- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up

DNS Server Isn't Responding? Easy Troubleshooting & Fixes
Last Updated: May 25, 2024 Fact Checked
Troubleshooting
Changing your dns servers.
This article was co-authored by Luigi Oppido and by wikiHow staff writer, Nicole Levine, MFA . Luigi Oppido is the Owner and Operator of Pleasure Point Computers in Santa Cruz, California. Luigi has over 25 years of experience in general computer repair, data recovery, virus removal, and upgrades. He is also the host of the Computer Man Show! broadcasted on KSQD covering central California for over two years. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 5,603,159 times.
Are you getting "DNS not responding" or "DNS server might be unavailable" errors? These errors occur when your device can't turn hostnames and domains into IP addresses . Although DNS server errors are frustrating and will keep you from browsing the web, we're here to help! Read on to learn how to fix DNS Not Responding problems on your computer for good.
DNS Server Not Responding: What It Means & How to Fix It
DNS server errors occur when your device can't turn domain names into IP addresses. There could be a problem with your DNS cache, internet connection, VPN, or the DNS servers themselves. You can stop the error by restarting your network, clearing your browser and computer's DNS caches, or changing your DNS servers.
- Go to Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Status .
- Click Network troubleshooter under "Change your network settings."
- Follow the steps in the troubleshooter. [1] X Trustworthy Source Microsoft Support Technical support and product information from Microsoft. Go to source
- Right-click the Wi-Fi, globe, or ethernet icon at the bottom-right corner (in the system tray) and select Diagnose network problems .
- If a problem is detected, you'll see an error.
- Press and hold Option as you click the Wi-Fi status icon in the menu bar. [2] X Research source
- Click Open Wireless Diagnostics and follow the on-screen instructions.
- If you see "DNS resolution failure," the issue is DNS related. If you see a broader error like "LAN Connectivity Failure," the issue is likely your connection to the internet.
- Type or paste chrome://net-internals/#dns into the address bar at the top of your browser and press Enter or Return .
- Click Clear host cache and then restart your browser.
- If you don't see the Develop menu when Safari is open, enable it in Safari > Settings > Advanced > Show features for web developers . [3] X Research source
- Click the Develop menu and select Empty Caches .
- Restart Safari and try browsing again.

Tip: If you're having trouble with a specific website, try accessing it using mobile data. If you still can't access the site, the issue is on the site's end.

- Close your web browser and all open programs.
- Press the Windows key , type cmd , and press Enter to open Command Prompt .
- Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter .
- In your Launchpad, type terminal , then click Terminal in the search results.
- Type sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder and press Return .
- Type your password when prompted to complete the flush.

- If your router and modem are two separate devices, unplug the power cords from each device. If you have one combined unit, unplug it. Wait about a minute.
- Plug the modem back in and wait 3-5 minutes. If you have a separate router, don't plug it back in yet.
- (If your modem/router is not combined into one unit): Once the modem is back up (after 3-5 minutes), plug your router back in and wait another 3-5 minutes.
- When the modem and router (or combo gateway) are back online, reconnect to Wi-Fi if your computer doesn't connect automatically, then try using the internet again.
- If you're unsure how to boot into safe mode, see our guide to booting into safe mode for Mac and Windows.
- Mac only: After about 15-20 seconds, press Ctrl + C to stop the ping.
- If you see "Request timed out" or "Destination host unreachable," there is a problem with your internet connection, not your DNS servers. See our guide to troubleshooting your internet connection .
- Now type ping dns.google and press Enter or Return .
- If you get an error like "Ping request could not find host," "Name or service not known," or "cannot resolve dns.google: Unknown host," but were able to ping 8.8.4.4, the DNS servers your computer is using are not working, but your internet is working. In this case, see this method to learn how to change your DNS servers to ones that won't give you errors.
If you still get DNS server errors after troubleshooting, and you were able to ping Google's IP address , changing your computer's DNS servers will usually fix the problem.

- Press Windows key , type control panel , and click Control Panel .
- Go to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings .
- Right-click your connection and select Properties .
- If you're using IPv6, select Internet Protocol Version 6 (TPC/IPv6) instead.
- If "Use the following DNS server addresses" is selected and IP addresses are listed, there's a problem with those server addresses. Before changing your DNS servers to the public Google servers, select "Obtain an IPv4/6 address automatically" first to see if that fixes the problem. If it doesn't, continue with this method.
- If using IPv6, enter 2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844 . [4] X Research source
- Click OK and OK again to save your changes.
- Restart your computer, and clear your browser cache once it comes back up. This should fix your DNS errors.
- If the DNS not resolving errors persist, contact your ISP.
- Open the Apple menu and go to System Settings > Network > Wi-Fi (or your network type).
- Go to Details > DNS . [5] X Research source
- If using IPv6, enter 2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844 .
- Remove the other DNS servers listed and click OK .
Community Q&A
- Resetting your router periodically is a good way to prevent DNS issues from happening. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- After resetting your DNS cache, your computer will load websites a bit slower the first time you visit them. This is because your computer establishes and verifies a new DNS address for the site. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/fix-wi-fi-connection-issues-in-windows-9424a1f7-6a3b-65a6-4d78-7f07eee84d2c
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/mac-help/use-wireless-diagnostics-mchlf4de377f/14.0/mac/14.0
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/safari/use-the-developer-tools-in-the-develop-menu-sfri20948/mac
- ↑ https://developers.google.com/speed/public-dns/docs/using
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/mac-help/change-dns-settings-on-mac-mh14127/mac
About This Article

To fix a DNS server not responding problem, try reaching the site with another device like a phone, since if this works you’ll know that the issue is with your other device. Alternatively, try to visit the site using a different web browser, such as Firefox or Chrome. If this works, try uninstalling and reinstalling your original browser to solve the problem. You could also try power cycling your modem and router by disconnecting them and letting them sit for at least 30 seconds. Then, reconnect them to the power supply, wait for them to reload, and try the website again. As another option, try connecting your device to the router with an Ethernet cable, since if you can access the site via the Ethernet it shows you have a problem with your wireless router. If this is the case, reset your router to resolve the issue. For tips on how to flush the DNS cache, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Apr 30, 2017
Is this article up to date?

Apr 15, 2017
Sep 10, 2018
Noel Meaney
Jan 31, 2017
Dec 9, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Computers and Electronics
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Keep up with tech in just 5 minutes a week!
Try using another web browser or device
Restart your devices, change your dns settings, flush your dns cache, update your network drivers, router, and modem, turn off your vpn and firewall, contact your isp, 8 ways to fix 'dns server not responding' errors on a mac or pc.
- You can fix a "DNS Server Not Responding" error by resetting your internet connection and computer.
- If the error keeps appearing, you can also flush your DNS cache and change the DNS settings.
- DNS errors might also come up if your ISP is having an outage.
DNS servers are like phonebooks – they help your computer find websites and load them properly. This means that if the DNS server stops responding, you won't be able to access any website or app.
Luckily, both Macs and PCs offer a few ways to fix "DNS Server Not Responding" issues. Here are eight ways to do it.
First, we need to figure out what's causing the issue: Is it your web browser, your computer, or your internet connection?
Using the same internet connection, try browsing the web using another browser. In other words, if you're using Google Chrome right now, try Microsoft Edge or Firefox instead. If the internet suddenly starts working, it means there's an issue with your original browser. Try clearing the cache , or uninstalling and reinstalling the app.
If it still doesn't work, try using another device. If the internet works on that device, the issue is coming from your computer. If you still run into internet problems, the issue is your connection.
Alternatively, try connecting to another internet signal on your computer. If the internet starts working, the issue is your connection; if it doesn't work, the issue is your computer.
Get closer to your internet router
It might seem too simple to be true, but a lot of DNS server issues are caused by weak internet signals. If you're too far away from the source of your internet connection – usually the router – your computer will have trouble reaching the DNS server.
Getting a stronger internet connection, either by moving closer to your internet router or removing obstructions, can solve this. You should also make sure that you're not taking up all your bandwidth by running too many websites or apps at once.
And if it's possible, consider connecting with an ethernet cable instead of Wi-Fi. Ethernet connections are way more stable than wireless ones , meaning you're much less likely to have DNS issues.
Before we delve into the more complicated troubleshooting steps, try restarting all your devices: Your computer, your router, and your modem. You'd be surprised by how many issues this can fix.
You can restart most routers and modems by unplugging them for about ten seconds, then plugging back in.
Once everything is running again, open a web browser and head to a website. There's a good chance that things will work now.
A lot of internet issues can be fixed by changing the DNS settings on your computer. These settings control how your computer interacts with the internet connection, and if they're not set up correctly, it can cause problems.
Specifically, you'll want to make sure that the DNS server is being obtained automatically. Or if it's already automatic and you're having trouble, you'll want to set one manually.
In Windows 10 and 11
1. Open the Control Panel and click Network and Internet , then Network and Sharing Center , and then Change adapter settings .
2. Right-click on your Wi-Fi network and select Properties .
3. In the list that appears, double-click on the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) option.
You'll be given a menu that lets you set your DNS server. There are two options that let you obtain the DNS server either automatically or manually.
4. Click whatever option isn't already selected. If you're switching from automatic to manual, you'll also need to enter two DNS servers.
5. Click OK to save the changes.
See if the internet works now. If it doesn't, go back to the Properties menu and do the same steps for the Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) option.
1. Open the System Preferences app and select Network .
2. Select the connection that you're trying to fix from the left sidebar, then click Advanced… in the bottom-right corner.
3. Select DNS from the tabs at the top.
4. Select the DNS Servers box and click the plus sign at the bottom, then enter a new DNS server you want to connect with.
5. Click OK to save your changes.
Most people know that every program and app has a cache, a small storage space for data that the app has loaded recently. Your DNS server has a cache too, which it uses to collect IP addresses and DNS records that you've connected with recently.
And just like other caches, letting the DNS cache get too full can cause problems. You can clear the DNS and refresh your IP address through the Command Prompt and Terminal apps.
1. Search your computer for "Command Prompt." When it appears in the results, right-click it and select Run as administrator .
2. In the Command Prompt window, type and submit these five commands in order. Type one of them, press Enter , and then wait a few moments before typing the next.
- netsh winsock reset
- netsh int ip reset
- ipconfig /release
- ipconfig /renew
- ipconfig /flushdns
3. Restart your computer.
1. Search your computer for "Terminal" and open the app when it appears.
2. Type and submit the following code, without quotes: "sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder"
3. When prompted, enter your Mac's password. It won't look like you're typing anything, but don't worry, it's just hiding your password.
4. If you don't see any sort of response — Terminal just takes the command and gives you another blank entry line — it means it worked.
Even if you've just bought all your hardware, it's a good idea to check that everything is updated. There's a chance you might be using outdated software, which can lead to bugs.
First, your drivers. These are small pieces of software that tell the computer how to function . If you're using a Mac, all your drivers will update whenever you install a full computer update . But on a Windows PC, you'll likely need to update them separately.
You can do this by opening the Device Manager app, clicking the Network adapters tab, and right-clicking on your main internet driver. You'll likely have two of them, one for Wi-Fi and one for Ethernet (usually called the "Family Controller"). When you're asked how you want to search for drivers, pick the automatic option.
If that doesn't work, check your computer manufacturer's website to see if they offer drivers of their own. These might work better than the ones that come pre-installed.
Finally, you can also try uninstalling the driver and restarting your computer. This will force the driver to restart, which can clear away some issues.
When it comes to your router and modem, every model and brand has a different updating process. But in general, you'll probably need to log into your devices' settings pages using a web browser and update from there. Check the manual or call your ISP for exact steps.
This isn't as common, but if there's something standing between your computer and the open internet — say, a VPN or firewall — you can run into DNS issues.
Every VPN has a different method for turning it off, but look for a Disconnect option in the settings. You can also open the Network settings on your computer and disable all VPNs from there.
In Windows, you can disable the default firewall by searching for Windows Defender Firewall, then selecting Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off .
On a Mac, open the System Preferences app and select Security & Privacy . Click Firewall at the top, then select Turn Off Firewall . You might need to click the lock icon in the bottom-left corner first.
If you're using a third-party antivirus program, you might need to disable that app's firewall too.
Finally, you can pick up the phone and call your internet service provider. At the end of the day, they're the ones with total control over your internet service.
If none of these steps have worked, it might mean that your ISP is having an outage. Alternatively, they might have shut off your service due to unpaid bills, or might be throttling your connection because you hit a data cap. If you rent your internet equipment from the ISP, they can even send someone out to troubleshoot in person.
- Main content
- Irresistible Tech Gifts for That Special Dad
- Killer Smartphone Deals We Love
How to Fix DNS Server Not Responding Errors
Internet connection won't work? Take a deep breath; we've got the answers
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- University of Illinois
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ryanperiansquare-de5f69cde760457facb17deac949263e-180a645bf10845498a859fbbcda36d46.jpg)
- Western Governors University
In This Article
Jump to a Section
- Why You Can't Connect to a DNS Server
- Step-by-Step: Run Network Troubleshooter in Windows 10
- Step-by-Step: Run Network Troubleshooter in Windows 7 or 8
- Fix DNS Server Not Responding Problems
- Resolve TCP/IP and DHCP Failures
- Handle DNS Provider Problems
- Avoid Internet Blockages From Antivirus Programs
Recover or Replace a Malfunctioning Router or Modem
When you connect a device to your home network or a Wi-Fi hotspot with internet access, the internet connection may fail to work for a variety of reasons.
Instructions in this article apply to Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Reasons Why You Cannot Connect to a DNS Server
One class of failures are related to Domain Name System — the distributed name resolution service used by internet providers around the world. Windows 7, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 computers may report the following error messages in the Troubleshooting Problems found window:
The device will not be able to reach the internet when these failure conditions occur. These DNS server errors may appear for any of several different reasons. Step-by-step network troubleshooting steps can be used to diagnose and repair the problem as described below.
How to Run Windows Network Troubleshooter in Windows 10
On Microsoft Windows PCs, Windows Network Diagnostics can be run to help diagnose internet connection problems. If you're not sure whether or not your computer is reporting DNS Server Not Responding errors, follow these steps:
Select Start and then choose Settings .
Select Network & Internet . The Network Status window will open.
Select Network Troubleshooter under Change Your Network Settings. Windows Network Diagnostics will open.
Follow the steps to begin and wait for the troubleshooting tests to complete. The wizard will offer customized diagnostic assessments based on the errors it thinks it finds, so each pass-through will differ for different people. Look in the Problems found section of the window for the error message to better identify potential root causes.
How to Run Windows Network Troubleshooter in Windows 7 or 8
Open the Control Panel.
Open the Network and Sharing Center .
Click the Troubleshoot problems under Change your Networking Settings.
Click Internet Connections . A new Internet Connections window appears.
Click Next .
Click Run the Troubleshooter.
Click Troubleshoot my connection to the Internet .
Wait for the troubleshooting tests to complete and look in the Problems found section of the window for the error message.
You should be done!
How to Fix DNS Server Not Responding Problems
To properly fix these internet connection failures requires first isolating the problem down to its root cause. The sections below each cover common causes of these failures:
Misbehaving internet provider
Malfunctioning TCP/IP or DHCP services
Overly aggressive antivirus software
Malfunctioning router or modem
If not confident that your internet connection issues are truly related to DNS, try general connection troubleshooting techniques first .
Resolving TCP/IP and DHCP Failures
It’s possible for the TCP/IP software inside a client device’s operating system to malfunction and set its DNS server addresses incorrectly. Rebooting a Windows computer often clears these temporary glitches. A more elegant solution involves running TCP/IP utility programs that perform the standard procedure to release and renew the Windows IP address settings .
Similarly, most TCP/IP networks use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol service to assign IP addresses to clients. DHCP assigns not only the device's private IP address but also primary and secondary DNS server addresses. If DHCP is malfunctioning, a PC reboot is likely required to recover it.
Check to ensure both your device and the network router both have DHCP enabled. If either end of the connection is not using DHCP, internet connection errors normally result.
Handling DNS Provider Problems
Many people configure their home networks to automatically obtain DNS server addresses from their internet provider. When the provider's servers or network suffer an outage or are heavily loaded with traffic, their DNS services can suddenly stop working. Customers must wait until the provider fixes those problems before they can use the provider's DNS.
As an alternative to the private DNS servers supported by each provider, several providers, most notably Google and OpenDNS, offer free public DNS servers . A router administrator can switch their network's DNS setup over from a private to a public DNS configuration by manually entering the public DNS IP addresses into the router configuration settings.
DNS settings can also be applied on the Windows device itself through the Network and Sharing Center. However, this approach usually will not work as a permanent solution because devices normally obtain and override their local settings with those from the router through DHCP.
Avoiding Internet Blockages from Antivirus Programs
Antivirus programs that people install on their Windows PCs are designed to keep intruders out, but they also block internet access if they detect a misbehaving device.
Most antivirus programs work using special database files that the software vendors automatically update on a regular basis. PC users often don't realize when these install updates happen as they are triggered in the background and designed to not interrupt normal work.
Unfortunately, sometimes mistakes are made with these data updates that cause the antivirus program to believe a computer is infected when really it is a false alarm ( false positive test). These false positives can trigger Windows to suddenly start reporting DNS Server Not Responding errors.
To verify whether this is the cause for your device, temporarily disable the antivirus program and re-run the Windows Network Diagnostics. Then consult the antivirus vendor for either a new update or technical support. Although disabling antivirus does not work as a permanent solution, doing so to temporarily to troubleshoot the problem is normally (not always) safe.
A misbehaving broadband router or broadband modem can trigger these DNS error messages on home network devices. Restarting the router and modem will resolve intermittent router glitches, at least temporarily.
Routers and modems must eventually be replaced if they continue to exhibit failures. However, it is unlikely for either to fail in such a way that would cause DNS errors to be regularly generated. Failed routers and modems normally cannot power on at all or else generate errors related to the underlying network connection itself. If you connect to the router using a wired Ethernet port , try moving the Ethernet cable to use a different port instead.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- How to Fix It When There's No Internet Connection
- Hulu Error Codes: What They Are and How to Fix Them
- How to Change DNS Servers in Windows
- What to Do When Windows 11 Can't Connect to a Network
- The Best Free and Public DNS Servers (2024)
- How to Connect Two Routers on a Home Network
- How to Fix Amazon Error Code 1060
- DHCP Error: What It Is and How to Fix It
- DNS Servers: What Are They and Why Are They Used?
- How to Change DNS Server Settings on Home Computer Networks
- Is Twitch Down... Or Is It Just You?
- Troubleshooting Xbox One Network Failures
- How to Fix a YouTube Black Screen
- How to Fix the PS4 'Cannot Connect to the Wi-Fi Network' Error
- How to Fix Netflix Error Code NW-2-5 on Any Device
- How to Resolve Limited or No Connectivity Errors in Windows
How-To Geek
How to fix a "dns server is not responding" error on windows.
Get around your PC's DNS problems with these methods.
Quick Links
Why do you get a "dns server not responding" error, fixes for a dns server not responding error on windows, key takeaways.
To resolve DNS issues on Windows, try opening your site in a different web browser, restarting your router, disabling your VPN, or running the "Internet Connections" troubleshooter. Other options include deleting your DNS cache, trying another device on the same network or another DNS server, updating your network adapter drivers, turning off your antivirus or IPv6, deactivating other network adapters, and booting your PC in safe mode.
DNS servers' unavailability causes your Windows PC to display a "DNS Server Is Not Responding" error. Various items can cause your DNS servers not to work. Luckily, it's easy to fix many of those items and resolve your problem. Here's how to do just that.
A "DNS server not responding" error appears when the server your device uses to resolve domain names is down or otherwise can't be reached. If that's confusing, let's review the function of a DNS server.
When you type in a domain name in your PC's web browser, your web browser asks your DNS server to translate your domain name to an IP address . Your browser then uses this IP address to locate your site on the internet and let you access its contents.
Related: What Is DNS, and Should I Use Another DNS Server?
When your DNS server is down or is experiencing an issue, your web browser can't retrieve your site's IP address , resulting in an error message. Many problems can cause your DNS servers to go down, and other issues could simply prevent your PC from connecting to your specific DNS servers.
Some of those potential problems are a malfunctioning router, a faulty web browser, an incompatible VPN app, a corrupt DNS cache, and more.
Related: How Do IP Addresses Work?
To resolve your Windows DNS error and access your sites, use the methods below that fix the underlying items causing the problem. Once you've resolved the issues, your DNS error will be gone, and the sites you're trying to reach will open just as they should.
Use a Different Web Browser
When you encounter a DNS issue in a web browser, the first thing to do is try accessing your site in another web browser . This helps you find out if your issue is device-specific or browser-specific.
To do that, launch a different web browser on your PC and try to access your site. If your site loads in this browser, your previous browser likely had issues. In this case, apply some fixes like clearing your previous browser's cache ( Chrome , Firefox , Edge ), turning off your browser's extensions ( Chrome , Firefox , Edge ), and resetting your web browser ( Chrome , Firefox , Edge ).
If you get the same error in your other browser, read on to discover more fixes.
Related: Why You Should Use Multiple Web Browsers
Reboot Your Router
Your router may be acting up, causing your PC not to reach your DNS servers. In this case, give your router a reboot to possibly fix your issue .
You can restart most routers by pressing the Power button on them. If yours hasn't got a Power button, unplug it from the power socket to turn the router off and (after at least 10 seconds) back on. Then, launch your web browser and try to access your site.
Related: Why Rebooting Your Router Fixes So Many Problems (and Why You Have to Wait 10 Seconds)
Turn Off Your VPN
Your VPN app transmits your data via a third-party server, letting you bypass your ISP's restrictions. Sometimes, this mechanism causes issues with your DNS servers, leading to errors like the one you're experiencing.
To verify that, turn off your VPN service and see if your site loads. If it does, reach out to your VPN provider to seek a permanent solution.
Use the Internet Connections Troubleshooter
Windows has many troubleshooters to help you fix issues with your PC's various components. When you have trouble connecting to the internet , use your PC's Internet Connections troubleshooter to find and fix all the faults with your connection.
To run the troubleshooter on Windows 11, navigate to Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other Troubleshooters. On the open page, next to "Internet Connections," click "Run."
If you're on Windows 10, head into Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Additional Troubleshooters. Click "Internet Connections" and choose "Run the Troubleshooter."
Follow the troubleshooter's instructions to detect and resolve your DNS issues.
Related: Internet Connection Not Working? 10 Troubleshooting Tips
Flush Your DNS Cache
Windows caches your DNS queries to help you quickly translate domain names to IP addresses. It's possible this cache has become corrupted, causing issues with your web browsers.
In this case, clear your bad DNS cache , and your issue will be resolved. Note that you don't lose any personal data when you do this.
To start, open the "Start" menu, find "Command Prompt", and launch the utility. In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
ipconfig /flushdns
Windows will clear your current DNS cache, and you're all set.
Use Another Device on the Same Network
To ensure your router configuration isn't the cause of the issue, use another device on your network and see if you can access your site on it. You can use any of your devices to do this, including iPhone, Android, Windows, Mac, Linux, Chromebook, or any other machines.
Related: How to See Your Wi-Fi Password on Windows 11
If your site fails to load on your other device and you get the same DNS error, your router likely has an issue. In this case, speak to your internet service provider (ISP) for help. Another thing you can do is reset your router to the default settings , but you'll need your ISP's configuration to re-configure your router and make it work with your current internet company.
In case your site opens just fine on your other device, your Windows PC has a problem. In this case, read on to learn more fixes.
Change Your PC's DNS Servers
If your DNS servers are down or are experiencing technical glitches, that may be why you can't access sites on your PC. In this case, change the current DNS servers on your PC to fix your issue.
We've already written guides on how to change your DNS servers on Windows 11 and Windows 10 , so check them out to learn how to perform the procedure.
Update Your Network Adapter Drivers
Your network adapter drivers tell your physical adapter how to communicate with your PC. If these drivers are outdated or corrupted, that may be why Windows displays a DNS error message.
In this case, resolve your issue by updating your drivers . Do this by first right-clicking the "Start" menu and choosing "Device Manager."
Then, expand "Network Adapters," right-click your adapter, and choose "Update Driver."
Select "Search Automatically for Drivers" and download and install the available drivers.
Restart your PC, and try to access your site.
Related: How to Update Drivers on Windows 11
Temporarily Disable Your Antivirus
Your PC's antivirus program may be interfering with your browsing sessions, causing your browsers to display a DNS error message. Usually, this happens when your antivirus detects a potential threat in your browsers.
If you trust your site and your DNS servers, temporarily turn off your antivirus protection to see if you can then load your site. Check out our guide on how to turn off Microsoft Defender Antivirus to learn how to do that.
Make sure to turn real-time protection back on when you've checked your site.
Turn Off IPv6 on Your PC
IPv6 is the latest Internet Protocol version, which aims to fix many IP-related issues on your devices. Sometimes, when this protocol version is enabled, you can get errors like a DNS server not responding.
To fix that, disable IPv6 on your PC, and your issue will be resolved.
To turn off IPv6, head into Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change Adapter Settings. Right-click your adapter and choose "Properties." Disable "Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)" and click "OK."
And that's it.
Related: Are You Using IPv6 Yet? Should You Even Care?
Disable Other Network Connections
Your computer might have other network connections, causing an issue with your DNS queries. If you don't use those other adapters, it's a good idea to turn them off to potentially resolve your problem.
To do that, navigate to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. Find an unused adapter, right-click it, and choose "Disable."
Repeat the above step for each unused adapter to disable it on your PC.
Reboot Your PC in Safe Mode
With Windows' safe mode, you can turn on your computer by only loading the essential files. This helps you find out if a third-party app installed on your PC is causing the problem. And if that's the case, you can remove that app from your PC.
Check out our guide on how to use Windows' safe mode . When in safe mode, if your web browser can open your site without the DNS error message, your third-party apps are likely the culprit.
You can start fixing the issue by removing your recently installed apps . Feel free to uninstall any app that you think might be the cause of the issue.
And that's how you resolve a "DNS Server Is Not Responding" error on a Windows 11 or Windows 10 PC. Enjoy browsing your favorite sites!
Related: How to Fix "This Site Can't Be Reached" ERR_ADDRESS_UNREACHABLE in Chrome
How to diagnose and fix DNS problems
Dead websites, page loading issues, web not working as it should? Here's what to do next.

