
Problem Solving Through Programming in C
In this lesson, we are going to learn Problem Solving Through Programming in C. This is the first lesson while we start learning the C language.
So let’s start learning the C language.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Problem Solving Through Programming in C
Regardless of the area of the study, computer science is all about solving problems with computers. The problem that we want to solve can come from any real-world problem or perhaps even from the abstract world. We need to have a standard systematic approach to problem solving through programming in c.
computer programmers are problem solvers. In order to solve a problem on a computer, we must know how to represent the information describing the problem and determine the steps to transform the information from one representation into another.
In this chapter, we will learn problem-solving and steps in problem-solving, basic tools for designing solution as an algorithm, flowchart , pseudo code etc.
A computer is a very powerful and versatile machine capable of performing a multitude of different tasks, yet it has no intelligence or thinking power.
The Computer performs many tasks exactly in the same manner as it is told to do. This places responsibility on the user to instruct the computer in a correct and precise manner so that the machine is able to perform the required job in a proper way. A wrong or ambiguous instruction may sometimes prove dangerous.
The computer cannot solve the problem on its own, one has to provide step by step solutions of the problem to the computer. In fact, the task of problem-solving is not that of the computer.
It is the programmer who has to write down the solution to the problem in terms of simple operations which the computer can understand and execute.
Problem-solving is a sequential process of analyzing information related to a given situation and generating appropriate response options.
In order to solve a problem with the computer, one has to pass through certain stages or steps. They are as follows:
Steps to Solve a Problem With the Computer

Step 1: Understanding the Problem:
Here we try to understand the problem to be solved in totally. Before with the next stage or step, we should be absolutely sure about the objectives of the given problem.
Step 2: Analyzing the Problem:
After understanding thoroughly the problem to be solved, we look at different ways of solving the problem and evaluate each of these methods.
The idea here is to search for an appropriate solution to the problem under consideration. The end result of this stage is a broad overview of the sequence of operations that are to be carried out to solve the given problem.
Step 3: Developing the solution:
Here, the overview of the sequence of operations that was the result of the analysis stage is expanded to form a detailed step by step solution to the problem under consideration.
Step 4: Coding and Implementation:
The last stage of problem-solving is the conversion of the detailed sequence of operations into a language that the computer can understand. Here, each step is converted to its equivalent instruction or instructions in the computer language that has been chosen for the implantation.
The vehicle for the computer solution to a problem is a set of explicit and unambiguous instructions expressed in a programming language. This set of instruction is called a program with problem solving through programming in C .
A program may also be thought of as an algorithm expressed in a programming language. an algorithm, therefore, corresponds to a solution to a problem that is independent of any programming language .
To obtain the computer solution to a problem once we have the program we usually have to supply the program with input or data. The program then takes this input and manipulates it according to its instructions. Eventually produces an output which represents the computer solution to the problem.
The problem solving is a skill and there are no universal approaches one can take to solving problems. Basically one must explore possible avenues to a solution one by one until she/he comes across the right path to a solution.
In general, as one gains experience in solving problems, one develops one’s own techniques and strategies, though they are often intangible. Problem-solving skills are recognized as an integral component of computer programming.
Note: Practice C Programs for problem solving through programming in C.
Problem Solving Steps
Problem-solving is a creative process which defines systematization and mechanization. There are a number of steps that can be taken to raise the level of one’s performance in problem-solving.
A problem-solving technique follows certain steps in finding the solution to a problem. Let us look into the steps one by one:
1. Problem Definition Phase:
The success in solving any problem is possible only after the problem has been fully understood. That is, we cannot hope to solve a problem, which we do not understand. So, the problem understanding is the first step towards the solution of the problem.
In the problem definition phase, we must emphasize what must be done rather than how is it to be done. That is, we try to extract the precisely defined set of tasks from the problem statement.
Inexperienced problem solvers too often gallop ahead with the task of the problem – solving only to find that they are either solving the wrong problem or solving the wrong problem or solving just one particular problem.
2. Getting Started on a Problem:
There are many ways of solving a problem and there may be several solutions. So, it is difficult to recognize immediately which path could be more productive. Problem solving through programming in C.
Sometimes you do not have any idea where to begin solving a problem, even if the problem has been defined. Such block sometimes occurs because you are overly concerned with the details of the implementation even before you have completely understood or worked out a solution.
The best advice is not to get concerned with the details. Those can come later when the intricacies of the problem have been understood.
3. Use of Specific Examples:
To get started on a problem, we can make use of heuristics i.e the rule of thumb. This approach will allow us to start on the problem by picking a specific problem we wish to solve and try to work out the mechanism that will allow solving this particular problem.
