

Online Equation Solver
Solve linear, quadratic and polynomial systems of equations with wolfram|alpha.
- Natural Language
More than just an online equation solver
Wolfram|Alpha is a great tool for finding polynomial roots and solving systems of equations. It also factors polynomials, plots polynomial solution sets and inequalities and more.
Learn more about:
- Equation solving
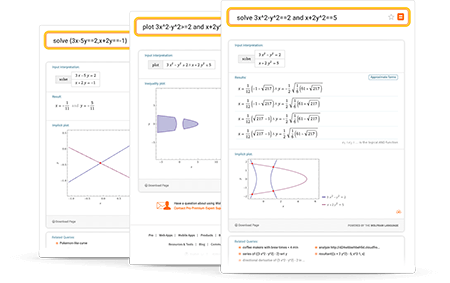
Tips for entering queries
Enter your queries using plain English. To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary. Here are some examples illustrating how to formulate queries.
- find roots to quadratic x^2-7x+12
- plot inequality x^2-7x+12<=0
- solve {3x-5y==2,x+2y==-1}
- plot inequality 3x-5y>=2 and x+2y<=-1
- solve 3x^2-y^2==2 and x+2y^2==5
- plot 3x^2-y^2>=2 and x+2y^2<=5
- View more examples
Access instant learning tools
Get immediate feedback and guidance with step-by-step solutions and Wolfram Problem Generator
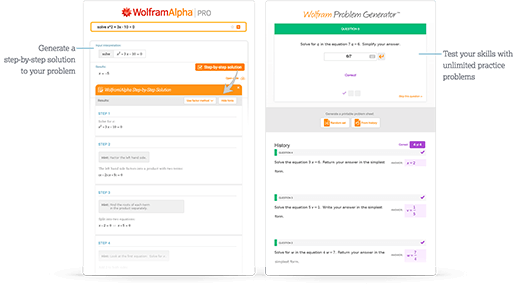
- Step-by-step solutions
- Wolfram Problem Generator
About solving equations
A value is said to be a root of a polynomial if ..
The largest exponent of appearing in is called the degree of . If has degree , then it is well known that there are roots, once one takes into account multiplicity. To understand what is meant by multiplicity, take, for example, . This polynomial is considered to have two roots, both equal to 3.
One learns about the "factor theorem," typically in a second course on algebra, as a way to find all roots that are rational numbers. One also learns how to find roots of all quadratic polynomials, using square roots (arising from the discriminant) when necessary. There are more advanced formulas for expressing roots of cubic and quartic polynomials, and also a number of numeric methods for approximating roots of arbitrary polynomials. These use methods from complex analysis as well as sophisticated numerical algorithms, and indeed, this is an area of ongoing research and development.
Systems of linear equations are often solved using Gaussian elimination or related methods. This too is typically encountered in secondary or college math curricula. More advanced methods are needed to find roots of simultaneous systems of nonlinear equations. Similar remarks hold for working with systems of inequalities: the linear case can be handled using methods covered in linear algebra courses, whereas higher-degree polynomial systems typically require more sophisticated computational tools.
How Wolfram|Alpha solves equations
For equation solving, Wolfram|Alpha calls the Wolfram Language's Solve and Reduce functions, which contain a broad range of methods for all kinds of algebra, from basic linear and quadratic equations to multivariate nonlinear systems. In some cases, linear algebra methods such as Gaussian elimination are used, with optimizations to increase speed and reliability. Other operations rely on theorems and algorithms from number theory, abstract algebra and other advanced fields to compute results. These methods are carefully designed and chosen to enable Wolfram|Alpha to solve the greatest variety of problems while also minimizing computation time.
Although such methods are useful for direct solutions, it is also important for the system to understand how a human would solve the same problem. As a result, Wolfram|Alpha also has separate algorithms to show algebraic operations step by step using classic techniques that are easy for humans to recognize and follow. This includes elimination, substitution, the quadratic formula, Cramer's rule and many more.
Math Solver
Geogebra math solver.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills!

Equation Solver
What do you want to calculate.
- Solve for Variable
- Practice Mode
- Step-By-Step
Example (Click to try)
How to solve your equation, solving equations video lessons.
- Solving Simple Equations
Need more problem types? Try MathPapa Algebra Calculator

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 2: Solving equations & inequalities
About this unit.
There are lots of strategies we can use to solve equations. Let's explore some different ways to solve equations and inequalities. We'll also see what it takes for an equation to have no solution, or infinite solutions.
Linear equations with variables on both sides
- Why we do the same thing to both sides: Variable on both sides (Opens a modal)
- Intro to equations with variables on both sides (Opens a modal)
- Equations with variables on both sides: 20-7x=6x-6 (Opens a modal)
- Equation with variables on both sides: fractions (Opens a modal)
- Equation with the variable in the denominator (Opens a modal)
- Equations with variables on both sides Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equations with variables on both sides: decimals & fractions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Linear equations with parentheses
- Equations with parentheses (Opens a modal)
- Reasoning with linear equations (Opens a modal)
- Multi-step equations review (Opens a modal)
- Equations with parentheses Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equations with parentheses: decimals & fractions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Reasoning with linear equations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Analyzing the number of solutions to linear equations
- Number of solutions to equations (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: number of solutions to equations (Opens a modal)
- Creating an equation with no solutions (Opens a modal)
- Creating an equation with infinitely many solutions (Opens a modal)
- Number of solutions to equations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Number of solutions to equations challenge Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Linear equations with unknown coefficients
- Linear equations with unknown coefficients (Opens a modal)
- Why is algebra important to learn? (Opens a modal)
- Linear equations with unknown coefficients Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Multi-step inequalities
- Inequalities with variables on both sides (Opens a modal)
- Inequalities with variables on both sides (with parentheses) (Opens a modal)
- Multi-step inequalities (Opens a modal)
- Using inequalities to solve problems (Opens a modal)
- Multi-step linear inequalities Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Using inequalities to solve problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Compound inequalities
- Compound inequalities: OR (Opens a modal)
- Compound inequalities: AND (Opens a modal)
- A compound inequality with no solution (Opens a modal)
- Double inequalities (Opens a modal)
- Compound inequalities examples (Opens a modal)
- Compound inequalities review (Opens a modal)
- Solving equations & inequalities: FAQ (Opens a modal)
- Compound inequalities Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Solve for x
Solve for x is all related to finding the value of x in an equation of one variable that is x or with different variables like finding x in terms of y. When we find the value of x and substitute it in the equation, we should get L.H.S = R.H.S.
What Does Solve for x Mean?
Solve for x means finding the value of x for which the equation holds true. i.e when we find the value of x and substitute in the equation, we should get L.H.S = R.H.S If I ask you to solve the equation 'x + 1 = 2' that would mean finding some value for x that satisfies the equation. Do you think x = 1 is the solution to this equation? Substitute it in the equation and see. 1 + 1 = 2 2 = 2 L.H.S = R.H.S That’s what solving for x is all about.
How Do You Solve for x?
To solve for x, bring the variable to one side, and bring all the remaining values to the other side by applying arithmetic operations on both sides of the equation. Simplify the values to find the result. Let’s start with a simple equation as, x + 2 = 7 How do you get x by itself? Subtract 2 from both sides ⇒ x + 2 - 2 = 7 - 2 ⇒ x = 5 Now, check the answer, x = 5 by substituting it back into the equation. We get 5 + 2= 7. L.H.S = R.H.S
Solve for x in the Triangle
Solve for x" the unknown side or angle in a triangle we can use properties of triangle or the Pythagorean theorem.
Let us understand solve for x in a triangle with the help of an example.
△ ABC is right-angled at B with two of its legs measuring 7 units and 24 units. Find the hypotenuse x.

In △ABC by using the Pythagorean theorem,
we get AC 2 = AB 2 + BC 2
⇒ x 2 = 7 2 + 24 2
⇒ x 2 = 49 + 576
⇒ x 2 = 625
⇒ x = 25 units
Solve for x to find Missing Angle of Triangle
Suppose angle A = 50°, angle B = 60°, and angle C = x are the angles of a triangle. ABC. By using the angle sum property we can find the value of x.
angle A + angle B + angle C = 180 degrees.
50° + 60° + x° = 180° ⇒ x = 70°
Solve for x in Fractions
Solve for x in fractions , we simply do the cross multiplication and simplify the equation to find x.
For example: Solve for x for equation ⇒ 2/5 = x/10.
Cross multiply the fractions ⇒ 2 × 10 = 5 × x Solve the equation for x ⇒ x = 20 / 5 Simplify for x ⇒ x = 4 To verify the x value put the result, 4 back into the given equation ⇒ 2/5 = 4/10 Cross multiply the fractions ⇒ 2 × 10 = 4 × 5 ⇒ 20 = 20 L.H.S = R.H.S
Solve for x Equations
We can use a system of equations solver to find the value of x when we have equations with different variables.
We solve one of the equations for the x variable (solve for x in terms of y) and then substitute it in the second equation, and then solve for the y variable.
Finally, we substitute the value of the x variable that we found in one of the equations and solve for the other variable.
Let us understand solve for x and y with the help of an example.
For example, Solve for x: 2x - y = 5, 3x + 2y = 11
⇒ 2x - y = 5
Adding y on both sides we get,
⇒ 2x - y + y = 5 + y
⇒ 2x = 5 + y
⇒ x = (5 + y) / 2
Above equation is known as x in terms of y.
Substitute x = (5 + y) / 2 in second equation 3(5 + y) / 2 + 2y = 11
⇒ (15 + 3y) / 2 + 2y = 11
⇒ (15 + 3y + 4y) / 2 = 11
⇒ (15 + 7y) / 2 = 11
⇒15 +7y = 22
⇒ 7y = 22 - 15
Now, substitute y = 1 in x = (5+y) / 2
⇒ x = (5 + 1) / 2
⇒ 6 / 2 = 3
Thus, the solution of the given system of equations is x = 3 and y = 1.
Important Notes on Solve for x
- To solve for x (the unknown variable in the equation), apply arithmetic operations to isolate the variable.
- For solving 'x' number of equations we need exactly 'x' number of variables.
- Solve for x and y can be done by the substitution method, elimination method, cross-multiplication method, etc.
☛ Related Articles
Here is a solve for x calculator for you to get your answers quickly. Try now. Also, check out these interesting articles to know more about solve for x.
- System of Equations Solver
- Polynomial Equations
- Linear Equations
- Linear Equations in Two Variables
Solve for x Examples
Example1: Solve for x: 2 ( 3x + 1 ) + 3 ( 5x + 2 ) = x - 1
Solution: 2 (3x + 1) + 3 (5x + 2) = x - 1
⇒ 6x + 2 + 15x + 6 = x - 1
⇒ 8 + 21x = x - 1
⇒ x = -9/20
Example 2: It is given that x is the one side of the chessboard and it is smaller than its perimeter by 18 inches. Form an equation and solve for x?
Solution: The side of chessboard = 'x' inches
Since the chessboard is square (all sides are equal), therefore its perimeter will be '4x' inches
According to the given condition,
Perimeter = x + 18
⇒ 4x = x + 18
⇒ 4x - x = 18
The side of the chessboard is 6 inches.
Example 3: The ages of Roony and Herald are 5x and 7x. If four years later, the sum of their ages will be 56 years, then form an equation and solve for x.
Solution: The Rooney and Herald's age is 5x and 7x.
The sum of their ages after 4 years = 56
According to given condition,
⇒ (5x+4) + (7x+4) = 56
⇒ 5x + 7x + 4 + 4 = 56
⇒ 12x + 8 = 56
⇒ 12x = 56 - 8
⇒ x = 48/12
⇒ x = 4 The age of Roony = 5 × 4 = 20 years The age of Herald = 7× 4 = 28 years
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Solve For x
How do you solve for x in a bracket.
To solve for x in a bracket we use distributive law and remove the bracket, move all the x terms to one side and constant to the other side and find the unknown x. For example, 2(x−3) = 4 By using distributive law, 2x - 6 = 4 ⇒ 2x = 4 + 6 ⇒ 2x = 10 ⇒ x = 10/2 ⇒ x = 5
How Do You Solve for x in a Fraction?
To solve for x in fractions we have to eliminate the denominator by cross multiplication and then solve for x. For example, x/4 + 1/2 = 5/2 ⇒ (2x+4)/8 = 5/2 By doing cross multiplication we get, 2(2x + 4) = 8(5) ⇒ 4x + 8 = 40 ⇒ 4x = 40 - 8 ⇒ 4x = 32 ⇒ x = 32 / 4 ⇒ x = 8
How Do You Solve for x for the Equation 4x + 2 = -8?
To solve for x follow the points.
- Start with 4x + 2 = -8
- Subtract 2 from both sides: 4x = -8 - 2 = -10
- Divide by 4: x = -10 ÷ 4 = -5/2
How Do You Solve for x for the Equation 3x - 7 = 26?
- Start with 3x - 7 = 26
- Add 7 to both sides: 3x - 7 + 7 = 26 + 7
- Calculate: 3x = 33
- Divide by 3: x = 33 ÷ 3
How Do You Solve for x in Vertical Angles?
Vertical angles are congruent , or we can say they have same measure. For example, if a vertical angle equals 2x and the other equals 90 - x, we would simply form an equation 2x = 90 - x. 2x = 90 - x Add x to both sides, 2x + x = 90 -x + x 3x = 90 x = 30

