How to Write an Annotated Bibliography - APA Style (7th Edition)
What is an annotation, how is an annotation different from an abstract, what is an annotated bibliography, types of annotated bibliographies, descriptive or informative, analytical or critical, to get started.
An annotation is more than just a brief summary of an article, book, website, or other type of publication. An annotation should give enough information to make a reader decide whether to read the complete work. In other words, if the reader were exploring the same topic as you, is this material useful and if so, why?
While an abstract also summarizes an article, book, website, or other type of publication, it is purely descriptive. Although annotations can be descriptive, they also include distinctive features about an item. Annotations can be evaluative and critical as we will see when we look at the two major types of annotations.
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources (like a reference list). It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100–200 words in length.
Depending on the assignment, an annotated bibliography might have different purposes:
- Provide a literature review on a particular subject
- Help to formulate a thesis on a subject
- Demonstrate the research you have performed on a particular subject
- Provide examples of major sources of information available on a topic
- Describe items that other researchers may find of interest on a topic
There are two major types of annotated bibliographies:
A descriptive or informative annotated bibliography describes or summarizes a source as does an abstract; it describes why the source is useful for researching a particular topic or question and its distinctive features. In addition, it describes the author's main arguments and conclusions without evaluating what the author says or concludes.
For example:
McKinnon, A. (2019). Lessons learned in year one of business. Journal of Legal Nurse Consulting , 30 (4), 26–28. This article describes some of the difficulties many nurses experience when transitioning from nursing to a legal nurse consulting business. Pointing out issues of work-life balance, as well as the differences of working for someone else versus working for yourself, the author offers their personal experience as a learning tool. The process of becoming an entrepreneur is not often discussed in relation to nursing, and rarely delves into only the first year of starting a new business. Time management, maintaining an existing job, decision-making, and knowing yourself in order to market yourself are discussed with some detail. The author goes on to describe how important both the nursing professional community will be to a new business, and the importance of mentorship as both the mentee and mentor in individual success that can be found through professional connections. The article’s focus on practical advice for nurses seeking to start their own business does not detract from the advice about universal struggles of entrepreneurship makes this an article of interest to a wide-ranging audience.
An analytical or critical annotation not only summarizes the material, it analyzes what is being said. It examines the strengths and weaknesses of what is presented as well as describing the applicability of the author's conclusions to the research being conducted.
Analytical or critical annotations will most likely be required when writing for a college-level course.
McKinnon, A. (2019). Lessons learned in year one of business. Journal of Legal Nurse Consulting , 30 (4), 26–28. This article describes some of the difficulty many nurses experience when transitioning from nursing to a nurse consulting business. While the article focuses on issues of work-life balance, the differences of working for someone else versus working for yourself, marketing, and other business issues the author’s offer of only their personal experience is brief with few or no alternative solutions provided. There is no mention throughout the article of making use of other research about starting a new business and being successful. While relying on the anecdotal advice for their list of issues, the author does reference other business resources such as the Small Business Administration to help with business planning and professional organizations that can help with mentorships. The article is a good resource for those wanting to start their own legal nurse consulting business, a good first advice article even. However, entrepreneurs should also use more business research studies focused on starting a new business, with strategies against known or expected pitfalls and issues new businesses face, and for help on topics the author did not touch in this abbreviated list of lessons learned.
Now you are ready to begin writing your own annotated bibliography.
- Choose your sources - Before writing your annotated bibliography, you must choose your sources. This involves doing research much like for any other project. Locate records to materials that may apply to your topic.
- Review the items - Then review the actual items and choose those that provide a wide variety of perspectives on your topic. Article abstracts are helpful in this process.
- The purpose of the work
- A summary of its content
- Information about the author(s)
- For what type of audience the work is written
- Its relevance to the topic
- Any special or unique features about the material
- Research methodology
- The strengths, weaknesses or biases in the material
Annotated bibliographies may be arranged alphabetically or chronologically, check with your instructor to see what he or she prefers.
Please see the APA Examples page for more information on citing in APA style.
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2023 11:27 AM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/annotated-bibliography-apa


