Find out how Siemens has benefited from our services
of the DAX 30 companies work with us
- Solutions Use cases Answer to your HR questions. smartData Market Intelligence Access to the world’s largest labor market database to tune your business and HR. smartPlan Future Workforce Planning Design your future workforce & uncover skills risks and gaps. smartPeople Skills Fulfillment Discover your internal skills and build a future-fit workforce.
- Podcasts & interviews
- ROI calculator
- HR Glossary
See why 100+ companies choose HRForecast.
- Book a demo

How to assess problem-solving skills

Human beings have been fascinated and motivated by problem-solving for as long as time. Let’s start with the classic ancient legend of Oedipus. The Sphinx aggressively addressed anyone who dared to enter Thebes by posing a riddle. If the traveler failed to answer the riddle correctly, the result was death. However, the Sphinx would be destroyed when the answer was finally correct.
Alas, along came Oedipus. He answered correctly. He unlocked this complex riddle and killed the Sphinx.
However, rationality was hardly defined at that time. Today, though, most people assume that it simply takes raw intelligence to be a great problem solver. However, it’s not the only crucial element.
Introduction to key problem-solving skills
You’ve surely noticed that many of the skills listed in the problem-solving process are repeated. This is because having these abilities and talents are so crucial to the entire course of getting a problem solved. Let’s look at some key problem-solving skills that are essential in the workplace.
Communication, listening, and customer service skills
In all the stages of problem-solving, you need to listen and engage to understand what the problem is and come to a conclusion as to what the solution may be. Another challenge is being able to communicate effectively so that people understand what you’re saying. It further rolls into interpersonal communication and customer service skills, which really are all about listening and responding appropriately.
Data analysis, research, and topic understanding skills
To produce the best solutions, employees must be able to understand the problem thoroughly. This is possible when the workforce studies the topic and the process correctly. In the workplace, this knowledge comes from years of relevant experience.
Dependability, believability, trustworthiness, and follow-through
To make change happen and take the following steps towards problem-solving, the qualities of dependability, trustworthiness, and diligence are a must. For example, if a person is known for not keeping their word, laziness, and committing blunders, that is not someone you’ll depend on when they provide you with a solution, will you?
Leadership, team-building, and decision-making
A true leader can learn and grow from the problems that arise in their jobs and utilize each challenge to hone their leadership skills. Problem-solving is an important skill for leaders who want to eliminate challenges that can otherwise hinder their people’s or their business’ growth. Let’s take a look at some statistics that prove just how important these skills are:
A Harvard Business Review study states that of all the skills that influence a leader’s success, problem-solving ranked third out of 16.
According to a survey by Goremotely.net, only 10% of CEOs are leaders who guide staff by example .
Another study at Havard Business Review found a direct link between teambuilding as a social activity and employee motivation.
Are you looking for a holistic way to develop leaders in your workplace?
Numerous skills and attributes define a successful one from a rookie when it comes to leaders. Our leadership development plan (with examples!) can help HR leaders identify potential leaders that are in sync with your company’s future goals.
Why is problem solving important in the workplace?
As a business leader, when too much of your time is spent managing escalations, the lack of problem-solving skills may hurt your business. While you may be hiring talented and capable employees and paying them well, it is only when you harness their full potential and translate that into business value that it is considered a successful hire.
The impact of continuing with poor problem-solving skills may show up in your organization as operational inefficiencies that may also manifest in product quality issues, defects, re-work and non-conformance to design specifications. When the product is defective, or the service is not up to the mark, it directly affects your customer’s experience and consequently reflects on the company’s profile.
At times, poor problem-solving skills could lead to missed market opportunities, slow time to market, customer dissatisfaction, regulatory compliance issues, and declining employee morale.
Problem-solving skills are important for individual business leaders as well. Suppose you’re busy responding to frequent incidents that have the same variables. In that case, this prevents you from focusing your time and effort on improving the future success of business outcomes.
Proven methods to assess and improve problem-solving skills
Pre-employment problem-solving skill assessment .
Recent research indicates that up to 85% of resumes contain misleading statements. Similarly, interviews are subjective and ultimately serve as poor predictors of job performance .
To provide a reliable and objective means of gathering job-related information on candidates, you must validate and develop pre-employment problem-solving assessments. You can further use the data from pre-employment tests to make informed and defensible hiring decisions.
Depending on the job profile, below are examples of pre-employment problem-solving assessment tests:
Personality tests: The rise of personality testing in the 20th century was an endeavor to maximize employee potential. Personality tests help to identify workplace patterns, relevant characteristics, and traits, and to assess how people may respond to different situations.
Examples of personality tests include the Big five personality traits test and Mercer | Mettl’s Dark Personality Inventory .
Cognitive ability test: A pre-employment aptitude test assesses individuals’ abilities such as critical thinking, verbal reasoning, numerical ability, problem-solving, decision-making, etc., which are indicators of a person’s intelligence quotient (IQ). The test results provide data about on-the-job performance. It also assesses current and potential employees for different job levels.
Criteria Cognitive Aptitude test , McQuaig Mental Agility Test , and Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory are commonly used cognitive ability assessment tests.
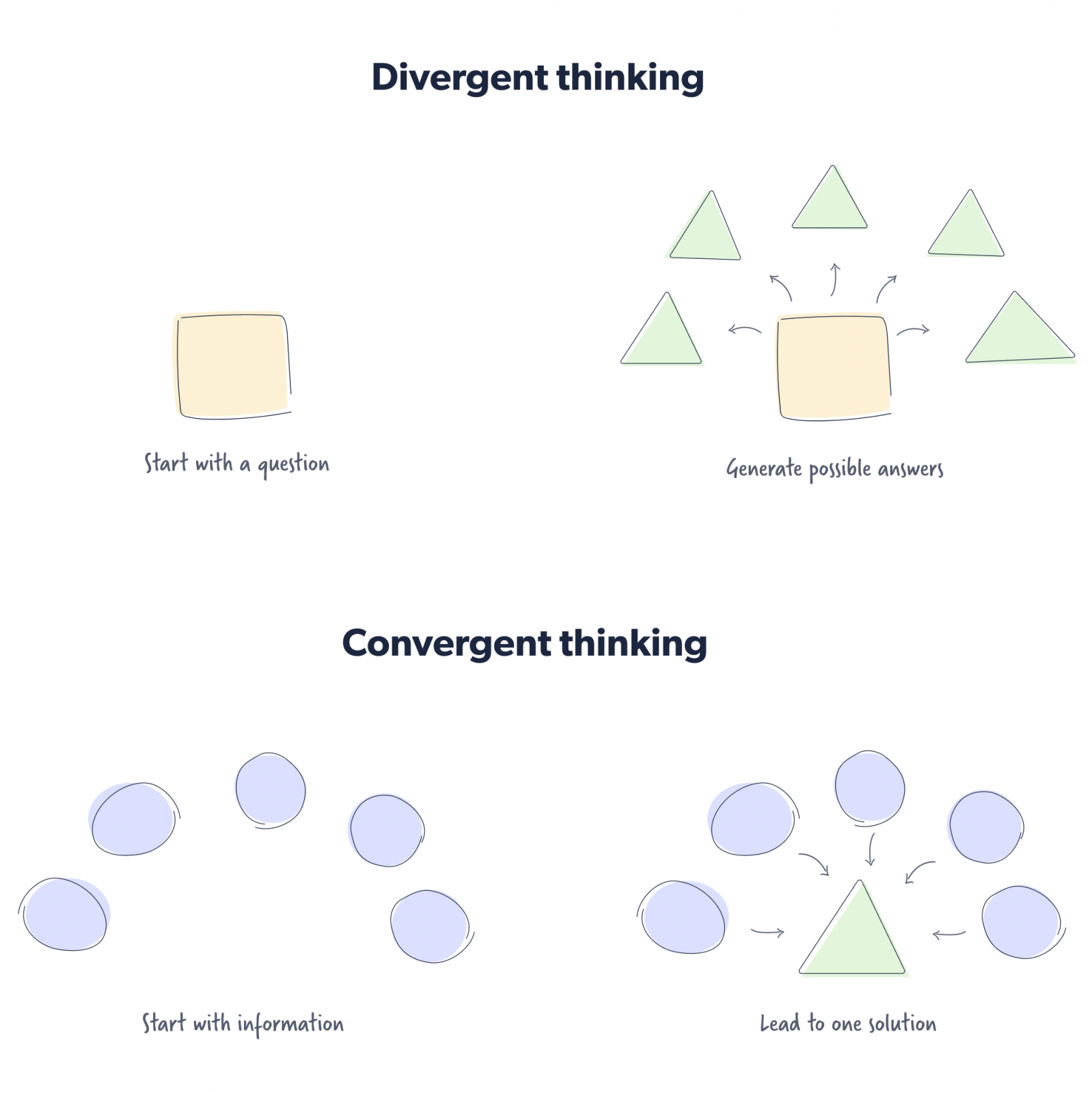
Convergent and divergent thinking methods
American psychologist JP Guilford coined the terms “convergent thinking” and “divergent thinking” in the 1950s.
Convergent thinking involves starting with pieces of information and then converging around a solution. An example would be determining the correct answer to a multiple-choice question.
The nature of the question does not demand creativity but rather inherently encourages a person to consider the veracity of each answer provided before selecting the single correct one.
Divergent thinking, on the other hand, starts with a prompt that encourages people to think critically, diverging towards distinct answers. An example of divergent thinking would be asking open-ended questions.
Here’s an example of what convergent thinking and a divergent problem-solving model would look like.
The 5 whys method , developed by Sakichi Toyoda, is part of the Toyota production system. In this method, when you come across a problem, you analyze the root cause by asking “Why?” five times. By recognizing the countermeasure, you can prevent the problem from recurring. Here’s an example of the 5 whys method.
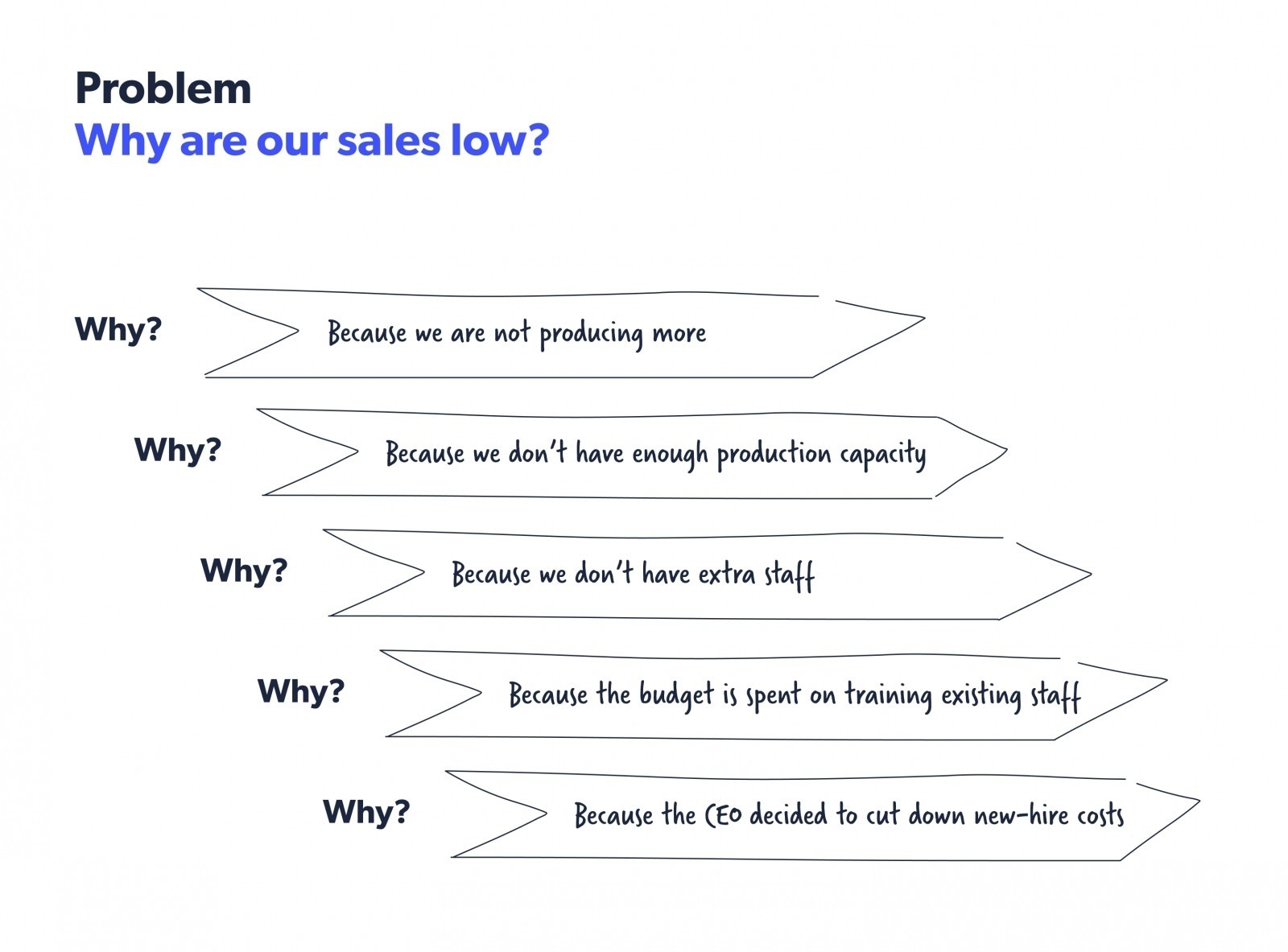
Source: Kanbanzie
This method is specifically useful when you have a recurring problem that reoccurs despite repeated actions to address it. It indicates that you are treating the symptoms of the problem and not the actual problem itself.
Starbursting
While brainstorming is about the team coming together to try to find answers, starbursting flips it over and asks everyone to think of questions instead. Here’s an example of the starbursting method.
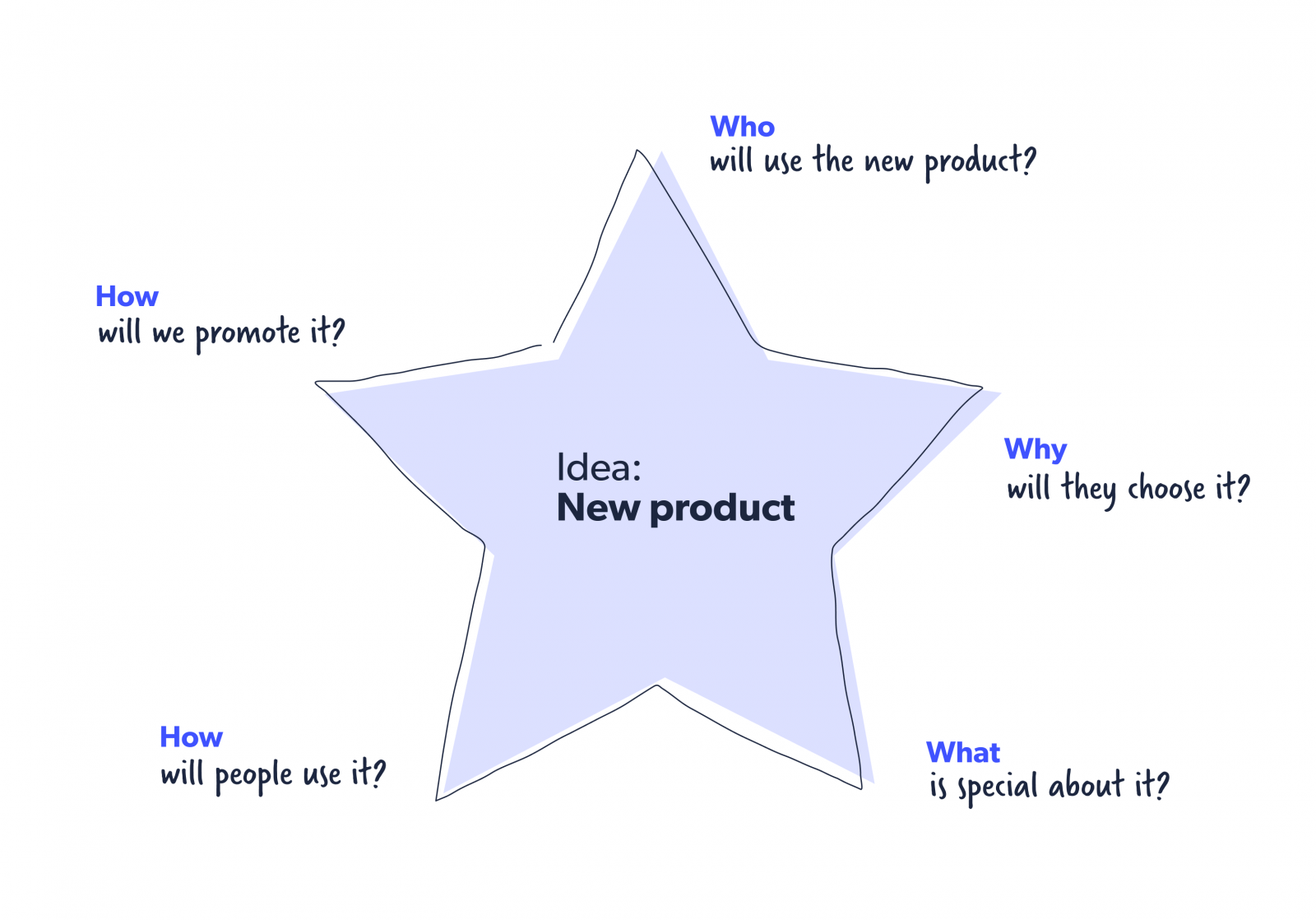
The idea of this method is to go and expand from here, layering more and more questions until you’ve covered every eventuality of the problem.
Use of data analysis to measure improvement in problem-solving skills for your organization
Problem-solving and data analytics are often used together. Supporting data is very handy whenever a particular problem occurs. By using data analytics, you can find the supporting data and analyze it to use for solving a specific problem.
However, we must emphasize that the data you’re using to solve the problem is accurate and complete. Otherwise, misleading data may take you off track of the problem at hand or even make it appear more complex than it is. Moreover, as you gain knowledge about the current problem, it further eases the way to solve it.
Let’s dig deeper into the top 3 reasons data analytics is important in problem-solving.
1. Uncover hidden details
Modern data analytics tools have numerous features that let you analyze the given data thoroughly and find hidden or repeating trends without needing any extra human effort. These automated tools are great at extracting the depths of data, going back way into the past.
2. Automated models
Automation is the future. Businesses don’t have enough time or the budget to encourage manual workforces to go through loads of data to solve business problems. Instead, the tools can collect, combine, clean, and transform the relevant data all by themselves and finally use it to predict the solutions.
3. Explore similar problems
When you use a data analytics approach to solve problems, you can collect all the data available and store it. It can assist you when you find yourself in similar problems, providing references for how such issues were tackled in the past.
If you’re looking for ways to help develop problem-solving skills in the workplace and want to build a team of employees who can solve their own problems, contact us to learn how we can help you achieve it.
Stay up to date with our newsletter
Every month, we’ll send you a curated newsletter with our updates and the latest industry news.
More stories we think you will like

Human-Computer Interaction – What the Future Ep. 1

Recruiting, Bias, Technology – What the Future Ep. 16

Redefining success. The rise of high-paying blue-collar careers
HRForecast newsletter
Get only relevant and insightful letters from us every month

Not a customer yet? Contact us

Career at HRForecast
Why hrforecast.
- Customer Stories
- Trust and Security
- Data Analytics Approach
- IT Skills Analytics
- smartPeople

2023 © Copyright - HRForecast | Imprint | Privacy policy | Terms and conditions (MSA)

Reimagining Assessment Assessing the Transfer of Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills

Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him) Director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute in Washington, DC
Educators are rethinking the purposes, forms, and nature of assessment. Beyond testing mastery of traditional content knowledge—an essential task, but not nearly sufficient—educators are designing assessment for learning as an integral part of the learning process.
Two Rivers embarked on a multi-year project to define and assess critical thinking and problem solving in project-based learning expeditions.
Two Rivers Public Charter School in Washington, D.C., is a network of EL Education schools serving over 700 students in preschool through 8th grade. Throughout our twelve-year history, we have continued to champion the importance of embracing a broader definition of student success than what has been handed to us by state and national policy. While we believe that it is essential for all students to be proficient in math, literacy, and the sciences, we believe that that is not enough. Students also need a rich set of social and cognitive skills that span beyond any given discipline.
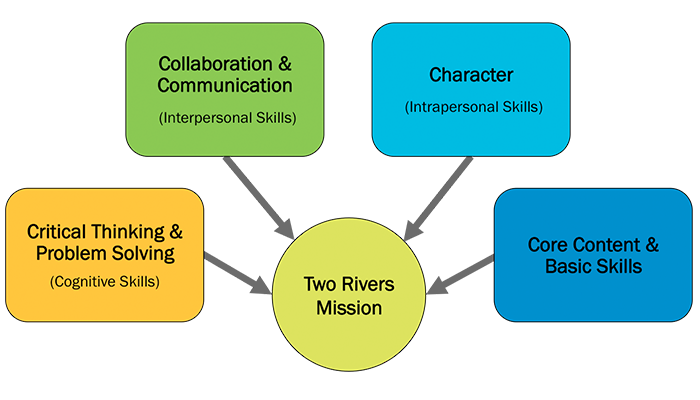
Furthermore, we believe that we can best teach students these skills through hands-on interdisciplinary project-based learning. As EL Education schools, our projects are defined as expeditions lasting 10 to 12 weeks in which students tackle messy, real world problems that don’t have easy paths to solutions nor do they have one clear right answer. Through intentional design of these projects, teachers address the core content and basic skills defined by literacy and content standards; the social skills of collaboration and communication; the intrapersonal skills defined by character; and the broadly applicable cognitive skills of critical thinking and problem solving.
In the life of our schools, we have seen the powerful way that our students through project-based learning have embraced deeper learning outcomes, and exhibited the habits of effective critical thinking, collaboration, and personal character. However, our evidence that this is working is only found in anecdotes and in the quality of student work. We have been unable to demonstrate neither the degree to which students are developing these skills within projects nor their ability to transfer the skills beyond the context of the current project.
Focusing just on the dimensions of critical thinking and problem solving, our teachers expressed frustration at not knowing in concrete terms what those cognitive skills looked like when students exhibited them. Building on our understanding of the essential role that assessment for learning plays in the learning process and the very practical consideration of how we help teachers and students define and work towards developing these skills, we have embarked on a multi-year project to define and assess critical thinking and problem solving.
Critical thinking and problem solving, as we define it, are the set of non-discipline specific cognitive skills people use to analyze vast amounts of information and creatively solve problems. We have broken those skills down into these five core components:
- Schema Development: The ability to learn vast amounts of information and organize it in ways that are useful for understanding
- Metacognition and Evaluation: The ability to think critically about what one is doing and evaluate many potential choices
- Effective Reasoning: The ability to create claims and support them with logical evidence
- Problem Solving: The ability to identify the key questions in a problem, develop possible paths to a solution, and follow through with a solution
- Creativity and Innovation: The ability to formulate new ideas that are useful within a particular context
Our project is working to create learning progressions in each of these core components with accompanying rubrics. The progressions of learning and rubrics will both help define for students and teachers the skills that all students should be developing as well as function as evaluative tools to provide a picture where each student sits in the development of these skills and what are the next steps for further learning.
However, we believe it is not enough for students to be able to develop these skills within the highly scaffolded context of our expeditions. If they have truly learned the skills, they should have the ability to transfer them. With this in mind, we are working to create short content-neutral performance tasks that will give teachers and students valuable information about each of the five core components listed above. Our hypothesis is that through having students tackle short novel tasks, we will be able to draw clear conclusions about their learning of critical thinking and problem solving skills.
Through the course of this work, we hope that our process will be useful to other educators interested in achieving deeper learning outcomes for their students. We realize that deeper learning will not become a reality in most schools until teachers and leaders have a clear vision for what it looks like on a day-to-day basis and how we can clearly demonstrate student growth in these essential skills. We hope that our work will help to inform how to make deeper learning a concrete reality. It is a work in progress, and we invite you to share your thoughts and follow our progress at our website https://learn.tworiverspcs.org .
Learn more about Two Rivers' Assessment for Learning Project on their grantee page .
Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him)
Director of the two rivers learning institute.
Jeff Heyck-Williams is the director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute and a founder of Two Rivers Public Charter School. He has led work around creating school-wide cultures of mathematics, developing assessments of critical thinking and problem-solving, and supporting project-based learning.
Read More About Reimagining Assessment

Three Ways Franklin Is Doing High School Differently
Carisa Corrow (she/hers)
November 13, 2023

Testing for Dummies: 5 Facts about Standardized Testing
John Tanner
August 31, 2023

Grades vs. Continuous Learning: Learners Are Entitled to the A
Catherine Thorn
August 24, 2023
Measuring, Assessing and Evaluating Thinking Skills in Educational Settings: A Necessity for Twenty-First Century
- First Online: 02 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Yalçın Dilekli ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0264-0231 3 , 5 &
- Erdoğan Tezci ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2055-0192 4
Part of the book series: Integrated Science ((IS,volume 13))
664 Accesses
1 Citations
The twenty-first century is very different from other centuries as mobilization of the people is very rapid, and the spread of knowledge has reached unbelievable levels, which has caused rapid changes in all disciplines. Under these circumstances, the traditional educational philosophy cannot meet the needs of the twenty-first century. The modern approach advocates that education should aim to raise thinking generations. A thinking generation means that individuals should be competent in terms of analytical, critical, and creative thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving. The transition from the traditional educational approach to the modern one has resulted in some problems called barriers in teaching thinking skills. These barriers can be summed up as attitudes of schools’ administrators, teachers, and parents. The major reason for this attitude is the difficulty of measuring and assessing these skills. The skills cannot be measured and assessed by traditional ways that measure remembering and memorizing. However, 21st-century skills are higher-order analysis, evaluation, and creation. These skills are measured and assessed using multiple-choice and open-ended questions and performance-based works. Furthermore, the evaluation process is not from a single perspective; instead, it is from multiple perspectives as self-evaluation, peer evaluation, and teacher evaluation. This chapter focuses on how teachers can measure and evaluate students’ thinking skills by focusing on concrete examples.
Graphical Abstract/Art Performance

Thinking skills.
Education is not learning of facts, but training of mind to think . Albert Einstein
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Onosko JJ (1991) Barriers to the promotion of higher-order thinking in social studies. Theor Res Soc Educ 19(4):341–366
Article Google Scholar
Baumfield V, Oberski I (1998) What do teachers think about thinking skills? Qual Assur Educ 6(1):44–51
Dilekli Y (2015) The relationship among teachers’ classroom practices for teaching thinking skills, teachers’ self-efficacy towards teaching thinking skills and teachers’ teaching styles. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation, Balikesir University, Balikesir, Turkey
Google Scholar
Hashim R (2003) Malaysian teachers’ attitudes, competency and practices in the teaching of thinking. Intellectual Discourse 11(1):27–50
Dilekli Y (2019) Teaching thinking skills with activities. Pegem Publishing, Ankara, Turkey
Dilekli Y, Tezci E (2016) The relationship among teachers’ classroom practices for teaching thinking skills, teachers’ self-efficacy towards teaching thinking skills and teachers’ teaching styles. Thinking Skills Creativity 21:144–151
Dilekli Y (2019) What are the dimensions of thinking skills in Turkish literature? A content analysis study. Int J Eval Res Educ 8(1):110–118
Care E, Griffin P, McGaw B (2012) Assessment and teaching of 21st century skills. Springer, Melbourne, AU
Costa AL (2001) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. ASCD, Melbourne, AU
Swartz RJ, Parks S (1994) Infusing the teaching of critical and creative thinking into content instruction: a lesson design handbook for the elementary grades. ERIC, Critical Thinking & Software Pacific Grove CA
McGuinness C (1999) From thinking skills to thinking classrooms: a review and evaluation of approaches for developing pupils’ thinking. Department for Education and Employment London, Nottingam, UK
Sternberg RJ (1987) Teaching critical thinking: eight easy ways to fail before you begin. Phi Delta Kappan 68(6):456–459
Coffman DM (2013) Thinking about thinking: an exploration of preservice teachers’ views about higher order thinking skills. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation, University of Kansas, USA
Nair S, Ngang TK (2012) Exploring parents’ and teachers’ views of primary pupils’ thinking skills and problem solving skills. Creat Educ 3(01):30–36
Tebbs TJ (2000) Assessing teachers’ self-efficacy towards teaching thinking skills. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation, University of Connecticut, USA
Jürges H, Schneider K (2010) Central exit examinations increase performance... but take the fun out of mathematics. J Popul Econ 23 (2):497–517
Kızkapan O, Nacaroğlu O (2019) Science teacher science teachers’ opinions about central exams (LGS). Nevşehir Hacı Bektaş Veli Üniversitesi SBE Dergisi 9(2):701–719
McGuinnes C, Sheey N, Curry C, Eakin A (2003) ACTs II Sustainable thinking in classrooms: a methodology for enhancing thinking across the curriculum. Materials available from Professor C McGuinness, School of Psychology, Queen’s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland
Dilekli Y, Tezci E (2019) Adaptation of teachers’ teaching thinking practices scale into English. Euro J Educ Res 8(4):943–953
Brookhart SM (2010) How to assess higher-order thinking skills in your classroom. ASCD, Melbourne, Australia
Norris SP, Ennis RH (1989) Evaluating critical thinking. The practitioners’ guide to teaching thinking series. Critical Thinking Press & Software Pacific Grove, CA
Dwyer C, Hogan MJ, Stewart I (2011) The promotion of critical thinking skills through argument mapping. Nova Science, Australia
Facione PA (1990) Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research Findings and Recommendations. The Delphi Report Millbrae, California, USA
Anderson LW, Krathwohl DR, Airasian PW, Cruikshank KA, Mayer RE, Pintrich PR, Raths J, Wittrock MC (2001) A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: a revision of bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, abridged edition. Longman, White Plains, NY
McMillan JH, Myran S, Workman D (2002) Elementary teachers’ classroom assessment and grading practices. J Educ Res 95(4):203–213
Sasson I, Yehuda I, Malkinson N (2018) Fostering the skills of critical thinking and question-posing in a project-based learning environment. Thinking Skills Creativity 29:203–212
Perry A, Karpova E (2017) Efficacy of teaching creative thinking skills: A comparison of multiple creativity assessments. Thinking Skills Creativity 24:118–126
Jaušovec N, Jaušovec K (2000) Differences in resting EEG related to ability. Brain Topogr 12(3):229–240
Royer JM, Feldman RS, Chase P, Schulze K (1984) Instructor’s manual for educational psychology: applications and theory. Random House, New York, USA
Tezci E (2002) The effects of constructivist instructional design on the success and creativity of fifth-year students in primary schools. Unpublished doctoral dissertation Fırat University, Elazığ, Turkey
Sweller J (2009) Cognitive bases of human creativity. Educ Psychol Rev 21(1):11–19
Azzam AM (2009) Why creativity now? A conversation with Sir Ken Robinson. Educ Leadersh 67(1):22–26
Lee YC (2007) Developing decision-making skills for socio-scientific issues. J Biol Educ 41(4):170–177
Lee B, Lee Y (2020) A study examining the effects of a training program focused on problem-solving skills for young adults. Thinking Skills Creativity 37:100692
Runco MA, Acar S, Cayirdag N (2017) A closer look at the creativity gap and why students are less creative at school than outside of school. Thinking Skills Creativity 24:242–249
Bransford JD, Stein BS (1993) The IDEAL problem solver. W. H. Freeman, New York, USA
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Science, Faculty of Education, Aksaray University, Aksaray, Turkey
Yalçın Dilekli
Necatibey Faculty of Education, Balıkesir University, Balıkesir, Turkey
Erdoğan Tezci
Bahçesaray M. Merkez Kampüs, Aksaray, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yalçın Dilekli .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Universal Scientific Education and Research Network (USERN), Stockholm, Sweden
Nima Rezaei
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Dilekli, Y., Tezci, E. (2022). Measuring, Assessing and Evaluating Thinking Skills in Educational Settings: A Necessity for Twenty-First Century. In: Rezaei, N. (eds) Integrated Education and Learning. Integrated Science, vol 13. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15963-3_22
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15963-3_22
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-15962-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-15963-3
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
How to improve your problem solving skills and build effective problem solving strategies

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
Effective problem solving is all about using the right process and following a plan tailored to the issue at hand. Recognizing your team or organization has an issue isn’t enough to come up with effective problem solving strategies.
To truly understand a problem and develop appropriate solutions, you will want to follow a solid process, follow the necessary problem solving steps, and bring all of your problem solving skills to the table.
We’ll first guide you through the seven step problem solving process you and your team can use to effectively solve complex business challenges. We’ll also look at what problem solving strategies you can employ with your team when looking for a way to approach the process. We’ll then discuss the problem solving skills you need to be more effective at solving problems, complete with an activity from the SessionLab library you can use to develop that skill in your team.
Let’s get to it!
What is a problem solving process?
- What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
Problem solving strategies
What skills do i need to be an effective problem solver, how can i improve my problem solving skills.
Solving problems is like baking a cake. You can go straight into the kitchen without a recipe or the right ingredients and do your best, but the end result is unlikely to be very tasty!
Using a process to bake a cake allows you to use the best ingredients without waste, collect the right tools, account for allergies, decide whether it is a birthday or wedding cake, and then bake efficiently and on time. The result is a better cake that is fit for purpose, tastes better and has created less mess in the kitchen. Also, it should have chocolate sprinkles. Having a step by step process to solve organizational problems allows you to go through each stage methodically and ensure you are trying to solve the right problems and select the most appropriate, effective solutions.
What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
All problem solving processes go through a number of steps in order to move from identifying a problem to resolving it.
Depending on your problem solving model and who you ask, there can be anything between four and nine problem solving steps you should follow in order to find the right solution. Whatever framework you and your group use, there are some key items that should be addressed in order to have an effective process.
We’ve looked at problem solving processes from sources such as the American Society for Quality and their four step approach , and Mediate ‘s six step process. By reflecting on those and our own problem solving processes, we’ve come up with a sequence of seven problem solving steps we feel best covers everything you need in order to effectively solve problems.
1. Problem identification
The first stage of any problem solving process is to identify the problem or problems you might want to solve. Effective problem solving strategies always begin by allowing a group scope to articulate what they believe the problem to be and then coming to some consensus over which problem they approach first. Problem solving activities used at this stage often have a focus on creating frank, open discussion so that potential problems can be brought to the surface.
2. Problem analysis
Though this step is not a million miles from problem identification, problem analysis deserves to be considered separately. It can often be an overlooked part of the process and is instrumental when it comes to developing effective solutions.
The process of problem analysis means ensuring that the problem you are seeking to solve is the right problem . As part of this stage, you may look deeper and try to find the root cause of a specific problem at a team or organizational level.
Remember that problem solving strategies should not only be focused on putting out fires in the short term but developing long term solutions that deal with the root cause of organizational challenges.
Whatever your approach, analyzing a problem is crucial in being able to select an appropriate solution and the problem solving skills deployed in this stage are beneficial for the rest of the process and ensuring the solutions you create are fit for purpose.
3. Solution generation
Once your group has nailed down the particulars of the problem you wish to solve, you want to encourage a free flow of ideas connecting to solving that problem. This can take the form of problem solving games that encourage creative thinking or problem solving activities designed to produce working prototypes of possible solutions.
The key to ensuring the success of this stage of the problem solving process is to encourage quick, creative thinking and create an open space where all ideas are considered. The best solutions can come from unlikely places and by using problem solving techniques that celebrate invention, you might come up with solution gold.
4. Solution development
No solution is likely to be perfect right out of the gate. It’s important to discuss and develop the solutions your group has come up with over the course of following the previous problem solving steps in order to arrive at the best possible solution. Problem solving games used in this stage involve lots of critical thinking, measuring potential effort and impact, and looking at possible solutions analytically.
During this stage, you will often ask your team to iterate and improve upon your frontrunning solutions and develop them further. Remember that problem solving strategies always benefit from a multitude of voices and opinions, and not to let ego get involved when it comes to choosing which solutions to develop and take further.
Finding the best solution is the goal of all problem solving workshops and here is the place to ensure that your solution is well thought out, sufficiently robust and fit for purpose.
5. Decision making
Nearly there! Once your group has reached consensus and selected a solution that applies to the problem at hand you have some decisions to make. You will want to work on allocating ownership of the project, figure out who will do what, how the success of the solution will be measured and decide the next course of action.
The decision making stage is a part of the problem solving process that can get missed or taken as for granted. Fail to properly allocate roles and plan out how a solution will actually be implemented and it less likely to be successful in solving the problem.
Have clear accountabilities, actions, timeframes, and follow-ups. Make these decisions and set clear next-steps in the problem solving workshop so that everyone is aligned and you can move forward effectively as a group.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved.
6. Solution implementation
This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind.
Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully. Only then can you ensure that you are solving the right problem but also that you have developed the correct solution and can then successfully implement and measure the impact of that solution.
Project management and communication skills are key here – your solution may need to adjust when out in the wild or you might discover new challenges along the way.
7. Solution evaluation
So you and your team developed a great solution to a problem and have a gut feeling its been solved. Work done, right? Wrong. All problem solving strategies benefit from evaluation, consideration, and feedback. You might find that the solution does not work for everyone, might create new problems, or is potentially so successful that you will want to roll it out to larger teams or as part of other initiatives.
None of that is possible without taking the time to evaluate the success of the solution you developed in your problem solving model and adjust if necessary.
Remember that the problem solving process is often iterative and it can be common to not solve complex issues on the first try. Even when this is the case, you and your team will have generated learning that will be important for future problem solving workshops or in other parts of the organization.
It’s worth underlining how important record keeping is throughout the problem solving process. If a solution didn’t work, you need to have the data and records to see why that was the case. If you go back to the drawing board, notes from the previous workshop can help save time. Data and insight is invaluable at every stage of the problem solving process and this one is no different.
Problem solving workshops made easy
Problem solving strategies are methods of approaching and facilitating the process of problem-solving with a set of techniques , actions, and processes. Different strategies are more effective if you are trying to solve broad problems such as achieving higher growth versus more focused problems like, how do we improve our customer onboarding process?
Broadly, the problem solving steps outlined above should be included in any problem solving strategy though choosing where to focus your time and what approaches should be taken is where they begin to differ. You might find that some strategies ask for the problem identification to be done prior to the session or that everything happens in the course of a one day workshop.
The key similarity is that all good problem solving strategies are structured and designed. Four hours of open discussion is never going to be as productive as a four-hour workshop designed to lead a group through a problem solving process.
Good problem solving strategies are tailored to the team, organization and problem you will be attempting to solve. Here are some example problem solving strategies you can learn from or use to get started.
Use a workshop to lead a team through a group process
Often, the first step to solving problems or organizational challenges is bringing a group together effectively. Most teams have the tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to solve their challenges – they just need some guidance in how to use leverage those skills and a structure and format that allows people to focus their energies.
Facilitated workshops are one of the most effective ways of solving problems of any scale. By designing and planning your workshop carefully, you can tailor the approach and scope to best fit the needs of your team and organization.
Problem solving workshop
- Creating a bespoke, tailored process
- Tackling problems of any size
- Building in-house workshop ability and encouraging their use
Workshops are an effective strategy for solving problems. By using tried and test facilitation techniques and methods, you can design and deliver a workshop that is perfectly suited to the unique variables of your organization. You may only have the capacity for a half-day workshop and so need a problem solving process to match.
By using our session planner tool and importing methods from our library of 700+ facilitation techniques, you can create the right problem solving workshop for your team. It might be that you want to encourage creative thinking or look at things from a new angle to unblock your groups approach to problem solving. By tailoring your workshop design to the purpose, you can help ensure great results.
One of the main benefits of a workshop is the structured approach to problem solving. Not only does this mean that the workshop itself will be successful, but many of the methods and techniques will help your team improve their working processes outside of the workshop.
We believe that workshops are one of the best tools you can use to improve the way your team works together. Start with a problem solving workshop and then see what team building, culture or design workshops can do for your organization!
Run a design sprint
Great for:
- aligning large, multi-discipline teams
- quickly designing and testing solutions
- tackling large, complex organizational challenges and breaking them down into smaller tasks
By using design thinking principles and methods, a design sprint is a great way of identifying, prioritizing and prototyping solutions to long term challenges that can help solve major organizational problems with quick action and measurable results.
Some familiarity with design thinking is useful, though not integral, and this strategy can really help a team align if there is some discussion around which problems should be approached first.
The stage-based structure of the design sprint is also very useful for teams new to design thinking. The inspiration phase, where you look to competitors that have solved your problem, and the rapid prototyping and testing phases are great for introducing new concepts that will benefit a team in all their future work.
It can be common for teams to look inward for solutions and so looking to the market for solutions you can iterate on can be very productive. Instilling an agile prototyping and testing mindset can also be great when helping teams move forwards – generating and testing solutions quickly can help save time in the long run and is also pretty exciting!
Break problems down into smaller issues
Organizational challenges and problems are often complicated and large scale in nature. Sometimes, trying to resolve such an issue in one swoop is simply unachievable or overwhelming. Try breaking down such problems into smaller issues that you can work on step by step. You may not be able to solve the problem of churning customers off the bat, but you can work with your team to identify smaller effort but high impact elements and work on those first.
This problem solving strategy can help a team generate momentum, prioritize and get some easy wins. It’s also a great strategy to employ with teams who are just beginning to learn how to approach the problem solving process. If you want some insight into a way to employ this strategy, we recommend looking at our design sprint template below!
Use guiding frameworks or try new methodologies
Some problems are best solved by introducing a major shift in perspective or by using new methodologies that encourage your team to think differently.
Props and tools such as Methodkit , which uses a card-based toolkit for facilitation, or Lego Serious Play can be great ways to engage your team and find an inclusive, democratic problem solving strategy. Remember that play and creativity are great tools for achieving change and whatever the challenge, engaging your participants can be very effective where other strategies may have failed.

LEGO Serious Play
- Improving core problem solving skills
- Thinking outside of the box
- Encouraging creative solutions
LEGO Serious Play is a problem solving methodology designed to get participants thinking differently by using 3D models and kinesthetic learning styles. By physically building LEGO models based on questions and exercises, participants are encouraged to think outside of the box and create their own responses.
Collaborate LEGO Serious Play exercises are also used to encourage communication and build problem solving skills in a group. By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking.
Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack of creative thinking. Some problems are not suited to LEGO Serious Play and require a different problem solving strategy.
Card Decks and Method Kits
- New facilitators or non-facilitators
- Approaching difficult subjects with a simple, creative framework
- Engaging those with varied learning styles
Card decks and method kids are great tools for those new to facilitation or for whom facilitation is not the primary role. Card decks such as the emotional culture deck can be used for complete workshops and in many cases, can be used right out of the box. Methodkit has a variety of kits designed for scenarios ranging from personal development through to personas and global challenges so you can find the right deck for your particular needs.
Having an easy to use framework that encourages creativity or a new approach can take some of the friction or planning difficulties out of the workshop process and energize a team in any setting. Simplicity is the key with these methods. By ensuring everyone on your team can get involved and engage with the process as quickly as possible can really contribute to the success of your problem solving strategy.
Source external advice
Looking to peers, experts and external facilitators can be a great way of approaching the problem solving process. Your team may not have the necessary expertise, insights of experience to tackle some issues, or you might simply benefit from a fresh perspective. Some problems may require bringing together an entire team, and coaching managers or team members individually might be the right approach. Remember that not all problems are best resolved in the same manner.
If you’re a solo entrepreneur, peer groups, coaches and mentors can also be invaluable at not only solving specific business problems, but in providing a support network for resolving future challenges. One great approach is to join a Mastermind Group and link up with like-minded individuals and all grow together. Remember that however you approach the sourcing of external advice, do so thoughtfully, respectfully and honestly. Reciprocate where you can and prepare to be surprised by just how kind and helpful your peers can be!
Mastermind Group
- Solo entrepreneurs or small teams with low capacity
- Peer learning and gaining outside expertise
- Getting multiple external points of view quickly
Problem solving in large organizations with lots of skilled team members is one thing, but how about if you work for yourself or in a very small team without the capacity to get the most from a design sprint or LEGO Serious Play session?
A mastermind group – sometimes known as a peer advisory board – is where a group of people come together to support one another in their own goals, challenges, and businesses. Each participant comes to the group with their own purpose and the other members of the group will help them create solutions, brainstorm ideas, and support one another.
Mastermind groups are very effective in creating an energized, supportive atmosphere that can deliver meaningful results. Learning from peers from outside of your organization or industry can really help unlock new ways of thinking and drive growth. Access to the experience and skills of your peers can be invaluable in helping fill the gaps in your own ability, particularly in young companies.
A mastermind group is a great solution for solo entrepreneurs, small teams, or for organizations that feel that external expertise or fresh perspectives will be beneficial for them. It is worth noting that Mastermind groups are often only as good as the participants and what they can bring to the group. Participants need to be committed, engaged and understand how to work in this context.
Coaching and mentoring
- Focused learning and development
- Filling skills gaps
- Working on a range of challenges over time
Receiving advice from a business coach or building a mentor/mentee relationship can be an effective way of resolving certain challenges. The one-to-one format of most coaching and mentor relationships can really help solve the challenges those individuals are having and benefit the organization as a result.
A great mentor can be invaluable when it comes to spotting potential problems before they arise and coming to understand a mentee very well has a host of other business benefits. You might run an internal mentorship program to help develop your team’s problem solving skills and strategies or as part of a large learning and development program. External coaches can also be an important part of your problem solving strategy, filling skills gaps for your management team or helping with specific business issues.
Now we’ve explored the problem solving process and the steps you will want to go through in order to have an effective session, let’s look at the skills you and your team need to be more effective problem solvers.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after, whatever industry or team you work in. Organizations are keen to employ people who are able to approach problems thoughtfully and find strong, realistic solutions. Whether you are a facilitator , a team leader or a developer, being an effective problem solver is a skill you’ll want to develop.
Problem solving skills form a whole suite of techniques and approaches that an individual uses to not only identify problems but to discuss them productively before then developing appropriate solutions.
Here are some of the most important problem solving skills everyone from executives to junior staff members should learn. We’ve also included an activity or exercise from the SessionLab library that can help you and your team develop that skill.
If you’re running a workshop or training session to try and improve problem solving skills in your team, try using these methods to supercharge your process!
Active listening
Active listening is one of the most important skills anyone who works with people can possess. In short, active listening is a technique used to not only better understand what is being said by an individual, but also to be more aware of the underlying message the speaker is trying to convey. When it comes to problem solving, active listening is integral for understanding the position of every participant and to clarify the challenges, ideas and solutions they bring to the table.
Some active listening skills include:
- Paying complete attention to the speaker.
- Removing distractions.
- Avoid interruption.
- Taking the time to fully understand before preparing a rebuttal.
- Responding respectfully and appropriately.
- Demonstrate attentiveness and positivity with an open posture, making eye contact with the speaker, smiling and nodding if appropriate. Show that you are listening and encourage them to continue.
- Be aware of and respectful of feelings. Judge the situation and respond appropriately. You can disagree without being disrespectful.
- Observe body language.
- Paraphrase what was said in your own words, either mentally or verbally.
- Remain neutral.
- Reflect and take a moment before responding.
- Ask deeper questions based on what is said and clarify points where necessary.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Analytical skills
All problem solving models require strong analytical skills, particularly during the beginning of the process and when it comes to analyzing how solutions have performed.
Analytical skills are primarily focused on performing an effective analysis by collecting, studying and parsing data related to a problem or opportunity.
It often involves spotting patterns, being able to see things from different perspectives and using observable facts and data to make suggestions or produce insight.
Analytical skills are also important at every stage of the problem solving process and by having these skills, you can ensure that any ideas or solutions you create or backed up analytically and have been sufficiently thought out.
Nine Whys #innovation #issue analysis #liberating structures With breathtaking simplicity, you can rapidly clarify for individuals and a group what is essentially important in their work. You can quickly reveal when a compelling purpose is missing in a gathering and avoid moving forward without clarity. When a group discovers an unambiguous shared purpose, more freedom and more responsibility are unleashed. You have laid the foundation for spreading and scaling innovations with fidelity.
Collaboration
Trying to solve problems on your own is difficult. Being able to collaborate effectively, with a free exchange of ideas, to delegate and be a productive member of a team is hugely important to all problem solving strategies.
Remember that whatever your role, collaboration is integral, and in a problem solving process, you are all working together to find the best solution for everyone.
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Communication
Being an effective communicator means being empathetic, clear and succinct, asking the right questions, and demonstrating active listening skills throughout any discussion or meeting.
In a problem solving setting, you need to communicate well in order to progress through each stage of the process effectively. As a team leader, it may also fall to you to facilitate communication between parties who may not see eye to eye. Effective communication also means helping others to express themselves and be heard in a group.
Bus Trip #feedback #communication #appreciation #closing #thiagi #team This is one of my favourite feedback games. I use Bus Trip at the end of a training session or a meeting, and I use it all the time. The game creates a massive amount of energy with lots of smiles, laughs, and sometimes even a teardrop or two.
Creative problem solving skills can be some of the best tools in your arsenal. Thinking creatively, being able to generate lots of ideas and come up with out of the box solutions is useful at every step of the process.
The kinds of problems you will likely discuss in a problem solving workshop are often difficult to solve, and by approaching things in a fresh, creative manner, you can often create more innovative solutions.
Having practical creative skills is also a boon when it comes to problem solving. If you can help create quality design sketches and prototypes in record time, it can help bring a team to alignment more quickly or provide a base for further iteration.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the fundamental problem solving skills you’ll want to develop when working on developing solutions. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, rationalize and evaluate while being aware of personal bias, outlying factors and remaining open-minded.
Defining and analyzing problems without deploying critical thinking skills can mean you and your team go down the wrong path. Developing solutions to complex issues requires critical thinking too – ensuring your team considers all possibilities and rationally evaluating them.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Data analysis
Though it shares lots of space with general analytical skills, data analysis skills are something you want to cultivate in their own right in order to be an effective problem solver.
Being good at data analysis doesn’t just mean being able to find insights from data, but also selecting the appropriate data for a given issue, interpreting it effectively and knowing how to model and present that data. Depending on the problem at hand, it might also include a working knowledge of specific data analysis tools and procedures.
Having a solid grasp of data analysis techniques is useful if you’re leading a problem solving workshop but if you’re not an expert, don’t worry. Bring people into the group who has this skill set and help your team be more effective as a result.
Decision making
All problems need a solution and all solutions require that someone make the decision to implement them. Without strong decision making skills, teams can become bogged down in discussion and less effective as a result.
Making decisions is a key part of the problem solving process. It’s important to remember that decision making is not restricted to the leadership team. Every staff member makes decisions every day and developing these skills ensures that your team is able to solve problems at any scale. Remember that making decisions does not mean leaping to the first solution but weighing up the options and coming to an informed, well thought out solution to any given problem that works for the whole team.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
Dependability
Most complex organizational problems require multiple people to be involved in delivering the solution. Ensuring that the team and organization can depend on you to take the necessary actions and communicate where necessary is key to ensuring problems are solved effectively.
Being dependable also means working to deadlines and to brief. It is often a matter of creating trust in a team so that everyone can depend on one another to complete the agreed actions in the agreed time frame so that the team can move forward together. Being undependable can create problems of friction and can limit the effectiveness of your solutions so be sure to bear this in mind throughout a project.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important skill for any successful team member, whether communicating internally or with clients or users. In the problem solving process, emotional intelligence means being attuned to how people are feeling and thinking, communicating effectively and being self-aware of what you bring to a room.
There are often differences of opinion when working through problem solving processes, and it can be easy to let things become impassioned or combative. Developing your emotional intelligence means being empathetic to your colleagues and managing your own emotions throughout the problem and solution process. Be kind, be thoughtful and put your points across care and attention.
Being emotionally intelligent is a skill for life and by deploying it at work, you can not only work efficiently but empathetically. Check out the emotional culture workshop template for more!
Facilitation
As we’ve clarified in our facilitation skills post, facilitation is the art of leading people through processes towards agreed-upon objectives in a manner that encourages participation, ownership, and creativity by all those involved. While facilitation is a set of interrelated skills in itself, the broad definition of facilitation can be invaluable when it comes to problem solving. Leading a team through a problem solving process is made more effective if you improve and utilize facilitation skills – whether you’re a manager, team leader or external stakeholder.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Flexibility
Being flexible is a vital skill when it comes to problem solving. This does not mean immediately bowing to pressure or changing your opinion quickly: instead, being flexible is all about seeing things from new perspectives, receiving new information and factoring it into your thought process.
Flexibility is also important when it comes to rolling out solutions. It might be that other organizational projects have greater priority or require the same resources as your chosen solution. Being flexible means understanding needs and challenges across the team and being open to shifting or arranging your own schedule as necessary. Again, this does not mean immediately making way for other projects. It’s about articulating your own needs, understanding the needs of others and being able to come to a meaningful compromise.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Working in any group can lead to unconscious elements of groupthink or situations in which you may not wish to be entirely honest. Disagreeing with the opinions of the executive team or wishing to save the feelings of a coworker can be tricky to navigate, but being honest is absolutely vital when to comes to developing effective solutions and ensuring your voice is heard.
Remember that being honest does not mean being brutally candid. You can deliver your honest feedback and opinions thoughtfully and without creating friction by using other skills such as emotional intelligence.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Initiative
The problem solving process is multi-faceted and requires different approaches at certain points of the process. Taking initiative to bring problems to the attention of the team, collect data or lead the solution creating process is always valuable. You might even roadtest your own small scale solutions or brainstorm before a session. Taking initiative is particularly effective if you have good deal of knowledge in that area or have ownership of a particular project and want to get things kickstarted.
That said, be sure to remember to honor the process and work in service of the team. If you are asked to own one part of the problem solving process and you don’t complete that task because your initiative leads you to work on something else, that’s not an effective method of solving business challenges.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Impartiality
A particularly useful problem solving skill for product owners or managers is the ability to remain impartial throughout much of the process. In practice, this means treating all points of view and ideas brought forward in a meeting equally and ensuring that your own areas of interest or ownership are not favored over others.
There may be a stage in the process where a decision maker has to weigh the cost and ROI of possible solutions against the company roadmap though even then, ensuring that the decision made is based on merit and not personal opinion.
Empathy map #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis An empathy map is a tool to help a design team to empathize with the people they are designing for. You can make an empathy map for a group of people or for a persona. To be used after doing personas when more insights are needed.
Being a good leader means getting a team aligned, energized and focused around a common goal. In the problem solving process, strong leadership helps ensure that the process is efficient, that any conflicts are resolved and that a team is managed in the direction of success.
It’s common for managers or executives to assume this role in a problem solving workshop, though it’s important that the leader maintains impartiality and does not bulldoze the group in a particular direction. Remember that good leadership means working in service of the purpose and team and ensuring the workshop is a safe space for employees of any level to contribute. Take a look at our leadership games and activities post for more exercises and methods to help improve leadership in your organization.
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
In the context of problem solving, mediation is important in keeping a team engaged, happy and free of conflict. When leading or facilitating a problem solving workshop, you are likely to run into differences of opinion. Depending on the nature of the problem, certain issues may be brought up that are emotive in nature.
Being an effective mediator means helping those people on either side of such a divide are heard, listen to one another and encouraged to find common ground and a resolution. Mediating skills are useful for leaders and managers in many situations and the problem solving process is no different.
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Planning
Solving organizational problems is much more effective when following a process or problem solving model. Planning skills are vital in order to structure, deliver and follow-through on a problem solving workshop and ensure your solutions are intelligently deployed.
Planning skills include the ability to organize tasks and a team, plan and design the process and take into account any potential challenges. Taking the time to plan carefully can save time and frustration later in the process and is valuable for ensuring a team is positioned for success.
3 Action Steps #hyperisland #action #remote-friendly This is a small-scale strategic planning session that helps groups and individuals to take action toward a desired change. It is often used at the end of a workshop or programme. The group discusses and agrees on a vision, then creates some action steps that will lead them towards that vision. The scope of the challenge is also defined, through discussion of the helpful and harmful factors influencing the group.
Prioritization
As organisations grow, the scale and variation of problems they face multiplies. Your team or is likely to face numerous challenges in different areas and so having the skills to analyze and prioritize becomes very important, particularly for those in leadership roles.
A thorough problem solving process is likely to deliver multiple solutions and you may have several different problems you wish to solve simultaneously. Prioritization is the ability to measure the importance, value, and effectiveness of those possible solutions and choose which to enact and in what order. The process of prioritization is integral in ensuring the biggest challenges are addressed with the most impactful solutions.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Project management
Some problem solving skills are utilized in a workshop or ideation phases, while others come in useful when it comes to decision making. Overseeing an entire problem solving process and ensuring its success requires strong project management skills.
While project management incorporates many of the other skills listed here, it is important to note the distinction of considering all of the factors of a project and managing them successfully. Being able to negotiate with stakeholders, manage tasks, time and people, consider costs and ROI, and tie everything together is massively helpful when going through the problem solving process.
Record keeping
Working out meaningful solutions to organizational challenges is only one part of the process. Thoughtfully documenting and keeping records of each problem solving step for future consultation is important in ensuring efficiency and meaningful change.
For example, some problems may be lower priority than others but can be revisited in the future. If the team has ideated on solutions and found some are not up to the task, record those so you can rule them out and avoiding repeating work. Keeping records of the process also helps you improve and refine your problem solving model next time around!
Personal Kanban #gamestorming #action #agile #project planning Personal Kanban is a tool for organizing your work to be more efficient and productive. It is based on agile methods and principles.
Research skills
Conducting research to support both the identification of problems and the development of appropriate solutions is important for an effective process. Knowing where to go to collect research, how to conduct research efficiently, and identifying pieces of research are relevant are all things a good researcher can do well.
In larger groups, not everyone has to demonstrate this ability in order for a problem solving workshop to be effective. That said, having people with research skills involved in the process, particularly if they have existing area knowledge, can help ensure the solutions that are developed with data that supports their intention. Remember that being able to deliver the results of research efficiently and in a way the team can easily understand is also important. The best data in the world is only as effective as how it is delivered and interpreted.
Customer experience map #ideation #concepts #research #design #issue analysis #remote-friendly Customer experience mapping is a method of documenting and visualizing the experience a customer has as they use the product or service. It also maps out their responses to their experiences. To be used when there is a solution (even in a conceptual stage) that can be analyzed.
Risk management
Managing risk is an often overlooked part of the problem solving process. Solutions are often developed with the intention of reducing exposure to risk or solving issues that create risk but sometimes, great solutions are more experimental in nature and as such, deploying them needs to be carefully considered.
Managing risk means acknowledging that there may be risks associated with more out of the box solutions or trying new things, but that this must be measured against the possible benefits and other organizational factors.
Be informed, get the right data and stakeholders in the room and you can appropriately factor risk into your decision making process.
Decisions, Decisions… #communication #decision making #thiagi #action #issue analysis When it comes to decision-making, why are some of us more prone to take risks while others are risk-averse? One explanation might be the way the decision and options were presented. This exercise, based on Kahneman and Tversky’s classic study , illustrates how the framing effect influences our judgement and our ability to make decisions . The participants are divided into two groups. Both groups are presented with the same problem and two alternative programs for solving them. The two programs both have the same consequences but are presented differently. The debriefing discussion examines how the framing of the program impacted the participant’s decision.
Team-building
No single person is as good at problem solving as a team. Building an effective team and helping them come together around a common purpose is one of the most important problem solving skills, doubly so for leaders. By bringing a team together and helping them work efficiently, you pave the way for team ownership of a problem and the development of effective solutions.
In a problem solving workshop, it can be tempting to jump right into the deep end, though taking the time to break the ice, energize the team and align them with a game or exercise will pay off over the course of the day.
Remember that you will likely go through the problem solving process multiple times over an organization’s lifespan and building a strong team culture will make future problem solving more effective. It’s also great to work with people you know, trust and have fun with. Working on team building in and out of the problem solving process is a hallmark of successful teams that can work together to solve business problems.
9 Dimensions Team Building Activity #ice breaker #teambuilding #team #remote-friendly 9 Dimensions is a powerful activity designed to build relationships and trust among team members. There are 2 variations of this icebreaker. The first version is for teams who want to get to know each other better. The second version is for teams who want to explore how they are working together as a team.
Time management
The problem solving process is designed to lead a team from identifying a problem through to delivering a solution and evaluating its effectiveness. Without effective time management skills or timeboxing of tasks, it can be easy for a team to get bogged down or be inefficient.
By using a problem solving model and carefully designing your workshop, you can allocate time efficiently and trust that the process will deliver the results you need in a good timeframe.
Time management also comes into play when it comes to rolling out solutions, particularly those that are experimental in nature. Having a clear timeframe for implementing and evaluating solutions is vital for ensuring their success and being able to pivot if necessary.
Improving your skills at problem solving is often a career-long pursuit though there are methods you can use to make the learning process more efficient and to supercharge your problem solving skillset.
Remember that the skills you need to be a great problem solver have a large overlap with those skills you need to be effective in any role. Investing time and effort to develop your active listening or critical thinking skills is valuable in any context. Here are 7 ways to improve your problem solving skills.
Share best practices
Remember that your team is an excellent source of skills, wisdom, and techniques and that you should all take advantage of one another where possible. Best practices that one team has for solving problems, conducting research or making decisions should be shared across the organization. If you have in-house staff that have done active listening training or are data analysis pros, have them lead a training session.
Your team is one of your best resources. Create space and internal processes for the sharing of skills so that you can all grow together.
Ask for help and attend training
Once you’ve figured out you have a skills gap, the next step is to take action to fill that skills gap. That might be by asking your superior for training or coaching, or liaising with team members with that skill set. You might even attend specialized training for certain skills – active listening or critical thinking, for example, are business-critical skills that are regularly offered as part of a training scheme.
Whatever method you choose, remember that taking action of some description is necessary for growth. Whether that means practicing, getting help, attending training or doing some background reading, taking active steps to improve your skills is the way to go.
Learn a process
Problem solving can be complicated, particularly when attempting to solve large problems for the first time. Using a problem solving process helps give structure to your problem solving efforts and focus on creating outcomes, rather than worrying about the format.
Tools such as the seven-step problem solving process above are effective because not only do they feature steps that will help a team solve problems, they also develop skills along the way. Each step asks for people to engage with the process using different skills and in doing so, helps the team learn and grow together. Group processes of varying complexity and purpose can also be found in the SessionLab library of facilitation techniques . Using a tried and tested process and really help ease the learning curve for both those leading such a process, as well as those undergoing the purpose.
Effective teams make decisions about where they should and shouldn’t expend additional effort. By using a problem solving process, you can focus on the things that matter, rather than stumbling towards a solution haphazardly.
Create a feedback loop
Some skills gaps are more obvious than others. It’s possible that your perception of your active listening skills differs from those of your colleagues.
It’s valuable to create a system where team members can provide feedback in an ordered and friendly manner so they can all learn from one another. Only by identifying areas of improvement can you then work to improve them.
Remember that feedback systems require oversight and consideration so that they don’t turn into a place to complain about colleagues. Design the system intelligently so that you encourage the creation of learning opportunities, rather than encouraging people to list their pet peeves.
While practice might not make perfect, it does make the problem solving process easier. If you are having trouble with critical thinking, don’t shy away from doing it. Get involved where you can and stretch those muscles as regularly as possible.
Problem solving skills come more naturally to some than to others and that’s okay. Take opportunities to get involved and see where you can practice your skills in situations outside of a workshop context. Try collaborating in other circumstances at work or conduct data analysis on your own projects. You can often develop those skills you need for problem solving simply by doing them. Get involved!
Use expert exercises and methods
Learn from the best. Our library of 700+ facilitation techniques is full of activities and methods that help develop the skills you need to be an effective problem solver. Check out our templates to see how to approach problem solving and other organizational challenges in a structured and intelligent manner.
There is no single approach to improving problem solving skills, but by using the techniques employed by others you can learn from their example and develop processes that have seen proven results.
Try new ways of thinking and change your mindset
Using tried and tested exercises that you know well can help deliver results, but you do run the risk of missing out on the learning opportunities offered by new approaches. As with the problem solving process, changing your mindset can remove blockages and be used to develop your problem solving skills.
Most teams have members with mixed skill sets and specialties. Mix people from different teams and share skills and different points of view. Teach your customer support team how to use design thinking methods or help your developers with conflict resolution techniques. Try switching perspectives with facilitation techniques like Flip It! or by using new problem solving methodologies or models. Give design thinking, liberating structures or lego serious play a try if you want to try a new approach. You will find that framing problems in new ways and using existing skills in new contexts can be hugely useful for personal development and improving your skillset. It’s also a lot of fun to try new things. Give it a go!
Encountering business challenges and needing to find appropriate solutions is not unique to your organization. Lots of very smart people have developed methods, theories and approaches to help develop problem solving skills and create effective solutions. Learn from them!
Books like The Art of Thinking Clearly , Think Smarter, or Thinking Fast, Thinking Slow are great places to start, though it’s also worth looking at blogs related to organizations facing similar problems to yours, or browsing for success stories. Seeing how Dropbox massively increased growth and working backward can help you see the skills or approach you might be lacking to solve that same problem. Learning from others by reading their stories or approaches can be time-consuming but ultimately rewarding.
A tired, distracted mind is not in the best position to learn new skills. It can be tempted to burn the candle at both ends and develop problem solving skills outside of work. Absolutely use your time effectively and take opportunities for self-improvement, though remember that rest is hugely important and that without letting your brain rest, you cannot be at your most effective.
Creating distance between yourself and the problem you might be facing can also be useful. By letting an idea sit, you can find that a better one presents itself or you can develop it further. Take regular breaks when working and create a space for downtime. Remember that working smarter is preferable to working harder and that self-care is important for any effective learning or improvement process.
Want to design better group processes?
Over to you
Now we’ve explored some of the key problem solving skills and the problem solving steps necessary for an effective process, you’re ready to begin developing more effective solutions and leading problem solving workshops.
Need more inspiration? Check out our post on problem solving activities you can use when guiding a group towards a great solution in your next workshop or meeting. Have questions? Did you have a great problem solving technique you use with your team? Get in touch in the comments below. We’d love to chat!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Self-Assessment • 20 min read
How Good Is Your Problem Solving?
Use a systematic approach..
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Good problem solving skills are fundamentally important if you're going to be successful in your career.
But problems are something that we don't particularly like.
They're time-consuming.
They muscle their way into already packed schedules.
They force us to think about an uncertain future.
And they never seem to go away!
That's why, when faced with problems, most of us try to eliminate them as quickly as possible. But have you ever chosen the easiest or most obvious solution – and then realized that you have entirely missed a much better solution? Or have you found yourself fixing just the symptoms of a problem, only for the situation to get much worse?
To be an effective problem-solver, you need to be systematic and logical in your approach. This quiz helps you assess your current approach to problem solving. By improving this, you'll make better overall decisions. And as you increase your confidence with solving problems, you'll be less likely to rush to the first solution – which may not necessarily be the best one.
Once you've completed the quiz, we'll direct you to tools and resources that can help you make the most of your problem-solving skills.
How Good Are You at Solving Problems?
Instructions.
For each statement, click the button in the column that best describes you. Please answer questions as you actually are (rather than how you think you should be), and don't worry if some questions seem to score in the 'wrong direction'. When you are finished, please click the 'Calculate My Total' button at the bottom of the test.
Answering these questions should have helped you recognize the key steps associated with effective problem solving.
This quiz is based on Dr Min Basadur's Simplexity Thinking problem-solving model. This eight-step process follows the circular pattern shown below, within which current problems are solved and new problems are identified on an ongoing basis. This assessment has not been validated and is intended for illustrative purposes only.
Below, we outline the tools and strategies you can use for each stage of the problem-solving process. Enjoy exploring these stages!
Step 1: Find the Problem (Questions 7, 12)
Some problems are very obvious, however others are not so easily identified. As part of an effective problem-solving process, you need to look actively for problems – even when things seem to be running fine. Proactive problem solving helps you avoid emergencies and allows you to be calm and in control when issues arise.
These techniques can help you do this:
PEST Analysis helps you pick up changes to your environment that you should be paying attention to. Make sure too that you're watching changes in customer needs and market dynamics, and that you're monitoring trends that are relevant to your industry.
Risk Analysis helps you identify significant business risks.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis helps you identify possible points of failure in your business process, so that you can fix these before problems arise.
After Action Reviews help you scan recent performance to identify things that can be done better in the future.
Where you have several problems to solve, our articles on Prioritization and Pareto Analysis help you think about which ones you should focus on first.
Step 2: Find the Facts (Questions 10, 14)
After identifying a potential problem, you need information. What factors contribute to the problem? Who is involved with it? What solutions have been tried before? What do others think about the problem?
If you move forward to find a solution too quickly, you risk relying on imperfect information that's based on assumptions and limited perspectives, so make sure that you research the problem thoroughly.
Step 3: Define the Problem (Questions 3, 9)
Now that you understand the problem, define it clearly and completely. Writing a clear problem definition forces you to establish specific boundaries for the problem. This keeps the scope from growing too large, and it helps you stay focused on the main issues.
A great tool to use at this stage is CATWOE . With this process, you analyze potential problems by looking at them from six perspectives, those of its Customers; Actors (people within the organization); the Transformation, or business process; the World-view, or top-down view of what's going on; the Owner; and the wider organizational Environment. By looking at a situation from these perspectives, you can open your mind and come to a much sharper and more comprehensive definition of the problem.
Cause and Effect Analysis is another good tool to use here, as it helps you think about the many different factors that can contribute to a problem. This helps you separate the symptoms of a problem from its fundamental causes.
Step 4: Find Ideas (Questions 4, 13)
With a clear problem definition, start generating ideas for a solution. The key here is to be flexible in the way you approach a problem. You want to be able to see it from as many perspectives as possible. Looking for patterns or common elements in different parts of the problem can sometimes help. You can also use metaphors and analogies to help analyze the problem, discover similarities to other issues, and think of solutions based on those similarities.
Traditional brainstorming and reverse brainstorming are very useful here. By taking the time to generate a range of creative solutions to the problem, you'll significantly increase the likelihood that you'll find the best possible solution, not just a semi-adequate one. Where appropriate, involve people with different viewpoints to expand the volume of ideas generated.
Tip: Don't evaluate your ideas until step 5. If you do, this will limit your creativity at too early a stage.
Step 5: Select and Evaluate (Questions 6, 15)
After finding ideas, you'll have many options that must be evaluated. It's tempting at this stage to charge in and start discarding ideas immediately. However, if you do this without first determining the criteria for a good solution, you risk rejecting an alternative that has real potential.
Decide what elements are needed for a realistic and practical solution, and think about the criteria you'll use to choose between potential solutions.
Paired Comparison Analysis , Decision Matrix Analysis and Risk Analysis are useful techniques here, as are many of the specialist resources available within our Decision-Making section . Enjoy exploring these!
Step 6: Plan (Questions 1, 16)
You might think that choosing a solution is the end of a problem-solving process. In fact, it's simply the start of the next phase in problem solving: implementation. This involves lots of planning and preparation. If you haven't already developed a full Risk Analysis in the evaluation phase, do so now. It's important to know what to be prepared for as you begin to roll out your proposed solution.
The type of planning that you need to do depends on the size of the implementation project that you need to set up. For small projects, all you'll often need are Action Plans that outline who will do what, when, and how. Larger projects need more sophisticated approaches – you'll find out more about these in the article What is Project Management? And for projects that affect many other people, you'll need to think about Change Management as well.
Here, it can be useful to conduct an Impact Analysis to help you identify potential resistance as well as alert you to problems you may not have anticipated. Force Field Analysis will also help you uncover the various pressures for and against your proposed solution. Once you've done the detailed planning, it can also be useful at this stage to make a final Go/No-Go Decision , making sure that it's actually worth going ahead with the selected option.
Step 7: Sell the Idea (Questions 5, 8)
As part of the planning process, you must convince other stakeholders that your solution is the best one. You'll likely meet with resistance, so before you try to “sell” your idea, make sure you've considered all the consequences.
As you begin communicating your plan, listen to what people say, and make changes as necessary. The better the overall solution meets everyone's needs, the greater its positive impact will be! For more tips on selling your idea, read our article on Creating a Value Proposition and use our Sell Your Idea Skillbook.
Step 8: Act (Questions 2, 11)
Finally, once you've convinced your key stakeholders that your proposed solution is worth running with, you can move on to the implementation stage. This is the exciting and rewarding part of problem solving, which makes the whole process seem worthwhile.
This action stage is an end, but it's also a beginning: once you've completed your implementation, it's time to move into the next cycle of problem solving by returning to the scanning stage. By doing this, you'll continue improving your organization as you move into the future.
Problem solving is an exceptionally important workplace skill.
Being a competent and confident problem solver will create many opportunities for you. By using a well-developed model like Simplexity Thinking for solving problems, you can approach the process systematically, and be comfortable that the decisions you make are solid.
Given the unpredictable nature of problems, it's very reassuring to know that, by following a structured plan, you've done everything you can to resolve the problem to the best of your ability.
This assessment has not been validated and is intended for illustrative purposes only. It is just one of many Mind Tool quizzes that can help you to evaluate your abilities in a wide range of important career skills.
If you want to reproduce this quiz, you can purchase downloadable copies in our Store .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Problem Solving
4 Logical Fallacies
Avoid Common Types of Faulty Reasoning
Add comment
Comments (2)
Afkar Hashmi
😇 This tool is very useful for me.
over 1 year
Very impactful

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Negotiating With Confrontational Customers

Managing Your Emotions at Work
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Coaching for team performance.
Improving Productivity by Improving Relationships
Empathy at Work
Developing Skills to Understand Other People
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Sharing creativity around.
A Group Exercise That Encourages Creativity Through Interpretation
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Decision Making
Member Podcast
An Effective Assessment Method of Higher-Order Thinking Skills (Problem-Solving, Critical Thinking, Creative Thinking, and Decision-Making) in Engineering and Humanities
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cognitive ability test: A pre-employment aptitude test assesses individuals' abilities such as critical thinking, verbal reasoning, numerical ability, problem-solving, decision-making, etc., which are indicators of a person's intelligence quotient (IQ). The test results provide data about on-the-job performance.
A variety of assessment techniques that may be used for assessing problem-solving skills and other higher-order thinking skills (as listed by Angelo and Cross) are listed below. Each can be readily modified for use in a range of curricula. To determine which assessment technique to use for which course, review the "Pros," "Cons," and "Caveats ...
Research is needed to compare and contrast assessment methods with problem-solving types. What has become obvious is the premise that in order to adequately assess problem-solving skills and abilities, it is necessary to use more than one form of assessment.
Assessing complex problem-solving skills through the lens of decision making by Carl Wieman, Argenta Price. Introduction: Scientific problem solving as a core competency ... whether the solution method works; and so on. How well these decisions are made, in a relevant context, is amenable to accurate assessment. Such assessment provides a ...
with the problem is a central feature of the assessment. PISA 2012 problem solving is an assessment of individual problem-solving competency. Collaborative problem-solving skills - the skills required to solve problems as a member of a group - are essential for successful future employment,
of successful problem solving in all domains as "skill", "metaskill" and "will". The problem-solving assessment in PISA 2012 focuses on students' general reasoning skills, their ability to regulate problem-solving processes, and their willingness to do so, by confronting students with problems that do not require
Assessment and teaching are closely linked, because without accurate ways to measure problem-solving skills, it is impossible to evaluate and improve the methods for teaching these skills. Different aspects of expertise, problem-solving, and assessment of problem-solving have been studied over many decades.
Abstract. Arguably, constructive alignment has been the major challenge for assessment in the context of problem-based learning (PBL). PBL focuses on promoting abilities such as clinical reasoning, team skills and metacognition. PBL also aims to foster self-directed learning and deep learning as opposed to rote learning.
ASSESSING PROBLEM-SOLVING SKILLS Part I: The Context for Assessment* DONALD R. Wooos, THEODORA KouRTI, P HILIP E. Woon, HEATHER SHEARDOWN, CAMERON M. CROWE, AND JAMES M. DICKSON McMaster University • Hamilton, Ontario, CANADA LBS 4L7 An analysis of the future of engineering education suggests that problem-solving skills are needed by
Methods for assessing problem-solving learning outcomes vary with the nature of the problem. For simpler well-structured problems, answer correctness and process may be used along with ...
Critical thinking is one of the most frequently discussed higher order skills, believed to play a central role in logical thinking, decision making, and problem solving (Butler, 2012; Halpern, 2003).It is also a highly contentious skill in that researchers debate about its definition; its amenability to assessment; its degree of generality or specificity; and the evidence of its practical ...
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. ... This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams. ... and assess the seriousness of the ...
Critical thinking and problem solving, as we define it, are the set of non-discipline specific cognitive skills people use to analyze vast amounts of information and creatively solve problems. We have broken those skills down into these five core components: Schema Development: The ability to learn vast amounts of information and organize it in ...
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
3.5 Problem-Solving Skills. Problem-solving is "a cognitive-behavioral process that includes identifying a problem, transforming a problem into a goal state, and finding and implementing alternative approaches to achieve the goals" . In the traditional approach, memorizing formulas and content in the book is the only way to solve a problem.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved. 6. Solution implementation. This is what we were waiting for!
mathematical problem-solving skills, and effect/role of assessments on students' mathematical problem-solving skills' as keywords, 63 studies were obtained. With a deep analysis of the collected data, 32 studies were related to teaching strategies in enhancing problem-solving skills, and these studies were filtered out, while
The exclusion criteria include: a) "collaborative problem solving skills" is not investigated by the research; (b) the article is a conceptual or theoretical work, or an analysis of CPS behaviors or processes, or a review of existing studies; (c) no information on assessment is reported; and (d) computer-based technologies are not used in ...
These questions assess both problem-solving skills and content knowledge, because students would need to know about or research the resources and methods available to farmers and the local government. When asking questions that have multiple proposed solutions, you can also ask students to evaluate ...
Problem-solving is a vital skill for coping with various challenges in life. This webpage explains the different strategies and obstacles that can affect how you solve problems, and offers tips on how to improve your problem-solving skills. Learn how to identify, analyze, and overcome problems with Verywell Mind.
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Enjoy exploring these stages! Step 1: Find the Problem (Questions 7, 12) Some problems are very obvious, however others are not so easily identified. As part of an effective problem-solving process, you need to look actively for problems - even when things seem to be running fine.
Learning skills include the ability to learn or acquire basic knowledge and concepts across multiple dimensions, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, creative thinking, and decision-making.This work presents an assessment approach intended for evaluating and assessing students' higher-order thinking (HOT) skills. The assessment of higher-order thinking skills includes four subthinking ...
Cognitive Problem solving skills analytical and creative thinking were the top two in demand skills of 2023 and are also the top two skills predicted to grow in importance in the future. ... In the ever changing world of cyber security it is next to impossible to second guess the methods that hackers might use to infiltrate a network. However ...