
10 Case Study Advantages and Disadvantages
A case study in academic research is a detailed and in-depth examination of a specific instance or event, generally conducted through a qualitative approach to data.
The most common case study definition that I come across is is Robert K. Yin’s (2003, p. 13) quote provided below:
“An empirical inquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident.”
Researchers conduct case studies for a number of reasons, such as to explore complex phenomena within their real-life context, to look at a particularly interesting instance of a situation, or to dig deeper into something of interest identified in a wider-scale project.
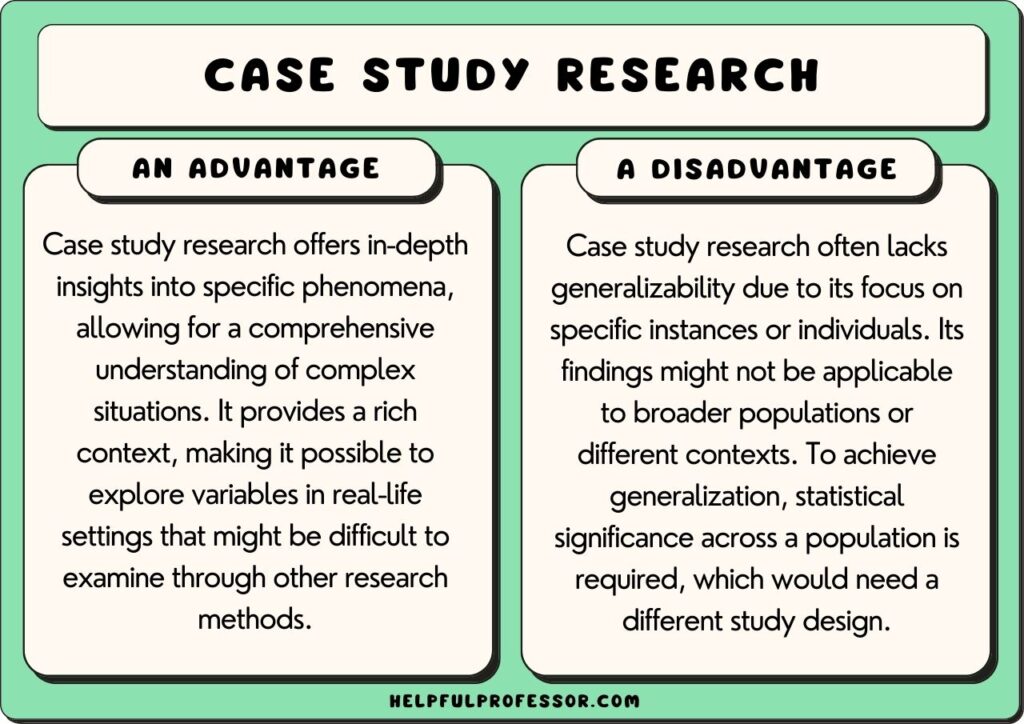
While case studies render extremely interesting data, they have many limitations and are not suitable for all studies. One key limitation is that a case study’s findings are not usually generalizable to broader populations because one instance cannot be used to infer trends across populations.
Case Study Advantages and Disadvantages
1. in-depth analysis of complex phenomena.
Case study design allows researchers to delve deeply into intricate issues and situations.
By focusing on a specific instance or event, researchers can uncover nuanced details and layers of understanding that might be missed with other research methods, especially large-scale survey studies.
As Lee and Saunders (2017) argue,
“It allows that particular event to be studies in detail so that its unique qualities may be identified.”
This depth of analysis can provide rich insights into the underlying factors and dynamics of the studied phenomenon.
2. Holistic Understanding
Building on the above point, case studies can help us to understand a topic holistically and from multiple angles.
This means the researcher isn’t restricted to just examining a topic by using a pre-determined set of questions, as with questionnaires. Instead, researchers can use qualitative methods to delve into the many different angles, perspectives, and contextual factors related to the case study.
We can turn to Lee and Saunders (2017) again, who notes that case study researchers “develop a deep, holistic understanding of a particular phenomenon” with the intent of deeply understanding the phenomenon.
3. Examination of rare and Unusual Phenomena
We need to use case study methods when we stumble upon “rare and unusual” (Lee & Saunders, 2017) phenomena that would tend to be seen as mere outliers in population studies.
Take, for example, a child genius. A population study of all children of that child’s age would merely see this child as an outlier in the dataset, and this child may even be removed in order to predict overall trends.
So, to truly come to an understanding of this child and get insights into the environmental conditions that led to this child’s remarkable cognitive development, we need to do an in-depth study of this child specifically – so, we’d use a case study.
4. Helps Reveal the Experiences of Marginalzied Groups
Just as rare and unsual cases can be overlooked in population studies, so too can the experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of marginalized groups.
As Lee and Saunders (2017) argue, “case studies are also extremely useful in helping the expression of the voices of people whose interests are often ignored.”
Take, for example, the experiences of minority populations as they navigate healthcare systems. This was for many years a “hidden” phenomenon, not examined by researchers. It took case study designs to truly reveal this phenomenon, which helped to raise practitioners’ awareness of the importance of cultural sensitivity in medicine.
5. Ideal in Situations where Researchers cannot Control the Variables
Experimental designs – where a study takes place in a lab or controlled environment – are excellent for determining cause and effect . But not all studies can take place in controlled environments (Tetnowski, 2015).
When we’re out in the field doing observational studies or similar fieldwork, we don’t have the freedom to isolate dependent and independent variables. We need to use alternate methods.
Case studies are ideal in such situations.
A case study design will allow researchers to deeply immerse themselves in a setting (potentially combining it with methods such as ethnography or researcher observation) in order to see how phenomena take place in real-life settings.
6. Supports the generation of new theories or hypotheses
While large-scale quantitative studies such as cross-sectional designs and population surveys are excellent at testing theories and hypotheses on a large scale, they need a hypothesis to start off with!
This is where case studies – in the form of grounded research – come in. Often, a case study doesn’t start with a hypothesis. Instead, it ends with a hypothesis based upon the findings within a singular setting.
The deep analysis allows for hypotheses to emerge, which can then be taken to larger-scale studies in order to conduct further, more generalizable, testing of the hypothesis or theory.
7. Reveals the Unexpected
When a largescale quantitative research project has a clear hypothesis that it will test, it often becomes very rigid and has tunnel-vision on just exploring the hypothesis.
Of course, a structured scientific examination of the effects of specific interventions targeted at specific variables is extermely valuable.
But narrowly-focused studies often fail to shine a spotlight on unexpected and emergent data. Here, case studies come in very useful. Oftentimes, researchers set their eyes on a phenomenon and, when examining it closely with case studies, identify data and come to conclusions that are unprecedented, unforeseen, and outright surprising.
As Lars Meier (2009, p. 975) marvels, “where else can we become a part of foreign social worlds and have the chance to become aware of the unexpected?”
Disadvantages
1. not usually generalizable.
Case studies are not generalizable because they tend not to look at a broad enough corpus of data to be able to infer that there is a trend across a population.
As Yang (2022) argues, “by definition, case studies can make no claims to be typical.”
Case studies focus on one specific instance of a phenomenon. They explore the context, nuances, and situational factors that have come to bear on the case study. This is really useful for bringing to light important, new, and surprising information, as I’ve already covered.
But , it’s not often useful for generating data that has validity beyond the specific case study being examined.
2. Subjectivity in interpretation
Case studies usually (but not always) use qualitative data which helps to get deep into a topic and explain it in human terms, finding insights unattainable by quantitative data.
But qualitative data in case studies relies heavily on researcher interpretation. While researchers can be trained and work hard to focus on minimizing subjectivity (through methods like triangulation), it often emerges – some might argue it’s innevitable in qualitative studies.
So, a criticism of case studies could be that they’re more prone to subjectivity – and researchers need to take strides to address this in their studies.
3. Difficulty in replicating results
Case study research is often non-replicable because the study takes place in complex real-world settings where variables are not controlled.
So, when returning to a setting to re-do or attempt to replicate a study, we often find that the variables have changed to such an extent that replication is difficult. Furthermore, new researchers (with new subjective eyes) may catch things that the other readers overlooked.
Replication is even harder when researchers attempt to replicate a case study design in a new setting or with different participants.
Comprehension Quiz for Students
Question 1: What benefit do case studies offer when exploring the experiences of marginalized groups?
a) They provide generalizable data. b) They help express the voices of often-ignored individuals. c) They control all variables for the study. d) They always start with a clear hypothesis.
Question 2: Why might case studies be considered ideal for situations where researchers cannot control all variables?
a) They provide a structured scientific examination. b) They allow for generalizability across populations. c) They focus on one specific instance of a phenomenon. d) They allow for deep immersion in real-life settings.
Question 3: What is a primary disadvantage of case studies in terms of data applicability?
a) They always focus on the unexpected. b) They are not usually generalizable. c) They support the generation of new theories. d) They provide a holistic understanding.
Question 4: Why might case studies be considered more prone to subjectivity?
a) They always use quantitative data. b) They heavily rely on researcher interpretation, especially with qualitative data. c) They are always replicable. d) They look at a broad corpus of data.
Question 5: In what situations are experimental designs, such as those conducted in labs, most valuable?
a) When there’s a need to study rare and unusual phenomena. b) When a holistic understanding is required. c) When determining cause-and-effect relationships. d) When the study focuses on marginalized groups.
Question 6: Why is replication challenging in case study research?
a) Because they always use qualitative data. b) Because they tend to focus on a broad corpus of data. c) Due to the changing variables in complex real-world settings. d) Because they always start with a hypothesis.
Lee, B., & Saunders, M. N. K. (2017). Conducting Case Study Research for Business and Management Students. SAGE Publications.
Meir, L. (2009). Feasting on the Benefits of Case Study Research. In Mills, A. J., Wiebe, E., & Durepos, G. (Eds.). Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (Vol. 2). London: SAGE Publications.
Tetnowski, J. (2015). Qualitative case study research design. Perspectives on fluency and fluency disorders , 25 (1), 39-45. ( Source )
Yang, S. L. (2022). The War on Corruption in China: Local Reform and Innovation . Taylor & Francis.
Yin, R. (2003). Case Study research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Home » Pros and Cons » 12 Case Study Method Advantages and Disadvantages
12 Case Study Method Advantages and Disadvantages
A case study is an investigation into an individual circumstance. The investigation may be of a single person, business, event, or group. The investigation involves collecting in-depth data about the individual entity through the use of several collection methods. Interviews and observation are two of the most common forms of data collection used.
The case study method was originally developed in the field of clinical medicine. It has expanded since to other industries to examine key results, either positive or negative, that were received through a specific set of decisions. This allows for the topic to be researched with great detail, allowing others to glean knowledge from the information presented.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of using the case study method.
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method
1. it turns client observations into useable data..
Case studies offer verifiable data from direct observations of the individual entity involved. These observations provide information about input processes. It can show the path taken which led to specific results being generated. Those observations make it possible for others, in similar circumstances, to potentially replicate the results discovered by the case study method.
2. It turns opinion into fact.
Case studies provide facts to study because you’re looking at data which was generated in real-time. It is a way for researchers to turn their opinions into information that can be verified as fact because there is a proven path of positive or negative development. Singling out a specific incident also provides in-depth details about the path of development, which gives it extra credibility to the outside observer.
3. It is relevant to all parties involved.
Case studies that are chosen well will be relevant to everyone who is participating in the process. Because there is such a high level of relevance involved, researchers are able to stay actively engaged in the data collection process. Participants are able to further their knowledge growth because there is interest in the outcome of the case study. Most importantly, the case study method essentially forces people to make a decision about the question being studied, then defend their position through the use of facts.
4. It uses a number of different research methodologies.
The case study method involves more than just interviews and direct observation. Case histories from a records database can be used with this method. Questionnaires can be distributed to participants in the entity being studies. Individuals who have kept diaries and journals about the entity being studied can be included. Even certain experimental tasks, such as a memory test, can be part of this research process.
5. It can be done remotely.
Researchers do not need to be present at a specific location or facility to utilize the case study method. Research can be obtained over the phone, through email, and other forms of remote communication. Even interviews can be conducted over the phone. That means this method is good for formative research that is exploratory in nature, even if it must be completed from a remote location.
6. It is inexpensive.
Compared to other methods of research, the case study method is rather inexpensive. The costs associated with this method involve accessing data, which can often be done for free. Even when there are in-person interviews or other on-site duties involved, the costs of reviewing the data are minimal.
7. It is very accessible to readers.
The case study method puts data into a usable format for those who read the data and note its outcome. Although there may be perspectives of the researcher included in the outcome, the goal of this method is to help the reader be able to identify specific concepts to which they also relate. That allows them to discover unusual features within the data, examine outliers that may be present, or draw conclusions from their own experiences.
List of the Disadvantages of the Case Study Method
1. it can have influence factors within the data..