APA 7th Edition Style Guide
- Changes/updates
- The Concise APA Handbook: APA 7th Edition
- Article Examples
- Book Examples
- Internet Resources and Other Examples
- Media Examples
- Finding the DOI
- APA Reference Quick Guide
- Legal Cases
- Sample Annotated Student Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Handouts and Guides
More examples
- Annotated bibliography example - UNT Dallas Library
- Annotated bibliography template - UNT Dallas Library
- APA 7th Edition Publication Manual - Sample Annotated Bibliography (See Fig. 9.3, p. 308)
What is an annotated bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources, each of which is followed by a brief note or “annotation.”
These annotations do one or more of the following:
- describe the content and focus of the book or article
- suggest the source’s usefulness to your research
- evaluate its method, conclusions, or reliability
- record your reactions to the source.
The process of writing an annotated bibliography provides a structured process to learn about a research topic. It causes you to read the available research (also referred to as "the literature") more closely as you develop a better understanding of the topic, related issues, and current trends.
Source: The University of Wisconsin-Madison: The Writing Center
Writing a strong annotation
The hardest part of this assignment is writing the annotation, but knowing what it entails can make this task less daunting.
While not all of these are necessary, an annotation could/will:
- Summarize the central theme and scope of the document
- Evaluates the authority, credibility, and/or background of the author(s)
- Comments on the intended audience (who was meant to read the document)
- Assesses the source’s strengths and weaknesses (Interesting? Helpful? Strong/weak argument? Strong/weak evidence?)
- Compares or contrast this work with others you have cited
- Critiques the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the source
- Evaluates the methods, conclusions/findings, and reliability of the source
- Shares how the source reinforces or contradicts your own argument
- Records your reactions to the reading
- States how the source will be used in your paper
Source: UNT Dallas Learning Commons: Annotated Bibliography
Formatting rules
General Formatting Rules:
- Format and order references in alphabetical order just as you would a reference list
- Each annotation should be a new paragraph below its reference entry
- Indent the entire annotation 0.5 inch from the left margins just as you would a block quotation
- If the annotation spans multiple paragraphs, indent the first line of the second and any subsequent paragraphs an addition 0.5 inch the same as you would a block quotation with multiple paragraphs
Source: Section 9.51 Annotated Bibliographies in the APA 7th Edition Publication Manual
Sample annotated bibliography
Excelsior OWL Sample Annotated Bibliography
- << Previous: Sample Annotated Student Paper
- Next: Handouts and Guides >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 5:21 PM
- URL: https://libguides.eku.edu/apastyleguide
EO/AA Statement | Privacy Statement | 103 Libraries Complex Crabbe Library Richmond, KY 40475 | (859) 622-1790 ©
University Libraries University of Nevada, Reno
- Skill Guides
- Subject Guides
MLA Citation Guide (MLA 9th Edition): Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Understanding Core Elements
- Formatting Appendices and Works Cited List
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Academic Honesty and Citation
- In-Text Citation
- Charts, Graphs, Images, and Tables
- Class Notes and Presentations
- Encyclopedias and Dictionaries
- Generative AI
- In Digital Assignments
- Interviews and Emails
- Journal and Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Social Media
- Special Collections
- Videos and DVDs
- When Information Is Missing
- Citation Software
Annotations
What is an annotation.
An annotation is a short (100-300 words) summary or critical evaluation of a source. Annotations can help you learn about your topic, develop a thesis statement, decide if a source will be useful for your assignment, and determine if there is enough valid information available to complete your project.
What is an annotated bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations for various books, articles, and other sources. The annotated bibliography looks like a Works Cited page but it also includes an annotation after each source cited. Annotated bibliographies are a great research tool.
What Goes Into an Annotation?
Most annotations both summarize and evaluate. Be sure to check with your professors to know what they want in annotations.
A summary describes the source by answering who wrote the document and their overall argument. You don't need to include every part of the argument; just the parts that are most relevant to your topic.
An evaluation critically assesses the work for accuracy, relevance, and quality. Check for any biases, holes, or particular strengths. Try out this Quick-How-To about Evaluating Sources for detailed guidance on assessing a source.
Tip: Annotations are original descriptions that you create after reading the document. You may find a short summary, often titled "abstract," at the beginning of journal articles. Do not copy the abstract as that would be plagiarism.
Writing an Annotation
Cite the source using MLA style.
Describe the main ideas, arguments, themes, theses, or methodology, and identify the intended audience.
Explain the author’s expertise, point of view, and any bias he/she may have.
Compare to other sources on the same topic that you have also cited to show similarities and differences.
Explain why each source is useful for your research topic and how it relates to your topic.
Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each source.
Identify the observations or conclusions of the author.
Tips on Writing and Formatting
Each annotation should be one or two paragraphs and between three to six sentences long (about 100- 300 words total).
All lines should be double-spaced (unless your professor has noted a different format).
Do not add an extra line between the citations.
Try to be objective, and give explanations if you state any opinions.
Use the third person (e.g., he, she, the author) instead of the first person (e.g., I, my, me), unless discussing your own research.
Sample Annotation
London, Herbert. “Five Myths of the Television Age.” Television Quarterly , vol. 10, no. 1, Mar. 1982, pp. 81-89.
Herbert London, the Dean of Journalism at New York University and author of several books and articles, explains how television contradicts five commonly believed ideas. He uses specific examples of events seen on television, such as the assassination of John Kennedy, to illustrate his points. His examples have been selected to contradict such truisms as: “seeing is believing”; “a picture is worth a thousand words”; and “satisfaction is its own reward.” London uses logical arguments to support his ideas which are his personal opinion. He does not refer to any previous works on the topic. London’s style and vocabulary would make the article of interest to any reader. The article clearly illustrates London’s points, but does not explore their implications leaving the reader with many unanswered questions.
Adapted from: "How to Write Annotated Bibliographies." Memorial University Libraries , www.library.mun.ca/researchtools/guides/writing/annotated_bibl/ .
- << Previous: Formatting Appendices and Works Cited List
- Next: Academic Honesty and Citation >>
How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography: The Annotated Bibliography
- The Annotated Bibliography
- Fair Use of this Guide
Explanation, Process, Directions, and Examples
What is an annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.
Annotations vs. Abstracts
Abstracts are the purely descriptive summaries often found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles or in periodical indexes. Annotations are descriptive and critical; they may describe the author's point of view, authority, or clarity and appropriateness of expression.
The Process
Creating an annotated bibliography calls for the application of a variety of intellectual skills: concise exposition, succinct analysis, and informed library research.
First, locate and record citations to books, periodicals, and documents that may contain useful information and ideas on your topic. Briefly examine and review the actual items. Then choose those works that provide a variety of perspectives on your topic.
Cite the book, article, or document using the appropriate style.
Write a concise annotation that summarizes the central theme and scope of the book or article. Include one or more sentences that (a) evaluate the authority or background of the author, (b) comment on the intended audience, (c) compare or contrast this work with another you have cited, or (d) explain how this work illuminates your bibliography topic.
Critically Appraising the Book, Article, or Document
For guidance in critically appraising and analyzing the sources for your bibliography, see How to Critically Analyze Information Sources . For information on the author's background and views, ask at the reference desk for help finding appropriate biographical reference materials and book review sources.
Choosing the Correct Citation Style
Check with your instructor to find out which style is preferred for your class. Online citation guides for both the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA) styles are linked from the Library's Citation Management page .
Sample Annotated Bibliography Entries
The following example uses APA style ( Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th edition, 2019) for the journal citation:
Waite, L., Goldschneider, F., & Witsberger, C. (1986). Nonfamily living and the erosion of traditional family orientations among young adults. American Sociological Review, 51 (4), 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
This example uses MLA style ( MLA Handbook , 9th edition, 2021) for the journal citation. For additional annotation guidance from MLA, see 5.132: Annotated Bibliographies .
Waite, Linda J., et al. "Nonfamily Living and the Erosion of Traditional Family Orientations Among Young Adults." American Sociological Review, vol. 51, no. 4, 1986, pp. 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
Versión española
Tambíen disponible en español: Cómo Preparar una Bibliografía Anotada
Content Permissions
If you wish to use any or all of the content of this Guide please visit our Research Guides Use Conditions page for details on our Terms of Use and our Creative Commons license.
Reference Help

- Next: Fair Use of this Guide >>
- Last Updated: Sep 29, 2022 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/annotatedbibliography

- General Education Courses
- School of Business
- School of Design
- School of Education
- School of Health Sciences
- School of Justice Studies
- School of Nursing
- School of Technology
- CBE Student Guide
- Online Library
- Ask a Librarian
- Learning Express Library
- Interlibrary Loan Request Form
- Library Staff
- Databases A-to-Z
- Discovery Search
- Publication Finder
- Video Databases
NoodleTools
- Library Guides
- Course Guides
- Writing Lab
- Rasmussen Technical Support (PSC)
- Copyright Toolkit
- Faculty Toolkit
- Suggest a Purchase
- Refer a Student Tutor
- Live Lecture/Peer Tutor Scheduler
- Faculty Interlibrary Loan Request Form
- Professional Development Databases
- Publishing Guide
- Professional Development Guides (AAOPD)
- Rasmussen University
- Library and Learning Services Guides
APA 7th Edition Guide
- Annotated Bibliographies
- APA Paper Basics
- Preventing Plagiarism
- Academic Integrity Video
- Setting Up Your Paper
- In-Text Citations
- eTextbooks and Course Materials
- Images & Audiovisual Media
- Legal Resources
- Personal Communications & Secondary Sources
- Missing Reference Information
- Citing Sources in PowerPoint Presentations
- Finding Help
- Additional Resources from the APA
Creating an Annotated Bibliography
- What is an Annotated Bibliography
Writing an Annotation
Formatting an annotated bibliography.
- Resources and Tools
- Creating an Annotated Bibliography Video
Components of an Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography is an APA reference list that includes a brief summary and analysis -- the annotation -- under the reference entry.
An annotated bibliography includes:
- APA Title page
- Pages are numbered beginning with title page
- References centered and bolded at top of page
- Entries listed in alphabetical order
- Annotations begin under its associated reference
- Annotations are indented 0.5 inches from the left margin
- The entire document is double spaced; no extra space between entries
Example of an annotated bibliography entry:

An an n otated bibliography is composed of the full APA reference for a source followed by notes and commentary about that so urce. T he word “annotate” means “critical or explanatory notes” and the word “bibliography” means “a list of sources”. Annotation s are meant to be critical in addition to being descriptive.
Annotations are generally between five to seven sentences in length and appear directly under the APA reference. The entire annotation is indented 0.5 inch from the left margin and lines up with the hanging indent of the APA reference.
Use the question prompts below as a guide when writing annotations:
• 2 to 4 sentences to summarize the main idea(s) of the source.
- What are the main arguments?
- What is the point of this book/article?
- What topics are covered?
• 1 or 2 sentences to assess and evaluate the source.
- How does it compare with other sources in your bibliography?
- Is this information reliable? current?
- Is the author credible? have the background to write on this topic?
- Is the source objective or biased?
• 1 or 2 sentences to reflect on the source.
- Was this source helpful to you?
- How can you use this source for your research project?
- Has it changed how you think about your topic?
- a title page, and
- the annotated bibliography which begins on its own page with the word References bolded and centered at the top of the page.
Each entry begins with an APA reference for the resource with the annotation appearing directly beneath. The entire annotation is indented 0.5 inches from the left margin.
Entries are listed in alphabetical order. The entire document is typed on one of the six approved font styles and sizes and is double spaced. There is no additional space between entires.
Consider using Academic Writer or NoodleTools to create and format your annotated bibliography.