Browsing the web is so easy, simple and straightforward that it feels almost automatic. Sure, you know there's a lot of low-level tech making this happen, but who cares when it just works?
That only makes it more frustrating when you suddenly get major page loading issues, though, dead websites everywhere, and all kinds of other web-based complications.
Internet connectivity problems across multiple websites can look like something you'll never fix yourself, but that's not always true – they're often related to DNS (Domain Name System) problems. In this article we'll look at how to identify these, and then get your system working again.
- Get security, streaming and more with today's best VPNs
What is DNS?
Accessing a new website looks simple, at least from user's point of view. Enter the URL in a browser, wait a few seconds, website appears, that's about it. Peek under the hood, though, and there's a lot more going on.
Your browser can't access a web server from a domain name like techradar.com, for instance. It can only find and download websites when it has a server IP address , such as 199.232.198.114.
A device normally handles this by asking your ISP's DNS server to translate the domain name into an IP address. Easy.
But what if DNS fails, and the server doesn't always return the IP address you need? Then you'll see major web problems.
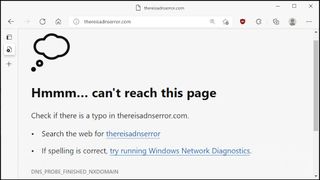
What does a DNS issue look like?
If your DNS fails entirely then it's likely you'll see timeouts, DNS or other errors with all your internet apps. It might look like your entire internet is dead.
Other DNS failures are partial, though, affecting some websites only. Maybe you'll access sites a, b and c as usual, but x, y and z all seem to be down.
Partial failures can also cause odd-looking page loading issues. What if DNS allows you to access bigsite.com, but not the domain where it hosts its images, scripts or contact forms?
You might see image placeholders, empty spaces where content used to be, or buttons and other site features not working as they should. It's this mix of problems across multiple sites that's one of the tell-tale signs of a DNS problem.
Diagnosing a DNS issue
The simplest DNS problem to diagnose is an issue with your current server. Try the same websites on a connection using another DNS server, and if they're now accessible and work correctly, it looks like you have a DNS issue.
If you've problems on a mobile device connected to your home Wi-Fi, for example, switching to your mobile network allows you to test a site with new DNS servers.
Or if you're on the move and already using your mobile network, look for a free hotspot you can try. (Just for a quick connectivity test, though – free Wi-Fi can be a security risk causing more problems than it solves, and you should always use at least a cheap VPN to stay safe on these networks.)
No other connections available? Try the virtual online browser Browserling . If you can reach it, choose Chrome as your preferred browser, enter the URL in the address box and click Test Now! Browserling uses its own DNS to connect to the site, so if it gets you access and your own connection doesn't, it could be a DNS issue.
Test your DNS server
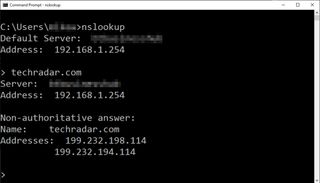
A more advanced test is to manually ask your DNS server for the IP address of the domain you're trying to access. If the server can't find the IP or displays an error, that points to a DNS difficulty.
To try this on Windows, click Start , type CMD and open Command Prompt , then type NSLOOKUP and press Enter. ( NSLOOKUP is often available on Macs and Linux – try opening it from your terminal window.)
NSLOOKUP launches and displays the name and IP address of your current DNS server (or 192.168.* if devices get their DNS via your router's connection.)
Now type the name of any domain you can't currently access, press Enter, and NSLOOKUP queries your DNS server.
If NSLOOKUP displays the site IP address, it looks like DNS is working correctly.
But if NSLOOKUP displays an error like ' can't find Google .com: Non-existent domain ', that's pretty conclusive evidence that something is screwed up at the DNS level. Although there is one more quick trick you should try.
Try another DNS server
You've proved that your DNS server can't find an IP address for a domain, but will other DNS servers do any better? NSLOOKUP makes it really, really easy to find out.
Type SERVER 1.1.1.1 , press Enter , and NSLOOKUP changes its default DNS server to the IP address 1.1.1.1. (That's Cloudflare. If you know you were using Cloudflare before and that's the DNS with the problem, switch to Google's 8.8.8.8 , instead.)
Now enter whatever domain you couldn't reach earlier, and NSLOOKUP sends its DNS query to Cloudflare (or Google), instead.
If NSLOOKUP failed earlier but successfully gets an IP with Cloudflare, that looks like a problem affecting your DNS server only.
Test this by entering the IP address in your browser, instead of the regular domain. Use 142.250.179.238 for Google, for instance. If you can't access the website when you enter a domain, but it at least begins to load with the IP address, that confirms your DNS issues.
How to fix DNS problems
If it looks like your ISP's DNS isn't working, the quickest and most effective solution is to switch to a free public DNS server . Google and Cloudflare offer fast and reliable services which anyone can use, no registration required.
Changing DNS servers normally involves tweaking your device network settings. The Cloudflare support site has guides on setting up Cloudflare DNS for Windows, Mac, Android, iOS, routers, gaming consoles, Linux and more. These are sometimes very basic ('install app X to do it for you'), but Google's equivalent page has more detailed advice if you need it.
Whatever changes you make, be sure to note down your original settings first, just in case you need to switch them back later.
Reboot your device when you're done, and it should now be using your (hopefully) problem-free new DNS server.
If you still have internet connectivity problems, though, it's time to ask your ISPs support team for help. Tell them what you've tried, and that should help them diagnose the issue and get your connection running smoothly again.
- Get protected online for less with a great cheap VPN
- Stop logging of your PC activities with our Windows 10 privacy guide
- These streaming VPNs will help you get around geo-restrictions
Are you a pro? Subscribe to our newsletter
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Mike is a lead security reviewer at Future, where he stress-tests VPNs , antivirus and more to find out which services are sure to keep you safe, and which are best avoided. Mike began his career as a lead software developer in the engineering world, where his creations were used by big-name companies from Rolls Royce to British Nuclear Fuels and British Aerospace. The early PC viruses caught Mike's attention, and he developed an interest in analyzing malware, and learning the low-level technical details of how Windows and network security work under the hood.
Hostinger becomes the world’s fastest growing web hosting company
Innovation and revenue growth to be the focus of AI use rather than lowering costs and optimization according to business leaders (but they’re not sure how)
Apple says it's prioritizing iPhones that ‘never fail’ over ‘super-easy to repair’ handsets – but it’s not that simple
Most Popular
- 2 World Exclusive: We tested the first 2TB microSD card and no, it's not a fake — AGI's card defies laws of physics with record-breaking storage capacity on pinkie-size surface area
- 3 I've been walking 10,000 steps a day for a year – here are five unexpected benefits I've experienced
- 4 Nvidia RTX 4080 Super gets tempting discounts – but are bigger price cuts coming, prompted by the RTX 5080 GPU?
- 5 Ticketmaster breached — data of over 500 million users allegedly put up for sale online
- 2 Jaw-dropping 256-core CPU will debut in 2025 as Arm partner turns heat up on AMD and Nvidia — Ampere conspicuously leaves Intel out of equation as it claims CPU leadership ahead of Epyc
- 3 Hardly any of us are using AI tools like ChatGPT, study says – here’s why
- 4 These are the best iPhone apps and games of 2024 so far, according to Apple
- 5 This hidden iPhone feature will change the way you emoji

How to Resolve DNS Issues on Windows 11/10
Tweak a few options here and there
Windows 10 and 11 Domain Name System (DNS) issues aren’t uncommon. You may experience these problems when a DNS server faces an outage , or your PC has a network problem.
There are a variety of DNS error messages that you may see on your computer. These errors range from messages like DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN and DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NO_INTERNET to DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_BAD_CONFIG .
Luckily, it’s easy to fix most DNS-related issues on Windows, as this mostly only involves tweaking a few settings here and there on your machine.

Restart Your Router
When DNS issues occur , the simplest solution you can use is to reboot your router. Doing so refreshes your router’s connection, giving the device a chance to fix minor glitches.
You can reboot your router by opening your router’s settings page in your web browser, accessing the Maintenance or similar tab, and choosing Reboot The Router .
If you aren’t sure how to access your router’s settings page, press the Power button on the router to turn the device off. Then, press the same button to turn the router back on. You may also use the power socket switch to turn your modem off and back on.
Flush the DNS Cache and Release and Renew Your IP Address
One possible reason you’re experiencing DNS problems with your Windows PC is that your DNS cache is corrupt. This makes your PC unable to translate domains into IP addresses, resulting in various DNS error messages.
A quick way to get around this problem is to clear your PC’s DNS cache. This fixes nearly all your DNS-related issues without affecting the personal data you’ve stored on your computer.
You can clear your DNS cache and release and renew your IP address as follows:
- Open the Start menu, search for Command Prompt , and select Run as administrator .
- Select Yes in the User Account Control prompt.
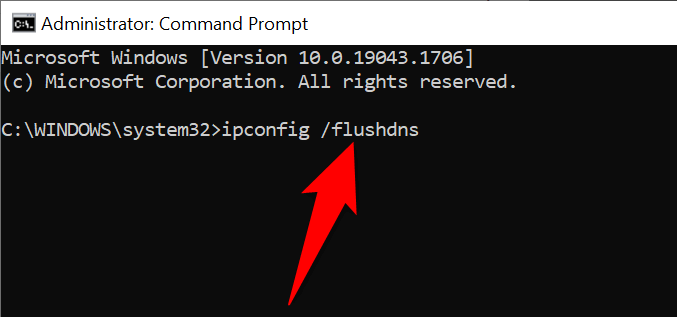
- Close the Command Prompt window when the commands have finished executing.
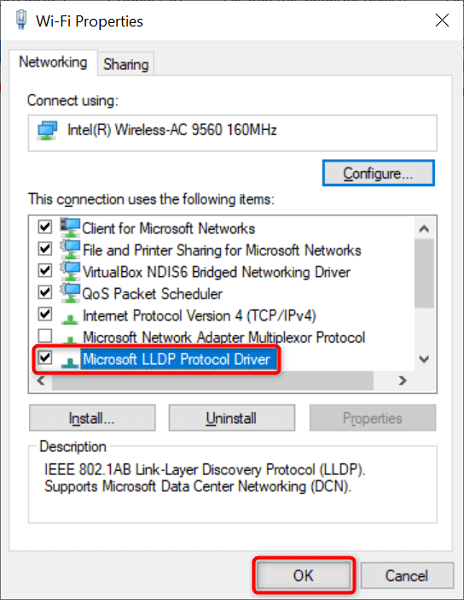
Enable the Microsoft LLDP Protocol Driver
When your PC suffers from DNS issues, consider enabling Microsoft’s LLDP protocol driver. This driver comes with both Windows 10 and Windows 11 PCs.
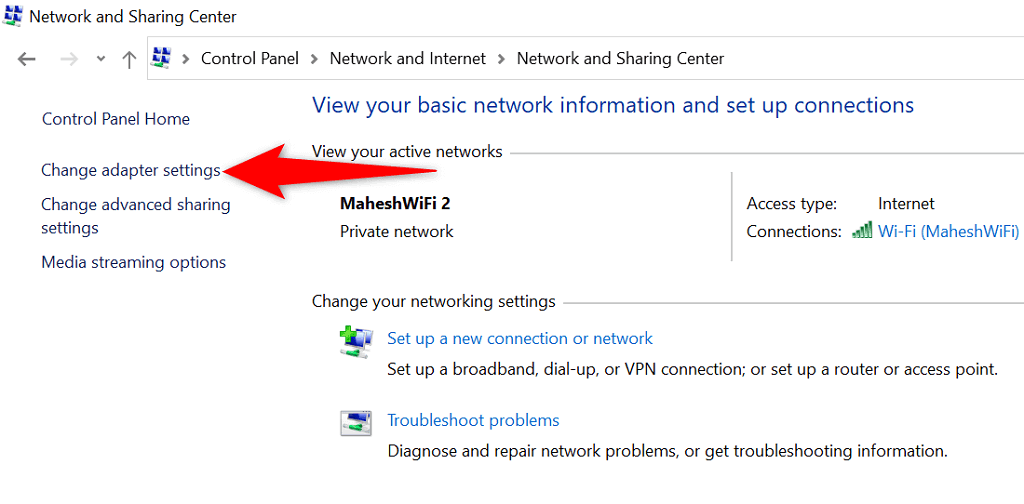
- Access the Start menu, search for Control Panel , and select Control Panel in the search results.
- Choose Network and Internet on the Control Panel window.
- Select Network and Sharing Center .
- Right-click your network adapter and select Properties .
Use Alternative DNS Servers
Unless you’ve configured a third-party DNS server, your Windows PC uses your internet service provider’s default DNS servers. These may not always work the best. So when you experience DNS problems, it’s worth switching to alternate DNS servers.
You have several free and reliable DNS servers to choose from. You simply need to add these servers to your network settings , and your PC will start using them. We’ll show you how to add Google’s public DNS to your Windows PC.
- Open Control Panel and head to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings .
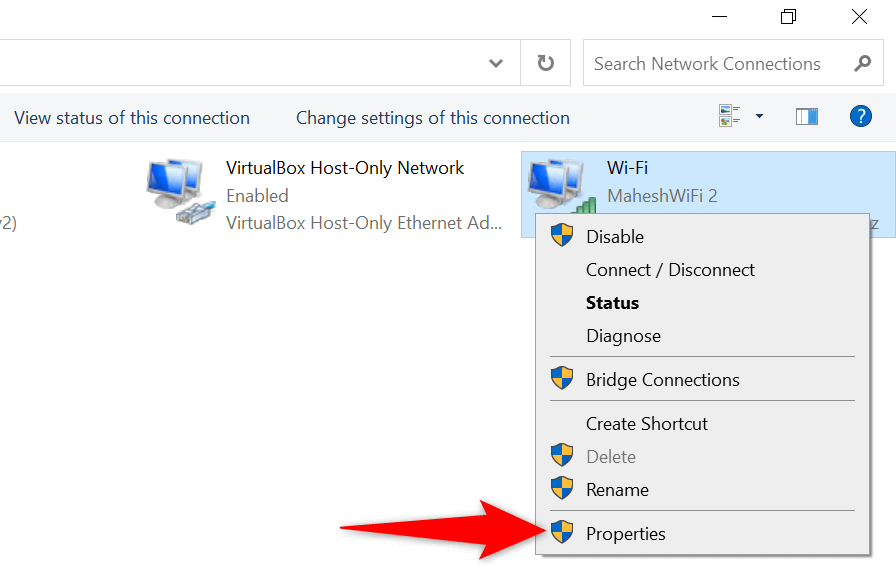
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and choose Properties .
- Enable the Use the following DNS server addresses option.
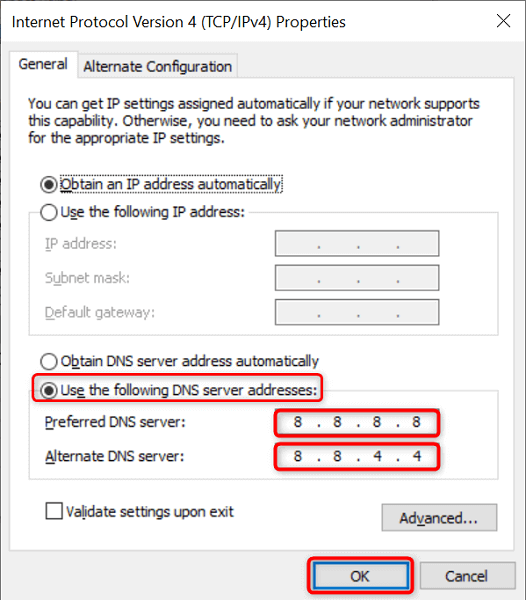
- Select OK at the bottom to save your settings.
Use the Internet Connections Troubleshooter
Microsoft’s Windows 10 and 11 operating systems include multiple troubleshooters. These troubleshooters help you quickly find and fix various common problems on your machine. One of these is an Internet Connections troubleshooter , and, often, it can resolve DNS problems.
The troubleshooter runs on automatic mode, for the most part, so you don’t have to specify any options in the tool manually.
- Open Settings by pressing Windows + I at the same time.
- Select Update & Security on the Settings window.
- Choose Troubleshoot in the pane on the left.

- Wait for the troubleshooter to find and fix your DNS issues.
Change Your Network Adapter’s Power Settings
Your power settings control your PC’s various components to some extent. If you’ve chosen to disable certain adapter functions when your machine is on battery or is plugged in, you’ll have to tweak those options to resolve your DNS problems.
It’s easy to change your power plan’s settings on Windows 10 and 11.
- Select Change advanced power settings .
- Expand Wireless Adapter Settings followed by Power Saving Mode .
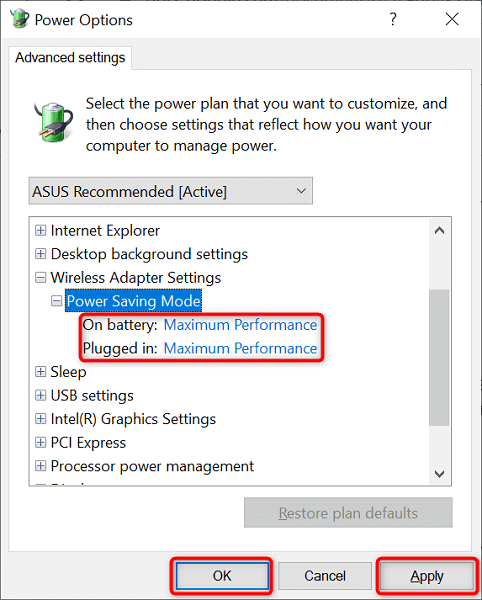
- Select Apply followed by OK at the bottom to save your changes.
Update Your Network Adapter Drivers
Outdated hardware drivers can cause various issues, including DNS problems. So, you should keep your network adapter and other drivers up to date. This should likely fix the DNS issues you’re experiencing on your PC.
- Launch the Start menu, search for Device Manager , and select that tool in the search results.
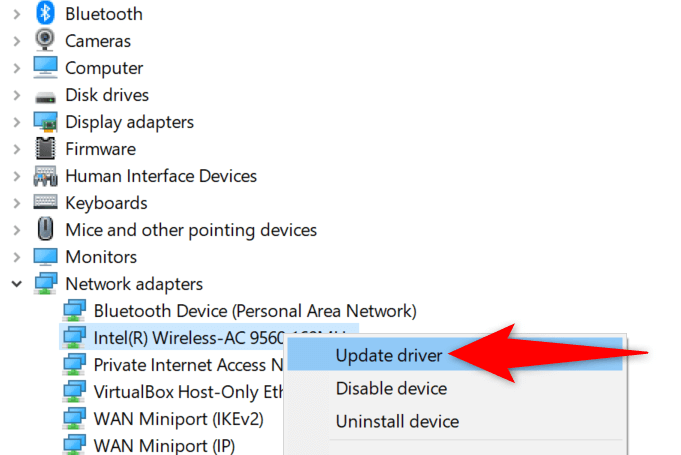
- Allow Windows to find and install the latest network adapter drivers.
Reinstall Your Network Adapter Drivers
Faulty network adapter drivers can prevent you from connecting to the internet. You may be unable to fix such drivers by running an update check. However, you can uninstall and reinstall the drivers to eliminate the issue.
Windows 10 and 11’s Device Manager makes it easy to tweak your adapter drivers.
- Open Device Manager on your PC.
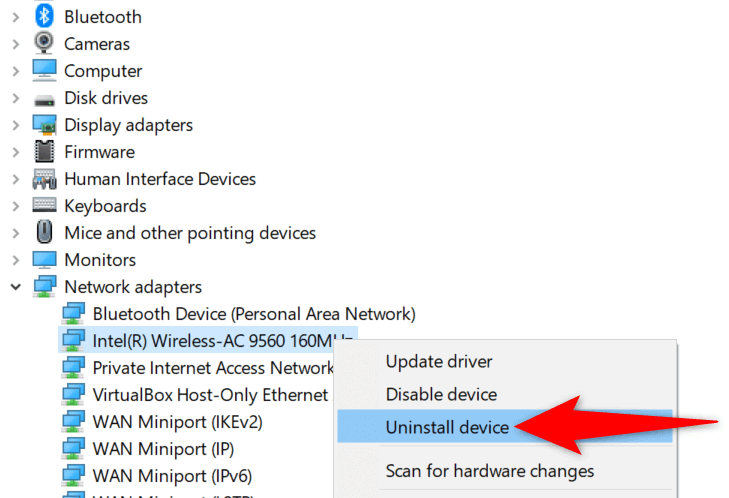
- Restart your PC when the drivers are uninstalled.
- Open your network adapter manufacturer’s website, download the latest drivers, and install those drivers on your PC.
Clean Boot Your Windows 10 or 11 System
If your DNS issues persist, one or more of the installed tools on your PC may be the culprit. One way to check if this is the case is by clean booting your Windows PC. Doing so keeps your installed tools from running, which helps find the problematic item.
We have written a guide on how to clean boot your Windows PC , so check that out to learn the procedure. Once you’ve identified the app that causes problems, use either Settings or Control Panel to remove that item from your computer.
Experience DNS Issues No More on Your Windows 10 or 11 PC
DNS plays an important role in connecting your PC to the internet. If this component ever experiences problems, you’re basically disconnected from the world wide web. However, you can fix most DNS-related issues with ease.
Once you tweak a few options here and there on your Windows system, your DNS issues are likely gone, and you’re back on the internet.
Mahesh has been obsessed with technology since he got his first gadget a decade or so ago. Over the last few years, he's written a number of tech articles on various online publications including but not limited to MakeTechEasier and Android AppStorm. Read Mahesh's Full Bio
Read More Posts:

