
- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …

Analytical Thinking vs Problem Solving: A Comprehensive Comparison

Analytical thinking and problem solving are crucial skills in various aspects of life, including personal and professional situations. While they may seem interchangeable, there are distinct differences between the two. Analytical thinking focuses on breaking down complex information into smaller, manageable components to understand a situation and evaluate alternatives effectively. On the other hand, problem solving involves devising practical solutions to overcome challenges or resolve issues that arise in daily life or the workplace.

Both analytical thinking and problem-solving skills contribute to making well-informed decisions, managing risks, and achieving success in various areas of life. By understanding these skills’ distinctions and applying them effectively, individuals can enhance their performance in the workplace, handle complex situations with ease, and make better choices in their personal lives.
Key Takeaways
- Analytical thinking is about understanding complex situations, while problem-solving focuses on finding practical solutions.
- Mastery of both skills leads to informed decision-making and improved risk management.
- These abilities are essential for workplace success and overall personal growth.
Understanding Analytical Thinking

Nature of Analytical Thinking
Analytical thinking refers to a mental process in which a person systematically breaks down complex problems or situations into smaller, manageable components. This enables the identification of essential elements and their relationships, leading to an effective solution. Analytical thinkers excel in identifying patterns, interpreting data, and drawing conclusions based on factual information. Unlike reactive problem-solving, which focuses on finding immediate remedies, analytical thinking is strategic in nature, seeking long-term solutions by addressing the root causes of a problem.
Key components of analytical thinking include reasoning, fact-checking, and questioning assumptions. This skill set allows individuals to approach problems with an open mind, meticulously gather and analyze data, and make well-informed decisions. Ultimately, analytical thinking leads to more informed and strategic decision-making, increasing the likelihood of success in professional and personal endeavors.
How Analytical Thinking Works
The process of analytical thinking unfolds in several stages:
- Identify the problem or situation : Determine the issue that needs addressing and clearly define its scope.
- Gather relevant data : Collect information related to the problem from various sources, ensuring its accuracy and reliability.
- Break down the problem : Dissect the problem into smaller, manageable parts to gain a better understanding of its intricacies.
- Analyze and interpret data : Examine the data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships, and derive insights using logical reasoning.
- Question assumptions : Challenge any preconceived notions or biases that may skew the analysis and arrive at the most objective conclusions possible.
- Generate solutions : Propose potential solutions based on the analysis, weighing their pros and cons.
It is important to note that analytical thinking is not solely reserved for mathematicians or scientists but is a valuable skill applicable to a wide range of disciplines and professions. From business analysts, who require analytical thinking and problem-solving skills to identify and implement changes, to daily decision-making in personal lives, analytical reasoning plays a vital role in successfully navigating through various complexities.
Significance of Problem Solving
Features of problem solving.
Problem solving is an essential skill that helps individuals and organizations tackle challenges effectively. Problem-solving skills enable individuals to identify problems or obstacles, analyze the situation, and find appropriate solutions. These skills include critical thinking, analytical reasoning, decision-making, and learning from the process. People with strong problem-solving abilities can better cope with stress, handle risk, and adapt to change in a fast-paced environment.
In the context of decision-making, problem solving requires individuals to evaluate multiple options and select the one with the highest probability of success. A well-developed thinking process is crucial to identifying and analyzing creative solutions, as it helps individuals see beyond the apparent issues and delve deeper into the underlying causes.
Process of Problem Solving
The process of problem-solving typically involves several stages:
- Identify the problem : Recognizing the issue at hand and understanding its impact on the situation.
- Gather information : Collecting relevant data and facts that will help in understanding the problem.
- Analyze the problem : Examining the situation, breaking it into smaller parts, and identifying the root causes.
- Generate solutions : Brainstorming various possible solutions and evaluating their feasibility.
- Choose the best solution : Using decision-making skills to select the most suitable solution based on available information.
- Implement the solution : Putting the chosen solution into action and monitoring its effectiveness.
- Evaluate and learn : Reflecting on the outcomes and learning from the experience for future problem-solving situations.
By sharpening problem-solving skills and employing an organized thinking process, individuals can enhance their abilities to overcome challenges and make informed decisions, leading to personal and professional growth.
Comparing Analytical Thinking and Problem Solving
Similarities.
Both analytical thinking and problem solving involve the process of breaking down complex situations into smaller, manageable components. In both approaches, individuals need to evaluate the information at hand, identify patterns, and derive conclusions based on the evidence. This often involves receiving feedback, adapting to new information, and adjusting one’s approach.
Moreover, practicing both analytical thinking and problem-solving techniques can lead to improved decision-making abilities. This development, in turn, translates into greater efficiency and effectiveness in personal and professional contexts.
Differences
While analytical thinking and problem solving share some similarities, they also have notable differences. Analytical thinking typically follows a linear and sequential process, whereas problem solving might involve iterative processes and creative solutions.
Analytical thinking often focuses on dissecting a situation or a problem, looking for underlying patterns, and finding ways to logically deduce solutions. On the other hand, problem solving might require a combination of analytical and creative thinking, especially when faced with novel or ambiguous challenges. Problem solvers often need to develop unique strategies and evaluate alternative solutions before settling on the most effective approach.
In conclusion, analytical thinking and problem-solving, while both essential skills, have distinct applications and methods, and their effective use can be instrumental in achieving success in various aspects of life.
Ways to Improve Both Techniques
Developing analytical thinking.
Developing analytical thinking is vital for individuals seeking to improve their problem-solving abilities. One effective strategy is to practice creative activities, such as brainstorming or solving puzzles, to challenge the brain and foster development. Engaging in these tasks allows for the creation of new connections and enhances cognitive flexibility.
Another useful approach is to focus on communication and the art of listening. Active listening enables a better understanding of various perspectives and leads to well-informed decisions. Moreover, discussing complex topics can strengthen one’s ability to analyze and evaluate information effectively.
Collaborating with others can also help individuals enhance their analytical thinking skills. By working together, people can build on each other’s strengths and overcome challenges. Additionally, they can exchange ideas and learn from different viewpoints, which may lead to innovative solutions.
Enhancing Problem Solving Skills
To enhance problem-solving skills, one must be willing to take action and embrace challenges. Tackling problems head-on allows for growth and the development of practical strategies. Regular practice is essential for refining these skills and building confidence in decision-making.
Integrating soft skills, such as empathy and adaptability, play an essential role in problem-solving. Employing these abilities can improve interpersonal communication and contribute to the formation of more effective solutions.
Utilizing a methodical approach to problem-solving can also yield positive results. Techniques like breaking down complex issues into manageable steps or generating multiple possible solutions can enable a more comprehensive analysis, increasing the likelihood of success in overcoming challenges.
Finally, don’t shy away from seeking feedback from peers and mentors. Constructive criticism can highlight areas for improvement and further facilitate the development of both analytical thinking and problem-solving skills. Remember, the key to growth lies in continuous learning and adapting to new situations with confidence and clarity.
Importance in Workplace and Career Success
Relevance in the workplace.
Analytical thinking and problem solving play crucial roles in the workplace. These skills enable employees to efficiently tackle a variety of tasks and challenges. Analytical thinking refers to gathering, organizing, and evaluating information to detect patterns and identify problems. Effective problem solving involves devising creative solutions based on these findings 1 . In the modern workplace, individuals with strong analytical thinking skills can identify issues and make well thought-out decisions that contribute to overall company success 2 .
Effective communication is an important aspect of analytical thinking and problem solving. In a professional setting, employees must often convey their findings and ideas to stakeholders, ensuring that solutions are implemented appropriately and any concerns are addressed. This communication can lead to improved collaboration, clearer goals, and faster resolution of issues 3 .
Implication for Career Success
In addition to benefitting the workplace as a whole, strong analytical thinking and problem-solving skills are critical for individual career success. These skills can help professionals stand out among their peers and demonstrate their value to their organization. Professionals who can apply analytical thinking and problem-solving techniques are viewed as being able to think critically, make decisions, and take initiative, which are all highly valued by employers 4 .
Individuals who possess these skills are often able to make more informed judgments and sound decisions. This can lead to career advancement and job stability, as they are viewed as capable and dependable. Developing analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities can also open doors to new opportunities and industries, making individuals more versatile and efficient in their careers 5 .
Role in Decision Making and Risk Management
Influence on decision making.
Analytical thinking plays a crucial role in decision making, as it involves breaking things down into their component parts and using deductive reasoning to draw conclusions from given evidence and assumptions source . This allows individuals and organizations to carefully consider the pros and cons of each option, determine the feasibility of implementing potential solutions, and weigh the costs and benefits associated with each decision.
Problem-solving, on the other hand, is an analytical method that focuses on identifying potential solutions to specific situations source , sometimes requiring personal decision-making that may involve judgments or decisions on the way to find the best outcome. Both analytical thinking and problem-solving contribute to effective decision-making processes, as they provide tools and techniques for examining different courses of action and limiting uncertainties.
Contribution to Risk Management
Risk management is a critical aspect of decision-making, as it helps organizations and individuals identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks associated with various decisions. Analytical thinking contributes to risk management by enabling decision-makers to collect and analyze data, evaluate risks and their potential consequences, and make informed decisions based on the results source .
Similarly, problem-solving assists in risk management by addressing potential challenges that may arise during the implementation of solutions, such as examining potential obstacles, resource constraints, and other factors that may impact the success of an initiative source . By combining the strengths of both analytical thinking and problem-solving, decision-makers can enhance their risk management strategies and ensure a higher probability of success in their respective decisions.
In summary, analytical thinking and problem-solving are essential tools in decision-making and risk management, as they provide the necessary framework for evaluating options, weighing potential outcomes, and identifying potential challenges. By utilizing these methods, decision-makers can make more informed choices and mitigate potential risks associated with their decisions.
Utilization in Business Analysis
Application in business analysis.
Analytical thinking and problem solving are essential skills for business analysts in their day-to-day work. They are responsible for identifying, researching, and understanding complex business problems, as well as finding effective solutions to address them. By using their analytical thinking skills, business analysts can gather, assess, and interpret data from various sources to develop a comprehensive understanding of the situation at hand [1] .
When approaching a problem, business analysts consider several key factors, such as people, processes, and technology. They employ systems thinking to understand the enterprise holistically and how all these elements interact. This mindset helps them to not only identify the root cause of a problem, but also to develop solutions that address the underlying issues effectively [2] .
Understanding Financial Data
One key area where business analysts apply their analytical and problem-solving skills is in the realm of financial data. Here, they are tasked with interpreting complex financial information to derive valuable insights and make informed decisions for the organization.
In this context, their analytical thinking skills enable business analysts to:
- Gather relevant financial data from multiple sources
- Identify patterns, trends, and potential issues
- Assess the quality and accuracy of the data
- Develop conclusions and recommendations based on the analyzed data
By employing problem-solving skills, business analysts can:
- Understand the impact of financial data on business processes and performance
- Identify potential areas for improvement or optimization
- Propose and evaluate relevant solutions for financial issues [3]
Overall, business analysis relies heavily on the combination of analytical thinking and problem-solving skills to address various challenges faced by organizations. The ability to understand and interpret financial data significantly contributes to the success and growth of any enterprise.
Real Life Examples
Analytical thinking and problem solving are essential skills in both personal and professional life. They allow individuals to tackle complex issues, identify the root causes, and develop effective solutions. Let’s examine some real-life examples that emphasize the differences between these two thought processes.
In the workplace, an employee might face a challenge in increasing sales. Applying analytical thinking , the individual would gather data, identify patterns, and evaluate market trends to understand the factors impacting sales performance. With this information, they can determine which areas need improvement and develop targeted strategies to address the issue. For example, they may discover that customers are dissatisfied with the available products in a particular category, prompting changes in the company’s product offering.
On the other hand, problem-solving involves addressing specific situations, such as dealing with a dissatisfied customer. In this instance, the employee would need to rely on their experience and emotional intelligence to find a solution. They would listen to the customer’s concerns, empathize with their feelings, and proactively offer options to resolve the problem. This process may include correcting mistakes made during a transaction or offering compensation for a negative experience.
Another example can be found in the realm of personal finance. Analytical thinking would be employed to evaluate one’s financial situation and understand patterns in spending habits. This analysis could reveal areas where money may be saved or better utilized. For instance, it may uncover excessive spending on dining out or ineffective monthly budgeting practices.
Conversely, problem-solving can come into play when an unexpected financial emergency occurs. In such cases, one would need to quickly evaluate the situation and devise creative solutions to address the crisis. This might involve temporarily reducing non-essential expenses, seeking additional sources of income, or negotiating payment plans with creditors.
In both of these real-life scenarios, analytical thinking and problem-solving work in tandem, complementing each other to achieve effective outcomes. While individuals may favor one approach over the other, it is crucial to recognize and develop both skillsets to navigate the complexities of modern life successfully.
- https://www.glassdoor.com/blog/guide/analytical-thinking/ ↩
- https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/problem-solving-and-decision-making ↩
- https://www.radford.edu/content/cobe/innovation-analytics/analytics/career-prep/report-e.html ↩
- https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/critical-thinking-vs-problem-solving ↩
- https://www.amanet.org/analytical-thinking-problem-solving-and-decision-making/ ↩
You may also like

