Writing a Bibliography | Definition, Types & Examples
TK Waters has been an adjunct professor of religion at Western Kentucky University for six years. They have a master's degree in religious studies from Western Kentucky University and a bachelor's degree in English literature and religious studies from Western Kentucky University.
Doresa holds a Ph.D. in Communication Studies.

What should a bibliography look like?
Bibliographies look different depending on the citation style. The bibliography structure always includes citing the author's name, the title of the work, the year of publication, and the publisher for each source one consults for a paper or project. Although specific formatting details differ for each citation style, the basics are universal for each type, with the bibliography alphabetized by the author's last name for each source.
What do you write in a bibliography?
A bibliography is a detailed list of all the sources consulted and cited in a research paper or project. The bibliography structure always includes citing the author's name, the title of the work, the year of publication, and the publisher for each source one consults for a paper or project. Although the formatting details differ for each citation style, the basics are universal, and the bibliography is always alphabetized by the author's last name for each source.
How do you write a bibliography for a website?
A website is cited similarly to a book or article by including the author, title, publisher, date of publication, and URL for the source. The bibliographic entry style varies depending on the utilization of Chicago, APA, or MLA style, but all of these elements are always included when available.
How do you begin a bibliography?
The best way to begin a bibliography is by keeping a list of sources consulted during the research. Upon completion of the study, one should follow the required citation style (usually Chicago, APA, or MLA) and put all of the information about the source, such as author and title, into that format.
How do you write a bibliography?
The bibliography structure always includes citing the author's name, the title of the work, the year of publication, and the publisher for each source one consults for a paper or project. Although the details of how this is formatted differ for each citation style, the basics are universal, with the bibliography alphabetized by the author's last name for each source.
What is a bibliography for an essay?
A bibliography is a list of sources reviewed when writing the essay; this can include references cited in the body of the paper and sources from general information.
Table of Contents
What is a bibliography, types of bibliographies, how to write a bibliography, lesson summary.
Most high schools, colleges, and universities require research papers and projects, so students need to know how to write a bibliography to cite the research sources they use. A bibliography is a list of sources one consults and references in a research paper or project. What does bibliography mean? The word "bibliography" is Greek. The Greek words biblio and graphia literally mean "the writing of/about books."
Bibliographies are required whenever a writer consults a source for their research, whether they directly or indirectly use information from the reference. This application gives credit to the original author of that information. It keeps the person writing the research paper from committing plagiarism or making information from other sources seem like the writer's own idea. While bibliographies originally were lists of books, in the 21st century, bibliographies can include books, journal articles , websites, newspaper articles, films, and even social media pages -anything that the writer consults in their research.
For any paper or project where research transpires, the writer should include a bibliography. The format and title of the bibliography depend on what citation style the writer uses. For example, a writer using Chicago style would use "Bibliography" as the title of their source page; in APA style, this would be "References," while in MLA style it would be "Works Cited." This practice extends to when the writer is researching a topic they might want to do more research on in the future, presenting new information in their field of study, or even critiquing another person's work, such as in a book review.
Bibliographies not only provide a way to cite sources but also help give the writer credibility. A writer can use references and bibliographies to inform their readers which evidence supports their ideas, who or what influenced the writer's ideas and work, and what sources were used if a reader decides to use the writer's work for their research or a critique.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account

An error occurred trying to load this video.
Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support.
You must c C reate an account to continue watching
Register to view this lesson.
As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed.
Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons.
Already registered? Log in here for access
Resources created by teachers for teachers.
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
You're on a roll. Keep up the good work!
Just checking in. are you still watching.
- 0:13 Why Do We Use Bibliographies?
- 2:52 Types of Bibliographies
- 3:47 How Do You Create a…
- 5:25 When Do You Need a…
Although the concept of a bibliography might seem straightforward, many different types of bibliographies exist and are necessary for different situations. These types include, but are not limited to, the following:
- an enumerative/systematic bibliography,
- an annotated bibliography,
- a working bibliography,
- a period bibliography,
- and a subject bibliography.
Enumerative Bibliography
The most commonly used type of bibliography is the enumerative bibliography , sometimes called a systematic bibliography. This type of bibliography is simply a list of the sources consulted and cited in a research paper or project ordered in a particular way, usually alphabetically by each author's last name. Whenever an assignment or instructor requests a "bibliography" without any other details, they typically refer to an enumerative bibliography.
Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography is a type of bibliography usually used early on in research projects. Annotated bibliographies have a list of sources to support a research project and brief "annotations" about each source. These annotations are usually around 150 words each and explain what the source is about and why it would be helpful to consult in the research project.
Working Bibliography
A working bibliography is similar to a rough draft version of a bibliography. A working bibliography is what one uses in drafting a research project or paper. This means that the working bibliography will change over time as new sources are added to it when the author continues their research. A working bibliography is not always a polished version of the bibliography. Depending on the requirements for an assignment, it might not even be in alphabetical order since the author has not finalized the bibliography yet.
Other Bibliographies
Enumerative, annotated, and working bibliographies are the most common types of bibliographies used in academic settings. Depending on the field of study, however, there are other types of bibliographies one might use. One of these is a period bibliography, which includes sources from a specific era, usually to aid in historical research. These bibliographies might accompany a project, but they might also be published separately just as a list of sources for others to consult if they are researching over that period. A subject bibliography works in much the same way as a period bibliography but covers a particular subject instead of a time.
Being able to understand what a bibliography is and how to do a bibliography are entirely different concepts. Many students in high schools, colleges, and even universities might be comfortable writing a research paper but still wonder, "How do you write a bibliography?" The bibliography in a research paper or project is typically one of the last pages of the paper, occurring after the bulk of the writing but before appendices. All bibliographies must include all of the references used to create the paper or project and what bibliographic information is available for a source; this includes:
- the name(s) of the author(s),
- the year of publication,
- the date of publication,
- the publisher,
- the containing work (journal, newspaper, anthology),
- the internet retrieval location (when applicable),
- and other necessary information for someone to be able to find the source.
Different citation styles determine how the bibliography should be formatted. Usually, an instructor or assignment will indicate the required citation style for the class or assignment. The three primary citation styles are the Chicago Manual of Style, the APA Style, and the MLA Style. While the Chicago style uses "bibliography" to refer to the bibliographies in their papers, APA style uses "references" while MLA style uses "works cited." The names refer to the same information, but each style guide has different requirements for formatting.
Chicago Style
The Chicago Manual of Style is the style used most commonly in history, anthropology, religious studies, and other humanities fields. Chicago style uses "Bibliography" to title the list of sources at the end of a paper. In addition to a bibliography, writers should include footnotes or endnotes in the body of their work. As the readers are reading, these notes detail where outside information was used. The basic information in a Chicago style bibliographic entry is as follows and in this order:
- author's last name,
- author's first name,
- title of work,
- publication location,
- and year of publication.
This information varies depending on the source cited, but the general order stays the same in Chicago style. What does a Chicago-style bibliography look like? Here are a few examples of different sources (book, journal article, film, and newspaper article) formatted in Chicago style. The author's last name alphabetizes all sources, only the first line of each entry is aligned to the left margin while subsequent lines are indented, and URLs are included for internet sources. Page ranges for articles appear after the volume number and issue number.
Although the Chicago style is the only formatting style that uses the term "bibliography" for sources, APA and MLA styles are the most commonly used citation styles. APA Style , which the American Psychological Association produced, is a style guide for fields like sociology, psychology, and other social sciences, as well as some natural sciences or scientific journals. Because most of these fields continue developing research and recent work is usually the most up-to-date, APA style puts the year of each source as the secondary focus after the author. In-text and parenthetical citations are in the body of the paper and bibliography, which is titled "References." The basic information in each APA style bibliographic entry includes, in order:
- author's first and middle initials,
- publisher name,
- and DOI (digital object identifier).
There are a few unique aspects that distinguish APA style bibliographic entries from what other citation styles require:
- The year appears directly after the author in parentheses.
- The work's title, whether a book or an article, uses sentence-style capitalization, which means that only the first word, words after colons and semicolons, ending punctuation, and proper nouns are capitalized. While this applies to book and article titles, it does not apply to journal and newspaper titles, which should still use title capitalization and have all major words capitalized.
- In the most recent edition, APA requires all sources to include a DOI (digital object identifier), if available, whether or not they were found on the internet.
- Volume numbers of journals are italicized, while issue numbers are in parentheses with page ranges following. Here are some examples of what APA style looks like on a reference page .
One of the most basic and widely used citation styles is MLA Style . MLA style, created by the Modern Language Association, is usually used in English, modern languages, cultural studies, and film study fields. MLA is one of the most approachable and straightforward to use styles, so it is often the first citation style one uses in an academic setting before learning the other types. In MLA, in-text and parenthetical citations are used to cite information in the body of the paper, while the bibliographic entries are organized on a page called " Works Cited ". MLA bibliographic entries typically include the following in order:
MLA style bibliographies look similar to Chicago style, with some exceptions. In MLA style, the abbreviation "pp." is used before a page range while "vol." and "no." are included before, respectively, a volume number and issue number. MLA also separates items in bibliographic entries primarily with commas instead of periods. One of the unique parts of an MLA entry is the formatting of the publisher's name. While Chicago and APA styles require the full publisher name, MLA style prefers that the publisher name stay short, one or two words if possible. If redundant words like "publisher," "publishing," "press," or "university" are part of the publisher's name, the omitting of these words are appropriate. Here are some examples of MLA bibliographic entries.
A bibliography is used in most academic writing to list works that an author consults in their research. This application gives the author credibility, lets their readers know where the author found the information and gives credit to other authors who have previously written various works. There are a few common types of bibliographies:
- an enumerative bibliography , which is a standard bibliography that lists all of the works and sources the author consulted in their research;
- an annotated bibliography , includes a bibliographic entry for each source an author is considering or has reviewed, along with a brief description and evaluation of the source;
- and a working bibliography , which includes what sources an author has consulted thus far and changes as the author continue researching and writing.
Many citation styles are used in academic settings to cite sources. These citation styles include:
- the Chicago Manual of Style , which is common in history and humanities fields;
- the APA Style , utilized primarily in the psychological and social sciences fields;
- and the MLA Style , commonly used in English, modern language, and film studies fields.
APA and MLA styles are the most commonly used citation styles. Each citation style has unique formatting requirements for how bibliographic entries should be formatted. However, all include basic information like the author's name, the title of the work, and the year of publication.
Video Transcript
Why do we use bibliographies.
Have you ever sat in a chair, looked out on a beautiful sunset and thought, 'what exactly is a bibliography?' Me either, but you may have to write one one day, so let's talk about what a bibliography is and why they are important.
Most often, when the word 'bibliography' is used in an academic setting it's referring to a list of sources used by the author to inform their work on a given topic . This means that you're going to include all the works that were read when researching the topic - whether or not they're used directly in your own writing.
There are several reasons why we use bibliographies. The first major reason for using a bibliography is to inform your reader on how widely you researched the topic on which you're writing. While you may cite only seven or eight sources within a paper, you may have read 25, 50, or even 100 different books, journal articles, or scholarly websites in finding those sources. Showing just how widely you researched your topic provides more credence and credibility to your work.
Another use for a bibliography is to allow your reader to know if you considered a work but chose not to include it within your piece, or if you didn't consult a particular author at all. For instance, I may be completing a research paper on the behavior of chimpanzees both in the wild and in captivity. If someone was reading through my piece and didn't see me cite Jane Goodall, one of the most famous chimpanzee experts of all time, they may be curious. A bibliography would let them know if I considered any of her famous works or if I failed to give her work any consideration at all. This would allow them to critique my own work on a much more informed basis.
One of the largest benefits for you personally in creating a bibliography is that it allows you to keep track of all the research you've consulted on a topic. For instance, when you are first writing a paper that you've researched, you may not initially utilize a source that you consulted. However, after you've done some rewriting and reworking of your paper, you may find that you really did need to include a source after all. Having a bibliography, it would be much easier for you to find the source information; you don't have to start all over again in the search process. Creating a bibliography allows you to build a small database of information on a number of given topics. While you're never going to write the same paper twice in an academic setting, you may write on a similar subject. Having a bibliography that you created as a place to start your research will put you much further ahead in the process.
What are the types on bibliographies? The first type you may find is an annotated bibliography , and that's going to give the citation of each source you consulted along with a brief description and evaluation of the source.
The second type is enumerative. An enumerative bibliography is a list of sources that were consulted, simply citing them in a proper format.
The third type of bibliography is a list of works published during a particular time in history - that's called a period bibliography . These are often used in anthropological, historical, or cultural research.
A subject bibliography is a list of sources on a particular subject, often considered a record of the most important works in any given field of study.
Now that you know the types of bibliography, let's talk about how you create one.
How Do You Create a Bibliography?
One of the first things you have to do in preparing to create a bibliography is to decide in advance what type of bibliography you are going to do - annotated, enumerative, period, or subject. In an academic setting, you are most likely going to do an annotated or enumerative bibliography. The second step is to decide on the citation formatting you're going to be using. The two most common types are APA and MLA, followed by Chicago formatting. The third step is to keep a record of the citations that you're going to be using, as well as keeping them in your chosen format.
Now, on your screen, you're going to see a sample annotated bibliography in APA format. This bibliography sample is provided to us by Purdue University. As you can see, the first step is to cite the source in proper formatting - that's the first paragraph that you see. That is an APA-formatted source: author's last name, year of publication, the title of the book, as well as the publishing information.
The second thing that you see is a brief summary of the work; that's that second paragraph. You see exactly what the book is about. Is it fiction or nonfiction? What is it based on, and what are the basic things that it covers? The final paragraph is a brief critique of the work from this particular researcher's point of view.
When Do You Need a Bibliography?
Now, how do you know when you need a bibliography? A good way to know is if your professor tells you to write one. On those occasions when it isn't clear - or isn't that clear - here are some good rules of thumb for deciding whether or not to utilize a bibliography:
1. When you are researching a topic you may want or need to do further research on in the future, you're going to want to do a bibliography. This includes any papers written in your major or minor field of study.
2. When you are writing a biography of a famous and/or historical person in which there are a lot of sources or a particularly large body of work.
3. When you are presenting new information in a field of study, or your conclusions are contrary or contrasting current trends or norms of the time.
4. When you are providing a critique of another author's piece of work.
5. When you are writing a paper for which others will be critiquing your conclusions.
6. When you have chosen to write on a more advanced topic and have chosen not to provide foundational information. This will allow the reader to know that you have looked at the foundations of the field, but chose to spend your limited writing space on more advanced information.
Lesson Objectives
After watching this lesson, you should be able to:
- Explain what a bibliography is and define the different types
- Describe how to write a bibliography
- Understand why and when you should write a bibliography
Unlock Your Education
See for yourself why 30 million people use study.com, become a study.com member and start learning now..
Already a member? Log In
Recommended Lessons and Courses for You
Related lessons, related courses, recommended lessons for you.

