
Topic Portal (1)
Teaching Case (1)
Portals (3)
Online Courses (1)
Thematic Lessons (2)
Teaching Pack Materials (6)
Activity (3)
Lesson Material (3)
Publication (2)
Web Portal (8)
Multimedia (1)
Middle-School Teachers (8)
High-School Teachers (10)
Digital/Media Literacy (5)
Data/Visualization (1)
Critical Thinking (10)
Leadership (1)
Global Learning (1)
Classroom (9)
Blended (10)
Online (11)
How can educators leverage the COVID-19 pandemic to engage students in active learning? This collection of resources was curated to support high-school and middle-school teachers in bringing timely, high-quality material on the current COVID-19 pandemic into the "classroom" whether it be online, hybrid or physical. Each tile within the collection brings together a key resource on the topic and some sample activities, discussion prompts, or tools to generate ideas for teaching and learning. This teaching pack is…

Teaching Pack: Lessons
How can educators leverage the COVID-19 pandemic to engage students in active learning? This collection of resources was curated to support high-school and middle-school teachers in bringing timely, high-quality material on the current COVID-19 pandemic into their "classrooms," whether digital or physical.
This online curriculum produced by the COVID-19 Student Response Team at Harvard Medical School (HMS) …
This online curriculum produced by the COVID-19 Student Response Team at Harvard Medical School (HMS) is a resource portal containing information about Coronavirus in three formats tailored to elementary school students, middle school students, and high school and college age students. Modules for elementary students include a guided series of printable coloring pages. Middle school students can learn the science behind viruses and the timeline of COVID-19 via a series of videos, readings, and interactive…
The purpose of this protocol is to design an art assignment that communicates public health …
The purpose of this protocol is to design an art assignment that communicates public health information. This is inspired by the United Nations Global Call Out to Creatives, a campaign to marshal creative efforts in translating critical public health message to different communities. A provocative or eye-catching piece of art, video, or audio can transform evidence into a format that is both attractive and memorable. Resources Students may want to refer to the following resources…
This collection of resources from The New York Times is designed to help students and …
This collection of resources from The New York Times is designed to help students and educators stay updated on the COVID-19 outbreak, think critically about information, consider the “essential” questions the pandemic raises about our world today. Popular resources include a lesson on how coronavirus hijacks cell function, weekly data literacy activities, short Film Club documentaries on COVID-related stories, and daily writing prompts for students. The page is regularly updated with new student-centered content from…
This video and facilitator guide from KQED, aimed at students, talks about the importance of …
This video and facilitator guide from KQED, aimed at students, talks about the importance of social distancing, even for young people. The facilitator guide includes prompts for students to practice their writing, specifically about their personal experiences social distancing and their tips for survival. Educators have the option to integrate the resource directly to Google Classroom.
These resources from BrainPOP offer multiple ways to teach about coronavirus that are most appropriate …
These resources from BrainPOP offer multiple ways to teach about coronavirus that are most appropriate for younger students. After watching the anchor video, students can take quizzes or make a visual map of their learning through BrainPOP’s web-based tool. It also includes a worksheet about prevention, graphic organizer on fact vs. fear, and vocabulary flash cards.
This resource collection from Scholastic Classroom Magazines brings together age-appropriate information for teaching about the …
This resource collection from Scholastic Classroom Magazines brings together age-appropriate information for teaching about the coronavirus. Among the resources for middle school and high school students is an interview with a physicist who explains how sneezes (and mucus droplets) spread the disease, as well as an accessible article on pandemic preparedness.
This web portal from the Viswanath Lab at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public …
This web portal from the Viswanath Lab at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health brings together a wide variety of credible Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) related information that is easy to access, digest, and act upon. The rapid spread of COVID-19 has simultaneously led to a rapid spread of information, misinformation, and disinformation related to the pandemic. This portal seeks to aid journalists, non-governmental organizations, and community members in navigating this deluge of…
These activities from Facing History and Ourselves encourage students to grapple with the ethics around …
These activities from Facing History and Ourselves encourage students to grapple with the ethics around social distancing, a new social norm with the spread of COVID-19. In particular, the activities in this resource help students explore the meaning of “common good” and consider its implications for collective action. Each activity includes reflection questions, which students can respond to through text, virtual discussion, or multimedia. This resource also includes student-facing Google Slides that can be integrated…
This resource library from National Geographic includes photos, videos, maps, and activities related to infectious …
This resource library from National Geographic includes photos, videos, maps, and activities related to infectious diseases. The resources within the collection focus on bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. The resources within the collection would be useful to educators seeking to contextualize COVID-19 within the context of other infectious disease prevention and treatment efforts. Educators can filter by content type (e.g., video, infographic, activity) or by subject (e.g., biology, social studies, geography). Most resources are suitable…
This case vignette will be most useful to high-school educators looking to introduce COVID-19 to …
This case vignette will be most useful to high-school educators looking to introduce COVID-19 to their classroom. The case focuses on understanding why local and federal governments need to "implement guidelines for social distancing". Students will learn what "social distancing" means, and how it can involve population-based measures such as canceling group events and closing public spaces as well as individual-level behavior change such as staying home, working remotely, and avoiding of crowds. Students will…
This documentary uncovers the history of the 1918 flu epidemic—the worst epidemic in American history, …
This documentary uncovers the history of the 1918 flu epidemic—the worst epidemic in American history, which killed over 600,000 people. Since 2018 represents the centenary of this deadly epidemic, many are drawing parallels to the current, deadly flu season. The film is accompanied by a teacher’s guide, a timeline tracking the disease’s spread, and a photo gallery of the medical investigation of influenza.
This article in the Biomedical Science Journal for Teens compares two non-pharmaceutical approaches for addressing …
This article in the Biomedical Science Journal for Teens compares two non-pharmaceutical approaches for addressing COVID-19: mitigation approaches, which emphasize protecting the most vulnerable in the population, and suppression approaches, which minimize the spread of the disease until treatment is available. This article, written in plain language accessible to middle school and high school audiences, bases this comparison on a computer model for flu pandemic simulations, modified for COVID-19. The authors find that suppression strategies—which…
Welcome to the Incubator's Digital Repository
Our digital repository is a searchable library of selected resources that support learning and teaching about interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary population health challenges across the globe. It includes general resources (e.g., reports, articles, country profiles, data, etc.) and teaching resources (e.g., teaching cases, curated resource packs, and lesson-based teaching packs). Open-access sources are prioritized, and include peer-reviewed journals, global reports from multilateral institutions and alliances, and knowledge-related public goods from reputable research and policy organizations.
Take a Video Tour
Download a 2-Page Explainer (PDF)
Download Self-Guided Tour (PDF)
- Create mode – the default mode when you create a requisition and PunchOut to Bio-Rad. You can create and edit multiple shopping carts
- Edit mode – allows you to edit or modify an existing requisition (prior to submitting). You will be able to modify only the cart that you have PunchedOut to, and will not have access to any other carts
- Inspect mode – when you PunchOut to Bio-Rad from a previously created requisition but without initiating an Edit session, you will be in this mode. You cannot modify any Cart contents
- Order Status
- Quick Order
- Bioprocessing
- Clinical Research
- Drug Discovery & Development
- Translational Research
- Wastewater Surveillance
- Diabetes / Hemoglobinopathies
- Hospital / Clinical Core Lab
- Infectious Disease
- Newborn Screening
- Transfusion Medicine
- Quality Control
- Food & Beverage Testing
- Classroom Education
- Bioprocess Analytics
- Bioprocess Chromatography
- Cell Line Development / Characterization
- Cell Research
- Gene Expression Analysis
- Mutation Detection
- Pathogen Detection
- Protein Expression / Characterization / Quantitation
- Viral / Vector Characterization
- Bacteriology
- Blood Typing, Screening & Antibody Identification
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Infectious Disease Testing
- Molecular Diagnostics
- Data Management Systems
- Proficiency Testing & EQAS
- Verification & Validation
- Food & Beverage Safety Testing
- Cannabis Testing
- Veterinary Diagnostics
- Water Quality Testing
- Biotechnology Textbook & Program
- DNA, PCR & Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
- Genetic Engineering, Microbiology & Model Organisms
- Proteins, Enzymes & ELISA
- COVID-19 Assay & Research
- Cell Isolation & Analysis
- Chromatography
- Digital PCR
- Electrophoresis & Blotting
- Flow Cytometers
- Immunoassays
- PCR & qPCR
- Sample Preparation & Quantitation
- Transfection
- Autoimmune Testing
- Blood Typing & Antibody Detection
- Diabetes Testing
- Hemoglobinopathy Testing
- Microbiology Testing
- Quality Controls
- Software & Data Analysis
- Molecular Testing
- B2B Commerce Solutions
- Custom PCR Plastics & Reagents
- Expert Care Service
- New Labs & New Grants
- Remote Diagnostic Services
- Supply Center Program
- Instrument Service Support Plans
- Trade-Up Program
- Certificate of Analysis
- Literature Library
- Electronic IFUs
- Product Safety Data Sheets
- Quality Management Systems Certificates
- Quality Control Inserts
- Life Science
- Clinical Testing Solutions
- Bioprocess Chromatography Resources
- Classroom Resources
- Product News
- Corporate News
COVID-19 Teaching Resources

Your students may have a lot of questions about COVID-19, from how it spreads to how it is detected and how it can be treated. This presents a rich opportunity to teach key concepts in biology through the lens of an ongoing real-world context. Bio-Rad offers a flexible array of hands-on kits, free resources, and lessons to help you teach the biology and detection of the SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The Biology of SARS-CoV-2 and Detection Methods

What Is the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus?
Help your students understand the biology of SARS-CoV-2 by reviewing its origin, structure, and ways to prevent the spread of infection. This PowerPoint presentation walks you and your students through key biology concepts of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
Download PPT (PPT 16.3 MB)

How Do We Detect COVID-19?
Every day brings new developments in the race for effective and accurate COVID-19 testing, but most strategies are based on a few key fundamental technologies. This PowerPoint presentation explains some fundamental techniques and emerging strategies in COVID-19 detection.
Download PPT (PPT 23.3 MB)
Hands-On Laboratory Activities for Your Students
Teach your students the science behind SARS-CoV-2 detection using these hands-on laboratory activities. Use these three Bio-Rad Explorer Classroom Kits to teach relevant life science concepts in the context of COVID-19.
ELISA Antibody Detection
Several existing and emerging SARS-CoV-2 detection methods rely on the specificity of antibodies. In this activity, use real antibodies to determine whether simulated patients are or were infected with SARS-CoV-2.
This activity uses the reagents and antibodies from the ELISA Immuno Explorer Kit .
Download the instructions and presentation (PPT 23.3 MB)