DNS Server Not Responding – How to Fix the Error in Windows 10

I think it's safe to say that the vast majority of professionals depend on the internet these days.
So being denied access to the internet when you are trying to mine nuggets of valuable information from your go-to web sites can be quite an ordeal. Especially when you are under pressure to complete a piece of urgently required work.
One particularly unwelcome cause of being denied access to the internet is the “DNS Server Not Responding” error. It’s like that old fable where a troll sits under a bridge and says “You shall not pass!”, or something about gobbling up those that wish to cross the bridge.
I’m happy to tell you that you should be able to defeat the troll and cross the bridge to internet access joy by following the simple trouble shooting steps discussed in this article.
What is the "DNS Server Not Responding" Error?
The “DNS Server Not Responding” error is a fairly common issue and is generally easy to fix. There are many reasons why this issue may occur. But fundamentally it is caused because the DNS server that is contacted during the processes of loading a web page is unable to find the site that contains the web page that you have requested.
This article explores what may have triggered this issue to occur and how you may go about fixing the issue.
Firstly, I think it is a good idea to gain at least a basic understanding of the “DNS Server Not Responding” error. To do this, let’s first understand DNS.
DNS stands for Domain Name System. A simple explanation of DNS is that it is a decentralised storage of human readable internet addresses, like the ones with which you will almost certainly be familiar (for example www.amazon.com or www.netlix.com).
The DNS maps these human readable URLs to their appropriate IP (Internet Protocol) addresses.
IP addresses are much less human readable, but are essential for the inner workings of the internet. IP addresses uniquely identify computers on the internet. The IP address associated with the URL, www.netflix.com, might for example, look like this, 69.53.224.255.
It is clearly easier for you to remember “ www.netflix.com ", rather than a string of numbers delimited by full stops, when you wish to access your favourite content on Netflix. So the DNS facilitates this for you, so that you don’t have to remember or manually lookup unfriendly strings of numeric data every time you wish to access a web site.
The common analogy to explain DSN is a telephone directory. Basically, as you would look up a telephone number using the name of the person you wish to call in a telephone directory, a similar look up is performed when you type in the URL (like www.amazon.com) of the web site you wish to view within your browser.
Thankfully you don’t have to manually look up the corresponding IP address for www.amazon.com, as this is performed behind the scenes for you automatically.
So the appropriate IP address is retrieved automatically every time you type in a URL into your browser. This IP address is then used to contact the appropriate server that hosts the relevant web site associated with the URL you have entered into your browser.
When the “DNS Server Not Responding” error occurs, this means that the decentralised naming systems responsible for automatically looking up the appropriate IP address based on the relevant hostname that you entered into you browser fails to respond.
There are many reasons why this error occurs, but fortunately there are also many solutions available to you to fix the issue.
An easy solution may be to simply change the web browser you are using or even simpler still, simply restart your computer. Yup, simply turning it off and then turning it on again could fix the issue.
However, if you are not so lucky and the problem still persists, don’t despair – there are many steps that you can take to find out the cause of the issue and subsequently fix it.
In this article you will learn a number of possible solutions to the “DNS Server Not Responding” error.
How to Fix "DNS Serger Not Responding"
Below, I've listed out the ways that you can try using to fix the “DNS Server Not Responding” error. The subsequent sections of this article provide details on each of these methods:
Use a Different Web Browser
- Try Accessing a Web Site with a Different Device
- Restart your Router
Investigate Possible Network Issues
- Manually Set your DNS Server
Clear the DNS Cache
Disable internet protocol version 6.
- Temporarily Deactivate your Firewall and Disable your Antivirus Software
- Reset your DNS Settings
Update the Network Adapter Driver
- Disable all Network Connections Except the Connection you are Using to Access the Internet
Restart your Computer in Safe Mode
A potential solution to the “DNS Server not Responding” issue that's really simple is to try accessing the relevant website using a different browser.
If, for example, you are using Microsoft Edge or Mozilla Firefox as your browser at the time that the issue occurs, try using a different browser like Google Chrome to access the relevant website.
If using a different browser solves the problem, then make the browser that works your default browser. But if the issue still persists, then we at least know that the browser you have been using is not the source of the issue and our investigation into finding a solution to the DNS Server not Responding” issue must continue…
Try Accessing a Website With a Different Device
Try to use a different device connected to your home network to access the website you were trying to access when you received the error.
For example, use Wi-Fi from your mobile phone to access the relevant web site. If the issue persists, you know that the issue isn’t just with your primary device and the problem may have something to do with your router.
Restart Your Router
The “DNS Server not Responding” issue may occur simply due to data traffic. It may be that simply restarting your router can fix this issue.
You can restart your router by pressing the power button on your router. You can then unplug your router's power cable. Wait for about 30 seconds then plug your router into the power outlet again and press the power button to restart it.
Running network diagnostics may point to network issues as the root cause of the issue.
Running Network Diagnostic is very simple on a Windows 10 OS. You can do this by following these steps:
- Open Control Panel. One way to do this is press the Windows Key + R to activate the “Run” box, then type “control” in the text box presented in the “Run” box and hit the enter key.

- Select the Network and Internet option presented within the Control Panel window.
- Click the Network and Sharing Center option from within the “Network and Internet” window.
- Click the Troubleshoot problems option presented under the "Change your network settings” heading within the “Network and Sharing Center” window.
- Click Additional troubleshooters -> Internet Connections -> Run the troubleshooter

The next step is to wait for the troubleshooter task to finish. If you are presented with any error messages, simply follow the steps on how to fix the relevant network issue.
Manually Set Your DNS Server
The source of your issue may be that your DNS server is down. In this case you’ll be pleased to know that you are able to manually change your DNS server.
You can change your DNS server to, for example, Googles Public DNS or CloudFlare’s public DNS. To change your DNS server, follow these steps:
- Invoke your Control Panel. One way to invoke your Control Panel is to activate your Start Menu and search for the Control Panel.
- In the Control Panel window click the Network and Internet option.
- In the Network and Internet window, click the Network and Sharing Center option.
- On the Network and Sharing Center window click on your active connection. For example, click the “ethernet” option if this is the connection currently being used or click the “Wi-Fi” option if it is clear that this is your active connection.
- In the dialog box that is presented to you, click the “Properties” button.
- In the dialog presented to you, you’ll see a list is presented under the “The connection uses the following items” heading.
- In this list, select the list item labelled “Internet protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” then click the “Properties” button.

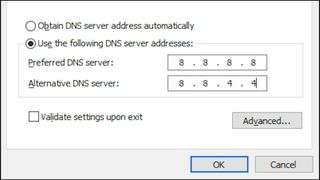
- You will be presented with another dialog box where you’ll see two fields. One will be labelled “Preferred DNS Server”, and the other which is directly under this field will be labelled “Alternate DNS Server”.
- First click the Use the following DNS server addresses radio button.
- To use Googles Public DNS server, enter 8.8.8.8 in the field labelled “Preferred DNS Server” and enter 8.8.4.4 into the field labelled “Alternate DNS Server”.

- You are also able to use CloudFlare’s DNS server for the same purpose. CloudFlare’s DNS address is simply 1.1.1.1
- Once you have entered your desired DNS server settings, ensure that the “Validate settings upon exit” checkbox is checked.
- Click the “OK” button to save your new DNS server settings.
- Restart your computer.
You are able to flush the DNS cache which may resolve the “DNS Server not Responding” issue. This action will clear IP addresses and other DNS related data from your cache.
You can clear the DNS cache by running a command using your command prompt.
One way to invoke the command prompt is to press Window Key + R to invoke the “Run” box. Type “cmd” within the “Run” box and press shift+ctrl+enter to run the command prompt as an administrator.

At the command prompt, type in the following command: “ipconfig /flushdns” and them press the enter key. If the command has executed successfully, you'll see the appropriate message in the command window.
At the time of writing this article, Internet Protocol Version 6 is the latest version of the internet protocol. Disabling the Internet Protocol Version 6 will not have detrimental effects on your computer’s operations, but it's been known to fix the “DNS Server not Responding” issue.
To disable the Internet Protocol version 6 on a Windows 10 operating system, just follow these steps:
- Go to Control Panel -> Network and Internet -> Network and Sharing Center
- Click on the relevant connection, for example “Wi-Fi”
- Click the “Properties” button on the dialog that is presented to you.
- In the list presented under the “This connection uses the following items” heading, uncheck the item labelled “Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)”.

- Press the “OK button”
Temporarily Deactivate your Firewall and Disable Antivirus
If your firewall is Defender, you can follow these steps to disable it:
- To open control panel, press Windows Key + R to activate the “Run” box, then type “control” in the text box presented in the “Run” box and hit the enter key.
- In the top right hand text box, type in “win”

- An option labelled "Windows Defender Firewall” should appear in the search results. Click the “Windows Defender Firewall” option.
- Click the “Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall” option.

- Click the “Change settings” button.

- From the list presented to you within the dialog box that has just been invoked, find the browser that you are using, for example Google Chrome. Then make sure that both the private and public checkboxes next to the relevant item are checked.

- Once you've done this, try to access the relevant website using the relevant browser and see if the issue has been fixed.
There is a chance that your firewall was preventing you from accessing external data through your browser.
Note that it is not recommended to leave your operating system unprotected by reliable antivirus software indefinitely. Disabling your antivirus software in this instance is only recommended for testing if the relevant antivirus software is the cause of the “DNS Server not Responding” issue.
To temporarily turn off Microsoft Defender antivirus protection, follow these steps:
- Select Start and then type in "Windows Security” in order to search for the relevant application.
- Select Windows Security App from the search results.
- Go to Virus & Threat Protection .
- Under Virus & threat protection settings select Manage settings.
- Switch Real-time protection off.

Attempt to access the relevant website through the relevant browser to test if the “DNS Server not Responding” issue still occurs.
Reset DNS Settings
To reset your DNS Settings, follow these steps:
- Run the command prompt as an administrator. To do this activate the “Run” box by pressing Windows key + R .
- In the run box type “cmd” and press shift + ctrl + enter
- Type the following commands in the command prompt. After entering each command press the enter key, so that each command is run individually.
ipconfig /registerdns
ipconfig /release
Ipconfig /renew
netsh winsock reset

Once you have run these commands, close the command prompt and restart your computer.
You can manually update your network adapter driver, but it is much easier to automate this task.
You can automate this through the use of free software like “Driver Easy” (https://www.drivereasy.com/download-free-version/). Simply download the free version of this software.
Make sure that before you run the free version of the Driver Easy software that you create a system restore point. This provides you with insurance, so in the unlikely event that you encounter a nasty surprise that adversely effects your computer, that you are able to return your Windows OS back to the state that it was in before you ran the Driver Easy software and encountered an unexpected issue.
To use the Driver Easy software, follow these steps:
- Run the software
- Click the “Scan Now” button
- Press the “Update” button next to any outdated drivers.
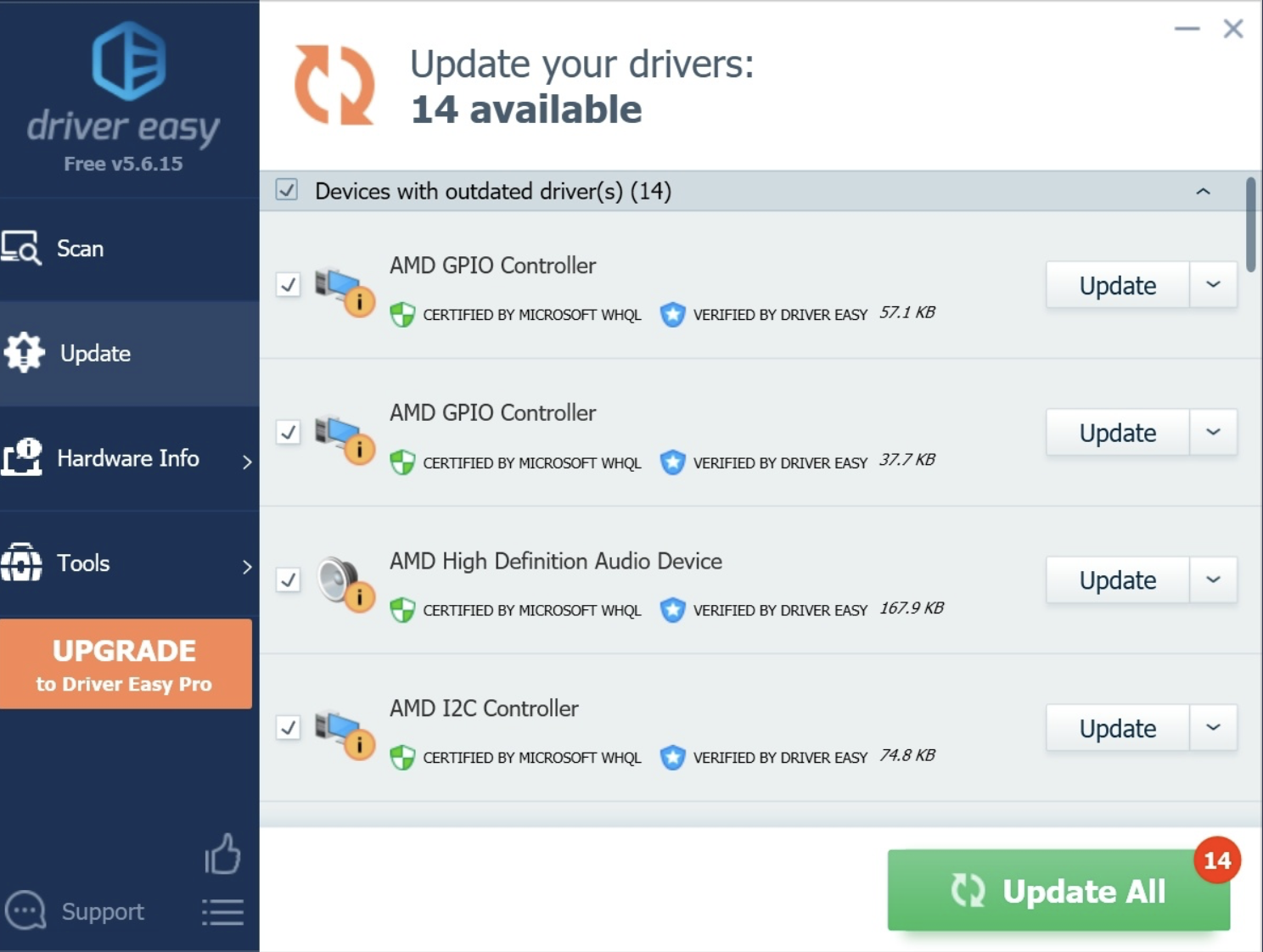
Disable all Network Connections Except for the Connection that you are Using
Disabling the additional network connections you may have setup on your computer (other than, for example, the Wi-Fi connection that you are using to access the internet) might fix the “DNS Server not Responding” issue.
To disable the relevant network connection, follow these steps:
- Firstly you must access your Network Connections. To access your Network Connections, press Windows Key + R to invoke the “Run” box
- In the “Run” box type in “ncpa.cpl” and press enter.
- Right click the relevant network connection and select “Disable” from the relevant context menu. Repeat this action until all connections except for the Wi-Fi connection you are using are disabled.

When you start your computer in Safe Mode, this means the Windows operating system loads with a limited set of drivers and files. This can help you diagnose what is causing your “DNS Server not Responding” issue through a process of illumination (as it were).
So to start your PC in Safe Mode, follow these steps:
- Press the Windows Key + I to open Settings.
- Select Update & Security -> Recovery
- Under Advanced startup , select Restart Now
- Once your PC has startup to the “Choose an option” screen, select Troubleshoot -> Advanced options -> Startup Settings -> Restart
- Once your PC has restarted you’ll see a list of options
- Select 5 or press F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
Try to access the web site that resulted in you getting the “DNS Server not Responding” issue. If the problem does not occur in safe mode this means that additional software may be the cause of the issue.
You can uninstall any additional software from your PC, one by one, and then test to see if the issue still occurs. If the issue does not occur after uninstalling particular software, this means that it is likely that this software was interfering with your internet access.
The “DNS Server not Responding” issue is relatively common and thankfully it is also relatively easy to fix.
It can be incredibly inconvenient to be denied access to the internet but hopefully the potential solutions outlined in this article will help you to once again have access to your favorite web sites.
Read more posts .
If this article was helpful, share it .
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Thank you for taking the time to respond. The NETGEAR documentation team uses your feedback to improve our knowledge base content.
Rating Submitted
Do you have a suggestion for improving this article?
Characters Left : 500

MyNETGEAR® Account
Welcome back
Access your NETGEAR

NETGEAR Support
How can I troubleshoot DNS resolution problems?
Was this article helpful? Yes No
The Domain Name System (DNS) server matches domain names (like www.netgear.com) to their IP addresses. For more information, see What is a Domain Name System (DNS) server?
If you experience a DNS resolution error when trying to use the Internet, the most likely cause is that your Internet connection is down. For more information about troubleshooting Internet connectivity, see What should I do if I can access my NETGEAR router but can’t connect to the Internet?
However, in some cases, the problem might be with a DNS server and not your Internet connection. By default, your Internet service provider (ISP) uses its own DNS servers. Rarely, their servers might have technical problems even when the rest of your Internet connection is working correctly.
If you think that you might be experiencing DNS resolution issues, you can configure one of your devices to use a popular free third-party DNS service like Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 or Google 8.8.8.8 . For instructions, select your type of device in one of the following external articles:
- Set up Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 resolver · Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 docs
- Get Started | Public DNS | Google Developers
If your DNS resolution problems are solved when you configure a device to use a third-party DNS service, your ISP’s DNS servers are likely experiencing problems. If this occurs frequently, you can configure your router to use a third-party DNS service for all devices on your network. For more information, see How do I set static Domain Name System servers on my NETGEAR router?
Last Updated:10/21/2022 | Article ID: 23
Was this article helpful?
This article applies to:.
- LBR20-1BNCNS
- LBR20-1H3NDS
- LBR20-1H3SDS
- LBR20-1USNAS
- NBR750-1BNCNS
- RBR350-1VNNZS
- RBS350-1VNNZS
- MBR1210-1BMCNS
- MBR1310-2H3ITS
- MBR1515-1GWNAS
- MBR1515-1VZNAS
- MBR1515A(R)-1VZNAS
- MBR1516-1BMCNS
- MR1100-1TLAUS
- MR1100RDMES
- MR5100-1TLAUS
- MR6110-111AUS
- MR6400-1Z1MES
- MR6500-1TLAUS
- MR6550-100APS
- MVBR1210C-1BMCNS
- C6300BD-1CXNAS
- C6300BD-1TLAUS
- R6300-2CHNAS
- XR1000-1RNNAS (ENTOUCH)
- XR1000-1RNNAS (GRANDE)
- XR1000-1RNNAS (RCN)
- XR1000-1RNNAS (WAVE)
- CG3000-1TDNDS
- CG3000D-1CHNAS
- CG3000D-1CXNAS
- CG3000D-1JCJPS
- CG3000D-2CXNAS
- WNDA3200-1VGUKS
- DGN1000SP-1RGUKS
- DGN1000SS-1VGUKS
- DGN2200-4DDAUS
- DGN2200M-2TKSAS
- DGN2200T-3BEGES
- DGND3300Bv2
- DGND3700Bv2
- DG834NU-2BEGES
- CENTRIA (WNDR4700/4720)
- JWNR2000-4EMRUS
- JWNR2000Tv3
- WNDR3400-1CANAS
- WNR1000-2VCNAS
- WNR2000-3XFNAS
- WNR2000UPPE
- WNR3500CEIF
- WNR612-2EMRUS
- WGR614-7VCNAS
- WGR614-8CONAS
- WGR614-9UMGRS
Looking for more about your product?
Get information, documentation, videos and more for your specific product.
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Quick and easy solutions are available for you in the NETGEAR community.
Need to Contact NETGEAR Support?
With NETGEAR’s round-the-clock premium support, help is just a phone call away.
Complimentary Support
NETGEAR provides complimentary technical support for NETGEAR products for 90 days from the original date of purchase.
NETGEAR Premium Support
Gearhead support for home users.
GearHead Support is a technical support service for NETGEAR devices and all other connected devices in your home. Advanced remote support tools are used to fix issues on any of your devices. The service includes support for the following:
- Desktop and Notebook PCs, Wired and Wireless Routers, Modems, Printers, Scanners, Fax Machines, USB devices and Sound Cards
- Windows Operating Systems (2000, XP or Vista), MS Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook and Adobe Acrobat
- Anti-virus and Anti-Spyware: McAfee, Norton, AVG, eTrust and BitDefender
ProSUPPORT Services for Business Users
NETGEAR ProSUPPORT services are available to supplement your technical support and warranty entitlements. NETGEAR offers a variety of ProSUPPORT services that allow you to access NETGEAR's expertise in a way that best meets your needs:
- Product Installation
- Professional Wireless Site Survey
- Defective Drive Retention (DDR) Service
Where to Find Your Model Number
To find the model/version number, check the bottom or back panel of your NETGEAR device.
Select a product or category below for specific instructions.

Nighthawk Routers

Powerline and Wall Plug Extenders

Cable and DSL Modem Routers

ReadyNAS Network Storage

Wireless Access Points

Other Business Products

Mobile Broadband
Stand for peace
Currently this site has a single message for our Russian friends: let’s stand together against the war in Ukraine!
If you are a SiteGround client looking to log into your Client Area, you can follow this link: https://login.siteground.com/login

How To Fix “DNS Server Not Responding” Error? (12 Methods)

While surfing the internet, on many occasions your browser must have shown an error message stating “ DNS server not responding ” or “ DNS server isn’t responding “. You start freaking out about what went wrong with the website, browser, or internet connection. But things are way different from what you are assuming.
This DNS server not responding generates an error when DNS fails to translate your hostnames into IP addresses. There can be multiple reasons that trigger this error message on your browser screen, which we will discuss in later sections of this post in detail.
But to your knowledge, most problems can be easily resolved with simple steps. The most common and effective method that would work is to restart your computer or switch to another web browser.
So, in this post, we try to cover all the aspects of “DNS Server not responding”, i.e. What is the meaning of DNS Server Not responding, what are the reasons that cause DNS Server not responding error and how can you fix them?
Keep on reading to get all your answers, Let’s get started!
Methods to fix DNS Server not Responding error (Windows)
- Check out different browsers
- Turn on your computer in Safe Mode
- Check with antivirus and Firewalls
- Restart your internet Modem or Router
- Update your Network Adapters with the latest version available
- Disable P2P feature to fix the DNS server not responding Windows 10
- Clear your DNS cache and reset your IP address
- Disable all connections other than the primary
- By changing the DNS settings on your Windows PC
- Temporarily Disable IPv6
- Check if disabling the Microsoft Virtual Wi-Fi Miniport Adapter fixes the issue?
- Contact your Internet service provider
Now you have got an idea about what the “ DNS server does not responding ” error means and what the possible reasons causing it. So, it is time for you to know how you can fix this error with the best possible methods available on both the platforms Windows as well as macOS.
1. Check out different browsers
One of the most common and basic methods that everyone should try first is to check if the error occurs in other browsers too. Sometimes, the DNS server not responding error can be fixed by simply changing the browser or updating the current one with its latest version available.
To start with, there are various other popular web browsers available on the internet such as Mozilla Firefox or Microsoft Edge you can try. If you are a macOS user and your default web browser is Safari you can try on either Chrome or Firefox instead.
If you don’t find a DNS server issue or an error message, it means there is an issue with your default current web browser. You can either reinstall it or update it with the latest version available.
However, if you still find the error message “DNS server not responding” after switching the browsers, it means, the source of this error is not your browsers.
2. Turn on your computer in Safe Mode
Sometimes, due to some issues in operating systems, your computer may show a DNS server not responding to error messages on your web browser. Hence, to figure out and resolve this issue you can turn your computer on in safe mode and check if it fixes the issue or not.
In safe mode, all the computer resources and files will be limited that are required to run the operating system, which can be an effective method to resolve this issue.
Turning Safe mode in Windows 7
For Windows 7 users, to turn on your computer in safe mode, you need to restart your computer by going to Power > Restart. After that, when the computer starts booting up, hold down the F8 key immediately. After that check, the issue DNS server not responding to Windows 7 was fixed or not.
Turning Safe mode in For Windows 10 or 11 users
Turning safe mode in both Windows 10 and 11 is quite the same but it is different from Windows 7. Let us see what steps you need to follow:
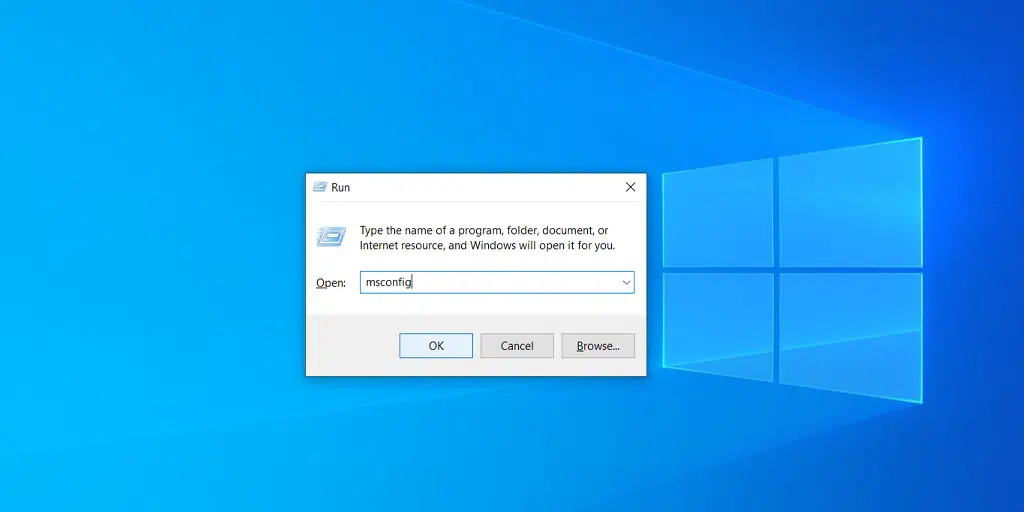
- Click on the Windows button as well as the key R simultaneously.
- Type “msconfig” in the box provided.
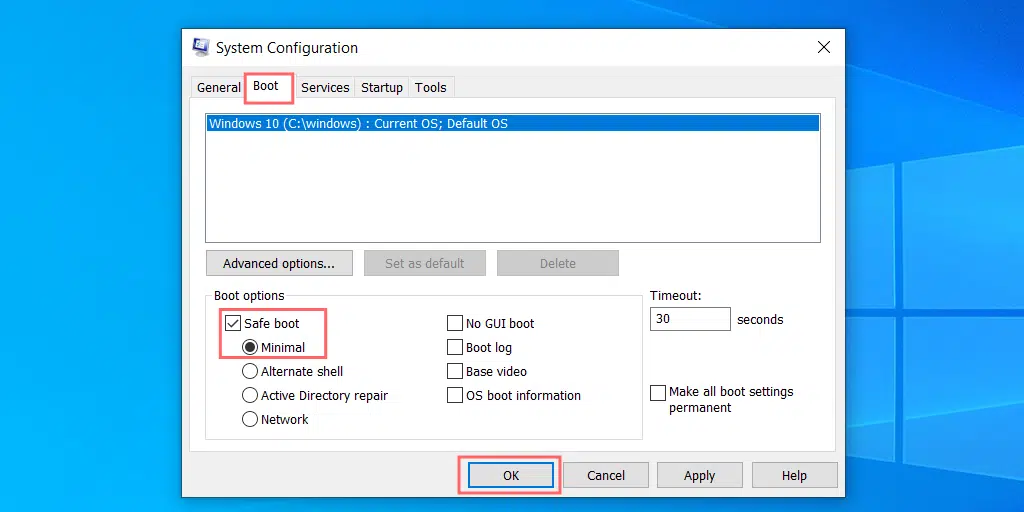
3. Select the Boot tab > Safe Boot option and click on the Apply button.
4. Now select the Restart button to apply the changes.
and your computer will boot up in safe mode. After that check, the issue of the DNS server not responding to Windows 10 or the DNS server not responding to Windows 11 has been fixed or not.
3. Check with antivirus and Firewalls
If checking with different browsers as well as accessing the website in safe mode does not help you to fix the issue, the next method you can try is to disable the antivirus and firewalls of your system temporarily.
Antivirus and Firewalls are some of the most important security measures of your system that secure your website from malicious attacks and intrusion. But sometimes they can also create problems for your system and with your connectivity. Hence to check whether firewalls or antivirus software are the culprits, you need to disable them temporarily and check if the issue persists or not.
If you are a Windows user, to disable the Windows antivirus application “Windows Defender” you need to go to your Control panel > Update and Security > Windows Security > Virus and Threat protection >Manage Settings .
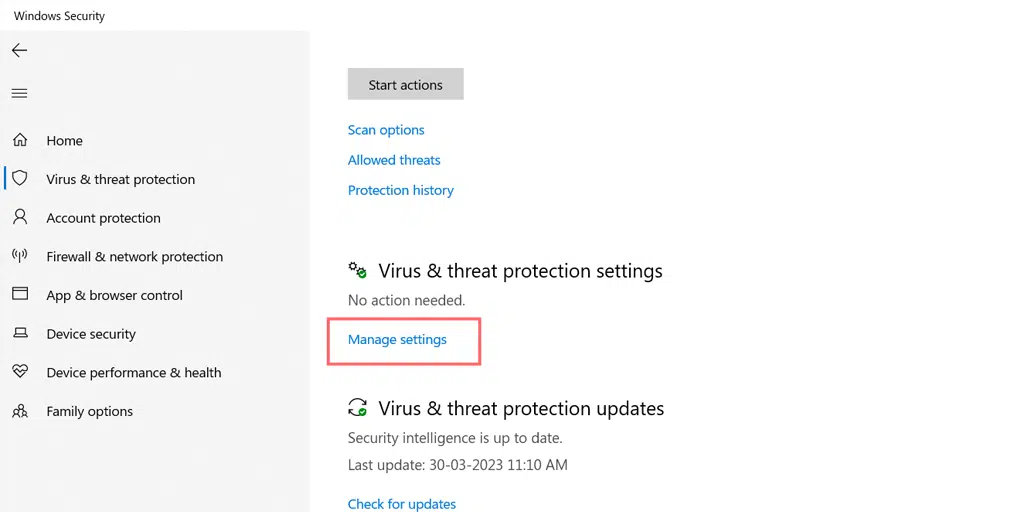
And turn off the Real-time Protection temporarily as shown in the picture below:
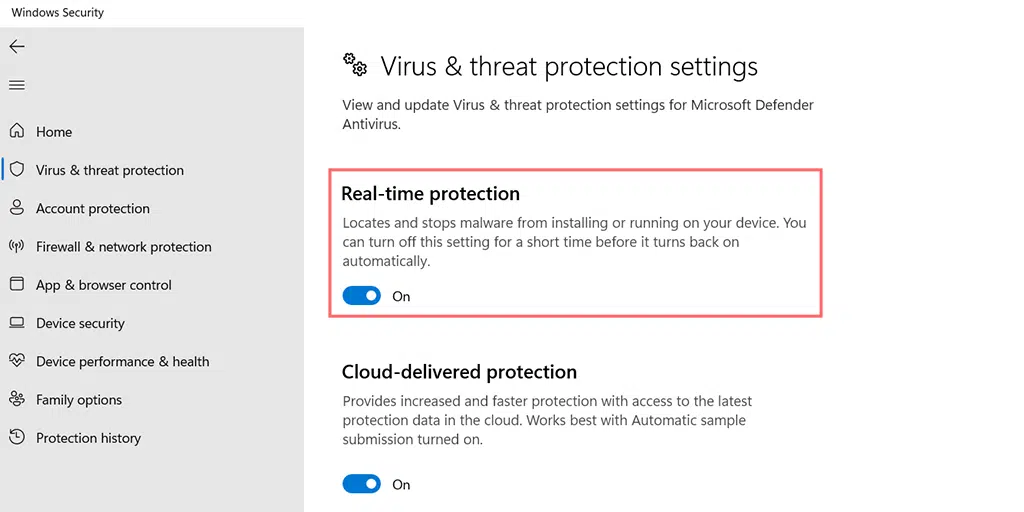
4. Restart your internet Modem or Router
Another easiest troubleshooting method to fix the DNS server not responding issue is by restarting your internet modem or Router. This method helps to clear out your router’s cache memory and that could help you to fix the issue.
To restart your modem, you can simply turn it off by pressing the power button until the LED lights stop blinking and wait for 10 seconds. Or it is better to remove the power source from the router/modem and wait for 30 seconds. After waiting for a while, turn on your modem or router or plug it into the power source again and wait till it can establish the connection.
After doing so, move back to your web browser and check if this method can resolve the “DNS server not responding issue” or not.
5. Update your Network Adapters with the latest version available
Another possible reason that you are facing the “DNS server not responding” issue can be due to an outdated version of your Network Adapters. So, in this situation, updating your network adapters with the latest version available can be the solution. You can update your Network Adapter manually or use tools to search for updates and install them for you automatically. If your network adapter provider is Intel you can easily get the latest version on their official website.
6. Disable the P2P feature to fix the DNS server not responding to Windows 10
If all the above-mentioned methods are not able to fix the DNS server not responding error. Another thing you can try is to disable the Windows P2P feature which is exclusive to Windows 10 users.
However, the above all saves your machine’s download bandwidth. This means it lets you download all the Windows updates once and after that, it uses your device as a medium to spread/share this latest version across all the computers that are available on your local network.
However, this feature can also be a culprit of triggering a DNS server not responding error and disrupting your DNS process. Hence, you need to disable it temporarily and check whether it is the culprit or not.
To disable this P2P feature, all you need to do is to click on Windows located at the down left corner of your machine and go to the Settings option followed by Update and Security as shown in the picture below:
Now Click on the Advanced options as shown in the picture below:
You will find the Delivery Optimization option just below the Advanced Options page as shown in the picture below:

Now to disable the P2P feature, you need to turn off the “Allow downloads from other PCs” option as shown in the picture below:
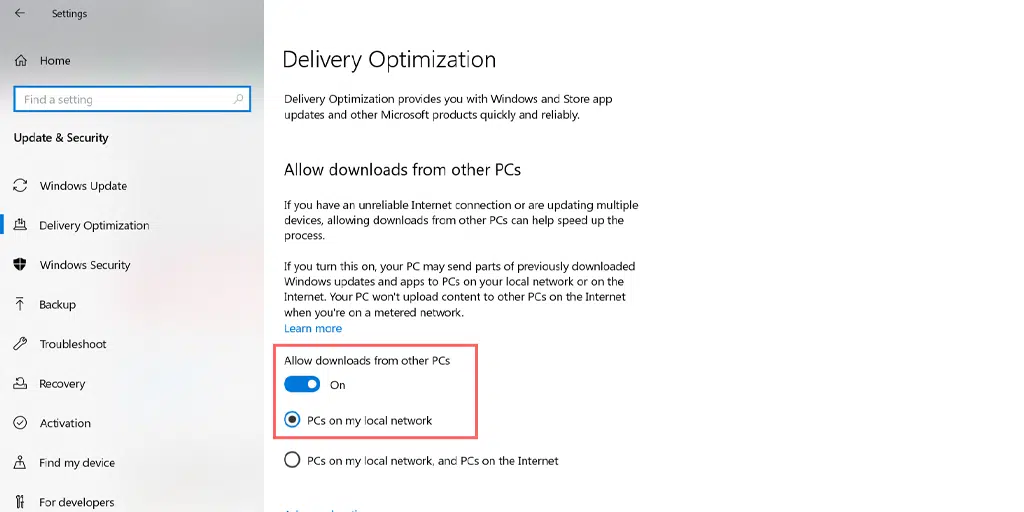
After following all the steps mentioned above, you need to restart your computer to make the changes effective and try to check if it can remove the issue or not. In case it doesn’t work we are going to provide you with more solutions that you can try.
7. Clear your DNS cache and reset your IP address
Earlier, you tried to restart your router to clear its cache but it didn’t work. Even if you tried the most effective and common methods it is still not able to fix it. Now it is time to get deeper and a little technical by looking at your DNS settings. Since the router has a cache present, it needs to be purged before establishing a connection to the internet.
For Windows users, you need to open your command prompt by typing the “ cmd ” in your Windows search bar and choosing the Command prompt application as shown:

Open the command prompt app and enter ipconfig/flushdns followed by pressing Enter:
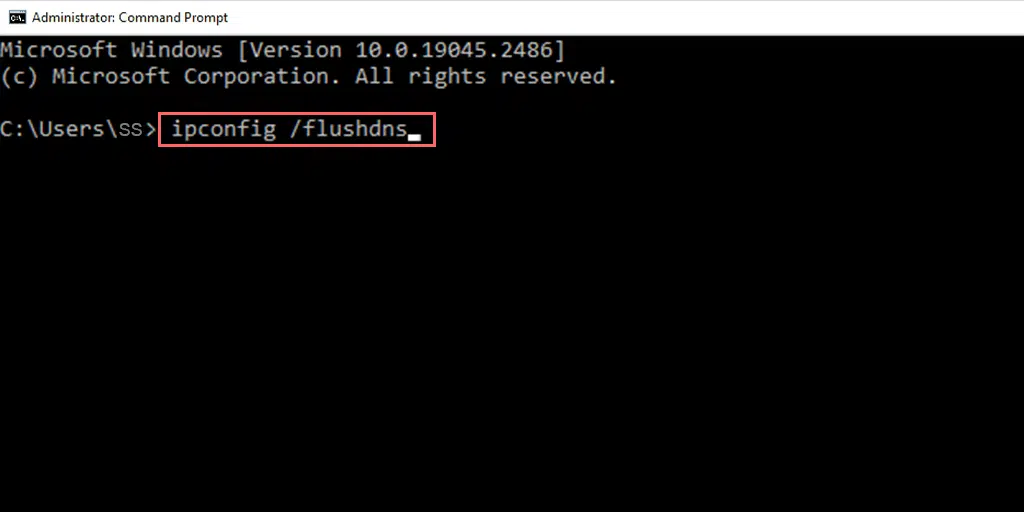
When hitting the Enter button, the Command prompt will flush your DNS instantly and a message will display stating “ Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache ” as shown in the picture below:
Similarly, repeat the same process by typing the following commands as mentioned below:
ipconfig /registerdns
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
8. Disable all connections other than the primary
Now, if disabling all the firewalls and antivirus applications on your machine doesn’t help you out with the DNS server not responding issue, another thing you can try out is to disable all the connections other than the primary one. It means you should not disable the current or active connection but other available connections.
For Windows 10 or 11 users, you need to go to your Windows icon located at the bottom corner left-hand side of your screen and click on it. Type “Network connections” in the search bar as shown in the picture below and select the View network connections application as shown below:
When you click on View Network connections, you will be directed to the Network Connections page, where you can see all the available connections you have. The active/current connection that you are using will be marked as green whereas the connections that are not in use will be marked as red cross as shown in the picture below.
Now select the connections which are not in use and disable them one by one. After successfully disabling all the secondary connections, you need to restart your computer and check whether it resolves the DNS server not responding issue by accessing the website on your browser.
9. By changing the DNS settings on your Windows PC
This method is getting a little technical and requires a lot of steps, which can be a little confusing for any beginner. But it is an effective method that you must try if all the above methods fail to fix the DNS server not responding issue.
If you are a Windows user, the first thing you need to do is to go to your Network Connections, Following the same process mentioned in Method 8. On the View Network connections page, choose the connection you are currently using or active and right-click on it to reveal options. Select properties.
When you click on the properties, a new window will open, in which you have to select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), as shown in the picture below:
A new window of Internet Protocol Version 4 will appear and you need to select the option “Use the following DNS server address” to assign a different DNS address manually.
you can fill Google ‘s public DNS IPv6 address in the Preferred DNS server as 8.8.8.8 and the Alternate DNS server as 8.8.4.4
10. Temporarily Disable IPv6
After IPv4, the latest internet protocol version that is primarily used is IPv6. Its main function is to route traffic between networks and the internet. But sometimes, it can also be the culprit for triggering a DNS server not responding error message on your computer screen. So, to check whether it is the main culprit behind this error or not, you need to open your Computer Network Connection page, just like you did in the above two methods. and select the active/current connection, right-click on it, and select the Properties option.
You will have a Network Connection properties window as shown below: Under the Networking tab of the panel that opens, scroll down until you see Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6):
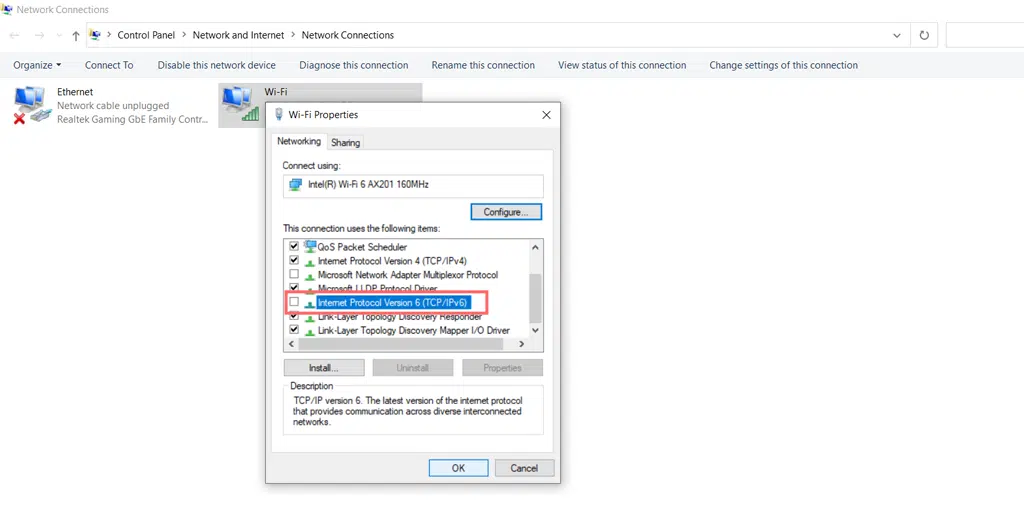
Now disable the IPv6 and unselect the box if it is selected by default as shown in the picture above. Now restart your web browser and check if the problem is resolved or not.
11. Check if disabling the Microsoft Virtual Wi-Fi Miniport Adapter fixes the issue.
To disable the Microsoft Virtual Wi-Fi Miniport Adapter, the first thing you need to do is press the Windows button and R key simultaneously on your keyboard. A run pop-up window will appear.
Now you need to type devmgmt.msc and hit the Enter key. This command will launch the Device Manager application on your computer screen. Now click on the View tab and select Show hidden Devices to show some new devices which are hidden in the list as shown in the picture below:
Click on the Network adapters category to expand and right-click on the Intel Virtual Wi-Fi Miniport Adapter to choose the uninstall device option.
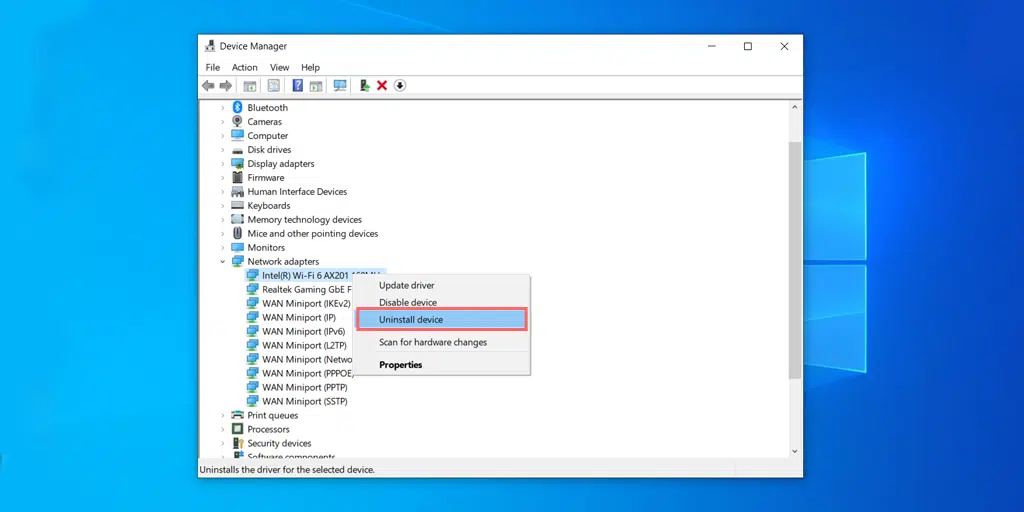
Do the same process with all the available Virtual Miniport Adapters and when done, close all the windows and restart your system.
12. Contact your Internet service provider
Although from the above 11 methods, any one method will be sufficient to fix the DNS server not responding error. But in case none of the above methods work, the only and final option left for you is to contact your Internet service provider.
Their technical knowledge and skills will help you to resolve this issue as soon as possible.
You can also read our other articles that are also based on similar kinds of errors such as:
- How to Fix DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN Error?
- How To Fix Error 404 Not Found?
Read: 🚩 chrome://net-internals/#dns – How to Clear DNS Cache Chrome
Methods to fix DNS Server not Responding error (macOS devices)
- Turning Safe mode in macOS
- Flush DNS cache in macOS devices
- Disable Secondary connections
- Temporarily Disable IPV6 in macOS
- Disable firewall in macOS
- Change DNS settings in macOS
Now that you have learned how to fix the DNS server not responding error in Windows devices, it’s worth noting that Mac users can use the methods listed below:
1. Turning Safe mode in macOS
For macOS users, the process is almost the same. When your machine is booting up you need to press the shift key unless or until the Apple logo appears. Once the logo appears, you can release the key and your Mac machine will start in safe mode.
After that, in safe mode, you can check whether the issue persists while accessing the website again or not. If in safe mode there is no internet or any connectivity issue and if the DNS server not respond issue occurs, it may be caused by any third-party application such as an antivirus.
2. Flush DNS cache in macOS devices
For macOS users, to purge or flush the DNS cache, you need to go to your Terminal application by pressing the Command as well as Space keys simultaneously and type the “terminal” keyword into the Spotlight. Open the Terminal application type the following command and hit enter:
dscacheutil -flushcache
Now you are done, this simple command will flush out the DNS cache instantly.
3. Disable Secondary connections
For macOS users, to disable secondary connections, the process is quite different. To do so, you need to navigate through the Apple icon similar to the Windows icon in Windows OS. Select System Preferences followed by Network.
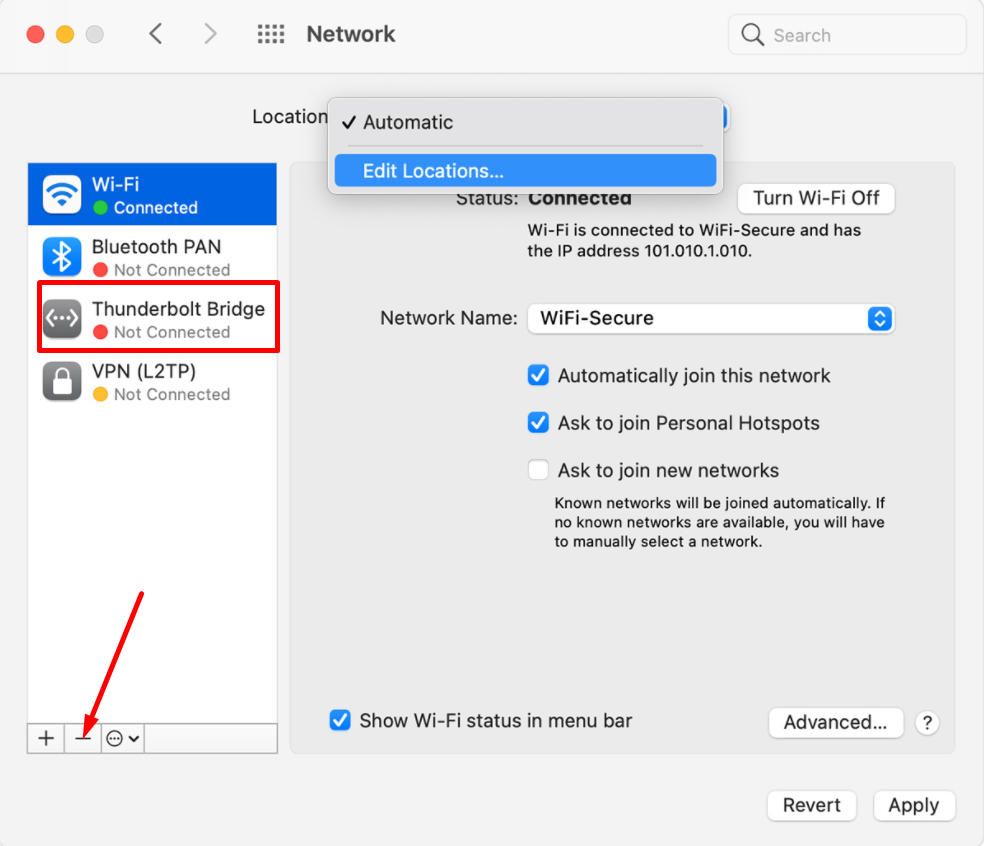
All the available network connections will be listed on the left side of the window as shown in the picture above. Now to disable any of the connections, you need to select the network and click on the (-) sign located at the bottom of the window as shown in the picture.
4. Temporarily Disable IPV6 in macOS
For macOS users, first of all, you need to open the Terminal application and enter the commands given below:
networksetup -listallnetworkservices
A complete list of all the available networks will appear. Now to disable IPv6 for Wi-Fi devices, you need to enter the command given below:
networksetup -setv6off Wi-Fi // for wifi connection
After that press the enter button, and you are done. You can check if this method is working or not by simply restarting your web browser and trying to access a website.
5. Disable the firewall in macOS
For Macintosh users to disable the Firewall temporarily, you need to go to your System Preferences > Security and Privacy > Firewall.
After successfully deactivating the antivirus or Firewalls, you can access the website from the website and check if the issue is still there or not. If the issue has been resolved, you can check the settings of your antivirus program and enable it.
6. Change DNS settings in macOS
However, if you are a macOS user, you can have this setting by navigating to your Apple icon > System preferences > Network.
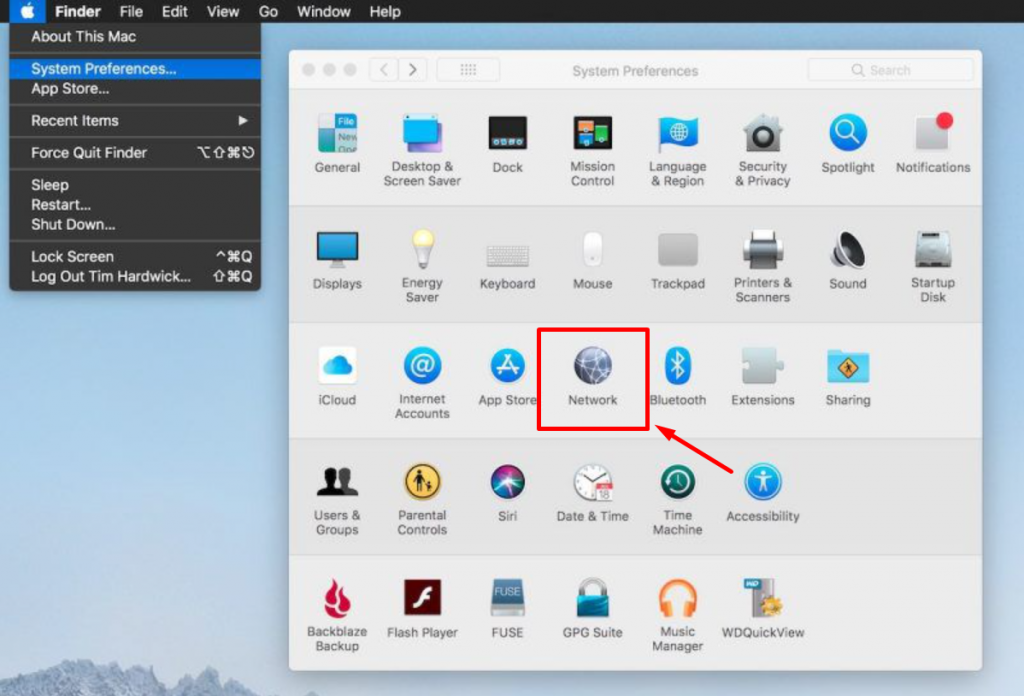
The next thing you need to select your current network and select the Advanced button.
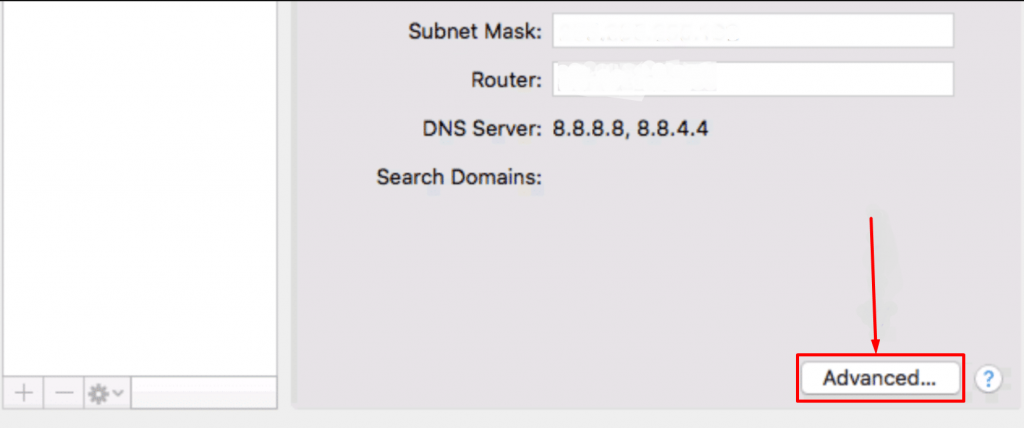
The moment you click on the Advanced button a new window will appear in which you need to enter a new DNS. Select the DNS tab click on the “+” button and press the Enter button.
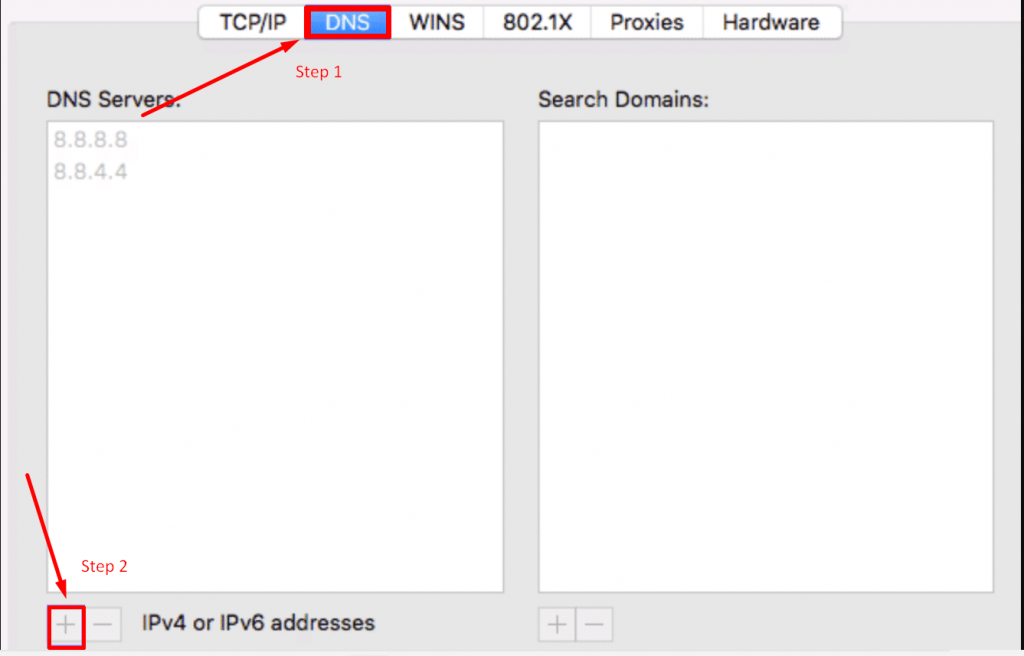
When you successfully enter the new DNS information, the next thing you need to do is to click on the Apply button and restart your web browser. You can access the website to check if the error DNS server not responding is resolved or not.
Intermittent DNS server not responding Issue
At times, there are certain occasions you may also experience an intermittent DNS server not responding error on your computer screen. The main culprit for triggering this error can be your faulty broadband router or modem. i.e the issue has been caused by your network adapter and you need to follow these steps to ensure it works properly:
- Restart your modem or router
- Update your network card drivers
- Try reconnecting your computer to the router
- Try disabling IPv6
- Reset Winsock
Step 1: All you need to Open a Cmd prompt with admin privileges
Step 2: Type netsh winsock reset catalog and press enter.
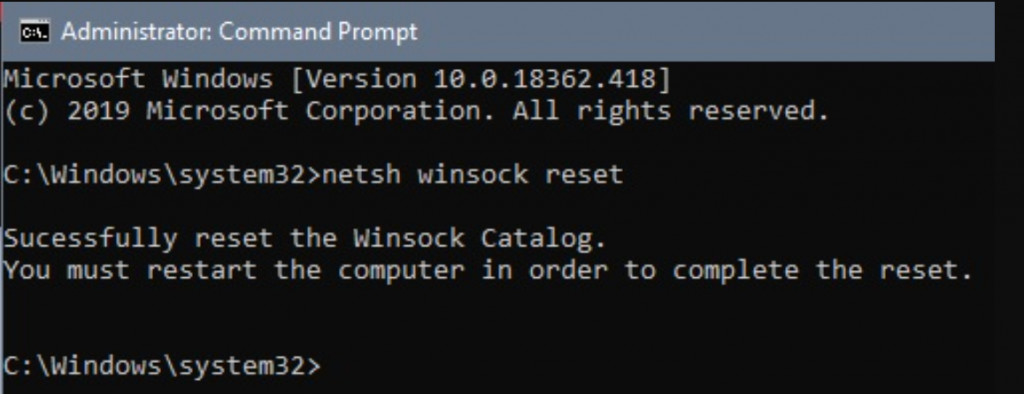
Step 3: Restart the computer and you are done.
However, if none of the methods mentioned above worked for you, you can try them out by performing a clean boot in Windows and disabling any antivirus program temporarily.
What is the meaning of a DNS Server Not Responding to an Error?
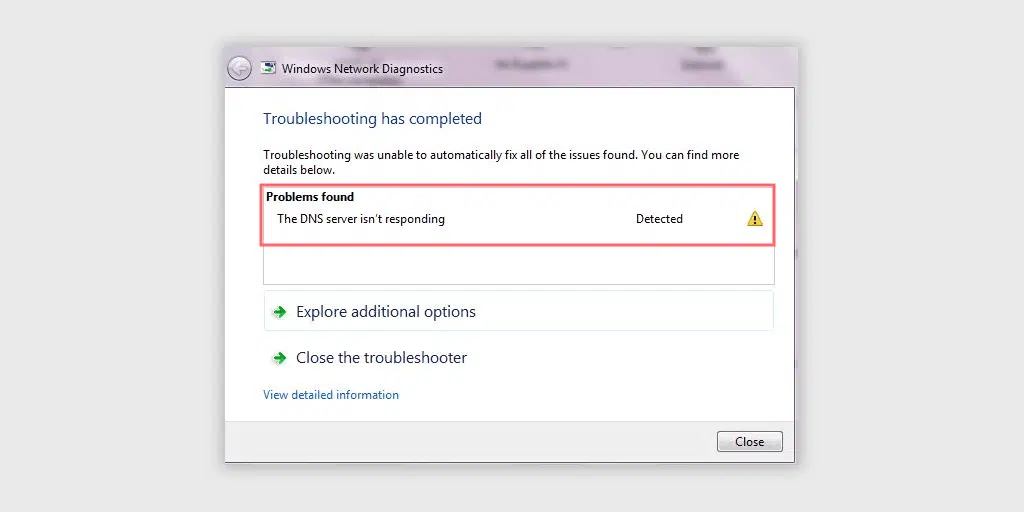
In simple words, a DNS or Domain Name Server is a translator that translates hostnames that are alphanumeric into IP addresses. Let us understand how it works in detail.
First of all, when you enter your web address or hostname in the address bar of your web browser, it is sent to a nearby DNS server via your router, where it gets translated into a numeric IP address. During this translation process, if anything goes wrong, the user will get notified by an error message on their web browser page stating “DNS server is not responding”. i.e. your web browser has not been able to make a successful connection to the internet.
Generally, this type of error occurs from the user end, either due to the user having a poor internet connection or not properly configured DNS. It is also possible that the user has not updated their web browsers or even the server is busy.
Hence, the most common and widely used solution that you must try to fix this issue is simply restarting your Personal computer or trying on other browsers.
Let us check out what are the possible reasons for DNS Server not responding on your PC, especially on your Windows device. Since Windows has the major Operating system market share in the world, let us see what are the reasons for the DNS servers not responding on Windows 10.
Possible Reasons for DNS Server not responding to Windows 10 devices
When a user enters the host’s name in the web browser, it gets translated into an IP address by DNS. The DNS saves all these IP addresses that the user requests in the form of a cache. Hence, from this, there can be only two possibilities that cause this error to happen in Windows 10 devices. They are:
- Exhausted Cache Memory: You have already read that all the IP addresses that the user request is stored in DNS as cache memory so that whenever the user likes to visit the website again, it does not go through the same process again and again.
- Malware attacks: Some malware or Computer viruses are assigned to steal data from your browser. Similarly, phishing is a data-stealing technique in which your computer is infected with some malware and Your web data is being stolen from the DNS cache or compromised. Due to this, you will start being redirected to some other potentially harmful websites.
Now you must be able to understand what are the possible causes that let this error message reflect on your webpage. Let us check out the different methods by which you can fix this issue as soon as possible.
Since only two dominating operating systems are used worldwide, i.e. Microsoft and Mac OS, we will talk about solutions for only these two platforms.
Encountering the error message “DNS server not responding” while accessing a website can be quite irritating and frustrating. Although the reason for triggering this error can be due to a variety of reasons, the best part is, that it can be resolved by following some simple methods. Such as:
- Trying to access the website on a different browser
- Turn your computer into safe mode
- Check with Antivirus and Firewalls
- Restart your Internet Modem and Router
- Disable the Windows P2P feature
- Disable all the connections rather than primarily the active one
- Change your DNS settings on Windows
- Disable IPv6
- Disable Microsoft Virtual Wi-Fi Miniport Adapter
- Contact your ISP
Apart from the above methods, if you have any more working methods that we have missed mentioning in this post, please do let us know in the comment section below.
Save your time, money, and resources, and give your website mammoth growth with WPOven’s the best wordpress vps hosting .
- 24X7 WordPress Expert support
- Cloudflare integration
- High-end Security
- Datacentres around the world, etc.
You can have all these features and much more in a single plan with unlimited Free migrations, unlimited staging, and a 14-day risk-free guarantee , Signup Now!
Frequently Asked Question
How do i fix the dns server that isn’t responding.
The 12 best methods to fix a DNS server not responding are: 1. Trying to access the website on a different browser 2. Turn your computer into safe mode 3. Check with Antivirus and Firewalls 4. Restart your Internet Modem and Router 5. Update your Network Adapters with the latest version available 6. Disable the Windows P2P feature 7. Clear your DNS cache and reset your IP address 8. Disable all the connections rather than primarily the active one 9. Change your DNS settings on Windows 10. Disable IPv6 11. Disable Microsoft Virtual Wi-Fi Miniport Adapter 12. Contact your ISP (Internet Service Provider)
How do you reset your DNS server?
To reset your DNS server, Do the following steps: 1. Open CMD by clicking on the Start button located at the bottom corner left-hand side of your Windows PC. 2. A black window of CMD will appear. 3. Type ipconfig /flushdns and hit enter 4. Now Restart your Windows PC
What is a DNS failure?
Due to any reason, DNS is not able to convert your hostname into an IP address in a TCP/IP network. It is termed a DNS failure.