Writing a Bibliography | Definition, Types & Examples Related Study Materials
- Related Topics
Browse by Courses
- Common Core ELA - Writing Grades 11-12: Standards
- Common Core ELA - Speaking and Listening Grades 11-12: Standards
- 12th Grade English: Homework Help Resource
- Comprehensive English: Overview & Practice
- Common Core ELA Grade 8 - Writing: Standards
- CAHSEE English Exam: Test Prep & Study Guide
- Common Core ELA Grade 8 - Literature: Standards
- Common Core ELA Grade 8 - Language: Standards
- 9th Grade English: High School
- 10th Grade English: High School
- 12th Grade English: Help and Review
- TOEFL iBT: Test Prep and Practice
- GRE Prep: Help and Review
- Technical Writing: Help and Review
- 10th Grade English: Credit Recovery
Browse by Lessons
- Creating a Bibliography: Lesson for Kids
- Enumerative Bibliography: Definition & Examples
- Period Bibliography: Definition & Examples
- Using Bibliographic Sources in a Library Media Program
- Pudd'nhead Wilson by Mark Twain | Summary, Themes & Analysis
- Pudd'nhead Wilson Setting
- Pudd'nhead Wilson Characters
- Pudd'nhead Wilson Themes
- Pudd'nhead Wilson Symbols
- The Tragedy of Pudd'nhead Wilson | Summary & Analysis
- The Adventures of Tom Sawyer Discussion Questions
- Absalom, Absalom! by William Faulkner | Summary & Characters
- Absalom, Absalom! by Faulkner: Themes & Analysis
- Brent Staples | Life, Books & Awards
- A Pact by Ezra Pound | Summary & Poem Analysis
Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Create an account
Explore our library of over 88,000 lessons
- Foreign Language
- Social Science
- See All College Courses
- Common Core
- High School
- See All High School Courses
- College & Career Guidance Courses
- College Placement Exams
- Entrance Exams
- General Test Prep
- K-8 Courses
- Skills Courses
- Teacher Certification Exams
- See All Other Courses
- Create a Goal
- Create custom courses
- Get your questions answered
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Bibliography in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
- APA Bibliography
- How to Create One
- Why You Need It
Sample Bibliography
An APA format bibliography lists all of the sources that might be used in a paper. A bibliography can be a great tool to help you keep track of information during the research and writing process. In some cases, your instructor may require you to include a bibliography as part of your assignment.
At a Glance
A well-written APA format bibliography can help you keep track of information and sources as you research and write your psychology paper. To create a bibliography, gather up all of the sources that you might use in your paper. Create an APA format reference for each source and then write a brief annotation. Your annotation should be a brief summary of what each reference is about. You can quickly refer to these annotations When writing your paper and determine which to include.
What Is an APA Format Bibliography?
An APA format bibliography is an alphabetical listing of all sources that might be used to write an academic paper, essay, article, or research paper—particularly work that is covering psychology or psychology-related topics. APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association (APA). This format is used by many psychology professors, students, and researchers.
Even if it is not a required part of your assignment, writing a bibliography can help you keep track of your sources and make it much easier to create your final reference page in proper APA format.
Creating an APA Bibliography
A bibliography is similar in many ways to a reference section , but there are some important differences. While a reference section includes every source that was actually used in your paper, a bibliography may include sources that you considered using but may have dismissed because they were irrelevant or outdated.
Bibliographies can be a great way to keep track of information you might want to use in your paper and to organize the information that you find in different sources. The following are four steps you can follow to create your APA format bibliography.
Start on a New Page
Your working bibliography should be kept separate from the rest of your paper. Start it on a new page, with the title "Bibliography" centered at the top and in bold text. Some people use the title "References" instead, so it's best to check with your professor or instructor about which they prefer you to use.
Gather Your Sources
Compile all the sources you might possibly use in your paper. While you might not use all of these sources in your paper, having a complete list will make it easier later on when you prepare your reference section.
Gathering your sources can be particularly helpful when outlining and writing your paper.
By quickly glancing through your working bibliography, you will be able to get a better idea of which sources will be the most appropriate to support your thesis and main points.
Reference Each Source
Your references should be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name, and they should be double-spaced. The first line of each reference should be flush left, while each additional line of a single reference should be a few spaces to the right of the left margin, which is known as a hanging indent.
The format of each source is as follows for academic journals:
- Last name of first author (followed by their first initial)
- The year the source was published in parentheses
- The title of the source
- The journal that published the source (in italics)
- The volume number, if applicable (in italics)
- The issue number, if applicable
- Page numbers (in parentheses)
- The URL or "doi" in lowercase letters followed by a colon and the doi number, if applicable
The following examples are scholarly articles in academic journals, cited in APA format:
- Kulacaoglu, F., & Kose, S. (2018). Borderline personality disorder (BPD): In the midst of vulnerability, chaos, and awe. Brain sciences , 8 (11), 201. doi:10.3390/brainsci8110201
- Cattane, N., Rossi, R., & Lanfredi, M. (2017). Borderline personality disorder and childhood trauma: exploring the affected biological systems and mechanisms. BMC Psychiatry, 18 (221). doi:10.1186/s12888-017-1383-2
Visit the American Psychological Association's website for more information on citing other types of sources including online media, audiovisual media, and more.
Create an Annotation for Each Source
Normally a bibliography contains only references' information, but in some cases you might decide to create an annotated bibliography. An annotation is a summary or evaluation of the source.
An annotation is a brief description of approximately 150 words describing the information in the source, your evaluation of its credibility, and how it pertains to your topic. Writing one of these for each piece of research will make your writing process faster and easier.
This step helpful in determining which sources to ultimately use in your paper. Your instructor may also require it as part of the assignment so they can assess your thought process and understanding of your topic.
Reasons to Write a Bibliography
One of the biggest reasons to create an APA format bibliography is simply to make the research and writing process easier.
If you do not have a comprehensive list of all of your references, you might find yourself scrambling to figure out where you found certain bits of information that you included in your paper.
A bibliography is also an important tool that your readers can use to access your sources.
While writing an annotated bibliography might not be required for your assignment, it can be a very useful step. The process of writing an annotation helps you learn more about your topic, develop a deeper understanding of the subject, and become better at evaluating various sources of information.
The following is an example of an APA format bibliography by the website EasyBib:
There are many online resources that demonstrate different formats of bibliographies, including the American Psychological Association website . Purdue University's Online Writing Lab also has examples of formatting an APA format bibliography.
Check out this video on their YouTube channel which provides detailed instructions on formatting an APA style bibliography in Microsoft Word.
You can check out the Purdue site for more information on writing an annotated APA bibliography as well.
What This Means For You
If you are taking a psychology class, you may be asked to create a bibliography as part of the research paper writing process. Even if your instructor does not expressly require a bibliography, creating one can be a helpful way to help structure your research and make the writing process more manageable.
For psychology majors , it can be helpful to save any bibliographies you have written throughout your studies so that you can refer back to them later when studying for exams or writing papers for other psychology courses.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 7th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2020.
Masic I. The importance of proper citation of references in biomedical articles. Acta Inform Med . 2013;21(3):148–155. doi:10.5455/aim.2013.21.148-155
American Psychological Association. How do you format a bibliography in APA Style?
Cornell University Library. How to prepare an annotated bibliography: The annotated bibliography .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

University of Pittsburgh Library System
- Collections
Course & Subject Guides
Citation styles: apa, mla, chicago, turabian, ieee.
- APA 7th Edition
- Turabian 9th
- Writing & Citing Help
- Understanding Plagiarism
Quick Links
Listed below are a few quick links to resources that will aid you in citing sources.
- Sign up for a Mendeley, EndNote, or Zotero training class.
- APA 7th Edition Published in October 2019. Visit this page for links to resources and examples.
- MLA Need help with citing MLA style? Find information here along with links to books in PittCat and free online resources.
- Chicago/Turabian Need help with citing Chicago/Turabian style? Find examples here along with links to the online style manual and free online resources.
Getting Started: How to use this guide
This LibGuide was designed to provide you with assistance in citing your sources when writing an academic paper.
There are different styles which format the information differently. In each tab, you will find descriptions of each citation style featured in this guide along with links to online resources for citing and a few examples.
What is a citation and citation style?
A citation is a way of giving credit to individuals for their creative and intellectual works that you utilized to support your research. It can also be used to locate particular sources and combat plagiarism. Typically, a citation can include the author's name, date, location of the publishing company, journal title, or DOI (Digital Object Identifier).
A citation style dictates the information necessary for a citation and how the information is ordered, as well as punctuation and other formatting.
How to do I choose a citation style?
There are many different ways of citing resources from your research. The citation style sometimes depends on the academic discipline involved. For example:
- APA (American Psychological Association) is used by Education, Psychology, and Sciences
- MLA (Modern Language Association) style is used by the Humanities
- Chicago/Turabian style is generally used by Business, History, and the Fine Arts
*You will need to consult with your professor to determine what is required in your specific course.
Click the links below to find descriptions of each style along with a sample of major in-text and bibliographic citations, links to books in PittCat, online citation manuals, and other free online resources.
- APA Citation Style
- MLA Citation Style
- Chicago/Turabian Citation Style
- Tools for creating bibliographies (CItation Managers)
Writing Centers
Need someone to review your paper? Visit the Writing Center or Academic Success Center on your campus.
- Oakland Campus
- Greensburg Campus
- Johnstown Campus
- Titusville Campus
- Bradford Campus
- Next: APA 7th Edition >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 9:46 AM
- URL: https://pitt.libguides.com/citationhelp

How to Format a Citation
Examples of apa, mla, and chicago manual of style, citation styles: american psychological association (apa), citation styles: chicago, citation styles: modern language association (mla), example: direct quote cited in a book, example: reference within a journal article.
- Zotero This link opens in a new window
- EndNote This link opens in a new window
- Compare Citation Management Software

There are two basic approaches to citation:
- In-text citations + a list of references at the end of the paper
- Endnotes or footnotes +/- a bibliography at the end of the paper
Scholars writing in the sciences and social sciences typically use in-text citations, while humanities scholars utilize endnotes/footnotes.
While the two basic approaches to citations are simple, there are many different citation styles.
What is a citation style?
The way that citations appear (format) depends on the citation style, which is a set of established rules and conventions for documenting sources.
Citation styles can be defined by an association, such as the Modern Language Association (MLA), publisher, such as the University of Chicago Press, or journal, such as The New England Journal of Medicine .
What citation style should I use?
The citation style that you use depends on the discipline in which you are writing, and where, or by whom, your work will be published or read.
When in doubt, ask your professor if there is a particular style that he/she would like you to use.
Where can I find more information on how to cite a specific type of source in a particular style?
The library has style manuals in print and online for several commonly used styles such as American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA) and Chicago. In addition, there are several excellent citation style guides on the web. (See below)
For examples of APA and MLA and Chicago Manual of Style, visit Purdue's OWL (Online Writing Lab) site.
Frank, H. (2011). Wolves, Dogs, Rearing and Reinforcement: Complex Interactions Underlying Species Differences in Training and Problem-Solving Performance. Behavior Genetics , 41 (6), 830-839.
- Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association Print manual for the APA style, available in the Sciences and Rockefeller libraries.
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab Well-organized, easy-to-follow guide, with numerous examples.
- APA Style American Psychological Association website for the APA Style. Provides tutorials, answers to frequently asked questions, and more.
Frank, H. 2011. "Wolves, Dogs, Rearing and Reinforcement: Complex Interactions Underlying Species Differences in Training and Problem-Solving Performance." Behavior Genetics 41 (6):830-839.
- The Chicago Manual of Style Older (15th edition) print manual, available at the Sciences, Rockefeller and Orwig libraries.
- The Chicago Manual of Style Online Current (16th) edition of the Chicago Manual of Style, and answers to frequently asked questions. Off-campus use requires Brown username and password.
Frank, H. "Wolves, Dogs, Rearing and Reinforcement: Complex Interactions Underlying Species Differences in Training and Problem-Solving Performance." Behavior Genetics 41.6 (2011): 830-39. Print.
- MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing Print manual for the MLA style. Available in the Rockefeller Library.
- MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers Print handbook for the MLA. Available in the Rockefeller Library.

Source: Gabriel, R. A. (2001). Gods of Our Fathers: The Memory of Egypt in Judaism & Christianity . Westport, CT, USA: Greenwood Press.

Source: Bradt, J., Potvin, N., Kesslick, A., Shim, M., Radl, D., Schriver, E., … Komarnicky-Kocher, L. T. (2015). The impact of music therapy versus music medicine on psychological outcomes and pain in cancer patients: a mixed methods study. Supportive Care in Cancer : Official Journal of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer , 23 (5), 1261–71.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Plagiarism >>
- Last Updated: May 24, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://libguides.brown.edu/citations
Brown University Library | Providence, RI 02912 | (401) 863-2165 | Contact | Comments | Library Feedback | Site Map
Library Intranet
- Utility Menu
fa3d988da6f218669ec27d6b6019a0cd
A publication of the harvard college writing program.
Harvard Guide to Using Sources
- The Honor Code
- Bibliography
If you are using Chicago style footnotes or endnotes, you should include a bibliography at the end of your paper that provides complete citation information for all of the sources you cite in your paper. Bibliography entries are formatted differently from notes. For bibliography entries, you list the sources alphabetically by last name, so you will list the last name of the author or creator first in each entry. You should single-space within a bibliography entry and double-space between them. When an entry goes longer than one line, use a hanging indent of .5 inches for subsequent lines. Here’s a link to a sample bibliography that shows layout and spacing . You can find a sample of note format here .
Complete note vs. shortened note
Here’s an example of a complete note and a shortened version of a note for a book:
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), 27-35.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated , 27-35.
Note vs. Bibliography entry
The bibliography entry that corresponds with each note is very similar to the longer version of the note, except that the author’s last and first name are reversed in the bibliography entry. To see differences between note and bibliography entries for different types of sources, check this section of the Chicago Manual of Style .
For Liquidated , the bibliography entry would look like this:
Ho, Karen, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009.
Citing a source with two or three authors
If you are citing a source with two or three authors, list their names in your note in the order they appear in the original source. In the bibliography, invert only the name of the first author and use “and” before the last named author.
1. Melissa Borja and Jacob Gibson, “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics: The Case of Evangelical Responses to Southeast Asian Refugees,” The Review of Faith & International Affairs 17, no. 3 (2019): 80-81, https://doi.org/10.1080/15570274.2019.1643983 .
Shortened note:
1. Borja and Gibson, “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics,” 80-81.
Bibliography:
Borja, Melissa, and Jacob Gibson. “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics: The Case of Evangelical Responses to Southeast Asian Refugees.” The Review of Faith & International Affairs 17. no. 3 (2019): 80–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/15570274.2019.1643983 .
Citing a source with more than three authors
If you are citing a source with more than three authors, include all of them in the bibliography, but only include the first one in the note, followed by et al. ( et al. is the shortened form of the Latin et alia , which means “and others”).
1. Justine M. Nagurney, et al., “Risk Factors for Disability After Emergency Department Discharge in Older Adults,” Academic Emergency Medicine 27, no. 12 (2020): 1271.
Short version of note:
1. Justine M. Nagurney, et al., “Risk Factors for Disability,” 1271.
Nagurney, Justine M., Ling Han, Linda Leo‐Summers, Heather G. Allore, Thomas M. Gill, and Ula Hwang. “Risk Factors for Disability After Emergency Department Discharge in Older Adults.” Academic Emergency Medicine 27, no. 12 (2020): 1270–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.14088 .
Citing a book consulted online
If you are citing a book you consulted online, you should include a URL, DOI, or the name of the database where you found the book.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), 27-35, https://doi-org.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/10.1215/9780822391371 .
Bibliography entry:
Ho, Karen. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009. https://doi-org.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/10.1215/9780822391371 .
Citing an e-book consulted outside of a database
If you are citing an e-book that you accessed outside of a database, you should indicate the format. If you read the book in a format without fixed page numbers (like Kindle, for example), you should not include the page numbers that you saw as you read. Instead, include chapter or section numbers, if possible.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), chap. 2, Kindle.
Ho, Karen. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009. Kindle.
- Citation Management Tools
- In-Text Citations
- Examples of Commonly Cited Sources
- Frequently Asked Questions about Citing Sources in Chicago Format
- Sample Bibliography
PDFs for This Section
- Citing Sources
- Online Library and Citation Tools
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Published on 1 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 7 November 2022.
In Harvard style , the bibliography or reference list provides full references for the sources you used in your writing.
- A reference list consists of entries corresponding to your in-text citations .
- A bibliography sometimes also lists sources that you consulted for background research, but did not cite in your text.
The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. If in doubt about which to include, check with your instructor or department.
The information you include in a reference varies depending on the type of source, but it usually includes the author, date, and title of the work, followed by details of where it was published. You can automatically generate accurate references using our free reference generator:
Harvard Reference Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Formatting a harvard style bibliography, harvard reference examples, referencing sources with multiple authors, referencing sources with missing information, frequently asked questions about harvard bibliographies.
Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading ‘Reference list’ or ‘Bibliography’ appears at the top.
Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used:

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Reference list or bibliography entries always start with the author’s last name and initial, the publication date and the title of the source. The other information required varies depending on the source type. Formats and examples for the most common source types are given below.
- Entire book
- Book chapter
- Translated book
- Edition of a book
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . City: Publisher. |
| Example | Coetzee, J. M. (2000) . London: Vintage. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Chapter title’, in Editor name (ed(s).) . City: Publisher, pp. page range. |
| Example | Greenblatt, S. (2010) ‘The traces of Shakespeare’s life’, in De Grazia, M. and Wells, S. (eds.) . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–14. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Translated from the [language] by ranslator name. City: Publisher. |
| Example | Saramago, J. (1997) . Translated from the Portuguese by G. Gontiero. London: Vintage. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Edition. City: Publisher. |
| Example | Danielson, D. (ed.) (1999) . 2nd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| Notes |
Journal articles
- Print journal
- Online-only journal with DOI
- Online-only journal without DOI
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), pp. page range. |
| Example | Maceachen, D. B. (1950) ‘Wilkie Collins and British law’, , 5(2), pp. 121–139. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), page range. DOI. |
| Example | Adamson, P. (2019) ‘American history at the foreign office: Exporting the silent epic Western’, , 31(2), pp. 32–59. doi:10.2979/filmhistory.31.2.02. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), pagerange. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Theroux, A. (1990) ‘Henry James’s Boston’, , 20(2), pp. 158–165. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20153016 (Accessed: 13 February 2020). |
| Notes |
- General web page
- Online article or blog
- Social media post
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Google (2019) . Available at: https://policies.google.com/terms?hl=en-US (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Rakich, N. (2020) ‘How does Biden stack up to past Democratic nominees?’, , 28 April. Available at: https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-does-biden-stack-up-to-past-democratic-nominees/ (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. [username] (Year) or text [Website name] Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Dorsey, J. [@jack] (2018) We’re committing Twitter to help increase the collective health, openness, and civility of public conversation … [Twitter] 1 March. Available at: https://twitter.com/jack/status/969234275420655616 (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) [Medium]. Institution, City or Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Bosch, H. (1482) [Triptych]. Groeningemuseum, Bruges. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Vox (2020) . 10 April. Available at: https://youtu.be/BE-cA4UK07c (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
Newspapers and magazines
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , date, p. page number. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Butler, S. (2020) ‘Women’s fashion manufacturer to make reusable gowns for NHS’, , 28 April. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/society/2020/apr/28/womens-fashion-manufacturer-to-make-reusable-gowns-for-nhs (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue) or (Month) or (Season), pp. page range. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Newman, J. (2020) ‘For autistic youths entering adulthood, a new world of challenges awaits’, , (May), pp. 20–24. |
| Notes |
When a source has up to three authors, list all of them in the order their names appear on the source. If there are four or more, give only the first name followed by ‘ et al. ’:
| Number of authors | Reference example |
|---|---|
| 1 author | Davis, V. (2019) … |
| 2 authors | Davis, V. and Barrett, M. (2019) … |
| 3 authors | Davis, V., Barrett, M. and McLachlan, F. (2019) … |
| 4+ authors | Davis, V. (2019) … |
Sometimes a source won’t list all the information you need for your reference. Here’s what to do when you don’t know the publication date or author of a source.
Some online sources, as well as historical documents, may lack a clear publication date. In these cases, you can replace the date in the reference list entry with the words ‘no date’. With online sources, you still include an access date at the end:
When a source doesn’t list an author, you can often list a corporate source as an author instead, as with ‘Scribbr’ in the above example. When that’s not possible, begin the entry with the title instead of the author:
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a difference in meaning:
- A reference list only includes sources cited in the text – every entry corresponds to an in-text citation .
- A bibliography also includes other sources which were consulted during the research but not cited.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
| In-text citation | Reference list | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | (Smith, 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
| 2 authors | (Smith and Jones, 2014) | Smith, T. and Jones, F. (2014) … |
| 3 authors | (Smith, Jones and Davies, 2014) | Smith, T., Jones, F. and Davies, S. (2014) … |
| 4+ authors | (Smith , 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
In Harvard style referencing , to distinguish between two sources by the same author that were published in the same year, you add a different letter after the year for each source:
- (Smith, 2019a)
- (Smith, 2019b)
Add ‘a’ to the first one you cite, ‘b’ to the second, and so on. Do the same in your bibliography or reference list .
To create a hanging indent for your bibliography or reference list :
- Highlight all the entries
- Click on the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the ‘Paragraph’ tab in the top menu.
- In the pop-up window, under ‘Special’ in the ‘Indentation’ section, use the drop-down menu to select ‘Hanging’.
- Then close the window with ‘OK’.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, referencing books in harvard style | templates & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