PCR Detection
Investigate the real life spread of SARS-CoV-2 that occurred in a restaurant. In this activity, students use agarose gel electrophoresis to analyze pre-amplified DNA samples from simulated patients and propose ways the virus may have spread.
This activity uses the Virus Detection and Transmission Kit .
Download the instructions and presentation (PPT 13.4 MB)
Real-Time PCR Detection
Real-time PCR is currently the gold standard for COVID-19 diagnosis. In this activity, use real-time PCR to detect SARS-CoV-2 in simulated patient samples. Students analyze amplification and melt curves to determine which patients are positive and then quantify viral RNA.
This activity uses the reagents and DNA samples from the Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Real-Time PCR Starter Kit .
Download the instructions and presentation (PPT 27.4 MB)
Additional Resources
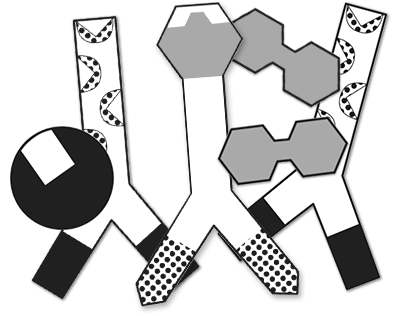
ELISA Paper Model Activity
Your students can use this paper model activity to get a solid grasp of the components of an ELISA and how they work together in antibody/antigen detection.
Download PDF (PDF 2.6 MB) Download PPT (PPT 65.9 MB)
Animation: ELISA Antibody Test Animation: ELISA Antigen Test
Visualize two types of ELISA in these step-by-step animations.
Animation: Polymerase Chain Reaction
The steps of PCR are best visualized through animation.
These pages list our product offerings in these areas. Some products have limited regional availability. If you have a specific question about products available in your area, please contact your local sales office or representative .
- Bio-rad LinkedIn Bio-rad Antibodies LinkedIn
- Bio-rad YouTube Bio-rad Antibodies YouTube
- Bio-rad Twitter Bio-rad Antibodies Twitter
- Bio-rad Facebook Bio-rad Antibodies Facebook
- Bio-rad Instagram
- Bio-rad Pinterest
About Bio-Rad
Bioradiations, sustainability, investor relations.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction
The global outbreak of COVID-19 has certainly taken an overwhelming toll on everyone. People have lost their jobs, their homes, and even their lives. There is no getting past the fact that the overall impact on the world has been negative, but it is important to realize that positive aspects of the pandemic have been overshadowed by the many negative ones. In an attempt to slow the spread of the disease, many governments made the decision to implement lockdowns, forcing billions to work and take classes from home, in many cases for the first times in their lives. Not only have these lockdowns altered the way that people work and go to school, but they have altered the mental health of everyone and the environmental health of the world around us.
Connection to STS Theory
The positive impacts of technology during the pandemic stems from the Modernization Theory, posing that there is a relationship between societal and technological advancements as societies shift to become updated as opposed to traditional. Technology has brought about lots of resistance to COVID that would not have been possible without the drastic advancements in science over the years. Thanks to these advancements, relationships can stay connected, students can continue to learn, jobs can stay open, and the environment can subtly improve. Our modernized world is well enough suited to take on the troubling times that COVID-19 has brought along.
Technology with School – Relates to College Students
Remote learning has allowed each of us to learn from the comfort of our homes. Working remotely has also allowed us to work from our living rooms. The perks of both are not having to wake up early to drive to work in the mornings, not having to sit at an office desk for eight hours a day, and not having to walk to class. Working remotely and remote learning has also been a time saver for many individuals.
According to Business Insider, there are a few tips that will help students be successful while being virtual. One tip is to clean your workspace. It is important to have a space, just like you would at a desk in a classroom, to ensure that you are paying attention to the professor. It is always important to engage with your professor. It is important to contact your professor outside of the class section to ensure that you are retaining the information. Another tip that the Business Insider recommends is to connect with your classmates. It is vital to build connections with your classmates that will help everyone have a comfortable environment to ask questions.
Personal Growth
In March 2020, the COVID-19 outbreak hit the United States. College students were forced to leave their beloved campuses and go home to finish their semesters online. For some, it meant their schoolwork load was lightened and they could sleep until noon. For others, it meant their plans of graduating and having a job for the summer were in jeopardy. Regardless of their situation, one thing was likely the same for all: lots of time alone. Students found things to do to pass the time. Some learned to cook, some started exercising at home, and others had more time to do what they already loved.
Ethan, a student at the University of South Carolina, used the time to start lifting weights in his home gym. In the United States, sales of home gym equipment doubled, reaching nearly $2.4 Billion in revenue. Store shelves were entirely sold out of exercise equipment. Many students like Ethan report that exercising was one of the biggest changes they made during COVID lockdown.
Other students, such as Cam, found an opportunity to get in a better place mentally. “I learned not to take things for granted. My relationship with my family has gotten better. I’m a much stronger person,” the Clemson student reported. Grayson, an athlete at Winthrop University, reported that it made him have a more positive outlook on being by himself. A student that elected to remain anonymous was just happy they could wake up later and not have to brush their teeth as much because of masks. Whether a dentist would approve of that habit or not, an improvement in mental health is a win in anyone’s book.
A select few students decided to challenge themselves in a world where all odds are stacked against them. Dean, a freshman at the University of South Carolina, decided to start his own bracelet and T-Shirt business in a time when small businesses all over the country were facing a grave threat of going out of business. All the while, he learned to play the guitar and uploaded his songs to SoundCloud, he reported.
Whether college students decided to get a six-pack or learned how to sew, almost everyone found something constructive and positive to do with their extra free time. The college students of COVID-19 learned what it meant to make the best of an unfortunate situation. Things may have looked bleak and frightening, but they learned how to manage those feelings and make something positive out of it.
Change in Workforce
Before the pandemic, many companies did not allow employees to work from home. Also, many companies would not even allow employees to take home items, such as laptops, as a safety precaution. According to Stanford Medicine, rapid innovation and implementation of technology has allowed for the employees to navigate the challenges. It states that it is clear that technology has transformed our typical daily workflow. Technology has also made it easier to connect with the patients during the pandemic.
The Pew Research Center states “about half of new teleworkers say they have more flexibility now and that majority who are working in person worry about virus exposure.” In December 2020, 71% of the workers that were surveyed were doing their job from home all or most of the time. Of those workers, more than half said if they were given the choice that they would want to keep working from home even after the pandemic. Among those who are currently working from home, most say that it has been easy to meet deadlines and complete projects on time without interruptions.
Environmental Improvements
Before the COVID-19 outbreak, a typical day consisted of billions of people across the globe commuting to work or school, whether that be through public buses or trains, driving themselves in cars, or some other means of transportation. As all these vehicles were used, immeasurable amounts of gases and chemicals were released into the atmosphere. As infection numbers and the death toll increased, most nations began enforcing lockdown protocols, and these mandates affected almost 3 billion people (Rume & Islam, 2020). Businesses and factories shut down or people began working from home, meaning they no longer needed to drive to work. In an attempt to stunt transmission, the majority of international travel was halted, limiting tourism, which also had a great impact. Since industrialization has advanced in major cities across the globe, the amount of Greenhouse Gases that have been emitted is alarming. Cars, buses, trains, industries, factories all release harmful chemicals due to the burning of fossil fuels or other energy sources. When these pollutants enter the atmosphere, they cause a variety of issues. It decreases overall air quality and visibility, and can be dangerous to those inhali ng the m.
According to research performed by Shakeel Ahmad Bhat and a group of other scientists from India, China, and the United Kingdom, Delhi, India is one of the most polluted cities in the world (Bhat et al, 2021). The city is highly industrialized and densely populated, contributing to the elevated levels of particulate matter in the air. Particulate matter is small pollutant liquid droplets and solid particles in the air (Environmental Protection Agency, 2020). When inhaled, they can burrow deep into the lungs and even the bloodstream and cause serious damage to a person, “particularly respiratory ailments” (Bhat et al, 2021). The two types of particulate matter are PM10 and PM2.5, and their numbers correspond to the size of the particles (their diameters in units of micrometers). The smaller the particle, the more harmful they are. By National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS), the level of particulate matter in Delhi is well above the tolerable limits. In 2016 alone, the amount of deaths caused by the poor air quality in India “was approximately 4.2 million” (Bhat et al, 2021).
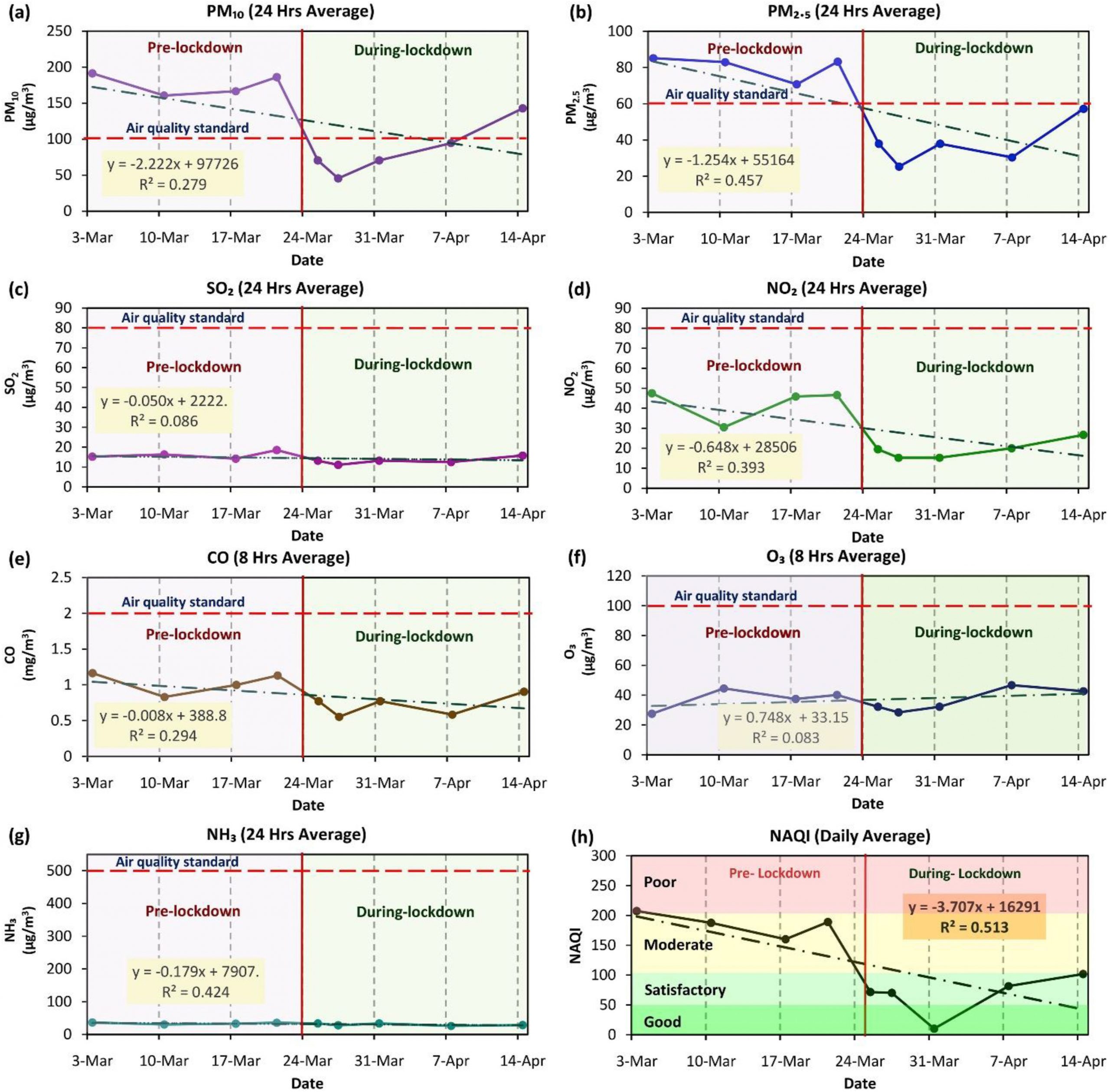
Lockdowns positively affe cted more than just the air quality around the world; additionally, water quality and beaches were a major beneficiary. Tourism for centuries has led to a significant overuse of beach resources such as fishing and leisure activities, and these in turn led to pollution of the water. If people are using jet skis and boating in lakes or oceans, the fuel and exhaust often leak into the water which can cause significant harm to the wildlife that lives in it. Restricting beach access has allowed them to recover and regain their resources, and has also decreased the pollution levels in the water. The water flowing in the Venice canals are cleaner now than they have been before (Bhat et al, 2021). pH levels, electric conductivity, dissolved oxygen levels, biochemical oxygen demand, and chemical oxygen demand have all decreased as a result of the lockdowns (Rume & Islam, 2020). These decreases all contribute to the fact that overall water quality levels have increased.
Noise pollution is an often-overlooked type of pollution that affects the world, especially in highly urbanized regions. Noise pollution is elevated levels of sound which are typically caused by human activities including transportation, machines, factories, etc. When the noise levels are elevated for extended periods of time, it negatively affects all organisms in the area. It leads to hearing loss, lack of concentration, high stress levels, interrupted sleep, and many other issues in humans. As for the wildlife, their abilities to detect and avoid predators and prey are hindered by noise pollution. It affects the invertebrates responsible for the control of many environmental processes that maintain balance in the ecosystem (Rume & Islam, 2020). When lockdowns were implemented, traveling and transportation stopped, industries shut down, flights were canceled, and people stayed home. The environment was able to recover and the people and organisms within the ecosystem enjoy a higher quality of life as a result.
Reflection Questions
- What kinds of positive experiences have you had during the pandemic?
- As stated in the chapter, there are many students who spent their time working out or picked up new hobbies. What new things were you able to focus on during the lockdowns?
Bhat, Shakeel Ahmad et al. “Impact of COVID-Related Lockdowns on Environmental and Climate Change Scenarios.” Environmental research 195 (2021): 110839–110839. Web. https://www-sciencedirect-com.libproxy.clemson.edu/science/article/pii/S001393512100133X?via%3Dihub.
DiDonato, S., Forgo, E., & Manella, H. (2020, June 5). Here’s how technology is helping residents during the COVID-19 pandemic . Scope Blog. https://scopeblog.stanford.edu/2020/06/04/how-technology-is-helping-residents-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/.
Environmental Protection Agency. (2020, October 1). Particulate Matter (PM) Basics. EPA. https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/particulate-matter-pm-basics.
Merkle, Steffen. “Positive Experiences During COVID-19.” Survey. 18 April 2021.
Parker, K., Horowitz, J. M., & Minkin, R. (2021, February 9). How Coronavirus Has Changed the Way Americans Work . Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2020/12/09/how-the-coronavirus-outbreak-has-and-hasnt-changed-the-way-americans-work/.
Rume, T., & Islam, S. M. D.-U. (2020, September 17). Environmental effects of COVID-19 pandemic and potential strategies of sustainability. Heliyon. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7498239/#bib42.
Shaban, Hamza. “The Pandemic’s Home-Workout Revolution May Be Here to Stay.” The Washington Post, WP Company, 8 Jan. 2021, www.washingtonpost.com/road-to-recovery/2021/01/07/home-fitness-boom/.
Thompson, K. L. (2021, February 2). I’m a college professor who’s teaching virtually during the pandemic. Here are 7 things my most successful students do on Zoom. Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/tips-for-zoom-success-as-remote-student-professor-advice-2021-2.
To the extent possible under law, Yang Wu; Allie Messenger; Arnaut Aguilar; Ashley Bui; Ava Kramer; Ben Jablonski; Blake Busking; Blake Moore; Carrie Pohlman; Brenna Turpin; Brooke Baker; Caroline Edwards; Chris Leroux; Claudia Sisk; Clayton Trentham; Davey Crouch; Eli Packer; Elle Wagner; Eliza Nix; Ellie Vensel; Erin Kennedy; Emily Cleveland; Ethan May; Ethan Hirsch; Frances Laughlin; George Easter; Grace Arnold; Grace D'Egidio; Grace Towe; Hope Wilde; Jack Sanford; Jake Brazinski; Jason McNult; Jason Saadeh; John Fuller; John Griffen; Julia Wood; Kasey Kiser; Katie Herbolsheimer; Katrina Campos; Kerrigan Donnelly; Kierstyn Stevens; Laurence Innes; Luke Dotson; Macey Coulter; Marco Guareschi; Meg Botts; Michael Havasy; Mikel Zoeller; Mitchell Wallin; Patrick Reed; Reagan Beach; Ryan Cook; Ryan Kennedy; Spencer Dalley; Steffen Merkle; Tayler Smith; Thomas Williams; Tim Egan; Tres Key; Tyler Parker; Virginia Lundeen; Will Gosnell; William Carroll; and Zoe Sabbert have waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to COVID 19: A Student Perspective , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
What do you think? Leave a respectful comment.
What impact is ‘the covid slide’ having on students.

