is 60 square meters .
Now let's try the example from the top of the page:

Example: Sam and Alex play Tennis. On the weekend Sam played 4 more games than Alex did, and together they played 12 games. How many games did Alex play?
- Use S for how many games Sam played
- Use A for how many games Alex played
We know that Sam played 4 more games than Alex, so: S = A + 4
And we know that together they played 12 games: S + A = 12
We are being asked for how many games Alex played: A
Which means that Alex played 4 games of tennis.
Check: Sam played 4 more games than Alex, so Sam played 8 games. Together they played 8 + 4 = 12 games. Yes!
A slightly harder example:

Example: Alex and Sam also build tables. Together they make 10 tables in 12 days. Alex working alone can make 10 in 30 days. How long would it take Sam working alone to make 10 tables?
- Use a for Alex's work rate
- Use s for Sam's work rate
12 days of Alex and Sam is 10 tables, so: 12a + 12s = 10
30 days of Alex alone is also 10 tables: 30a = 10
We are being asked how long it would take Sam to make 10 tables.
30a = 10 , so Alex's rate (tables per day) is: a = 10/30 = 1/3
Which means that Sam's rate is half a table a day (faster than Alex!)
So 10 tables would take Sam just 20 days.
Should Sam be paid more I wonder?
And another "substitution" example:

Example: Jenna is training hard to qualify for the National Games. She has a regular weekly routine, training for five hours a day on some days and 3 hours a day on the other days. She trains altogether 27 hours in a seven day week. On how many days does she train for five hours?
- The number of "5 hour" days: d
- The number of "3 hour" days: e
We know there are seven days in the week, so: d + e = 7
And she trains 27 hours in a week, with d 5 hour days and e 3 hour days: 5d + 3e = 27
We are being asked for how many days she trains for 5 hours: d
The number of "5 hour" days is 3
Check : She trains for 5 hours on 3 days a week, so she must train for 3 hours a day on the other 4 days of the week.
3 × 5 hours = 15 hours, plus 4 × 3 hours = 12 hours gives a total of 27 hours
Some examples from Geometry:
Example: A circle has an area of 12 mm 2 , what is its radius?
- Use A for Area: A = 12 mm 2
- Use r for radius
And the formula for Area is: A = π r 2
We are being asked for the radius.
We need to rearrange the formula to find the area
Example: A cube has a volume of 125 mm 3 , what is its surface area?
Make a quick sketch:
- Use V for Volume
- Use A for Area
- Use s for side length of cube
- Volume of a cube: V = s 3
- Surface area of a cube: A = 6s 2
We are being asked for the surface area.
First work out s using the volume formula:
Now we can calculate surface area:
An example about Money:

Example: Joel works at the local pizza parlor. When he works overtime he earns 1¼ times the normal rate. One week Joel worked for 40 hours at the normal rate of pay and also worked 12 hours overtime. If Joel earned $660 altogether in that week, what is his normal rate of pay?
- Joel's normal rate of pay: $N per hour
- Joel works for 40 hours at $N per hour = $40N
- When Joel does overtime he earns 1¼ times the normal rate = $1.25N per hour
- Joel works for 12 hours at $1.25N per hour = $(12 × 1¼N) = $15N
- And together he earned $660, so:
$40N + $(12 × 1¼N) = $660
We are being asked for Joel's normal rate of pay $N.
So Joel’s normal rate of pay is $12 per hour
Joel’s normal rate of pay is $12 per hour, so his overtime rate is 1¼ × $12 per hour = $15 per hour. So his normal pay of 40 × $12 = $480, plus his overtime pay of 12 × $15 = $180 gives us a total of $660
More about Money, with these two examples involving Compound Interest
Example: Alex puts $2000 in the bank at an annual compound interest of 11%. How much will it be worth in 3 years?
This is the compound interest formula:
So we will use these letters:
- Present Value PV = $2,000
- Interest Rate (as a decimal): r = 0.11
- Number of Periods: n = 3
- Future Value (the value we want): FV
We are being asked for the Future Value: FV
Example: Roger deposited $1,000 into a savings account. The money earned interest compounded annually at the same rate. After nine years Roger's deposit has grown to $1,551.33 What was the annual rate of interest for the savings account?
The compound interest formula:
- Present Value PV = $1,000
- Interest Rate (the value we want): r
- Number of Periods: n = 9
- Future Value: FV = $1,551.33
We are being asked for the Interest Rate: r
So the annual rate of interest is 5%
Check : $1,000 × (1.05) 9 = $1,000 × 1.55133 = $1,551.33
And an example of a Ratio question:
Example: At the start of the year the ratio of boys to girls in a class is 2 : 1 But now, half a year later, four boys have left the class and there are two new girls. The ratio of boys to girls is now 4 : 3 How many students are there altogether now?
- Number of boys now: b
- Number of girls now: g
The current ratio is 4 : 3
Which can be rearranged to 3b = 4g
At the start of the year there was (b + 4) boys and (g − 2) girls, and the ratio was 2 : 1
b + 4 g − 2 = 2 1
Which can be rearranged to b + 4 = 2(g − 2)
We are being asked for how many students there are altogether now: b + g
There are 12 girls !
And 3b = 4g , so b = 4g/3 = 4 × 12 / 3 = 16 , so there are 16 boys
So there are now 12 girls and 16 boys in the class, making 28 students altogether .
There are now 16 boys and 12 girls, so the ratio of boys to girls is 16 : 12 = 4 : 3 At the start of the year there were 20 boys and 10 girls, so the ratio was 20 : 10 = 2 : 1
And now for some Quadratic Equations :
Example: The product of two consecutive even integers is 168. What are the integers?
Consecutive means one after the other. And they are even , so they could be 2 and 4, or 4 and 6, etc.
We will call the smaller integer n , and so the larger integer must be n+2
And we are told the product (what we get after multiplying) is 168, so we know:
n(n + 2) = 168
We are being asked for the integers
That is a Quadratic Equation , and there are many ways to solve it. Using the Quadratic Equation Solver we get −14 and 12.
Check −14: −14(−14 + 2) = (−14)×(−12) = 168 YES
Check 12: 12(12 + 2) = 12×14 = 168 YES
So there are two solutions: −14 and −12 is one, 12 and 14 is the other.
Note: we could have also tried "guess and check":
- We could try, say, n=10: 10(12) = 120 NO (too small)
- Next we could try n=12: 12(14) = 168 YES
But unless we remember that multiplying two negatives make a positive we might overlook the other solution of (−14)×(−12).
Example: You are an Architect. Your client wants a room twice as long as it is wide. They also want a 3m wide veranda along the long side. Your client has 56 square meters of beautiful marble tiles to cover the whole area. What should the length of the room be?
Let's first make a sketch so we get things right!:
- the length of the room: L
- the width of the room: W
- the total Area including veranda: A
- the width of the room is half its length: W = ½L
- the total area is the (room width + 3) times the length: A = (W+3) × L = 56
We are being asked for the length of the room: L
This is a quadratic equation , there are many ways to solve it, this time let's use factoring :
And so L = 8 or −14
There are two solutions to the quadratic equation, but only one of them is possible since the length of the room cannot be negative!
So the length of the room is 8 m
L = 8, so W = ½L = 4
So the area of the rectangle = (W+3) × L = 7 × 8 = 56
There we are ...
... I hope these examples will help you get the idea of how to handle word questions. Now how about some practice?
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
Introduction to Word Problems
These lessons, with videos, examples, solutions and worksheets, help Grade 5 students learn how to solve word problems.
Related Pages More Grade 5 Math Word Problems More Lessons for Grade 5 Math Math Worksheets
The following diagram gives some examples of word problems keywords or clue words. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions of word problems.
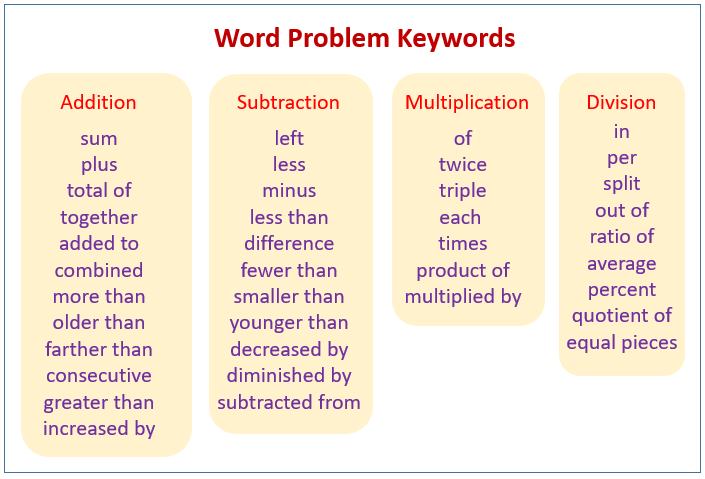
Introduction to Word Problem Terms
Problem Solving Strategies
Explain the meanings of the four basic operations–addition, subtraction, multiplication and division–so that you can understand how to solve word problems correctly.
Helpful hints for solving word problems