Rahul Kumar is a web enthusiast, and content strategist specializing in WordPress & web hosting. With years of experience and a commitment to staying up-to-date with industry trends, he creates effective online strategies that drive traffic, boosts engagement, and increase conversions. Rahul’s attention to detail and ability to craft compelling content makes him a valuable asset to any brand looking to improve its online presence.
Related Posts:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How To Fix the DNS Server Not Responding Error – 12 Simple Ways
Is your site launch-ready.
Get your free checklist and avoid costly launch delays & errors
Download is Just A Click Away!
Enter your email address and be the first to learn about updates and new features.
Seeing a DNS Server Not Responding error when trying to use the internet? Can’t visit your favorite websites all of a sudden? This blog post can help!
The DNS server not responding error is displayed either by the browser you’re using or by your operating system. Either way, it means the device cannot reach the Domain Name Servers it needs to talk to in order to locate the website you want to visit.
The cause could be your computer, browser or could be a network issue on the internet.
The vast majority of DNS errors you’ll come across will be with your own network so the majority of our troubleshooting will look at your computer, browser, router and software configurations.
By the end of this article, you should know what DNS is, how it works and what to do when things go wrong!
Disable Internet Protocol Version 6
What is dns.
The Domain Name System ( DNS ) links domain names to web server IP addresses .
It’s like a phone book, a series of distributed databases that link the www.mydomainname.com name to IP addresses of a web server.
Without DNS, the web wouldn’t work.
Servers use IP addresses to communicate with each other and it’s not realistic for humans to remember a string of numbers. Certainly not now we are shifting from IPv4 to IPv6!
An IP address looks like 192.168.1.1 if IPv4 or 2439:cd44:1078:1::s722:d7k2 if IPv6.
Good luck remembering those!
The answer is to use more memorable words to create domain names for websites and use a system behind the scenes to link them to the IP address of the web servers hosting your website.
Most ISPs will have their own DNS servers to connect customers immediately to the web.
There are also centralized DNS servers that hold more records. We’ll show you how it all works in a little while.
What Does a DNS Server Do?
A Domain Name Server has one job. To hold and constantly update its DNS database.
There are a couple of levels of DNS servers out there.
There’s the one your ISP has, that holds thousands of local DNS records for websites it may host and one addresses are often searched for by its customers.
Those are called recursive DNS servers.
Then there’s the central DNS servers. Larger servers that hold hundreds of thousands or millions of DNS records. Those are called authoritative DNS servers.
A web query does something like this:
- You type a URL into your browser or click a favorite
- The browser sends the query to your ISPs recursive DNS server
- If the server has the DNS record, it returns it to your browser and your browser visits the web server hosting the desired website
- If the recursive DNS server doesn’t have the record, it queries the closest authoritative DNS server and requests the record
- Once your ISP DNS server receives the record, it caches it in case you, or someone else, needs it again and sends a copy to your browser
- Your browser then visits the hosting server hosting that website
If you manually set your DNS to something else like Google or OpenDNS, the query at step 2 queries those DNS servers and not your ISP.
Looking for a new web host? Check out the 9 fastest web hosts for WordPress!
What Causes DNS Server Not Responding Errors?
DNS server not responding errors literally means the browser cannot reach the DNS server, or it didn’t get a response from that server.
The most common causes are local issues with your device, your home network or your ISP.
It can also be caused by network issues. It could be a physical issue with the server or with the network connection to the server, a software fault, DDoS ( Distributed Denial of Service ) attack or similar, but these are rare.
As DNS is such an important aspect of the web, they are usually well protected and use multiple backups.
That doesn’t mean they never go wrong though!
There are frequent stories of DNS outages like the one at Salesforce or Microsoft or Register.com . These are usually localized outages and not global though.
How to Fix DNS Server Not Responding Errors
Here are the ways to fix “DNS Server Not Responding” errors. In the upcoming sections, we’ll delve into each method.
Force Refresh the Web Page
Test with a different browser, disconnect from vpn, restart your device and router, use the netsh command in windows, disable your antivirus software and firewall, flush dns settings, change computer dns settings, manually set dns on your router, install the latest windows network driver, reset the network adapter on mac.
As you now know, the majority of DNS errors are likely to be local to you. Your computer or phone or your router.
So that’s where we’ll begin our troubleshooting.
This article “DNS Server Not Responding” is mainly about Windows and Mac, some of these fixes will work on phones or games consoles too.
The exact methods may differ but the principles will be exactly the same!
If you try to visit a website and see the DNS error, forcing a refresh of the page should always be your first fix.
A forced refresh tells the browser to go fetch a fresh copy of the page, which means a new DNS query. If the issue was temporary, a refresh should overcome it and load the page.
Use one of these shortcut combinations to force refresh your browser.
- Chrome on Windows: Ctrl + F5
- Chrome on Mac: Command + Shift + R
- Firefox on Windows: Ctrl + F5
- Firefox on Mac: Command + Shift + R
- Safari: Command + Option + R
- Microsoft Edge: Ctrl + F5
As the browser is front and center in all this, it makes sense to make sure it isn’t something with the browser causing the error.
That’s easy to find out by using a different browser.
Most of us have more than one browser on our device so try another. Load the same page you were trying and see what happens.
If you regularly use a VPN, Virtual Private Network, make sure that’s not connected when you’re trying the website giving you DNS server errors.
VPNs add a whole new layer to networking that can cause a number of errors when not configured correctly or when the network itself isn’t running right.
Before performing any fixes, make sure you’re not connected to your VPN.
IT techs will always get you to reboot your device but there is a reason behind it. Whether it’s a phone, tablet, laptop or desktop, they all use software that can be corrupted.
Data corruption can happen anywhere at any time. A piece of data in memory that was accidentally overwritten, a device driver that was partially loaded or something completely different.
A reboot forces the device to load everything from afresh, which can fix the corruption or whatever it was causing the error.
Do that next.
Reboot your device and retest.
If the DNS error is still there, reboot your router and retest, just in case.
Windows handles networking differently than macOS and there is an extra potential fix to the DNS server error you can try. It’s an IP and Winsock reset.
These two services handle networking within Windows. Winsock has a history of causing issues within Windows so this is definitely one to try.
- Type ‘ cmd ’ into the Windows search box
- Right click the Command Prompt entry in the menu and select Open as Administrator
- Type ‘ netsh int ip reset ’ and hit Enter
- Type ‘ netsh winsock reset ’ and hit Enter
- Reboot your computer
This fix requires a system reboot to allow Windows to reload the network configuration. It won’t work until you do, so don’t retry the website until you have rebooted.
You should run both antivirus and a software firewall on Windows and potentially on Mac too. Even if you have a hardware firewall on your router, you should always use a software firewall for defense in depth.
Macs definitely need antivirus but a firewall isn’t so necessary due to how Apple apps handle ‘listening’ to internet-enabled ports. macOS does come with a firewall though.
If you do use a software firewall, temporarily disable them and retest.
In Windows:
- Open the Windows notification window in the bottom right of the Task Bar
- Select Windows Security
- Select Virus and Threat Protection from the left menu of the new settings window
- Select Manage Settings from the center pane
- Toggle Real-time Protection to off
- Select Firewall and Network Protection from the left menu
- Select Private Network in the center
- Toggle the firewall to off
- Repeat for Domain and Public networks
If you use a third party firewall, you can right click its icon in the notification area at the bottom right of the task bar. There should be an option to disable the firewall.
Once done, retest the website and see if the DNS server error is still there.
Mac is a little more complicated. It has its own antivirus in XProtect which is part of System Integrity Protection. Apple doesn’t like you turning this off as Apple knows best.
But there is a way.
If you use the Apple firewall, that’s much easier to disable so you might like to try that first.
Disable it using System Preferences > Security & Privacy > Firewall .
To disable System Integrity Protection, do this:
- Select the Apple icon in the menu
- Select Restart and hold down Command + R to boot into Recovery Mode
- Select Utilities once loaded
- Select Terminal
- Type ‘ csrutil disable ’ and hit Enter
- Select the Apple icon in the menu and select Restart
You can retest the website once macOS has loaded to see if the DNS server error is local to you or not.
You’ll need to repeat the above process and type ‘ csrutil enable ’ to restart SIP once you’re done testing.
The DNS cache doesn’t usually cause DNS server isn’t responding errors but we may as well check, just in case.
Flushing the DNS cache will drop all entries held in memory and make your computer retrieve new settings from your DNS server.
To flush DNS, do the following:
- Type ‘ ipconfig /flushdns ’ and hit Enter
- Type ‘ ipconfig /renew ’ and hit Enter
- Open a terminal
- Type ‘ dscacheutil -flushcache ’ and hit Enter
- Retry the website
If it was the DNS cache, you should see the website load normally.
If the DNS server isn’t responding error still appears, we can temporarily change your DNS settings.
Your computer gets the DNS server settings from two places. One, on the computer itself and two, on your router. The computer DNS setting will override the router, so let’s change that first.
Change DNS settings in Windows:
- Type ‘ ethernet ’ into the Windows search box and select Ethernet Properties
- Select Change Adapter Options in the new window
- Right click the Ethernet adapter in the next screen and select Properties
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) in the center and select the Properties button underneath
- Select ‘ Use the following DNS server address ’ at the bottom of the new window
- Enter 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 for Google DNS or 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220 for OpenDNS
Change DNS settings on Mac:
- Select System Preferences and Network
- Select Advanced and the DNS tab
- Select the ‘ + ’ icon to add a DNS server
- Select OK and then Apply
Retest the website using your new setting to see if the DNS error is still present.
If it is, let’s change the DNS setting on your router.
Even though your local computer DNS should override the router settings, it’s worth changing the router configuration just in case.
Every router works differently so it’s impossible to outline exactly what to do. Instead, we’ll walk you through how it works on ours as it could be similar to yours.
Type 192.168.1.1 in a browser window to take you to the router admin page
- Log into your router
- Select Internet or Network and locate DNS settings
- Select to edit or modify those settings
- Save the change
Some routers will perform a soft reboot to load the new configuration ready for use, others will be ready right away. Once your router is ready to work, retest the website.
Old or corrupted network drivers can cause DNS issues as we have seen it first hand. Updating the driver only takes a minute and is good practice so let’s do that next.
- Right click the Windows button and select Device Manager
- Select Network Adapters and expand the list
- Select your Ethernet adapter
- Right click and select Update Driver
- Select Search Automatically for Drivers and let Windows find a new driver
If Windows cannot find a new driver, download the latest driver from the hardware manufacturer and manually install it. Even if it’s the same driver version, it could fix the problem.
macOS handles drivers differently so you don’t need to install the latest drivers. Instead, we’ll reset the network adapter to see if that works.
- Open a Terminal
- Type ‘ sudo ifconfig en0 down ’ and hit Enter
- Type ‘ sudo ifconfig en0 up ’ and hit Enter
This assumes that your Ethernet adapter is ‘en0’. You can check that in System Preferences and Network .
Even though IPv6 is in widespread use, it is still causing occasional issues with networking. These issues are much less common than before, which is why this fix is last.
However, as we have exhausted almost everything else, it’s worth trying.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) in the center and uncheck the box to the left of it
If you need to enable IPv6 again, just repeat and check the box again.
- Open Terminal
- Type ‘ networksetup -listallnetworkservices ’ and hit Enter
- Type ‘ networksetup -setv6off Ethernet ’ and hit Enter
- Retest the website
To restore IPv6 in Mac, type ‘ networksetup -setv6on Ethernet ’ and hit Enter.
That’s the limit of what you can do at home if you see DNS server not responding errors. If you have tried all the above but are still seeing DNS server errors, chances are, the error isn’t with your computer or home network!

DNS Server Errors and Their Fixes
DNS is central to how the internet operates and the web wouldn’t be the same without it. While the system seems complicated, if you just think of it like the web’s phone book, you won’t go far wrong.
Whether you use Windows or Mac, there are several things you can do when you see DNS server not responding errors in your browser. We have covered the vast majority of fixes we know that work, so there should be the fix within this page.
Don’t forget though, DNS server errors are often computer errors but not always. If you try all these fixes and it still isn’t fixed, it might be a wider internet issue so don’t throw the computer out the window just yet!
Recommended Articles:
- What is the err_connection_refused error?
Do you know of any fixes for DNS server isn’t responding errors that we didn’t cover? Tell us about them below if you do!
Get exclusive access to new tips, articles, guides, updates, and more.
Disclosure: This blog may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through one of these links, we may receive a small commission. Read disclosure . Rest assured that we only recommend products that we have personally used and believe will add value to our readers. Thanks for your support!
I was getting dns address could not be found, then dns_probe_possible. Then the page would load after a few seconds. After clearing browser stuff, trying a diff browser, dns flush and restarting router and modem, it still happened, but only on my pc. Then I found this article! The netsh commands seem to have fixed it. I really appreciate it.
That’s awesome, Will! 🙂
I looked at several sites before I found yours. Your suggestion on the resets worked right away. You saved me hours of agony. Thanks ever so much.
So glad to hear that! 🙂
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
We believe creating beautiful websites should not be expensive. That's why Astra is free for everyone. Get started for free and extend with affordable packages.
Download is Just A Click Away!
YEAR IN REVIEW
How To Fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error (6 Methods)

You may run into a wide variety of issues when browsing the internet or trying to access a website. One of the most common is the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error message.
While inconvenient, this Domain Name Server (DNS) problem isn’t anything to panic about. You can use a handful of relatively easy, quick, and straightforward solutions to resolve the issue and get back to a smooth browsing experience.
In this post, we’ll explain what the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error means and its common causes. Then we’ll walk you through six methods you can use to resolve it. Let’s dive in!
Check Out Our Video Guide to Fixing the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error
What the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error Means
The DNS_PROBE_STARTED error message typically indicates an issue with your DNS or network. Most often, it means that your computer was unable to connect to a DNS server :

DNS, sometimes referred to as the phonebook of the Internet, is the system that lets people connect to websites using easy-to-remember domain names instead of hard-to-remember IP addresses . For example, it will convert an IP address such as 104.18.42.131 into a site name such as www.kinsta.com .
A DNS probe is a network diagnostic tool used to test the reachability of a given hostname or IP address. A DNS probe can also test the performance of a DNS server by measuring the time it takes for the server to resolve a given hostname .
There are various types of DNS-related errors that can occur. Other examples include:
- DNS_PROBE_BAD_CONFIG (which can be caused by VPN apps)
- DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN (Common with Android & iOS)
- DNS SERVER NOT RESPONDING
DNS_PROBE_STARTED is an error message that indicates that the DNS probe failed to start. This can happen due to several factors. While DNS_PROBE_STARTED in Chrome is the most common occurrence, it can also happen in other browsers, including Microsoft Edge and Android browsers.
Common Causes of the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Message
There are a few common causes of the DNS_PROBE_STARTED message. Firstly, your DNS server may be down. This issue commonly occurs because of a misconfiguration of your DNS or network settings.
It could also be attributed to a problem with your network adapter or router. If you have antivirus or firewall software installed, it may be blocking DNS requests, leading to this error message.
Now that we understand more about this error, let’s get into how you can resolve it. Below are six methods to use to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error.
Note that for the following tutorial, we’ll be using Windows/Chrome since this is where you will most likely encounter this error. However, if you’re using a Mac device or another browser, you can follow the same steps by substituting the commands with the OS/browser equivalents.
1. Change Your IPv4/IPv6 DNS Address
The first solution you can try is changing your IPv4/IPv6 DNS address . Without getting into the nitty-gritty, these internet protocols have slight technical differences. While IPv6 is the newest version, IPv4 is still the most popular.
To get started, navigate to your control panel and click on Network & Internet > Network and Sharing Center . From the menu on the left, select Change adapter settings :

This will open the Network Connections window. Right-click on your network and then select Properties :

In the window that opens, click on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) from the list, then select Properties again:

Click on Use the following DNS server addresses . You can enter “8.8.8.8” for the Preferred DNS server and “8.8.4.4” for the Alternate DNS server :

When you’re done, click on the OK button to save your changes. Close all the windows, then try reaccessing the website to see if the error is still present. If the problem isn’t fixed, you can move on to the next potential solution.
2. Refresh Your DNS
DNS caching involves your OS/browser saving your recently visited IP addresses in a database. However, an outdated database can lead to network connectivity issues, such as the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error.
Therefore, the next method you should try to resolve this issue is to flush your DNS cache to refresh it. Open the Command Prompt. To do this, press the Windows key + R , type “cmd” into the Run box, and press Enter :

If you’re using macOS, you can navigate to Utilities > Terminal . In the command prompt window, type the following:
Press your Enter key. This will clear any incorrect DNS entries from your computer’s cache. Next, enter the following command:
This will renew your computer’s IP address. Finally, you can input:
Press Enter to run the command. This will register your computer’s DNS settings with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). You can type in “exit,” and press Enter to close the command prompt.
3. Clear Your Browser Cache and Cookies
If you’re still seeing the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error message, clearing your cache and cookies is the next method you can try. The exact steps for this process will vary depending on your browser.
For example, in Google Chrome, you can select the three vertical dots in the upper right corner, then navigate to More tools > Clear browsing data :

In the window that opens, you can select all three options under Basic . Then click on Clear data :

You can follow similar steps if you’re using a Mac device or another web browser. For detailed guidance, you can refer to our guide on How to Clear Cache for All Major Browsers .
4. Uninstall and Reinstall Your Network Driver(s)
Many issues can arise from outdated network drivers. One of them is the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error message.
Therefore, if you’re still seeing the error, you can try uninstalling and then reinstalling your network drivers through your Device Manager. In Windows, press the Windows key + R , then type “devmgmt.msc” into the Run box and hit Enter.
In the Device Manager window, click to expand Network adapters . Then right-click on your network adapter, and select Uninstall device :

Close the Device Manager window and restart your computer. Once your computer has restarted, open the Device Manager again and select your network adapter. Click on Action > Scan for hardware changes from the menu bar:

This will reinstall your network driver(s). Now try loading the website again.
5. Disable Antivirus and Firewall Software
Antivirus and firewall tools are important because they can safeguard you against various issues, including multiple types of malware .
However, if you’re still having trouble with the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error, your antivirus software may be blocking DNS requests. Therefore, you can try disabling it temporarily to see if that fixes the problem.
You can also temporarily disable your firewall. Alternatively, you may want to try adjusting its settings.
To check your firewall settings, open your control panel and type “control” into the search field, followed by your Enter key. Select System and Security , then under Windows Defender Firewall , pick Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall:

In the next window, click on Change settings :

If your DNS client is not listed, you can add it by clicking on the plus ( + ) icon. When you’re done, select the OK button to save your changes.
6. Restart Your Router/Modem
Finally, the last method you can try is to restart your router or modem. This will reset the connection between your computer and DNS servers.
You can skip this step if you only see the DNS_PROBE_STARTED message in one browser, such as Chrome, but not in others, like Edge . In this scenario, the issue is likely with your browser settings rather than your network or internet connection.
After you power off your computer, router/modem, unplug them from the outlet(s) and wait a few minutes. Then turn on your router/modem and, after another minute or two, your computer.
Dealing with DNS problems can be a real pain, especially if you don’t know what’s causing the issue. However, if you come across the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error, you can take a handful of troubleshooting steps to resolve it.
As we discussed in this post, there are six methods you can use to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED error. If one does not work, then try the next one. You should be able to successfully resolve the issue using one of the methods above.
Do you want to switch to hosting that can help you quickly identify, troubleshoot, and resolve problems with your website? Learn how our application, database, and managed WordPress hosting plans , user-friendly MyKinsta dashboard, and Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tool can help!
Related Articles

An Introduction to “DNS Poisoning” (And How to Prevent It)

How to fix the “DNS server not responding” error on Windows and Mac

How to Fix DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN (Desktop & Mobile)
Before you go...
Check out today's top deals.
Plus, get free shipping and easy returns.
HP TECH TAKES /...

How to Resolve DNS Issues
What is DNS?
Signs of a dns error.
- Type the numerical IP address directly into your browser. If the webpage loads, then your problem is DNS related. You can try with Google’s IP address: “ 172.217.4.46 ”.
- Perform a ping test by typing “ cmd ” into your Windows Start Menu search bar. Select Open Command Prompt . When the black box comes up, type in “ ping 172.217.4.46 ” then wait to see the results. If all four pings come back successful, it may be a DNS problem.
- ping Amazon.com
- ping Google.com
- Or the site you want to test
How to resolve DNS issues
- Right-click on the internet icon in your task tray.
- Select Troubleshoot problems .
- Let the wizard go through all the steps. This may take a few minutes.
- If it doesn’t fix your problem, move on to the solutions below, which are designed for Windows 10 users.
1. Rule out ISP issues
- Look for the WAN or internet port label on the back of your wireless router, and disconnect the cable going into that port.
- Take the free end of this same cable and plug it directly into the Ethernet port on your computer.
- Turn off the wireless router, so you don’t accidentally connect to it.
- Give your computer a minute or two to recognize the new connection. Be sure you are using an Ethernet or LAN connection, and not your WiFi. You may have to restart your computer for the new settings to take effect.
2. Restart your networking equipment
3. Flush DNS cache and reset winsock
- Type “cmd” in the Windows Start Search bar, and select Open Command Prompt.
- Type the following exactly as written, and hit enter after each line is typed out
4. Perform a clean reboot
- Push the Win + R keys at the same time.
- In the Run dialog box that comes up, type “ msconfig ”. Alternately, you can type “ msconfig ” in the search bar at the bottom of the Windows Start Menu, and select Open for the System Configuration app.
- Click on the Services tab within the System Configuration app.
- Check Hide all Microsoft services .
- Select the Disable all option.
- Click the Apply button, then the OK button to save your preferences.
- Click on the Startup tab .
- Click Open Task Manager .
- Start with the first application, and click on the Disable option next to it. Continue doing this for all applications until they are all disabled.
- Close the application window.
- Restart your computer.
- Go back into the System Configuration App .
- Click on the Services tab.
- One by one, select an application and click to enable it. After you enable each app, see if you can connect to the internet.
5. Run the Microsoft LLDP Protocol Driver
- Press Windows + X keys to open the Quick Link Menu . Select Network Connections . Alternatively, you can click on the internet icon in your task tray to bring up your available networks. Click on Network and Internet Setting link .
- Click Change Connection Properties or Change Adapter Settings .
- In the new window that pops up, right-click on the connect you are using. Select Properties .
- Check the list for Microsoft LLDP Protocol Driver . Make sure the box next to it is checked.
- Click OK to exit.
6. Update network adapter driver and reinstall if needed
- Type devmgmt into the Windows Start Menu search bar and open the Device Manager app.
- Go to the Network adapters section in the list, and click to expand it.
- Find your network device, and right-click to choose Update driver .
- When prompted, choose Search automatically for updated driver software . This may take a few moments to complete.
- If a driver is available, Windows will install it.
- Restart your computer, and check to see if the DNS error still exists.
- Repeat steps 1 and 2 above.
- Find your driver, and right-click Uninstall .
- Use the driver software downloaded from the manufacturer’s website for your driver to reinstall the driver.
- Restart your computer and check the DNS again.
7. Change to public Google DNS servers
- Click on the internet icon in your task tray to bring up your available networks. Click on Network and Internet Setting link .
- In the new window, right-click on the connection you are using. Select Properties .
- Choose Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) from the list, and click the Properties button.
- Choose Use the following DNS server address option.
- Type 8.8.8.8 into the Preferred DNS server fields.
- Type 8.8.4.4 into the Alternate DNS Server fields.
- Click OK to save and exit the TCP/IPv4 window. Click OK to save again to exit the Properties window.
8. Check power settings
- Type Control Panel into the Search box from the Start Menu .
- Click to open the Control Panel .
- Select Hardware & Sound .
- Look for the Power Options category, and then Choose or customize a power plan .
- Click the Change Plan Settings link.
- Click the Change Advanced Power settings link.
- In the new window, find Wireless Adapter Settings . Click to expand.
- Click the Power Saving Mode option to expand.
- Change both On battery and Plugged in to Maximum Performance .
- Click OK to save and exit.
What to do if your DNS issues aren’t resolved
About the author.
Linsey Knerl is a contributing writer for HP® Tech Takes. Linsey is a Midwest-based author, public speaker, and member of the ASJA. She has a passion for helping consumers and small business owners do more with their resources via the latest tech solutions.
Popular articles
- 10 Best Minecraft Seeds for 2024
- How to Screenshot on HP Laptop or Desktop Computers
- How to Enter BIOS Setup on Windows PCs
- How Do I Fix a Laptop that Won’t Turn On?
- 3 Different Ways to Charge a Laptop without a Charger
- How to Boot from a USB Drive on Windows 10 PCs
- 7 Ways to Improve Your Computer Performance
- 10 Best Minecraft Shaders for 2024
- How to Turn Keyboard Lighting On / Off
- Lag! Top 5 Reasons your Ping is so High
Related tags
- business software
- computer processors

Article archives
- 2023 Articles
- 2022 Articles
- 2021 Articles
- 2020 Articles
- 2019 Articles
- 2018 Articles
Recommended articles

What is the HP OMEN Command Center?

What You Should Know About the Intel Core i9 Processor

How to Uninstall Programs on Windows 10

Best Screencasting Software for Teachers 2024

Why Should I Upgrade to an Intel Xeon Processor?

What is Processor Speed and Why Does It Matter?

How to Transfer Files from PC to PC

How to Upgrade Your Laptop

GPU vs CPU: What Matters Most for PC Gaming?