Stephanie Sy Stephanie Sy

Courtney Norris Courtney Norris
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/show/what-impact-is-the-covid-slide-having-on-students
The questions around when to re-open more schools for in-person classes remains front and center for millions of Americans. Data show about 42 percent of all students between kindergarten and high school are in virtual-only schooling right now. Christopher Morphew, dean of the School of Education at Johns Hopkins University, joins Stephanie Sy to discuss.
Read the Full Transcript
Notice: Transcripts are machine and human generated and lightly edited for accuracy. They may contain errors.
Judy Woodruff:
The questions around when to reopen more schools for in person classes remains front and center for millions of Americans. Data show about 42 percent of all students between kindergarten and high school are in virtual-only schooling right now.
As we reported, there was more fuel for the debates around this today when CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky said there's growing evidence that schools can reopen safely. And she said that's even before all teachers can be vaccinated.
Stephanie Sy has our conversation again tonight.
Stephanie Sy:
Judy, teachers and school staff say they need enough protective gear and safety measures in place before they return to in person school. They also want more access to the COVID vaccine.
Only about half of states are specifically prioritizing teachers as an eligible group for vaccines right now, although teachers may still qualify because of their age or medical conditions.
Last night, we heard from the head of the largest teachers union.
Now, for a different perspective, I'm joined by Christopher Morphew, dean of the School of Education at Johns Hopkins University.
Dr. Morphew, thank you so much for joining us on the "NewsHour."
There are K-12-age students that have not been in, in person school since last March. How much learning has been lost?
Christopher Morphew:
Well, first of all, thanks for inviting me, Stephanie. I really appreciate being here.
You know, we're starting to see some evidence around a learning loss, and it looks pretty darn significant. Last June, a colleague and I, Josh Sharfstein here at Hopkins, wrote a piece in "JAMA."
And we were at that time talking about what we had — and others were calling the COVID slide, which was our prediction about what would happen as a result of closing schools during the pandemic, and we were predicting something that looked like a nine-to-10-month summer melt in students.
And the early findings we're seeing from studies are substantiating just that. We're seeing evidence right now of students falling behind. And, most importantly, we're seeing lots of evidence of the students who are most at risk and who entered into the pandemic and entered into the schools' closures behind falling further and further behind.
So we're seeing evidence and data now that suggests we're looking at students who were behind losing another nine to 11 months. And these are students who entered into the pandemic, as I said, maybe one or two years already behind their peers in terms of learning.
So, it's those most at-risk students that we're primarily concerned about here as a result of the closure. But we're seeing general agreement from teachers, parents, and students that remote learning is not as high-quality as the learning that had been taking place beforehand.
But the loss goes beyond academics, doesn't it?
Your Web site says these same disadvantaged groups you're talking about, students of color, low-income families, have — quote — "faced compounded threats" to their physical, emotional, and educational well-being, that, for them, the most is at stake.
Yes, what we're seeing now, I think one study I was just reading described it as a collective trauma that students are experiencing.
You know, I have two students in K-12 schools, and I'm seeing some of the mental health effects that other parents are seeing. And, again, we're starting to see from descriptive studies and national polls that, you know, 30 percent or more of parents are reporting significant mental health — significant changes in mental health.
So that's greatly concerning. Findings suggest that, as I said, students are experiencing the sort of collective trauma that is likely to have long-lasting impacts well past the pandemic.
And one of the things that we're concerned about here at Hopkins is looking at the cases of abuse that are going undiscovered as a result of schools being closed. Schools are a primary and essential piece for identifying evidence of abuse. And what we're really concerned about is that the pandemic is very likely exacerbating this in communities and homes around the country.
But students aren't in schools, so we weren't seeing the effects of this the way that counselors and teachers and school leaders have been trained to identify. So, we're concerned about that as well.
So, the priority, it sounds like, should be getting all kids back to in person learning.
And you now have the new head of the CDC saying that this can be done safely even without all teachers getting vaccinated. But you have major unions in big districts disagreeing with that.
What's the best path out of that impasse?
I think it's realizing that vaccines are only one part of this.
We know that — we know a lot more about the virus. We know a lot more about how to reopen schools safely than we did nine months ago, and we need to take all of that into consideration even beyond vaccines. The federal government really needs to think innovatively and act big when it comes to reopening schools.
And that means stepping in, and making sure districts have the resources they need to provide PPE, to engage in the asymptomatic testing that we now have at hand. They need to think innovatively about summer to step in and to act to sure that our children, and particularly our at-risk children, don't experience the kind of COVID slide and the nine to 10 months of summer melt that we were just talking about in terms of learning loss.
The federal government really has an opportunity here for its rhetoric to be matched by action.
Christopher Morphew, the dean of the school of education at Johns Hopkins, thank you so much.
Thanks, Stephanie.
Listen to this Segment

Watch the Full Episode
Stephanie Sy is a PBS NewsHour correspondent and serves as anchor of PBS NewsHour West. Throughout her career, she served in anchor and correspondent capacities for ABC News, Al Jazeera America, CBSN, CNN International, and PBS NewsHour Weekend. Prior to joining NewsHour, she was with Yahoo News where she anchored coverage of the 2018 Midterm Elections and reported from Donald Trump’s victory party on Election Day 2016.
Courtney Norris is the deputy senior producer of national affairs for the NewsHour. She can be reached at [email protected] or on Twitter @courtneyknorris
Support Provided By: Learn more
More Ways to Watch
- PBS iPhone App
- PBS iPad App
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

11 templates

67 templates

21 templates

environmental science
36 templates

9 templates

holy spirit
It seems that you like this template, covid-19 presentation, premium google slides theme and powerpoint template.
The coronavirus outbreak has become one of the most notorious events of the decade, if not the current century. Every bit of information helps a lot, so let us help you create useful and informative presentations about this virus with our latest template.
We’ve got a serious matter at hand, which in turn requires a serious tone. Our slide deck makes use of realistic 3D backgrounds of viruses and microorganisms to put everything in context at first glance while grabbing attention. The control and prevention of this disease can be the main pillar of your talking points, so our nicely designed infographics will come in handy. To build trust in your audience, the palette revolves around blue and turquoise, and there’s a sans-serif title font with some scientific vibes and a monospaced font for body copy.
Features of this template
- An abstract multi-purpose design with 3D backgrounds and useful infographics
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 30 different slides to impress your audience
- Available in five colors: blue, green, purple, red, and orange
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics, maps and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free and premium resources used
What are the benefits of having a Premium account?
What Premium plans do you have?
What can I do to have unlimited downloads?
Combines with:
This template can be combined with this other one to create the perfect presentation:

Don’t want to attribute Slidesgo?
Gain access to over 24300 templates & presentations with premium from 1.67€/month.
Are you already Premium? Log in
Available colors
Original Color
Related posts on our blog

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides


How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


- Student Support
- RedHawk Hub
- About Seattle U
- Inclusive Excellence
- Campus Sustainability
- Centers and Institutes
- Facts and Figures
- Faculty and Staff Resources
- Directories
- Undergraduate Majors and Degrees
- Graduate Programs and Degrees
- Colleges and Schools
- Lemieux Library
- Service Learning
- Education Abroad
- Student Academic Services
- Online Programs
- Redhawk Service Center
- Student Life
- Housing and Residence Life
- Dining Services
- Center for Community Engagement
- Center for Student Involvement
- Health and Personal Wellness
- Diversity and Multicultural Resources
- Career Engagement Office
- Parent and Family Engagement
- Public Safety
- Campus Store
- Campus Calendar
- University Recreation
- First Year Applicants
- International Students
- Transfer Students
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- School of Law
- Campus Tours
- Accepted Students
- Tuition and Aid
- Net Price Calculator
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships and Grants
- Student Billing and Payment
- Student Financial Services
- Authorized User Login
- Forms & Documents
- Jesuit Tradition
- Campus Ministry
- Center for Jesuit Education
- Institute for Catholic Thought and Culture
- Chapel of St. Ignatius
- Center for Ecumenical and Interreligious Engagement
- All Things Jesuit
- Jesuits of Seattle U
CEJS 2023-2024 Student and Faculty Fellowship Presentations
No Proper Link Provided
Posted: May 15, 2024
Tuesday, May 28, 12:30 p.m. Stuart Rolfe Room in ADAL RSVP for the event Light lunch will be served.
Join the Center for Environmental Justice and Sustainability for the 2023-2024 Student and Faculty Fellowship presentations.
- Laudato Si’ Faculty Fellows are Tapoja Chaudhuri , presenting “Putting Down Roots,” and Lauren Bibin , whose study focuses on “Seattle University Sustainability Transformation Assessment in Nursing.”
- Gary L. Chamberlain Student Fellows, Gabe Veltr i and Olivia Roberts , will present “Composition of Moss Dwelling Invertebrate Communities in Southern Seattle: Duwamish Valley vs. Seattle Parks.”
- Francis Student Fellow, Angela Su , will present on her study “Examining Sexual and Reproductive Health Education Strategies and Their Impact on Measures of Social Sustainability.”
For more information, visit CEJS Fellows .
By using our website, you agree to our cookie policy
Kentucky doctor reacts to new COVID-19 FLiRT variant
LEXINGTON, Ky. (WKYT)—It’s been roughly four years since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, and as the world has navigated the virus, it has developed as well.
CBS News reported just days ago that nearly one-third of the country’s COVID-19 cases are linked to a new variant.
“It’s called FLiRT because they named it due to some minimal changes on what we call the spike protein. It is now becoming the most predominant variant,” said Dr. Jeff Foxx, a family physician.
The variant also coined the name FLiRT because of its minor changes to previous variants. CBS reported that this strain is not any more severe than recent strains, according to the CDC.
Dr. Foxx says if you get it, you may not even notice a difference.
“At this point and time it doesn’t change anything that we do significantly. Most of it’s respiratory. So it still appears clinically to look like the other COVID variants,” said Foxx.
He says that because it’s not too different from what we’ve seen before, we can’t get complacent about treating it.
As the summer nears, taking proper precautions is always the best call.
“The good thing about summertime is a lot of stuff is outside. The airflow is better, the risk is less even though we may see a spike in the summer. If you’re gonna be in a large gathering, especially indoors, do things like washing your hands, social distancing, keeping your vaccines up to date,” said Foxx.
Health officials recommend staying away from others if you believe you’re contagious.
The CDC has not made any changes to its current vaccine recommendations, which were last updated in April.
Copyright 2024 WKYT. All rights reserved.

Dine-and-dashers caught on camera at Lexington restaurant

Doctor and his 2 adult children die in plane crash while traveling to Kentucky

Changes from Visa mean Americans will carry fewer physical credit, debit cards in their wallets

Pair facing charges after kids, 24 animals found living in extremely poor conditions

Man charged with deadly stabbing of woman inside retirement home has previous murder conviction
Latest news.

World No. 1 golfer Scottie Scheffler released from LMDC after being arrested by Louisville Metro police

Wednesday night's MN House debate could impact end of session negotiations

WATCH | Jim Caldwell's FastCast

Jim Caldwell's Forecast | Showers & storms will fill our Kentucky skies

Lexington Council approves changes to downtown parking
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

The impact of COVID-19 on student experiences and expectations: Evidence from a survey ☆
Esteban m. aucejo.
a Department of Economics, Arizona State University, CEP & NBER, United States of America
Jacob French
b Department of Economics, Arizona State University, United States of America
Maria Paola Ugalde Araya
Basit zafar.
c Department of Economics, University of Michigan, & NBER, United States of America
In order to understand the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on higher education, we surveyed approximately 1500 students at one of the largest public institutions in the United States using an instrument designed to recover the causal impact of the pandemic on students' current and expected outcomes. Results show large negative effects across many dimensions. Due to COVID-19: 13% of students have delayed graduation, 40% have lost a job, internship, or job offer, and 29% expect to earn less at age 35. Moreover, these effects have been highly heterogeneous. One quarter of students increased their study time by more than 4 hours per week due to COVID-19, while another quarter decreased their study time by more than 5 hours per week. This heterogeneity often followed existing socioeconomic divides. Lower-income students are 55% more likely than their higher-income peers to have delayed graduation due to COVID-19. Finally, we show that the economic and health related shocks induced by COVID-19 vary systematically by socioeconomic factors and constitute key mediators in explaining the large (and heterogeneous) effects of the pandemic.
- • Due to COVID: 13% of students delayed graduation, 40% lost a job, internship, or offer, and 29% expect to earn less at 35.
- • The effects of the pandemic have been highly heterogeneous.
- • Lower-income students are 55% more likely than their higher-income peers to have delayed graduation due to COVID-19.
- • COVID-19's economic and health shocks vary by socioeconomic status and act as key mediators explaining pandemic's effects.
1. Introduction
The disruptive effects of the COVID-19 outbreak have impacted almost all sectors of our society. Higher education is no exception. Anecdotal evidence paints a bleak picture for both students and universities. According to the American Council on Education, enrollment is likely to drop by 15% in the fall of 2020, while at the same time many institutions may have to confront demands for large tuition cuts if classes remain virtual. 1 In a similar vein, students face an increasingly uncertain environment, where financial and health shocks (for example, lack of resources to complete their studies or fear of becoming seriously sick), along with the transition to online learning may have affected their academic performance, educational plans, current labor market participation, and expectations about future employment.
This paper attempts to shed light on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on college students. First, we describe and quantify the causal effects of the COVID-19 outbreak on a wide set of students' outcomes/expectations. In particular, we analyze enrollment and graduation decisions, academic performance, major choice, study and social habits, remote learning experiences, current labor market participation, and expectations about future employment. Second, we study how these effects differ along existing socioeconomic divides and whether the pandemic has exacerbated existing inequalities. Finally, we present suggestive evidence on the mechanisms behind the heterogeneous COVID-19 effects by quantifying the relationship between individual-level (financial and health) shocks and students' academic decisions and labor market expectations.
For this purpose, we surveyed about 1500 undergraduate students at Arizona State University (ASU), one of the largest public universities in the United States, in late April 2020. The survey was explicitly designed to not only collect student outcomes and expectations after the onset of the pandemic, but also to recover counterfactual outcomes in the absence of the outbreak. Specifically, the survey asked students about their current experiences/expectations and what those experiences/expectations would have been had it not been for the pandemic. Because we collect information conditional on both states of the world (with the COVID-19 pandemic, and without) from each student , we can directly analyze how each student believes COVID-19 has impacted their current and future outcomes. 2 For example, by asking students about their current GPA in a post-COVID-19 world and their expected GPA in the absence of COVID-19, we can back out the subjective treatment effect of COVID-19 on academic performance. The credibility of our approach depends on: (1) students having well-formed beliefs about outcomes in the counterfactual scenario. This is a plausible assumption in our context since the counterfactual state is a realistic and relevant one - it was the status quo less than two months before the survey, and (2) there being no systematic bias in the reporting of the data - an assumption that is implicitly made when using any survey data. 3
Our findings on academic outcomes indicate that COVID-19 has led to a large number of students delaying graduation (13%), withdrawing from classes (11%), and intending to change majors (12%). Moreover, approximately 50% of our sample separately reported a decrease in study hours and in their academic performance. Predicting the longer-term impact of the pandemic on student achievement is more difficult, but students reported that they expect to take a break from college in the fall 2020 semester at more than twice the rate in previous years. Historically, 28% of students who fail to re-enroll do not return to ASU or another university after 5 years (authors' calculations from ASU first-time freshmen transcript data for the 2012–2014 spring semesters), suggesting that the pandemic may have a lasting impact on the educational achievement of current students. We also find that students report a decreased preference for online instruction as a result of their recent experiences.
As expected, the COVID-19 outbreak also had large negative effects on students' current labor market participation and expectations about post-college labor outcomes. Working students suffered a 31% decrease in their wages and a 37% drop in weekly hours worked, on average. Moreover, around 40% of students lost a job, internship, or a job offer, and 61% reported to have a family member that experienced a reduction in income. The pandemic also had a substantial impact on students' expectations about their labor market prospects post-college. For example, their perceived probability of finding a job before graduation decreased by almost 20%, and their expected earnings when 35 years old (around 15 years from the outbreak) declined by approximately 2.5%. This last finding suggests that students expect the pandemic to have a long-lasting impact on their labor market prospects, which is qualitatively consistent with the literature on graduating during a recession. For instance, Oreopoulos et al. (2012) and Schwandt and von Wachter (2019) find significant reductions in earnings 5 and 10 years after graduation, respectively, and Kahn (2010) finds an even longer-lasting effect on wages. On the other hand, although we are measuring the probability of finding a job before graduating, not unemployment directly, our estimated quantitative effect on students' expectations of finding a job seems to be larger relative to the literature ( Kahn, 2010 ; Altonji et al., 2016 ; and Rothstein, 2020 ).
The data also show that while all subgroups of the population have experienced negative effects due to the outbreak, the size of the effects are heterogeneous. For example, compared to their more affluent peers, lower-income students are 55% more likely to delay graduation due to COVID-19 and are 41% more likely to report that COVID-19 impacted their major choice. Further, COVID-19 nearly doubled the gap between higher- and lower-income students' expected GPA. 4 There also is substantial variation in the pandemic's effect on preference for online learning, with Honors students and males revising their preferences down more than 2.5 times as much as their peers. However, despite appearing to be more disrupted by the switch to online learning, the impact of COVID-19 on Honors students' academic outcomes is consistently smaller than the impact on non-Honors students.
Finally, we evaluate the extent to which mitigating factors associated with more direct economic and health shocks from the pandemic (for example, a family member losing income due to COVID-19, or the expected probability of hospitalization if contracting COVID-19) can explain the heterogeneity in pandemic effects. We find that both types of shock (economic and health) are systematically correlated with students' COVID-19 experiences. For example, the expected probability of delaying graduation due to COVID-19 increases by approximately 25% if either a student's subjective probability of being late on a debt payment in the following 90 days (a measure of financial fragility) or subjective probability of requiring hospitalization conditional on contracting COVID-19 increases by one standard deviation. As expected, the magnitude of health and economic shocks are not homogeneous across the student population. The average of the principal component for the economic and health shocks is about 0.3–0.4 standard deviations higher for students from lower-income families. Importantly, we find that the disparate economic and health impacts of COVID-19 can explain 40% of the delayed graduation gap (as well as a substantial part of the gap for other outcomes) between lower- and higher-income students. This analysis should be viewed as descriptive in nature and not necessarily causal, since omitted factors that are correlated both with the shocks and the outcomes may be driving these relationships.
To our knowledge, this is the first paper to shed light on the effects of COVID-19 on college students' experiences. The treatment effects that we find are large in economic terms. Whether students are overreacting in their response to the COVID-19 shock is not clear. We do find that previous cumulative GPA is a strong predictor of expected semester GPA without COVID-19, suggesting that students' reported expectations are meaningful. However, we know that individuals generally tend to overweight recent experiences ( Malmendier and Nagel, 2016 ; Kuchler and Zafar, 2019 ). Whether students' subjective treatment effects are “correct” in some ex-post sense is beside the point. As long as students are reporting their subjective beliefs without any systematic bias, it is the perceived treatment effects, not actual ones, – regardless of whether they are correct or not – which are fundamental to understanding choices. For example, if students (rightly or wrongly) perceive a negative treatment effect of COVID-19 on the returns to a college degree, this belief will have an impact on their future human capital decisions (such as continuing with their education, choice of major, etc.).
Our results underscore the fact that the COVID-19 shock is likely to exacerbate socioeconomic disparities in higher education. This is consistent with findings regarding the impacts of COVID-19 on K-12 students. Kuhfeld et al. (2020) project that school closures are likely to lead to significant learning losses in math and reading. However, they estimate heterogeneous effects, and conclude that high-performing students are likely to make gains. Likewise, Chetty et al. (2020) find that, post-COVID, student progress on an online math program decreased significantly more in poorer ZIP codes. Our analysis reveals that the heterogeneous economic and health burden imposed by COVID-19 can partially explain these varying impacts. This suggests that by addressing the economic and health impacts imposed by COVID-19, policy makers may be able to prevent COVID-19 from widening existing gaps in higher education.
2.1. Survey
Our data come from an original survey of undergraduate students at Arizona State University (ASU), one of the largest public universities in the United States. Like other higher educational institutions in the US, the Spring 2020 semester started in person. However, in early March during spring break, the school announced that instruction would be transitioned online and that students were advised not to return to campus.
The study was advertised on the My ASU website, accessible only through the student's ASU ID and password. Undergraduate students were invited to participate in an online survey about their experiences and expectations in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, for which they would be paid $10. The study was posted during the second to last week of instruction for the spring semester (April 23rd). Our sample size was constrained by the research funds to 1500 students, and the survey was closed once the desired sample size was reached, which happened within 3 days of posting the survey.
The survey was programmed in Qualtrics. It collected data on students' demographics and family background, their current experiences (both for academic outcomes and non-academic outcomes), and their future expectations. Importantly for the purposes of this study, the survey collected data on what these outcomes/expectations would have been in the counterfactual state, without COVID-19. The survey instrument (with only the relevant sections) can be found here .
2.2. Sample
A total of 1564 respondents completed the survey. 5 90 respondents were ineligible for the study (such as students enrolled in graduate degree programs or diploma programs) and were dropped from the sample. Finally, responses in the 1st and 99th percentile of survey duration were further excluded, leading to a final sample size of 1446. The survey took 38 min to complete, on average (median completion time was 26 min).
The first five columns of Table 1 show how our sample compares with the broader ASU undergraduate population and the average undergraduate student at other large flagship universities (specifically, the largest public universities in each state). Relative to the ASU undergraduate population, our sample has a significantly higher proportion of first-generation students (that is, students with no parent with a college degree), and a smaller proportion of international students. The demographic composition of our sample compares reasonably well with that of students in flagship universities. Our sample is also positively selected in terms of SAT/ACT scores relative to these two populations. The sample may also differ from the student body at other large public schools in that 30% report living on campus, which is not always the norm at other large institutions and may play an important role in how disruptive the pandemic has been. 6
Summary statistics.
Notes: Data in columns (2), (3) and (8) is from IPEDS 2018. The flagship universities are the 4-year public universities with the highest number of undergraduate students in each state. Means for these columns are weighted by total number of undergraduates in each institution. ACT and SAT data are weighted averages of 2018–2015 years from IPEDS. P -value columns show the p -value of a difference in means test between the two columns indicated by the numbers in the heading.
The better performance on admission tests could be explained by the high proportion of Honors students in our sample (22% compared to 18% in the ASU population). The last four columns of Table 1 show how Honors students compare with ASU students and the average college student at a top-10 university. We see that they perform better than the average ASU student (which is expected) and just slightly worse than the average college student at a top-10 university. The share of white Honors students in our sample (60%) is higher than the proportion in the ASU population and much higher than the proportion of white students in the top-10 universities.
Overall, we believe our sample of ASU students is a reasonable representation of students at other large public schools, while the Honors students may provide insight into the experiences of students at more elite Institutions. Though, it is important to acknowledge that elite institutions may have additional resources to address a global pandemic.
3. Analytic framework
We next outline a simple analytic framework that guides the empirical analysis. Let O i ( COVID – 19) be the potential outcome of individual i associated with COVID-19 treatment. We are interested in the causal impact of COVID-19 on student outcomes:
where the first term on the right-hand side is student i 's outcome in the state of the world with COVID-19, and the second term being student i 's outcome in the state of the world without COVID-19. Recovering the treatment effect at the individual level entails comparison of the individual's outcomes in two alternate states of the world. With standard data on realizations, a given individual is observed in only one state of the world (in our case, COVID – 19 = 1). The alternate outcomes are counterfactual and unobserved. A large econometric and statistics literature studies how to identify these counterfactual outcomes and moments of the counterfactual outcomes (such as average treatment effects) from realized choice data (e.g., Heckman and Vytlacil, 2005 ; Angrist and Pischke, 2009 ; Imbens and Rubin, 2015 ). Instead, the approach we use in this paper is to directly ask individuals for their expected outcomes in both states of the world. From the collected data, we can then directly calculate the individual-level subjective treatment effect. As an example, consider beliefs about end-of-semester GPA. The survey asked students “ What semester-level GPA do you expect to get at the end of this semester ?” This is the first-term on the right-hand side of Eq. (1) . The counterfactual is elicited as follows “ Were it not for the COVID-19 pandemic , what semester-level GPA would you have expected to get at the end of the semester ?”. The difference in the responses to these two questions gives us the subjective expected treatment effect of COVID-19 on the student's GPA. For certain binary outcomes in the survey, we directly ask students for the Δ i . For example, regarding graduation plans, we simply ask a student if the Δ i is positive, negative, or zero: “ How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected your graduation plan ? [ graduate later ; graduation plan unaffected ; graduate earlier ].”
The approach we use in this paper follows a small and growing literature that uses subjective expectations to understand decision-making under uncertainty. Specifically, Arcidiacono et al. (2020) and Wiswall and Zafar (2020) ask college students about their beliefs for several outcomes associated with counterfactual choices of college majors, and estimate the ex-ante treatment effects of college majors on career and family outcomes. Shapiro and Giustinelli (2019) use a similar approach to estimate the subjective ex-ante treatment effects of health on labor supply. There is one minor distinction from these papers: while these papers elicit ex-ante treatment effects, in our case, we look at outcomes that have been observed (for example, withdrawing from a course during the semester) as well as those that will be observed in the future (such as age 35 earnings). Thus, some of our subjective treatment effects are ex-post in nature while others are ex-ante.
The soundness of our approach depends on a key assumption that students have well-formed expectations for outcomes in both the realized state and the counterfactual state. Since the outcomes we ask about are absolutely relevant and germane to students, they should have well-formed expectations for the realized state. In addition, given that the counterfactual state is the one that had been the status quo in prior semesters (and so students have had prior experiences in that state of the world), their ability to have expectations for outcomes in the counterfactual state should not be a controversial assumption. 7 As evidence that students' expectations exhibit meaningful variation, Appendix Fig. A1 shows that previous cumulative GPA is a strong predictor of expected semester GPA with COVID-19.
4. Empirical analysis
4.1. treatment effects.
We start with the analysis of the aggregate-level treatment effects, which are presented in Table 2 . The outcomes are organized in two groups, academic and labor market (see Appendix Table A1 for a complete list of outcomes). The first two columns of the table show the average beliefs for those outcomes where the survey elicited beliefs in both states of the world. The average treatment effects shown in column (3) are of particular interest. Since we can compute the individual-level treatment effects, columns (4)–(7) of the table show the cross-sectional heterogeneity in the treatment effects.
Subjective treatment effects.
Notes: Δ : change. Prop. Δ >0: proportion of students for whom the individual level Δ is positive. Prop. Δ =0: proportion of students for whom the individual level Δ is zero. 25th and 75th percentiles of the cross-sectional distribution of Δ . Standard deviation in parentheses. ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
We see that the average treatment effects are statistically and economically significant for all outcomes. The average impacts on academic outcomes, shown in Panel A, are mostly negative. For example, the average subjective treatment effect of COVID-19 on semester-level GPA is a decline of 0.17 points. More than 50% of the students in our sample expect a decrease in their GPA due to the treatment (versus only 7% expecting an increase). Additionally, 13% of the participants delayed their graduation, 11% withdrew from a class during the spring semester, and 12% stated that their major choice was impacted by COVID-19. 8
While almost no students report planning to drop out due to COVID-19, on average they expect to take a break from ASU in the fall 2020 semester at nearly twice the historical rate. Admittedly, the decision to take a break during a pandemic may be different than in more normal times. However, a substantial increase in the share of students failing to continue their studies is concerning, as historically 28% of students who fail to re-enroll for a fall semester do not return to ASU or another university within 5 years.
Regarding the impact of the pandemic on major choice, students who report that COVID-19 impacted their major choice were more likely to be in lower-paying majors before the pandemic; mean pre-COVID major-specific annual earnings were $43,053 ($46,943) for students whose major choice was (not) impacted by COVID-19. 9 Impacted students were also 9.3 percentage points less likely to be in a science, technology, engineering, or math (STEM) major before COVID-19. 10 We are only able to observe pre- and post-COVID major choices for the subset of students who had switched their major by the date of the survey. 11 Within this selected subsample of switchers, students chose to move into higher paying majors, with an average change in first-year earnings of $3,340. These patterns are generally consistent with the finding that students tend to gravitate towards higher-paying majors when exposed to adverse economic conditions when in college ( Blom et al., 2019 ).
An interesting and perhaps unanticipated result reported in Table 2 is that, on average, students are 4 percentage points less likely to opt for online instruction if given the choice between online and in-person instruction due to their experience with online instruction during the pandemic. 12 13 However, there is a substantial amount of variation in terms of the direction of the effect: 31% (47%) of the participants are now more (less) likely to enroll in online classes. We explore this heterogeneity in more detail in the next section, but it seems that prior experience with online classes somewhat ameliorates the negative experience; the average treatment effect for students with prior experience in online classes is a 2.4 percentage points decrease in their likelihood of enrolling in online classes, versus a 9.5 percentage points decline for their counterparts (difference statistically significant at the 0.1% level).
This large variation in the treatment effects of COVID-19 is apparent in several of the other outcomes, such as study hours, where the average treatment effect of COVID-19 on weekly study hours is −0.9 (that is, students spend 0.9 less hours studying per week due to COVID-19). The interquartile range of the across-subject treatment effect demonstrates substantial variation, with the pandemic decreasing study time by 5 hours at the 25th percentile and increasing study time by 4 hours at the 75th.
Overall, these results suggest that COVID-19 represents a substantial disruption to students' academic experiences, and is likely to have lasting impacts through changes in major/career and delayed graduation timelines. Students' negative experiences with online teaching, perhaps due to the abruptness of the transition, also has implications for the willingness of students to take online classes in the future.
Turning to Panel B in Table 2 , we see that students' current and expected labor market outcomes were substantially disrupted by COVID-19. As for the extensive margin of current employment, on average, 29% of the students lost the jobs they were working at prior to the pandemic (67% of the students were working prior to the pandemic), 13% of students had their internships or job offers rescinded, and 61% of the students reported that a close family member had lost their job or experienced an income reduction. The last statistic is in line with findings from other surveys of widespread economic disruption across the US. 14 Respondents experienced an average decrease of 11.5 hours of work per week and a 21% decrease in weekly earnings, although there was no change in weekly earnings for 52% of the sample, which again reflects substantial variation in the effects of COVID-19 across students.
In terms of labor market expectations, on average, students foresee a 13 percentage points decrease in the probability of finding a job by graduation, a reduction of 2% in their reservation wages, and a 2.3% decrease in their expected earnings at age 35.
The significant changes in reservation wages and expected earnings at age 35 demonstrate that students expect the treatment effects of COVID-19 to be long-lasting. Qualitatively, this is broadly consistent with the literature on graduating during recession. Oreopoulos et al. (2012) finds that graduating during a recession in which the unemployment rate increases 5% implies an initial loss in earnings of 9%, that decreases to 4.5% within 5 years and disappears after 10 years for a sample of male college graduates in Canada. Similarly, Schwandt and von Wachter (2019) find a 2.6% reduction in earnings 10 years after graduation for a 3-percentage point increase in unemployment at graduation, and Kahn (2010) finds an even longer-lasting effect on wages.
A large literature has investigated the impact of graduating during recessions on unemployment rates. Kahn (2010) finds that during the 1980's recession, the probability of being employed right after graduation for white males was largely unaffected by economic conditions. Altonji et al. (2016) only find what they term modest impacts. On the other hand, Rothstein (2020) finds that, for 22 to 23-year-olds graduating from college during the Great Recession, the probability of being employed decreases by 0.7 percentage point for every 1 percentage point increase in the unemployment rate. Using the estimates in Rothstein (2020) and the approximate 10 percentage point increase in the unemployment rate during April 2020, a back-of-the-envelope calculation indicates a 7 percentage point reduction in the probability of being employed for the graduating cohort in our sample. We find that students who are graduating in spring or summer 2020 expect a 35 percentage point decline in the likelihood of finding a job before graduation. While it is difficult to precisely map pre-graduation job finding rates to unemployment over the subsequent year, a 7 percentage point increase in unemployment appears low compared to the impact on students' expectations. It could be the case that the literature estimates are not appropriate for a situation as unexpected and different as a global pandemic, where the economic recession goes hand in hand with health concerns. Having said that, it could also be that students are overreacting to the COVID-19 shock. Data that tracks students' expectations and outcomes over time may be able to shed light on this.
4.2. Heterogeneous effects
We next explore demographic heterogeneity in the treatment effects of COVID-19. Fig. 1 plots the average treatment effects across several relevant demographic divisions including gender, race, parental education, and parental income. Honors college status and cohort are also included as interesting dimensions of heterogeneity in the COVID-19 context. The figure shows the impacts for six of the more economically meaningful outcomes from Table 2 (additional outcomes can be found in Appendix Fig. A2 ).

Treatment effects by demographic group.
(a) Delay Graduation due to COVID (0/1)
(b) Semester GPA ( Δ 0–4)
(c) Change major due to COVID (0/1)
(d) Likelihood take online classes ( Δ 0–1)
(e) Probability job before graduate ( Δ 0–1)
(f) Expected earnings at age 35 (Pct. Δ )
Notes: bars denote 90% confidence interval.
At least four patterns of note emerge from Fig. 1 . First, compared to their classmates, students from disadvantaged backgrounds (lower-income students defined as those with below-median parental income, racial minorities, and first-generation students) experienced larger negative impacts for the academic outcomes, as shown in the first three panels of the figure. 15 The trends are most striking for lower-income students, who are 55% more likely to delay graduation due to COVID-19 than their more affluent classmates (0.16 increase in the proportion of those expecting to delay graduation versus 0.10), expect 30% larger negative effects on their semester GPA due to COVID-19, and are 41% more likely to report that COVID-19 impacted their major choice (these differences are statistically significant at the 5% level). For some academic outcomes, COVID-19 had similarly disproportionate effects on nonwhite and first-generation students, with nonwhite students being 70% more likely to report changing their major preference compared to their white peers and first-generation students being 50% more likely to delay their graduation than students with college-educated parents. Thus, while on average COVID-19 negatively impacted several measures of academic achievement for all subgroups, the effects are significantly more pronounced for socioeconomic groups which were predisposed towards worse academic outcomes pre-COVID. 16 The pandemic's widening of existing achievement gaps can be seen directly in students' expected Semester GPA. Without COVID-19, lower-income students expected a 0.052 lower semester GPA than their higher-income peers. With COVID-19, this gap nearly doubles to 0.098. 17
Second, Panel (d) of Fig. 1 shows that the switch to online learning was substantially harder for some demographic groups; for example, men are 7 percentage points less likely to opt for an online version of a course as a result of COVID-19, while women do not have a statistically significant change in their online preferences. We also see that Honors students revise their preferences by more than 2.5 times the amount of non-Honors students. As we show later (in Table 4 ), these gaps persist after controlling for household income, major, and cohort, suggesting that the switch to online learning mid-semester may have been substantially more disruptive for males and Honors students. While the effect of COVID-19 on preferences for online learning looks similar for males and Honors students, our survey evidence indicates that different mechanisms underpin these shifts. Based on qualitative evidence, it appears that Honors students had a negative reaction to the transition to online learning because they felt less challenged, while males were more likely to struggle with the learning methods available through the online platform. 18 One speculative explanation for the gender difference is that consumption value of college amenities is higher for men (however, Jacob et al. (2018) , find little gender difference in willingness to pay for the amenities they consider).
Composition of COVID effects.
Notes: Standard errors in parentheses bootstrapped with 1000 replications. Each column reports results from a separate OLS regression of the dependent variable onto the covariates (row variables). Dependent variables measured in percentage points. ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
The third trend worth highlighting from Fig. 1 is that Honors students were better able to mitigate the negative effect of COVID-19 on their academic outcomes (panels a, b, and c), despite appearing to be more disrupted by the move to online learning (panel d). Honors students report being less than half as likely as non-Honors students to delay graduation and change their major due to COVID-19. Extrapolating from these patterns provides suggestive evidence that academic impacts for students attending elite schools– the group more comparable to these Honors students– are likely to have been small relative to the impacts for the average student at large public schools.
Finally, the last two panels of Fig. 1 present the COVID effect on two labor market expectations and show much less meaningful heterogeneity across demographic groups compared to the academic outcomes in previous panels. This suggests that, while students believe COVID-19 will impact both their academic outcomes and future labor market outcomes, they do not believe there is a strong connection between these domains. Supporting this observation, the individual-specific treatment effect on semester GPA is only weakly correlated with the individual-specific treatment effects on finding a job before graduation (corr = 0.0497, p = 0.065) and expected earnings at 35 (corr = 0.0467, p = 0.077).
The one notable exception to the lack of heterogeneity in panels (e) and (f) of Fig. 1 are seniors, who on average revised their subjective probability of finding a job before graduation three times as much as other cohorts. Appendix Fig. A3 further breaks down the estimated COVID-19 effects by expected year of graduation. Perhaps unsurprisingly, the 2020 cohort expects much larger effects on immediate job market outcomes such as reservation wages and probability of finding a job before graduation. While average expected changes to job market outcomes are noisier for academically younger students, perhaps reflecting additional uncertainty about the longer-term impacts of COVID-19, they appear to anticipate meaningful changes to their future labor market prospects. Conversely, younger students also expected larger disruptions to academic outcomes such as semester GPA and study time.
5. Understanding the heterogeneous effects
This section presents mediation analysis on the drivers of the underlying heterogeneity in the treatment effects. The COVID-19 pandemic serves as both an economic and a health shock. However, these shocks may have been quite heterogeneous across the various groups, and that could partly explain the heterogeneous treatment effects we documented in the previous section.
5.1. Economic and health mediating factors
We proxy for the financial and health shocks due to COVID-19 by relying on a small but relevant set of covariates which capture more fundamental or first-order disruptions from the pandemic. Financial shocks are characterized based on whether a student lost a job due to COVID-19, whether a student's family members lost income due to COVID-19, the change in a student's monthly earnings due to COVID-19, and the likelihood a student will fail to fully meet debt payments in the next 90 days. To measure health shocks, we consider a student's belief about the likelihood that they will be hospitalized if they contract COVID-19, a student's belief about the likelihood that they will have contracted COVID-19 by summer, and a student's subjective health assessment. Finally, in order to summarize the combined effect of each set of proxies, we construct principal component scores as one-dimensional measures of the financial and health shock to students. 19
Table 3 reports summary statistics of the different economic and health proxies by demographic group. Given the results in Fig. 1 , the remainder of the analysis will focus on three socioeconomic divisions: parental income, gender, and Honors college status. Our data indicate that lower-income students faced larger health and economic shocks as compared to their more affluent peers. In particular, they are almost 10 percentage points more likely to expect to default on their debt payments compared to their higher-income counterparts. Additionally, lower-income students are 16 percentage points more likely to have had a close family member experience an income reduction due to COVID-19. Regarding the health proxies, lower-income students rate their health as worse than higher-income students and perceive a higher probability of being hospitalized if they catch the virus. Finally, the differences in economic and health shocks between lower and higher-income students, as summarized by the principle components of the selected proxy variables, are statistically significant.
Summary statistics for economic and health proxies.
Notes: P-value columns report the p-value of a difference in means test between the two columns indicated by the numbers in the heading.
Columns (5)–(7) of Table 3 show that both economic and health shocks are larger for non-Honors students. In fact, the average differences in the principal component scores for both the economic and health factors is larger for these two groups than for the income groups. Likewise, the last three columns of the table show that women experienced larger COVID-19 shocks due to economic and health factors. These differences are partly driven by the fact that, in our sample, females are more likely to report that they belong to a lower-income household than males (50% vs. 42%).
In short, Table 3 makes clear that the impacts of COVID-19 on the economic well-being and health of students have been quite heterogeneous, with lower-income and lower-ability students being more adversely affected.
5.2. The role of economic and health shocks on explaining the COVID-19 effects
To investigate the role of economic and health shocks in explaining the heterogeneous treatment effects (in Section 4.2 ), we estimate the following specification:
where Δ i is the COVID-19 treatment effect for outcome O on student i . Demog i is a vector including indicators for gender, lower-income, Honors status, and dummies for cohort year and major. FinShock i and HealthShock i are vectors containing the shock proxies or their principal component. Finally, ε i denotes an idiosyncratic shock.
The parameters of interest are α 2 and α 3 . A causal interpretation of these parameters requires FinShock i and HealthShock i to be independent of ε i . This seems unlikely in our context as unobservables correlated with FinShock i and HealthShock i may also modulate COVID-19's impact on academic outcomes. Therefore, we prefer to interpret α 2 and α 3 as simple correlations. Nevertheless, we believe this descriptive evidence can be informative from a policy perspective.
Table 4 shows estimates of Eq. (2) for four different outcomes ( Appendix Table A2 shows the estimates for additional outcomes). For each outcome, five specifications are reported ranging from controlling for only demographic variables in the first specification to controlling for both economic and health factors in the fourth specification. Finally, the last column includes only the principal component of each shock to provide insight about overall effects, given that certain shock proxies show high levels of correlation (see Appendix Table A4 for the correlations within each set of proxies).
Several important messages emerge from Table 4 . First, both shocks are (economically and statistically) significant correlates of the COVID-19 effects on students' outcomes. In particular, F-tests show that the financial and health shock proxies are jointly significant across almost all specifications. 20 This is also reflected in the statistical significance of the principal components. Moreover, the fact that the effect of key proxy variables remains robust when we simultaneously control for both shocks demonstrates the robustness of our results. For example, we find that a 50 percentage point increase in the probability of being late on debt payments is associated with an increase in the probability of delaying graduation and switching majors due to COVID-19 of 6.9 and 6.4 percentage points respectively. These effects are large given that they represent more than half of the overall COVID-19 treatment effect for these variables. Similarly, we find that an analogous increase in the probability of hospitalization if contracting COVID-19 is associated with a 6 and 5 percentage points increase in the probability of delaying graduation and switching majors due to COVID-19.
Second, in terms of labor market expectations, we find that the change in the expected probability of finding a job before graduation strongly depends on having a family member that lost income (which is also correlated with the student himself losing a job). In particular, the size of this effect represents 32% of the overall COVID-19 treatment effect. Therefore, this finding suggests that students' labor market expectations are driven in large part by personal/family experiences.
Third, although the proxies play an important role in explaining the pandemic's impact on students, there is still a substantial amount of variation in COVID-19 treatment effects left unexplained. Across the four outcomes in Table 4 , the full set of proxies explain less than a quarter of the variation in outcomes across individuals. Appendix Fig. A4 visualizes this variation by plotting the distribution of several continuous outcomes with and without controls. While the interquartile range noticeably shrinks after conditioning on the proxy variables, these plots highlight the large amount of variation in treatment effects remaining after conditioning on the proxies.
Finally, our results show that the financial and health shocks play an important role in explaining the heterogeneous effects of the COVID-19 outbreak. In particular, columns (4) and (9) demonstrate that economic and health factors together can explain approximately 40% and 70% of the income gap in COVID-19's effect on delayed graduation and changing major respectively. The gap between Honors and non-Honors students is likewise reduced by 27% and 39% for the same outcomes. Taken together, these results imply that differences in the magnitude of COVID-19's economic and health impact can explain a significant proportion of the demographic gaps in COVID-19's effect on the decision to delay graduation, the decision to change major, and preferences for online learning. These results are important and suggest that focusing on the needs of students who experienced larger financial or health shocks from COVID-19 may be an effective way to minimize the disparate disruptive effects and prevent COVID-19 from exacerbating existing achievement gaps in higher education.
6. Conclusions
This paper provides the first systematic analysis of the effects of COVID-19 on higher education. To study these effects, we surveyed 1500 students at Arizona State University, and present quantitative evidence showing the negative effects of the pandemic on students' outcomes and expectations. For example, we find that 13% of students have delayed graduation due to COVID-19. Expanding upon these results, we show that the effects of the pandemic are highly heterogeneous, with lower-income students 55% more likely to delay graduation compared to their higher-income counterparts. We further show that the negative economic and health impacts of COVID-19 have been significantly more pronounced for less advantaged groups, and that these differences can partially explain the underlying heterogeneity that we document. Our results suggest that by focusing on addressing the economic and health burden imposed by COVID-19, as measured by a relatively narrow set of mitigating factors, policy makers may be able to prevent COVID-19 from widening existing achievement gaps in higher education.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no relevant or material financial interests that relate to the research described in this paper. There are no declarations of interest.
☆ Noah Deitrick and Adam Streff provided excellent research assistance. All errors that remain are ours.
1 See, the New York Times article “ After Coronavirus , Colleges Worry : Will Students Come Back ?” (April 15, 2020) for a discussion surrounding students' demands for tuition cuts.
2 In some cases, instead of asking students for the outcomes in both states of the world, we directly ask for the difference. For example, the survey asked how the pandemic had affected the student's graduation date.
3 This approach has been used successfully in several other settings, such as to construct career and family returns to college majors ( Arcidiacono et al., 2020 ; Wiswall and Zafar, 2020 ), and the causal impact of health on retirement ( Shapiro and Giustinelli, 2019 ).
4 The income gap in GPA increased from 0.052 to 0.098 on a 4 point scale. It is significant at the 1% level in both scenarios.
5 The 64 people taking the survey at the moment the target sample size (1500) was reached were allowed to finish.
6 59% of Honors students in our sample report living on campus.
7 This is different from asking students in normal times about their expected outcomes in a state with online teaching and no campus activities (COVID-19) since most students would not have had any experience with this counterfactual prior to March this year.
8 Altonji et al. (2016) finds a small but positive effect on the probability of attending graduate school when graduating into a recession. This is suggestive evidence that students try to avoid entering the labor market when economic conditions are adverse. Our results on delayed graduation are consistent with students avoiding entering the labor market at inopportune times.
9 For this calculation, we take earnings data from the US Department of Education College Scorecard dataset. Major-specific earnings are calculated using median first-year earnings for ASU graduates in 2015 and 2016 by two-digit CIP code. Observable earnings averaged within major category.
10 STEM major designation made using two-digit CIP code and The STEM Designated Degree Program from the US Department of Homeland Security.
11 This includes 77 respondents, or 43% of those who say COVID-19 impacted their major choice.
12 The relevant survey question read: “ Suppose you are given the choice to take a course online/remote or in-person . [ Had you NOT had experience with online/remote classes this semester ], what is the percent chance that you would opt for the online/remote option ?”
13 This result is in line with a survey about eLearning experiences across different universities in Washington and New York that concludes that 75% of the students are unhappy with the quality of their classes after moving to online learning due to COVID-19.
14 According to the US Census Bureau Household Pulse Survey Week 3, 48% of the surveyed households have experienced a loss in employment income since March 13 2020.
15 The cutoff for median parental income in our sample is $80,000.
16 Based on analysis of ASU administrative data including transcripts, we find that, relative to their counterparts, first-generation, lower-income, and non-white students drop out at higher rates, take longer to graduate, have lower GPAs at graduation, and are more likely to switch majors when in college (see Appendix Table A3 ).
17 The difference is significant at 1% in both cases.
18 Honors students were as likely as non-Honors students to say that classes got easier after they went online but, conditional on saying classes got easier, were 47% more likely to say “homework/test questions got easier.” Conversely, males were marginally more likely to say classes got harder after they went online (10% more likely, p = 0.055) and, conditional on this, were 14% more likely to say that “online material is not clear”.
19 Eigenvalues indicate the presence of only one principal component for each of the shocks.
20 The only exception is the financial shock when explaining changes in the probability of taking classes online.

Expected and previous academic performance.
Notes: Figure plots mean expected GPA with COVID-19 against students' cumulative GPA up to the spring 2020 semester. The 45 degree line is also plotted for reference.

More treatment effects by demographic group.
(a) Withdrew from Class due to COVID (0/1); (b) Social Events per Week ( Δ 0–14); (c) Move in With Family due to COVID (0/1); (d) Weekly Study Hours ( Δ 0–40); (e) Reservation Wage (Pct. Δ )
Notes: Bars denote 90% confidence interval.

Cohort trends.
Notes: Figure plots average COVID-19 effects for a series of outcomes. The x-axis variable in each panel is expected academic year of graduation (after COVID), with summer graduation dates included in the previous academic year. Bars denote 90% confidence interval.

Distribution of individual effects.
Notes: Data winsorized below 5% and above 95%. Controls include cohort fixed effects, major fixed effects, and the economic/health proxies in Table 3 . Conditional distribution adjusted to preserve unconditional mean. Within each plot: middle line represents median, edges of box represent interquatile range (IQR), edge of whisker represents the adjacent values or the 25th(75th) percentile plus(minus) 1.5 times the IQR. Outlier observations past adjacent values plotted as individual points.
Composition of COVID effects: more outcomes.
Notes: Standard errors in parentheses bootstrapped with 1000 replications. Each column reports results from a separate OLS regression of the dependent variable onto the covariates (row variables). Dependent variables measured in percentage points (except GPA). ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
Existing achievement gaps.
Notes: Sample includes all first time freshman at ASU's main campus who started within the last 10 years. N = 58,426. ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
Correlation of shock proxies.
Notes: Table reports correlation matrix for indicated variables.
- Altonji J., Arcidiacono P., Maurel A. Handbook of the Economics of Education. vol. 5. Elsevier; Cambridge, MA: 2016. The analysis of field choice in college and graduate school: determinants and wage effects; pp. 305–396. [ Google Scholar ]
- Angrist J.D., Pischke J.-S. Princeton University Press; Princeton: 2009. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: An Empiricist’s Companion. OCLC: ocn231586808. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arcidiacono P., Hotz V.J., Maurel A., Romano T. Ex ante returns and occupational choice. J. Polit. Econ. 2020 (forthcoming) [ Google Scholar ]
- Blom E., Cadena B.C., Keys B.J. 2019. Investment Over the Business Cycle: Insights from College Major Choice. (Working Paper) [ Google Scholar ]
- Chetty R., Friedman J.N., Hendren N., Stepner M. 2020, May. Real-Time Economics: A New Platform to Track the Impacts of COVID-19 on People, Businesses, and Communities Using Private Sector Data. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heckman J.J., Vytlacil E. Structural equations, treatment effects, and econometric policy evaluation. Econometrica. 2005, May; 73 (3):669–738. [ Google Scholar ]
- Imbens G., Rubin D.B. Causal inference: for statistics, social and biomedical sciences: an introduction. OCLC. 2015; 985493948 [ Google Scholar ]
- Jacob B., McCall B., Stange K. College as country club: do colleges cater to students’ preferences for consumption? J. Labor Econ. 2018; 36 (2):40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kahn L.B. The long-term labor market consequences of graduating from college in a bad economy. Labour Econ. 2010, April; 17 (2):303–316. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuchler T., Zafar B. Personal experiences and expectations about aggregate outcomes. J. Financ. 2019, October; 74 (5):2491–2542. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhfeld M., Soland J., Tarasawa B., Johnson A., Ruzek E., Liu J. 2020, May. Projecting the Potential Impacts of COVID-19 School Closures on Academic Achievement. Publisher: EdWorkingPapers.com. [ Google Scholar ]
- Malmendier U., Nagel S. Learning from inflation experiences *. Q. J. Econ. 2016, February; 131 (1):53–87. [ Google Scholar ]
- Oreopoulos P., von Wachter T., Heisz A. The short- and long-term career effects of graduating in a recession. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 2012, January; 4 (1):1–29. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rothstein J. 2020, May. The Lost Generation? Labor Market Outcomes for Post Great Recession Entrants. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwandt H., von Wachter T. Unlucky cohorts: estimating the long-term effects of entering the labor market in a recession in large cross-sectional data sets. J. Labor Econ. 2019; 37 (S1):S161–S198. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shapiro M., Giustinelli P. 2019, July. SeaTE: Subjective ex Ante Treatment Effect of Health on Retirement. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiswall M., Zafar B. Human capital investments and expectations about career and family. J. Polit. Econ. 2020 (forthcoming) [ Google Scholar ]

Biden Mangles Statistic About Hispanic Students
By Robert Farley
Posted on May 10, 2024
Este artículo estará disponible en español en El Tiempo Latino .
According to the Department of Education, about 28% of U.S. students are Hispanic. According to Census Bureau data, about 15% of U.S. students speak Spanish at home. And about 21% of students come from homes where at least one person speaks Spanish.

Three different statistics. Three different numbers.
But in remarks to Latino audiences whose votes he hopes to win , President Joe Biden routinely conflates these statistics, sometimes in the course of the same speech or interview.
For example, in remarks at a Cinco de Mayo reception at the White House on May 6, Biden called Latinos “the future of our nation.”
“You know, everybody says … why have I always been so fundamentally focused on Latinos,” Biden said. “Simple proposition: You make up 28% of the students in America. Think — think about it. Twenty-eight percent of all the students in high school and grade school in America are Latino.”
Right so far. The Department of Education’s National Center for Education Statistics says that by the fall of 2021, about 28% of students enrolled in public schools in prekindergarten through 12th grade were Hispanic/Latino.
But later in the speech, Biden said, “You know, when you have 28% of all the students in our schools up to high school — 28% speaking Spanish, how in God’s name can we not pay attention?”
That’s not accurate. It assumes all Hispanic students speak Spanish, and they do not.
We wouldn’t normally write about an elected official botching a statistic that he had repeatedly gotten right on other occasions. But in this case, it’s a statistic Biden has mangled numerous times, and for years.
For example, on a Spanish-language radio show recorded May 6 , Biden was asked why it was important for him to have events like the Cinco de Mayo reception.

“The Hispanic community’s part of the future of America,” Biden said. “Twenty-eight out of every 100 students in school speak Spanish — 28! The idea that we’d ignore that? That’s our future.” (The Republican National Committee called Biden out on that one, commenting on X , “He completely made that statistic up.” But Biden didn’t invent the figure; he confused it with a different statistic, as this story makes clear.)
On other occasions, Biden has cited similar figures as the percentage of students who come from Spanish-speaking homes, as he did in an April 9 interview on Univision and in remarks at the Congressional Hispanic Caucus gala on Sept. 21, 2022.
Analyzing data from the Census Bureau’s 2022 American Community Survey, Jeffrey Passel , senior demographer at the Pew Research Center, concluded that about 21% of U.S. students live in a home where at least one person speaks Spanish.
In fairness, Biden has gotten the statistic right numerous times as well, such as during remarks at the Americas Economic Leadership Summit on Nov. 3, when he said, “About a quarter of the children in our public schools today are Hispanic.” But quite ofte n , Biden conflates the percentage of Hispanic students in the U.S. with the percentage of U.S. students who speak Spanish .
The mix-up prompted PolitiFact to weigh in with two fact-checks when Biden repeatedly got it wrong on the campaign trail in September 2020, and again in June.
At least once, the White House press office has corrected the president in the official transcript. When Biden, in remarks at a Hispanic Heritage Month reception on Sept. 30, 2022, said, “Twenty-six percent of every single child who’s in school today speaks Spanish,” the press office later clarified that he meant “is Latino.”
There is a difference between being Latino and speaking Spanish. According to the Census Bureau’s 2022 American Community Survey , about 45% of Hispanics born in the U.S. speak only English. Another 45% speak another language but also speak English “very well.” As one would expect, a far smaller percentage of foreign-born Hispanic people — who make up about a third of the Hispanic population in the country — speak only English (6.5%) or speak another language but also speak English “very well” (31%).
According to Passel of the Pew Research Center, the American Community Survey shows about 26% of K-12 students are Hispanic (a little higher for public than private school). That’s close to the 28% cited by Biden, and, as we said, the Department of Education reports the figure as 28%.
As for the percentage of U.S. students who speak Spanish, the American Community Survey questions don’t make it easy to answer that precisely.
Analyzing available data from the survey — not whether someone speaks Spanish, but whether it is “spoken at home” — for those aged 5 and over, Passel said about 15% of K-12 students speak Spanish at home, representing about 55% of the Hispanic students. We looked at the survey data another way — people aged 5 to 17 (so school age but not necessarily students) — and found, similarly, nearly 15% of that population speaks Spanish.
Analyzing 2022 American Community Survey data — the latest available — Passel estimated the share of K-12 students who come from a home where somebody speaks Spanish is 21%.
Again, Biden mixes up these statistics, often inflating the percentage of students who speak Spanish.
We reached out to the White House press office for comment or backup for the president’s claims, but we did not get a response.
Editor’s note: FactCheck.org does not accept advertising. We rely on grants and individual donations from people like you. Please consider a donation. Credit card donations may be made through our “Donate” page . If you prefer to give by check, send to: FactCheck.org, Annenberg Public Policy Center, 202 S. 36th St., Philadelphia, PA 19104.
- History, Facts & Figures
- YSM Dean & Deputy Deans
- YSM Administration
- Department Chairs
- YSM Executive Group
- YSM Board of Permanent Officers
- FAC Documents
- Current FAC Members
- Appointments & Promotions Committees
- Ad Hoc Committees and Working Groups
- Chair Searches
- Leadership Searches
- Organization Charts
- Faculty Demographic Data
- Professionalism Reporting Data
- 2022 Diversity Engagement Survey
- State of the School Archive
- Faculty Climate Survey: YSM Results
- Strategic Planning
- Mission Statement & Process
- Beyond Sterling Hall
- COVID-19 Series Workshops
- Previous Workshops
- Departments & Centers
- Find People
- Biomedical Data Science
- Health Equity
- Inflammation
- Neuroscience
- Global Health
- Diabetes and Metabolism
- Policies & Procedures
- Media Relations
- A to Z YSM Lab Websites
- A-Z Faculty List
- A-Z Staff List
- A to Z Abbreviations
- Dept. Diversity Vice Chairs & Champions
- Dean’s Advisory Council on Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer and Intersex Affairs Website
- Minority Organization for Retention and Expansion Website
- Office for Women in Medicine and Science
- Committee on the Status of Women in Medicine Website
- Director of Scientist Diversity and Inclusion
- Diversity Supplements
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recruitment
- By Department & Program
- News & Events
- Executive Committee
- Aperture: Women in Medicine
- Self-Reflection
- Portraits of Strength
- Mindful: Mental Health Through Art
- Event Photo Galleries
- Additional Support
- MD-PhD Program
- PA Online Program
- Joint MD Programs
- How to Apply
- Advanced Health Sciences Research
- Clinical Informatics & Data Science
- Clinical Investigation
- Medical Education
- Visiting Student Programs
- Special Programs & Student Opportunities
- Residency & Fellowship Programs
- Center for Med Ed
- Organizational Chart
- Leadership & Staff
- Committee Procedural Info (Login Required)
- Faculty Affairs Department Teams
- Recent Appointments & Promotions
- Academic Clinician Track
- Clinician Educator-Scholar Track
- Clinican-Scientist Track
- Investigator Track
- Traditional Track
- Research Ranks
- Instructor/Lecturer
- Social Work Ranks
- Voluntary Ranks
- Adjunct Ranks
- Other Appt Types
- Appointments
- Reappointments
- Transfer of Track
- Term Extensions
- Timeline for A&P Processes
- Interfolio Faculty Search
- Interfolio A&P Processes
- Yale CV Part 1 (CV1)
- Yale CV Part 2 (CV2)
- Samples of Scholarship
- Teaching Evaluations
- Letters of Evaluation
- Dept A&P Narrative
- A&P Voting
- Faculty Affairs Staff Pages
- OAPD Faculty Workshops
- Leadership & Development Seminars
- List of Faculty Mentors
- Incoming Faculty Orientation
- Faculty Onboarding
- Past YSM Award Recipients
- Past PA Award Recipients
- Past YM Award Recipients
- International Award Recipients
- Nominations Calendar
- OAPD Newsletter
- Fostering a Shared Vision of Professionalism
- Academic Integrity
- Addressing Professionalism Concerns
- Consultation Support for Chairs & Section Chiefs
- Policies & Codes of Conduct
- First Fridays
- Fund for Physician-Scientist Mentorship
- Grant Library
- Grant Writing Course
- Mock Study Section
- Research Paper Writing
- Establishing a Thriving Research Program
- Funding Opportunities
- Join Our Voluntary Faculty
- Child Mental Health: Fostering Wellness in Children
- Faculty Resources
- Research by Keyword
- Research by Department
- Research by Global Location
- Translational Research
- Research Cores & Services
- Program for the Promotion of Interdisciplinary Team Science (POINTS)
- CEnR Steering Committee
- Experiential Learning Subcommittee
- Goals & Objectives
- Issues List
- Print Magazine PDFs
- Print Newsletter PDFs
- YSM Events Newsletter
- Social Media
- Patient Care
INFORMATION FOR
- Residents & Fellows
- Researchers
Students and Faculty Mentors Celebrated at Student Research Day
Student research day scientific poster session, student research day, shelli farhadian, md, phd, and john k. forrest, md, peter aronson, md, c.n.h. long professor of medicine (nephrology) and professor of cellular and molecular physiology.
On May 7, 2024, students and faculty mentors were celebrated at Yale School of Medicine’s (YSM) Student Research Day (SRD), an annual tradition at YSM since 1988. Five medical students (Chinye Ijile, Amanda Lieberman, Kingson Lin, Victoria Marks, and Jamieson O’Marr) made thesis presentations, and over 75 students, from across Yale’s health profession schools, displayed scientific posters and engaged with attendees during the poster session.
“Today we’re showcasing a diverse range of mentored research—spanning from fundamental basic science, to implementation science—performed by student investigators from across the health professions schools,” Associate Dean for Student Research Sarwat Chaudhry, MD, professor of medicine (general medicine), said in opening remarks. Associate Dean for Student Research Erica Herzog, MD, PhD, John Slade Ely Professor of Medicine (pulmonary) and professor of pathology, added, “We take immense pride in Yale’s deep-rooted tradition of embedding research within medical education. For our students, experience in scientific investigation isn't merely a stepping stone towards a successful residency match or a career in academic research; it's foundational training for their lifelong commitment to medicine.”
Farr Lecture
The Lee E. Farr MD Endowed Lectureship and the presentation of the Dr. John N. Forrest, Jr., Mentorship Award, which bookended the student thesis presentations, honored YSM faculty for their outstanding mentorship. In introducing Peter Aronson, MD, C.N.H. Long Professor of Medicine (Nephrology) and professor of cellular and molecular physiology, as the Farr lecturer, Nancy J. Brown, MD, Jean and David W. Wallace Dean and C.N.H. Long Professor of Internal Medicine, explained that the lecture aims to stimulate thinking and to inspire students to strive to achieve more effective leadership and educational roles in society. Brown said that Aronson, who has been at YSM for 50 years since joining as a nephrology fellow in 1974, “epitomizes these qualities as a physician-scientist, educator, mentor, and colleague. As such, there is no one more fitting to speak at today’s event.”
As chief of the Section of Nephrology from 1987-2002, Brown said, Aronson nurtured the development of numerous physician-scientists, both as faculty and fellows, many of whom became recognized leaders—and many of whom remain at Yale and were present on SRD. “It goes without saying” Brown concluded, “that Dr. Aronson’s stewardship is one reason for the enduring strength of Yale’s 200-year tradition of medical student research,” noting he had been part of the tradition for one quarter of the 200 years. (In comments after Aronson spoke, Herzog noted several of his student evaluations simply said GOAT: “Greatest Of All Time.”)
Using his own experiences as examples in his lecture titled From Sugar to Salt to Stones: Serendipitous Journey as Mentee and Mentor, Aronson noted the importance of chance events and serendipitous research findings in determining the course of his academic development and research career. ( This article describes his remarks in detail .) In closing, Aronson honored the late John N. Forrest, Jr., professor emeritus of medicine and the founding director of YSM’s Office of Student Research (OSR). Forrest, he said, “exemplified extraordinary commitment to the process of education and mentorship,” adding “we should all be inspired by his example of what is most gratifying in academic medicine.”
Dr. John N. Forrest, Jr., Mentorship Award
Chaudhry similarly honored John N. Forrest, Jr. in introducing the mentorship award established to recognize his legacy. “As many of you know, Dr. Forrest died earlier this year, and so this year’s Forrest Prize holds special meaning.” OSR “was his pride and joy,” Chaudhry said, adding that since starting their roles as associate deans of student research in 2020, “Dr. Herzog and I have continually been impressed by Dr. Forrest’s care and foresight in establishing the Office of Student Research. Dr. Forrest’s legacy lives on in the enduring strength of YSM’s medical student research program.”
Before Forrest’s son, John K. Forrest, MD, associate professor of medicine (cardiovascular medicine), announced the award recipient— Shelli Farhadian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine (infectious diseases); assistant professor, epidemiology of microbial diseases —he shared, “My family and I are grateful to the numerous people who reached out after our father’s passing. Some of the most touching correspondence we received were from medical students, residents, and fellows whom he had mentored while at Yale. There is no greater evidence of the lasting impact that mentorship plays in the lives of young physicians that the words contained in those letters.”
Turning to the awardee, Forrest said, “Dr. Farhadian is an exemplary mentor,” and pointed to her role “in shaping the careers of her mentees, many of whom have garnered multiple awards and recognition, and published first author manuscripts under her tutelage.”
He then shared what a student wrote about Farhadian: “Dr. Farhadian is such a fantastic mentor and person. As my mentor she encouraged me to apply for grants and submit to conferences and journals and has always made herself available to answer any questions that I have. She also facilitates an environment in which her mentees feel comfortable coming to her with questions and offers help in connecting me with doctors in my fields of interest. Beyond my research with Dr. Farhadian, she has also proved to be an invaluable resource in terms of developing as a student and a future doctor. She is an inspiring woman in medicine, and I hope to become as caring and capable as a doctor and mentor as she models.”
Upon receiving the award, Farhadian said, “It means a great deal for me to receive this award in Dr. Forrest’s name. I was lucky to cross paths with Dr. Forrest when I was an intern, and I will always remember how kind he was to everyone in the hospital, no matter how small their role.” Farhadian added, “I feel very lucky to have had my own exceptional research mentors along the way, and I have tried to emulate them when mentoring my own trainees.”
Student Thesis Presentations
Chinye Ijile
Medicaid Coverage for Undocumented Children in Connecticut: A Political History
Faculty mentor: Naomi Rogers, PhD, professor in the history of medicine and of history; acting chair, Spring 2024, History of Medicine
Amanda Lieberman
Multilevel Barriers to Methadone for HIV Prevention Among People Who Inject Drugs in Kazakhstan
Faculty mentor: Frederick Altice, MD, MA, professor of medicine (infectious diseases) and of epidemiology (microbial diseases)
Kingson Lin, MD-PhD
Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Novel MGMT-Dependent, MMR-Independent Agents for the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)
Faculty mentors: Ranjit Bindra, MD, PhD, Harvey and Kate Cushing Professor of Therapeutic Radiology and professor of pathology; and Seth Herzon, PhD, Milton Harris ’29 Ph.D. Professor of Chemistry
- Victoria Marks
Association between Medical Insurance, Access to Care, and Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Uveal Melanoma in the United States
Faculty mentor: Michael Leapman, MD, MHS, associate professor of urology; assistant professor, chronic disease epidemiology
Jamieson O’Marr
Ballistic and Explosive Orthopaedic Trauma Epidemiology and Outcomes in a Global Population
Faculty mentor: Brianna Fram, MD, assistant professor of orthopaedics & rehabilitation
Featured in this article
- Frederick Lewis Altice, MD, MA
- Peter S. Aronson, MD
- Ranjit S. Bindra, MD, PhD
- Nancy J. Brown, MD
- Sarwat Chaudhry, MD
- Shelli Farhadian, MD, PhD
- John K Forrest, MD, FACC, FSCAI
- Brianna R. Fram, MD
- Erica Herzog, MD, PhD
- Seth Herzon, PhD
- Chinye Ijeli
- Michael S. Leapman, MD, MHS
- Amanda Liberman
- Kingson Lin
- Jamieson O'Marr, MS
- Naomi Rogers, PhD
Related Links
- Student Research Day Program

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This presentation summarizes important basic information on the current pandemic. It was written for high school and college non-science-major students/teachers. Feel free to use, share, and send suggestions for improvements. ... COVID-19 is an infectious disease of the human respiratory system caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2.
If you want to make COVID-19 understandable for your middle school students, we recommend using this editable template from Slidesgo. With it you can explain the symptoms, prevention measures, how the transmission occurs, what treatments are available, etc. We have included tables, maps, infographics and lists that will be of great help.
People with COVID-19 can have no symptoms or develop mild, severe, or fatal illness. Kids may have less severe disease (2% of confirmed cases in China occurred among those <20 years old) Current case fatality rate ~2% among those with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19. Risk factors for severe illness may include:
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. After a year and a half, has society really learned a lesson about the COVID-19 pandemic? What about in education? These are questions that you can answer by customizing this new template for educational presentations. Teaching and classes in general might be ...
This collection of resources from The New York Times is designed to help students and educators stay updated on the COVID-19 outbreak, think critically about information, consider the "essential" questions the pandemic raises about our world today. Popular resources include a lesson on how coronavirus hijacks cell function, weekly data literacy activities, short Film Club documentaries on ...
Coronavirus Presentation templates ... The COVID-19 vaccine has improved the pandemic situation. We are gradually returning to our pre-COVID-19 lifestyle. ... If you want to make COVID-19 understandable for your middle school students, we recommend using this editable template from Slidesgo. With it you can explain the symptoms, prevention ...
This PowerPoint presentation walks you and your students through key biology concepts of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Download PPT (PPT 16.3 MB) How Do We Detect COVID-19? Every day brings new developments in the race for effective and accurate COVID-19 testing, but most strategies are based on a few key fundamental technologies.
3. Be a leader in keeping yourself, your school, family and community healthy. Share what you learn about preventing disease with your family and friends, especially with younger children. Model good practices such as sneezing or coughing into your elbow and washing your hands, especially for younger family members. 4.
Through this program, ED and HHS are offering interested public school districts, including public charter school districts, over-the-counter (OTC) rapid antigen COVID-19 self-tests free of charge for their students, families, staff, and school community. These self-tests are easy to use and can play an important role in containing the spread ...
COVID-19 presentation for educators - Google Slides. JavaScript isn't enabled in your browser, so this file can't be opened.
INTRODUCTION. With incendiary speed, COVID-19 has transformed economies, health services, and education structures, informing new methods for remote teaching ().The global impact of school closures in early March affected over 1.725 billion students in 193 countries ().Guidelines provided by the U.S. state health organizations, state education departments, and state education licensing ...
COVID-19 has led to some of the same changes high schools and colleges have adopted, specifically, replacement of large in-person lectures with small group activities small group discussion and virtual lectures. 32 The transition to an online format for medical education has been rapid and impacted both students and faculty. 33, 34 In a survey ...
Introduction. The global outbreak of COVID-19 has certainly taken an overwhelming toll on everyone. People have lost their jobs, their homes, and even their lives. There is no getting past the fact that the overall impact on the world has been negative, but it is important to realize that positive aspects of the pandemic have been overshadowed ...
The aim of this survey study is to investigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the education, health, and lifestyle of students from different age-groups. 2.2. Statistical analysis. In this study, we conducted a cross-sectional survey with a sample size of 1182 students from different educational institutions.
COVID-19: 13% of students have delayed graduation, 40% lost a job, internship, or a job offer, and 29% expect to earn less at age 35. Moreover, these effects have been highly heterogeneous. One quarter of students increased their study time by more than 4 hours per week due to COVID-19, while another quarter decreased their study time by more ...
The questions around when to re-open more schools for in-person classes remains front and center for millions of Americans. Data show about 42 percent of all students between kindergarten and high ...
Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. The coronavirus outbreak has become one of the most notorious events of the decade, if not the current century. Every bit of information helps a lot, so let us help you create useful and informative presentations about this virus with our latest template. We've got a serious matter at hand ...
If a patient tests negative by Rapid Antigen Test (RAT) FDA recommends. If symptomatic, test at least twice 48 hours apart. A third test might be needed if the patient is concerned they have COVID-19. If asymptomatic, but believe they have been exposed, test with RAT at least 3 times, each 48 hours apart to be considered truly negative.
PK !aŽF | 'u [Content_Types].xml ¢ ( Ì ]oÛ6 †ï ì? º lI--ÉEœbh7`À¶ h ì-'h[¾&ÑNòïGÉ uR%-|Èò½ ¢ >'È÷% éæíC-Žv¼ª""_ZîÄ ...
A Mental Wellness Project Supports Students During COVID-19. Researchers are working with children in Baltimore to learn about student resilience during the pandemic. Feature. Measuring the Psychological Distress of COVID-19. People from many racial and ethnic minority groups reported experiencing less distress than White adults.
Tool 4. Presentation template - 28 April 2021. 28 April 2021. | COVID-19: Critical preparedness, readiness and response. Download (3.8 MB)
List of Presentation Topic Ideas for Students. We know how difficult it is to come up with an interesting presentation topic idea on the fly. That's why we put together a list of more than 200 ideas to help you out. We've organized these presentation topics for students by subject so you can easily browse through and find what you're looking for.
Students graduating from college in spring or summer 2024 are eligible. Your insights will contribute to a deeper understanding of the challenges and triumphs faced during these unprecedented times. ... at the University of Arkansas are conducting a research study aimed at understanding the narratives of college students during the COVID-19 ...
AAMC Guidelines on Student Involvement in Direct Patient Contact - March 2020. ''. For medical schools in locales in which there is significant, active current or anticipated COVID-19 community spread, and/or limited availability of PPE and/or limited availability of COVID-19 testing, the AAMC guidance remains that, unless there is a critical ...
Join the Center for Environmental Justice and Sustainability for the 2023-2024 Student and Faculty Fellowship presentations. Laudato Si' Faculty Fellows are Tapoja Chaudhuri, presenting "Putting Down Roots," and Lauren Bibin, whose study focuses on "Seattle University Sustainability Transformation Assessment in Nursing."
The COVID‐19 pandemic continues to upend the lives of students in higher education institutions. Students' mental health has become a paramount concern to institutional leaders: over 90% of college presidents were concerned about students' mental health during the pandemic (Lederman, 2020 ).
CBS News reported just days ago that nearly one-third of the country's COVID-19 cases are linked to a new variant. "It's called FLiRT because they named it due to some minimal changes on ...
Due to COVID-19: 13% of students have delayed graduation, 40% have lost a job, internship, or job offer, and 29% expect to earn less at age 35. Moreover, these effects have been highly heterogeneous. One quarter of students increased their study time by more than 4 hours per week due to COVID-19, while another quarter decreased their study time ...
According to the Department of Education, about 28% of U.S. students are Hispanic. According to Census Bureau data, about 15% of U.S. students speak Spanish at home. And about 21% of students come ...
COVID-19 Series Workshops. Previous Workshops. Departments & Centers. Find People. Giving to YSM. Cancer. Biomedical Data Science. Health Equity. Inflammation. Neuroscience. ... Student Thesis Presentations. Chinye Ijile . Medicaid Coverage for Undocumented Children in Connecticut: A Political History. Faculty mentor: Naomi Rogers, PhD ...