- Essay Check
- Chicago Style
- APA Citation Examples
- MLA Citation Examples
- Chicago Style Citation Examples
- Writing Tips
- Plagiarism Guide
- Grammar Rules
- Student Life
- Create Account

MLA Website Citation
- powered by chegg, create citations for free.
Website Book Journal Other
←Back to MLA Citation Examples
How to cite a website in a bibliography using MLA
The most basic entry for a website consists of the author name(s), webpage title, website title, *sponsoring institution/publisher, publication date, and DOI or URL.
Author Last Name, First Name. “Webpage Title.” Website Title , *Sponsoring Institution/Publisher, Publication Date, DOI or URL.
Owoseje, Toyin. “Britney Spears Apologizes to Fans for ‘Pretending’ to be OK in her Conservatorship.” CNN , 25 June 2021, cnn.com/2021/06/25/entertainment/britney-spears-conservatorship-instagram-intl-scli/index.html.
*If the sponsoring institution or publisher’s name is the same as the website title, do not include it. MLA prefers to avoid duplicating information in citations.
The first author’s name should be reversed, with a comma after the last name, followed by a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears on the website. Titles and affiliations associated with the author should generally be omitted. A suffix, such as a roman numeral or Jr./Sr. should appear after the author’s given name, preceded by a comma.
For a page with two or more authors, list them in the order they appear on the website. Only the first author’s name should be reversed, while the others are written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word “and” before the last author’s name.
Sanchez, Ray, and Eric Levenson. “Derek Chauvin Sentenced to 22.5 Years in Death of George Floyd.” CNN , 25 June 2021, cnn.com/2021/06/25/us/derek-chauvin-sentencing-george-floyd/index.html.
For pages with three or more authors, reverse the first author’s name as described above and follow it with a comma and the abbreviation “et al.” Do not italicize “et al.” in parenthetical citations or works-cited list entries.
Rebaza, Claudia, et al. “John McAfee Was Not Suicidal, Says Widow of Antivirus Software Magnate.” CNN , 25 June 2021, cnn.com/2021/06/25/tech/john-mcafee-wife-janice-intl/index.html.
If the article was written by a news service or organization, include the name in the author position and remove any introductory articles (e.g., A, An, The) from the name.
Associated Press. “Obama Inaugurated as President.” CNN , 21 Jan. 2009, cnn.com/2009/01/21/politics/obama-inaugurated-as-president/index.html.
If no author is available, begin the citation with the webpage title.
“Obama Inaugurated as President.” CNN , 21 Jan. 2009, cnn.com/2009/01/21/politics/obama-inaugurated-as-president/index.html.
The webpage title should be placed within quotation marks. Place a period after the webpage title within the quotation marks. The webpage title is followed by the name of the larger website container in italics, and it’s usually followed by a comma and any additional information such as version, number, publisher, publication date, or URL. The punctuation before the version element varies depending on whether the webpage is part of a larger work or “container.” When it is part of a larger work, use a comma followed by the version. When it is a work that stands alone, use a period followed by the version.
Smith, John. “Obama Inaugurated as President.” CNN , Version 12.1.1., 21 Jan. 2009, cnn.com/2009/01/21/politics/obama-inaugurated-as-president/index.html.
Include the sponsoring institution or publisher with a comma after the website title (or version number, if available). The sponsoring institution/publisher can usually be found at the bottom of the website in the footer. You may omit the publisher’s name when there is no publisher or when the publisher name isn’t required (for example, when the publisher title matches the website title or the website doesn’t list the publisher responsible for producing the work).
Smith, John. “Obama Inaugurated as President.” CNN , 21 Jan. 2009, cnn.com/2009/01/21/politics/obama-inaugurated-as-president/index.html.
Next, state the publication date of the webpage. In works-cited list entries, use only the day-month-year style. Month names should be abbreviated, except for May, June, and July, and followed by a period. In some cases, a specific date might not be available, and the date published may only be specific to a month or even year. Provide whatever date information is available. When using seasons in the date, lowercase the season (spring 2021 not Spring 2021). If there is no date available, you may omit the publication date element from your citation. However, you may wish to include an access date in the supplemental element slot after the URL.
Smith, John. “Obama Inaugurated as President.” CNN , cnn.com/2009/01/21/politics/obama-inaugurated-as-president/index.html.
Smith, John. “Obama Inaugurated as President.” CNN , cnn.com/2009/01/21/politics/obama-inaugurated-as-president/index.html. Accessed 21 Jan. 2021.
According to MLA’s 9th edition, updated in 2021, you may usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them or unless instructed otherwise. When in doubt, ask your instructor. If a DOI is available, use that instead of the URL. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. Use a period after the DOI and the URL.
Smith, John. “Obama Inaugurated as President.” CNN , 21 Jan. 2009, https://doi.org/12.3456/789.1011.1213.
←Back to MLA Citation Guide

“A word after a word after a word is power.” — Margaret Atwood
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
For an online news source with more than two authors (3+), use “ et al ” after the first author to indicate “ and others ” in your works cited entry. With this format, you do not have to write all the authors’ names since you are indicating the same using “et al.”
Last Name, First Name1, et al. “Title of the article.” Title of the newspaper , Date of publication, URL.
Kamelion, North, et al. “How do Zebras stay awake in the forest amidst a scavenger hunt?” Taj Road Journal , 9 Aug. 2020, www.tajroadjournal.com/posts/253839.
If you have the same author as the first author in more than one entry, then distinguish these entries by listing two authors in the entries and using “et al” for the other authors.
If there is no author given for an online news source, then the in-text citation should include the first main word or words of the article title within the quotation marks. For example:
In a works-cited entry, you will include the article title, newspaper name, publication date, and URL. See below for the format and example.
“Article Title.” Newspaper , Date, URL.
“High Winds Blow Michigan Anglers, Ice Shanty about a Mile across Saginaw Bay.” Detroit Free Press , 2022 March 7, https://www.freep.com/story/news/local/michigan/2022/03/07/saginaw-bay-ice-shanty-winds/9411709002/.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Website in MLA
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, citing a website in mla, how to create an mla website citation:.
When citing a website, you’re often actually citing a specific page on a website. You’re not actually citing the entire website.
Here is the most common way to cite a page on a website:
- Start the citation with the name of the author who wrote the information on the page. If there isn’t an author listed, do not include this information in the citation. Start the citation with the title.
- The title of the individual page is placed in quotation marks, followed by a period.
- Next, place the name of the website in italics, followed by a comma.
- If the name of the publisher matches the name of the author or the name of the title, do not include the publisher’s information in the citation.
- The date the page or website was published comes next.
