
146+ Informative Speech Examples, Samples, Outlines, and Topics: Get Inspired
May 2, 2024

May 2, 2024 | Blog
Have you ever wondered what makes a speech truly informative and engaging? In exploring informative speech examples, we’ll dissect the elements that make a speech impactful and provide insights on crafting your compelling narrative. Whether you’re gearing up for a class presentation or simply curious about effective communication, we’ve got you covered.
What exactly is an informative speech, you ask? Well, think of it as a chance to share knowledge with your audience, like being a friendly guide on a journey of information. Unlike persuasive speeches aiming to sway opinions, informative speeches focus on presenting facts, ideas, or explanations.
So, let’s delve into this world of words, where you’ll discover the nuances of different speech types, from brief and concept speeches to autobiographical gems.
Ready to dive in? Let’s roll!
What Are Informative Speeches
Imagine you’re sharing cool facts with your friends. That’s an informative speech! It’s a type of speech where you deliver fascinating details to your audience.
But wait, isn’t that the same as an explanatory speech? Not quite!
While an explanatory speech clarifies, an informative one educates. So, think of yourself as a friendly guide, not a textbook.
Your mission? Present relevant information, explain concepts, and make sure your audience leaves enlightened. No convincing is informative and needed; just sharing knowledge like a pro!
Ready to inform? Let’s roll!
Effective Informative Speaking Vs. Persuasive Speaking
Let’s talk about the difference between effective informativeand persuasive speaking. Imagine you’re presenting a persuasive speech – you’re on a mission to convince your audience to see things your way. It’s like being a smooth talker, aiming to sway opinions.
Conversely, informative peaking is like a friendly guide, sharing facts without pushing a particular viewpoint. So, how do you think you could spot the variance?
In persuasive speeches, your closing statement is like the grand finale, the big persuasion moment. In informative speeches, it’s more about leaving your audience with a clear understanding.
Remember, it’s not about convincing; it’s about enlightening. So, when choosing a topic, ask yourself, “Am I trying to persuade or inform?” That’s the key to crafting a speech that hits the right notes for your audience.
How do you write a good informative speech?
Let’s dive into the art of crafting a stellar informative speech. Have you ever wondered what makes public speaking a task and an opportunity to share knowledge? Here’s your guide:
- Start with a Clear Purpose: Ask yourself, “What’s my goal here? Am I educating, explaining, or demonstrating?” Knowing your purpose helps shape your entire speech.
- Know Your Audience: Who are you talking to? I think it’s important that you understand your audience’s knowledge level. Are they familiar with the topic, or is it new territory?
- Choose a Relevant Topic: Pick something your audience can connect with. Remember, it’s about them understanding, not you impressing.
- Research Like a Pro: Dive into your topic like a detective. Gather facts, examples, and anecdotes. The more well-researched your speech, the more credible you become.
- Craft a Clear Structure: Organize your speech logically. Start with an introduction, followed by main points, and end with a memorable conclusion. Think of it as a journey with a roadmap.
- Engage with Your Audience: Connect with nonverbal cues – eye contact and gestures. Imagine you’re having a conversation, not delivering a monologue.
- Keep It Simple: Explain complex concepts in simple terms. Avoid jargon that might confuse your audience.
- Be Passionate: Even if your topic seems dry, let your enthusiasm shine through. Your passion is contagious!
How To Start An Informative Speech Examples
Have you ever wondered how to kick off an informative speech and grab your audience’s attention? Let’s break it down:
- Hook Your Audience: To start an informative speech, begin with a captivating fact, a relatable story, or a surprising statistic. Think of it as reeling in your audience, making them eager to hear more.
- Establish a Friendly Tone: In your introduction for an informative speech, set a welcoming atmosphere. Imagine you’re chatting with friends, creating a connection from the get-go.
- Declare Your Purpose: Could you explain why you’re there? Are you going to educate the audience on a fascinating topic or perhaps deliver an informative speech to clarify a concept?
- Please look over the Journey: Outline the main points you’ll cover. It’s like giving your audience a roadmap for the upcoming adventure. Could you let them know what to expect? Connect with nonverbal cues – eye contact and gestures
- Engage Your Audience: Interact with your audience members. Ask questions and share relatable experiences – make them part of the conversation. After all, an informative speech is a two-way street.
What does a good informative speech look like?
So, you’re curious about what a good informative speech looks like? Fantastic! Let’s paint a picture together:
- Clear Introduction: A great informative speech kicks off with a bang. Imagine it like a friendly invitation – you want your audience excited to join you on this learning journey. Ask a thought-provoking question or share an intriguing fact to grab their attention.
- Defined Purpose: Right out of the gate, your audience should know what type of speech they’re in for. Are you here to educate, explain, or show something cool? Make it crystal clear.
- Organized Structure: Picture your speech like a well-arranged book. Start with a captivating introduction, smoothly move through your main points, and wrap it up with a memorable conclusion. Think of it as a roadmap guiding your audience through the information.
- Engaging Content: Sprinkle your speech with relatable examples, anecdotes, or even a touch of humor. Keep your audience on their toes – you want them to remember your words.
- Visual Aids: If you’re explaining a process or showing statistics, use visuals. A picture is worth a thousand words.
- Connect with Your Audience: It’s about delivering information and connecting. Imagine you’re having a friendly chat, not delivering a lecture. Engage with your audience through eye contact and a conversational tone.
- Avoid Overloading with Information: While you want to be informative, avoid overwhelming your audience with a data dump. Pick the juiciest, most relevant information to keep them interested.
- Memorable Conclusion: Wrap things up with a bow. Summing up your main points and leaving your audience with a clear understanding. It’s like leaving a lasting impression after a great conversation.
What are examples of informative writing?

The following is an informative speaking excerpt on smoking:
It is general knowledge that smoking is bad for your health. Yet, the number of smokers globally increases each year. In 2018, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 1.1 billion people in the world use tobacco. That number might rise to 1.6 billion by 2025.
Tobacco kills, which smokers ignore until they get cancer or another terminal disease. It results in 6 million deaths per year. That means that there is one tobacco-related death every six seconds.
That said, a lack of information about the effects of smoking is a significant contributor to this pandemic. A survey conducted in China revealed that only 38% of tobacco smokers knew the habit could lead to heart disease, and only as few as 27% were aware smoking could cause a stroke.
Ignorance is no defense. So, today, I will present the adverse effects of tobacco and back them up with facts and real-world statistics.
The following is another informative speaking excerpt on global warming:
A global warming search on Google brings back 65 million results pages. The subject has drawn a lot of attention due to adverse climate change . In a speech presented at the UN Summit in 2019, Barrack Obama said that we must solve climate change swiftly and boldly or risk leaving future generations to an irreversible catastrophe.
A YouTube Influencer, Prince EA, addressed this issue by saying that our descendants will know it as the Amazon Desert instead of the Amazon Rainforest if we are not careful. Imagining the Amazon as a dessert should give you chills, and it seems so farfetched, but it could be a reality if global warming is not addressed.
But what exactly is global warming? What causes it? And what can we do to stop it? In this short but informative speech, I will answer these questions effectively.
Examples of Informative Speeches in Literature or Popular Culture:
Excerpt from Marie Curie’s speech on the discovery of radium:
I could tell you many things about radium and radioactivity, and it would take a long time. But as we can not do that, I shall only give you a short account of my early work about radium. Radium is no longer a baby; it is more than twenty years old, but the discovery conditions were somewhat peculiar, so remembering and explaining them is always of interest. We must go back to the year 1897. Professor Curie and I worked then in the School of Physics and Chemistry laboratory, where Professor Curie held his lectures. I was engaged in some work on uranium rays which had been discovered two years before by Professor Becquerel.***I spent some time studying the way of making good measurements of the uranium rays, and then I wanted to know if there were other elements, giving out rays of the same kind. So I took up work about all known elements and their compounds and found that uranium compounds and all thorium compounds are active, but other elements were not found active, nor were their compounds. As for the uranium and thorium compounds, I found that they were active in proportion to their uranium or thorium content.
The impassioned political speech by President George W. Bush’s address to the nation as the US attacked Iraq begins as an informative speech:
At this hour, American and coalition forces are in the early stages of military operations to disarm Iraq, free its people, and defend the world from grave danger.
On my orders, coalition forces began striking selected targets of military importance to undermine Saddam Hussein’s ability to wage war. These are the opening stages of a broad and concerted campaign.
More than 35 countries are giving crucial support, from using naval and air bases to help with intelligence and logistics to deploying combat units. Every nation in this coalition has chosen to bear the duty and share the honor of serving in our common defense.
Informative Speech Examples
- Example Of A Speech
- Example Of A Written Speech
- Example Of An Outline For An Informative Speech
- Example Of Informative Outline – The Importance of Regular Physical Exercise
- Example Of Informative Presentation on The Fascinating World of Honeybees
- Example Of Informative Speech Introduction
- Example Of Informative Speech Outline
- Example Of Informative Speech Topics
- Example Of Introduction In Informative Speech
- Example Of Short Speech
- Example Of Speech Format
- Example Of Thesis Statement For Informative Speech
- Example Outline For Informative Speech
- Example Speeches For Students
- Example Topic Of Informative Speech
- Examples For Informative Speech
- Examples Of A How To Speech
- Examples Of A Informative Speech
- Examples Of An Informative Speech
- Examples Of An Informative Speech Outline
- Examples Of Informative Presentations
- Examples Of Informative Speech Outlines
- Examples Of Informative Speech Thesis Statements
- Examples Of Introduction Speeches
- Examples Of Introductory Speeches
- Examples Of Preview Statements
- Examples Of Speech Outlines
- Examples Of Speeches
- Examples Speech Writing
- Explanatory Speech Examples on the Power of Sleep
- Expository Speech Example
- An Example Of An Informative Speech
- Brief Speech Example
- Concept Speech Examples
- Description Speech Example
- Example For A Speech
- Example For Informative Speech
- Example In Speech
- Expository/Informative Speech Examples
- Inform Speech Examples
- Informal Speech Examples
- Informative Example
- Informative Presentation Examples
- Informative Presentation Outline Example
- Informative Speaking Examples
- Informative Speech Conclusion Example
- Informative Speech Examples About Life
- Informative Speech Examples For Students
- Informative Speech Intro Examples
- Informative Speech Introduction Example
- Informative Speech Introduction Examples
- Informative Speech Thesis Examples
- Informative Speech Thesis Statement Examples
- Informative Speech Topic Examples
- Informative Speech Topics Examples
- Informative Topic Examples
- Introduction In Speech Example
- Introduction Informative Speech Examples
- Introduction Speech Example
- Introduction Speech Examples For Students
- Introduction To Informative Speech Examples
- Outline Example For Informative Speech
- Outline Of Informative Speech Example
- Personal Speech Examples
- Preview Statement Examples
- Short Speech Examples
- Short Speech Examples For Students
- Speech Examples For Students
- Speech Examples Informative
- Speech Informative Example
- Speech Introduction Examples
- Speech Of Explanation Examples
- Speech Script Example
- Speech Story Example
- Speech To Inform Examples
- Speech Writing Example
- Speech Writing Examples
- Thesis Examples For Informative Speech
- Thesis Examples For Speeches
- Thesis For Informative Speech Examples
- Written Speech Examples
- Informative Speech Worksheet Example
- Literature Informative Speech
- Short Informative Speech Examples
- Short Informative Speech on Smoking
- Literature Informative Speech Examples
- Informative Business Speech on New Product or Business Launch
- Business Informative Speech Examples
- Free Informative Speech
Informative Speech Samples
- Sample How To Speech
- Sample Informative Speech Outline
- Sample Of An Informative Speech
- Sample Of Informative Speech
- Sample Of Informative Speech Outline
- Sample Of Speech Introduction
- Sample Of Speech To Inform
- Sample Short Speech
- Sample Speech Outline Informative
- Sample Speech To Inform
- a sample of a speech
- best speech sample
- expository speech samples
- famous informative speeches
- great informative speeches
- intro of a speech sample
- personal experience speech samples
- short sample speech
- speech about informative
- speech samples for students
- Sample Informative Speech
- Student Informative Speech
- Informative Speech about Love
- Informative Speech about Friendship
- Example Informative Speech Outline
How To Write An Informative Speech Outline