APA Citation Style Resources and Tools
Apa academic writer.
Use the tools in the References tab to create APA references for the resources in your annotated bibliography. The form includes a text box for your annotation. You can create your title page and assemble your annotated bibliography in the Write tab in this authoritative resource.

Create and format your annotated bibliography in NoodleTools . Find information on how to create an account, create APA references, and creating and formatting an annotated bibliography in the NoodleTools Guide.
- NoodleTools Guide
This video below provides an overview of how to create an annotated bibliography including evaluating resources, writing annotations, creating APA references, and formatting the final document in the APA style.
- << Previous: Citing Sources in PowerPoint Presentations
- Next: Finding Help >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 11:23 AM
- URL: https://guides.rasmussen.edu/apa

APA Style & Citation 7th edition
- What's new with the 7th edition
Annotated Bibliography
- PowerPoint and APA
- Citations: References
- Citations: In-Text
- Library Databases
- Books and Ebooks
- Media (includes videos)
- Other types of sources
- Numbers, Capitalization, Italics
- Additional Resources
Information on Annotated Bibliographies can be found in Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.)
- Title page, page numbers, font style and size, etc. See Format basics
- Alphabetical with hanging indents etc. See Citations: references
- The annotation - the notes you have about the source - appear in a new paragraph below its reference entry, indented 0.5 inches from the left margin
- Annotated bibliography example To use as a template, open the document with Word, replace the text with your own but keep the formatting intact.
- << Previous: Format Basics
- Next: PowerPoint and APA >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2023 5:31 PM
- URL: https://guides.centralpenn.edu/APA7th