- End the citation with the URL or DOI. When including the URL, copy the URL directly from the address bar or link in your browser window.
Last name, First name of author. “Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Date published, URL.
Rothfeld, Lindsay. “Smarter Education: The Rise of Big Data in the Classroom.” Mashable, 3 Sept. 2014, mashable.com/2014/09/03/education-data-video/#hViqdPbFbgqH.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx.
If you’re still confused and feeling the urge to type “How to cite a website MLA” into Google, try out our free generator at the top of this page. Our citation generator MLA site is easy to use!
Social media:
If the user’s handle and real name are similar, you may include the real name and leave out the handle as long as a URL is also included. If the user’s real name and handle are different, include the hand in brackets after the real name.
Gates, Melinda. “Today, Bill and I were deeply humbled to accept France’s Legion of Honour award on behalf of all our foundation’s partners and grantees.” Twitter, 21 Apr. 2017, twitter.com/melindagates/status/855535625713459200.
Sandler, Adam. “California Strong celebrity softball game this Sunday at Pepperdine. All proceeds go to the victims of the wildfires and shooting in Thousand Oaks.” Facebook, 11 Jan. 2019, www.facebook.com/Sandler/.
Mizuhara, Kiko [@I_am_kiko]. “@vivi_mag_official shot by my sis @ashley_yuka.” Instagram, 25 June 2020, www.instagram.com/p/CB27SYahBpo.
Featured links:
MLA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interviews | PDFs
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

Thursday, February 23: The Clark Library is closed today.
MLA Style (9th Edition) Citation Guide: Websites
- Introduction to MLA Style
- Journal Articles
- Magazine/Newspaper Articles
- Books & Ebooks
- Government & Legal Documents
- Biblical Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Videos/DVDs/TV Shows
- How to Cite: Other
- 9th Edition Updates
- Additional Help
Table of Contents
Entire website - no separate pages or sections, page or section from a website.
Note: For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
It can sometimes be difficult to find out who the author of a website is. Remember that an author can be a corporation or group, not only a specific person. Author information can sometimes be found under an "About" section on a website.
If there is no known author, start the citation with the title of the website instead.
The best date to use for a website is the date that the content was last updated. Otherwise look for a copyright or original publication date. Unfortunately this information may not be provided or may be hard to find. Often date information is put on the bottom of the pages of a website.
If you do not know the complete date, put as much information as you can find. For example you may have a year but no month or day. If the source does not include a copyright/last modified date, then omit the date and include an access date in your citation instead.
Access Date
Date of access is optional in MLA 8th/9th edition; it is recommended for pages that may change frequently or that do not have a copyright/publication date.
In your works cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
Author, or compiler name (if available). Title of Website, Name of Organization Affiliated with the Website, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed access date.
Works Cited List Example:
Mabillard, Amanda. Shakespeare Online, 29 Dec. 2011, www.shakespeare-online.com. Accessed 6 July 2016.
In-Text Citation Example:
(Author's Last Name)
(Mabillard)
Note: In this example, the name of the organization affiliated with the website is omitted since it is the same as the website title.
Created by an Unknown Author, or the Author is the same as the Website Title/Publisher
"Title of Section." Title of Website, Publisher or Sponsoring Organization, Date of publication or last modified date, URL. Accessed Date Month (abbreviated) Year.
Note: The publisher or sponsoring organization can often be found in a copyright notice at the bottom of the home page or on a page that gives information about the site . If the website publisher is the same as the author and title of the web site , then include only the title of the web site.
“ Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview.” WebMD, 25 Sept. 2014, www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/tc/athletes-foot-topic-overview.
("Title of Section")
(“Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview”)
Created by a Known Author
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Page or Document." Title of Website, Publisher or Sponsoring Organization, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed Date Month (abbreviated) Year.
Morin, Amy. "How to Prevent the Media From Damaging Your Teen's Body Image." Verywell Family, About Inc., 6 Oct. 2019, www.verywellfamily.com/media-and-teens-body-image-2611245. Accessed 1 Nov. 2019.
- << Previous: Government & Legal Documents
- Next: Biblical Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 1:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.up.edu/mla
- Bibliography Answers
How to cite a website in APA, MLA, or Harvard style

There are many different ways to cite a website, depending on which citation style you need to format it in.
The easy way to cite a website in any citation style
Use our citation generator below to automatically cite a website in any style, including APA, MLA 7 and 8, and Harvard. Just select the style you need, copy the URL into the search box, and press search. We’ll do the rest.
The manual way to cite a website
To cite a website by hand just follow the instructions below. For the 3 most popular styles–APA, MLA 8, and Harvard–this is as follows:
In APA style
You need to locate these details for the website: page or article author, page or article title, website name, published date, access date, page URL (web address) .
- The author can typically be found on the page, but if there isn’t one listed you can use the website name in its place.
- The page title can be found near the top of the page, and you can also find it by hovering your mouse over the browser tab.
- The website name can usually be found in the web address or by looking for a logo or similar at the very top of the page.
- There often isn’t a publish date , but if there is it’ll be very close to the page title.
- The access date is the date you took information from the article (usually today).
- The page URL can be copied straight from the address bar of your browser and will start with either http:// or https://.
Then use this template, replacing the colored placeholders with the information you found on the page:
Author last name , author first name initial . ( published year , published month and day ). Page title . Retrieved accessed month and day , accessed year , from article URL .
The final formatted citation should look like this:
Ingle, S. (2018, February 11). Winter Olympics was hit by cyber-attack, officials confirm. Retrieved July 24, 2018, from https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2018/feb/11/winter-olympics-was-hit-by-cyber-attack-officials-confirm.
For a more comprehensive guide, including what to do when you can’t find certain details, have a look at our more in-depth guide to citing a website in APA format .
In MLA 8 style
Here are the specific details you need to find on the page: page or article author, page or article title, website name, published date, access date, page URL (web address) .
Then use this template:
Author last name , author first name . “ Page title .” website name , published date day, month, year , page URL . Accessed accessed date day, month, year .
Ingle, Sean. “Winter Olympics Was Hit by Cyber-Attack, Officials Confirm.” The Guardian , 11 Feb. 2018, https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2018/feb/11/winter-olympics-was-hit-by-cyber-attack-officials-confirm. Accessed 13 July 2018.
For a more comprehensive guide, including what to do when you can’t find certain details, have a look at our more in-depth guide to citing a website in MLA 8 format .
In Harvard style
First, find these details for the website: page or article author, page or article title, website name, published date, access date, page URL (web address) .
Author last name , author firstname initial ( published date year ). Page title . [online] website name . Available at: page URL [Accessed accessed date day, month, year ].