- Start with a Clear Purpose: Before diving into the details, ask yourself, “What’s the goal here?” Is it to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint or inform them about a topic?
- Pick Your Main Points: Could you identify the key ideas you want to convey? Imagine telling a friend about your favorite movie – what would you highlight?
- Organize Your Thoughts: Arrange your main points logically. Think of it as creating a roadmap for your audience. You want them to follow along easily.
- Add Supporting Details: Each main point needs backup dancers! Sprinkle in facts, examples, or anecdotes. This isn’t a demonstrative speech , but adding a story here and there keeps it engaging.
- Create a Memorable Introduction: Your introduction is like the trailer for a movie. It should grab attention and hint at what’s coming. Consider posing a question or sharing a surprising fact.
- Conclude Strong: Summing up your main points and leave a lasting impression. A good conclusion for an informative speech should tell your audience, “Wow, I learned something valuable!”
- Practice Your Timing: A well-prepared speaker keeps an eye on the clock. Ensure your speech runs smoothly or cut smoothly, not run too long or cut too short.
- Be Open to Adjustments: Sometimes, the best ideas appear during practice. Be flexible and tweak your outline if needed. For tutoring, check out Spark on how to create an informative speech outline.
Informative Speech Outline Examples
- Example Of An Informative Speech Outline
- Autobiographical Speech Outline
- Informative Outline Example
- Informative Outline Examples
- Informative Speech Outline Format Example
- Informative Speech Outline Samples
- Informative Speech Outline Topics
- Informative Speech Template Outline
Informative Speech Format Examples
10+ informative speech examples & samples in pdf, alliteration examples in literature , informative speeches about concepts, informative speeches about objects, list of informative speech topics: ideas to spark your creativity, informative speeches topics for history and the humanities.
1. The Olympics in Ancient Greece
2. Explore the history of tattoos and body art
3. Economic divisions and the Vietnam War
4. Burial practices in ancient cultures and societies
5. How escaped enslaved people communicated along the Underground Railroad
6. Immigration history in America
7. Mahatma Gandhi and Indian apartheid
8. Innovations that came out of the great wars
9. The assassination of John F Kennedy
10. Sculpture in the Renaissance
11. The Salem Witch Trials
12. Colonization and its impact on the European powers in the Age of Exploration and beyond
13. The Gold Rush in California and its impact or significance
14. Fashion in Victorian Britain
15. Japanese Kamikaze fighters during World War II
16. The significance of the Stonewall Riots
17. The Spanish Flu
18. Rum running during Prohibition
19. Society and life in the Dark Ages
20. The mystery of Leonardo DaVinci’s Mona Lisa painting
Interesting Topic Ideas For English And Classic Literature
1. Depictions of classic literature in modern films
2. Depictions of the apocalypse in literature and fiction
3. Common themes in Victorian literature from the th century
4. How to beat writer’s block
5. Symbolism in Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird
6. The history of spirits or the supernatural in classic literature
7. The concept of madness in William Shakespeare’s tragedies
8. War poetry from any period
9. How Shakespeare’s plays helped shape the modern language
10. Ernest Hemingway’s narrative on masculinity
11. How to define the canons of classic literature
12. Which books published today would be classic literature in the future?
13. Common themes in Gothic literature
14. Feminist theory and the works of Charlotte Perkins Gilman
15. The practice of banning books and literature from schools
16. Rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” speech
17. Satire in Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice
18. Human nature in Plato’s The Republic
19. The impact of modern technology on literature and publishing
20. Rationality in William Golding’s Lord of the Flies
Intriguing Topics About Current Affairs, Social Issues, And Human Rights
1. Current social movements such as Black Lives Matter or the Occupy Wall Street movement
2. The influence of cultural traditions on human rights in various countries
3. Benefits of social media for collective action in areas where human rights are being contested
4. Support and guidance for troubled children in the current foster care system
5. The prevalence of child abuse in modern society
6. The United Nations Human Rights Council and its purpose/function
7. Women’s rights/freedoms in third world countries
8. Human trafficking in first-world countries
9. Patterns in America’s fastest-growing cities
10. Generational divisions and tensions between Baby Boomers, Millennials, or Generation Z
11. The concept of universal human rights
12. What our society has learned from the COVID- pandemic
13. Uses of torture to extract information from high-level criminals or terrorists
14. The influence of Westernization on human rights in other countries
15. The role of the United Nations in the interest of global human rights
16. Racial prejudice in the workplace
17. Explore modern protest culture
18. Idolization of celebrities in modern society
19. “Viral” culture in today’s society
20. Social media influencers and Tik Tok stars and their celebrity status among Generation Z
Creative Ideas For Film, Music, And Popular Culture
1. Mythology in popular culture
2. Censorship issues in music
3. Superhero culture in society
4. Focus on a music subculture and how it has empowered that group of people
5. Modern horror films and “shock value”
6. The importance of teaching music in elementary and high schools
7. The impact of a historical musician or musical group and their impact on today’s music
8. How streaming services have changed the film/television or music industry
9. Domestic violence in the media
10. Disney princesses and their impact on young girls in society
11. The history of jazz music in New Orleans
12. Crime scene television – accuracies and inaccuracies
13. Which popular cultural artifacts will archaeologists study in the future to learn about our society?
14. The role of music in social movements
15. Originality in today’s music, movies, or television shows
16. Religious symbolism in Star Wars
17. The current status of the idea of the “Blockbuster” movie
18. Child stars and the problems they face as they age
19. Sexuality and messaging in film and television
20. The power of satire in comedy
What are some good topics for an informative speech?
Example Informative Speech Topics
Informational Topics For Speeches Informative Speech Ideas Informative Speech About A Person Informative Speech Essay Informative Speech Intro Informative Speech Introduction Informative Speech Meaning
Sample Informative Speech Topics
Topics To Do Informative Speeches On Things To Write An Informative Speech About What To Write An Informative Speech About What To Write An Informative Speech On
Get Help With Your Informative Speech Writing
Need help with your informative speech? Fret not! Essay Freelance Writers has your back. Our expert team excels in crafting top-notch speeches tailored just for you. How do I nail that conclusion for an informative speech? We’ve got the perfect formula. But hey, what exactly is an informative speech, you ask? It’s a dynamic way to inform the audience and share knowledge. Our skilled writers present information effectively and ensure your speech leaves a lasting impact. Whether you need to define informative speech elements or deliver a compelling information speech, our team guides you. So, why stress? Click that ORDER NOW button to make your informative speech shine!
What is an example of an informative speech?
An example of informative speaking could be a presentation on climate change, providing facts and data to educate the audience.
What are good informative speech topics?
Good informative speech topics include subjects like space exploration, sustainable living, or the history of ancient civilizations.
What is an example of an informative speech about objects?
An informative speech about objects could focus on the history and significance of a specific artifact, like the Rosetta Stone.
What is a good introduction for an informative speech?
A good introduction for an informative speech grabs attention, such as posing a thought-provoking question or sharing a relevant anecdote, setting the tone for the presentation.

With a passion for helping students navigate their educational journey, I strive to create informative and relatable blog content. Whether it’s tackling exam stress, offering career guidance, or sharing effective study techniques
People Also Read
- 78 Sports Informative Speech Topics To Wow Your Audience
- Master the Art of Writing an Informative Essay with These 10 Examples
- Top 293 Speech Topics for Students: Persuasive, Descriptive, Informative Speech Topics

Most Popular Articles
Racism thesis statement example, how to rephrase a thesis statement, capstone project topic suggestions, how to write an abortion essay, should students wear school uniforms essay, list causal essay topics write, respect essay, signal words, great synonyms, informative speech examples, essay writing guide, introduction paragraph for an essay, argumentative essay writing, essay outline templates, write an autobiographical essay, personal narrative essay ideas, descriptive essay writing, how to write a reflective-essay, how to write a lab report abstract, how to write a grant proposal, point of view in an essay, debate topics for youth at church, theatre research paper topics, privacy overview.
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Informative Speech Outline – Template & Examples

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Informative speeches are used in our day-to-day lives without even noticing it, we use these speeches whenever we inform someone about a topic they didn’t have much knowledge on, whenever we give someone instructions on how to do something that they haven’t done before, whenever we tell someone about another person. Informative speaking is fairly new to the world of public speaking. Ancient philosophers like Aristotle, Cicero and, Quintilian envisioned public speaking as rhetoric, which is inherently persuasive.
In this article:
What is an Informative Speech?
Here are some ways to prepare for your speech, 1. develop support for your thesis, 2. write your introduction and conclusion, 3. deliver the speech, example of an informative speech outline.