Annotated Bibliographies
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain why annotated bibliographies are useful for researchers, provide an explanation of what constitutes an annotation, describe various types of annotations and styles for writing them, and offer multiple examples of annotated bibliographies in the MLA, APA, and CBE/CSE styles of citation.
Introduction
Welcome to the wonderful world of annotated bibliographies! You’re probably already familiar with the need to provide bibliographies, reference pages, and works cited lists to credit your sources when you do a research paper. An annotated bibliography includes descriptions and explanations of your listed sources beyond the basic citation information you usually provide.
Why do an annotated bibliography?
One of the reasons behind citing sources and compiling a general bibliography is so that you can prove you have done some valid research to back up your argument and claims. Readers can refer to a citation in your bibliography and then go look up the material themselves. When inspired by your text or your argument, interested researchers can access your resources. They may wish to double check a claim or interpretation you’ve made, or they may simply wish to continue researching according to their interests. But think about it: even though a bibliography provides a list of research sources of all types that includes publishing information, how much does that really tell a researcher or reader about the sources themselves?
An annotated bibliography provides specific information about each source you have used. As a researcher, you have become an expert on your topic: you have the ability to explain the content of your sources, assess their usefulness, and share this information with others who may be less familiar with them. Think of your paper as part of a conversation with people interested in the same things you are; the annotated bibliography allows you to tell readers what to check out, what might be worth checking out in some situations, and what might not be worth spending the time on. It’s kind of like providing a list of good movies for your classmates to watch and then going over the list with them, telling them why this movie is better than that one or why one student in your class might like a particular movie better than another student would. You want to give your audience enough information to understand basically what the movies are about and to make an informed decision about where to spend their money based on their interests.
What does an annotated bibliography do?
A good annotated bibliography:
- encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, their place within a field of study, and their relation to your own research and ideas.
- proves you have read and understand your sources.
- establishes your work as a valid source and you as a competent researcher.
- situates your study and topic in a continuing professional conversation.
- provides a way for others to decide whether a source will be helpful to their research if they read it.
- could help interested researchers determine whether they are interested in a topic by providing background information and an idea of the kind of work going on in a field.
What elements might an annotation include?
- Bibliography according to the appropriate citation style (MLA, APA, CBE/CSE, etc.).
- Explanation of main points and/or purpose of the work—basically, its thesis—which shows among other things that you have read and thoroughly understand the source.
- Verification or critique of the authority or qualifications of the author.
- Comments on the worth, effectiveness, and usefulness of the work in terms of both the topic being researched and/or your own research project.
- The point of view or perspective from which the work was written. For instance, you may note whether the author seemed to have particular biases or was trying to reach a particular audience.
- Relevant links to other work done in the area, like related sources, possibly including a comparison with some of those already on your list. You may want to establish connections to other aspects of the same argument or opposing views.
The first four elements above are usually a necessary part of the annotated bibliography. Points 5 and 6 may involve a little more analysis of the source, but you may include them in other kinds of annotations besides evaluative ones. Depending on the type of annotation you use, which this handout will address in the next section, there may be additional kinds of information that you will need to include.
For more extensive research papers (probably ten pages or more), you often see resource materials grouped into sub-headed sections based on content, but this probably will not be necessary for the kinds of assignments you’ll be working on. For longer papers, ask your instructor about their preferences concerning annotated bibliographies.
Did you know that annotations have categories and styles?
Decisions, decisions.
As you go through this handout, you’ll see that, before you start, you’ll need to make several decisions about your annotations: citation format, type of annotation, and writing style for the annotation.
First of all, you’ll need to decide which kind of citation format is appropriate to the paper and its sources, for instance, MLA or APA. This may influence the format of the annotations and bibliography. Typically, bibliographies should be double-spaced and use normal margins (you may want to check with your instructor, since they may have a different style they want you to follow).
MLA (Modern Language Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic MLA bibliography formatting and rules.
- MLA documentation is generally used for disciplines in the humanities, such as English, languages, film, and cultural studies or other theoretical studies. These annotations are often summary or analytical annotations.
- Title your annotated bibliography “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Following MLA format, use a hanging indent for your bibliographic information. This means the first line is not indented and all the other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- Begin your annotation immediately after the bibliographic information of the source ends; don’t skip a line down unless you have been told to do so by your instructor.
APA (American Psychological Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic APA bibliography formatting and rules.
- Natural and social sciences, such as psychology, nursing, sociology, and social work, use APA documentation. It is also used in economics, business, and criminology. These annotations are often succinct summaries.
- Annotated bibliographies for APA format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References” designation.
- Like MLA, APA uses a hanging indent: the first line is set flush with the left margin, and all other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line.
- The entire annotation is indented an additional two spaces, so that means each of its lines will be six spaces from the margin (if your instructor has said that it’s okay to tab over instead of using the four spaces rule, indent the annotation two more spaces in from that point).
CBE (Council of Biology Editors)/CSE (Council of Science Editors)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic CBE/CSE bibliography formatting and rules.
- CBE/CSE documentation is used by the plant sciences, zoology, microbiology, and many of the medical sciences.
- Annotated bibliographies for CBE/CSE format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References,” “Cited References,” or “Literature Cited,” and set it flush with the left margin.
- Bibliographies for CSE in general are in a slightly smaller font than the rest of the paper.
- When using the name-year system, as in MLA and APA, the first line of each entry is set flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines, including the annotation, are indented three or four spaces.
- When using the citation-sequence method, each entry begins two spaces after the number, and every line, including the annotation, will be indented to match the beginning of the entry, or may be slightly further indented, as in the case of journals.
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line. The entire annotation follows the indentation of the bibliographic entry, whether it’s N-Y or C-S format.
- Annotations in CBE/CSE are generally a smaller font size than the rest of the bibliographic information.
After choosing a documentation format, you’ll choose from a variety of annotation categories presented in the following section. Each type of annotation highlights a particular approach to presenting a source to a reader. For instance, an annotation could provide a summary of the source only, or it could also provide some additional evaluation of that material.
In addition to making choices related to the content of the annotation, you’ll also need to choose a style of writing—for instance, telescopic versus paragraph form. Your writing style isn’t dictated by the content of your annotation. Writing style simply refers to the way you’ve chosen to convey written information. A discussion of writing style follows the section on annotation types.
Types of annotations
As you now know, one annotation does not fit all purposes! There are different kinds of annotations, depending on what might be most important for your reader to learn about a source. Your assignments will usually make it clear which citation format you need to use, but they may not always specify which type of annotation to employ. In that case, you’ll either need to pick your instructor’s brain a little to see what they want or use clue words from the assignment itself to make a decision. For instance, the assignment may tell you that your annotative bibliography should give evidence proving an analytical understanding of the sources you’ve used. The word analytical clues you in to the idea that you must evaluate the sources you’re working with and provide some kind of critique.
Summary annotations
There are two kinds of summarizing annotations, informative and indicative.
Summarizing annotations in general have a couple of defining features:
- They sum up the content of the source, as a book report might.
- They give an overview of the arguments and proofs/evidence addressed in the work and note the resulting conclusion.
- They do not judge the work they are discussing. Leave that to the critical/evaluative annotations.
- When appropriate, they describe the author’s methodology or approach to material. For instance, you might mention if the source is an ethnography or if the author employs a particular kind of theory.
Informative annotation
Informative annotations sometimes read like straight summaries of the source material, but they often spend a little more time summarizing relevant information about the author or the work itself.
Indicative annotation
Indicative annotation is the second type of summary annotation, but it does not attempt to include actual information from the argument itself. Instead, it gives general information about what kinds of questions or issues are addressed by the work. This sometimes includes the use of chapter titles.
Critical/evaluative
Evaluative annotations don’t just summarize. In addition to tackling the points addressed in summary annotations, evaluative annotations:
- evaluate the source or author critically (biases, lack of evidence, objective, etc.).
- show how the work may or may not be useful for a particular field of study or audience.
- explain how researching this material assisted your own project.
Combination
An annotated bibliography may combine elements of all the types. In fact, most of them fall into this category: a little summarizing and describing, a little evaluation.
Writing style
Ok, next! So what does it mean to use different writing styles as opposed to different kinds of content? Content is what belongs in the annotation, and style is the way you write it up. First, choose which content type you need to compose, and then choose the style you’re going to use to write it
This kind of annotated bibliography is a study in succinctness. It uses a minimalist treatment of both information and sentence structure, without sacrificing clarity. Warning: this kind of writing can be harder than you might think.
Don’t skimp on this kind of annotated bibliography. If your instructor has asked for paragraph form, it likely means that you’ll need to include several elements in the annotation, or that they expect a more in-depth description or evaluation, for instance. Make sure to provide a full paragraph of discussion for each work.
As you can see now, bibliographies and annotations are really a series of organized steps. They require meticulous attention, but in the end, you’ve got an entire testimony to all the research and work you’ve done. At the end of this handout you’ll find examples of informative, indicative, evaluative, combination, telescopic, and paragraph annotated bibliography entries in MLA, APA, and CBE formats. Use these examples as your guide to creating an annotated bibliography that makes you look like the expert you are!
MLA Example
APA Example
CBE Example
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
American Psychological Association. 2010. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 6th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Bell, I. F., and J. Gallup. 1971. A Reference Guide to English, American, and Canadian Literature . Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press.
Bizzell, Patricia, and Bruce Herzburg. 1991. Bedford Bibliography for Teachers of Writing , 3rd ed. Boston: Bedford Books.
Center for Information on Language Teaching, and The English Teaching Information Center of the British Council. 1968. Language-Teaching Bibliography . Cambridge: Cambridge University.
Engle, Michael, Amy Blumenthal, and Tony Cosgrave. 2012. “How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography.” Olin & Uris Libraries. Cornell University. Last updated September 25, 2012. https://olinuris.library.cornell.edu/content/how-prepare-annotated-bibliography.
Gibaldi, Joseph. 2009. MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th ed. New York: The Modern Language Association of America.
Huth, Edward. 1994. Scientific Style and Format: The CBE Manual for Authors, Editors, and Publishers . New York: University of Cambridge.
Kilborn, Judith. 2004. “MLA Documentation.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated March 16, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/research/mla.html.
Spatt, Brenda. 1991. Writing from Sources , 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s.
University of Kansas. 2018. “Bibliographies.” KU Writing Center. Last updated April 2018. http://writing.ku.edu/bibliographies .
University of Wisconsin-Madison. 2019. “Annotated Bibliography.” The Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/annotatedbibliography/ .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: MLA Annotated Bibliography
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
Annotated Bibliography
- Updated MLA Ninth Edition Annotated Bibliography Template
This template includes a space to add your topic and thesis statement as this is preferred for the annotated bibliography assignments in ENC courses taught at IRSC. Always follow your professor's instructions over any instructions on this LibGuide or inside the MLA Handbook.
Your professor may ask that you create an annotated bibliography in MLA style. An annotated bibliography is similar to the Works Cited page found at the end of a paper. The paper formatting is the same but instead of following a full research paper, the student will write a brief annotation for each source which will directly follow the source's Works Cited entry. The annotations contain descriptive or evaluative comments about your sources. Annotations should be short, typically no longer than one paragraph. Indent the annotation an inch from the start of the entry. Each citation should adhere to MLA guidelines. The title might be 'Annotated Bibliography' or 'Annotated List of Works Cited'.
Below is an example of an annotated bibliography in MLA style. You are welcome to use the template linked above to get you started with the correct formatting.

- << Previous: Formatting Your Works Cited List
- Next: MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 5:26 PM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla
Generate accurate Chicago citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- Chicago Style
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography in Chicago/Turabian Style
Published on October 15, 2019 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on April 9, 2024.
While a standard Chicago style bibliography provides publication details of your sources, an annotated bibliography also provides a summary (and often an evaluation) of each source.
Turabian style , a version of Chicago style specifically designed for students and researchers, provides formatting guidelines for an annotated bibliography. A typical entry might look like this:
Kenny, Anthony. A New History of Western Philosophy: In Four Parts . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Chicago Citation Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write annotations, how to format an annotated bibliography.
The purpose of annotations is to give the reader relevant information about each source you have consulted. There are two main types of annotation.
Descriptive annotations simply describe your sources, briefly summarizing their arguments and ideas . They are useful for keeping a record of your reading and giving a quick overview of sources related to your topic.
Evaluative annotations go into more detail and provide your own perspective on each source. For example, you may evaluate your sources by:
- assessing the strength of the author’s arguments.
- describing the ways in which the source is helpful or unhelpful to your own research.
- evaluating the evidence presented in the source, discussing the credibility .
Check the requirements of your assignment to find out whether you need to write descriptive or evaluative annotations.
How long should annotations be?
Annotations can vary in length according to the approach taken and the length of the source. You may write a couple of sentences describing the argument of an essay, or several paragraphs summarizing and evaluating a book .
A good guideline is to aim for 50 to 200 words for each source. Consult your instructor to check how long your annotated bibliography should be and how many sources you need to include.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Each entry starts with a Chicago style citation , which gives full publication details of the source. The citation is formatted the same as a normal bibliography entry:
- Single-spaced
- Each line after the first indented ( hanging indent )
- Organized in alphabetical order by author last name
The annotation appears on a new line directly after the source citation. The whole annotation is indented, to make it clear when the annotation ends and a new source appears.
According to Turabian guidelines, annotations should be formatted the same as the main text of any paper:
- Double-spaced
- Left-aligned
- Indent the first line of each new paragraph