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
Algebra Word Problem Solvers
- Inspiration
Word problems
Here is a list of all of the skills that cover word problems! These skills are organized by grade, and you can move your mouse over any skill name to preview the skill. To start practicing, just click on any link. IXL will track your score, and the questions will automatically increase in difficulty as you improve!
Here is a list of all of the skills that cover word problems! To start practicing, just click on any link.
Pre-K skills
- V.8 Addition word problems with pictures - sums up to 5
- W.8 Addition word problems with pictures - sums up to 10
- X.7 Subtraction word problems with pictures - numbers up to 5
- Y.7 Subtraction word problems with pictures - numbers up to 10
Kindergarten skills
- Q.1 Build cube trains to solve addition word problems - sums up to 5
- Q.2 Addition word problems with pictures - sums up to 5
- Q.3 Write addition sentences for word problems with pictures - sums up to 5
- Q.4 Addition word problems - sums up to 5
- Q.5 Model and write addition sentences for word problems - sums up to 5
- U.1 Build cube trains to solve addition word problems - sums up to 10
- U.2 Addition word problems with pictures - sums up to 10
- U.3 Write addition sentences for word problems with pictures - sums up to 10
- U.4 Addition word problems - sums up to 10
- U.5 Model and write addition sentences for word problems - sums up to 10
- V.4 Subtraction sentences up to 5 - what does the cube train show?
- X.1 Subtraction word problems with pictures - numbers up to 5
- X.2 Write subtraction sentences for word problems with pictures - up to 5
- X.3 Use cube trains to solve subtraction word problems - up to 5
- X.4 Subtraction word problems - numbers up to 5
- X.5 Model and write subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 5
- Y.4 Subtraction sentences up to 10 - what does the cube train show?
- AA.1 Subtraction word problems with pictures - numbers up to 10
- AA.2 Write subtraction sentences for word problems with pictures - up to 10
- AA.3 Use cube trains to solve subtraction word problems - up to 10
- AA.4 Subtraction word problems - numbers up to 10
- AA.5 Model and write subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 10
- CC.1 Addition and subtraction word problems with pictures
- CC.2 Use cube trains to solve addition and subtraction word problems - up to 10
- CC.3 Addition and subtraction word problems
- CC.4 Model and write addition and subtraction sentences for word problems
First-grade skills
- C.6 Skip-counting patterns - with tables
- H.1 Addition word problems with pictures - sums up to 10
- H.2 Write addition sentences for word problems with pictures - sums up to 10
- H.3 Build cube trains to solve addition word problems - sums up to 10
- H.4 Addition word problems - sums up to 10
- H.5 Model and write addition sentences for word problems - sums up to 10
- H.6 Addition sentences for word problems - sums up to 10
- I.5 Subtraction sentences up to 10: what does the cube train show?
- L.1 Subtraction word problems with pictures - up to 10
- L.2 Write subtraction sentences for word problems with pictures - up to 10
- L.3 Use cube trains to solve subtraction word problems - up to 10
- L.4 Subtraction word problems - up to 10
- L.5 Model and write subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 10
- L.6 Subtraction sentences for "take apart" word problems - up to 10
- L.7 Subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 10
- N.1 Comparison word problems up to 10: how many more?
- N.2 Subtraction sentences for comparison word problems up to 10: how many more?
- N.3 Comparison word problems up to 10: how many fewer?
- N.4 Subtraction sentences for comparison word problems up to 10: how many fewer?
- N.5 Comparison word problems up to 10: how many more or fewer?
- N.6 Subtraction sentences for comparison word problems up to 10: how many more or fewer?
- N.7 Comparison word problems up to 10: what is the larger amount?
- N.8 Comparison word problems up to 10: what is the smaller amount?
- N.9 Comparison word problems up to 10
- O.1 Addition and subtraction word problems with pictures - up to 10
- O.2 Use cube trains to solve addition and subtraction word problems - up to 10
- O.3 Word problems with unknown sums and differences - up to 10
- O.4 Addition and subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 10
- O.5 Word problems with change unknown - up to 10
- O.6 Word problems with start unknown - up to 10
- O.7 Word problems with one addend unknown - up to 10
- O.8 Word problems with both addends unknown - up to 10
- O.9 Word problems involving addition and subtraction - up to 10
- O.10 Match word problems to addition and subtraction sentences - up to 10
- R.1 Addition word problems with models - sums up to 20
- R.2 Addition word problems - sums up to 20
- R.3 Addition sentences for word problems - sums up to 20
- R.4 Add three numbers - word problems
- U.1 Subtraction word problems - up to 20
- U.2 Subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 20
- W.1 Comparison word problems up to 20: how many more or fewer?
- W.2 Comparison word problems up to 20: what is the larger amount?
- W.3 Comparison word problems up to 20: what is the smaller amount?
- W.4 Comparison word problems up to 20: part 1
- W.5 Comparison word problems up to 20: part 2
- X.1 Word problems with one addend unknown - up to 20
- X.2 Word problems with both addends unknown - up to 20
- X.3 Use models to solve word problems involving addition and subtraction - up to 20
- X.4 Word problems involving addition and subtraction - up to 20
- X.5 Addition and subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 20
- X.6 Match word problems to addition and subtraction sentences - up to 20
- BB.4 Compare numbers up to 100: word problems
- DD.13 Addition word problems - one-digit plus two-digit numbers
- DD.14 Addition sentences for word problems - one-digit plus two-digit numbers
- EE.11 Customary units of length: word problems
- EE.13 Metric units of length: word problems
- FF.7 Time and clocks: word problems
- HH.8 Money - word problems
Second-grade skills
- B.5 Greatest and least - word problems - up to 100
- B.6 Greatest and least - word problems - up to 1,000
- C.6 Skip-counting stories
- C.10 Skip-counting puzzles
- G.4 Addition word problems - sums to 20
- G.5 Addition sentences for word problems - sums to 20
- G.10 Addition word problems - three one-digit numbers
- G.12 Addition word problems - four or more one-digit numbers
- I.3 Subtraction word problems - up to 20
- I.4 Subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 20
- K.1 Comparison word problems - up to 20
- K.2 Use models to solve addition and subtraction word problems - up to 20
- K.3 Addition and subtraction word problems - up to 20
- K.4 Match word problems to addition and subtraction sentences - up to 20
- K.5 Two-step addition and subtraction word problems - up to 20
- K.6 Solve word problems using guess-and-check - up to 20
- L.16 Guess the number
- N.8 Addition word problems - up to two digits
- N.16 Addition word problems - three numbers up to two digits each
- N.19 Addition word problems - four numbers up to two digits each
- P.10 Subtraction word problems - up to two digits
- R.1 Addition and subtraction word problems - up to 100
- R.2 Two-step addition and subtraction word problems - up to 100
- T.5 Addition word problems - up to three digits
- V.6 Subtraction word problems - up to three digits
- W.4 Addition and subtraction word problems - up to 1,000
- X.6 Solve word problems using repeated addition - sums to 25
- AA.14 Making change
- BB.2 Add money up to $1: word problems
- BB.4 Subtract money up to $1: word problems
- BB.6 Add and subtract money up to $1: word problems
- GG.6 Compare lengths: customary units
- GG.7 Customary units of length: word problems
- HH.4 Compare lengths: metric units
- HH.5 Metric units of length: word problems
Third-grade skills
- A.6 Place value word problems
- A.7 Guess the number
- B.5 Ordering puzzles
- D.3 Estimate sums by rounding: word problems
- E.3 Estimate differences by rounding: word problems
- F.3 Estimate sums and differences: word problems
- G.7 Add two numbers up to three digits: word problems
- G.12 Add three numbers up to three digits each: word problems
- H.7 Subtract numbers up to three digits: word problems
- I.3 Add two numbers up to four digits: word problems
- I.7 Add three numbers up to four digits each: word problems
- J.3 Subtract two numbers up to four digits: word problems
- K.6 Addition and subtraction word problems
- K.7 Age puzzles
- K.8 Find two numbers based on sum and difference
- M.3 Skip-counting puzzles
- S.1 Use equal groups and arrays to solve multiplication word problems
- S.2 Multiplication word problems with factors up to 5
- S.3 Use strip models to solve multiplication word problems
- S.4 Multiplication word problems with factors up to 10
- S.5 Multiplication word problems with factors up to 5: find the missing number
- S.6 Multiplication word problems with factors up to 10: find the missing number
- S.7 Compare numbers using multiplication: word problems
- T.7 Multiply one-digit numbers by two-digit numbers: word problems
- T.9 Multiply three numbers: word problems
- Y.1 Use equal groups to solve division word problems
- Y.2 Use arrays to solve division word problems
- Y.3 Use equal groups and arrays to solve division word problems
- Y.4 Division word problems
- Z.6 Multiplication and division word problems
- AA.4 Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division word problems
- AA.5 Find two numbers based on sum, difference, product, and quotient
- BB.1 Two-step addition and subtraction word problems
- BB.2 Two-step multiplication and division word problems
- BB.3 Two-step mixed operation word problems
- BB.4 Two-step word problems: identify reasonable answers
- CC.5 Write equations with unknown numbers to represent word problems: multiplication and division only
- CC.6 Write equations with unknown numbers to represent word problems
- FF.1 Unit fractions: modeling word problems
- FF.2 Unit fractions: word problems
- FF.3 Fractions of a whole: modeling word problems
- FF.4 Fractions of a whole: word problems
- FF.5 Fractions of a group: word problems
- KK.5 Compare fractions in recipes
- MM.12 Find the area of rectangles: word problems
- MM.13 Find the missing side length of a rectangle: word problems
- NN.6 Perimeter: word problems
- OO.1 Find the area, perimeter, or side length: word problems
- SS.3 Find the end time: word problems
- SS.4 Find the elapsed time: word problems
- SS.5 Find start and end times: two-step word problems
- UU.6 Measurement word problems
- WW.6 Making change
- WW.10 Add money amounts - word problems
Fourth-grade skills
- A.9 Place value word problems
- B.5 Find the order
- C.5 Rounding puzzles
- D.2 Estimate sums: word problems
- D.4 Add two multi-digit numbers: word problems
- E.2 Estimate differences: word problems
- E.4 Subtract two multi-digit numbers: word problems
- F.8 Compare numbers using multiplication: word problems
- F.9 Comparison word problems: addition or multiplication?
- G.2 Divisibility rules: word problems
- H.4 Estimate products word problems: identify reasonable answers
- H.10 Multiply 1-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers: word problems
- H.11 Multiply 1-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers: multi-step word problems
- H.17 Multiply 1-digit numbers by 3-digit or 4-digit numbers: word problems
- H.18 Multiply 1-digit numbers by 3-digit or 4-digit numbers: multi-step word problems
- I.3 Multiply two multiples of ten: word problems
- I.5 Estimate products: word problems
- I.11 Multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number: word problems
- I.12 Multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number: multi-step word problems
- J.2 Division facts to 10: word problems
- J.4 Division facts to 12: word problems
- L.1 Divide numbers ending in zeros by 1-digit numbers: word problems
- L.2 Divide 2-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers: interpret remainders
- L.3 Divide 2-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers: word problems
- L.4 Divide larger numbers by 1-digit numbers: interpret remainders
- L.5 Divide larger numbers by 1-digit numbers: word problems
- M.2 Estimate sums, differences, products, and quotients: word problems
- M.5 Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division word problems
- M.7 Find two numbers based on sum and difference
- M.9 Find two numbers based on sum, difference, product, and quotient
- M.11 Write equations to represent word problems
- M.13 Use equations to solve addition and subtraction word problems
- N.1 Multi-step addition and subtraction word problems
- N.2 Multi-step word problems with strip diagrams
- N.3 Use strip diagrams to represent and solve multi-step word problems
- N.4 Multi-step word problems
- N.5 Multi-step word problems involving remainders
- N.6 Multi-step word problems: identify reasonable answers
- N.7 Word problems with extra or missing information
- N.8 Solve word problems using guess-and-check
- O.7 Number patterns: word problems
- P.1 Fractions of a whole: word problems
- P.2 Fractions of a group: word problems
- T.4 Add and subtract fractions with like denominators: word problems
- T.5 Add and subtract fractions with like denominators in recipes
- T.12 Add and subtract mixed numbers with like denominators in recipes
- T.13 Add and subtract mixed numbers with like denominators: word problems
- U.7 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators: word problems
- V.6 Multiply unit fractions by whole numbers: word problems
- W.7 Multiply fractions by whole numbers: word problems
- W.10 Multiply fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers in recipes
- W.13 Fractions of a number: word problems
- Z.7 Add and subtract decimals: word problems
- Z.10 Add 3 or more decimals: word problems
- Z.13 Solve decimal problems using diagrams
- AA.5 Find the change, price, or amount paid
- AA.8 Multi-step word problems with money: addition and subtraction only
- AA.9 Multi-step word problems with money
- CC.5 Elapsed time: word problems
- CC.6 Find start and end times: multi-step word problems
- FF.1 Measurement word problems
- FF.2 Measurement word problems with fractions
- HH.8 Relationship between area and perimeter
- HH.9 Area and perimeter: word problems
- HH.10 Rectangles: relationship between perimeter and area word problems
Fifth-grade skills
- B.2 Estimate sums and differences: word problems
- B.4 Add and subtract whole numbers: word problems
- D.3 Multiply numbers ending in zeros: word problems
- D.6 Estimate products: word problems
- D.8 Multiply by 1-digit numbers: word problems
- D.13 Multiply by 2-digit numbers: word problems
- E.3 Divide numbers ending in zeros: word problems
- E.7 Divide by 1-digit numbers: interpret remainders
- E.8 Divide multi-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers: word problems
- E.12 Divide 2-digit and 3-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers: word problems
- E.14 Divide 4-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers: word problems
- F.5 Divisibility rules: word problems
- G.2 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers: word problems
- I.1 Write numerical expressions for word problems
- I.2 Multi-step word problems
- I.3 Multi-step word problems involving remainders
- I.4 Multi-step word problems: identify reasonable answers
- L.7 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators: word problems
- L.9 Add 3 or more fractions: word problems
- M.6 Add and subtract mixed numbers: word problems
- M.7 Add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers in recipes
- O.3 Multiply fractions by whole numbers: word problems
- O.6 Fractions of a number: word problems
- P.2 Multiply two fractions: word problems
- R.7 Multiplication with mixed numbers: word problems
- R.8 Multiply fractions and mixed numbers in recipes