An informative speech is designed to inform the audience about a certain topic of discussion and to provide more information. It is usually used to educate an audience on a particular topic of interest. The main goal of an informative speech is to provide enlightenment concerning a topic the audience knows nothing about. The main types of informative speeches are descriptive, explanatory, demonstrative, and definition speeches. The topics that are covered in an informative speech should help the audience understand the subject of interest better and help them remember what they learned later. The goal of an informative speech isn’t to persuade or sway the audience to the speaker’s point of view but instead to educate. The details need to be laid out to the audience so that they can make an educated decision or learn more about the subject that they are interested in.
It is important for the speaker to think about how they will present the information to the audience.
Informative Speech Preparation

When you are preparing your informative speech, your preparation is the key to a successful speech. Being able to carry your information across to the audience without any misunderstanding or misinterpretation is very important.
1. Choose Your Topic
Pick a topic where you will explain something, help people understand a certain subject, demonstrate how to use something.
2. Make a Thesis Statement
Think about what point you are trying to get across, What is the topic that you want to educate your audience on? “I will explain…” “I will demonstrate how to…” “I will present these findings…”
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
3. Create Points That Support Your Thesis
Take a moment to think about what would support your thesis and take a moment to write the points down on a sheet of paper. Then, take a moment to elaborate on those points and support them.
Typical Organization for an Informative Speech:
How to Speech: 4 Key steps to doing what you are talking about.
Example: Step One: Clean the chicken of any unwanted feathers and giblets. Step Two: Spice the chicken and add stuffings. Step Three: Set oven to 425 degrees Fahrenheit. Step Four: Place chicken in the oven and cook for an hour.
History/ What Happened Speech: Points listing from the beginning to the latest events that you want to discuss in your speech.
Example: First, Harry met Sally. Second, Harry took Sally out to the roadhouse. Third, Harry and Sally started their courtship. Fourth, Harry and Sally moved in together and adopted a dog named Paco.
What is it Speech: Two to Four main points that discuss the key elements of your subject.
Example: First, there must be four wheels. Second, the car’s engine must be functioning. Third, the doors must be functional. Fourth, in order to get to your destination, the car’s steering has to be functional.
Explain it Speech: Two to Four main points that go through the key elements of the topic to explain it.
Example: Firstly, the car drives by the engine that powers it to move forward. Secondly, by the wheels that rotate in a forward or backward motion. Thirdly, the car’s engine is powered by gas which gives it the ability to function and essentially move the car.
Write down support for your points. Take some time to research your topic thoroughly. It is good to gather statistics, expert opinions, facts, and much more to make your speech unique and effective.
There are three main types of support you should use to strengthen your speech:
Interest supports.
Interest supports are used to increase the audience’s interest in the topic you are presenting.
- Personal experiences
- Interaction (e.g., Questions to the audience)
Evidence Supports
Evidence increases solid factual support in your speech. Examples of evidence supported are statistics, expert opinions, direct quotations. Studies, surveys, and facts.
Multimedia Aids
Multimedia aids such as posters with pictures and writing, DVDs, music or recordings on a stereo player, videotapes, and PowerPoint presentations.
Write your introduction. Provide a quick attention getter, state your thesis, elaborate on why it is important to you and your audience. It is expected that you preview your main points in the introduction by listing all your main points of discussion in your introduction.
Write your conclusion. Tie the speech together, build to a higher point and give it a sense of conclusion.
Practice your speech until you feel confident. Present your material as effectively as possible.
Informative Speech Outline

Creating an outline for an informative speech will help you organize your ideas and information to share with your audience in an effective manner. A well-planned outline will ensure that all the important information is included in your speech and ensure that you don’t wander off-topic.
Topic: This will be the title of your speech.
Purpose: To inform the audience about the topic.
Thesis: A theme statement that clearly describes the topic and points made in the presentation.
- Introduction
- Attention-grabbing opening statement
- Reason to listen to the speech
- Thesis statement
- Preview of points to be covered
- First main point
- First subpoint
- Supporting detail
- Second subpoint
- Second main point
- Third main point
- Restatement of main points
- Restatement of thesis
- Concluding remarks
When developing an outline, follow these rules to ensure a successful speech:
- Include one idea for every point, subpoint, or supporting detail.
- If there is one point, there must be a second point. If there is one supporting point, there should be a second supporting point.
- Be consistent. If you are using full sentences to describe points and subpoints, use full sentences throughout the outline. Ensure that the verb tense is consistent throughout your outline as well.
Informative Speech Outline Examples

Topic: Adoption
Purpose: To inform people about adoption
Thesis: Adoption is the act of transferring parental rights and duties to someone other than the adopted person’s biological parents. The number of children adopted each year by American families is an estimate only.
- What do Edgar Allan Poe, John Lennon, Steve Jobs, and Eleanor Roosevelt all have in common? They were all adopted. Adoption is the act of transferring parental rights and duties to someone other than the adopted person’s biological parents. The adoption process is lengthy, expensive, and varies from country to country and even state to state. Not only does adoption vary from state to state, but sometimes the adoption process even varies within regions of a state.
- Many children get adopted every year. No one knows how adoption works.
- Adoption is a life-changing event, not just for the children involved but also for every single family made whole through adoption.
- Adoption processes vary from place to place. Types of adoption. Benefits and detriments to adoption. Many children who are adopted have experienced neglect and abuse.
- Adoption processes vary from place to place.
- The adoption process varies from state to state.
- It is more expensive in certain states than in others.
- The amount of paperwork throughout the process also depends on the state legislature.
- The adoption process varies within a state.
- In certain states, the adoption process is different from one region to the next.
- The process is different depending on the child protection laws set in each region inside a state.
- Types of adoption
- There are different types of adoption.
- There is step-parent or other family member adoption
- There is also adoption across state lines
- The more traditional adoption types are commonly known.
- There is private adoption which is most commonly found throughout the U.S.
- Adoption through foster care is a good thing to try for first-time adopters.
- The adoption process is expensive.
- There are a lot of upfront expenses.
- You are subjected to adoption agency fees to help you find a suitable match for your family.
- You also have to pay to adopt the child you want to adopt.
- There are a lot of big expenses in terms of the child too.
- Readying a living space to suit a child’s wants and needs can be expensive.
- Many new expenses come to light like healthcare, school, etc.
- Adoption processes vary from state to state. There are many different types of adoption. Adoption can be expensive, so you have to ensure that you are financially capable of caring for another human being.
- Adoption is the act of transferring parental rights and duties to someone other than the adopted person’s biological parents. The number of children adopted each year by American families is an estimate only.
- Adoption is an absolutely life-changing adventure, but everyone needs to be more educated before walking into a demanding process. There will be many emotions, expenses, and frustration, but it truly is worth it in the end.
Topic: Snakebites and how they’re treated
Purpose: To inform the audience of the dangers of snakes and how to respond to being bitten by a snake.
Thesis: Snakebites are dangerous and could ultimately lead to loss of life if not acted upon correctly.
- Imagine that you and your friend are walking in the woods, one sunny day in the fall when leaves cover the ground. Suddenly, your friend accidentally steps on a snake and gets bitten.
- Your friend’s chance of survival depends on your knowledge of acting promptly and taking proper measures in this situation.
- Today I will inform you about three common poisonous snakes seen in our country and explain to you the effects of a snake bite.
- Three poisonous snakes. Effects of the snake’s venom. How to administer first aid in the event of a snake bite.
- Three poisonous snakes
- There are two types of Rattlesnakes.
- William Pinkston: Responsible for more deaths in this country.
- Western diamondback: found from Texas to Eastern California.
- Copperhead and Cottonmouth
- Before striking, it opens its mouth wide to reveal its white inside.
- That’s how it got its name.
- The effects of snake venom on the human body
- Hepatotoxic
- Destroys blood vessels and red blood cells.
- Deadly and fatal to the victim.
- It affects the optic nerves in the eyes, causing blindness.
- It affects the nerves controlling the respiratory muscles, causing suffocation and eventually leading to death if left untreated.
- How to administer first aid in the event of a snake bite.
- Immobilize the bitten area slightly lower than the heart.
- Apply a flat constricting band 2-4 inches above the bite.
- With a sterile scalpel or knife, make one incision that connects the fang marks.
- Squeeze venom gently from the incision with your fingers for 30 minutes.
- Get the victim to the hospital as soon as possible.
- Snake bites are dangerous and could ultimately lead to loss of life if not acted upon correctly.
- Snake bites are dangerous and could ultimately lead to loss of life if they are not cared for properly, and the victim doesn’t get the necessary treatment in time.
Informative speeches have one main goal: to inform the audience of a specific topic of interest. For you to have an effective and successful informative speech, it is important to do your research and draw up an informative speech outline. The speech outline ensures that you do not wander off topic or get carried away with one point.
If, on the other hand, you have to prepare persuasive speech, we have a guide on outlining and preparing for it the right way right here .
Avoid Any Awkward Silence With These 35+ Topics to Talk About
16 Tips to Help You Write Like a Pro
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