Game Central
Inequalities, absolute value and rounding, related concepts.
Solve For x
Instructions: Use calculator to solve for x for any given equation that you provide, showing all the steps. Please type in the equation you need to solve for x in the box below.

How to Solve for x
This calculator will allow you to solve for x for any given equation you provide, showing all the steps of the process in case that a solution can be found, which is not always the case .
You can provide an expression like 'y = x + 1' which is a simple linear function where x appears, or you can have something more complex , like 'x^2 + y^2 = 1', where you will have more than one solution.
Once you have provided a valid expression that involves x, you can click on "Calculate" for the process to get started, and the calculator will attempt to solve for x, by solving the equation needed. Notice the word "attempt", because you will find that some equations cannot be solved.

How do you solve for x?
There is not really one answer to that, as it heavily depends on the structure of the equation that x appears in. Linear equations will be simple to deal with as it is just about moving terms around and dividing the equality by a number if need.
Or for quadratic equations you will have a simple type of formula, the well know quadratic formula that will tell you exactly how to solve for x.
But for anything more complex than, it is no man's land, and each equation will require its own approach, if any, to be solved.
That is why having an equation calculator is so important, because it will have a way to solve the most common types of equation, plus it will have some tricks to try in case of a difficult one, increasing your chances of success.
Steps for solving for x
- Step 1: First, try to identify the type of equation: linear, quadratic, polynomial, rational, radical, logarithmic, exponential, etc.
- Step 2: If you have identified the type, then that specific type will have some specific rules to be solved. Ex: if you find that the equation for x is exponential, the usual trick for that kind of equations is to set a common base and equate exponents in order to solve the equation
- Step 3: If no specific type of equation has been identified, then you just can follow some generic type of roadmap: Try to isolate all the terms involving x on one side of the equation (Depending on the type of equation, that may not be possible)
- Step 4: Can you apply a suitable substitution? Can you simplify things by applying a function or some operation to both sides of the equality? That is pretty much the general advice to get you started
Honest, that is all about that you can know as a general rule to solve equations and to solve for x. The rest will come from the specific structure of the equation you are dealing with.
So, there is no formula for x?
Not in general, unfortunately. For the easier types, you will be able to find a formula for x, something like x = g(y), and sometimes this formula will help you define an inverse function , but sometimes you won't find any kind of formula, or sometimes you will find more than one solution.
Sometimes you will have to restrict the variables by solving an inequality in order to find a solution for x. This is, in such cases solving for x is successful only on some restricted region.

Is there a difference between solving for x and solving for y?
Yes, from the point of view that the target variable you want to solve would be different, but no from from a methodological point of view, as the steps you take to solve for x are the same steps you would take to solve for y.
Solving for x or y or z involves the same process, which is solving for a specific variable, which requires the same methodology. There are cases where symmetry plays a role, and it is even literally the same. Just to see it concretely, if you have the equation \(x^2+y^2=1\), solving for x would lead to the same exact steps than solving for y would. That is true only for this kind of symmetric equations.

Example: Solve for x
Find x in terms of y for : \(\frac{1}{3} y = \frac{x-1}{x+4} - \frac{5}{6}\)
Solution: In this case we have a simple linear equation, so then solving for x is all about putting x on one side:
Then, by manipulating terms in the above equation, we obtain the solution:
Therefore, solving for \(x\) for the given equation leads to the solution \(x=-\frac{2\cdot \left(4y+13\right)}{2y-1}\).
Graphically
The following is the graphical representation of the solutions obtained with \(y\) expressed in terms of \(\):

Example: Can you solve for x?
Can you solve for x in this case: \(y = x^2 - 1\)
Solution: In this case, we get directly that
This implies that we are able to find two solutions, or "branches", which are \(x = \sqrt{ y + 1 }\) and \(x = -\sqrt{ y + 1 }\).
Other useful equation calculators
As we saw here, solving for x relies heavily in solving equations , which can certainly be a challenging process for the more complex types that are not linear or quadratic equations.
The idea of solving for x is tightly related with finding the inverse and also finding the graph of the inverse , as that is precisely how you start when you are dealing with inverses.
Equations can get more complicated when dealing with simultaneous equations, which require some specific techniques. One common procedure that we can deal with is solving systems of linear equations , using either graphical or analytical methods
Related Calculators

log in to your account
Reset password.
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Mathematics

How to Solve for X
Last Updated: May 3, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by David Jia . David Jia is an Academic Tutor and the Founder of LA Math Tutoring, a private tutoring company based in Los Angeles, California. With over 10 years of teaching experience, David works with students of all ages and grades in various subjects, as well as college admissions counseling and test preparation for the SAT, ACT, ISEE, and more. After attaining a perfect 800 math score and a 690 English score on the SAT, David was awarded the Dickinson Scholarship from the University of Miami, where he graduated with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration. Additionally, David has worked as an instructor for online videos for textbook companies such as Larson Texts, Big Ideas Learning, and Big Ideas Math. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 810,515 times.
There are a number of ways to solve for x, whether you're working with exponents and radicals or if you just have to do some division or multiplication. No matter what process you use, you always have to find a way to isolate x on one side of the equation so you can find its value. Here's how to do it:
How do you solve for X in equations?
- For basic linear equations: Follow the order of operations (using PEMDAS) to resolve the equation.
- For exponents: Separate the exponent variable from the rest of the equation and find the square root of each side.
- For fractions: Cross-multiply to create a fraction-less equation, combine any like terms, and divide both sides by the x-value's coefficient.
Using a Basic Linear Equation