It is usually much easier to work out the details of a solution to a specific problem because the relationship between the mechanism and the problem is more clearly defined.
This approach of focusing on a particular problem can give us the foothold we need for making a start on the solution to the general problem.
4. Similarities Among Problems:
One way to make a start is by considering a specific example. Another approach is to bring the experience to bear on the current problems. So, it is important to see if there are any similarities between the current problem and the past problems which we have solved.
The more experience one has the more tools and techniques one can bring to bear in tackling the given problem. But sometimes, it blocks us from discovering a desirable or better solution to the problem.
A skill that is important to try to develop in problem-solving is the ability to view a problem from a variety of angles.
One must be able to metaphorically turn a problem upside down, inside out, sideways, backwards, forwards and so on. Once one has developed this skill it should be possible to get started on any problem.
5. Working Backwards from the Solution:
In some cases, we can assume that we already have the solution to the problem and then try to work backwards to the starting point. Even a guess at the solution to the problem may be enough to give us a foothold to start on the problem.
We can systematize the investigations and avoid duplicate efforts by writing down the various steps taken and explorations made.
Another practice that helps to develop the problem-solving skills, once we have solved a problem, to consciously reflect back on the way we went about discovering the solution.
General Problem Solving Strategies:

There are a number of general and powerful computational strategies that are repeatedly used in various guises in computer science.
Often it is possible to phrase a problem in terms of one of these strategies and achieve considerable gains in computational efficiency.
1. Divide and Conquer:
The most widely known and used strategy, where the basic idea is to break down the original problem into two or more sub-problems, which is presumably easier or more efficient to solve.
The Splitting can be carried on further so that eventually we have many sub-problems, so small that further splitting is no necessary to solve them. We shall see many examples of this strategy and discuss the gain in efficiency due to its application.
2. Binary Doubling:
This is the reverse of the divide and conquers strategy i.e build-up the solution for a larger problem from solutions and smaller sub-problems.
3. Dynamic Programming:
Another general strategy for problem-solving which is useful when we can build-up the solution as a sequence of the intermediate steps. Problem Solving through programming in C.
The travelling salesman problem falls into this category. The idea here is that a good or optimal solution to a problem can be built-up from good or optimal solutions of the sub-problems.
4. General Search, Back Tracking and Branch-and-Bound:
All of these are variants of the basic dynamic programming strategy but are equally important.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Related posts.

What is Preprocessor in C

What is File Handling in C

Introduction
- Historical Development of C
- Importance of C
- Basic Structure of C Program
- Executing a C Program
- Compiler, Assembler, and Interpreter
Problem Solving Using Computer
- Problem Analysis
- Types of Errors
- Debugging, Testing, and Program Documentation
- Setting up C Programming Environment
C Fundamentals
- Character Set
- Identifiers and Keywords
- Data Types
- Constants and Variables
- Variable/Constant Declaration
- Pre-processor Directive
- Symbolic Constant
C Operators and Expressions
- Operators and Types
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Conditional Operator
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Special Operators
- Precedence and Associativity
C Input and Output
- Input and Output functions
- Unformatted I/O
- Formatted I/O
C Decision-making Statements
- Decision-making Statements in C
- Nested if else
- Else-if ladder
- Switch Case
- Loop Control Statements in C
C Functions
- Get Started
- First Program

Problem Analysis in C
- < 1 minute
The initial stage of any kind of software development is the problem/requirement/feasibility analysis of the project. The programming part starts once everything is analyzed and approved. To solve the client’s requirement with the computer-based system, good quality software needs to be developed. Initially, we have to model and map the real-world problem to our computer programs to work. So, the problem analysis is the initial process before starting the real computer program development. The basic problem analysis involves the following.
- Objectives – The problem should be stated clearly without any ambiguity. Some simple problem can be stated easily but complex problem may need complex analysis and analysis the problem dividing into smaller sub-problems.
- Output Requirements – We should know the output or what comes from the system thus developed. It is better to design the output requirements based on end user/ real users of the system developed.
- Input Requirements – To get the required output it is required to define the input data and the sources of input data. for example: student data from college administration, survey data of the road.
- Processing Requirements – This is where thre actual raw input data are processed to produce required output. any kind of algorithms/formulas are implemented. In processing requirement there may be hardware platform, software platform, and manpower etc.
- Evaluating Feasibility – In this phase where we decide whether the proposed software development task is technically and economically feasible or not.
