
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons

Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.2e: Exercises - Right Angle Trigonometry
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 69486
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
A: Given three sides of a right triangle, find all six trigonometric ratios
Exercise \(\PageIndex{A}\)
\( \bigstar \) Given right triangle \(ABC\) where the right angle is angle \(C\) in each figure below, (a) Label the remaining sides and angles (b) Designate the hypotenuse, adjacent side or opposite side to angle \(A\). Determine the trigonometric ratios for (c) \(\sin A\), (d) \(\cos A\), (e) \(\tan A\), (f) \(\sec A\), (g) \(\csc A\), (h) \(\cot A\). Give simplified exact answers - reduce fractions, rationalize all denominators!

B: Given two sides of right triangle, find all trigonometric ratios of the acute angles
Exercise \(\PageIndex{B}\)
\( \bigstar \) Find the exact values of all six trigonometric functions of angles \(A\) and \(B \) in the right triangle \(\triangle\,ABC \) illustrated below . Simplify!

\( \bigstar \) In each of the triangles below, find \(\sin \left(A\right), \; \cos \left(A\right),\; \tan \left(A\right),\; \sec \left(A\right),\; \csc \left(A\right),\; \cot \left(A\right)\).

For all triangles #5-16, the trigonometric ratios can be determined using the following formulas: \( \sin A = \cos B = \frac{a}{c}, \) \( \cos A = \sin B = \frac{b}{c}, \) \( \tan A = \cot B = \frac{a}{b}, \) \( \csc A = \sec B = \frac{c}{a}, \) \( \sec A = \csc B = \frac{c}{b}, \) \( \cot A = \tan B = \frac{b}{a}, \) The missing side needed to calculate these ratios is given below: 5. \(a = 5\) 7. \(b = 24\) 9. \(c = 41 \) 11. \( c = \sqrt{10} \) 13. \(b = \sqrt{11} \) 15. a = \( \sqrt{15} \)
17. \(\sin \left(A\right) = \frac{5\sqrt{41}}{41}, \; \cos \left(A\right) = \frac{4\sqrt{41}}{41},\; \tan \left(A\right) = \frac{5}{4},\; \sec \left(A\right) = \frac{\sqrt{41}}{4},\; \csc \left(A\right)= \frac{\sqrt{41}}{5},\; \cot \left(A\right) = \frac{4}{5}\)
C: Given one trigonometric ratio of an acute angle, find all the others
Exercise \(\PageIndex{C}\)
\( \bigstar \) Find the exact values of the other five trigonometric functions of the acute angle \(A \) given the indicated value of one of the functions. Simplify!
21. \( \sin A = \frac{1}{2}\) , \( \cos A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \), \( \tan A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\), \(\csc A = 2\), \( \sec A = \frac{2\sqrt{3}}{3}\), \( \cot A = \sqrt{3} \) 23. \( \sin A = \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{5} \), \( \cos A = \frac{1}{5} \) , \( \tan A = 2\sqrt{6} \), \( \csc A = \frac{5\sqrt{6}}{12} \), \( \sec A = 5 \), \( \cot A = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{12} \) 25. \( \sin A = \frac{3}{5} \), \( \cos A = \frac{4}{5} \), \( \tan A = \frac{3}{4} \) , \( \csc A = \frac{5}{3} \), \( \sec A = \frac{5}{4} \), \( \cot A = \frac{4}{3} \) 27. \( \sin A = \frac{3}{7} \), \( \cos A = \frac{2\sqrt{10}}{7} \), \( \tan A = \frac{3\sqrt{10}}{20} \), \( \csc A = \frac{7}{3} \) , \( \sec A = \frac{7\sqrt{10}}{20} \), \( \cot A = \frac{2\sqrt{10}}{3} \) 29. \( \sin A = \frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3} \), \( \cos A = \frac{1}{3} \), \( \tan A = 2\sqrt{2} \), \( \csc A = \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{4} \), \( \sec A = 3\) , \( \cot \theta = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{4} \) 31. \( \sin A = \frac{\sqrt{101}}{101} \), \( \cos A = \frac{10\sqrt{101}}{101} \), \( \tan A = \frac{1}{10} \), \( \csc A =\sqrt{101} \), \( \sec A= \frac{\sqrt{101}}{10} \), \( \cot A = 10 \)
D: Cofunctions
Exercise \(\PageIndex{D}\)
Use cofunctions of complementary angles to write an equivalent expression.
37. \(\dfrac{π}{6}\) 39. \(\dfrac{π}{4}\)
E: Given one side and an acute angle of a right triangle, find the other sides and angles
Exercise \(\PageIndex{E}\)
\( \bigstar \) In each of the following triangles, solve for \(x\) to the nearest tenth.
41. \(6.4\) 43. \(7.7\) 45. \(11.9\) 47. \(8.4\) 49. \(44.8\) 51. \(7.8\)
53. \(20.5\) 55. \(14.5\) 57. \(7.3\) 59. \(4.8\)
\( \bigstar \) In each of the following triangles, solve for the unknown sides and angles. Give answers to 4 decimal digits.

69. \(a=5,\) angle opposite side \(a\) is \( ∡ A=60^∘\)
70. Hypotenuse \(c=12,\) and one acute angle is \( ∡ A=45^∘\)
\( \bigstar \) Find \(x\). Give answers to 4 decimal digits.

61. \(b \approx 12.1244\), \( c =14\), \( B = 60^{\circ} \) 63. \(a \approx 5.3171\), \( c \approx 11.3257\), \( A = 28^{\circ} \) 65. \(a \approx 9.0631\), \( b \approx 4.2262\), \( B = 25^{\circ} \) 67. \(a = 15\), \( b = 15\), \( A = 45^{\circ} \) 69. \(b \approx 2.8868\), \( c \approx 5.7735\), \( B = 30^{\circ} \) 71. \(188.3159\) 73. \(200.6737\)
F: Right Triangle Applications
Exercise \(\PageIndex{F}\)
Solve. Round answers to the nearest \(10^{th}\) unless otherwise specified.
81. A \(23\)-ft ladder leans against a building so that the angle between the ground and the ladder is \(80°\). How high does the ladder reach up the side of the building?
82. A \(33\)-ft ladder leans against a building so that the angle between the ground and the ladder is \(80°\). How high does the ladder reach up the side of the building?
83. A 20 foot ladder is leaning against a wall, It makes an angle of \(70^{\circ}\) with the ground. How high is the top of the ladder from the ground (nearest tenth of a foot)?
84. A 275 foot guy wire is attached to the top of a communication tower. If the wire makes an angle of \(53^{\circ}\) with the ground, how tall is the tower?
ANGLE OF ELEVATION

85. At a point 50 feet from a tree the angle of elevation of the top of the tree is \(43^{\circ}\). Find the height of the tree to the nearest tenth of a foot.
86. At a point 60 feet from a tree the angle of elevation of the top of the tree is \(40^{\circ}\). Find the height of the tree to the nearest tenth of a foot.
87. The angle of elevation to the top of a mountain from a point 20 miles away from the base of the mountain is \(6^{\circ}\). How high is the mountain to the nearest foot? One mile is \(5280\) feet.