Ingle, S. (2018). Winter Olympics was hit by cyber-attack, officials confirm . [online] The Guardian. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2018/feb/11/winter-olympics-was-hit-by-cyber-attack-officials-confirm [Accessed 13 Jul. 2018].
Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
Citing a website in MLA style
When citing a website in MLA style, your citation should follow one of the basic formats below.
Webpage with an individual author
When citing websites, MLA usually requires you to abbreviate the names of months to three letters. For example, January becomes Jan.
Author Last Name, First Name. “Title.” Title of Site , Sponsor or Publisher [include only if different from website title or author], Day Month Year, URL.
Hamilton, Jon. “Think You’re Multitasking? Think Again.” National Public Radio , 2 Oct. 2008, www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=95256794 .
Webpage with no author or group author
If no author is available, or the webpage is authored by a group or organization, begin with the title of the webpage. If the title of the site is the same as the sponsor or publisher, omit the sponsor or publisher.
“Title.” Title of Site , Sponsor or Publisher, Day Month Year, URL.
“Turmeric.” National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health , Sep. 2016, nccih.nih.gov/health/turmeric/ataglance.htm.
Webpage with no date
If the webpage does not have any date information, or the page updates its content frequently (e.g., a wiki site), you should include an accessed date at the end of your citation to indicate when you were viewing the content.
Author Last Name, First Name. “Title.” Website name , URL. Accessed Day Month Year.
Gillingham, Kim. “How to Use the Dewey Decimal System.” Wikihow , https://www.wikihow.com/Use-the-Dewey-Decimal-System . Accessed 6 July 2023.
More information
To see more examples and other situations of citing books in MLA style, see the library's online MLA Citation Guide . You can also find the MLA Handbook (9th edition) in the Knowledge Center’s reference collection and in the Book Stacks. Purdue’s Online Writing Lab also has a comprehensive guide to MLA style .
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format
MLA Format: Everything You Need to Know Here
Welcome to an overview of “What is MLA Format?” in relation to paper formatting. You’ll find in-depth guidelines, examples, and visual samples to help you easily format your paper. This guide does not serve as a reference for MLA citation format.
For help determining the proper structure for citing, refer to the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here is another informative site which may help with further understanding of MLA citation format.
Guidelines for Formatting a Paper in MLA
- Use white 8 ½ x 11” paper.
- Make 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and sides.
- The first word in every paragraph should be indented one half inch.
- Indent set-off or block quotations one half inch from the left margin.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read, such as Times New Roman. Make sure that italics look different from the regular typeface.
- Use 12-point size.
- Double space the entire research paper, even the Works Cited page.
- Leave one space after periods and other punctuation marks, unless your instructor tells you to leave two spaces.
These guidelines come from the MLA Style Center’s web page “Formatting a Research Paper.”
MLA Guide Overview
There are various sections in this guide. Each section provides an in-depth overview of the different components to keep in mind when developing an MLA paper.
This guide includes the following sections:
- Format background
- General paper formatting
- MLA heading format & title page instructions
- Running head & page numbers
- Paraphrases
- Abbreviations
- Numbers (includes the use of numbers in MLA outline format)
- Images, tables, and musical scores
- MLA works cited format
- MLA citation format (for in-depth citation rules visit this MLA citation guide or MLA in-text citation guide)
- Edits & proofreading
If you need more guidance, a website like EasyBib.com usually has guides and tools to help you out. There’s also resources on other styles, like our guide on “ APA reference page ”, otherwise known as a “References” page.
MLA Format Background
The Modern Language Association (MLA) is an organization responsible for developing MLA format. It was developed as a means for researchers, students, and scholars in the literature and language fields to uniformly format their papers and assignments. This uniform, or consistent, method to developing a paper or assignment allows for easy reading. Today, MLA is not only used in literature and language subject areas; many others have adopted it as well.
The Modern Language Association released the 9th and most current edition of their MLA Handbook in April 2021. The Handbook provides thorough instructions on citing, as well as guidelines for submitting work that adheres to the Modern Language Association’s rules and standards. Although we’re not affiliated with the MLA, our citation specialists bring you this thoughtful and informative guide on the format.
Looking for information about previous editions to the Handbook ? Want to learn more about the origin of “What is MLA format?” Click here to learn about the previous editions to the Handbook .
Actually, are you looking for help on using another style? See how to cite an APA journal , learn to create an APA book citation , and more!
Formatting the Header in MLA
To create a header for your first page, follow these steps:
- Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin.
- Type your name, your instructor’s name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
- Double space once more and center the title. Do NOT underline, bold, or type the title in all capital letters. Only italicize words that would normally be italicized in the text. Example: Character Development in The Great Gatsby
- Do not place a period after the title or after any headings
- Double space between the title and first lines of the text

General Paper Formatting
Paper choice.
While many professors, instructors, and publications allow electronic submission, some prefer printed, hard copies of papers. This section focuses on the type of paper to use for printed submission.
If you choose to print your paper, use white paper only. Do not use ivory, off-white, or any other shades or colors.
Choose a standard, high quality paper to print your project on. Do not use cardstock. It is not necessary to use resum é paper. Use typical, high quality printer or copy paper.
When it comes to size, 8 ½-by-11-inch paper is the recommended size. If you’d like to use a different size, ask your teacher prior to submission.
Use One-Inch Margins in MLA
Use one-inch margins around the entire page. The running head should be the only item seen in the one inch margin (see below for more on running heads).
Most word processing programs automatically default to using one inch margins. Check the page settings section of the program to locate the margin size.
Indenting Paragraphs in MLA
Indent the first word in every paragraph. Sentences should begin one half inch from the left margin.
It is not necessary to manually measure half an inch. Use the “tab” button on the keyboard to create a half inch space.
Double Space Paragraphs in MLA
MLA research paper format requires that the entire research paper or MLA format essay includes double-spaced lines. Double-spaced lines should be found in between the written body of the work, in the heading, and also on the MLA reference page.
While it may seem tempting to place a few extra lines between the heading, title, and beginning of the paper, lines should all be double spaced.
Font and Font Size in MLA
In an MLA paper, it is acceptable to use any font type that is easy to read. Many source types, such as books and articles, use fonts that are easy to read, so if you’re seeking an appropriate font style, look at other sources for guidance. Two of the most commonly used fonts are Arial and Times New Roman.
It is important for the reader to be able to distinguish the difference between italicized and regular font, so if you choose a font style different than Arial or Times New Roman, make sure the difference between the two type styles is evident.
The use of a 12-point font size is recommended as this is the default size for many word processing programs. It is acceptable to use another standard size, such as 11-point or 11.5-point.
