
Free MLA Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What is the Cite This For Me MLA Citation Generator?
Are you looking for an easy and reliable way to cite your sources in the MLA format? Look no further because Cite This For Me’s MLA citation generator is designed to remove the hassle of citing. You can use it to save valuable time by auto-generating all of your citations.
The Cite This For Me citation machine accesses information from across the web, assembling all of the relevant material into a fully-formatted works cited MLA format page that clearly maps out all of the sources that have contributed to your paper. Using a generator simplifies the frustrating citing process, allowing you to focus on what’s important: completing your assignment to the best of your ability.
Have you encountered an unusual source, such as a microfiche or a handwritten manuscript, and are unsure how to accurately cite this in the MLA format? Or are you struggling with the dozens of different ways to cite a book? If you need a helping hand with creating your citations, Cite This For Me’s accurate and powerful generator and handy MLA format template for each source type will help to get you one step closer to the finishing line.
Continue reading our handy style guide to learn how to cite like a pro. Find out exactly what a citation generator is, how to implement the MLA style in your writing, and how to organize and present your work according to the guidelines.
Popular MLA Citation Examples
- Archive material
- Book Chapter
- Dictionary entry
- E-book or PDF
- Image online or video
- Presentation or lecture
- Video, film, or DVD
Why Do I Need To Cite?
Whenever you use someone else’s ideas or words in your own work, even if you have paraphrased or completely reworded the information, you must give credit where credit is due to avoid charges of plagiarism. There are many reasons why.
First, using information from a credible source lends credibility to your own thesis or argument. Your writing will be more convincing if you can connect it to information that has been well-researched or written by a credible author. For example, you could argue that “dogs are smart“ based on your own experiences, but it would be more convincing if you could cite scientific research that tested the intelligence of dogs.
Second, you should cite sources because it demonstrates that you are capable of writing on an academic or professional level. Citations show that your writing was thoughtfully researched and composed, something that you would not find in more casual writing.
Lastly, and most importantly, citing is the ethical thing to do. Imagine that you spent months of your life on a paper: researching it, writing it, and revising it. It came out great and you received many compliments on your thesis and ideas. How would you feel if someone took those ideas (or even the whole paper) and turned them in as their own work without citations? You’d probably feel terrible.
For all of these reasons, be sure that all of the source material that has contributed to your work is cited. There are two steps:
- Acknowledge a source with an MLA in-text citation (also known as a parenthetical citation )
- Feature a full citation for the source in your works cited list
Create citations, whether manually or by using the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator, to maintain accuracy and consistency throughout your project.
Do I Have to Cite Everything?
When writing a research paper, any information used from another source needs to be cited. The only exceptions to this rule are everyday phrases (e.g., all the world’s a stage) and common knowledge (e.g., President Kennedy was killed in 1963).
Also, your own work does not need to be cited. That includes your opinions, ideas, and visuals (e.g., graphs, photos, etc.) you created. However, you do need to cite your own work if you have previously published it or used it in another assignment. Otherwise it’s considered self plagiarism . For example, submitting a paper that you wrote and already turned in for another class is still plagiarism, even though it is your own work.
If you have any doubts about whether or not something you’ve written requires a citation, it’s always better to cite the source. While it may be a tedious process without an MLA citation machine, attributing your research is essential in validating the statements and conclusions you make in your work. What’s more, drawing on numerous sources elevates your understanding of the topic, and accurately citing these sources reflects the impressive research journey that you have embarked on.
Consequences of Not Citing
The importance of crediting your sources goes far beyond ensuring that you don’t lose points on your assignment for citing incorrectly. Plagiarism, even when done unintentionally, can be a serious offense in both the academic and professional world.
If you’re a student, possible consequences include a failing assignment or class grade, loss of scholarship, academic probation, or even expulsion. If you plagiarize while writing professionally, you may suffer legal ramifications as well, such as fines, penalties, or lawsuits.
The consequences of plagiarism extend beyond just the person who plagiarized: it can result in the spread of misinformation. When work is copied and/or improperly cited, the facts and information presented can get misinterpreted, misconstrued, and mis-paraphrased. It can also be more difficult or impossible for readers and peers to check the information and original sources, making your work less credible.
What is the MLA Format?
The MLA format was developed by the Modern Languages Association as a consistent way of documenting sources used in academic writing. In 2021, the Modern Languages Association replaced its 8th edition of the guidelines with the current 9th edition. Most of these changes were made to reflect the expanding digital world and how researchers and writers cite online information resources. MLA is a concise style predominantly used in the liberal arts and humanities, first and foremost in research focused on languages, literature, and culture. You can find out more here .
It is important to present your work consistently, regardless of the style you are using. Accurately and coherently crediting your source material both demonstrates your attention to detail and enhances the credibility of your written work. The MLA format provides a uniform framework for consistency across a scholarly document, and caters to a large variety of sources. So, whether you are citing a website, an article, or even a podcast, the style guide outlines everything you need to know to correctly format all of your MLA citations.* The style also provides specific guidelines for formatting your research paper, and useful tips on the use of the English language in your writing.
The Cite This For Me style guide is based on the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook. Our citation generator also uses the 9th edition — allowing you to shift focus from the formatting of your citations to what’s important — how each source contributes to your work.
MLA has been widely adopted by scholars, professors, journal publishers, and both academic and commercial presses across the world. However, many academic institutions and disciplines prefer a specific style of referencing (or have even developed their own unique format) so be sure to check which style you should be using with your professor. Whichever style you’re using, be consistent!
So, if you’re battling to get your citations finished in time, you’ve come to the right place. The generator above will create your citations in MLA style by default, or it can cite any source in 7,000+ styles. So, whether your discipline uses the APA citation style, or your institution requires you to cite in the Chicago style citation , simply go to the Cite This For Me website to find generators and style guides for ASA , IEEE , AMA , Harvard and many more.
*You may need to cite a source type that is not covered by the format manual – for these instances we have developed additional guidance and MLA format examples, which stick as closely as possible to the spirit of the style. Where examples are not covered in the official handbook, this is clearly indicated.
How Do I Create and Format MLA In-text Citations?
The MLA format is generally simpler than other referencing styles as it was developed to emphasize brevity and clarity. The style uses a straightforward two-part documentation system for citing sources: parenthetical citations in the author-page format that are keyed to an alphabetically ordered MLA works cited page. This means that the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text as a parenthetical citation, and a complete corresponding reference should appear in your works cited list.
Keep your MLA in-text citations brief, clear and accurate by only including the information needed to identify the sources. Furthermore, each parenthetical citation should be placed close to the idea or quote being cited, where a natural pause occurs – which is usually at the end of the sentence. Essentially you should be aiming to position your parenthetical citations where they minimize interruption to the reading flow, which is particularly important in an extensive piece of written work.
Check out the examples below…
MLA Format Examples
In-text citation MLA examples:
- Page specified, author mentioned in text:
If the author’s name already appears in the sentence itself then it does not need to appear in the parentheses. Only the page number appears in the citation.
Here is an MLA format example for a source with one author :
Sontag has theorized that collecting photographs is a way “to collect the world” (3).
Here is an MLA format example for a source with two authors :
According to MacDougall and Sanders-Parks, “employers seldom expect you to know every aspect of a new job” (31).
- Page specified, author not mentioned in text:
Include the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken in a parenthetical citation after the quote. This way of citing foregrounds the information being cited.
Example for source with one author :
“To collect photographs is to collect the world” (Sontag 3).
Example for a source with two authors :
“But employers seldom expect you to know every aspect of a new job” (MacDougall and Sanders-Parks 31).
When the author is referred to more than once in the same paragraph, you may use a single MLA in-text citation at the end of the paragraph (as long as the work cannot be confused with others cited).
If you are citing two works by the same author, you should put a comma after the author’s surname and add a shortened title to distinguish between them. If there are two authors with the same surname, be sure to include their first initial in your citation to avoid confusion.
- Website, author known:
Books are not the only sources you will cite; odds are that you will also use many web-based sources. An MLA website citation in the text of your paper looks similar to a book citation, except that it does not include a page number.
“Photography reflects, records and advertises our lives online” (O’Hagan).
- Website, unknown author:
Many web pages don’t have a clear author listed. In these cases, MLA citation format guidelines say to include the title of the web page. You can shorten the title if it is long.
“The most expensive photograph ever sold was not by a photographer, nor was the photograph taken by the artist” (“Photography Market”).
For any in-text citation, don’t forget to include a corresponding full citation in your bibliography. If you are struggling with how to cite a website in MLA, try the Cite This For Me MLA generator at the top of this page.
Works cited / bibliography example:
Unlike an MLA in-text citation, you must include all of the publication information in your works cited entries.
Franke, Damon. Modernist Heresies: British Literary History, 1883-1924. Ohio State UP, 2008.
O’Hagan, Sean. “What Next for Photography in the Age of Instagram?” The Guardian , 14 Oct. 2018, www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2018/oct/14/future-photography-in-the-age-of-instagram-essay-sean-o-hagan..
“The Photography Market is About Not Just Names.” The Economist , 13 Jul. 2017, www.economist.com/books-and-arts/2017/07/13/the-photography-market-is-about-not-just-names.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography . Penguin, 2008.
Luckily for you, we know where the commas go, and the Cite This For Me citation generator will put them there for you.
If citing is giving you a headache, use the Cite This For Me free, accurate MLA citation generator to add all of your source material to your works cited page with just a few clicks.
How Do I Format My MLA Works Cited Page?
A works cited page is a comprehensive list of all the sources that directly contributed to your work – each entry links to the brief parenthetical citations in the main body of your work. An in-text citation only contains enough information to enable readers to find the source in the works cited MLA format list, so you’ll need to include the complete publication information for the source in your works cited entries.
Your works cited MLA page should appear at the end of the main body of text on a separate page. Each entry should start at the left margin and be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name (note that if there is no author, you can alphabetize by title). For entries that run for more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) – this format is called a ‘hanging indentation.’
The title of the page should be neither italicized nor bold – it is simply center-aligned. Like the rest of your MLA format paper the list should be double-spaced, both between and within entries.
Sometimes your professor will ask you to also list the works that you have read throughout your research process, but didn’t directly cite in your paper. This list should be called ‘Work Cited and Consulted,’ and is an excellent opportunity to demonstrate the full extent of the research you have carried out.
Remember, indicate all of your sources via both parenthetical citations and an MLA format works cited list, to acknowledge the work of other authors.
Works cited examples:
Anderson, Benedict. Imagined Communities. Verso, 1983.
Fox, Claire F. The Fence and the River: Culture and Politics at the U.S.-Mexico Border. U of Minnesota P, 1999.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography. Penguin, 2008.
MLA Style Research
When you are gathering sources in your research phase, be sure to make note of the following bibliographical items:
- Name of original source owner: author, editor, translator, illustrator, or director
- Titles: article or newspaper title, title of publication, series title
- Important dates: date of publication, date of composition, issue date, event date, date accessed
- Publishing information: publisher name
- Identifying information: number of volumes, volume number, issue number, edition, chapter, pages, lines
If you’re still in your research phase, why not try out Cite This For Me for Chrome? It’s an intuitive and easy-to-use browser extension that enables you to instantly create and edit a citation for any online source whilst you browse the web.
Racing against the clock? If your deadline has crept up on you and you’re running out of time, the Cite This For Me MLA citation maker will help collect and add any source to your MLA bibliography with just a click.
In today’s digital age, source material comes in all shapes and sizes. Thanks to Cite This For Me’s citation generator, citing is no longer a chore. Accurately and easily cite any type of source in a heartbeat, whether it be a musical score, a work of art, or even a comic strip. Cite This For Me elevates students’ research to the next level by enabling them to cite a wide range of sources.
MLA Citation Formatting Guidelines
Accurately citing sources for your assignment doesn’t just prevent the appearance or accusations of plagiarism – presenting your source material in a clear and consistent way also ensures that your work is accessible to your reader. So, whether you’re following the MLA format citation guidelines or using the Cite This For Me generator, be sure to abide by the presentation rules on font type, margins, page headers and line spacing.
To format your research paper according to the guidelines:
- Set the margins to 1 inch (or 2.5 cm) on all sides
- Choose an easily readable font, recommended Times New Roman
- Set font size to 12 point
- Set double space for your entire paper
- Indent every new paragraph by ½ inch – you can simply use your tab bar for this
- In the header section – on the top right corner of the pages – give your last name followed by the respective page number
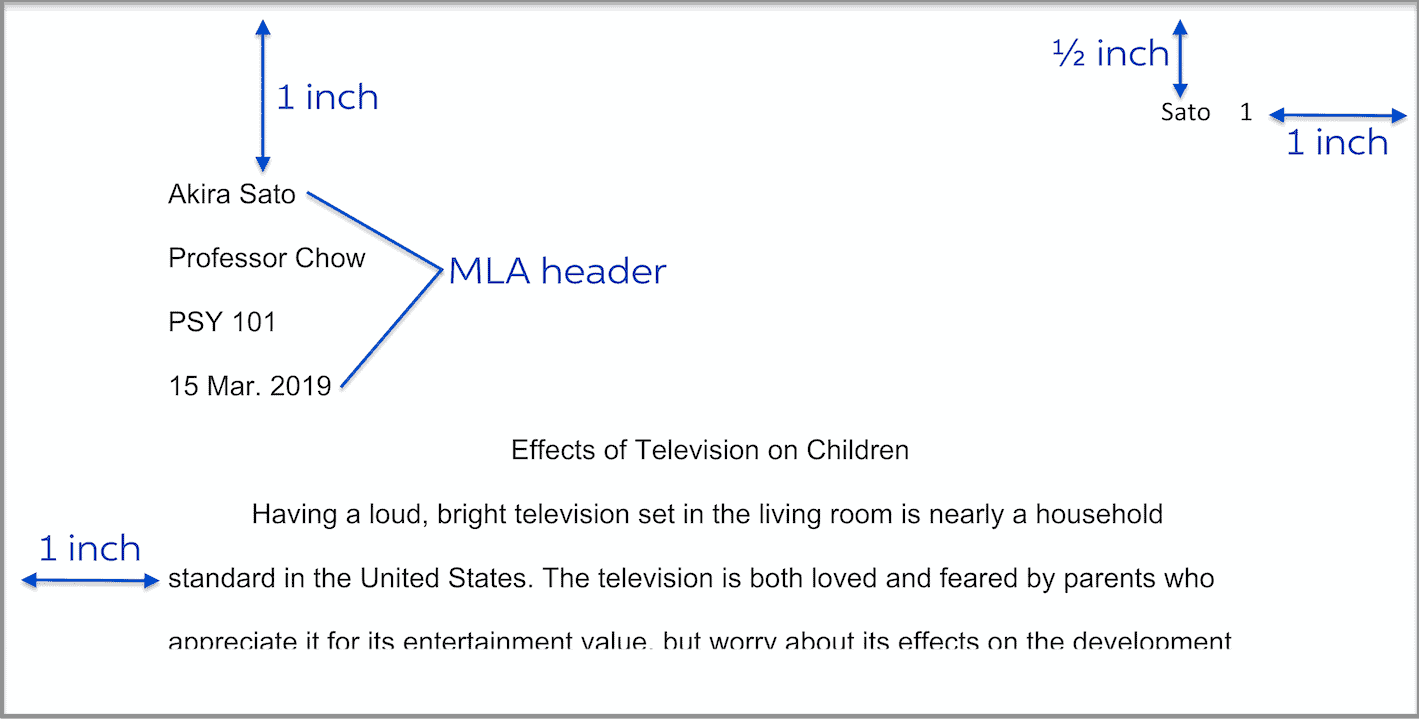
MLA format heading, title, and running head: Within this formatting style, an MLA title page isn’t necessary. What’s needed instead is a header. The header is a small section added to the first page of your paper and it includes all of the same basic information a title page would.
To format your MLA header and title:
- On the first page, ensure the text is left-aligned and then give your details: starting with your full name in line one, followed by the name of your teacher or professor, the course name and number, and the date in separate lines
- Center align your heading – do not italicize, bold or underline, or use a period after the title
- The body of your text should start in the next line, left-aligned with an indentation
On every page, you will also need to include what is called a “running head.” Follow these directions to create one:
- On the top right corner of each page – give your last name followed by the respective page number. This is your running head.
- It should be positioned ½ an inch from the top of the page, and 1 inch from the right edge of the page.
If your instructor asks for or insists on having an MLA cover page for your paper, ask them to show you a cover page example. That’s the best way to know what your instructor will be looking for.
Here is a visual MLA format template for the first page of your paper:
MLA Style 9th Edition - Changes From Previous Editions
It is worth bearing in mind that the MLA format is constantly evolving to meet the various challenges facing today’s researchers. Using Cite This For Me’s generator will help you to stay ahead of the game without having to worry about the ways in which the style has changed.
Below is a list outlining the key ways in which the style has developed since previous editions.
- Titles of independent works (such as books and periodicals) are now italicized rather than underlined .
- Listing URLs for web citations is now always encouraged, and you should no longer include “https://” at the beginning of the URL with the exception of DOIs.
- You no longer are required to list the place of publication for a source unless the version of the work changes based on location, or it was published prior to 1900.
- You are no longer required to provide medium information in your citations (e.g. ‘Print.’, ‘Web.’, ‘DVD.’ etc.)
- The style guidelines now call for the inclusion of both volume and issue numbers in listings for journal articles.
How Do I Cite My Sources With the Cite This For Me Citation Machine for MLA?
If you’re frustrated by the time-consuming process of citing, the Cite This For Me multi-platform citation management tool will transform the way you conduct your research. Using this fast, accurate and accessible generator will give you more time to work on the content of your paper, so you can spend less time worrying about tedious references.
To use the MLA format generator:
- Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g. website, book, journal & video
- Enter the URL , DOI , ISBN , title, or other unique source information to locate your source
- Click the ‘Search’ button (If there is more than one result, review the sources presented and select one)
- See what information was found on your source, then click the “Continue” button
- Review or edit your citation information, then click “Complete citation” to create it
- Copy your fully-formatted citation into your works cited list</li/>
- Repeat the same process for each source that has contributed to your work
As well as making use of the powerful citation generator on this MLA citation website, you can cite with our Chrome add-on or Word add-on.
Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool.
Published October 1, 2015. Updated July 21, 2021.
- For educators
- Go to my projects
- Português (PT)
- Português (BR)
BibGuru MLA Citation Generator
Cite websites, books, articles, ...
Your Works Cited page in MLA
- A closer look at MLA's core elements
In-text citations in MLA
Formatting your paper in mla, helpful resources on mla style, the ultimate guide to citing in mla.
The MLA citation style was developed by the Modern Language Association of America, an association of scholars and teachers of language and literature.
The MLA publishes several academic journals, and the MLA Handbook , a citation guide for high school and undergrad students. The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for writing and documenting research, as well as tips for the use of the English language in your writing.
MLA is a very popular citation style. However, if you are unsure which citation style to use in your paper, ask your instructor. There are many different citation styles and using the style your instructor or institution has established correctly can have a positive impact on your grade.
This guide is based on the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook and aims at helping you cite correctly in MLA. The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for a large variety of sources and uses a two-part documentation system for citing sources:
- in-text parenthetical citations (author, page)
- a reference list at the end of paper with all literature used in text.
Each source that was cited in the text or notes of your paper should appear in a list at the end of the paper. MLA calls the reference list a "Works Cited" page.