89. At a point 100 feet from a tall building the angle of elevation of the top of the building is \(65^{\circ}\). Find the height of the building to the nearest foot.
90. The angle of elevation to the top of a building in New York is found to be \(9\) degrees from the ground at a distance of \(1\) mile from the base of the building. Using this information, find the height of the building in feet. One mile is \(5280\) feet.
91. The angle of elevation to the top of a building in Seattle is found to be \(2\) degrees from the ground at a distance of \(2\) miles from the base of the building. Using this information, find the height of the building in feet. One mile is \(5280\) feet.
93. Assuming that a \(370\)-foot tall giant redwood grows vertically, if I walk a certain distance from the tree and measure the angle of elevation to the top of the tree to be \(60°\), how far from the base of the tree am I?
94. The CN Tower in Toronto is 1815 feet tall. When the angle of elevation to the top of the tower is observed to be \(40°\), how far away from the Tower is that location?
ANGLE OF DEPRESSION

95. From the top of a building 125 feet tall, the angle of depression of an intersection is \(34^{\circ} .\) How far from the base of the building is the intersection? Notice that the angle of elevation will be equal to the corresponding angle of depression.
96. A helicopter that is 700 feet in the air measures the angle of depression to a landing pad as \(24^{\circ} .\) How far is the landing pad from the point directly beneath the helicopter's current position?

97. From the top of a 100 foot lighthouse the angle of depression of a boat is \(15^{\circ}\). How far is the boat from the bottom of the lighthouse (nearest foot)?
98. From the top of a lighthouse 180 feet above sea level, the angle of depression to a ship in the ocean is \(28^{\circ} .\) How far is the ship from the base of the lighthouse?

99. From an airplane 5000 feet above the ground the angle of depression of an airport is \(5^{\circ}\). How far away is the airport to the nearest hundred feet?
100. From a helicopter 1000 feet above the ground the angle of depression of a heliport is \(10^{\circ}\). How far away is the heliport to the nearest foot?
TWO ANGLES of DEPRESSION and/or ELEVATION
101. A radio tower is located \(325\) feet from a building. From a window in the building, a person determines that the angle of elevation to the top of the tower is \(43°\), and that the angle of depression to the bottom of the tower is \(31°\). How tall is the tower?
102. A radio tower is located \(400\) feet from a building. From a window in the building, a person determines that the angle of elevation to the top of the tower is \(36°\), and that the angle of depression to the bottom of the tower is \(23°\). How tall is the tower?
103. A \(400\)-foot tall monument is located in the distance. From a window in a building, a person determines that the angle of elevation to the top of the monument is \(18°\), and that the angle of depression to the bottom of the monument is \(3°\). How far is the person from the monument?
104. A \(200\)-foot tall monument is located in the distance. From a window in a building, a person determines that the angle of elevation to the top of the monument is \(15°\), and that the angle of depression to the bottom of the tower is \(2°\). How far is the person from the monument?
105. There is lightning rod on the top of a building. From a location \(500\) feet from the base of the building, the angle of elevation to the top of the building is measured to be \(36°\). From the same location, the angle of elevation to the top of the lightning rod is measured to be \(38°\). Assuming the lightning rod is situated at the edge of the building facing the observer, find the height of the lightning rod.
106. There is an antenna on the top of a building. From a location \(300\) feet from the base of the building, the angle of elevation to the top of the building is measured to be \(40°\). From the same location, the angle of elevation to the top of the antenna is measured to be \(43°\). Find the height of the antenna.
81. \(22.7\) ft 83. \(18.8\) ft 85. \(46.6\) feet. 87. \(11,099\) feet. 89. \(214\) feet. 91. \(368.8\) ft 93. \(213.6\) ft 95. \(d \approx 185.32\) ft 97. \(373.2\) ft 99. \(57,300\) feet 101. \(498.3\) ft 103. \(1060.1\) ft 105. \(27.4\) ft
G: Find an angle given 2 sides of a right triangle
Exercise \(\PageIndex{G}\)
\( \bigstar \) Find the angle \(x\) to the nearest tenth of a degree:
111. \(41.8^{\circ}\) 113. \(36.9^{\circ}\) 115. \(56.3^{\circ}\) 117. \(48.2^{\circ}\)
H: Applications Finding an Angle
Exercise \(\PageIndex{H}\)
121. If a 20 foot telephone pole casts a shadow of 43 feet , what is the angle of elevation of the sun to the nearest tenth?

122. An 88 foot tree casts a shadow that is 135 feet long. What is the angle of elevation of the sun to the nearest tenth?
123. A road rises 30 feet in a horizontal distance of 300 feet. Find the angle the road makes with the horizontal to the nearest tenth of a degree.

124. A road rises 10 feet in a horizontal distance of 400 feet. Find the angle the road makes with the horizontal to the nearest tenth of a degree.
121. \( 24.9^{\circ} \) 123. \(5.7^{\circ}\)
I: Calculator Practice
Exercise \(\PageIndex{I}\)
\( \bigstar \) Use a calculator to find the value to four decimal digits. Be sure your calculator is in the appropriate mode!
131. \(\sin 10^{\circ}\) 132. \(\sin 30^{\circ}\) 133. \(\cos 80^{\circ}\) 134. \(\cos 60^{\circ}\) 135. \(\tan 45^{\circ}\)
136. \(\tan 60^{\circ}\) 137. \(\sin 18^{\circ}\) 138. \(\cos 72^{\circ}\) 139. \(\tan 50^{\circ}\) 140. \(\tan 80^{\circ}\)
141. \(\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi}{12} \right) \) 142. \(\sin \left( \dfrac{5\pi}{12} \right) \) 143. \(\cos \left( \dfrac{3\pi}{8} \right) \) 144. \(\cos \left( \dfrac{3\pi}{8} \right) \) 145. \(\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi}{3} \right) \) 146. \(\tan \left( 0.8 \right) \) 147. \(\sin \left( 1.5 \right) \) 148. \(\cos \left( 1.0 \right) \)
131. \(0.1736\) 133. \(0.1736\) 135. \(1\) 137. \(0.3090\) 139. \(1.1918\) 141. \(0.2588\) 143. \(0.3827\) 145. \(1.7321\) 147. \(0.9975\)
\( \bigstar \) Use a calculator to find the value (a) in degrees and (b) in radians to four decimal digits.
151. \(\sin^{-1} (.1)\) 152. \(\sin^{-1} (.1)\) 153. \(\cos^{-1} (.3)\) 154. \(\cos^{-1} (.9)\)
155. \(\tan^{-1} (.5)\) 156. \(\tan^{-1} (4)\) 157. \(\sin^{-1} (3)\) 158. \(\cos^{-1} (2)\)
151. (a) \(6.7392^{\circ}\) (b) \(.1002\) (radians) 153. (a) \(72.5425^{\circ}\) (b) \(1.2661\) (radians) 155. (a) \(26.5651^{\circ}\) (b) \(1.3258\) (radians) 157. Undefined ("Domain Error")
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
Curriculum / Math / 10th Grade / Unit 4: Right Triangles and Trigonometry / Lesson 12
Right Triangles and Trigonometry
Lesson 12 of 19
Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor problems.
- Problem Set
Target Task
Additional practice.
Describe the relationship between slope and the tangent ratio of the angle of elevation/depression. Use the tangent ratio of the angle of elevation or depression to solve real-world problems.
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson
Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry
G.SRT.C.8 — Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. Modeling is best interpreted not as a collection of isolated topics but in relation to other standards. Making mathematical models is a Standard for Mathematical Practice, and specific modeling standards appear throughout the high school standards indicated by a star symbol (★). The star symbol sometimes appears on the heading for a group of standards; in that case, it should be understood to apply to all standards in that group.
Foundational Standards
The foundational standards covered in this lesson
Expressions and Equations
8.EE.B.5 — Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. For example, compare a distance-time graph to a distance-time equation to determine which of two moving objects has greater speed.
8.EE.B.6 — Use similar triangles to explain why the slope m is the same between any two distinct points on a non-vertical line in the coordinate plane; derive the equation y = mx for a line through the origin and the equation y = mx + b for a line intercepting the vertical axis at b.
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Describe how the slope of a line compares to the tangent of the angle of depression.
- Use the context of the problem to determine whether the angle is an elevation or a depression.
- Explain that the ratios of any right angle formed from a single line where the line is the hypotenuse will be equal (slope triangles from 8th grade).
- Describe that the angle of elevation is congruent to the angle of depression, but they are not the same angle.
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
- This lesson is an extension of 8.EE.6 by relating slope to the tangent ratio. As a result, students may need to review the concept of slope before they can fully access this lesson. It is recommended to spend time outside of class building this skill.
- This is the first lesson out of two that begins to have students model real-world examples of trigonometric ratios.
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Problems designed to teach key points of the lesson and guiding questions to help draw out student understanding
Brandon and Madison use different triangles to determine the slope of the line shown below.

Brandon started at (0,-1) and drew a right triangle going up 2 units and right 3 units. Madison started at (-3,-3) and drew a right triangle going up 6 units and right 9 units.
- Draw and label both triangles on the graph.
- How can Brandon and Madison use their triangles to find the slope?
- What trigonometric ratio do Brandon and Madison use to find the slope?
Guiding Questions
Below is a line segment on a coordinate grid.

- Draw the right triangle that you can use to find the length of this line segment.
- Find the length of the line segment.
- Find the measure of all of the angles of the triangle formed.
Standing on the gallery of a lighthouse (the deck at the top of a lighthouse), a person spots a ship at an angle of depression of 20°. The lighthouse is 28 meters tall and sits on a cliff 45 meters tall as measured from sea level. What is the horizontal distance between the lighthouse and the ship?
Geometry > Module 2 > Topic E > Lesson 29 of the New York State Common Core Mathematics Curriculum from EngageNY and Great Minds . © 2015 Great Minds. Licensed by EngageNY of the New York State Education Department under the CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 US license. Accessed Dec. 2, 2016, 5:15 p.m..
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
Samuel is at the top of a tower and will ride a trolley down a zip line to a lower tower. The total vertical drop of the zip line is 40 feet. The zip line’s angle of elevation from the lower tower is 11.5°. Sam’s friend is not going to zip-line but wants to walk along the ground from the tall tower to the lower tower. How far will Sam’s friend walk to meet him?
The following resources include problems and activities aligned to the objective of the lesson that can be used for additional practice or to create your own problem set.
- Include word problems where students are required to draw a diagram with the angle of elevation or depression.
- EngageNY Mathematics Geometry > Module 2 > Topic E > Lesson 29 — Example 1, Example 2, Exercise 2, and Problem Set
- Mathematics Vision Project: Secondary Mathematics Two Module 6: Similarity and Right Triangle Trigonometry — Lessons 10 and 11 (Focus on the questions regarding angle of elevation and depression)
- CK-12 Angles of Elevation and Depression
Topic A: Right Triangle Properties and Side-Length Relationships
Define the parts of a right triangle and describe the properties of an altitude of a right triangle.
G.CO.A.1 G.SRT.B.4
Define and prove the Pythagorean theorem. Use the Pythagorean theorem and its converse in the solution of problems.
Define the relationship between side lengths of special right triangles.
G.SRT.B.4 G.SRT.B.5
Multiply and divide radicals. Rationalize the denominator.
A.SSE.A.2 N.RN.A.2
Add and subtract radicals.
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Right Triangle Trigonometry
Define and calculate the sine of angles in right triangles. Use similarity criteria to generalize the definition of sine to all angles of the same measure.
Define and calculate the cosine of angles in right triangles. Use similarity criteria to generalize the definition of cosine to all angles of the same measure.
Derive the relationship between sine and cosine of complementary angles in right triangles, and describe sine and cosine as angle measures approach 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°.
Describe and calculate tangent in right triangles. Describe how the value of tangent changes as the angle measure approaches 0°, 45°, and 90°.
G.SRT.C.6 G.SRT.C.7
Solve for missing sides of a right triangle given the length of one side and measure of one angle.
Topic C: Applications of Right Triangle Trigonometry
Find the angle measure given two sides using inverse trigonometric functions.
Solve a modeling problem using trigonometry.
Topic D: The Unit Circle
Define angles in standard position and use them to build the first quadrant of the unit circle.
Use the first quadrant of the unit circle to define sine, cosine, and tangent values outside the first quadrant.
Topic E: Trigonometric Ratios in Non-Right Triangles
Derive the area formula for any triangle in terms of sine.
Verify algebraically and find missing measures using the Law of Sines.
Verify algebraically and find missing measures using the Law of Cosines.
Use side and angle relationships in right and non-right triangles to solve application problems.
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.
Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

Effective Instruction Made Easy
Access rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free

Chapter 5: Equations and Identities
Exercises: Chapter 5 Review Problems
Suggested problems.
Exercises for Chapter 5 Review
Exercise group.
For Problems 1–4, evaluate the expressions for [latex]x = 120°,~ y = 225°,[/latex] and [latex]z = 90°{.}[/latex] Give exact values for your answers.
[latex]\sin^2 x \cos y[/latex]
[latex]\sin z - \dfrac{1}{2} \sin y[/latex]
[latex]\tan (z - x) \cos (y - z)[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{\tan^2 x}{2 \cos y}[/latex]
For Problems 5–8, evaluate the expressions using a calculator. Are they equal?
- [latex]\sin (20° + 40°)[/latex]
- [latex]\sin 20° + \sin 40°[/latex]
- [latex]\cos^2 70° - \sin^2 70°[/latex]
- [latex]\cos (2\cdot 70°)[/latex]
- [latex]\dfrac{\sin 55°}{\cos 55°}[/latex]
- [latex]\tan 55°[/latex]
- [latex]\tan 80° - \tan 10°[/latex]
- [latex]\tan (80° - 10°)[/latex]
For Problems 9–12, simplify the expression.
[latex]3\sin x - 2\sin x \cos y + 2\sin x - \cos y[/latex]
[latex]\cos t + 3\cos 3t - 3\cos t - 2\cos 3t[/latex]
[latex]6 \tan^2 \theta + 2\tan \theta - (4\tan \theta )^2[/latex]
[latex]\sin \theta (2\cos \theta - 2) + \sin \theta (1 - \sin \theta)[/latex]
For Problems 13–16, decide whether or not the expressions are equivalent. Explain.
[latex]\cos \theta + \cos 2\theta;~~\cos 3\theta[/latex]
[latex]1 + \sin^2 x;~~(1 + \sin x)^2[/latex]
[latex]3\tan^2 t - \tan^2 t;~~2\tan^2 t[/latex]
[latex]\cos 4\theta;~~2\cos 2\theta[/latex]
For Problems 17–20, multiply or expand.
[latex](\cos \alpha + 2)(2\cos \alpha - 3)[/latex]
[latex](1 - 3\tan \beta)^2[/latex]
[latex](\tan \phi - \cos \phi)^2 = 0[/latex]
[latex](\sin \rho - 2\cos \rho)(\sin \rho + \cos \rho)[/latex]
For Problems 21–24, factor the expression.
[latex]12\sin 3x - 6\sin 2x[/latex]
[latex]2\cos^2 \beta + \cos \beta[/latex]
[latex]1 - 9\tan^2 \theta[/latex]
[latex]\sin^2 \phi - \sin \phi \tan \phi - 2\tan^2 \phi[/latex]
For Problems 25–30, reduce the fraction.
[latex]\dfrac{\cos^2 \alpha - \sin^2 \alpha}{\cos \alpha - \sin \alpha}[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{1 - \tan^2 \theta}{1 - \tan \theta}[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{3\cos x + 9}{2\cos x + 6}[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{5\sin \theta - 10}{\sin^2 \theta - 4}[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{3\tan^2 C - 12}{\tan^2 C - 4\tan C + 4}[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{\tan^2 \beta - \tan \beta - 6}{\tan \beta - 3}[/latex]
For Problems 31–32, use a graph to solve the equation for [latex]0° \le x \lt 360°{.}[/latex] Check your solutions by substitution.
[latex]8\cos x - 3 = 2[/latex]
[latex]6\tan x - 2 = 8[/latex]
For Problems 33–40, find all solutions between [latex]0°[/latex] and [latex]360°{.}[/latex] Give exact answers.
[latex]2\cos^2 \theta + \cos \theta = 0[/latex]
[latex]\sin^2 \alpha - \sin \alpha = 0[/latex]
[latex]2\sin^2 x - \sin x - 1 = 0[/latex]
[latex]\cos^2 B + 2\cos B + 1 = 0[/latex]
[latex]\tan^2 x = \dfrac{1}{3}[/latex]
[latex]\tan^2 t - \tan t = 0[/latex]
[latex]6\cos^2 \alpha - 3\cos \alpha - 3 = 0[/latex]
[latex]2\sin^2 \theta + 4\sin \theta + 2 = 0[/latex]
For Problems 41–44, solve the equation for [latex]0° \le x \lt 360°{.}[/latex] Round your answers to two decimal places.
[latex]2 - 5\tan \theta = -6[/latex]
[latex]3 + 5\cos \theta = 4[/latex]
[latex]3\cos^2 x + 7\cos x = 0[/latex]
[latex]8 - 9\sin^2 x = 0[/latex]
A light ray passes from glass to water, with a [latex]37°[/latex] angle of incidence. What is the angle of refraction? The index of refraction from water to glass is 1.1.
A light ray passes from glass to water, with a [latex]76°[/latex] angle of incidence. What is the angle of refraction? The index of refraction from water to glass is 1.1.
For Problems 47–50, decide which of the following equations are identities. Explain your reasoning.
[latex]\cos x\tan x = \sin x[/latex]
[latex]\sin \theta = 1 - \cos \theta[/latex]
[latex]\tan \phi + \tan \phi = \tan 2\phi[/latex]
[latex]\tan^2 x = \dfrac{\sin^2 x}{1 - \sin^2 x}[/latex]
For Problems 51–54, use graphs to decide which of the following equations are identities.
[latex]\cos 2\theta = 2 \cos \theta[/latex]
[latex]\cos (x - 90°) = \sin x[/latex]
[latex]\sin 2x = 2\sin x \cos x[/latex]
[latex]\cos (\theta + 90°) = \cos \theta - 1[/latex]
For Problems 55–58, show that the equation is an identity by transforming the left side into the right side.
[latex]\dfrac{1 - \cos^2 \alpha}{\tan \alpha} = \sin \alpha \cos \alpha[/latex]
[latex]\cos^2 \beta \tan^2 \beta + \cos^2 \beta = 1[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{\tan \theta - \sin \theta \cos \theta}{\sin \theta \cos \theta} = \sin \theta[/latex]
[latex]\tan \phi - \dfrac{\sin^2 \phi}{\tan \phi} = \tan \phi \sin^2 \phi[/latex]
For Problems 59–62, simplify, using identities as necessary.
[latex]\tan \theta + \dfrac{\cos \theta}{\sin \theta}[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{1 - 2\cos^2 \beta}{\sin \beta \cos \beta} + \dfrac{\cos \beta}{\sin \beta}[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{1}{1 - \sin^2 v} - \tan^2 v[/latex]
[latex]\cos u + (\sin u)(\tan u)[/latex]
For Problems 63–66, evaluate the expressions without using a calculator.
[latex]\sin 137° - \tan 137° \cdot \cos 137°[/latex]
[latex]\cos^2 8° + \cos 8° \cdot \tan 8° \cdot \sin 8°[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{1}{\cos^2 54°} - \tan^2 54°[/latex]
[latex]\dfrac{2}{\cos^2 7°} - 2\tan^2 7°[/latex]
For Problems 67–70, use identities to rewrite each expression.
Write [latex]\tan^2 \beta + 1[/latex] in terms of [latex]\cos^2 \beta{.}[/latex]
Write [latex]2\sin^2 t + \cos t[/latex] in terms of [latex]\cos t{.}[/latex]
Write [latex]\dfrac{\cos x}{\tan x}[/latex] in terms of [latex]\sin x{.}[/latex]
For Problems 71–74, find the values of the three trigonometric functions.
[latex]7\tan \beta - 4 = 2, ~~ 180° \lt \beta \lt 270°[/latex]
[latex]3\tan C + 5 = 3, ~~-90° \lt C \lt 0°[/latex]
[latex]5\cos \alpha + 3 = 1, ~~ 90° \lt \alpha \lt 180°[/latex]
[latex]3\sin \theta + 2 = 4, ~~ 90° \lt \beta \lt 180°[/latex]
For Problems 75–82, solve the equation for [latex]0° \le x \lt 360°{.}[/latex] Round angles to three decimal places if necessary.
[latex]\sin w + 1 = \cos^2 w[/latex]
[latex]\cos^2 \phi - \cos \phi - \sin^2 \phi = 0[/latex]
[latex]\cos x + \sin x = 0[/latex]
[latex]3\sin \theta = \sqrt{3} \cos \theta[/latex]
[latex]2\sin \beta - \tan \beta = 0[/latex]
[latex]6\tan \theta \cos \theta + 6 = 0[/latex]
[latex]\cos^2 t - \sin^2 t = 1[/latex]
[latex]5\cos^2 \beta - 5\sin^2 \beta = -5[/latex]
Trigonometry Copyright © 2024 by Bimal Kunwor; Donna Densmore; Jared Eusea; and Yi Zhen. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
HIGH SCHOOL
- ACT Tutoring
- SAT Tutoring
- PSAT Tutoring
- ASPIRE Tutoring
- SHSAT Tutoring
- STAAR Tutoring
GRADUATE SCHOOL
- MCAT Tutoring
- GRE Tutoring
- LSAT Tutoring
- GMAT Tutoring
- AIMS Tutoring
- HSPT Tutoring
- ISAT Tutoring
- SSAT Tutoring
Search 50+ Tests
Loading Page
math tutoring
- Elementary Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry

science tutoring
Foreign languages.
- Mandarin Chinese
elementary tutoring
- Computer Science
Search 350+ Subjects
- Video Overview
- Tutor Selection Process
- Online Tutoring
- Mobile Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- How We Operate
- Our Guarantee
- Impact of Tutoring
- Reviews & Testimonials
- Media Coverage
- About Varsity Tutors
Trigonometry : Solving Word Problems with Trigonometry
Study concepts, example questions & explanations for trigonometry, all trigonometry resources, example questions, example question #1 : solving word problems with trigonometry.

You can draw the following right triangle using the information given by the question:

Since you want to find the height of the platform, you will need to use tangent.

You can draw the following right triangle from the information given by the question.
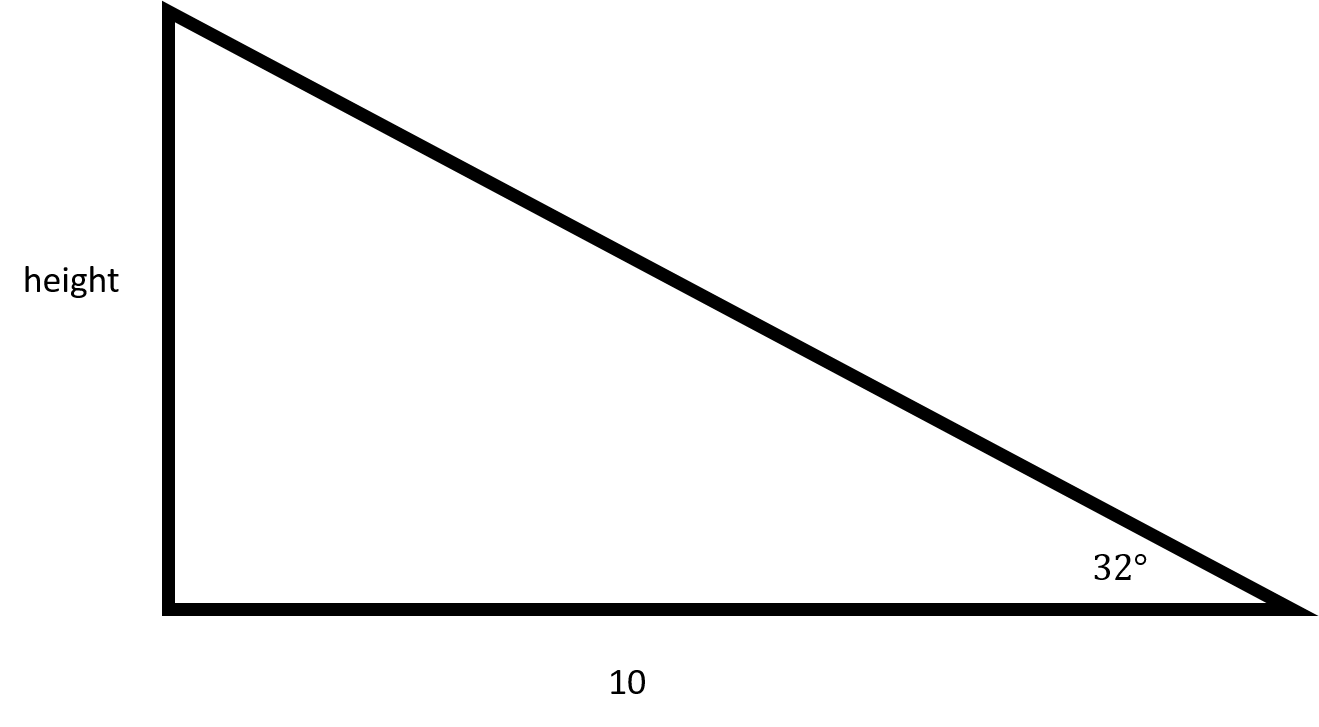
In order to find the height of the flagpole, you will need to use tangent.

You can draw the following right triangle from the information given in the question:
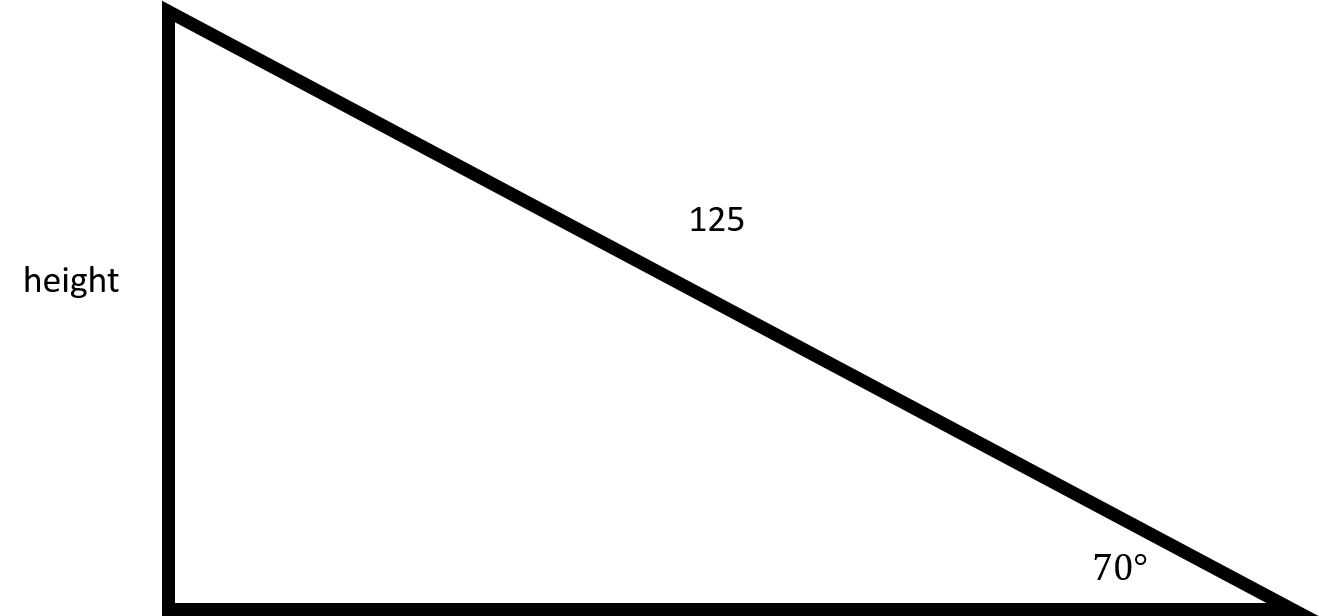
In order to find out how far up the ladder goes, you will need to use sine.

In right triangle ABC, where angle A measures 90 degrees, side AB measures 15 and side AC measures 36, what is the length of side BC?

This triangle cannot exist.

Example Question #5 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
A support wire is anchored 10 meters up from the base of a flagpole, and the wire makes a 25 o angle with the ground. How long is the wire, w? Round your answer to two decimal places.
23.81 meters

28.31 meters
21.83 meters
To make sense of the problem, start by drawing a diagram. Label the angle of elevation as 25 o , the height between the ground and where the wire hits the flagpole as 10 meters, and our unknown, the length of the wire, as w.
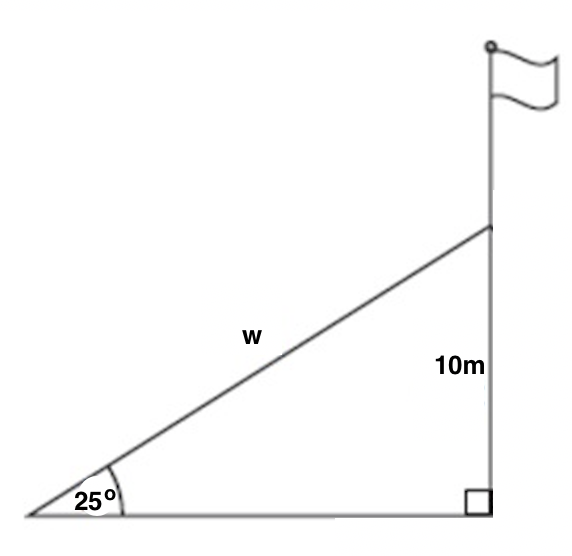
Now, we just need to solve for w using the information given in the diagram. We need to ask ourselves which parts of a triangle 10 and w are relative to our known angle of 25 o . 10 is opposite this angle, and w is the hypotenuse. Now, ask yourself which trig function(s) relate opposite and hypotenuse. There are two correct options: sine and cosecant. Using sine is probably the most common, but both options are detailed below.
We know that sine of a given angle is equal to the opposite divided by the hypotenuse, and cosecant of an angle is equal to the hypotenuse divided by the opposite (just the reciprocal of the sine function). Therefore:

To solve this problem instead using the cosecant function, we would get:

The reason that we got 23.7 here and 23.81 above is due to differences in rounding in the middle of the problem.