14.5: Sample Informative Speeches and Speech Outlines
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 174388
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Sample Informative Speech Outline
By Shannon Stanley
Topic: Lord Byron
Specific Purpose: To inform my audience about the life of George Gordon, Lord Byron.
Central Idea: George Gordon, Lord Byron overcame physical hardships, was a world-renowned poet, and an advocate for the Greek’s war for freedom.
Introduction
A. Attention step : Imagine an eleven year old boy who has been beaten and sexually abused repeatedly by the very person who is supposed to take care of him. B. Reveal topic/thesis : This is one of the many hurdles that George Gordon, better known as Lord Byron, overcame during his childhood. Lord Byron was also a talented poet with the ability to transform his life into the words of his poetry. Byron became a serious poet by the age of fifteen and he was first published in 1807 at the age of nineteen. Lord Byron was a staunch believer in freedom and equality, so he gave most of his fortune, and in the end, his very life, supporting the Greek’s war for independence. C. Establish credibility : While many of you have probably never heard of Lord Byron, his life and written work will become more familiar to you when you take Humanities 1201, as I learned when I took it last semester. D. Preview body of speech : In this speech I will talk about Lord Byron’s early childhood, accomplishments, and life outside of poetry
Transition : Let me start with Lord Byron’s childhood.
A. Main point 1: Lord Byron’s childhood
I. Subpoint 1: Birth and disability
a. Lord Byron was born on January 22, 1788 to Captain John Byron and Catherine Gordon Byron. b. According to Paul Trueblood, the author of Lord Byron, Lord Byron’s father only married Catherine for her dowry, which he quickly went through, leaving his wife and child nearly Penniless. c. By the age of two, Lord Byron and his mother had moved to Aberdeen in Scotland and shortly thereafter, his father died in France at the age of thirty-six. d. Lord Byron was born with a clubbed right foot, which is a deformity that caused his foot to turn sideways instead of remaining straight, and his mother had no money to seek treatment for this painful and embarrassing condition. e. He would become very upset and fight anyone who even spoke of his lameness f. Despite his handicap, Lord Byron was very active and liked competing with the other boys.
II. Subpoint 2: Later childhood, sexual abuse.
a. At the age of ten, his grand-uncle died leaving him the title as the sixth Baron Byron of Rochdale. With this title, he also inherited Newstead Abbey, a dilapidated estate that was in great need of repair. b. Because the Abbey was in Nottinghamshire England, he and his mother moved there and stayed at the abbey until it was rented out to pay for the necessary repairs. c. During this time, May Gray, Byron’s nurse had already begun physically and sexually abusing him. A year passed before he finally told his guardian, John Hanson, about May’s abuse; she was fired immediately. Unfortunately, the damage had already been done. d. In the book Lord Byron, it is stated that years later he wrote “My passions were developed very early- so early, that few would believe me if I were to state the period, and the facts which accompanied it.”
Transition : Although Lord Byron had many obstacles to overcome, during his childhood, he became a world-renowned poet by the age of 24.
B. Main point 2: Lord Byron’s accomplishments as a poet
I. Subpoint 1: Beginning of the career
a. Lord Byron experienced the same emotions we all do, but he was able to express those emotions in the form of his poetry and share them with the world. b. According to Horace Gregory, The author of Poems of, George Gordon, Lord Byron, the years from 1816 through 1824 is when Lord Byron was most known throughout Europe. c. But according to Paul Trueblood, Childe Harold was published in 1812 and became one of the best-selling works of literature in the 19th century. d. Childe Harold was written while Lord Byron was traveling through Europe after graduating from Trinity College. e. Many authors such as Trueblood, and Garrett, the author of George Gordon, Lord Byron, express their opinion that Childe Harold is an autobiography about Byron and his travels.
II. Subpoint 2: Poem topics
a. Lord Byron often wrote about the ones he loved the most, such as the poem “She Walks in Beauty” written about his cousin Anne Wilmont, and “Stanzas for Music” written for his half-sister, Augusta Leigh. b. He was also an avid reader of the Old Testament and would write poetry about stories from the Bible that he loved. One such story was about the last king of Babylon. This poem was called the “Vision of Belshazzar,” and is very much like the bible version in the book of Daniel.
Transition : Although Lord Byron is mostly known for his talents as a poet, he was also an advocate for the Greek’s war for independence.
C. Main point 3: Lord Byron’s life other than poetry
I. Sub point 1: Byron arrived in Greece in 1823 during a civil war.
a. Lord Byron, after his self-imposed exile from England, took the side of the Greek’s in their war for freedom from Turkish rule. b. The Greek’s were too busy fighting amongst themselves to come together to form a formidable army against the Turks. According to Martin Garrett, Lord Byron donated money to refit the Greek’s fleet of ships, but did not immediately get involved in the situation. He had doubts as to if or when the Greek’s would ever come together and agree long enough to make any kind of a difference in their war effort. c. Eventually the Greek’s united and began their campaign for the Greek War of Independence. d. He began pouring more and more of his fortune into the Greek army and finally accepted a position to oversee a small group of men sailing to Missolonghi. e. Lord Byron set sail for Missolonghi in Western Greece in 1824. He took a commanding position over a small number of the Greek army despite his lack of military training. f. He had also made plans to attack a Turkish held fortress but became very ill before the plans were ever carried through.
II. Sub point II: Death
a. Lord Byron died on April 19, 1824 at the age of 36 due to the inexperienced doctors who continued to bleed him while he suffered from a severe fever. b. After Lord Byron’s death, the Greek War of Independence, due to his support, received more foreign aid which led to their eventual victory in 1832. c. Lord Byron is hailed as a national hero by the Greek nation d. Many tributes such as statues and road-names have been devoted to Lord Byron since the time of his death.
A. Signal end of speech (transition) : In conclusion, B. Review main points and summarize : Lord Byron overcame great physical hardships to become a world-renowned poet, and is seen as a hero to the Greek nation and is mourned by them still today. C. Sense of completeness/clincher/memorable ending : I have chosen not to focus on Lord Byron’s more liberal way of life, but rather to focus on his accomplishments in life. He was a man who owed no loyalty to Greece, yet gave his life to support their cause. Most of the world will remember Lord Byron primarily through his written attributes, but Greece will always remember him as the “Trumpet Voice of Liberty.”
Sample Informative Speech by Pamela Meyer
Garrett, M. (2000). George Gordon, Lord Byron. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Gregory, H. (1969). Poems of George Gordon, Lord Byron. New York, NY: Thomas Y. Crowell Company.
Trueblood, P. G. (1969). Lord Byron. (S. E. Bowman, Ed.). New York, NY:Twayne Publishers.

13.4 Sample Informative Speeches and Speech Outlines
Sample informative speech outline.
By Shannon Stanley
Topic: Lord Byron
Specific Purpose: To inform my audience about the life of George Gordon Byron, Lord Byron.
Central Idea: George Gordon (Lord Byron) overcame physical hardships, was a world-renowned poet, and was an advocate for the Greek’s war for freedom.
Introduction
A. Attention step : Imagine an eleven-year-old boy who has been beaten and sexually abused repeatedly by the very person who is supposed to take care of him. B. Reveal topic/thesis : This is one of the many hurdles that George Gordon, better known as Lord Byron, overcame during his childhood. Lord Byron was also a talented poet with the ability to transform his life into the words of his poetry. Byron became a serious poet by the age of fifteen, and he was first published in 1807 at the age of nineteen. Lord Byron was a staunch believer in freedom and equality, so he gave most of his fortune, and in the end, his very life, supporting the Greek’s war for independence. C. Establish credibility : While many of you have probably never heard of Lord Byron, his life and written work will become more familiar to you when you take Humanities 1201, as I learned when I took it last semester. D. Preview body of speech : In this speech I will talk about Lord Byron’s early childhood, accomplishments, and life outside of poetry
Transition : Let me start with Lord Byron’s childhood.
Body A. Main point 1: Lord Byron’s childhood
I. Subpoint 1: Birth and disability
a. Lord Byron was born on January 22, 1788, to Captain John Byron and Catherine Gordon Byron. b. According to Paul Trueblood, the author of Lord Byron, Lord Byron’s father only married Catherine for her dowry, which he quickly went through, leaving his wife and child nearly Penniless. c. By the age of two, Lord Byron and his mother had moved to Aberdeen in Scotland and shortly thereafter, his father died in France at the age of thirty-six. d. Lord Byron was born with a clubbed right foot, which is a deformity that caused his foot to turn sideways instead of remaining straight, and his mother had no money to seek treatment for this painful and embarrassing condition. e. He would become very upset and fight anyone who even spoke of his lameness f. Despite his handicap, Lord Byron was very active and liked competing with the other boys.
II. Subpoint 2: Later childhood, sexual abuse.
a. At the age of ten, his grand-uncle died, leaving him the title as the sixth Baron Byron of Rochdale. With this title, he also inherited Newstead Abbey, a dilapidated estate that was in great need of repair. b. Because the Abbey was in Nottinghamshire England, he and his mother moved there and stayed at the abbey until it was rented out to pay for the necessary repairs. c. During this time, May Gray, Byron’s nurse, had already begun physically and sexually abusing him. A year passed before he finally told his guardian, John Hanson, about May’s abuse; she was fired immediately. Unfortunately, the damage had already been done. d. In the book Lord Byron , it is stated that years later, he wrote, “My passions were developed very early—so early, that few would believe me if I were to state the period, and the facts which accompanied it.”
Transition : Although Lord Byron had many obstacles to overcome, during his childhood, he became a world-renowned poet by the age of 24.
B. Main point 2: Lord Byron’s accomplishments as a poet
I. Subpoint 1: Beginning of the career
a. Lord Byron experienced the same emotions we all do, but he was able to express those emotions in the form of his poetry and share them with the world. b. According to Horace Gregory, the author of Poems of George Gordon, Lord Byron , the years from 1816 through 1824 is when Lord Byron was most known throughout Europe. c. But according to Paul Trueblood, Childe Harold was published in 1812 and became one of the best-selling works of literature in the 19th century. d. Childe Harold was written while Lord Byron was traveling through Europe after graduating from Trinity College. e. Many authors such as Trueblood, and Garrett, the author of George Gordon, Lord Byron, express their opinion that Childe Harold is an autobiography about Byron and his travels.
II. Subpoint 2: Poem topics
a. Lord Byron often wrote about the ones he loved the most, such as the poem “She Walks in Beauty” written about his cousin Anne Wilmont, and “Stanzas for Music” written for his half-sister, Augusta Leigh. b. He was also an avid reader of the Old Testament and would write poetry about stories from the Bible that he loved. One such story was about the last king of Babylon. This poem was called the “Vision of Belshazzar,” and is very much like the bible version in the book of Daniel.
Transition : Although Lord Byron is mostly known for his talents as a poet, he was also an advocate for the Greek’s war for independence.
C. Main point 3: Lord Byron’s life other than poetry
I. Sub point 1: Byron arrived in Greece in 1823 during a civil war.
a. Lord Byron, after his self-imposed exile from England, took the side of the Greeks in their war for freedom from Turkish rule. b. The Greeks were too busy fighting amongst themselves to come together to form a formidable army against the Turks. According to Martin Garrett, Lord Byron donated money to refit the Greek’s fleet of ships, but did not immediately get involved in the situation. He had doubts as to if or when the Greeks would ever come together and agree long enough to make any kind of a difference in their war effort. c. Eventually the Greeks united and began their campaign for the Greek War of Independence. d. He began pouring more and more of his fortune into the Greek army and finally accepted a position to oversee a small group of men sailing to Missolonghi. e. Lord Byron set sail for Missolonghi in Western Greece in 1824. He took a commanding position over a small number of the Greek army despite his lack of military training. f. He had also made plans to attack a Turkish held fortress but became very ill before the plans were ever carried through.
II. Sub point II: Death
a. Lord Byron died on April 19, 1824, at the age of 36 due to the inexperienced doctors who continued to bleed him while he suffered from a severe fever. b. After Lord Byron’s death, the Greek War of Independence, due to his support, received more foreign aid which led to their eventual victory in 1832. c. Lord Byron is hailed as a national hero by the Greek nation d. Many tributes such as statues and road-names have been devoted to Lord Byron since the time of his death.
A. Signal end of speech (transition) : In conclusion, B. Review main points and summarize : Lord Byron overcame great physical hardships to become a world-renowned poet, and is seen as a hero to the Greek nation and is mourned by them still today. C. Sense of completeness/clincher/memorable ending : I have chosen not to focus on Lord Byron’s more liberal way of life, but rather to focus on his accomplishments in life. He was a man who owed no loyalty to Greece, yet gave his life to support their cause. Most of the world will remember Lord Byron primarily through his written attributes, but Greece will always remember him as the “Trumpet Voice of Liberty.”
Sample Informative Speech by Pamela Meyer
Garrett, M. (2000). George Gordon, Lord Byron. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Gregory, H. (1969). Poems of George Gordon, Lord Byron. New York, NY: Thomas Y. Crowell Company.
Trueblood, P. G. (1969). Lord Byron. (S. E. Bowman, Ed.). New York, NY: Twayne Publishers.
It’s About Them: Public Speaking in the 21st Century Copyright © 2022 by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Informative Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples

What is an informative speech?
An informative speech uses descriptions, demonstrations, and strong detail to explain a person, place, or subject. An informative speech makes a complex topic easier to understand and focuses on delivering information, rather than providing a persuasive argument.
Types of informative speeches
The most common types of informative speeches are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration.

A definition speech explains a concept, theory, or philosophy about which the audience knows little. The purpose of the speech is to inform the audience so they understand the main aspects of the subject matter.
An explanatory speech presents information on the state of a given topic. The purpose is to provide a specific viewpoint on the chosen subject. Speakers typically incorporate a visual of data and/or statistics.
The speaker of a descriptive speech provides audiences with a detailed and vivid description of an activity, person, place, or object using elaborate imagery to make the subject matter memorable.
A demonstrative speech explains how to perform a particular task or carry out a process. These speeches often demonstrate the following:
How to do something
How to make something
How to fix something
How something works

How to write an informative speech
Regardless of the type, every informative speech should include an introduction, a hook, background information, a thesis, the main points, and a conclusion.
Introduction
An attention grabber or hook draws in the audience and sets the tone for the speech. The technique the speaker uses should reflect the subject matter in some way (i.e., if the topic is serious in nature, do not open with a joke). Therefore, when choosing an attention grabber, consider the following:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?

Common Attention Grabbers (Hooks)
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way (e.g., a poll question where they can simply raise their hands) or ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic in a certain way yet requires no response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, which is typically done using data or statistics. The statement should surprise the audience in some way.
Provide a brief anecdote that relates to the topic in some way.
Present a “what if” scenario that connects to the subject matter of the speech.
Identify the importance of the speech’s topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
The thesis statement shares the central purpose of the speech.
Demonstrate

Preview the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose. Typically, informational speeches will have an average of three main ideas.
Body paragraphs
Apply the following to each main idea (body) :
Identify the main idea ( NOTE: The main points of a demonstration speech would be the individual steps.)
Provide evidence to support the main idea
Explain how the evidence supports the main idea/central purpose
Transition to the next main idea

Review or restate the thesis and the main points presented throughout the speech.
Much like the attention grabber, the closing statement should interest the audience. Some of the more common techniques include a challenge, a rhetorical question, or restating relevant information:
Provide the audience with a challenge or call to action to apply the presented information to real life.
Detail the benefit of the information.
Close with an anecdote or brief story that illustrates the main points.
Leave the audience with a rhetorical question to ponder after the speech has concluded.
Detail the relevance of the presented information.

Before speech writing, brainstorm a list of informative speech topic ideas. The right topic depends on the type of speech, but good topics can range from video games to disabilities and electric cars to healthcare and mental health.
Informative speech topics
Some common informative essay topics for each type of informational speech include the following:
Informative speech examples
The following list identifies famous informational speeches:
“Duties of American Citizenship” by Theodore Roosevelt
“Duty, Honor, Country” by General Douglas MacArthur
“Strength and Dignity” by Theodore Roosevelt
Explanation
“Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” by Patrick Henry
“The Decision to Go to the Moon” by John F. Kennedy
“We Shall Fight on the Beaches” by Winston Churchill
Description
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
“Pearl Harbor Address” by Franklin Delano Roosevelt
“Luckiest Man” by Lou Gehrig
Demonstration
The Way to Cook with Julia Child
This Old House with Bob Vila
Bill Nye the Science Guy with Bill Nye
- 2024 Calendar
- 2025 Calendar
- Monthly Calendar
- Blank Calendar
- Julian Calendar 2024
- Personal Letter
- Personal Reference Letter
- Collection Letter
- Landlord Reference Letter
- Letter of Introduction
- Notarized Letter
- Lease Renewal Letter
- Medication Schedule
- Bank Statement
- 100 Envelope Challenge
- Landscaping Invoice
- Credit Application Form
- Plane Ticket
- Child Support Agreement
- Payment Agreement
- Cohabitation Agreement
- Residential Lease Agreement
- Land Lease Agreement
- Real Estate Partnership Agreement
- Master Service Agreement
- Profit Sharing Agreement
- Subcontractor Agreement
- Military Time
- Blood Sugar Chart
- Reward Chart
- Foot Reflexology
- Hand Reflexology
- Price Comparison Chart
- Baseball Score Sheet
- Potluck Signup Sheet
- Commission Sheet
- Silent Auction Bid Sheet
- Time Tracking Spreadsheet
Free Printable Informative Speech Outline Templates [PDF, Word] Example
Are you tired of delivering dull and unengaging informative speeches ? Whether you’re a student or a business owner, the ability to make your speeches interesting is a valuable skill. Your audience will be more likely to listen and retain the information you present if they find the speech engaging. So, how can you make your informative speech more interesting?
There are various techniques you can use, such as using humor, incorporating interactive elements, and incorporating real-life examples. In this article, we’ll explore different ways to make your informative speeches more engaging and memorable for your audience.
Table of Contents
What is an Informative Speech?

An informative speech is a type of public speaking that aims to educate and inform the audience about a specific topic or subject. The goal of an informative speech is to provide the audience with knowledge, understanding, and insight into the topic being discussed.
The speaker delivers information in a clear and concise manner, using examples, facts, and other supporting materials to help the audience understand the topic. Unlike persuasive or argumentative speeches, the objective of an informative speech is not to persuade the audience to take a particular action or adopt a certain viewpoint, but simply to provide them with valuable information. Informative speeches can be delivered in a variety of settings, including classrooms, business meetings , and public events, and can be used to inform people about a wide range of topics, from science and technology, to history and culture.
Informative Speech Templates
Deliver impactful and organized presentations with our collection of Informative Speech Outline templates . These templates serve as a roadmap for structuring your speech, ensuring that your content is clear, engaging, and well-organized. Whether you’re delivering a speech in an academic setting, business environment, or any other professional context , our templates provide a framework to effectively convey information to your audience.
With sections for introduction, main points, supporting details, and conclusion, these templates help you organize your thoughts and present your ideas in a logical and compelling manner. Customize the templates to fit your specific topic, add visuals, and enhance the overall flow of your speech. Download our Informative Speech Outline templates and captivate your audience with a well-structured and impactful presentation.
Types of Informative Speeches
There are several types of informative speeches, including:

Definition speech
A definition speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker defines and explains a specific term or concept. The goal of a definition speech is to provide the audience with a clear and concise understanding of the term or concept being discussed. The speaker may provide a brief history of the term or concept, as well as its origin and evolution over time. The speaker may also use examples, illustrations, and analogies to help the audience understand the meaning of the term or concept.
The key to a successful definition speech is to provide accurate and relevant information in a clear and easy-to-understand manner, so that the audience leaves with a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Definition speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from technical terms in a specific field to commonly misunderstood concepts in society.
Descriptive speech
A descriptive speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker provides a detailed description of a person, place, or object. The goal of a descriptive speech is to create a vivid mental image for the audience so that they can imagine the person, place, or object being described. The speaker may use sensory details such as sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell to help the audience understand the subject being described.
The speaker may also use comparisons and contrasts to help the audience understand the unique qualities and characteristics of the person, place, or object. A successful descriptive speech requires the speaker to be imaginative and creative in their descriptions, and to use language that is both descriptive and easy to understand. Descriptive speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from famous historical landmarks to unique cultural experiences.
Explanatory speech
An explanatory speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker provides a step-by-step explanation of how to perform a task or process. The goal of an explanatory speech is to provide the audience with the knowledge and understanding they need to successfully perform the task or follow the process being discussed. The speaker may use diagrams, illustrations, and other visual aids to help the audience understand the steps involved.
The speaker may also use examples and anecdotes to help the audience understand the purpose and importance of each step. A successful explanatory speech requires the speaker to be organized and clear in their presentation, and to use language that is easy to follow and understand. Explanatory speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from technical processes in a specific field to everyday tasks such as cooking or home maintenance.
Process speech
A process speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker outlines the steps or stages involved in a process or event. The goal of a process speech is to provide the audience with a clear understanding of the sequence of events that take place in a particular process or event. The speaker may use diagrams, illustrations, and other visual aids to help the audience understand the steps involved.
The speaker may also use examples and anecdotes to help the audience understand the purpose and importance of each step. A successful process speech requires the speaker to be organized and clear in their presentation, and to use language that is easy to follow and understand. Process speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from complex industrial processes to everyday events such as baking a cake or preparing for a trip.
Demonstration speech
A demonstration speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker physically demonstrates how to perform a task or process. The goal of a demonstration speech is to provide the audience with a clear and hands-on understanding of how to perform the task or process being discussed. The speaker may use visual aids, props, and actual products to help the audience understand the steps involved.
The speaker may also use examples and anecdotes to help the audience understand the purpose and importance of each step. A successful demonstration speech requires the speaker to be confident and engaging in their presentation, and to use language that is easy to follow and understand. Demonstration speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from technical procedures in a specific field to everyday tasks such as cooking or home maintenance.
Object speech
An object speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker provides information about a specific object or item. The goal of an object speech is to provide the audience with a clear understanding of the characteristics, features, and history of the object being discussed. The speaker may use visual aids, props, and actual products to help the audience understand the object being described.
The speaker may also use comparisons and contrasts to help the audience understand the unique qualities and characteristics of the object. A successful object speech requires the speaker to be knowledgeable and descriptive in their presentation, and to use language that is easy to follow and understand. Object speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from famous works of art to unique technological devices.
Compare and contrast speech
A compare and contrast speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker discusses the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. The goal of a compare and contrast speech is to provide the audience with a clear understanding of the similarities and differences between the subjects being discussed. The speaker may use visual aids, examples, and anecdotes to help the audience understand the similarities and differences being discussed. The speaker may also use comparisons and contrasts to help the audience understand the unique qualities and characteristics of each subject. A successful compare and contrast speech requires the speaker to be organized and clear in their presentation, and to use language that is easy to follow and understand. Compare and contrast speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from different historical events to different types of products or services.
Cause and effect speech
A cause and effect speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker discusses the relationship between two events or conditions, where one event or condition is the result of the other. The goal of a cause and effect speech is to provide the audience with a clear understanding of the reasons behind an event or condition, and the consequences that result from it. The speaker may use examples, statistics, and anecdotes to help the audience understand the cause and effect relationship being discussed.
The speaker may also use cause and effect diagrams, illustrations, or other visual aids to help the audience understand the relationship between the events or conditions being discussed. A successful cause and effect speech requires the speaker to be organized and clear in their presentation, and to use language that is easy to follow and understand. Cause and effect speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from social and political issues to natural disasters and medical conditions.
Historical speech
A historical speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker discusses a particular event, person, or era in history. The goal of a historical speech is to provide the audience with a clear understanding of the subject being discussed, including its background, context, and significance. The speaker may use visual aids, props, and primary sources to help the audience understand the historical context of the event, person, or era being discussed. The speaker may also use anecdotes and storytelling techniques to help the audience understand the subject in a more engaging and memorable way.
A successful historical speech requires the speaker to be knowledgeable and passionate about their subject, and to use language that is easy to follow and understand. Historical speeches can be used to educate people about a wide range of subjects, from famous historical figures to important events in world history.
Checklist for Your Informative Speech
Here is a checklist that you can use when preparing and delivering an informative speech:
Choose a relevant and interesting topic: Make sure your topic is relevant and interesting to your audience, and that you have enough information to provide a comprehensive overview of the subject.
Research the topic: Gather as much information as possible about your topic, and use credible sources to ensure the accuracy of your information.
Organize your speech: Decide on the best way to present your information, and organize your speech into clear and concise sections.
Develop an introduction: Start your speech with an attention-grabbing introduction that will engage your audience and provide context for your topic.
Use visual aids: Consider using visual aids, such as slides, props, or videos, to help illustrate your points and make your speech more engaging.
Use clear and concise language: Make sure your language is clear, concise, and easy to understand, and use examples and anecdotes to help illustrate your points.
Rehearse your speech: Practice your speech several times, and consider recording yourself so you can get an idea of how it will sound when you deliver it.
Timing: Make sure you have enough time to cover all of the important points in your speech, but also be mindful of your audience’s attention span and keep your speech within a reasonable length.
Engage with your audience: Make eye contact, use gestures, and engage with your audience to help keep their attention and interest.
Practice good posture and delivery: Stand up straight, use confident body language, and project your voice so that everyone in the audience can hear you.
How to Write an Informative Speech?
Writing an informative speech can be a challenging task, but with the right preparation and strategy, it can also be a rewarding experience. Here are the steps you should follow to write an informative speech:
Choose a topic: Start by choosing a topic that is relevant and interesting to your audience. The topic should also be something that you are knowledgeable and passionate about, as this will make it easier for you to convey your information with enthusiasm and energy.
Research the topic: Once you have chosen a topic, it is time to research it thoroughly. Make sure you use credible sources to gather information, and take notes on the key points you want to cover in your speech.
Organize your information: Now that you have gathered all of your information, it’s time to organize it in a way that makes sense to your audience. Consider dividing your speech into clear and concise sections, and use headings or subheadings to help guide the audience through your information.
Write an introduction: Start your speech with an attention-grabbing introduction that will grab your audience’s attention and provide context for your topic. This could include a personal story, a surprising statistic, or a thought-provoking question.
Develop the body of your speech: Use the information you have gathered to develop the body of your speech, making sure to include clear and concise explanations of each key point you want to make. Consider using examples, anecdotes, and visual aids to help illustrate your points and make your speech more engaging.
Write a conclusion: End your speech with a powerful conclusion that summarizes your key points and leaves a lasting impression on your audience. This could include a call to action, a personal reflection, or a thought-provoking question.
Edit and revise: Once you have written your speech, take the time to review it and make any necessary changes. This could include correcting any errors, refining your language, and adding any additional information that you think would be beneficial to your audience.
Rehearse your speech: Once you have completed your final draft, it’s time to rehearse your speech. Practice speaking it out loud, paying close attention to your tone, pacing, and body language. Consider recording yourself so you can get an idea of how it will sound when you deliver it.
Delivery: Finally, it’s time to deliver your speech. Remember to make eye contact with your audience, use gestures to help illustrate your points, and project your voice so that everyone can hear you.
Here are a few examples of informative speech topics:
- The history of chocolate
- The benefits of meditation
- How to start a small business
- The science of climate change
- Understanding the human brain
- The benefits of a plant-based diet
- The history of the internet
- The dangers of plastic pollution
- Understanding renewable energy sources
- The benefits of practicing gratitude.
What is an informative speech outline?
An informative speech outline is a plan or framework for constructing and delivering a speech that aims to inform or educate the audience on a specific topic. It typically includes an introduction, main points, and a conclusion, and helps the speaker organize their content in a coherent and logical manner.
Why is an informative speech outline important?
An informative speech outline is crucial because it helps to organize ideas, ensures a coherent structure for the speech, aids in remembering key points, and contributes to effective delivery. It also helps to manage the timing of the speech and ensures all important points are covered.
What should be included in the introduction of an informative speech outline?
The introduction should include an attention-grabber, a statement on the importance of the topic, your credibility, a thesis statement , and a preview of the main points you will be covering in your speech.
How do you conclude an informative speech outline?
In the conclusion of your outline, restate the thesis statement, summarize the main points, and provide a closing statement that leaves a lasting impression or calls the audience to further think about the topic.
How detailed should an informative speech outline be?
The level of detail in your outline may depend on your familiarity with the topic and the complexity of the material. However, it should be detailed enough to help you remember your key points and maintain a logical flow, without reading it word-for-word during your speech.
Can I use visual aids in my informative speech?
Yes, visual aids can be very effective in enhancing understanding and retention of the information presented. Incorporate them in your outline at the relevant points to ensure a seamless integration into your speech.
How do I cite sources in an informative speech outline?
Sources should be cited in your outline to give credit to the original authors and enhance your credibility. You can use a standard citation format like APA, MLA, or Chicago, and include a reference list at the end of your outline. During your speech, verbally acknowledge the sources of your information.
How do you write an informative speech outline?
- Start by researching and understanding your topic thoroughly.
- Decide on a specific purpose and thesis statement for your speech.
- List the main points you want to cover in the body of your speech.
- Draft an engaging introduction to grab the audience’s attention.
- Write a conclusion to summarize the main points and restate the thesis.
- Use bullet points and sub-points to organize ideas under each main point.
- Practice delivering your speech using the outline to ensure a smooth flow and adherence to time constraints.
![Free Printable Booklet Templates [Word, Powerpoint] 1 Booklet Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Booklet-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
A booklet is an excellent tool for promoting your business or products. It allows you to promote your business without spending too much advertising money. When people can hold the…
![Free Printable Bubble Map Templates [PDF, Word] Editable 2 Bubble Map](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Bubble-Map-1-150x150.jpg)
Bubbles maps are for you if you’re into brainstorming and organizing ideas. It’s a great way to organize multiple ideas and categories in one place. You can use these templates when…
![Free Printable Newsletter Templates [Editable PDF, Word, Excel] 3 Newsletter Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Newsletter-Template-150x150.jpg)
A newsletter might seem like an outdated, old idea, but it is still very helpful because it provides you with a way to regularly communicate information to your members and…
![Free Printable Indemnification Agreement Templates [PDF, Word] Hold Harmless 4 Indemnification Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Indemnification-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
Are you planning on protecting your company or business against any loss? Say hello to indemnification agreements. No doubt you might have thought of the term liability, which can connect…
![Free Printable Cease and Desist Letter Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 5 Cease and Desist Letter](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Cease-and-Desist-Letter-1-150x150.jpg)
A cease and desist letter is defined as a legal document that demands someone to stop an activity or behavior immediately. It's mainly used to defend the rights of someone…
![Free Printable Flat Stanley Templates [PDF] Letter Girl, Boy 6 Flat Stanley](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Flat-Stanley-1-150x150.jpg)
In 1996, the Flat Stanley Project was launched by teacher Dale Hubert in Ontario, Canada. It was inspired by an old folk tale from the Toyland of Oz and a…

Betina Jessen
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Business Templates
- Sample Speeches
FREE 8+ Informative Speech Samples in MS Word | PDF
When you need to educate a given audience about a certain aspect through a speech, you need an information speech. The function of an information speech is to prevent the people from straying from the topic or to lose the flow of words. There are several Informative Speech Examples available in the websites, and you can check them out for your convenience. You can go through the persuasive speech examples and get a complete idea about these speeches.
Informative Speech
Sample speech outline template - 9+ free documents download ..., speech examples - 23+ download free documents in pdf , word, sample informative speech - 11+ documents in pdf, word, informative speech outline example.

Size: 70 KB
This is the format in which the document is presented. The introduction, body, and conclusion are subdivided into other sections, each highlighting the materials that are to be included in the speech.
Informative Speech Statement Example

Size: 48 KB
An introduction speech needs a catchy beginning to get going with the topic. Here, the Self-introduction Speech has been further divided into attention statement, subject statement, the significance of the subject and point review.
Informative Speech Assignment Example

Size: 41 KB
An information speech assignment has a definite purpose, followed by other essential factors like the time limit, point value, outline and so in. The references are also mentioned here, along with self-evaluation and visual aids.
What is an Information Speech Made Up of?
An Information Speech has three main parts. These are the introduction, which makes the people acquainted with a particular topic, a captivating body that keeps them engaged till the end and a stunning conclusion that will be remembered long after the speech is delivered.
Again, there are certain divisions among these parts. The respective time allotted for reciting each of the parts are written by the sides. For instance, the introduction consists of attention device, thesis statement, main points and other parts.
Informative Speech Worksheet Format

Size: 131 KB
This worksheet looks like a form and has different heads to be filled up. These include purpose, preview, attention getter and so on. The body of the write-up has further segments.
Sample Informative Speech Evaluation Example
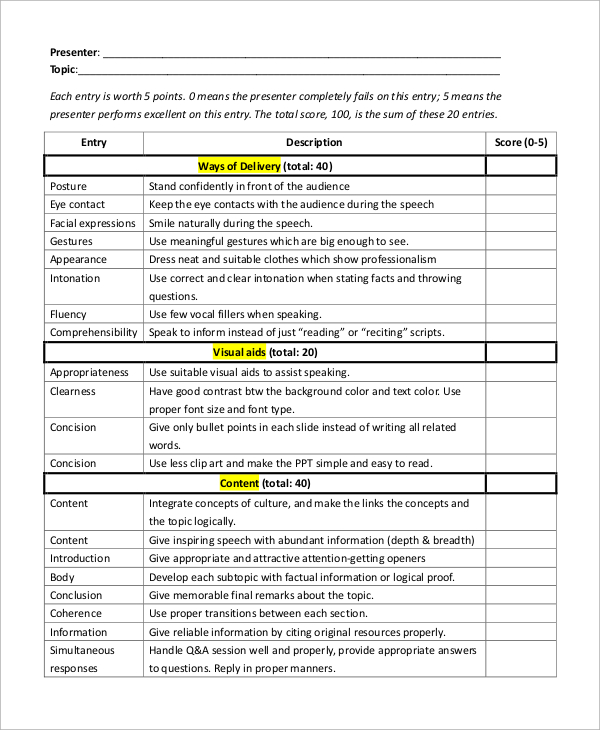
Size: 54 KB
The names of presenter and topic are included at the top of the sheet. There is a chart showing the entry and description of the topics. These are evaluated in the third column. You may also see the Elevator Speech Samples .
Research Informative Speech Sample

Size: 73 KB
Supplemental Informative Speech Example

Size: 110 KB
Informative Speech Introduction Example

How to Make an Information Speech Effective?
Certain strategies can make an information speech more efficient. You need to decide the topic at the outset and think of starting off with a positive note. Do not include unnecessary details in the introduction itself. You can browse the website for Graduation Speech Examples .
These speeches have to be authentic, as the sources sometimes turn out to be biased. Each section can contain three to four sub-topics. You need to know the areas that you are weak in and get the right information in place. Make sure that you do the necessary research.
Who Needs an Information Speech?
An Information Speech can be of use to a vast range of professionals. Academicians are often in need of these speeches so that they can deliver speeches with confidence. Apart from this, when students leave a particular institution, they have to give a speech and to ensure the accuracy of facts; an information speech can be of good help. People who are participating in an individual program or willing to deliver a speech before an audience also require these speeches.
All the sections of an information speech are divided for the ease of the speaker. It ends with a clincher to draw maximum attention. Information speeches can be of various types and they can be used on any given topic.
If you have any DMCA issues on this post, please contact us .
Related Posts
Free 8+ sample speech outline templates in pdf | ms word, free 6+ sample commemorative speech in pdf, free what is a speech [ how to plan a speech, importance ], free 9+ informative speech samples in pdf, company profile samples, sample dot papers, sample lined paper templates, isometric papers, sample printable kite templates, sample packing checklist templates, sample movie reviews, travel budget templates, design document samples, article writing samples & templates, research papers, article summary template - 8+ samples , examples & formats, sample outline - 15+ examples in pdf, word, ppt, sample speech outline - 8+ documents in pdf, word, sample elevator pitch template - 11+ free documents in pdf , word.
All Formats
Outline Templates
7+ informative speech outline templates for the podium – pdf.
It has been two weeks since Martin Luther King Jr. day, which is around the date of the Civil Rights Movement’s leader’s birthday. More than 40 years ago, at the height of the Civil Rights Movement, in the fight to end legal racial segregation in the country, Martin Luther King delivered his impassioned “I Have A Dream” speech from the steps of the Lincoln Memorial, cementing his place in not only American but also world history. It was given at the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, echoing to the corners of the troubled Deep South and resonating across all 50 states. You may also like formal outline templates .

- Speech Outline Templates
- Best Outline Examples
Informative Speech Outline

Informative Speech Outline Sample

Informative Speech Outline for Students

Informative Speech Discussion Guide

Informative Speaking Sample

Discussion Paper on Informative Speeches

Outline for Informative Speech

Sample Informative Speech Outline

Informative Speech Outline for Healthy Eating

More in Outline Templates
- 10+ Training Outline Templates – PDF, Word, Apple Pages
- 24+ Autobiography Outline Templates & Samples – DOC, PDF
- 10+ Project Proposal Outline in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | Editable PDF | InDesign | Photoshop | Publisher | PDF
- 12+ Literature Review Outline Templates – PDF, DOC
- 15+ Thesis Outline Templates – Sample, Example
- 11+ Outline Report Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Production Outline Templates
- 12+ Project Outline Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF | XLS
- 15+ Meeting Outline Templates in PDF | DOC
- 8+ Project Proposal Outline Templates
- 12+ Outline Templates in Apple Pages
- 10+ Outline Templates in Word
- 10+ Outline Templates
- 15+ Topic Proposal Outline Templates – PDF, Word
- 12+ Research Project Proposal Outline Templates – PDF, Word, Pages
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.

Narrative Speech
Narrative speech generator.

Try to let this scenario ply out in your head. It is the first day of school. You see children running around the hallways and the canteen. You see the teachers in the faculty room taking their 15-minute break before the start of the school bell at 7:30 in the morning. You see the high school students doing typical teenager things (e.g. texting, putting make up on, chatting the day away, sleeping, doing their homework at the very last minute, etc…). As the bell begins to ring, the students start to sing the country’s national anthem followed by a patriotic oath to the country then, sometimes the school hymn. You may also see narrative writings .
- Speech Examples
- Informative Speech
As the students take their seats, the first period teacher walks in the classroom and begins to introduce herself as Ms. Katniss Everdeen. As she was just finishing doing her introductions, the principal made an announcement requesting all the students and faculty to assemble in the school’s multi-purpose room for welcoming remarks of the first day of school. After settling down, the principal walked up to the stage and said: “Here to talk about pursuing your dreams at a young age, I would like to introduce to you the speaker of today’s special talk. You may also see personal narrative essay .
May we please give a special round of applause to none other than Eleven herself from Stranger Things, Millie Bobbie Brown?”
We all wish our first day of school was like that… Oh well. Now considering that you are placed in her shoes and will be asked to talk about a similar topic to that, how would you go about it?
Narrative Speeches
But then, you remembered something. It is actually not that difficult since this speech is all about you, and how that experience allowed you to become a better version yourself. Personal narrative speeches give focus on a specific real life event that served as a turning point for the writer. Speeches are often given as an assignment or a project by the teacher. But in order to write a strong personal narrative about yourself, try to think of an idea that might pique the audience’s curiosity.
Just like every good speech, great books, and awesome movies, it must have an introduction, the middle events, the climax, and finally, the end of the story. Here is an example of a personal narrative that might be able to help you out in writing your own personal narrative. You may also see informative speech .
Basic Personal Narrative Outline Example