Some professors or instructors will provide guidance on how to secure hard copies of projects. If your instructor does not provide you with any expectations or guidance, a simple staple in the top left corner should suffice. If a stapler is not available, some instructors allow paper or binder clips.
Do not fold the top left corner down to secure the pages together. The page could easily unfold, causing a mess of papers. While binders and plastic holders are cute, in reality, they add bulk to a professor or instructor who may like to take the papers home for grading purposes. Keep the binding simple and clean. Staples work best, and binder and paper clips are the next best option.
As always, follow any instructions your professor or teacher may provide. The guidelines found here are simply recommendations.
MLA Heading & Title Page Instructions
The web page “Formatting a Research Paper” gives two options when it comes to creating the header for your project:
- An MLA format heading can be placed at the top of the first page
- A title page can grace the front of the assignment. If you choose to create a title page, keep in mind that there aren’t any official title page or cover page guidelines in MLA format. See more information below.
If choosing option one, creating an MLA heading, you’ll need to include four main components:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The name and number of the course or class
- The assignment’s due date
The first item typed on the paper should be your full name.
- Position your name one inch from the top and left margins of the page.
- Add a double space beneath your name, and type the name of your instructor.
- Below the professor or instructor’s name should be a double space, followed by the name of the course, class, or section number (if available).
- Below it, include another double space and add the assignment’s due date (Day Month Year).
Here’s an example:

The assignment’s title should be placed below the due date, after a double space. Align the title so it sits in the center of the MLA format paper. The title should be written in standard lettering, without underlines, bold font, italicized font, or any quotation marks. Only include italics or quotation marks if your title includes the title of another source.
Here is an example of an MLA header for an MLA format essay, paper, or assignment:
Neal E. Bibdarsh
Professor Haujeemoto
English 201
The Trials and Tribulations of Lincoln’s Reciting of “The Gettysburg Address”
*Note: The quotation marks here are around the title of a speech included in the paper’s title.
Most research papers use a standard MLA format heading, like the one seen above. If your instructor requires you to create a standalone title page, ask him or her for specifications. MLA does not have specific instructions for developing an MLA title page. We recommend you use an MLA header for your project.
If your teacher or professor requires a standalone title page, but has not provided any guidance or specifications, here are a few suggestions from EasyBib.com and this MLA guide :
- Center and double space all of the text on your page.
- Place the name of your school at the top of the page.
- Skip down to about the center of the page and type the title of your paper. Do not bold the title, italicize the entire title, place quotation marks around it, or type the title out in capital letters.
- Use italics for the titles of any sources in the title of your paper. Example: An Analysis of Mythical Creatures in Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
- first letter of the title
- first letter of the last word
- first letter of any adjectives, adverbs, nouns, pronouns, and verbs
- If your paper has a subtitle, include on the next line below your title.
- Skip down to the bottom third of the page and add your name, the the name of your instructor, the name/number of the course or class, and the assignment’s due date on four separate lines.
- Keep the font size at 12 pt., or a size close to it, to make it look professional.
- Use the same font as the text of the paper. The Modern Language Association recommends any font that is easy to read and has a clear distinction between italics and standard font. Times New Roman and Arial are recommended, but many other fonts work as well.
- Include a page number in the top right corner of the paper. For more information on how to style page numbers, check out the next section, “Running Head and Page Numbers.”
- We do not recommend adding any images or cover art to the title page.
Click additional information about essays to see an example of a formatted header.
You can either create a title page using the EasyBib Title Page creator or omit the title page completely and use a header.
Running Head & Page Numbers in MLA
A running head is a brief heading that is placed in the top right corner of every page in a project. The Modern Language Association Style Center (online) states that the running head consists of:
- Last name of the paper’s author
- Page number
General tips to keep in mind:
- The running head is placed in the upper right-hand corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin of the page.
- Type your last name before the page number.
- The last name and page number should be separated by a single space.
- Do not place the word “page” or use an abbreviation, such as p. or pg., before the page number.
- Quite often, the running head begins on the second page, but your instructor may ask you to include the running head on the first page of the assignment. As always, if your instructor provides you with specific directions, follow his or her guidelines.

Before adding this information manually onto every single page, check to see if the word processor you’re using has the capability to automatically add this information for you. Try looking in the settings area where page numbers or headers can be added or modified.
Google Docs: Adding a header
- Go to the menu section “Insert.”
- Select “Page numbers” and select the option that places the page number in the upper-right corner.
- A page number will appear; your cursor will blink next to it.
- Move your cursor to the left of the page number.
- Type your last name. Add a space between your name and the page number.
- You should now have a properly formatted header on every page!
Microsoft Word Document: Adding a header
- Double-click in the space at the top of the page (where the page number is).
- OR Go to the “Insert” menu, select “Header,” and select “Edit Header.”
- Type your last name next to page number. If it isn’t already right-aligned, go to the “Home” menu and right-align your name.
Quotations in MLA
Quotes are added into assignments to help defend an argument, prove a point, add emphasis, or simply liven up a project.
Quotes should not take up the majority of your paper or assignment. Quotes should be sprinkled sparingly throughout, and quotes longer than 4 lines should be formatted as MLA block quotes . Use direct quotes from outside sources to enhance and expand on your own writing and ideas.
Words from quotes belong to the individual who spoke or wrote them, so it is essential to credit that individual’s work. Credit him or her by adding what is called an “in-text citation” into the body of the project.
There are three ways to add quotes: 1. With the author’s name in the sentence (a citation in prose).
Dan Gutman shares a glimpse into the overall plot by stating, “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman is the author of the book that this quote is pulled from.
2. Without the author’s name in the sentence (a parenthetical citation).
The main character’s confusing experience is realized and explained when he states “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (Gutman 5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman’s name isn’t included in the sentence. It’s included in the parentheses at the end of the sentence. This is an example of a proper MLA style citation in the body of a project.
3. In a block quote, which is used when a large quote, of 4 lines or more, is added into a project.
Using footnotes and endnotes
The Modern Language Association generally promotes the use of references as described in the sections above, but footnotes and endnotes are also acceptable forms of references to use in your paper.
Footnotes and endnotes are helpful to use in a variety of circumstances. Here are a few scenarios when it may seem appropriate to use this type of referencing:
- When you are referring to a number of various sources, by various authors, in a section of your paper. In this situation, it is a good idea to use a footnote or endnote to share information for parenthetical references. This will encourage the reader to stay focused on the text of the research paper, instead of having to read through all of the reference information.
- When you are sharing additional information that doesn’t quite fit into the scope of the paper, but is beneficial for the reader. These types of footnotes and endnotes are helpful when explaining translations, adding background information, or sharing counterexamples to research.
To include a footnote or endnote, add a superscript number at the end of the sentence the footnote or endnote refers to. They can be included mid-sentence if necessary, but be sure to add it after any punctuation, such as commas or periods. Find a location that doesn’t distract the reader from the content and flow of the paper.
Within the text example:
Numerous well-known children’s books include characters from a wide range of races and ethnicities, thus promoting diversity and multiculturalism.¹
At the bottom of the page (footnote) or at the end of the section (endnote):
¹See Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez. While Parr’s work features characters of various colors, such as pink or blue, children easily correlate it with individuals of different races and ethnicities.
On the last page of the assignment, the writer includes the full references for the books by Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez.
For more on block quotes and a further, detailed explanation on the use of quotes, including MLA footnotes, refer to our MLA In-Text Citation and Parenthetical Citations Guide. In this guide you’ll find further information including directions for the use of quotes without an author, page numbers, and how to properly credit work from electronic sources.
For guides on citations in another style, check out APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation .
Paraphrases in MLA
Paraphrases are created when text or speech from another source are added into a project, but the writer chooses to summarize them and weave in his or her own writing and writing style.
Even though the writer modifies the information from another source, it is still necessary to credit the source using proper format ( Handbook 98). Paraphrased information uses the same MLA reference format as stated in the section directly above this one.
Here is an acceptable paraphrase:
Original text:
“Stay hungry. Stay foolish.” Steve Jobs
Paraphrase:
Steve Jobs encouraged students at Stanford to continue with their determination, drive, and ambitious behavior. They should never be simply satisfied with the status quo. They should continue to push themselves despite possible obstacles and failures.
To develop a well-written paraphrase, follow these simple, step-by-step instructions.
- Find a phrase, sentence, paragraph, or section of original text you’d like to turn into a paraphrase.
- Read the text carefully and make sure you fully comprehend its meaning. A writer can only develop a well-written paraphrase if the information has been fully grasped and understood. If you’re having difficulty understanding the information, take a few minutes to read up on tricky words and background information. If all else fails, ask a friend to see if they’re able to make sense of the concepts.
- After analyzing and completely understanding the original text, put it to the side. Take a moment to think about what you’ve read and connect the idea to your own assignment.
- Now that the information is completely understood, take a moment to rewrite what you’ve read, in your own words and writing style. Do not simply substitute words in the original text with synonyms. That’s plagiarism! Show off and demonstrate your ability to process the original information, connect it to the content in your paper, and write it in your own individual and unique writing style.
- Include an in-text reference next to the paraphrase. All paraphrases include references, similar to direct quotes. See the “Quotations” section of this guide to learn how to properly attribute your paraphrased information.
- Give yourself a pat on the back! Paraphrasing is an important part of the research and writing process.
Wondering if it’s better to quote or paraphrase?
An essential part of the research process involves adding direct quotes and paraphrases into projects. Direct quotes provide word-for-word evidence and allow writers to use another author’s eloquent words and language in their own projects. When it comes to paraphrases, writers are able to take a block of text and shrink the scope of it into the their papers. Paper writers can also use paraphrases to demonstrate their ability to analyze and reiterate information in a meaningful and relevant way.
If you’re wondering which one is better to consistently use, quotes or paraphrases, there’s a clear winner. Paraphrases come out on top. Sure, direct quotes are incredibly beneficial, but copying and pasting too many of these into a project can cause a reader to lose sight of the writer’s own voice. Mixing your own voice with another author’s too much can make for choppy and disjointed reading.
The ultimate goal of a research project is to have your voice and research merged together as one. Paraphrases allow just that. When you combine information from outside sources with your own writing style, it demonstrates your ability as a researcher to showcase your understanding and analyzation of a topic.
Remember, whether you’re adding direct quotes or paraphrases into a project, both types of additions need references. References are placed after the quotes and paraphrases, and also at the end of an assignment.
If you’re looking for additional help with your punctuation or grammar, check out the EasyBib plagiarism checker !
Using Abbreviations in MLA
Abbreviations are commonly used in many source types including websites, blog posts, books, and journal articles. It is acceptable to use abbreviations in all of these sources.
When it comes to school and research assignments, however, the MLA Handbook states that abbreviations should be used rarely in the prose of your paper (293). Spelling out abbreviations into their full words and meanings is recommended. This ensures understanding and avoids any confusion from your reader.
There are times when you may feel it is perfectly acceptable to use an abbreviation rather than its typed out counterpart in a paper. If you do abbreviate, be sure you are using commonly accepted abbreviations, which you can find in the dictionary. You can also review Appendix 1 in the MLA Handbook .
General Abbreviation Tips
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus can be abbreviated to HIV, not H.I.V.
- United States should be US, not U.S.
- Digital video disc should be DVD, not D.V.D.
- For lower case abbreviations, it is acceptable to include periods between the letters.
- The abbreviation, “For example” = e.g.
- If there is a mix of lower case and upper case letters, do not use periods if the majority of the letters are upper case. Examples include PhD and EdD
Abbreviating Months
Type out entire month names when being used in the body of a research paper or assignment.
She rented out the beach house from May through September
When it comes to references, MLA bibliography format requires months longer than four letters to be abbreviated.
- July = July
- November = Nov.
Other abbreviations that are perfectly acceptable to use in a bibliography (not the body of a project) include:
- p. or pp. for page and page numbers
- ch. for chapter
- ed. for edition
- trans. for translation or translated
- vol. for volume
- no. for number
- rev. for revised
Again, these abbreviations should only be used in the final page(s) of a project, the MLA Works Cited list. They should not be used in the body of a project.
For more information on bibliographies, see our MLA format Works Cited List page.
Abbreviating Publishers
One of the quirkiest things about this particular style is how publisher names are structured on the final page of references. Certain words are abbreviated, some words are omitted, and other words are written in full.
Words describing what type of business the publisher is are omitted from the works cited. Here’s a breakdown of the words that should be excluded:
- Co. (Company)
- Corp. (Corporation)
- Inc. (Incorporated)
- Ltd. (Limited)
- The (when at the beginning of the name)
If a publisher’s name contains the words “University” and “Press” (or the equivalent in another language), the words should be abbreviated to the letters “U” and “P” in your citation. But if only one of the words appears, it should be written out normally.
Here are a few examples:
- University of Delaware
- U College of London P
All other words related to the names of publishers should be written out in full.
Abbreviating Titles
Certain classical and biblical works are abbreviated in a bibliography, but also in any parenthetical references in the text.