What is a Bibliographic Citation? Examples & Best Practices
- Posted on May 26, 2023
Whenever you dip your toes into the research world, one term you will likely encounter is “citation.” The term is familiar as every research work needs to contain a bibliography with a list of the sources consulted during the research process. You also have to ensure that the sources you include are appropriately cited. This is where bibliographic citation comes into the picture.
But what is a bibliographic citation? And how can you ensure that you follow the best practices when citing your sources? Read on to explore the definition, examples, and best practices of bibliographic citations.
What is a Bibliographic Citation?
A bibliographic citation is a reference to a book, article, web page, or other published item that provides the necessary information for readers to locate and retrieve that source. It includes the following information:
- Author’s last name
- Date of publication
- Page numbers of your sources
- Online sources
When writing a research paper, it is important to cite sources and paraphrase to avoid plagiarism . There are different source types that require other citation formats, such as journal articles, magazine articles, online articles, electronic sources, conference proceedings, and book reviews.
You should include the author’s last name and the publication year in parentheses for in-text citations. If you cite multiple sources, list them alphabetically by the author’s last name.
For reference entries, the format will vary depending on the source type. For example, a journal article citation should include the author’s last name and initials, the publication year, the article title, the journal title, the volume number, and the page numbers.
An online source citation should include the author’s last name and initials, the publication date, the article title, the website name, the URL or HTML, and the date you accessed the source.
During citation, it is essential to provide detailed information for each source you cite to help readers locate the source. You should also ensure your research paper is accurate and credible for easy organizing.
When writing quoted information, knowing the difference between summarizing and paraphrasing is vital. If you use direct wording without changing them, it could lead to high plagiarism scores.
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a collection of specific notes on a source. The bibliographies include two parts: the citation and the annotation. The citation provides basic information about the source, such as the author’s name(s), publication date, title of work, and publisher.
At the same time, annotations are brief summaries or evaluations describing how valuable each information source was for your research project.
For an annotated bibliography, in-text citations should be included within parentheses after any direct quote or paraphrase from another author’s work (basic format).
You can also create a reference list with all works cited at the end of the paper. It is essential to list the citations alphabetically by last name and first initial followed by year publication information enclosed in parentheses (Publication Manual).
- Last Name, First Initial. (Year Published). Title of Book/Article/Journal/Magazine/Newspaper/etc., Publisher/City Where Published.
- Doe JF Jr., Smith AB III. (2019) Marketing strategies for small businesses: A case study approach. Wiley & Sons Inc, New York City.
Bibliographies can be an incredibly helpful tool when conducting research or writing papers. They provide detailed information about sources used in your work, which can ensure you’re citing all relevant materials correctly.
What are Endnotes?
Endnotes citation provide additional information or clarification on a specific point within the text. You can place them at the end of a page, so readers can easily locate them without disrupting the writing’s continuity.
Unlike in-text citations, which use parentheses and can be found directly after the quoted or paraphrased material, endnotes utilize superscript numbers that correspond with their respective entries in an organized reference list at the conclusion of your thesis.
To properly format an endnote, include essential details such as the author’s name, publication date, title, and publisher, separated by commas.
3 Examples of Bibliographic Citations
There are different formats for bibliographic citations, depending on the source type. Here are three examples of bibliographic citations:
1. Book Citation
Here is an American Psychological Association (APA) style book citation:
- Author Last Name, Author First Name. (Publication Year) Title. Publisher’s City: Publisher. Page numbers
In this citation, the author’s last name comes first, followed by their first name. The publication year is enclosed in parentheses, followed by the book’s title, the publisher’s city, the publisher, and the page numbers.
For example, Smith, John. (2010) The Great Gatsby. New York: Scribner. 167-250.2. Journal article citation
It is essential to consider if the book has more than one writer, as this can change the formatting of the above citation. For instance, you have to write all the writers’ names in the same format, Last Name, First Name.
2. Journal Article Citation
Here is an APA-style journal article citation:
- Author Last Name, Author First Name. (Publication Date—could be more than a year) “Article Title.”Publication Title, Vol. #. (Issue #), Page numbers
When citing a journal article, you should include the author’s last name and first name, the publication date, the article title, the publication title, the volume and issue numbers, and the page numbers. You can also input a doi if the publisher provides one.
For example, Johnson, Emily. (2018) “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health.” Psychology Today, 35(4), 12-23.
3. Website Citation
Here is an American Psychological Association (APA-style) journal article citation:
- Author. (Date of Internet Publication—could be more than a year) “Document Title.” Title of Publication. Retrieved on: Date from Full Web Address, starting with http://
A website citation should include the author’s name, date of internet publication, document title, title of publication, and the full web address.
For example, Smith, Mark. (2020) “The Benefits of Meditation.” Healthline. Retrieved on August 15, 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/12-benefits-of-meditation . Note that the data retrieved should correspond with the precise date you visited the website for research.
You can also use different bibliographic citations to cite the same information. Be keen on the changes, as they can be slightly confusing.
Best Practices for Bibliographic Citations
Incorporating bibliographic citations effectively is crucial in any research paper or article. Follow these best practices to ensure accuracy and consistency:
- Choose the appropriate citation style based on your field (e.g., humanities, social sciences).
- Use quotation marks for direct quotes and italics for titles of longer works.
- Include parenthetical citations with relevant information, such as the author’s last name, publication date, and page number.
- List all sources alphabetically by the author’s last name on a separate reference page.
- Avoid unnecessary abbreviations and maintain consistent formatting throughout your work.
To better understand the citation rules, it is ideal to understand the different exemplary bibliographic citations such as American Psychological Association (APA 7th edition), Chicago, or Modern Language Association (MLA 8th edition). The styles have specific formatting requirements for different types of sources of information like articles and web pages.
For more guidance on citing different sources , refer to this comprehensive citation guide on how to use citations with various styles like APA, MLA style, and the Chicago Manual of Style:
Every research individual can ask, “What is a bibliographic citation?” Bibliographic citations are an essential part of any research paper or publication. They provide detailed information about the sources used in the work and allow readers to locate and verify the information cited.
Annotated bibliographies and endnotes are also valuable tools for organizing and presenting sources. It is essential to follow best practices, including all necessary information, formatting correctly, and citing multiple sources properly, to ensure your work is credible and reliable.
If you need assistance with creating accurate bibliographic citations or other aspects of your marketing materials or publications, visit our website today !
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

Essential Comma Rules for Business Emails
- Posted on June 7, 2024

How to Write Polished, Professional Emails With AI
- Posted on May 30, 2024

A Safer Learning Environment: The Impact of AI Detection on School Security
- Posted on May 17, 2024

Rethinking Academic Integrity Policies in the AI Era
- Posted on May 10, 2024 May 10, 2024

Jargon Phrases to Avoid in Business Writing
- Posted on May 3, 2024 May 3, 2024

Comparing Two Documents for Plagiarism: Everything You Need to Know
- Posted on April 26, 2024 April 26, 2024

Mastering Tone in Email Communication: A Guide to Professional Correspondence
- Posted on April 17, 2024

Mastering End-of-Sentence Punctuation: Periods, Question Marks, Exclamation Points, and More
- Posted on April 12, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Directories
- What are citations and why should I use them?
- When should I use a citation?
- Why are there so many citation styles?
- Which citation style should I use?
- Chicago Notes Style
- Chicago Author-Date Style
- AMA Style (medicine)
- Bluebook (law)
- Additional Citation Styles
- Built-in Citation Tools
- Quick Citation Generators
- Citation Management Software
- Start Your Research
- Research Guides
- University of Washington Libraries
- Library Guides
- UW Libraries
- Citing Sources
Citing Sources: What are citations and why should I use them?
What is a citation.
Citations are a way of giving credit when certain material in your work came from another source. It also gives your readers the information necessary to find that source again-- it provides an important roadmap to your research process. Whenever you use sources such as books, journals or websites in your research, you must give credit to the original author by citing the source.
Why do researchers cite?
Scholarship is a conversation and scholars use citations not only to give credit to original creators and thinkers, but also to add strength and authority to their own work. By citing their sources, scholars are placing their work in a specific context to show where they “fit” within the larger conversation. Citations are also a great way to leave a trail intended to help others who may want to explore the conversation or use the sources in their own work.
In short, citations
(1) give credit
(2) add strength and authority to your work
(3) place your work in a specific context
(4) leave a trail for other scholars
"Good citations should reveal your sources, not conceal them. They should honeslty reflect the research you conducted." (Lipson 4)
Lipson, Charles. "Why Cite?" Cite Right: A Quick Guide to Citation Styles--MLA, APA, Chicago, the Sciences, Professions, and More . Chicago: U of Chicago, 2006. Print.
What does a citation look like?
Different subject disciplines call for citation information to be written in very specific order, capitalization, and punctuation. There are therefore many different style formats. Three popular citation formats are MLA Style (for humanities articles) and APA or Chicago (for social sciences articles).
MLA style (print journal article):
Whisenant, Warren A. "How Women Have Fared as Interscholastic Athletic Administrators Since the Passage of Title IX." Sex Roles Vol. 49.3 (2003): 179-182.
APA style (print journal article):
Whisenant, W. A. (2003) How Women Have Fared as Interscholastic Athletic Administrators Since the Passage of Title IX. Sex Roles , 49 (3), 179-182.
Chicago style (print journal article):
Whisenant, Warren A. "How Women Have Fared as Interscholastic Athletic Administrators Since the Passage of Title IX." Sex Roles 49, no. 3 (2003): 179-182.
No matter which style you use, all citations require the same basic information:
- Author or Creator
- Container (e.g., Journal or magazine, website, edited book)
- Date of creation or publication
- Publisher
You are most likely to have easy access to all of your citation information when you find it in the first place. Take note of this information up front, and it will be much easier to cite it effectively later.
- << Previous: Basics of Citing
- Next: When should I use a citation? >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 12:48 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uw.edu/research/citations

Citation Guide
- What is a Citation?
- Citation Generator
- Chicago/Turabian Style
- Paraphrasing and Quoting
- Examples of Plagiarism
What is a Bibliography?
What is an annotated bibliography, introduction to the annotated bibliography.
- Writing Center
- Writer's Reference Center
- Helpful Tutorials
- the authors' names
- the titles of the works
- the names and locations of the companies that published your copies of the sources
- the dates your copies were published
- the page numbers of your sources (if they are part of multi-source volumes)
Ok, so what's an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is the same as a bibliography with one important difference: in an annotated bibliography, the bibliographic information is followed by a brief description of the content, quality, and usefulness of the source. For more, see the section at the bottom of this page.
What are Footnotes?
Footnotes are notes placed at the bottom of a page. They cite references or comment on a designated part of the text above it. For example, say you want to add an interesting comment to a sentence you have written, but the comment is not directly related to the argument of your paragraph. In this case, you could add the symbol for a footnote. Then, at the bottom of the page you could reprint the symbol and insert your comment. Here is an example:
This is an illustration of a footnote. 1 The number “1” at the end of the previous sentence corresponds with the note below. See how it fits in the body of the text? 1 At the bottom of the page you can insert your comments about the sentence preceding the footnote.
When your reader comes across the footnote in the main text of your paper, he or she could look down at your comments right away, or else continue reading the paragraph and read your comments at the end. Because this makes it convenient for your reader, most citation styles require that you use either footnotes or endnotes in your paper. Some, however, allow you to make parenthetical references (author, date) in the body of your work.
Footnotes are not just for interesting comments, however. Sometimes they simply refer to relevant sources -- they let your reader know where certain material came from, or where they can look for other sources on the subject. To decide whether you should cite your sources in footnotes or in the body of your paper, you should ask your instructor or see our section on citation styles.
Where does the little footnote mark go?
Whenever possible, put the footnote at the end of a sentence, immediately following the period or whatever punctuation mark completes that sentence. Skip two spaces after the footnote before you begin the next sentence. If you must include the footnote in the middle of a sentence for the sake of clarity, or because the sentence has more than one footnote (try to avoid this!), try to put it at the end of the most relevant phrase, after a comma or other punctuation mark. Otherwise, put it right at the end of the most relevant word. If the footnote is not at the end of a sentence, skip only one space after it.
What's the difference between Footnotes and Endnotes?
The only real difference is placement -- footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page, while endnotes all appear at the end of your document. If you want your reader to read your notes right away, footnotes are more likely to get your reader's attention. Endnotes, on the other hand, are less intrusive and will not interrupt the flow of your paper.
If I cite sources in the Footnotes (or Endnotes), how's that different from a Bibliography?
Sometimes you may be asked to include these -- especially if you have used a parenthetical style of citation. A "works cited" page is a list of all the works from which you have borrowed material. Your reader may find this more convenient than footnotes or endnotes because he or she will not have to wade through all of the comments and other information in order to see the sources from which you drew your material. A "works consulted" page is a complement to a "works cited" page, listing all of the works you used, whether they were useful or not.
Isn't a "works consulted" page the same as a "bibliography," then?
Well, yes. The title is different because "works consulted" pages are meant to complement "works cited" pages, and bibliographies may list other relevant sources in addition to those mentioned in footnotes or endnotes. Choosing to title your bibliography "Works Consulted" or "Selected Bibliography" may help specify the relevance of the sources listed.
This information has been freely provided by plagiarism.org and can be reproduced without the need to obtain any further permission as long as the URL of the original article/information is cited.
How Do I Cite Sources? (n.d.) Retrieved October 19, 2009, from http://www.plagiarism.org/plag_article_how_do_i_cite_sources.html
The Importance of an Annotated Bibliography
An Annotated Bibliography is a collection of annotated citations. These annotations contain your executive notes on a source. Use the annotated bibliography to help remind you of later of the important parts of an article or book. Putting the effort into making good notes will pay dividends when it comes to writing a paper!
Good Summary
Being an executive summary, the annotated citation should be fairly brief, usually no more than one page, double spaced.
- Focus on summarizing the source in your own words.
- Avoid direct quotations from the source, at least those longer than a few words. However, if you do quote, remember to use quotation marks. You don't want to forget later on what is your own summary and what is a direct quotation!
- If an author uses a particular term or phrase that is important to the article, use that phrase within quotation marks. Remember that whenever you quote, you must explain the meaning and context of the quoted word or text.
Introduction and example
When using BiBTeX , the bibliography style is set and the bibliography file is imported with the following two commands:
where bibfile is the name of the bibliography .bib file, without the extension, and stylename is one of values shown in the table below .
Here is an example that you can open in Overleaf—the .bib file is created for you:
Open in Overleaf (a suitable .bib file is generated)
Table of stylename values
| stylename | output |
|---|---|
Further reading
For more information see:
- Bibliography management with bibtex
- BibTeX documentation at CTAN web site
- tocbind package documentation
- Bibliography management with natbib
- Bibliography management with biblatex
- Table of contents
- Management in a large project
- Multi-file LaTeX projects
- Documentation Home
- Learn LaTeX in 30 minutes
Overleaf guides
- Creating a document in Overleaf
- Uploading a project
- Copying a project
- Creating a project from a template
- Using the Overleaf project menu
- Including images in Overleaf
- Exporting your work from Overleaf
- Working offline in Overleaf
- Using Track Changes in Overleaf
- Using bibliographies in Overleaf
- Sharing your work with others
- Using the History feature
- Debugging Compilation timeout errors
- How-to guides
- Guide to Overleaf’s premium features
LaTeX Basics
- Creating your first LaTeX document
- Choosing a LaTeX Compiler
- Paragraphs and new lines
- Bold, italics and underlining
Mathematics
- Mathematical expressions
- Subscripts and superscripts
- Brackets and Parentheses
- Fractions and Binomials
- Aligning equations
- Spacing in math mode
- Integrals, sums and limits
- Display style in math mode
- List of Greek letters and math symbols
- Mathematical fonts
- Using the Symbol Palette in Overleaf
Figures and tables
- Inserting Images
- Positioning Images and Tables
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- Drawing Diagrams Directly in LaTeX
- TikZ package
References and Citations
- Natbib bibliography styles
- Natbib citation styles
- Biblatex bibliography styles
- Biblatex citation styles
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using polyglossia and fontspec
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using babel and fontspec
- International language support
- Quotations and quotation marks
Document structure
- Sections and chapters
- Cross referencing sections, equations and floats
- Nomenclatures
- Lengths in L a T e X
- Headers and footers
- Page numbering
- Paragraph formatting
- Line breaks and blank spaces
- Text alignment
- Page size and margins
- Single sided and double sided documents
- Multiple columns
- Code listing
- Code Highlighting with minted
- Using colours in LaTeX
- Margin notes
- Font sizes, families, and styles
- Font typefaces
- Supporting modern fonts with X Ǝ L a T e X
Presentations
- Environments
Field specific
- Theorems and proofs
- Chemistry formulae
- Feynman diagrams
- Molecular orbital diagrams
- Chess notation
- Knitting patterns
- CircuiTikz package
- Pgfplots package
- Typesetting exams in LaTeX
- Attribute Value Matrices
Class files
- Understanding packages and class files
- List of packages and class files
- Writing your own package
- Writing your own class