Size: 130 KB
Part 1. Brainstorming Ideas for the Narrative
Every good piece of literature or movie must always have a great idea to begin the story. Once you have an idea on what you would want to share with the audience, it makes things easier for you to explain as you just have to boil down to the specifics on what experiences can best go with the theme you are going to share. Listed below are some of the ways to brainstorm ideas:
Think of a memorable event or a moment in your life. Sure there are many moments and memories in your life that you have felt and experienced over the years. But there are only so few that have struck you to the depths of your soul that you cannot help but not forget that instance, even when you become old and gray. It does not have to be something major, it can even be as something simple as your first date with her and how you felt whenever she was with you. You may also see declamation speech .
For example, you can write about how your best friend stood up to you when you were getting bullied by a bunch of jerks in middle school or the time when you and your friends went to the club for the very first time and got wasted. You may also see launch speech .
Expand on an important conflict in your life. Everyone just loves watching drama. When you have found the perfect dramatic event to be included in your speech, include it in the speech and elaborate in detail. You may also see youth speech .
For example, you can write about the time your one and only best friend ditched you to start hanging out with those “plastic” losers and you were abandoned and treated like garbage afterwards by everyone in your class after your “best friend” spread some lies about you. You may also see graduation speech .
Think about a particular theme or idea. When deciding your speech, decide what the message you want to deliver the audience as a jumping off point for the narrative. Base your theme on your personal experiences that you would like to share. Once you have thought about it, ask yourself as to whether it has transformed you for the better or for the worst. Poverty, patience, sacrifice, and endurance are all good choices for a personal narrative. You may also see award speech .
For example, you may want to include in your experience on how a boy with no father or mother makes a living for himself by selling street food and how poverty has made you become more generous and thoughtful for others who are suffering on the streets. You may also see retirement speech .
Read examples of personal narrative. Finally, in order to write a good narrative, you must learn how others o it as well. To quote from the Jedi Master Yoda, he states: “You must unlearn what you have learned”. Very philosophical, but it is true. One cannot claim to know everything. And even if you did know everything, to learn something new, you must be open to change and new things in order to enhance and improve your skill. Here are some reading references you might want to glance at before starting:
- The Boys of My Youth by Jo Ann Beard
- Slouching Towards Bethlehem by Joan Didion
- Me Talk Pretty One Day by David Sedaris
- The Lives section of The New York Times
David Becomes King Narrative Speech Outline Example

Size: 292 KB
Part 2. Writing the Personal Narrative
Now that you have brainstormed some ideas needed to start with your personal narrative, it is finally time to get to your computer and ignite the thought train full speed ahead.
Start with a hook. First impressions matter! If you have successfully bored out the audience in their chairs, then congratulations, only a few people are going to pay attention to what you have to say throughout the rest of your speech. Attention-grabbers often come in the form of a story, a quote, a personal experience. You may also see valedictorian speech .
For example, you can mention in the first line of your personal narrative: “I remember this one time when I accidentally slipped and fell down on the lake when I was fishing while everyone was staring at me.”
Set the scene with action. Every good story will not be complete without providing some background information and supporting details to the characters in your story.
Move chronologically through the events. When you begin your speech with your four year-old self accidentally drowning in a swimming pool just because he saw a slide and he wanted to get on it, do not immediately proceed to when you nine years old and you accidentally punched someone in the face because he was a jerk. It is important to set things in order as to avoid confusion between the timeline of your story. Finish explaining everything that occurred in event A before proceeding to event B and finally concluding with event C. You may also see acceptance speech .
Use sensory detail and description. They say it is important to show and not just simply to tell. Most speeches would allow visual aids or props to be presented at the front to give an audience a better idea on what the speaker is describing. But if not, then you must be able to use your imagination describing the object or event you have felt using the five senses. You may also see persuasive speech .
Finish with a moral or takeaway. Wrap your personal narrative up with a reflection or analysis of the transpired events. It is important that at the end of your speech, the audience is left with something to recall even if he forgets everything else. Allow them to leave the room with the moral and lessons that they have learned from your speech. You may also see elevator speech .
Speech 101 Narrative Speech Outline Example

Size: 75 KB
At the end of the day, speech writing is one challenge. The next challenge is on how you are going to deliver it in front of the audience. You may refer to these examples for guidance if ever you are still struggling with writing a narrative speech. With that, we would like to end here and wish you the best of luck in your speech writing journey!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a narrative speech about a life-changing travel experience
2. Help me write a narrative speech on overcoming adversity

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An Informative Speech focus on educating an audience through the use of facts and evidence to establish credibility. It can include definitions, explanations, descriptions, visual images, demonstrations. It should focus on speaking about objects, events, processes, concepts, and examples. An informative speech does not attempt to persuade and ...
Take care to be clear and understandable when creating and presenting a speech about a concept. When selecting a concept, remember you are crafting an informative speech. Often, speeches about concepts take on a persuasive tone. Focus your efforts toward providing unbiased information and refrain from making arguments.
10+ Informative Speech Examples & Samples in PDF. Alliteration Examples in Literature . Informative Speeches about Concepts. Informative Speeches about Objects. List of Informative Speech Topics: Ideas to Spark Your Creativity. Informative Speeches Topics For History And The Humanities. 1.
Explain why they should care about the information you're going to present. 6. Set the Tone: Consider the tone of your speech. Depending on your topic, you may want to set a serious, informative, motivational, or humorous tone. Ensure that the tone aligns with the subject matter and the audience's expectations.
Public Speaking Center: Sample Informative Speech (Full Sentence Outline) I. Introduction a. Attention Getter: When I was in high school, I did an experiment for a ... This speech was written and delivered by Kristen Nathe as a CST 110 Student at UW-La Crosse in Spring 2020. Be sure to consult with your instructor if they have specific ...
Informative Speech Outline Examples. Example 1. Topic: Adoption. Purpose: To inform people about adoption. Thesis: Adoption is the act of transferring parental rights and duties to someone other than the adopted person's biological parents. The number of children adopted each year by American families is an estimate only.
The specific purpose of a speech is its goal, stated in a complete sentence. If the general purpose of your speech is to inform, then your specific purpose will be a statement of the particular information you will present to the audience. Example: Joel's general purpose in his speech about place-kicking is to inform. His specific
This page titled 14.5: Sample Informative Speeches and Speech Outlines is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Sara Kim, Douglas Marshall, June Pulliam, Victoria VanNest, and James Yeargain (LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the ...
Informative speeches about concepts can be about seemingly simple theories like evolution or more complex philosophies like ... Take, for example, a speech about a medical treatment program. This is a fairly complicated subject; however, if the speaker explains what is involved at each treatment step, why it must go in that order, and how the ...
Let his head, arms, and upper torso hang forward. Make a fist with one hand and place it thumb side in against the victim's abdomen—slightly above the navel but below the rib cage. Then cover the first with your other hand and press into the abdomen with a quick upward thrust, bending your arms at the elbows.
13.4 Sample Informative Speeches and Speech Outlines Sample Informative Speech Outline. By Shannon Stanley. Topic: Lord Byron Specific Purpose: To inform my audience about the life of George Gordon Byron, Lord Byron. Central Idea: George Gordon (Lord Byron) overcame physical hardships, was a world-renowned poet, and was an advocate for the Greek's war for freedom.
Template: INFORMATIVE SPEECH PREPARATION OUTLINE (Your outline must use complete sentences) General Purpose: To Inform . Specific Purpose: At the end of my speech the audience will know more about [my topic] I. Introduction . A. Attention-getter/Grabber: ...
For example, replace "Suppor-ng Idea #1" with a sentence that introduces your first suppor-ng idea for that Main Idea. Remember, this is a full-sentence outline. Each numeral or leHer of the outline should be followed by a full sentence. Finally, remember this is only a template. It is flexible. You may have more or fewer suppor-ng ideas ...
The most common types of informative speeches are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration. A definition speech explains a concept, theory, or philosophy about which the audience knows little. The purpose of the speech is to inform the audience so they understand the main aspects of the subject matter.
Programming offers built in plot (example: many historical events were embroiled in scandal like the Kinsey Report and the carbon dating of the shroud of Turin. Watching how these events unfold is incredibly interesting) C. Learn while you relax watching TV (example: Georgia Outdoors demonstrates activities available in the state of
Conclusion: "In closing, I encourage each of you to take a small but vital step towards a healthier. and happier life by incorporating regular exercise into your daily routine. The benefits are. immeasurable, and the journey begins with that first step. Remember, you have the power to.
Informative Speech Templates. Deliver impactful and organized presentations with our collection of Informative Speech Outline templates. These templates serve as a roadmap for structuring your speech, ensuring that your content is clear, engaging, and well-organized. Whether you're delivering a speech in an academic setting, business ...
Download. The above-mentioned informative Welcome Speech Examples contain all the guidelines required to deliver mind-blowing speeches in school, colleges, competitions and even in corporate events. It lists multiple statements to be used to get attention at once. It also contains a list of action words and phrases.
An informative speech thesis statement conveys the main idea of your speech, providing an overview of what listeners should expect. It aims to educate, enlighten, and provide essential details on a specific topic without persuading or arguing a perspective. Today, we'll explore the mysterious world of the deep sea and the creatures that ...
PDF. Size: 405 KB. Download. The Informative Speech Product Launch Template helps you to provide accurate, detailed, and streamlined description of your newly launched products and services with ease. You can use these templates to enlist product features, their USPs, price, availability, and other valid information.
Details. File Format. PDF. Size: 54 KB. Download. The names of presenter and topic are included at the top of the sheet. There is a chart showing the entry and description of the topics. These are evaluated in the third column. You may also see the Elevator Speech Samples.
10+ Report Outline Templates - PDF, Google DOC, Apple Pages, Word. Program Outline Template - 7+ Free Free Word, PDF Format Download! Sermon Outline Template - 9+ Free Sample, Example, Format Download! 6+ Free Chapter Outline Templates - Word, PDF. 17+ Proposal Outline Templates - DOC, PDF.
2. Persuasive. Sales presentations and demonstrations are the type of speeches that aim to entice the audience into taking the desired action after the persuasive speech. Most sales and marketing personnel make use of such speeches with the aim of having the listeners purchase a product or service. 3.
Just like every good speech, great books, and awesome movies, it must have an introduction, the middle events, the climax, and finally, the end of the story. Here is an example of a personal narrative that might be able to help you out in writing your own personal narrative. You may also see informative speech. Basic Personal Narrative Outline ...