The official handbook provides a lengthy list, spanning over multiple pages, of the preferred abbreviations to use for classical and biblical works ( Handbook 295-301), but here’s a quick snapshot of some of the commonly used ones:
Hebrew Bible or Old Testament = OT
- Deut. = Deuteronomy
- Gen. = Genesis
- Lev. = Leviticus
- Num. = Numbers
- Ps. = Psalms
New Testament = NT
- 1 Cor. = 1 Corinthians
- Jas. = James
- Matt. = Matthew
Shakespeare:
- Ado = Much Ado about Nothing
- 3H6 = Henry VI, Part 3
- JC = Julius Caesar
- Mac. = Macbeth
- MND = A Midsummer Night’s Dream
- Oth. = Othello
- Rom. = Romeo and Juliet
Again, the titles above are allowed to be abbreviated both in references in parentheses in the body of a project and also on the final page of references. If you’re wondering why, it’s because they’re cited often and it’s unnecessary to type out the entire title names.
Formatting Numbers in MLA
Use of numerals.
If the project calls for frequent use of numbers (such as a scientific study or statistics), use numerals that precede measurements.
- 247 milligrams
Other items to keep in mind:
In divisions, use numbers, ex: In page 5 of the study

Arabic Numbers
When including a number in a paper, spell out the number if it can be written as one word (such as six ) or two words (such as sixty-two ). For fractions, decimals, or longer numbers, type them out using digits. For larger numbers, write the number itself ( Handbook 82-84).
- twenty-seven
- one hundred
If the number comes before a unit of measurement or label, type the number using digits.
- 8 tablespoons
- 3 July 2018
- 25 King Street
More on Numbers
Starting a sentence with a number is generally frowned upon. Try modifying the sentence so that the number, or number word, is found elsewhere.
Instead of:
225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Use this sentence:
A total of 225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
If modifying the sentence is not possible or does not work well with the flow of the assignment or paper, type out the written number:
Two hundred twenty five children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Do not include any ISBN numbers in your paper.
Outline Format
The Modern Language Association does not have any requirements regarding the structure of an outline. If your teacher asks you to create an MLA outline, we recommend using roman numerals, capital and lowercase letters, and numbers.
Here is an example of a recommended outline structure:

In addition to outlines, use roman numerals for suffixes.
- King George IV
Using Images, Tables, & Musical Scores in MLA
Photographs, data sets, tables, graphs, and other images are often added into projects or papers to promote or aid understanding. They provide meaningful visuals for the reader. If the illustration or visual image does not enhance the quality of the paper, do not include it in the project.
Tables and illustrations should be placed as close as possible to the text that they most closely refer to.
For an image to be significant and easily identifiable, place it as close as possible to the text in the project where it is discussed.
It is not acceptable to simply place an image in a project without including identifiable information. All images must include information about its origin.
Here are the directions to properly attribute an image:
- Assign an Arabic number. The image closest to the beginning of the project should be labeled as Fig. 1. The next image in the project should be Fig. 2. and so on.
- Provide a caption. The caption should be a brief explanation or the title of the contents of the image. Place the caption directly next to the label.
- Immediately following the caption, it is acceptable to include attribution information. If the image is not discussed further in the rest of the paper or project, it is acceptable to include the MLA bibliography format citation below the image and omit it from the bibliography or MLA format works cited page.
In the text of the project or paper where the figure is discussed, include the label in parentheses to ensure the reader knows where to find the figure in your paper.
In the text:
Sarah’s tattoo design was filled with two of her favorite flowers: lilies and daffodils along a thinly curved vine (fig. 1).
Image formatting:
(Image Would Be Here) Fig. 1. Sarah’s Tattoo. barneyWILLIAMSable, Deviant Art , 2011, barneywilliamsable.deviantart.com/art/Sarah-s-Tattoo-design-193048938.
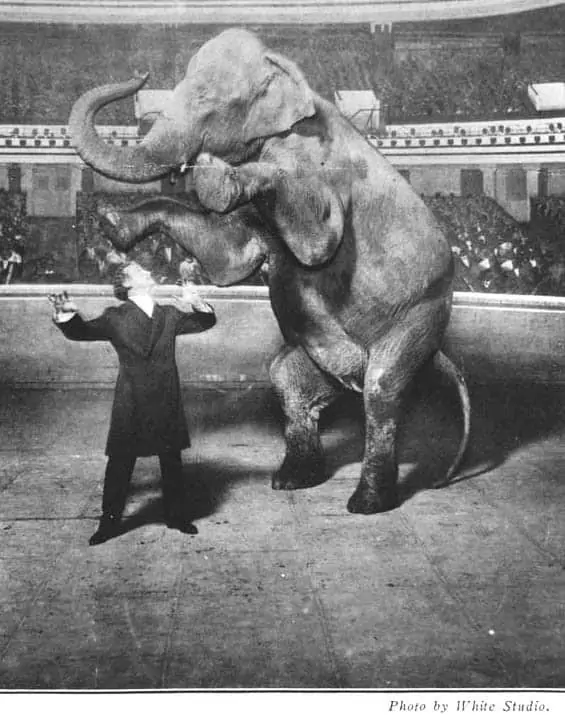

Fig. 1. White Studio. “Houdini and Jennie, the Elephant, Performing at the Hippodrome, New York.” Library of Congress , www.loc.gov/item/96518833/.
When adding a table or data set into a project, it is formatted a little differently. Above the data set, include the label “Table” with an Arabic numeral, and title it. The table number and title should be located flush left and on separate lines. The first table seen in the project is labeled as Table 1. The second table in the project is Table 2, and so on. The table’s title should be written in title case form (the first letter of each word is capitalized, except for small, insignificant words).
Underneath the table, provide the source and any notes. Notes should be labeled with a letter, rather than a numeral, so the reader is able to differentiate between the notes of the text and the notes of the table.
International Scholars from India Enrolled at Yale University a
Source: “International Scholars Academic Year 2015-2016.” Yale University , Office of International Students and Scholars, yale.app.box.com/v/scholar-2015-2016. a. The numbers reflect students who are enrolled full-time.
The information included above and below any images or table should be double spaced, similar to the rest of the project or paper.
Musical Scores
Musical scores need to be labeled as well. When including a musical score in a project, label musical scores with “Ex.” which is short for example. This label should be placed below the musical score. Next to the abbreviation “Ex.”, assign the score an Arabic numeral. The first musical score in the project should be labeled as Ex. 1. The second musical score found in an assignment should be labeled as Ex. 2., and so on.
If possible, provide a caption after to the label. If the caption below the sheet music includes enough information about the source, it is not necessary to include the full reference at the end of the assignment.
Here is an example of a possible label and caption:
Ex. 4. Scott Joplin, The Entertainer, piano, C major.
Another example:

Here’s more on tables and illustrations.
Using Lists in MLA
It’s appropriate to add lists into an MLA format essay as long as the proper rules are followed.
Lists created using MLA essay format look different than a grocery list or any other type of vertical listing of items. Items in a list are included in your prose, rather than the traditional vertical style.
Often, you will use a colon between the introductory sentence and the list. But you should not include a colon if the first item in the list is part of the sentence.
List Example #1
Here is an example of how a list may look incorporated into the prose of a research project or assignment:
William Shakespeare wrote numerous plays, many of which were considered tragedies: Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear .
List Example #2 Here is an example of how a list may look in a research project or assignment when the list is part of the introductory sentence:
Many of William Shakespeare’s were tragedies. Some of his most popular tragedies include Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear.
MLA Works Cited Format
EasyBib.com has a full, comprehensive guide to creating a proper works cited MLA format , but here are a few items to keep in mind when developing this portion of a project:
- The list of citations should be the very last page of a research project or essay.
- The top of the page should include the running head and the page number.
- All entries should be placed in alphabetical order by the first item in the MLA format citation.
- The entire page should be double spaced.
For more detailed information, make sure to check out the EasyBib guide to MLA format Works Cited pages.
MLA Citation Format
The majority of this guide focuses on MLA formatting in regards to MLA paper format rules and guidelines. If you’re seeking information related to the proper formatting of an MLA citation, refer to our individual pages and posts on various types of citations.
If you’re simply looking for the general structure for full references, which are found on the final pages of projects, here’s the proper order:
Author’s Last name, Author’s First name. “Title of Source.”* Title of Container , Names of other contributors along with their specific roles, version of the source (if it differs from the original or is unique), any key numbers associated with the source that aren’t dates (such as journal issue numbers or volume numbers), Name of the Publisher, publication date, location (such as the URL or page numbers).
*Note: A title may be in italics instead of quotation marks, depending of the type of source. The general rule is that works that are self-contained (like books, journals, or television shows) are formatted in italics. Works that are part of a larger work (like articles, chapters, or specific episodes) are formatting in quotation marks.
MLA Format Citing FAQs:
“What in the world are containers?”
Containers are what hold the source. If you’re creating a reference for a chapter in a book, the title of the chapter is the title of the source , and the container is the title of the book . The book holds the chapter, so it’s the container. If you’re searching for how to cite a website, here’s a tip: the title of the source is the name of the individual page and the title of the container is the name of the full website.
“This seems like a lot of information for a reference. Is it all necessary?”
The short answer is “No!” When citing, only include the components that help the reader locate the exact same source themselves.
It isn’t necessary to go digging for items such as numbers, version types, or names of other individuals or contributors associated with the source if they aren’t applicable. If you think it’s beneficial for the reader, then include it.
Related to citations, here are helpful pages on:
- MLA citation website format
- Citing a book
- Citing a journal
- What is a DOI ?
- More on PDFs
If you’re looking for an MLA citation generator, head to the EasyBib homepage. Our formatter will help you create citations quickly and easily!
Need APA, too? There are also EasyBib tools and an APA citation website reference guide to help you learn the basics.
Edits and Proofreading
Editing and proofreading your assignment prior to submission is an incredibly important step in the research process. Editing involves checking the paper for the following items:
- Spelling : Are all words spelled correctly? Review all proper names, places, and other unique words to ensure correct spelling. When finished, run the project through a spell checker. Many word processing programs, such as Microsoft Word and Google Drive, provide a free spell checking feature. While spell checks are beneficial, they do not always spot every mistake, so make sure you take the time to read through the assignment carefully. If you’re still not sure if your project contains proper spelling, ask a friend to read through it. They may find a mistake you missed!
- Grammar : Check your assignment to make sure you’ve included proper word usage. There are numerous grammar checkers available to review your project prior to submission. Again, take the time to review any recommendations from these programs prior to accepting the suggestions and revisions.
- Punctuation : Check to make sure the end of every sentence has an ending punctuation mark. Also make sure commas, hyphens, colons, and other punctuation marks are placed in the appropriate places.
- Attribution : Do all quotes and paraphrases include a citation? Did you create an in-text citation for each individual piece of information?
Smart idea: running your paper through a paper checker before you turn it in. EasyBib Plus offers a checker that scans for grammar errors and unintentional plagiarism.
Check out our MLA sample papers . Also, check out the EasyBib MLA Annotated Bibliography Guide.
Don’t forget to use the EasyBib citation generator to develop your Modern Language Association style references.EasyBib.com also has helpful guides on APA format and more styles . Lastly, stay up-to-date on what’s coming by following our EasyBib Twitter account.
Works Cited
“Formatting a Research Paper.” The MLA Style Center , Modern Language Association of America, style.mla.org/formatting-papers/.
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. You can find her here on Twitter. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The works-cited list provides the reader full information so that a reader can locate the source for further use.
Basic formatting
The works-cited list appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes if they are present.
Page margins
All margins (top, bottom, left, and right) should be set at 1 inch.
Running head
Write the running head in the top right of the page at 0.5 inch from the top. Use the running head “Surname Page #.”
The font should be clear enough to read. For example, Times New Roman font set to 12 points.
Formatting entries
Entries should be double-spaced, including a double-space between the heading and the first entry. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Formatting the title
The title should be “Works Cited.” Center the title. Do not bold, italicize, or underline the title. If you cite only one source in the list, the title should be “Work Cited.” If you include sources that you only consulted and didn’t cite directly, the title should be changed accordingly to “Works Cited and Consulted.”
Arranging works cited
Works-cited-list entries are arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name (or the editor’s last name for entire edited collections). Double-space all entries. Begin each entry flush with the left margin. If any entry runs over more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin (sometimes called a hanging indent).
Example works cited
Damasio, Antonio. The Feeling of What Happens: Body, Emotion and the Making of Consciousness . Vintage, 2000.
Hill, R. T. “Legitimizing Colonial Privilege: Native Americans at a Quincentenary of Discourse.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 16, no. 1, 1996, pp. 92–100.
MacDonald, Shauna M. “Performance as Critical Posthuman Pedagogy.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 34, no. 2, 2014, pp. 164–81.
Zilio, M. “Canada Will Not Move Embassy to Jerusalem, Federal Government Says.” The Globe and Mail . 7 Sept. 2017, www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/canada-will-not-move-embassy-to-jerusalem-federal-government-says/article37219576/ .
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed in the text. It is styled in two ways: a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when directly quoting text from the source being cited. When including a page number, do not include a comma or any other punctuation mark between the author’s surname and the page number.