Critical thinking and Goal setting
If you are interested in learning more about critical thinking and goal setting, you aren’t alone. A lot of people want to […]

Unleash Your True Mental Power with These 10 Critical Thinking Habits
Critical thinking is an extremely useful skill no matter where you are in life. Whether you are with the top decision-making bodies […]

Critical thinking jokes
Critical thinking can make life smoother and smarter, solving all kinds of academic, professional and everyday problems. But it’s not something you […]

Decision Making Framework: A Guide to Smarter Choices
Effective decision making is crucial for success in both personal and organizational contexts. The complexity of modern life, with its vast array […]
Mind by Design

Critical thinking vs analytical thinking: The differences and similarities
The ability to think clearly and make informed decisions is paramount to life. This article delves deep into the realms of analytical thinking and critical thinking, shedding light on their differences and how they complement each other. By understanding these thinking styles, you’ll be better equipped to tackle complex problems, evaluate information, and make well-informed decisions. Let’s dive in!
Introduction to Analytical and Critical Thinking
Analytical and critical thinking are two skills essential for solving problems and making decisions in various aspects of life. While both involve the use of logic and reasoning, they differ in their approach and outcomes. Analytical thinking involves breaking down complex information into smaller parts, while critical thinking involves taking a holistic view and evaluating information from different angles. Analytical thinking involves the ability to dissect a problem or situation into its individual components and examining each part separately. It requires careful observation and the ability to identify patterns and relationships. This type of thinking is essential for tasks such as data analysis, problem-solving, and troubleshooting.

Critical thinking, on the other hand, involves the ability to assess information objectively, evaluate its credibility, and make logical judgments. It involves questioning assumptions, examining evidence, and considering different perspectives. Critical thinking is crucial for making informed decisions, weighing pros and cons, and avoiding biases and fallacies.
Both analytical and critical thinking complement each other and are necessary for effective problem-solving and decision-making. Analytical thinking provides a structured and systematic approach to understanding complex problems , while critical thinking helps evaluate different options and make sound judgments.
Developing analytical and critical thinking skills can greatly benefit individuals in various aspects of life. In academia, these skills are necessary for understanding and interpreting complex subjects, conducting research, and writing analytical essays. In the workplace, analytical and critical thinking skills are highly valued by employers as they enable employees to solve problems efficiently and make informed decisions. In daily life, these skills are essential for evaluating information, distinguishing between fact and opinion, and making rational choices.
There are various ways to improve analytical and critical thinking skills. Engaging in activities that require logical reasoning, such as puzzles, brain teasers, and mathematical problems, can help develop analytical thinking abilities. Reading diverse sources of information, questioning assumptions, and actively seeking different perspectives can enhance critical thinking skills . Additionally, engaging in debates, discussions, and problem-solving exercises can promote both analytical and critical thinking.
Analytical and critical thinking skills are essential for problem-solving and decision-making in various aspects of life. They involve breaking down complex information and evaluating it from different angles. Developing these skills can lead to more effective problem-solving, informed decision-making, and overall improved cognitive abilities.
Traits of an Analytical Thinker
An analytical thinker is one who is adept at breaking down complex problems into smaller parts. This type of thinking is linear and involves analyzing cause and effect relationships. Analytical thinking uses logic and reasoning to come to a conclusion, often relying on data and facts. Some key traits of an analytical thinker include:
- The ability to dissect complex information into smaller pieces.
- A knack for recognizing patterns and relationships.
- A methodical approach to problem-solving.
What Does It Mean to Think Critically?
Critical thinking, on the other hand, is a type of higher-order thinking that requires a more holistic approach. Critical thinkers are often skeptical, questioning the validity of information before accepting it. They are adept at evaluating information from various sources and are not easily swayed by outside information. Key aspects of critical thinking include :
- The ability to form an opinion based on evidence.
- Considering multiple perspectives before making a decision.
- Recognizing biases and challenging one’s own assumptions.
Analytical Thinking vs Critical Thinking: The Major Differences
While both analytical and critical thinking are essential for solving problems, they differ in several key ways:
- Approach : Analytical thinking is more linear and focuses on breaking down complex information into smaller parts. Critical thinking, however, is holistic and looks at the bigger picture.
- Use of Information : Analytical thinkers rely heavily on facts and data, while critical thinkers use facts in conjunction with other pieces of information and perspectives.
- Outcome : Analytical thinking often leads to a single logical conclusion, whereas critical thinking might result in multiple potential solutions or outcomes.

The Processes: Analytical Thinking Process vs Critical Thinking Process
Both styles of thinking have distinct processes:
- Analytical Thinking Process : Starts with gathering data, followed by breaking down complex problems, analyzing the cause and effect relationships, and finally drawing a conclusion.
- Critical Thinking Process : Begins with gathering diverse pieces of information, evaluating their validity, considering various perspectives, and finally forming an opinion or decision.
Using Analytical and Critical Thinking in Real Life Scenarios
In real-life scenarios, these thinking styles can be applied in various ways. For instance, when faced with a business decision, an analytical thinker might focus on the numbers and statistics, while a critical thinker might consider the potential impact on employees, company culture, and external stakeholders.
Analytical thinking can be particularly useful when analyzing financial data and making data-driven decisions. For example, a business owner might use analytical thinking to analyze the company’s financial statements and determine the profitability and financial health of the business. They might examine key financial ratios, such as return on investment or gross profit margin, to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of various business operations.
On the other hand, critical thinking can be applied when evaluating different options and considering the potential consequences of each option. For example, when considering a potential business expansion, a critical thinker may explore the potential impact on existing employees, the company’s culture, and the external stakeholders. They may assess the potential risks and benefits of the expansion, considering factors such as increased competition, resource allocation, and market demand.
Analytical and critical thinking can also be applied in personal decision-making. For example, when considering a major life decision such as buying a house or changing careers, analytical thinking can help weigh the financial implications, such as the monthly mortgage payments or future earning potential. Critical thinking can help evaluate the potential impact on personal goals, values, and overall satisfaction.
In everyday life, analytical thinking can be useful when evaluating product options or making purchasing decisions. For example, comparing different phone models based on features, specifications, and customer reviews can help individuals make an informed choice. Critical thinking can be applied when assessing the potential consequences of a decision, such as considering the long-term environmental impact of a product or the ethical practices of a particular company.
Both analytical and critical thinking are valuable skills in problem-solving. They can help individuals identify the root causes of a problem, analyze potential solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness. Whether it’s troubleshooting a technical issue, resolving a conflict, or devising strategies to improve personal or professional performance, these thinking styles can be instrumental in finding effective solutions.
Analytical and Critical Thinking in Problem-Solving
Problem-solving requires a combination of both analytical and critical thinking. Analytical thinking helps break the problem into manageable parts, while critical thinking helps in evaluating potential solutions and considering their implications.
The Importance of Combining Both Thinking Styles
While both styles are powerful on their own, combining analytical and critical thinking skills can lead to more robust solutions. This combination allows for a thorough analysis of a problem while also considering the broader implications and potential consequences of a decision.
Mistakes to Avoid: Misconceptions about Analytical and Critical Thinking
Many assume that analytical thinking and critical thinking are one and the same, but this is a misconception. It’s important to recognize their distinct differences and strengths. Another common mistake is over-relying on one style and neglecting the other, leading to potential oversights in decision-making.

Key Takeaways: The Future of Analytical and Critical Thinking
In summary, here are the most important things to remember:
- Distinct yet Complementary : While analytical and critical thinking have distinct processes and outcomes, they are complementary and can be used together for more effective decision-making.
- Real-world Applications : Both styles are essential in various aspects of life, from business decisions to personal choices.
- Continuous Learning : As the world becomes more complex, honing both analytical and critical thinking skills will be crucial for success.
Embrace both styles of thinking and watch as your decision-making skills, problem-solving abilities, and overall understanding of complex situations improve dramatically.
Q: What is the difference between critical thinking and analytical thinking?
A: Critical thinking and analytical thinking are similar thinking skills, but there are some differences between the two. Critical thinking involves gathering information, evaluating and interpreting it, and then making a judgment or decision based on that information. Analytical thinking, on the other hand, focuses more on breaking down complex problems into smaller components, analyzing the relationships between these components, and coming up with solutions based on this analysis. So while both skills involve a logical and systematic approach to thinking, critical thinking is more focused on making judgments and decisions, whereas analytical thinking is more focused on problem-solving and analysis.
Q: How do I use critical thinking in everyday life?
A: Critical thinking is a valuable skill that can be applied in various aspects of everyday life. To use critical thinking, you need to approach situations and problems with an open and questioning mind. This involves challenging your own assumptions and beliefs, gathering and evaluating information from different sources, considering alternative perspectives, and making informed decisions based on evidence and logical reasoning. By using critical thinking, you can enhance your problem-solving skills, improve your decision-making abilities , and think more creatively and independently.
Q: How do I use analytical thinking in my professional life?
A: Analytical thinking is an important skill in many professional fields. To use analytical thinking, you need to be able to break down complex problems or tasks into smaller parts, analyze the relationships between these parts, and come up with logical and well-reasoned solutions. This involves gathering and evaluating relevant data, identifying patterns or trends, and using logical reasoning to draw conclusions. By using analytical thinking, you can improve your problem-solving and decision-making abilities, demonstrate a logical and organized approach to your work, and effectively communicate your analysis and solutions to others.
Q: Can critical thinking and analytical thinking be used together?
A: Yes, critical thinking and analytical thinking are complementary skills that can be used together. Both skills involve a systematic and logical approach to thinking, and they can reinforce each other in problem-solving and decision-making processes. Critical thinking provides the framework for evaluating and interpreting information, while analytical thinking provides the tools for breaking down complex problems and finding solutions. By using both skills together, you can enhance your ability to think critically and analytically, make more informed decisions, and solve problems more effectively.
Q: What are the differences between analytical reasoning and critical thinking?
A: Analytical reasoning and critical thinking are related skills that involve a logical and systematic approach to thinking. However, there are some differences between the two. Analytical reasoning is more focused on the process of breaking down complex problems or arguments, identifying logical relationships between different elements, and drawing conclusions based on this analysis. Critical thinking, on the other hand, is a broader skill that involves evaluating and interpreting information, questioning assumptions and biases, and making judgments or decisions based on evidence and logical reasoning. While analytical reasoning is an important part of critical thinking, critical thinking encompasses a wider range of cognitive processes and skills.
Q: How can I develop and improve my analytical thinking skills?
A: To develop and improve your analytical thinking skills, you can engage in activities that stimulate your logical and problem-solving abilities. This may involve practicing with puzzles and brainteasers, analyzing case studies or real-life scenarios, participating in debates or discussions, learning and applying different analytical frameworks or models, and seeking feedback on your analytical thinking from others. Additionally, you can also cultivate your analytical thinking skills by staying curious, asking thoughtful questions, and continuously seeking new knowledge and perspectives. With practice and perseverance, you can enhance your analytical thinking abilities and become a more effective problem solver and decision maker.
Q: How can I become a critical thinker?
A: Becoming a critical thinker requires a conscious effort to develop and refine your thinking skills. Here are some steps you can take to become a critical thinker : 1. Cultivate intellectual humility and open-mindedness: Be willing to consider alternative viewpoints and challenge your own assumptions and beliefs. 2. Develop strong analytical and reasoning skills: Learn to gather and evaluate evidence, identify logical fallacies, and draw logical and well-supported conclusions. 3. Practice active listening and effective communication: Listen attentively to others’ perspectives, ask thoughtful questions, and communicate your own ideas clearly and persuasively. 4. Seek out diverse sources of information: Expose yourself to different perspectives and viewpoints to broaden your understanding and avoid bias. 5. Reflect and evaluate your own thinking: Regularly reflect on your own thinking processes, identify any biases or logical gaps, and work on improving your critical thinking skills.
Q: What role does critical thinking play in problem-solving?
A: Critical thinking is a fundamental skill in problem-solving. It helps you approach problems with a logical and systematic mindset, evaluate potential solutions, and make informed decisions. Critical thinking allows you to gather and analyze relevant information, identify patterns or trends, consider different perspectives or alternatives, weigh the pros and cons, and choose the most effective solution. By using critical thinking in problem-solving, you can enhance your ability to find creative and innovative solutions, overcome obstacles, and make well-informed decisions that are based on sound reasoning and evidence.
Q: Why is critical thinking important?
A: Critical thinking is important because it enables you to think independently, make informed decisions, solve problems effectively, and evaluate information and arguments critically. In a rapidly changing and complex world, critical thinking allows you to navigate through information overload, identify biases or misinformation, and make sense of a wide range of conflicting information. It also helps you develop a deep understanding of concepts and ideas, construct well-reasoned arguments, and communicate your thoughts effectively. In both personal and professional contexts, critical thinking is a valuable skill that empowers you to be a more effective and successful individual.
Q: How does analytical thinking contribute to problem-solving?
A: Analytical thinking is a key component of problem-solving. It involves breaking down complex problems into smaller components, analyzing the relationships between these components, and identifying patterns or trends. Analytical thinking helps you understand the underlying causes of problems, explore different possible solutions, and evaluate their feasibility and effectiveness. By using analytical thinking, you can approach problems in a structured and systematic way, make well-informed decisions, and find creative and innovative solutions. Analytical thinking provides a solid foundation for problem-solving, enabling you to effectively address challenges and find solutions in various domains.
Similar Posts