How to Overclock Your PC’s CPU

PC Upgrade Guide: Which Components to Upgrade and When

Hyper-Threading and Everything You Need to Know

How to Build a Really Fast Desktop Computer

Best Computer Processor (CPU) for Business
- HP Fraud Alert
- Mobile Workstation Laptop
- HP Standard Laptop
- Nvidia Geforce Laptop
- Nvidia Laptop
- NVIDIA Laptops
- Nvidia Quadro Laptop
- Chrome OS Laptop
- Windows 10 Laptop
- Windows Laptops
- Windows 7 Laptop
- Laptop Bundles
- Custom 2-in-1 Laptop
- Custom Build Workstation
- Windows 10 Laptop W/ AMD Processor
- HP Intel Celeron
- i3 Windows 10 Laptop
- i5 Windows 10 Laptop
Disclosure: Our site may get a share of revenue from the sale of the products featured on this page.
FREE shipping & Easy returns
Order by Phone 877-203-4758
Student discounts

HP for Business
Offers subject to change, not combinable with all other offers, and exclusions may apply, while supplies last. HP may impose a purchase quantity limit (for example, 3 units per order). Taxes, shipping, and other fees may apply as applicable. HP reserves the right to cancel orders arising from pricing or other errors. Prices, specifications, availability, and terms of offers may change without notice. Price protection, price matching or price guarantees do not apply to Intra-day, Daily Deals or limited-time promotions. These terms apply only to products sold by HP.com; reseller offers may vary. Items sold by HP.com are not for immediate resale. Orders that do not comply with HP.com terms, conditions, and limitations may be cancelled. Contract and volume customers not eligible.
HP’s MSRP is subject to discount. HP’s MSRP price is shown as either a stand-alone price or as a strike-through price with a discounted or promotional price also listed. Discounted or promotional pricing is indicated by the presence of an additional higher MSRP strike-through price.
Microsoft and Windows are US registered of Microsoft Corporation. Ultrabook, Celeron, Celeron Inside, Core Inside, Intel, Intel Logo, Intel Atom, Intel Atom Inside, Intel Core, Intel Inside, Intel Inside Logo, Intel vPro, Itanium, Itanium Inside, Intel Evo, Intel Optane, Iris, Itanium, MAX, Pentium, Pentium Inside, vPro Inside, Xeon, Xeon Phi and Xeon Inside are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries.
Not all features are available in all editions or versions of Windows. Systems may require upgraded and/or separately purchased hardware, drivers, software or BIOS update to take full advantage of Windows functionality. Windows is automatically updated and enabled. High speed internet and Microsoft account required. ISP fees may apply and additional requirements may apply over time for updates. See http://www.windows.com.
Earn HP Rewards on select products from the following categories: Laptops, Desktops, Printers, Business PC’s, select Accessories, and select Ink, Toner & Paper. Exclusions apply, and program membership required. See details HP Rewards
The personal information you provide will be used according to the HP Privacy Statement
*America’s most trusted printer brand: Based on 2022 semi-annual internal brand surveys commissioned by HP.
*2 years of ink included with the best print quality every time: Based upon 150 and 200 pages per month of HP Smart Tank customers’ usage. Actual yield varies considerably based on content of printed pages and other factors. Average yield based on ISO/IEC 24711 or HP testing methodology and continuous printing. Some ink from included bottles is used to start up the printer. For details, see: www.hp.com/go/learnaboutsupplies. Print quality tested on everyday paper. Compared to the majority of in-class, 3:1 and 4:1 duplex, wireless A4 ink tank printers under $552 USD. Printers selected by market share as reported by IDC Quarterly Hardcopy Peripherals Tracker – Final Historical CYQ2 2023. Claim based on publicly available information as of September 2023 and Keypoint Intelligence hands-on testing and study in September 2023 commissioned by HP. Details: www.keypointintelligence.com/hpbesteverydayprintquality.
**Copilot in Windows (in preview) is available in select global markets and will be rolled out to additional markets over time. See microsoft.com/en-us/windows/windows-10-specifications for more information.
How to Fix DNS Server Not Responding on Windows 11
A DNS server connection is vital for easy web browsing. Here's how to fix a DNS server not responding on Windows 11.
DNS or Domain Name System is the decentralized naming system that identifies computers, servers, and other resources that the internet can reach. It basically helps identify your PC and traffic that comes in. However, you may experience some errors if your computer can’t access the DNS server.
If you are getting a “DNS Server Not Responding” error on your Windows 11, don’t panic. It is still a new system, and bugs can affect it from time to time. Just follow the fixes below, and you’ll get your system back up in no time.
How to Fix DNS Server Not Responding Error on Windows 11 Computer
There are many reasons why you are getting this error. In most cases, your computer can’t establish a connection with the internet. Sometimes, Windows misidentifies network-related problems as DNS issues, while in some cases, it’s caused by a third-party app interfering with your connection.
Whatever the reason, you can try the fixes below to solve the "DNS server not responding" error on Windows 11.
Important reminder: Before trying any fixes, make sure that you have a working internet connection. As mentioned, this is usually caused by network-related issues, so it’s best to eliminate this cause right away. If you have problems with your internet, fix it first before going through all these steps.
1. Disable Third-Party Antivirus
If you have a third-party antivirus installed on your computer, like Avast AVG, or McAfee, it might be the reason why you’re receiving this error. Sometimes, it can interfere with your network and cause various errors such as DNS issues.
Related: What Is DNS and Why Is It Important?
To check if this is causing the issue, temporarily turn off your third-party antivirus software and check if you still have a DNS server problem. If it works properly, the program is likely the cause, and you should consider other ways to protect your computer.
You can either uninstall it completely and use the Windows 11 built-in security program, Microsoft Defender, or wait for a new Windows 11 update and see if it will fix this issue.
2. Flush Your DNS
This is the most popular way to fix most DNS problems, especially if it’s due to misconfigured settings in your device. Here’s how you can flush and renew your DNS on Windows 11.
- Open Run by pressing and holding Win + R keys. Then, type cmd and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
Related: How to Find the Fastest DNS to Optimize Your Internet Speed
3. Change the DNS on Your Windows PC
In some cases, using your network provider’s default DNS can cause issues to your system. If you haven’t changed yours yet, we recommend switching to a free DNS provider. You can either change it from your router settings or your computer’s network adapter setting. Here are some of the free DNS providers and addresses you can use:
- Google : 8.8.8.8 | 8.8.4.4
- OpenDNS Home : 208.67.222.222 | 208.67.220.220
- Cloudflare : 1.1.1.1 | 1.0.0.1
- AlternateDNS : 76.76.19.19 | 76.223.122.150
- AdGuard DNS : 94.140.14.14 | 94.140.15.15
- Quad9 : 9.9.9.9 | 149.112.112.112
Follow the instructions below to change your DNS setting on your Windows 11 computer:
- Press and hold Windows + I keys to open Settings.
- On the Settings app, click ‘Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Hardware Properties .
- From the DNS server assignment, click Edit.
4. Update Drivers
If you want to quickly update the essential drivers of your computer, you can download and use a free driver updater for Windows . However, if you don’t like installing other programs on your computer, you can manually update them using the Windows settings. Follow these steps:
- Open Settings by pressing and holding the Windows + I keys.
- Then, click Windows Update and then, click the Check for updates button.
- Once your computer booted, check if you’re receiving the same error.
Related: How to Find & Replace Outdated Windows Drivers
5. Boot into Safe Mode
If you’re still experiencing the issue even after doing all the troubleshooting steps mentioned above, it’s best to restart your PC in Safe mode. In Safe mode, Windows will only run basic settings and \remove any settings that could cause the error. Here’s how you can boot into Safe mode.
- Open the Start menu, and click the Power icon.
- Then, press and hold the Shift key and click Restart .
- On Recovery Options, click Troubleshoot
A Better Windows 11 Experience
The “DNS Server Not Responding” error can be frustrating and concerning, especially when you’re trying to access important pages and settings on your Windows 11 system. There are several reasons you're experiencing this issue, but there is no need to panic. You can easily solve the problem, even if you’re not too technical.
What Is DNS? Definition & How It Works

- by Lauren Ballejos , IT Editorial Expert
- Last updated May 31, 2024
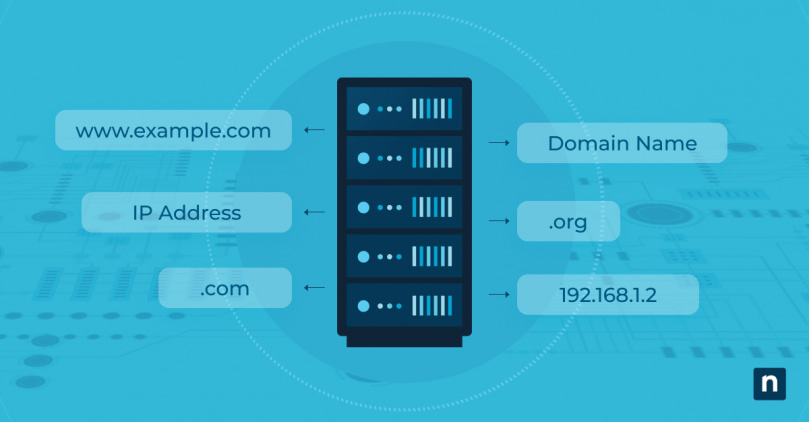
The Domain Name System , commonly known as DNS, is a fundamental component of the internet, yet it remains a mystery to many users. Simply put, DNS is like the phonebook of the internet, translating human-friendly domain names such as www.ninjaone.com into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
Without DNS, browsing the web would be a cumbersome process, requiring us to remember complicated numerical addresses for every website we want to visit.
In this article, we will demystify DNS, explaining its importance, how it works, and its critical role in our everyday online activities. Whether you’re a beginner looking to understand the basics or a tech enthusiast seeking deeper insights, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the DNS protocol.
What is DNS and why is it used?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and decentralized naming system used to identify computers, services, and other resources reachable through the internet or other IP networks. Essentially, DNS converts user-friendly domain names into IP addresses, enabling browsers to locate and load internet resources.
For example, when you type “www.example.com” into your browser, DNS translates this domain name into an IP address like “192.0.2.1,” directing your browser to the correct website.
DNS operates through a series of DNS servers:
- DNS resolver: This server receives queries from client machines, such as your computer or smartphone.
- Root name server: This server responds to requests for records in the root zone and directs queries to the appropriate top-level domain (TLD) servers.
- TLD name server: This server handles requests for specific TLDs, such as .com or .org, directing queries to the authoritative name servers for the requested domain.
- Authoritative same server: This server contains the actual DNS records for the requested domain and responds with the IP address corresponding to the domain name.
The evolution of DNS
Before DNS was established, early internet users relied on a simple text file called the HOSTS file, which mapped domain names to IP addresses. This method quickly became impractical as the number of hosts on the ARPANET (the precursor to the modern internet) grew exponentially.
In 1983, Paul Mockapetris proposed DNS as a scalable solution to this problem, and by 1984, DNS was formally implemented in the ARPANET. The introduction of DNS marked a significant milestone, as it allowed the internet to grow without the limitations of manually updated HOSTS files.
Over the years, DNS has evolved to support various advanced features such as DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC), caching mechanisms, and Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs).
The role of DNS in simplifying internet navigation
DNS plays a crucial role in making the internet accessible and user-friendly. Imagine if, instead of typing “www.google.com,” you had to remember and enter “172.217.16.196” every time you wanted to perform a web search. DNS abstracts these complex numerical IP addresses , allowing us to use easy-to-remember domain names.
Moreover, DNS enables:
- Scalability: By distributing the load across multiple servers, DNS ensures that no single server becomes a bottleneck, thus supporting the vast number of queries generated by billions of internet users.
- Redundancy: Multiple DNS servers provide resilience against failures, ensuring that internet services remain accessible even if some servers go down.
- Load balancing: DNS can distribute traffic across multiple servers hosting the same content, improving performance and reliability.
Still asking “what is DNS needed for?” The simple answer is this: Think of DNS as a cornerstone of internet infrastructure, allowing us to use the URLs and domain names that we all depend on when navigating the internet and sending emails.
How DNS works
So, how does the Domain Name System (DNS) translate domain names into IP addresses? Here’s a detailed breakdown of how DNS works:
The DNS query process
When you enter a domain name (e.g., www.example.com) into your web browser, a series of steps is triggered to resolve this domain name into an IP address:
Step 1: User’s request
- User action: You type the domain name into your browser and press enter.
- DNS resolver: The browser sends a query to the local DNS resolver, usually managed by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Step 2: Recursive query
- Recursive resolver: The local DNS resolver acts as a recursive resolver, meaning it will perform a sequence of queries to resolve the domain name fully.
Step 3: Root name server query
- Root server query: The recursive resolver queries a root name server to find out which authoritative server is responsible for the top-level domain (TLD) of the requested domain (e.g., “.com”).
- Root server response: The root server responds with the IP address of the TLD name server.
Step 4: TLD name server query
- TLD server query: The recursive resolver queries the TLD name server specified by the root server to find out which authoritative name server is responsible for the second-level domain (e.g., “example”).
- TLD server response: The TLD server responds with the IP address of the authoritative name server for the domain “example.com.”
Step 5: Authoritative name server query
- Authoritative server query: The recursive resolver queries the authoritative name server to get the IP address of the specific domain (e.g., “www.example.com”).
- Authoritative server response: The authoritative name server responds with the IP address associated with the domain name.
Step 6: Response to user
- Resolver to browser: The recursive resolver returns the IP address to the user’s browser.
- Connection established: The browser uses the IP address to establish a connection with the web server, retrieving the website content.
Components of DNS
- DNS resolver: This is the first point of contact for the user’s DNS query. It is responsible for handling the query and passing it along to other servers if needed.
- Root name server: The root name server is the top-level DNS server that responds to queries for TLDs (e.g., .com, .org, .net) and directs the query to the appropriate TLD server.
- TLD name server: The TLD server manages domain names within the top-level domain. For example, the .com TLD server handles requests for all .com domains.
- Authoritative name server: This server holds the DNS records for specific domains and responds with the IP address or other information related to the domain.
Caching and TTL (Time to Live)
To improve efficiency and reduce load times, DNS employs caching mechanisms:
- Local cache: Both the user’s browser and the DNS resolver cache the DNS responses for a certain period.
- TTL (Time to Live): Each DNS record has a TTL value, specifying how long it should be cached before a new request is made. Lower TTL values result in more frequent updates but higher server load, while higher TTL values reduce server load but may serve outdated information.
Security enhancements
DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions): DNSSEC adds a layer of security by allowing DNS responses to be verified through digital signatures, ensuring that the responses have not been tampered with.
Load balancing and failover
DNS can also be used for load balancing by distributing traffic among multiple servers hosting the same service, enhancing reliability and performance. For failover purposes, multiple DNS records can be configured to ensure that if one server goes down, another can take its place without disrupting the user experience.
What are the types of DNS records?
DNS relies on various record types to direct traffic appropriately. The most common DNS record types include:
- A Record (Address Record): Maps a domain name to an IPv4 address.
- AAAA Record: Maps a domain name to an IPv6 address.
- CNAME Record (Canonical Name Record): Alias of one domain name to another. Useful for pointing multiple domain names to the same IP address.
- MX Record (Mail Exchange Record): Specifies the mail server responsible for receiving email on behalf of a domain.
- TXT Record: Stores text information related to the domain, often used for security purposes like SPF (Sender Policy Framework) or DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail).
Common DNS issues and troubleshooting
Dns server outages.
When DNS servers go down due to maintenance, cyber-attacks, or technical failures, users cannot resolve domain names to IP addresses. This results in the inability to access websites, effectively cutting off internet connectivity.
DNS propagation delays
Changes to DNS records (such as changing the IP address of a domain) can take time to propagate across all DNS servers worldwide due to the TTL settings. During this period, some users might get the old DNS information while others get the updated information.
DNS cache poisoning (DNS Spoofing)
Malicious actors can corrupt the DNS cache, causing users to be directed to fraudulent or malicious sites instead of the intended websites. This can lead to phishing attacks, data theft, and other security issues.
Misconfigured DNS records
Incorrect DNS configurations, such as wrong IP addresses or mistyped domain names, can lead to failure in resolving the domain names properly.
Network congestion and latency
High traffic volumes or network congestion can slow down the DNS query process, leading to delayed responses and slower access to websites.
How to diagnose and resolve DNS issues
Checking network connectivity.
Ensure that your internet connection is stable. A disconnected or unstable network can mimic DNS issues.
Diagnosis tools: Ping, tracert (Windows) or traceroute (Mac/Linux).
Resolution: Fix any network connection problems, such as reconnecting to the network or restarting the router.
Verifying DNS server settings
Ensure that your DNS settings are correct and pointing to valid DNS servers.
Diagnosis tools: Command prompt/terminal commands like ipconfig /all (Windows) or cat /etc/resolv.conf (Linux/Mac).
Resolution: Correct any misconfigured DNS server settings in your network or device settings.
Flushing the DNS cache
Clear the DNS cache to ensure that outdated or corrupt DNS records are not causing the issue.
Diagnosis tools: None needed.
Resolution: Use commands like ipconfig /flushdns (Windows), sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder (Mac), or sudo systemd-resolve –flush-caches (Linux).
Testing with different DNS servers
Switch to alternative DNS servers, such as Google DNS (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1), to see if the issue is with your current DNS server.
Diagnosis tools: Change DNS settings on your device or router and test.
Resolution: Use reliable and fast public DNS servers if your ISP’s DNS servers are experiencing issues.
Using nslookup or dig Commands
Use these commands to manually query DNS records and diagnose issues with specific domains.
Diagnosis Tools: nslookup (Windows) or dig (Linux/Mac).
Resolution: Analyze the output to identify where the DNS query is failing and take appropriate action (e.g., updating DNS records or contacting your DNS provider).
Tools and techniques for DNS troubleshooting
A command-line tool for querying DNS to obtain domain name or IP address mapping and other DNS records.
Usage: nslookup www.example.com
dig (Domain Information Groper)
A powerful command-line tool used for querying DNS servers and diagnosing DNS problems.
Usage: dig www.example.com
traceroute/tracert
Tools that trace the path packets take from your computer to the destination, helping identify where the connection is failing.
Usage: tracert www.example.com (Windows) or traceroute www.example.com (Linux/Mac).
A basic network tool to test the reachability of a host and measure round-trip time for messages sent.
Usage: ping www.example.com
Online DNS tools
Web-based tools like DNSstuff, MXToolbox, and What’s My DNS can provide insights into DNS propagation, lookups, and performance.
Usage: Visit the tool’s website and enter the domain name to diagnose.
Browser developer tools
Most modern web browsers include developer tools that can help diagnose DNS and network issues.
Usage: Open the developer tools (F12 in most browsers), navigate to the “Network” tab, and observe DNS resolution times and any errors.
DNS security and best practices
Common dns vulnerabilities and threats.
DNS spoofing (DNS cache poisoning): Attackers manipulate DNS cache to return incorrect IP addresses, directing users to malicious sites instead of the intended destination. This exposes users to phishing attacks, malware, and data theft.
DDoS attacks on DNS servers : Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks flood DNS servers with excessive queries, overwhelming them and causing service outages. This results in websites becoming unreachable, disrupting services, and causing potential financial losses.
DNS hijacking: Attackers take control of DNS settings, redirecting traffic from legitimate websites to malicious sites. This leads to compromised user data, financial loss, and damage to brand reputation.
Man-in-the-middle attacks: Attackers intercept DNS queries and responses, altering them to redirect users or steal sensitive information. This results in unauthorized access to user data, breach of privacy, and exposure to further attacks.
DNS tunneling: Exploiting the DNS protocol to tunnel malware or data through DNS queries and responses. This leads to data exfiltration, unauthorized communication channels, and network security breaches.
Implementing DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) for enhanced security
DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) add a layer of security to DNS by enabling DNS responses to be verified through digital signatures, ensuring data integrity and authenticity. Here are the steps to implement DNSSEC:
Zone signing
- Key Generation: Generate a pair of cryptographic keys (public and private) for your DNS zone.
- Sign the Zone: Use the private key to sign DNS records in your zone, creating a digital signature for each record.
Publishing keys
- Publish public key: Publish the public key in the DNS zone as a DNSKEY record.
- Parent zone update: Update the parent zone with a Delegation Signer (DS) record that contains a hash of your public key, establishing a chain of trust.
Resolver configuration
- DNSSEC-aware Resolvers: Ensure that DNS resolvers are configured to validate DNSSEC signatures by checking the authenticity of the responses using the chain of trust.
Best practices for DNS management and configuration
- Use reliable DNS providers: Choose reputable and secure DNS hosting providers that offer features like DNSSEC, DDoS protection, and robust infrastructure.
- Regularly update DNS software: Ensure that DNS server software is up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Implement DNSSEC: Enable DNSSEC for your domains to protect against tampering and spoofing.
- Monitor DNS traffic: Continuously monitor DNS traffic for unusual patterns or anomalies that could indicate an attack.
- Use split-horizon DNS: Implement split-horizon DNS to provide different DNS responses based on the source of the request, enhancing security for internal and external queries.
- Limit zone transfers: Restrict zone transfers to specific IP addresses and use TSIG (Transaction Signature) keys to authenticate zone transfer requests.
- Apply least privilege principle: Ensure that only authorized personnel have access to DNS configuration and management.
- Regularly review DNS records: Periodically audit DNS records to remove outdated or unnecessary entries and to ensure accuracy.
Protecting against DNS spoofing and cache poisoning
- Implement DNSSEC: Deploy DNSSEC as discussed above to validate DNS responses and ensure data integrity.
- Use secure DNS resolvers: Utilize resolvers that support DNSSEC validation and have features to detect and mitigate spoofing attempts.
- Employ DNS filtering: Use DNS filtering services to block access to known malicious domains and IP addresses.
- Enable DNS query rate limiting: Implement rate limiting on DNS queries to reduce the risk of cache poisoning through flood attacks.
- Regularly flush DNS cache: Periodically clear DNS caches to minimize the risk of poisoned entries lingering and affecting users.
- Use randomized source ports and transaction IDs: Randomize source ports and transaction IDs for DNS queries to make it more difficult for attackers to guess and spoof responses.
- Monitor and analyze DNS logs: Continuously monitor DNS logs for signs of suspicious activity, such as repeated queries for the same domain or unusual response patterns.
- Educate users: Educate users about the risks of phishing and the importance of verifying website URLs to reduce the likelihood of falling victim to spoofing attacks.
How to perform a DNS lookup
Performing a DNS lookup involves querying a DNS server to obtain the IP address associated with a domain name. Here is a step-by-step guide:
1. Open a terminal or command prompt: Access the command-line interface on your computer. For Windows, use Command Prompt or PowerShell; for macOS and Linux, use the Terminal.
- Choose a DNS query tool: Select a tool such as nslookup or dig.
- Enter the DNS query command:
- For nslookup, type: nslookup [domain name]
- For dig, type: dig [domain name]
- Press Enter: Execute the command to send the DNS query.
4. Review the results: Analyze the response returned by the DNS server, which includes the IP address and additional DNS information.
Online DNS lookup tools
Several web-based tools are available for performing DNS lookups without needing to use the command line. These options are convenient for quick checks and are accessible from any device with an internet connection. Popular online DNS lookup tools include:
What’s My DNS : Provides global DNS propagation status by checking DNS records from multiple locations worldwide.
MXToolbox: Offers a variety of DNS lookup services, including A, MX, CNAME, and TXT record queries, as well as blacklisting checks.
DNSstuff: Provides comprehensive DNS tools for checking DNS records, propagation, and troubleshooting issues.
DNS Spy: Monitors DNS records and alerts users about changes or potential issues.
These online tools are user-friendly and typically require entering the domain name and selecting the record type to perform the lookup.
Interpreting DNS lookup results
Understanding the results of a DNS lookup is crucial for diagnosing and resolving DNS-related issues. Here’s how to interpret common fields in DNS lookup results:
A Record (Example: www.example.com A 93.184.216.34)
Indicates the IP address associated with a domain name.
MX Record (Example: example.com MX 10 mail.example.com)
Lists the mail servers for a domain, with priority values indicating the order in which servers should be used.
CNAME Record (Example: www.example.com CNAME example.com)
Shows alias records, which point one domain name to another.
NS Record (Example: example.com NS ns1.example.com)
Displays the authoritative name servers for the domain.
TXT Record (Example: example.com TXT “v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com ~all”)
Contains text information for various purposes, such as SPF or DKIM configurations.
SOA Record (Example: example.com SOA ns1.example.com admin.example.com 2024051701 3600 900 1209600 3600)
The Start of Authority record provides administrative information about the domain, including the primary name server, responsible party email, and domain serial number.
Interpreting these results helps in understanding how a domain is configured, identifying potential misconfigurations, and troubleshooting issues related to DNS resolution.
Understanding DNS (Domain Name System) is crucial for navigating the internet effectively and ensuring secure, efficient access to web services. By following these guidelines, users and administrators can ensure robust DNS configurations, enhancing both the performance and security of their internet experience.
Building an efficient and effective IT team requires a centralized solution that acts as your core service deliver tool. NinjaOne enables IT teams to monitor, manage, secure, and support all their devices, wherever they are, without the need for complex on-premises infrastructure.
Learn more about Ninja Endpoint Management , check out a live tour , or start your free trial of the NinjaOne platform .
- Category: IT Ops
You might also like