Advanced TeX/LaTeX
- In-depth technical articles on TeX/LaTeX
Get in touch
Have you checked our knowledge base ?
Message sent! Our team will review it and reply by email.
Email:
- Essay Check
- Chicago Style
APA Citation Examples
- MLA Citation Examples
- Chicago Style Citation Examples
- Writing Tips
- Plagiarism Guide
- Grammar Rules
- Student Life
- Create Account
- powered by Chegg
Cite in apa automatically with bibme, create apa citations for free.
Website Book Journal Other
←Back to All Citation Guides
APA (American Psychological Association) style is most frequently used within the social sciences, in order to cite various sources. This APA Citation Guide provides the general format for in-text citations and the reference page. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th ed.
In APA style, two citations are used to cite a source:
- A short citation used in the text (called the in-text citation ).
- A full citation (called the reference ) in the reference list at the end of a paper.
The in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The in-text citation lets the reader know that the information came from the cited source. The reference list entry provides complete details of a source and is shown at the end of a document.
In order to properly cite a source in APA style, you must have both citation types in your paper. Every in-text citation has a reference list entry. Every reference list entry has at least one (maybe more) corresponding in-text citation.
In-text citations
The basic elements needed for an in-text citation are the author’s surname and the publication year . Sometimes, page numbers are also included, especially when quotes are mentioned in the text. In-text citations are mentioned in the text in two ways: as a narrative citation or a parenthetical citation.
Narrative citations are incorporated into the text and act as a part of the sentence. Usually, narrative citations use the author’s name in the text and the publication year is enclosed in parenthesis after the name. An example of a narrative citation for one author is given below:
Barbarin (2013) examined socioemotional learning in African boys.
Parenthetical
Parenthetical citations add the author’s name and the publication year at the end of the sentence in parenthesis. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
Inhibition and working memory in young children were studied extensively (Aase, 2014).
When are page numbers are included?
Page numbers are referred to within in-text citations when quotes are used. Examples of both narrative citations and parenthetical citations are given below.
Ahmed (2004, p. 44)
Ahmed (2004, pp. 53–56)
Parenthetical:
(Ahmed, 2004, p. 44)
(Ahmed, 2004, pp. 53–56)
Examples of in-text citations
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for a different number of authors:
Use the surname of the author in in-text citations. Use a comma before the publication year in parenthetical citations.
Narrative:
Bucher (2018)
Parenthetical:
(Bucher, 2018)
Two authors
Separate the author surnames with an “and” in narrative citations. Use an ampersand symbol (&) in parenthetical citations.
Popescu and Pennacchiotti (2010)
(Popescu & Pennacchiotti, 2010)
Three or more authors
Use the first author surname name followed by et al.
van Dijck et al. (2018)
(van Dijck et al., 2018)
Group author
Treat the group author similar to how you would treat author names.
Auger Collaboration (2003)
(Auger Collaboration, 2018)
If there is no author for the source, use the source title in place of the author’s name. In general, sources with no author appear as parenthetical citations.
When you add such in-text citations, you will either italicize the text or place it in quotations. If the source title is italicized in the reference list entry, italicize the title in the in-text citation. If the title is not italicized, place it in quotation marks.
Parenthetical, book:
( Nothing here , 1997)
Parenthetical, journal article:
(“Examination of parrotfish impact on coral reefs,” 2018)
Reference list entries
Reference list entries are also called full citations. There are four main details that most reference list entries have:
- The author field.
- The publication year.
- The title of the work ( italicized or in “quotation marks”).
- The source from where the reference can be obtained (e.g., URL, DOI, etc.).
Depending on the source type, you will also need additional details like volume number, publication title, contributors, medium, etc.
Examples of reference list entries
Below are a few examples of different types of reference entries along with their templates. The examples given are for one author. Note that “F” and “M” in the templates denote the first and the middle initials of an author’s name.
The title of the book is set in italics and sentence case.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the book . Publisher.
Ahmed, S. (2014). The cultural politics of emotion . Edinburgh University Press.
Journal article
The title of the article is in sentence case. The first word of a subtitle is capitalized. The journal title and the volume number are set in italics. If an article has a DOI it should always be included. Use “https://doi.org/” before the DOI. If there is no DOI for an online journal, include the URL instead. Do not use a period after the DOI or URL.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. URL or DOI
Collins, R. (2004). Rituals of solidarity and security in the wake of terrorist attack. Sociological Theory, 22 (1), 53–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9558.2004.00204.x
Newspaper or magazine article
Newspaper and magazine articles take the same style. The title of the article is in plain text and sentence case; the title of the newspaper or the magazine is set in italics. Follow the format given in the template and example for setting the date, month, and year.
Surname, F. M. (Date of publication). Title of the article. Title of the Newspaper or Magazine . URL
TNN. (2021, July 18). Parents have a habit of comparing kids to others but you don’t need to. The Times of India . https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com//home/sunday-times/parents-have-a-habit-of-comparing-kids-to-others-but-you-dont-need-to/articleshow/84507857.cms
The webpage title is in plain text, while the Website name is set in italics. Follow the format given in the template and example for setting the date, month, year, and URL.
Author or Organization Name. (Year, Month Day of Publication ). Webpage title. Title of the Website. URL
Lamberth, H. (2021, August 12). Binge drinking is problem drinking: How to get back in control. PSYCOM . https://www.psycom.net/binge-drinking-problem-drinking
YouTube video
The video title is set in sentence case and italicized. The first word after a colon is capitalized. The word “Video” is enclosed in brackets after the video title. This is followed followed by the word “YouTube.” Finally, the link is given. Note that a period is not given after the URL.
Uploader’s name, F. (Year, Month Day Published). Video title [Video]. YouTube. URL
Ananta, P. (2021, February 21). APJ Abdul Kalam inspirational quotes [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pjfL51RFL2k
Reference entries for different number of authors
The number of authors in the source decides how the author name(s) will be set in the references list. Here, you will see many journal references with different numbers of authors.
List the author name followed by the publication year.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range.
Spitka, T. (2017). Mediating among mediators: Building a consensus in multilateral interventions. International Negotiation, 23 , 1–30.
Separate the author names by an ampersand. Use a comma between the first author’s initial and the ampersand symbol.
Author Surname, F. M., & Author Surname, F. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
Bernstein, B., & Solomon, J. (1999). Pedagogy, identity and the construction of a theory of symbolic control: Basil Bernstein questioned by Joseph Solomon. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 20 (2), 265–279. https://doi:10.1080/01425699995443
When you add two organizations in the author field, do not use a comma before the ampersand.
Organization 1 & Organization 2. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
American Psychological Association & American Psychological Society. (2020). Psychology of children. Journal of Child Psychology, 34 (23), 1–12.
3–20 authors
List all author names. Do not forget to insert an “ampersand” before the last author. The example given below is for three authors.
Author Surname, F. M., Author Surname, F. M., & Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
Pyysiäinen, J., Halpin, D., & Guilfoyle, A. (2017). Neoliberal governance and ‘responsibilization’ of agents: Reassessing the mechanisms of responsibility-shift in neoliberal discursive environments. Distinktion: Journal of Social Theory, 18 (2), 215–235. https://doi:10.1080/1600910X.2017.1331858
More than 20 authors
List the names of the first 19 authors followed by an ellipsis. Add the final author name after the ellipsis but without the ampersand symbol before the last author name.
Author Surname1, F. M., Author Surname2, F. M., Author Surname3, F. M., Author Surname4, F. M., Author Surname5, F. M., Author Surname6, F. M., Author Surname7, F. M., Author Surname8, F. M., Author Surname9, F. M., Author Surname10, F. M., Author Surname11, F. M., Author Surname12, F. M., Author Surname13, F. M., Author Surname14, F. M., Author Surname15, F. M., Author Surname16, F. M., Author Surname17, F. M., Author Surname18, F. M., Author Surname19, F. M,¼ Last Author name, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
Fox, J., Harper, D., Bird, A., Kindler, F. A., Feng, H.-G., Seng, A. L., Sevel, K., Ed, E., Nell, A., Ten, T., Elin, K. J., Thomas, A., Thendy, S., Fall, W., Fint, E., Gurdy, A. K., Dondy, D., Egert, E., Nanda, A. L., ¼ Long, G. (2015). Pedagogising knowledge: Bernstein’s theory of the pedagogic device. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 23 (4), 571–582.
For additional information on APA format, select from one of the source types below. For help creating APA citations, check out the BibMe APA citation generator.
Source Types:
- How to cite a Book in APA
- How to cite a Magazine in APA
- How to cite a Newspaper in APA
- How to cite a Website in APA
- How to cite a Journal Article in APA
- How to cite a Film in APA
- How to cite an Interview in APA
- How to cite a Lecture in APA
- How to cite a TV Show / Radio Broadcast in APA
- How to cite an Encyclopedia in APA
- How to cite a Photograph in APA
- APA 7 Updates
APA Format:
- In-Text Citation Basics
- Reference Page
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
As per Section 8.17 from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , for any work that has three or more authors, the name of the first author and “et al.” should be used as in-text citation. The Latin phrase “et al” means “and others” and is used to reduce the citation length.
Example In-Text Citation Entry:
No stretch of reason can categorize cultural appropriation as imaginary (Rahim et al., 2020).
Sometimes, the same set of initial authors and the same publication year appear in a paper. In such rare circumstances, as per Section 8.18 of the APA manual, write out as many names as needed to differentiate between these similar references.
Example In-Text Citation Entries:
Miller, John, Reighstag et al. (2018)
Miller, John, Amudsen, et al. (2018)
As per Section 8.21 and Table 8.1 of the APA Publication Manual , a citation for a group author may be abbreviated in in-text citations. It is not compulsory to do so; however, if the group author is well known or if it appears at least thrice in the paper, then the name of the group may be abbreviated.
Parenthetical in-text citation template and example:
(Full Name of the Group [Abbreviation], year)
(National Institute of Mental Health [NIMH], 2018)
Whether it is a narrative or parenthetical in-text citation, the full name of the group should be mentioned in the first instance, along with the abbreviation.
Narrative in-text citation examples:
The American Psychological Association (APA, 2017) argues that… (first instance)
As per the APA (2017), it is standard practice that… (subsequent instances)
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / Creating an MLA Bibliography
Creating an MLA Bibliography
If you write a research paper in MLA format, then you will need to include a Works Cited page according to the current 9th edition of the Modern Language Association (MLA) guidelines. Along with citing your sources within the body of your paper, you also need to include full citations of all sources at the end of your paper. The references in a bibliography are formatted in the same way as they would be in a Works Cited page. However, a bibliography refers to all works that you have consulted in your research, even if you did not use their information directly in your paper.
When you use the correct MLA bibliography format, it shows the reader what sources you consulted, makes finding your sources easier for the reader, and gives credibility to your work as a researcher and writer. This MLA sample paper will show you how the bibliography is incorporated into the rest of your paper. We also have a guide on APA reference pages , if you are following APA style in your paper.
Works cited or bibliography?
You may be wondering, what is a bibliography, and how is it different from a Works Cited page? The difference between the two is that while a bibliography refers to any source you consulted to write your research paper, a Works Cited page only includes full citations of the sources you quoted or paraphrased within your paper.
Typically, when someone says, “MLA bibliography” they really mean a Works Cited page, since the MLA format usually uses a Works Cited page instead of a bibliography.
A bibliography in MLA format may also refer to a Works Consulted page. If you used other sources that you did not directly quote or paraphrase within the paper, you will need to create a Works Consulted/Additional Resources page. A Works Consulted page starts on a separate page and follows the Works Cited page. It follows the same formatting guidelines as a Works Cited page, but you will use Works Consulted (or Additional Resources) as the title.
If you’re unsure of what to include in your citations list (works cited, works consulted, or both), ask your instructor. For the rest of this article, we will refer to this page as the MLA bibliography.
MLA bibliography formatting guidelines
These are the formatting rules you need to follow to create your bibliography according to MLA’s current edition guidelines. Your first page(s) will be your Works Cited page(s) and include the references that you directly refer to in your paper. Usually, this is all that is needed. If your instructor wants you to also include the works you consulted but did not include in your paper (more like a bibliography), then add Works Consulted or Additional Resources page for these sources.
- Your MLA Works Cited (and Works Consulted or Additional Resources pages) should begin on a separate page or pages at the end of your essay.
- Your essay should have a header on every page that includes your last name and the page number.
- The last name/page number header should be on the top right of each page with a ½ inch margin from the top of the page.
- One-inch margins.
- Title the page Works Cited (no italicization or quotation marks) unless otherwise instructed. Center the title. The top should look like this:

- Only center the Works Cited title; all citations should be left-justified.
- Double-space citations.
- Do not add an additional space between citations.
- After the first line, use a hanging indent of ½ inch on all additional lines of a citation. The hanging indent should look like this:

- Typically, this is the author’s last name, but sometimes it could be the title of the source if the author’s name is not available.

If you have a Works Consulted or Additional Resources page after your Works Cited page, format it in the same way, but with the title of Works Consulted or Additional Resources instead of Works Cited. Alternatively, your instructor may require a bibliography. If this is the case, all your sources, whether they are cited in your paper are not, are listed on the same page.
MLA citation guidelines
These are the rules you need to follow to create citations for an MLA bibliography. This section contains information on how to correctly use author names, punctuation, capitalization, fonts, page numbers, DOIs, and URLS in the citations on your MLA bibliography.
Author names
After the title Works Cited, the last name of the author of a source should be the first thing to appear on your page.
List the author’s last name followed by a comma, then the first name followed by the middle name or middle initial if applicable, without a comma separating the first and middle names. Add a period after the name.
Rowling, J.K.
Smith, Alexander McCall.
- Do not include titles such as Dr., Mrs., etc. or professional qualifications such as PhD, M.S., etc. with author names.
- Include suffixes such as Jr. or III after the author’s first name. Separate the first name and the suffix by a comma unless the suffix is a numeral. For example, to cite an author named John Smith, Jr., you would type Smith, John, Jr.
Sources with two authors
For a source with two authors, list the author names in your citation in the order they appear on the source, not alphabetically.
Type the last name of the first author listed on the source followed by a comma, then the first author’s first name followed by a comma. Then type the word “and” then list the second author’s first name and last name in the standard order. Follow the second name with a period.
Include middle names or initials and suffixes when applicable according to the guidelines for one author as listed above.
1st Author’s Last Name, First Name, and 2nd Author’s First Name Last Name.
Lutz, Lisa, and David Hayward.
Clark, Mary Higgins, and Alafair Burke.
Sources with three or more authors
For a source with three or more authors, only type the last and first name of the first author listed in the source, followed by a comma and the phrase et al., which is Latin for “and others.” Be sure to always place a period after the al in et al. but never after the et.
1st Author’s Last Name, First Name, et al.
Charaipotra, Sona, et al.
Williams, Beatriz, et al. All the Ways We Said Goodbye . HarperLuxe, 2020.
Organizations and corporations as authors
For sources with organizations or corporations listed as the author, type the name of the corporation in place of an author’s name. If the organization begins with an article like a, an, or the, it should be excluded in the Works Cited entry.
Modern Language Association of America. MLA Handbook . 2016.
*Note: If the organization is listed as both the author and the publisher, begin the citation with the title and include the organization’s name within the publisher field instead.
For a source with no author listed, simply omit the author’s name and begin the citation with the title of the source. Use the first letter of the title when considering alphabetical order in your MLA bibliography.
Capitalization
Use MLA title case when citing titles of sources.
- Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, and subordinating conjunctions should be capitalized.
- Articles, prepositions, and coordinating conjunctions should not be capitalized.
Font formatting
- Italicize the titles of larger works such as magazines and books. Also, italicize database and website names.
- Instead of italicization, use quotation marks around titles of shorter works such as poems, short stories, and articles.
- End all bibliography citations with a period.
Page numbers
Include page numbers in your full citations whenever possible. This helps the reader find the information you cited more quickly than if you just cited the entire source and lends more credibility to your argument. If you cite different pages from the same source within your paper, you should cite the entire source on your MLA bibliography instead of listing all of the page numbers you used.
When including page numbers in a citation, use the abbreviation p. to cite one page and the abbreviation pp. to cite multiple pages with a hyphen between the page numbers.
p. 25 or pp. 16-37
When citing page numbers in MLA, omit the first set of repeated digits.
pp. 365-69, not pp. 365-369
DOIs and URLs
A Digital Object Identifier (DOI) is used to locate and identify an online source. While URLs may change or web pages might be edited or updated, a DOI is permanent and therefore more useful in a source citation.
- Use a DOI (digital object identifier) whenever possible. Otherwise use a permalink or URL.
- DOIs should be formatted with “https://doi.org/” before the DOI number.
- Do not include “http://” or “https://” in your URLs.
- As either one will be the last part of your citation, place a period after the DOI or URL. (Note that this period is not part of the DOI or URL.)
Butarbutar, R, et al. “Analyzing of Puzzle Local Culture-Based in Teaching English for Young Learners.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science , vol. 343, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/343/1/012208.
Accessed dates
Since the previous 8th edition of the MLA Handbook was published, you do NOT need to list an accessed date for a stable source (e.g., online newspaper article, journal article, photograph, etc.). However, including an access date is good to include when a source does not have a publishing date, and some instructors will request that accessed dates be included for all sources.
If you do include an access date, here’s how to format it:
- Place it at the end of the citation without “http://” or “https://”.
- Write “Accessed” first, followed by the date accessed.
- The date accessed should be formatted as Day Month (abbreviated) Year.
Butarbutar, R, et al. “IOPscience.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science , IOP Publishing, 1 Oct. 2019, iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/343/1/012208/meta. Accessed 8 Oct. 2020.
Note: If you choose to list an accessed date after a DOI, the accessed date part of the citation will follow the period after the DOI and will end with a period at the end of the citation
Butarbutar, R, et al. “Analyzing of Puzzle Local Culture-Based in Teaching English for Young Learners.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science , vol. 343, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/343/1/012208. Accessed 8 Oct. 2020.
MLA 8 th edition vs MLA 9 th edition
The 9 th edition of the MLA handbook re-introduces guidelines regarding paper formatting (which were not present in the 8 th edition). The guidance in the 9 th addition is consistent with the guidance in previous editions and expands on the formatting of tables, figures/illustrations, and lists. The 9 th edition also offers new guidance in areas like annotated bibliographies, inclusive language, and footnotes/endnotes.
Many of the differences between the 8 th edition and 9 th edition have to do with the formatting of the core elements in reference list entries. Some of the main changes include:
| DOI format: doi:10.1353/aeh.2021.0012 | DOI format: https://doi.org/10.1353/aeh.2021.0012 |
| Seasons for publications capitalized: Winter 2021 | Seasons for publications not capitalized: winter 2021 |
| Publisher format: Use “U” for University and “P” for Press in publisher names (i.e., MIT P) | Publisher format: Use “U” for University and “P” for Press in publisher names unless the word “university” is not present (in any language) (e.g., MIT Press) |
| Organization authors: full name should be used | Organization authors: if the organization has a long name, it should be shortened in the in-text citation (i.e., American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals = American Society) |
| Social media: author’s username should be used | Social media: author’s real name or account name (if available) should be used |
| URLs: include full URL | URLs: Shorten URL if longer than 3 lines (include at least the host) and always eliminate the https:// except in DOIs |
| Pseudonyms: include in parentheses | Pseudonyms: include in square brackets |
Written by Grace Turney , freelance writer and artist. Grace is a former librarian and has a Master’s degree in Library Science and Information Technology.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
Annotated Bibliography
Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An MLA bibliography is similar to the Works Cited list that you include at the end of your paper. The only difference between a Works Cited list and a bibliography is that for the former, you need to include the entries for only the sources you cited in the text, whereas for the latter you can also include the sources you consulted to write your paper but didn’t directly cite in your writing. MLA generally prefers Works Cited lists to bibliographies.
If your instructor advises you to create an MLA bibliography, follow the same guidelines you would follow for creating an MLA Works Cited list.
The bibliography list appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes if they are present.
All margins (top, bottom, left, and right) should be set at 1 inch.
Write the running head in the top right of the page at 0.5 inch from the top. Use the running head “Surname Page #.”
The font should be clear enough to read. Use Times New Roman font of size 12 points.
Entries should be double-spaced. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent lines of the entry 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Bibliographic entries are arranged alphabetically according to the first item in each entry.
Title your bibliography as “Bibliography.”
Braidotti, Rosi. The Posthuman . Polity, 2013.
Brisini, Travis. “Phytomorphizing Performance: Plant Performance in an Expanded Field.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 39, 2019, pp. 1–2.
Riccio, Thomas. “Reimagining Yup’ik and Inupiat Performance.” Northwest Theatre Review , vol. 12, no. 1, 1999, pp. 1–30.
General rules for creating an annotated bibliography
The annotation is given after the source entry and is generally about 100-150 words in length. The annotation should be indented 1 inch from the left margin to distinguish it from the hanging indent within the citation entry.
The annotation, in general, should be written as short phrases. However, you may use full sentences as well.
The annotation for each source is usually no longer than one paragraph. However, if multiple paragraphs are included, indent the second and subsequent paragraphs without any extra line space between them.
The annotation provides basic information about the source, but does not include details about the source, quotes from the author, etc. The information can be descriptive (by generally describing what the source covers) or evaluative (by evaluating the source’s usefulness to the argument in your paper).
Example annotated bibliography
The below is an example of an annotated bibliography:
Morritt, Robert D. Beringia: Archaic Migrations into North America . Cambridge Scholars Pub, 2011.
The author studies the migration of cultures from Asia to North America. The connection between the North American Athabaskan language family and Siberia is presented, together with comparisons and examinations of the implications of linguistics from anthropological, archaeological, and folklore perspectives. This book explores the origins of the earliest people in the Americas, including Siberian, Dene, and Navajo Creation myths; linguistic comparisons between Siberian Ket Navajo and Western Apache; and comparisons between indigenous groups that appear to share the same origin.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Culture
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business History
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- Ethnic Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Theory
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment
Referencing styles
Author-date citations (Harvard) Numbered notes Numbered reference citations (Vancouver) OSCOLA
Introduction
Source references are vital to academic works (both print and digital) and so it is essential that they are clear, complete, and consistently formatted. Online bibliographical material is hyperlinked to provide readers with instant access to relevant sources or additional information.
Reference styles vary greatly across disciplines. This section details the main reference styles supported by OUP (Harvard, Vancouver, and OSCOLA) and provides examples that you can follow. If you are in doubt, your OUP editorial contact will be able to advise you on the best citation system for your text.
Author-date citations (Harvard)
The author-date style is an efficient and clear method of providing citations to published sources, which appear in a reference list at the end of the chapter or book. No superscripts are used, which means that reordering of the text does not require renumbering of notes. Instead of superscript numbers, a parenthetical citation (consisting of author name and date of publication) appears in the text and leads the reader to a full entry in a reference list that appears at the end of the chapter or book.
The method works particularly well when most of your citations are to published books or journal articles. It works less well if you are citing a lot of unauthored material or untraditional sources. Unlike numbered notes, author-date citations cannot accommodate translations or commentary outside the main text, although it is possible to combine author-date citations (for bibliographic citations) with numbered notes (for explanatory text).
In-text citation
References are cited within the text by including the author’s last name and a date parenthetically. A page number can be added if needed. If the author’s name appears in the sentence containing the citation, you need only use the date. Complete bibliographical reference information is listed at the end of the chapter or text.
Up to two author names can be used in the in-text citation. When citing a work with three or more authors, use the first author’s last name plus ‘et al.’
If you cite multiple references by the same author that were published in the same year, distinguish between them by adding labels (e.g. ‘a’ and ‘b’) to the year, in both the citation and the reference list.
Structure of the reference list
The reference list appears at the end of the chapter or text in alphabetical order. The name of the first author is inverted. In science literature, initials are often used in place of author first names.
The bibliographic elements listed below are required for the most common types of reference citations. Additional elements are mentioned that may be optional or to be used in only certain instances (e.g. a page number or other locator that is required if you are quoting a precise part of a large work, but not if the reference is to the work as a whole). Consistency in application is important.
Do not use long dashes (“—") to substitute for the name of an author who is identified in the bibliography due to how that entry will be linked in digital versions. Because the entry may not appear immediately following the entry with the full name, repeat the name in full.
Examples of author-date references in British style
Authored book.
Required elements
Lastname, Firstname/initials. Year of Publication. Title of Work .
With optional elements
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname/initials Lastname. Year of Publication. Title of Work , 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher.
Chapter in an edited book
Lastname, Firstname/initials, Year of Publication. ‘Title of Chapter in an Edited Book’. In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname.
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname/initials Lastname. Year of Publication. ‘Title of Chapter in an Edited Book’. In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname, page number(s) [or alternative locator info]. 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher.
Journal article
Lastname, Firstname/initials,Year of Publication. ‘Title of Article’. Name of Journal vol. number: start page.
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname/initials Lastname. Year of Publication. ‘Title of Article’. Name of Journal vol. number (issue number) (Month or Season): start page–end page. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Magazine article
Lastname, Firstname/initials, Year of Publication. ‘Title of Article’. Day and Month of Pub. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname/initials Lastname. Year of Publication. ‘Title of Article’. Name of Magazine , Day and Month of Pub. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Required elements if a magazine article has no stated author
‘Title of Article’. Year of Publication. Name of Magazine , Month of Pub. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Website or other source
Include as much of the following as possible in your bibliographic entry: author; title or description of the content; owner/publisher; month and/or day of publication, most recent revision (or, failing that, date accessed); and URL. The year of publication should be the second element in the entry.
Some flexibility is acceptable to accommodate the wide variety of content available, particularly online.
Website names are usually set in roman type, but the names of online magazines and books are italicized (like their print counterparts).
As you write ...
Example: author–date citation with a reference list and further reading —british style.
Psychoanalytic studies, along with other literary and cultural texts, not only contribute to the new discourse of the jungle but also reflect the imperialist history that brings West Europeans and Americans into contact with the geographic jungles of India, Africa, and other parts of the world (Rogers et al. 2010, 1). This colonial context needs to be sketched here as well in order to reveal how the birth of the jungle eventually produces new constructions of sexuality in the United States. Billops (1999a) notes that the word ‘jungle’ comes from the Hindi and Marathi word jangal, meaning ‘desert’, ‘waste’, ‘forest’; as well as from the Sanskrit jangala, meaning ‘dry’, ‘dry ground’, or ‘desert’. Its first appearance in English is in 1776, with its meaning already shifted towards what might be more recognizable today: ‘Land overgrown with underwood, long grass, or tangled vegetation; also, the luxuriant and often almost impenetrable growth of vegetation covering such a tract’ (Dreft and Smithers 1978, 87). Brought into English as a result of an imperialist presence in India, ‘jungle’ is intimately related to the larger rise of Western imperialism around the world, particularly in the nineteenth century (Billops 1999b). Western powers such as Britain and France went from controlling 35 per cent of the earth’s surface in 1800 to, by 1914, ‘a grand total of roughly 85 per cent of the earth as colonies, protectorates, dependencies, dominions, and commonwealths’ (Said 1993, ch.2, ‘Colonial impacts’).
Reference list
Billops, Camille. 1999a. ‘Indo-European Loan Words’. Annals of Linguistics 21 (4): pp. 38–44.
Billops, Camille. 1999b. ‘Indo-European Vowel Shift: Evidence and Interpretation’. Annals of Linguistics 21 (4): p. 45.
Dreft, Edward, and Susan Smithers. 1978. ‘Words Working’. International Journal of American Linguistics 62 (3): pp. 227–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb25475.x.
Rogers, Jason, Millicent Eng, and Rene Woo. 2010. ‘English-Based African Creoles’. In Spreading the People: Colonizing Languages in the Raj , edited by Jason Rogers, pp. 310–330. 2nd ed. London: Verso.
Said, Eleanor. 1993. The European Dream of Africa . New York: Random House.
Further reading
Bickerton, Derek. 2008. Bastard Tongues: A Trail-Blazing Linguist Finds Clues to Our Common Humanity in the World’s Lowliest Languages . New York: Hill and Wang.
‘Evolutionary Linguistics’. 2012. Wikipedia. Updated 4 November. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolutionary_linguistics.
Mfuti, Miriam. 2001. ‘Pidgin Town’. In The Oxford Handbook of Pidgins and Creoles , edited by Alain Smet, pp. 107–112. New York: Oxford University Press.
Rambow, John. 2007. ‘Will This Demon Fit in My Carry-On?’ Bangalore Monkey blog. 21 December. http://www.bangaloremonkey. com/2007/12/will-this-demon-fit-in-my-carry-on.html.
Examples of author-date references in US style
Lastname, Firstname/initials, Year of Publication. Title of Work .
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname Lastname/initials. Year of Publication. Title of Work , 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher.
Lastname, Firstname/initials, Year of Publication. “Title of Chapter in an Edited Book.” In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname.
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname Lastname/initials. Year of Publication. “Title of Chapter in an Edited Book.” In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname, page number(s) [or alternative locator info]. 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher.
Lastname, Firstname/initials,Year of Publication. “Title of Article.” Name of Journal vol. number, start page.
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname Lastname/initials. Year of Publication. “Title of Article.” Name of Journal vol. number (issue number) (Month or Season Year): start page–end page. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Lastname, Firstname/initials, Year of Publication. “Title of Article.” Name of Magazine , Month of Pub.
Lastname, Firstname/initials, and Firstname Lastname/initials. Year of Publication. “Title of Article.” Name of Magazine , Month and Day of Pub. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Required elements If a magazine article has no stated author:
“Title of Article.” Year of Publication. Name of Magazine , Month of Pub.
“Title of Article.” Year of Publication. Name of Magazine , Month and Day of Pub, doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Include as much of the following as possible in your bibliographic entry: author; title or description of the content; owner/publisher; month and/or day of publication, most recent revision (or, failing that, date accessed); and URL. The year of publication should be the second element in the entry. Some flexibility is acceptable to accommodate the wide variety of content available, particularly online.
The names of websites are usually set in roman type, but the names of online magazines and books are italicized (like their print counterparts).
Reference list vs. bibliography
Note that a reference list in the author-date system can contain only items that are actually cited in the work. The reference list must contain all of those items. This differs from a bibliography in the numbered-note system, which can contain both cited items and items of interest that have not been specifically cited. If there are uncited works that you would like to draw to the reader’s attention, these can be placed after the references in a separate listed titled ‘Further reading’.
Example: author–date citation with a reference list and further reading—US style
Psychoanalytic studies, along with other literary and cultural texts, not only contribute to the new discourse of the jungle but also reflect the imperialist history that brings West Europeans and Americans into contact with the geographic jungles of India, Africa, and other parts of the world (Rogers et al. 2010, 1). This colonial context needs to be sketched here as well in order to reveal how the birth of the jungle eventually produces new constructions of sexuality in the United States. Billops (1999a) notes that the word “jungle” comes from the Hindi and Marathi word jangal, meaning “desert,” “waste,” “forest”; as well as from the Sanskrit jangala, meaning “dry,” “dry ground,” or “desert.” Its first appearance in English is in 1776, with its meaning already shifted toward what might be more recognizable today: “Land overgrown with underwood, long grass, or tangled vegetation; also, the luxuriant and often almost impenetrable growth of vegetation covering such a tract” (Dreft and Smithers 1978, 87). Brought into English as a result of an imperialist presence in India, “jungle” is intimately related to the larger rise of Western imperialism around the world, particularly in the nineteenth century (Billops 1999b). Western powers such as Britain and France went from controlling 35 percent of the earth’s surface in 1800 to, by 1914, “a grand total of roughly 85 percent of the earth as colonies, protectorates, dependencies, dominions, and commonwealths” (Said 1993, ch.2, “Colonial impacts”).
Billops, Camille. 1999a. “Indo-European Loan Words.” Annals of Linguistics 21 (4): pp. 38–44.
Billops, Camille. 1999b. “Indo-European Vowel Shift: Evidence and Interpretation.” Annals of Linguistics 21 (4): p. 45.
Dreft, Edward, and Susan Smithers. 1978. “Words Working.” International Journal of American Linguistics 62 (3): pp. 227–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb25475.x.
Rogers, Jason, Millicent Eng, and Rene Woo. 2010. “English-Based African Creoles.” In Spreading the People: Colonizing Languages in the Raj , edited by Jason Rogers, pp. 310–330. 2nd ed. London: Verso.
“Evolutionary Linguistics.” 2012. Wikipedia. Updated November 4. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolutionary_linguistics.
Mfuti, Miriam. 2001. “Pidgin Town.” In The Oxford Handbook of Pidgins and Creoles , edited by Alain Smet, pp. 107–112. New York: Oxford University Press.
Rambow, John. 2007. “Will This Demon Fit in My Carry-On?” Bangalore Monkey blog. December 21. http://www.bangaloremonkey. com/2007/12/will-this-demon-fit-in-my-carry-on.html.
Numbered notes
Using numbered notes is a common method of citing sources, particularly in the humanities. Sequential superscript numbers appear in the text to direct the reader to bibliographic or explanatory information that appears in a note.
This is a flexible style that allows authors to combine bibliographic information with annotation, translation, or other commentary. Scholars who frequently cite unpublished material will find numbered notes more useful than author-date citations.
Endnotes or footnotes?
In print publishing, notes can be placed at the bottom of the page as footnotes or at the end of a chapter or book in a separate section as endnotes.
Footnotes are preferred in cases where the information in the note is important enough that readers need it to fully engage with the material. Please note that in a digital context, footnotes in the traditional sense are not possible. Depending on the format, footnotes can appear at the end of a section or chapter, or they may be viewed by clicking or hovering over the superscript numbers in the text to display individual footnotes.
Endnotes are a better choice in print if the material in the notes does not need immediate engagement by the reader. For digital publications where individual chapters may be made available to readers, the notes should appear with the chapter, rather than separately at the end of the work. This varies according to discipline, so please consult your OUP editorial contact if you are unsure.
The formatting of bibliographic information is identical for footnotes and endnotes.
Please use the following guidance:
- Numbered notes appear sequentially in the text as superscripts, ideally at the end of a sentence, following the closing punctuation.
- Use Arabic numerals.
- Numbers should restart at 1 at the beginning of each chapter and run consecutively to the end of each chapter. Do not start renumbering within a chapter (e.g. per page or per double-page spread) or use asterisks, as this will cause confusion in a digital environment.
- Do not number the notes continuously throughout a book, because a later change would necessitate extensive renumbering.
Note structure and format
Required bibliographic elements are given below for the most common types of reference citations, along with optional elements that if used, must be consistent.
- Page numbers are useful locators when referencing in print publications.
- Give page ranges using the fewest number of figures as possible (e.g. pp. 126–27, not pp. 126–127).
- When referencing a digital publication, you may not have access to a print page number. Cite a specific locator (e.g. chapter titles and sub-headings). Do not use location numbers from a proprietary e-reader (e.g. Kindle location numbers).
- Edition numbers are not required when citing a first edition but are necessary for subsequent editions.
Numbered notes in British style
Firstname Lastname, Title of Work (Year of Publication).
Firstname Lastname, Title of Work , 2nd ed. (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication), page number(s) [or alternative locator info].
- Michael Murray, Climate Change at the Poles (New York: Scribner, 2007), p. 9.
- Darian Ibrahim and Carol Marche, Financing the Next Silicon Valley , 3rd ed. (San Francisco: Upbeat Press, 2010).
Edited book
Firstname Lastname, ed., Title of Work (Year of Publication).
Firstname Lastname, eds., Title of Work , 2nd ed. (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication), page number(s) [or alternative locator info].
- Anton Smirov, ed., Eastern Europe After the Iron Curtain (London: Chatto and Windus, 2012).
Firstname Lastname, ‘Title of Chapter in an Edited Volume’, in Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (Year of Publication).
Firstname Lastname, ‘Title of Chapter in an Edited Volume’, in Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication), page number(s) [or alternative locator info].
Hanna Growiszc, ‘Far Right Ideologies in Czech Literature’, in Eastern Europe After the Iron Curtain , edited by Anton Smirov (London: Chatto and Windus, 2012), ch. 7.
Authored book with an editor or translator
Firstname Lastname, Title of Work , ed./trans. Firstname Lastname, (Year of Publication).
Firstname Lastname, Title of Work , ed./trans. Firstname Lastname, 2nd ed. (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication), page number(s) [or alternative locator info].
- Günter Grass, The Tin Drum , trans. Breon Mitchell (New York: Houghton Mifflin, 2009).
Aristotle, Nicomachean Ethics , ed. and trans. Terence Irwin (Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing, 1999).
Multi-volume work
References to multi-volume book citations can take a variety of forms, depending on whether an individual volume or the entire work is being cited, and the authorship of the work.
Citing one volume of a multi-volume work
- Robert Caro, The Path to Power , vol. 1, The Years of Lyndon Johnson (New York: Knopf, 1982), p. 267.
Citing a multi-volume work as a whole
Robert Caro, The Years of Lyndon Johnson , 4 vols (New York: Knopf, 1982–2012).
Allison Wyste, ed. Indian and Tibetan Cooking , vol. 6, Cuisines of Asia, ed. Robert Trautmann (London: Brill Books, 2007).
Multi-volume work with series editor and individual author/editors
Whenever possible, include a DOI (preferred) or a stable URL for citations to journal articles. However, a URL or DOI is not sufficient to stand alone as a reference.
Firstname Lastname, ‘Title of Article’, Name of Journal vol. number, (Year): start page.
Firstname Lastname, ‘Title of Article’, Name of Journal vol. number, issue number (Month or Season Year): start page–end page, doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Barbara Eckstein, ‘The Body, the Word, and the State: J. M. Coetzee’s “Waiting for the Barbarians”’, Novel: A Forum on Fiction 22, no. 2 (Winter 1989): pp. 175–198, http://www.jstor.org/stable/1345802.
David Hyun-Su Kim, ‘The Brahmsian Hairpin’, 19th Century Music 36, no. 1 (Summer 2012): pp. 46–47, doi:10.1525/ncm.2012.36.1.046.
A DOI or URL can be included for articles that you consulted online. The citations for online-only magazines follow the same pattern as print-based magazines, with the addition of URLs. If an online journal or magazine has a stable home page that allows a user to search for articles by title or author, it is acceptable to include the URL for that page (rather than the longer, more specific URL).
‘Title of Article’, Name of Magazine , Month of Pub, Year.
Firstname Lastname, ‘Title of Article’, Name of Magazine , Month and Day of Pub, Year, doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Mary Rose Himler, ‘Religious Books as Best Sellers’, Publishers Weekly , 19 February 1927.
‘Amazon Best Books 2012 Revealed’, Publishers Weekly , 13 November 2012, http://www.publishersweekly.com/pw/by-topic/industry-news/publisher-news/article/54738-amazon-best-books-2012-revealed.html.
Fritz Allhoff, ‘The Paradox of Nonlethal Weapons’, Slate , 13 November 2012, http://www.slate.com.
Law citation styles vary widely depending on jurisdiction. The following examples are for citing law cases in a non-specialist academic context. If you are writing specialist legal content, see ‘Citing of Legal Materials’ for detailed citation information.
Case Number Name of Case [Year] Report VolNo-FirstPageNo
Case C-34/89 P Smith v EC Commission [1993] ECR I-454
Name of Case [Year] VolNo Report, PageNo
Ridge v Baldwin [1964] AC 40, 78
Name of Case , VolNo Reporter SeriesNo (Year)
Name of Case , VolNo Reporter SeriesNo (Name of Court Year)
Bowers v Hardwick 478 US 186 (1986).
Unpublished or informally published content
The titles of unpublished works are set in quotation marks rather than italics. In place of a publisher, location or institutional information can be given.
Troy Thibodeaux, ‘Modernism in Greenwich Village, 1908–1929’ (PhD dissertation, New York University, 1999), p. 59.
Mary Koo, ‘Prakriti and Purusha: Dualism in the Yoga of Patanjali’ (lecture, Theosophical Society, Chennai, India, 17 May 2008).
To cite a website or other source that does not fall within those covered here, include as much of the following as possible (in this order) in your citation: author; title or description of the content; owner/publisher; date of publication or most recent revision (or, failing that, date accessed); and URL. Some flexibility is acceptable to accommodate the wide variety of content available, especially online.
The names of websites are usually set in roman type but the names of online magazines and books are italicized (like their print counterparts).
- ‘The Board of Directors of the Coca-Cola Company Authorizes New Share Repurchase Program’, Coca- Cola Company, 18 October 2012, http://www.coca-colacompany.com/media-center/press-releases/the-board-of-directors-of-the-coca-cola-company-authorizes-new-share-repurchase-program.
- John Rambow, ‘Will This Demon Fit in My Carry-On?’, Bangalore Monkey blog, 21 December 2007, http://www.bangaloremonkey.com/2007/12/will-this-demon-fit-in-my-carry-on.html.
- Wikimedia privacy policy, Wikimedia Foundation, accessed 26 November 2010, http://wikimediafoundation.org/wiki/ Privacy policy.
Numbered notes in US style
Firstname Lastname, Title of Work , (Year of Publication).
Firstname Lastname, eds., Title of Work , (Year of Publication).
- Hanna Growiszc, “Far Right Ideologies in Czech Literature,” in Eastern Europe After the Iron Curtain , edited by Anton Smirov (London: Chatto and Windus, 2012), ch. 7.
- Aristotle, Nicomachean Ethics , ed. and trans. Terence Irwin (Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing, 1999).
Multi-volume book citations can take a variety of forms, depending on whether an individual volume or the work as a whole is being cited, and on how the multi-volume work was authored or edited.
- Robert Caro, The Years of Lyndon Johnson , 4 vols. (New York: Knopf, 1982–2012).
- Allison Wyste, Indian and Tibetan Cooking , vol. 6, Cuisines of Asia, ed. Robert Trautmann (London: Brill Books, 2007).
Firstname Lastname, “Title of Chapter in an Edited Volume,” in Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (Year of Publication).
Firstname Lastname, “Title of Chapter in an Edited Volume,” in Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication), page number(s) [or alternative locator info].
Firstname Lastname, “Title of Article,” Name of Journal vol. number, (Year): start page.
Firstname Lastname, “Title of Article,” Name of Journal vol. number, issue number (Month or Season Year): start page–end page, doi: DOI [or stable URL].
- Barbara Eckstein, “The Body, the Word, and the State: J. M. Coetzee’s ‘Waiting for the Barbarians,’” Novel: A Forum on Fiction 22, no. 2 (Winter 1989): pp. 175–198, http://www.jstor.org/stable/1345802.
- David Hyun-Su Kim, “The Brahmsian Hairpin,” 19th Century Music 36, no. 1 (Summer 2012): pp. 46–47, doi:10.1525/ncm.2012.36.1.046.
A DOI or URL can be included for articles that you consulted online. Online-only magazines follow the same pattern as print-based magazines, with the addition of URLs. If an online journal or magazine has a stable home page that allows a user to search for articles by title or author, it is acceptable to cite that page rather than a longer, more specific URL.
“Title of Article,” Name of Magazine , Month of Pub, Year.
Firstname Lastname, “Title of Article,” Name of Magazine, Month and Day of Pub, Year, doi: DOI [or stable URL].
- Mary Rose Himler, “Religious Books as Best Sellers,” Publishers Weekly , February 19, 1927.
- “Amazon Best Books 2012 Revealed,” Publishers Weekly , November 13, 2012, http://www.publishersweekly.com/pw/by-topic/industry-news/publisher-news/article/54738-amazon-best-books-2012-revealed.html.
- Fritz Allhoff, “The Paradox of Nonlethal Weapons,” Slate , November 13, 2012, http://www.slate.com.
Law - case law
Law citation styles can vary widely depending on jurisdiction. These examples are for citing legal case law in a non-specialist academic context. If you are writing specialist legal content, see ‘Citing of legal materials’ for detailed information on law citation.
Name of Case [Year] VolNo Report PageNo
Ridge v. Baldwin [1964] AC 40, 78
Name of Case , Vol No. Reporter Series No. (Year)
Bowers v Hardwick , 478 U.S. 186 (1986)
Name of Case , Vol No. Reporter Series No. (Name of Court Year)
Bowers v. Hardwick 478 U.S. 186 (1986)
The titles of unpublished works are set in quotation marks rather than italics. Since there is no publisher, location or institutional information can be cited.
- Troy Thibodeaux, “Modernism in Greenwich Village, 1908–1929” (PhD dissertation, New York University, 1999), p. 59.
- Mary Koo, “Prakriti and Purusha: Dualism in the Yoga of Patanjali’ (lecture, Theosophical Society, Chennai, India, May 17, 2008).
If you need to cite a website or other source that does not fall within those covered here, include as much of the following as possible (in this order): author; title or description of the content; owner/publisher; date of publication or most recent revision (or, failing that, date accessed); and URL. Some flexibility is acceptable to accommodate the wide variety of content available, especially online.
- “The Board of Directors of the Coca-Cola Company Authorizes New Share Repurchase Program,” Coca-Cola Company, October 18, 2012, http://www.coca-colacompany.com/media-center/press-releases/the-board-of-directors-of-the-coca-cola-company-authorizes-new-share-repurchase-program.
- John Rambow, “Will This Demon Fit in My Carry-On?,” Bangalore Monkey blog, December 21, 2007, http://www.bangaloremonkey. com/2007/12/will-this-demon-fit-in-my-carry-on.html.
- Wikimedia privacy policy, Wikimedia Foundation, accessed November 26, 2010, http://wikimediafoundation.org/wiki/ Privacy_policy.
Short citations
When a work is cited for the first time in a chapter, full bibliographic information should be given (for an alternative, see ‘Numbered notes in combination with a bibliography’). Subsequent citations should be shortened as in the following examples.
Legal short citations
Give the first mention of legal cases in full. Subsequent mentions within the same article or chapter can be shortened to the case name alone, given in italics (even if italics are not used in the original citation)
- Case C–34/89 P Smith v EC Commission [1993] ECR I–454
- P Smith v EC Commission.
Example: short citations in US style
- See, for example, Alan Hess, Googie: Fifties Coffee Shop Architecture (San Francisco: Chronicle Books, 1985) and Noah Sheldon, Ranch House (New York: Harry S. Abrams, 2004).
- Sheldon, Ranch House , p. 207.
- Ashraf Salama, “Evolutionary Paradigms in Mosque Architecture,” Faith & Form 40, no. 1 (2007): pp. 16–17.
- Salama, “Evolutionary Paradigms.”
- Hess, Googie , p. 21.
- Wikimedia privacy policy, para. 16.
Numbered notes in combination with a bibliography
It is possible to combine notes and bibliography so that all the notes, including the first reference, are short citations that lead the reader to a full citation in the bibliography. This system results in shorter notes and less work for the reader, since complete information is easily available in the alphabetical bibliography and need not be hunted for through all the chapter notes. This requires that all cited sources appear in a bibliography, which can also contain works that are not cited but are germane to the topic.
Structure of a bibliography entry
Bibliographies are structured similarly to notes, but there are some important differences. The first author name (and only the first) is inverted for alphabetization. Punctuation format also varies slightly between notes and bibliographic entries.
Do not use long dashes (e.g. “—") to substitute for an author’s name if it is repeated in the bibliography. Repeat the name in full because in a digital version, the shortened entry may not follow the complete one immediately.
Bibliography entries in British Style
Lastname, Firstname, Title of Work , (Year of Publication).
Lastname, Firstname, and Firstname Lastname. Title of Work , 2nd ed. (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication).
Lastname, Firstname. ‘Title of Chapter in an Edited Book’. In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (Year of Publication).
Lastname, Firstname, and Firstname Lastname. ‘Title of Chapter in an Edited Book’. In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication), page number(s) [or alternative locator info].
Lastname, Firstname,‘Title of Article’. Name of Journal vol. number, no. X (Year): start page.
Lastname, Firstname, and Firstname Lastname. ‘Title of Article’. Name of Journal vol. number, no. X (Month or Season Year): start page–end page. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
‘Title of Article’. Name of Magazine , Month Year of Pub.
Lastname, Firstname, and Firstname Lastname. ‘Title of Article’. Name of Magazine , Day Month Year of Pub, doi: DOI [or stable URL].
If you need to cite a website or other source that does not fall within those covered here, include as much of the following as possible (in this order): author; title or description of the content; owner/publisher; date of publication, most recent revision (or, failing that, date accessed); and URL. Some flexibility is acceptable to accommodate the wide variety of content available, especially online.
Sample bibliography
Growiszc, Hanna. ‘Far Right Ideologies in Czech Literature’. In Eastern Europe After the Iron Curtain , edited by Anton Smirov (London: Chatto and Windus, 2012), ch. 7.
Himler, Mary Rose. ‘Religious Books as Best Sellers’. Publishers Weekly , 19 February 1927.
Khan, Imran, and Richard Collins. ‘True Belief: Hindu Metanarratives in Bollywood’. Journal of Cinema Studies 7, no. 4 (2009): pp. 104–115. doi:10.1086/jcs113.3.752.
Murray, Michael. ‘The Antarctic Summer Lengthens’. Journal of Climate Studies 20, no. 9 (2011): p. 203.
Murray, Michael. Climate Change at the Poles (New York: Scribner, 2007).
Rambow, John. ‘Will This Demon Fit in My Carry-On?’ Bangalore Monkey blog. 21 December 2007. http://www.bangaloremonkey.com/2007/12/will-this-demon-fit-in-my-carry-on.html.
Bibliography entries in US style
Lastname, Firstname, “Title of Chapter in an Edited Book.” In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (Year of Publication).
Lastname, Firstname, and Firstname Lastname. “Title of Chapter in an Edited Book.” In Title of Edited Volume , edited by Firstname Lastname (City of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication), page number(s) [or alternative locator info].
Lastname, Firstname,“Title of Article.” Name of Journal vol. number, no. X (Year): start page.
Lastname, Firstname, and Firstname Lastname. “Title of Article.” Name of Journal vol. number, no. X (Month or Season Year): start page–end page. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
“Title of Article.” Name of Magazine , Month of Pub, Year.
Lastname, Firstname, and Firstname Lastname. “Title of Article.” Name of Magazine , Month and Day of Pub, Year, doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Growiszc, Hanna. “Far Right Ideologies in Czech Literature.” In Eastern Europe After the Iron Curtain, edited by Anton Smirov (London: Chatto and Windus, 2012), ch. 7.
Himler, Mary Rose. “Religious Books as Best Sellers.” Publishers Weekly, February 19, 1927.
Khan, Imran, and Richard Collins. “True Belief: Hindu Metanarratives in Bollywood.” Journal of Cinema Studies 7, no. 4 (2009): pp. 104–115. doi:10.1086/jcs113.3.752.
Murray, Michael. “The Antarctic Summer Lengthens.” Journal of Climate Studies 20, no. 9 (2011): p. 203.
Rambow, John. “Will This Demon Fit in My Carry-On?” Bangalore Monkey blog. December 21, 2007. http://www.bangaloremonkey.com/2007/12/will-this-demon-fit-in-my-carry-on.html.
Numbered reference citations (Vancouver)
Numbered reference citations (also known as author–number or Vancouver references) are used in scientific and medical texts. In this system, each reference used is assigned a number. When that reference is cited in the text, its number appears, either in parentheses or brackets or as a superscript. All cited references appear in a numbered reference list at the end of the chapter or book.
An advantage of numbered references over the author–date style is that less space in the main text is required for in-text citations. The system also avoids ambiguity in the case of two works by the same author published the same year, an occasional issue in author–date citations. A disadvantage is that late addition or removal of references usually requires renumbering of both the reference list and the citations. Numbered reference citations cannot be used to provide commentary or other explanatory material to the text.
References are cited within the text by using a number in a superscript, in parentheses, or in square brackets. Although each of these variants is acceptable, only one can be used in a single text. The examples in this guide will enclose citation numbers in parentheses. Note that although citations are numbered in the order of their first appearance in the text, non-consecutive note numbers are possible, to allow references to be cited more than once. Citations can take the form of a range: for example (4–7) would cite references 4, 5, 6, and 7 simultaneously. If it is necessary to cite specific page numbers that are not present in the reference list, page numbers can be inserted into the citation: for example (4p6, 5pp1–11).
Please note the following:
- Author first names are usually given as initials only, with no full stops (e.g. “AN” not “A.N.”) between initials. In the case of multiple authors, you can list up to six full names; for more than six authors, list the first three plus ‘et al’. All author names are inverted (i.e. last name, first name).
- Names of journals can be abbreviated, as in the examples in this section, but must follow the standard abbreviations used by PubMed. Journal article titles are given without quotation marks and in sentence-style capitalization.
- Do not use long dashes (e.g. “—") to substitute for the name of an author whose name is repeated in the bibliography. Repeat the name in full because linking in a digital publication may not immediately follow the entry with the full name.
- Citations are numbered in the order in which they first appear in the text.
Required bibliographic elements are given below for the most common types of reference citations, along with optional elements (if used, be consistent). Other elements below are required if applicable (for example, you need a page number or other locator if you are quoting a precise part of a large work, but you can skip it if the reference is to the work as a whole).
Numbered reference citations in British style
Lastname FI, Title of Work , Year of Publication.
Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI. Title of Work , 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher; Year of Publication: startpage–endpage [or alternative locator info].
Unauthored book (books published by committee, agency, or group)
Title of Work . Year of Publication.
Title of Work . 16th ed. City of Publication: Publisher; Year of Publication: startpage–endpage [or alternative locator info].
Lastname FI. Title of chapter in sentence case. In: Lastname FI, eds. Title of Work. Year of Publication.
Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI. Title of chapter in sentence case. In: Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI, eds. Title of Work . 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher; Year of Publication: startpage–endpage [or alternative locator info].
Lastname FI, Title of article in sentence case. Abbreviated Journal Title . Year of Publication; Volume No.
Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI, et al. Title of article in sentence case. Abbreviated Journal Title . Year of Publication; Volume No. (Issue No.) (Supplement No.): startpage–endpage [or alternative locator info]. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Magazine or newspaper article
Lastname FI. Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title . Month and Year of Publication.
Lastname FI. Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title . Day Month and Year of Publication: startpage–endpage. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
If the article has no stated author:
Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title . Month and Year of Publication.
Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title . Day Month and Year of Publication: startpage–endpage. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Include of the following (in this order) in your bibliographic entry: author; title or description of the content; owner/publisher; date of publication or most recent revision (or, failing that, date accessed); and URL. Some flexibility is acceptable to accommodate the wide variety of content available online and in non-traditional formats. Follow the capitalization and italicization patterns of the examples here as much as possible.
If the nature of the material you are citing is not clear from the bibliographic information, you can provide a descriptor in brackets after the first element of the reference.
Example: Numbered reference citations and reference list—British style
Colorectal cancer (cRc) is one of the most common malignancies and the second leading cause of death from cancer in Europe and North America (1). While early stage cRc is associated with an excellent 5-year survival rate (90% for localized disease), approximately 20% of patients present with metastatic disease, and many patients diagnosed with stage ii or iii cancer will experience a recurrence and develop distant metastases (2). At present, established clinico-pathological criteria are used to estimate risks of recurrence in stage ii and iii disease, and this is routinely used in the selection of patients or adjuvant systemic therapy following surgical resection. The clinical outcome of patients who receive such adjuvant treatment can, however, vary widely, when additional molecular factors are taken into consideration. Identification of novel prognostic markers is, therefore, vital in improving the prognosis of this disease (3). One of the recently described substances important for angiogenesis is endoglin. Endoglin, also known as cD105, is a receptor for transforming growth factor-ß1 molecule, which binds preferentially to the activated endothelial cells that participate in tumour angiogenesis, with weak or negative expression in vascular endothelium of normal tissues. Endoglin is induced by hypoxia. Therefore, it is very useful for assessment of neo-angiogenesis of malignant neoplasms (4–6). Many reports indicate that endoglin assessed immunohistochemically in colorectal cancer correlates not only with tumour microvessel density, but also with survival. It has also been reported as a valuable parameter predicting patients having an increased risk of developing metastatic disease. Endoglin is expressed not only on cell surfaces since its soluble form (sol-end) can be detected also in blood (4–7). A few studies evaluated the clinical significance of elevated sol-end levels in colorectal cancer patients (7).
1. Ferlay J, Autier P, Boniol M, Heanue M, Colombet M, Boyle P. Estimates of the cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol . 2007; 18: pp. 581–592.
2. Meyerhardt JA, Mayer RJ. Systemic therapy for colorectal cancer. In: Boniol M, Smith J, eds. Oncological Research Reviews . 16th ed. New York, NY: Dekker; 2005; pp. 476–487.
3. Allegra CJ, Paik S, Colangelo LH, et al. Prognostic value of thymidylate synthase, Ki-67, and p53 in patients with Dukes’ B and C colon cancer: a National Cancer Institute-National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project collaborative study. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21: pp. 241–250.
4. Drug Topics Red Book . Montvale, NJ: Thomson Healthcare, 2009: p. 232.
5. FDA approves new treatment for advanced colorectal cancer. 2012. US Food and Drug Administration website. 27 September. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm321271.htm.
6. Stivarga [package insert]. Wayne, NJ: Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, 2012.
7. Mysliwiec P, Pawlak K, Kuklinski A, Kedra B. Combined perioperative plasma endoglin and vegF-a assessment in colorectal cancer patients. Folia Histochem Cytobiol . 2008; 46(2)(suppl. 1): pp. 487–49.
Numbered reference citations and reference list in US style
Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI. Title of Work , 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher; Year of Publication.
Title of Work. Year of Publication.
Title of Work. 16th ed. City of Publication: Publisher; Year of Publication: startpage–endpage [or alternative locator info].
Lastname FI, Title of chapter in sentence case. In: Lastname FI, ed. Title of Work. Year of Publication.
Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI. Title of chapter in sentence case. In: Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI, eds. Title of Work. 2nd ed. City of Publication: Publisher; Year of Publication: startpage–endpage [or alternative locator info].
Lastname FI, Title of article in sentence case. Abbreviated Journal Title. Year of Publication; Volume No. (Issue No.)
Lastname FI, Lastname FI, Lastname FI, et al. Title of article in sentence case. Abbreviated Journal Title. Year of Publication; Volume No. (Issue No.)(SupplementNo): startpage–endpage [or alternative locator info]. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Lastname FI. Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title. Month, Day, and Year of Publication.
Lastname FI. Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title. Month, Day, and Year of Publication: startpage–endpage. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title. Month, Day, and Year of Publication.
Title of article in sentence case. Magazine or Newspaper Title. Month, Day, and Year of Publication: startpage–endpage. doi: DOI [or stable URL].
Include as much of the following as possible in your bibliographic entry (in this order): author; title or description of the content; owner/publisher; date of publication or most recent revision, or, failing that, date accessed; and URL if available. Some flexibility is acceptable to accommodate the wide variety of content available online and in non-traditional formats. Follow the capitalization and italicization patterns of these examples.
Example: Numbered reference citations and reference list—US style
Colorectal cancer (cRc) is one of the most common malignancies and the second leading cause of death from cancer in Europe and North America (1). While early stage cRc is associated with an excellent 5-year survival rate (90% for localized disease), approximately 20% of patients present with metastatic disease, and many patients diagnosed with stage ii or iii cancer will experience a recurrence and develop distant metastases (2). At present, established clinico-pathological criteria are used to estimate risks of recurrence in stage ii and iii disease, and this is routinely used in the selection of patients or adjuvant systemic therapy following surgical resection. The clinical outcome of patients who receive such adjuvant treatment can, however, vary widely, when additional molecular factors are taken into consideration. Identification of novel prognostic markers is, therefore, vital in improving the prognosis of this disease (3). One of the recently described substances important for angiogenesis is endoglin. Endoglin, also known as cD105, is a receptor for transforming growth factor-ß1 molecule, which binds preferentially to the activated endothelial cells that participate in tumor angiogenesis, with weak or negative expression in vascular endothelium of normal tissues. Endoglin is induced by hypoxia. Therefore it is very useful for assessment of neo-angiogenesis of malignant neoplasms (4–6). Many reports indicate that endoglin assessed immunohistochemically in colorectal cancer correlates not only with tumor microvessel density, but also with survival. It has also been reported as a valuable parameter predicting patients having an increased risk of developing metastatic disease. Endoglin is expressed not only on cell surfaces, since its soluble form (sol-end) can be detected also in blood (4–7). A few studies evaluated the clinical significance of elevated sol-end levels in colorectal cancer patients (7).
1. Ferlay J, Autier P, Boniol M, Heanue M, Colombet M, Boyle P. Estimates of the cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol. 2007; 18: pp. 581–592.
2. Meyerhardt JA, Mayer RJ. Systemic therapy for colorectal cancer. In: Boniol M, Smith J, eds. Oncological Research Reviews. 16th ed. New York, NY: Dekker; 2005; pp. 476–487.
3. Allegra CJ, Paik S, Colangelo LH, et al. Prognostic value of thymidylate synthase, Ki-67, and p. 53 in patients with Dukes’ B and C colon cancer: a National Cancer Institute-National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project collaborative study. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21: pp. 241–250.
4. Drug Topics Red Book. Montvale, NJ: Thomson Healthcare, 2009: p. 232.
5. FDA approves new treatment for advanced colorectal cancer. US Food and Drug Administration website. September 27, 2012. http://www.fda. gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm321271.htm.
7. Mysliwiec P, Pawlak K, Kuklinski A, Kedra B. Combined perioperative plasma endoglin and vegF-a assessment in colorectal cancer patients. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2008; 46(2)(suppl. 1): pp. 487–492.
For legal works, we recommend that you follow The Oxford University Standard for Citation of Legal Authorities (OSCOLA). The fourth edition (published in 2012) covers International Law. The full set of guidance can be found at https://www.law.ox.ac.uk/sites/default/files/migrated/oscola_4th_edn_hart_2012.pdf
Information on how to apply OSCOLA style in EndNote, Latex, Refworks and Zotero can be found at https://www.law.ox.ac.uk/research-subject-groups/publications/oscola-styles-endnote-latek-refworks-and-zotero
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Frequently asked questions
What are the different types of citation styles.
There are many different citation styles used across different academic disciplines, but they fall into three basic approaches to citation:
- Parenthetical citations : Including identifying details of the source in parentheses —usually the author’s last name and the publication date, plus a page number if available ( author-date ). The publication date is occasionally omitted ( author-page ).
- Numerical citations: Including a number in brackets or superscript, corresponding to an entry in your numbered reference list.
- Note citations: Including a full citation in a footnote or endnote , which is indicated in the text with a superscript number or symbol.
Frequently asked questions: Citing sources
A scientific citation style is a system of source citation that is used in scientific disciplines. Some commonly used scientific citation styles are:
- Chicago author-date , CSE , and Harvard , used across various sciences
- ACS , used in chemistry
- AMA , NLM , and Vancouver , used in medicine and related disciplines
- AAA , APA , and ASA , commonly used in the social sciences
A source annotation in an annotated bibliography fulfills a similar purpose to an abstract : they’re both intended to summarize the approach and key points of a source.
However, an annotation may also evaluate the source , discussing the validity and effectiveness of its arguments. Even if your annotation is purely descriptive , you may have a different perspective on the source from the author and highlight different key points.
You should never just copy text from the abstract for your annotation, as doing so constitutes plagiarism .
Most academics agree that you shouldn’t cite Wikipedia as a source in your academic writing , and universities often have rules against doing so.
This is partly because of concerns about its reliability, and partly because it’s a tertiary source. Tertiary sources are things like encyclopedias and databases that collect information from other sources rather than presenting their own evidence or analysis. Usually, only primary and secondary sources are cited in academic papers.
A Wikipedia citation usually includes the title of the article, “Wikipedia” and/or “Wikimedia Foundation,” the date the article was last updated, and the URL.
In APA Style , you’ll give the URL of the current revision of the article so that you’re sure the reader accesses the same version as you.
There’s some disagreement about whether Wikipedia can be considered a reliable source . Because it can be edited by anyone, many people argue that it’s easy for misleading information to be added to an article without the reader knowing.
Others argue that because Wikipedia articles cite their sources , and because they are worked on by so many editors, misinformation is generally removed quickly.
However, most universities state that you shouldn’t cite Wikipedia in your writing.
Hanging indents are used in reference lists in various citation styles to allow the reader to easily distinguish between entries.
You should apply a hanging indent to your reference entries in APA , MLA , and Chicago style.
A hanging indent is used to indent all lines of a paragraph except the first.
When you create a hanging indent, the first line of the paragraph starts at the border. Each subsequent line is indented 0.5 inches (1.27 cm).
APA and MLA style both use parenthetical in-text citations to cite sources and include a full list of references at the end, but they differ in other ways:
- APA in-text citations include the author name, date, and page number (Taylor, 2018, p. 23), while MLA in-text citations include only the author name and page number (Taylor 23).
- The APA reference list is titled “References,” while MLA’s version is called “ Works Cited .”
- The reference entries differ in terms of formatting and order of information.
- APA requires a title page , while MLA requires a header instead.
A parenthetical citation in Chicago author-date style includes the author’s last name, the publication date, and, if applicable, the relevant page number or page range in parentheses . Include a comma after the year, but not after the author’s name.
For example: (Swan 2003, 6)
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
APA Style distinguishes between parenthetical and narrative citations.
In parenthetical citations , you include all relevant source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence or clause: “Parts of the human body reflect the principles of tensegrity (Levin, 2002).”
In narrative citations , you include the author’s name in the text itself, followed by the publication date in parentheses: “Levin (2002) argues that parts of the human body reflect the principles of tensegrity.”
In a parenthetical citation in MLA style , include the author’s last name and the relevant page number or range in parentheses .
For example: (Eliot 21)
A parenthetical citation gives credit in parentheses to a source that you’re quoting or paraphrasing . It provides relevant information such as the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number(s) cited.
How you use parenthetical citations will depend on your chosen citation style . It will also depend on the type of source you are citing and the number of authors.
APA does not permit the use of ibid. This is because APA in-text citations are parenthetical and there’s no need to shorten them further.
Ibid. may be used in Chicago footnotes or endnotes .
Write “Ibid.” alone when you are citing the same page number and source as the previous citation.
When you are citing the same source, but a different page number, use ibid. followed by a comma and the relevant page number(s). For example:
- Ibid., 40–42.
Only use ibid . if you are directing the reader to a previous full citation of a source .
Ibid. only refers to the previous citation. Therefore, you should only use ibid. directly after a citation that you want to repeat.
Ibid. is an abbreviation of the Latin “ibidem,” meaning “in the same place.” Ibid. is used in citations to direct the reader to the previous source.
Signal phrases can be used in various ways and can be placed at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence.
To use signal phrases effectively, include:
- The name of the scholar(s) or study you’re referencing
- An attributive tag such as “according to” or “argues that”
- The quote or idea you want to include
Different citation styles require you to use specific verb tenses when using signal phrases.
- APA Style requires you to use the past or present perfect tense when using signal phrases.
- MLA and Chicago requires you to use the present tense when using signal phrases.
Signal phrases allow you to give credit for an idea or quote to its author or originator. This helps you to:
- Establish the credentials of your sources
- Display your depth of reading and understanding of the field
- Position your own work in relation to other scholars
- Avoid plagiarism
A signal phrase is a group of words that ascribes a quote or idea to an outside source.
Signal phrases distinguish the cited idea or argument from your own writing and introduce important information including the source of the material that you are quoting , paraphrasing , or summarizing . For example:
“ Cognitive psychologist Steven Pinker (1994) insists that humans possess an innate faculty for comprehending grammar.”
If you’re quoting from a text that paraphrases or summarizes other sources and cites them in parentheses , APA and Chicago both recommend retaining the citations as part of the quote. However, MLA recommends omitting citations within a quote:
- APA: Smith states that “the literature on this topic (Jones, 2015; Sill, 2019; Paulson, 2020) shows no clear consensus” (Smith, 2019, p. 4).
- MLA: Smith states that “the literature on this topic shows no clear consensus” (Smith, 2019, p. 4).
Footnote or endnote numbers that appear within quoted text should be omitted in all styles.
If you want to cite an indirect source (one you’ve only seen quoted in another source), either locate the original source or use the phrase “as cited in” in your citation.
In scientific subjects, the information itself is more important than how it was expressed, so quoting should generally be kept to a minimum. In the arts and humanities, however, well-chosen quotes are often essential to a good paper.
In social sciences, it varies. If your research is mainly quantitative , you won’t include many quotes, but if it’s more qualitative , you may need to quote from the data you collected .
As a general guideline, quotes should take up no more than 5–10% of your paper. If in doubt, check with your instructor or supervisor how much quoting is appropriate in your field.
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
To paraphrase effectively, don’t just take the original sentence and swap out some of the words for synonyms. Instead, try:
- Reformulating the sentence (e.g., change active to passive , or start from a different point)
- Combining information from multiple sentences into one
- Leaving out information from the original that isn’t relevant to your point
- Using synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning
The main point is to ensure you don’t just copy the structure of the original text, but instead reformulate the idea in your own words.
“ Et al. ” is an abbreviation of the Latin term “et alia,” which means “and others.” It’s used in source citations to save space when there are too many authors to name them all.
Guidelines for using “et al.” differ depending on the citation style you’re following:
To insert endnotes in Microsoft Word, follow the steps below:
- Click on the spot in the text where you want the endnote to show up.
- In the “References” tab at the top, select “Insert Endnote.”
- Type whatever text you want into the endnote.
If you need to change the type of notes used in a Word document from footnotes to endnotes , or the other way around, follow these steps:
- Open the “References” tab, and click the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the “Footnotes” section.
- In the pop-up window, click on “Convert…”
- Choose the option you need, and click “OK.”
To insert a footnote automatically in a Word document:
- Click on the point in the text where the footnote should appear
- Select the “References” tab at the top and then click on “Insert Footnote”
- Type the text you want into the footnote that appears at the bottom of the page
Footnotes are notes indicated in your text with numbers and placed at the bottom of the page. They’re used to provide:
- Citations (e.g., in Chicago notes and bibliography )
- Additional information that would disrupt the flow of the main text
Be sparing in your use of footnotes (other than citation footnotes), and consider whether the information you’re adding is relevant for the reader.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page they refer to. This is convenient for the reader but may cause your text to look cluttered if there are a lot of footnotes.
Endnotes appear all together at the end of the whole text. This may be less convenient for the reader but reduces clutter.
Both footnotes and endnotes are used in the same way: to cite sources or add extra information. You should usually choose one or the other to use in your text, not both.
An in-text citation is an acknowledgement you include in your text whenever you quote or paraphrase a source. It usually gives the author’s last name, the year of publication, and the page number of the relevant text. In-text citations allow the reader to look up the full source information in your reference list and see your sources for themselves.
If you are reusing content or data you used in a previous assignment, make sure to cite yourself. You can cite yourself just as you would cite any other source: simply follow the directions for that source type in the citation style you are using.
Keep in mind that reusing your previous work can be considered self-plagiarism , so make sure you ask your professor or consult your university’s handbook before doing so.
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Peer review is a process of evaluating submissions to an academic journal. Utilizing rigorous criteria, a panel of reviewers in the same subject area decide whether to accept each submission for publication. For this reason, academic journals are often considered among the most credible sources you can use in a research project– provided that the journal itself is trustworthy and well-regarded.
Academic dishonesty can be intentional or unintentional, ranging from something as simple as claiming to have read something you didn’t to copying your neighbor’s answers on an exam.
You can commit academic dishonesty with the best of intentions, such as helping a friend cheat on a paper. Severe academic dishonesty can include buying a pre-written essay or the answers to a multiple-choice test, or falsifying a medical emergency to avoid taking a final exam.
Academic dishonesty refers to deceitful or misleading behavior in an academic setting. Academic dishonesty can occur intentionally or unintentionally, and varies in severity.
It can encompass paying for a pre-written essay, cheating on an exam, or committing plagiarism . It can also include helping others cheat, copying a friend’s homework answers, or even pretending to be sick to miss an exam.
Academic dishonesty doesn’t just occur in a classroom setting, but also in research and other academic-adjacent fields.
To apply a hanging indent to your reference list or Works Cited list in Word or Google Docs, follow the steps below.
Microsoft Word:
- Highlight the whole list and right click to open the Paragraph options.
- Under Indentation > Special , choose Hanging from the dropdown menu.
- Set the indent to 0.5 inches or 1.27cm.
Google Docs:
- Highlight the whole list and click on Format > Align and indent > Indentation options .
- Under Special indent , choose Hanging from the dropdown menu.
When the hanging indent is applied, for each reference, every line except the first is indented. This helps the reader see where one entry ends and the next begins.
For a published interview (whether in video , audio, or print form ), you should always include a citation , just as you would for any other source.
For an interview you conducted yourself , formally or informally, you often don’t need a citation and can just refer to it in the text or in a footnote , since the reader won’t be able to look them up anyway. MLA , however, still recommends including citations for your own interviews.
The main elements included in a newspaper interview citation across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the names of the interviewer and interviewee, the interview title, the publication date, the name of the newspaper, and a URL (for online sources).
The information is presented differently in different citation styles. One key difference is that APA advises listing the interviewer in the author position, while MLA and Chicago advise listing the interviewee first.
The elements included in a newspaper article citation across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author name, the article title, the publication date, the newspaper name, and the URL if the article was accessed online .
In APA and MLA, the page numbers of the article appear in place of the URL if the article was accessed in print. No page numbers are used in Chicago newspaper citations.
Untitled sources (e.g. some images ) are usually cited using a short descriptive text in place of the title. In APA Style , this description appears in brackets: [Chair of stained oak]. In MLA and Chicago styles, no brackets are used: Chair of stained oak.
For social media posts, which are usually untitled, quote the initial words of the post in place of the title: the first 160 characters in Chicago , or the first 20 words in APA . E.g. Biden, J. [@JoeBiden]. “The American Rescue Plan means a $7,000 check for a single mom of four. It means more support to safely.”
MLA recommends quoting the full post for something short like a tweet, and just describing the post if it’s longer.
The main elements included in image citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the name of the image’s creator, the image title, the year (or more precise date) of publication, and details of the container in which the image was found (e.g. a museum, book , website ).
In APA and Chicago style, it’s standard to also include a description of the image’s format (e.g. “Photograph” or “Oil on canvas”). This sort of information may be included in MLA too, but is not mandatory.
The main elements included in a lecture citation across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the name of the speaker, the lecture title, the date it took place, the course or event it was part of, and the institution it took place at.
For transcripts or recordings of lectures/speeches, other details like the URL, the name of the book or website , and the length of the recording may be included instead of information about the event and institution.
The main elements included in a YouTube video citation across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the name of the author/uploader, the title of the video, the publication date, and the URL.
The format in which this information appears is different for each style.
All styles also recommend using timestamps as a locator in the in-text citation or Chicago footnote .
Each annotation in an annotated bibliography is usually between 50 and 200 words long. Longer annotations may be divided into paragraphs .
The content of the annotation varies according to your assignment. An annotation can be descriptive, meaning it just describes the source objectively; evaluative, meaning it assesses its usefulness; or reflective, meaning it explains how the source will be used in your own research .
Any credible sources on your topic can be included in an annotated bibliography . The exact sources you cover will vary depending on the assignment, but you should usually focus on collecting journal articles and scholarly books . When in doubt, utilize the CRAAP test !
An annotated bibliography is an assignment where you collect sources on a specific topic and write an annotation for each source. An annotation is a short text that describes and sometimes evaluates the source.
The elements included in journal article citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the name(s) of the author(s), the title of the article, the year of publication, the name of the journal, the volume and issue numbers, the page range of the article, and, when accessed online, the DOI or URL.
In MLA and Chicago style, you also include the specific month or season of publication alongside the year, when this information is available.
In APA , MLA , and Chicago style citations for sources that don’t list a specific author (e.g. many websites ), you can usually list the organization responsible for the source as the author.
If the organization is the same as the website or publisher, you shouldn’t repeat it twice in your reference:
- In APA and Chicago, omit the website or publisher name later in the reference.
- In MLA, omit the author element at the start of the reference, and cite the source title instead.
If there’s no appropriate organization to list as author, you will usually have to begin the citation and reference entry with the title of the source instead.
The main elements included in website citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author, the date of publication, the page title, the website name, and the URL. The information is presented differently in each style.
When you want to cite a specific passage in a source without page numbers (e.g. an e-book or website ), all the main citation styles recommend using an alternate locator in your in-text citation . You might use a heading or chapter number, e.g. (Smith, 2016, ch. 1)
In APA Style , you can count the paragraph numbers in a text to identify a location by paragraph number. MLA and Chicago recommend that you only use paragraph numbers if they’re explicitly marked in the text.
For audiovisual sources (e.g. videos ), all styles recommend using a timestamp to show a specific point in the video when relevant.
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
The main elements included in all book citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author, the title, the year of publication, and the name of the publisher. A page number is also included in in-text citations to highlight the specific passage cited.
In Chicago style and in the 6th edition of APA Style , the location of the publisher is also included, e.g. London: Penguin.
A block quote is a long quote formatted as a separate “block” of text. Instead of using quotation marks , you place the quote on a new line, and indent the entire quote to mark it apart from your own words.
The rules for when to apply block quote formatting depend on the citation style:
- APA block quotes are 40 words or longer.
- MLA block quotes are more than 4 lines of prose or 3 lines of poetry.
- Chicago block quotes are longer than 100 words.
In academic writing , there are three main situations where quoting is the best choice:
- To analyze the author’s language (e.g., in a literary analysis essay )
- To give evidence from primary sources
- To accurately present a precise definition or argument
Don’t overuse quotes; your own voice should be dominant. If you just want to provide information from a source, it’s usually better to paraphrase or summarize .
Every time you quote a source , you must include a correctly formatted in-text citation . This looks slightly different depending on the citation style .
For example, a direct quote in APA is cited like this: “This is a quote” (Streefkerk, 2020, p. 5).
Every in-text citation should also correspond to a full reference at the end of your paper.
A quote is an exact copy of someone else’s words, usually enclosed in quotation marks and credited to the original author or speaker.
The DOI is usually clearly visible when you open a journal article on an academic database. It is often listed near the publication date, and includes “doi.org” or “DOI:”. If the database has a “cite this article” button, this should also produce a citation with the DOI included.
If you can’t find the DOI, you can search on Crossref using information like the author, the article title, and the journal name.
A DOI is a unique identifier for a digital document. DOIs are important in academic citation because they are more permanent than URLs, ensuring that your reader can reliably locate the source.
Journal articles and ebooks can often be found on multiple different websites and databases. The URL of the page where an article is hosted can be changed or removed over time, but a DOI is linked to the specific document and never changes.
When a book’s chapters are written by different authors, you should cite the specific chapter you are referring to.
When all the chapters are written by the same author (or group of authors), you should usually cite the entire book, but some styles include exceptions to this.
- In APA Style , single-author books should always be cited as a whole, even if you only quote or paraphrase from one chapter.
- In MLA Style , if a single-author book is a collection of stand-alone works (e.g. short stories ), you should cite the individual work.
- In Chicago Style , you may choose to cite a single chapter of a single-author book if you feel it is more appropriate than citing the whole book.
Articles in newspapers and magazines can be primary or secondary depending on the focus of your research.
In historical studies, old articles are used as primary sources that give direct evidence about the time period. In social and communication studies, articles are used as primary sources to analyze language and social relations (for example, by conducting content analysis or discourse analysis ).
If you are not analyzing the article itself, but only using it for background information or facts about your topic, then the article is a secondary source.
A fictional movie is usually a primary source. A documentary can be either primary or secondary depending on the context.
If you are directly analyzing some aspect of the movie itself – for example, the cinematography, narrative techniques, or social context – the movie is a primary source.
If you use the movie for background information or analysis about your topic – for example, to learn about a historical event or a scientific discovery – the movie is a secondary source.
Whether it’s primary or secondary, always properly cite the movie in the citation style you are using. Learn how to create an MLA movie citation or an APA movie citation .
To determine if a source is primary or secondary, ask yourself:
- Was the source created by someone directly involved in the events you’re studying (primary), or by another researcher (secondary)?
- Does the source provide original information (primary), or does it summarize information from other sources (secondary)?
- Are you directly analyzing the source itself (primary), or only using it for background information (secondary)?
Some types of source are nearly always primary: works of art and literature, raw statistical data, official documents and records, and personal communications (e.g. letters, interviews ). If you use one of these in your research, it is probably a primary source.
Primary sources are often considered the most credible in terms of providing evidence for your argument, as they give you direct evidence of what you are researching. However, it’s up to you to ensure the information they provide is reliable and accurate.
Always make sure to properly cite your sources to avoid plagiarism .
Common examples of secondary sources include academic books, journal articles , reviews, essays , and textbooks.
Anything that summarizes, evaluates or interprets primary sources can be a secondary source. If a source gives you an overview of background information or presents another researcher’s ideas on your topic, it is probably a secondary source.
Common examples of primary sources include interview transcripts , photographs, novels, paintings, films, historical documents, and official statistics.
Anything you directly analyze or use as first-hand evidence can be a primary source, including qualitative or quantitative data that you collected yourself.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.

In-Text Citations
In scholarly writing, it is essential to acknowledge how others contributed to your work. By following the principles of proper citation, writers ensure that readers understand their contribution in the context of the existing literature—how they are building on, critically examining, or otherwise engaging the work that has come before.
APA Style provides guidelines to help writers determine the appropriate level of citation and how to avoid plagiarism and self-plagiarism.
We also provide specific guidance for in-text citation, including formats for interviews, classroom and intranet sources, and personal communications; in-text citations in general; and paraphrases and direct quotations.

Academic Writer ®
Master academic writing with APA’s essential teaching and learning resource

Course Adoption
Teaching APA Style? Become a course adopter of the 7th edition Publication Manual

Instructional Aids
Guides, checklists, webinars, tutorials, and sample papers for anyone looking to improve their knowledge of APA Style
BibTeX bibliography style: plain
The plain BibTeX style is one of the four standard bibliography styles in BibTeX.
CTAN » tex-archive » biblio » bibtex » base » plain.bst

- Bibliography examples for all BibTeX entries
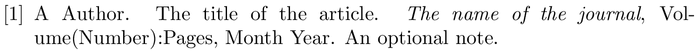
incollection

inproceedings

mastersthesis
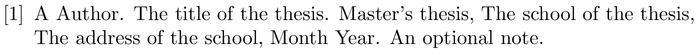
proceedings

unpublished
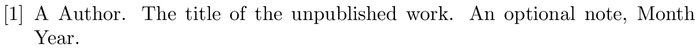
- Supported BibTeX fields
- howpublished
- institution
- organization
- Other styles
- elsarticle-num
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Sample Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper
This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication). These differences mostly extend to the title page and running head. Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper.
However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style.
Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples. Those authored by [AF] denote explanations of formatting and [AWC] denote directions for writing and citing in APA 7.
APA 7 Student Paper:
Apa 7 professional paper:.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Website
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, citing a website in apa.
Once you’ve identified a credible website to use, create a citation and begin building your reference list. Citation Machine citing tools can help you create references for online news articles, government websites, blogs, and many other website! Keeping track of sources as you research and write can help you stay organized and ethical. If you end up not using a source, you can easily delete it from your bibliography. Ready to create a citation? Enter the website’s URL into the search box above. You’ll get a list of results, so you can identify and choose the correct source you want to cite. It’s that easy to begin!
If you’re wondering how to cite a website in APA, use the structure below.
Author Last Name, First initial. (Year, Month Date Published). Title of web page . Name of Website. URL
Example of an APA format website:
Austerlitz, S. (2015, March 3). How long can a spinoff like ‘Better Call Saul’ last? FiveThirtyEight. http://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-long-can-a-spinoff-like-better-call-saul-last/
Keep in mind that not all information found on a website follows the structure above. Only use the Website format above if your online source does not fit another source category. For example, if you’re looking at a video on YouTube, refer to the ‘YouTube Video’ section. If you’re citing a newspaper article found online, refer to ‘Newspapers Found Online’ section. Again, an APA website citation is strictly for web pages that do not fit better with one of the other categories on this page.
Social media:
When adding the text of a post, keep the original capitalization, spelling, hashtags, emojis (if possible), and links within the text.
Facebook posts:
Structure: Facebook user’s Last name, F. M. (Year, Monday Day of Post). Up to the first 20 words of Facebook post [Source type if attached] [Post type]. Facebook. URL
Source type examples: [Video attached], [Image attached]
Post type examples: [Status update], [Video], [Image], [Infographic]
Gomez, S. (2020, February 4). Guys, I’ve been working on this special project for two years and can officially say Rare Beauty is launching in [Video]. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/Selena/videos/1340031502835436/
Life at Chegg. (2020, February 7) It breaks our heart that 50% of college students right here in Silicon Valley are hungry. That’s why Chegg has [Images attached] [Status update]. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/LifeAtChegg/posts/1076718522691591
Twitter posts:
Structure: Account holder’s Last name, F. M. [Twitter Handle]. (Year, Month Day of Post). Up to the first 20 words of tweet [source type if attached] [Tweet]. Twitter. URL
Source type examples: [Video attached], [Image attached], [Poll attached]
Example: Edelman, J. [Edelman11]. (2018, April 26). Nine years ago today my life changed forever. New England took a chance on a long shot and I’ve worked [Video attached] [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/Edelman11/status/989652345922473985
Instagram posts:
APA citation format: Account holder’s Last name, F. M. [@Instagram handle]. (Year, Month Day). Up to the first 20 words of caption [Photograph(s) and/or Video(s)]. Instagram. URL
Example: Portman, N. [@natalieportman]. (2019, January 5). Many of my best experiences last year were getting to listen to and learn from so many incredible people through [Videos]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/p/BsRD-FBB8HI/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link
If this guide hasn’t helped solve all of your referencing questions, or if you’re still feeling the need to type “how to cite a website APA” into Google, then check out our APA citation generator on CitationMachine.com, which can build your references for you!
Featured links:
APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDF
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Help | Advanced Search
Electrical Engineering and Systems Science > Audio and Speech Processing
Title: style mixture of experts for expressive text-to-speech synthesis.
Abstract: Recent advances in style transfer text-to-speech (TTS) have improved the expressiveness of synthesized speech. Despite these advancements, encoding stylistic information from diverse and unseen reference speech remains challenging. This paper introduces StyleMoE, an approach that divides the embedding space, modeled by the style encoder, into tractable subsets handled by style experts. The proposed method replaces the style encoder in a TTS system with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) layer. By utilizing a gating network to route reference speeches to different style experts, each expert specializes in aspects of the style space during optimization. Our experiments objectively and subjectively demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in increasing the coverage of the style space for diverse and unseen styles. This approach can enhance the performance of existing state-of-the-art style transfer TTS models, marking the first study of MoE in style transfer TTS to our knowledge.
| Subjects: | Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Sound (cs.SD) |
| Cite as: | [eess.AS] |
| (or [eess.AS] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences. MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities. Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history. Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Now among citation pages, there are three different types: reference list, bibliography and works cited. A reference list and a works cited list only the ideas or quotes used in the body of the paper. A bibliography, on the other hand, will list all the sources used in the creation of the body of the paper, even if they weren't cited in the ...
A bibliography is a detailed list of all the sources consulted and cited in a research paper or project. The bibliography structure always includes citing the author's name, the title of the work ...
To create a bibliography, gather up all of the sources that you might use in your paper. Create an APA format reference for each source and then write a brief annotation. Your annotation should be a brief summary of what each reference is about. You can quickly refer to these annotations When writing your paper and determine which to include.
The citation style sometimes depends on the academic discipline involved. For example: APA (American Psychological Association) is used by Education, Psychology, and Sciences. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is used by the Humanities. Chicago/Turabian style is generally used by Business, History, and the Fine Arts.
What is a citation style? The way that citations appear (format) depends on the citation style, which is a set of established rules and conventions for documenting sources. Citation styles can be defined by an association, such as the Modern Language Association (MLA), publisher, such as the University of Chicago Press, or journal, such as The ...
Bibliography. If you are using Chicago style footnotes or endnotes, you should include a bibliography at the end of your paper that provides complete citation information for all of the sources you cite in your paper. Bibliography entries are formatted differently from notes. For bibliography entries, you list the sources alphabetically by last ...
Formatting a Harvard style bibliography. Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading 'Reference list' or 'Bibliography' appears at the top. Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used: Harvard bibliography example.
A bibliographic citation is a reference to a book, article, web page, or other published item that provides the necessary information for readers to locate and retrieve that source. It includes the following information: When writing a research paper, it is important to cite sources and paraphrase to avoid plagiarism.
The 2 styles. The first style is the notes and bibliography style. This style uses footnotes or endnotes to point readers to the original source of the information. This style also often provides a bibliography at the end that readers consult, but this is not always necessary if sources are cited in full in your text.
Citation Styles & Tools Quick MLA, APA, and Chicago style guides for bibliographies; tools for storing and organizing sources. Course Reserves Library materials reserved for your classes. Collections & Archives Unique online and physical collections on specific subjects, in distinct formats, and in special archives.
A bibliography is a list of all of the sources you have used in the process of researching your work. In general, a bibliography should include: the authors' names. the titles of the works. the names and locations of the companies that published your copies of the sources. the dates your copies were published.
When it is time to turn in your Bibliography, type all of your sources into a list. Use the examples in MLA Format Examples or APA Format Examples as a template to insure that each source is formatted correctly. List the sources in alphabetical order using the author's last name.
When using BiBTeX, the bibliography style is set and the bibliography file is imported with the following two commands: \bibliographystyle{ stylename } \bibliography{ bibfile } where bibfile is the name of the bibliography .bib file, without the extension, and stylename is one of values shown in the table below .
The in-text citation lets the reader know that the information came from the cited source. The reference list entry provides complete details of a source and is shown at the end of a document. In order to properly cite a source in APA style, you must have both citation types in your paper. Every in-text citation has a reference list entry.
Type the last name of the first author listed on the source followed by a comma, then the first author's first name followed by a comma. Then type the word "and" then list the second author's first name and last name in the standard order. Follow the second name with a period.
The author-date style is an efficient and clear method of providing citations to published sources, which appear in a reference list at the end of the chapter or book. ... Bibliography entries in US style Authored book. Required elements. Lastname, Firstname, Title of Work, (Year of Publication). With optional elements. Lastname, Firstname, and ...
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field. APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences. MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
A reference list contains works that specifically support the ideas, claims, and concepts in a paper; in contrast, a bibliography provides works for background or further reading and may include descriptive notes (e.g., an annotated bibliography). The Publication Manual (see Section 9.51) provides formatting guidance and examples for annotated ...
APA Style ® calls for a list of references instead of a bibliography.. The requirements of a reference list are that all references cited in the text of a paper must be listed alphabetically by first author's last name in the list of references and that all references listed must be cited within the text.
APA Style provides guidelines to help writers determine the appropriate level of citation and how to avoid plagiarism and self-plagiarism. We also provide specific guidance for in-text citation, including formats for interviews, classroom and intranet sources, and personal communications; in-text citations in general; and paraphrases and direct quotations.
Usage. \documentclass[a4paper,10pt] { article } \begin { document } This is an example of a paragraph with in-text. citations using the plain BibTeX style. Here is a reference to a journal article with. a single author \cite { article1 }, to a journal. article with two authors \cite { article2 } and. three authors \cite { article3 }, and to a book.
Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper. However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style. Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples.
Enter the website's URL into the search box above. You'll get a list of results, so you can identify and choose the correct source you want to cite. It's that easy to begin! If you're wondering how to cite a website in APA, use the structure below. Structure: Author Last Name, First initial.
Recent advances in style transfer text-to-speech (TTS) have improved the expressiveness of synthesized speech. Despite these advancements, encoding stylistic information from diverse and unseen reference speech remains challenging. This paper introduces StyleMoE, an approach that divides the embedding space, modeled by the style encoder, into tractable subsets handled by style experts. The ...