Every person has their own unconscious bias. Although the case study method is designed to limit the influence of this bias by collecting fact-based data, it is the collector of the data who gets to define what is a “fact” and what is not. That means the real-time data being collected may be based on the results the researcher wants to see from the entity instead. By controlling how facts are collected, a research can control the results this method generates.
2. It takes longer to analyze the data.
The information collection process through the case study method takes much longer to collect than other research options. That is because there is an enormous amount of data which must be sifted through. It’s not just the researchers who can influence the outcome in this type of research method. Participants can also influence outcomes by given inaccurate or incomplete answers to questions they are asked. Researchers must verify the information presented to ensure its accuracy, and that takes time to complete.
3. It can be an inefficient process.
Case study methods require the participation of the individuals or entities involved for it to be a successful process. That means the skills of the researcher will help to determine the quality of information that is being received. Some participants may be quiet, unwilling to answer even basic questions about what is being studied. Others may be overly talkative, exploring tangents which have nothing to do with the case study at all. If researchers are unsure of how to manage this process, then incomplete data is often collected.
4. It requires a small sample size to be effective.
The case study method requires a small sample size for it to yield an effective amount of data to be analyzed. If there are different demographics involved with the entity, or there are different needs which must be examined, then the case study method becomes very inefficient.
5. It is a labor-intensive method of data collection.
The case study method requires researchers to have a high level of language skills to be successful with data collection. Researchers must be personally involved in every aspect of collecting the data as well. From reviewing files or entries personally to conducting personal interviews, the concepts and themes of this process are heavily reliant on the amount of work each researcher is willing to put into things.
These case study method advantages and disadvantages offer a look at the effectiveness of this research option. With the right skill set, it can be used as an effective tool to gather rich, detailed information about specific entities. Without the right skill set, the case study method becomes inefficient and inaccurate.
Related Posts:
- 25 Best Ways to Overcome the Fear of Failure
- Monroe's Motivated Sequence Explained [with Examples]
- 21 Most Effective Bundle Pricing Strategies with Examples
- Force Field Analysis Explained with Examples
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
- First Online: 27 October 2022
Cite this chapter

- R. M. Channaveer 4 &
- Rajendra Baikady 5
2531 Accesses
1 Citations
This chapter reviews the strengths and limitations of case study as a research method in social sciences. It provides an account of an evidence base to justify why a case study is best suitable for some research questions and why not for some other research questions. Case study designing around the research context, defining the structure and modality, conducting the study, collecting the data through triangulation mode, analysing the data, and interpreting the data and theory building at the end give a holistic view of it. In addition, the chapter also focuses on the types of case study and when and where to use case study as a research method in social science research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Ang, C. S., Lee, K. F., & Dipolog-Ubanan, G. F. (2019). Determinants of first-year student identity and satisfaction in higher education: A quantitative case study. SAGE Open, 9 (2), 215824401984668. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244019846689
Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2015). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report . Published. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2008.1573
Bhatta, T. P. (2018). Case study research, philosophical position and theory building: A methodological discussion. Dhaulagiri Journal of Sociology and Anthropology, 12 , 72–79. https://doi.org/10.3126/dsaj.v12i0.22182
Article Google Scholar
Bromley, P. D. (1990). Academic contributions to psychological counselling. A philosophy of science for the study of individual cases. Counselling Psychology Quarterly , 3 (3), 299–307.
Google Scholar
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 11 (1), 1–9.
Grässel, E., & Schirmer, B. (2006). The use of volunteers to support family carers of dementia patients: Results of a prospective longitudinal study investigating expectations towards and experience with training and professional support. Zeitschrift Fur Gerontologie Und Geriatrie, 39 (3), 217–226.
Greenwood, D., & Lowenthal, D. (2005). Case study as a means of researching social work and improving practitioner education. Journal of Social Work Practice, 19 (2), 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/02650530500144782
Gülseçen, S., & Kubat, A. (2006). Teaching ICT to teacher candidates using PBL: A qualitative and quantitative evaluation. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 9 (2), 96–106.
Gomm, R., Hammersley, M., & Foster, P. (2000). Case study and generalization. Case study method , 98–115.
Hamera, J., Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). Performance ethnography . SAGE.
Hayes, N. (2000). Doing psychological research (p. 133). Open University Press.
Harrison, H., Birks, M., Franklin, R., & Mills, J. (2017). Case study research: Foundations and methodological orientations. In Forum qualitative sozialforschung/forum: Qualitative social research (Vol. 18, No. 1).
Iwakabe, S., & Gazzola, N. (2009). From single-case studies to practice-based knowledge: Aggregating and synthesizing case studies. Psychotherapy Research, 19 (4–5), 601–611. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503300802688494
Johnson, M. P. (2006). Decision models for the location of community corrections centers. Environment and Planning b: Planning and Design, 33 (3), 393–412. https://doi.org/10.1068/b3125
Kaarbo, J., & Beasley, R. K. (1999). A practical guide to the comparative case study method in political psychology. Political Psychology, 20 (2), 369–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/0162-895x.00149
Lovell, G. I. (2006). Justice excused: The deployment of law in everyday political encounters. Law Society Review, 40 (2), 283–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5893.2006.00265.x
McDonough, S., & McDonough, S. (1997). Research methods as part of English language teacher education. English Language Teacher Education and Development, 3 (1), 84–96.
Meredith, J. (1998). Building operations management theory through case and field research. Journal of Operations Management, 16 (4), 441–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-6963(98)00023-0
Mills, A. J., Durepos, G., & Wiebe, E. (Eds.). (2009). Encyclopedia of case study research . Sage Publications.
Ochieng, P. A. (2009). An analysis of the strengths and limitation of qualitative and quantitative research paradigms. Problems of Education in the 21st Century , 13 , 13.
Page, E. B., Webb, E. J., Campell, D. T., Schwart, R. D., & Sechrest, L. (1966). Unobtrusive measures: Nonreactive research in the social sciences. American Educational Research Journal, 3 (4), 317. https://doi.org/10.2307/1162043
Rashid, Y., Rashid, A., Warraich, M. A., Sabir, S. S., & Waseem, A. (2019). Case study method: A step-by-step guide for business researchers. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 18 , 160940691986242. https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406919862424
Ridder, H. G. (2017). The theory contribution of case study research designs. Business Research, 10 (2), 281–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40685-017-0045-z
Sadeghi Moghadam, M. R., Ghasemnia Arabi, N., & Khoshsima, G. (2021). A Review of case study method in operations management research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 20 , 160940692110100. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069211010088
Sommer, B. B., & Sommer, R. (1997). A practical guide to behavioral research: Tools and techniques . Oxford University Press.
Stake, R. E. (2010). Qualitative research: Studying how things work .
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research . Sage Publications.
Stoecker, R. (1991). Evaluating and rethinking the case study. The Sociological Review, 39 (1), 88–112.
Suryani, A. (2013). Comparing case study and ethnography as qualitative research approaches .
Taylor, S., & Berridge, V. (2006). Medicinal plants and malaria: An historical case study of research at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the twentieth century. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 100 (8), 707–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.11.017
Tellis, W. (1997). Introduction to case study. The Qualitative Report . Published. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/1997.2024
Towne, L., & Shavelson, R. J. (2002). Scientific research in education . National Academy Press Publications Sales Office.
Widdowson, M. D. J. (2011). Case study research methodology. International Journal of Transactional Analysis Research, 2 (1), 25–34.
Yin, R. K. (2004). The case study anthology . Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Design and methods. Case Study Research , 3 (9.2).
Yin, R. K. (1994). Case study research: Design and methods (2nd ed.). Sage Publishing.
Yin, R. (1984). Case study research: Design and methods . Sage Publications Beverly Hills.
Yin, R. (1993). Applications of case study research . Sage Publishing.
Zainal, Z. (2003). An investigation into the effects of discipline-specific knowledge, proficiency and genre on reading comprehension and strategies of Malaysia ESP Students. Unpublished Ph. D. Thesis. University of Reading , 1 (1).
Zeisel, J. (1984). Inquiry by design: Tools for environment-behaviour research (No. 5). CUP archive.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Social Work, Central University of Karnataka, Kadaganchi, India
R. M. Channaveer
Department of Social Work, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rajendra Baikady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to R. M. Channaveer .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Centre for Family and Child Studies, Research Institute of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates
M. Rezaul Islam
Department of Development Studies, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Niaz Ahmed Khan
Department of Social Work, School of Humanities, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Channaveer, R.M., Baikady, R. (2022). Case Study. In: Islam, M.R., Khan, N.A., Baikady, R. (eds) Principles of Social Research Methodology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_21
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_21
Published : 27 October 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-5219-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-5441-2
eBook Packages : Social Sciences
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Communication
- Recreational

Pros and Cons of case studies
- Post author: admin
- Post published: March 27, 2020
- Post category: Education
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case studies are research methodologies that are used and analyzed in order to depict principles; they have been usually used in social sciences. They are research strategies and experiential inquiries that seek to examine various phenomena within a real-life context. Case studies seek to explain and give details in the analysis of people and events. There are several pros that back case studies and there are cons too that criticize them. The pros and cons are listed below.
1 . They show client observations- Since case studies are strategies that are used and analyzed in order to describe principles therefore it seeks to show indeed the client investigated and experienced a particular phenomenon.
2 . Makes practical improvements- Case studies present facts that categorically describe particular people or events in order to make some of the necessary improvements. Case studies data is what supports a particular belief.
3 . They are an influential way of portraying something- If a researcher wants to prove a particular principle to be true, he or she must back it by case studies in order to make the other people and the naysayers believe.
4 . They turn opinions into facts- Case studies present real data on a particular phenomenon. Since facts about various things are presented then it can be verified through this kind of data if the information presented is in the positive or negative development of opinion.
5 . It is relevant to all the parties that are involved- Case studies help the researchers in actively focusing on the data collection process and the participants’ knowledge is bettered. At the end of the process, everybody is able to defend his position through facts.
6 . A number of different research methodologies can be used in case the studies- Case study method goes beyond the interview and direct observations. Secondary data can be obtained from various historical sources that can be used to back the method.
7 . Case studies can be done remotely- It is not essential for a researcher to be present in the specific location of the study in order to effectively use the case study method. Other forms of communication come in to cover that gap for the researcher.
8 . It has a very high cost- If you put this research method in comparison to the others, this one seems more expensive because the cost of accessing data is very high.
9 . Readers can access data from this method very easily- The The format in which case studies present their data is very useful to the readers and easily note the outcomes of the same.
10 . Collects data that cannot be collected by another method- The type of data collected by case studies is much richer and greater in-depth than that of the other experimental methods.
1 . Data collected cannot be generalized- The data collected by the case study method was collected from a smaller population it cannot be generalized to the wider population.
2 . Some of the case studies are not scientific- The weakness of the data collected in some of the case studies that are not scientific is that it cannot be generalized.
3 . It is very difficult to draw a definite cause/effect from case studies- The the kind of data that case studies present cannot be used to draw a definite cause-effect relationship.
4 . Case studies concentrate on one experiment- The problem associated with concentrating on one experiment or a specific group of people is that the data presented might contain some kind of bias.
5 . It takes a lot of time to analyze the data- This process takes longer to analyze the data because there is a very large amount of data that must be collected. Participants might take a lot of time in giving answers or giving inaccurate information.
6 . Case studies can be inefficient processes- Sometimes the researchers are not present in the study areas which means they will not be able to notice whether the information provided is accurate or not terming the whole process inefficient.
7 . Case study method can only be effective with a small sample size- If a very large sample size is involved in the case study it is likely for it to become inefficient because the method requires a small sample size to get the data and analyze it.
8 . The method requires a lot of labor in data collection- The researcher is seriously needed in the data collection of this method. They have to be personally involved in order to be able to identify the quality of the data provided.
9 . There are factors that can influence the data- The method of data collection is meant to collect fact-based data but the power to determine what fact is and what is not is the person who is collecting the data.
10 . There is no right answer in case studies- Case studies do not present any specific answer that is right, the problem arises in the validation of solutions because there is more than one way of looking at things.
You Might Also Like

Pros and cons of co education
Pros and Cons of P/E Ratio

Pros and Cons of Using Technology in Education System
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Case Study Method: What are the Advantages and Disadvantages?
by Antony W
January 25, 2023
Case study method employs investigative inquiry to acquire data on certain demographics. The strategy is applicable to individuals, organizations, groups, and events.
Each participant receives an equal amount of engagement, providing data that may help to discover novel insights on particular patterns, ideas, or hypotheses.
In this guide, we look at the advantages and the disadvantages of case stud method as a technique of collecting data.
What is Case Study Method?
The case study method was a technique first established to generate and support hypotheses in clinical medicine. The technique was adapted to other sectors because of the benefits uncovered by these initiatives, allowing for the analysis of results through suggested decisions, procedures, or outcomes.
Its distinctive approach to knowledge enables others to discover special insights that foster development.
What are the Advantages of Case Study Methods?
The following are the advantages of case study methods:
1. It Offers a Detailed Examination of a Particular Unit.
When adopting the case study technique, researchers must document independently verifiable data from firsthand observations. The work provides information on the input mechanisms that contribute to the hypothesis under consideration .
2. Case Study Method is Useful When Creating a Hypothesis
Researchers will use this technique to test a proposed hypothesis. After finishing this effort, it is not unusual for the acquired facts to inspire the formation of new concepts.
This approach fosters more research because it permits notions to change as individuals do in their social and physical settings. This implies that a comprehensive data set may be collected depending on the abilities of the researcher and the candor of the participants in the study.
3. Case Study Method Provide Constant Examination of Facts
Using the case study technique, researchers will examine the social group’s facts in a continuous manner. This indicates there are no disruptions in the process that might compromise the authenticity of the data obtained for this project.
This benefit lowers the need to make assumptions when taking conclusions from the data, hence enhancing the long-term validity of the study’s findings. Thus, the conclusion becomes crucial to both sides of the equation, as it may either confirm certain hypotheses or refute the theory under discussion.
Due to the sheer volume of data being examined by academics, this benefit might result in inefficiency. It is the responsibility of the persons concerned to determine what is helpful and significant and what is not.
4. The Technique Allows for Comparison
Individual insights gleaned from collective settings comprise the human experience.
Certain demographics may think, behave, or respond to stimuli in certain ways, yet each member of that group will contribute a little portion to a whole.
The case study methodology enables researchers to compare information from each demographic group. This information can then lead to ideas that either support or disprove a theory.
5. It Gives an Expansion of Knowledge.
The case study technique equips everyone with the ability to expand his or her knowledge via analysis. This advantage is attainable due to the employment of a range of methods to collect data and evaluate hypotheses.
Researchers prefer to accomplish their job through direct observation and interviews, however surveys can also be beneficial. Participants may be required to record their experiences in a notebook or diary, and the information may help to analyze behaviors or decisions.
Some researchers use memory tests and experimental activities to predict how social groups would interact with or respond to particular scenarios. All of this information then serves to confirm the hypothesized possibilities.
6. Case Study Method Doesn’t Require Data Sampling
This research technique examines social units holistically as opposed to isolating and analyzing individual data pieces. Therefore, no sample is necessary when employing the case study technique.
The hypothesis under examination is supported because it seeks to transform views into facts by validating or rejecting future ideas that may be used by outside observers.
Although researchers may pay attention to specific incidences or results based on broader behaviors or concepts, the study itself will not sample such instances. Instead, it looks at the “larger picture.”
What are Disadvantages of Case Study Methods?
The following are the disadvantages of case study methods:
1. Case Study Methodology Provides Limited Representation
The use of the case study technique is restricted to a particular subset of representatives.
When selecting this option, researchers are targeting a certain demographic. This indicates that it is impossible to generalize the findings of this study to the rest of society, an organization, or a wider community.
Utilizing the case study technique is advantageous when seeking to determine the particular reasons why some individuals behave in a certain manner. But if researchers want something more generic, they must choose a different technique.
2. Case Study Method Makes Categorization Impossible
This shortcoming is also a result of the case study method’s small sample size.
Because researchers are examining such a small unit, group, or demography, categorization is impossible. Since the abilities of the researcher affect the quality of the data obtained to evaluate the validity of a hypothesis, the procedure might be inefficient.
Some individuals may be hesitant to answer or participate, while others may make educated guesses to support the conclusion.
3. It Doesn’t Exclude the Possibility of Errors
Individuals have an unconscious bias that shapes their actions and decisions.
Due to its emphasis on uncovering facts, the case study technique may quickly identify outliers that contradict a theory, but it is up to the researchers to choose what material counts as such.
If the outcomes of the case study technique are unexpected or contradict the opinions of the participants, it is still possible that the information is not 100 percent correct.
Researchers must have rules in place that regulate the process of data collection. The outcomes of the study cannot be reliable in the absence of this restriction due to the presence of bias.
4. Case Study Method is a Subjective Research Methodology
Although the goal of the case study research technique is to collect data, the information acquired is but opinion. It employs the subjective technique as opposed to the objective method for analyzing data, which implies that the information considered may have an additional layer of mistakes.
Imagine that a researcher undertaking direct observation misinterprets a participant’s answer as “anger” when the subject was actually experiencing “shame” due to a decision they made.
The gap between these two emotions is substantial, and it might lead to information disturbances that could be detrimental for the final proof of the hypothesis.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

Case Study: Types, Advantages And Disadvantages
Case Study: Types, Advantages And Disadvantages
Case study is both method and tool for research. Case study is the intensive study of a phenomenon, but it gives subjective information rather than objective. It gives detailed knowledge about the phenomena and is not able to generalize beyond the knowledge.
Case studies aim to analyze specific issues within the boundaries of a specific environment, situation or organization. According to its design, case study research method can be divided into three categories: explanatory, descriptive and exploratory.
Explanatory case studies aim to answer ‘how’ or ‘why’ questions with little control on behalf of the researcher over occurrence of events. This type of case study focuses on phenomena within the contexts of real-life situations.
Descriptive case studies aim to analyze the sequence of interpersonal events after a certain amount of time has passed. Case studies belonging to this category usually describe culture or sub-culture, and they attempt to discover the key phenomena.
Exploratory case studies aim to find answers to the questions of ‘what’ or ‘who’. Exploratory case study data collection method is often accompanied by additional data collection method(s) such as interviews, questionnaires, experiments etc.
DEFINITION OF CASE STUDY
The case study or case history method is not a newer thing, but it is a linear descendent of very ancient methods of sociological description and generalization namely, the ‘parable’, the ‘allegory’, the ‘story’ and the ‘novel’.
According to P.V. Young . “A fairly exhaustive study of a person or group is called a life of case history.”
Thus, the case study is more intensive in nature; the field of study is comparatively limited but has more depth in it.

TYPES OF CASE STUDY
Six types of case studies are conducted which are as follows:
Community Studies: The community study is a careful description and analysis of a group of people living together in a particular geographic location in a corporative way. The community study deals with such elements of the community as location, appearance, prevailing economic activity, climate and natural sources, historical development, how the people live, the social structure, goals and life values, an evaluation of the social institutions within the community that meet the human needs etc. Such studies are case studies, with the community serving as the case under investigation.
Casual Comparative Studies: Another type of study seeks to find the answers to the problems through the analysis of casual relationships. What factors seem to be associated with certain occurrences, conditions or types of behaviour? By the methodology of descriptive research, the relative importance of these factors may be investigated.
Activity Analysis: The analysis of the activities or processes that an individual is called upon to perform is important, both in industry and in various types of social agencies. This process of analysis is appropriate in any field of work and at all levels of responsibility. In social system, the roles of superintendent, the principal, the teacher and the custodian have been carefully analyzed to discover what these individuals do and need to be able to do.
Content or Document Analysis: Content analysis, sometimes known as document analysis. Deals with the systematic examination of current records or documents as sources of data. In documentary analysis, the following may be used as sources of data: official records and reports, printed forms, text-books, reference books, letters, autobiographies diaries, pictures, films and cartoons etc . But in using documentary sources, one must bear in mind the fact that data appearing in print is not necessarily trustworthy. This content or document analysis should serve a useful purpose in research, adding important knowledge to a field to study or yielding information that is helpful in evaluating and improving social or educational practices.
A Follow-up Study: A follow-up study investigates individuals who have left an institution after having completed programme, a treatment or a course of study, to know what has been the impact of the institutions and its programme upon them. By examining their status or seeking their opinions, one may get some idea of the adequacy or inadequacy of the institutes programme. Studies of this type enable an institution to evaluate various aspects of its programme in the light of actual results.
Trend Studies: The trend or predictive study is an interesting application of the descriptive method. In essence, it is based upon a longitudinal consideration of recorded data, indicating what has been happening in the past, what does the present situation reveal and on the basis of these data, what will be likely to happen in the future.
Whatever type of case study is to conduct, it’s important to first identify the purpose, goals, and approach for conducting methodologically sound research.
ADVANTAGES OF CASE STUDY
The main points of advantages of case study are given below:
Formation of valid hypothesis: Case study helps in formulating valid hypothesis. Once the various cases are extensively studied and analyze, the researcher can deduce various generalizations, which may be developed into useful hypotheses. It is admitted by all that the study of relevant literature and case study form the only potent sources of hypothesis.
Useful in framing questionnaires and schedules: Case study is of great help in framing questionnaires, schedules or other forms. When a questionnaire is prepared after thorough case study the peculiarities of the group as well as individual units, become known also the type of response likely to be available, liking and aversions of the people. This helps in getting prompt response.
Sampling: Case study is of help in the stratification of the sample. By studying the individual units the researcher can put them in definite classes or types and thereby facilitate the perfect stratification of the sample.
Location of deviant cases: The case study makes it possible to locate deviant cases. There exists a general tendency to ignore them, but for scientific analysis, they are very important. The analysis of such cases is of valuable help in clarifying the theory itself.
Study of process: In cases where the problem under study constitutes a process and not one incident e.g. courtship process, clique formation etc., case study is the appropriate method as the case data is essential for valid study of such problems.
Enlarges experience: The range of personal experience of the researcher is enlarged by the case study on the other hand in statistical methods a narrow range of topics is selected, and the researcher’s knowledge is restricted to the particular aspect only.
Qualitative analysis in actual situation: Case study enables the establishment of the significance of the recorded data when the individual is alive and later on within the life of the classes of individuals. The researcher has the opportunity to come into contact with different classes of people and he is in a position to watch their life and hear their experiences. This provides him with an opportunity to acquire experiences of such life situations which he is never expected to lead.
This discussion highlights the advantages of the case data in social research. Social scientists developed the techniques to make it more perfect and remove the chances of bias.
LIMITATIONS/DISADVANTAGES OF CASE STUDY METHOD
Subjective bias: Research subjectivity in collecting data for supporting or refuting a particular explanation, personal view of investigation influences the findings and conclusion of the study.
Problem of objectivity: Due to excessive association with the social unit under investigation the researcher may develop self-justificatory data which are far from being factual.
Difficulty in comparison: Because of wide variations among human beings in terms of their response and behaviour, attitudes and values, social setting and circumstances, etc., the researcher actually finds it difficult to trace out two social units which are identical in all respects. This hinders proper comparison of cases.
A time, energy and money consuming method: The preparation of a case history involves a lot of time and expenditure of human energy, therefore, there is every possibility that most of the cases may get stray. Due to such difficulties, only a few researchers can afford to case study method.
Time span: Long time span may be another factor that is likely to distort the information provided by the social unit to the researcher.
Unreliable source material: The two major sources of case study are: Personal documents and life history. But in both these cases, the records or the own experience of the social units may not present a true picture. On the contrary, the social unit may try to suppress his unpleasant facts or add colour to them. As a result, the conclusions drawn do not give a true picture and dependable findings.
Scope for wrong conclusions: The case study is laden with inaccurate observation, wrong inferences, faulty reporting, memory failure, repression or omission of unpleasant facts in an unconscious manner, dramatization of facts, more imaginary description, and difficulty in choosing a case typical of the group. All these problems provide the researcher with every possibility of drawing wrong conclusions and errors.
Case studies are complex because they generally involve multiple sources of data, may include multiple cases within a study and produce large amounts of data for analysis. Researchers from many disciplines use the case study method to build upon theory, to produce new theory, to dispute or challenge theory, to explain a situation, to provide a basis to apply solutions to situations, to explore, or to describe an object or phenomenon. The advantages of the case study method are its applicability to real-life, contemporary, human situations and its public accessibility through written reports. Case study results relate directly to the common readers everyday experience and facilitate an understanding of complex real-life situations.
__________________________________________________________________________
Research Methodology Methods and Techniques~C. R. Kothari (p.113) - Link
Fundamental of Research Methodology and Statistics~Yogesh Kumar Singh (Chapter–10: Case Study Method p. 147) - Link
Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches~W. Lawrence Neuman (p.42) - Link
The Basics of Social Research~Earl Babbie (p.280) - Link
Social Science Research Principles, Methods, and Practices~Anol Bhattacherjee (93) - Link
PREPARING A CASE STUDY: A Guide for Designing and Conducting a Case Study for Evaluation Input - Link
A Case in Case Study Methodology - Link
Case Study Method - Link1 & Link 2
Unit-4 Case Study - Link
Case study as a research method - Link
Case_Study~Tanya Sammut-Bonnici and John McGee - Link
Post a Comment
Contact form.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Professor of Business Administration, Distinguished University Service Professor, and former dean of Harvard Business School.
Partner Center

Case Study Method – 18 Advantages and Disadvantages
The case study method uses investigatory research as a way to collect data about specific demographics. This approach can apply to individuals, businesses, groups, or events. Each participant receives an equal amount of participation, offering information for collection that can then find new insights into specific trends, ideas, of hypotheses.
Interviews and research observation are the two standard methods of data collection used when following the case study method.
Researchers initially developed the case study method to develop and support hypotheses in clinical medicine. The benefits found in these efforts led the approach to transition to other industries, allowing for the examination of results through proposed decisions, processes, or outcomes. Its unique approach to information makes it possible for others to glean specific points of wisdom that encourage growth.
Several case study method advantages and disadvantages can appear when researchers take this approach.
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method
1. It requires an intensive study of a specific unit. Researchers must document verifiable data from direct observations when using the case study method. This work offers information about the input processes that go into the hypothesis under consideration. A casual approach to data-gathering work is not effective if a definitive outcome is desired. Each behavior, choice, or comment is a critical component that can verify or dispute the ideas being considered.
Intensive programs can require a significant amount of work for researchers, but it can also promote an improvement in the data collected. That means a hypothesis can receive immediate verification in some situations.
2. No sampling is required when following the case study method. This research method studies social units in their entire perspective instead of pulling individual data points out to analyze them. That means there is no sampling work required when using the case study method. The hypothesis under consideration receives support because it works to turn opinions into facts, verifying or denying the proposals that outside observers can use in the future.
Although researchers might pay attention to specific incidents or outcomes based on generalized behaviors or ideas, the study itself won’t sample those situations. It takes a look at the “bigger vision” instead.
3. This method offers a continuous analysis of the facts. The case study method will look at the facts continuously for the social group being studied by researchers. That means there aren’t interruptions in the process that could limit the validity of the data being collected through this work. This advantage reduces the need to use assumptions when drawing conclusions from the information, adding validity to the outcome of the study over time. That means the outcome becomes relevant to both sides of the equation as it can prove specific suppositions or invalidate a hypothesis under consideration.
This advantage can lead to inefficiencies because of the amount of data being studied by researchers. It is up to the individuals involved in the process to sort out what is useful and meaningful and what is not.
4. It is a useful approach to take when formulating a hypothesis. Researchers will use the case study method advantages to verify a hypothesis under consideration. It is not unusual for the collected data to lead people toward the formulation of new ideas after completing this work. This process encourages further study because it allows concepts to evolve as people do in social or physical environments. That means a complete data set can be gathered based on the skills of the researcher and the honesty of the individuals involved in the study itself.
Although this approach won’t develop a societal-level evaluation of a hypothesis, it can look at how specific groups will react in various circumstances. That information can lead to a better decision-making process in the future for everyone involved.
5. It provides an increase in knowledge. The case study method provides everyone with analytical power to increase knowledge. This advantage is possible because it uses a variety of methodologies to collect information while evaluating a hypothesis. Researchers prefer to use direct observation and interviews to complete their work, but it can also advantage through the use of questionnaires. Participants might need to fill out a journal or diary about their experiences that can be used to study behaviors or choices.
Some researchers incorporate memory tests and experimental tasks to determine how social groups will interact or respond in specific situations. All of this data then works to verify the possibilities that a hypothesis proposes.
6. The case study method allows for comparisons. The human experience is one that is built on individual observations from group situations. Specific demographics might think, act, or respond in particular ways to stimuli, but each person in that group will also contribute a small part to the whole. You could say that people are sponges that collect data from one another every day to create individual outcomes.
The case study method allows researchers to take the information from each demographic for comparison purposes. This information can then lead to proposals that support a hypothesis or lead to its disruption.
7. Data generalization is possible using the case study method. The case study method provides a foundation for data generalization, allowing researches to illustrate their statistical findings in meaningful ways. It puts the information into a usable format that almost anyone can use if they have the need to evaluate the hypothesis under consideration. This process makes it easier to discover unusual features, unique outcomes, or find conclusions that wouldn’t be available without this method. It does an excellent job of identifying specific concepts that relate to the proposed ideas that researchers were verifying through their work.
Generalization does not apply to a larger population group with the case study method. What researchers can do with this information is to suggest a predictable outcome when similar groups are placed in an equal situation.
8. It offers a comprehensive approach to research. Nothing gets ignored when using the case study method to collect information. Every person, place, or thing involved in the research receives the complete attention of those seeking data. The interactions are equal, which means the data is comprehensive and directly reflective of the group being observed.
This advantage means that there are fewer outliers to worry about when researching an idea, leading to a higher level of accuracy in the conclusions drawn by the researchers.
9. The identification of deviant cases is possible with this method. The case study method of research makes it easier to identify deviant cases that occur in each social group. These incidents are units (people) that behave in ways that go against the hypothesis under consideration. Instead of ignoring them like other options do when collecting data, this approach incorporates the “rogue” behavior to understand why it exists in the first place.
This advantage makes the eventual data and conclusions gathered more reliable because it incorporates the “alternative opinion” that exists. One might say that the case study method places as much emphasis on the yin as it does the yang so that the whole picture becomes available to the outside observer.
10. Questionnaire development is possible with the case study method. Interviews and direct observation are the preferred methods of implementing the case study method because it is cheap and done remotely. The information gathered by researchers can also lead to farming questionnaires that can farm additional data from those being studied. When all of the data resources come together, it is easier to formulate a conclusion that accurately reflects the demographics.
Some people in the case study method may try to manipulate the results for personal reasons, but this advantage makes it possible to identify this information readily. Then researchers can look into the thinking that goes into the dishonest behaviors observed.
List of the Disadvantages of the Case Study Method
1. The case study method offers limited representation. The usefulness of the case study method is limited to a specific group of representatives. Researchers are looking at a specific demographic when using this option. That means it is impossible to create any generalization that applies to the rest of society, an organization, or a larger community with this work. The findings can only apply to other groups caught in similar circumstances with the same experiences.
It is useful to use the case study method when attempting to discover the specific reasons why some people behave in a specific way. If researchers need something more generalized, then a different method must be used.
2. No classification is possible with the case study method. This disadvantage is also due to the sample size in the case study method. No classification is possible because researchers are studying such a small unit, group, or demographic. It can be an inefficient process since the skills of the researcher help to determine the quality of the data being collected to verify the validity of a hypothesis. Some participants may be unwilling to answer or participate, while others might try to guess at the outcome to support it.
Researchers can get trapped in a place where they explore more tangents than the actual hypothesis with this option. Classification can occur within the units being studied, but this data cannot extrapolate to other demographics.
3. The case study method still offers the possibility of errors. Each person has an unconscious bias that influences their behaviors and choices. The case study method can find outliers that oppose a hypothesis fairly easily thanks to its emphasis on finding facts, but it is up to the researchers to determine what information qualifies for this designation. If the results from the case study method are surprising or go against the opinion of participating individuals, then there is still the possibility that the information will not be 100% accurate.
Researchers must have controls in place that dictate how data gathering work occurs. Without this limitation in place, the results of the study cannot be guaranteed because of the presence of bias.
4. It is a subjective method to use for research. Although the purpose of the case study method of research is to gather facts, the foundation of what gets gathered is still based on opinion. It uses the subjective method instead of the objective one when evaluating data, which means there can be another layer of errors in the information to consider.
Imagine that a researcher interprets someone’s response as “angry” when performing direct observation, but the individual was feeling “shame” because of a decision they made. The difference between those two emotions is profound, and it could lead to information disruptions that could be problematic to the eventual work of hypothesis verification.
5. The processes required by the case study method are not useful for everyone. The case study method uses a person’s memories, explanations, and records from photographs and diaries to identify interactions on influences on psychological processes. People are given the chance to describe what happens in the world around them as a way for researchers to gather data. This process can be an advantage in some industries, but it can also be a worthless approach to some groups.
If the social group under study doesn’t have the information, knowledge, or wisdom to provide meaningful data, then the processes are no longer useful. Researchers must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of the case study method before starting their work to determine if the possibility of value exists. If it does not, then a different method may be necessary.
6. It is possible for bias to form in the data. It’s not just an unconscious bias that can form in the data when using the case study method. The narrow study approach can lead to outright discrimination in the data. Researchers can decide to ignore outliers or any other information that doesn’t support their hypothesis when using this method. The subjective nature of this approach makes it difficult to challenge the conclusions that get drawn from this work, and the limited pool of units (people) means that duplication is almost impossible.
That means unethical people can manipulate the results gathered by the case study method to their own advantage without much accountability in the process.
7. This method has no fixed limits to it. This method of research is highly dependent on situational circumstances rather than overarching societal or corporate truths. That means the researcher has no fixed limits of investigation. Even when controls are in place to limit bias or recommend specific activities, the case study method has enough flexibility built into its structures to allow for additional exploration. That means it is possible for this work to continue indefinitely, gathering data that never becomes useful.
Scientists began to track the health of 268 sophomores at Harvard in 1938. The Great Depression was in its final years at that point, so the study hoped to reveal clues that lead to happy and healthy lives. It continues still today, now incorporating the children of the original participants, providing over 80 years of information to sort through for conclusions.
8. The case study method is time-consuming and expensive. The case study method can be affordable in some situations, but the lack of fixed limits and the ability to pursue tangents can make it a costly process in most situations. It takes time to gather the data in the first place, and then researchers must interpret the information received so that they can use it for hypothesis evaluation. There are other methods of data collection that can be less expensive and provide results faster.
That doesn’t mean the case study method is useless. The individualization of results can help the decision-making process advance in a variety of industries successfully. It just takes more time to reach the appropriate conclusion, and that might be a resource that isn’t available.
The advantages and disadvantages of the case study method suggest that the helpfulness of this research option depends on the specific hypothesis under consideration. When researchers have the correct skills and mindset to gather data accurately, then it can lead to supportive data that can verify ideas with tremendous accuracy.
This research method can also be used unethically to produce specific results that can be difficult to challenge.
When bias enters into the structure of the case study method, the processes become inefficient, inaccurate, and harmful to the hypothesis. That’s why great care must be taken when designing a study with this approach. It might be a labor-intensive way to develop conclusions, but the outcomes are often worth the investments needed.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Benefits of Learning Through the Case Study Method

- 28 Nov 2023
While several factors make HBS Online unique —including a global Community and real-world outcomes —active learning through the case study method rises to the top.
In a 2023 City Square Associates survey, 74 percent of HBS Online learners who also took a course from another provider said HBS Online’s case method and real-world examples were better by comparison.
Here’s a primer on the case method, five benefits you could gain, and how to experience it for yourself.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is the Harvard Business School Case Study Method?
The case study method , or case method , is a learning technique in which you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it. After working through it yourself and with peers, you’re told how the scenario played out.
HBS pioneered the case method in 1922. Shortly before, in 1921, the first case was written.
“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it?” says HBS Professor Jan Rivkin, former senior associate dean and chair of HBS's master of business administration (MBA) program, in a video about the case method . “That skill—the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry to choose a course of action—that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
Originally developed for the in-person MBA classroom, HBS Online adapted the case method into an engaging, interactive online learning experience in 2014.
In HBS Online courses , you learn about each case from the business professional who experienced it. After reviewing their videos, you’re prompted to take their perspective and explain how you’d handle their situation.
You then get to read peers’ responses, “star” them, and comment to further the discussion. Afterward, you learn how the professional handled it and their key takeaways.
HBS Online’s adaptation of the case method incorporates the famed HBS “cold call,” in which you’re called on at random to make a decision without time to prepare.
“Learning came to life!” said Sheneka Balogun , chief administration officer and chief of staff at LeMoyne-Owen College, of her experience taking the Credential of Readiness (CORe) program . “The videos from the professors, the interactive cold calls where you were randomly selected to participate, and the case studies that enhanced and often captured the essence of objectives and learning goals were all embedded in each module. This made learning fun, engaging, and student-friendly.”
If you’re considering taking a course that leverages the case study method, here are five benefits you could experience.
5 Benefits of Learning Through Case Studies
1. take new perspectives.
The case method prompts you to consider a scenario from another person’s perspective. To work through the situation and come up with a solution, you must consider their circumstances, limitations, risk tolerance, stakeholders, resources, and potential consequences to assess how to respond.
Taking on new perspectives not only can help you navigate your own challenges but also others’. Putting yourself in someone else’s situation to understand their motivations and needs can go a long way when collaborating with stakeholders.
2. Hone Your Decision-Making Skills
Another skill you can build is the ability to make decisions effectively . The case study method forces you to use limited information to decide how to handle a problem—just like in the real world.
Throughout your career, you’ll need to make difficult decisions with incomplete or imperfect information—and sometimes, you won’t feel qualified to do so. Learning through the case method allows you to practice this skill in a low-stakes environment. When facing a real challenge, you’ll be better prepared to think quickly, collaborate with others, and present and defend your solution.
3. Become More Open-Minded
As you collaborate with peers on responses, it becomes clear that not everyone solves problems the same way. Exposing yourself to various approaches and perspectives can help you become a more open-minded professional.
When you’re part of a diverse group of learners from around the world, your experiences, cultures, and backgrounds contribute to a range of opinions on each case.
On the HBS Online course platform, you’re prompted to view and comment on others’ responses, and discussion is encouraged. This practice of considering others’ perspectives can make you more receptive in your career.
“You’d be surprised at how much you can learn from your peers,” said Ratnaditya Jonnalagadda , a software engineer who took CORe.
In addition to interacting with peers in the course platform, Jonnalagadda was part of the HBS Online Community , where he networked with other professionals and continued discussions sparked by course content.
“You get to understand your peers better, and students share examples of businesses implementing a concept from a module you just learned,” Jonnalagadda said. “It’s a very good way to cement the concepts in one's mind.”
4. Enhance Your Curiosity
One byproduct of taking on different perspectives is that it enables you to picture yourself in various roles, industries, and business functions.
“Each case offers an opportunity for students to see what resonates with them, what excites them, what bores them, which role they could imagine inhabiting in their careers,” says former HBS Dean Nitin Nohria in the Harvard Business Review . “Cases stimulate curiosity about the range of opportunities in the world and the many ways that students can make a difference as leaders.”
Through the case method, you can “try on” roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career .
5. Build Your Self-Confidence
Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader’s perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career.
According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey , 84 percent of HBS Online learners report feeling more confident making business decisions after taking a course.
“Self-confidence is difficult to teach or coach, but the case study method seems to instill it in people,” Nohria says in the Harvard Business Review . “There may well be other ways of learning these meta-skills, such as the repeated experience gained through practice or guidance from a gifted coach. However, under the direction of a masterful teacher, the case method can engage students and help them develop powerful meta-skills like no other form of teaching.”

How to Experience the Case Study Method
If the case method seems like a good fit for your learning style, experience it for yourself by taking an HBS Online course. Offerings span seven subject areas, including:
- Business essentials
- Leadership and management
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Finance and accounting
- Business in society
No matter which course or credential program you choose, you’ll examine case studies from real business professionals, work through their challenges alongside peers, and gain valuable insights to apply to your career.
Are you interested in discovering how HBS Online can help advance your career? Explore our course catalog and download our free guide —complete with interactive workbook sections—to determine if online learning is right for you and which course to take.

About the Author
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Review article, modernizing and harmonizing regulatory data requirements for genetically modified crops—perspectives from a workshop.

- 1 Corteva™ Agriscience, Indianapolis, IN, United States
- 2 CropLife International, Arlington, VA, United States
- 3 BASF Corporation, Research Triangle Park, NC, United States
- 4 Corteva™ Agriscience, Johnston, IA, United States
- 5 Syngenta Seeds LLC, Research Triangle Park, NC, United States
- 6 Bayer Crop Science, Chesterfield, MO, United States
Genetically modified (GM) crops that have been engineered to express transgenes have been in commercial use since 1995 and are annually grown on 200 million hectares globally. These crops have provided documented benefits to food security, rural economies, and the environment, with no substantiated case of food, feed, or environmental harm attributable to cultivation or consumption. Despite this extensive history of advantages and safety, the level of regulatory scrutiny has continually increased, placing undue burdens on regulators, developers, and society, while reinforcing consumer distrust of the technology. CropLife International held a workshop at the 16th International Society of Biosafety Research (ISBR) Symposium to examine the scientific basis for modernizing global regulatory frameworks for GM crops. Participants represented a spectrum of global stakeholders, including academic researchers, GM crop developers, regulatory consultants, and regulators. Concurrently examining the considerations of food and feed safety, along with environmental safety, for GM crops, the workshop presented recommendations for a core set of data that should always be considered, and supplementary (i.e., conditional) data that would be warranted only on a case-by-case basis to address specific plausible hypotheses of harm. Then, using a case-study involving a hypothetical GM maize event expressing two familiar traits (insect protection and herbicide tolerance), participants were asked to consider these recommendations and discuss if any additional data might be warranted to support a science-based risk assessment or for regulatory decision-making. The discussions during the workshop highlighted that the set of data to address the food, feed, and environmental safety of the hypothetical GM maize, in relation to a conventional comparator, could be modernized compared to current global regulatory requirements. If these scientific approaches to modernize data packages for GM crop regulation were adopted globally, GM crops could be commercialized in a more timely manner, thereby enabling development of more diverse GM traits to benefit growers, consumers, and the environment.
1 Introduction
Genetically modified (GM) crops that have been engineered to express transgenes have been commercially cultivated since 1995 and are annually grown on 200 million hectares globally. These crops have delivered important societal benefits, such as increased crop yields, resilience to adverse growing conditions, reduced tillage leading to improved soil health, reduction in the need for crop protection inputs, preservation of natural resources, and improved rural economies ( Klümper and Qaim, 2014 ; Dively et al., 2018 ; Zilberman et al., 2018 ; Smyth, 2020 ; Ala-Kokko et al., 2021 ; Macall et al., 2021 ; Peshin et al., 2021 ; Brookes, 2022a ; Brookes, 2022b ; Brookes, 2022c ). These benefits have led to rapid adoption of GM technology for agricultural production, including 80% of global cotton and 73% of global soybean. One-third of global maize production includes GM traits for herbicide tolerance, insect protection, or both ( AgbioInvestor, 2023 ). GM traits have been introduced in other row crops such as oilseed rape, sugar beet, and alfalfa and, at a smaller scale, in specialty crops such as apples, eggplant, squash and potatoes ( ISAAA, 2020 ). Hundreds of studies have been conducted to assess the safety of GM crops, and there have been no substantiated cases of resulting harm to people or livestock that consume GM crops or to the environment in which they are grown ( European Commission, 2010 ; Snell et al., 2012 ; Van Eenennaam and Young, 2014 ; NASEM, 2016 ).
Despite this track record of safety and benefits, regulatory data requirements for approval and commercialization of GM crops have continued to grow globally. GM technology is primarily limited to major global crops, like maize and soybean, and to major input traits, such as insect protection and herbicide tolerance. While there are many efforts underway to use GM technology for other traits and to improve minor crops, especially for small holders in the developing world ( David, 2009 ; Shelton, 2021 ; Woodruff, 2024 ), securing the regulatory approvals to enable cultivation and avoid potential trade disruptions can present often insurmountable challenges to commercialization. Only a few large multinational developers can afford the US$115 million cost and also persist for the 16 years that it currently takes, on average, to bring a new trait to the global market. More than one-third of those costs, and more than one-half of that time, are taken by the regulatory process ( AgbioInvestor, 2022 ). These extensive and complex regulatory systems also mean that governments must invest significant resources in developing and maintaining regulatory bodies staffed with sufficient people and expertise, creating a burden on taxpayers and society. Countries that cannot afford such an investment are missing out on the benefits of GM crops.
CropLife International and its member companies that develop GM crops (BASF, Bayer Crop Science, Corteva™ Agriscience, and Syngenta) have proposed a modernized regulatory framework and streamlining of data requirements for GM crops that is based on scientific rationale and builds on the 25 years of experience with the technology, and the history of its safe use ( Mathesius et al., 2020 ; Anderson et al., 2021 ; Bachman et al., 2021 ; Brune et al., 2021 ; Goodwin et al., 2021 ; McClain et al., 2021 ; Roper et al., 2021 ; Waters et al., 2021 ). The development of the proposed framework was motivated and guided by considering four key questions. 1) Are today’s regulations for GM crop approvals risk-proportionate? 2) Do today’s data requirements act as an unnecessary barrier to beneficial innovation? 3) How can knowledge and experience accumulated over the last 25 years inform modernization of regulations? 4) Can data requirements be streamlined and harmonized across countries and authorities? These questions were used to guide the determination of the types of data that are necessary to ensure GM crops are developed and deployed without increased risks for food and feed safety or the environment compared to conventional crops. Under this framework, core data, which are important for the problem formulation step of the risk assessment of the GM crop, were identified. The core data are used for problem formulation to identify plausible cause-and-effect hypotheses of harm from the GM crop. Depending upon the outcome of the problem formulation for a specific crop by trait combination, additional supplementary (i.e., conditional) studies may be needed, on a case-by-case basis, to analyze any plausible risk identified. Figure 1A outlines proposed core and supplemental studies for a Food and Feed Safety Assessment; Figure 1B outlines proposed core and supplemental studies for an Environmental Risk Assessment. CropLife International took an approach that is consistent with principles of risk assessment such that the proposed data requirements can fully inform decision-making by a regulatory agency, without the extraneous data present in many current regulatory submissions that does not meaningfully contribute to the risk assessment of the GM crop.
Figure 1 . (A) proposes a set of data recommended for a science-based food and feed safety assessment for a typical GM crop and considers as core studies: basic molecular characterization, protein characterization and expression, and protein safety (i.e., history of safe use of the protein and source organism and bioinformatics to identify potential toxins and allergens). The outcomes of these core data are used to inform the problem formulation step and decide, on a case-by-case basis which, if any, supplementary studies are needed to make a conclusion on safety ( Brune et al., 2021 ; Waters et al., 2021 ). (A) is adapted from Brune et al., 2021 and Waters et al., 2021 . (B) proposes a set of data recommended for a science-based environmental risk assessment for a typical GM crop and considers as data: understanding the receiving environment and the basic biology of the unmodified plant; assessing the agronomic similarity of the GM crop to its conventional counterparts (i.e., agronomic comparative assessment); and understanding the intended trait of the GM plant and assessment of how the intended trait may lead to environmental harm. The core data should be used first to inform the problem formulation. If a conclusion cannot be made about the pathway to harm using the core data, additional case-by-case hypothesis-driven supplementary studies should be considered ( Anderson et al., 2021 ).
To further examine whether CropLife International’s proposed modernized data requirements are sufficient for food and feed safety assessments and for environmental risk assessments, a workshop was held at the 16th International Society of Biosafety Research (ISBR) Symposium (St. Louis, USA) in 2023. Using a case study of a hypothetical GM maize event containing two familiar transgenic traits (herbicide resistance and insect protection). The workshop participants were charged with considering whether the proposed data in the case study are scientifically both necessary and sufficient to determine the food, feed and environmental safety of the hypothetical GM crop.: CropLife International member representatives that served as moderators during the workshop authored this publication to report the outcomes and summarize the discussions that took place among the participants. The participants varied in their backgrounds and prior experience with risk assessment and included individuals from regulatory agencies, technology developers, consultant groups, and academia. A wide range of geographical areas were represented.
2 Case study description
For the case study, a hypothetical GM maize event was presented to the workshop participants for evaluation. The hypothetical event was intentionally simple for this exercise (i.e., a familiar crop with traits that are similar to many transgenic events that have already been reviewed and approved by regulatory agencies globally, with several in commercial production for many years), which enabled the participants to analyze in greater depth the need for data that is routinely submitted but may not contribute to the safety assessment. More specifically, a maize ( Zea mays ) event containing a single insertion encoding for two proteins from a single T-DNA introduced using standard disarmed Agrobacterium tumefaciens-based transformation was described. The two hypothetical traits provide protection against lepidopteran pests and tolerance to treatment with glyphosate herbicide, using a hypothetical Cry1 protein from Bacillus thuringiensis ( Bt ) and a hypothetical EPSPS protein variant isolated from maize, respectively. The workshop participants were asked to separately consider a food and feed safety assessment or an environmental risk assessment for this same hypothetical GM maize event. Additional distinctions between the presentation of the case study for the different assessments are outlined below.
2.1 Food and feed safety assessment
For the Food and Feed Safety Assessment, the results from hypothetical evaluations of core data on the characterization and safety assessment of the event were provided (summarized in Table 1 ). Throughout this paper, the term ‘data’ refers to both the results of experiments or studies as well as information gathered from literature reviews, consensus documents and other similar sources. As described in Waters et al. (2021) , the core data for a food and feed safety assessment are: 1) molecular characterization, 2) protein characterization, and 3) protein safety (allergenicity and toxicity). The results of the molecular characterization demonstrated that there was an insertion of a single T-DNA sequence into the maize genomic DNA without any vector backbone sequences. There were no changes in the intended protein coding sequence and constitutive expression of both proteins were driven by familiar promoter elements (35S from cauliflower mosaic virus and ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays , respectively). Finally, the inserted DNA and the traits were indicated as being stable over three generations. The protein characterization data given to participants indicated that the molecular weight and amino acid sequence were as expected for both proteins. The function of the hypothetical Cry1 protein was established as having activity limited to target lepidopteran pest species, with no activity against other insect orders. Field tolerance to glyphosate from the hypothetical EPSPS protein variant was also as expected. The protein safety data indicated that both proteins are similar to proteins that have a history of safe use for food and feed; neither EPSPS proteins nor Cry proteins have any known toxicity or allergenicity concerns. Bioinformatics analysis comparing the amino acid sequences of both hypothetical proteins to a protein database also demonstrated that neither protein is related to any protein of toxicological concern nor related to any allergens in the qualified allergen database.
Table 1 . Summary of food and feed safety assessment core data of the hypothetical GM maize.
A familiar crop with familiar traits and minimal genetic disruptions was used for the workshop to promote discussion of what data is really needed to establish the food and feed safety of a GM crop event. It was also noted to workshop participants that extensive protein expression data in the plant was not obtained, nor was detailed proximate or nutrient composition data included. Further, while it was established that bioinformatics confirmed no homology to known allergens or toxins, no exposure assessments, no animal feeding studies, or other more direct assessments of potential for harm from the hypothetical event were included. As presented, the case study stated that considering 1) the assessment from the core data, 2) the familiarity of the crop and traits, and 3) the lack of direct interaction with other metabolic pathways of the plant, there was no hypothesis of food and/or feed safety risks for the new GM maize crop, and therefore additional supplementary data are not warranted to establish food and feed safety, in accordance with the approach established in Brune et al. (2021) , McClain et al. (2021) and Roper et al. (2021) .
2.2 Environmental risk assessment
For Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA), the intention of the case study was to model how problem formulation and core data should be leveraged to inform ERA of a GM crop for cultivation safety. Problem formulation is a process used in the ERA to develop plausible pathways to harm resulting from cultivation of the GM crop. Problem formulation first considers core data, then considers other data on a case-by-case basis if it is deemed necessary to inform the risk assessment. For ERA, core data includes information related to the receiving environment, description of basic biology of the unmodified plant, assessment of the agronomic similarity of the GM crop to its conventional counterparts, and characterization of the intended traits of the GM crop (summarized in Table 2 ). For the purpose of the case study, the protection goal was broadly stated as protection of biodiversity, specifically protection of beneficial or charismatic species. For the purposes of the workshop, the core characteristics of the event as described for the food and feed assessment were considered the same (e.g., molecular features), with additional information focused on agronomic and environmental aspects provided to guide the ERA discussion.
Table 2 . Summary of environmental risk assessment core data.
The participants were presented with the following set of core data (summarized in Table 2 ) and were asked to consider if a plausible pathway to harm could be developed related to weediness, invasiveness, gene flow to wild relatives or hazard to non-target organisms: 1) assessment of the receiving environment indicating no wild relatives of maize present in the cultivation country and no changes to the standard agronomic practices relative to non-modified maize; 2) assessment of the basic biology of maize, using consensus documents, demonstrating non-modified maize has no weediness characteristics and requires human intervention for propagation and survival; 3) multilocation field trial data demonstrating hypothetical maize was agronomically similar to non-modified maize; and 4) assessment of the intended phenotype (i.e., insect protection and herbicide tolerant traits are not intended to increase fitness or survival in the environment).
Based on the core data assessed, the case study proposed that there are no plausible hypotheses for how cultivation of the hypothetical maize could result in environmental harm related to weediness, invasiveness, and gene flow to wild relatives. Thus, additional data will not further contribute to meaningful assessment of environmental safety. However, the case study proposed that a plausible pathway to harm to non-target organisms could be developed based on the intended insect protection phenotype. The hypothetical Cry1 protein was presented as providing protection against specific lepidopteran insect pests (European corn borer, Asian corn borer, Southwestern corn borer, corn earworm, and fall armyworm).
The mode of action of Cry proteins in GM crops is well-documented ( Bravo et al., 2007 ; OECD, 2007 ). In this case study, additional supplemental protein expression data and non-target organism hazard data were provided to the participants, and they were asked to consider if additional plausible pathways to harm could be developed. The set of supplemental data (summarized in Table 3 ) was as follows: 1) multilocation field trial data measuring the concentration of the hypothetical Cry1 protein in several plant tissues to inform exposure assessment; 2) an exposure assessment for different non-target organisms to consider the likelihood and magnitude of exposure to the hypothetical Cry1 protein; and 3) results of non-target organism Tier I hazard studies for several surrogate species representing different taxonomic orders (e.g., ladybird beetle, a soil dwelling organism, and a non-target predator) conducted with the Cry1 protein in the diet.
Table 3 . Summary of environmental risk assessment supplementary data.
The multilocation field trial data showed that the Cry1 protein was only detectable (above the limit of detection) in the leaf and whole plant, with the highest concentration found in R1 leaf. The protein was below the limit of detection of the analytical assay in pollen and root. Based on the tissue expression, the exposure assessment concluded that since there is no expression of the Cry1 protein in pollen, there would be no route of exposure to non-target pollen feeding organisms (e.g., honeybee). Finally, the Tier I hazard studies indicated that no hazard was observed at concentrations that exceeded >10x the expected environmental concentration.
Usually, the assessment of adverse effects in non-target organisms follows a tiered approach that starts with laboratory studies at levels that exceed worst-case exposure conditions ( Romeis et al., 2011 ). Tier I laboratory studies with non-target organisms are typically conducted using at least 10X the worst-case expected environmental concentration. In this case, the results of the hypothetical Tier I dietary studies indicated no hazard (i.e., adverse effects) at concentrations that exceeded 10x the worst-case expected environmental concentration, and thus a conclusion that evidence is sufficient without conducting additional hazard testing was indicated. Based on data from the exposure assessment and non-target hazard assessment studies, the case study proposed that there were no plausible pathways to harm to non-target organisms due to lack of exposure and/or lack of risk because there were no adverse effects at concentrations that exceeded 10X the worst-case expected environmental concentration. Participants were asked to consider whether they agreed with the conclusions proposed by the case study based on core data and additional supplementary data related to protein expression, non-target organism exposure, and non-target organism hazard.
Additional information such as molecular data to confirm that the insert is an intact single copy, stable across generations, and that there is no insertion of DNA from the plasmid backbone were not provided in the ERA case study. These additional data for product characterization have historically been submitted to regulators as part of cultivation applications, but they are not directly relevant to ERA ( Anderson et al., 2021 ).
3 Learnings from breakout group discussions
After participants attended the introductory presentation session of the workshop, they were distributed into smaller discussion groups of approximately 10 people, with CropLife International member representatives serving as moderators. Each participant had the opportunity to choose either the Food and Feed Safety Assessment or the Environmental Risk Assessment, depending on their respective areas of interest.
The goal of the smaller group discussion sessions was to allow participants to go into deeper conversations about the proposed modernized paradigm for a risk assessment of a GM crop. Discussions were aided by a distribution of a printed booklet that included a description of the hypothetical GM maize event and the data collected, and that outlined the key concepts of using the core data for a Food and Feed Safety Assessment and Environmental Risk Assessment. Moderators provided some time for the participants to review the information and then introduced the case study by giving a brief overview of the information provided in each data section of the case study. Participants were encouraged to provide feedback and to bring up questions and/or comments about topics/elements of the case study that they considered not sufficiently covered by the data provided. They were also asked to complete a worksheet allowing for comments on the specific steps of the assessment process.
Discussions during this small group session were productive and highly informative. Overall, the participants were engaged, willing to discuss, and mostly supportive of the general assessment framework of primarily using core data and only using further assessments on a case-by-case basis.
A summary of key points from the breakout group discussions is shared below. This section is not intended to be a complete summary of the discussion, rather the authors have captured points of interest with an emphasis on points that are worth considering for future workshops and discussions on this topic.
3.1 Food and feed safety assessment
In the small group session, participants were asked to consider 1) the assessment from the core studies (see Table 1 ), 2) the familiarity of the crop and traits, and 3) the lack of direct interaction with other metabolic pathways of the plant, and then decide whether there was a hypothesis of food and/or feed safety risks for the new GM maize crop. Because of these considerations, the position for the case-study was that, for the hypothetical event, additional supplemental studies are not warranted to establish food and feed safety, and the participants discussed whether they agreed with this position.
Below are some key feedback and questions captured during the workshop regarding the proposed approach for the assessment of Food and Feed Safety of the hypothetical GM maize event.
3.1.1 Molecular characterization (transformation method, transformation construct, DNA insert characterization)
Overall, the participants agreed that the proposed molecular characterization core data is aligned with what is currently provided and that the information was sufficient to inform a food and feed safety assessment. One potential exception to the core data package that was discussed is data demonstrating that the insert is stable over at least three generations. The participants suggested that this study could be considered as supplemental, and not necessarily required as part of the core data package, if the insert is demonstrated to be inserted into the chromosome and is not interrupting endogenous genes or regulatory elements, and there is no other reason to expect that the insert might be unstable (e.g., insertion site near a transposon). There was some discussion that three generations of data may not be considered enough by all regulatory agencies and that additional generations could be required for polyploid crop species. Additionally, participants raised questions about Agrobacterium transformation not being targeted and discussed providing data on whether any internal genes were modified. It was also noted by workshop participants that the use of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) to characterize the insert is not yet accepted by all regulatory agencies, but also there was recognition of the utility of NGS to provide a more comprehensive characterization of the insert and the insertion site compared to traditional methods (e.g., Southern blots).
3.1.2 Protein characterization (molecular weight, protein sequence confirmation, protein function)
Participants agreed that the protein characterization information was sufficient to inform the food and feed safety assessment, with some discussions around whether a registrant would always be able to provide what is required, as some proteins may be more challenging to characterize (e.g., difficulties in isolating the proteins in an active form, generating specific antibodies, or generating SDS-PAGE and Western blot data). A question was also raised on maize codon optimization and if the protein would still be considered the same as the native version. Future workshops can reinforce that maize codon optimization of the GM trait gene does not alter the trait protein sequence. Thus, it should not change the safety profile of the protein if there is no change to the amino acid sequence. Discussion also occurred regarding familiarity with promoters and the relationship to expression levels. The participants discussed if there might be a need to better understand the protein expression levels for unfamiliar promoters and also if increased expression levels might raise a concern of potentially increased allergenicity risk.
3.1.3 Protein safety/toxicology/allergenicity (background, source, history of safe use, bioinformatics)
Participants agreed that the EPSPS protein information for safety was sufficient to inform the food and feed risk assessments, but questions were raised about Cry proteins around digestibility and heat stability. There was also discussion regarding how similar a protein would need to be to a known protein to be considered familiar. Additionally, concerns were raised in the small group discussion on the limited protein expression data provided in the case study as it related to an exposure assessment. In response, the moderators noted that an exposure assessment is not necessary, because no hazard was identified from the proteins. However, when a hazard is identified, then protein expression levels are needed to enable assessment of potential exposure ( Brune et al., 2021 ).
3.1.4 Additional information needed to determine event safety
It was stated by one participant that if there was a disruption of a native gene, then composition data could be requested. Discussion also occurred regarding the concept of History of Safe Use (HOSU), and the amount of data, time and similarity (e.g., consideration of minor protein sequence differences) needed to establish something as having sufficient familiarity to be considered safe without additional data. One participant suggested that protein sequence data would be needed to demonstrate a HOSU and could be useful in determining the activity of the protein.
3.1.5 General feedback for food and feed safety assessment
Although participants generally agreed that the case study with a familiar crop and familiar traits is a good starting point for the discussions, several suggestions were made for further discussions to also provide a case study on an unfamiliar event or protein, to lay out how each study informs the safety assessment, to provide more on the problem formulation process, and to provide more graphics and to use examples. Discussion also occurred around the challenges of communicating and making changes to the currently provided data in regulatory applications. On this topic, proposals from participants included suggestions to emphasize more the end goal of getting needed products on the market sooner with less regulatory burden for all stakeholders and to publish more data prior to submission of the application in the scientific literature, and to be ready to provide additional data upon request.
3.2 Environmental risk assessment
After introducing the case study, the CropLife International moderator described a list (provided with the case study) of the specific potential pathways to harm that are relevant to the cultivation of the hypothetical maize event. Additionally, an explanation for how the core data can be used to sufficiently assess environmental risk was provided. For plausible pathways to harm that may not be sufficiently addressed by the core data (i.e., potential harm to non-target organisms), another list of potential pathways to harm that are specific to non-target organism (NTO) exposure was also presented.
Below are some key feedback and questions captured during the workshop regarding the proposed approach for the Environmental Risk Assessment of the hypothetical GM maize event.
3.2.1 Weediness potential
There was an overall consensus among the workshop groups that weediness can be adequately assessed using only core data. Participants agreed that there is not a plausible pathway to harm in the case study since maize is highly domesticated and volunteers will not survive without human intervention and management. One group discussed questions around the potential for dormancy, which may be a weediness trait, and whether it can be assessed in the core data (multilocation field trial; Table 2 ). It was concluded within the groups that the similarity in agronomic characteristics between the GM maize event and the non-GM maize in the case study core data is sufficient to show that there is a highly unlikely risk of weediness potential. This follows the principle of placing risk in the context of current practice (i.e., that the modified maize will have no greater risk than that of cultivation of the non-modified maize) ( Raybould and MacDonald, 2018 ). However, one workshop group had unresolved discussions on whether a difference in agronomic performance between different geographical regions may result in differences in the risk assessment and what specific agronomic elements are the most relevant to consider. Some participants in this group proposed scenarios in which the agronomic data generated in field trials performed outside of the cultivation country may not sufficiently represent the agronomic outcomes of field trials performed within the cultivation country.
3.2.2 Gene flow potential to wild relatives
There was general consensus that there is no environmental safety concern of gene flow in the case study based on the core data because there were no wild relatives present in the hypothetical cultivating environment. There was some interest from participants in further exploring how the risk assessment and data requirements will change if the cultivation environment did contain wild relatives. Also, there was some discussion on the threshold of relatedness between the GM maize and a wild relative species that constitutes a safety concern in terms of gene flow. Ultimately, there was additional consensus that product registrants should demonstrate that there are no wild relative species that are reproductively compatible with GM maize (regardless of species relatedness) to position that there is no gene flow concern. Alternatively, if there are wild relative species in the area of cultivation an assessment of the likelihood and consequences of trait introgression into the wild relative population may be warranted based on a problem formulation approach ( Anderson et al., 2021 ). Participants generally stressed the importance of citing published literature (e.g., accepted consensus references on crop-specific biology) as part of the core data to support the environmental risk assessment. Although it was acknowledged that gene flow will not likely occur between GM maize and wild relatives in the case study example, there was some discussion around whether gene flow may occur between the GM maize and adjacent local non-GM maize varieties and negatively impact crop integrity and biodiversity. The case study focused on assessing plausible pathways to harm related to gene flow between GM maize and sexually compatible weedy relatives. Future workshops can address concerns that were raised about coexistence of GM and non-GM cropping systems. Such a workshop may have to distinguish between environmental risks and market or socio-political concerns. For example, countries that have landrace populations for which the genetic make-up per se is a protection goal may have societal concerns about coexistence (for example, there could be changes the genetic identity of the landrace).
3.2.3 Plausible pathways to harm for non-target organisms (NTO)
All groups aligned that the only plausible pathway to harm from the case study that could not be sufficiently addressed with core data alone was the potential for harm to NTOs from potential exposure to the hypothetical Cry1 protein ( Table 2 ). Participants discussed the plausible pathways to harm that are specific to NTOs. There was general agreement that no additional data was needed to assess the potential for the EPSPS protein conferring the herbicide tolerance trait to cause harm to NTOs. However, participants acknowledged that public perception of herbicide tolerance traits could influence regulatory decisions and may need to be considered when determining the registrability of a GM crop. Such perceptions are not reflective of an actual risk, and the additional data generated do not inform the science-based risk assessment. For other pathways to harm, there was consensus that if there was either no hazard or no detectable exposure, then there is low risk to NTOs. For example, honeybees that may directly consume maize pollen and NTO lepidopterans that may indirectly consume maize pollen that drifts onto their host plants should have low risk in the ERA case study since the GM maize event has expression less than the limit of detection (LOD) of the insecticidal protein in pollen tissue ( Table 2 ). It was generally accepted by workshop participants that if expression of the insecticidal protein is <LOD in tissues that might be consumed by an NTO, further toxicity testing to determine hazard is not warranted.
Participants were also mostly aligned that aquatic environments generally experience minimal exposure to GM crop tissue and so additional toxicity testing is not needed for aquatic NTO species in most situations. However, some participants expressed uncertainty on whether this may be an issue if GM crops are cultivated very close to aquatic environments, which may affect exposure levels to NTO aquatic species. For NTO species where there is a plausible pathway to harm, all groups agreed that further data (exposure assessment or NTO Tier I laboratory testing) might be needed. Some discussions among participants regarding appropriate surrogate species to use for NTO testing and to what extent test species need to match those found in the cultivation regions were not resolved in the workshop. There was some additional discussion around the large body of scientific literature describing the surrogate species concept for testing Cry proteins and other types of plant incorporated protectants (e.g., Romeis, et al., 2011 ; Romeis et al., 2013 ; Bachman et al., 2021 ). While the terms “focal species” and “indicator species” were not discussed directly as part of the workshop, understanding protection goals and selecting appropriate surrogate species or indicator species to inform the science-based assessment of risk is an important consideration ( Rose, 2007 ; Roberts et al., 2020 ). Despite the lack of consensus on species selection, there was clear alignment among participants that NTO species representatives should only be tested if there is a valid hypothesis that there is a plausible pathway to harm for that specific organism type. For this reason, NTO studies should only be conducted when hypothesis-driven ( Figure 1B ).
3.2.4 General feedback and future considerations for ERA
Although participants agreed that a generic ERA case study is a good starting place, participants indicated that future workshops using a modified case study tailored for specific geographical regions will be even more helpful. As different countries have different sets of questions and concerns from local regulatory agencies, using more country-specific scenarios and less familiar pest-control traits in a case study may be more directly relevant in that region.
Related to gene flow, there was not a consensus about potential for harm in small team discussions. Future workshops would benefit from guided discussion to help develop problem formulation for gene flow. For example, it could be established as a baseline that for gene flow to occur naturally in the environment, and when assessing the potential for harm from gene flow between GM maize and local maize varieties, it should be compared to potential for harm from gene flow of non-GM maize and local maize varieties ( OECD, 2023 ). Furthermore, future workshops can reinforce that if gene flow to local maize varieties is a relevant concern for a specific cultivation country, then there is a large body of literature to leverage to assess if additional data is needed to inform the risk assessment (See OECD, 2023 Annex B for recent review) such a workshop would need to distinguish between the true environmental impact and concerns related to trade or economic issues.
Also, there were productive discussions on the topic of data transportability. Participants generally accepted the concept of transportability for lab study data. However, due to a lack of time for discussion, some unresolved questions remained regarding the transportability of field study data. Future workshops will benefit from guided discussion to help explain the principle of data transportability. An underlying principle of data transportability is that if no biologically relevant differences between a GM crop and its conventional counterparts are observed in one country or region, data from these studies can be used to inform the risk assessment in another country, regardless of agroclimatic zone ( Bachman et al., 2021 ). Following the recommendations for modernizing global regulatory frameworks for GM crops, additional agronomic data should only be collected in the local environment if there are plausible pathways for harm that cannot be fully informed by the core data.
Furthermore, there was some interest from participants in discussing how the proposed risk assessment paradigm might apply to combined GM products (i.e., breeding stacks), yield and stress traits (e.g., drought resistance), and streamlining of import registrations.
One topic that generated discussion across groups was the value of product characterization data in an environmental risk assessment. In the proposed modernized regulatory framework ( Anderson et al., 2021 ), underlying characterization data for the GM event are not regarded as core to the regulatory assessments (such as molecular data to confirm that the insert is an intact single copy, stable across generations, and that there is no plasmid backbone DNA). Although these data do not directly inform the ERA ( Anderson et al., 2021 ), it was discussed that an understanding of the characteristics of the GM product provides foundational information that enables the regulatory assessments to focus on the intended introduced trait during the problem formulation stage. Therefore, it was proposed to consider including, as part of the modernized ERA framework, a set of foundational information and data from the characterization of the GM event that confirms that (1) the intended gene sequence was inserted and functions as intended, as well as the number of such insertions; (2) the plants produce the intended newly expressed protein (NEP); (3) the intended phenotype is achieved.
4 Key considerations and takeaways from the workshop
The case study for the workshop considered a single event, albeit one that contained genetic material encoding for two proteins leading to two distinct traits (herbicide tolerance and insect protection). However, the majority of commercialized products contain multiple GM events that are combined through conventional breeding (also known as stacked trait products). The typical regulatory process first assesses all single events, before applying regulatory processes, if any, to the stacked trait products. In this sense, the case study used for the workshop reflected a realistic scenario in which regulators assess a single event regardless of whether the event will be commercialized as a single event or as a stacked trait product.
Regulatory processes for stacked trait products vary globally, with many countries recognizing the long, safe history of conventional breeding and not requiring additional assessment once all the single events are approved. It is the position of CropLife International that additional safety assessment of a stacked trait product produced by conventional breeding should not be required unless there is a plausible and testable hypothesis for interaction of the traits ( Goodwin et al., 2021 ). This case study did not address stacked trait products however, further iterations could include consideration of stacked trait products and how to evaluate possible interaction of traits.
The workshop was convened to explore the proposed modernized data requirements for regulatory assessments of GM crops ( Anderson et al., 2021 ; Waters et al., 2021 ). The participants were charged with considering whether currently implemented regulations for GM crops are risk-proportionate or whether they create an unwarranted barrier to the introduction of new traits. The organizers presented a position that knowledge and experience from 25 years of research and development could inform regulatory modernization and that streamlined data requirements could advance harmonization across countries and authorities.
Overall, considering the case study discussed, the participants at the workshop found the proposed modernized data requirements generally to be necessary and sufficient for decision making to support the safe commercial introduction of a new GM crop. There was a clear consensus that some of the current data requirements are no longer routinely warranted for familiar traits such as that discussed in the case study, given the track record of GM crops not presenting unexpected or unintended effects on food or feed safety or environmental risk relative to their conventional counterparts. Participants appreciated the benefit of harmonized hypothesis-based risk assessments to enable future deployment of GM crops that can address emerging agricultural challenges associated with increasing demand for affordable healthy food and changing agricultural environments. The points discussed in this publication will be used to further clarify recommendations for supplementary case-by-case data and guide the development of future, more targeted workshops and related discussions. In particular, applying the proposed framework to traits and crops with which there is less familiarity and established HOSU than those used in the case study may be associated with greater uncertainty in the foundational information of the GM event. Additional case studies involving less familiar traits and different crops should be used to further test the robustness of the modernized regulatory framework.
The workshop focused on what data was scientifically necessary and sufficient to make a conclusion on the food, feed and environmental safety of the GM crop. However, several participants noted that certain data not included in the case study was either required in their jurisdiction or routinely submitted by applicants. While it was beyond the scope of this workshop, future targeted workshops or symposia could address the extent to which regulatory authorities have the flexibility to decide, on a case-by-case basis, what data is necessary to make a conclusion on safety. In some jurisdictions the recommendations of the modernization project could be implemented by applicants by including a scientific rationale in their submission for why a specific study is not necessary. In other cases, changes to laws, regulations, or written guidance would be needed to implement these recommendations.
The case study for the first workshop, as described in this publication, was a valuable tool to foster discussion about science-based data requirements for the assessment of GM crops. If these scientific approaches to modernize data packages for GM crop regulation were adopted globally, delays to the commercialization of GM crops could be reduced, thereby allowing farmers access to new GM traits that will benefit not just growers, but consumers and the environment as well. For more information on the case study used in the workshop, or if there is interest in hosting a similar workshop, please contact the corresponding author.
Author contributions
NS: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AS: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JA: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MH: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. DM: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. CM: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. SS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. EU-W: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. CropLife International supported the open access publication of this work. The funder was not involved in the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Conflict of interest
Authors NS, JA, and CM were employed by Corteva™ Agriscience. Author AS was employed by CropLife International. Authors JS and MS were employed by BASF Corporation. Authors MH and SS were employed by Syngenta Seeds LLC. Authors DM and E-UW were employed by Bayer Crop Science. BASF Corporation, Bayer Crop Science, Corteva™ Agriscience, and Syngenta Seeds LLC are commercial developers of GM crops.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
AgbioInvestor (2022). Time and cost to develop a new GM trait. Available at: https://agbioinvestor.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/AgbioInvestor-Time-and-Cost-to-Develop-a-New-GM-Trait.pdf (Accessed November 18, 2023).
Google Scholar
AgbioInvestor (2023). Global GM crop area review. Available at: https://gm.agbioinvestor.com/downloads (Accessed November 29, 2023).
Ala-Kokko, K., Lanier Nalley, L., Shew, A. M., Tack, J. B., Chaminuka, P., Matlock, M. D., et al. (2021). Economic and ecosystem impacts of GM maize in South Africa. Glob. Food Secur. 29, 100544. doi:10.1016/j.gfs.2021.100544
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Anderson, J., Bachman, P. M., Burns, A., Chakravarthy, S., Goodwin, L., Privalle, L., et al. (2021). Streamlining data requirements for the environmental risk assessment of genetically modified (GM) crops for cultivation approvals. J. Regul. Sci. 9 (1), 26–37. doi:10.21423/jrs-v09i1anderson
Bachman, P. M., Anderson, J., Burns, A., Chakravarthy, S., Goodwin, L., Privalle, L., et al. (2021). Data transportability for studies performed to support an environmental risk assessment for genetically modified (GM) crops. J. Regul. Sci. 9 (1), 38–44. doi:10.21423/jrs-v09i1bachman
Bravo, A., Gill, S. S., and Soberón, M. (2007). Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 49 (4), 423–435. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.11.022
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Brookes, G. (2022a). Farm income and production impacts from the use of genetically modified (GM) crop technology 1996-2020. Gm. Crops Food 13 (1), 171–195. doi:10.1080/21645698.2022.2105626
Brookes, G. (2022b). Genetically modified (GM) crop use 1996–2020: environmental impacts associated with pesticide use change. Gm. Crops Food 13 (1), 262–289. doi:10.1080/21645698.2022.2118497
Brookes, G. (2022c). Genetically modified (GM) crop use 1996–2020: impacts on carbon emissions. Gm. Crops Food 13 (1), 242–261. doi:10.1080/21645698.2022.2118495
Brune, P., Chakravarthy, S., Graser, G., Mathesius, C. A., McClain, S., Petrick, J. S., et al. (2021). Core and supplementary studies to assess the safety of genetically modified (GM) plants used for food and feed. J. Regul. Sci. 9 (1), 45–60. doi:10.21423/jrs-v09i1brune
Clark, B. W., Phillips, T. A., and Coats, J. R. (2005). Environmental fate and effects of Bacillus thuringiensis (bt) proteins from transgenic crops: a review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53 (12), 4643–4653. doi:10.1021/jf040442k
David, M. A. (2009). GAIN report: Nigeria agricultural biotechnology annual report. Available at: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/Report/DownloadReportByFileName?fileName=AGRICULTURAL%20BIOTECHNOLOGY%20ANNUAL_Lagos_Nigeria_8-3-2009 (Accessed February 12, 2024).
Dively, G. P., Venugopal, P. D., Bean, D., Whalen, J., Holmstrom, K., Kuhar, T. P., et al. (2018). Regional pest suppression associated with widespread Bt maize adoption benefits vegetable growers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115 (13), 3320–3325. doi:10.1073/pnas.1720692115
European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation (2010). A decade of EU-funded GMO research (2001-2010) . Brussels: European Commission . doi:10.2777/97784
Goodwin, L., Hunst, P., Burzio, L. A., Rowe, L., Money, S., and Chakravarthy, S. (2021). Stacked trait products are as safe as non-genetically modified (GM) products developed by conventional breeding practices. J. Regul. Sci. 9 (1), 22–25. doi:10.21423/jrs-v09i1goodwin
Icoz, I., and Stotzky, G. (2008). Fate and effects of insect-resistant Bt crops in soil ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 40 (3), 559–586. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.11.002
International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA) (2020). Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops in 2019 (brief 55). Available at: https://www.isaaa.org/resources/publications/briefs/55/executivesummary/default.asp .
International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA) (2023). ISAAA’s GM approval database. Available at: https://www.isaaa.org/gmapprovaldatabase (Accessed September 14, 2023).
Klümper, W., and Qaim, M. (2014). A meta-analysis of the impacts of genetically modified crops. PLoS ONE 9 (11), e111629. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111629
Macall, D. M., Trabanino, C. R., Soto, A. H., and Smyth, S. J. (2020). Genetically modified maize impacts in Honduras: production and social issues. Transgenic Res. 29 (5), 575–586. doi:10.1007/s11248-020-00221-y
Mathesius, C. A., Sauve-Ciencewicki, A., Anderson, J., Cleveland, C., Fleming, C., Frierdich, G. E., et al. (2020). Recommendations for assessing human dietary exposure to newly expressed proteins in genetically modified crops. J. Regul. Sci. 8, 1–12. doi:10.21423/JRS-V08MATHESIUS
McClain, S., Herman, R. A., Islamovic, E., Ranjan, R., Silvanovich, A., Song, P., et al. (2021). Allergy risk assessment for newly expressed proteins (NEPs) in genetically modified (GM) plants. J. Regul. Sci. 9 (1), 67–75. doi:10.21423/jrs-v09i1mcclain
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (2016). Genetically engineered crops: experiences and prospects . Washington, DC, USA: The National Academies Press US . doi:10.17226/23395
OECD (2003). Consensus document on the biology of Zea mays subsp. mays (maize) . ENV/JM/MONO(2007)14. Paris, France: Organisation for Economic Cooperative Development . Available at: https://one.oecd.org/document/env/jm/mono(2003)11/en/pdf .
OECD (2007). Consensus document on safety information on transgenic plants expressing Bacillus thuringiensis - derived insect control protein . ENV/JM/MONO(2003)11. Paris, France: Organisation for Economic Cooperative Development . Available at: https://one.oecd.org/document/env/jm/mono(2007)14/en/pdf .
OECD (2023). Consensus document on environmental considerations for the release of transgenic plants, harmonisation of regulatory oversight in biotechnology . ENV/CBC/MONO(2023)30. Paris, France: Organisation for Economic Cooperative Development . doi:10.1787/62ed0e04-en
Peshin, R., Hansra, B. S., Singh, K., Nanda, R., Sharma, R., Yangsdon, S., et al. (2021). Long-term impact of Bt cotton: an empirical evidence from North India. J. Clean. Prod. 312, 127575. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127575
Raybould, A., and Macdonald, P. (2018). Policy-led comparative environmental risk assessment of genetically modified crops: testing for increased risk rather than profiling phenotypes leads to predictable and transparent decision-making. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 6, 43. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2018.00043
Raybould, A., Stacey, D., Vlachos, D., Graser, G., Li, X., and Joseph, R. (2007). Non-target organism risk assessment of MIR604 maize expressing mCry3A for control of corn rootworm. J. Appl. Entomology 131 (6), 391–399. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0418.2007.01200.x
Roberts, A., Boeckman, C. J., Mühl, M., Romeis, J., Teem, J. L., Valicente, F. H., et al. (2020). Sublethal endpoints in non-target organism testing for insect-active GE crops. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 556. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.00556
Romeis, J., Hellmich, R., Candolfi, M., Carstens, K., De Schrijver, A., Gatehouse, A., et al. (2011). Recommendations for the design of laboratory studies on non-target arthropods for risk assessment of genetically engineered plants. Transgenic Res. 20 (1), 1–22. doi:10.1007/s11248-010-9446-x
Romeis, J., McLean, M. A., and Shelton, A. M. (2013). When bad science makes good headlines: bt maize and regulatory bans. Nat. Biotech. 31 (5), 386–387. doi:10.1038/nbt.2578
Roper, J., Lipscomb, E. A., Petrick, J. S., Ranjan, R., Sauve-Ciencewicki, A., and Goodwin, L. (2021). Toxicological assessment of newly expressed proteins (NEPs) in genetically modified (GM) plants. J. Regul. Sci. 9 (1), 61–66. doi:10.21423/jrs-v09i1roper
Rose, R. I. (2007). White paper on tier-based testing for the effects of proteinaceous insecticidal plant-incorporated protectants on NonTarget arthropods for regulatory risk assessments. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/tier-based-testing.pdf (Accessed April 2, 2024).
Shelton, A. M. (2021). Bt eggplant: a personal account of using biotechnology to improve the lives of resource-poor farmers. Am. Entomologist 67 (3), 52–59. doi:10.1093/ae/tmab036
Smyth, S. J. (2020). The human health benefits from GM crops. Plant Biotechnol. J. 18 (4), 887–888. doi:10.1111/pbi.13261
Snell, C., Bernheim, A., Bergé, J.-B., Kuntz, M., Pascal, G., Paris, A., et al. (2012). Assessment of the health impact of GM plant diets in long-term and multigenerational animal feeding trials: a literature review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 50 (3), 1134–1148. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.048
Stotzky, G. (2005). Persistence and biological activity in soil of the insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis, especially from transgenic plants. Plant Soil 266 (1), 77–89. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-5945-6
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (2010). Bacillus thurigiensis Cry3Bb1 corn biopesticides registration action document. Available at: https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/pip/cry3bb1-brad.pdf .
Van Eenennaam, A. L., and Young, A. E. (2014). Prevalence and impacts of genetically engineered feedstuffs on livestock populations. J. Animal Sci. 92 (11), 4255–4278. doi:10.2527/jas.2014-8124
van Frankenhuyzen, K. (2009). Insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal proteins. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 101 (1), 1–16. doi:10.1016/j.jip.2009.02.009
Waters, S., Ramos, A., Henderson Culler, A., Hunst, P., Zeph, L., Gast, R., et al. (2021). Recommendations for science-based safety assessment of genetically modified (GM) plants for food and feed uses. J. Regul. Sci. 9 (1), 16–21. doi:10.21423/JRS-V09I1WATERS
Woodruff, S. (2024). Gardeners can now grow a genetically modified purple tomato made with snapdragon DNA. Available at: https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2024/02/06/1228868005/purple-tomato-gmo-gardeners .
Zilberman, D., Holland, T. G., and Trilnick, I. (2018). Agricultural GMOs—what we know and where scientists disagree. Sustainability 10 (5), 1514. doi:10.3390/su10051514
Keywords: genetically modified (GM), regulation, food and feed, safety assessment, environmental risk assessment (ERA), problem formulation, cultivation, data requirements
Citation: Storer NP, Simmons AR, Sottosanto J, Anderson JA, Huang MH, Mahadeo D, Mathesius CA, Sanches da Rocha M, Song S and Urbanczyk-Wochniak E (2024) Modernizing and harmonizing regulatory data requirements for genetically modified crops—perspectives from a workshop. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12:1394704. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1394704
Received: 02 March 2024; Accepted: 12 April 2024; Published: 10 May 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Storer, Simmons, Sottosanto, Anderson, Huang, Mahadeo, Mathesius, Sanches da Rocha, Song and Urbanczyk-Wochniak. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abigail R. Simmons, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Advancing Science in Support of Sustainable Bio-Innovation: 16th ISBR Symposium

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
Advantages. 1. In-depth analysis of complex phenomena. Case study design allows researchers to delve deeply into intricate issues and situations. By focusing on a specific instance or event, researchers can uncover nuanced details and layers of understanding that might be missed with other research methods, especially large-scale survey studies.
Even interviews can be conducted over the phone. That means this method is good for formative research that is exploratory in nature, even if it must be completed from a remote location. 6. It is inexpensive. Compared to other methods of research, the case study method is rather inexpensive.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data. Analysis of qualitative data from case study research can contribute to knowledge development.
A case study is an in-depth investigation of a single person, group, event, or community. This research method involves intensively analyzing a subject to understand its complexity and context. The richness of a case study comes from its ability to capture detailed, qualitative data that can offer insights into a process or subject matter that ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
1 Advantages of case studies. One of the main advantages of case studies is that they can capture the complexity and uniqueness of the phenomenon under study, without oversimplifying or ...
The quality of a case study does not only depend on the empirical material collection and analysis but also on its reporting (Denzin & Lincoln, 1998). A sound report structure, along with "story-like" writing is crucial to case study reporting. The following points should be taken into consideration while reporting a case study.
28) calls case study research design a 'craftwork'. This is rightly so, because how rigorous and sharp the design is constructed ultimately determines the efficacy, reliability and validity 3 of the final case study outcome. Research design is the key that unlocks before the both the researcher and the audience all the primary elements of ...
The popularity and reliability of a case study as a research method in multidisciplinary areas is based on the advantages of the case study method. In the following part, an attempt has been done to examine the advantages of a case study and its applicability in social science research. Case study method is extensively used in educational settings.
Cons: 1. Data collected cannot be generalized- The data collected by the case study method was collected from a smaller population it cannot be generalized to the wider population. 2. Some of the case studies are not scientific-The weakness of the data collected in some of the case studies that are not scientific is that it cannot be generalized.
Case study research involves an in-depth investigation of a contemporary, real-life phenomenon in its context. A case study can focus on one person, a group, an organization, or an event. Case ...
Researchers, economists, and others frequently use case studies to answer questions across a wide spectrum of disciplines, from analyzing decades of climate data for conservation efforts to developing new theoretical frameworks in psychology. Learn about the different types of case studies, their benefits, and examples of successful case studies.
The following are the advantages of case study methods: 1. It Offers a Detailed Examination of a Particular Unit. When adopting the case study technique, researchers must document independently verifiable data from firsthand observations. The work provides information on the input mechanisms that contribute to the hypothesis under consideration. 2.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
The main points of advantages of case study are given below: Formation of valid hypothesis: Case study helps in formulating valid hypothesis. Once the various cases are extensively studied and analyze, the researcher can deduce various generalizations, which may be developed into useful hypotheses. It is admitted by all that the study of ...
Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment ...
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method. 1. It requires an intensive study of a specific unit. Researchers must document verifiable data from direct observations when using the case study method. This work offers information about the input processes that go into the hypothesis under consideration.
Revised on June 22, 2023. A case-control study is an experimental design that compares a group of participants possessing a condition of interest to a very similar group lacking that condition. Here, the participants possessing the attribute of study, such as a disease, are called the "case," and those without it are the "control.".
Through the case method, you can "try on" roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career. 5. Build Your Self-Confidence. Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader's perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and ...
The biggest disadvantage to case studies is that the results only apply to the case studied and cannot be generalized. Explore all similar answers ... An equation of the line tangent to y=x3+3x2+2 at its point of inflection is A. y=−6x−6y is equal to negative 6 x minus 6 B. y=−3x+1y is equal to negative 3 x plus 1 C. y=2x+10y is equal to ...
2024 AP Exam Dates. The 2024 AP Exams will be administered in schools over two weeks in May: May 6-10 and May 13-17. AP coordinators are responsible for notifying students when and where to report for the exams. Early testing or testing at times other than those published by College Board is not permitted under any circumstances.
Although participants generally agreed that the case study with a familiar crop and familiar traits is a good starting point for the discussions, several suggestions were made for further discussions to also provide a case study on an unfamiliar event or protein, to lay out how each study informs the safety assessment, to provide more on the ...
Join us at 6 PM (WAT) this Thursday May 9, 2024, as our distinguish guest will be discussing the topic: GEN-Z ACCOUNTANTS: Redefining Traditional...