What causes low self-confidence?
Low self-confidence is caused by many different life circumstances. From feeling like an outsider to feeling like their achievements don’t matter, people can have low self-confidence because of a variety of scenarios. You can always work on ways to change your perspective and stop these negative thoughts from becoming a reality. Top 5 reasons for…

What is the opposite of stoicism?
The opposite of stoicism is the belief that feeling emotions are a natural, healthy, and important part of life. Stoicism emphasizes emotional control with the goal to eliminate negative emotions such as anger or fear. It is an unemotional state of mind. In contrast to stoicism, positive psychology’s approach to emotions is based on the…

How To Stop Relying on One Person for Happiness (13 Ways to Independence)
Relying on one person for happiness is a dangerous game. You will inevitably be crushed when that person leaves or falls out of your life. So how do you break free from the dependence on just one person for success? It’s simple: there are 13 steps of independence, which I’ve outlined below for you. 1)…

What is a growth mindset?
A growth mindset is a belief that intelligence can be developed through hard work, education and learning. This is in contrast to a fixed mindset which assumes intelligence is not changeable. These limiting beliefs can stunt children’s growth and learning, leading to underachievement. According to research, around 4% of the general population have a growth…

What are the 8 principles of Stoicism?
The philosophy of Stoicism was founded around 300 BC in Athens by a Phoenician called Zeno of Citium. It was first established as a school of thought. Its founding principles are that people should live in accordance with nature, which means to be helpful and tolerant towards others. It teaches that we shouldn’t be overly…

10 Reasons a Growth Mindset Is Key to Success in Athletes
A growth mindset and its benefits are often cited in popular psychology and business literature. But what does that mean for athletes? Contrary to the belief that some people are born with a natural advantage, success starts with the understanding that anyone can improve and grow. This post will detail 10 reasons why a growth…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy
- Find a Course
- For Business
- For Educators
- Product News
Analytical thinking: what it is and why it matters more than ever
January 30, 2024

Welcome back to our high-impact workplace skills series. We really enjoyed the conversations happening in the comments section of last week’s top skills of 2023 issue, so be sure to check those out for perspectives and insights from fellow members of our Career Chat community.
One comment that’s been on our mind came from Kendra Vivian Lewis , who asked some thoughtful questions about the comparative importance of workplace and technical skills and if there’s a way to forecast which skills will be important in the coming years. This week’s topic—analytical thinking, the number one skill on the list—is a great example as we explore both questions. Be sure to read to the end to discover a special offer that we’re running on Coursera Plus subscriptions through September 21.
What it means to think analytically
Analytical thinking involves using data to understand problems, identify potential solutions, and suggest the solution that’s most likely to have the desired impact. It’s similar to critical thinking skills , which are the skills you use to interpret information and make decisions.
In order to succeed as a strong analytical thinker, you also need to have strong technical skills in your field. Remember: technical skills describe the things you do, while workplace skills describe how you do them. So your workplace skills, used effectively, enhance your technical skills. That’s why we consider them to be high-impact—they stand to make your work more impactful than it would have been had you only used your technical skills.
To illustrate, suppose you just started a job as a data analyst for a think tank focused on climate change, and you’ve been tasked with raising community engagement in future climate action efforts.
You might start with your technical data analysis skills as you gather data from a few sources. Then, you’ll use your analytical thinking skills to determine the validity of each data source. Perhaps you’ll discard one source when you learn the research was funded by a firm with a financial stake in fossil fuel consumption. Your technical skills lead again as you clean data, and then you’ll return to your analytical thinking skills to analyze and interpret your findings, ultimately leading to your recommendation to start a transparency campaign to display water and energy use in the community.
Tell us in the comments: How do you use your analytical skills alongside your technical skills in your day-to-day work?
Why analytical skills top the list
To develop the skills list, the World Economic Forum surveyed 800+ global employers on their views of skills and jobs over the next five years, so this list is forward-looking. According to the Future of Jobs Report , employers believe analytical thinking skills will grow in importance by 72 percent in this timeframe.
The reason employers are keen to hire employees with strong analytical thinking skills is informed by trends in automation and technological advancements. While technical data analysis becomes easier with automation, reasoning and decision-making automation is advancing at a much slower pace—meaning employers anticipate that, within the next five years, we’ll have a wealth of data at our fingertips and too few people to interpret what that data means.
Where to begin
For a crash course in critical thinking, try the University of California, Davis’s Critical Thinking Skills for the Professional course. You can finish this beginner-level course in about 7 hours.
For a more comprehensive exploration into analytical thinking , try Duke University’s Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking Specialization . Over four courses, you’ll learn how to effectively argue and reason using logic.
For a technical process to guide your analytical thinking, try Google’s Data Analytics Professional Certificate . Ground your analytical thinking skills in technical know-how in this eight-course series.
Interested in multiple programs? Don’t miss this special offer!
Through September 21, we’re offering $100 off annual Coursera Plus subscriptions for new subscribers. With this offer, you’ll pay less than $25 per month for one year of access to 6,100 courses, Specializations, and Professional Certificates with flexibility to start new courses and move between programs at your pace.
This offer is a great choice if you are frequently tempted to enroll in multiple courses at once or plan to complete a Specialization or Professional Certificate within the next year. If that sounds like you, take a closer look at the offer and the Coursera Plus course catalog.
That’s all for this week! Join us next week to talk about motivation and self-awareness skills.
Keep reading
- Enhance your resume with ChatGPT
- Blueprint for success: Lisa’s degree story began with two certificates from HEC Paris
- Top skill alert: Open doors with spreadsheets

Critical Thinking vs Analytical Thinking: What’s the Difference?
What is critical thinking, what is analytical thinking, traits of critical thinkers, traits of analytical thinkers, for example, why are critical thinking and analytical skills important, how to develop a critical thinking and analytical mind , critical thinking vs analytical thinking faqs.
Other Related Blogs
- Curious: They possess a natural curiosity and an insatiable desire to learn and understand. They constantly ask questions and seek deeper knowledge.
- Structured Problem-Solving : Analytical thinkers approach problems systematically. They break down complex issues into smaller, manageable components for thorough analysis.
- Data-driven: They rely on data and evidence to support their conclusions. Data analysis is a key aspect of their decision-making process.
- Critical Evaluation: They critically assess the quality and reliability of information sources. They are discerning about the credibility of data.
- Logical Reasoning: They employ logical reasoning to connect facts and deduce insights. Their arguments are based on sound logic.
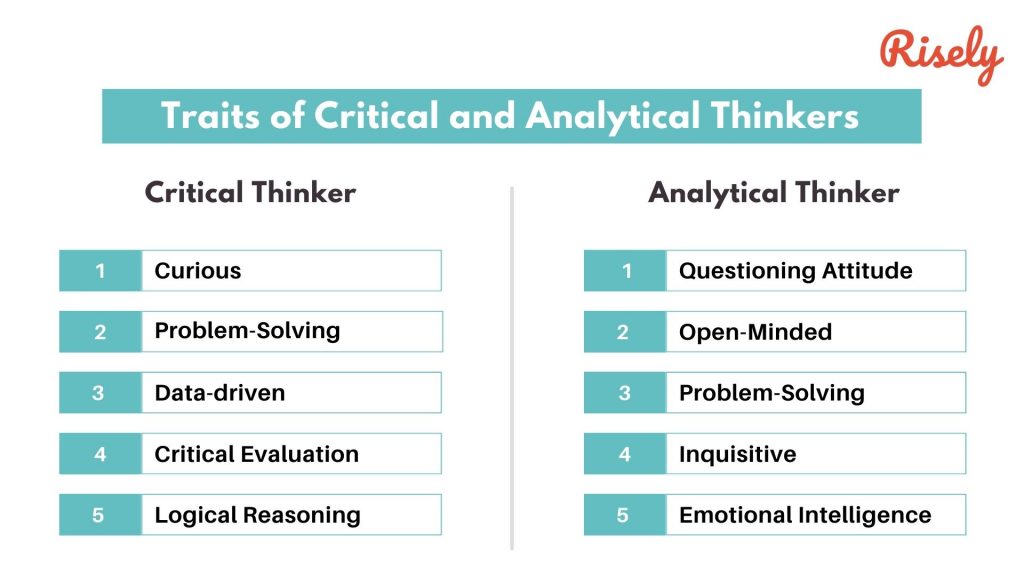
- Questioning Attitude: Critical thinkers question assumptions, statements, and conventional wisdom. They challenge ideas to seek deeper understanding.
- Open-Minded: They maintain an open mind, considering multiple perspectives and being receptive to new information.
- Problem-Solving: Critical thinkers approach problems by examining all angles, evaluating evidence, and identifying the best possible solutions.
- Inquisitive: They have a natural curiosity and an appetite for knowledge. They are motivated to dig deeper into subjects.
- Emotional Intelligence : They are attuned to emotions, both their own and those of others. This awareness helps them understand human behavior and reactions.
Critical Thinking vs Analytical Thinking for Managers
- A retail store manager might use analytical thinking skills to analyze sales data to identify patterns and trends. For example, they might examine sales data to determine which products are selling well and at what times of day or year. They might then use this information to adjust inventory levels, schedule staff, or develop marketing campaigns to capitalize on trends.
- A manager might use analytical thinking skills to analyze financial data to identify cost savings or revenue growth opportunities. For example, they might analyze expense data to identify areas where costs are higher than expected and develop strategies to reduce them. They might also analyze sales data to identify opportunities to expand into new markets or increase revenue from existing customers.
- A manager might use critical thinking skills to evaluate competing proposals for a new project. For example, they might consider each proposal based on feasibility, cost, the potential impact on the organization, and alignment with its strategic goals. They might then use this evaluation to make an informed decision about which proposal to pursue.
- A manager might use critical thinking skills to evaluate the performance of individual employees or teams. For example, they might evaluate employee performance based on factors such as productivity, quality of work, and adherence to company policies and procedures. They might then use this evaluation to decide on promotions, training, development, or disciplinary action.
- Types of Negotiations: Your Ultimate Toolkit for Effective Communication
- 9 Tips to Master the Art of Delegation for Managers
- 8 Effective problem-solving strategies for managers
- Understanding The Role Of Team Dynamics To Make A Healthy Work Environment
- Learning Automation in the Workplace: Top Examples, pros & Cons and 3 Types
- Negotiation and Communication Skills: Top Examples for Managers to Learn From
- 7 Effective Ways To Manage Stress At Work For Managers
- 6-step template to make Reverse Brainstorming the Key to Unlocking Innovation
- Acing Mid-year Performance Reviews: 7 Useful Tips for Managers
- Human Resources Manager Training: A 6 Step Framework
- Effective problem-solving: Critical thinking and analytical skills are essential for identifying, analyzing, and solving complex problems. By breaking down problems into smaller parts and evaluating each part objectively, individuals can develop effective solutions to complex problems .
- Improved decision-making: Critical thinking and analytical skills help individuals make well-informed decisions by evaluating and synthesizing information from multiple sources. By objectively assessing information, individuals can make decisions based on evidence rather than biases or emotions.
- Increased creativity: Analytical thinking skills can help individuals identify patterns and connections between seemingly unrelated pieces of information, leading to creative problem-solving and innovative solutions.
- Better communication: Critical thinking skills help individuals evaluate the quality of arguments and evidence presented by others, leading to more transparent and effective communication .
- Success in the workplace: Employers value critical thinking and analytical skills because they enable individuals to be more effective problem-solvers and decision-makers, leading to better business outcomes and increased success.

- Ask questions: Ask questions to clarify information, evaluate evidence, and challenge assumptions. This helps you better understand the information and think more critically about it.
- Seek out diverse perspectives: Engage with people who have different backgrounds and experiences from your own. This helps you to see problems from different angles and gain new insights.
- Evaluate sources: Practice evaluating the credibility of sources, such as news articles or research studies. This helps you develop a critical eye and avoid being swayed by false information.
- Practice active listening: When engaging in conversation, try to listen to others and truly understand their perspectives. This helps you to evaluate information objectively and avoid making assumptions.
- Practice problem-solving: Regularly engage in problem-solving activities like puzzles or brain teasers. This helps you to develop your analytical skills and practice thinking creatively.
- Practice analyzing data: Analyze data from different sources and identify patterns or trends. This helps you to develop your analytical skills and practice thinking critically about information.
- Reflect on your thinking: Regularly reflect on your thinking processes and evaluate how you approach problems or make decisions. This helps you identify improvement areas and develop better critical thinking habits.
- Seek feedback: Ask for feedback from others on your critical thinking and analytical skills. This helps you to identify areas where you can improve and develop new strategies for thinking more critically.
- Practice decision-making: Practice decision making based on evidence and logical reasoning rather than emotions or biases. This helps you to develop more effective decision-making skills.
- Engage in a debate: Participate in debates or discussions where you are challenged to defend your position and evaluate opposing arguments. This helps you to practice critical thinking and develop more effective communication skills.
Test your critical thinking skills for free!
Start the free critical thinking skills assessment for managers .
Is analyzing a critical thinking skill?
Can you be both an analytical and critical thinker, how can i be critical and analytical .

Critical Thinking Training For Managers Simplified
6 steps to beat common critical thinking barriers at work, how to develop the 8 conceptual skills every manager needs, 7 ways to develop critical thinking skills as a manager.

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Analytical Thinking: An Introduction
Get introduced to "Analytical Thinking" with this comprehensive blog. Delve into the core concept of analytical thinking, exploring its characteristics such as curiosity, systematic approach, problem-solving aptitude and open-mindedness. By the end of this exploration, you'll have a clear understanding of what analytical thinking is and why it's a crucial skill.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Leadership Skills Training
- Instructional Design Training
- Design Thinking Course
- Business Development Training
- Leadership and Management Course

Table of Contents
1) What is Analytical Thinking?
2) Why is Analytical Thinking important?
3) Important elements of Analytical Thinking
4) How to master Analytical Thinking?
5) Conclusion
What is Analytical Thinking ?
Analytical Thinking is the cognitive process of dissecting intricate problems, data, or situations into smaller components to discern patterns, relationships, and underlying principles. It involves critical observation, logical reasoning, and systematic analysis to arrive at informed conclusions or solutions.

Why is Analytical Thinking important?
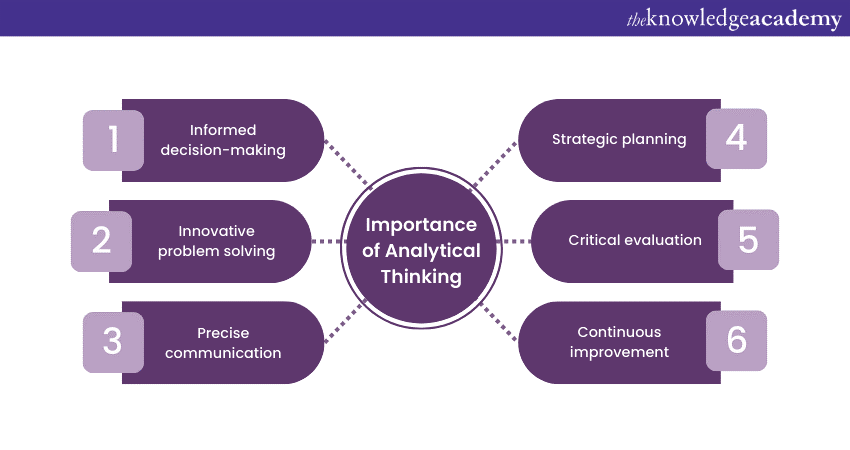
Informed decision-making
At its core, Analytical Thinking equips individuals with the tools to dissect intricate scenarios, distil pertinent information, and make informed decisions. From someone pondering a career move, considering a significant investment to someone deciding on a course of action, Analytical Thinking allows you to assess the pros and cons, identify potential pitfalls, and forecast outcomes.

Innovative problem solving
Innovation often springs from the ability to connect disparate dots and unearth hidden solutions. Analytical thinkers possess the capability for dissecting complex problems, breaking them into manageable components, and reassembling them in novel ways. This cognitive dexterity breeds innovation, as it enables individuals to envision alternative paths and approaches that might otherwise remain concealed.
Precise communication
Clear and effective communication is essential in all walks of life. Analytical Thinking fosters the capacity to organise thoughts logically, structure arguments coherently, and present ideas with precision. Regardless of whether you're explaining a concept to a colleague, delivering a persuasive pitch, or writing a research paper, the analytical thinker's ability to present complex ideas succinctly and comprehensibly is an invaluable asset.
Strategic planning
From business strategies to personal goals, strategic planning hinges on the ability to anticipate outcomes, devise contingencies, and adapt to changing circumstances. Analytical Thinking lends itself to strategic prowess by enabling individuals to assess multiple variables, foresee potential roadblocks, and chart a course that maximises the likelihood of success.
Critical evaluation
In a world rife with misinformation and biased narratives, the skill of critical evaluation is more crucial than ever. Analytical Thinking empowers individuals to sift through a barrage of information, discern credible sources, and separate fact from fiction. This aptitude for discernment is a bulwark against being swayed by superficial allure or baseless assertions.
Continuous improvement
Analytical thinkers possess an innate curiosity that propels them towards constant learning and growth. They see challenges not as insurmountable obstacles but as opportunities for enhancement. This drive for self-improvement extends beyond their capabilities; analytical thinkers often seek to refine processes, systems, and products, contributing to advancing their fields and industries.
Unlock your creative potential and enhance your Analytical Thinking skills with our comprehensive Creative and Analytical Thinking Training !
Important Elements of Analytical Thinking
Now that you know the meaning of Analytical Thinking, let's explore its characteristics. Analytical Thinking is more than a mere mental exercise; it's a unique cognitive approach that involves a specific set of traits and habits. Those with these characteristics are adept at dissecting complexities, drawing insights from data, and arriving at well-reasoned conclusions. Here are the key attributes that define Analytical thinkers:
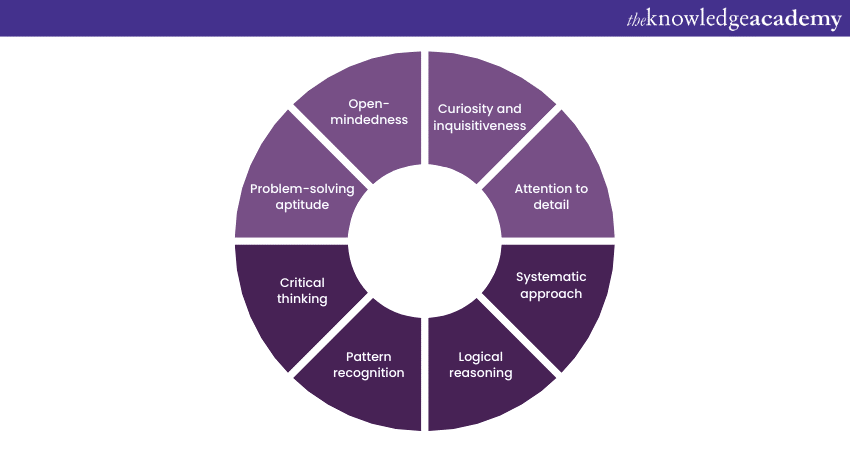
Curiosity and inquisitiveness
Analytical Thinkers exhibit a natural curiosity about the world around them. They possess an insatiable desire to understand how things work and why they are the way they are. This curiosity fuels their exploration of concepts, data, and problems, leading them to uncover hidden connections and unexpected insights.
Attention to detail
One of the hallmarks of Analytical Thinking is an unwavering attention to detail. Analytical individuals have a knack for spotting even the minutest discrepancies, anomalies, or patterns within data or scenarios that might go unnoticed by others. This acute attention to detail is instrumental in identifying potential issues and crafting precise solutions.
Systematic approach
Analytical Thinkers approach problems methodically. They break down complex issues into manageable parts, which allows them to analyse each component individually before synthesising a comprehensive understanding. This systematic approach enables them to unravel intricate challenges and address them step by logically.
Logical reasoning
Logical reasoning is the bedrock of Analytical Thinking . Those who possess this trait are skilled at constructing and deconstructing arguments, identifying flaws in reasoning, and evaluating the validity of information. This ability helps them sift through the noise and reach well-founded conclusions based on evidence and logic.
Pattern recognition
Analytical Thinkers excel at recognising patterns and trends across various data sets or scenarios. They have an innate ability to identify similarities and differences, allowing them to generalise principles from specific instances and apply them to broader contexts.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is a cornerstone of Analytical Thinking . Individuals with this characteristic are not content with accepting information at face value; they question assumptions, challenge norms, and seek underlying reasons. This intellectual rigour ensures that their conclusions are well-substantiated and comprehensive.
Problem-solving aptitude
Analytical Thinkers thrive on solving complex problems. They approach challenges with a blend of creativity and logic, devising innovative solutions that address the root causes rather than merely treating symptoms. Their ability to dissect problems and explore multiple angles empowers them to tackle even the most daunting issues.
Open-mindedness
While Analytical Thinkers possess strong reasoning skills, they also embrace open-mindedness. They acknowledge that not all problems have linear solutions and are willing to explore unconventional ideas and viewpoints. This adaptability allows them to adapt their approach when encountering new and unexpected scenarios.
Unlock your potential with our Decision-Making Skills Training - empower your choices and lead with confidence!
How to master Analytical Thinking?
In order to master your Analytical Thinking skills, you can adapt the following skills:
1) Analysing information involves thoroughly examining data or a situation to identify crucial elements, assess their strengths and weaknesses, and leverage this understanding to construct a compelling argument, offer recommendations, or address a problem effectively.
2) Breaking down problems simplifies significant challenges by dividing them into more minor, manageable issues that are easier to solve individually.
3) Gathering information requires asking pertinent questions of oneself and others to gain valuable insights, facilitating more informed decision-making when tackling problems.
4) Identifying issues and problems involves honing the skill of recognising underlying issues or challenges through analysing trends, associations, and cause-effect relationships within datasets.
5) Identifying the root cause is conducting a thorough analysis to pinpoint the fundamental cause of a problem, ensuring that efforts are focused on addressing the actual issue rather than just its symptoms.
6) Organising information entails systematically arranging and integrating all collected data to derive insights and generate ideas, laying the groundwork for potential solutions to the problems at hand.
Conclusion
Analytical Thinking emerges as an invaluable beacon in a world demanding ever-greater insight and adaptability. Its ability to unravel complexity, innovate solutions, and foster critical evaluation empowers individuals across diverse domains. By cultivating a curious mind, attention to detail and logic, we can get started on a journey of continuous improvement. Hope we could answer all your queries about “What is Analytical Thinking”!
Unlock your l eadership potential with our comprehensive Leadership Training - J oin now for a transformative learning journey!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here's how you can enhance Analytical Thinking skills:
a) Practice regularly: Solve puzzles and engage in analytical games.
b) Read widely: Explore diverse topics for a broader perspective.
c) Critical reflection: Reflect on experiences and decisions critically.
d) Ask questions: Challenge information and seek underlying reasons.
e) Break down issues: Analyse complex problems by breaking them into parts.
f) Seek feedback: Discuss analyses with peers for valuable insights.
g) Learn from mistakes: Analyse failures for continuous improvement.
h) Data literacy: Understand and interpret data for informed decisions.
i) Stay curious: Cultivate curiosity to explore various problem angles.
j) Take on projects: Apply analytical skills in practical scenarios for hands-on experience.
Analytical Thinking is vital for career growth, enabling strategic decision-making and effective problem-solving. It empowers professionals to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, and drive innovation. Those skilled in Analytical Thinking excel in strategic planning, problem-solving, and efficient decision-making. They contribute to organisational success by optimising operations, fostering innovation, and exhibiting leadership qualities. This skill enhances adaptability in dynamic environments, encourages continuous learning, and improves communication with diverse stakeholders.
Individuals with strong analytical skills can create detailed plans, identify critical milestones, and allocate resources efficiently by breaking down complex projects into manageable components. This approach allows setting of precise timelines and realistic goal-setting. Analytical thinkers excel at anticipating potential challenges, enabling proactive problem-solving and risk mitigation. They prioritise tasks based on strategic importance and resource availability, ensuring optimal time utilisation. Additionally, Analytical Thinking aids in assessing project progress through data analysis, facilitating informed adjustments when necessary.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide. Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue , encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA . The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses , including Leadership Skills, Creative Leader Thinking and Creative and Analytical Thinking. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Leadership Qualities Our Leadership Training blogs covers a range of topics related to leadership and analytical thinking, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Leadership skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 7th Jun 2024
Fri 2nd Aug 2024
Fri 4th Oct 2024
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
- Career Advice
- Job Search & Interview
- Productivity
- Public Speaking and Presentation
- Social & Interpersonal Skills
- Professional Development
- Remote Work
Eggcellent Work
Critical thinking vs problem solving: what’s the difference.
In our blog “Importance of Problem Solving Skills in Leadership ,” we highlighted problem solving skills as a distinct skill set. We outlined a 7-step approach in how the best leaders solve problems.
Table of Contents
Critical thinking vs. problem solving
But are critical thinking and problem solving the same? Also, if there are differences, what are they? Although many educators and business leaders lump critical thinking and problem solving together, there are differences:
Problem solving uses many of the same skills required for critical thinking; e.g., observation, analysis, evaluation, interpretation, and reflection. Critical thinking is an important ingredient of problem solving.
Critical thinking vs. problem solving: Not all problems require critical thinking skills
Not every problem-solving skill is a critical thinking skill. That is because not every problem requires thinking. A problem like opening a stubborn pickle jar could simply require brute strength. On the other hand, it becomes a thinking skill when you remember to tap the edge of the pickle jar lid to loosen the seal.
Also, some problem-solving skills are the exact opposite of critical thinking. When you follow directions or use muscle memory or rote (memorization) thinking, there is no critical thinking required. Likewise, skills of persuasion or public oratory are thinking skills, but aren’t necessarily critical thinking skills.
Critical thinking vs. problem solving: The role of emotional intelligence
In our blog “ What is the role of communication in critical thinking ?” we highlighted one author’s argument that critical thinking and problem solving is not always a purely rational process. While critical thinkers are in great demand in the hiring marketplace, employees who are emotionally intelligent bring even greater value to an organization.
Writing for Business News Daily , editor Chad Brooks describes emotional intelligence as “the ability to understand your emotions and recognize the emotions and motivations of those around you.”
So, when looking for star performers, research shows “that emotional intelligence counts for twice as much as IQ and technical skills combined in determining who will be a star performer.”
Further, in today’s collaborative workplace environment, “hiring employees who can understand and control their emotions – while also identifying what makes those around them tick—is of the utmost importance.”
Finally, one expert notes that dealing with emotions is an important part of critical thinking. Emotions can be at the root of a problem. They are frequently symptomatic of problems below the surface. Problem solving when dealing with emotions requires openness to authentic emotional expressions. It requires the understanding that when someone is in pain, it is a problem that is real.
- The Ultimate Guide To Critical Thinking
- Is Critical Thinking A Soft Skill Or Hard Skill?
- How To Improve Critical Thinking Skills At Work And Make Better Decisions
- 5 Creative and Critical Thinking Examples In Workplace
- 25 In-Demand Jobs That Require Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
- Brainstorming: Techniques Used To Boost Critical Thinking and Creativity
Critical thinking and problem solving: A deeper dive
A recap of the distinct differences between critical thinking and problem solving.
Critical thinking, according to an article on Drexel University’s Graduate College webpage “utilizes analysis, reflection, evaluation, interpretation, and inference to synthesize information that is obtained through reading, observing, communicating, or experience.”
The goal of critical thinking is to evaluate the credibility of both the information and its source. It questions the central issue and how the information will inform intelligent decisions. Finally, it asks the question, “Where does this information lead me?”
Problem solving , as previously mentioned, uses many of those skills, but “it takes the process a step further to identify obstacles and then to strategically map out a set of solutions to solve the problem. That extra step in problem solving is identifying obstacles as well as mapping out a strategic set of solutions to resolve the problem.
How to develop critical thinking skills to become a better problem solver
1. develop your analytical skills..
Pay attention and be more observant. Ask the questions “who, what, where, and why” and learn as much as possible about the topic or problem. Map everything out to imprint or gain a visual understanding and focus on the differences between fact, opinion, and your own bias.
2. Learn the skill of evaluating
As a subset of analysis, you can become skilled in evaluation by:
- comparing similar and related topics, programs, and issues. How are they different, and where are the similarities?
- looking for trends that support (or refute) what you intuitively feel is the solution
- recognizing barriers or conflicts to successful problem resolution
- asking questions and gathering information—assuming nothing, ever.
3. Interpretation with the help of a mentor or someone more experienced
Interpreting a problem accurately employs both analytical and evaluating skills. With practice, you can develop this skill, but to hone your interpretation skills, it is advisable to seek the help of an experienced mentor.
You’ll need to do the following:
- know how your own biases or opinions can be a roadblock to the best decision making
- recognize that cultural differences can be a barrier to communication
- look at the problem from the point of view of others
- learn as much as you can about the problem, topic, or experience
- synthesize everything you have learned in order to make the connections and put the elements of a problem together to form its solution
4. Acquire the skill and habit of reflection.
Being reflective is applicable to almost every aspect of your personal and professional life. To open your mind to reflection, think back to your educational experience. Your instructor may have asked you to keep a reflective journal of your learning-related experiences. A reflective journal requires expressive writing, which, in turn, relieves stress.
Perhaps you have just had a disagreement with a coworker, who became abusive and personal. Not everyone can come up with those instant snappy comebacks on the spot, and it is usually best to disengage before the situation gets worse.
Here’s where reflective journaling helps. When you’re in a calmer state of mind, you can journal the incident to:
- gain deeper insights into your thought processes and actions—How do you feel about not defending yourself from the colleague’s accusations or personal abuse? What was the perfect response that eluded you in the stress of the moment?
- build a different approach to problems—It could be that your co-worker perceives you as unapproachable or unreceptive to suggestions and criticism. Maybe it’s time to have a frank discussion to help you see yourself through the eyes of the coworker.
- get closer to making significant changes in your life—Your journal entries may have displayed a pattern of your behavior on the job, which elicits consistent negative reactions from more than one co-worker.
Your takeaways:
- When evaluating critical thinking vs. problem solving, the elements of both appear to blend into a distinction without a difference.
- Good problem solvers employ the steps of critical thinking, but not all problem solving involves critical thinking.
- Emotional intelligence is an attribute that is a hybrid skill of problem solving and critical thinking.
- You can hone your critical thinking skills to become a better problem solver through application of analysis, evaluation, interpretation, and reflection.
- 10 Best Books On Critical Thinking And Problem Solving
- 12 Common Barriers To Critical Thinking (And How To Overcome Them)
- How To Promote Critical Thinking In The Workplace
Is Critical Thinking Overrated? Disadvantages Of Critical Thinking
11 principles of critical thinking .
Jenny Palmer
Founder of Eggcellentwork.com. With over 20 years of experience in HR and various roles in corporate world, Jenny shares tips and advice to help professionals advance in their careers. Her blog is a go-to resource for anyone looking to improve their skills, land their dream job, or make a career change.
Further Reading...

17 Tips To Improve Your Ability To Work Independently
No comments, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What Is The Role Of Communication In Critical Thinking?
Critical Thinking vs Problem Solving: Navigating Cognitive Approaches

JTN Article

Critical thinking and problem solving are closely related skills that often go hand in hand. Critical thinking is a prerequisite for effective problem-solving. While they are distinct concepts, they are interdependent and complement each other in various ways. Here's a breakdown of the relationship between critical thinking and problem solving, and strategies to strengthen both skill sets.
Critical Thinking vs. Problem Solving
Critical thinking involves the ability to analyze, evaluate, and assess information, ideas, or arguments in a logical and systematic manner. It includes skills such as reasoning, analyzing evidence, identifying biases, and making informed judgments. Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to specific challenges or issues. It typically involves defining a problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating those solutions, and implementing the best one.
Critical thinking is often considered the foundation of effective problem solving. To solve a problem effectively, you first need to critically assess and understand the problem itself. Critical thinking helps you define the problem, identify its root causes, and gather relevant information.
Both critical thinking and problem solving contribute to informed decision-making. Critical thinking helps individuals evaluate the pros and cons of different solutions, while problem-solving skills help in selecting the most suitable solution. Critical thinking and problem-solving skills promote continuous improvement within an organization in response to changing needs and conditions. Individuals who engage in critical thinking continuously refine their problem-solving abilities, leading to more effective solutions over time.
In summary, critical thinking and problem solving are interconnected skills that support each other. Critical thinking provides the analytical and evaluative tools needed to approach problems effectively, while problem solving puts critical thinking into action by applying these skills to real-world challenges. Together, they enable individuals and teams to make well-informed decisions and find innovative solutions to complex issues.
Understanding Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a cognitive skill and a mental process that involves the objective, deliberate, and systematic evaluation of information, ideas, situations, or problems in order to form well-reasoned judgments, make informed decisions, and solve complex issues. It is a fundamental human capability that goes beyond mere acceptance of information at face value and instead encourages individuals to approach information critically, examining its validity, relevance, and potential biases.
At its core, critical thinking involves these key components:
- Analysis: Critical thinkers carefully examine information or situations by breaking them down into their constituent parts. They dissect complex ideas or problems into manageable components, making it easier to understand and address.
- Evaluation: Critical thinking requires individuals to assess the quality and credibility of information or arguments. It involves considering the source, evidence, and reasoning behind a statement or claim, and determining whether it is well-founded.
- Inference: Critical thinkers draw logical and reasonable conclusions based on available evidence and information. They avoid making assumptions or jumping to unwarranted conclusions.
- Problem-Solving : Critical thinking is a valuable problem-solving tool. It involves identifying problems, exploring potential solutions, and evaluating those solutions to determine the most effective course of action.
- Decision-Making: Informed decision-making is a crucial aspect of critical thinking. It helps individuals choose the most appropriate course of action among several options, taking into account the potential consequences and ethical considerations.
- Reflection: Critical thinkers engage in self-reflection, questioning their own beliefs and assumptions. This self-awareness allows for personal growth and intellectual development.
The Power of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking skills are essential for analyzing complex problems within your organization. When faced with a problem, individuals and teams must critically examine the various components, potential causes, and consequences of the issue. Critical thinking helps break down complex problems into manageable parts. Critical thinking skills also play a crucial role in identifying problems accurately. Without the ability to critically assess situations, individuals may misinterpret problems or focus on symptoms rather than root causes.
Informed Decision-Making
Critical thinking enables leaders and employees to make informed decisions. It involves evaluating information, considering alternatives, and weighing the pros and cons before choosing the best course of action. In a business context, this can lead to better strategic decisions, efficient resource allocation, and effective problem-solving.
Problem Solving
Businesses face a wide range of complex challenges. Critical thinking equips individuals with the skills to analyze problems, identify root causes, and develop innovative solutions. This is crucial for addressing issues promptly and effectively, whether they involve market competition, operational inefficiencies, or customer satisfaction.
Innovation
Critical thinking fosters creativity and innovation. It encourages employees to think outside the box, challenge conventional wisdom, and explore unconventional solutions. This is essential for staying competitive and developing new products, services, or processes.
Conflict Resolution
Conflicts are inevitable in any organization. Critical thinking skills enable individuals to approach conflicts objectively, understand the underlying issues, and propose constructive solutions. This promotes a healthier work environment and fosters collaboration.
Customer Satisfaction
Understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations are crucial in business. Critical thinking helps organizations analyze customer feedback, identify areas for improvement, and innovate to provide better products or services.
Ethical Decision-Making
In an age where ethics and corporate responsibility are paramount, critical thinking plays a role in ethical decision-making. It helps individuals and organizations assess the ethical implications of their actions and make choices that align with their values and societal expectations.
Competitive Advantage
Businesses that encourage and develop critical thinking skills in their employees can gain a competitive advantage. A workforce that can analyze data, adapt to changes, and innovate is more likely to thrive in a rapidly evolving market.
Enhancing Critical Thinking Abilities
Enhancing critical thinking abilities is a valuable skill that can improve decision-making, problem solving, and overall cognitive function. Here are some strategies to help you develop and enhance your critical thinking abilities:
Ask Questions: Encourage curiosity by asking open-ended questions about the information or situation at hand. Questions like "Why?" and "How?" can prompt deeper thinking and analysis.
Gather Information: Seek out diverse sources of information and perspectives. Be open to exploring various viewpoints, even if they challenge your existing beliefs or assumptions.
Evaluate Sources: Assess the credibility and reliability of information sources. Consider the author's qualifications, the publication's reputation, and potential biases.
Analyze Arguments: Break down arguments into their components. Identify premises, conclusions, and any logical fallacies. Evaluate the strength of the evidence and the soundness of the reasoning.
Practice Reflective Thinking: Regularly take time to reflect on your thoughts, experiences, and decisions. Consider what you've learned and how you can apply it to future situations.
Consider Alternative Perspectives: Put yourself in someone else's shoes and try to understand their viewpoint, even if you disagree. This helps you develop empathy and a more comprehensive understanding of issues.
Socratic Questioning: Employ Socratic questioning techniques, which involve asking a series of probing questions to explore ideas and uncover deeper insights.
Problem-Solving Exercises: Regularly tackle problems or puzzles that require analytical thinking. This can be anything from brain teasers to real-world challenges.
Debate and Discussion: Engage in debates and discussions with others, particularly those with different viewpoints. Constructive debates can sharpen your critical thinking skills as you defend your position and respond to counter-arguments.
Continual Learning: Embrace a growth mindset and a commitment to lifelong learning. New information and experiences can challenge and expand your thinking.
Seek Feedback: Encourage others to provide constructive feedback on your thoughts and ideas. Constructive criticism can help you refine your thinking.
Use Critical Thinking Tools: Familiarize yourself with critical thinking tools like the SWOT analysis, the 5 Whys technique, and decision matrices. These tools can help structure your thinking and decision-making process.
Take Courses: Consider enrolling in courses or workshops focused on critical thinking and problem solving. Many educational institutions and online platforms offer such courses.
Collaborate: Collaborate with others on projects or problem-solving tasks. Different perspectives and skills can enhance your critical thinking abilities.
Remember that developing critical thinking is an ongoing process, and improvement takes time. Be patient with yourself and continuously practice these strategies to enhance your critical thinking abilities over time.
Problem Solving: A Key Skillset
Developing critical thinking skills will help you and your team become better problem-solvers. A strong problem-solving skillset is of paramount importance in a professional or business context for several compelling reasons. In the complex and ever-evolving landscape of modern work environments, individuals and organizations alike face a myriad of challenges that demand effective problem-solving abilities.
First and foremost, problem-solving skills empower individuals to tackle obstacles and setbacks with confidence and efficiency. In a professional context, this means overcoming workplace challenges, meeting project deadlines, and addressing unexpected issues head-on. Whether it's resolving technical glitches, navigating interpersonal conflicts, or devising strategies to meet changing market demands, problem-solving is the linchpin that ensures operations run smoothly.
Moreover, in business, problem-solving is intricately linked to innovation and growth. Companies that foster a culture of problem-solving encourage their employees to think creatively and proactively identify opportunities for improvement. These organizations not only respond effectively to market disruptions but also stay ahead of the competition by consistently delivering innovative products, services, and solutions. Problem-solving skillsets, therefore, serve as a catalyst for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in today's fast-paced business world.
Additionally, problem-solving skills facilitate effective decision-making. Professionals who can critically analyze information, weigh alternatives, and assess potential risks are better equipped to make sound decisions that align with their organizations' strategic objectives. From financial choices to resource allocation and market entry strategies, well-honed problem-solving skills are instrumental in choosing the most suitable and advantageous courses of action.
In conclusion, the importance of a problem-solving skillset in a professional or business context cannot be overstated. It empowers individuals to navigate challenges, fosters innovation, supports effective decision-making, and ultimately contributes to the success and growth of both individuals and organizations. In today's dynamic and competitive work environments, honing problem-solving abilities is an investment with dividends that extend far beyond immediate problem resolution.
Unleashing Problem-Solving Abilities
Developing and honing problem-solving abilities at work is a valuable skill that can enhance your effectiveness and contribute to your career growth. Here are some practical strategies to help you cultivate and improve your problem-solving skills in the workplace:
Recognize the Importance: Acknowledge the significance of problem-solving skills in your job and career. Understand that the ability to solve problems efficiently is a valuable asset that can set you apart.
Understand the Problem: Take the time to fully understand the problem at hand. Define the problem clearly and identify its root causes. This step is crucial for finding effective solutions.
Gather Information: Collect relevant data and information related to the problem. This may involve research, data analysis, or consulting with colleagues who have expertise in the area.
Break It Down: Divide complex problems into smaller, more manageable components. This can make the problem-solving process less daunting and help you focus on solving one aspect at a time.
Brainstorm Solutions: Encourage brainstorming sessions with colleagues or team members. Diverse perspectives can lead to innovative solutions. Be open to ideas and avoid judgment during this phase.
Evaluate Solutions: Assess each potential solution objectively. Consider the pros and cons, feasibility, and potential risks associated with each option. Critical thinking is essential at this stage.
Select the Best Solution: Based on your evaluation, choose the solution that seems most effective and suitable for the situation. Consider both short-term and long-term implications.
Create an Action Plan: Develop a clear and actionable plan to implement the chosen solution. Define roles and responsibilities, set deadlines, and allocate resources as needed.
Implement and Monitor: Put the plan into action, and closely monitor its progress. Be prepared to make adjustments if necessary as you encounter new information or challenges.
Learn from Failure: Understand that not all solutions will be successful. When problems persist or new ones arise, view them as opportunities for growth and learning. Analyze what went wrong and use that knowledge to improve.
Seek Feedback: Don't hesitate to seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or supervisors. Constructive criticism can provide valuable insights and help you refine your problem-solving skills.
Continuous Learning: Stay updated on industry trends, best practices, and emerging technologies. Expanding your knowledge base can provide you with new tools and perspectives for problem-solving.
Practice Patience: Complex problems may not have immediate solutions. Exercise patience and persistence, and don't get discouraged if a solution doesn't come quickly.
Embrace Challenges: Seek out challenging projects or assignments that require problem-solving skills. The more you practice, the more confident and skilled you'll become.
Mentorship: If possible, find a mentor or coach who excels in problem-solving. Learning from someone with experience can accelerate your growth.
Use Problem-Solving Tools: Familiarize yourself with problem-solving methodologies and tools like the 5 Whys technique, root cause analysis, SWOT analysis, and decision matrices. These frameworks can guide your problem-solving process.
Develop Soft Skills: Effective problem-solving often involves strong communication, teamwork, and interpersonal skills. Work on improving these soft skills to collaborate effectively with others in solving problems.
Problem Solving in Action
Here are some real-life examples of problem-solving in action in various organizational or business contexts:
- Customer Complaint Resolution: A customer service team at an e-commerce company receives numerous complaints about delayed deliveries. The team investigates the root causes, which may include inefficient order processing or problems with third-party couriers. They implement process improvements, streamline communication with courier services, and provide proactive delivery updates to customers to address the issue and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Cost Reduction Initiative: A manufacturing company realizes that its production costs are escalating, affecting its profit margins. To solve this problem, the company engages in a cost reduction initiative. They scrutinize every aspect of their operations, identify inefficiencies, negotiate better deals with suppliers, optimize production processes, and implement energy-saving measures, ultimately reducing production costs without compromising quality.
- Employee Engagement Improvement: An organization observes declining employee engagement levels, leading to increased turnover. HR and management collaborate to identify the underlying issues, which may include inadequate training, lack of career growth opportunities, or poor work-life balance. They develop and implement employee engagement strategies, such as training programs, mentorship initiatives, and flexible work arrangements, to boost morale and retain talent.
- Product Quality Enhancement: A technology company receives customer complaints about a particular product's reliability and performance. The engineering team conducts root cause analysis, identifies design flaws, and works on product improvements. They also set up a system for gathering feedback from customers to continuously refine the product's quality.
These real-life examples demonstrate that problem-solving is an essential skill in organizations and businesses across various sectors. Effective problem-solving often involves collaboration among teams, data analysis, creative thinking, and the implementation of well-thought-out solutions to overcome challenges and achieve strategic objectives.
Unraveling the Critical Thinking Puzzle
In a professional or organizational context, the relationship between critical thinking and problem-solving is symbiotic and indispensable. Critical thinking serves as the foundational framework that underpins effective problem-solving, while problem-solving is the practical application of critical thinking skills to address real-world challenges. Together, they form a dynamic duo that drives success and innovation.
Critical thinking equips individuals and teams with the capacity to analyze information, evaluate alternatives, and make informed decisions. It encourages open-mindedness, skepticism, and the ability to see beyond the surface, fostering a culture of intellectual rigor. In the context of problem-solving, critical thinking helps define the problem accurately, assess potential solutions objectively, and identify the most appropriate course of action.
Problem-solving, on the other hand, puts critical thinking into action. It involves taking the insights gained through critical analysis and applying them to real-world scenarios. Effective problem-solving hinges on the ability to break down complex challenges, generate creative solutions, and adapt strategies as circumstances evolve—all skills deeply rooted in critical thinking.
In sum, critical thinking without effective problem-solving remains theoretical, and problem-solving without critical thinking lacks depth and efficacy. In the professional and organizational realm, these two capabilities complement and strengthen each other, fostering innovation, informed decision-making, and the ability to navigate the complexities of today's dynamic business environments. Together, they empower individuals and organizations to thrive, adapt, and excel in a world where challenges and opportunities abound.

Kaitlyn is a member of the training team at JTN Group in New York. She's a master facilitator with experience leading workshops & training programs for SMBs through to Enterprise organizations. Learn about JTN Group here.
Get in Touch With Us
United States
4th Floor 667 Madison Avenue New York, NY 10065 United States +1 877 465 7740 [email protected]
United Kingdom
30th Floor 122 Leadenhall Street London EC3V 4AB United Kingdom +44 20 7099 5535 [email protected]

JTN works globally with ambitious B2B organizations. Let’s stay in touch.
JTN is a registered trademark used under license.
Radford University
Center for Innovation and Analytics
Departments
- Academic Affairs
- Audit and Advisory Services
- Finance and Administration
- Human Resources
- Information Technology
- Office of the President
- Student Affairs
- University Advancement
- University Relations
- Other Offices and Departments
- About the Center for Innovation and Analytics
- Areas of Growth in Analytics
- Analytics Career Preparation
- Microsoft Office Specialist Certifications
- Executives in Residence in Analytics
- Success Stories
- Analytics Events
- SAS Joint Graduate Certificate in Business Analytics
- Analytics Resources
- Online SAS Joint Graduate Certificate in Business Analytics Certificate
- The Background to Support the Center
- What the Center Provides
- Skills Required by Employers
- Director's Bio
P.O. Box 6953 Radford, VA 24142 Kyle Hall Suite 231 540.831.5513 cia@radford.edu cia-analytics@radford.edu cia-innovation@radford.edu
Dr. Wil Stanton, Director wstanton@radford.edu cia-analytics@radford.edu
Vicki Perkins, Administrative Assistant vperkins1@radford.edu
Problem Solving, Critical Thinking, and Analytical Reasoning Skills Sought by Employers
In this section:
Problem Solving
- Critical Thinking
Analytical Reasoning
View the content on this page in a Word document.
Critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and problem-solving skills are required to perform well on tasks expected by employers. 1 Having good problem-solving and critical thinking skills can make a major difference in a person’s career. 2
Every day, from an entry-level employee to the Chairman of the Board, problems need to be resolved. Whether solving a problem for a client (internal or external), supporting those who are solving problems, or discovering new problems to solve, the challenges faced may be simple/complex or easy/difficult.
A fundamental component of every manager's role is solving problems. So, helping students become a confident problem solver is critical to their success; and confidence comes from possessing an efficient and practiced problem-solving process.
Employers want employees with well-founded skills in these areas, so they ask four questions when assessing a job candidate 3 :
- Evaluation of information: How well does the applicant assess the quality and relevance of information?
- Analysis and Synthesis of information: How well does the applicant analyze and synthesize data and information?
- Drawing conclusions: How well does the applicant form a conclusion from their analysis?
- Acknowledging alternative explanations/viewpoints: How well does the applicant consider other options and acknowledge that their answer is not the only perspective?
When an employer says they want employees who are good at solving complex problems, they are saying they want employees possessing the following skills:
- Analytical Thinking — A person who can use logic and critical thinking to analyze a situation.
- Critical Thinking – A person who makes reasoned judgments that are logical and well thought out.
- Initiative — A person who will step up and take action without being asked. A person who looks for opportunities to make a difference.
- Creativity — A person who is an original thinker and have the ability to go beyond traditional approaches.
- Resourcefulness — A person who will adapt to new/difficult situations and devise ways to overcome obstacles.
- Determination — A person who is persistent and does not give up easily.
- Results-Oriented — A person whose focus is on getting the problem solved.
Two of the major components of problem-solving skills are critical thinking and analytical reasoning. These two skills are at the top of skills required of applicants by employers.
- Return to top of page -
Critical Thinking 4
“Mentions of critical thinking in job postings have doubled since 2009, according to an analysis by career-search site Indeed.com.” 5 Making logical and reasoned judgments that are well thought out is at the core of critical thinking. Using critical thinking an individual will not automatically accept information or conclusions drawn from to be factual, valid, true, applicable or correct. “When students are taught how to use critical thinking to tap into their creativity to solve problems, they are more successful than other students when they enter management-training programs in large corporations.” 6
A strong applicant should question and want to make evidence-based decisions. Employers want employees who say things such as: “Is that a fact or just an opinion? Is this conclusion based on data or gut feel?” and “If you had additional data could there be alternative possibilities?” Employers seek employees who possess the skills and abilities to conceptualize, apply, analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information to reach an answer or conclusion.
Employers require critical thinking in employees because it increases the probability of a positive business outcome. Employers want employees whose thinking is intentional, purposeful, reasoned, and goal directed.
Recruiters say they want applicants with problem-solving and critical thinking skills. They “encourage applicants to prepare stories to illustrate their critical-thinking prowess, detailing, for example, the steps a club president took to improve attendance at weekly meetings.” 7
Employers want students to possess analytical reasoning/thinking skills — meaning they want to hire someone who is good at breaking down problems into smaller parts to find solutions. “The adjective, analytical, and the related verb analyze can both be traced back to the Greek verb, analyein — ‘to break up, to loosen.’ If a student is analytical, you are good at taking a problem or task and breaking it down into smaller elements in order to solve the problem or complete the task.” 9
Analytical reasoning connotes a person's general aptitude to arrive at a logical conclusion or solution to given problems. Just as with critical thinking, analytical thinking critically examines the different parts or details of something to fully understand or explain it. Analytical thinking often requires the person to use “cause and effect, similarities and differences, trends, associations between things, inter-relationships between the parts, the sequence of events, ways to solve complex problems, steps within a process, diagraming what is happening.” 10
Analytical reasoning is the ability to look at information and discern patterns within it. “The pattern could be the structure the author of the information uses to structure an argument, or trends in a large data set. By learning methods of recognizing these patterns, individuals can pull more information out of a text or data set than someone who is not using analytical reasoning to identify deeper patterns.” 11
Employers want employees to have the aptitude to apply analytical reasoning to problems faced by the business. For instance, “a quantitative analyst can break down data into patterns to discern information, such as if a decrease in sales is part of a seasonal pattern of ups and downs or part of a greater downward trend that a business should be worried about. By learning to recognize these patterns in both numbers and written arguments, an individual gains insights into the information that someone who simply takes the information at face value will miss.” 12
Managers with excellent analytical reasoning abilities are considered good at, “evaluating problems, analyzing them from more than one angle and finding a solution that works best in the given circumstances”. 13 Businesses want managers who can apply analytical reasoning skills to meet challenges and keep a business functioning smoothly
A person with good analytical reasoning and pattern recognition skills can see trends in a problem much easier than anyone else.
- Wigan and Leigh College
- Learning Resources
- Study Skills Guides
- Employability Skills
- Problem Solving and Analytical Skills
- Employability
- Communication & Interpersonal Skills
- Written Communication Skills
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Adaptability & Flexibility Skills
- Persuading, Influencing & Negotiation
- Teamworking Skills
- Leadership Skills
- Planning and Organisation Skills
How to develop and demonstrate your problem-solving skills
Analytical and critical thinking skills, why employers want these skills, examples of how analytical or problem solving skills can be developed or evidenced, final thought....
- Self-motivation & Initiative
- Working under pressure
- The Employable Digital Student
- Using Social Media for job hunting and networking
- Developing Professionalism
- Online Safety & Security This link opens in a new window
- Tutorial Quiz This link opens in a new window
We all solve problems on a daily basis, in academic situations, at work and in our day-to-day lives. Some of the problems that are typically faced by students include:
- Putting together an argument for an essay
- Dealing with an awkward customer when working part-time in a shop or restaurant
- Thinking about how you are going to manage your budget to keep you going until the end of term
- Working out why your printer won’t respond
- Developing a strategy to reach the next level of a computer game.
Any job will also bring problems to be faced. It is important to show to a recruiter that you have the right skills to resolve these problems, and the personal resilience to handle the challenges and pressure they may bring. You need to be able to:
- Evaluate information or situations
- Break them down into their key components
- Consider various ways of approaching and resolving them
- Decide on the most appropriate of these ways
Solving these problems involves both analytical and creative skills . Which particular skills are needed will vary, depending on the problem and your role in the organisation, but the following skills are key to problem-solving:

- Lateral Thinking
- Logical Reasoning
- Persistence
Analytical and critical thinking skills help you to evaluate the problem and to make decisions. A l ogical and methodical approach is best in some circumstances: for example, you will need to be able to draw on your academic or subject knowledge to identify solutions of a practical or technical nature. In other situations, using creativity or l ateral thinking will be necessary to come up with ideas for resolving the problem and find fresh approaches Not everyone has these two types of skills in equal measure: for this reason, team working is often a key component in problem-solving. Further skills, such as communication, persuasion and negotiation , are important in finding solutions to problems involving people.

Whatever issue you are faced with, some steps are fundamental:
- I dentify the problem
- D efine the problem
- E xamine the options
- A ct on a plan
- L ook at the consequences
This is the IDEAL model of problem-solving. The final stage is to put the solution you have decided on into practice and check the results.
Any workplace, project or task will have challenges or obstacles which need to be overcome. If an organisation employs people who are adept at solving problems at all levels, it reduces the need for complex chains of command or lessens demand on managers' time. In short, it will help save time and therefore money. Analytical skills are perhaps becoming increasingly important; we are all bombarded with huge amounts of information every day. Being able to quickly yet comprehensively identify and evaluate the most important or relevant information for the organisation or your specific job role will be an increasingly useful skill.
- Leisure activities (e.g. chess, logic games, computing).
- Overcoming obstacles to achieve an ambition or goal.
- Working in a customer environment and resolving complaints, particularly in situations where there is no protocol.
- Research (e.g. for essays or projects, or within the workplace).
- Particular achievements in the workplace (e.g. devising new working practices to improve efficiency, information systems development, diagnosing and rectifying faults or issues).
- Creative solutions to coursework problems.
- Identifying appropriate source material for assignments.
A large cosmetics company had a problem in that some of the soap boxes coming off the production lines were empty. The problem was quickly isolated to the assembly line, which transported the packaged boxes of soap to the delivery department: some soap boxes went through the assembly line empty. The management asked its engineers to solve the problem. They spent much time and money in designing a machine with high-resolution monitors manned by staff; to scan all the boxes on the line to make sure they weren't empty. A workman hearing about this, came up with another solution. He got a powerful industrial fan and pointed it at the assembly line. As each soap box passed the fan, the empty boxes were blown off the line. Moral: the simplest solution is usually the best!
- << Previous: Planning and Organisation Skills
- Next: Self-motivation & Initiative >>
- Last Updated: Jan 15, 2024 1:11 PM
- URL: https://libguides.wigan-leigh.ac.uk/Employability_Skills

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making - What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking and decision-making -, what is critical thinking, critical thinking and decision-making what is critical thinking.

Critical Thinking and Decision-Making: What is Critical Thinking?
Lesson 1: what is critical thinking, what is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is a term that gets thrown around a lot. You've probably heard it used often throughout the years whether it was in school, at work, or in everyday conversation. But when you stop to think about it, what exactly is critical thinking and how do you do it ?
Watch the video below to learn more about critical thinking.
Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions . It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better.
This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical thinking is a broad skill that can be applied to so many different situations. You can use it to prepare for a job interview, manage your time better, make decisions about purchasing things, and so much more.
The process
As humans, we are constantly thinking . It's something we can't turn off. But not all of it is critical thinking. No one thinks critically 100% of the time... that would be pretty exhausting! Instead, it's an intentional process , something that we consciously use when we're presented with difficult problems or important decisions.
Improving your critical thinking

In order to become a better critical thinker, it's important to ask questions when you're presented with a problem or decision, before jumping to any conclusions. You can start with simple ones like What do I currently know? and How do I know this? These can help to give you a better idea of what you're working with and, in some cases, simplify more complex issues.
Real-world applications

Let's take a look at how we can use critical thinking to evaluate online information . Say a friend of yours posts a news article on social media and you're drawn to its headline. If you were to use your everyday automatic thinking, you might accept it as fact and move on. But if you were thinking critically, you would first analyze the available information and ask some questions :
- What's the source of this article?
- Is the headline potentially misleading?
- What are my friend's general beliefs?
- Do their beliefs inform why they might have shared this?

After analyzing all of this information, you can draw a conclusion about whether or not you think the article is trustworthy.
Critical thinking has a wide range of real-world applications . It can help you to make better decisions, become more hireable, and generally better understand the world around you.

/en/problem-solving-and-decision-making/why-is-it-so-hard-to-make-decisions/content/

Analytical Thinking vs. Critical Thinking
There are two important phrases in business which are bandied about a lot. Analytical Thinking and Critical Thinking .
Like some terms in business, there isn’t always a clear definition. In my opinion, some definitions are simply head-scratching. Other definitions of Analytical Thinking sound like Critical Thinking, and vice versa. In many cases, the differences are so vague that often sound like synonyms.
For many years, I’ve used two definitions that wouldn’t win any scientific or academic applause. But, they work for me, and seem to have helped others primarily the definitions try to also explain what you should be doing when using either style. I also know from experience when the definitions are concise and the application is simple, there’s more transparency among the team, and individuals have more clarity about what’s required of them to do to be more successful.
Part of these definitions are aligned with two other aspects I’ve used for many years:
- The Information Chain , a step-by-step process of how we turn general data into specific ideas
- The Hourglass Figure , a linear path showing how strategic/creative thinking and convergent/divergent thinking fit together, and in fact, need each other to be effective.
Analytical Thinking
Think about a time at work when you wanted to analyse something. What did you do?
For a simple example, let’s use a single invoice from a hypothetical vendor. If you analysed it, what information could you take away? Such as …
- Invoice number and date, perhaps a purchase order from your company
- Description of goods purchased
- Price per unit
- GST or sales tax, plus a grand total
- Payment terms and instructions
Each individual piece of information (e.g., a price) is a part – a sub-set as it were – of the larger whole (the invoice). This information you extracted tells you a little, but frankly, it doesn’t tell you a lot. In the right context (like anything), this info might be useful.
In other words, Analytical Thinking is thinking inside itself . All the information gained comes from the original item. The picture to the right demonstrates what I mean.

Critical Thinking
Let’s use the same example of the vendor’s invoice. This time, let’s use Critical Thinking.
The critical word is … well, critical . To be critical, you have to critique. To critique, you hae to compare or contrast one item against something else.
So, Critical Thinking requires two things, not just one, like Analytical Thinking. To use Critical Thinking, you need the original thing (invoice #1) and then something else (invoice #2). I hope it’s obvious that the two items should be similar: apples vs. oranges, as it were.
Using the two inovices, you compare and contrast them against each other. More so, you get a lot more information.
- Hold on … the second invoice doesn’t have a P.O., why not?
- Hold on … the descriptions for the same items are different. Did we buy different things?
- Hold on … the per unit costs changed. Why did the second invoice have a higher cost?
- Hold on … The first one had GST inclusive . The second one had GST exclusive . Why the difference?
- Hold on … Why are the payments terms different? We pay the first voice in 30 days, but we pay the second in 45 days?
By comparing and contrasting – whether it’s information, insight, ideas or decisions – you can extract much more information. In other words, Critical Thinking is thinking outside of itself .
The aspect of examining one thing against another thing allows you to decide if one is right or wrong , good or average , better or worst , preferable or undesirable , prettier or uglier , and on and on.
In Critical Thinking, you aren’t just looking at the thing, you’re looking at two. Exponentially I could be wrong, but Critical Thinking gives you “double” the information over Analytical Thinking.

Definitions for Analytical Thinking and Critical Thinking
Analytical Thinking breaks down a specific thing (a piece of information, insight, idea or decision) into smaller, discrete components or elements to better understand the whole. By understanding the whole, you may be able to apply the learning to anything else. Analytical Thinking is thinking inside itself.
Critical Thinking evaluates or critiques a specific thing (a piece of information, insight, idea or decision) by comparing and contrasting it against something else to better understand it. Critical Thinking is thinking outside of itself.
Two important aspects:
One way of thinking is not better than the other. They both have benefits and drawbacks, like every other way of thinking, in business or not.
Second, and with due apologies for paraphrasing Walter Shewhart : Information without context is useless.

Some questions to get started
Here are some general questions which may help you analyse and understand your thinking process to produce the best outcomes, whichever style of thinking you choose.
Are you starting with the right goal? Who says? Is the goal S.M.A.R.T. ?
- To the last point above, have you ever started (or given) a project without the ‘T’ (time specific)? If you don’t have agreement from the start when the goal must be accomplished, when will you or anyone else actually finish it? (The wrong answer is ‘whenever’ .)
Are you addressing the real problem? Are you sure it’s the problem and not the symptom? Worse, are you solving the wrong problem?
Where are you gathering research? How do you know it’s a quality source? Are you gathering the ‘right’ research? Again, how do you know?
Are you only gathering information which you agree with, or supports your opinion? That’s bias, pure and simple, which means your solution will be as well. As a good rule of thumb, you should be trying to prove yourself wrong as often as you try to prove yourself right .
Are you analysing information deeply enough? Go beyond the first page of Google. Look for sources which might disprove each other. Try to understand why they disagree. (One of them likely has an agenda.)
Are you comparing/contrasting the right information? Apples to apples as it were, not apples to oranges.
Are you extracting a true insight? This is something my brilliant university professor John Bennett used to tell us. When you finish your research, put it down and push it away. Turn to any other trusted person and tell them what you learnt.
Also, here is what an insight is not. If anyone (including you) says: “Well, I knew that already” then it’s not an insight. More often than not, an insight is:
- Something new you learnt
- Something you didn’t know
- Something that surprised you
- Something that was unexpected
- Something you forgot but realised again how incredibly important that piece of information was
Are you generating enough ideas (even bad ideas)? The key is volume. You want as many ideas as possible to allow Sturgeon’s Law to work.
How are you selecting the best ideas? What criteria are you using to pick the best idea? Does your criteria match what your decision maker or client might use?
Do your ideas actually address the business problem? If your idea doesn’t address the problem, it’s a bad idea.
Some related information, if it helps
The benefits of Analytical Thinking and Critical Thinking are linked to a few related topics.
By looking at information …
You need to know where a piece of information is good. What makes a Source of Information Good?
You need to extract information with five useful qualities. What are the Five Useful Qualities of a Piece of Information.
You need to put information to use. That’s knowing The Difference Between Strategic and Creative Thinking .
Last, if you want a PDF of the large picture, click here .
No doubt this launch many questions and arguments. How have you defined either Analytical or Critical Thinking in the past? What else would you contribute (or disagree) with? Please add your thoughts and comments below.

No comment yet, add your voice below!
Add a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
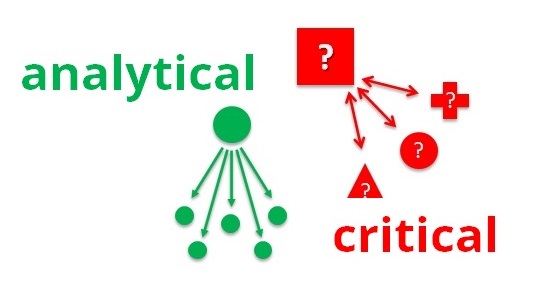
- No Comments
- Categories: Analytical and Critical Thinking , Most Popular Tools
- Tags: analytical thinking , critical thinking , curiosity , definitions , downloads , hourglass figure , information , information chain , insights , research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Key Takeaways. Analytical thinking is about understanding complex situations, while problem-solving focuses on finding practical solutions. Mastery of both skills leads to informed decision-making and improved risk management. These abilities are essential for workplace success and overall personal growth.
Analytical thinking involves using a systemic approach to make decisions or solve problems. By breaking down information into parts, analytical thinkers can better understand it and come to a sensible conclusion. For instance, once analytical thinkers identify a problem, they typically gather more information, develop possible solutions, test ...
Critical thinking vs. problem-solving Critical thinking and problem-solving can both help you resolve challenges, but the two practices have distinct purposes and strategies. Here are some differences between the two skills: Critical thinking This is a mode of thinking, compared to problem-solving, which is a set of solution-oriented strategies.
Critical thinking vs analytical thinking can be mistaken for the same thing but they are indeed different. Critical thinking is the process of reasoning through information, concepts, or data that are acquired by sensory experience. Analytical thinking is the type of thought that typically centres on problem-solving in many areas. Analytical thinking can be applied in various ways to solve ...
If used correctly, analytical thinking will help you: Understand connections between information and occurrences; Recognise the validity of different information and arguments; Recognise the mistakes you make in your thinking and improve; Solve problems and make decisions effectively. 2.1 Importance of Analytical thinking in the workplace.
Analytical thinking involves using data to understand problems, identify potential solutions, and suggest the solution that's most likely to have the desired impact. It's similar to critical thinking skills, which are the skills you use to interpret information and make decisions. In order to succeed as a strong analytical thinker, you also ...
Critical Thinking versus Problem Solving. Many people lump critical thinking and problem-solving together into one basket, and while there are similarities, there are also distinct differences. Critical thinking utilizes analysis, reflection, evaluation, interpretation, and inference to synthesize information that is obtained through reading ...
Analytical Thinking, Critical Analysis, and Problem Solving Guide. Analytical thinking; is a mental process that entails dissecting an issue or situation into its constituent parts, investigating their relationships, and reaching conclusions based on facts and logic. It is not about trusting instincts or making assumptions; rather, it is about ...
Problem-Solving: Analytical thinking is essential for solving scientific problems, such as identifying research gaps, developing new methodologies, and finding innovative solutions to complex issues.
Critical thinking involves asking questions, defining a problem, examining evidence, analyzing assumptions and biases, avoiding emotional reasoning, avoiding oversimplification, considering other interpretations, and tolerating ambiguity. Dealing with ambiguity is also seen by Strohm & Baukus (1995) as an essential part of critical thinking ...
Traits of Analytical Thinkers. Questioning Attitude: Critical thinkers question assumptions, statements, and conventional wisdom.They challenge ideas to seek deeper understanding. Open-Minded: They maintain an open mind, considering multiple perspectives and being receptive to new information. Problem-Solving: Critical thinkers approach problems by examining all angles, evaluating evidence ...
The skill of Analytical Thinking empowers individuals to make well-judged decisions, innovate creatively, and communicate complex ideas. Analytical Thinking is a bedrock of effective problem-solving, enabling individuals to navigate challenges with precision and adaptability, whether in daily life, business, or academic pursuits.
Although many educators and business leaders lump critical thinking and problem solving together, there are differences: Problem solving uses many of the same skills required for critical thinking; e.g., observation, analysis, evaluation, interpretation, and reflection. Critical thinking is an important ingredient of problem solving.
Critical Thinking vs. Problem Solving. Critical thinking involves the ability to analyze, evaluate, and assess information, ideas, or arguments in a logical and systematic manner. It includes skills such as reasoning, analyzing evidence, identifying biases, and making informed judgments. Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to ...
Critical Thinking 4 "Mentions of critical thinking in job postings have doubled since 2009, according to an analysis by career-search site Indeed.com." 5 Making logical and reasoned judgments that are well thought out is at the core of critical thinking. Using critical thinking an individual will not automatically accept information or conclusions drawn from to be factual, valid, true ...
Analytical thinking and problem solving are foundational thinking skills that involve breaking things down into their component parts. They also involve deductive reasoning, drawing conclusions from givens and applying judgments to reach conclusions from a combination of evidence and assumptions. This seminar introduces you to fundamental ...
Analytical thinking is a method for analyzing a problem and finding a solution. This is a way for processing and breaking down complex information. ... Analytical thinking vs. critical thinking ... distinguished between primary and secondary issues or included others' input when you were solving a problem. Consider ways to incorporate these ...
Analytical and critical thinking skills help you to evaluate the problem and to make decisions. A logical and methodical approach is best in some circumstances: for example, you will need to be able to draw on your academic or subject knowledge to identify solutions of a practical or technical nature. In other situations, using creativity or lateral thinking will be necessary to come up with ...
Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions. It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better. This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical thinking is a ...
BABOK Applied. Analytical thinking and problem solving skills are required for business analysts to analyze problems and opportunities effectively, identify which changes may deliver the most value, and work with stakeholders to understand the impact of those changes.
Enhanced problem-solving. Integrating both holistic and analytic thinking approaches enhances problem-solving. Holistic thinking, with its focus on the bigger picture, creativity, and empathy, is valuable in understanding human behavior, art, design, and complex societal issues. Analytic thinking excels in precision and systematic problem ...
Analytical Thinking is thinking inside itself. Critical Thinking evaluates or critiques a specific thing (a piece of information, insight, idea or decision) by comparing and contrasting it against something else to better understand it. Critical Thinking is thinking outside of itself. Two important aspects:
Problem solving, reasoning, and analytical thinking are defined and described as teachable repertoires. This paper describes work performed at a school serving special needs children, Morningside Academy, that has resulted in specific procedures developed over the past 15 years. These procedures include modifying "Think Aloud Pair Problem Solving"(after Whimbey & Lochhead, 1991) methods ...
Showcase your problem-solving skills in an interview, by focusing on your analytical approach. Describe how you systematically identify issues, collect relevant data, perform thorough analyses ...