- 2 2 (x+3) + 9 - 5 = 32

- 4(x+3) + 9 - 5 = 32

- 4x + 12 + 9 - 5 = 32

- 4x+21-5 = 32
- 4x + 16 - 16 = 32 - 16

- 4x/4 = 16/4
Joseph Meyer
To solve an equation for a variable like "x," you need to manipulate the equation to isolate x. Use techniques like the distributive property, combining like terms, factoring, adding or subtracting the same number, and multiplying or dividing by the same non-zero number to isolate "x" and find the answer.

- 2 2 (x+3)+ 9 - 5 = 32
- 2 2 (4+3)+ 9 - 5 = 32
- 2 2 (7) + 9 - 5 = 32
- 4(7) + 9 - 5 = 32
- 28 + 9 - 5 = 32
- 37 - 5 = 32
With Exponents

- 2x 2 + 12 = 44

- 2x 2 +12-12 = 44-12

- (2x 2 )/2 = 32/2
- 4 Take the square root of each side of the equation. [6] X Research source Taking the square root of x 2 will cancel it out. So, take the square root of both sides. You'll get x left over on one side and plus or minus the square root of 16, 4, on the other side. Therefore, x = ±4.
- 2(4) 2 + 12 = 44
- 2(16) + 12 = 44
- 32 + 12 = 44
Using Fractions

- (x + 3)/6 = 2/3

- (x + 3) x 3 = 3x + 9
- 3x + 9 = 12

- 3x + 9 - 9 = 12 - 9

- (1 + 3)/6 = 2/3
Using Radical Signs

- √(2x+9) - 5 = 0

- √(2x+9) - 5 + 5 = 0 + 5
- √(2x+9) = 5

- (√(2x+9)) 2 = 5 2
- 2x + 9 = 25

- 2x + 9 - 9 = 25 - 9

- √(2(8)+9) - 5 = 0
- √(16+9) - 5 = 0
- √(25) - 5 = 0
Using Absolute Value

- |4x +2| - 6 = 8

- |4x +2| - 6 + 6 = 8 + 6
- |4x +2| = 14

- 4x + 2 = 14
- 4x + 2 - 2 = 14 -2

- 4x + 2 = -14
- 4x + 2 - 2 = -14 - 2
- 4x/4 = -16/4

- |4(3) +2| - 6 = 8
- |12 +2| - 6 = 8
- |14| - 6 = 8
- |4(-4) +2| - 6 = 8
- |-16 +2| - 6 = 8
- |-14| - 6 = 8
Practice Problems and Answers

Expert Q&A

- To check your work, plug the value of x back into the original equation and solve. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Radicals, or roots, are another way of representing exponents. The square root of x = x^1/2. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ David Jia. Academic Tutor. Expert Interview. 23 February 2021
- ↑ https://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/Classes/Alg/SolveLinearEqns.aspx
- ↑ https://www.purplemath.com/modules/solvelin.htm
- ↑ https://sciencing.com/tips-for-solving-algebraic-equations-13712207.html
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LMS1NR4gZN8
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/fractions-algebra.html
- ↑ http://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/radical-equations-solving.html
- ↑ http://www.sosmath.com/algebra/solve/solve0/solve0.html
About This Article

To solve for x in a basic linear equation, start by resolving the exponent using the order of operations. Then, isolate the variable to get your answer. To solve for x when the equation includes an exponent, start by isolating the term with the exponent. Then, isolate the variable with the exponent by dividing both sides by the coefficient of the x term to get your answer. If the equation has fractions, start by cross-multiplying the fractions. Then, combine like terms and isolate x by dividing each term by the x coefficient. If you want to learn how to solve for x if the equation has radicals or absolute values, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Zukisa Buhle Denge
Jun 18, 2016
Did this article help you?
Mbali Palesa
Jul 25, 2020
Jun 6, 2016
Phumla Miya
Nov 18, 2018
Henry Statin
Jan 25, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Math Lessons
- Math Formulas
- Calculators
Math Calculators, Lessons and Formulas
It is time to solve your math problem
- HW Help (paid service)
- Solving Equations
- Step-by-step Equation Solver
Step by step equation solver
This is an online calculator for solving algebraic equations. Simply enter the equation, and the calculator will walk you through the steps necessary to simplify and solve it. Each step is followed by a brief explanation.
- Factoring Polynomials
- Polynomial Roots
- Synthetic Division
- Polynomial Operations
- Graphing Polynomials
- Simplify Polynomials
- Generate From Roots
- Simplify Expression
- Multiplication / Division
- Addition / Subtraction
- Rationalize Denominator
- Simplifying
- Quadratic Equations Solver
- Polynomial Equations
- Solving Equations - With Steps
- Solving (with steps)
- Quadratic Plotter
- Factoring Trinomials
- Equilateral Triangle
- Right Triangle
- Oblique Triangle
- Square Calculator
- Rectangle Calculator
- Circle Calculator
- Hexagon Calculator
- Rhombus Calculator
- Trapezoid Calculator
- Triangular Prism
- Distance calculator
- Midpoint Calculator
- Triangle Calculator
- Graphing Lines
- Lines Intersection
- Two Point Form
- Line-Point Distance
- Parallel/Perpendicular
- Circle Equation
- Circle From 3 Points
- Circle-line Intersection
- Modulus, inverse, polar form
- Vectors (2D & 3D)
- Add, Subtract, Multiply
- Determinant Calculator
- Matrix Inverse
- Characteristic Polynomial
- Eigenvalues
- Eigenvectors
- Matrix Decomposition
- Limit Calculator
- Derivative Calculator
- Integral Calculator
- Arithmetic Sequences
- Geometric Sequences
- Find n th Term
- Degrees to Radians
- Trig. Equations
- Long Division
- Evaluate Expressions
- Fraction Calculator
- Greatest Common Divisor GCD
- Least Common Multiple LCM
- Prime Factorization
- Scientific Notation
- Percentage Calculator
- Dec / Bin / Hex
- Probability Calculator
- Probability Distributions
- Descriptive Statistics
- Standard Deviation
- Z - score Calculator
- Normal Distribution
- T-Test Calculator
- Correlation & Regression
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Amortization Calculator
- Annuity Calculator
- Work Problems
Hire MATHPORTAL experts to do math homework for you.
Prices start at $3 per problem.
1. Rational Equations - an extensive tutorial with exercises.
2. Solving Rational Equations - video tutorial.
3. Solving Simple Equations - Purplemath.
4. Practice problems with solutions
Welcome to MathPortal. This website's owner is mathematician Miloš Petrović. I designed this website and wrote all the calculators, lessons, and formulas .
If you want to contact me, probably have some questions, write me using the contact form or email me on [email protected]
Email (optional)