How to Use Disk Cleanup in Windows to Optimize Your System
How to Use Windows Command Prompt
What Is an IT Roadmap and How to Create One
Running the Windows Kill Process: 4 Methods

How to Replace Notepad with Notepad++ in Windows 10 & 11

How to Fix Notepad++ Crash After Startup
Ready to become an it ninja.
Learn how NinjaOne can help you simplify IT operations.
See NinjaOne in action!
Start a Free Trial of the #1 Endpoint Management Software on G2
No credit card required, full access to all features

NinjaOne Terms & Conditions
By clicking the “I Accept” button below, you indicate your acceptance of the following legal terms as well as our Terms of Use :
- Ownership Rights : NinjaOne owns and will continue to own all right, title, and interest in and to the script (including the copyright). NinjaOne is giving you a limited license to use the script in accordance with these legal terms.
- Use Limitation : You may only use the script for your legitimate personal or internal business purposes, and you may not share the script with another party.
- Republication Prohibition : Under no circumstances are you permitted to re-publish the script in any script library belonging to or under the control of any other software provider.
- Warranty Disclaimer : The script is provided “as is” and “as available”, without warranty of any kind. NinjaOne makes no promise or guarantee that the script will be free from defects or that it will meet your specific needs or expectations.
- Assumption of Risk : Your use of the script is at your own risk. You acknowledge that there are certain inherent risks in using the script, and you understand and assume each of those risks.
- Waiver and Release : You will not hold NinjaOne responsible for any adverse or unintended consequences resulting from your use of the script, and you waive any legal or equitable rights or remedies you may have against NinjaOne relating to your use of the script.
- EULA : If you are a NinjaOne customer, your use of the script is subject to the End User License Agreement applicable to you (EULA).

Xbox Forum Top Contributors: SwordofWhedon - Smwutches - StuartATrueRed - [EX] - KindGryphon ✅
May 10, 2024
Xbox Forum Top Contributors:
SwordofWhedon - Smwutches - StuartATrueRed - [EX] - KindGryphon ✅
Contribute to the Xbox forum! Click here to learn more 💡
April 9, 2024
Contribute to the Xbox forum!
Click here to learn more 💡
- Click here and we’ll get you to the right game studio to help you. When you open the page, go to the "Help with games" section in order to find the right path to look for help. .
- Additional information on Game support can be found here: How do I get the right game support?
January 12, 2024
Hey gamers! Are you experiencing a problem with a specific game?
- Search the community and support articles
- Gaming and Xbox
- Hardware and network
- Search Community member
Ask a new question
How to fix 100% packet loss?
My internet connection is fine, I just have 100% packet loss so I can’t play online. I have restarted the console, restarted the router. I have changed DNS, and I have even reset the console, and nothing has worked. I have no idea what to do now.
- Subscribe to RSS feed
Report abuse
Reported content has been submitted
Replies (0)
Question info.
- Networking help
- Norsk Bokmål
- Ελληνικά
- Русский
- עברית
- العربية
- ไทย
- 한국어
- 中文(简体)
- 中文(繁體)
- 日本語
- Answer HQ English
- EA Services
- Bug Reports
How to fix Error Code EC:10000 or EC:10500 in EA app?
- Answers HQ Community
- AHQ Community Resources
- Answers HQ Heroes and Champions
- Public Information
- Answers HQ Guardians
- EA Services – Announcements
- EA Services – General Questions
- Information, Guides and Announcements for the EA app
- General Discussion
- Technical Issues - PC
- Technical Issues - Mac
- Origin Mac Client - Technical Support
- Information and Announcements about EA Play
- EA Play - PC
- EA Play - Console
- EA Community Playtesting
- News & Announcements
- Accessibility
- Accessibility News & Resources
- Technical Issues
- Apex Legends
- Cross-Progression
- News & Game Updates
- General Feedback
- Legends Feedback
- Weapons & Loot Feedback
- Map Feedback
- Battlefield
- Battlefield V
- Battlefield 1
- Battlefield 4
- Battlefield 3
- Other Battlefield Games
- Battlefield General Discussion
- Battlefield 2042
- Battlefield Announcements
- Command and Conquer
- Other Command & Conquer Games
- C&C: Tiberium Alliances
- Tips & Guides
- Suggestions & Feedback
- Technical Issues, Tools & Scripts
- Public Test Environment
- Dead Space Games
- Other Dead Space Games
- Dragon Age: Inquisition
- Other Dragon Age Games
- EA Originals
- Immortals of Aveum
- Wild Hearts
- EA Originals Games
- Tales of Kenzera™: ZAU
- Technical Issues & Bug Reports
- College Football 25
- EA SPORTS FC™ 24
- The Locker Room
- Real Football
- Career Mode
- Career Mode - Stories
- Clubs & Volta Football
- Switch Feedback
- EA SPORTS FC™ 24 Info Hub
- Campaigns & Promotions
- Pitch Notes
- How to stay up to date?
- Useful Articles
- Ultimate Team™
- Ultimate Team™ Content
- Ultimate Team™ Evolutions
- EA SPORTS FC™ MOBILE
- Updates, News & Announcements
- FC TACTICAL
- EA SPORTS™ PGA Tour
- EA SPORTS™ WRC
- Guides & Documentation
- Game Suggestions
- Technical Issues - VR Beta
- Other F1® Games
- Updates & News
- Other FIFA Games
- GRID™ Games
- Madden NFL Football
- Madden NFL 23
- Other Madden Games
- Madden NFL Mobile
- Madden NFL 25
- Madden NFL 24
- General Discussion, Updates, & News
- Madden NFL Ultimate Team
- Mass Effect
- Mass Effect Legendary Edition
- Other Mass Effect Games
- NBA Live Mobile
- Other NBA Live Games
- NEED FOR SPEED™
- NEED FOR SPEED™ HEAT
- Other Need for Speed Games
- NEED FOR SPEED™ Unbound
- Other NHL Games
- General Discussion & News
- Franchise Mode
- Hockey Ultimate Team
- World of CHEL
- Plants vs. Zombies
- Plants vs. Zombies 2
- Other Plants vs. Zombies Games
- Plants vs. Zombies™ 3
- News & Infos
- General Discussion & Feedback
- Technical Help
- Pogo Classic
- SimCity BuildIt
- Other SimCity Games
- Other Skate Games
- STAR WARS Jedi: Survivor™️
- STAR WARS™ Battlefront™ II
- Other STAR WARS™ Games
- STAR WARS™: Galaxy of Heroes
- Game Information
- STAR WARS™: The Old Republic™
- General Discussion & Technical Issues
- Super Mega Baseball
- Super Mega Baseball 4
- The Simpsons: Tapped Out
- FAQs & Guides
- Finding Friends
- Springfield Showcase
- Bugs & Technical Issues
- Project Rene Community Discussion
- The Sims FreePlay
- Other The Sims Games
- In-Game Help
- Game Issues
- Game Questions
- The Gallery
- Mods & Custom Content
- Mods & CC Discussion
- Mods & CC Issues
- The Sims 4 Creative Corner
- Art and Videos
- Lots Showcase
- Sims & Modeling Showcase
- Challenges, Stories & Legacies
- The Sims 4 General Discussion
- Game Feedback & Ideas
- General Chat
- Pack Discussion
- Store Issues
- Technical Issues – PC
- Technical Issues – Mac
- Creative Corner
- The Sims Mobile
- Titanfall Games
- Other UFC Games
- Other EA Games
- Real Racing 3
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Printer Friendly Page
- « Message Listing
- « Previous Topic
- Next Topic »
- Previous
- Next
Original Post
Re: mac ea app - error ec:106 when launching ea app for mac.
- Mark as New
- Get shareable link
Re: HELP!!! EA app not opening
EC:10500 EA app does not work
Error Code: EC:10500 on Mac
Re: EC:10500
- Prev

What's EA Play?
New name, new look, same great benefits: EA Access and Origin Access are now EA Play.
Forget your EA Account ID or password?
Reset, update, or link your account information.
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products, Solutions, and Services
Want some help finding the Cisco products that fit your needs? You're in the right place. If you want troubleshooting help, documentation, other support, or downloads, visit our technical support area .
Contact Cisco
- Get a call from Sales
Call Sales:
- 1-800-553-6387
- US/CAN | 5am-5pm PT
- Product / Technical Support
- Training & Certification
Products by technology

- Software-defined networking
- Cisco Silicon One
- Cloud and network management
- Interfaces and modules
- Optical networking
- See all Networking

Wireless and Mobility
- Access points
- Outdoor and industrial access points
- Controllers
- See all Wireless and Mobility

- Secure Firewall
- Secure Endpoint
- Secure Email
- Secure Access
- Multicloud Defense
- See all Security

Collaboration
- Collaboration endpoints
- Conferencing
- Cisco Contact Center
- Unified communications
- Experience Management
- See all Collaboration

Data Center
- Servers: Cisco Unified Computing System
- Cloud Networking
- Hyperconverged infrastructure
- Storage networking
- See all Data Center
- Nexus Dashboard Insights
- Network analytics
- Cisco Secure Network Analytics (Stealthwatch)

- Video endpoints
- Cisco Vision
- See all Video

Internet of Things (IoT)
- Industrial Networking
- Industrial Routers and Gateways
- Industrial Security
- Industrial Switching
- Industrial Wireless
- Industrial Connectivity Management
- Extended Enterprise
- Data Management
- See all industrial IoT
- Cisco+ (as-a-service)
- Cisco buying programs
- Cisco Nexus Dashboard
- Cisco Networking Software
- Cisco DNA Software for Wireless
- Cisco DNA Software for Switching
- Cisco DNA Software for SD-WAN and Routing
- Cisco Intersight for Compute and Cloud
- Cisco ONE for Data Center Compute and Cloud
- See all Software
- Product index
Products by business type

Service providers

Small business

Midsize business
Cisco can provide your organization with solutions for everything from networking and data center to collaboration and security. Find the options best suited to your business needs.
- By technology
- By industry
- See all solutions
CX Services
Cisco and our partners can help you transform with less risk and effort while making sure your technology delivers tangible business value.
- See all services
Design Zone: Cisco design guides by category
Data center
- See all Cisco design guides
End-of-sale and end-of-life
- End-of-sale and end-of-life products
- End-of-Life Policy
- Cisco Commerce Build & Price
- Cisco Software Central
- Cisco Feature Navigator
- See all product tools
- Cisco Mobile Apps
- Design Zone: Cisco design guides
- Cisco DevNet
- Marketplace Solutions Catalog
- Product approvals
- Product identification standard
- Product warranties
- Cisco Security Advisories
- Security Vulnerability Policy
- Visio stencils
- Local Resellers
- Technical Support
- Patch Notes
- Hardware and Tech
- PC Invasion Staff
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy

How to fix Wolters Pearson error in Modern Warfare 3 (MW3)
The Wolters Peason or Pearson error code in Modern Warfare 3 will prevent you from being able to play the game at all, but there are a few ways to fix it. These should get you back to clicking heads immediately.
Wolters Peason (Pearson) error code fix in MW3
The problem is most likely with your game files on PS5, Xbox, and PC, so you will have to verify them to fix the Wolters Pearson error. This is a simple enough process , and if it doesn’t work, there are other methods.
Verify files
Files can become corrupted after an update, and we all know MW3 has enough of those. If you are experiencing the Wolters Pearson error, you may need to verify your files are all where they are supposed to be. This is a quick process.
- PC – Open your Modern Warfare 3 game launcher. On Steam, right-click on the game, select Properties, select Installed Files, and Verify the Integrity of Files. With Battle.net, click the cog symbol next to the game, and verify files.

- Console – The only way to check for corrupted files on a console is by completely reinstalling the game. However, before you do this, try turning your console off and back on. This will check for missing or necessary files in Modern Warfare 3.
If there are missing files in Modern Warfare 3, you will receive the Wolters Pearson (Peason) error. However, a file check will reinstall them and get you back in the game.
Try resetting your router
A quick router reset can often fix the Wolters Pearson error in MW3. Simply find your router, switch it off at the wall, and wait 10 seconds. This will give the router time to clear its memory and reopen any closed gateways. Once you reboot it, make sure your console or PC is connected to the internet and boot MW3 back up.
Check MW3 server status
The problem is more often than not with the game files integrity. However, if your local servers for MW3 are down , you may receive the Wolters Pearson error code and be unable to play. Check the Twitter and down status website for news on Call of Duty server status.


XDefiant: How To Fix Mike-01 Error
Quick links, what is the mike-01 error in xdefiant, how to fix the mike-01 error in xdefiant.
Being unable to play a game due to a random issue is one of the most frustrating things in gaming. XDefiant isn't free from this occurance, either. Some errors can prevent you from playing this multiplayer shooter from Ubisoft, and one of the most common is called Mike-01. This issue can be quite problematic to deal with. But don’t worry; this guide will tell you how to fix the Mike-01 error in XDefiant .
XDefiant: Every Assault Rifle, Ranked
From the MDR to the ACR 6.8, here is every Assault Rifle in XDefiant, ranked!
The Mike-01 error appears when your device has problems connecting to Ubisoft servers . This can happen for various reasons, and sometimes, there's very little you can do about it. So, let’s find out how to resolve this issue and where it might come from.
The way to fix the Mike-01 error in XDefiant depends on why it occurred. Sometimes, you don’t have to do anything at all. Here is a list of ways to deal with this error:
Check The Status Of Ubisoft Servers
Of course, if there is some scheduled maintenance, you won’t be able to play. If this prevents you from starting a match , you'll just have to wait until Ubisoft servers are up and running. You can check the status of Ubisoft servers to see if there are any problems with them. For this purpose, you can use the XDefiant Twitter account or Ubisosft Help.
Check For New Updates
The Mike-01 error can also occur if you don’t have the latest patch. So, check for new updates and install them if necessary. This should fix the error and allow you to play XDefiant .
Try Rebooting Your Device Or Router
Sometimes, restarting your device can help you deal with this issue. So, turn off your PC or console and then turn it on. If this doesn’t help, you can try rebooting your router, which may also resolve the problem.
Confirm That Ubisoft+ Is Available In Your Country
Some countries don’t have access to Ubisoft+. Use this link to check if the service is available to you. If you don’t have access, you can try using a VPN to play the game.
The Mike-01 error can be annoying, and it usually occurs due to issues with Ubisoft servers. In most cases, you just need to wait until the server-side issue is resolved, but having a checklist of potentially useful things to try can make a world of difference.
Platform(s) Xbox Series X, PS5, PC
Released May 21, 2024
Developer(s) Ubisoft San Francisco
Publisher(s) Ubisoft
Genre(s) FPS


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Press the Windows key, type cmd, and press Enter to open Command Prompt. Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter. Mac: In your Launchpad, type terminal, then click Terminal in the search results. Type sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder and press Return. Type your password when prompted to complete the flush.
Select the connection that you're trying to fix from the left sidebar, then click Advanced… in the bottom-right corner. 3. Select DNS from the tabs at the top. 4. Select the DNS Servers box and ...
If you're not sure whether or not your computer is reporting DNS Server Not Responding errors, follow these steps: Select Start and then choose Settings . Select Network & Internet. The Network Status window will open. Select Network Troubleshooter under Change Your Network Settings. Windows Network Diagnostics will open.
On the open page, next to "Internet Connections," click "Run." If you're on Windows 10, head into Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Additional Troubleshooters. Click "Internet Connections" and choose "Run the Troubleshooter." Follow the troubleshooter's instructions to detect and resolve your DNS issues.
networksetup -setv6off Ethernet. Then hit the Enter key, and refresh your browser to see if the issue is resolved. 11. Change the default DNS server on your Windows computer. Another solution you can try in order to fix "DNS server not responding" in Windows is to change your default DNS server.
Test your DNS server. A more advanced test is to manually ask your DNS server for the IP address of the domain you're trying to access. If the server can't find the IP or displays an error, that ...
If you are experiencing DNS issues, start by performing the following steps before going on to in-depth troubleshooting: Check cables. If using a wired connection, make sure everything is connected properly. On wireless networks, check if WiFi is turned on and connected. Check the router if all cables are functional.
Navigate to System Preferences > Network and select your primary internet connection in the sidebar. Click Details (or Advanced on older Macs) then select DNS. At the bottom of the DNS servers list, click the + button and enter your new DNS address. Make sure to click Apply before leaving the Network screen.
Flushing Your DNS (Windows) The most effective method for fixing the issue with the DNS server being unavailable is to flush it using Command Prompt. Pull up the Run dialog by simultaneously pressing the Windows key and R key. Type cmd into the field and press Enter. In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.
Open Control Panel and head to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings. Right-click your network adapter and choose Properties. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and choose Properties. Enable the Use the following DNS server addresses option.
You can do this by following these steps: Open Control Panel. One way to do this is press the Windows Key + R to activate the "Run" box, then type "control" in the text box presented in the "Run" box and hit the enter key. Select the Network and Internet option presented within the Control Panel window.
If you think that you might be experiencing DNS resolution issues, you can configure one of your devices to use a popular free third-party DNS service like Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 or Google 8.8.8.8. For instructions, select your type of device in one of the following external articles: Set up Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 resolver · Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 docs.
On Mac, open System Settings > Network > click on your active network > Details > DNS. The DNS server addresses are listed under the section DNS servers. Alternatively, you can use Terminal to obtain your DNS server addresses. Open Finder, and from the menu bar on top of the screen, select Go > Utilities > Terminal.
Consider TCP/IP settings. One of the most common issues that causes DNS errors is the TCP/IP settings. You can check these by going to the control panel, and choosing "Manage network connections.". You can then look in the Local Area Connections properties, and look at the IPv4 and IPv6 properties. See what's written under these items ...
5. Update your Network Adapters with the latest version available. Another possible reason that you are facing the "DNS server not responding" issue can be due to an outdated version of your Network Adapters. So, in this situation, updating your network adapters with the latest version available can be the solution.
Type ' networksetup -listallnetworkservices ' and hit Enter. Type ' networksetup -setv6off Ethernet ' and hit Enter. Retest the website. To restore IPv6 in Mac, type ' networksetup -setv6on Ethernet ' and hit Enter. That's the limit of what you can do at home if you see DNS server not responding errors.
Get all your applications, databases, and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes: Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard; 24/7 expert support
Restart your computer. Go back into the System Configuration App. Click on the Services tab. One by one, select an application and click to enable it. After you enable each app, see if you can connect to the internet. If you can reconnect after disabling an application, this is the one causing DNS issues.
Here's how you can flush and renew your DNS on Windows 11. Open Run by pressing and holding Win + R keys. Then, type cmd and press Enter to open the Command Prompt. On the Command Prompt, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter to execute the command. Then, type ipconfig /registerdns and press Enter .
chrome://flags. The page shows individual Chrome flags and their status. 2. Click the Reset all button to reset the flags to default settings. Alternatively, check the individual flags and change their status. 3. Restart Chrome and attempt to access the website to see if the issue persists. 9. Clear Browser DNS Cache.
Find out how to fix the DNS Server Not Responding error in this video. Start your online journey with Hostinger web hosting 👉 https://bit.ly/3qfhiw1💥 Use t...
Resolution: Fix any network connection problems, such as reconnecting to the network or restarting the router. Verifying DNS server settings; Ensure that your DNS settings are correct and pointing to valid DNS servers. Diagnosis tools: Command prompt/terminal commands like ipconfig /all (Windows) or cat /etc/resolv.conf (Linux/Mac).
Head to System Preferences on your Macbook and then click Network. Next, inside the Wi-Fi tab, click the 'Advanced' button and head to DNS settings. Add Google's Public DNS - '8.8.8.8' and select the OK button to make changes. Refresh the site to see if it loads now. Conclusion: Final Thoughts.
Steps: Open the Control Panel and go to Network and Sharing Center. Click on Change adapter settings. Right-click your network adapter and select Disable. Wait a few seconds, then right-click it ...
Last updated June 2, 2024 Views 14 Applies to: Gaming and Xbox. /. Hardware and network. /. Networking help. My internet connection is fine, I just have 100% packet loss so I can't play online. I have restarted the console, restarted the router. I have changed DNS, and I have even reset the console, and.
So far ive tried everything i can think of from resetting my router, Flushing Dns, setting up Dns towards Google, ipconfig renew's, restart the pc, clear cache, repair app, Update app (its already up to date) uninstall and reinstall the app, safe boot, and many more things. its getting quite frustrating as ive payed for EA play pro and have ...
Cisco buying programs. Cisco Nexus Dashboard. Cisco Networking Software. Cisco DNA Software for Wireless. Cisco DNA Software for Switching. Cisco DNA Software for SD-WAN and Routing. Cisco Intersight for Compute and Cloud. Cisco ONE for Data Center Compute and Cloud. See all Software.
Assuming Wuthering Waves servers are live, and you are still facing the network and login errors, use the below steps to fix it: Unplug the power cable from your router and wait for a few seconds ...
PC - Open your Modern Warfare 3 game launcher. On Steam, right-click on the game, select Properties, select Installed Files, and Verify the Integrity of Files. With Battle.net, click the cog ...
Some errors can prevent you from playing this multiplayer shooter from Ubisoft, and one of the most common is called Mike-01. This issue can be quite problematic to deal with. This issue can be ...