Fundamentals of C Programming/Problem Analysis
‹ Back to Contents ‹ Back to Introduction to C Programming
Problem Analysis [ edit | edit source ]
If we are to use the computer as a problem-solving tool, then we must have a good analysis of the problem given. Here are some suggested steps on how to go about analyzing a certain problem for computer application:
1. Review the problem carefully and understand what you are asked to do.
2. Determine what information is given(input) and what result must be produced(output).
3. Assign names to each input and output items.
4. Determine the manner of processing that must be done on the input data to come up with the desired output(i.e., determine what formulas are needed to manipulate the given data).
Given the scores for the two departmental quizzes, two machine projects, final exam, and teacher's evaluation, write a program that will compute for the final grade based on the following computation:
- Book:Fundamentals of C Programming
Navigation menu
- Announcements
- Explore Courses
Problem solving through Programming In C
- BE/BTech in all disciplines
- BCA/MCA/M. Sc
- All IT Industries
65741 students have enrolled already!!

In association with

Problem Solving with Computer
By Bipin Tiwari
Problem Solving is a scientific technique to discover and implement the answer to a problem. The computer is the symbol manipulating device that follows the set of commands known as program.
Program is the set of instructions which is run by the computer to perform specific task. The task of developing program is called programming.
Problem Solving Technique:
Sometimes it is not sufficient just to cope with problems. We have to solve that problems. Most people are involving to solve the problem. These problem are occur while performing small task or making small decision. So, Here are the some basic steps to solve the problems
Step 1: Identify and Define Problem
Explain you problem clearly as possible as you can.
Step 2: Generate Possible Solutions
- List out all the solution that you find. Don’t focus on the quality of the solution
- Generate the maximum number of solution as you can without considering the quality of the solution
Step 3: Evaluate Alternatives
After generating the maximum solution, Remove the undesired solutions.
Step 4: Decide a Solution
After filtering all the solution, you have the best solution only. Then choose on of the best solution and make a decision to make it as a perfect solution.
Step 5: Implement a Solution:
After getting the best solution, Implement that solution to solve a problem.
Step 6: Evaluate the result
After implementing a best solution, Evaluate how much you solution solve the problem. If your solution will not solve the problem then you can again start with Step 2 .
Algorithm is the set of rules that define how particular problem can be solved in finite number of steps. Any good algorithm must have following characteristics
- Input: Specify and require input
- Output: Solution of any problem
- Definite: Solution must be clearly defined
- Finite: Steps must be finite
- Correct: Correct output must be generated
Advantages of Algorithms:
- It is the way to sole a problem step-wise so it is easy to understand.
- It uses definite procedure.
- It is not dependent with any programming language.
- Each step has it own meaning so it is easy to debug
Disadvantage of Algorithms:
- It is time consuming
- Difficult to show branching and looping statement
- Large problems are difficult to implement
The solution of any problem in picture form is called flowchart. It is the one of the most important technique to depict an algorithm.
Advantage of Flowchart:
- Easier to understand
- Helps to understand logic of problem
- Easy to draw flowchart in any software like MS-Word
- Complex problem can be represent using less symbols
- It is the way to documenting any problem
- Helps in debugging process
Disadvantage of Flowchart:
- For any change, Flowchart have to redrawn
- Showing many looping and branching become complex
- Modification of flowchart is time consuming
Symbol Used in Flowchart:
Example: Algorithm and Flowchart to check odd or even
Coding, Compiling and Execution
Question's answer.
Share this link via
Or copy link
Copyright 2022 | HAMROCSIT.COM | All Right Reserved
What Is Problem Solving? How Software Engineers Approach Complex Challenges

From debugging an existing system to designing an entirely new software application, a day in the life of a software engineer is filled with various challenges and complexities. The one skill that glues these disparate tasks together and makes them manageable? Problem solving .
Throughout this blog post, we’ll explore why problem-solving skills are so critical for software engineers, delve into the techniques they use to address complex challenges, and discuss how hiring managers can identify these skills during the hiring process.

What Is Problem Solving?
But what exactly is problem solving in the context of software engineering? How does it work, and why is it so important?
Problem solving, in the simplest terms, is the process of identifying a problem, analyzing it, and finding the most effective solution to overcome it. For software engineers, this process is deeply embedded in their daily workflow. It could be something as simple as figuring out why a piece of code isn’t working as expected, or something as complex as designing the architecture for a new software system.
In a world where technology is evolving at a blistering pace, the complexity and volume of problems that software engineers face are also growing. As such, the ability to tackle these issues head-on and find innovative solutions is not only a handy skill — it’s a necessity.
The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills for Software Engineers
Problem-solving isn’t just another ability that software engineers pull out of their toolkits when they encounter a bug or a system failure. It’s a constant, ongoing process that’s intrinsic to every aspect of their work. Let’s break down why this skill is so critical.
Driving Development Forward
Without problem solving, software development would hit a standstill. Every new feature, every optimization, and every bug fix is a problem that needs solving. Whether it’s a performance issue that needs diagnosing or a user interface that needs improving, the capacity to tackle and solve these problems is what keeps the wheels of development turning.
It’s estimated that 60% of software development lifecycle costs are related to maintenance tasks, including debugging and problem solving. This highlights how pivotal this skill is to the everyday functioning and advancement of software systems.
Innovation and Optimization
The importance of problem solving isn’t confined to reactive scenarios; it also plays a major role in proactive, innovative initiatives . Software engineers often need to think outside the box to come up with creative solutions, whether it’s optimizing an algorithm to run faster or designing a new feature to meet customer needs. These are all forms of problem solving.
Consider the development of the modern smartphone. It wasn’t born out of a pre-existing issue but was a solution to a problem people didn’t realize they had — a device that combined communication, entertainment, and productivity into one handheld tool.
Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
Good problem-solving skills can save a lot of time and resources. Effective problem-solvers are adept at dissecting an issue to understand its root cause, thus reducing the time spent on trial and error. This efficiency means projects move faster, releases happen sooner, and businesses stay ahead of their competition.
Improving Software Quality
Problem solving also plays a significant role in enhancing the quality of the end product. By tackling the root causes of bugs and system failures, software engineers can deliver reliable, high-performing software. This is critical because, according to the Consortium for Information and Software Quality, poor quality software in the U.S. in 2022 cost at least $2.41 trillion in operational issues, wasted developer time, and other related problems.
Problem-Solving Techniques in Software Engineering
So how do software engineers go about tackling these complex challenges? Let’s explore some of the key problem-solving techniques, theories, and processes they commonly use.
Decomposition
Breaking down a problem into smaller, manageable parts is one of the first steps in the problem-solving process. It’s like dealing with a complicated puzzle. You don’t try to solve it all at once. Instead, you separate the pieces, group them based on similarities, and then start working on the smaller sets. This method allows software engineers to handle complex issues without being overwhelmed and makes it easier to identify where things might be going wrong.
Abstraction
In the realm of software engineering, abstraction means focusing on the necessary information only and ignoring irrelevant details. It is a way of simplifying complex systems to make them easier to understand and manage. For instance, a software engineer might ignore the details of how a database works to focus on the information it holds and how to retrieve or modify that information.
Algorithmic Thinking
At its core, software engineering is about creating algorithms — step-by-step procedures to solve a problem or accomplish a goal. Algorithmic thinking involves conceiving and expressing these procedures clearly and accurately and viewing every problem through an algorithmic lens. A well-designed algorithm not only solves the problem at hand but also does so efficiently, saving computational resources.
Parallel Thinking
Parallel thinking is a structured process where team members think in the same direction at the same time, allowing for more organized discussion and collaboration. It’s an approach popularized by Edward de Bono with the “ Six Thinking Hats ” technique, where each “hat” represents a different style of thinking.
In the context of software engineering, parallel thinking can be highly effective for problem solving. For instance, when dealing with a complex issue, the team can use the “White Hat” to focus solely on the data and facts about the problem, then the “Black Hat” to consider potential problems with a proposed solution, and so on. This structured approach can lead to more comprehensive analysis and more effective solutions, and it ensures that everyone’s perspectives are considered.
This is the process of identifying and fixing errors in code . Debugging involves carefully reviewing the code, reproducing and analyzing the error, and then making necessary modifications to rectify the problem. It’s a key part of maintaining and improving software quality.
Testing and Validation
Testing is an essential part of problem solving in software engineering. Engineers use a variety of tests to verify that their code works as expected and to uncover any potential issues. These range from unit tests that check individual components of the code to integration tests that ensure the pieces work well together. Validation, on the other hand, ensures that the solution not only works but also fulfills the intended requirements and objectives.
Explore verified tech roles & skills.
The definitive directory of tech roles, backed by machine learning and skills intelligence.
Explore all roles
Evaluating Problem-Solving Skills
We’ve examined the importance of problem-solving in the work of a software engineer and explored various techniques software engineers employ to approach complex challenges. Now, let’s delve into how hiring teams can identify and evaluate problem-solving skills during the hiring process.
Recognizing Problem-Solving Skills in Candidates
How can you tell if a candidate is a good problem solver? Look for these indicators:
- Previous Experience: A history of dealing with complex, challenging projects is often a good sign. Ask the candidate to discuss a difficult problem they faced in a previous role and how they solved it.
- Problem-Solving Questions: During interviews, pose hypothetical scenarios or present real problems your company has faced. Ask candidates to explain how they would tackle these issues. You’re not just looking for a correct solution but the thought process that led them there.
- Technical Tests: Coding challenges and other technical tests can provide insight into a candidate’s problem-solving abilities. Consider leveraging a platform for assessing these skills in a realistic, job-related context.
Assessing Problem-Solving Skills
Once you’ve identified potential problem solvers, here are a few ways you can assess their skills:
- Solution Effectiveness: Did the candidate solve the problem? How efficient and effective is their solution?
- Approach and Process: Go beyond whether or not they solved the problem and examine how they arrived at their solution. Did they break the problem down into manageable parts? Did they consider different perspectives and possibilities?
- Communication: A good problem solver can explain their thought process clearly. Can the candidate effectively communicate how they arrived at their solution and why they chose it?
- Adaptability: Problem-solving often involves a degree of trial and error. How does the candidate handle roadblocks? Do they adapt their approach based on new information or feedback?
Hiring managers play a crucial role in identifying and fostering problem-solving skills within their teams. By focusing on these abilities during the hiring process, companies can build teams that are more capable, innovative, and resilient.
Key Takeaways
As you can see, problem solving plays a pivotal role in software engineering. Far from being an occasional requirement, it is the lifeblood that drives development forward, catalyzes innovation, and delivers of quality software.
By leveraging problem-solving techniques, software engineers employ a powerful suite of strategies to overcome complex challenges. But mastering these techniques isn’t simple feat. It requires a learning mindset, regular practice, collaboration, reflective thinking, resilience, and a commitment to staying updated with industry trends.
For hiring managers and team leads, recognizing these skills and fostering a culture that values and nurtures problem solving is key. It’s this emphasis on problem solving that can differentiate an average team from a high-performing one and an ordinary product from an industry-leading one.
At the end of the day, software engineering is fundamentally about solving problems — problems that matter to businesses, to users, and to the wider society. And it’s the proficient problem solvers who stand at the forefront of this dynamic field, turning challenges into opportunities, and ideas into reality.
This article was written with the help of AI. Can you tell which parts?
Get started with HackerRank
Over 2,500 companies and 40% of developers worldwide use HackerRank to hire tech talent and sharpen their skills.
Recommended topics
- Hire Developers
- Problem Solving
Does a College Degree Still Matter for Developers in 2024?

Problem solving through Programming In C
- Formulate simple algorithms for arithmetic and logical problems
- Translate the algorithms to programs (in C language)
- Test and execute the programs and correct syntax and logical errors
- Implement conditional branching, iteration and recursion
- Decompose a problem into functions and synthesize a complete program using divide and conquer approach
- Use arrays, pointers and structures to formulate algorithms and programs
- Apply programming to solve matrix addition and multiplication problems and searching and sorting problems
- Apply programming to solve simple numerical method problems, namely rot finding of function, differentiation of function and simple integration
Note: This exam date is subjected to change based on seat availability. You can check final exam date on your hall ticket.
Page Visits
Course layout, books and references, instructor bio.

Prof. Anupam Basu
Course certificate.
- Assignment score = 25% of average of best 8 assignments out of the total 12 assignments given in the course.
- ( All assignments in a particular week will be counted towards final scoring - quizzes and programming assignments).
- Unproctored programming exam score = 25% of the average scores obtained as part of Unproctored programming exam - out of 100
- Proctored Exam score =50% of the proctored certification exam score out of 100

DOWNLOAD APP

SWAYAM SUPPORT
Please choose the SWAYAM National Coordinator for support. * :
- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Class 8 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 11 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
- Graphical Solution of Linear Programming Problems
- Linear Programming
- Solving Linear Inequalities Word Problems
- Stars and Bars Algorithms for Competitive Programming
- Python | Linear search on list or tuples
- Top 50 Dynamic Programming Coding Problems for Interviews
- Dynamic Programming (DP) Tutorial with Problems
- Program to find all types of Matrix
- Dynamic Programming | High-effort vs. Low-effort Tasks Problem
- Python | Linear Programming in Pulp
- C++ Program for the Fractional Knapsack Problem
- Transportation Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- Algorithms | Dynamic Programming | Question 7
- Algorithms | Dynamic Programming | Question 4
- Algorithms | Dynamic Programming | Question 3
- Algorithms | Dynamic Programming | Question 2
- How to begin with Competitive Programming?
- Dynamic Programming (DP) on Grids
- Knuth's Optimization in Dynamic Programming
Types of Linear Programming Problems
Linear programming is a mathematical technique for optimizing operations under a given set of constraints. The basic goal of linear programming is to maximize or minimize the total numerical value. It is regarded as one of the most essential strategies for determining optimum resource utilization. Linear programming challenges include a variety of problems involving cost minimization and profit maximization, among others. They will be briefly discussed in this article.
The purpose of this article is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the different types of linear programming problems and their solutions.
What is Linear Programming?
Linear programming (LP) is a mathematical optimization technique used to maximize or minimize a linear objective function, subject to a set of linear equality and inequality constraints. It is widely used in various fields such as economics, engineering, operations research, and management science to find the best possible outcome given limited resources.
Components of Linear Programming
Components of linear programming include:
- Objective Function: This is a linear function that needs to be optimized (maximized or minimized). It represents the quantity to be maximized or minimized, such as profit, cost, time, etc.
- Decision Variables: These are the variables that represent the choices or decisions to be made. They are the unknown quantities that the optimization process seeks to determine. Decision variables must be continuous and can take any real value within a specified range.
- Constraints: These are restrictions or limitations on the decision variables that must be satisfied. Constraints can be expressed as linear equations or inequalities. They represent the limitations imposed by available resources, capacity constraints, demand requirements, etc.
- Feasible Region: The feasible region is the set of all possible combinations of decision variables that satisfy all constraints. It is defined by the intersection of the constraint boundaries.
- Optimal Solution: This is the best possible solution that maximizes or minimizes the objective function while satisfying all constraints. In graphical terms, it is the point within the feasible region that maximizes or minimizes the objective function.
Linear programming provides a systematic and efficient approach to decision-making in situations where resources are limited and objectives need to be optimized.
Different Types of Linear Programming Problems
The following are the types of linear programming problems:
- Manufacturing problems
- Diet problems
- Transportation problems
- Optimal alignment problem
Let’s discuss more about each of them.
Manufacturing Problems
In these problems, we evaluate the number of units of various items that should be produced and sold by a company when each product requires a given number of workforce, machine hours, labour hours per unit of product, warehouse space per unit of output, and so on, to maximize profit.
Manufacturing problems involve maximizing the production rate or net profits of manufactured products, which might measure the available workspace, the number of workers, machine hours, packing materials used, raw materials required, the product’s market value, and other factors. These are commonly used in the industrial sector to anticipate a company’s future capital increase over time.
Diet Problems
In these challenges, we assess how many components or nutrients a diet should contain in order to lower the cost of the desired diet while guaranteeing the minimal amount of each vitamin.
As the name suggests, diet-related problems can be resolved by eating more particular foods that are rich in essential nutrients and can support the adoption of a particular diet plan. Finding a set of meals that will satisfy a set of daily nutritional demands for the least amount of money is the aim of a diet problem.
Transportation Problems
In these problems , we create a transportation schedule to discover the most cost-effective method of carrying a product from various plants/factories to various markets.
The study of transportation routes or how items from diverse production sources are transported to various markets to minimize the total transportation cost is linked to transportation difficulties. Analyzing such challenges is crucial for large firms with several production units and a broad customer base.
Optimal Assignment Problems
This problem addresses a company’s completion of a given task/assignment by selecting a specific number of employees to complete the assignment within the required timeframe, assuming that each person works on only one job. Event planning and management in major organizations, for example, are examples of such problems.
Constraints and Objective Function of Each Linear Programming Problem
Steps for solving linear programming problems.
Step 1: Identify the decision variables : The first step is to determine which choice factors control the behaviour of the objective function. A function that needs to be optimised is an objective function. Determine the decision variables and designate them with X, Y, and Z symbols.
Step 2: Form an objective function : Using the decision variables, write out an algebraic expression that displays the quantity we aim to maximize.
Step 3: Identify the constraints : Choose and write the given linear inequalities from the data.
Step 4: Draw the graph for the given data : Construct the graph by using constraints for solving the linear programming problem.
Step 5: Draw the feasible region : Every constraint on the problem is satisfied by this portion of the graph. Anywhere in the feasible zone is a viable solution for the objective function.
Step 6: Choosing the optimal point : Choose the point for which the given function has maximum or minimum values.
Solved Problems of Linear Programming Problems
Question 1. A factory manufactures two types of gadgets, regular and premium. Each gadget requires the use of two operations, assembly and finishing, and there are at most 12 hours available for each operation. A regular gadget requires 1 hour of assembly and 2 hours of finishing, while a premium gadget needs 2 hours of assembly and 1 hour of finishing. Due to other restrictions, the company can make at most 7 gadgets a day. If a profit of $20 is realized for each regular gadget and $30 for a premium gadget, how many of each should be manufactured to maximize profit?
We define our unknowns:
Let the number of regular gadgets manufactured each day = x
and the number of premium gadgets manufactured each day = y
The objective function is
P = 20x + 30y
We now write the constraints. The fourth sentence states that the company can make at most 7 gadgets a day. This translates as
Since the regular gadget requires one hour of assembly and the premium gadget requires two hours of assembly, and there are at most 12 hours available for this operation, we get
x + 2y ≤ 12
Similarly, the regular gadget requires two hours of finishing and the premium gadget one hour. Again, there are at most 12 hours available for finishing. This gives us the following constraint.
2x + y ≤ 12
The fact that x and y can never be negative is represented by the following two constraints:
x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
We have formulated the problem as follows :
Maximize P=20x + 30y Subject to : x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 122, x + y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
In order to solve the problem, we next graph the constraints and feasible region.
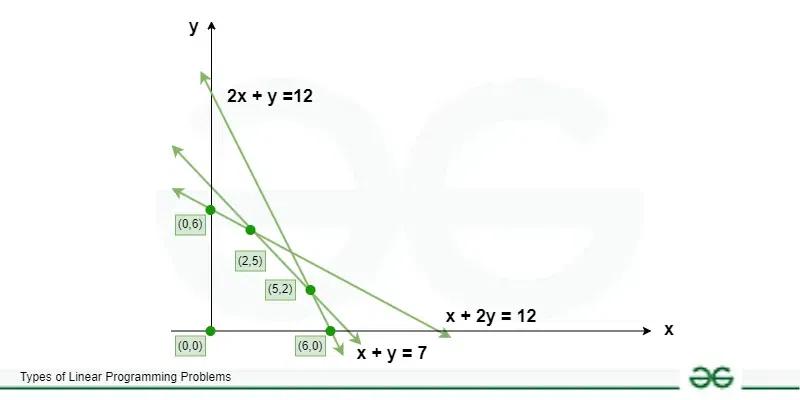
Again, we have shaded the feasible region, where all constraints are satisfied.
Since the extreme value of the objective function always takes place at the vertices of the feasible region, we identify all the critical points. They are listed as (0, 0), (0, 6), (2, 5), (5, 2), and (6, 0). To maximize profit, we will substitute these points in the objective function to see which point gives us the maximum profit each day. The results are listed below.
FAQ on Linear programming
How many methods are there in lpp.
There are different methods to solve a linear programming problem. Such as Graphical method, Simplex method, Ellipsoid method, Interior point methods.
What are the four 4 special cases in linear programming?
Four special cases and difficulties arise at times when using the graphical approach to solving LP problems: (1) infeasibility, (2) unboundedness, (3) redundancy, and (4) alternate optimal solutions.
What are the 3 components of linear programming?
The basic components of the LP are as follows: Decision Variables. Constraints. Objective Functions.
What are the applications of LPP?
LPP applications may include production scheduling, inventory policies, investment portfolio, allocation of advertising budget, construction of warehouses, etc.
What are the limitations of LPP?
Constraints (limitations) should be expressed in mathematical form. Relationships between two or more variables should be linear. The values of the variables should always be non-negative or zero. There should always be finite and infinite inputs and output numbers.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Maths-Class-12
- School Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: Practice C Programs for problem solving through programming in C. Problem Solving Steps. Problem-solving is a creative process which defines systematization and mechanization. There are a number of steps that can be taken to raise the level of one's performance in problem-solving. A problem-solving technique follows certain steps in ...
In this article, we will be tackling problem-solving through C programming. For embedded devices, C is the most extensively used language. C is a structured programming language with a large number of built-in functions and operators that can be used to create complicated programs.
This self-readable and student-friendly text provides a strong programming foundation to solve problems with C language through its well-supported structured programming methodology, rich set of operators and data types. It is designed to help students build efficient and compact programs. The book, now in its second edition, is an extended version of Dr. M.T. Somashekara's previous book ...
Share your videos with friends, family, and the world
The basic problem analysis involves the following. Objectives - The problem should be stated clearly without any ambiguity. Some simple problem can be stated easily but complex problem may need complex analysis and analysis the problem dividing into smaller sub-problems. Output Requirements - We should know the output or what comes from the ...
Here are some suggested steps on how to go about analyzing a certain problem for computer application: 1. Review the problem carefully and understand what you are asked to do. 2. Determine what information is given (input) and what result must be produced (output). 3. Assign names to each input and output items.
Basic Math. Simple math concepts required to solve programming problems. Lesson. Addition and multiplication. Lesson. Subtraction and division. 3.
Learners enrolled: 29073. ABOUT THE COURSE : This course is aimed at enabling the students to. Formulate simple algorithms for arithmetic and logical problems. Translate the algorithms to programs (in C language) Test and execute the programs and correct syntax and logical errors. Implement conditional branching, iteration and recursion.
Problem solving through Programming In C. ABOUT THE COURSE This course is aimed at enabling the students to. ·formulate simple algorithms for arithmetic and logical problems·translate the algorithms to programs (in C language)·test and execute the programs and correct syntax and logical errors·implement conditional branching, iteration and ...
Step 1: Identify and Define Problem. Explain you problem clearly as possible as you can. Step 2: Generate Possible Solutions. List out all the solution that you find. Don't focus on the quality of the solution. Generate the maximum number of solution as you can without considering the quality of the solution.
Documentation - Techniques of Problem Solving - Problem solving aspects - Top- Down aspects - Implementation of algorithms - Program verification - Flowcharting, decision table, algorithms, Structured programming concepts, Programming methodologies viz. top-down and bottom-up programming. Basic Concepts of Computer
The best way to learn C programming is by practicing and solving the C programs (C problems). We have 30+ C programs with solutions which are categorized below. Practice these C programs to learn and enhance your C problem-solving skills. If you have mastered programming, you must have experienced the beginning of problem solving or solving ...
You'll develop your ability to produce good code and your problem-solving skills. This course provides all the information on "why" you are doing the things that you are doing in addition to teaching you how to write in the C programming language. You will have a thorough understanding of the C programming language's principles at the end of ...
Join over 23 million developers in solving code challenges on HackerRank, one of the best ways to prepare for programming interviews. ... For Loop in C. Easy C (Basic) Max Score: 10 Success Rate: 93.70%. Solve Challenge. Sum of Digits of a Five Digit Number. Easy C (Basic) Max Score: 15 Success Rate: 98.66%.
C Programs. C Programs: Practicing and solving problems is the best way to learn anything. Here, we have provided 100+ C programming examples in different categories like basic C Programs, Fibonacci series in C, String, Array, Base Conversion, Pattern Printing, Pointers, etc.
C is called a structured programming language because to solve a large problem, C programming language divides the problem into smaller modules called functions or procedures each of which handles a particular responsibility. The program which solves the entire problem is a collection of such functions.
As you can see, problem solving plays a pivotal role in software engineering. Far from being an occasional requirement, it is the lifeblood that drives development forward, catalyzes innovation, and delivers of quality software. By leveraging problem-solving techniques, software engineers employ a powerful suite of strategies to overcome ...
10. You might try solving some of the problems on Project Euler. The first few are pretty simple, but they get very challenging very quickly. I think it's a lot of fun trying to come up with the shortest code or highly optimized code to compute the results (though, I generally use C++ or Python, not C).
Solve these beginner friendly problems online to get better at C language. ... Get hands-on experience with Practice C programming practice problem course on CodeChef. Solve a wide range of Practice C coding challenges and boost your confidence in programming. ... CodeChef Learn Problem Solving: 287: Multiple Choice Question: NA: Learning SQL ...
Q2: Write a Program to find the Sum of two numbers entered by the user. In this problem, you have to write a program that adds two numbers and prints their sum on the console screen. For Example, Input: Enter two numbers A and B : 5 2. Output: Sum of A and B is: 7.
C is a general-purpose, imperative computer programming language, supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope and recursion, while a static type system prevents many unintended operations. C was originally developed by Dennis Ritchie between 1969 and 1973 at Bell Labs.
C language was designed at Bell laboratories in the early 1970's by Dennis Ritchie. C being popular in the modern computer world can be used in Mathematical Scientific, Engineering and Commercial applications The most popular Operating system UNIX is written in C language. This language also has the features of low level languages and hence ...
Problem solving through Programming In C. By Prof. Anupam Basu | IIT Kharagpur. Learners enrolled: 61372. This course is aimed at enabling the students to. Formulate simple algorithms for arithmetic and logical problems. Translate the algorithms to programs (in C language) Test and execute the programs and correct syntax and logical errors.
Problem solving strategy 3: Split the problem into parts. A problem halved is a problem solved. Source: Author. It makes complete sense that splitting a problem into smaller parts will help you to solve it. However, it is also important to consider how the parts are then 'put back together'. The example below highlights how the sum of the ...
Steps for Solving Linear Programming Problems. Step 1: Identify the decision variables: The first step is to determine which choice factors control the behaviour of the objective function. A function that needs to be optimised is an objective function. Determine the decision variables and designate them with X, Y, and Z symbols.