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.3: Determining a Linear Equation
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 147254

- Rupinder Sekhon and Roberta Bloom
- De Anza College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
In this section, you will learn to:
- Find an equation of a line if a point and the slope are given.
- Find an equation of a line if two points are given.
Prerequisite Skills
Before you get started, take this prerequisite quiz.
1. Simplify each expression:
a. \(3(2x-5)\)
b. \(-7(4x-2)\)
a. \(6x-15\)
b. \(-28x+14\)
If you missed any part of this problem, review here . (Note that this will open a different textbook in a new window.)
2. Find the slope of the line containing each given pair of points.
a. (1, 4) and (5, -2)
b. (-2, 5) and (10, -4).
a. \(-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b. \(-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
If you missed any part of this problem, review Section 1.2 . (Note that this will open in a new window.)
3. Solve: \(\frac { 1 } { 3 } x + \frac { 1 } { 5 } = \frac { 1 } { 5 } x - 1\).
If you missed this problem, review Section 1.1 . (Note that this will open in a new window.)
So far, we were given an equation of a line and were asked to give information about it. For example, we were asked to find points on the line, find its slope and even find intercepts. Now we are going to reverse the process. That is, we will be given either two points, or a point and the slope of a line, and we will be asked to find its equation.
An equation of a line can be written in three forms, the slope-intercept form , the point-slope form, or the standard form . We will discuss each of them in this section.
A line is completely determined by two points, or by a point and slope. The information we are given about a particular line will influence which form of the equation is most convenient to use. Once we know any form of the equation of a line, it is easy to re-express the equation in the other forms if needed.
THE SLOPE-INTERCEPT FORM OF A LINE: \(y = mx + b\)
In the last section we learned that the equation of a line whose slope = \(m\) and \(y\)-intercept = \(b\) is \[y=mx+b.\] This is called the slope-intercept form of the line and is the most commonly used form.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Find an equation of a line whose slope is 5, and \(y\)-intercept is 3.
Since the slope is \(m = 5\), and the \(y\)- intercept is \(b = 3\), the equation is \(y = 5x + 3\).
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Find the equation of the line that passes through the point (\(2, 7\)) and has slope \(3\).
Since \(m = 3\), the partial equation is \(y = 3x + b\).
Now \(b\) can be determined by substituting the point (\(2, 7\)) in the equation \(y = 3x + b\).
\begin{aligned} &7=3(2)+b \nonumber \\ &b=1 \nonumber \end{aligned}
Therefore, the equation is \(y = 3x + 1\).
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Find an equation of the line that passes through the points (-1, 2), and (1, 8).
We need to find the slope of the line containing these points first. Remember that if (\(x_1\), \(y_1\)) and (\(x_2\), \(y_2\)) are two different points on a line, the slope of the line is
\[\text{slope}=m=\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1} \label{slope}\nonumber\]
\(m=\frac{8-2}{1-(-1)}=\frac{6}{2}=3\). So the partial equation is \(y = 3x + b\).
We can use either of the two points (-1, 2) or (1, 8), to find \(b\). Substituting (-1, 2) gives
\begin{aligned} &2=3(-1)+b \nonumber \\ &5=b \nonumber \end{aligned}
So the equation is \(y = 3x +5\).
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Find an equation of the line that has \(x\)-intercept 3, and \(y\)-intercept 4.
\(x\)-intercept = 3, and \(y\)-intercept = 4 correspond to the points (3, 0), and (0, 4), respectively.
\[ m=\frac{4-0}{0-3} = -\frac{4}{3} \nonumber \]
We are told the \(y\)-intercept is 4; thus \(b\) = 4
Therefore, the equation is \(y = -\frac{4}{3} x + 4\).
THE POINT-SLOPE FORM OF A LINE: \(y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)\)
The point-slope form is useful when we know two points on the line and want to find the equation of the line.
The definition of a slope leads us to the point-slope formula. Using two points (\(x_1\), \(y_1\)) and any other (\(x,y\)), the slope is \( \frac{y-y_1}{x-x_1}= m\).
Multiplying both sides by (\(x-x_1\)) gives the point-slope form: \(y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)\).
A line with slope m which contains a specific point (\(x_1, y_1)\) can be expressed in the form \[y - y_1 = m(x - x_1).\]
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Find the point-slope form of the equation of the line given in Example \(\PageIndex{2}\). ( Find the equation of the line that passes through the point (\(2, 7\)) and has slope \(3\). ) Show that the two forms of the equations are equivalent.
Substituting the point \((x_1,y_1) = (2,7)\) and \(m= 3\) in the point-slope formula, we get
\[\mathbf{y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)} \nonumber \]
\[y - 7 = 3(x - 2) \nonumber \]
We can show that the forms are equivalent by solving this equation for \(y\).
\[y - 7 = 3x - 6 \nonumber \]
\[y = 3x + 1 \nonumber \]
This is the slope-intercept form of the equation that we found in Example \(\PageIndex{2}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Find the point-slope form of the equation of a line that has slope \(\frac{1}{2}\) and passes through the point (12,4). Then write the equation in slope-intercept form.
Substituting the point \((x_1,y_1) = (12,4)\) and \(m= \frac{1}{2}\) in the point-slope formula, we get
\[y - 4 = \frac{1}{2}(x - 12) \nonumber \]
\[y - 4 = \frac{1}{2}x - 6 \nonumber \]
\[y = \frac{1}{2}x - 2 \nonumber \]
THE STANDARD FORM OF A LINE: \(Ax + By = C\)
Another useful form of the equation of a line is the standard form.
If we know the equation of a line in point-slope form, \(y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)\), or if we know the equation of the line in slope-intercept form \(y = mx + b\), we can simplify the formula to have all terms for the \(x\) and \(y\) variables on one side of the equation, and the constant on the other side of the equation.
The result is referred to as the standard form of the line: \(Ax + By = C\) where \(A, B,\) and \(C\) are integers and \(A>0\).
We should always be able to convert from one form of an equation to another. For example, if we are given a line in the slope-intercept form, we should be able to express it in the standard form, and vice versa.
Example \(\PageIndex{7}\)
Write the equation \(y = -\frac{2}{3}x + 3\) in the standard form.
Multiplying both sides of the equation by 3, we get
\begin{aligned} &3y = -2x + 9 \\ &2x + 3y = 9 \quad \text { Standard Form } \end{aligned}
Example \(\PageIndex{8}\)
Write the equation \(3x - 4y = 10\) in the slope-intercept form.
Solving for \(y\), we get
\begin{aligned} &-4y = -3x + 10 \\ &y = \frac{3}{4}x - \frac{5}{2} \quad \text { Standard Form } \end{aligned}
Example \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Using the point-slope formula, find the standard form of an equation of the line that passes through the point (2, 3) and has slope \(-3/5\).
Solution: Substituting the point (2, 3) and \(m= - 3/5\) in the point-slope formula, we get
\[y - 3 = - 3/5(x - 2) \nonumber \]
Multiplying both sides by 5 gives us
\begin{aligned} &5(y-3)=-3(x-2)\\ &5 y-15=-3 x+6\\ &3 x+5 y=21 \quad \text { Standard Form } \end{aligned}
Example \(\PageIndex{10}\)
Find the standard form of the line that passes through the points (1, -2), and (4, 0).
First we find the slope: \(m = \frac{0-(-2)}{4-1} = \frac{2}{3}\)
Then, the point-slope form is: \(y - (-2) = \frac{2}{3}(x -1)\)
Multiplying both sides by 3 gives us
\begin{aligned}&3(y+2)=2(x-1) \\ &3 y+6=2 x-2\\ &-2 x+3 y=-8\\ &2 x-3 y=8 \quad \text{ Standard Form } \end{aligned}
We summarize the forms for equations of a line below:
Slope Intercept form: \(\mathbf{y = mx + b}\), where \(m\) = slope, \(b\) = \(y\)-intercept
Point Slope form: \(\mathbf{y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)}\), where \(m\) = slope, \((x_1,y_1)\) is a point on the line
Standard form: \(\mathbf{Ax + By = C}\)
Horizontal Line: \(\mathbf{y = b}\) where \(b\) = \(y\)-intercept
Vertical Line: \(\mathbf{x = a}\) where \(a\) = \(x\)-intercept
Real World Examples of Quadratic Equations
A Quadratic Equation looks like this:
Quadratic equations pop up in many real world situations!
Here we have collected some examples for you, and solve each using different methods:
- Factoring Quadratics
- Completing the Square
- Graphing Quadratic Equations
- The Quadratic Formula
- Online Quadratic Equation Solver
Each example follows three general stages:
- Take the real world description and make some equations
- Use your common sense to interpret the results