Parenthetical citations usually add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Sometimes they include a page number or other locator. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
The spiritual geography of the landscape is explained (Cooper).
If you want to cite a chapter number, a scene, or a line number, follow the abbreviation guidelines below:
When including a more specific locator number rather than a page number, place a comma between the author’s surname and the label.
(Cooper, ch. 2).
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for sources with different numbers or types of authors:
Use only the surname of the author in parenthetical citations. If you want to add a page number (or another indicator of the place in a work), add it after the author’s surname without any punctuation between the surname and the page number.
(Abraham 7).
Two authors
Add only the surnames of the authors. Use “and” to separate the two authors.
(Langmuir and Einstein).
Three or more authors
Add only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
(Low et al.).
Corporate author
Shorten the organization name wherever possible, excluding any initial articles and using the shortest noun phrase (e.g., shorten Literary Society of Tamil Culture to Literary Society).
(Literary Society).
If there is no author for the source, use the source title in place of the author’s surname.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them is shortened to Fantastic Beasts .
( Fantastic Beasts 160).
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Using MLA Format

Document Sources
Works cited quick guide.
Learn how to use the MLA format template.
Digital Citation Tool
Build citations with our interactive template.
In-Text Citations
Get help with in-text citations.
Endnotes and Footnotes
Read our guide about using notes in MLA style.

Set Up Your Paper
Setting up a research paper.
Get our guidelines for setting up academic research papers.
Formatting Captions
Learn how to format captions.
Sample Papers
Read sample papers written in MLA style.
Annotated Bibliographies
Learn how to set up an annotated bibliography.

Get Writing and Teaching Tips
Ask the mla.
Browse answers and ask MLA editors questions.
Writing Tips
Improve your writing with these suggestions.
Teaching Resources and Advice
Get teaching advice, lesson plans, and activities.
Test your knowledge with these fun quizzes.
Recent questions from Ask the MLA
How do i alphabetize a works-cited-list entry that begins with a hashtag or another symbol.
The MLA recommends that writers should “ignore symbols when alphabetizing” (“How”). This includes hashtags. Thus, if an entry begins with a hashtag or another symbol,… Read More
How do I cite a work accessed through Wayback Machine ?
Wayback Machine is an archive of websites that lives on the Internet Archive ’s site, so you would treat the Internet Archive as the container of… Read More
How do I style the title of a fairy tale?
Fairy tales are typically enclosed in quotation marks, in the style of other short-form works. Some people may not know that Disney’s 1989 film The … Read More
How do I cite an anonymously translated poem?
If a translator’s name is not provided in the source, then skip that element in your works-cited-list entry. Follow the MLA template of core elements,… Read More
How do I cite a work that has incorrect citation information on its cover sheet?
Some works, especially works contained in databases, may list citation information for the work on a cover sheet or in a footer. If that citation… Read More
How do I cite Twitter now that its name has changed to X?
In 2023 the social media platform Twitter changed its name to X . What does this change mean for citations? When you cite a post published… Read More
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead. If the publication date is unknown, or if the content is ...
Write the author's name in last name, first name format with a period following. Next, write the name of the website in italics. Write the contributing organization's name with a comma following. List the date in day, month, year format with a comma following. Lastly, write the URL with a period following.
Type the last name of the first author listed on the source followed by a comma, then the first author's first name followed by a comma. Then type the word "and" then list the second author's first name and last name in the standard order. Follow the second name with a period.
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application.These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
author's given name, preceded by a comma. For a page with two or more authors, list them in the order they appear on the website. Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the others are written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the last author's name.
How to Cite an Online Work. To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an online work, list the author, the title of the work, the title of the website as the title of the container, and the publication details. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of work (e.g., book, scholarly article, blog post) and how you accessed ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Start the citation with the title. The title of the individual page is placed in quotation marks, followed by a period. Next, place the name of the website in italics, followed by a comma. If the name of the publisher matches the name of the author or the name of the title, do not include the publisher's information in the citation.
In MLA style, the list of Works Cited (also known as a reference list or bibliography) appears at the end of your paper. It gives full details of every source that you cited in an MLA in-text citation. Like the rest of an MLA format paper, the Works Cited should be left-aligned and double-spaced with 1-inch margins.
Works Cited List Example: Mabillard, Amanda. Shakespeare Online, 29 Dec. 2011, www.shakespeare-online.com. Accessed 6 July 2016. In-Text Citation Example: (Author's Last Name) (Mabillard) Note: In this example, the name of the organization affiliated with the website is omitted since it is the same as the website title.
Then use this template: Author last name, author first name. " Page title ." website name, published date day, month, year, page URL. Accessed accessed date day, month, year. The final formatted citation should look like this: Ingle, Sean. "Winter Olympics Was Hit by Cyber-Attack, Officials Confirm.".
Overview of how to create MLA in-text citations and reference lists In-Text Citations. Resources on using in-text citations in MLA style. The Basics General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Works Cited Page. Resources on writing an MLA style works cited page, including citation formats ...
Webpage with an individual author. When citing websites, MLA usually requires you to abbreviate the names of months to three letters. For example, January becomes Jan. Author Last Name, First Name. "Title.". Title of Site, Sponsor or Publisher [include only if different from website title or author], Day Month Year, URL.
Formatting the Header in MLA. To create a header for your first page, follow these steps: Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin. Type your name, your instructor's name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
The nine core elements of MLA citations. 1. Author. Begin each source entry with the name of the author (s) or creator (s). The name of the first author is always inverted (Last name, First name). When a source has two authors, the second author's name is shown in the normal order (First name Last name).
Get started with MLA style. Learn how to document sources, set up your paper, and improve your teaching and writing. Document Sources Works Cited Quick Guide Learn how to use the MLA format template. Digital Citation Tool Build citations with our interactive template. In-Text Citations Get help with in-text citations. Endnotes and Footnotes Read our …
Author's last name, first name. "Article title." Periodical title Volume # Date: inclusive pages. Note: If an edition is named on the masthead, add a comma after the date and specify the edition. Examples: Hall, Trish. "IQ Scores Are Up, and Psychologists Wonder Why." New York Times 24 Feb. 1998, late ed.: F1+.
Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. It should have the same one-inch margins and last name, page number header as the rest of your paper. Label the page Works Cited (do not italicize the words Works Cited or put them in quotation marks) and center the words Works Cited at the top of the page.
Works Cited page. The Works Cited list is included on a separate page at the end of your paper. You list all the sources you referenced in your paper in alphabetical order. Don't include sources that weren't cited in the paper, except potentially in an MLA annotated bibliography assignment.. Place the title "Works Cited" in the center at the top of the page.
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.