I want to cite a ...
Your Works Cited list identifies the sources you cite in the body of your research project. Works that you consult during your research, but don't use and cite in your paper, are not included. Your Works Cited list is ordered alphabetically by the part of the author's name that comes first in each entry.
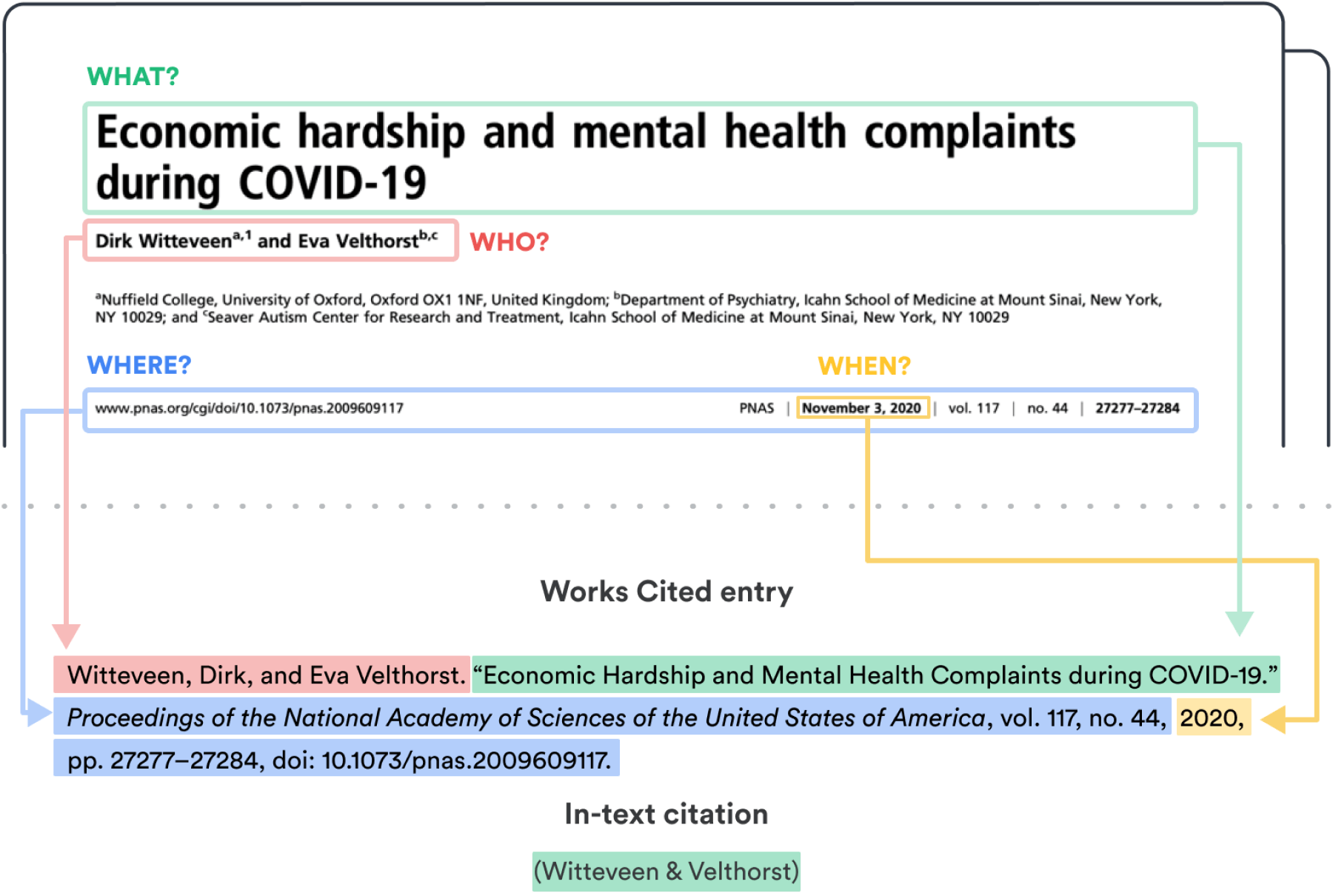
Entries in the list of works cited are made up of core elements given in a specific order, and there are optional elements that may be included. The core elements in your works cited list are the following, given in the order in which they should appear, followed by the correct punctuation mark. The final element in an MLA reference should end with a period:
- Title of source.
- Title of container,
- Contributor,
- Publication date,
To use this template of core elements, first evaluate what you are citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then list each element relevant to your source in the order given on the template. For a work containing another work (e.g. an article published in a journal and contained in a database), you can repeat the process by filling out the template again from Title of container to Location , listing all elements that apply to the container.
Step-by-step guide to create a Works Cited entry
Let's try this with a journal article. If you wanted to cite the article , “What Should We Do with a Doctor Here?”: Medical Authority in Austen’s Sanditon ," from the journal, Nineteenth-Century Contexts , the process would look like this:
- First, you would determine the author. In this case, that's Amy Mallory-Kani. so the first part of your reference would be: Mallory-Kani, Amy.
- Next, you'd want to include the title of the source in quotation marks, followed by a period: “What Should We Do with a Doctor Here?”: Medical Authority in Austen’s Sanditon."
- After the title of the source, you need to list the container. In this case, it's the journal's name, Nineteenth-Century Contexts , italicized and followed by a comma.
- For journal articles, the title of the container needs to be followed by version, or the volume number of the journal, separated by a comma from the issue number: vol. 39, no. 4,
- Since there is not typically a publisher listed for journal articles, the next step is to include the date, followed by a comma: 2017,
- Finally, you'll end your reference by adding the page numbers for the article, followed by an ending period: pp. 313-26.
If we put this all together, the full reference will look like this:
EXAMPLE Journal article
Mallory-Kani, Amy. “'What Should We Do with a Doctor Here?': Medical Authority in Austen’s Sanditon ”. Nineteenth-Century Contexts , vol. 39, no. 4, 2017, pp. 313-26.
MLA has a specific rule about how to structure page numbers in a works cited entry. Use pp. and then list the number. If the page range is within ten or one hundred digits, you don't need to repeat the first digit. For example, you would write pp. 51-8 or pp. 313-26.
The following section takes a deeper look at the core elements of an MLA works cited entry to help you get your citation right.
A closer look at MLA's core elements
When formatting the author element, make sure to follow these guidelines:
- When a work is published without an author's name, do not list it as Anonymous . Skip the author element instead and begin with the Title of source .
- Begin the entry with the last name of the author, so it can be alphabetized under this name. Follow the last name with a comma and the rest of the name as presented by the work.
- When a source has two authors, include them in the order in which they are presented in the work. Reverse the first of the names as described above.
- When a source has three or more authors, reverse the first of the names as described above and follow it with a comma and the abbreviation, et al.
EXAMPLE Source with two authors
Gabrielle, Matthew, and David M. Perry. The Bright Ages: A New History of Medieval Europe . Harper, 2021.
In the Title of Source element, you list the title of the work you are citing:
EXAMPLE Title of Source element
Cox, Taylor. Creating the Multicultural Organization: A Strategy for Capturing the Power of Diversity . Jossey-Bass, 2001.
In general, titles in your Works Cited list are given in full exactly as they are found in the source, except that capitalization, punctuation between the main title and a subtitle, and the styling of titles that normally appear in italic typeface are standardized. The Title of Source element is followed by a period unless the title ends in a question mark or exclamation point.
A container in the context of the MLA template is a work that contains another work. An example of a container can be:
- A periodical, such as a journal, magazine or newspaper is the container of an article published there.
- A website or database can be the container of a post, a review, a song, a film, or other media.
- An art exhibit is the container of an artwork featured in it.
In the example below, the Journal of Postsecondary Education and Disability is the container of the article “Vocabulary Knowledge of Deaf and Hearing Postsecondary Students”:
EXAMPLE Title of Container
Sarchet, Thomastine, et al. “Vocabulary Knowledge of Deaf and Hearing Postsecondary Students.” Journal of Postsecondary Education and Disability , vol. 27, no. 2, Summer 2014, pp. 161–178.
Importantly, a website or a database is not always automatically the container of a work that can be found there. If you click on a Facebook link that takes you to a New York Times article, Facebook is not the container of the article, but the New York Times website is. Be careful to make the distinction here.
The title of Container is normally italicized and followed by a comma.
People, groups, and organizations can be contributors to a work without being its primary creator. There can be a primary author, but a work can also be created by a group of people. Key contributors should always be listed in your entry. Other contributors can be listed on a case-by-case basis. Whenever you list a contributor, include a label describing the role. These kinds of contributors should always be listed in your entry:
- translators
- editors responsible for scholarly editions and anthologies
- editors responsible for edited collections of works by various primary authors from which you cite an individual contribution
EXAMPLE Translator of a work with a primary author
Chartier, Roger. The Order of Books: Readers, Authors, and Libraries in Europe between the Fourteenth and Eighteenth Centuries. Translated by Lydia G. Cochrane, Stanford UP, 1994.
It may be necessary to include other types of contributors if they shaped the overall presentation of the work. Use labels (in lowercase) to describe the contributor's role, such as:
- translated by
EXAMPLE Creator of a television show
"Strike Up the Band." The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel , created by Amy Sherman-Palladino, season 3, episode 1, Amazon Studios, 2019.
When a source has three or more contributors in the same role, list the first contributor, followed by et al.
EXAMPLE Three or more contributors
Balibar, Étienne. Politics and the Other Scene . Translated by Christine Jones et al., Verso, 2002.
If a source is a version of a work released in more than one form, you need to identify the version in your entry. For example, books are commonly issued in versions called editions .
When citing versions in your Works Cited list, write original numbers with arabic numerals and no superscript. Abbreviate revised (rev.) and edition (ed.) .
EXAMPLE Edition of a work
Black, Joseph, et al., editors. The Broadview Anthology of British Literature: The Victorian Era . 3rd ed., Broadview, 2021.
The source you are documenting may be part of a sequence, like a volume, issue, or episode. Include that number in your entry:
EXAMPLE Work with a number
Warren, R., et al. “The Projected Effect on Insects, Vertebrates, and Plants of Limiting Global Warming to 1.5°C Rather than 2°C.” Science (New York, N.Y.) , vol. 360, no. 6390, 2018, pp. 791–795, doi:10.1126/science.aar3646.
Always use arabic numerals in the Number element. If necessary, convert roman numerals or spelled out numerals to arabic numerals.
The publisher is the entity primarily responsible for making the work available to the public. The publisher element may include the following:
- book publisher
- studio, network, company, or distributor that produced or broadcast a television show
- institution responsible for creating website content
- agency that produced government publication
A publisher's name may be omitted when there is none, or when it doesn't need to be given, for example in:
- some periodicals (when publication is ongoing)
- works published by their authors or editors (self-published)
- websites not involved in producing the content they make available (e.g. Youtube)
This element tells your reader when the version of the book you are citing was published. In the example below, the book was published in 2018:
EXAMPLE Publication date
Lavelle, Christophe, editor. Molecular Motors: Methods and Protocols. 2nd ed., Humana Press, 2018, doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-8556-2.
If roman numerals are used, convert them to arabic numerals. Use the day-month-year style to minimize commas in your entry and use the most specific date you can find in your source. Include day, month, and year if your source does:
EXAMPLE Specific Publication date
Merrill, Stephen. "Teaching through a Pandemic: A Mindset for This Moment." Edutopia , 19 Mar. 2020, www.edutopia.org/article/teaching-through-pandemic-mindset-moment.
When time is given and helps define and locate the work, include it.
For paginated print or similar formats (e.g. PDFs), the location is the page range. In other cases, additional information may need to be included with the page numbers so that the work can be found. In this overview, you can see examples for locations:
As mentioned above, Works Cited list entries in MLA style are based on the template of core elements. In some cases, you may need or want to give additional information relevant to the work you are documenting. You can do so by adding supplements to the template. There are two sections where you can add supplements, either:
- after the Title of Source, or
- at the end of the entry.
A period should be placed after a supplemental element. Three pieces of information are the most likely to be placed after the Title of Source:
- A contributor other than the author
- The original publication date (for a work contained in another work)
- Generically labeled sections (if any part or section of the work has a unique title as well as generic label)
For example, inserting the contributors' roles and names after the Title of Source element tells the reader that Leila El Khalidi and Christopher Tingley translated only The Singing of the Stars , not all the other works in Short Arabic Plays :
EXAMPLE Supplemental elements
Fagih, Ahmed Ibrahim al-. The Singing of the Stars . Translated by Leila El Khalidi and Christopher Tingley. Short Arabic Plays: An Anthology , edited by Salma Khadra Jayyusi, Interlink Books, 2003, pp. 140-57.
If you need to clarify something about the entry as a whole, you can do it at the end of the entry , like:
- Date of access
- Medium of publication (when more than one version of a source is accessible on the same landing page and you are citing a version that is not the default version)
- Dissertations and theses
- Publication history
- Book series
- Columns, sections, and other recurring titled features
- Multivolume works
- Government documents
EXAMPLE Government documents
United States, Congress, House. Improving Broadband Access for Veterans Act of 2016. Congress.gov , www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/house-bill/6394/text. 114th Congress, 2nd session, House Resolution 6394, passed 6 Dec. 2016.
How to use Bibguru for MLA citations

In-text citations aim at directing the reader to the entry in your Works Cited list for the source. while creating the least possible interruption in the text. An in-text citation usually contains the author's name (or other first element in the entry in the works cited list) and a page number. The page number usually goes in a parenthesis, placed where there is a natural pause in the text.
A parenthetical citation that directly follows a quotation is placed after the closing quotation mark. No punctuation is used between the author's name (or the title) and a page number:
EXAMPLE Parenthetical citation
“It's silly not to hope. It's a sin he thought.” (Hemingway 96)
The author's name can appear in the text itself or before the page number in the parenthesis:
Cox names five strategies to implement Diversity Management in companies (50).
Here are some additional examples of in-text citations and their corresponding Works Cited entries:
EXAMPLE Citation in prose using author's name
Smith argues that Jane Eyre is a "feminist Künstlerroman " that narrativizes a woman's struggle to write herself into being (86).
Jane Eyre is a "feminist Künstlerroman " that narrativizes a woman's struggle to write herself into being (Smith 86).
EXAMPLE Works cited
Smith, Jane. Feminist Self-Definition in the Nineteenth-Century Novel . Cambridge UP, 2001.
How to correctly style your in-text citations
- If you are citing an author in your paper, give the full name at first mention and the last name alone thereafter.
- If you are citing a work with two authors, include both first and last names the first time you mention them in your paper. Then, in a following parenthetical citation, connect the two last names with and .
- If the source has three or more authors, you may list all the names or provide the name of the first collaborator followed by "and others" or "and colleagues". In a parenthetical citation, list the last name of the first author and et al .
Ditch the frustrations for stress-free citations
The MLA Handbook also provides guidelines on how to present your paper in a clear and consistent way. These are the general guidelines to format your paper correctly , according to MLA. For more details, refer to the MLA Handbook :
- Use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Font size should be 12 pt.
- Set the margins of your document to 1 inch on all sides.
- Double-space the entire text of your paper.
- Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks.
- Indent every new paragraph one half-inch from the left margin. You can use your tab bar for this.
- Create a header that numbers all pages consecutively in the upper right-hand corner, one half-inch from the top and flush with the right margin.
- Use italics for the titles of longer works.
- Do not make a title page for your paper unless specifically required.
- On the first page, make sure that the text is left-aligned. Then, list your name, the name of your teacher or professor, the course name and the date in separate lines.
- Center align your heading. Do not italicize, bold, or underline your title. Also, do not use a period after the title.
The MLA Handbook gives guidance for a multitude of different sources, like websites, television series, songs, articles, comic books, etc., and considers various types of contributors to these sources. BibGuru's MLA citation generator helps you create the fastest and most accurate MLA citations possible. If you want to learn more about MLA citations, check out our detailed MLA citation guides .
From our blog

More Bibguru MLA guides

Resources based on the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab (OWL)
- California State University, Northridge Library MLA Style Guide
- Columbia College Library MLA Style Guide
- McMaster University Library MLA Style Guide
- Spartanburg Community College Library MLA Style Guide
- Madison College Libraries MLA Style Guide
- California State University, Dominguez Hills Library MLA Style Guide
- University of Wisconsin-Parkside Library MLA Style Guide
The following resources are based on the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook , but still offer relevant insights on MLA style
- University of Washington Libraries MLA Style Guide
- University of North Texas Libraries MLA Style Guide
- Valencia College Library MLA Style Guide
- College of Southern Nevada Libraries MLA Style Guide
- University of Nevada, Reno Libraries MLA Style Guide
- Montana State University Library MLA Style Guide
- University of Michigan Library MLA Style Guide
- University of Vermont Libraries MLA Style Guide
- University of Illinois Library MLA Style Guide
- Hillsborough Community College Libraries MLA Style Guide
- Southern Connecticut State University Library MLA Style Guide
- Arizona State University Library MLA Style Guide
An in-text citation usually contains the author's name (or other first element in the entry in the works cited list) and a page number. The page number usually goes in a parenthesis, placed where there is a natural pause in the text.
In MLA style, audio-visual material uses the specific time of the audio/video for in-text citations. You need to cite the author's last name and the time or a short version of the title and the time within parentheses, e.g.:
The following scene exemplifies the performer's physical abilities (Thurman 00:15:43-00:20:07).
Anyone can use MLA style given its versatility. However, this format is often used by writers and students working in the arts and humanities, such as linguistics, literature, and history.
Yes, the BibGuru MLA citation generator is completely free and ready to use by students and writers adopting MLA guidelines.
The most recent version of the MLA guidelines is the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook, released in 2021. It is still very new so you should check with your instructor or institution to make sure you're using the right version.
Citation generators
Citation guides, alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test

MLA Citation Generator
powered by QuillBot
MLA Format Guide for MLA (9th Edition)
MLA citations have two main parts that work together to identify the sources you’ve used for a paper and each of the specific places in your paper where you directly quote or paraphrase from a source:
- A Works Cited list
- Located at the end of your paper
- Contains a list of full references for every source you cited in your paper
- Alphabetized by author’s last name
- In-text citations
- Appear in the text of your paper, after any place where you directly quote or paraphrase from a source
- Consist of just the author name and relevant page number of the quote source
- Are written inside
How to Write an MLA Works Cited
The Works Cited list (sometimes also called a reference list or bibliography) contains the full references for every source you used in writing your paper. The references are alphabetized in the list by author’s last name.
Every entry in an MLA Works Cited—whether for a book, website, journal, etc.—is built from up to nine components:
- Author. “Title of the Source.” Title of the Container , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location.
If a particular reference you are using doesn’t have any information for one of these components, then you just leave out that component.
Here's a bit more information about each of the components that will let you handle any type of MLA works cited entry.
Author in MLA Format
How you handle the author depends on how many authors the work has, or if the author is an organization rather than a single person.
- 1 author : Invert the author’s name (Last Name, First Name)
- Andrews, Julianne
- 2 authors : Include both authors in the order in which they appear on the work, inverting the first author’s name, followed by an “and” and then the second author’s name written normally.
- Andrews, Julianne and Arthur Smith
- 3+ authors : Include the first author listed on the work, inverted, followed by the phrase “et al”
- Andrews, Julianne, et al
- Organization : If the work was written by an Organization rather than by a person or group of people, then just write out the name of the organization.
- No author : If a work has no listed author at all, then you can leave out the Author component entirely and start with the Title of the Source. (Note: when alphabetizing the entry by the first letter of the Title of the Source, ignore articles that start the title such as “The,” “A,” etc.)
Title of the Source in MLA Format
Use the entire title of your source, including subtitles. Subtitles should be separated from the main title by a colon.
The formatting for the source depends on whether it’s self contained or part of a larger whole (such as an entire book, website, or movie), or is part of a larger work (such as a story in an anthology, an article in a magazine, etc.):
- If the source is a self contained unit : The title should be italicized.
- Andrews, Julianne. The Friendly Giraffe . Knopf, 2011.
- If the source is part of a larger work : The title should be placed within quotation marks.
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” Essays on Sports , Harcourt, 2017, pp. 17-31.
Regardless of whether it’s inside quotes or italicized, the title of the source should be written in title case, which means you capitalize every word other than articles, conjunctions, and prepositions.
Title of the Container in MLA Format
The “container” refers to a larger work that contains the source, such as a magazine that contains an article. If a source isn’t a part of a longer work (such as an entire book), then leave out the Title of Container component.
The Title of the Container should always be italicized:
Common examples of containers are:
- A book containing short stories or essays
- A magazine or newspaper containing articles
- An encyclopedia containing entries
- A website containing articles or other entries
- A TV series containing episodes
Other Contributors
If there are people who contributed to a work besides the author(s), include those names in the “Other Contributors” component.
Other contributors should be formatted by identifying what the person did and then the person’s name written out normally. For example:
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” Great Sports Writing of 2018 , edited by Carlos Mendes, Harcourt, 2017, pp. 17-31.
Common types of work that are result in people being included as contributors are:
- Translated by
- Illustrated by
- Directed by
If there are different versions or editions of your source, specify which version your specific source belongs to:
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” Great Sports Writing of 2018 , edited by Carlos Mendes, 3rd ed, Harcourt, 2017, pp. 17-31.
Common reasons for the inclusion of a version number for an entry are:
- A 2nd (or 3rd or 4th, etc.) edition of a source
- A director’s cut of a movie
- An anniversary or expanded edition
Many types of sources are numbered in some way, and in such cases the MLA entry should capture that numbering:
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” Great Sports Writing of 2018 , edited by Carlos Mendes, 3rd ed, vol. 3, Harcourt, 2017, pp. 17-31.
Numbering most often occurs for sources that have containers. Common examples include:
- Journals are often divided into volumes (“vol. 3”)
- Magazines and some periodicals may be numbered (“no. 16”)
- Television shows often have season and episode numbers (“Season 4, Episode 2”)
If a source has multiple numbers, separate the numbers with commas (“vol 3, no. 16”).
Not all sources will have a publisher—this component usually only applies to books and to movies. For movies, the production company is treated as the “publisher.”
Publication date
You should include as specific a publication date as possible, which can range from just the year all the way down to the minute. Ranges are acceptable.
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” Great Sports Writing of 2018, edited by Carlos Mendes, 3rd ed, vol. 3, Harcourt, 2017, pp. 17-31.
The most common ways to represent the publication date are:
- Year : 2001
- Month/Year : Apr. 1976 (note that months should be abbreviated to their first three letters followed by a period, such as “Apr.”)
- Day/Month/Year : 2 Apr. 1976 (note that the day should precede the month)
- Precise time and date : 2 Apr. 1976, 5:15 p.m.
- Year Range : 1975-1977
- Month/Year Range : Apr. 1976–Apr. 1977
- If there’s no date : If you can’t find a publication date, instead use the day/month/year format for the day on which you accessed the information and use the word “Accessed” to make clear the distinction.
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” Great Sports Writing , edited by Carlos Mendes, Accessed 2 Apr. 2018, www.greatsportswriting.com/best.
The location component generally only applies to references that either have containers or that is an event or physical object that occurred or you encountered in a physical place.
- For a chapter, essay, story, or other part of a book : Include a page range.
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” Great Sports Writing of 2018 , edited by Carlos Mendes, 3rd ed, vol. 3, Harcourt, 2017, pp. 217-231.
- For a web page : Include the URL, leaving out the “http://” or “https://”.
- For a printed periodical article : Include a page range.
- Andrews, Julianne. “The Best Game Ever Played.” The Sports Magazine, 2 Jan. 2022, 25-39.
- For an online journal : There are two options
- Include a URL, leaving out the “http://” or “https://”
- Andrews, Julianne. “A Statistical Analysis to Identify the Best Games Ever Played.” Sports Analytics , Accessed 2 Apr. 2018, www.sportsanalytics.org/1249.
- A DOI—digital object identifier—which are sometimes assigned to journal articles to provide a link to that article that will never change. If an article has one, use it instead of a URL
- Example: doi: 11.1633/tox.31266
- Andrews, Julianne. “A Statistical Analysis to Identify the Best Games Ever Played.” Sports Analytics , Accessed 2 Apr. 2018, doi: 11.1633/tox.31266.
- For a physical object located in a specific place : Include the place where you encountered the object, including the name of any institution and the location of that institution.
- Goldsworthy, Andy. The Wall that Went for a Walk . 1999, Storm King Art Center, Windsor, NY.
How to Write MLA In-Text Citations
In-text citations do two things:
- They identify the places in your paper where you either directly quote or paraphrase a source.
- They contain just enough information to refer to the full entry in the Works Cited list, so a reader can tell which source you quoted or paraphrased from.
MLA In-Text Citations Format
MLA in-text citations follow two basic formats:
- The author’s last name and a page number or other location inside parentheses:
- The greatest game ever played wasn’t “great because of what happened on the field, but because of what happened off of it” (Andrews 71).
- If the author is named in the sentence, then the in-text citation can include just the page:
- As Andrews puts it, the greatest game every played wasn’t “great because of what happened on the field, but because of what happened off of it” (71).
Additions to Basic In-Text Citations Format
There are a few scenarios in which the formatting of in-text MLA citations changes just a bit:
- Two authors : Use the last names of both authors separated by an “and.”
- (Andrews and Smith 71).
- Three authors : Within the parentheses, include the last name of the first author along with “et al.” When mentioning the authors outside the parentheses, use the last name of the first author along with the phrase “and colleagues.”
- (Andrews et al. 71).
- No author : Within the parentheses, include an abbreviated reference to the first two or three words of the source title in the Works Cited entry, and format the in-text citation to match the use of italicization or quotation marks in Works Cited entry. Outside the parentheses, use the entire source title, formatted correctly with quotation marks or italics.
- (The Best Game 71).