Balls, Arrows, Missiles and Stones
When you throw a ball (or shoot an arrow, fire a missile or throw a stone) it goes up into the air, slowing as it travels, then comes down again faster and faster ...
... and a Quadratic Equation tells you its position at all times!
Example: Throwing a Ball
A ball is thrown straight up, from 3 m above the ground, with a velocity of 14 m/s. when does it hit the ground.
Ignoring air resistance, we can work out its height by adding up these three things: (Note: t is time in seconds)
Add them up and the height h at any time t is:
h = 3 + 14t − 5t 2
And the ball will hit the ground when the height is zero:
3 + 14t − 5t 2 = 0
Which is a Quadratic Equation !
In "Standard Form" it looks like:
−5t 2 + 14t + 3 = 0
It looks even better when we multiply all terms by −1 :
5t 2 − 14t − 3 = 0
Let us solve it ...
There are many ways to solve it, here we will factor it using the "Find two numbers that multiply to give ac , and add to give b " method in Factoring Quadratics :
ac = −15 , and b = −14 .
The factors of −15 are: −15, −5, −3, −1, 1, 3, 5, 15
By trying a few combinations we find that −15 and 1 work (−15×1 = −15, and −15+1 = −14)
The "t = −0.2" is a negative time, impossible in our case.
The "t = 3" is the answer we want:
The ball hits the ground after 3 seconds!
Here is the graph of the Parabola h = −5t 2 + 14t + 3
It shows you the height of the ball vs time
Some interesting points:
(0,3) When t=0 (at the start) the ball is at 3 m
(−0.2,0) says that −0.2 seconds BEFORE we threw the ball it was at ground level. This never happened! So our common sense says to ignore it.
(3,0) says that at 3 seconds the ball is at ground level.
Also notice that the ball goes nearly 13 meters high.
Note: You can find exactly where the top point is!
The method is explained in Graphing Quadratic Equations , and has two steps:
Find where (along the horizontal axis) the top occurs using −b/2a :
- t = −b/2a = −(−14)/(2 × 5) = 14/10 = 1.4 seconds
Then find the height using that value (1.4)
- h = −5t 2 + 14t + 3 = −5(1.4) 2 + 14 × 1.4 + 3 = 12.8 meters
So the ball reaches the highest point of 12.8 meters after 1.4 seconds.
Example: New Sports Bike

You have designed a new style of sports bicycle!
Now you want to make lots of them and sell them for profit.
Your costs are going to be:
- $700,000 for manufacturing set-up costs, advertising, etc
- $110 to make each bike
Based on similar bikes, you can expect sales to follow this "Demand Curve":
Where "P" is the price.
For example, if you set the price:
- at $0, you just give away 70,000 bikes
- at $350, you won't sell any bikes at all
- at $300 you might sell 70,000 − 200×300 = 10,000 bikes
So ... what is the best price? And how many should you make?
Let us make some equations!
How many you sell depends on price, so use "P" for Price as the variable
Profit = −200P 2 + 92,000P − 8,400,000
Yes, a Quadratic Equation. Let us solve this one by Completing the Square .
Solve: −200P 2 + 92,000P − 8,400,000 = 0
Step 1 Divide all terms by -200
Step 2 Move the number term to the right side of the equation:
Step 3 Complete the square on the left side of the equation and balance this by adding the same number to the right side of the equation:
(b/2) 2 = (−460/2) 2 = (−230) 2 = 52900
Step 4 Take the square root on both sides of the equation:
Step 5 Subtract (-230) from both sides (in other words, add 230):
What does that tell us? It says that the profit is ZERO when the Price is $126 or $334
But we want to know the maximum profit, don't we?
It is exactly half way in-between! At $230
And here is the graph:
The best sale price is $230 , and you can expect:
- Unit Sales = 70,000 − 200 x 230 = 24,000
- Sales in Dollars = $230 x 24,000 = $5,520,000
- Costs = 700,000 + $110 x 24,000 = $3,340,000
- Profit = $5,520,000 − $3,340,000 = $2,180,000
A very profitable venture.
Example: Small Steel Frame
Your company is going to make frames as part of a new product they are launching.
The frame will be cut out of a piece of steel, and to keep the weight down, the final area should be 28 cm 2
The inside of the frame has to be 11 cm by 6 cm
What should the width x of the metal be?
Area of steel before cutting:
Area of steel after cutting out the 11 × 6 middle:
Let us solve this one graphically !
Here is the graph of 4x 2 + 34x :
The desired area of 28 is shown as a horizontal line.
The area equals 28 cm 2 when:
x is about −9.3 or 0.8
The negative value of x make no sense, so the answer is:
x = 0.8 cm (approx.)
Example: River Cruise
A 3 hour river cruise goes 15 km upstream and then back again. the river has a current of 2 km an hour. what is the boat's speed and how long was the upstream journey.
There are two speeds to think about: the speed the boat makes in the water, and the speed relative to the land:
- Let x = the boat's speed in the water (km/h)
- Let v = the speed relative to the land (km/h)
Because the river flows downstream at 2 km/h:
- when going upstream, v = x−2 (its speed is reduced by 2 km/h)
- when going downstream, v = x+2 (its speed is increased by 2 km/h)
We can turn those speeds into times using:
time = distance / speed
(to travel 8 km at 4 km/h takes 8/4 = 2 hours, right?)
And we know the total time is 3 hours:
total time = time upstream + time downstream = 3 hours
Put all that together:
total time = 15/(x−2) + 15/(x+2) = 3 hours
Now we use our algebra skills to solve for "x".
First, get rid of the fractions by multiplying through by (x-2) (x+2) :
3(x-2)(x+2) = 15(x+2) + 15(x-2)
Expand everything:
3(x 2 −4) = 15x+30 + 15x−30
Bring everything to the left and simplify:
3x 2 − 30x − 12 = 0
It is a Quadratic Equation!
Let us solve it using the Quadratic Formula :
Where a , b and c are from the Quadratic Equation in "Standard Form": ax 2 + bx + c = 0
Solve 3x 2 - 30x - 12 = 0
Answer: x = −0.39 or 10.39 (to 2 decimal places)
x = −0.39 makes no sense for this real world question, but x = 10.39 is just perfect!
Answer: Boat's Speed = 10.39 km/h (to 2 decimal places)
And so the upstream journey = 15 / (10.39−2) = 1.79 hours = 1 hour 47min
And the downstream journey = 15 / (10.39+2) = 1.21 hours = 1 hour 13min
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- One-Step Addition
- One-Step Subtraction
- One-Step Multiplication
- One-Step Division
- One-Step Decimals
- Two-Step Integers
- Two-Step Add/Subtract
- Two-Step Multiply/Divide
- Two-Step Fractions
- Two-Step Decimals
- Multi-Step Integers
- Multi-Step with Parentheses
- Multi-Step Rational
- Multi-Step Fractions
- Multi-Step Decimals
- Solve by Factoring
- Completing the Square
- Quadratic Formula
- Biquadratic
- Logarithmic
- Exponential
- Rational Roots
- Floor/Ceiling
- Equation Given Roots
- Newton Raphson
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Cramer's Rule
- Gaussian Elimination
- System of Inequalities
- Perfect Squares
- Difference of Squares
- Difference of Cubes
- Sum of Cubes
- Polynomials
- Distributive Property
- FOIL method
- Perfect Cubes
- Binomial Expansion
- Negative Rule
- Product Rule
- Quotient Rule
- Expand Power Rule
- Fraction Exponent
- Exponent Rules
- Exponential Form
- Logarithmic Form
- Absolute Value
- Rational Number
- Powers of i
- Complex Form
- Partial Fractions
- Is Polynomial
- Leading Coefficient
- Leading Term
- Standard Form
- Complete the Square
- Synthetic Division
- Linear Factors
- Rationalize Denominator
- Rationalize Numerator
- Identify Type
- Convergence
- Interval Notation
- Pi (Product) Notation
- Boolean Algebra
- Truth Table
- Mutual Exclusive
- Cardinality
- Caretesian Product
- Age Problems
- Distance Problems
- Cost Problems
- Investment Problems
- Number Problems
- Percent Problems
- Addition/Subtraction
- Multiplication/Division
- Dice Problems
- Coin Problems
- Card Problems
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions
Most Used Actions
Number line, algebra calculator.
The Algebra Calculator is a versatile online tool designed to simplify algebraic problem-solving for users of all levels. Here's how to make the most of it:
- Begin by typing your algebraic expression into the above input field, or scanning the problem with your camera.
- After entering the equation, click the 'Go' button to generate instant solutions.
- The calculator provides detailed step-by-step solutions, aiding in understanding the underlying concepts.
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- (x+5)(x-5)\gt 0
- 10^{1-x}=10^4
- \sqrt{3+x}=-2
- 6+11x+6x^2+x^3=0
- factor\:x^{2}-5x+6
- simplify\:\frac{2}{3}-\frac{3}{2}+\frac{1}{4}
- x+2y=2x-5,\:x-y=3
- How do you solve algebraic expressions?
- To solve an algebraic expression, simplify the expression by combining like terms, isolate the variable on one side of the equation by using inverse operations. Then, solve the equation by finding the value of the variable that makes the equation true.
- What are the basics of algebra?
- The basics of algebra are the commutative, associative, and distributive laws.
- What are the 3 rules of algebra?
- The basic rules of algebra are the commutative, associative, and distributive laws.
- What is the golden rule of algebra?
- The golden rule of algebra states Do unto one side of the equation what you do to others. Meaning, whatever operation is being used on one side of equation, the same will be used on the other side too.
- What are the 5 basic laws of algebra?
- The basic laws of algebra are the Commutative Law For Addition, Commutative Law For Multiplication, Associative Law For Addition, Associative Law For Multiplication, and the Distributive Law.
algebra-calculator
- Middle School Math Solutions – Inequalities Calculator Next up in our Getting Started maths solutions series is help with another middle school algebra topic - solving...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To solve the equation for different variables step-by-step clear any fractions by multiplying both sides of the equation by the LCM of the denominators. Get all the terms with the wanted variable on one side of the equation and all the other terms on the other side.
Algebra. Equation Solver. Step 1: Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor. The equation calculator allows you to take a simple or complex equation and solve by best method possible. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit and see the result! The equation solver allows you to enter your problem and solve the equation to see the result.
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Completing the square method is a technique for find the solutions of a quadratic equation of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0. This method involves completing the square of the quadratic expression to the form (x + d)^2 = e, where d and e are constants.
Linear equation. Arithmetic. Matrix. Simultaneous equation. Differentiation. Integration. Limits. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
In fact, solving an equation is just like solving a puzzle. And like puzzles, there are things we can (and cannot) do. ... Example: solve for x: 2xx − 3 + 3 = 6x − 3 (x≠3) We have said x≠3 to avoid a division by zero. Let's multiply through by (x − 3): 2x + 3(x−3) = 6.
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
Equation solving; Tips for entering queries. Enter your queries using plain English. To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary. Here are some examples illustrating how to formulate queries. find roots to quadratic x^2-7x+12; plot inequality x^2-7x+12<=0; solve {3x-5y==2,x+2y==-1} plot inequality 3x-5y>=2 and x+2y<=-1
Download our apps here: English / English (United States) Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems with the free GeoGebra Math Solver. Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now!
To solve your equation using the Equation Solver, type in your equation like x+4=5. The solver will then show you the steps to help you learn how to solve it on your own. Solving Equations Video Lessons. Solving Simple Equations; Need more problem types? Try MathPapa Algebra Calculator. ...
Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,100 Mastery points! There are lots of strategies we can use to solve equations. Let's explore some different ways to solve equations and inequalities. We'll also see what it takes for an equation to have no solution, or infinite solutions.
Solve for x in fractions, we simply do the cross multiplication and simplify the equation to find x. For example: Solve for x for equation ⇒ 2/5 = x/10. Cross multiply the fractions. ⇒ 2 × 10 = 5 × x. Solve the equation for x. ⇒ x = 20 / 5. Simplify for x.
Polynomial. In mathematics, a polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of indeterminates and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate x is x² − 4x + 7. An example with three indeterminates ...
Steps for solving for x. Step 1: First, try to identify the type of equation: linear, quadratic, polynomial, rational, radical, logarithmic, exponential, etc. Step 2: If you have identified the type, then that specific type will have some specific rules to be solved. Ex: if you find that the equation for x is exponential, the usual trick for ...
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
5. Isolate the variable. The last thing you have to do to solve for x is to isolate the variable by dividing both sides of the equation by 2, the coefficient of the x term. 2x/2 = x and 16/2 = 8, so you're left with x = 8. 6. Check your work. Plug 8 back in to the equation for x to see if you get the right answer:
Popular Calculators. Fractions Radical Equation Factoring Inverse Quadratic Simplify Slope Domain Antiderivatives Polynomial Equation Log Equation Cross Product Partial Derivative Implicit Derivative Tangent Complex Numbers. Symbolab: equation search and math solver - solves algebra, trigonometry and calculus problems step by step.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
Step 1: Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor. The equation calculator allows you to take a simple or complex equation and solve by best method possible. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit and see the result! The solve for x calculator allows you to enter your problem and solve the equation to see the result.
Step by step equation solver. This is an online calculator for solving algebraic equations. Simply enter the equation, and the calculator will walk you through the steps necessary to simplify and solve it. Each step is followed by a brief explanation.
MAT 1320 Finite Mathematics, 2e 1: Solving Linear Equations 1.3: Determining a Linear Equation Expand/collapse global location 1.3: Determining a Linear Equation ... We can show that the forms are equivalent by solving this equation for \(y\). \[y - 7 = 3(x - 2) \nonumber \] \[y - 7 = 3x - 6 \nonumber \]
Step 1 Divide all terms by -200. P 2 - 460P + 42000 = 0. Step 2 Move the number term to the right side of the equation: P 2 - 460P = -42000. Step 3 Complete the square on the left side of the equation and balance this by adding the same number to the right side of the equation: (b/2) 2 = (−460/2) 2 = (−230) 2 = 52900.
The Math Calculator will evaluate your problem down to a final solution. You can also add, subtraction, multiply, and divide and complete any arithmetic you need. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit and see your result! Math Calculator from Mathway will evaluate various math problems from basic arithmetic to advanced trigonometric expressions.
Solve the equation for different variables step-by-step. solve-for-equation-calculator. en. Related Symbolab blog posts. High School Math Solutions - Quadratic Equations Calculator, Part 1. A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial having the general form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c...
The Algebra Calculator is a versatile online tool designed to simplify algebraic problem-solving for users of all levels. Here's how to make the most of it: Begin by typing your algebraic expression into the above input field, or scanning the problem with your camera. After entering the equation, click the 'Go' button to generate instant solutions.
Free math problem solver answers your linear algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Linear Algebra. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry.