  - Math Forum/Help
- Problem Solver
- College Math
- Problem Solvers
Online Math Problem SolverAn absolutely free universal math problem solver: Solve your math problems online. The free version gives you just answers. If you would like to see complete solutions you need to sign up for an account. Basic Math PlanBasic Math Solver offers you solving online fraction problems, metric conversions, power and radical problems. You can find area and volume of rectangles, circles, triangles, trapezoids, boxes, cylinders, cones, pyramids, spheres. You can simplify and evaluate expressions, factor/multiply polynomials, combine expressions. Online Pre-Algebra(Geometry) SolverYou can solve all problems from the basic math section plus solving simple equations, inequalities and coordinate plane problems. You can also evaluate expressions, factor polynomials, combine/multiply/divide expressions. Online Algebra SolverOnline trigonometry solver. Solve all type of trigonometric (sin, cos, tan, sec, scs, cot) expressions, equations, inequalities. Graph trigonometric functions. Trigonometry of a right triangle. Online Pre-calculus SolverInclude everything above plus finding limits (lim), sums, matrices. Online Calculus SolverSolve integral problems - definite, indefinite integrals. Online Statistics SolverSolve your probability, combination, permutation problems. Statistics - find median, mean (arithmetic, geometric, quadratic), mode, dispersion, mormal distributions, t-Distribution. The solver successfully do Statistical hypothesis testing Online Chemistry SolverYou can online solve chemistry equations. Other calculators:Want Better Math Grades?✅ Unlimited Solutions ✅ Step-by-Step Answers ✅ Available 24/7 ➕ Free Bonuses ($1085 value!) On this page - Search IntMath
- Math interactives
- About (site info)
- Uses of Trignometry
- ASCIIMath input, KaTeX output
- ASCIIMath input, LaTeX and KaTeX output
- Send Math in emails
- Syntax for ASCIIMathML
- Math Display Experiments
- Scientific Notebook
Math Problem SolverRelated Sections Math Tutoring Need help? Chat with a tutor anytime, 24/7.  This tool combines the power of mathematical computation engine that excels at solving mathematical formulas with the power of artificial intelligence large language models to parse and generate natural language answers. This creates a math problem solver that's more accurate than ChatGPT, more flexible than a math calculator, and provides answers faster than a human tutor. Sign up for free here . Problem Solver SubjectsOur math problem solver that lets you input a wide variety of math math problems and it will provide a step by step answer. This math solver excels at math word problems as well as a wide range of math subjects. - Math Word Problems
- Pre-Algebra
- Geometry Graphing
- Trigonometry
- Precalculus
- Finite Math
- Linear Algebra
Here are example math problems within each subject that can be input into the calculator and solved. This list is constanstly growing as functionality is added to the calculator. Basic Math SolutionsBelow are examples of basic math problems that can be solved. - Long Arithmetic
- Rational Numbers
- Operations with Fractions
- Ratios, Proportions, Percents
- Measurement, Area, and Volume
- Factors, Fractions, and Exponents
- Unit Conversions
- Data Measurement and Statistics
- Points and Line Segments
Math Word Problem SolutionsMath word problems require interpreting what is being asked and simplifying that into a basic math equation. Once you have the equation you can then enter that into the problem solver as a basic math or algebra question to be correctly solved. Below are math word problem examples and their simplified forms. Word Problem: Rachel has 17 apples. She gives some to Sarah. Sarah now has 8 apples. How many apples did Rachel give her? Simplified Equation: 17 - x = 8 Word Problem: Rhonda has 12 marbles more than Douglas. Douglas has 6 marbles more than Bertha. Rhonda has twice as many marbles as Bertha has. How many marbles does Douglas have? Variables: Rhonda's marbles is represented by (r), Douglas' marbles is represented by (d) and Bertha's marbles is represented by (b) Simplified Equation: {r = d + 12, d = b + 6, r = 2 �� b} Word Problem: if there are 40 cookies all together and Angela takes 10 and Brett takes 5 how many are left? Simplified: 40 - 10 - 5 Pre-Algebra SolutionsBelow are examples of Pre-Algebra math problems that can be solved. - Variables, Expressions, and Integers
- Simplifying and Evaluating Expressions
- Solving Equations
- Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities
- Ratios, Proportions, and Percents
- Linear Equations and Inequalities
Algebra SolutionsBelow are examples of Algebra math problems that can be solved. - Algebra Concepts and Expressions
- Points, Lines, and Line Segments
- Simplifying Polynomials
- Factoring Polynomials
- Linear Equations
- Absolute Value Expressions and Equations
- Radical Expressions and Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Inequalities
- Complex Numbers and Vector Analysis
- Logarithmic Expressions and Equations
- Exponential Expressions and Equations
- Conic Sections
- Vector Spaces
- 3d Coordinate System
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Linear Transformations
- Number Sets
- Analytic Geometry
Trigonometry SolutionsBelow are examples of Trigonometry math problems that can be solved. - Algebra Concepts and Expressions Review
- Right Triangle Trigonometry
- Radian Measure and Circular Functions
- Graphing Trigonometric Functions
- Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions
- Verifying Trigonometric Identities
- Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Complex Numbers
- Analytic Geometry in Polar Coordinates
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Vector Arithmetic
Precalculus SolutionsBelow are examples of Precalculus math problems that can be solved. - Operations on Functions
- Rational Expressions and Equations
- Polynomial and Rational Functions
- Analytic Trigonometry
- Sequences and Series
- Analytic Geometry in Rectangular Coordinates
- Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
Calculus SolutionsBelow are examples of Calculus math problems that can be solved. - Evaluating Limits
- Derivatives
- Applications of Differentiation
- Applications of Integration
- Techniques of Integration
- Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
- Differential Equations
Statistics SolutionsBelow are examples of Statistics problems that can be solved. - Algebra Review
- Average Descriptive Statistics
- Dispersion Statistics
- Probability
- Probability Distributions
- Frequency Distribution
- Normal Distributions
- t-Distributions
- Hypothesis Testing
- Estimation and Sample Size
- Correlation and Regression
Finite Math SolutionsBelow are examples of Finite Math problems that can be solved. - Polynomials and Expressions
- Equations and Inequalities
- Linear Functions and Points
- Systems of Linear Equations
- Mathematics of Finance
- Statistical Distributions
Linear Algebra SolutionsBelow are examples of Linear Algebra math problems that can be solved. - Introduction to Matrices
- Linear Independence and Combinations
Chemistry SolutionsBelow are examples of Chemistry problems that can be solved. - Unit Conversion
- Atomic Structure
- Molecules and Compounds
- Chemical Equations and Reactions
- Behavior of Gases
- Solutions and Concentrations
Physics SolutionsBelow are examples of Physics math problems that can be solved. - Static Equilibrium
- Dynamic Equilibrium
- Kinematics Equations
- Electricity
- Thermodymanics
Geometry Graphing SolutionsBelow are examples of Geometry and graphing math problems that can be solved. - Step By Step Graphing
- Linear Equations and Functions
- Polar Equations
Looking for the old Mathway Calculator? We've moved it to here . Tips, tricks, lessons, and tutoring to help reduce test anxiety and move to the top of the class.Email Address Sign Up  Ask Questions Math SolverAbout upstudy ai math solver, what types of math problems can upstudy math solver handle.  UpStudy Math Solver with steps is versatile and capable of solving a wide range of mathematical problems, including pre-algebra, algebra, pre-calculus, inequalities, calculus, trigonometry, geometry, statistics and probability, and matrices. No matter the complexity of the problem, our tool aims to provide fast, clear, and step-by-step solutions. Is it free? Is there a limit to the number of problems I can solve per day?There is no limit to the number of problems you can solve using our free Math Solver. Our goal is to provide unrestricted access to help students and professionals alike with their mathematical needs at any time. Is it a picture math solver? Can it solve the question in the picture I sent?The Math Solver on this page does not currently support solving problems directly from pictures. However, UpStudy does provide this functionality, which is one of our proudest features. For the best experience, we recommend using our Android or iOS app, or you can visit our ' Ask AI ' page to try it out. What are the benefits of using the UpStudy Math Solver?There are many pros to UpStudy Math Solver: it gives instant and exact answers to complicated mathematical problems, saves time, and increases understanding of various mathematical concepts. With that, the users learn and apply mathematics in great detail because the principles are supposed to be worked out step by step. If you are a student or a teacher, or even a working professional who needs to do some important math calculations, Math Solver will provide the best solution for you. Moreover, its ability to handle a broad spectrum of math problems makes it versatile for a wide range of educational and professional applications. Tips & Fun Ideas for math problems solving in lifeSolving math problems can be more engaging and effective with the right approach. Here are some tips and fun ideas to enhance your problem-solving skills: Decompose: Begin with breaking a complex problem into smaller, doable parts. This will help with better understanding the problem as a whole, and the solution will be arrived at in a step-by-step manner. Use Visual Aids: This may include drawing diagrams, or even some physical objects to help visualize the problem at hand. It is most useful in Geometry, Trigonometry, and Algebra and can make abstract concepts more tangible. Practice regularly: Like any other skill, doing math is a habit. Schedule regular times for practicing math problems to build and keep your skills current. Play Math Games: Have fun doing math puzzles and games like Sudoku, KenKen or math riddles. These can make learning fun and improve your number skills and logical thinking. Understand the 'Why': Understand not just how to solve a problem, but why a particular method works. Through this, it is possible for you to understand methods better and apply them more productively in a wide range of other problems. Use AI Homework Helper: Tools like UpStudy Math Solver help you see solutions and approaches that you probably would not have thought of; it's going to show you insight in many solving methods. Join Study Groups: Trying to discuss the problems with peers can open a new point of view and way of trying. Also, this makes learning fun, not a lonely process. Apply Math to Real Life: Try to connect math problems with real-life scenarios. This not only makes the problems more interesting but also enhances your problem-solving skills by showing the practical application of math. Still have questions? Ask UpStudy onlineUnlimited numbers of questions - Step-by-step explanations
You can enjoy - Unlimited number of questions
- No interruptions
- Full access to answer and solution
- Limited Solutions
 Upload a screenshot and solve any math, physics, or accounting problem instantly with MathGPT!Drag & drop an image file here, or click to select an image.  Game Central Search formYou are here. Number Line- \mathrm{Lauren's\:age\:is\:half\:of\:Joe's\:age.\:Emma\:is\:four\:years\:older\:than\:Joe.\:The\:sum\:of\:Lauren,\:Emma,\:and\:Joe's\:age\:is\:54.\:How\:old\:is\:Joe?}
- \mathrm{Kira\:went\:for\:a\:drive\:in\:her\:new\:car.\:She\:drove\:for\:142.5\:miles\:at\:a\:speed\:of\:57\:mph.\:For\:how\:many\:hours\:did\:she\:drive?}
- \mathrm{The\:sum\:of\:two\:numbers\:is\:249\:.\:Twice\:the\:larger\:number\:plus\:three\:times\:the\:smaller\:number\:is\:591\:.\:Find\:the\:numbers.}
- \mathrm{If\:2\:tacos\:and\:3\:drinks\:cost\:12\:and\:3\:tacos\:and\:2\:drinks\:cost\:13\:how\:much\:does\:a\:taco\:cost?}
- \mathrm{You\:deposit\:3000\:in\:an\:account\:earning\:2\%\:interest\:compounded\:monthly.\:How\:much\:will\:you\:have\:in\:the\:account\:in\:15\:years?}
- How do you solve word problems?
- To solve word problems start by reading the problem carefully and understanding what it's asking. Try underlining or highlighting key information, such as numbers and key words that indicate what operation is needed to perform. Translate the problem into mathematical expressions or equations, and use the information and equations generated to solve for the answer.
- How do you identify word problems in math?
- Word problems in math can be identified by the use of language that describes a situation or scenario. Word problems often use words and phrases which indicate that performing calculations is needed to find a solution. Additionally, word problems will often include specific information such as numbers, measurements, and units that needed to be used to solve the problem.
- Is there a calculator that can solve word problems?
- Symbolab is the best calculator for solving a wide range of word problems, including age problems, distance problems, cost problems, investments problems, number problems, and percent problems.
- What is an age problem?
- An age problem is a type of word problem in math that involves calculating the age of one or more people at a specific point in time. These problems often use phrases such as 'x years ago,' 'in y years,' or 'y years later,' which indicate that the problem is related to time and age.
| 🌐 Languages | EN, ES, PT & more | | 🏆 Practice | Improve your math skills | |
| 😍 Step by step | In depth solution steps | | ⭐️ Rating | based on 20924 reviews | word-problems-calculator - High School Math Solutions – Inequalities Calculator, Exponential Inequalities Last post, we talked about how to solve logarithmic inequalities. This post, we will learn how to solve exponential...
Please add a message. Message received. Thanks for the feedback. More From ForbesThe most rigorous math program you've never heard of. - Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Math-M-Addicts students eagerly dive into complex math problems during class. In the building of the Speyer Legacy School in New York City, a revolutionary math program is quietly producing some of the city's most gifted young problem solvers and logical thinkers. Founded in 2005 by two former math prodigies, Math-M-Addicts has grown into an elite academy developing the skills and mindset that traditional schooling often lacks. "We wanted to establish the most advanced math program in New York," explains Ruvim Breydo, co-founder of Math-M-Addicts. "The curriculum focuses not just on mathematical knowledge, but on developing a mastery of problem-solving through a proof-based approach aligned with prestigious competitions like the International Mathematical Olympiad." From its inception, Math-M-Addicts took an unconventional path. What began as an attempt to attract only the highest caliber high school students soon expanded to offer multiple curriculum levels. "We realized we couldn't find enough kids at the most advanced levels," says Breydo. "So we decided to develop that talent from an earlier age." The program's approach centers on rigor. At each of the 7 levels, the coursework comprises just a handful of fiendishly difficult proof-based math problems every week. "On average, we expect them to get about 50% of the solutions right," explains instructor Natalia Lukina. "The problems take hours and require grappling with sophisticated mathematical concepts." But it's about more than just the content. Class sizes are small, with two instructors for every 15-20 students. One instructor leads the session, while the other teacher coordinates the presentation of the homework solutions by students. The teachers also provide customized feedback by meticulously reviewing each student's solutions. "I spend as much time analyzing their thought processes as I do teaching new material," admits instructor Bobby Lee. Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024. Lee and the Math-M-Addicts faculty embrace an unconventional pedagogy focused on developing logic, creativity, and a tenacious problem-solving mindset over procedures. "We don't dumb it down for them," says Breydo. "We use technical math language and allow students to struggle through the challenges because that's where real learning happens." Impressive results of Math-M-addicts students in selective math competitions highlight their ... [+] preparation and dedication. For the Math-M-Addicts team, finding the right teachers is as essential as shaping brilliant students. Prospective instructors go through a rigorous multi-stage vetting process. "We seek passionate mathematical problem solvers first," says program director Sonali Jasuja. "Teaching experience is great, but first and foremost, we need people who deeply understand and enjoy the reasoning behind mathematics." Even exceptional instructors undergo extensive training by co-teaching for at least a year alongside veteran Math-M-Addicts faculty before taking the lead role. "Our approach is different from how most US teachers learned mathematics," explains instructor Tanya Gross, the director of Girls Adventures in Math (GAIM) competition. "We immerse them in our unique math culture, which focuses on the 'why' instead of the 'how,' empowering a paradigm shift." That culture extends to the students as well. In addition to the tools and strategies imparted in class, Math-M-Addicts alumni speak of an unshakable confidence and camaraderie that comes from up to several thousands of hours grappling with mathematics at the highest levels alongside peers facing the same challenges. As Math-M-Addicts ramps up efforts to expand access through online classes and global partnerships, the founders remain devoted to their core mission. "Math education should not obsess with speed and memorization of math concepts," argues Breydo. "This is not what mathematics is about. To unlock human potential, we must refocus on cognitive reasoning and problem-solving skills. We are seeking to raise young people unafraid to tackle any complex challenge they face"  - Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The ConversationOne Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts. Forbes Community GuidelinesOur community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space. In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil. Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain: - False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in: - Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user? - Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service. Mathful Review: Unveiling the Innovative Math AI Solver for Enhanced Learning  Mahipal Nehra  Publish Date  In our digital age, educational tools have evolved radically, with Math AI technologies standing at the forefront of this transformation. One of the noteworthy entrants is Mathful, a platform that integrates a sophisticated math AI solver and a photo math solver, accompanied by a comprehensive step-by-step math calculator. This Mathful review delves into how the platform serves as an educational catalyst, leveraging technology to simplify and elucidate complex mathematical concepts.  The Essence of Mathful's AI SolverReinventing problem-solving. Mathful's core lies in its Math AI solver, a pioneering technology tailored to decipher a plethora of mathematical queries. What sets it apart is not just the ability to solve problems but to do so with an innovative and user-friendly approach. It's more than a mere calculator; it's a comprehensive learning companion designed for students and educators alike. With the ability to quickly interpret images of math problems and offer exhaustive step-by-step explanations, this photo math application surpasses conversational AI platforms like ChatGPT in both accuracy and efficiency. You can tap here for quick assistance if math homework or test prep is causing you stress. Photo Math Solver: A Snapshot to Solution The platform's photo math solver exemplifies innovation, enabling users to capture and upload a picture of a math problem. This feature underlines an understanding of the real-world challenges students face - the tediousness of inputting complex equations manually. Through this, Mathful diminishes barriers, offering an effortless bridge from problem to solution. Step-by-Step Math Calculator: Learning Through ProcessDistinctly, Mathful's calculator with steps reveals the "how" behind answers. Each solution is dismantled into digestible steps, fostering a deeper comprehension among users. This pedagogical approach is invaluable, positioning the platform as a learning tool rather than a mere answer generator. Critical Analysis: Accuracy, User Experience, and Coverage Precision and PromptnessMathful prides itself on the accuracy and speed of its math AI solver and calculator. Such claims place it in high regard, especially when swift, reliable answers are crucial. However, evaluating its effectiveness requires continuous user feedback and benchmarking against established standards in the field. Accessibility and DesignA platform is only as effective as its ease of use. Mathful excels in creating an accessible user interface, making intricate math problems manageable for users across all levels of expertise. Its round-the-clock availability further ensures that learners have an anytime, anywhere learning aid. Broad Spectrum of MathematicsFrom elementary arithmetic to more advanced calculus and geometry, Mathful's AI solves a vast array of mathematical problems. This wide-ranging coverage is commendable, catering to a diverse user base with varying educational needs. Prospects and PerspectivesWhile Mathful presents an array of advantages—from its nuanced photo math solver to the detailed calculator with steps—challenges remain. Reliance on technology and the nuances of accurately interpreting user-uploaded photos are areas needing vigilant refinement. Moreover, the learning curve associated with maximizing these sophisticated tools cannot be overlooked. Conclusion: The Role of Mathful in Modern LearningMathful stands as a testament to the potential of Math AI technology in enhancing educational experiences. Through its photo math solver and step-by-step calculator, it encourages not just solution-seeking but an in-depth understanding of mathematical concepts. As educational paradigms continue to evolve, tools like Mathful will be pivotal in shaping a future where technology and learning go hand in hand, making complex math more accessible and engaging for everyone involved. In navigating the path forward, Mathful's commitment to accuracy, user experience, and educational value will be key in its quest to redefine math problem solving for the digital age. Say Something!Get in touch. Let's delve into your project and craft something truly exceptional together. Recent Blogs- Computer Vision
- Federated Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
- Natural Language Processing
- New Releases
- Advisory Board Members
- 🐝 Partnership and Promotion
 Researchers from institutions including the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Singapore University of Technology and Design, Tongji University, and the National University of Singapore introduced Math-LLaVA, a model fine-tuned with a novel dataset called MathV360K. This dataset includes 40K high-quality images and 320K synthesized question-answer pairs designed to improve the breadth and depth of multimodal mathematical reasoning capabilities. Introducing Math-LLaVA represents a significant step forward in the field, addressing the gaps left by previous datasets and methods. The MathV360K dataset was constructed by selecting 40K high-quality images from 24 pre-existing datasets, focusing on subjects like algebra, geometry, and visual question answering. Researchers synthesized 320K new question-answer pairs based on these images to enhance the diversity and complexity of the dataset. This comprehensive dataset was then used to fine-tune the LLaVA-1.5 model, resulting in the development of Math-LLaVA. The selection process for these images involved rigorous criteria to ensure clarity and complexity, aiming to cover a wide range of mathematical concepts and question types. The synthesis of additional question-answer pairs involved generating diverse questions that probe different aspects of the images and require multiple reasoning steps, further enhancing the dataset’s robustness. 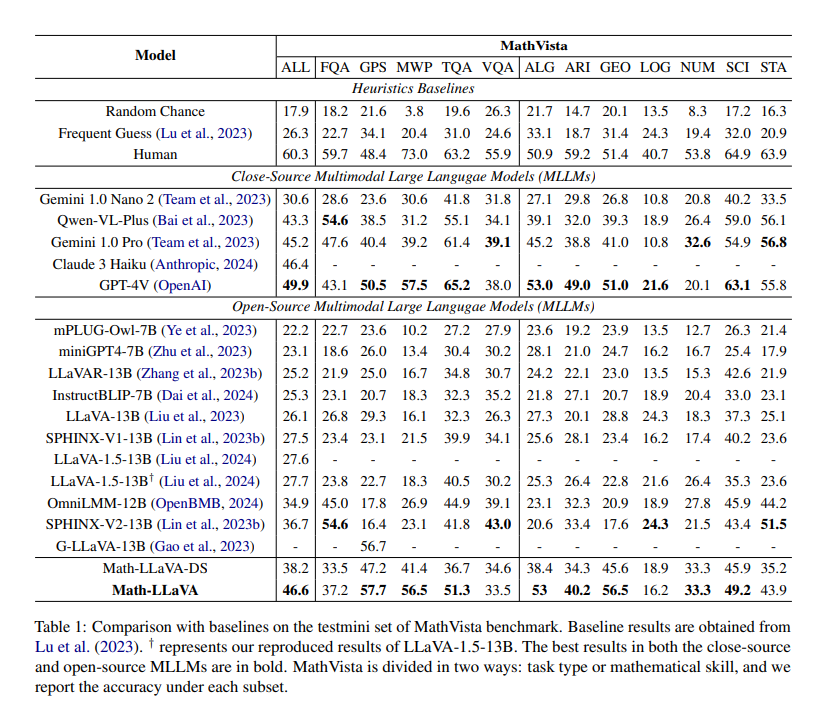 Math-LLaVA demonstrated significant improvements, achieving a 19-point increase on the MathVista minutest split compared to the original LLaVA-1.5 model. Furthermore, it showed enhanced generalizability and performed well on the MMMU benchmark. Specifically, Math-LLaVA achieved a 57.7% accuracy on the GPS subset, outperforming G-LLaVA-13B, trained on 170K high-quality geometric image-caption and question-answer pairs. These results highlight the effectiveness of the diverse and comprehensive MathV360K dataset in enhancing the multimodal mathematical reasoning capabilities of MLLMs. The model’s performance on different benchmarks underscores its ability to generalize across various mathematical reasoning tasks, making it a valuable tool for a wide range of applications. To conclude, the research underscores the critical need for high-quality, diverse multimodal datasets to improve mathematical reasoning in MLLMs. By developing and fine-tuning Math-LLaVA with MathV360K, researchers have significantly enhanced the model’s performance and generalizability, showcasing the importance of dataset diversity and synthesis in advancing AI capabilities. The MathV360K dataset and the Math-LLaVA model represent a substantial advancement in the field, providing a robust framework for future research and development. This work not only underscores the potential of MLLMs to transform various domains by integrating visual and textual data but also inspires hope for the future of AI, paving the way for more sophisticated and capable AI systems. Check out the Paper . All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter . Join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Gr oup . If you like our work, you will love our newsletter.. Don’t Forget to join our 45k+ ML SubReddit  Nikhil is an intern consultant at Marktechpost. He is pursuing an integrated dual degree in Materials at the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Nikhil is an AI/ML enthusiast who is always researching applications in fields like biomaterials and biomedical science. With a strong background in Material Science, he is exploring new advancements and creating opportunities to contribute. This AI Paper by Tencent AI Lab Researchers Introduces Persona-Hub: A Collection of One Billion Diverse Personas for Scaling Synthetic Data- This AI Paper by Narrative BI Introduces a Hybrid Approach to Business Data Analysis with LLMs and Rule-Based Systems
- WildTeaming: An Automatic Red-Team Framework to Compose Human-like Adversarial Attacks Using Diverse Jailbreak Tactics Devised by Creative and Self-Motivated Users in-the-Wild
- This AI Paper by UC Berkeley Explores the Potential of Self-play Training for Language Models in Cooperative Tasks
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHORGibbs diffusion (gdiff): a new bayesian blind denoising method with applications in image denoising and cosmology, 15 real-world examples of llm applications across different industries, meet bricksai: an open-core ai gateway that helps developers implement all essential features needed in any genai project, researchers at the university of toronto introduce a deep-learning model that outperforms google ai system to predict peptide structures, tigerbeetle: a distributed financial transactions database designed for mission critical safety and performance to power the online transaction processing oltp, this ai paper by tencent ai lab researchers introduces persona-hub: a collection of one..., gibbs diffusion (gdiff): a new bayesian blind denoising method with applications in image denoising..., meet bricksai: an open-core ai gateway that helps developers implement all essential features needed in any..., researchers at the university of toronto introduce a deep-learning model that outperforms google ai.... - AI Magazine
- Privacy & TC
- Cookie Policy
🐝 🐝 Join the Fastest Growing AI Research Newsletter... Thank You 🙌 Privacy Overview Towards Better Quantity Representations for Solving Math Word ProblemsNew citation alert added. This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to: You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited. To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below. New Citation Alert!Please log in to your account Information & ContributorsBibliometrics & citations, index terms. Computing methodologies Artificial intelligence Natural language processing RecommendationsNumber-enhanced representation with hierarchical recursive tree decoding for math word problem solving. Automatic solving math word problems (MWPs) is a number-intensive application in natural language processing (NLP). However, these existing methods are far from achieving acceptable levels of numeracy learning. As a result, the performance of ... - We propose a number-enhanced representation framework to model numbers and relations.
- We devise a new tree-structured decoder to address early-stage information loss.
- We outperform the state-of-the-art baselines on four benchmark ...
Reduced models for solving particle beams and plasma physics problemsIn recent years, modelling and solving numerically problems which couple charged particle to electro-magnetic fields has given rise to challenging mathematical and scientific computing developments. In the industry, a variety of examples can be thought ... Data Augmentation with In-Context Learning and Comparative Evaluation in Math Word Problem SolvingMath Word Problem (MWP) solving presents a challenging task in Natural Language Processing (NLP). This study aims to provide MWP solvers with a more diverse training set, ultimately improving their ability to solve various math problems. We ... InformationPublished in.  Association for Computing Machinery New York, NY, United States Publication HistoryCheck for updates, author tags. - Math word problem solving
- quantity representation
- attention mechanism
- auxiliary task
- Research-article
Funding Sources- National Key R&D Program of China
- National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS
ContributorsOther metrics, bibliometrics, article metrics. - 0 Total Citations
- 72 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 72
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 65
View OptionsLogin options. Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article. Full AccessView options. View or Download as a PDF file. View online with eReader . View this article in Full Text. Share this Publication linkCopying failed. Share on social mediaAffiliations, export citations. - Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ... We will inform you here when the file is ready. Your file of search results citations is now ready. Your search export query has expired. Please try again. - Comment Comments
- Save Article Read Later Read Later
AI Reveals New Possibilities in Matrix MultiplicationNovember 23, 2022 Matrix multiplication is not unlike solving an unthinkably large Rubik’s Cube. Mahmet Emin Güzel for Quanta Magazine IntroductionMathematicians love a good puzzle. Even something as abstract as multiplying matrices (two-dimensional tables of numbers) can feel like a game when you try to find the most efficient way to do it. It’s a little like trying to solve a Rubik’s Cube in as few moves as possible — challenging, but alluring. Except that for a Rubik’s Cube, the number of possible moves at each step is 18; for matrix multiplication, even in relatively simple cases, every step can present more than 10 12 options. Over the past 50 years, researchers have approached this problem in many ways, all based on computer searches aided by human intuition. Last month, a team at the artificial intelligence company DeepMind showed how to tackle the problem from a new direction, reporting in a paper in Nature that they’d successfully trained a neural network to discover new fast algorithms for matrix multiplication. It was as if the AI had found an unknown strategy for solving a monstrously complex Rubik’s Cube. “It’s a very neat result,” said Josh Alman , a computer scientist at Columbia University. But he and other matrix multiplication specialists also emphasized that such AI assistance will complement rather than replace existing methods — at least in the near term. “It’s like a proof of concept for something that could become a breakthrough,” Alman said. The result will simply help researchers on their quest. As if to prove the point, three days after the Nature paper came out, a pair of Austrian researchers illustrated how new and old methods might complement each other. They used a conventional computer-aided search to further improve one of the algorithms that the neural network had discovered. The results suggest that, like the process of solving a Rubik’s Cube, the path to better algorithms will be full of twists and turns.  Video : DeepMind researchers trained an AI system called AlphaTensor to find new, faster algorithms for matrix multiplication. AlphaTensor quickly rediscovered — and surpassed, for some cases — the reigning algorithm discovered by German mathematician Volker Strassen in 1969. Christopher Webb Young/ Quanta Magazine ; Emily Zhang for Quanta Magazine Multiplying MatricesMatrix multiplication is one of the most fundamental and ubiquitous operations in all of mathematics. To multiply a pair of n -by- n matrices, each with n 2 elements, you multiply and add these elements together in particular combinations to generate the product, a third n -by- n matrix. The standard recipe for multiplying two n -by- n matrices requires n 3 multiplication operations, so a 2-by-2 matrix, for example, requires eight multiplications. For larger matrices, with thousands of rows and columns, this process quickly becomes cumbersome. But in 1969, the mathematician Volker Strassen discovered a procedure for multiplying a pair of 2-by-2 matrices using seven rather than eight multiplication steps, at the cost of introducing more addition steps. Strassen’s algorithm is needlessly convoluted if you just want to multiply a pair of 2-by-2 matrices. But he realized it would also work for bigger matrices. That’s because the elements of a matrix can themselves be matrices. For example, a matrix with 20,000 rows and 20,000 columns can be reimagined as a 2-by-2 matrix whose four elements are each 10,000-by-10,000 matrices. Each of these matrices can then be subdivided into four 5,000-by-5,000 blocks, and so on. Strassen could apply his method to multiply 2-by-2 matrices at each level of this nested hierarchy. As the matrix size increases, the savings from fewer multiplications grows. Strassen’s discovery led to a search for efficient algorithms for matrix multiplication, which has since inspired two distinct subfields. One focuses on a question of principle: If you imagine multiplying two n -by- n matrices and let n run toward infinity, how does the number of multiplication steps in the fastest possible algorithm scale with n ? The current record for the best scaling, n 2.3728596 , belongs to Alman and Virginia Vassilevska Williams , a computer scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. (A recent unpublished preprint reported a tiny improvement using a new technique.) But these algorithms are of purely theoretical interest, winning out over methods like Strassen’s only for absurdly large matrices. The second subfield thinks on a smaller scale. Soon after Strassen’s work, the Israeli American computer scientist Shmuel Winograd showed that Strassen had reached a theoretical limit: It’s not possible to multiply 2-by-2 matrices with fewer than seven multiplication steps. But for all other matrix sizes, the minimum number of required multiplications remains an open question. And fast algorithms for small matrices could have an outsize impact, since repeated iterations of such an algorithm might beat Strassen’s algorithm when reasonably sized matrices are being multiplied. Unfortunately, the sheer number of possibilities is huge. Even for 3-by-3 matrices, “the number of possible algorithms exceeds the number of atoms in the universe,” said Alhussein Fawzi , a DeepMind researcher and one of the leaders of the new work. Faced with this dizzying menu of options, researchers have made progress by transforming matrix multiplication into what seems like a totally different math problem — one that is easier for computers to handle. It’s possible to represent the abstract task of multiplying two matrices as a specific kind of mathematical object: a three-dimensional array of numbers called a tensor. Researchers can then break this tensor up into a sum of elementary components, called “rank-1” tensors; each of these will represent a different step in the corresponding matrix multiplication algorithm. That means that finding an efficient multiplication algorithm amounts to minimizing the number of terms in a tensor decomposition — the fewer the terms, the fewer the steps involved. In this way, researchers have discovered new algorithms that multiply n -by- n matrices using fewer than the standard n 3 multiplication steps for many small matrix sizes. But algorithms that outperform not only the standard but also Strassen’s algorithm for small matrices have remained out of reach — until now. The DeepMind team approached the problem by turning tensor decomposition into a single-player game. They started with a deep learning algorithm descended from AlphaGo — another DeepMind AI that in 2016 learned to play the board game Go well enough to beat the top human players. All deep learning algorithms are built around neural networks: webs of artificial neurons sorted into layers, with connections that can vary in strength representing how much each neuron influences those in the next layer. The strength of these connections is tweaked over many iterations of a training procedure, during which the neural network learns to transform each input it receives into an output that helps the algorithm accomplish its overall goal. In DeepMind’s new algorithm, dubbed AlphaTensor, the inputs represent steps along the way to a valid matrix multiplication scheme. The first input to the neural network is the original matrix multiplication tensor, and its output is the rank-1 tensor that AlphaTensor has chosen for its first move. The algorithm subtracts this rank-1 tensor from the initial input, yielding an updated tensor that is fed back into the network as a new input. The process repeats until eventually every element in the starting tensor has been reduced to zero, meaning there are no more rank-1 tensors to take out. At that point, the neural network has discovered a valid tensor decomposition, since it’s mathematically guaranteed that the sum of all the rank-1 tensors is exactly equal to the starting tensor. And the steps it took to get there can be translated back into steps of the corresponding matrix multiplication algorithm. Here’s the game: AlphaTensor repeatedly decomposes a tensor to a set of rank-1 components. Each time, AlphaTensor gets rewarded if it finds a way to reduce the number of steps. But shortcuts to victory are not at all intuitive, just as you sometimes must scramble a perfectly ordered face on a Rubik’s Cube before you can solve the whole thing. The team now had an algorithm that could, theoretically, solve their problem. They just had to train it first. Like all neural networks, AlphaTensor needs a lot of data to train on, but tensor decomposition is a notoriously hard problem. There were few examples of efficient decompositions that the researchers could feed the network. Instead, they helped the algorithm get started by training it on the much easier inverse problem: adding up a bunch of randomly generated rank-1 tensors. “They’re using the easy problem to produce more data for the hard problem,” said Michael Littman , a computer scientist at Brown University. Combining this backward training procedure with reinforcement learning, wherein AlphaTensor generated its own training data as it blundered around looking for efficient decompositions, worked much better than either training method on its own. The DeepMind team trained AlphaTensor to decompose tensors representing the multiplication of matrices up to 12-by-12. It sought fast algorithms for multiplying matrices of ordinary real numbers and also algorithms specific to a more constrained setting known as modulo 2 arithmetic. (This is math based on only two numbers, so matrix elements can only be 0 or 1, and 1 + 1 = 0.) Researchers often start with this more restricted but still vast space, in hopes that algorithms discovered here can be adapted to work on matrices of real numbers. After training, AlphaTensor rediscovered Strassen’s algorithm within minutes. It then discovered up to thousands of new fast algorithms for each matrix size. These were different from the best-known algorithms but had the same number of multiplication steps. In a few cases, AlphaTensor even beat existing records. Its most surprising discoveries happened in modulo 2 arithmetic, where it found a new algorithm for multiplying 4-by-4 matrices in 47 multiplication steps, an improvement over the 49 steps required for two iterations of Strassen’s algorithm. It also beat the best-known algorithm for 5-by-5 modulo 2 matrices, reducing the number of required multiplications from the previous record of 98 to 96. (But this new record still lags behind the 91 steps that would be required to beat Strassen’s algorithm using 5-by-5 matrices.) The new high-profile result created a lot of excitement, with some researchers heaping praise on the AI-based improvement on the status quo. But not everyone in the matrix multiplication community was so impressed. “I felt like it was a little overhyped,” said Vassilevska Williams. “It’s another tool. It’s not like, ‘Oh, the computers beat the humans,’ you know?” Researchers also emphasized that immediate applications of the record-breaking 4-by-4 algorithm would be limited: Not only is it valid only in modulo 2 arithmetic, but in real life there are important considerations besides speed. Fawzi agreed that really, this is just the beginning. “There is a lot of room for improvement and research, and that’s a good thing,” he said. A Final TwistAlphaTensor’s greatest strength relative to well-established computer search methods is also its greatest weakness: It’s not constrained by human intuition about what good algorithms look like, so it can’t explain its choices. That makes it difficult for researchers to learn from its achievements. But this may not be as big a drawback as it seems. A few days after the AlphaTensor result, the mathematician Manuel Kauers and his graduate student Jakob Moosbauer , both of Johannes Kepler University Linz in Austria, reported another step forward.  Manuel Kauers tweaked the DeepMind approach to generate further improvements. Jakob Moosbauer When the DeepMind paper came out, Kauers and Moosbauer were in the process of searching for new multiplication algorithms using a conventional computer-aided search. But unlike most such searches, which start afresh with a new guiding principle, their method works by repeatedly tweaking an existing algorithm in hopes of squeezing more multiplication savings out of it. Taking AlphaTensor’s algorithm for 5-by-5 modulo 2 matrices as a starting point, they were surprised to find that their method reduced the number of multiplication steps from 96 to 95 after just a few seconds of computation. AlphaTensor also helped them make another improvement indirectly. Previously, Kauers and Moosbauer hadn’t bothered to explore the space of 4-by-4 matrices, believing that it would not be possible to beat two iterations of Strassen’s algorithm. The AlphaTensor result prompted them to reconsider, and after a week of computation time starting from scratch, their method turned up another 47-step algorithm unrelated to the one AlphaTensor had discovered. “If somebody had told us that there is something to discover for 4-by-4, we could have done that earlier,” said Kauers. “But OK, well, that’s how it works.” Littman expects more such surprises, likening the situation to the first time a runner finished a mile in under four minutes, a feat that had widely been considered impossible. “People were like, ‘Oh, wait, we can do this,’ and now lots of people can do it,” he said. Looking forward, Fawzi hopes to generalize AlphaTensor to tackle a broader range of mathematical and computational tasks, just as its ancestor AlphaGo eventually branched out into other games. Kauers sees this as the true litmus test for the application of machine learning to discovering new algorithms. He points out that the quest for fast matrix multiplication algorithms is a combinatorial problem to which computer searches, with or without human assistance, are well suited. But not all mathematical problems are so easy to pin down. If machine learning can discover a qualitatively new algorithmic idea, he said, “this would then be a game changer.” Get highlights of the most important news delivered to your email inbox Comment on this articleQuanta Magazine moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (New York time) and can only accept comments written in English.  Next articlePlease ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following: - a special character: @$#!%*?&
 | 



















IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. Take a photo of your math problem on the app. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math.
Type a math problem and get step-by-step solutions, graphs, and explanations. Practice algebra, calculus, trigonometry, and more with worksheets and videos.
QuickMath can answer algebra, equations, calculus and more problems faced by high-school and college students. Enter your problem and get instant solutions with detailed steps and graphs.
Popular Calculators. Fractions Radical Equation Factoring Inverse Quadratic Simplify Slope Domain Antiderivatives Polynomial Equation Log Equation Cross Product Partial Derivative Implicit Derivative Tangent Complex Numbers. Symbolab: equation search and math solver - solves algebra, trigonometry and calculus problems step by step.
Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app. ... Type a math problem. Examples. Quadratic equation { x } ^ { 2 } - 4 x - 5 = 0. Trigonometry. 4 \sin \theta \cos \theta = 2 \sin \theta ...
Symbolab offers free online calculators for various math topics, such as algebra, calculus, trigonometry, statistics and more. You can enter your problem and get step-by-step solutions with explanations and graphs.
QuickMath offers a step-by-step math problem solver for various equations and expressions, simplifying complex math tasks.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems with the free GeoGebra Math Solver. Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now!
Microsoft Math Solver
Understand the how and why See how to tackle your equations and why to use a particular method to solve it — making it easier for you to learn.; Learn from detailed step-by-step explanations Get walked through each step of the solution to know exactly what path gets you to the right answer.; Dig deeper into specific steps Our solver does what a calculator won't: breaking down key steps ...
Cymath | Math Problem Solver with Steps | Math Solving App ... \\"Solve
The Math Calculator will evaluate your problem down to a final solution. You can also add, subtraction, multiply, and divide and complete any arithmetic you need. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit and see your result! Math Calculator from Mathway will evaluate various math problems from basic arithmetic to advanced trigonometric expressions.
Basic Math Plan. Basic Math Solver offers you solving online fraction problems, metric conversions, power and radical problems. You can find area and volume of rectangles, circles, triangles, trapezoids, boxes, cylinders, cones, pyramids, spheres. You can simplify and evaluate expressions, factor/multiply polynomials, combine expressions.
Math Word Problem Solutions. Math word problems require interpreting what is being asked and simplifying that into a basic math equation. Once you have the equation you can then enter that into the problem solver as a basic math or algebra question to be correctly solved. Below are math word problem examples and their simplified forms.
UpStudy Math Solver with steps is versatile and capable of solving a wide range of mathematical problems, including pre-algebra, algebra, pre-calculus, inequalities, calculus, trigonometry, geometry, statistics and probability, and matrices. No matter the complexity of the problem, our tool aims to provide fast, clear, and step-by-step ...
MathGPT is an AI-powered math problem solver, integral calculator, derivative cacluator, polynomial calculator, and more! Try it out now and solve your math homework! Snap, Solve, Submit! Upload a screenshot and solve any math, physics, or accounting problem instantly with MathGPT! MathGPT MathGPT Vision PhysicsGPT AccountingGPT. MathGPT can ...
The Algebra Calculator is a versatile online tool designed to simplify algebraic problem-solving for users of all levels. Here's how to make the most of it: Begin by typing your algebraic expression into the above input field, or scanning the problem with your camera. After entering the equation, click the 'Go' button to generate instant solutions.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Many mathematical problems have been stated but not yet solved. These problems come from many areas of mathematics, such as theoretical physics, computer science, algebra, analysis, combinatorics, algebraic, differential, discrete and Euclidean geometries, graph theory, group theory, model theory, number theory, set theory, Ramsey theory, dynamical systems, and partial differential equations.
About the Curricula. A curriculum is how standards, or learning goals, for every grade and subject are translated into day-to-day activities. As part of the NYC Solves initiative, all high schools will use Illustrative Mathematics and districts will choose a comprehensive, evidence-based curricula for middle school math instruction from an approved list.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
For all academic inquiries, please contact: Math Student Services C-36 Padelford Phone: (206) 543-6830 Fax: (206) 616-6974 [email protected]
An age problem is a type of word problem in math that involves calculating the age of one or more people at a specific point in time. These problems often use phrases such as 'x years ago,' 'in y years,' or 'y years later,' which indicate that the problem is related to time and age.
Ruvim Breydo, founder of Math-M-Addicts, advocates for math education focused on cognitive reasoning and problem-solving to nurture fearless, challenge-ready students.
The Essence of Mathful's AI Solver Reinventing Problem-Solving. Mathful's core lies in its Math AI solver, a pioneering technology tailored to decipher a plethora of mathematical queries. What sets it apart is not just the ability to solve problems but to do so with an innovative and user-friendly approach.
Free math problem solver answers your homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. Take a photo of your math problem on the app. get Go. Basic Math. Basic Math.
Research on Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) focuses on integrating visual and textual data to enhance artificial intelligence's reasoning capabilities. By combining these modalities, MLLMs can interpret complex information from diverse sources such as images and text, enabling them to perform tasks like visual question answering and mathematical problem-solving with greater accuracy ...
Solving a math word problem requires selecting quantities in it and performing appropriate arithmetic operations to obtain the answer. For deep learning-based methods, it is vital to obtain good quantity representations, i.e., to selectively and emphatically aggregate information in the context of quantities.
The team now had an algorithm that could, theoretically, solve their problem. They just had to train it first. New Paths. Like all neural networks, AlphaTensor needs a lot of data to train on, but tensor decomposition is a notoriously hard problem. There were few examples of efficient decompositions that the researchers could feed the network.
Free math problem solver answers your calculus homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. Take a photo of your math problem on the app. get Go. Calculus.