Generate formatted bibliographies, citations, and works cited automatically
What is mybib.
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers.
If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically for books, journals, websites, and videos just by searching for a title or identifier (such as a URL or ISBN).
Plus, we're using the same citation formatting engine as professional-grade reference managers such as Zotero and Mendeley, so you can be sure our bibliographies are perfectly accurate in over 9,000 styles -- including APA 6 & 7, Chicago, Harvard, and MLA 7 & 8.
Quick features:
- Untitled Bibliography current
- Create new list
Bibcitation is a free citation generator that creates bibliographies, references and works cited. Automatically generate MLA, APA, Chicago and other citations and create an accurate bibliography in one click.
No citations yet
Our Complete Guide to Citing in MLA 9 Format

In academia, citations help you avoid plagiarism and demonstrate your credibility as a researcher. The MLA format is widely used for this purpose, particularly for writing papers in literature and humanities.
Our comprehensive MLA guide will walk you through the process of citing various types of sources in MLA, as well as formatting your Works Cited list. With plenty of specific examples and step-by-step instructions, you'll be able to master the art of MLA citation in no time.
Get ready to master the art of MLA citations!

Discover More Bibcitation Guides
Mla format overview.
The Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format is a widely used citation style for academic papers in the humanities and liberal arts. Designed to provide a clear and consistent method of citing sources, the MLA format helps writers avoid plagiarism and give proper credit to their sources. This citation style uses two main components: in-text citations and the Works Cited page.
In-text citations appear within the body of the paper, providing a brief reference to the source, usually including the author's last name and the page number where the information was found. In-text citations correspond to the full citation found on the Works Cited page, which is organized alphabetically by the author's last name.
The Works Cited page in the MLA citation format provides a comprehensive list of all sources used in the paper, offering detailed information about each source to help readers locate them. The format varies slightly based on the type of source, such as a book, journal article, or website. The MLA citation style prioritizes clarity and simplicity, making it easy for both writers and readers to understand and navigate the sources used in a paper.
Insert MLA In-text Citations
In the MLA citation format, in-text citations are brief references within the body of a paper that guide readers to the full citation in the Works Cited page. They typically include the author's last name and the page number where the information was found. Here you can find detailed examples of in-text citations in the MLA format:
Basic in-text citation: The most common in-text citation includes the author's last name and the page number(s) in parentheses, placed at the end of the sentence before the period. For example: (Smith 42) .
Multiple authors: If a source has two authors, include both last names in the citation, separated by "and." For example: (Smith and Johnson 58) . If a source has three or more authors, include the first author's last name followed by "et al." For example: (Smith et al. 22) .
Multiple works by the same author: If citing multiple works by the same author, include a shortened version of the title to differentiate between the sources. For example: (Smith, "A Journey into the Universe" 12) and (Queen, Rose Water 35) .
No author: If the source has no author, use a shortened version of the title in quotation marks for articles or in italics for longer works, such as books or websites. For example: ("Article Title" 5) or ( Book Title 32) .
Citing multiple sources in one sentence: If referencing multiple sources in one sentence, separate each citation with a semicolon. For example: (Smith 42; Bart 78) .
Indirect citations (quotations within a source): If citing a quotation from a source that is itself quoting another source, use the abbreviation "qtd. in" before the indirect source. For example: (qtd. in Smith 15) .
Electronic sources without page numbers: When citing electronic sources without page numbers, use the author's last name only or a shortened version of the title if no author is available. For example: (Smith) or ("Article Title") .
Audiovisual sources: If citing a film, television show, or other audiovisual source, use the title (italicized) and a timestamp (hours, minutes, and seconds) instead of a page number. For example: ( Citizen Kane 01:22:15) .
For long quotations, use a block quote format. Indent the entire quotation one inch from the left margin and do not use quotation marks. Place the in-text citation after the closing punctuation.
Smith emphasizes the importance of proper citation:
Citing sources correctly is essential for maintaining academic integrity and avoiding plagiarism. By giving credit to the original authors, you demonstrate respect for their work and allow readers to locate the sources you used. (25)
Format Your MLA Works Cited
A Works Cited page is an essential part of any research paper or academic work using the MLA citation format. It provides a comprehensive list of all sources cited in the paper, allowing readers to locate and verify the sources used.
Here are detailed instructions on how to format a Works Cited page in MLA format:
- Choose placement and title: The Works Cited page should begin on a separate page at the end of your paper. Center the title "Works Cited" (without quotation marks) at the top of the page. Do not bold, italicize, or underline the title.
- Use correct spacing and margins: Use double-spacing throughout the Works Cited page. Maintain 1-inch margins on all sides of the page. The first line of each citation should be flush with the left margin. Indent any additional lines by 0.5 inches (a hanging indent).
- Organize citations: Sort the list of sources in alphabetical order by the author's last name. If a source does not have an author, use the title to alphabetize the entry. Ignore articles ("a," "an," "the") when alphabetizing by title.
- Format entries correctly: Follow the general format for each source type (e.g., books, articles, websites) as specified in the MLA Handbook. Include the author's name, the title of the work, the container (if applicable), and other relevant information such as the publisher, publication date, and location.
- Don't forget about punctuation and capitalization: Use title case for titles, capitalizing the first word, the last word, and all other major words. Use punctuation marks consistently, following the guidelines in the MLA Handbook.
- Check for accuracy: Be sure to check each reference for accuracy, including spelling and punctuation, as well as proper capitalization and italics.

Remember to consult the MLA Handbook for specific guidelines and examples for various source types. As you add sources to your Works Cited page, be sure to double-check the formatting to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Cite Books in MLA
To cite a book in your Works Cited list, follow this format:
For example:
If the book is an edited volume, use the word "editor" or "editors" after the editor's name, depending on whether it is a single or multiple editors.
Citing an edited book:
For books with multiple editions, specify the edition after the title, using ordinal numbers (e.g., "2nd ed.").
Citing a book with multiple editions:
If a book is part of a series or multivolume set, include the volume number after the title, preceded by "vol." In cases where a book has no author, the citation should begin with the title.
When citing a book that has been translated, include the translator's name after the title, preceded by the word "Translated by."
Citing a translated book:
When citing a specific chapter or essay within an edited book or anthology, start with the author's name, followed by the title of the chapter or essay in quotation marks, then the title of the book, the editor's name, and the page numbers of the cited section.
Citing a specific portion of a book:
These examples cover various scenarios and exceptions for citing books in MLA format. Remember to consult the MLA Handbook for more information and specific guidelines when formatting your citations.
Cite Journal Articles in MLA
When citing a journal article in MLA format, follow this template:
For the journal articles that you accessed online, from JSTOR or a different online database, make sure to include the DOI or the URL if the DOI is unavailable.
Citing a journal article accessed online:
If an article has two authors, include both authors' names separated by "and."
Citing an article with two authors:
If an article has three or more authors, list only the first author, followed by "et al."
Citing an article with three authors:
In some cases, the journal article may not have an official author or some other elements, like the volume or issue number. In this situation, the title of the article is used in place of the author's name, while the volume and issue are omitted.
Citing an article without an author, volume or issue number:
Cite Websites in MLA
Citing a webpage on your MLA Works Cited page? Use the following format:
However, web pages may often not have an identified author. In this situation, the title of the article is used in place of the author's name. For example:
Citing a web page without an author:
When citing a website with an organization as the author, you can use the organization's name as both the author and the website name if they are the same.
Citing a website with an organization as the author:
If no publication date is available, use the abbreviation "n.d." (no date).
Moreover, for online sources without a publication date or for sources that can be updated or changed without notice (like web pages), it is recommended to include the "Accessed" date. This provides a clearer timeline of when the researcher viewed the material and ensures accuracy, as the content might have been updated or removed since that date. Using the "Accessed" date is especially useful for materials that are subject to change or when a source's stability cannot be guaranteed.
Cite Book Chapters in MLA
Citing a book chapter in MLA format requires you to include the chapter author and the book editor(s). The format is:
If the book is a translation, include the translator's name after the editor's name (if any), preceded by the phrase "translated by."
Citing a chapter in a translated book:
If the chapter has a unique title within a larger work, such as a play within an anthology or a collection of works by different authors, include the title of the larger work in italics, followed by the editor's name (if any) and the page numbers of the cited section.
Citing a chapter from a collection of works:
If the book is a multivolume set, include the volume number after the book title and edition (if available), preceded by "vol."
For chapters with supplementary materials or appendices, include the relevant page numbers or identifiers in the citation.
Cite Ebooks in MLA
Citing an ebook in MLA format follows similar guidelines to citing a printed book, but with a few additional details. The basic format for citing an ebook is as follows:
If the ebook has a DOI (Digital Object Identifier), the citation should include it at the end of the reference.
Citing an ebook with a DOI:
If your ebook was only available on a tablet, e-reader, or a reading app such as Kindle, all you need to do is to include the words "E-book ed."after the title.
Citing an ebook from a personal device:
In some scenarios, additional elements need to be included in the citation. If the ebook is part of a series, provide the series name and volume number after the publisher and before the publication date.
If the ebook is a translation, include the translator's name after the editor's name (if available), preceded by the phrase "translated by." For ebooks with supplementary materials, include the relevant page numbers or identifiers in the citation.
Cite Magazine Articles in MLA
To cite a magazine article in your MLA Works Cited page, use the following format:
If the magazine article is found online, you should also provide the URL or DOI at the end of the citation.
If the magazine is published seasonally (e.g., Winter, Spring, Summer, or Fall) rather than monthly, include the season and year as the publication date (e.g., Winter 2021).
Cite Newspaper Articles in MLA
For newspaper articles, the MLA citation format is similar to magazine articles:
If the article is found online, include the URL or the DOI (Digital Object Identifier) if available, but do not include the page numbers.
If the newspaper isn't widely recognized or is a local paper, include the name of the city in parentheses following the newspaper's title.
If the article is available in both print and digital formats, the citation should be identical for both, but for digital articles, you should also include a DOI or a URL at the end of the citation.
Cite Conference Papers in MLA
To cite published conference proceedings in MLA, use the following format:
After the author's name, make sure to include the title of the paper in quotation marks, followed by the title of the conference (italicized), the date and location of the conference, and any relevant publication information (for instance, whether the paper has been published).
When a conference paper is part of a published conference proceedings, include the editor's name (if available) preceded by "edited by," the title of the proceedings (italicized), the publisher, and the publication date.
For online conference papers, provide the URL or DOI (if available) at the end of the citation.
Citing an edited conference paper available online:
Remember that each specific conference paper may require additional information or variations in the citation format.
Cite Audio & Visual Media in MLA
For audiovisual materials like films, television series, and YouTube videos, include the contributor(s) most relevant to your source, such as the director, or if not available, then producer, or writer. The MLA citation format for films materials is:
However, there are some exceptions to this format. When citing a TV-show episode, make sure to include the show title, as well as the season and episode numbers.
Citing a TV-show episode:
If you’re looking to cite a song, your citation should include the song title, as well as the name of the album and format (if applicable), or URL or DOI (if available).
Citing a song:
Remember that different scenarios and exceptions may require you to adapt these structures. Always consult the MLA Handbook for more information and specific guidelines when formatting your citations for audio and visual materials.
Cite Podcasts in MLA
To cite a podcast episode in MLA format, use the following citation structure:
If the podcast episode does not have an episode number, omit it from the citation.
If you need to cite a specific guest on the podcast, include their name and the description "guest" after the title of the podcast.
Keep in mind that you may need to adapt your citation based on the specific information available for the podcast and the focus of your discussion.
Cite Social Media Posts in MLA
For social media posts, use the following format in your MLA Works Cited:
Citing an Instagram post:
If the account name and its corresponding handle are similar (e.g., @aliciakeys and Alicia Keys), it is generally recommended to exclude the handle when including a URL in the entry. However, if you are not providing a URL, such as when referencing a mobile version of the site, it is advisable to include the handle, as it can assist your reader in locating the specific post.
Citing a Twitter post:
Citing a Facebook post:
Moreover, if you are accessing a post on the mobile version of a social media site and the copyright date is not visible, it is recommended to include the date you accessed the post as an additional element at the end of the entry.
Cite Images & Artworks in MLA
To cite an online image or artwork in your MLA citation list, the format is:
For digital images or artwork viewed online, begin with the artist's name, the title of the artwork in italics, the date of creation (if known), the website hosting the artwork or the name of the database, and the URL or DOI (if available).
Citing an image or artwork viewed online:
In cases where the creation date or author name is unknown, you can make adjustments to the citation format to account for the missing information.
If the creation date of the artwork is unknown, you can use the abbreviation "n.d." (no date) in place of the date.
If the author of the artwork is unknown, you can start the citation with the title of the artwork in italics. If it's necessary to provide context or specify that the author is unknown, you can use the term “Unknown Artist”, “Anonymous” or “Anon.”.
Citing an artwork with an unknown author and creation date:
Remember that citation requirements may vary depending on the context and the focus of your work. Always consult the MLA Handbook for more information and specific guidelines when formatting your citations with unknown information.
Cite Theses & Dissertations in MLA
When citing a thesis or dissertation in your MLA paper, use the following format:
For a digital thesis or dissertation, begin with the author's name, the title of the work in italics, the year of completion, the institution where the work was completed, the description of the work as a thesis or dissertation, and the URL or DOI (if available).
Citing a thesis or dissertation published online:
Cite Databases & Data Sets in MLA
When citing datasets or statistical data, include the author, publication year, title of the dataset, version, publisher, and the DOI or URL in your MLA Works Cited page:
If you are citing a specific work within a database or using data from a data set, you should first cite the work or the data following the appropriate citation format for that type of source (e.g., a journal article, a book, a newspaper article), and then add the database or data set as a supplementary source at the end of the citation.
Cite Mobile Applications in MLA
Citing mobile applications in MLA format requires the author, the app's release year, the app's title, the version, and the platform in your reference list entry:
Keep in mind that you may need to modify these examples based on the specific information available for the mobile application and the focus of your discussion.
Cite Classical Works
Citing classical works in MLA format involves various scenarios, depending on factors such as the type of source (print or digital), the specific edition or translation being cited, and the availability of specific information (author, title, date, etc.).
Keep in mind that classical works often have unique citation requirements due to their historical context and the numerous editions, translations, or versions available.
Here is the general structure for citing classical works in MLA format:
N.B. When referencing classical works, the original publication year is often unknown or irrelevant; instead, provide the year of the translation or version you are using in parentheses, followed by a period.
Cite Legal Documents
For a legal document as the main focus of your MLA citation, provide the title of the document in italics, the document number or code, the name of the authority issuing the document, the publication date, and the URL or DOI (if available).
For court cases , the citation structure is a bit different:
When citing the Constitution , you can use the following format: Title of Constitution, jurisdiction or authority, publication date, URL or DOI (if available).
For more information and examples on how to cite different government documents in the MLA format, we suggest that you follow these guidelines from the MLA Style Center.
Cite Online Lectures & TED Talks
When citing online lectures, webinars, or TED Talks, include the speaker, the date, the title of the talk, and the URL in your APA reference list entry:
Cite Course Materials & Lectures in MLA
Course materials are considered unique academic sources and should be cited according to the guidelines for educational or instructional materials. Here is the general structure for citing course materials in MLA format:
Cite Personal Communications in MLA
In MLA format, personal communications, such as interviews, emails, letters, or personal conversations, are considered unpublished sources and are not typically included in the Works Cited list because they cannot be accessed by your readers.
Instead, you should provide a parenthetical citation within the text of your document, giving credit to the source.
When citing personal communications in your text, mention the source of the communication, the type of communication (e.g., email, letter, personal interview, etc.), and the date the communication took place.
Here is the general structure for citing personal communications in MLA format:
(Source's Last Name, Type of Communication, Date)
Keep in mind that you should only cite personal communications in the body of your text, as they cannot be accessed by your readers and, therefore, should not be listed in the Works Cited page.
- Personal interview: According to John Smith , the use of renewable energy has increased dramatically in the last decade (personal interview, 7 May 2023) .
- Email: Jane Doe mentioned in an email that her research findings support the use of electric vehicles to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (12 April 2023) .
- Letter: She recently expressed her concerns about the environmental impact of deforestation (Sarah Johnson, letter, 10 June 2022) .
Always ensure that you have the permission of the person you are citing to include their personal communication in your work, as this information is not publicly accessible and may involve privacy concerns.
MLA Style: Final Notes
As you can see, the MLA citation format provides a consistent and clear method for citing various types of sources in your research. By mastering the MLA citation style, you will not only make your work more professional but also help your readers easily locate the sources you have used.
We hope this comprehensive guide on MLA citation style has provided you with a solid foundation for citing sources in your research. Remember that Bibcitation is here to help you with your academic needs, offering accurate and easy-to-use tools.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- School access
The best papers start with EasyBib®
Powered by chegg.
Start a new citation or manage your existing projects.
Scan your paper for plagiarism and grammar errors.
Check your paper for grammar and plagiarism
Catch plagiarism and grammar mistakes with our paper checker
Wipe out writing errors with EasyBib® Plus
Double check for plagiarism mistakes and advanced grammar errors before you turn in your paper.
- expert check
Know you're citing correctly
No matter what citation style you're using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) we'll help you create the right bibliography
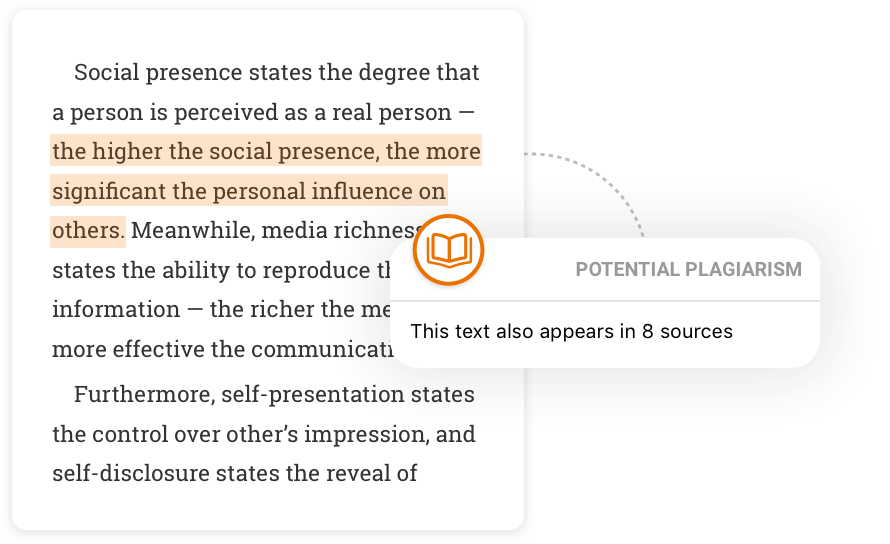
Check for unintentional plagiarism
Scan your paper the way your teacher would to catch unintentional plagiarism. Then, easily add the right citation
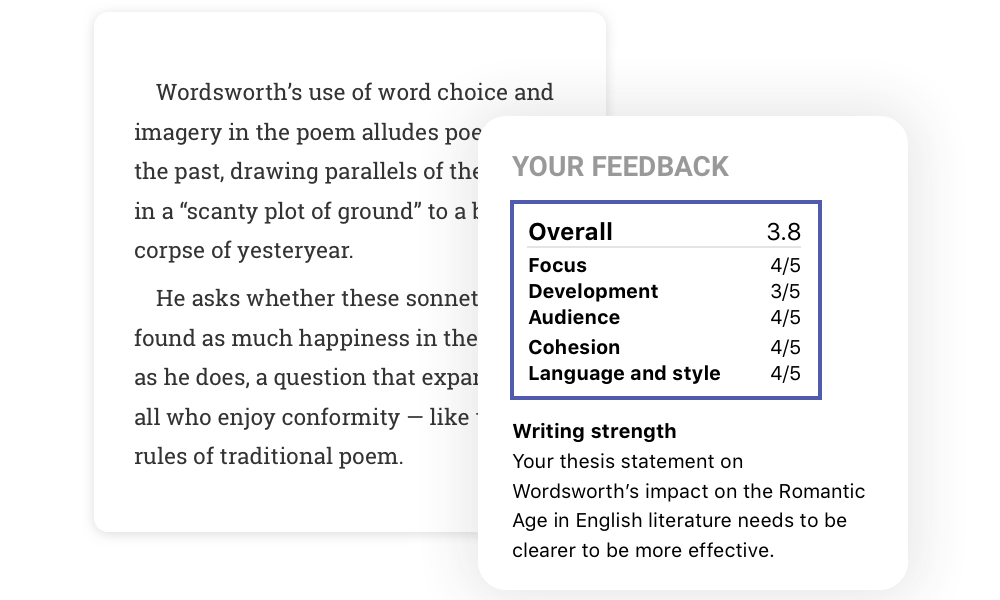
Strengthen your writing
Give your paper an in-depth check. Receive feedback within 24 hours from writing experts on your paper's main idea, structure, conclusion, and more.

Find and fix grammar errors
Don't give up sweet paper points for small mistakes. Our algorithms flag grammar and writing issues and provide smart suggestions
Choose your online writing help
Easybib® guides & resources, mla format guide.
This is the total package when it comes to MLA format. Our easy to read guides come complete with examples and step-by-step instructions to format your full and in-text citations, paper, and works cited in MLA style. There’s even information on annotated bibliographies.
Works Cited | In-Text Citations | Bibliography | Annotated Bibliography | Website | Book | Journal | YouTube | View all MLA Citation Examples
APA Format Guide
Get the facts on citing and writing in APA format with our comprehensive guides. Formatting instructions, in-text citation and reference examples, and sample papers provide you with the tools you need to style your paper in APA.
Reference Page | In-Text Citations | Annotated Bibliography | Website | Books | Journal | YouTube | View all APA citation Examples
Chicago Format Guide
Looking to format your paper in Chicago style and not sure where to start? Our guide provides everything you need! Learn the basics and fundamentals to creating references and footnotes in Chicago format. With numerous examples and visuals, you’ll be citing in Chicago style in no time.
Footnotes | Website | Book | Journal
Harvard Referencing Guide
Learn the requirements to properly reference your paper in Harvard style. The guides we have provide the basics and fundamentals to give credit to the sources used in your work.
In-Text Citations | Books | Article | YouTube | View all Harvard Referencing Examples
Check Your Paper
Avoid common grammar mistakes and unintentional plagiarism with our essay checker. Receive personalized feedback to help identify citations that may be missing, and help improve your sentence structure, punctuation, and more to turn in an error-free paper.
Grammar Check | Plagiarism Checker | Spell Check
Learn From Our Innovative Blog
Our blog features current and innovative topics to keep you up to speed on citing and writing. Whether you’re an educator, student, or someone who lives and breathes citations (it’s not as uncommon as you might think!), our blog features new and exciting articles to discover and learn from.
Looking for Other Tools and Resources?
Our Writing Center is jam-packed with tons of exciting resources. Videos, infographics, research guides, and many other citation-related resources are found here. Check it out to find what you need to succeed!
- EasyBib® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style Format
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
According to MLA style, you must have a Works Cited page at the end of your research paper. All entries in the Works Cited page must correspond to the works cited in your main text.
Basic rules
- Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. It should have the same one-inch margins and last name, page number header as the rest of your paper.
- Only the title should be centered. The citation entries themselves should be aligned with the left margin.
- Double space all citations, but do not skip spaces between entries.
- Indent the second and subsequent lines of citations by 0.5 inches to create a hanging indent.
- List page numbers of sources efficiently, when needed. If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp. 225-50). If the excerpt spans multiple pages, use “pp.” Note that MLA style uses a hyphen in a span of pages.
- If only one page of a print source is used, mark it with the abbreviation “p.” before the page number (e.g., p. 157). If a span of pages is used, mark it with the abbreviation “pp.” before the page number (e.g., pp. 157-68).
- If you're citing an article or a publication that was originally issued in print form but that you retrieved from an online database, you should type the online database name in italics. You do not need to provide subscription information in addition to the database name.
- For online sources, you should include a location to show readers where you found the source. Many scholarly databases use a DOI (digital object identifier). Use a DOI in your citation if you can; otherwise use a URL. Delete “http://” from URLs. The DOI or URL is usually the last element in a citation and should be followed by a period.
- All works cited entries end with a period.
Additional basic rules new to MLA 2021
New to MLA 2021:
- Apps and databases should be cited only when they are containers of the particular works you are citing, such as when they are the platforms of publication of the works in their entirety, and not an intermediary that redirects your access to a source published somewhere else, such as another platform. For example, the Philosophy Books app should be cited as a container when you use one of its many works, since the app contains them in their entirety. However, a PDF article saved to the Dropbox app is published somewhere else, and so the app should not be cited as a container.
- If it is important that your readers know an author’s/person’s pseudonym, stage-name, or various other names, then you should generally cite the better-known form of author’s/person’s name. For example, since the author of Alice's Adventures in Wonderland is better-known by his pseudonym, cite Lewis Carroll opposed to Charles Dodgson (real name).
- For annotated bibliographies , annotations should be appended at the end of a source/entry with one-inch indentations from where the entry begins. Annotations may be written as concise phrases or complete sentences, generally not exceeding one paragraph in length.
Capitalization and punctuation
- Capitalize each word in the titles of articles, books, etc, but do not capitalize articles (the, an), prepositions, or conjunctions unless one is the first word of the title or subtitle: Gone with the Wind, The Art of War, There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
- Use italics (instead of underlining) for titles of larger works (books, magazines) and quotation marks for titles of shorter works (poems, articles)
Listing author names
Entries are listed alphabetically by the author's last name (or, for entire edited collections, editor names). Author names are written with the last name first, then the first name, and then the middle name or middle initial when needed:
Do not list titles (Dr., Sir, Saint, etc.) or degrees (PhD, MA, DDS, etc.) with names. A book listing an author named "John Bigbrain, PhD" appears simply as "Bigbrain, John." Do, however, include suffixes like "Jr." or "II." Putting it all together, a work by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. would be cited as "King, Martin Luther, Jr." Here the suffix following the first or middle name and a comma.
More than one work by an author
If you have cited more than one work by a particular author, order the entries alphabetically by title, and use three hyphens in place of the author's name for every entry after the first:
Burke, Kenneth. A Grammar of Motives . [...]
---. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
When an author or collection editor appears both as the sole author of a text and as the first author of a group, list solo-author entries first:
Heller, Steven, ed. The Education of an E-Designer .
Heller, Steven, and Karen Pomeroy. Design Literacy: Understanding Graphic Design.
Work with no known author
Alphabetize works with no known author by their title; use a shortened version of the title in the parenthetical citations in your paper. In this case, Boring Postcards USA has no known author:
Baudrillard, Jean. Simulacra and Simulations. [...]
Boring Postcards USA [...]
Burke, Kenneth. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
Work by an author using a pseudonym or stage-name
New to MLA 9th edition, there are now steps to take for citing works by an author or authors using a pseudonym, stage-name, or different name.
If the person you wish to cite is well-known, cite the better-known form of the name of the author. For example, since Lewis Carroll is not only a pseudonym of Charles Dodgson , but also the better-known form of the author’s name, cite the former name opposed to the latter.
If the real name of the author is less well-known than their pseudonym, cite the author’s pseudonym in square brackets following the citation of their real name: “Christie, Agatha [Mary Westmacott].”
Authors who published various works under many names may be cited under a single form of the author’s name. When the form of the name you wish to cite differs from that which appears on the author’s work, include the latter in square brackets following an italicized published as : “Irving, Washington [ published as Knickerbocker, Diedrich].”.
Another acceptable option, in cases where there are only two forms of the author’s name, is to cite both forms of the author’s names as separate entries along with cross-references in square brackets: “Eliot, George [ see also Evans, Mary Anne].”.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
- powered by chegg.
Keep all of your citations in one safe place
Create an account to save all of your citations
Check your paper before your teacher does!
Avoid plagiarism — quickly check for missing citations and check for writing mistakes., your ultimate mla format guide & generator, what is mla.
MLA stands for the Modern Language Association , an organization that focuses on language and literature.
Depending on which subject area your class or research focuses on, your professor may ask you to cite your sources in MLA style. This is a specific way to cite, following the Modern Language Association's guidelines. There are other styles, such as APA format and Chicago citation style , but MLA format is often used for literature, language, liberal arts, and other humanities subjects. This guide extensively covers this format but is not associated with the organization.
What is MLA Citing?
The Modern Language Association Handbook is in its 9th edition and standardizes the way scholars document their sources and format their papers. When everyone documents their sources and papers in the same way, it is simple to recognize and understand the types of sources used for a project. Readers of your work will look at your citations not only to understand them but possibly to explore them as well.
When you're borrowing information from a source and placing it in your research or assignment, it’s important to give credit to the original author. This is done by creating an MLA citation. Depending on the type of information you're including in your work, you may place citations in the body of your project and in a works-cited list at the end of your project.
The handbook explains how to create MLA citations. This page summarizes the information in the handbook’s 9th edition.
There is also a section below on a recommended way to create an MLA header. These headers appear at the top of your assignment’s pages. Check with your instructor on whether they prefer a certain MLA format for the header.
What is MLA Format?
The 9th edition is the most recent and updated version for MLA citations. Released in April 2021, the citation format differs slightly from previous versions. This update follows the 2016 update for the 8th edition that contained many significant changes from previous editions.
For the 8th edition, the biggest difference and most exciting update was the use of one standard format for all source types. In previous versions, scholars were required to locate the citation format for the specific source that they used. There were different formats for books, websites, periodicals, and so on. After 2016, using one universal MLA citation format allowed scholars to spend less time trying to locate the proper format to document their sources and focus more on their research .
Other updates included the addition of “containers.” A container provides details on a work contained within a larger work. For example, books contain chapters, albums contain songs, and journals contain journal articles. The source is the larger work, such as a website, while the container is a smaller work within that source, such as a short story on the website.
MLA now encourages you to add DOIs or URLs to citations. Use a DOI instead of a URL when it’s available. According to the MLA 9th edition, you can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx).
Social media pseudonyms and usernames can replace the real name of the author. Volume and issue numbers are now abbreviated as “vol.” and “no.” Cities of publication and the source’s medium (such as print or web) are no longer included in citations. For academic presses/publishers, with the words “university” or “press,” shorten “university” to “U”, and “press” to “P” (Cambridge UP). Lowercase seasons when using them in the date field of a citation (spring 2021 not Spring 2021).
Bibliography vs. Works Cited - What's the Difference?
You may have heard the two terms, "Bibliography" and "Works Cited" thrown around interchangeably. The truth is that they are two different words with two completely different meanings.
A bibliography is a list of sources that the writer recommends for further reading. A works-cited list is a list of sources that were included in the author's writing.
Want to suggest some books and websites to your reader? Create an MLA format bibliography by creating a list of full citations and label the page as "Bibliography."
Did you use any quotes or place any paraphrases in your writing? Create in-text citations and place them in the body of your work. Then, create a list of full citations and place them at the end of the project. Label the page as "Works Cited."
The good news is that references in MLA bibliography format and regular works-cited lists are structured the exact same way.
Citing Basics
When adding information to your project from another source, you are required to add an MLA citation. There are two types of MLA format citations: in-text citations and full citations.
Full Citation Basics:
All sources used for a project are found on the MLA format “Works Cited” page, which is generally the last portion of a project.
MLA citing format often includes the following pieces of information, in this order:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Source." Title of Container , Other contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication Date, Location.
For more information about each individual element and for proper formatting rules, see the sections below on author names, titles, containers, names of other contributors, source versions, numbers, publishers, publication dates, and locations.
Find more in-depth rules regarding the works-cited list in MLA format on the page down below, along with a sample page.
Don't forget, our BibMe MLA citation generator is an MLA formatter that helps you create your citations quickly and easily!
Citation Components
The author's name is generally the first item in a citation (unless the source does not have an author). The author's name is followed by a period.
If the source has one author , place the last name first, add a comma, and then the first name.
MLA format:
Lee, Harper.
Fitzgerald, F. Scott.
If your source has two authors , place them in the same order they're shown on the source. The first author is in reverse order, add a comma and the word "and", then place the second author in standard form. Follow their names with a period.
Monsen, Avery, and Jory John.
For three or more authors , only include the first listed author's name. Place the first author's name in reverse order (Last name, First name) place a comma afterwards, and then add the Latin phrase "et al."
Borokhovic, Kenneth A., et al.
For social media posts, it's acceptable to use a screen name or username in place of the author's name. Start the citation with the user's handle.
@TheOnion. "Experts Warn Number of Retirees Will Completely Overwhelm Scenic Railway Industry by 2030." Twitter , 9 Oct. 2017, 9:50 a.m., twitter.com/TheOnion/status/917386689500340225.
No author listed? If there isn't an author, start the citation with the title and skip the author section completely.
Citations do not need to always start with the name of the author. When your research focuses on a specific individual that is someone other than the author, it is appropriate for readers to see that individual's name at the beginning of the citation. Directors, actors, translators, editors, and illustrators are common individuals to list at the beginning. Again, only include their name in place of the author if your research focuses on that specific individual.
To include someone other than the author at the beginning of the citation, place their name in reverse order, add a comma afterwards, and then the role of that individual followed by a period.
Fimmel, Travis, performer. Vikings . Created by Michael Hirst, History Channel, 2013-2016.
Gage, John T., editor. The Promise of Reason: Studies in the New Rhetoric . SIU Press, 2011.
Here's a helpful table to refer to when structuring author names:
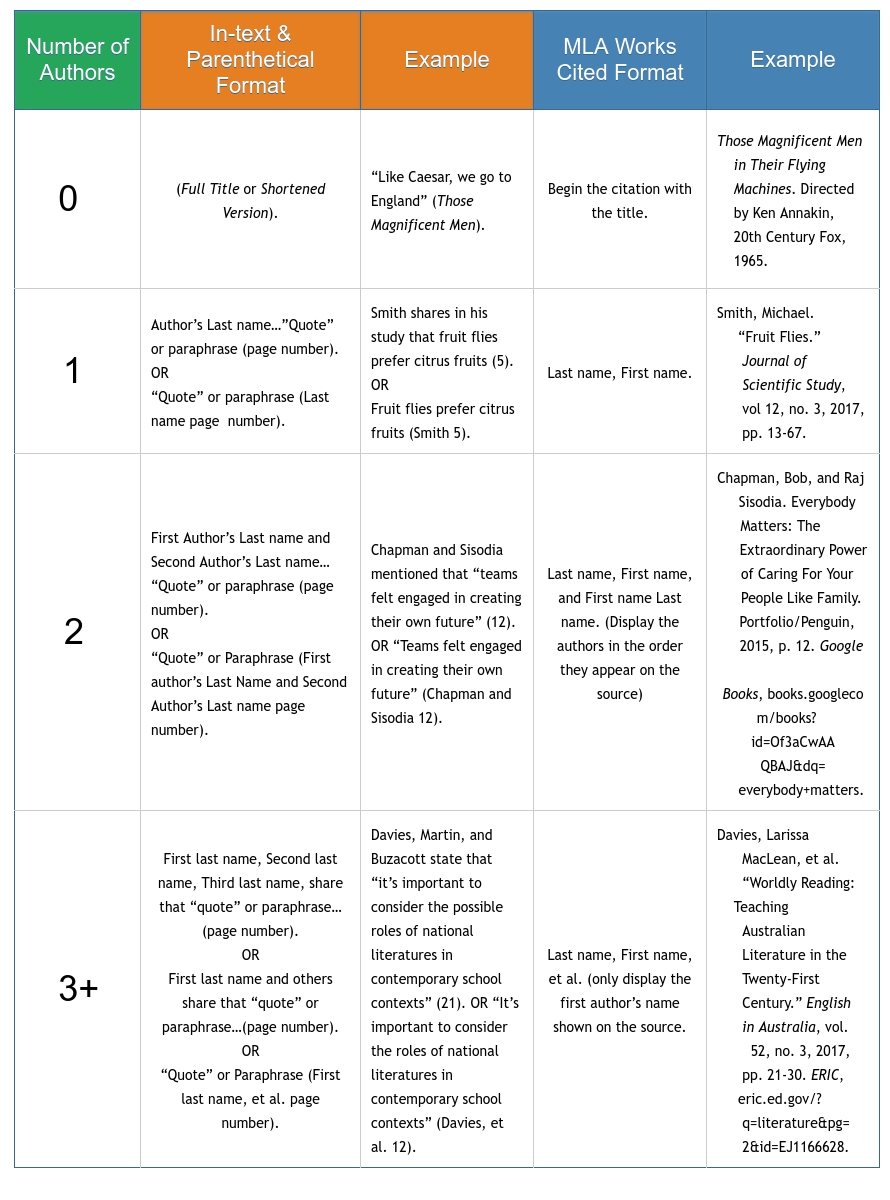
Titles and Containers:
Titles follow the name of the author and are written in title capitalization form.
If you're citing a source in its entirety, such as a full book, a movie, or a music album, then place the title in italics.
Franzen, Jonathan. The Corrections . Farrar, Straus, and Giroux, 2001.
Rufus Du Sol. Bloom . Sweat It Out! 2016.
If you're citing a source, such as a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a journal or website, then place the title of the piece in quotations and add a period afterwards. Follow it with the title of the full source, in italics, and then add a comma. This second portion is called the container . Containers house smaller works, such as songs, in larger comprehensive works, such as albums.
Examples with containers:
Wondering what to do with subtitles? Place a colon in between the title and subtitle. Write both parts in title capitalization form.
Nasar, Sylvia. A Beautiful Mind: The Life of Mathematical Genius and Nobel Laureate John Nash . Simon and Schuster, 2001.
If the source does not have a title , give a brief description and do not use quotation marks or italics.
Israel, Aaron. Brooklyn rooftop acrylic painting. 2012, 12 W 9th Street, New York City.
For a tweet , the full text of the tweet is placed where the title sits.
@LOCMaps. "#DYK the first public zoo to open in the US was the #Philadelphia Zoo? #50States." Twitter , 9 Feb. 2017, 3:14 p.m., twitter.com/LOCMaps/status/829785441549185024.
For email messages, the subject of the email is the title. Place this information in quotation marks.
Rabe, Leor. "Fwd: Japan Itinerary." Received by Raphael Rabe, 11 Feb 2017.
Citations with Two Containers:
It is possible for a source to sit in a second or larger container. A journal article sits in its first container, which is the journal itself, but it can also sit in a larger container, such as a database. A song can sit in its first container, which is the album it's found on. Then it can sit in its next container, which could be Spotify or iTunes.
It is important to include the second container because the content on one container may differ from content from another container.
MLA citing with two containers should be formatted like this:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Source." Title of Container , Other Contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication Date, Location. Title of Second Container , Other Contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication Date, Location.
In most cases, for the second container, only the title of the second container and the location is needed. Why? For readers to locate the source themselves, they'll most likely use the majority of the information found in the first part of the citation.
Examples of Citations with 2 Containers:
Sallis, James, et al. "Physical Education's Role in Public Health: Steps Forward and Backward Over 20 Years and Hope for the Future." Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport , vol. 83, no. 2, Jun. 2012, pp. 125-135. ProQuest , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=http://search.proquest.com/docview/1023317255?accountid=35635.
Baker, Martha. "Fashion: Isaac in Wonderland." New York Magazine , vol. 24, no. 3, 21 Jan. 1991, pp. 50-54. Google Books , books.google.com/books?id=PukCAAAAMBAJ&lpg=PP1&dq=magazine&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=magazine&f=false.
Remember, BibMe has an MLA works-cited generator that creates citations for you quickly and easily!
Format for Other Contributors:
In MLA citing, when there are other individuals (besides the author) who play a significant role in your research, include them in this section of the citation. Other contributors can also be added to help individuals locate the source themselves. You can add as many other contributors as you like.
Start this part of the citation with the individual's role, followed by the word "by". Notice that when adding other contributors after a period, you capitalize the first letter of the individual's role. When adding other contributors after a comma, you lowercase the first letter of the individual’s role.
Gaitskill, Mary. "Twilight of the Superheroes." The Scribner Anthology of Contemporary Short Fiction: 50 North American Stories Since 1970, edited by Lex Williford and Michael Martone, Simon and Schuster, 2012, pp. 228-238.
The Incredibles . Directed by Brad Bird, produced by John Walker, Pixar, 2004.
Gospodinov, Georgi. The Physics of Sorrow . Translated by Angela Rodel, Open Letter, 2015.
Format for Versions:
Sources can come in different versions. There are numerous bible versions; books can come in versions (such as numbered editions), and even movies and songs can have special versions.
When a source indicates that it is different than other versions, include this information in the citation. This will help readers locate the exact source that you used for your project.
The Bible . Lexham English Version, Logos, 2011, lexhamenglishbible.com.
Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion . 2nd ed., Clarendon, 1979.
Afrojack. "Take Over Control." Beatport , performance by Eva Simons, extended version, 2011, www.beatport.com/track/take-over-control-feat-eva-simons-extended/1621534.
Format for Numbers:
Any numbers related to a source that isn't the publication date, page range, or version number should be placed in the numbers position of the citation. This includes volume and issue numbers for journal articles, volume or series numbers for books, comic book numbers, and television episode numbers, to name a few.
When including volume and issue numbers, use the abbreviation “vol.” for volume and “no.” for number.
Zhai, Xiaojuan, and Jingjing Wang. "Improving Relations Between Users and Libraries: A Survey of Chinese Academic Libraries." The Electronic Library , vol. 34, no. 4, 2016, pp. 597-616. ProQuest Research Library , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=http://search.proquest.com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/1841764839?accountid=35635.
"Chestnut." Westworld , directed by Richard J. Lewis, season 1, episode 2, Warner Bros., 2016.
Publishers:
The publisher produces the source. In the citation, place the publisher before the date of publication. Include the publisher for any source type except websites when the name of the publisher is the same as the name of the website. Also, it’s not necessary to include the name of publishers for newspapers, magazines, or journal articles, since the name of the publisher is generally insignificant.
When sources have more than one publisher that share responsibility for the production of the source, place a slash between the names of the publishers.
Use the abbreviation “UP” when the name of the publisher includes the words “University Press.”
Cambridge UP
Publication Dates:
When including the date that the source was published, display the amount of information that is found on the source, whether it's the full date, the month and year, or just the year.
If the date includes a season rather than a month, make sure to lowercase the season (spring 2021 not Spring 2021). Do not capitalize the season.
2 Nov. 2016 or Nov. 2, 2016
When multiple dates are shown on the source, include the date that is most relevant to your work and research.
Abbreviate months longer than 4 letters.
The location refers to the place where the source can be found. This can be in the form of a URL, page number, disc number, or physical place.
When citing websites in MLA, include DOIs or URLs. Copy the DOI or URL directly from the address bar or link in your browser window. If a DOI number is present, use it in place of a URL. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx.
For page numbers, use the abbreviation “p.” when referring to only one page, and “pp.” for a range of pages.
In-Text & Parenthetical Citation Basics:
When using a direct quote or paraphrasing information from a source, add an in-text or parenthetical citation into the body of your work. Direct quotes are word-for-word quotes pulled from a source and added to your project. A paraphrase is when you take a section of information from a source and put it in your own words. Both direct quotes and paraphrases require an in-text or parenthetical citation to follow it.
Format your parenthetical or in-text citation in MLA as follows:
"Direct quote" or paraphrase (Author's last name and page number).
Author's last name said that "Direct Quote" or paraphrase (page number).
*See the comprehensive section below on MLA in-text citations for further clarification and instructions.
MLA In-Text and Parenthetical Citations
What is an in-text citation or parenthetical citation.
You used information from websites, articles, books, and other sources for your paper, right? Hopefully, you did, because the best research and writing projects validate claims using information from other sources.
The purpose of an in-text citation is to give the reader a brief idea about where you found the information used in your writing.
When you place a line of text, word for word (called a direct quote), or an idea (called a paraphrase) from another source into your writing, you, the writer, must display:
- who created that information (the original author's name)
- the page number you found it on
Check out this example:
"A main clause has to have a finite verb " (Cameron 94).
No author? No problem! Include the title, and if it's lengthy, shorten it.
The major thing to keep in mind is that whichever information you include in the in-text or parenthetical citation, whether it's the author's name or the title, it needs to match the first word in the full citation. The full citation is found on the “Works Cited” page in MLA.
Format your parenthetical and MLA in-text citation as follows:
"Direct quote" or Paraphrase (Author's last name and page number). This is an MLA parenthetical citation as the author's name is in parentheses.
Author's Last Name states, "Direct Quote" or paraphrase (page number). This is an MLA citation in prose as the author's name is in the prose of your sentence.
"Jim never got back with a bucket of water under an hour—and even then somebody generally had to go after him" (Twain 8).
Twain went on to say, “Jim never got back with a bucket of water under an hour—and even then somebody generally had to go after him” (8).
Other things to keep in mind:
If your in-text citation comes from a website or another source that does not have page numbers, use the following abbreviations:
- If the source has designated paragraph numbers, use par. or pars.
- If the source has designated sections, use sec. or secs.
- If the source has designated chapters, use ch. or chs.
- If the source has designated lines, use line or lines.
Example in MLA formatting:
Gregor's sister is quite persuasive, especially when she states to her parents, "It'll be the death of both of you, I can see it coming. We can't all work as hard as we have to and then come home to be tortured like this, we can't endure it" (Kafka, ch. 3).
- If there aren't page, paragraph, section, or chapter numbers, only include the author's name in the in-text or parenthetical citation.
- If the original source is an audio or video recording, after the author's name or title, place a timestamp.
The girl's affection towards Marley is clear when she blushes upon his arrival and shares that she would like to accompany him to the theater ( Tales of Times Ago 12:45).
- Two authors : place both names in the reference.
Malcolm and Knowles state... (12).
The smaller the class size, the more attention a student receives, which greatly impacts learning (Malcolm and Knowles 12).
- Three or more authors : place all three names in the in-text citation. It's also acceptable to use the phrase, "and others," or another cohesive term. For parenthetical citations, use the abbreviation et al.
Smith, Baker, and Klein share that.... (78). OR Smith and others share that.... (78).
Many lizards, including the Carolina anole, only eat when they're hungry. They'll ignore food until their body sends a signal to eat (Smith et al. 78).
- Authors with the same last name : Include the first initial of the author’s first name in the in-text or parenthetical citation.
One study shows that the average time spent on homework is 52 minutes (R. Brown 17). However, a more recent study, released in 2018, found that the average student spends 42 minutes completing homework (S. Brown 966).
- Quoted text : Share in the text that the quote comes from another individual.
Lawrence shares his insight by stating that “instructions need to be shared, not assumed” (Young 55).
Common Examples:
Citations for books:.
The basic entry for a book consists of the author's name, the book title, the publisher, and the year published.
Author's Last name, First name. Book Title . Publisher, Year Published.
MLA book citation example:
Shelley, Mary. Frankenstein . Lackington, Hughes, Harding, Mavor & Jones, 1818.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears on the title page.
For a book written by two authors:
- List them in order as they appear on the cover or title page.
- Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the second author's name is written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the second author's name.
Smith, John, and Bob Anderson. The Sample Book . Books For Us, 2017.
- For books with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by a comma and the abbreviation "et al."
Campbell, Megan, et al. The Best Noun Book . Books For Us, 2017.
The full title of the book, including any subtitles, should be italicized and followed by a period. If the book has a subtitle, the main title should be followed by a colon (unless the main title ends with a question mark or exclamation point).
The Best Books for Kids: A Complete Anthology.
Publication information can generally be found on the title page of a book. If it is not available there, it may also be found on the copyright page. State the name of the publisher.
If you are citing a specific page range from the book, include the page(s) at the end of the citation.
Smith, John, and Bob Anderson. The Sample Book . Books For Us, 2017, pp. 5-12.
When a book has no edition number/name present, it is generally a first edition. If you have to cite a specific edition of a book later than the first, see the section below on citing edited books.
Citations for Translated Books:
If the translation is the focus of your project, include the translator's name at the beginning of the citation, like this:
Translator's Last name, First name, translator. Title . By Original Author's First name Last name, Publisher, Year published.
If it's not the actual translation that is the focus, but the text itself, include the translator's name in the "other contributors" position, like this:
Original Author's Last name, First name. Title . Translated by First Name Last name. Publisher, Year published.
Citations for E-Books:
E-books are formatted differently than print books. Why? Some e-books have different, or extra, information than print books. In addition, e-book pages are often numbered differently. Since the content and format may differ from print books, e-book citations are structured differently. When citing an e-book from a website, format the e-book citation with the website title and URL. When citing an e-book in a digital book format, which lacks a URL or that requires software on an e-reader device, include “e-book ed.” for the Version element of the citation. If you know that the e-book file format (EPUB, MOBI, etc.) varies depending on the e-book publication, you may also include the file format as a supplemental element at the end of the entry.
Format for an e-book found on the Internet:
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-Book . Publisher, Year Published. Title of Website , URL.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . Duke UP, 2010. Google Books , books.google.com/books?id=syqTarqO5XEC&lpg=PP1&dq=electronic%20music&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=electronic%20music&f=false.
Format for an e-book found on an e-reader:
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-book. . E-Book ed., Publisher, Year Published.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . E-book ed., Duke UP, 2010. EPUB.
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-book. E-Book ed., Publisher, Year Published. File Format.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . E-Book ed., Duke UP, 2010. EPUB.
Citations for Chapters in Books:
Individual chapters are cited when a writer uses a book filled with many chapters, each written by different authors. When citing a specific chapter in a book or an anthology, structure the citation like this:
Last name, First name of Chapter's Author. "Title of Chapter." Title of Book , Other Contributors and their roles, Version (if there's a specific edition), Publisher, Year Published, Page or Page Range.
Levi-Strauss, Claude. "The Structural Study of Myth." Literary Adverb Theory: An Anthology , edited by Julie Rivkin and Michael Ryan, 3rd ed., Wiley Blackwell, 2017, pp. 178-195.
Citations for Edited Books:
If your book is not a first edition, you should note this in the citation. If the book is a revised edition or an edition that includes substantial new content, include the number, name, or year of the edition and the abbreviation "ed." after the book title. "Revised edition" should be abbreviated as "Revised ed." and "Abridged edition" should be "Abridged ed." The edition can usually be found on the title page, as well the copyright page, along with the edition's date.
Author's Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book . Numbered ed., Publisher, Year Published.
Ferraro, Gary, and Susan Andreatta, editors. Cultural Anthropology: An Applied Perspective . 10th ed., Cengage Learning, 2014.
Smith, John. The MLA Sample Paper Book . Revised ed., Books For Us, 2017.
If your edited book has more than one author, refer to the directions above under the heading "Authors."
Also, BibMe.org helps you create your citations with more than one author quickly and easily! Try our MLA formatter!
Citations for Websites:
Wondering how to cite a website in MLA? The most basic entry for an MLA website citation consists of the author name(s), page title, website title, sponsoring institution/publisher, date published, and the DOI or URL.
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Individual Web Page." Title of Website , Publisher, Date, DOI or URL.
Fosslien, Liz, and Mollie West. "3 Ways to Hack Your Environment to Help You Create." Huffpost Preposition Endeavor , Huffington Post, Dec. 7, 2016, www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/3-ways-to-hack-your-environment-to-help-you-create us 580f758be4b02444efa569bc.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears on the website.
For a page with two or more authors, list them in the order they appear on the website. Only the first author's name should be reversed, with the others written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the last author's name. For pages with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by the abbreviation "et al."
If no author is available, begin the citation with the page title.
The page title should be placed within quotation marks. Place a period after the page title within the quotation marks. The page title is followed by the name of the website, which is italicized, followed by a comma.
After the website title, include the sponsoring institution or publisher followed by a comma. The sponsoring institution/publisher can usually be found at the bottom of the website, in the footer. If the name of the publisher is the same as the name as the website, do not include the publisher information in your citation. In MLA format, it is not recommended to include duplicate information for a website.
Next, state the publication date of the page.In some cases, a specific date might not be available, and the date published may only be specific to a month or even a year. Provide whatever date information is available.
End the citation with the URL. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. End the entire citation with a period.
Looking for an MLA formatter to create your website citations quickly and easily? Check out the BibMe MLA citation machine! Our MLA format website creates your citations in just a few clicks.
Citations for Online Journal Articles:
The most basic entry for a journal consists of the author name(s), article title, journal name, volume number, issue number, year published, page numbers, name of website or database where the article was found, and URL or Direct Object Identifier (DOI).
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Journal Article." Title of Journal , vol. number, issue no., Date, Page Range. Database or Website Name , URL or DOI.
Snyder, Vivian. "The Effect Course-Based Reading Strategy Training on the Reading Comprehension Skills of Developmental College Students." Research and Teaching in Developmental Education , vol. 18, no. 2, spring 2002, pp. 37-41. *JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/42802532.
*According to MLA 9th edition, lowercase seasons (spring 2002 not Spring 2002). Do not capitalize seasons.
Most online journal articles have two containers. The first is the journal that the article is in, and the second is the website or database the journal is in.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears in the journal.
For an article written by two authors, list them in the order they appear in the journal. Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the second is written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the second author's name.
Krispeth, Klein, and Stewart Jacobs.
For articles with three or more authors, include the name of the first author in the citation, followed by a comma and the abbreviation "et al."
Jones, Langston, et al.
The article title should be placed within quotation marks. Place a period after the article title within the quotation marks, unless the article title ends with a question mark or exclamation mark. The article title is followed by the name of the journal, which is italicized.
Include the volume number of the journal, but use the abbreviation "vol." You may also need to include the issue number, depending on the journal. Use the abbreviation "no." before the journal's issue number.
Jones, Robert, et al. "Librarianship in the Future." Libraries Today , vol. 5, no. 2, Mar. 2017, pp. 89-103. Database Life , www.dbl.com/6854.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. If the article has a DOI, use the DOI instead of the URL.
Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs)
Simply put, a Digital Object Identifier (usually abbreviated as “DOI”) is an identification number or source link for a document or file. It’s a system that is widely used by journals today. The DOI is comprised of symbols, numbers, and letters.
Example: https://doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1805-z.
This unique number system is very beneficial to readers and authors since it can be used to immediately locate an exact document, even if a host web page or database has altered an article’s URL.
How do I find an article’s DOI?
In print or PDF form, the first place to check is the front page of the article. If it is an online article, look for the DOI near the top of the article, at the very end of the article, or wherever citation information is located. Here are a few examples:
Here is an example from The New England Journal of Medicine:

Here is an example from the bottom of a Nature article:
Where in a citation is the DOI included?
If a DOI for an article exists, place it at the end of the citation. Here’s an example for the New England Journal of Medicine article previously shown:
Thomas, Cristina, et al. “Facing Uncertainty.” New England Journal of Medicine , vol. 381, no. 23, 2019, pp. 2253–2259, https://doi:10.1056/nejmcps1906037.
Citations for Blogs:
Blogs can be good sources to use for research papers and projects since many are regularly updated and written by influencers and experts.
Blogs can belong to a single individual, a group of people, or a company. Most entries for a blog include a title for that day’s entry, the date it was posted, and the information.
To cite a blog, you’ll need the following pieces of information: * The author’s name(s) or the name of the company who posted the blog * The title of the individual blog post * The title of the blog * The name of the publisher (if it differs from the name of the author(s) or title of the blog) * The date the blog post was posted * The website address (URL) for the blog post
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Blog Post.” Title of Blog , Publisher, Date Published, URL.
BibMe. “How to Spell in English: British vs. American.” BibMe Blog, www.bibme.org/blog/writing-tips/how-to-spell-in-english-british-vs-american/.
Notice in the above example, the date is missing. If there is no date shown on the blog post, omit it from the full citation.
Williams, Lindsay. “How to Get the Most from Your Online Language Lessons with a Tutor.” Lindsay Does Languages , 2019 Feb. 12, www.lindsaydoeslanguages.com/how-to-get-the-most-from-your-online-language-lessons-with-a-tutor/.
Cite a blog post in the text of the paper using this format:
(Author’s Last name) OR Author’s Last name...
Since there isn’t a page number, only use the author’s last name.
Citations for Newspapers:
The most basic entry for a newspaper consists of the author name(s), article title, newspaper name, publication date, page numbers, and sometimes a URL if found online. Omit volume numbers, issue numbers, and the names of publishers from newspaper citations.
Format if found on a website:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Article." Title of Newspaper's Website , Publication Date, URL.
Format if found on a database:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Article." Title of Newspaper , Publication Date, Page or Page Range (if available). Title of Database , URL.
MLA format example:
This example is for a print newspaper:
Hageman, William. "Program Brings Together Veterans, Neglected Dogs." Chicago Tribune , 4 Jan. 2015, p. 10.
The full article title should be placed within quotations. Next, state the name of the newspaper in italics.
Towards the end of the citation, include the page numbers on which the article appears with a period. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
Don't forget, the BibMe citation generator in MLA creates citations for you quickly and easily! Also, check out BibMe Plus paper checker, which scans your paper for correct usage of language elements. Have a determiner out of place in your writing? A pronoun spelled incorrectly? An overused adjective ? No worries, BibMe Plus has you covered!
Citations for Photographs:
The most basic entry for a photograph consists of the photographer's name, the title of the photograph, the title of the book, website, or collection where the photograph can be located, the publisher of the photograph or publication where the image was located, the date the photograph was posted or taken, and the page number, location of the museum (such as a city and state), or URL if found online.
Photographer's Last name, First name. "Title of the Photograph." Title of the Book, Website, Collection, or other type of publication where the photograph was found , Date photograph was taken, Page Number (if applicable), Location (such as a city and state if necessary) where the photograph can be found, or URL.
Begin with the name of the photographer or main contributor (if available). This person's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (and any middle name).
For a photograph taken from a publication or website, include the title of the photograph in quotation marks followed by a period. If the photograph does not have a formal title, create a description. If you make your own description, only include a capital at the beginning of the description and at the beginning of any proper nouns. Do not place the description in italics or quotation marks.
Place the title of the publication in italics immediately following the description, followed by a comma.
Digital Image/Photograph found online:
Photograph of the Hudson Area Public Library. JMS Collective , 19 Apr. 2016, www.jmscollective.com/hudson-ny-3/historic-hudson-armory-now-public-\ library/.
*Note that the above photograph does not have a formal title, so the photograph citation contains a description instead.
Photograph or Image viewed in a museum:
Vishniac, Roman. "Red Spotted Purple." Roman Vishniac's Science Work , early 1950s - late 1960s, International Center of Photography at Mana, New Jersey.
Photograph or Image found in a book:
Barnard, Edwin. Photograph of Murray Street, Hobart. Exiled: The Port Arthur Convict Photographs , National Library of Australia, 2010, p. 20.
Citing Social Media in MLA Format:
It's not uncommon to see social media posts included in research projects and papers. Most social media citations use the following structure:
@Username (First name Last name, if known, and differs from handle). "Text of post." Social Media Platform , Date posted, URL.
If the post is a photo or image instead of text, include a description of the image. Only capitalize the first letter in the description and the first letter for any proper nouns. Do not place the description in quotation marks.
If the post is long or includes emojis or links, it is acceptable to include only the beginning of the tweet with an ellipsis at the end of the included portion.
Citing a Twee:
@BibMe. "Need help with MLA essay format? Here are 6 steps to getting it done..." Twitter , 3 Dec. 2018, twitter.com/bibme/status/1069682724716204032.
Citing a Facebook Post:
DeGeneres, Ellen. "Holiday party goals..." Facebook , 21 Dec. 2018, www.facebook.com/ellentv/photos/a.182755292239/10157188088077240/?type=3&theater.
Citing an Instagram Post:
@dualipa. "A lil Hollywood glam brunch! Thank you @variety for by Breakthrough Artist of the Year award and thank you for your continuous support...." Instagram , 2 Dec. 2018, www.instagram.com/p/Bq33SC2BAsr/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link.
Citations for Music:
Citing a Song from the Internet:
To cite this type of source, structure the reference as follows:
Singer's Last Name, First name OR Band Name. "Title of Song." Title of Website or Service , Other Contributors and their roles (if applicable), Version, Date Published, URL.
Lopez, Jennifer. "Us." Spotify , 2 Feb. 2018, open.spotify.com/track/2MMvonKGALz6YOJwaKDO3q.
Citing a song from an album or downloaded:
Singer's Last name, First name OR Band Name. "Title of Song." Title of Album , Other Contributors and their roles (if applicable), Version, Publisher, Date Published or Released.
Lopez, Jennifer. "On the Floor." LOVE? , performance by Pitbull, Island, 2011.
Citations for Films:
The most basic entry for a film consists of the title, director, publisher, and year of release. You may also choose to include the names of the writer(s), performer(s), and the producer(s), depending on who your research focuses on. You can also include certain individuals to help readers locate the exact source themselves.
Example of a common way to cite a film:
Film Title . Directed by First name Last name, performance by First Name Last Name, Publisher, Year.
BibMe: The Movie . Directed by John Smith, performance by Jane Doe, New York Stories, 2017.
If your research focuses on a specific individual, you can begin the citation with that individual's name (in reverse order) and their role. Format it the same way as you would an author's name.
Doe, Jane, performer. BibMe: The Movie . Directed by John Smith, New York Stories, 2017.
If the film is dubbed in English or does not have an English title, use the foreign language title in the citation, followed by a square bracket that includes the translated title.
Citas gobiernan el mundo [ Citations Rule the World ]. Directed by Sara Paul, Showcase Films, 2017.
If the film was found online, such as YouTube or another site, include the name of the website and the URL.
Last name, First name of Individual who posted the video OR Account name. "Film Title." Website Title , other individuals and their roles (if applicable), Publisher, Year Published, URL.
The New York Public Library. "2018 National Book Awards Finalists at NYPL." YouTube , 15 Nov. 2018, youtu.be/edJqg3NuF2Q.
*Note that the New York Public Library was not listed as the publisher of the video. Adding "The New York Public Library" in the citation twice is not necessary.
Since the citation has two titles included (the title of the film and the title of the website), the title of the film is placed in quotation marks and the title of the website is in italics.
Citations for TV/Radio:
The most basic MLA format citation for a radio/TV program consists of the individuals responsible for the creation of the episode (if they're important to your research), the episode title, program/series name, broadcasting network or publisher, the original broadcast date, and the URL.
"The Highlights of 100." Seinfeld , NBC, 2 Feb. 1995.
If your research focuses on a specific individual from a TV or radio broadcast, include their name at the beginning of the citation in the author position.
If relevant, you may also choose to include the names of personnel involved with the program. Depending if the personnel are relevant to the specific episode or the series as a whole, place the personnel names after the program/series name. You may cite narrator(s) preceded by "narrated by", writer(s) preceded by "written by", directors preceded by "directed by", performer(s) preceded by "performance by", and/or producer(s) preceded by "produced by" and then the individual names. Include as many individuals as you like. Write these personnel names in normal order --- do not reverse the first and last names.
"The Highlights of 100." Seinfeld , directed by Andy Ackerman, written by Peter Mehlman, NBC, 2 Feb. 1995.
Also include the name of the network on which the program was broadcasted, followed by a comma.
State the date on which your program was originally broadcasted, followed by a period. When including the URL, follow the date with a comma and place the URL at the end, followed by a period to end the citation. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them.
Citations for Lectures:
The most basic entry for a lecture consists of the speaker's name, presentation title, date conducted, and the name and location of the venue.
Speaker's Last name, First name. Title of Lecture . Date Conducted, Venue, Location.
Pausch, Randy. Really Achieving Your Childhood Dreams . 18 Sept. 2007, McConomy Auditorium, Pittsburgh.
Begin the citation with the name of the speaker. This person's name should be reversed. If the lecture has a title, place it in the citation in italics, followed by a period. State the date on which the lecture was conducted, followed by a comma. Conclude your citation with the location/venue name and the city in which it occurred, separated by a comma.
Citations for Encyclopedias
The most basic entry for an encyclopedia consists of the author name(s), article title, encyclopedia name, publisher, and year published.
Last Name, First Name. "Article Title." Encyclopedia Name , Publisher, Year Published.
Smith, John. "Internet." Encyclopedia Britannica , 2012.
Notice that the name of the publisher was not included in the example above. Only include the name of the publisher if it differs from the name of the encyclopedia. Encyclopedia Britannica is the name of the encyclopedia AND the name of the publisher. It is not necessary to include Encyclopedia Britannica twice in the citation.
If there are no authors for the article, begin the citation with the article title instead.
"Media." World Book Encyclopedia , 2010.
If the encyclopedia arranges articles alphabetically, do not cite the page number(s) or number of volumes. If articles are not arranged alphabetically, you may want to include page number(s) and/or volume number, which is preceded by the abbreviation "vol." The volume should be cited after the encyclopedia name (or any edition), and before any publication information. After the publication year, include the page numbers on which the article appears, along with a period. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
Saunders, Bill. "Treasure." Encyclopedia Britannica , vol. 18, 2012, p. 56.
If the encyclopedia entry is found on a website, use the following structure:
Last name, First name. "Encyclopedia Entry." Title of Encyclopedia Website , Publisher, Year published, URL.
Citations for Magazines:
The most basic entry for a magazine consists of the author name(s), article title, magazine name, the volume and issue numbers (if available), publication date, page numbers, and URL if found online.
Last name, First name. "Article Title." Magazine Name , vol. number, issue no., Publication Date, Page Numbers or URL.
Print example:
Pratt, Sybil. "A Feast of Tradition." BookPage , Oct. 2017, p. 8.
Online example:
Geagan, Kate. "Sweeter Swaps: How to Choose Sustainable Sweeteners." Clean Eating , no. 83, Nov./Dec. 2018, pp. 36-37. Flipster , cleaneating.eoncontent.ebscohost.com/1927216#&pageSet=19.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears in the magazine.
For an article written by two or more authors, list them in the order as they appear on the title page. Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the others are written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the last author's name. For articles with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by the abbreviation "et al."
The full article title should be placed within quotations. Unless there is punctuation that ends the article title, place a period after the title within the quotations. Next, state the name of the magazine in italics.
If volume and issue numbers are available, include them in the citation. Use the abbreviations “vol.” and “no.” before the volume number and issue number.
Example: vol. 6, no. 1
The date the magazine was published comes directly after the volume and issue number. Use whichever date the magazine includes, whether it's a complete date, a period spanning two months, a season (lowercased), or just a month and year. Follow this information with a comma.
Include the page number(s) on which the article appears. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
If the magazine article was found online, include the DOI or URL. Use a DOI instead of a URL when it is available. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. End the citation with a period.
Citations for Interviews:
Begin your citation with the name of the person interviewed. This person's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name).
For an interview that has been broadcast or published, if there is a title, include it after the name of the person interviewed.
Jolie, Angelina. "Being a Mother." Interview conducted by Steve Kroft, 60 Minutes , CBS, 3 Feb. 2009.
If there is no title, use the word "Interview" in place of a title and do not use quotation marks or italics. If the interviewer's name is known, add it, preceded by "Conducted by", after the word "Interview". Do not reverse the interviewer's name.
Jenkins, Lila. Interview. Conducted by Jessica Grossman. 5 Mar. 2017.
For published interviews found online, include the title of the website after the title of the interview. In addition, add the URL at the end of the citation.
Michaels, Jamye. "Fighting to Survive." Women's Magazine of Life , 2 Nov. 2016, www.womensmagazine.com/fightingtosurvive.com.
Citations for Dissertations and Theses:
In order to obtain a degree, most colleges and universities require students to submit a dissertation or thesis towards the end of their academic track. Dissertations and theses are lengthy essays or in-depth research projects that relate to the scope of the student’s learning.
For example, if a student is close to obtaining their Master’s in Library Science, the student could study and write about the Internet searching habits of elderly individuals, or perhaps focus on the research skills of economically disadvantaged adults.
Upon completion, this individual assignment is often presented to the main directors, committee members, or professors at the school for approval.
A dissertation is generally assigned to students who are completing their doctorate degree, and many graduate schools require students to hand in a thesis to obtain a master’s degree.
Since so much research and work went into these scholarly projects, and new ideas and conclusions are often produced, many colleges and universities publish the completed papers. You can find these projects on many school websites and databases.
Here’s one way you can reference a dissertation or thesis:
Author’s Last Name, First name. Title of Dissertation or Thesis . Year Completed. University or College, Degree Abbr. Database , DOI or URL.
Kim, Kee Han. Development of an Improved Methodology for Analyzing Existing Single-Family Residential Energy Use . 2014. Texas A & M U, PhD. ProQuest , https://ezproxy.nypl.org/socabs/docview/1665251619/abstract/E9D36166E31040AEPQ/1?accountid=35635.
Fletcher, Marissa. Influences of Nutrition and Pathogenicity from a Microbial Diet on Immunity and Longevity in Caenorhabditis Elegans . 2012. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, PhD. DSpace@MIT , https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/120633.
Using Visuals
Including a visual in your project is a great way to make information come to life, as visuals can complement written work and enhance understanding.
Photographs, maps, charts, graphs, line drawings, musical scores, and tables are images that can be included in a project.
Follow these directions to add an image to your research paper:
- Images should be placed close to where they’re mentioned in the text.
- Provide a brief explanation about the image in the written portion of the paper, but do not write out all data shown in the image. Doing so would make the image unnecessary. (See the visual “Table example” at the end of this section.)
Correct example: Table 1 shows commonly used words in Shakespeare’s plays and their English translation.
Incorrect example: Table 1 shows commonly used words in Shakespeare’s plays and their English translation. Brave translates to handsome , character means a letter or word , egal means equal , fancy is a term for desire , and honest translates to pure .
- Tables are titled Table X, figures are Fig. X, and examples are Ex. X.
- Any type of image that includes an illustration is considered a “Figure”.
- Musical scores or sheet music are considered “Examples”.
- If the information below the image contains all of the source information, a full reference on the “Works Cited” page is not necessary.
- Double space everything.
- The image should have the same 1-inch margins as the rest of the paper.
Check out the examples below to see how tables, figures, and musical scores are arranged.
Table Example:
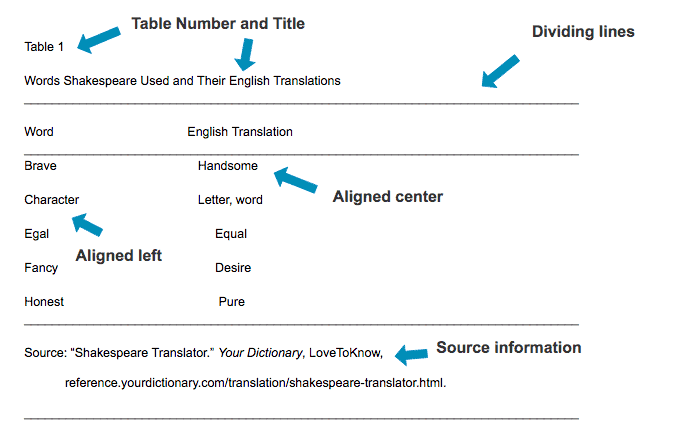
Figure Example:
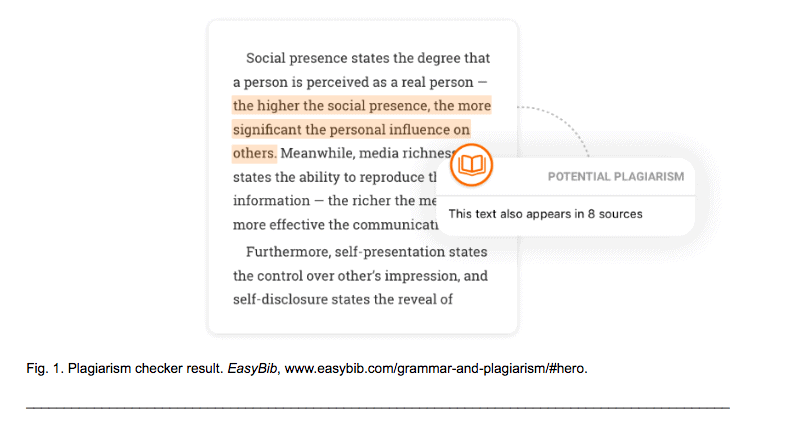
Musical score example:
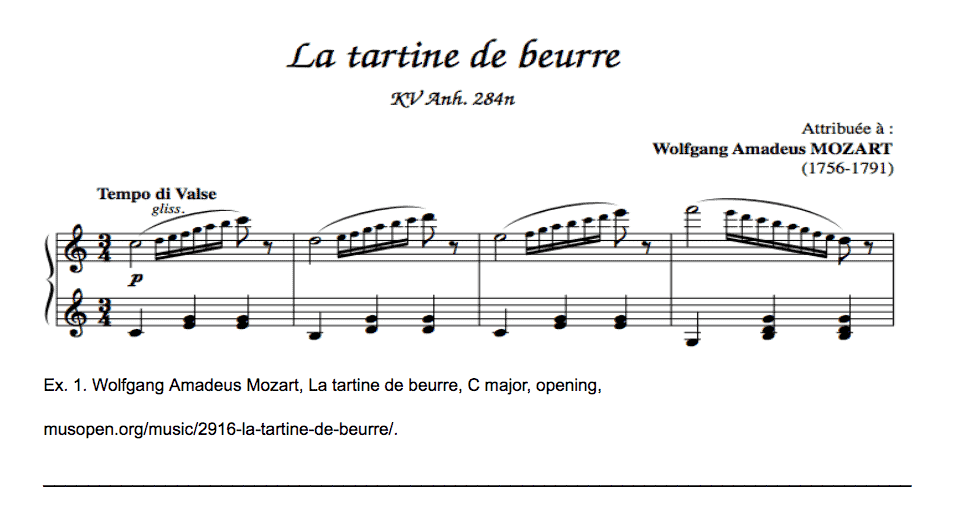
Your “Works Cited” Page
An MLA "Works Cited" or MLA "Work Cited" page contains all of the citations for a project.
- This page sits on its own and is found at the end of a project.
- If there is only one citation on the page, title the page: Work Cited. While it might seem silly to have a full page dedicated to one citation, a “Work Cited” page in MLA is still necessary. If there are multiple citations on the page, title the page: Works Cited.
- Double space the entire list of works cited.
- Include the writer's last name and the page number, at the top right corner of the page.
- Every in-text or parenthetical citation in the body of the project should correspond with its full citation listed on the MLA “Works Cited” or “Work Cited” page.
- All full citations in MLA formatting have a hanging indent. This means that the first line of the citation sits flush against the left margin. The second line, and any subsequent lines, are indented in another half inch. If you need a visual, all full citations on this page have a hanging indent.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first letter found in the citation.
- If there are multiple sources by the same author, only include the author's name in the first citation. For each citation afterwards, MLA formatting requires you to include three dashes and a period. Organize the citations by the title.
Example of a Works-Cited List with Multiple Works by Same Author:
Riggs, Ransom. Miss Peregrine's Home for Peculiar Children . Quirk, 2011.
---. Tales of the Peculiar . Dutton, 2016.
- When alphabetizing by titles, ignore “A,” “An,” and “The,” and use the next part of the title.
- If the title starts with a number, place the title where it would belong if the number was spelled out.
MLA formatting example:
1492: The Year Our World Began would be alphabetized under F (for fourteen)
Sample Works Cited:

Formatting Your Header:
The first page of your MLA format paper should include a header. An MLA cover page, or MLA title page, that sits on its own isn't necessary or recommended.
MLA heading format includes the following pieces of information, styled like this, in this order:
Your professor or teacher's name
The class and/or course number
Date of submission
- Double space everything on the page.
- In the top right corner, include your last name and the page number.
- The title should be centered in the middle of the page.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read for the entire paper.
- MLA paper format requires 12-point font, or another size close to it.
Sample MLA Header:

Using BibMe.org to Create Citations for your MLA Works Cited Page or MLA Bibliography
Wondering how to use MLA format? The BibMe automatic MLA format generator formats your citations for you. Enter a title, web address, ISBN number, or other identifying information into the MLA format template to automatically cite your sources. If you need help with BibMe.org or our citation machine in MLA, click here on more styles .
Try This Out:
The BibMe service is an extremely helpful resource that helps you create your citations for your project, but there's more. The BibMe service also has a feature that will help to proofread your entire MLA format essay. The BibMe Plus paper checker scans for proper spelling, punctuation, language elements, and syntax. It will tell you if a language element, such as a preposition , conjunction , or interjection , is a bit off. It also has a built-in plagiarism checker , which scans papers for instances of accidental plagiarism. Try it out now!

More Information:
Here's more information on the previous handbooks. There's further good information here , including MLA format examples and examples of MLA in-text citations.
Background Information and History:
The Modern Language Association was developed in 1883 and was created to strengthen the study and teaching of languages and literature. With over 25,000 current members worldwide, the Modern Language Association continuously strives to keep its members up-to-date on the best practices, methods, and trends related to language and literature. The Modern Language Association boasts an annual conference, journal, an online communication platform, numerous area-focused committees, and one of its most popular publications, the MLA Handbook, now in its 9th edition.
Updated June 25, 2021
Edited and written by Elise Barbeau and Michele Kirschenbaum. Elise is a citation expert and has her master’s degree in public history/library science. She has experience in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing. Michele is a certified library media specialist who loves citations and teaching. She’s been writing about citing sources since 2014.
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Works-Cited-List Entries
Citations by format.
Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements —facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you’re citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on the template.
The examples below show you how to cite five basic source types. Click on an entry to get more information, as well as links to posts with more examples. For hundreds of sample entries by format, check out the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Book by One Author
Mantel, Hilary. Wolf Hall . Picador, 2010.
Book by an Unknown Author
Beowulf . Translated by Alan Sullivan and Timothy Murphy, edited by Sarah Anderson, Pearson, 2004.
An Edited Book
Sánchez Prado, Ignacio M., editor. Mexican Literature in Theory . Bloomsbury, 2018.
Online Works
Article on a website.
Deresiewicz, William. “The Death of the Artist—and the Birth of the Creative Entrepreneur.” The Atlantic , 28 Dec. 2014, theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2015/01/ the-death-of-the-artist-and-the-birth-of-thecreative-entrepreneur/383497/.
Book on a website
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Masque of the Red Death.” The Complete Works of Edgar Allan Poe , edited by James A. Harrison, vol. 4, Thomas Y. Crowell, 1902, pp. 250-58. HathiTrust Digital Library , hdl.handle.net/2027/coo.31924079574368.
Journal Article in a Database
Goldman, Anne. “Questions of Transport: Reading Primo Levi Reading Dante.” The Georgia Review , vol. 64, no. 1, spring 2010, pp. 69-88. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/41403188.
Songs, Recordings, and Performances
Song from an album.
Snail Mail. “Thinning.” Habit , Sister Polygon Records, 2016. Vinyl EP.
Song on a website
Snail Mail. “Thinning.” Bandcamp , snailmailbaltimore.bandcamp.com.
Concert Attended in Person
Beyoncé. The “Formation” World Tour. 14 May 2016, Rose Bowl, Los Angeles.
Movies, Videos, and Television Shows
A movie viewed in person.
Opening Night. Directed by John Cassavetes, Faces Distribution, 1977.
A Movie Viewed Online
Richardson, Tony, director. Sanctuary . Screenplay by James Poe, Twentieth Century Fox, 1961. YouTube , uploaded by LostCinemaChannel, 17 July 2014, www.youtube.com/watch?v=IMnzFM_Sq8s .
A Television Show Viewed on Physical Media
“Hush.” 1999. Buffy the Vampire Slayer: The Complete Fourth Seaso n, created by Joss Whedon, episode 10, Mutant Enemy / Twentieth Century Fox, 2003, disc 3. DVD.
A Photograph Viewed in Person
Cameron, Julia Margaret. Alfred, Lord Tennyson . 1866, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City.
A Painting Viewed Online
Bearden, Romare. The Train . 1975. MOMA , www.moma.org/collection/works/65232?locale=en.
An Untitled Image from a Print Magazine
Karasik, Paul. Cartoon. The New Yorker , 14 Apr. 2008, p. 49.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Website in MLA
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, citing a website in mla, how to create an mla website citation:.
When citing a website, you’re often actually citing a specific page on a website. You’re not actually citing the entire website.
Here is the most common way to cite a page on a website:
- Start the citation with the name of the author who wrote the information on the page. If there isn’t an author listed, do not include this information in the citation. Start the citation with the title.
- The title of the individual page is placed in quotation marks, followed by a period.
- Next, place the name of the website in italics, followed by a comma.
- If the name of the publisher matches the name of the author or the name of the title, do not include the publisher’s information in the citation.
- The date the page or website was published comes next.
- End the citation with the URL or DOI. When including the URL, copy the URL directly from the address bar or link in your browser window.
Last name, First name of author. “Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Date published, URL.
Rothfeld, Lindsay. “Smarter Education: The Rise of Big Data in the Classroom.” Mashable, 3 Sept. 2014, mashable.com/2014/09/03/education-data-video/#hViqdPbFbgqH.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx.
If you’re still confused and feeling the urge to type “How to cite a website MLA” into Google, try out our free generator at the top of this page. Our citation generator MLA site is easy to use!
Social media:
If the user’s handle and real name are similar, you may include the real name and leave out the handle as long as a URL is also included. If the user’s real name and handle are different, include the hand in brackets after the real name.
Gates, Melinda. “Today, Bill and I were deeply humbled to accept France’s Legion of Honour award on behalf of all our foundation’s partners and grantees.” Twitter, 21 Apr. 2017, twitter.com/melindagates/status/855535625713459200.
Sandler, Adam. “California Strong celebrity softball game this Sunday at Pepperdine. All proceeds go to the victims of the wildfires and shooting in Thousand Oaks.” Facebook, 11 Jan. 2019, www.facebook.com/Sandler/.
Mizuhara, Kiko [@I_am_kiko]. “@vivi_mag_official shot by my sis @ashley_yuka.” Instagram, 25 June 2020, www.instagram.com/p/CB27SYahBpo.
Featured links:
MLA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interviews | PDFs
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Robertson Library
MLA Citation Guide
Mla 9th edition.
MLA 9th edition was released in the spring of 2021. Make sure that any resources or citation generators you use are for the correct edition.
We do not currently have online access to the MLA Handbook, but we do have a copy on reserve at the Library Service Desk. You can borrow it by asking at the desk.
Tutors in the Writing Centre can help you with MLA formatting and citations.
Official MLA Style Center resources for MLA 9th Edition:
- A quick guide to works cited
- Sample papers in MLA Style format
- An interactive practice template for works cited
- Formatting your paper
- "How do I cite generative AI in MLA style?"
Basics of MLA Citations
If you are citing sources in an MLA style paper, you'll have brief in-text citations throughout your paper as well as longer full citations on your Works Cited list.
In-text citations in MLA are usually parenthetical citations that include the author's surname and, if relevant, a page number. Usually, there are no commas or years. (If you're reading a paper that routinely has commas and/or years in its parenthetical citations, it might be in APA , Chicago , or another style.)
Full citations in MLA are based on the idea that works have an author or authors, a title , and one or more containers . The container could be something like a journal (for a journal article), a TV series (for a television episode), an anthology (for a short story), a scholarly book (for a book chapter), or a concert (when discussing the performance of a single work). Some works, like novels or films, are usually their own containers. If you're citing a journal article that you accessed through a library database, you'll need to include information for two containers (the journal and the database).
For examples, see " MLA Style Quick Guide " or " Poetry, Songs, and Plays " from the libraries at Memorial University of Newfoundland.
Last updated 29 November 2023

AI Generator

MLA format is a widely accepted style for writing and documenting scholarly papers, particularly in the humanities. It provides guidelines for formatting manuscripts , citing sources, and structuring works cited pages, ensuring consistency and clarity. Adhering to MLA format helps writers present their research in a professional and organized manner, facilitating readability and academic integrity.
What is MLA Format?
MLA format, established by the Modern Language Association, is a widely-used style for writing and documenting scholarly papers in the humanities. It features in-text citation , a “Works Cited” page, double-spacing, one-inch margins, and specific guidelines for formatting headings, titles, and quotations to ensure clarity and consistency in academic writing.
MLA Format Examples
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year of Publication.
- Example: Smith, John. The Art of Writing . Penguin, 2020.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal , vol. number, no. number, Year, pages.
- Example: Doe, Jane. “Exploring Literature.” Literary Journal , vol. 5, no. 3, 2019, pp. 45-67.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Date of Publication, URL.
- Example: Brown, Lisa. “Understanding MLA Format.” Writing Resources , Purdue OWL, 15 Mar. 2021, www.owl.purdue.edu/mlaformat .
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Chapter.” Title of Book , edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, Publisher, Year, pages.
- Example: Taylor, Robert. “Modern Poetry.” Anthology of Modern Literature , edited by Sarah Green, Norton, 2018, pp. 120-135.
- Editor’s Last Name, First Name, editor. Title of Book . Publisher, Year.
- Example : Anderson, Mary, editor. Cultural Studies . Routledge, 2017.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine , Date of Publication, pages.
- Example: Clark, Emily. “The Future of Education.” Education Today , 12 June 2021, pp. 22-25.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper , Date of Publication, pages.
- Example: Adams, Michael. “Tech Innovations in 2022.” The New York Times , 5 Jan. 2022, p. B1.
- Title of Film . Directed by Director’s First Name Last Name, performance by Lead Actor’s First Name Last Name, Production Company, Year.
- Example: Inception . Directed by Christopher Nolan, performance by Leonardo DiCaprio, Warner Bros., 2010.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Video.” Website , uploaded by Uploader’s Name, Date of Upload, URL.
- Example : Johnson, Mark. “ How to Write in MLA Format.” YouTube , uploaded by Academic Tips, 10 Feb. 2021, www.youtube.com/academic-tips-mla .
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Paper.” Title of Conference , Date, Location.
- Example: Lee, Anna. “The Impact of Social Media on Education.” International Conference on Education , 23 Apr. 2021, Boston, MA.
When to use MLA Format
MLA format is commonly used in the humanities, especially for writing papers and citing sources in subjects like:
- Essay , research papers, and articles analyzing novels, poems, plays, and other literary works.
- Papers exploring cultural phenomena, media studies, and societal impacts on culture.
- Research involving comparative literature, translations, and linguistic studies.
- Essays and papers discussing philosophical theories, arguments, and historical texts.
- Research papers analyzing art movements, specific artworks, and artist biographies.
- Analyses of plays, playwrights, theatrical performances, and historical context of theater.
- Humanities-focused historical research papers, particularly those involving textual analysis.
- Research involving film, television, digital media, and their cultural implications.
MLA format is preferred in these fields for its emphasis on detailed citation and textual analysis, ensuring clarity, consistency, and academic integrity in scholarly writing.
How to set up your paper in MLA Format
Setting up your paper in MLA format is crucial for academic writing, ensuring that your work meets the standards for scholarly communication. Follow these steps to format your paper correctly:
1. General Guidelines
- Font : Use a readable font like Times New Roman, size 12.
- Margins : Set all margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Line Spacing : Double-space the entire paper, including any notes and the works cited page.
- Indentation : Indent the first line of each paragraph one-half inch from the left margin. Use the Tab key instead of the space bar.
2. Header and Title
- Header : Create a header in the upper right-hand corner that includes your last name, followed by a space and the page number. Number all pages consecutively with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- In the upper left-hand corner, list your name, your instructor’s name, the course, and the date. Double-space this information.
- Center the title. Do not underline, italicize, or place your title in quotation marks. Write the title in Title Case (standard capitalization), not in all capital letters.
3. In-Text Citations
- When quoting or paraphrasing, include an in-text citation with the author’s last name and the page number from which the quote or paraphrase is taken, like this: (Smith 123).
4. Works Cited Page
- Title : Center the title “Works Cited” at the top of the page. Do not italicize or underline it.
- Entries : Begin each entry at the left margin; if an entry runs more than one line, indent the subsequent lines one-half inch from the left margin (hanging indent).
- Alphabetical Order : List the entries alphabetically by the author’s last name. If no author is given, alphabetize by the title.
Example of the First Page
Jane Doe Professor Smith English 101 20 May 2023 Centered Title in Title Case The first paragraph of your paper begins here, with the first line indented one-half inch. Subsequent paragraphs should also be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
Example of a Works Cited Entry
Works Cited Smith, John. The Great Gatsby . Scribner, 2004.
Formatting Header and Title in MLA
Formatting the header and title correctly is an important step in ensuring your paper adheres to MLA standards. Here’s a detailed guide on how to set up the header and title for your MLA paper:
The header in MLA format is placed in the upper right-hand corner of each page, including the first page. Here are the steps to set it up:
- Open your document in a word processing program like Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
- In Microsoft Word: Go to the “Insert” tab and select “Header.” Choose the “Blank” option.
- In Google Docs: Click on “Insert” and then “Headers & footers,” followed by “Header.”
- Type your last name followed by a space.
- In Microsoft Word: While the cursor is still in the header, go to the “Design” tab, click on “Page Number,” and choose “Top of Page” then “Plain Number 3.”
- In Google Docs: While the cursor is in the header, click on “Insert,” then “Page numbers,” and select the option to have the page numbers in the upper right corner.
- Set the font and size : Ensure the font is Times New Roman, size 12, matching the rest of your document.
2. Title Page Setup
MLA format does not require a separate title page unless specifically requested by your instructor. Instead, the title is placed on the first page of your paper. Here’s how to format it:
Information Block
- Position the cursor at the top of the first page.
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The course name or number
- The date in the format: Day Month Year (e.g., 20 May 2023)
- Double-space after the date.
- Center the title of your paper. The title should be in Title Case, which means you capitalize the major words.
- Do not use bold, italics, underline, or quotation marks for the title. Write it in plain text.
Example of the First Page Setup
Jane Doe Professor Smith English 101 20 May The Impact of Climate Change on Migration The first paragraph of your paper begins here, with the first line indented one-half inch. Subsequent paragraphs should also be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
Headings and Subheadings in MLA Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) format provides a flexible guideline for structuring your academic paper. While the MLA Handbook (9th edition) does not provide specific rules for headings and subheadings, it encourages consistency and clarity. Here’s a guide on how to create and format headings and subheadings in your MLA-style paper.
General Guidelines
- Font and Size: Use a readable font like Times New Roman, size 12.
- Consistency: Ensure that the format and style of headings and subheadings are consistent throughout the paper.
- No Bold or Italics: Headings should not be bolded or italicized. They should be in plain text, maintaining the same font and size as the rest of the paper.
- Title Case: Capitalize the first and last words and all principal words in headings and subheadings.
Levels of Headings
MLA does not have specific rules for the number of heading levels. However, using up to five levels of headings is common. Below is a suggested format for organizing your paper with headings and subheadings.
First-Level Heading (H2)
Centered, Title Case
Causes of Climate Change
Second-Level Heading (H3)
Left-aligned, Title Case
Human Activities
Third-Level Heading (H4)
Indented, Title Case, Ends with a Period.
Burning of Fossil Fuels.
Fourth-Level Heading (H5)
Indented, Sentence case, Ends with a period.
Deforestation and land use changes.
Fifth-Level Heading (H6)
Indented, italicized, Sentence case, Ends with a period.
Use of agricultural practices.
Examples of Headings in a Paper
Here’s an example of how to structure a paper using these headings:
Causes of Climate Change Human activities significantly contribute to climate change through various means. Human Activities Human activities that impact climate change include the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and certain agricultural practices. Burning of Fossil Fuels. The combustion of coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Deforestation and land use changes. The removal of trees decreases the planet’s capacity to absorb CO2. Use of agricultural practices. Certain farming practices, like livestock production, increase methane emissions. Natural Factors Natural factors also play a role in climate change, albeit to a lesser extent than human activities. Volcanic Eruptions. Eruptions release particles that can cool the Earth by blocking sunlight. Solar Variations Changes in solar energy affect the Earth’s climate cycles.
Quotations in MLA Format
Quotations are an essential part of academic writing, providing evidence and supporting arguments. MLA (Modern Language Association) format has specific guidelines for incorporating quotations into your text. Here’s a detailed guide on how to format both short and long quotations in MLA style.
1. Short Quotations
Short quotations are defined as fewer than four lines of prose or three lines of verse. These quotations should be incorporated into the text and enclosed in double quotation marks.
- Introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author’s last name followed by the page number in parentheses.
- Place the period after the parenthetical citation.
According to Smith, “climate change is the greatest challenge facing humanity today” (123).
2. Long Quotations
Long quotations, also known as block quotations, are used for prose that is more than four lines or verse that is more than three lines. These should be formatted as a freestanding block of text and indented one inch from the left margin. Quotation marks are not used.
- Introduce the block quotation with a signal phrase that ends with a colon.
- Start the quotation on a new line and indent the entire block one inch from the left margin.
- Double-space the quotation.
- Place the parenthetical citation after the period at the end of the quotation.
Smith discusses the impacts of climate change in detail:
Climate change affects all regions around the world. Polar ice caps are melting, sea levels are rising, and weather patterns are becoming more extreme. These changes threaten the habitats of countless species, and the economic and social systems of human communities are also at risk. Immediate action is required to mitigate these effects and adapt to the changes that are already underway. (123)
3. Adding or Omitting Words
Adding Words: When adding words for clarity, enclose the added text in square brackets.
Smith notes that “immediate action [by global leaders] is required to mitigate these effects” (123).
Omitting Words: To omit words from a quotation, use an ellipsis (…). Ensure that the omission does not change the meaning of the original text.
Smith argues that “climate change affects all regions…and weather patterns are becoming more extreme” (123).
4. Quoting Poetry
For quoting poetry, maintain the original formatting as much as possible. Use a slash (/) to indicate line breaks within the text.
Short Poetry Quotations:
- Enclose the quotation in double quotation marks.
- Use a slash (/) to indicate line breaks.
In Frost’s “The Road Not Taken,” the speaker reflects, “Two roads diverged in a yellow wood, / And sorry I could not travel both” (1-2).
Long Poetry Quotations:
- Introduce the quotation with a signal phrase ending with a colon.
- Maintain the original line breaks.
In his poem “The Road Not Taken,” Frost writes:
Two roads diverged in a yellow wood, And sorry I could not travel both And be one traveler, long I stood And looked down one as far as I could To where it bent in the undergrowth; (1-5)
5. Quoting Dialogue
When quoting dialogue from a play or script, each character’s speech begins on a new line, and the character’s name is written in all capital letters followed by a period.
- Introduce the quotation with a signal phrase.
- Start the quotation on a new line and indent each line of the characters’ speech one inch from the left margin.
- Double-space the dialogue.
In Shakespeare’s Macbeth , the witches proclaim:
FIRST WITCH. When shall we three meet again In thunder, lightning, or in rain? SECOND WITCH. When the hurlyburly’s done, When the battle’s lost and won. (1.1.1-4)
Paraphrases in MLA Format
Paraphrasing involves restating someone else’s ideas in your own words. In MLA (Modern Language Association) format, it’s essential to credit the original source even when you paraphrase. Here’s a detailed guide on how to properly format paraphrases in MLA style.
1. General Guidelines for Paraphrasing
- Restate the original text: Ensure that the paraphrase is in your own words and that it accurately reflects the meaning of the original text.
- Provide an in-text citation: Include the author’s last name and the page number where the original idea can be found.
- No quotation marks: Do not use quotation marks around a paraphrase since you are not using the exact words from the source.
2. In-Text Citations for Paraphrases
The in-text citation for a paraphrase is similar to that for a direct quotation. It includes the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses.
Basic Format: (Author’s Last Name Page Number)
Example: According to Smith, climate change poses a significant challenge to humanity, requiring immediate and concerted action from global leaders (123).
3. Incorporating Paraphrases into Your Text
You can introduce a paraphrase in several ways to smoothly integrate it into your writing. Here are some examples:
Using a Signal Phrase
Signal phrases introduce the source of the paraphrase and are typically followed by the paraphrased material and a parenthetical citation.
Example: Smith argues that immediate action is necessary to address the widespread impacts of climate change, which threaten both natural ecosystems and human societies (123).
Integrating the Paraphrase
Integrate the paraphrase directly into your sentence, ensuring it flows naturally with your own writing.
Example: The widespread impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels and more extreme weather patterns, require urgent action to mitigate damage to both ecosystems and human communities (Smith 123).
4. Multiple Authors
When paraphrasing a source with multiple authors, include all authors’ last names or use “et al.” for three or more authors.
Two Authors:
Example: According to Johnson and Smith, sustainable practices are essential for mitigating the effects of climate change (45).
Three or More Authors:
Example: Research indicates that sustainable practices are crucial for mitigating climate change impacts (Johnson et al. 45).
5. No Author
If the source has no author, use a shortened title of the work instead. Place the title in quotation marks if it’s an article or in italics if it’s a book or other standalone work.
Example: Measures to address climate change must be implemented urgently to prevent further environmental degradation (“Climate Action” 12).
6. Multiple Works by the Same Author
If you cite multiple works by the same author, include a shortened version of the title in the citation to differentiate between them.
Example: Smith argues that sustainable practices are necessary for environmental conservation (“Environmental Policies” 56) and that global cooperation is key to effective climate action (“Global Strategies” 78).
7. Citing Indirect Sources
If you need to paraphrase information from a source cited within another source, use “qtd. in” to indicate the original source.
Example: According to Brown, environmental education plays a crucial role in raising awareness about climate change (qtd. in Smith 89).
Example of a Paragraph with Paraphrases
Original Text: “Climate change affects all regions around the world. Polar ice caps are melting, sea levels are rising, and weather patterns are becoming more extreme. These changes threaten the habitats of countless species, and the economic and social systems of human communities are also at risk. Immediate action is required to mitigate these effects and adapt to the changes that are already underway” (Smith 123). Paraphrased Paragraph: Smith notes that climate change has a global impact, causing the melting of polar ice caps, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather events. These environmental changes endanger numerous species’ habitats and pose risks to human economic and social structures. Therefore, Smith emphasizes the need for swift measures to mitigate and adapt to these evolving challenges (123).
Using Abbreviations in MLA Format
Abbreviations can help make your writing more concise and clear. However, it is important to use them correctly and consistently. Here is a guide on how to use abbreviations in MLA (Modern Language Association) format.
- Introduce Abbreviations: When you first introduce an abbreviation, spell out the full term followed by the abbreviation in parentheses. After this initial introduction, you can use the abbreviation alone.
- Consistency: Use the abbreviation consistently throughout your paper after introducing it.
- Periods: Use periods with certain abbreviations (e.g., a.m., p.m., U.S.), but do not use them for acronyms (e.g., NASA, MLA).
Types of Abbreviations
Acronyms and initialisms.
Acronyms are formed from the initial letters of words and pronounced as words (e.g., NASA). Initialisms are formed from the initial letters but pronounced as individual letters (e.g., FBI).
Example: The Modern Language Association (MLA) provides guidelines for formatting academic papers. According to MLA guidelines, authors should use consistent formatting throughout their work.
When citing sources, abbreviate the names of months (except May, June, and July) in the Works Cited page.
Example: Jan., Feb., Mar., Apr., Aug., Sept., Oct., Nov., Dec.
Works Cited Entry Example: Smith, John. “The Effects of Climate Change.” Environmental Studies Journal , vol. 12, no. 4, Aug. 2020, pp. 123-45.
Common Latin Abbreviations
Certain Latin abbreviations are commonly used in academic writing. Here are a few examples:
- e.g. (exempli gratia): means “for example”
- i.e. (id est): means “that is”
- etc. (et cetera): means “and so on”
- et al. (et alii): means “and others”
Example: There are many theories on climate change (e.g., greenhouse effect, solar variability).
Abbreviating Titles and Terms
Use standard abbreviations for titles and terms when they appear in citations.
- ed. (edition)
- rev. ed. (revised edition)
- vol. (volume)
- no. (number)
Examples: Doe, Jane, ed. Anthology of Modern Poetry . 3rd ed., Penguin Books, 2019. Brown, Sarah. History of Medieval Europe . Rev. ed., vol. 2, Academic Press, 2018.
Abbreviating Locations in Works Cited
Abbreviate the names of U.S. states and countries in publisher locations.
- Cambridge, MA
Works Cited Entry Example: Smith, John. The Great Migration . Cambridge UP, 2015.
In-Text Citations with Abbreviations
Use abbreviations in in-text citations as necessary to keep them concise. For example, abbreviate the titles of works that are long or frequently cited within the text.
Example: (Tolkien, LOTR 23)
Abbreviating Corporate Authors
When a corporate author is commonly known by an abbreviation, you can use the abbreviation after introducing it.
Example: The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has made significant advancements in space exploration. According to NASA, the Mars rover has sent back valuable data (NASA).
Common MLA Abbreviations
- ch. (chapter)
- sec. (section)
- trans. (translator)
- UP (University Press)
Example of Proper Abbreviation Usage in a Paragraph
When citing sources, the Modern Language Association (MLA) recommends abbreviating the names of months except for May, June, and July. For instance, an article published in March would be cited as “Mar.” (MLA Handbook 123). Additionally, when referring to organizations like the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the abbreviation can be used after the first mention. NASA has reported new findings from the Mars rover mission (NASA).
Formatting Numbers in MLA Format
When writing papers in MLA (Modern Language Association) format, it’s important to know the guidelines for formatting numbers. Here’s a concise guide to help you understand when to use numerals and when to spell out numbers.
General Rules
- Spell out numbers that can be written in one or two words.
- Examples: one, thirty-six, ninety-nine, one hundred, fifteen hundred
- Use numerals for numbers that require more than two words.
- Examples: 101, 1,250, 7,891
Specific Cases
- Spell out numbers when they begin a sentence.
- Example: One hundred students attended the lecture.
- Note: If rewriting the sentence to avoid starting with a number, it is acceptable. Example: There were 100 students who attended the lecture.
- Use numerals for dates.
- Example: June 5, 2024
- Use numerals with a.m. and p.m.
- Examples: 10:30 a.m., 5:00 p.m.
- For round numbers, you may spell out the time if clarity is preserved.
- Example: He arrived at six o’clock in the evening.
- Use numerals and the percent symbol (%).
- Example: The survey showed that 75% of participants agreed.
- Always use numerals.
- Example: Please refer to page 45 for more information.
- Use a combination of numerals and words for very large round numbers.
- Example: 2.5 million, 3 billion
- Spell out simple fractions and use numerals for more complex fractions.
- Examples: Two-thirds of the class, 3/8 of an inch
- Use numerals for decades and spell out centuries.
- Examples: the 1990s, the twenty-first century
Examples in Context
- There are fifty-two weeks in a year.
- The population of the city is approximately 1.2 million.
- She bought three dozen eggs.
- On April 15, 2022, the event will take place.
- The meeting starts at 9:00 a.m.
- About 40% of the respondents disagreed with the statement.
- The results are discussed on page 23.
- He has lived here since the 1980s.
- The twentieth century saw many technological advances.
- There are 52 weeks in a year. (Should be spelled out)
- The population of the city is approximately one million two hundred thousand. (Use numerals)
- She bought 3 dozen eggs. (Spell out)
Using Lists in MLA Format
Lists can be a useful way to present information clearly and concisely. In MLA (Modern Language Association) format, there are specific guidelines for incorporating lists into your writing. Here’s a guide on how to format both bulleted and numbered lists according to MLA style.
- Introduce the list with a complete sentence followed by a colon.
Example: There are several reasons to visit the museum:
- Ensure that each item in the list follows the same grammatical structure.
- Free admission
- Guided tours
- Educational workshops
Bulleted Lists
Bulleted lists are used to present items that do not need to be in a specific order.
- Introduce the list with a complete sentence.
- Use a colon at the end of the introductory sentence.
- Begin each item with a capital letter.
- Use a period after each item if the items are complete sentences; otherwise, do not use periods.
Example: The museum offers the following activities:
- Art exhibitions
- Interactive workshops
Numbered Lists
Numbered lists are used to present items that need to be in a specific order, such as steps in a process.
- Use periods after each item if the items are complete sentences.
Example: Follow these steps to register for the workshop:
- Visit the museum’s website.
- Click on the “Events” tab.
- Select the desired workshop.
- Complete the registration form.
In-Text Lists
In-text lists are used within a sentence and are typically introduced with a colon or parentheses.
Comma-Separated Lists:
- Use commas to separate items in a simple list within a sentence.
- Example: The museum offers guided tours, art exhibitions, and interactive workshops.
Semicolon-Separated Lists:
- Use semicolons to separate items in a complex list within a sentence.
- Example: The museum offers several activities: guided tours for all ages; art exhibitions featuring local artists; and interactive workshops on weekends.
Lists with Complete Sentences
When each item in the list is a complete sentence, use periods at the end of each item.
- The museum offers free admission every first Sunday of the month.
- It has a wide range of art exhibitions from contemporary to classical art.
- Interactive workshops are available for children and adults alike.
Example in Context
Here is an example of how to integrate a list into an MLA-formatted paper:
Text Example:
Visiting the museum can be a rewarding experience for several reasons:
- Free Admission: The museum offers free admission every first Sunday of the month.
- Diverse Exhibitions: It features a wide range of art exhibitions, from contemporary to classical art.
- Interactive Workshops: There are interactive workshops available for both children and adults.
In addition to these activities, the museum also provides guided tours and educational programs, making it an excellent destination for visitors of all ages.
MLA Format vs. APA Format
What is mla format.
MLA format is a style guide for writing and documenting research in the humanities, particularly in English studies, provided by the Modern Language Association.
How do you cite a book in MLA format?
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year of Publication. Example: Smith, John. The Great Gatsby . Scribner, 2004.
How do you format the first page of an MLA paper?
Include your name, instructor’s name, course, and date in the upper left corner. Center the title, and start the text on a new line, double-spaced.
What should be included in an MLA Works Cited page?
List all sources cited in the text, alphabetized by the author’s last name. Include full publication details for each source.
How do you format in-text citations in MLA?
nclude the author’s last name and page number in parentheses after the quote or paraphrase. Example: (Smith 123).
Do I need a title page in MLA format?
No, MLA format typically does not require a separate title page unless specified by the instructor.
How do you cite a website in MLA format?
Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Publication Date, URL.
How do you handle multiple authors in an MLA citation?
For two authors, use both last names (Smith and Jones). For three or more, use the first author’s last name followed by “et al.” (Smith et al.).
How are block quotes formatted in MLA?
Indent the entire quote one inch from the left margin, double-space, and omit quotation marks. Place the parenthetical citation after the period.
What font and size should be used in MLA format?
Use a readable font like Times New Roman, size 12, and double-space the entire document.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Ask A Librarian Help

The links in the MLA Style Center reflect MLA Style 9th Edition.

The links in Purdue OWL reflect MLA Style 9th Edition.
- Citation Style Chart via Purdue OWL:
- MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) Websites, pages on websites, eBooks, images, eArticles, social media...
- MLA Works Cited: Other Common Sources Interviews; speeches, lectures, or presentations; panel discussions; painting, sculpture, or photograph; conference proceedings, song or album; film or movie; podcasts; digital files
- MLA Works Cited Page: Books in Print
- MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals in Print (Journals, Magazines & Newspapers)
- MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics
- MLA Style Sample Paper
- MLA Style Sample Works Cited
- MLA 9th PowerPoint Presentation

- << Previous: Finding and Accessing eBooks Tutorial
- Next: Library Instruction Recap >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 1:54 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ggc.edu/ENGL_4412_Weiss