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, April 09). How to Write an Annotated Bibliography in Chicago/Turabian Style. Scribbr. Retrieved June 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/chicago-style/chicago-annotated-bibliography/

Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is an annotated bibliography | examples & format, creating a chicago style bibliography | format & examples, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- MJC Library & Learning Center
- Research Guides
Ready, Set, Cite (Chicago)
- Annotated Bibliography
- Chicago Style Basics
- Formatting the Paper
- Citation Basics
- Plagiarism & Its Consequences
- Citations: Author-Date References System
- Notes-Bibliography System
What is an Annotated Bibliography & Why Write One
Chicago style annotated bibliography example, what is an annotated bibliography.
A bibliograph y is a list of sources (books, journals, Web sites, periodicals, etc.) you used for researching your topic. Bibliographies are called "Works Cited" (in MLA Style) and "References" (in APA Style) Your bibliography will include the bibliographic information (i.e., the author, title, publisher, etc.) that your reader would need to identify and locate the original source you're citing.
An annotation is a summary and/or evaluation of a source.
Therefore, an annotated bibliography includes your citation followed by a summary and/or evaluation of each of your sources. Depending on your project or the assignment, your annotations may do one or more of the following.
- Summarize: Some annotations merely summarize the source. What are the main arguments? What is the point of this book or article? What topics are covered? If someone asked what this article/book is about, what would you say?
- Assess: After summarizing a source, it may be helpful to evaluate it. Is it a useful source? How does it compare with other sources in your bibliography? Is the information reliable? Is this source biased or objective? What is the goal of this source?
- Reflect: Once you've summarized and assessed a source, you need to ask how it fits into your research. Was this source helpful to you? How does it help you shape your argument? How can you use this source in your research project? Has it changed how you think about your topic?
Your annotated bibliography may include some of these, all of these, or even others.
Be sure to always follow the specific instructions your instructor gives you.
Why Write an Annotated Bibliography
Every good research paper is an argument. The purpose of research is to state and support a thesis. So, a very important part of research is developing a thesis that is debatable, interesting, and current. Writing an annotated bibliography can help you gain a good perspective on what is being said about your topic. By reading and responding to a variety of sources on a topic, you'll start to see what the issues are, what people are arguing about, and you'll then be able to develop your own point of view.
Writing an annotated bibliography is excellent preparation for a research project. Just collecting sources for a bibliography is useful, but when you have to write annotations for each source, you're forced to read each source more carefully. You begin to read more critically instead of just collecting information.
Chicago Style
Formatting rules.
- Order your references in alphabetical order as you would in your Bibliography.
- Each annotation should be a new paragraph below its reference entry. Indent the entire annotation 0.5 in. from the left margin.
- Do not indent the first line of the annotation.
Because your teachers generally set all the other requirements for your annotated bibliography, ask your teacher for specific instructions. For example, ask if your annotated bibliography should include a title page.
Sample Annotated Bibliography Using Chicago Style

- << Previous: Notes-Bibliography System
- Next: Get Help >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2024 12:04 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mjc.edu/chicago
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 and CC BY-NC 4.0 Licenses .

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Annotated Bibliography – Formatting Rules And Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

An annotated bibliography or an analytical bibliography includes the bibliographic reference of a set of works and a brief synthesis or review of these works. When citing sources , this descriptive or critical commentary aims either to inform the reader about the main ideas of a work or to measure the quality of a work by evaluating its credibility, accuracy, and relevance. This article provides insights into the format of an annotated bibliography and how to find relevant sources.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Annotated Bibliography – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Annotated bibliography
- 3 Annotated bibliography formatting
- 4 Writing an annotated bibliography
- 5 Finding sources for your annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliography – In a Nutshell
- An annotated bibliography consists of two parts: A reference list and a source summary.
- Learn how to format an annotated bibliography correctly.
- Primary, secondary, and tertiary sources should be included in the annotated bibliography.
Definition: Annotated bibliography
An annotated bibliography (or analytical bibliography) consists of a list of references, each subject to a commentary by the person carrying out the exercise.
First, a bibliography is the list of sources referenced in a document. You should be familiar with this method for any academic essay you’ve written:
- Think about the APA-style references you usually include.
- Include important source information, such as author name, article title, publication date, and page number
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources used in the body of the work, including a brief summary of each source. These summary annotations assess the accuracy and quality of the information sources and identify any possible reason for bias.
An annotated bibliography should present the sources alphabetically in list form, like a standard bibliography. Source summaries are usually around 150 words, although this may vary depending on the nature of the original.
Annotated bibliography formatting
There are several recognized ways of formatting an annotated bibliography. Use the style recommended by your institution of learning.
1. APA style
Formatting your annotated bibliography is the same as formatting an APA reference list. You use the same author-date style and place the elements in the same order.
Here’s a quick rundown of the guidelines for an annotated bibliography in APA style :
- Right-aligned page number
- Running header (Optional)
- One-inch margins
- Double-spaced
- The title “Annotated Bibliography” centered
- Hanging indent for the second and subsequent lines of the citation
- Indent annotation of five spaces
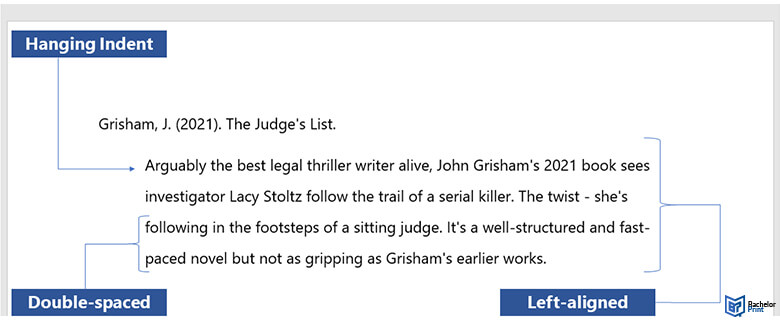
Grisham, J. (2021). The Judge’s List
Arguably the best legal thriller writer alive, John Grisham’s 2021 book sees investigator Lacy Stoltz follow the trail of a serial killer. The twist – she’s following in the footsteps of a sitting judge. It’s a well-structured and fast-paced novel but not as gripping as Grisham’s earlier works.
In MLA , each annotation should be one paragraph, between three and six sentences long (about 150 – 200 words). Start with the same format as a regular Works Cited list .
All lines should be double-spaced . Do not add an extra line between the citations.
Kenny, Anthony. A New History of Western Philosophy: In Four Parts. Oxford UP, 2010.
Broad history of Western philosophy from the ancient Greeks to the present day. Divided into four periods—ancient, medieval, early modern, and modern—each section begins with a chronological overview of the key thinkers, followed by chapters dedicated to each significant subfield in the period: metaphysics, political philosophy, God, etc.

3. Chicago style
An annotated bibliography in Chicago style should be formatted as the following:
- The text should be double-spaced.
- Numbering starts on the first page of writing (not the title page) at the top right of the page.
- Reference list entries must have a hanging indent (to do this in Microsoft Word 2003, click Format, then Paragraph, then Special, and choose Hanging).
- There should be 1-inch (2.54 cm) margins all around (top, bottom, left, and right) on each page.
- Use Times Roman font or a similar serif font.
- Each paragraph should be indented using the tab key.
Collins, Michael. “Carrying the Fire”, Pan Macmillan, 1974
Collins was the Command Module Pilot on the Apollo Mission. When the Lunar Lander descended to the surface of the moon, it was his task to stay with the Command Module in Lunar orbit. Collins is a man who has been extraordinarily close to the moon without walking on the surface. “Carrying the Fire” is a personal and mesmerizing account of his entire life and career.

Writing an annotated bibliography
Follow these steps when writing an annotated bibliography:
| | |
| Heading | • Use a heading that indicates the subject of the entries • Center the heading at the top of the page |
| Introduction Optional | • Check your assignment instructions |
| Source entry A | • 100 - 200 words, depending on assignment instructions |
| Full citation | • Use the required referencing style as specified in your assignment instructions |
| Summary | • Concise description of the source • Including a summary of the key points and findings (check assignment instructions for the level of detail required) |
| Evaluation | • Briefly comment on the strengths and limitations of the source and the research it describes |
| Reflection | • Comment on the relevance of the source to your topic or field of study |
| Subheadings | • Optional (check assignment instructions) |
| Conclusion | • Optional (check your assignment instructions) |
Types of Annotations
| • Describe the book, article, or another source • Information about whom the author(s) of the work are and their credentials, and a summary of the work's main points | • Also known as "critical" annotations • Summarize the essential ideas in a document and provide judgments about their quality (negative, positive, or both) • Typically, three to four sentences long | • Reflection on how useful the source is for your own research (for instance, if you are writing the annotated bibliography in preparation for a research essay) • You could be asked to reflect on how the source relates to the themes in your unit |
Finding sources for your annotated bibliography
Research projects and compositions, especially argumentative or positional texts, require you to collect sources, develop a thesis , and then support that thesis through an analysis of the evidence, including sources, that you have compiled, ideally from visiting the university library.
Start by gathering all materials, including books, Google Scholar, websites, professional journals, periodicals, and papers that may contain valuable insights on your topic. Your annotated bibliography should include primary, secondary, and even tertiary sources to achieve the best marks in an academic essay.

How does an annotated bibliography in APA differ to MLA?
The main differences between the APA style and MLA formats are:
- Creation of the title page
- In-text citations
- Reference lists
MLA uses the author-page number style for in-text citations, while an APA annotated bibliography uses the author-date citation style.
What goes into an annotated bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations, which can include books, journal articles, and documents.
Each citation is usually followed by a brief description of the text and, more importantly, a critical evaluation.
What is essential in an annotated bibliography?
The annotated bibliography adds descriptive and evaluative comments (i.e., an annotation), assessing the nature and value of the cited works. The addition of commentary provides the future reader or researcher essential critical information and a foundation for further research.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
- ENC Learning Commons
Annotated Bibliography
- Sample ASA Annotation
- URL: https://libguides.enc.edu/writing_basics/annotatedbib
- Definition and Descriptions
- Evaluation Tools
- Parts of an Annotation
- Sample APA Annotation
- Sample Chicago Annotation
- Sample MLA Annotation
Research Tools
American Sociological Association (ASA) Annotations
Creating an annotated bibliography in ASA style
The Publication Manual of the American Sociological Association is kept behind the IRC Desk on the Ground Floor.
General guidelines
Some anno tatio ns are merely descriptive , summarizing the authors' qualifications, research methods, and arguments. Your professor might also ask you to identify the authors' theoretical frameworks .
Many annotations evaluate the quality of scholarship in a book or article. You might want to consider the logic of authors' arguments, and the quality of their evidence. Your findings can be positive, negative, or mixed.
Your professor might also want you to explain why the source is relevant to your assignment. Some instructors require you to identify the authors' theoretical models as well.
Sample Page: ASA-formatted annotated bibliography
|
|
Rules! rules! rules!
The Publication Manual of the American Sociological Association (1997) states the following formatting rules, but check your course outline in case your professor has other requirements!
- All text should be double-spaced.
- Reference list entries must have a hanging indent (to do this in Microsoft Word 2003, click Format, then Paragraph, then Special, and choose Hanging).
- There should be 1 1/4 inch margins on each page.
- Use 12 point Times Roman font, or a similar serif font.
- Start counting pages on the first page of text, but numbers should only appear from the second page onward (as 2, etc.).
- Each paragraph should be indented.
- The reference list is alphabetical by authors' last names.
- When a work has more than one author, the name of the first author is inverted (Lastname, Firstname). The names of additional authors are not inverted.
More Sample Annotations
The Memorial University of Newfoundland presents these examples of both descriptive and critical annotations . Cornell University Library offers these examples of both APA and MLA format descriptive bibliographies.
- << Previous: Sample APA Annotation
- Next: Sample Chicago Annotation >>
- Last Updated: Nov 7, 2023 8:23 AM
- Find A Local Contest
- Get Started
- Contest Rules & Evaluation
- Find Your Local Contest (Affiliate)
- National Contest
- Classroom Tools
- Teaching Research Skills
- Advising NHD Students
- News & Events
- Why NHD Works
- People of NHD
- Find Your Local Affiliate
- 50 Years of NHD
- Sponsors and Supporters
- Volunteer to Judge
- Alumni Network
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
Learn what an annotated bibliography is, how to cite sources, and annotation requirements for your NHD project. Watch the videos below or review the annotated bibliography guide.

Annotations

Related Resources

Documentary Project Example 4: Wade in the Water: How African Americans Got Back Into the Pool

Documentary Project Example 3: “¡Sί Se Puede!” How the United Farm Workers Grape Boycott Broke Barriers for Social Movements
Support the teaching and learning of history.
Your support of National History Day is an investment in the future
Judges needed
Judges make the NHD contest possible. See how you can provide students a high-quality educational experience
National History Day ®
Influencing the future through discovery of the past
- Job Openings
Read our newsletter for the latest resources, events, and training.
We use cookies to analyze how visitors use our website so we can provide the best possible experience. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device. For more information, please view our Privacy Policy.

Reference Examples
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual . Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual .
To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of work (e.g., journal article ) and follow the relevant example.
When selecting a category, use the webpages and websites category only when a work does not fit better within another category. For example, a report from a government website would use the reports category, whereas a page on a government website that is not a report or other work would use the webpages and websites category.
Also note that print and electronic references are largely the same. For example, to cite both print books and ebooks, use the books and reference works category and then choose the appropriate type of work (i.e., book ) and follow the relevant example (e.g., whole authored book ).
Examples on these pages illustrate the details of reference formats. We make every attempt to show examples that are in keeping with APA Style’s guiding principles of inclusivity and bias-free language. These examples are presented out of context only to demonstrate formatting issues (e.g., which elements to italicize, where punctuation is needed, placement of parentheses). References, including these examples, are not inherently endorsements for the ideas or content of the works themselves. An author may cite a work to support a statement or an idea, to critique that work, or for many other reasons. For more examples, see our sample papers .
Reference examples are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 10 and the Concise Guide Chapter 10
Related handouts
- Common Reference Examples Guide (PDF, 147KB)
- Reference Quick Guide (PDF, 225KB)
Textual Works
Textual works are covered in Sections 10.1–10.8 of the Publication Manual . The most common categories and examples are presented here. For the reviews of other works category, see Section 10.7.
- Journal Article References
- Magazine Article References
- Newspaper Article References
- Blog Post and Blog Comment References
- UpToDate Article References
- Book/Ebook References
- Diagnostic Manual References
- Children’s Book or Other Illustrated Book References
- Classroom Course Pack Material References
- Religious Work References
- Chapter in an Edited Book/Ebook References
- Dictionary Entry References
- Wikipedia Entry References
- Report by a Government Agency References
- Report with Individual Authors References
- Brochure References
- Ethics Code References
- Fact Sheet References
- ISO Standard References
- Press Release References
- White Paper References
- Conference Presentation References
- Conference Proceeding References
- Published Dissertation or Thesis References
- Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis References
- ERIC Database References
- Preprint Article References
Data and Assessments
Data sets are covered in Section 10.9 of the Publication Manual . For the software and tests categories, see Sections 10.10 and 10.11.
- Data Set References
- Toolbox References
Audiovisual Media
Audiovisual media are covered in Sections 10.12–10.14 of the Publication Manual . The most common examples are presented together here. In the manual, these examples and more are separated into categories for audiovisual, audio, and visual media.
- Artwork References
- Clip Art or Stock Image References
- Film and Television References
- Musical Score References
- Online Course or MOOC References
- Podcast References
- PowerPoint Slide or Lecture Note References
- Radio Broadcast References
- TED Talk References
- Transcript of an Audiovisual Work References
- YouTube Video References
Online Media
Online media are covered in Sections 10.15 and 10.16 of the Publication Manual . Please note that blog posts are part of the periodicals category.
- Facebook References
- Instagram References
- LinkedIn References
- Online Forum (e.g., Reddit) References
- TikTok References
- X References
- Webpage on a Website References
- Clinical Practice References
- Open Educational Resource References
- Whole Website References
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / How to Cite Sources
How to Cite Sources
Here is a complete list for how to cite sources. Most of these guides present citation guidance and examples in MLA, APA, and Chicago.
If you’re looking for general information on MLA or APA citations , the EasyBib Writing Center was designed for you! It has articles on what’s needed in an MLA in-text citation , how to format an APA paper, what an MLA annotated bibliography is, making an MLA works cited page, and much more!
MLA Format Citation Examples
The Modern Language Association created the MLA Style, currently in its 9th edition, to provide researchers with guidelines for writing and documenting scholarly borrowings. Most often used in the humanities, MLA style (or MLA format ) has been adopted and used by numerous other disciplines, in multiple parts of the world.
MLA provides standard rules to follow so that most research papers are formatted in a similar manner. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the information. The MLA in-text citation guidelines, MLA works cited standards, and MLA annotated bibliography instructions provide scholars with the information they need to properly cite sources in their research papers, articles, and assignments.
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Documentary
- Encyclopedia
- Google Images
- Kindle Book
- Memorial Inscription
- Museum Exhibit
- Painting or Artwork
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Sheet Music
- Thesis or Dissertation
- YouTube Video
APA Format Citation Examples
The American Psychological Association created the APA citation style in 1929 as a way to help psychologists, anthropologists, and even business managers establish one common way to cite sources and present content.
APA is used when citing sources for academic articles such as journals, and is intended to help readers better comprehend content, and to avoid language bias wherever possible. The APA style (or APA format ) is now in its 7th edition, and provides citation style guides for virtually any type of resource.
Chicago Style Citation Examples
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes ) or at the end of a paper (endnotes).
The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but the Turabian style is geared towards student published papers such as theses and dissertations, while the Chicago style provides guidelines for all types of publications. This is why you’ll commonly see Chicago style and Turabian style presented together. The Chicago Manual of Style is currently in its 17th edition, and Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations is in its 8th edition.
Citing Specific Sources or Events
- Declaration of Independence
- Gettysburg Address
- Martin Luther King Jr. Speech
- President Obama’s Farewell Address
- President Trump’s Inauguration Speech
- White House Press Briefing
Additional FAQs
- Citing Archived Contributors
- Citing a Blog
- Citing a Book Chapter
- Citing a Source in a Foreign Language
- Citing an Image
- Citing a Song
- Citing Special Contributors
- Citing a Translated Article
- Citing a Tweet
6 Interesting Citation Facts
The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there’s more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations , and other formatting specifications. Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
Ever wonder what sets all the different styles apart, or how they came to be in the first place? Read on for some interesting facts about citations!
1. There are Over 7,000 Different Citation Styles
You may be familiar with MLA and APA citation styles, but there are actually thousands of citation styles used for all different academic disciplines all across the world. Deciding which one to use can be difficult, so be sure to ask you instructor which one you should be using for your next paper.
2. Some Citation Styles are Named After People
While a majority of citation styles are named for the specific organizations that publish them (i.e. APA is published by the American Psychological Association, and MLA format is named for the Modern Language Association), some are actually named after individuals. The most well-known example of this is perhaps Turabian style, named for Kate L. Turabian, an American educator and writer. She developed this style as a condensed version of the Chicago Manual of Style in order to present a more concise set of rules to students.
3. There are Some Really Specific and Uniquely Named Citation Styles
How specific can citation styles get? The answer is very. For example, the “Flavour and Fragrance Journal” style is based on a bimonthly, peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1985 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original research articles, reviews and special reports on all aspects of flavor and fragrance. Another example is “Nordic Pulp and Paper Research,” a style used by an international scientific magazine covering science and technology for the areas of wood or bio-mass constituents.
4. More citations were created on EasyBib.com in the first quarter of 2018 than there are people in California.
The US Census Bureau estimates that approximately 39.5 million people live in the state of California. Meanwhile, about 43 million citations were made on EasyBib from January to March of 2018. That’s a lot of citations.
5. “Citations” is a Word With a Long History
The word “citations” can be traced back literally thousands of years to the Latin word “citare” meaning “to summon, urge, call; put in sudden motion, call forward; rouse, excite.” The word then took on its more modern meaning and relevance to writing papers in the 1600s, where it became known as the “act of citing or quoting a passage from a book, etc.”
6. Citation Styles are Always Changing
The concept of citations always stays the same. It is a means of preventing plagiarism and demonstrating where you relied on outside sources. The specific style rules, however, can and do change regularly. For example, in 2018 alone, 46 new citation styles were introduced , and 106 updates were made to exiting styles. At EasyBib, we are always on the lookout for ways to improve our styles and opportunities to add new ones to our list.
Why Citations Matter
Here are the ways accurate citations can help your students achieve academic success, and how you can answer the dreaded question, “why should I cite my sources?”
They Give Credit to the Right People
Citing their sources makes sure that the reader can differentiate the student’s original thoughts from those of other researchers. Not only does this make sure that the sources they use receive proper credit for their work, it ensures that the student receives deserved recognition for their unique contributions to the topic. Whether the student is citing in MLA format , APA format , or any other style, citations serve as a natural way to place a student’s work in the broader context of the subject area, and serve as an easy way to gauge their commitment to the project.
They Provide Hard Evidence of Ideas
Having many citations from a wide variety of sources related to their idea means that the student is working on a well-researched and respected subject. Citing sources that back up their claim creates room for fact-checking and further research . And, if they can cite a few sources that have the converse opinion or idea, and then demonstrate to the reader why they believe that that viewpoint is wrong by again citing credible sources, the student is well on their way to winning over the reader and cementing their point of view.
They Promote Originality and Prevent Plagiarism
The point of research projects is not to regurgitate information that can already be found elsewhere. We have Google for that! What the student’s project should aim to do is promote an original idea or a spin on an existing idea, and use reliable sources to promote that idea. Copying or directly referencing a source without proper citation can lead to not only a poor grade, but accusations of academic dishonesty. By citing their sources regularly and accurately, students can easily avoid the trap of plagiarism , and promote further research on their topic.
They Create Better Researchers
By researching sources to back up and promote their ideas, students are becoming better researchers without even knowing it! Each time a new source is read or researched, the student is becoming more engaged with the project and is developing a deeper understanding of the subject area. Proper citations demonstrate a breadth of the student’s reading and dedication to the project itself. By creating citations, students are compelled to make connections between their sources and discern research patterns. Each time they complete this process, they are helping themselves become better researchers and writers overall.
When is the Right Time to Start Making Citations?
Make in-text/parenthetical citations as you need them.
As you are writing your paper, be sure to include references within the text that correspond with references in a works cited or bibliography. These are usually called in-text citations or parenthetical citations in MLA and APA formats. The most effective time to complete these is directly after you have made your reference to another source. For instance, after writing the line from Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times…,” you would include a citation like this (depending on your chosen citation style):
(Dickens 11).
This signals to the reader that you have referenced an outside source. What’s great about this system is that the in-text citations serve as a natural list for all of the citations you have made in your paper, which will make completing the works cited page a whole lot easier. After you are done writing, all that will be left for you to do is scan your paper for these references, and then build a works cited page that includes a citation for each one.
Need help creating an MLA works cited page ? Try the MLA format generator on EasyBib.com! We also have a guide on how to format an APA reference page .
2. Understand the General Formatting Rules of Your Citation Style Before You Start Writing
While reading up on paper formatting may not sound exciting, being aware of how your paper should look early on in the paper writing process is super important. Citation styles can dictate more than just the appearance of the citations themselves, but rather can impact the layout of your paper as a whole, with specific guidelines concerning margin width, title treatment, and even font size and spacing. Knowing how to organize your paper before you start writing will ensure that you do not receive a low grade for something as trivial as forgetting a hanging indent.
Don’t know where to start? Here’s a formatting guide on APA format .
3. Double-check All of Your Outside Sources for Relevance and Trustworthiness First
Collecting outside sources that support your research and specific topic is a critical step in writing an effective paper. But before you run to the library and grab the first 20 books you can lay your hands on, keep in mind that selecting a source to include in your paper should not be taken lightly. Before you proceed with using it to backup your ideas, run a quick Internet search for it and see if other scholars in your field have written about it as well. Check to see if there are book reviews about it or peer accolades. If you spot something that seems off to you, you may want to consider leaving it out of your work. Doing this before your start making citations can save you a ton of time in the long run.
Finished with your paper? It may be time to run it through a grammar and plagiarism checker , like the one offered by EasyBib Plus. If you’re just looking to brush up on the basics, our grammar guides are ready anytime you are.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The On-Campus and Online versions of Purdue OWL assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue OWL serves the Purdue West Lafayette and Indianapolis campuses and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Published on March 9, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 23, 2022. An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper, or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic.
MLA provides guidelines for writing and formatting your annotated bibliography. An example of a typical annotation is shown below. Example of an MLA source annotation. Kenny, Anthony. A New History of Western Philosophy: In Four Parts. Oxford UP, 2010. Broad history of Western philosophy from the ancient Greeks to the present day.
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources (like a reference list). It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100-200 words in length. ... Write the citation and annotation - When writing your annotation, the complete citation should always come ...
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources, each of which is followed by a brief note or "annotation." ... General Formatting Rules: Format and order references in alphabetical order just as you would a reference list; Each annotation should be a new paragraph below its reference entry;
The MLA Style Center provides the following guidance for formatting an MLA annotated bibliography: ... The MLA follows the rules set forth in James L. Harner's On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography, 2nd edition, which they published in 2000. Harner submits that the typical organization for this type of work "…consists of three parts ...
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations for various books, articles, and other sources on a topic. The annotated bibliography looks like a References page but includes an annotation after each source cited. ... The formatting of annotated bibliographies can vary. The University Libraries recommend the format exhibited in the examples ...
What is an annotated bibliography? An annotated bibliography is a list of citations for various books, articles, and other sources. The annotated bibliography looks like a Works Cited page but it also includes an annotation after each source cited. Annotated bibliographies are a great research tool.
What Is an Annotated Bibliography? An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources ...
According to the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (2019, p. 307) 9.51 Annotated Bibliographies: Format and order references in an annotated bibliography in alphabetical order, the same as you would order entries in a reference list (see Sections 9.43-9.44)
An annotated bibliography includes: APA Title page. Pages are numbered beginning with title page. APA formatted reference list beginning on own page. References centered and bolded at top of page. Entries listed in alphabetical order. Annotations begin under its associated reference. Annotations are indented 0.5 inches from the left margin.
Information on Annotated Bibliographies can be found in Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) The format of your annotated bibliography follow the same format as any APA paper. Title page, page numbers, font style and size, etc. See Format basics. Alphabetical with hanging indents etc.
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic MLA bibliography formatting and rules. MLA documentation is generally used for disciplines in the humanities, such as English, languages, film, and cultural studies or other theoretical studies. ... Annotated bibliographies for CBE/CSE format do not require a special title. Use the usual ...
An annotated bibliography is similar to the Works Cited page found at the end of a paper. The paper formatting is the same but instead of following a full research paper, the student will write a brief annotation for each source which will directly follow the source's Works Cited entry. The annotations contain descriptive or evaluative comments ...
How to Format an APA Annotated Bibliography. Formatting your annotated bibliography is the same as formatting an APA reference list. You use the same author-date style and place the elements in the same order. ... Make sure you are ready to play the game in the academic field by having all the rules for any APA style project at your fingertips.
The American Psychological Association states that your instructor should set the guidelines for your annotated bibliography, but does ask that the list be formatted according to their standard reference page rules (see Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual).Since there are no set rules for creating one, you may be wondering how to create an annotated APA bibliography.
In the absence of other guidance, format an annotated bibliography as follows: Format and order reference in alphabetical order, the same as you would order entries in a reference list. Each annotation should be a new paragraph below its reference entry. Indent the entire annotation 0.5 in. from the left margin, the same as you would a block ...
A bibliography is a list of sources (books, journals, Web sites, periodicals, etc.) one has used for researching a topic. Bibliographies are sometimes called "References" or "Works Cited" depending on the style format you are using. A bibliography usually just includes the bibliographic information (i.e., the author, title, publisher, etc.).
The annotation appears on a new line directly after the source citation. The whole annotation is indented, to make it clear when the annotation ends and a new source appears. According to Turabian guidelines, annotations should be formatted the same as the main text of any paper: Double-spaced. Left-aligned.
An annotated bibliography is an alphabetical list of source citations with a short description and/or evaluation of that material under the citation. The purpose of an annotated bibliography is to present your critique, analysis, description and/or usefulness of a particular source listed.
Therefore, an annotated bibliography includes your citation followed by a summary and/or evaluation of each of your sources. Depending on your project or the assignment, your annotations may do one or more of the following. ... Formatting Rules. Order your references in alphabetical order as you would in your Bibliography.
1. APA style. Formatting your annotated bibliography is the same as formatting an APA reference list. You use the same author-date style and place the elements in the same order. Here's a quick rundown of the guidelines for an annotated bibliography in APA style: Right-aligned page number. Running header (Optional)
Creating an annotated bibliography in ASA style. The Publication Manual of the American Sociological Association is kept behind the IRC Desk on the ... states the following formatting rules, but check your course outline in case your professor has other requirements! All text should be double-spaced. Reference list entries must have a hanging ...
Research Skill. Learn what an annotated bibliography is, how to cite sources, and annotation requirements for your NHD project. Watch the videos below or review the annotated bibliography guide. DOWNLOAD THE Annotated bibliography HANDBOOK.
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual.Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual.. To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of ...
6 Interesting Citation Facts. The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there's more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations, and other formatting specifications.Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue.