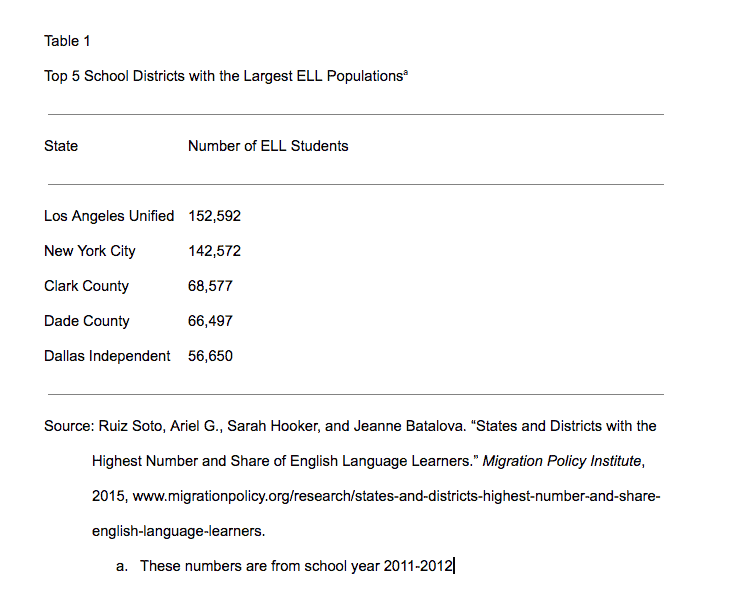
Works-Cited-List Entries
Citations by format.
Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements —facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you’re citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on the template.
The examples below show you how to cite five basic source types. Click on an entry to get more information, as well as links to posts with more examples. For hundreds of sample entries by format, check out the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .

Book by One Author
Mantel, Hilary. Wolf Hall . Picador, 2010.
Book by an Unknown Author
Beowulf . Translated by Alan Sullivan and Timothy Murphy, edited by Sarah Anderson, Pearson, 2004.
An Edited Book
Sánchez Prado, Ignacio M., editor. Mexican Literature in Theory . Bloomsbury, 2018.
Online Works
Article on a website.
Deresiewicz, William. “The Death of the Artist—and the Birth of the Creative Entrepreneur.” The Atlantic , 28 Dec. 2014, theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2015/01/ the-death-of-the-artist-and-the-birth-of-thecreative-entrepreneur/383497/.
Book on a website
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Masque of the Red Death.” The Complete Works of Edgar Allan Poe , edited by James A. Harrison, vol. 4, Thomas Y. Crowell, 1902, pp. 250-58. HathiTrust Digital Library , hdl.handle.net/2027/coo.31924079574368.
Journal Article in a Database
Goldman, Anne. “Questions of Transport: Reading Primo Levi Reading Dante.” The Georgia Review , vol. 64, no. 1, spring 2010, pp. 69-88. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/41403188.
Songs, Recordings, and Performances
Song from an album.
Snail Mail. “Thinning.” Habit , Sister Polygon Records, 2016. Vinyl EP.
Song on a website
Snail Mail. “Thinning.” Bandcamp , snailmailbaltimore.bandcamp.com.
Concert Attended in Person
Beyoncé. The “Formation” World Tour. 14 May 2016, Rose Bowl, Los Angeles.
Movies, Videos, and Television Shows
A movie viewed in person.
Opening Night. Directed by John Cassavetes, Faces Distribution, 1977.
A Movie Viewed Online
Richardson, Tony, director. Sanctuary . Screenplay by James Poe, Twentieth Century Fox, 1961. YouTube , uploaded by LostCinemaChannel, 17 July 2014, www.youtube.com/watch?v=IMnzFM_Sq8s .
A Television Show Viewed on Physical Media
“Hush.” 1999. Buffy the Vampire Slayer: The Complete Fourth Seaso n, created by Joss Whedon, episode 10, Mutant Enemy / Twentieth Century Fox, 2003, disc 3. DVD.
A Photograph Viewed in Person
Cameron, Julia Margaret. Alfred, Lord Tennyson . 1866, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City.
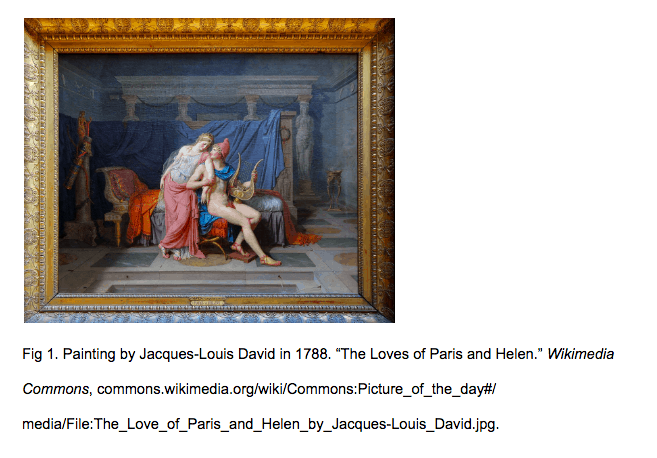
A Painting Viewed Online
Bearden, Romare. The Train . 1975. MOMA , www.moma.org/collection/works/65232?locale=en.
An Untitled Image from a Print Magazine
Karasik, Paul. Cartoon. The New Yorker , 14 Apr. 2008, p. 49.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Citation Styles and Management Tools Guide
Mla 9th edition citation guides, mla handbook (9th edition), core elements.
- Citing Business Sources
- Citation Management Tools
- Other Online Citation Tools
- UConn MLA 9th Edition (PDF) Citation Style Guide Guide to citing using MLA with examples. Created by UConn Librarians.
- Purdue OWL MLA Guide Comprehensive guide to using the MLA style from Purdue University.
- MLA Works Cited: A Quick Guide Highly recommended resource! Examples of the core elements, practice identifying "containers," and a practice template to make your own citation!
MLA focuses on the core elements that are common to all the different types of citations you might make. Remember, one of the points of a citation is to help others find the work you have consulted. Keep that in mind as you put together your core elements!
Not every source is going to all of these elements.
- Title of Source (e.g. a book, article, chapter, song, or episode)
- Title of Container (e.g. a journal, a book, album, or TV show)
- Other Contributors (e.g. translator, editors, producers)
- Publication date
The creator of the source you're citing.
Title of the Source
Title of the Container - This can be a tricky one!
The Container is the larger whole that the source is part of. If you have a chapter in a book, it's a book. If you're citing a TV episode, it's the whole TV show. "In some cases, a container might be within a larger container. You might have read a book of short stories on Google Books, or watched a television series on Netflix. You might have found the electronic version of a journal on JSTOR. It is important to cite these containers within containers so that your readers can find the exact source that you used." (Purdue OWL)
Publication Date
"The same source may have been published on more than one date, such as an online version of an original source. For example, a television series might have aired on a broadcast network on one date, but released on Netflix on a different date. When the source has more than one date, it is sufficient to use the date that is most relevant to your use of it. If you’re unsure about which date to use, go with the date of the source’s original publication." (Purdue OWL)
Other Contributors
In addition to the author, there may be other contributors to the source who should be credited, such as editors, illustrators, translators, etc. If their contributions are relevant to your research, or necessary to identify the source, include their names in your documentation. (Purdue OWL)
If a source is listed as an edition or version of a work, include it in your citation. (Purdue OWL)
If a source is part of a numbered sequence, such as a multi-volume book, or journal with both volume and issue numbers, those numbers must be listed in your citation. (Purdue OWL)
The publisher produces or distributes the source to the public. (Purdue OWL)
The same source may have been published on more than one date, such as an online version of an original source. For example, a television series might have aired on a broadcast network on one date, but released on Netflix on a different date. When the source has more than one date, it is sufficient to use the date that is most relevant to your use of it. If you’re unsure about which date to use, go with the date of the source’s original publication. (Purdue OWL)
This refers to a location like page numbers, a URL, or the physical location of a physical object.
- MLA Interactive Practice Template

Test your ability to use MLA format in this quick, interactive exercise!
- << Previous: Chicago
- Next: ASA >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 8:36 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/citationguides