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.1: Creating MLA Works Cited Entries
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 59575
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Because of the wide variety of source formats, MLA 8 now requires that researchers follow a simple set of guidelines to create appropriate citations (instead of looking up one of the fifty-nine types of sources inside the previous handbook and following the instructions). Although there are still distinct rules you need to follow to create a citation, the rules are less rigid and allow for you to look for the main components of a citation and construct it yourself. This means you will need to think about the source and its information, select the appropriate components, and organize it in a logical and useful manner.
Regardless of the source type, you are now asked to locate the same “core elements” from your sources and place them in a standard order in order to create citations. These core elements are explained in detail below. Note that you do not need to memorize every step of this process , but should take this opportunity to understand how citations are created. You can always return to this page, to the MLA handbook, the MLA Style Center , or to other online resources to help you create the citations you need for your paper. Click through the following slides to learn more about each component and to see examples of MLA citations.
You can also download the presentation here .
Watch this video to see examples of how to identify the core elements needed in a citation:
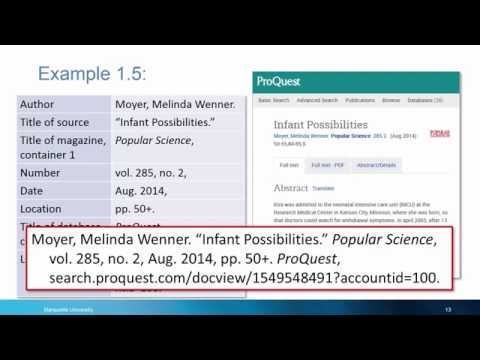
A YouTube element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: http://pb.libretexts.org/itl/?p=114
Practice your mastery of MLA documentation by correctly ordering the following citations from the Santa Fe College library :
- Book – Desktop Version | Touchscreen Version
- Chapter in an Edited Book – Desktop Version | Touchscreen Version
- Article from a Print Journal – Desktop Version | Touchscreen Version
- Journal Article from a Library Database – Desktop Version | Touchscreen Version
- Web Page – Desktop Version | Touchscreen Version
- Video – Desktop Version | Touchscreen Version
Contributors and Attributions
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- MLA Format (8th Ed.), information for presentation. Authored by : EasyBib. Located at : http://www.easybib.com/guides/citation-guides/mla-8/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- MLA Style, 8th Edition: An Introduction. Authored by : MU Libraries. Located at : https://youtu.be/lSekgYAdQcU?t=2m7s . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship
- Difference between Copyright and Patent
- Difference Between Call by Value and Call by Reference in C
- Difference Between Call by Value and Call by Reference in C++
- Difference between useRef and createRef in ReactJS
- Difference Between Trip and Tour
- Difference between SRAM and DRAM
- Difference between Register and Memory
- Difference between Linker and Loader
- Difference Between Mirror and Lens
- Difference Between Hotel and Motel
- Difference between RAM and Cache
- Difference Between Object And Class
- Difference between Source Code and Object Code
- Difference between Class and Structure in C#
- Difference between RAM and SRAM
- Difference between Identifiers and Variables in C
- Difference Between Source Code and Byte Code
- Difference between Keyword and Identifier
- Difference between React.js and Node.js
Difference between Citation and Reference
Citation and Reference are often used interchangeably but they have distinct meanings in academic writing. A citation is a brief notation within the body of a text that indicates the source of information, ideas, or quoted material; whereas, a reference is a detailed entry at the end of a document that provides full information about a source cited in the text.
What is Citation?
A citation is a brief notation within the body of a text that indicates the source of information, ideas, or quoted material. Citations typically appear in parentheses or as footnotes/endnotes and correspond to a more detailed entry in a bibliography or reference list.
Features of Citation:
- Brevity: Citations are concise, providing just enough information to identify the source without interrupting the flow of the text. They typically include the author’s last name, publication year, and page number (if applicable).
- Placement: Citations are placed within the text where the source is referenced, ensuring readers can easily locate the corresponding source material. They can appear as in-text (parenthetical) citations, footnotes, or endnotes, depending on the citation style used.
- Correspondence: Each citation corresponds to a full reference entry in the bibliography or reference list at the end of the document. This ensures that readers can find complete information about the sources cited in the text.
- Citation Styles: Various citation styles dictate the format and placement of citations, including APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard. Each style has specific rules for how citations should be formatted, such as the order of elements and punctuation.
What is Reference?
A reference is a detailed entry at the end of a document that provides full information about a source cited in the text. It includes comprehensive details such as the author’s name, title of the work, publication date, publisher, and other relevant information.
Features of Reference:
- Comprehensive Information: References provide full bibliographic details about the sources cited in the text, including the author’s name, title of the work, publication date, publisher, and other relevant information.
- Location: References are typically located at the end of the document, in a separate section known as the bibliography or reference list. This allows readers to easily locate and consult the sources cited in the text.
- Correspondence with Citations: Each reference entry corresponds to one or more citations in the text. This ensures that readers can match the abbreviated information provided in the citations with the full details provided in the reference list.
- Formatting Consistency: References adhere to specific formatting guidelines dictated by the chosen citation style, such as APA, MLA, Chicago, or Harvard. This consistency ensures clarity and uniformity in documenting sources.
Citation and Reference – FAQs
How do i create a reference list or bibliography.
A reference list or bibliography should be arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name or by the title of the work, depending on the citation style used. Each reference entry should be formatted according to the rules of the chosen citation style.
Can I use websites as references in academic writing?
Yes, websites can be used as references in academic writing, but it’s important to evaluate the credibility and reliability of the website and include all relevant information in the reference entry, such as the author, publication date, and URL.
Do I need to include page numbers in citations for electronic sources?
Page numbers are not always available for electronic sources, so it’s not always necessary to include them in citations. However, if page numbers are available (e.g., for PDF documents), it’s recommended to include them in the citation.
How do I cite sources with multiple authors?
The format for citing sources with multiple authors varies depending on the citation style used. Generally, you would list all authors’ last names in the citation, separated by commas, and use an “&” before the last author’s name.
How do I cite sources that are cited within another source?
This is known as secondary source citation. In such cases, you should cite the original source and indicate that you accessed it through another source. The exact format may vary depending on the citation style used.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Commerce - Difference Between
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
What is a citation generator?
Lenovo Pro Business Store
Log In / Sign Up
{{SalesNumber}}
{{SmallBusinessNumber}}
Chat Now >
Visit Sales Support Page >
Order Support:
Order Lookup >
Visit Order Support Page >
Technical Support >
- About Lenovo
- Lenovo Pro for Business Business Store Benefits Small Business Medium Business Partners Business Community
- Shop Shop all Education Education Sale Laptops by Major Education Accessories Warranties & Services
- Explore Education Discounts Lenovo EDU Community More in Lenovo Education
- Shop Shop All Gaming Gaming Laptops Gaming Desktops Gaming Accessories Gaming Sale
- Explore Lenovo Legion Lenovo LOQ Legion Go Legion Ultimate Support Legion Gaming Community
Sign in / Create Account Keep track of your wishlist, orders, and My Lenovo rewards, all in one place
Access your orders, subscriptions, saved carts, rewards balance, and profile
Create a wishlist of your favorite products
Create an account to earn or view your rewards
View & track your orders
Product Registration
Register your product and/or update your warranty dates
- Laptops by Use Work Gaming Education Laptops by Brand Yoga & Lenovo Slim ThinkPad ThinkBook Legion Gaming LOQ Gaming IdeaPad
- Laptops by Type 2-in-1 Laptops Traditional Laptops Build Your Own Laptop Mobile Workstations Chromebooks Shop All Laptops
- Best Selling Laptops ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 11 ThinkPad E16 Intel LOQ Gaming (16" AMD) Legion Pro 7i Gaming (16" Intel) Yoga 7 (16” AMD) 2 in 1 Laptop IdeaPad Pro 5i (16″ Intel) Quick Links New Arrivals Pick Up at Best Buy Laptop Deals
- Desktops by Type Traditional Towers Small Form Factor All-in-One Tiny Desktops Thin Client Desktop Workstations Build Your Own Desktops
- Desktops by Use Work Gaming Everyday Desktops by Brand Legion Gaming LOQ Gaming ThinkCentre IdeaCentre ThinkStation
- Best Selling Desktops ThinkCentre M80q Tiny (Intel) ThinkCentre Neo 50s Gen 4 (Intel) ThinkCentre M70q Tiny (Intel) IdeaCentre AIO 3 (24" AMD) Legion Tower 7i Gaming (Intel) Quick Links New Arrivals Desktop Deals
- Workstations by Type Desktop Workstations Mobile Workstations Shop All Workstations
- Workstations by Brand ThinkPad ThinkStation Quick links Workstation Deals Compare Best Selling Workstations Workstations for AI
- Best Selling Workstations ThinkPad P1 Gen 6 ThinkPad P16s Gen 2 ThinkPad P16 Gen 2 ThinkPad P16v ThinkPad P14s Gen 4 ThinkStation P3 Tiny ThinkPad P3 Tower
- Accessories by Category Docking Stations Keyboards & Mice Cases & Bags Audio Chargers & Batteries Cables & Adapters Webcams Lenovo Go Accessories Printers & Scanners Wireless & Networking Privacy & Protection
- Memory & Storage Stylus Pens & Supplies Stands & Mounts Furniture Graphics Cards Hubs Tablet Accessories VR Headsets Smart Home Devices Wearables Gaming Accessories
- Software & Subscriptions PDF Editors Graphics & Creativity Security Utilities Monthly Subscriptions Microsoft 365 Google Workspace Dropbox Lenovo Vantage Amazon Music Shop All Software
- Quick Links Find Compatible Accessories Web Exclusives Yes, Lenovo Sells That Brand Bundle & Save Accessory Deals New Arrivals PC Support Warranty Lookup & Extension Teens Accessories
- Monitors by Size 29″ or more 27″ - 28″ 23″ - 24.5″ Less than 23″ Portable Monitors
- Monitors by Use Gaming Monitors Business Monitors Business for Professionals Docking Monitors Monitors for Home
- Monitors by Resolution & Shape 4K - Best QHD - Better FHD - Good Curved & Ultrawide
- Quick Links Monitor Deals Shop All Monitors Monitor Buying Guide Monitor Accessories
- Explore Tablets Android Tablets Tablets for Business Tablet Accessories Tablet Deals Shop All Tablets
- Explore Smartphones ThinkPhone by Motorola Moto G Series Moto Edge Series Moto Care Phone Accessories Smartphone Deals
- Best Selling Tablets Lenovo Tab M11 Lenovo Tab M8 Lenovo Tab M9 Lenovo Tab M10 Plus Lenovo Tab P11 Pro Lenovo Tab P12
- Explore Servers Rack Servers Tower Servers Edge Servers Mission Critical Servers Multi-Node Servers Supercomputing Servers Options & Accessories
- Explore By Processor AMD Servers Intel Servers Explore Software Infrastructure Software Management Software Lenovo Open Cloud Automation Cloud Marketplace
- Hyperconverged Infrastructure ThinkAgile HX Series (with Nutanix) ThinkAgile MX and SXM Series (with Microsoft) ThinkAgile VX Series (with VMware) Explore Storage Unified Storage Storage-Area Network Direct-Attached Storage Tape Storage Options & Accessories
- Explore Furniture Desks Office Chairs & Seating Bookcases Tables Boards Shop All Furniture
- Office Supplies Office Accessories Notetaking Writing Cleaning Products Storage Binders Shredders Shop All Office Supplies
- Smart Office Conference Cameras Presentation Remote Controllers Printers & Scanners ThinkSmart Bar Speakers ThinkReality Smart Glasses Shop All ThinkSmart Office Devices
- Smart Devices Smart Lighting Smart Glasses VR headsets Smartwatches
- PC Deals Laptop Deals ThinkPad Deals Gaming Deals 2-in-1 Laptop Deals Desktop Deals Workstation Deals Build Your Own PC
- Other Deals Clearance Outlet Accessories & Electronics Monitor Deals Tablets & Phones Deals Server & Storage Deals
- Membership & Programs Lenovo Coupons Lenovo Trade-in Lenovo Pro for Business My Lenovo Rewards Lenovo Financing All Discount Programs
- Digital Workplace Solutions Digital Workplace Offerings Virtual Desktop Infrastructure Smart Collaboration
- Hybrid Cloud Multi Cloud Solutions Cloud Service Provider
- TruScale Hybrid Cloud Deloitte-Hybrid Cloud Microsoft-Hybrid Cloud Nutanix-Hybrid Cloud SAP-Hybrid Cloud VMware-Hybrid Cloud
- AI for All Edge AI Edge Computing Lenovo AI Innovators
- Sustainability Lenovo Value Recovery Asset Recovery Services CO2 Offset Services
- TruScale TruScale IaaS TruScale DaaS TruScale Data Management TruScale HPC TruScale Infinte Storage TruScale DaaS Calculator
- Solutions by Industry Architecture, Engineering & Construction Education Government Healthcare
- Manufacturing Media & Entertainment OEM Infrastructure Solutions OEM Solutions
- Product Development Retail SMB Infrastructure Solutions Telco Infrastructure Solutions
- Alliance Partners AMD Intel Lenovo Solutions Accelerated by Intel Microsoft
- NVIDIA Red Hat SAP VMWare Lenovo AI Innovators
- Other Solutions AR/VR Backup & Disaster Recovery Big Data & Analytics Business Applications Database
- Data Management High-Performance Computing Kubernetes & Containers SAP Solutions Windows 11
- Resources Customer Success Stories Smarter Infrastructure Customer Stories Storage Customer Stories
- Resource Library Lenovo Press Tech Today Resource Center
- Lenovo StoryHub Infrastructure Solutions Events Lenovo Executive Briefing Center
- Consumer Services
- Advisory Services Sustainability Workshop AI
- Deployment Services Chrome OS Zero-Touch Smart Collaboration
- Managed Services Digital Workplace Solutions Managed Services Managed Services for Collaboration Suite Lenovo Device Intelligence Plus Managed Services
- Security Services Cyber Resiliency as a Service ThinkShield Accidental Damage Protection Smart Lock
- Premier Support Premier Support Plus
- Hardware Support Premium Care Premium Care Plus Sealed Battery Keep Your Drive Smart Performance
- Gaming Support Legion Ultimate Support
- TruScale TruScale DaaS TruScale Infrastructure Services TruScale Hybrid Cloud TruScale DaaS Calculator
- Warranty Lookup
- Sales Support For Home 1-855-253-6686 For Business 1-866-426-0911 Visit Sales Support
- Order Support Track Your Order Warranty Lookup For Home 1-855-253-6686 For Business 1-866-426-0911
- Technical Support
- Track Your Order
- Who We Are Our Leadership Our History
- Our Impact Diversity & Inclusion Ethics & Security Sustainability
- Investor Relations
- Sponsorships
Memorial Day! Save up to {savingPercent} on laptops & accessories! Plus, extra savings the more you buy. Shop Now >
Shopping for a business? New Lenovo Pro members get $100 off first order of $1,000+, exclusive savings & 1:1 tech support. Learn More >
Need it today? Buy online, pick up select products at Best Buy. Shop Pick Up >
My Lenovo Rewards! Join for free or sign in to your account and earn 2X rewards (that's 6% back). Hurry, ends 5/27 Join for Free >
Bad credit or no credit? No problem! Katapult offers a simple lease to own payment option to help get what you need. See if you Prequalify >
{{tabItem?.headline?.t_id}}
A citation generator is a tool that helps you create bibliographic references for the sources of information you use in your work. You plug in the details about your source—like the author's name, title, and publication date—and the tool formats this information into a citation that complies with your chosen style guide. This can be incredibly helpful, as it ensures that you are giving proper credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Can a citation generator save me time on my research project?
Absolutely. A citation generator streamlines the process of creating accurate references. Instead of manually checking each citation against a style guide, you simply input your source’s information, and the citation generator does the rest. So, yes, it can save you a significant amount of time, allowing you to focus on the research itself rather than the intricacies of referencing.
Does a citation generator support different citation styles?
Yes, most citation generators are quite versatile, supporting a range of citation styles such as American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), Chicago, and Harvard, among others. You can usually select your desired style, and the tool will generate the citation accordingly. This is crucial because different academic fields and journals may require different citation formats.
What happens if I input incorrect information into the citation generator?
It's important to remember that a citation generator works with the information you provide. If you input incorrect details, the citation created will also be incorrect. Your role is to ensure the accuracy of the data entered; the generator's role is to format that data according to the selected citation style.
Could automated citation generators be considered a form of artificial intelligence?
While citation generators do automate a task that requires understanding of citation rules, they might not be considered artificial intelligence in the same way that more complex AI systems are. Citation generators follow a set of programmed rules to format data, which is a task that typically doesn't require learning or adaptation, key features in more advanced AI.
Would the use of a citation generator be suitable for all types of documents?
Citation generators are ideal for academic papers, research articles, and any type of written work where it is necessary to credit sources. However, for more informal documents or in cases where citations are not required or follow a very specific format, such as certain legal documents, they might not be the best tool to use.
What should I do if my source doesn’t fit into standard categories in the citation generator?
For sources that don't neatly fit into standard categories, many citation generators offer an "Other" or "Manual entry" option which you can use to construct the reference manually within the generator’s framework. You will need to apply the principles of your citation style to properly format the reference.
Can a citation generator create in-text citations as well as full references?
Yes, many citation generators can create both in-text citations and full bibliographic references. The generator will usually ask what type of citation you need and format it accordingly.
Does using a citation generator help me learn how to cite sources manually?
Using a citation generator can be educational. As you observe the correct formats being generated, you would likely begin to understand the patterns and rules of citation for different source types and citation styles.
When citing a book with multiple authors, how does a citation generator handle that?
When you’re citing a book with multiple authors, citation generators ask you to input all the authors' names. The tool then applies the rules of the citation style you’ve chosen to format the names correctly, whether it’s including all the names or using ‘et al.’ after the first author, dependent on the number of authors and the rules of the citation style.
Can a citation generator compile a full bibliography for my paper?
Certainly. Once you've entered all your sources, the citation generator can compile these entries into a complete bibliography that can be directly inserted into your paper. However, you should still review it for any errors or inconsistencies.
How do I know if my institution accepts citations made by a citation generator?
In most cases, if the citations generated are in the correct format as dictated by your institution's preferred citation style, they should be accepted. However, it's always a wise move to check with your instructor or institution's writing center for approval. Some institutions may have specific guidelines about the use of these tools.
What happens if the citation generator is outdated and uses an old citation style?
If the citation generator hasn’t been updated to the latest version of a citation style, the references it creates might not meet current standards. Always check that the generator has options for the most recent edition of the style guide, especially since guides like APA and MLA periodically update.
Can citation generators handle sources like tweets or YouTube videos?
Modern citation generators typically include options for digital sources such as social media posts and videos. If you input the correct details, these tools can generate the proper reference.
Does using a citation generator ensure my paper will be free from plagiarism?
Using a citation generator can help prevent plagiarism by creating accurate citations for your sources, which is an important part of recognizing others' work. However, avoiding plagiarism isn't just about properly citing sources; it’s also about ensuring that the work you submit is genuinely your own and that all sources are credited appropriately.
What can I do if the citation style I need isn't available on the citation generator I am using?
If your specific citation style isn't available, you might need to either find a different generator that does support your style or manually construct your citations according to the style guide. Even without the exact style, familiarizing yourself with similar styles can sometimes help in manually adapting your citations.
How do I choose the best citation generator for my needs?
Consider what you value most: Is it the number of citation styles supported, ease of use, cost, or the ability to store and manage multiple citations? Look for a generator that balances these factors effectively for your specific requirements.
Could I use a citation generator if I’m co-writing a paper and have different devices?
Yes, citation generators, especially those with cloud-based functionality, can be used by multiple people on different devices. This can be particularly helpful for ensuring uniform citations across a collaborative document.
Can citation generators be integrated into word processing software?
Many citation generators can integrate with word processing software, either as add-ons or built-in features. This integration allows for seamless citation management within your writing environment.
When should I double-check the output of a citation generator?
You should always double-check, but it's critical when dealing with atypical sources or when your generator doesn't include the latest updates to a citation style. Remember, the accuracy of your references is ultimately your responsibility.
While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, this glossary is provided for reference purposes only and may contain errors or inaccuracies. It serves as a general resource for understanding commonly used terms and concepts. For precise information or assistance regarding our products, we recommend visiting our dedicated support site , where our team is readily available to address any questions or concerns you may have.

- Our Company
- Smarter Technology For All
- Investors Relations
- Product Recycling
- Product Security
- Product Recalls
- Executive Briefing Center
- Lenovo Cares
- Formula 1 Partnership
- Products & Services
- Laptops & Ultrabooks
- Desktop Computers
- Workstations
- Servers, Storage, & Networking
- Accessories & Software
- Services & Warranty
- Product FAQs
- Lenovo Coupons
- Cloud Security Software
- Windows 11 Upgrade
- Shop By Industry
- Small Business Solutions
- Large Enterprise Solutions
- Government Solutions
- Healthcare Solutions
- Higher Education Solutions
- Education Discounts
- Discount Programs
- Legion Gaming Community
- Lenovo EDU Community
- Lenovo Pro Community
- Lenovo Pro for Business
- My Lenovo Rewards
- Lenovo Financing
- Lenovo Trade-in
- Customer Discounts
- Affiliate Program
- Affinity Program
- Employee Purchase Program
- Lenovo Partner Hub
- Laptop Buying Guide
- Where to Buy
- Customer Support
- Policy FAQs
- Return Policy
- Shipping Information
- Order Lookup
- Register a Product
- Replacement Parts
- Provide Feedback

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically with MyBib, a software tool for academic papers. Choose from various sources, styles, and formats, and download or autocite your works cited page.
Create MLA citations for websites, books, journals, and more with this free online tool. Learn how to format your paper and avoid plagiarism with the complete guide to MLA style.
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
Cite This For Me helps you create accurate and reliable citations in the MLA format for various source types. Learn how to cite like a pro, avoid plagiarism, and format your paper according to the MLA style guide.
Learn how to format your Works Cited page in MLA style with our free template and citation generator. Find examples of Works Cited entries for common source types and tips for ordering and indenting your list.
The Cite This For Me style guide is based on the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook. Our citation generator also uses the 9th edition — allowing you to shift focus from the formatting of your citations to what's important — how each source contributes to your work. MLA has been widely adopted by scholars, professors, journal publishers, and ...
BibGuru helps you cite websites, books, articles, and more in MLA style. Learn the rules and examples of MLA citation format, in-text citations, and Works Cited page.
Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text citations using Scribbr's APA Citation Generator, MLA Citation Generator, Harvard Referencing Generator, and Chicago Citation Generator. Plagiarism Checker: Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to ...
MLA Format Guide for MLA (9th Edition) MLA citations have two main parts that work together to identify the sources you've used for a paper and each of the specific places in your paper where you directly quote or paraphrase from a source: A Works Cited list. Located at the end of your paper. Contains a list of full references for every ...
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers. If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically ...
Format Your MLA Works Cited. A Works Cited page is an essential part of any research paper or academic work using the MLA citation format. It provides a comprehensive list of all sources cited in the paper, allowing readers to locate and verify the sources used. Here are detailed instructions on how to format a Works Cited page in MLA format:
EasyBib® has tools to help you create citations for over 50 source types in this style, as well as a guide to show you how an MLA paper should be formatted. Review the guide to learn how to format a paper's title page, paragraphs, margins, quotations, abbreviations, numbers, tables, and more! There are even tips on editing, as well as on the ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Stay up to date! Get research tips and citation information or just enjoy some fun posts from our student blog. Citation Machine® helps students and professionals properly credit the information that they use. Cite sources in APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and Harvard for free.
Generate flawless MLA citations with our user-friendly MLA format generator. Simplify referencing with our MLA citation generator for precise citation generation and formatting.
MLA Format Guide. This is the total package when it comes to MLA format. Our easy to read guides come complete with examples and step-by-step instructions to format your full and in-text citations, paper, and works cited in MLA style. There's even information on annotated bibliographies.
If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp ...
Find more in-depth rules regarding the works-cited list in MLA format on the page down below, along with a sample page. ... Remember, BibMe has an MLA works-cited generator that creates citations for you quickly and easily! Format for Other Contributors: In MLA citing, when there are other individuals (besides the author) who play a significant ...
Citations by Format. Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements—facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you're citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on ...
Start the citation with the title. The title of the individual page is placed in quotation marks, followed by a period. Next, place the name of the website in italics, followed by a comma. If the name of the publisher matches the name of the author or the name of the title, do not include the publisher's information in the citation.
A quick guide to works cited; Sample papers in MLA Style format; An interactive practice template for works cited; Formatting your paper "How do I cite generative AI in MLA style?" Basics of MLA Citations. If you are citing sources in an MLA style paper, you'll have brief in-text citations throughout your paper as well as longer full citations ...
MLA format is a widely accepted style for writing and documenting scholarly papers, particularly in the humanities. It provides guidelines for formatting manuscripts, citing sources, and structuring works cited pages, ensuring consistency and clarity.Adhering to MLA format helps writers present their research in a professional and organized manner, facilitating readability and academic integrity.
Citations by Format Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements—facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you're citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on the template.
This means you will need to think about the source and its information, select the appropriate components, and organize it in a logical and useful manner. Regardless of the source type, you are now asked to locate the same "core elements" from your sources and place them in a standard order in order to create citations.
MLA format is a widely used citation style for academic papers. Learn how to format your title page, header, and Works Cited page with our free template and examples. Watch our 3-minute video to see how easy it is to apply MLA rules to your document.
You should always include a citation for the sources you use to support any academic text. In-text citations must accompany any material that is quoted, paraphrased, or summarized. The in-text citation should direct the reader to the full reference entry in the references list or bibliography. The format of your citations and reference entries ...
An author-date citation in running text or at the end of a block quotation consists of the last (family) name of the author, followed by the year of publication of the work in question. In this context, author may refer not only to one or more authors or an institution but also to one or more editors, translators, or compilers. No punctuation ...
A citation is located within the text as an in-text citation, footnote, or endnote. A reference is located at the end of the document, in the bibliography or reference list. Purpose. A citation briefly indicates the source of specific information within the text. A reference provides full details of the sources cited in the text.
A citation generator is a tool that helps you create bibliographic references for the sources of information you use in your work. You plug in the details about your source—like the author's name, title, and publication date—and the tool formats this information into a citation that complies with your chosen style guide.