- V.2 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions and mixed numbers: word problems
- X.6 Compare, order, and round decimals: word problems
- AA.6 Add and subtract decimals: word problems
- CC.8 Multiply decimals and whole numbers: word problems
- FF.7 Division with decimal quotients: word problems
- GG.2 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals: word problems
- HH.2 Add and subtract money: word problems
- HH.3 Add and subtract money: multi-step word problems
- HH.5 Multiply money amounts: word problems
- HH.6 Multiply money amounts: multi-step word problems
- HH.8 Divide money amounts: word problems
- HH.11 Find the number of each type of coin
- II.10 Multi-step problems with customary unit conversions
- JJ.8 Multi-step problems with metric unit conversions
- JJ.9 Multi-step problems with customary or metric unit conversions
- KK.5 Number patterns: word problems
- MM.2 Write variable expressions: word problems
- MM.4 Write variable equations: word problems
- TT.7 Area and perimeter: word problems
- UU.4 Volume of rectangular prisms made of unit cubes: word problems
- UU.6 Volume of cubes and rectangular prisms: word problems
- UU.7 Compare volumes and dimensions of rectangular prisms: word problems
- VV.1 Income and payroll taxes: understanding pay stubs
- VV.2 Income and payroll taxes: word problems
- VV.3 Sales and property taxes: word problems
- VV.9 Reading financial records
- VV.10 Keeping financial records
Sixth-grade skills
- A.2 Add and subtract whole numbers: word problems
- B.2 Multiply whole numbers: word problems
- B.4 Multiply numbers ending in zeros: word problems
- C.3 Divide numbers ending in zeros: word problems
- E.2 Add, subtract, multiply, or divide two whole numbers: word problems
- E.3 Estimate to solve word problems
- E.4 Multi-step word problems
- E.5 Multi-step word problems: identify reasonable answers
- F.10 GCF and LCM: word problems
- H.2 Add and subtract decimals: word problems
- H.3 Add and subtract money amounts: word problems
- I.6 Divide decimals by whole numbers: word problems
- I.11 Multiply and divide decimals: word problems
- J.2 Add, subtract, multiply, or divide two decimals: word problems
- K.2 Add and subtract fractions with like denominators: word problems
- K.4 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators: word problems
- K.7 Add and subtract mixed numbers: word problems
- L.3 Multiply fractions by whole numbers: word problems
- L.7 Multiply fractions: word problems
- L.14 Multiply mixed numbers: word problems
- M.5 Divide fractions by whole numbers in recipes
- M.12 Divide fractions and mixed numbers: word problems
- N.2 Add, subtract, multiply, or divide two fractions: word problems
- O.10 Absolute value and integers: word problems
- P.8 Add and subtract integers: word problems
- Q.6 Compare and order rational numbers: word problems
- S.3 Write a ratio: word problems
- S.8 Equivalent ratios: word problems
- S.11 Calculate speed, distance, or time: word problems
- S.12 Ratios and rates: complete a table and make a graph
- S.13 Use tape diagrams to solve ratio word problems
- S.14 Compare ratios: word problems
- S.15 Compare rates: word problems
- S.16 Ratios and rates: word problems
- S.19 Scale drawings: word problems
- T.3 Identify proportional relationships by graphing
- T.4 Interpret graphs of proportional relationships
- U.5 Convert between percents, fractions, and decimals: word problems
- U.7 Compare percents and fractions: word problems
- V.5 Percents of numbers: word problems
- V.8 Find what percent one number is of another: word problems
- V.11 Solve percent word problems
- W.10 Compare temperatures above and below zero
- X.7 Percents - calculate tax, tip, mark-up, and more
- Y.3 Write variable expressions: word problems
- Y.7 Evaluate variable expressions: word problems
- AA.13 Solve one-step addition and subtraction equations: word problems
- AA.14 Solve one-step multiplication and division equations: word problems
- AA.15 Write a one-step equation: word problems
- AA.16 Solve one-step equations: word problems
- AA.17 Which word problem matches the one-step equation?
- BB.4 Write and graph inequalities: word problems
- CC.2 Identify independent and dependent variables in tables and graphs
- CC.4 Identify independent and dependent variables: word problems
- CC.6 Find a value using two-variable equations: word problems
- CC.7 Solve word problems by finding two-variable equations
- CC.13 Graph a two-variable equation
- CC.14 Interpret a graph: word problems
- GG.17 Area of quadrilaterals and triangles: word problems
- HH.3 Volume of cubes and rectangular prisms: word problems
- JJ.10 Interpret measures of center and variability
- KK.1 Counting principle
- LL.1 Compare checking accounts
Seventh-grade skills
- A.6 Quantities that combine to zero: word problems
- B.14 Add and subtract integers: word problems
- D.2 Add and subtract decimals: word problems
- D.4 Multiply decimals and whole numbers: word problems
- D.6 Divide decimals by whole numbers: word problems
- D.9 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals: word problems
- E.4 GCF and LCM: word problems
- F.1 Understanding fractions: word problems
- F.4 Fractions: word problems with graphs and tables
- F.7 Compare fractions: word problems
- G.2 Add and subtract fractions: word problems
- G.4 Add and subtract mixed numbers: word problems
- G.10 Multiply fractions and mixed numbers: word problems
- G.14 Divide fractions and mixed numbers: word problems
- G.16 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions and mixed numbers: word problems
- I.6 Identify quotients of rational numbers: word problems
- I.11 Multi-step word problems with positive rational numbers
- L.4 Equivalent ratios: word problems
- L.7 Compare ratios: word problems
- L.8 Compare rates: word problems
- L.10 Do the ratios form a proportion: word problems
- L.12 Solve proportions: word problems
- L.13 Estimate population size using proportions
- N.1 Find the constant of proportionality from a table
- N.2 Write equations for proportional relationships from tables
- N.3 Identify proportional relationships by graphing
- N.4 Find the constant of proportionality from a graph
- N.5 Write equations for proportional relationships from graphs
- N.10 Interpret graphs of proportional relationships
- N.11 Write and solve equations for proportional relationships
- O.7 Percents of numbers: word problems
- O.9 Solve percent equations: word problems
- O.11 Percent of change: word problems
- O.12 Percent of change: find the original amount word problems
- O.13 Percent error: word problems
- P.1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide money amounts: word problems
- P.8 Find the percent: tax, discount, and more
- P.10 Multi-step problems with percents
- R.3 Write variable expressions: word problems
- S.14 Identify equivalent linear expressions: word problems
- T.11 Choose two-step equations: word problems
- T.12 Solve two-step equations: word problems
- U.6 One-step inequalities: word problems
- V.5 Sequences: word problems
- X.1 Identify independent and dependent variables
- X.8 Interpret a graph: word problems
- BB.4 Area and perimeter: word problems
- BB.7 Circles: word problems
- CC.6 Volume of cubes and rectangular prisms: word problems
- DD.2 Scale drawings: word problems
- DD.3 Scale drawings: scale factor word problems
- HH.9 Make inferences from multiple samples
- HH.10 Compare populations using measures of center and spread
- II.4 Experimental probability
- II.10 Find the number of outcomes: word problems
Eighth-grade skills
- A.6 Add and subtract integers: word problems
- B.7 Add and subtract rational numbers: word problems
- B.10 Multiply and divide rational numbers: word problems
- B.14 Multi-step word problems
- G.2 Solve proportions: word problems
- G.3 Estimate population size using proportions
- G.4 Scale drawings: word problems
- G.5 Scale drawings: scale factor word problems
- H.4 Find what percent one number is of another: word problems
- H.7 Percents of numbers: word problems
- H.11 Percent of change: word problems
- H.12 Percent of change: find the original amount word problems
- I.6 Find the percent: tax, discount, and more
- I.8 Multi-step problems with percents
- K.4 Write variable expressions: word problems
- L.9 Identify equivalent linear expressions: word problems
- M.10 Solve one-step and two-step equations: word problems
- M.14 Solve equations with variables on both sides: word problems
- T.5 Pythagorean theorem: word problems
- V.3 Area and perimeter: word problems
- V.5 Circles: word problems
- X.1 Find the constant of proportionality from a table
- X.2 Write equations for proportional relationships from tables
- X.3 Identify proportional relationships by graphing
- X.4 Find the constant of proportionality from a graph
- X.5 Write equations for proportional relationships from graphs
- X.8 Identify proportional relationships: word problems
- X.9 Graph proportional relationships and find the slope
- X.10 Interpret graphs of proportional relationships
- X.11 Write and solve equations for proportional relationships
- X.12 Compare proportional relationships represented in different ways
- BB.3 Identify independent and dependent variables
- CC.4 Interpret points on the graph of a linear function
- CC.6 Interpret the slope and y-intercept of a linear function
- CC.10 Write linear functions: word problems
- FF.5 Sequences: word problems
- GG.3 Solve a system of equations by graphing: word problems
- GG.9 Solve a system of equations using substitution: word problems
- GG.11 Solve a system of equations using elimination: word problems
- GG.13 Solve a system of equations using any method: word problems
- II.10 Interpret lines of best fit: word problems
- JJ.3 Experimental probability
- JJ.10 Counting principle
Algebra 1 skills
- C.9 Solve one-step and two-step linear equations: word problems
- C.11 Consecutive integer problems
- C.16 Solve linear equations with variables on both sides: word problems
- D.1 Area and perimeter: word problems
- E.1 Scale drawings: word problems
- E.5 Multi-step problems with unit conversions
- E.6 Rate of travel: word problems
- E.7 Weighted averages: word problems
- M.3 Identify independent and dependent variables
- N.4 Evaluate a linear function from its graph: word problems
- N.5 Interpret the slope and y-intercept of a linear function
- N.8 Domain and range of linear functions: word problems
- O.3 Solve a system of equations by graphing: word problems
- O.9 Solve a system of equations using substitution: word problems
- O.11 Solve a system of equations using elimination: word problems
- O.13 Solve a system of equations using augmented matrices: word problems
- O.15 Solve a system of equations using any method: word problems
- P.5 Write two-variable inequalities: word problems
- V.7 Write exponential functions: word problems
- V.8 Exponential growth and decay: word problems
- Z.7 Solve quadratic equations: word problems
- AA.5 Write linear and exponential functions: word problems
- JJ.6 Interpret lines of best fit: word problems
- JJ.8 Interpret regression lines
- JJ.9 Analyze a regression line of a data set
- KK.6 Identify independent and dependent events
- KK.8 Counting principle
- KK.9 Permutations
Geometry skills
- A.1 Identify hypotheses and conclusions
- A.2 Counterexamples
- P.1 Pythagorean theorem
- V.9 Calculate density, mass, and volume
- AA.5 Counting principle
- AA.6 Permutations
- AA.15 Find probabilities using the addition rule
Algebra 2 skills
- B.3 Solve linear equations: word problems
- E.3 Solve a system of equations by graphing: word problems
- E.7 Solve a system of equations using substitution: word problems
- E.9 Solve a system of equations using elimination: word problems
- E.11 Solve a system of equations using any method: word problems
- F.1 Write two-variable linear inequalities: word problems
- O.7 Solve quadratic equations: word problems
- Z.3 Write exponential functions: word problems
- Z.9 Exponential growth and decay: word problems
- CC.4 Compound interest: word problems
- CC.5 Continuously compounded interest: word problems
- OO.2 Counting principle
- OO.4 Find probabilities using combinations and permutations
- OO.5 Find probabilities using two-way frequency tables
- OO.10 Find conditional probabilities using two-way frequency tables
- OO.11 Find probabilities using the addition rule
- PP.8 Write the probability distribution for a game of chance
- PP.9 Expected values for a game of chance
- PP.10 Choose the better bet
- QQ.1 Find probabilities using the binomial distribution
- RR.5 Find confidence intervals for population means
- RR.6 Find confidence intervals for population proportions
- RR.7 Interpret confidence intervals for population means
- RR.8 Experiment design
- RR.9 Analyze the results of an experiment using simulations
- SS.5 Interpret regression lines
- SS.6 Analyze a regression line of a data set
- TT.19 Solve a system of equations using augmented matrices: word problems
Precalculus skills
- D.9 Solve quadratic equations: word problems
- K.5 Exponential growth and decay: word problems
- K.6 Compound interest: word problems
- N.2 Solve a system of equations by graphing: word problems
- N.5 Solve a system of equations using substitution: word problems
- N.7 Solve a system of equations using elimination: word problems
- N.9 Solve a system of equations using augmented matrices: word problems
- CC.3 Find probabilities using combinations and permutations
- CC.4 Find probabilities using two-way frequency tables
- CC.8 Find conditional probabilities using two-way frequency tables
- CC.9 Find probabilities using the addition rule
- DD.8 Write the probability distribution for a game of chance
- DD.9 Expected values for a game of chance
- DD.10 Choose the better bet
- EE.1 Find probabilities using the binomial distribution
- EE.2 Mean, variance, and standard deviation of binomial distributions
- EE.9 Use normal distributions to approximate binomial distributions
- FF.5 Find confidence intervals for population means
- FF.6 Find confidence intervals for population proportions
- FF.7 Interpret confidence intervals for population means
- FF.8 Experiment design
- FF.9 Analyze the results of an experiment using simulations
- GG.5 Interpret regression lines
- GG.6 Analyze a regression line of a data set
- GG.7 Analyze a regression line using statistics of a data set
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Praxis Core Math
Course: praxis core math > unit 1.
- Algebraic properties | Lesson
- Algebraic properties | Worked example
- Solution procedures | Lesson
- Solution procedures | Worked example
- Equivalent expressions | Lesson
- Equivalent expressions | Worked example
- Creating expressions and equations | Lesson
- Creating expressions and equations | Worked example
Algebraic word problems | Lesson
- Algebraic word problems | Worked example
- Linear equations | Lesson
- Linear equations | Worked example
- Quadratic equations | Lesson
- Quadratic equations | Worked example
What are algebraic word problems?
What skills are needed.
- Translating sentences to equations
- Solving linear equations with one variable
- Evaluating algebraic expressions
- Solving problems using Venn diagrams
How do we solve algebraic word problems?
- Define a variable.
- Write an equation using the variable.
- Solve the equation.
- If the variable is not the answer to the word problem, use the variable to calculate the answer.
What's a Venn diagram?
- 7 + 10 − 13 = 4 brought both food and drinks.
- 7 − 4 = 3 brought only food.
- 10 − 4 = 6 brought only drinks.
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
- (Choice A) $ 4 A $ 4
- (Choice B) $ 5 B $ 5
- (Choice C) $ 9 C $ 9
- (Choice D) $ 14 D $ 14
- (Choice E) $ 20 E $ 20
- (Choice A) 10 A 10
- (Choice B) 12 B 12
- (Choice C) 24 C 24
- (Choice D) 30 D 30
- (Choice E) 32 E 32
- (Choice A) 4 A 4
- (Choice B) 10 B 10
- (Choice C) 14 C 14
- (Choice D) 18 D 18
- (Choice E) 22 E 22
Things to remember
Want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
- 1-800-234-2933
- [email protected]

Word Problems Calculators: (41) lessons
2 number word problems.
Free 2 number Word Problems Calculator - This calculator handles word problems in the format below: * Two numbers have a sum of 70 and a product of 1189 What are the numbers? * Two numbers have a sum of 70. Their difference 32
2 Unknown Word Problems
Free 2 Unknown Word Problems Calculator - Solves a word problem based on two unknown variables
Age Difference
Free Age Difference Calculator - Determines the ages for an age difference word problem.
Age Word Problems
Free Age Word Problems Calculator - Determines age in age word problems
Angle of Elevation
Free Angle of Elevation Calculator - Solves angle of elevation word problems
Free Break Even Calculator - Given a fixed cost, variable cost, and revenue function or value, this calculates the break-even point
Coin Combinations
Free Coin Combinations Calculator - Given a selection of coins and an amount, this determines the least amount of coins needed to reach that total.
Coin Total Word Problems
Free Coin Total Word Problems Calculator - This word problem lesson solves for a quantity of two coins totaling a certain value with a certain amount more or less of one coin than another
Coin Word Problems
Free Coin Word Problems Calculator - This word problem lesson solves for a quantity of two coins totaling a certain value
Collinear Points that form Unique Lines
Free Collinear Points that form Unique Lines Calculator - Solves the word problem, how many lines can be formed from (n) points no 3 of which are collinear.
Compare Raises
Free Compare Raises Calculator - Given two people with a salary and annual raise amount, this determines how long it takes for the person with the lower salary to catch the person with the higher salary.
Consecutive Integer Word Problems
Free Consecutive Integer Word Problems Calculator - Calculates the word problem for what two consecutive integers, if summed up or multiplied together, equal a number entered.
Cost Revenue Profit
Free Cost Revenue Profit Calculator - Given a total cost, variable cost, revenue amount, and profit unit measurement, this calculates profit for each profit unit
Free Decay Calculator - Determines decay based on an initial mass and decay percentage and time.
Distance Catch Up
Free Distance Catch Up Calculator - Calculates the amount of time that it takes for a person traveling at one speed to catch a person traveling at another speed when one person leaves at a later time.
Distance Rate and Time
Free Distance Rate and Time Calculator - Solves for distance, rate, or time in the equation d=rt based on 2 of the 3 variables being known.
Find two numbers word problems
Free Find two numbers word problems Calculator - Given two numbers with a sum of s where one number is n greater than another, this calculator determines both numbers.
Inclusive Number Word Problems
Free Inclusive Number Word Problems Calculator - Given an integer A and an integer B, this calculates the following inclusive word problem questions: 1) The Average of all numbers inclusive from A to B 2) The Count of all numbers inclusive from A to B 3) The Sum of all numbers inclusive from A to B
Free Map Scale Calculator - Solves map scale problems based on unit measurements
Markup Markdown
Free Markup Markdown Calculator - Given the 3 items of a markup word problem, cost, markup percentage, and sale price, this solves for any one of the three given two of the items. This works as a markup calculator, markdown calculator.
Numbers Word Problems
Free Numbers Word Problems Calculator - Solves various basic math and algebra word problems with numbers
Free Overtime Calculator - Solves overtime wage problems
Percent Off Problem
Free Percent Off Problem Calculator - Given the 3 items of a percent word problem, Reduced Price, percent off, and full price, this solves for any one of the three given two of the items.
Percentage of the Pie Word Problem
Free Percentage of the Pie Word Problem Calculator - This takes two or three fractions of ownership in some good or object, and figures out what remaining fraction is left over.
Percentage Word Problems
Free Percentage Word Problems Calculator - Solves percentage word problems
Population Doubling Time
Free Population Doubling Time Calculator - Determines population growth based on a doubling time.
Population Growth
Free Population Growth Calculator - Determines population growth based on an exponential growth model.
Product of Consecutive Numbers
Free Product of Consecutive Numbers Calculator - Finds the product of (n) consecutive integers, even or odd as well. Examples include: product of 2 consecutive integers product of 2 consecutive numbers product of 2 consecutive even integers product of 2 consecutive odd integers product of 2 consecutive even numbers product of 2 consecutive odd numbers product of two consecutive integers product of two consecutive odd integers product of two consecutive even integers product of two consecutive numbers product of two consecutive odd numbers product of two consecutive even numbers product of 3 consecutive integers product of 3 consecutive numbers product of 3 consecutive even integers product of 3 consecutive odd integers product of 3 consecutive even numbers product of 3 consecutive odd numbers product of three consecutive integers product of three consecutive odd integers product of three consecutive even integers product of three consecutive numbers product of three consecutive odd numbers product of three consecutive even numbers product of 4 consecutive integers product of 4 consecutive numbers product of 4 consecutive even integers product of 4 consecutive odd integers product of 4 consecutive even numbers product of 4 consecutive odd numbers product of four consecutive integers product of four consecutive odd integers product of four consecutive even integers product of four consecutive numbers product of four consecutive odd numbers product of four consecutive even numbers product of 5 consecutive integers product of 5 consecutive numbers product of 5 consecutive even integers product of 5 consecutive odd integers product of 5 consecutive even numbers product of 5 consecutive odd numbers product of five consecutive integers product of five consecutive odd integers product of five consecutive even integers product of five consecutive numbers product of five consecutive odd numbers product of five consecutive even numbers
Ratio Word Problems
Free Ratio Word Problems Calculator - Solves a ratio word problem using a given ratio of 2 items in proportion to a whole number.
Rebound Ratio
Free Rebound Ratio Calculator - Calculates a total downward distance traveled given an initial height of a drop and a rebound ratio percentage
Slope Word Problems
Free Slope Word Problems Calculator - Solves slope word problems
Solution Mixture
Free Solution Mixture Calculator - Determines a necessary amount of a Solution given two solution percentages and 1 solution amount.
Split Fund Interest
Free Split Fund Interest Calculator - Given an initial principal amount, interest rate on Fund 1, interest rate on Fund 2, and a total interest paid, calculates the amount invested in each fund.
Sum of Consecutive Numbers
Free Sum of Consecutive Numbers Calculator - Finds the sum of (n) consecutive integers, even or odd as well. Examples include: sum of 2 consecutive integers sum of 2 consecutive numbers sum of 2 consecutive even integers sum of 2 consecutive odd integers sum of 2 consecutive even numbers sum of 2 consecutive odd numbers sum of two consecutive integers sum of two consecutive odd integers sum of two consecutive even integers sum of two consecutive numbers sum of two consecutive odd numbers sum of two consecutive even numbers sum of 3 consecutive integers sum of 3 consecutive numbers sum of 3 consecutive even integers sum of 3 consecutive odd integers sum of 3 consecutive even numbers sum of 3 consecutive odd numbers sum of three consecutive integers sum of three consecutive odd integers sum of three consecutive even integers sum of three consecutive numbers sum of three consecutive odd numbers sum of three consecutive even numbers sum of 4 consecutive integers sum of 4 consecutive numbers sum of 4 consecutive even integers sum of 4 consecutive odd integers sum of 4 consecutive even numbers sum of 4 consecutive odd numbers sum of four consecutive integers sum of four consecutive odd integers sum of four consecutive even integers sum of four consecutive numbers sum of four consecutive odd numbers sum of four consecutive even numbers sum of 5 consecutive integers sum of 5 consecutive numbers sum of 5 consecutive even integers sum of 5 consecutive odd integers sum of 5 consecutive even numbers sum of 5 consecutive odd numbers sum of five consecutive integers sum of five consecutive odd integers sum of five consecutive even integers sum of five consecutive numbers sum of five consecutive odd numbers sum of five consecutive even numbers
Sum of Five Consecutive Integers
Free Sum of Five Consecutive Integers Calculator - Finds five consecutive integers, if applicable, who have a sum equal to a number. Sum of 5 consecutive integers
Sum of Four Consecutive Integers
Free Sum of Four Consecutive Integers Calculator - Finds four consecutive integers, if applicable, who have a sum equal to a number. Sum of 4 consecutive integers
Sum of the First (n) Numbers
Free Sum of the First (n) Numbers Calculator - Determines the sum of the first (n) * Whole Numbers * Natural Numbers * Even Numbers * Odd Numbers * Square Numbers * Cube Numbers * Fourth Power Numbers
Sum of Three Consecutive Integers
Free Sum of Three Consecutive Integers Calculator - Finds three consecutive integers, if applicable, who have a sum equal to a number. Sum of 3 consecutive integers
Free Sun Shadow Calculator - This solves for various components and scenarios of the sun shadow problem
Unit Savings
Free Unit Savings Calculator - A discount and savings word problem using 2 people and full prices versus discount prices.
Work Word Problems
Free Work Word Problems Calculator - Given Person or Object A doing a job in (r) units of time and Person or Object B doing a job in (s) units of time, this calculates how long it would take if they combined to do the job.
An Automated Online Math Tutor serving 8.1 million parents and students in 235 countries and territories.

Our Services
- All Subjects
- A.I. Training Data and Analytics
- Get Paid as an Affiliate

Top Categories
- Trigonometry
- Pre-Algebra
- Pre-Calculus
- Join the MathCelebrity Skool Group
- Post a Math Problem


- Math for Kids
- Parenting Resources
- ELA for Kids
- Teaching Resources

How to Teach Number Recognition to Kids in 8 Easy Steps
How to Teach One to One Correspondence To Kids: 4 Easy Steps
How to Teach Odd and Even Numbers in 4 Easy Steps
How to Teach Long Division to Kids in 6 Easy Steps
15 Famous Mathematicians in History That Kids Should Know
How to Prepare a Schedule for Kindergarten With Examples
How to Prepare a Schedule for Preschoolers With Sample
12 Best Funny Short Stories for Kids to Read in 2024
6 Best Alternatives to Public Schooling: A Guide for Parents
How to Cope With Test Anxiety in 12 Easy Ways
List of 58 Best R Words for Kids in 2024
List of 180 Animal Names in English for Kids
How to Teach Pronouns to Beginners in 6 Easy Steps
12 Best Spelling Apps For Kids in 2024
How to Teach Parts of Speech: 15 Fun Ways for Kids
13 Best Assessment Tools for Teachers in 2024
12 Best STEM Programs for Kids in 2024
12 Best Tips for Substitute Teachers
30 Best Classroom Reward Ideas for Elementary Students
12 Best Websites for English Teachers

10 Best Strategies for Solving Math Word Problems
1. Understand the Problem by Paraphrasing
2. identify key information and variables, 3. translate words into mathematical symbols, 4. break down the problem into manageable parts, 5. draw diagrams or visual representations, 6. use estimation to predict answers, 7. apply logical reasoning for unknown variables, 8. leverage similar problems as templates, 9. check answers in the context of the problem, 10. reflect and learn from mistakes.
Have you ever observed the look of confusion on a student’s face when they encounter a math word problem ? It’s a common sight in classrooms worldwide, underscoring the need for effective strategies for solving math word problems . The main hurdle in solving math word problems is not just the math itself but understanding how to translate the words into mathematical equations that can be solved.
SplashLearn: Most Comprehensive Learning Program for PreK-5

SplashLearn inspires lifelong curiosity with its game-based PreK-5 learning program loved by over 40 million children. With over 4,000 fun games and activities, it’s the perfect balance of learning and play for your little one.
Generic advice like “read the problem carefully” or “practice more” often falls short in addressing students’ specific difficulties with word problems. Students need targeted math word problem strategies that address the root of their struggles head-on.
A Guide on Steps to Solving Word Problems: 10 Strategies
One of the first steps in tackling a math word problem is to make sure your students understand what the problem is asking. Encourage them to paraphrase the problem in their own words. This means they rewrite the problem using simpler language or break it down into more digestible parts. Paraphrasing helps students grasp the concept and focus on the problem’s core elements without getting lost in the complex wording.
Original Problem: “If a farmer has 15 apples and gives away 8, how many does he have left?”
Paraphrased: “A farmer had some apples. He gave some away. Now, how many apples does he have?”
This paraphrasing helps students identify the main action (giving away apples) and what they need to find out (how many apples are left).
Play these subtraction word problem games in the classroom for free:

Students often get overwhelmed by the details in word problems. Teach them to identify key information and variables essential for solving the problem. This includes numbers , operations ( addition , subtraction , multiplication , division ), and what the question is asking them to find. Highlighting or underlining can be very effective here. This visual differentiation can help students focus on what’s important, ignoring irrelevant details.
- Encourage students to underline numbers and circle keywords that indicate operations (like ‘total’ for addition and ‘left’ for subtraction).
- Teach them to write down what they’re solving for, such as “Find: Total apples left.”
Problem: “A classroom has 24 students. If 6 more students joined the class, how many students are there in total?”
Key Information:
- Original number of students (24)
- Students joined (6)
- Looking for the total number of students
Here are some fun addition word problems that your students can play for free:

The transition from the language of word problems to the language of mathematics is a critical skill. Teach your students to convert words into mathematical symbols and equations. This step is about recognizing keywords and phrases corresponding to mathematical operations and expressions .
Common Translations:
- “Total,” “sum,” “combined” → Addition (+)
- “Difference,” “less than,” “remain” → Subtraction (−)
- “Times,” “product of” → Multiplication (×)
- “Divided by,” “quotient of” → Division (÷)
- “Equals” → Equals sign (=)
Problem: “If one book costs $5, how much would 4 books cost?”
Translation: The word “costs” indicates a multiplication operation because we find the total cost of multiple items. Therefore, the equation is 4 × 5 = $20
Complex math word problems can often overwhelm students. Incorporating math strategies for problem solving, such as teaching them to break down the problem into smaller, more manageable parts, is a powerful approach to overcome this challenge. This means looking at the problem step by step rather than simultaneously trying to solve it. Breaking it down helps students focus on one aspect of the problem at a time, making finding the solution more straightforward.
Problem: “John has twice as many apples as Sarah. If Sarah has 5 apples, how many apples do they have together?”
Steps to Break Down the Problem:
Find out how many apples John has: Since John has twice as many apples as Sarah, and Sarah has 5, John has 5 × 2 = 10
Calculate the total number of apples: Add Sarah’s apples to John’s to find the total, 5 + 10 = 15
By splitting the problem into two parts, students can solve it without getting confused by all the details at once.
Explore these fun multiplication word problem games:

Diagrams and visual representations can be incredibly helpful for students, especially when dealing with spatial or quantity relationships in word problems. Encourage students to draw simple sketches or diagrams to represent the problem visually. This can include drawing bars for comparison, shapes for geometry problems, or even a simple distribution to better understand division or multiplication problems .
Problem: “A garden is 3 times as long as it is wide. If the width is 4 meters, how long is the garden?”
Visual Representation: Draw a rectangle and label the width as 4 meters. Then, sketch the length to represent it as three times the width visually, helping students see that the length is 4 × 3 = 12
Estimation is a valuable skill in solving math word problems, as it allows students to predict the answer’s ballpark figure before solving it precisely. Teaching students to use estimation can help them check their answers for reasonableness and avoid common mistakes.
Problem: “If a book costs $4.95 and you buy 3 books, approximately how much will you spend?”
Estimation Strategy: Round $4.95 to the nearest dollar ($5) and multiply by the number of books (3), so 5 × 3 = 15. Hence, the estimated total cost is about $15.
Estimation helps students understand whether their final answer is plausible, providing a quick way to check their work against a rough calculation.
Check out these fun estimation and prediction word problem worksheets that can be of great help:

When students encounter problems with unknown variables, it’s crucial to introduce them to logical reasoning. This strategy involves using the information in the problem to deduce the value of unknown variables logically. One of the most effective strategies for solving math word problems is working backward from the desired outcome. This means starting with the result and thinking about the steps leading to that result, which can be particularly useful in algebraic problems.
Problem: “A number added to three times itself equals 32. What is the number?”
Working Backward:
Let the unknown number be x.
The equation based on the problem is x + 3x = 32
Solve for x by simplifying the equation to 4x=32, then dividing by 4 to find x=8.
By working backward, students can more easily connect the dots between the unknown variable and the information provided.
Practicing problems of similar structure can help students recognize patterns and apply known strategies to new situations. Encourage them to leverage similar problems as templates, analyzing how a solved problem’s strategy can apply to a new one. Creating a personal “problem bank”—a collection of solved problems—can be a valuable reference tool, helping students see the commonalities between different problems and reinforcing the strategies that work.
Suppose students have solved a problem about dividing a set of items among a group of people. In that case, they can use that strategy when encountering a similar problem, even if it’s about dividing money or sharing work equally.
It’s essential for students to learn the habit of checking their answers within the context of the problem to ensure their solutions make sense. This step involves going back to the original problem statement after solving it to verify that the answer fits logically with the given information. Providing a checklist for this process can help students systematically review their answers.
Checklist for Reviewing Answers:
- Re-read the problem: Ensure the question was understood correctly.
- Compare with the original problem: Does the answer make sense given the scenario?
- Use estimation: Does the precise answer align with an earlier estimation?
- Substitute back: If applicable, plug the answer into the problem to see if it works.
Problem: “If you divide 24 apples among 4 children, how many apples does each child get?”
After solving, students should check that they understood the problem (dividing apples equally).
Their answer (6 apples per child) fits logically with the number of apples and children.
Their estimation aligns with the actual calculation.
Substituting back 4×6=24 confirms the answer is correct.
Teaching students to apply logical reasoning, leverage solved problems as templates, and check their answers in context equips them with a robust toolkit for tackling math word problems efficiently and effectively.
One of the most effective ways for students to improve their problem-solving skills is by reflecting on their errors, especially with math word problems. Using word problem worksheets is one of the most effective strategies for solving word problems, and practicing word problems as it fosters a more thoughtful and reflective approach to problem-solving
These worksheets can provide a variety of problems that challenge students in different ways, allowing them to encounter and work through common pitfalls in a controlled setting. After completing a worksheet, students can review their answers, identify any mistakes, and then reflect on them in their mistake journal. This practice reinforces mathematical concepts and improves their math problem solving strategies over time.
3 Additional Tips for Enhancing Word Problem-Solving Skills
Before we dive into the importance of reflecting on mistakes, here are a few impactful tips to enhance students’ word problem-solving skills further:
1. Utilize Online Word Problem Games

Incorporate online games that focus on math word problems into your teaching. These interactive platforms make learning fun and engaging, allowing students to practice in a dynamic environment. Games can offer instant feedback and adaptive challenges, catering to individual learning speeds and styles.
Here are some word problem games that you can use for free:

2. Practice Regularly with Diverse Problems

Consistent practice with a wide range of word problems helps students become familiar with different questions and mathematical concepts. This exposure is crucial for building confidence and proficiency.
Start Practicing Word Problems with these Printable Word Problem Worksheets:

3. Encourage Group Work
Solving word problems in groups allows students to share strategies and learn from each other. A collaborative approach is one of the best strategies for solving math word problems that can unveil multiple methods for tackling the same problem, enriching students’ problem-solving toolkit.
Conclusion
Mastering math word problems is a journey of small steps. Encourage your students to practice regularly, stay curious, and learn from their mistakes. These strategies for solving math word problems are stepping stones to turning challenges into achievements. Keep it simple, and watch your students grow their confidence and skills, one problem at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can i help my students stay motivated when solving math word problems.
Encourage small victories and use engaging tools like online games to make practice fun and rewarding.
What's the best way to teach beginners word problems?
Begin with simple problems that integrate everyday scenarios to make the connection between math and real-life clear and relatable.
How often should students practice math word problems?
Regular, daily practice with various problems helps build confidence and problem-solving skills over time.
- Pre-Kindergarten
- Kindergarten
Most Popular

76 Best Report Card Comments Samples for Teachers

117 Best Riddles for Kids (With Answers)

40 Best Good Vibes Quotes to Brighten Your Day
Recent posts.

40 Best Scavenger Hunt Riddles For Kids [With Answers]

How to Teach One to One Correspondence To Kids: 4 Easy...
Math & ela | prek to grade 5, kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free

- Games for Kids
- Worksheets for Kids
- Math Worksheets
- ELA Worksheets
- Math Vocabulary
- Number Games
- Addition Games
- Subtraction Games
- Multiplication Games
- Division Games
- Addition Worksheets
- Subtraction Worksheets
- Multiplication Worksheets
- Division Worksheets
- Times Tables Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Writing Games
- Phonics Games
- Sight Words Games
- Letter Tracing Games
- Reading Worksheets
- Writing Worksheets
- Phonics Worksheets
- Sight Words Worksheets
- Letter Tracing Worksheets
- Prime Number
- Order of Operations
- Long multiplication
- Place value
- Parallelogram
- SplashLearn Success Stories
- SplashLearn Apps
- [email protected]
© Copyright - SplashLearn

Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free

Word Problem Practice Questions with Answer Key
- Posted by Brian Stocker
- Date February 13, 2019
- Comments 11 comments
Problem Solving – Word Problems
Word problems are mathematical problems using everyday language and real-world situations. Some information is given and one or more pieces or information (variables) are missing. You must understand the given information, identify the mathematical operations necessary to solve the problem, and then carry out those operations to obtain the missing information or variables.
The Biggest Tip!
Tackling word problems is much easier if you have a systematic approach which we outline below.
Here is the biggest tip for word problems practice. Practice regularly and systematically. Sounds simple and easy right? Yes it is, and yes it really does work. Word problems are a way of thinking and require you to translate a real world problem into mathematical terms.
Some math instructors go so far as to say that learning how to think mathematically is the main reason for teaching word problems. So what do we mean by Practice regularly and systematically? Studying word problems and math in general requires a logical and mathematical frame of mind. The only way that you can get this is by practicing regularly, which means everyday.
How to Solve Word Problems
Types of Word Problems
Most Common Word Problem Mistakes on a Test
It is critical that you practice word problems everyday for the 5 days before the exam as a bare minimum. If you practice and miss a day, you have lost the mathematical frame of mind and the benefit of your previous practice is pretty much gone. Anyone who has done any number of math tests will agree – you have to practice everyday.
See Also Algebra Word Problems
Effective problem-solving skills are essential in many areas of life, from academia to the workplace and beyond. Developing the ability to solve word problems requires practice and patience, as well as a strong understanding of basic mathematical concepts and operations.
Try a FREE Quiz
Word problem practice questions.
1. A box contains 7 black pencils and 28 blue ones. What is the ratio between the black and blue pens?
a. 1:4 b. 2:7 c. 1:8 d. 1:9
2. The manager of a weaving factory estimates that if 10 machines run at 100% efficiency for 8 hours, they will produce 1450 meters of cloth. Due to some tech¬nical problems, 4 machines run of 95% efficiency and the remaining 6 at 90% efficiency. How many meters of cloth can these machines will produce in 8 hours?
a. 1334 meters b. 1310 meters c. 1300 meters d. 1285 meters
3. In a local election at polling station A, 945 voters cast their vote out of 1270 registered voters. At poll¬ing station B, 860 cast their vote out of 1050 regis¬tered voters and at station C, 1210 cast their vote out of 1440 registered voters. What is the total turnout from all three polling stations?
a. 70% b. 74% c. 76% d. 80%
4. If Lynn can type a page in p minutes, what portion of the page can she do in 5 minutes?
a. p/5 b. p – 5 c. p + 5 d. 5/p
5. If Sally can paint a house in 4 hours, and John can paint the same house in 6 hours, how long will it take for both to paint a house?
a. 2 hours and 24 minutes b. 3 hours and 12 minutes c. 3 hours and 44 minutes d. 4 hours and 10 minutes
6. Employees of a discount appliance store receive an additional 20% off the lowest price on any item. If an employee purchases a dishwasher during a 15% off sale, how much will he pay if the dishwasher originally cost $450?
a. $280.90 b. $287.00 c. $292.50 d. $306.00
7. The sale price of a car is $12,590, which is 20% off the original price. What is the original price?
a. $14,310.40 b. $14,990.90 c. $15,108.00 d. $15,737.50
8. Richard gives ‘s’ amount of salary to each of his ‘n’ employees weekly. If he has ‘x’ amount of money, how many days he can employ these ‘n’ employees.
a. sx/7n b. 7x/nx c. nx/7s d. 7x/ns
9. A distributor purchased 550 kilograms of potatoes for $165. He distributed these at a rate of $6.4 per 20 kilograms to 15 shops, $3.4 per 10 kilograms to 12 shops and the remainder at $1.8 per 5 kilo¬grams. If his total distribution cost is $10, what will his profit be?
a. $10.40 b. $8.60 c. $14.90 d. $23.40
10. How much pay does Mr. Johnson receive if he gives half of his pay to his family, $250 to his land¬lord, and has exactly 3/7 of his pay left over?
a. $3600 b. $3500 c. $2800 d. $175042
11. The cost of waterproofing canvas is .50 a square yard. What’s the total cost for waterproofing a canvas truck cover that is 15’ x 24’?
a. $18.00 b. $6.67 c. $180.00 d. $20.00
1. A The ratio between black and blue pens is 7 to 28 or 7:28. Bring to the lowest terms by dividing both sides by 7 gives 1:4.
2. A At 100% efficiency 1 machine produces 1450/10 = 145 m of cloth. At 95% efficiency, 4 machines produce 4 * 145 * 95/100 = 551 m of cloth. At 90% efficiency, 6 machines produce 6 * 145 * 90/100 = 783 m of cloth. Total cloth produced by all 10 machines = 551 + 783 = 1334 m Since the information provided and the question are based on 8 hours, we did not need to use time to reach the answer.
The turnout at polling station A is 945 out of 1270 registered voters. So, the percentage turnout at station A is:
(945/1270) × 100% = 74.41%
The turnout at polling station B is 860 out of 1050 registered voters. So, the percentage turnout at station B is:
(860/1050) × 100% = 81.90%
The turnout at polling station C is 1210 out of 1440 registered voters. So, the percentage turnout at station C is:
(1210/1440) × 100% = 84.03%
To find the total turnout from all three polling stations, we need to add up the total number of voters and the total number of registered voters from all three stations:
Total number of voters = 945 + 860 + 1210 = 3015
Total number of registered voters = 1270 + 1050 + 1440 = 3760
The overall percentage turnout is:
(3015/3760) × 100% = 80.12%
Therefore, the total turnout from all three polling stations is 80.12% — rounding to 80%.
4. D This is a simple direct proportion problem: If Lynn can type 1 page in p minutes, then she can type x pages in 5 minutes We do cross multiplication: x * p = 5 * 1 Then, x = 5/p
5. A This is an inverse ratio problem. 1/x = 1/a + 1/b where a is the time Sally can paint a house, b is the time John can paint a house, x is the time Sally and John can together paint a house. So, 1/x = 1/4 + 1/6 … We use the least common multiple in the denominator that is 24: 1/x = 6/24 + 4/24 1/x = 10/24 x = 24/10 x = 2.4 hours. In other words; 2 hours + 0.4 hours = 2 hours + 0.4•60 minutes = 2 hours 24 minutes
The original price of the dishwasher is $450. During a 15% off sale, the price of the dishwasher will be reduced by:
15% of $450 = 0.15 x $450 = $67.50
So the sale price of the dishwasher will be:
$450 – $67.50 = $382.50
As an employee, the person receives an additional 20% off the lowest price, which is $382.50. We can calculate the additional discount as:
20% of $382.50 = 0.20 x $382.50 = $76.50
So the final price that the employee will pay for the dishwasher is:
$382.50 – $76.50 = $306.00
Therefore, the employee will pay $306.00 for the dishwasher.
7. D Original price = x, 80/100 = 12590/X, 80X = 1259000, X = 15,737.50.
8. D We are given that each of the n employees earns s amount of salary weekly. This means that one employee earns s salary weekly. So; Richard has ‘ns’ amount of money to employ n employees for a week. We are asked to find the number of days n employees can be employed with x amount of money. We can do simple direct proportion: If Richard can employ n employees for 7 days with ‘ns’ amount of money, Richard can employ n employees for y days with x amount of money … y is the number of days we need to find. We can do cross multiplication: y = (x * 7)/(ns) y = 7x/ns
9. B The distribution is done at three different rates and in three different amounts: $6.4 per 20 kilograms to 15 shops … 20•15 = 300 kilograms distributed $3.4 per 10 kilograms to 12 shops … 10•12 = 120 kilograms distributed 550 – (300 + 120) = 550 – 420 = 130 kilograms left. This 50 amount is distributed in 5 kilogram portions. So, this means that there are 130/5 = 26 shops. $1.8 per 130 kilograms. We need to find the amount he earned overall these distributions. $6.4 per 20 kilograms : 6.4•15 = $96 for 300 kilograms $3.4 per 10 kilograms : 3.4 *12 = $40.8 for 120 kilograms $1.8 per 5 kilograms : 1.8 * 26 = $46.8 for 130 kilograms So, he earned 96 + 40.8 + 46.8 = $ 183.6 The total distribution cost is given as $10 The profit is found by: Money earned – money spent … It is important to remember that he bought 550 kilograms of potatoes for $165 at the beginning: Profit = 183.6 – 10 – 165 = $8.6
10. B We check the fractions taking place in the question. We see that there is a “half” (that is 1/2) and 3/7. So, we multiply the denominators of these fractions to decide how to name the total money. We say that Mr. Johnson has 14x at the beginning; he gives half of this, meaning 7x, to his family. $250 to his landlord. He has 3/7 of his money left. 3/7 of 14x is equal to: 14x * (3/7) = 6x So, Spent money is: 7x + 250 Unspent money is: 6×51 Total money is: 14x Write an equation: total money = spent money + unspent money 14x = 7x + 250 + 6x 14x – 7x – 6x = 250 x = 250 We are asked to find the total money that is 14x: 14x = 14 * 250 = $3500
11. D First calculate total square feet, which is 15 * 24 = 360 ft 2 . Next, convert this value to square yards, (1 yards 2 = 9 ft 2 ) which is 360/9 = 40 yards 2 . At $0.50 per square yard, the total cost is 40 * 0.50 = $20.
- Not reading the problem carefully and thoroughly, so that you either misunderstand or solve the problem incorrectly.
- Not identifying the important information in the problem, such as the quantities, units, and the operation to be performed.
- Not translating the information in the problem into mathematical language and equations.
- Not checking the units of measure and making sure they match your final answer.
- Not double-checking the answer to ensure it makes sense.
- Not understanding the underlying mathematical concept or operation the problem is asking for.
- Not using estimation or approximations as a tool to check the reasonableness of your answer.
Try a FREE Math Quiz
Got a Question? Email me anytime - [email protected]
Previous post
Pythagorean Geometry - Tutorial and Practice Questions
Calculate the slope of a line - practice questions, you may also like.

Basic Math Video Tutorials
How to answer basic math multiple choice, how to solve linear inequalities – quick review and practice.
Basic linear inequalities have one of the following forms: ax + b > 0 ax + b < 0 ax + b > 0 ax + b < 0 where a and b are some real numbers. Our solution to …
11 Comments
Will we need to know units and their conversions such as yards to feet? Should we memorise those?
are we allowed to use a calculator? To expect someone to complete these in their head is absurd especially with a time limit. The second question requires multiplication by decimals, which would be okay if you got a whole number but you dont, you get a fraction and the only way to get it to 551 is by then multiplying that number by 4. Doubt anyone would be required to do these kind of calculations in a real world scenario especially unaided and under time constraints.
Hi Depends on the test – what test are you studying for?
is this preparation for the CAAT level C???
These questions vary in subject and difficulty level to give students practice on different types of questions for different types of tests. They are not specific to one test or one level.
Yes the LEAST common multiple of 6 and 4 is 12 – i did it with 24 – it will give the same answer no matter which way you do it. Good point though – perhaps for simplicity sake 12 would be better.
Are these questions appeared on the Cbest?
The are the same TYPE of questions – not exactly
sorry for the message above, i like your site and i have won 1st place in an exam due to this site
I used Chat GPT. Solved every one…. perfectly. I’m still dumb as a rock though.
Oh Really? You may want to check that again!! It gave me wrong answers and weird steps to calculate for 2 of them!
Leave A Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Core Math Worksheets
Addition worksheets, subtraction worksheets, multiplication worksheets, division worksheets, fact family worksheets, long division worksheets, negative numbers, exponents worksheets, order of operations worksheets, fraction worksheets, fractions worksheets, graphic fractions, equivalent fractions, reducing fractions, comparing fractions, adding fractions, subtracting fractions, multiplying fractions, dividing fractions, fractions as decimals, fraction decimal percent, word problems, pre-algebra word problems, money word problems, combining like terms, properties of multiplication, exponent rules, linear equations, one step equations, two step equations, factoring polynomials, quadratic equations, other worksheets, place value, percentages, rounding numbers, ordering numbers, standard, expanded, word form, mean median mode range, ratio worksheets, probability worksheets, roman numerals, factorization, gcd, lcm, prime and composite numbers, pre-algebra, geometry worksheets, blank clocks, telling analog time, analog elapsed time, greater than and less than, arithmetic sequences, geometric sequences, venn diagram, graph worksheets, measurement & conversions, inches measurement, metric measurement, metric si unit conversions, customary unit conversions, customary and metric, patterns and puzzles, number patterns, patterns with negatives, missing operations, magic square, number grid puzzles, word search puzzles, color by number, addition color by number, subtraction color by number, multiplication color by number, division color by number, color by number, holiday & seasonal, valentine's day, st. patrick's day, thanksgiving, early learning, base ten blocks, printable flash cards, number matching, number tracing, missing numbers, picture math addition, picture math subtraction, picture math multiplication, picture math division, multiplication chart, multiplication table, prime numbers chart, hundreds chart, place value chart, roman numerals chart, handwriting paper, graph paper, coordinate plane, spaceship math check-off, square root chart, fraction chart, probability chart, measurement chart, number line, comic strip template, calculators, age calculator, factoring calculator, fraction calculator, slope calculator, degrees to radians, percentage calculator, prime factorization calculator, roman numeral converter, long division calculator, multiplication calculator, math worksheets by grade, preschool math worksheets, kindergarten math worksheets, 1st grade math worksheets, 2nd grade math worksheets, 3rd grade math worksheets, 4th grade math worksheets, 5th grade math worksheets, 6th grade math worksheets, worksheet news.
Word problems are one of the first ways we see applied math, and also one of the most anxiety producing math challenges many grade school kids face. This page has a great collection of word problems that provide a gentle introduction to word problems for all four basic math operations. You'll find addition word problems, subtraction word problems, multiplication word problems and division word problems, all starting with simple easy-to-solve questions that build up to more complex skills necessary for many standardized tests. As they progress, you'll also find a mix of operations that require students to figure out which type of story problem they need to solve. And if you need help, check out word problem tricks at the bottom of this page!
Addition Word Problems
20 word problems worksheets.
These introductory word problems for addition are perfect for first grade or second grade applied math.

Subtraction Word Problems
These worksheets include simple word problems for subtraction with smaller quantities. Watch for words like difference and remaining.

Mixed Addition and Subtraction Word Problems
8 word problems worksheets.
This set of worksheets includes a mix of addition and subtraction word problems. Students are required to figured out which operation to apply given the problem context.

Multiplication Word Problems
This is the first set of word problem worksheets the introduces multiplication. These worksheets include only multiplication story problems; see worksheets in the following sections for mixed operations.

Division Word Problems
These division story problems deal with only whole divisions (quotients without remainders.) This is a great first step to recognizing the keywords that signal you are solving a division word problem.
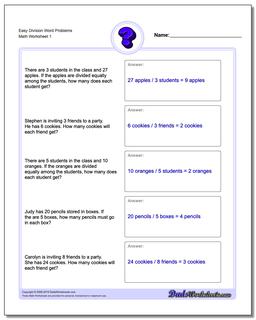
Girl Scout Cookie Division
If you've been working as Troop Cookie Mom (or Dad!) you'll know what kind of math we've been practicing... These worksheets are primarily division word problems that introduce remainders. Pull your tagalongs or your thin mints out of the box and figure out how many remainders you'll be allowed to eat!

Division With Remainders Word Problems
24 word problems worksheets.
The worksheets in this section are made up of story problems using division and involving remainders. These are similar to the Girl Scout problems in the prior section, but with different units.

Mixed Multiplication and Division Word Problems
This worksheets combine basic multiplication and division word problems. The division problems do not include remainders. These worksheets require the students to differentiate between the phrasing of a story problem that requires multiplication versus one that requires division to reach the answer.

Mixed Operation Word Problems
The whole enchilada! These workshes mix addition, subtraction, multiplication and division word problems. These worksheets will test a students ability to choose the correct operation based on the story problem text.

Extra Facts Addition Word Problems
One way to make a word problem slightly more complex is to include extra (but unused) information in the problem text. These worksheets have addition word problems with extra unused facts in the problem.

Extra Facts Subtraction Word Problems
Word problem worksheets for subtraction with extra unused facts in each problem. The worksheets start out with subtraction problems with smaller values and progress through more difficult problems.

Extra Facts Addition and Subtraction Word Problems
Mixed operation addition and subtraction word problem worksheets with extra unused facts in the problems.

Extra Facts Multiplication Word Problems
Word problems for multiplication with extra unused facts in the problem. The worksheets in this set start out with multiplication problems with smaller values and progress through more difficult problems.
Extra Facts Division Word Problems
The worksheets in this section include math word problems for division with extra unused facts in the problem. The quotients in these division problems do not include remainders.

Extra Facts Multiplication and Division Word Problems
16 word problems worksheets.
This is a collection of worksheets with mixed multiplication and division word problems and extra unused facts in the problem. The quotients in these division problems do not include remainders.

Travel Time Word Problems (Customary)
28 word problems worksheets.
These story problems deal with travel time, including determining the travel distance, travel time and speed using miles (customary units). This is a very common class of word problem and specific practice with these worksheets will prepare students when they encounter similar problems on standardized tests.

Travel Time Word Problems (Metric)
Wondering when the train arrives? These story problems deal with travel time, including determining the travel distance, travel time and speed using kilometers (metric units).

Tricks for Solving Word Problems
The math worksheets on this section of the site deal with simple word problems appropriate for primary grades. The simple addition word problems can be introduced very early, in first or second grade depending on student aptitude. Follow those worksheets up with the subtraction word problems once subtraction concept are covered, and then proceed with multiplication and division word problems in the same fashion.
Word problems are often a source of anxiety for students because we tend to introduce math operations in the abstract. Students struggle to apply even elementary operations to word problems unless they have been taught consistently to think about math operations in their day to day routines. Talking with kids regularly about 'how many more do you need' or 'how many do you have left over' or other seemingly simple questions when asked regularly can build that basic number sense that helps enormously when word problems and applied math start to show up.
There are many tricks for solving word problems that can bridge the gap, and they can be helpful tools if students are either struggling with where to start with a problem or just need a way to check their thinking on a particular problem.
Make sure your student reads the entire problem first. It is very easy to start reading a word problem and think after the first sentence or two that 'I know what they're asking for...' and then have the problem take an entirely different turn. Overcoming this early solution bias can be difficult, and it is much better to develop the habit of making a complete pass over the problem before deciding on a path to the solution.
There are particular words that seem to show up in word problems for different operations that can tip you off to what might be the correct operation to apply. These key words aren't a sure-fire way to know what to do with a problem, but they can be a useful starting point.
For example, phrases like 'combined,' 'total,' 'together' or 'sum' are very often signals that the problem is going to involve addition.
Subtraction word problems very often use words such as 'difference,' 'less,' or 'decrease' in their wording. Word problems for younger kids will also use verbs like 'gave' or 'shared' as a stand-in for subtraction.
The key phrases to watch out for multiplication word problems include obvious ones like 'times' and 'product,' but also be on the look out for 'for each' and 'every.'
Learning when to apply division in a word problem can be tricky, especially for younger kids who haven't fully developed a concept of what division can be used for... But that's exactly why division word problems can be so useful! If you see words like 'per' or 'among' in the word problem text, your division radar should be sounding off loud and clear. Pay attention to 'shared among' and make sure students don't confuse this phrasing with a subtraction word problem. That's a clear example of when paying attention to the language is very important.
Number Line
The Algebra Calculator is a versatile online tool designed to simplify algebraic problem-solving for users of all levels. Here's how to make the most of it:
- Begin by typing your algebraic expression into the above input field, or scanning the problem with your camera.
- After entering the equation, click the 'Go' button to generate instant solutions.
- The calculator provides detailed step-by-step solutions, aiding in understanding the underlying concepts.
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- (x+5)(x-5)\gt 0
- 10^{1-x}=10^4
- \sqrt{3+x}=-2
- 6+11x+6x^2+x^3=0
- factor\:x^{2}-5x+6
- simplify\:\frac{2}{3}-\frac{3}{2}+\frac{1}{4}
- x+2y=2x-5,\:x-y=3
algebra-calculator
word problem
- High School Math Solutions – Systems of Equations Calculator, Elimination A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with the same set of variables. In this blog post,...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.

Addition (Basic)
Addition (Multi-Digit)
Algebra & Pre-Algebra
Comparing Numbers
Daily Math Review
Division (Basic)
Division (Long Division)
Hundreds Charts
Measurement
Multiplication (Basic)
Multiplication (Multi-Digit)
Order of Operations
Place Value
Probability
Skip Counting
Subtraction
Telling Time
Word Problems (Daily)
More Math Worksheets
Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension Gr. 1
Reading Comprehension Gr. 2
Reading Comprehension Gr. 3
Reading Comprehension Gr. 4
Reading Comprehension Gr. 5
Reading Comprehension Gr. 6
Reading & Writing
Reading Worksheets
Cause & Effect
Fact & Opinion
Fix the Sentences
Graphic Organizers
Synonyms & Antonyms
Writing Prompts
Writing Story Pictures
Writing Worksheets
More ELA Worksheets
Consonant Sounds
Vowel Sounds
Consonant Blends
Consonant Digraphs
Word Families
More Phonics Worksheets
Early Literacy
Build Sentences
Sight Word Units
Sight Words (Individual)
More Early Literacy
Punctuation
Subjects and Predicates
More Grammar Worksheets
Spelling Lists
Spelling Grade 1
Spelling Grade 2
Spelling Grade 3
Spelling Grade 4
Spelling Grade 5
Spelling Grade 6
More Spelling Worksheets
Chapter Books
Charlotte's Web
Magic Tree House #1
Boxcar Children
More Literacy Units
Animal (Vertebrate) Groups
Butterfly Life Cycle
Electricity
Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas)
Simple Machines
Space - Solar System
More Science Worksheets
Social Studies
Maps (Geography)
Maps (Map Skills)
More Social Studies
Mother's Day
Father's Day
More Holiday Worksheets
Puzzles & Brain Teasers
Brain Teasers
Logic: Addition Squares
Mystery Graph Pictures
Number Detective
Lost in the USA
More Thinking Puzzles
Teacher Helpers
Teaching Tools
Award Certificates
More Teacher Helpers
Pre-K and Kindergarten
Alphabet (ABCs)
Numbers and Counting
Shapes (Basic)
More Kindergarten
Worksheet Generator
Word Search Generator
Multiple Choice Generator
Fill-in-the-Blanks Generator
More Generator Tools
Full Website Index
Math Word Problems
Word problems (or story problems) allow kids to apply what they've learned in math class to real-world situations. Word problems build higher-order thinking, critical problem-solving, and reasoning skills.
Logged in members can use the Super Teacher Worksheets filing cabinet to save their favorite worksheets.
Quickly access your most used files AND your custom generated worksheets!
Please login to your account or become a member and join our community today to utilize this helpful feature.

Addition and Subtraction Mixed
Multiplication.
Word problems where students use reasoning and critical thinking skill to solve each problem.
Mixed word problems (stories) for skills working on subtraction,addition, fractions and more.
A full index of all math worksheets on this site.
Images of Worksheets

PDF with answer key:
PDF no answer key:
















IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Translate the problem into mathematical expressions or equations, and use the information and equations generated to solve for the answer. How do you identify word problems in math? Word problems in math can be identified by the use of language that describes a situation or scenario.
Problem Solver Subjects. Our math problem solver that lets you input a wide variety of math math problems and it will provide a step by step answer. This math solver excels at math word problems as well as a wide range of math subjects. Here are example math problems within each subject that can be input into the calculator and solved.
Click to see solution. Problem 17. A biker covered half the distance between two towns in 2 hr 30 min. After that he increased his speed by 2 km/hr. He covered the second half of the distance in 2 hr 20 min. Find the distance between the two towns and the initial speed of the biker. Click to see solution. Problem 18.
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
Word Problem Calculator. Get detailed solutions to your math problems with our Word Problem step-by-step calculator. Practice your math skills and learn step by step with our math solver. Check out all of our online calculators here. Go! Symbolic mode. Text mode.
For example, students may need a way to figure out what 7 × 8 is or have previously memorized the answer before you give them a word problem that involves finding the answer to 7 × 8. There are a number of strategies used in solving math word problems; if you don't have a favorite, try the Math-Drills.com problem-solving strategy:
Our solver can interpret math word problems and determine what mathematical operations needs to be used to solve the problem. Snap a Pic Easily snap a picture from your phone or upload a screenshot from your computer or copy/paste into the solver to get your step by step math solution.
Turning English into Algebra. To turn the English into Algebra it helps to: Read the whole thing first; Do a sketch if possible; Assign letters for the values; Find or work out formulas; You should also write down what is actually being asked for, so you know where you are going and when you have arrived!. Also look for key words:
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. Take a photo of your math problem on the app. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math.
Introduction to Word Problems. These lessons, with videos, examples, solutions and worksheets, help Grade 5 students learn how to solve word problems. The following diagram gives some examples of word problems keywords or clue words. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions of word problems.
Solve the equation. Find the remaining variables. The older brother Bob is two year older than his little sister Alice. Taken together, the sum of their ages is 8. Bob is two years older than Alice. Bob's age plus Alice's age = 8. Bob's age B and Alice's age A. Get rid of B. Bob is 2 years older than Alice, so you can use A+2 instead of B.
IXL brings learning to life with over 200 different word-problem skills. Engaging questions and fun visuals motivate students to master new concepts. ... Use strip diagrams to represent and solve multi-step word problems N.4 ... .5 Multi-step word problems involving remainders N.6 Multi-step word problems: identify reasonable answers N.7 Word ...
Algebraic word problems are questions that require translating sentences to equations, then solving those equations. The equations we need to write will only involve. basic arithmetic operations. and a single variable. Usually, the variable represents an unknown quantity in a real-life scenario.
Students can generate multiple word problems of each type for problem-solving practice. Teachers can use the word problem generators to create word problems for students. Once you answer a word problem the answer is shown in a proof. The equation is created and solved in detail and can be used to check your own work. The best way for you to ...
Free Inclusive Number Word Problems Calculator - Given an integer A and an integer B, this calculates the following inclusive word problem questions: 1) The Average of all numbers inclusive from A to B 2) The Count of all numbers inclusive from A to B 3) The Sum of all numbers inclusive from A to B. Calculator · Watch the Video.
6. Use Estimation to Predict Answers. Estimation is a valuable skill in solving math word problems, as it allows students to predict the answer's ballpark figure before solving it precisely. Teaching students to use estimation can help them check their answers for reasonableness and avoid common mistakes.
Answer Key. 1. The ratio between black and blue pens is 7 to 28 or 7:28. Bring to the lowest terms by dividing both sides by 7 gives 1:4. 2. At 100% efficiency 1 machine produces 1450/10 = 145 m of cloth. At 95% efficiency, 4 machines produce 4 * 145 * 95/100 = 551 m of cloth.
This page has a great collection of word problems that provide a gentle introduction to word problems for all four basic math operations. You'll find addition word problems, subtraction word problems, multiplication word problems and division word problems, all starting with simple easy-to-solve questions that build up to more complex skills ...
These mixed operations word problems worksheets will produce addition, multiplication, subtraction and division problems with 1 or 2 digit numbers. These word problems worksheets will produce ten problems per worksheet. These word problems worksheets are appropriate for 3rd Grade, 4th Grade, and 5th Grade.
The Algebra Calculator is a versatile online tool designed to simplify algebraic problem-solving for users of all levels. Here's how to make the most of it: Begin by typing your algebraic expression into the above input field, or scanning the problem with your camera. After entering the equation, click the 'Go' button to generate instant solutions.
Multiplication Word Problems: 2-digit by 1-digit. Several two-digit by one-digit multiplication word problems. (example: 22 x 8) 3rd and 4th Grades. View PDF. Multiplication Word Problems: 3-digit by 1 digit. A sheet of three-digit by one-digit multiplication word problems. (example: 340 x 7) 3rd through 5th Grades.
solving word problems. Have a question about using Wolfram|Alpha? Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music….
Word Problems with example. 1. Arithmetic Progression. 1. For given arithemetic progression series 1,4,7,10,13 ,... find 10 th term and addition of first 10 th terms. 2. For arithemetic progression addition of 3 terms is 27 and their multiplication is 648, then that nos. 3.
Subtraction word problems. Best for:1st grade, second grade 9. Subtracting to 10: There were 3 pizzas in total at the pizza shop.A customer bought 1 pizza. How many pizzas are left? 10. Subtracting to 20: Your friend said she had 11 stickers.When you helped her clean her desk, she only had a total of 10 stickers.
Today's crossword puzzle clue is a quick one: Believing that all problems are fixable, perhaps. We will try to find the right answer to this particular crossword clue. Here are the possible solutions for "Believing that all problems are fixable, perhaps" clue. It was last seen in Daily quick crossword. We have 1 possible answer in our database.
Step 4: Solve the problem. Now all we have to do is solve our problem. Like with any problem, we can solve this one by following the order of operations. f is already alone on the left side of the equation, so all we have to do is calculate the right side.