Citation Guide
- APA Style - 7th Edition
Introduction to MLA Style
Creating mla citations: examples, paper formatting guidelines & sample papers, in-text citations & the list of works cited, examples of works cited & in-text citations, software tools for mla style, works cited for this page.
- Chicago/Turabian Style
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
- Tools for Managing Citations
- Citation Season!
What is MLA Style?
MLA stands for Modern Language Association. MLA Style is an established style for formatting your paper and giving credit to your sources.
This page provides resources for all the elements of a preparing a paper in MLA Style, including formatting, in-text citations, and the works cited list.
Disciplines at Caldwell that use MLA Style include English, history, theology, philosophy, and others.
MLA Quick Links
- Quoting and Paraphrasing in MLA Format This video course is all about quoting and paraphrasing sources in your paper! Learn rules of quoting and paraphrasing responsibly, and see examples of in-text citations in MLA format.
- Purdue OWL Guide to MLA Style Purdue OWL has resources about many citation styles. Here is their section on MLA

An Article from a Journal Found in a Library Database (a source in two containers)
from MLA Handbook chapter 5.100-103, The Three Most Common Types of Entries

A Chapter or Section of a Book Accessed through an Online Repository (a source with two containers)

An Episode of a TV Show Watched on an Online Platform (a source in two containers)

A Chapter or Section of a Print Book (a source in one container)

A Print Book (a source that is self-contained)
- Sample MLA Papers These sample student papers show MLA formatting for all details of a research paper. Look a the structure of the page, how quotes are incorporated, and how works are cited.
- Formatting Your Research Project (MLA Handbook, Ch. 1) Instructions for formatting your paper in MLA style, including margins, title, headers and footers, headings and subheadings, etc.
- The Writing Process Purdue OWL's Guide to academic writing in MLA Style, including grammar, mechanics, and punctuation.
- Mechanics of Prose (MLA Handbook, Ch. 2) Guidance on all the details of writing, such as spelling, grammar, punctuation, how format titles and names in your paper.
In-Text Citations
- In-Text Citations: The Basics Basic instructions from Purdue OWL about how to format in-text citations in MLA Style. This is how you credit your sources when you mention them in the text of your paper.
- Citing Sources in the Text (MLA Handbook, Ch. 6) This chapter starts with the basics of citing your sources in the text of your paper. It covers many situations you might encounter.
Works Cited Page
- MLA Style 101 This video course goes through each "element" of the MLA works cited page entry (like author, title, publisher) and shows how to identify what belongs in each element. This will help you create works cited page entries and know how to edit citations that a database generates!
- Interactive Practice Template Learn how to create citations for your Works Cited page!
- How to Cite Books This page from Purdue OWL covers the basics of citing books as well as what to do in a variety of situations. This page has guidance on multiple authors, an organization as author, translations, anthologies, and more.
- How to Cite Electronic Resources (aka things you found online) This page from Purdue OWL covers works cited page entries for most kinds of online sources, including scholarly journal articles in a library database, ebooks, government agency websites, online news, a YouTube video, personal email correspondence, and more.
- Citation Examples from the MLA Handbook This is a regularly updated list of citations for a wide variety of sources. It's organized by source, so scroll down or use ctrl-F to search the page for the kind of source you want to see, like "translated book" or "YouTube Video".
Journal Article Found in a Library Database
Works cited page entry.
Lorensen, Jutta. “Between Image and Word, Color, and Time: Jacob Lawrence’s The Migration Series.” African American Review , vol. 40, no. 3, 2006, pp. 571-86. Academic Search Premier, each.ebscohost.com/login.aspx? Drect=true&db=f5h&AN=24093790&site=eho st-live.
In-text citation
(Lorensen 577)
Newspaper Article Found in a Library Database
Fessenden, Ford, et al. "The Battle for New York's Key Voting Blocs in the Primaries." New York Times , 19 Apr. 2016, p. A 14. ProQuest Central , ezproxy.caldwell.edu:2048/login?url=http:// search.proquest.com/ docview/1781721245?accountid=26523.
(Fessenden et al. A14)
Article from an Online News Source
Chang, Kenneth. “NASA Will Send More Helicopters to Mars.” The New York Times , 27 July 2022, www.nytimes.com/2022/07/27/science/mars-sample-mission-nasa.html.
Dorris, Michael, and Louise Erdrich. The Crown of Columbus . HarperCollins Publishers, 1999.
(Dorris and Erdrich 110-12)
Article or Specific Chapter from a Book
Copeland, Edward. “Money.” The Cambridge Companion to Jane Austen , edited by Copeland and Juliet McMaster, Cambridge UP, 1997, pp. 131-48.
(Copeland 135)
Webpage on a Website
“Infographic: Benefits of Language Learning.” Modern Language Association , 2022, www.mla.org/Resources/Advocacy/Infographics/Infographic-Benefits-of-Language-Learning.
("Inforgraphic: Benefits of Language Learning")
Film on an App
Mamma Mia . Directed by Phyllida Lloyd, Universal Pictures, 2008. Netflix app.
( Mamma Mia ) or ( Mamma Mia 59:03-61:23) - cite a specific scene with timestamps in the page number spot
There are many tools that can help you create, manage, and organize your citations and your references page. Here are some that the library provides or recommends for students and faculty.
- NoodleTools This link opens in a new window NoodleTools is an online tool that helps you take notes and correctly format citations. MLA, APA, and Chicago/Turabian citation styles are included. Use throughout your research project to track sources, take notes, create outlines, collaborate with classmates, and format bibliographies. Use this link to create an account.
- ZoteroBib ZoteroBib is a free service that helps you build a bibliography from any computer or device, without creating an account or installing any software. It's from the team behind the open source citation management app Zotero. ZBib can create a draft citation from a link or ISBN and has helpful templates for you to use to manually create citations. You can use it for MLA, APA, or Chicago Style.
The information on this page comes from the MLA Handbook, 9th Edition. This book can be cited in MLA style like this:
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
The elements used here are: [2. Title of source] MLA Handbook. [5. Version] 9th ed., [7. Publisher] Modern Language Association of America, [8. Publication date] 2021. Because the publisher is an organization who is also the author, this organization - the Modern Language Association - is only listed once, as the publisher.
An in-text citation for this handbook could be ( MLA Handbook 45) to refer specifically to something on page 45.
- << Previous: APA Style - 7th Edition
- Next: Chicago/Turabian Style >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 9:53 AM
- URL: https://libguides.caldwell.edu/citations
Please sign in
You need to log in to use the bookmarking feature.