Example Question #6 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
When the sun is 22 o above the horizon, how long is the shadow cast by a building that is 60 meters high?
To solve this problem, first set up a diagram that shows all of the info given in the problem.
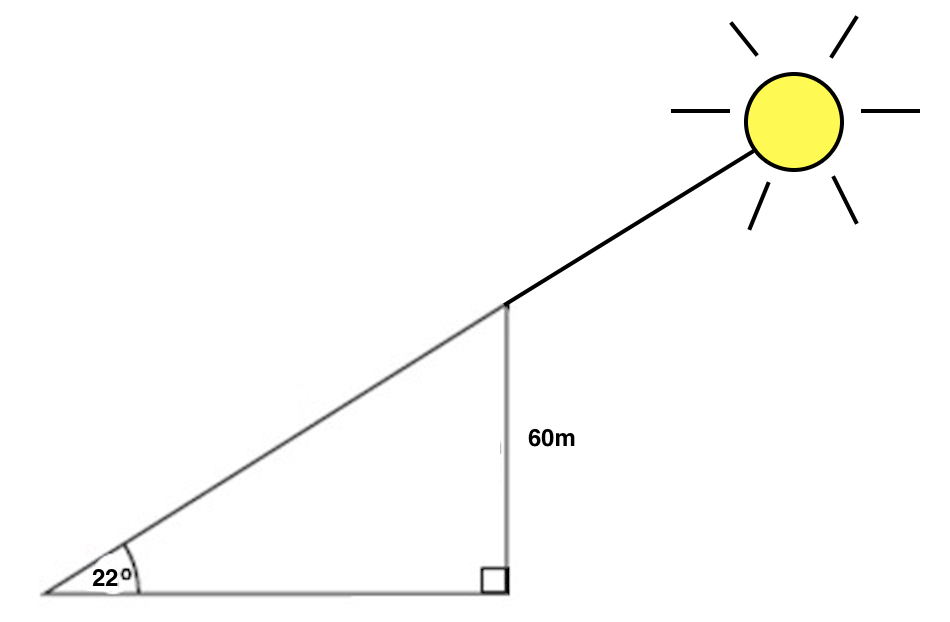
Next, we need to interpret which side length corresponds to the shadow of the building, which is what the problem is asking us to find. Is it the hypotenuse, or the base of the triangle? Think about when you look at a shadow. When you see a shadow, you are seeing it on something else, like the ground, the sidewalk, or another object. We see the shadow on the ground, which corresponds to the base of our triangle, so that is what we'll be solving for. We'll call this base b.

Therefore the shadow cast by the building is 150 meters long.
If you got one of the incorrect answers, you may have used sine or cosine instead of tangent, or you may have used the tangent function but inverted the fraction (adjacent over opposite instead of opposite over adjacent.)
Example Question #7 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
From the top of a lighthouse that sits 105 meters above the sea, the angle of depression of a boat is 19 o . How far from the boat is the top of the lighthouse?
423.18 meters
318.18 meters
36.15 meters
110.53 meters
To solve this problem, we need to create a diagram, but in order to create that diagram, we need to understand the vocabulary that is being used in this question. The following diagram clarifies the difference between an angle of depression (an angle that looks downward; relevant to our problem) and the angle of elevation (an angle that looks upward; relevant to other problems, but not this specific one.) Imagine that the top of the blue altitude line is the top of the lighthouse, the green line labelled GroundHorizon is sea level, and point B is where the boat is.
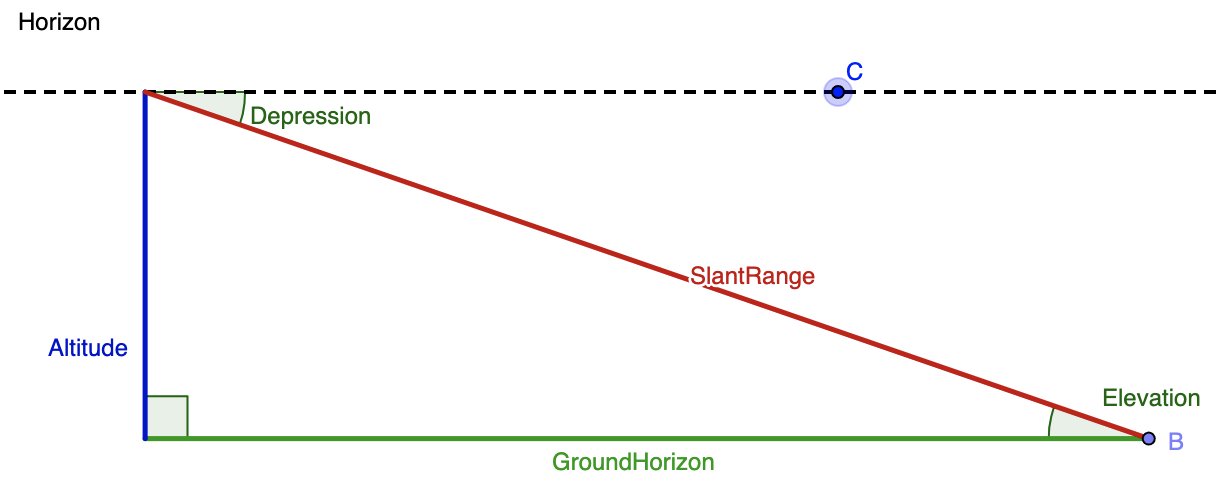
Merging together the given info and this diagram, we know that the angle of depression is 19 o and and the altitude (blue line) is 105 meters. While the blue line is drawn on the left hand side in the diagram, we can assume is it is the same as the right hand side. Next, we need to think of the trig function that relates the given angle, the given side, and the side we want to solve for. The altitude or blue line is opposite the known angle, and we want to find the distance between the boat (point B) and the top of the lighthouse. That means that we want to determine the length of the hypotenuse, or red line labelled SlantRange. The sine function relates opposite and hypotenuse, so we'll use that here. We get:

Example Question #8 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
Angelina just got a new car, and she wants to ride it to the top of a mountain and visit a lookout point. If she drives 4000 meters along a road that is inclined 22 o to the horizontal, how high above her starting point is she when she arrives at the lookout?
9.37 meters
1480 meters
3708.74 meters
10677.87 meters
1616.1 meters
As with other trig problems, begin with a sketch of a diagram of the given and sought after information.
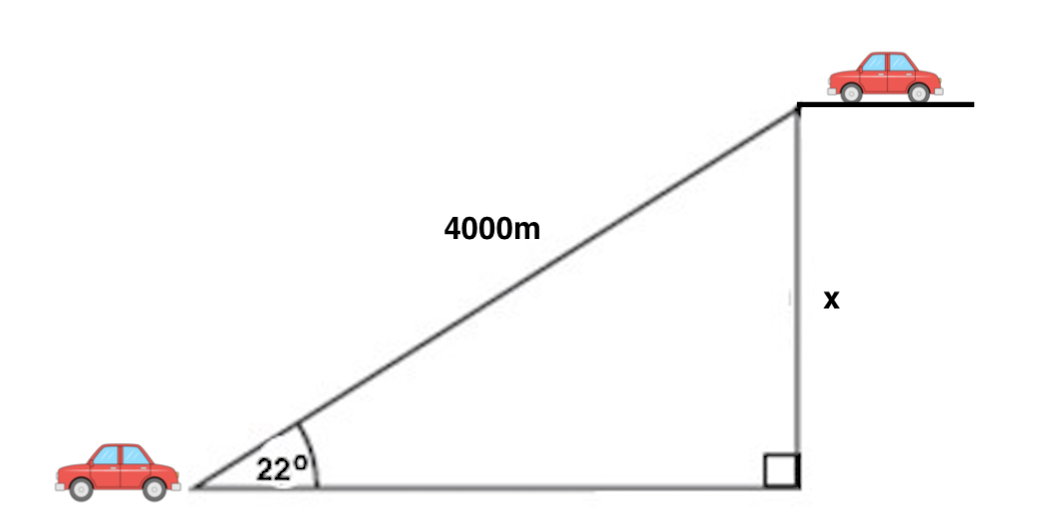
Angelina and her car start at the bottom left of the diagram. The road she is driving on is the hypotenuse of our triangle, and the angle of the road relative to flat ground is 22 o . Because we want to find the change in height (also called elevation), we want to determine the difference between her ending and starting heights, which is labelled x in the diagram. Next, consider which trig function relates together an angle and the sides opposite and hypotenuse relative to it; the correct one is sine. Then, set up:

Therefore the change in height between Angelina's starting and ending points is 1480 meters.
Example Question #9 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
Two buildings with flat roofs are 50 feet apart. The shorter building is 40 feet tall. From the roof of the shorter building, the angle of elevation to the edge of the taller building is 48 o . How high is the taller building?
To solve this problem, let's start by drawing a diagram of the two buildings, the distance in between them, and the angle between the tops of the two buildings. Then, label in the given lengths and angle.
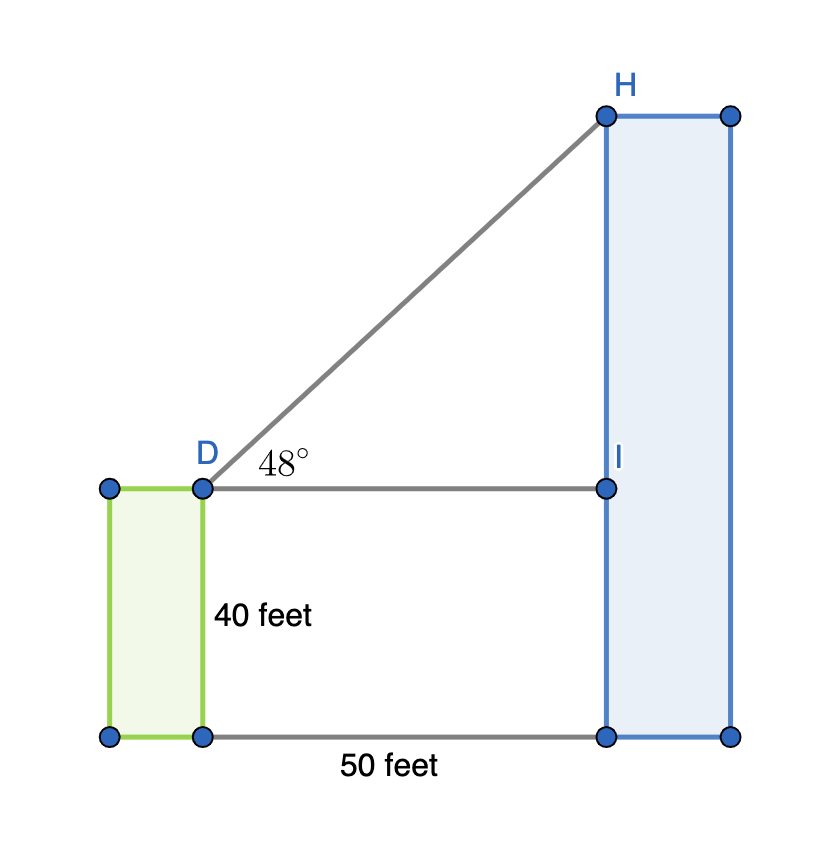
Example Question #10 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
Two buildings with flat roofs are 80 feet apart. The shorter building is 55 feet tall. From the roof of the shorter building, the angle of elevation to the edge of the taller building is 32 o . How high is the taller building?
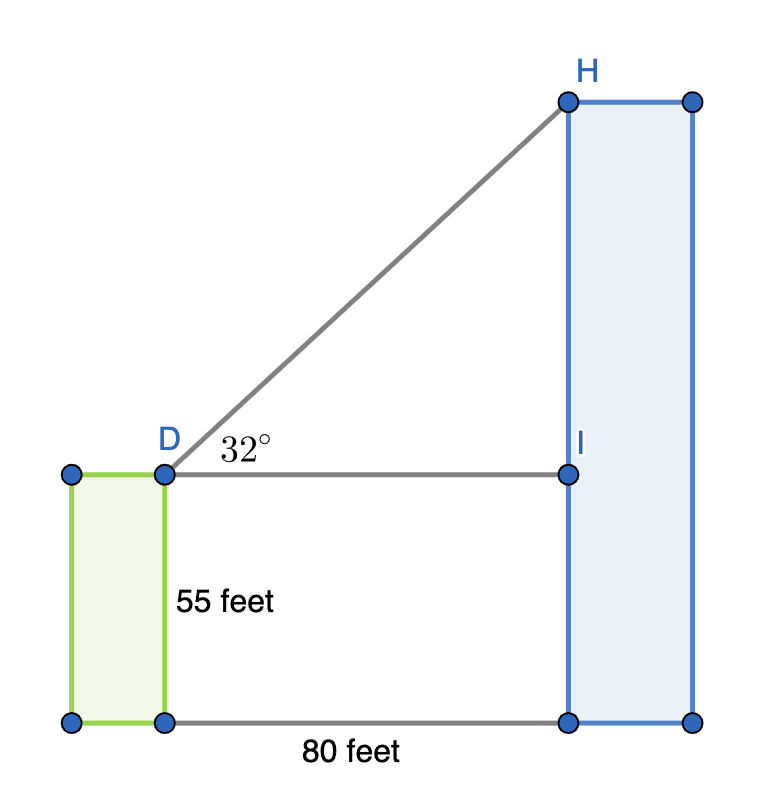
Report an issue with this question
If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources.
DMCA Complaint
If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing the information described below to the designated agent listed below. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors.
Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects.org.
Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney.
Please follow these steps to file a notice:
You must include the following:
A physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf; An identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed; A description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content; for example we require a link to the specific question (not just the name of the question) that contains the content and a description of which specific portion of the question – an image, a link, the text, etc – your complaint refers to; Your name, address, telephone number and email address; and A statement by you: (a) that you believe in good faith that the use of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright is not authorized by law, or by the copyright owner or such owner’s agent; (b) that all of the information contained in your Infringement Notice is accurate, and (c) under penalty of perjury, that you are either the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf.
Send your complaint to our designated agent at:
Charles Cohn Varsity Tutors LLC 101 S. Hanley Rd, Suite 300 St. Louis, MO 63105
Or fill out the form below:
Contact Information
Complaint details.

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 8: Trigonometry
About this unit.
In this unit we'll start by learning all about the law of sines and the law of cosines, which can help us figure out the side lengths or angles of a triangle. We'll also get to explore the unit circle, and how it connects to trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent. Finally, we'll have some fun graphing these functions and learning how to transform them. Get ready to get triggy with it!
Law of sines
- Solving for a side with the law of sines (Opens a modal)
- Solving for an angle with the law of sines (Opens a modal)
- Proof of the law of sines (Opens a modal)
- Solve triangles using the law of sines Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Law of cosines
- Solving for a side with the law of cosines (Opens a modal)
- Solving for an angle with the law of cosines (Opens a modal)
- Proof of the law of cosines (Opens a modal)
- Solve triangles using the law of cosines Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Solving general triangles
- Trig word problem: stars (Opens a modal)
- Laws of sines and cosines review (Opens a modal)
- General triangle word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Unit circle introduction
- Unit circle (Opens a modal)
- The trig functions & right triangle trig ratios (Opens a modal)
- Trig unit circle review (Opens a modal)
- Unit circle Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Intro to radians (Opens a modal)
- Radians & degrees (Opens a modal)
- Degrees to radians (Opens a modal)
- Radians to degrees (Opens a modal)
- Radian angles & quadrants (Opens a modal)
- Radians & degrees Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Unit circle (with radians) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
The Pythagorean identity
- Proof of the Pythagorean trig identity (Opens a modal)
- Using the Pythagorean trig identity (Opens a modal)
- Pythagorean identity review (Opens a modal)
- Use the Pythagorean identity Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Trigonometric values of special angles
- Trig values of π/4 (Opens a modal)
- Trig values of special angles Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Graphs of sin(x), cos(x), and tan(x)
- Graph of y=sin(x) (Opens a modal)
- Intersection points of y=sin(x) and y=cos(x) (Opens a modal)
- Graph of y=tan(x) (Opens a modal)
Amplitude, midline, & period
- Features of sinusoidal functions (Opens a modal)
- Midline, amplitude, and period review (Opens a modal)
- Midline of sinusoidal functions from graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Amplitude of sinusoidal functions from graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Period of sinusoidal functions from graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Transforming sinusoidal graphs
- Amplitude & period of sinusoidal functions from equation (Opens a modal)
- Transforming sinusoidal graphs: vertical stretch & horizontal reflection (Opens a modal)
- Transforming sinusoidal graphs: vertical & horizontal stretches (Opens a modal)
- Amplitude of sinusoidal functions from equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Midline of sinusoidal functions from equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Period of sinusoidal functions from equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Graphing sinusoidal functions
- Example: Graphing y=3⋅sin(½⋅x)-2 (Opens a modal)
- Example: Graphing y=-cos(π⋅x)+1.5 (Opens a modal)
- Sinusoidal function from graph (Opens a modal)
- Graph sinusoidal functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Construct sinusoidal functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Graph sinusoidal functions: phase shift Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Sinusoidal models
- Interpreting trigonometric graphs in context (Opens a modal)
- Trig word problem: modeling daily temperature (Opens a modal)
- Trig word problem: modeling annual temperature (Opens a modal)
- Trig word problem: length of day (phase shift) (Opens a modal)
- Interpreting trigonometric graphs in context Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Modeling with sinusoidal functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Modeling with sinusoidal functions: phase shift Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!

Trigonometry Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers.
Answers – Version 1
Answers – Version 2
GCSE Revision Cards

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In Exercises 10-12, give each answer to the nearest tenth of a unit. 10. ... Lesson 12.5 • Problem Solving with Trigonometry. Name Period Date. 1. While floating down a river with a 2.75 mi/h current, Alicia decides ... LESSON 12.5 • Problem Solving with Trigonometry. 1. About 2.85 mi/h; about 15°
Unit 1: Right triangles & trigonometry. 0/700 Mastery points. Ratios in right triangles Introduction to the trigonometric ratios Solving for a side in a right triangle using the trigonometric ratios. Solving for an angle in a right triangle using the trigonometric ratios Sine and cosine of complementary angles Modeling with right triangles The ...
Yearly. Trigonometry 4 units · 36 skills. Unit 1 Right triangles & trigonometry. Unit 2 Trigonometric functions. Unit 3 Non-right triangles & trigonometry. Unit 4 Trigonometric equations and identities. Course challenge. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course. Start Course challenge.
Exercise 5.2e. ★ Given right triangle ABC where the right angle is angle C in each figure below, (a) Label the remaining sides and angles. (b) Designate the hypotenuse, adjacent side or opposite side to angle A. Determine the trigonometric ratios for (c) sin A, (d) cos A, (e) tan A, (f) sec A, (g) csc A, (h) cot A.
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Trigonometry. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus.
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Trigonometry 5th Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Trigonometry includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take ...
Lesson 12.5 • Problem Solving with Trigonometry Name Period Date 1. While floating down a river with a 2.75 mi/hr current, Alicia decides to swim toward the river bank. She can swim 0.75 mi/hr in still water. What is the actual speed at which she moves toward the bank? At what angle will she approach the bank, measured with respect to the ...
Right triangle trigonometry problems are all about understanding the relationship between side lengths, angle measures, and trigonometric ratios in right triangles. In this lesson, we'll learn to: Use the Pythagorean theorem and recognize Pythagorean triples. Find the sine, cosine, and tangent of similar triangles.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 12 Lesson 12: ... students more opportunities to use trigonometric functions to solve problems in modeling. This lesson is the first in which the model is based on time; that is, ... In the discussion of the problem, be sure to remind the students how the values of
Exercise 113. Exercise 114. Exercise 115. Exercise 116. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Trigonometry - 9780321839855, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
Problem 1. Brandon and Madison use different triangles to determine the slope of the line shown below. Brandon started at (0,-1) and drew a right triangle going up 2 units and right 3 units. Madison started at (-3,-3) and drew a right triangle going up 6 units and right 9 units. Draw and label both triangles on the graph.
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Trigonometry 8th Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Trigonometry includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take ...
Choose the appropriate trig ratio and write an equation, then solve the problem. 35. The gondola cable for the ski lift at Snowy Peak is [latex]2458[/latex] yards long and climbs [latex]1860[/latex] feet.
Answer to the nearest degree, or state an exact solution where possible. a) Find the reference angles for 116°, 265°, 289°, 323°. b) Evaluate the three trigonometric ratios for the angles above. c) Find a coterminal angle with the angles above. 3 sin θ = -2. 5 tan θ + 4 = -2 tan θ. 3 sin θ + 1 = 0.
Solving cos (θ)=1 and cos (θ)=-1. Trig word problem: solving for temperature. "This module revisits trigonometry that was introduced in Geometry and Algebra II, uniting and further expanding the ideas of right triangle trigonometry and the unit circle. New tools are introduced for solving geometric and modeling problems through the power of ...
Exercise Group. For Problems 1-4, evaluate the expressions for x = 120°, y = 225°, x = 120 °, y = 225 °, and z = 90°. z = 90 °. Give exact values for your answers.
Correct answer: 23.81 meters. Explanation: To make sense of the problem, start by drawing a diagram. Label the angle of elevation as 25 o, the height between the ground and where the wire hits the flagpole as 10 meters, and our unknown, the length of the wire, as w. Now, we just need to solve for w using the information given in the diagram.
Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 2,000 Mastery points! In this unit we'll start by learning all about the law of sines and the law of cosines, which can help us figure out the side lengths or angles of a triangle. We'll also get to explore the unit circle, and how it connects to trigonometric functions like sine, cosine ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to enVision Geometry - 9780328931583, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Section 8-5: Problem Solving with Trigonometry. Page 380: Topic Review. Page 345: Explore and Reason. Page 346: Try It! ... Section 12-5: Expected Value. Section 12-6: Probability and ...
Answers - Version 1. Answers - Version 2. Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Trigonometry.
Area Formula for a Triangle in Terms of its Side Lengths. The area of ABC with sides a, b, and c. Area =½bc (sin A) Area =½ac (sin B) Area =½ab (sin C) Lesson 13.1 : Tangent Lesson 13.2 : Sine and Cosine Ratios Lesson 13.3 : Special Right Triangles Lesson 13.4 : Problem Solving with Trigonometry.
trigonometry • To find the area of a triangle using trigonometry. . .And Why To find the area of a courtyard, as in Example 2 In Lesson 10-3, you learned to find the area of a regular polygon by using the formula A = ap, where a is the apothem and p is the perimeter. By using this formula and trigonometric ratios, you can solve other types ...
Simplify the trigonometric expression. 1. Which of the following is a trigonometric identity? Tan^2theta=sin^2theta x sec^2 theta. Use the unit circle to find the inverse function value in degrees. sin^-1 (sqrt3/2) 60. Use the unit circle to find the inverse function value in degrees. tan^-1 sqrt3. 60.