- Baker Library
- Special Collections
- Fast Answers
- All Services
- Plan Your Visit
- Working Knowledge
- Academic Programs
- Faculty & Research
- Harvard Business Review
- Initiatives
- Map / Directions
Purdue Owl: MLA Formatting & Style Guide
Developed by the Purdue Online Writing Lab. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Author/Editor (By:)
Contributor, corporate author, related organizations, citation type.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
Keep all of your citations in one safe place
Create an account to save all of your citations
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper
The complete guide to mla & citations, what you’ll find in this guide.
This page provides an in-depth overview of MLA format. It includes information related to MLA citations, plagiarism, proper formatting for in-text and regular citations, and examples of citations for many different types of sources.
Looking for APA? Check out the Citation Machine’s guide on APA format . We also have resources for Chicago citation style as well.
How to be a responsible researcher or scholar
Putting together a research project involves searching for information, disseminating and analyzing information, collecting information, and repurposing information. Being a responsible researcher requires keeping track of the sources that were used to help develop your research project, sharing the information you borrowed in an ethical way, and giving credit to the authors of the sources you used. Doing all of these things prevents plagiarism.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the act of using others’ information without giving credit or acknowledging them. There are many examples of plagiarism. Completely copying another individual’s work without providing credit to the original author is a very blatant example of plagiarism. Plagiarism also occurs when another individual’s idea or concept is passed off as your own. Changing or modifying quotes, text, or any work of another individual is also plagiarism. Believe it or not, you can even plagiarize yourself! Reusing a project or paper from another class or time and saying that it’s new is plagiarism. One way to prevent plagiarism is to add citations in your project where appropriate.
What is a Citation?
A citation shows the reader of your project where you found your information. Citations are included in the body of a project when you add a quote to your project. Citations are also included in the body when you’re paraphrasing another individual’s information. These citations in the body of a research paper are called in-text citations. They are found directly next to the information that was borrowed and are very brief to avoid causing distraction while reading a project. These brief citations include the last name of the author and a page number. Scroll down for an in-depth explanation and examples of MLA in-text citations.
In-text citations provide us with a brief idea as to where you found your information, though they usually don't include the title and other components. Look on the last page of a research project to find complete citations.
Complete citations are found on what MLA calls a works-cited list, which is sometimes called an MLA bibliography. All sources that were used to develop a research project are found on the works-cited list. Complete citations are also created for any quotes or paraphrased information used in the text. Complete citations include the author’s name, the title, publisher, year published, page numbers, URLs, and a few other pieces of information.
Looking to create your citations in just a few clicks? Need an MLA format website or book citation? Visit Citation Machine.net! Our Citation Machine MLA generator, which is an MLA citation website, will create all of your citations in just a few clicks. Click here to see more styles .
Why Does it Matter?
Citing your sources is an extremely important component of your research project. It shows that you’re a responsible researcher and that you located appropriate and reputable sources that support your thesis or claim. In addition, if your work ends up being posted online or in print, there is a chance that others will use your research project in their own work!
Scroll down to find directions on how to create citations.
How the Modern Language Association Helps You Become a Responsible Researcher
What is mla format.
The Modern Language Association is an organization that was created to develop guidelines on everything language and literature related. They have guidelines on proper grammar usage and research paper layouts. In addition, they have English and foreign language committees, numerous books and journal publications, and an annual conference. They are not connected with this guide, but the information here reflects the association’s rules for formatting papers and citations.
What are citations?
The Modern Language Association is responsible for creating standards and guidelines on how to properly cite sources to prevent plagiarism. Their style is most often used when writing papers and citing sources in the liberal arts and humanities fields. “Liberal arts” is a broad term used to describe a range of subjects including the humanities, formal sciences such as mathematics and statistics, natural sciences such as biology and astronomy, and social sciences such as geography, economics, history, and others. The humanities focuses specifically on subjects related to languages, art, philosophy, religion, music, theater, literature, and ethics.
Believe it or not, there are thousands of other types of citation styles. While this citation style is most often used for the liberal arts and humanities fields, many other subjects, professors, and schools prefer citations and papers to be styled in MLA format.
What’s the difference between a bibliography and a works-cited list?
Great question. The two terms cause a lot of confusion and are consistently misused not only by students but educators as well! Let’s start with what the two words mean.
A bibliography displays the sources the writer used to gain background knowledge on the topic and also research it in-depth. Before starting a research project, you might read up on the topic in websites, books, and other sources. You might even dive a bit deeper to find more information elsewhere. All of these sources you used to help you learn about the topic would go in an MLA format bibliography. You might even include other sources that relate to the topic.
A works-cited list displays all of the sources that were mentioned in the writing of the actual paper or project. If a quote was taken from a source and placed into a research paper, then the full citation goes on the works-cited list.
Both the works-cited list and bibliography go at the end of a paper. Most teachers do not expect students to hand in both a bibliography AND a works-cited list. Teachers generally expect to see a works-cited list, but sometimes erroneously call it a bibliography. If you’re not sure what your teacher expects, a page in MLA bibliography format, a works-cited list, or both, ask for guidance.
Why do we use this MLA style?
These specific guidelines and standards for creating citations were developed for numerous reasons. When scholars and researchers in literature, language, and numerous other fields all cite their sources in the same manner, it makes it easier for readers to look at a citation and understand the different components of a source. By looking at an MLA citation, we can see who the author is, the title of the source, when it was published, and other identifiable pieces of information.
Imagine how difficult it would be to understand the various components of a source if we didn’t all follow the same guidelines! Not only would it make it difficult to understand the source that was used, but it would also make it difficult for readers to locate it themselves. This streamlined process aides us in understanding a researcher’s sources.

How is the new version different than previous versions?
This citation style has changed dramatically over the past couple of years. The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition.
The new version expands upon standards previously set in the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook, including the core elements. The structure of citations remains the same, but some formatting guidance and terminology have changed.
- DOI numbers are now formatted as https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx
- Seasons in publishing daters are lowercased: spring 2020
- The term “optional elements” is now “supplemental elements”
- “Narrative in-text citations” are called “citations in prose”
In addition, new information was added on the following:
- Hundreds of works-cited-list entries
- MLA formatting for papers
- Punctuation, spelling, and other mechanics of prose
- Chapter on inclusive language
- Notes (bibliographic and content)
For more information on MLA 9, click here .
A Deeper Look at Citations
What do they look like.
There are two types of citations. The first is a full, or complete, citation. These are found at the end of research projects. These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves.
Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a DOI, URL, or page range).
There are times when additional information is added into the full citation.
Not sure how to transfer the information from your source into your citation? Confused about the term, “containers”? See below for information and complete explanations of each citation component.
The second type of citation, called an “in-text citation,” is included in the main part, or body, of a project when a researcher uses a quote or paraphrases information from another source. See the next section to find out how to create in-text citations.
What are in-text citations?
As stated above, in-text citations are included in the main part of a project when using a quote or paraphrasing a piece of information from another source. We include these types of citations in the body of a project for readers to quickly gain an idea as to where we found the information.
These in-text citations are found directly next to the quote or paraphrased information. They contain a small tidbit of the information found in the regular MLA citation. The regular, or complete, citation is located at the end of a project, on the works-cited list.
Here’s what a typical in-text citation looks like:
In the book The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements…. Too much fire and you have a bad temper...too little wood and you bent too quickly...too much water and you flowed in too many directions” (Tan 31).
This specific in text citation, (Tan 31), is called an MLA parenthetical citation because the author’s name is in parentheses. It’s included so the reader sees that we are quoting something from page 31 in Tan’s book. The complete, regular citation isn’t included in the main part of the project because it would be too distracting for the reader. We want the reader to focus on our work and research, not get caught up on our sources.
Here’s another way to cite in the text:
In Tan’s novel The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements... Too much fire and you have a bad temper... too little wood and you bent too quickly... too much water and you flowed in too many directions" (31).
If the reader would like to see the source’s full information, and possibly locate the source themselves, they can refer to the last part of the project to find the regular citation.
The regular citation, at the end of the project looks like this:
%%Tan, Amy. The Joy Luck Club. Penguin, 1989, p. 31.
Notice that the first word in the full citation (Tan) matches the “Tan” used in the body of the project. It’s important to have the first word of the full citation match the term used in the text. Why? It allows readers to easily find the full citation on the works-cited list.
If your direct quote or paraphrase comes from a source that does not have page numbers, it is acceptable to place a line number (use line or lines), paragraph number (use the abbreviation par. or pars.), sections (sec. or secs.), or chapters (ch. or chs.). Only use these other terms if they are actually labeled on the source. If it specifically says on the source, “Section 1,” for example, then it is acceptable to use “sec. 1” in the in-text citation.
If there are no numbers to help readers locate the exact point in the source, only include the author’s last name.
To determine how to create in-text citations for more than one author, no authors, or corporate authors, refer to the “Authors” section below.
More about quotations and how to cite a quote:
- Use quotes from outside sources to help illustrate and expand on your own points. The majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas.
- Include the quote exactly as you found it. It is okay to use only certain words or phrases from the quote, but keep the words (spelling and capitalization) and punctuation the same.
- It is acceptable to break up a direct quote with your own writing.
Example from a movie:
Dorothy stated, "Toto," then looked up and took in her surroundings, "I’ve a feeling we’re not in Kansas anymore" ( Wizard of Oz ).
- The entire paper should be double-spaced, including quotes.
- If the quote is longer than four lines, it is necessary to make a block quote. Block quotes show the reader that they are about to read a lengthy amount of text from another source.
- Start the quote on the next line, half an inch from the left margin.
- Do not use any indents at the beginning of the block quote.
- Only use quotation marks if there are quotation marks present in the source.
- If there is more than one paragraph in the block quote, indent the beginning of the paragraphs after the first one an additional half an inch from the left margin.
- Add your in-text citation after the final period of the block quote. Do not add an additional period after the parenthetical citation.
While his parents sat there in surprise, Colton went onto say:
“Cause I could see you,” Colon said matter-of-factly. “I went up and out of my body and I was looking down and I could see the doctor working on my body. And I saw you and Mommy. You were in a little room by yourself, praying; and Mommy was in a different room, and she was praying and talking on the phone.” (Burpo xxi)
How to create a paraphrase:
As stated above, the majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas. It’s acceptable to include quotes, but they shouldn’t crowd your paper. If you’re finding that you’re using too many quotes in your paper, consider adding paraphrases. When you reiterate a piece of information from an outside source in your own words, you create a paraphrase.
Here’s an example:
Readers discover in the very first sentence of Peter Pan that he doesn’t grow up (Barrie 1).
What paraphrases are:
- Recycled information in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.
- They’re still references! Include an in-text citation next to the paraphrased information.
What paraphrases are not:
- A copy and pasted sentence with a few words substituted for synonyms.
Confused about whether footnotes and endnotes should be used?
Footnotes and endnotes are completely acceptable to use in this style. Use a footnote or endnote if:
- Adding additional information will help the reader understand the content. This is called a content note .
- You need to cite numerous sources in one small section of your writing. Instead of clogging up a small paragraph with in-text citations (which could cause confusion for the reader), include a footnote or endnote. This is called a bibliographic note .
Keep in mind that whether you choose to include in-text citations or footnotes/endnotes, you need to also include a full reference on the MLA format works-cited list.
Content note example:
Even Maurice Sendak’s work (the mastermind behind Where the Wild Things Are and numerous other popular children’s picture books) can be found on the banned books list. It seems as though nobody is granted immunity. 1
- In the Night Kitchen ’s main character is nude on numerous pages. Problematic for most is not the nudity of the behind, but the frontal nudity.
Work Cited:
%%Sendak, Maurice. In The Night Kitchen. Harper Collins, 1996.
Bibliographic note example:
Dahl had a difficult childhood. Both his father and sister passed away when he was a toddler. He was then sent away by his mother to boarding school (de Castella). 1
- Numerous books, such as Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG, all feature characters with absent or difficult parents.
MLA Works Cited:
Include 4 full citations for: de Castella’s article, Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG .
Don’t forget to create full, or regular citations, and place them at the end of your project.
If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net can help. Our MLA citation generator is simple and easy to use!
Common Knowledge: What Is It and How Will It Affect My Writing?
Footnotes, endnotes, references, proper structuring. We know it’s a lot. Thankfully, you don’t have to include a reference for EVERY piece of information you add to your paper. You can forget about including a reference when you share a piece of common knowledge.
Common knowledge is information that most people know. For example, these are a few facts that are considered common knowledge:
- The Statue of Liberty is located in New York City
- Tokyo is the capital of Japan
- Romeo and Juliet is a play written by William Shakespeare
- English is the language most people speak in England
- An elephant is an animal
We could go on and on. When you include common knowledge in your paper, omit a reference. One less thing to worry about, right?
Before you start adding tons of common knowledge occurrences to your paper to ease the burden of creating references, we need to stop you right there. Remember, the goal of a research paper is to develop new information or knowledge. You’re expected to seek out information from outside sources and analyze and distribute the information from those sources to form new ideas. Using only common knowledge facts in your writing involves absolutely zero research. It’s okay to include some common knowledge facts here and there, but do not make it the core of your paper.
If you’re unsure if the fact you’re including is common knowledge or not, it doesn’t hurt to include a reference. There is no such thing as being overly responsible when it comes to writing and citing.
Wikipedia - Yay or Nay?
If you’re wondering whether it’s okay to use Wikipedia in your project, the answer is, it depends.
If Wikipedia is your go-to source for quick information on a topic, you’re not alone. Chances are, it’s one of the first websites to appear on your results page. It’s used by tons of people, it’s easily accessible, and it contains millions of concise articles. So, you’re probably wondering, “What’s the problem?”
The issue with Wikipedia is that it’s a user-generated site, meaning information is constantly added and modified by registered users. Who these users are and their expertise is somewhat of a mystery. The truth is anyone can register on the site and make changes to articles.
Knowing this makes some cringe, especially educators and librarians, since the validity of the information is questionable. However, some people argue that because Wikipedia is a user-generated site, the community of registered users serve as “watchdogs,” ensuring that information is valid. In addition, references are included at the bottom of each article and serve as proof of credibility. Furthermore, Wikipedia lets readers know when there’s a problem with an article. Warnings such as “this article needs clarification,” or “this article needs references to prove its validity” are shared with the reader, thus promoting transparency.
If you choose to reference a Wikipedia article in your research project, and your teacher or professor says it’s okay, then you must reference it in your project. You would treat it just as you would with any other web source.
However, you may want to instead consider locating the original source of the information. This should be fairly easy to do thanks to the references at the bottom of each article.
Specific Components of a Citation
This section explains each individual component of the citation, with examples for each section for full citations and in-text citations.
Name of the author
The author’s name is usually the first item listed in the MLA citation. Author names start with the last name, then a comma is added, and then the author’s first name (and middle name if applicable) is at the end. A period closes this information.
Here are two examples of how an author’s name can be listed in a full citation:
Twain, Mark.
Poe, Edgar Allan.
For in-text:
(Author’s Last name page number) or Author’s Last name... (page).
Wondering how to format the author’s name when there are two authors working jointly on a source? When there are two authors that work together on a source, the author names are placed in the order in which they appear on the source. Place their names in this format:
Author 1’s Last Name, First name, and Author 2’s First Name Last Name.
Here are two examples of how to cite two authors:
Clifton, Mark, and Frank Riley.
Paxton, Roberta J., and Michael Jacob Fox.
(Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name page number) or Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name... (page).
There are many times when three or more authors work together on a source. This often happens with journal articles, edited books, and textbooks.
To cite a source with three or more authors, place the information in this format:
Author 1’s Last name, First name, et al.
As you can see, only include the first author’s name. The other authors are accounted for by using “et al.” In Latin, et al. is translated to “and others.” If using the Citation Machine citation generator, this abbreviation is automatically added for you.
Here’s an example of a citation for three or more authors:
%%Warner, Ralph, et al. How to Buy a House in California. Edited by Alayna Schroeder, 12th ed., Nolo, 2009.
(Author 1’s Last name et al. page number)
Is there no author listed on your source? If so, exclude the author’s information from the citation and begin the citation with the title of the source.
For in-text: Use the title of the source in parentheses. Place the title in italics if the source stands alone. Books and films stand alone. If it’s part of a larger whole, such as a chapter in an edited book or an article on a website, place the title in quotation marks without italics.
( Back to the Future )
(“Citing And Writing”)
Other in-text structures:
Authors with the same last name in your paper? MLA essay format requires the use of first initials in-text in this scenario.
Ex: (J. Silver 45)
Are you citing more than one source by the same author? For example, two books by Ernest Hemingway? Include the title in-text.
Example: (Hemingway, For Whom The Bell Tolls 12).
Are you citing a film or song? Include a timestamp in the format of hours:minutes:seconds. ( Back to the Future 00:23:86)
Was the source found on social media, such as a tweet, Reddit, or Instagram post? If this is the case, in an MLA format paper, you are allowed to start the citation with the author’s handle, username, or screen name.
Here is an example of how to cite a tweet:
%%@CarlaHayden. “I’m so honored to talk about digital access at @UMBCHumanities. We want to share the @libraryofcongress collection.” Twitter , 13 Apr. 2017, 6:04 p.m., twitter.com/LibnOfCongress/status/852643691802091521.
While most citations begin with the name of the author, they do not necessarily have to. Quite often, sources are compiled by editors. Or, your source may be done by a performer or composer. If your project focuses on someone other than the author, it is acceptable to place that person’s name first in the citation. If you’re using the MLA works cited generator at Citation Machine.net, you can choose the individual’s role from a drop-down box.
For example, let’s say that in your research project, you focus on Leonardo DiCaprio’s performances as an actor. You’re quoting a line from the movie Titanic in your project, and you’re creating a complete citation for it in the works-cited list.
It is acceptable to show the reader that you’re focusing on Leonardo DiCaprio’s work by citing it like this in the MLA works-cited list:
%%DiCaprio, Leonardo, performer. Titanic . Directed by James Cameron. Paramount, 1997.
Notice that when citing an individual other than the author, place the individual’s role after their name. In this case, Leonardo DiCaprio is the performer.
This is often done with edited books, too. Place the editor’s name first (in reverse order), add a comma, and then add the word editor.
If you’re still confused about how to place the authors together in a citation, the tools at CitationMachine.net can help! Our website is easy to use and will create your citations in just a few clicks!
Titles and containers
The titles are written as they are found on the source and in title form, meaning the important words start with a capital.
Here’s an example of a properly written title:
Practical Digital Libraries: Books, Bytes, and Bucks.
Wondering whether to place your title in italics or quotation marks? It depends on whether the source sits by itself or not. If the source stands alone, meaning that it is an independent source, place the title in italics. If the title is part of a larger whole, place the title of the source in quotation marks and the source it is from in italics.
When citing full books, movies, websites, or albums in their entirety, these titles are written in italics.
However, when citing part of a source, such as an article on a website, a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a scholarly journal, the part is written with quotation marks and then the titles of the sources that they are found in are written in italics.
Here are some examples to help you understand how to format titles and their containers.
To cite Pink Floyd’s entire album, The Wall , cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. The Wall. Columbia, 1979.
To cite one of the songs on Pink Floyd’s album in MLA formatting, cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. “Another Brick in the Wall (Part I).” The Wall, Columbia, 1979, track 3.
To cite a fairy tale book in its entirety, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. The Land of Stories. Little Brown, 2016.
To cite a specific story or chapter in the book, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. “Little Red Riding Hood.” The Land of Stories, Little Brown, 2016, pp. 58-65.
More about containers
From the section above, you can see that titles can stand alone, or they can sit in a container. Many times, sources can sit in more than one container. Wondering how? When citing an article in a scholarly journal, the first container is the journal. The second container? It’s the database that the scholarly journal is found in. It is important to account for all containers, so readers are able to locate the exact source themselves.
When citing a television episode, the first container is the name of the show and the second container is the name of the service that it could be streaming on, such as Netflix .
If your source sits in more than one container, the information about the second container is found at the end of the citation.
Use the following format to cite your source with multiple containers :
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
If the source has more than two containers, add on another full section at the end for each container.
Not all of the fields in the citation format above need to be included in your citation. In fact, many of these fields will most likely be omitted from your citations. Only include the elements that will help your readers locate the source themselves.
Here is an example of a citation for a scholarly journal article found in a database. This source has two containers: the journal itself is one container, and the site it sits on is the other.
%%Zanetti, Francois. “Curing with Machine: Medical Electricity in Eighteenth-Century Paris.” Technology and Culture, vol. 54, no. 3, July 2013, pp. 503-530. Project Muse, muse.jhu.edu/article/520280.
If you’re still confused about containers, the Citation Machine MLA cite generator can help! MLA citing is easier when using the tools at CitationMachine.net.
Other contributors
Many sources have people besides the author who contribute to the source. If your research project focuses on an additional individual besides the author, or you feel as though including other contributors will help the reader locate the source themselves, include their names in the citation.
To include another individual in the citation, after the title, place the role of the individual, the word “by,” and then their name in standard order.
If the name of the contributor comes after a period, capitalize the first letter in the role of the individual. If it comes after a comma, the first letter in the role of the individual is lowercased.
Here’s an example of a citation for a children’s book with the name of the illustrator included:
%%Rubin, Adam. Dragons Love Tacos. Illustrated by Daniel Salmieri, Penguin, 2012.
The names of editors, directors, performers, translators, illustrators, and narrators can often be found in this part of the citation.
If the source that you’re citing states that it is a specific version or edition, this information is placed in the “versions” section of the citation.
When including a numbered edition, do not type out the number, use the numeral. Also, abbreviate the word “edition” to “ed.”
Here is an example of a citation with a specific edition:
%%Koger, Gregory. “Filibustering and Parties in the Modern State.” Congress Reconsidered, edited by Lawrence C. Dodd and Bruce I. Oppenheimer, 10th ed., CQ Press, 2013, pp. 221-236. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=b7gkLlSEeqwC&lpg=PP1&dq=10th%20edition&pg=PR6#v=onepage&q=10th%20edition&f=false.
Many sources have numbers associated with them. If you see a number different than the date, page numbers, or editions, include this information in the “numbers” section of the citation. For MLA citing, this includes volume and/or issue numbers (use the abbreviations vol. and no.), episode numbers, track numbers, or any other numbers that will help readers identify the specific source that you used. Do not include ISBN (International Standard Book Numbers) in the citation.
It is important to include the name of the publisher (the organization that created or published the source), so that readers can locate the exact source themselves.
Include publishers for all sources except periodicals. Also, for websites, exclude this information when the name of the publisher matches the name of the website. Furthermore, the name of the publisher is often excluded from the citation for second containers, since the publisher of the second container is not necessarily responsible for the creation or production of the source’s content.
Publication dates
Publication dates are extremely important to include in citations. They allow the reader to understand when sources were published. They are also used when readers are attempting to locate the source themselves.
Dates can be written in MLA in one of two ways. Researchers can write dates as:
Day Mo. Year
Mo. Day, Year
Whichever format you decide to use, use the same format for all of your citations. If using the Citation Machine citation generator, the date will be formatted in the same way for each citation.
While it isn’t necessary to include the full date for all source citations, use the amount of information that makes the most sense to help your readers understand and locate the source themselves.
Wondering what to do when your source has more than one date? Use the date that is most applicable to your research.
The location generally refers to the place where the readers can find the source. This includes page ranges, URLs, DOI numbers, track numbers, disc numbers, or even cities and towns.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx .
For page numbers, when citing a source found on only one page, use p.
Example: p. 6.
When citing a source that has a page range, use pp. and then add the page numbers.
Example: pp. 24-38.
Since the location is the final piece of the citation, place a period at the end. When it comes to URLs, many students wonder if the links in citations should be live or not. If the paper is being shared electronically with a teacher and other readers, it may be helpful to include live links. If you’re not sure whether to include live links or not, ask your teacher or professor for guidance.
Looking for an online tool to do the work for you? Citation Machine citing tools could help! Our site is simple (and fun!) to use.
Need some more help? There is further good information here .
Common Citation Examples
ALL sources use this format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). *Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
*If the source does not have a second container, omit this last part of the citation.
Remember, the Citation Machine MLA formatter can help you save time and energy when creating your citations. Check out our MLA Citation Machine pages to learn more.
- Journal Articles
How to Format a Paper
When it comes to formatting your paper or essay for academic purposes, there are specific MLA paper format guidelines to follow.
- Use paper that is 8½-by-11 inch in size. This is the standard size for copier and printer paper.
- Use high quality paper.
- Your research paper or essay should have a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the paper.
- While most word processors automatically format your paper to have one-inch margins, you can check or modify the margins of your paper by going to the “Page setup” section of your word processor.
Which font is acceptable to use?
- Use an easily readable font, specifically one that allows readers to see the difference between regular and italicized letters.
- Times New Roman, Arial, and Helvetica are recommended options.
- Use 12-point size font.
Should I double-space the paper, including citations?
- Double-space the entire paper.
- There should be a double space between each piece of information in the heading.
- Place a double space between the heading and the title.
- Place a double space between the title and the beginning of the essay.
- The works-cited list should be double-spaced as well. All citations are double-spaced.
Justification & Punctuation
- Text should be left-justified, meaning that the text is aligned, or flush, against the left margin.
- Indents signal to the reader that a new concept or idea is about to begin.
- Use the “tab” button on your keyboard to create an indent.
- Add one space after all punctuation marks.
Heading & Title
- Include a proper heading and title
- The heading should include the following, on separate lines, starting one inch from the top and left margins:
- Your full name
- Your teacher or professor’s name
- The course number
- Dates in the heading and the body of your essay should be consistent. Use the same format, either Day Month Year or Month Day, Year throughout the entire paper
- Examples: 27 July 2017 or July 27, 2017
- The title should be underneath the heading, centered in the middle of the page, without bold, underlined, italicized, or all capital letters.
Page numbers
- Number all pages, including the very first page and the works-cited list.
- Place page numbers in the top right corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin.
- Include your last name to the left of the page number. Example: Jacobson 4
Here’s an example to provide you with a visual:

If you need help with sentence structure or grammar, check out our paper checker. The paper checker will help to check every noun , verb , and adjective . If there are words that are misspelled or out of place, the paper checker will suggest edits and provide recommendations.
- If a citation flows onto the second line, indent it in half an inch from the left margin (called a “hanging indent”).
- For more information on the works-cited list, refer to “How to Make a Works Cited Page,” which is found below.
How to Create a Title Page
According to the Modern Language Association’s official guidelines for formatting a research paper, it is unnecessary to create or include an individual title page, or MLA cover page, at the beginning of a research project. Instead, follow the directions above, under “Heading & Title,” to create a proper heading. This heading is featured at the top of the first page of the research paper or research assignment.
If your instructor or professor does in fact require or ask for an MLA title page, follow the directions that you are given. They should provide you with the information needed to create a separate, individual title page. If they do not provide you with instructions, and you are left to create it at your own discretion, use the header information above to help you develop your research paper title page. You may want to include other information, such as the name of your school or university.
How to Make a Works Cited Page
The MLA Works Cited page is generally found at the end of a research paper or project. It contains a list of all the citations of sources used for the research project. Follow these directions to format the works-cited list to match the Modern Language Association’s guidelines.
- The “Works Cited” page has its own page at the end of a research project.
- Include the same running head as the rest of the project (Your last name and then the page number). The “Works Cited” page has the final page number for the project.
- Name the page “Works Cited,” unless your list only includes one citation. In that case, title it in MLA “Work Cited.”
- The title of the page (either “Works Cited” or “Work Cited”) is placed one inch from the top of the page, centered in the middle of the document.
- Double space the entire document, even between the title of the page and the first citation.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the citation (usually the last name of the author or the first word in the title if the citation does not include the author’s name. Ignore “A,” “An,” and “The” if the title begins with these words.)
- If there are multiple citations by the same author, place them in chronological order by the date published.
- Also, instead of writing the author’s name twice in both citations, use three hyphens.
%%Angelou, Maya. I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings. Random House, 2009.
%%---. Gather Together in My Name. Random House, 1974.
- All citations begin flush against the left margin. If the citation is long and rolls onto a second or third line, indent the lines below the first line half an inch from the left margin. This is called a “hanging indent.” The purpose of a hanging indent is to make the citations easier to read. If you’re using our MLA citation machine, we’ll format each of your references with a hanging indent for you.
%%Wai-Chung, Ho. “Political Influences on Curriculum Content and Musical Meaning: Hong Kong Secondary Music Education, 1949-1997.” Journal of Historical Research in Music Education, vol. 22, no. 1, 1 Oct. 2000, pp. 5-25. Periodicals Index Online, search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/pio/docview/1297849364/citation/6B70D633F50C4EA0PQ/78?accountid=35635.
- MLA “Works Cited” pages can be longer than one page. Use as many pages as necessary. If you have only one source to cite, do not place the one citation below the text of your paper. In MLA, a “Work Cited” page is still created for that individual citation.
Here’s a sample paper to give you an idea of what an MLA paper could look like. Included at the end is an MLA “Works Cited” page example.

Looking to add a relevant image, figure, table, or musical score to your paper? Here’s the easy way to do it, while following guidelines set forth by the Modern Language Association:
- Place the image, figure, table, or music close to where it’s mentioned in the text.
- Provide source information and any additional notes directly below the image, figure, table, or music.
For tables:
- Label the table as “Table” followed by an arabic numeral such as “1.” Table 1 is the table closest to the beginning of the paper. The next table mentioned in the text would be Table 2, and so on.
- Create a title for the table and place it below the label. Capitalize all important words.
- The label (Table 1) and the title should be flush against the left margin.
- Double-space everything.
- A figure can be a map, photograph, painting, pie chart, or any other type of image.
- Create a label and place it below the figure. The figure first mentioned in the text of the project is either “Figure 1” or “Fig 1.” Though figures are usually abbreviated to “Fig.” Choose one style and use it consistently. The next mentioned figure is “Figure 2” or “Fig. 2.”, and so on.
- Place a caption next to the label. If all of the source information is included in the caption, there isn’t a need to replicate that information in the works-cited list.
MLA Final Checklist
Think you’re through? We know this guide covered a LOT of information, so before you hand in that assignment, here’s a checklist to help you determine if you have everything you need:
_ Are both in-text and full citations included in the project? Remember, for every piece of outside information included in the text, there should be a corresponding in-text citation next to it. Include the full citation at the end, on the “Works Cited” page.
_ Are all citations, both in-text and full, properly formatted in MLA style? If you’re unsure, try out our citation generator!
_ Is your paper double-spaced in its entirety with one inch margins?
_ Do you have a running header on each page? (Your last name followed by the page number)
_ Did you use a font that is easy to read?
_ Are all citations on the MLA format works-cited list in alphabetical order?
Our plagiarism checker scans for any accidental instances of plagiarism. It scans for grammar and spelling errors, too. If you have an adverb , preposition , or conjunction that needs a slight adjustment, we may be able to suggest an edit.
Common Ways Students Accidentally Plagiarize
We spoke a bit about plagiarism at the beginning of this guide. Since you’re a responsible researcher, we’re sure you didn’t purposely plagiarize any portions of your paper. Did you know students and scholars sometimes accidentally plagiarize? Unfortunately, it happens more often than you probably realize. Luckily, there are ways to prevent accidental plagiarism and even some online tools to help!
Here are some common ways students accidentally plagiarize in their research papers and assignments:
1. Poor Paraphrasing
In the “How to create a paraphrase” section towards the top of this page, we share that paraphrases are “recycled information, in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.” If you attempt to paraphrase a few lines of text and it ends up looking and sounding too close to the original author’s words, it’s a poor paraphrase and considered plagiarism.
2. Incorrect Citations
If you cite something incorrectly, even if it’s done accidentally, it’s plagiarism. Any incorrect information in a reference, such as the wrong author name or the incorrect title, results in plagiarism.
3. Forgetting to include quotation marks
When you include a quote in your paper, you must place quotation marks around it. Failing to do so results in plagiarism.
If you’re worried about accidental plagiarism, try our Citation Machine Plus essay tool. It scans for grammar, but it also checks for any instances of accidental plagiarism. It’s simple and user-friendly, making it a great choice for stress-free paper editing and publishing.
Updated June 15, 2021
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Wendy Ikemoto. Michele Kirschenbaum has been an awesome school librarian since 2006 and is an expert in citing sources. Wendy Ikemoto has a master’s degree in library and information science and has been working for Citation Machine since 2012.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Citation Guide
- A Quick Guide to Resources
Subject Guide

Changes in 9th edition
The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook was published in 2021. In this update, the format for both in-text and Works Cited citations is the same as the 8th edition. The 9th edition also includes this clarification on citing a film/DVD.
A film/DVD: Generally list film directors as key contributors in the Contributor element Blade Runner . 1982. Directed by Ridley Scott, director’s cut, Warner Bros., 1992.
Examples of MLA Style
In-text Citation
Creating a Works Cited Page
With MLA style, you must include a Works Cited page at the end of your paper. A Works Cited page is an alphabetical listing of the resources cited in your paper. Below are some examples of MLA style citations. Note: Some instructors may require access dates for websites or other pieces of information. Please check with your instructor if you have any questions.
- Official MLA Style Center
A Modern Language Association hosted website with information on MLA citation and related resources. The MLA Style Center does not contain the full text of the handbook, although it walks users through the process of creating an entry in the works cited list.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab
Online writing lab with formatting tips and sample papers. The "Cite your source automatically" feature on Purdue Owl pages is part of another website, and not recommended.
- Excelsior Writing Lab
Citation examples, videos, and formatting guides for MLA, APA, and Chicago styles.
- Citing Government Information using MLA
Information on citing government print and electronic resources using MLA citation style. (Courtesy of the University of Nevada-Reno)
- << Previous: Basic APA
- Next: If I Apply >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2023 4:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.pnw.edu/c.php?g=1300509

MLA citation guides online
Mla citation guides in the library, webster university's writing center, citing chatgpt and other generative ai applications in mla.
Ask A Librarian for help finding sources, narrowing or expanding your topic, and more!
- Research Desk: 314-246-6950
- Toll-free: 800-985-4279
- Visit us: Library hours
- Search our FAQs or email us
- Purdue OWL: MLA formatting and style MLA citation help from the Purdue Online Writing Lab (9th edition)
- MLA Style Center MLA's own online citation help for the 9th edition
- Webster University Libraries: MLA style guide
MLA 9 th edition came out in April 2021. Check with your instructor to see which version you should use.
Whether you are an experienced academic writer or this is your first paper, Webster University's Writing Center offers writing support for students. Find help with all kinds of research projects, including "reports; résumés and cover letters; admission essays and personal statements; summaries, critical analyses, and literature reviews; research and term papers; theses and dissertations; and more." Writing Center coaches are available at all stages of the writing process from brainstorming to draft revision and everything in-between.
Visit Writing Support to:
- Schedule an appointment with a writing coach
- Submit a paper online to the Writing Center for review
- Select Writing Resources to find help with citation, grammar, avoiding plagiarism, and more
ChatGPT and similar tools are not credible sources of information; however, if your instructor allows other uses of AI applications in your course, you will still need to cite the output of those applications as you would any other source you use in your academic work. Citing the output of generative AI, for example large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, is a unique challenge in that these applications are not "authors," and the output itself is irretrievable by others even when referenced. Therefore, you may need to provide additional documentation when submitting your work, for example, the full prompts you used to generate the output along with transcriptions or screenshots of the output. Style guides differ greatly on how and when to cite AI-generated content, so it's important to read the style guidelines for full details . Below are examples from the MLA Style Center for how to cite generative AI in MLA style.
- How do I cite generative AI in MLA style? (MLA Style Center) Full explanation of how to cite generative AI in MLA.
Works-cited list:
“Describe the symbolism of the green light in the book The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald” prompt. ChatGPT , 13 Feb. version, OpenAI, 8 Mar. 2023, chat.openai.com/chat.
Paraphrased in your prose:
While the green light in The Great Gatsby might be said to chiefly symbolize four main things: optimism, the unattainability of the American dream, greed, and covetousness (“Describe the symbolism”), arguably the most important—the one that ties all four themes together—is greed.
- Last Updated: May 6, 2024 3:33 PM
- URL: https://library.webster.edu/mlastyle
- Collection Development Plan
- Staff Directory
- Library Policies
- GC Recommends
- Reserving spaces
- Instruction
- Off campus access
- Course Reserves
- Interlibrary Loan
- Visitor, Guest, & Alumni Policy
- Collections
- Databases & Electronic Resources
- Research Guides
Service Alert

Citation Styles and How to Guide
- Chicago & Turabian
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Writing & Citing Help
MLA Style is a citation style created by the Modern Language Association, which is how it got its name! Although it's most commonly used in the humanities, MLA can be used across many disciplines. Therefore, the current citation style for this edition is more like a set of guidelines rather than strict rules.
MLA Style is currently in the 9th edition. For an overview of changes between the 8th and 9th editions of MLA, check out this article from the Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL).
MLA Citation Style Basics
- Resources for Getting Started
- Formatting Paper
- In-Text Citations
- Works Cited
These are some recommended resources for getting started citing in MLA Style.
A collection of frequently asked questions about MLA style answered by the Modern Language Association.
From the creators of MLA Style, this is a great resource for getting started with MLA.
Purdue OWL provides a wealth of information in their MLA Formatting and Style Guide.
You must format your paper according to MLA guidelines if you are citing using MLA Style.
Purdue OWL provides some general guidelines for formatting your paper in MLA Style, which include:
- Papers should be typed
- Use double spacing
- 1 inch margins
- Use 12 pt. size font
- The first line of each paragraph should be indented with the Tab key
- On the first page of your paper, you should include the following information indented left: your name, your instructor's name, the course that the assignment is for, and the date. All subsequent pages should have a header in the top right corner with the page number.
- A Works Cited page at the end of your paper that includes all the sources
For MLA Style formatting examples, take a look at MLA Style Center's Sample Papers and Purdue OWL's Sample Papers .
MLA Style's in-text citations use parenthetical citations that consist of an author-page style.
The author's last name and page number(s) from where the quotation or paraphrase is taken appears in the text. The structure of the in-text citation will depend on whether you are paraphrasing or quoting the text. This in-text citation will correspond to a complete reference on the Works Cited page.
For example, if you are citing something paraphrased by Jasmine Plott on page 3 of her work, you would provide an in-text citation that looks as follows: (Plott 3) . The full citation would appear in the works cted page.
For more information about how to craft an in-text citation, refer to Purdue OWL's guidance available here .
Your Works Cited page appears at the end of your paper and will alphabetically lists all the sources that you included as in-text citations in your paper. For MLA Style, there are a set of core elements that serve as general guidelines for what should go into a citation. Structure your citations using the core elements listed below. Don't forget to include the punctuation after each element in the below list, since that is an important part of the citation too!
Try to include as many core elements as you can in your citation, but don't sweat it if some of the information simply isn't available. For instance, only some sources will have containers , which are bigger sources where that particular source is held. As an example, an entry in an encyclopedia would be the source, and the encyclopedia itself would be the container.
MLA Style Center's Works Cited: A Quick Guide, and Purdue OWL's MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format are recommended resources for getting more information about how to structure your Works Cited page. Check out the selected links from MLA Style Center and Purdue OWL for more detailed information!
MLA Style Center's overview of how to structure citations for a Works Cited page
Purdue OWL's information about the general format of a Works Cited page
MLA Style Center's examples for how to cite five basic source types: (1) books; (2) online works; (3) songs, recordings, and performances; (4) movies, videos, and television shows; and (5) images
Purdue OWL's guidance for basic book formatting, books with more than one author, book chapter, other print sources, etc.
Purdue OWL's guidance for scholarly journals, magazines, newspapers
Purdue OWL's guidance for websites, images, articles in databases, YouTube videos, etc
Purdue OWL's guidance for interviews, artwork, films, music, etc.
Purdue OWL's sample Works Cited page
Add / Reorder
- << Previous: APA
- Next: Chicago & Turabian >>
- Last Updated: Nov 1, 2023 4:04 PM
- URL: https://libguides.greensboro.edu/citationguide
MLA Format Guidelines
- Getting Started
- General Document Format
- Formatting Visuals
- In-Text Citations
- List of Sources
- Bias Free Language
For more guidance, visit Purdue OWL's MLA In-Text citation page.
- Purdue OWL's MLA In-Text Citation
Recommended MLA Websites
- MLA Citation Guide - Purdue Owl MLA style guidelines for formatting manuscripts and using the English language in writing.
- MLA In-Text Citations - Purdue Owl Describes how to write In-Text citations in your research assignments.
- MLA Works Cited Page - Purdue Owl How to format your Works Cited Page.
- MLA Works Cited Page - Purdue Owl A sample works cited page.
- Purdue OWL Sample Paper - MLA
Include the source's author (last name only) and page number (if applicable) in parentheses either at the end of sentence before the sentence-ending punctuation or before a natural break in the sentence, such as a semicolon or comma.
- Human beings have been described as "symbol-using animals" (Burke 3).
If the author's name is used in the sentence, include the page number in parentheses before a natural break or at the end of the sentence.
- Wordsworth stated that Romantic poetry was marked by a "spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings" (263).
If a quotation is more than four lines long in your document, indent it 0.5 inches on a new line without quotation marks around it. Double space the quotation, and insert closing punctuation before the parenthetical citation at the end.
At the end of Lord of the Flies the boys are struck with the realization of their behaviour:
The tears began to flow and sobs shook him. He gave himself up to them now for the first time on the island; great, shuddering spasms of grief that seemed to wrench his whole body. His voice rose under the black smoke before the burning wreckage of the island; and infected by that emotion, the other little boys began to shake and sob too. (Golding 186)
- The line before your long quotation, when you're introducing the quote, usually ends with a colon.
- The long quotation is indented half an inch from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- There are no quotation marks around the quotation.
- The period at the end of the quotation comes before your in-text citation as opposed to after , as it does with regular quotations.
Paraphrase or Summary
Unlike a direct quotation, a summary or paraphrase still relays ideas from a source but in your own words to make it fit better with your document. A paraphrase is a specific idea from a source that needs a citation with author and page number.
Paraphrasing from One Page
Include a full in-text citation with the author name and page number (if there is one). For example:
- Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65).
Paraphrasing from Multiple Pages
If the paraphrased information/idea is from several pages, include them.
- Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 50, 55, 65-71).
One or Multiple Authors
Citation rules vary based on how many authors a source. Consult the following table for how to handle these different situations.
Indirect (Secondary) Sources
When citing a quotation from a source, include the quotation's original author in text and insert a parenthetical citation that begins with the phrase "qtd. in" to indicate the source from which the quotation came.
- According to Allegeria, biology "revolves around the idea that the cell is a fundamental unit of life" (qtd. in Smith 15).
Authors with the Same Surname
In addition to the author's name and the page number(s), include a shortened version of the title to distinguish which source is being referenced.
- Mattias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, were scientists who formulated cell theory in 1838 (Smith, "Cell Theory" 20).
Anonymous Author
When a source's author is unknown, cite the first few words of the source's reference list entry, usually the title with appropriate formatting if an article (quotation marks) or book (italicized).
- Cell biology is an area of science that focuses on the structure and function of cells ( Cell Biology 15).
- << Previous: Formatting Visuals
- Next: List of Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 6:12 PM
- URL: https://tstc.libguides.com/mla
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

- Ask a Librarian
Locating and Using Images for Presentations and Coursework
- Free & Open Source Images
- How to Cite Images
- Alt Text Image Descriptions
Copyright Resources
- Copyright Term and the Public Domain in the United States from Cornell University Library
- Copyright Overview from Purdue University
- U.S. Copyright Office
- Fair Use Evaluator
- Visual Resources Association's Statement of Fair Use of Images for Teaching, Research, and Study
- Creative Commons Licenses
Attribution
Again, the majority of images you find are under copyright and cannot be used without permission from the creator. There are exceptions with Fair Use, but this Libguide is intended to help you locate images you can use with attribution (and in some case, the images are free to use without attribution when stated, such as with stock images from pixabay). ***Please read about public domain . These images aren't under copyright, but it's still good practice to include attribution if the information is available. Attribution : the act of attributing something, especially the ascribing of a work (as of literature or art) to a particular author or artist. When you have given proper attribution, it means you have given the information necessary for people to know who the creator of the work is.
Citation General Guidelines
Include as much of the information below when citing images in a paper and formal presentations. Apply the appropriate citation style (see below for APA, MLA examples).
- Image creator's name (artist, photographer, etc.)
- Title of the image
- Date the image (or work represented by the image) was created
- Date the image was posted online
- Date of access (the date you accessed the online image)
- Institution (gallery, museum) where the image is located/owned (if applicable)
- Website and/or Database name
Citing Images in MLA, APA, Chicago, and IEEE
- Directions for citing in MLA, APA, and Chicago MLA: Citing images in-text, incorporating images into the text of your paper, works cited APA 6th ed.: Citing images in-text and reference list Chicago 17th ed.: Citing images footnotes and endnotes and bibliography from Simon Fraser University
- How to Cite Images Using IEEE from the SAIT Reg Erhardt Library
- Image, Photograph, or Related Artwork (IEEE) from the Rochester Institute of Technology Library
Citing Images in Your PPT
Currently, citing images in PPT is a bit of the Wild West. If details aren't provided by an instructor, there are a number of ways to cite. What's most important is that if the image is not a free stock image, you give credit to the author for the work. Here are some options:
1. Some sites, such as Creative Commons and Wikimedia, include the citation information with the image. Use that citation when available. Copy the citation and add under the image. For example, an image of a lake from Creative Commons has this citation next to it: "lake" by barnyz is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 .
2. Include a marker, such as Image 1. or Figure 1., and in the reference section, include full citation information with the corresponding number
3. Include a complete citation (whatever the required format, such as APA) below the image
4. Below the image, include the link to the online image location
5. Hyperlink the title of the image with the online image location
- << Previous: Free & Open Source Images
- Next: Alt Text Image Descriptions >>
- Last Edited: Jun 8, 2023 3:28 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/images

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Purdue OWL, Purdue U Writing Lab. Accessed 18 Jun. 2018. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations ...
Resources on using in-text citations in MLA style. The Basics General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Works Cited Page. Resources on writing an MLA style works cited page, including citation formats. Basic Format
If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp ...
Cite a book automatically in MLA. The 8 th edition of the MLA handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any ...
Cite your source automatically in MLA. Use the following format for all sources: Author. Title. Title of container (self contained if book), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs URL or DOI). 2 nd container's title, Other contributors ...
Citations by Format. Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements—facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you're citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on ...
The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services. A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is ...
Purdue OWL MLA Guide. Comprehensive guide to using the MLA style from Purdue University. MLA Handbook (9th Edition) ... If a source is listed as an edition or version of a work, include it in your citation. (Purdue OWL) Number. If a source is part of a numbered sequence, such as a multi-volume book, or journal with both volume and issue numbers ...
This vidcast introduces the viewers to the basics of MLA style documentation, focusing on the list of works cited. For more information on this, please see t...
Formatting Your Research Project (MLA Handbook, Ch. 1) Instructions for formatting your paper in MLA style, including margins, title, headers and footers, headings and subheadings, etc. The Writing Process. Purdue OWL's Guide to academic writing in MLA Style, including grammar, mechanics, and punctuation.
Developed by the Purdue Online Writing Lab. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead. If the publication date is unknown, or if the content is ...
MLA - Purdue Owl The MLA Formatting and Style Guide page on Purdue OWL is a comprehensive resource for learning how to format papers and cite sources in MLA style. The guide covers all aspects of MLA style, from the basic formatting of a paper to the specific citation formats for different types of sources.
These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author's last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves. Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format: %%Last name of the author, First name of the author. "Source's Title.".
Basic MLA - Citation Guide - Library Guides at Purdue University Northwest. MLA. Changes in 9th edition. The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook was published in 2021. In this update, the format for both in-text and Works Cited citations is the same as the 8th edition. The 9th edition also includes this clarification on citing a film/DVD.
MLA citation guides in the library. MLA 9 th edition came out in April 2021. Check with your instructor to see which version you should use. MLA Handbook (9th ed.) Call Number: LB2369 .M52 2021. Copies of this can be found both in Reference on Level 2 and on Level 3. MLA Handbook (8th ed.) Call Number: LB 2369 .G53 2016.
MLA Style Center's examples for how to cite five basic source types: (1) books; (2) online works; (3) songs, recordings, and performances; (4) movies, videos, and television shows; and (5) images. MLA Works Cited Page: Books. Purdue OWL's guidance for basic book formatting, books with more than one author, book chapter, other print sources, etc ...
Include a full in-text citation with the author name and page number (if there is one). For example: Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65). Paraphrasing from Multiple Pages. If the paraphrased information/idea is from several pages, include them.
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
MLA: Citing images in-text, incorporating images into the text of your paper, works cited APA 6th ed.: Citing images in-text and reference list ... Purdue University, 610 Purdue Mall, West Lafayette, IN, 47907, 765-494-4600. Purdue University Libraries is a congressionally designated depository for U.S. Government information.
2/12/13 Purdue OWL. In-Text Citations: Author-Page Style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page.