- BEST PRACTICES

Knowledge Management Case Studies
Since researching and consulting on knowledge management from the mid-1990s, I have collected over 400 examples of knowledge management in practice in organizations large and small around the world. About 30 of these are in-depth case studies from our own research and interviews that have been published in our reports and books; around 50 are from academic journals; about 150 from conferences or articles in magazines by those involved, and the remainder are 'caselets' that illustrate the use of specific KM techniques.
As this section develops we shall pick a selection from our database and publish them in a standard format. To give a flavour of what is to follow we start with the following three examples:
- Best practices yields one free fab plant (Texas Instruments) - this is one of KM's classic examples dating from the 1990s. It demonstrates how sharing best practices across their world-wide operations Texas Instruments saved of the order of $500 million.
- Holistic KM at the Department of Health - a good example of how a KM strategy embraces several inter-related dimensions including people, processes, technology, content and also top-down, bottom-up and middle-out approaches.
- Telling Stories to Capture Lessons Learned (British Council) - the use of narrative techniques in workshops to capture lessons learned.
Other Examples
Throughout our resources, especially the articles and presentations , you will find short abstracts and references to many other cases. Here are some examples:
- Hoffman La Roche - by considering the knowledge needed to prepare clinical trials documentation for the approval authorities have contributed to faster time to market for new drugs.
- NEC - when this Japanese electronics company articulated its core knowledge base, it helped redefine the company's mission as 'computers and communications', markets in which it has shown continuing success.
- Dow Chemical - by auditing its intellectual property that was in its patent portfolio it generated significant additional revenues through licensing and other agreements.
- Skandia - in the late 1990s this Swedish based insurance company developed methods to measure it intellectual capital (the knowledge in its people and processes); this focus by its senior managers helped it grow from a small regional company to number five in the world in its market segment.
- Steelcase - this office products supplier used ethnography techniques to find how people working in offices interacted; as a result they put the lessons learned into practice in designing office environments that increased productivity through an appropriate mix of 'caves and commons' workspaces.
You'll also find examples in our archive - see the site map - cases .
Last updated: 9th April 2011
CASE STUDIES
- blog (new tab)
- presentations
- periodicals
- organizations
I 3 Update/ Entovation International News
This newsletter was published regularly between 1993 and 2003. Its many articles still provide food for thought and practical tips for knowledge managers; you'll also find other case examples.
Go to the newsletter archive
IN OUR ARCHIVE:
- Case snippets
What's the difference between leaders and laggards in knowledge management?
Read this article which spells out the differences.
Top Knowledge Management Use Cases (with Real World Examples)
Knowledge Management (KM) is presently experiencing a rebirth, with greater executive interest and organizational commitment. Driven by the post-Covid transition to hybrid and remote work, the employee churn during the great resignation, and the explosion of AI driven by knowledge graphs and large language models, the value that KM offers is better understood, and KM initiatives are being prioritized like never before.
At EK, we’ve worked tirelessly over the last decade to ensure KM is understood for the business value it offers and considered in terms of practical solutions and measurable results. We’ve found that defining use cases is one of the best ways to help organizations understand this value, and moreover, prioritize what really matters for them, their mission, and their stakeholders.
There is a lot of writing about KM outcomes, or features, but there is a surprising dearth of writing regarding Knowledge Management Use Cases. In this article, I’ve captured the top ten use cases for KM Transformations. It’s important to note that these aren’t enabling features or software like search or online discussions, nor are they expected outcomes or results like improved findability, knowledge sharing, or knowledge retention. Rather, these are the actual use cases, the reasons why people do KM and what it actually means to the organization’s operations and people.
Of the top ten Knowledge Management use cases, six are what I’d consider “classics,” in that they’ve been present as the leading use cases for much of the short history of KM. The other four are the cool new ones, which are presently driving the industry and will be top organizational priorities for the near future as well.
The following six are the “classic” KM use cases. They hold as much value today, if not more, as they always have. The solutions and technologies we can apply against these use cases have changed over the years, though the use cases themselves remain largely the same.
Use Case #1: Knowledge Sharing and Retention
Perhaps no use case is more central to KM than Knowledge Sharing and Retention. Organizations have consistently sought to retain the knowledge and expertise held within the minds of their employees. This tacit knowledge walks out the door with employees if not properly shared with others or transferred into an explicit format that may be captured and managed. KM for Knowledge Sharing and Retention will counteract this “brain drain,” ensuring that information is shared, used, and reused, thereby improving the collective knowledge of the organization and saving countless hours that otherwise would have been spent re-creating lost knowledge (or worse yet, repeating mistakes already made).
Real World Example:
We recently led a “Knowledge Transfer Menu” effort with a global development bank, which was concerned with their increasing attrition at all levels, recognizing their expertise and associated experience was walking out the door. Given the wide number of potential knowledge transfer and sharing techniques, we worked with them to develop a menu of different techniques, allowing them to quickly test a selection of each, ranging in scale, type, and complexity (none, limited, or high technology) to determine what would be most natural to their unique business and employees—to facilitate knowledge sharing either one-to-one, one-to-many, or as a larger community. As a result, the organization adopted a subset of the Knowledge Transfer techniques to establish enterprise wide, and we helped them implement a simple knowledge base to ensure this new knowledge would be managed and easily findable.
Use Case #2: Onboarding and Learning

To be fair, onboarding and learning could easily be considered two separate use cases, but both are solved by many of the same solutions and tend to produce similar outcomes. The Onboarding and Learning use cases are all about providing the employee with everything they need to perform, from day one of their job through the entire employee journey. This is much more than employee self-service. The Onboarding and Learning use cases cover the delivery of knowledge at the point of need, connecting learners with teachers or experts, and guiding a learner to develop and extend their knowledge. Effective Onboarding and Learning will result in employee satisfaction, which further leads to higher employee retention.
A large public agency was seeking to transform from a traditional to modern learning environment. With a highly distributed workforce, the agency needed an innovative means of helping their employees of all levels and tenures connect and learn from each other. We designed and implemented an advanced learning platform for them that integrated all elements of their learning and performance ecosystem so that any employee could intuitively find and discover classes, self-serve learning content, experts, and cohorts with which to engage. The result was a single place for employees to craft their learning journey and managers to track and manage these journeys, while also capturing new knowledge through communities of practice and learning cohorts.
Use Case #3: Customer Support
The Customer Support use case covers call centers, help desks, and the associated knowledge bases responding agents use to deliver concise, complete, and consistent customer service. This use case addresses common customer complaints that they were “bounced around” from person to person, given inconsistent guidance, had to repeat themselves, and were stuck in “on hold” purgatory. Just as the Onboarding and Learning use case results in employee satisfaction and retention, the Customer Support use case results in customer satisfaction and retention. Moreover, appropriate customer support can yield higher revenues and faster deal close times, depending on the industry.
One of the largest insurance companies in the United States found that nearly half of their help desk calls were unresolved, requiring escalation or follow-up. Not surprisingly, less than 30% of their customers were satisfied with overall customer support. We helped to reengineer their customer support systems by designing a new tagging structure and taxonomy for their knowledge base, implementing new content governance for their knowledge base content, and creating new incentives and measurements for their agents to identify and improve lower-end knowledge base content. As a result, their Tier 1 call resolution improved to nearly 80%, with similar trends for overall customer satisfaction.
Use Case #4: Self-Service
This use case connects to the two preceding, in that it may be either employee self-service or customer self-service. As the name states, this use case is creating easy and intuitive mechanisms to get the right people the information they need, without having to make a call, send an email, or otherwise rely on others. Generationally, end users are increasingly wanting to get their questions answered or complete their desired action via self-service. This use case delivers the right knowledge, information, and data at the point of need, and when delivered properly, does so quickly and intuitively. Self-service can be a major cost saver for an organization, while also improving user satisfaction and delivering a more complete and more customized “answer.”
One of the world’s largest employers recognized their host of employees was struggling to get fast answers to simple HR and payroll questions. As part of a 360-Degree Employee Satisfaction effort, we helped them redesign their employee self-service system, including the ability for employees to crowd-source questions and answers to a variety of questions, up-vote ideas and priorities for management, and independently track and complete simple changes to their benefits and employee data.
Use Case #5: Idea Generation and Innovation

In an increasingly distributed world, the opportunity for water cooler meetings and moments of professional kismet are waning. The Idea Generation and Innovation use case counteracts those trends, creating KM-driven opportunities to share knowledge, ideas, problems, and challenges, invoking the collective expertise of individuals to help. This use case isn’t just about coming up with the next “Flamin’ Hot Cheetos” scale of idea, but also about day-to-day problem solving, small ideas, and incremental wins that can collectively make a big difference for an organization and its performance.
A leading software company dramatically shifted to a largely remote work environment following the pandemic. However, they recognized that this sudden and permanent shift would eliminate many of the natural opportunities for the “water cooler talk,” moments of happenstance collaboration, and whiteboard innovation that had previously helped them to thrive. We helped them envision and execute a complete menu of techniques to help them transition to remote work while continuing to collaborate and innovate. This included new traditions like virtual brown bags and topic-based online meetups, new tools for synchronous and asynchronous collaboration, and new processes to capture knowledge at the point of generation and deliver it at the point of need.
Use Case #6: Regulatory Compliance and Preparedness

This use case isn’t about addressing the lack of knowledge, information, or data within an organization; rather, it’s about addressing the proliferation of bad knowledge, information, and data. Many organizations have a poor handle on their content, maintaining years of old, obsolete, and incorrect legacy content, which exposes them to undue risk. For some organizations, this presents a regulatory risk, which if unaddressed can result in millions of dollars of fines, lawsuits, and accidents. Successfully implementing this use case not only addresses these types of risks and costs, but it also vastly improves the findability and manageability of content by removing all the potential wrong answers and dead ends.
During an audit, a global manufacturing company in a highly regulated industry identified a major risk to their operations, finding scores of obsolete, outdated, and incorrect information hosted on their servers. We helped them engineer a content audit and cleanup process to confront this risk, which included a blend of system analytics, automated semantic analysis, and targeted expert reviews to eliminate their “bad” content and also enhance and promote “good” content to new systems so that it could be better leveraged. This process not only removed or archived over 80% of their total content, it also highlighted hidden gems of lessons learned and thought pieces that helped the organization maintain their expertise.
The final four KM use cases are the cool new ones, which have gained great traction only recently and promise high value and organizational prioritization for years to come. These are the ones that are getting the largest budgets and most attention today.
Use Case #7: Getting the Most out of a Digital Transformation

The previous decade was marked by massive investments in digital transformations, with organizations seeking to fundamentally update their processes and systems with streamlined technologies and more “online” modes of work. Millions were invested in these transformations, but few organizations reported the results they were expecting. The missing piece for many was KM. Though systems and processes had been updated, insufficient attention was paid to the core content and means of harnessing organizational expertise. This use case focuses on ameliorating those omissions by helping the state of an organization’s knowledge, information, and data “catch up” with the digital transformation.
A global pharmaceutical company invested millions of dollars in a digital transformation—modernizing, consolidating, and integrating their assorted document, content, and data management systems and implementing a leading enterprise search product. As the multi-year transformation was well underway, however, the organization was not realizing the return on investment they’d anticipated. We conducted an assessment of the organization and helped them pinpoint the critical points of knowledge, information, and data management that would help them realize true business value. These included design and implementation of taxonomy/ontology with auto-tagging of content, improved knowledge capture workflows, design and implementation of search hit types, and a knowledge retention measurement plan. Within six months, they were capturing the returns they’d initially expected from the overall digital transformation.
Use Case #8: Measurement and Efficacy

Keying off of previous use cases, with millions invested in digital transformations, more advanced delivery systems and interfaces, and greater customization, organizations are asking whether they’re getting the promised returns and desired impacts to their business. Though always an important question for a business to answer, in the face of a recession, this becomes all the more critical. This use case seeks to answer that question by delivering detailed insights into how people are using an organization’s content and what they’re doing as a result. Are people learning as they should? Are they taking the appropriate actions as a result? This use case delivers a comprehensive view not just into usage, but impacts, allowing organizations to make the right decisions as a result.
A global financial organization had invested heavily in the creation of an array of new multichannel learning and performance content, as well as improved analytics to track its usage. They had the new content and data, but they lacked the insights to understand it and make decisions as a result of it. We worked with them to go beyond measurement of usage to measurement of efficacy, plotting out the desired impacts and outcomes of each learning topic, then creating measures of performance for each. In cases where the outcomes weren’t reached, we developed processes to engage internal stakeholders and external subject matter experts to help address the underlying issues with the learning content, creating a consistent and positive learning loop to help the organization’s learning environment evolve. We also identified opportunities to use this same process to identify gaps in organizational knowledge and leveraged the same approach to proactively fill those gaps.
Use Case #9: Content Assembly and Customization

A big box retailer with highly complex logistics and a massive fluctuation of employees was constantly struggling to keep key documents like employee handbooks, required safety documents, learning materials, and store-specific guidelines up to date. We worked with the organization to deconstruct this content and then build a content assembly engine to automatically create customized documents for each individual based on their home store, geography, role, and dozens of other factors. This drastically reduced human error and administrative burden while delivering a more customized experience to the individual stakeholders.
Use Case #10: Powering AI

The hottest new use case is no doubt around AI. Most every conversation seems to involve an organization’s vision for their own Chat GPT, bespoke large language models, and organizational Artificial Intelligence. The questions tend to be the same in many of these organizations. How do we make AI happen? This use case is the enabler for organizational AI, creating the structured content, knowledge maps and ontologies, and integrated systems that will truly make AI real for these organizations in their production environments across the enterprise.
For many years, we’ve worked with a global development bank to progress towards Knowledge Management maturity. Over the years, we helped them clean up their content, design and apply an enterprise taxonomy, improve their knowledge capture techniques (for consistency and completeness), and implement more consistent information architectures. Each of these KM initiatives yielded its own value for the organization, but the culmination of the work was the creation of a knowledge graph powered by an ontology and connected to the key content and data stores across 12 different applications. This solution allowed them to realize an array of Artificial Intelligence capabilities, including an intelligent chatbot, a recommendation engine, and an application to identify at-risk knowledge topics in the organization, triggering prioritized knowledge transfer and capture techniques.
At this moment, the organizational understanding of KM continues to increase, executives show a growing willingness to support and invest in it, and the associated technologies continue to progress to help KM Transformations become a reality. These use cases can all be faster, easier, better, and more tangible than in the past, making the overall opportunity for meaningful KM Transformations as high as it has ever been.
For more details and use cases visit Enterprise Knowledge .
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Knowledge Management Analysis: A Case Study

Related Papers
Murray Jennex
Study Presented at 2 nd International …
Mustafa Sagsan
Bhairav Mehta Mehta
E-business has changed the face of most business functions in competitive enterprises. E-business functions are enterprise resource planning (ERP) and related systems such as supply chain management (SCM) and customer relationship management (CRM), are incorporating decision support tools and technologies. Data mining has matured as a field of basic and applied research in e-business. Effective knowledge management (KM) enhances products, improves operational efficiency, speeds deployment, increases sales and profits, and creates customer satisfaction. The aim of this study is to make an association with e-business, KM and data mining. Therefore, firstly, it will brief review the existing on knowledge management, e-business, and data mining, decision support system. We then present on linkages or supplementary relationships between the knowledge management and e-business with data mining. Secondly, knowledge, knowledge management and knowledge process is defined, and point out the need for integration with e-business. Thirdly, it introduces data mining and examined data mining in data warehouse environment. Fourth, the e-business is defined. Using this definition, it can drive e-business application architecture and knowledge process frameworks with business process. Finally, Integrating Intelligent Decision Support System and knowledge management with data mining model is discussed. It presents the proposed KM architecture and discusses how decision support system and data mining can enhance KM. In this study some suggestions are made to get knowledge with data mining, which will help, for the improvement of e-business. Chinese Motor Corporation's knowledge and Sequent Computer's knowledge are discussed.
Craig Furneaux
Case Studies in …
Elayne Coakes
Amir Shafie
Munusamy Natarajan
Public Administration and Public Policy
Csaba Csaki
Dr. Rajesh K Shakya
The outcome of public procurement reforms being carried out in most developing countries is negligible and has not provided significant support for good governance in the procurement sector despite having sound objectives with the initiatives. Presently, most of the governments around the world are implementing e-government procurement (e-GP) systems as a tool for public procurement reform for better governance in the public procurement sector. The implementation of e-procurement has been accepted as one of the most promising and feasible options for governments in delivering enhanced governance in the acquisition of goods, works, and services for the public sector. This action research analyzed the implementation of the e-GP system in a developing country using quantitative and qualitative methods of data analysis following the utilization-focused evaluation framework. The study focused in the utility of the e-GP system, addressing different dimensions of good governance and emphasizing transparency, accountability, corruption control, efficiency, effectiveness and predictability, easy access, rule of law and equity, and civil society awareness. It studied the users’ perception about the role of the e-GP system in public procurement good governance, the users’ attitude towards e-GP system use, and the e-GP system’s impact on good governance. The research revealed that an e-GP system significantly enables and enhances good governance in the public procurement sector. The research indicated that an e-GP system can be fully leveraged for enhancing good governance if, among other things, a comprehensive e-GP system implementation framework is followed with adequate planning, phasing of implementation is based on the procurement cycle basis rather than an incremental functional basis, and the e-GP system addresses all the key aspects of good governance rather than focusing only on 1 or 2 aspects in isolation.
Tiffany Espinosa , Jara Raphaelson
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Information and Software Technology
Jesus Favela
Kiran Nuthanapati
Knowledge management: an evolutionary view
Patrick S . W . Fong
Rajiv Sabherwal
Mani Subramani
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, knowledge management enablers: a case study.
Industrial Management & Data Systems
ISSN : 0263-5577
Article publication date: 1 July 2006
To analyze the crucial role that enablers play in carrying out knowledge management within the enterprise.
Design/methodology/approach
This research uses the method of a case study and has directed the survey on Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Inc. (ASE) and VIA Technologies, Inc. (VIA). It is anticipated through the case study of these two companies that it will be possible to verify the finding of enablers concluded by other papers, thus showing the inter‐relationship between theory and business.
It is found that among the enablers: on the part of strategy and leadership; obtaining top managements' support is most important; among organization culture enablers is the forming of an atmosphere and culture of sharing is most important but needs to be supplemented by informational technology; among people enablers, other than training courses and channels that provide learning, employee incentive program is one of the executing key factor; and among informational technology enablers, other than the digitization of documents, the function of speedy search of information for its re‐use is becoming more and more important.
Practical implications
The result of this study not just validates theory with reality; it also provides a reference for the academia as well as the business field.
Originality/value
This paper has discovered that establishing a dedicated unit for implementing knowledge management is also one of the key enablers. Its role does not just stop at managing knowledge, but instead it plays the role of furthering knowledge management by taking on the duty of assisting and coordinating different departments in their communication.
- Knowledge management
- Knowledge management systems
- Corporate strategy
- Organizational culture
- Communication technologies
Yeh, Y. , Lai, S. and Ho, C. (2006), "Knowledge management enablers: a case study", Industrial Management & Data Systems , Vol. 106 No. 6, pp. 793-810. https://doi.org/10.1108/02635570610671489
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2006, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support

- Vision 2025
- APO Members
- Secretary-General
- Organization
- Annual Reports
- Focus Areas
- Types of Programs
- List of Projects
- Information for Participants
- Flagship Programs
- Centers of Excellence
- Special Projects
- Press Releases
Publications
- Careers@APO
- Procurement Notice
- Digital Learning
Select Page
| Year | 2009 |
| Description | This casebook is an accompaniment to Knowledge Management: Facilitators’ Guide, with case studies from Scotland and the UK as well as from APO members the ROC, Japan, Singapore, and Vietnam. It is meant to inspire and guide more SMEs to apply KM techniques. |
| Download |
- PUBLICATIONS
- DIGITAL LEARNING
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Intelligent text mining for ontological knowledge graph refinement and patent portfolio analysis—case study of net-zero data center innovation management.

1. Introduction
2. literature review, 2.1. ontological knowledge graph (okg), 2.2. keyword extraction, 2.3. clustering method, 2.4. topic modeling, 2.5. technology maturity analysis, 3. methodology, 3.1. dc net-zero technologies’ okg construction, 3.2. patent data retrieval strategy design, 3.3. major patenting trend analysis, 3.4. clustering and topic modeling for enhancing domain okg.
- Combination of K-means Clustering and KeyBERT Keyword Extraction
- CorEx Topic Modeling
3.5. Critical Patent Portfolio Analysis Based on Refined OKG
- KeyBERT-based Technology Function Matrix (KeyBERT-based eTFM)
- Technology Maturity Analysis

4. Discover Enhanced OKG and Patent Analysis—Case of Net-Zero DC Innovations
4.1. major patenting trend analysis, 4.2. clustering and topic modeling for enhancing domain okg, 4.3. critical patent portfolio analysis based on refined okg.
- KeyBERT-based eTFM Analysis
- Technology Maturity Analysis (s-curve)
5. Conclusions, Limitations and Future Works
Author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Paulheim, H. Knowledge graph refinement: A survey of approaches and evaluation methods. Semant. Web 2017 , 8 , 489–508. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Staab, S.; Studer, R. “What Is an Ontology?”, Handbook on Ontologies ; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mizoguchi, R.; Ikeda, M. Towards ontology engineering. J.-Jpn. Soc. Artif. Intell. 1998 , 13 , 9–10. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arregoces, M.; Portolani, M. Data Center Fundamentals ; Cisco Press: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- IEA. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/6b2fd954-2017-408e-bf08-952fdd62118a/Electricity2024-Analysisandforecastto2026.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Datacenter Dynamic. Available online: https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/news/european-energy-efficiency-directive-published-with-mandatory-data-center-reporting/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Fankhauser, S.; Smith, S.M.; Allen, M.; Axelsson, K.; Hale, T.; Hepburn, C.; Kendall, J.M.; Khosla, R.; Lezaun, J.; Mitchell-Larson, E.; et al. The meaning of net-zero and how to get it right. Nat. Clim. Change 2022 , 12 , 15–21. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Strandburg, K.J. Users as innovators: Implications for patent doctrine. Univ. Colo. Law Rev. 2008 , 79 , 467. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gruber, T.R. A translation approach to portable ontology specifications. Knowl. Acquis. 1993 , 5 , 199–220. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Lin, G.B.; Chen, H.K.; Chen, M.C. A comprehensive analysis of global patent landscape for recent R&D in agricultural drone technologies. World Pat. Inf. 2023 , 74 , 102216. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Wei, A.Y.; Chen, N.K.; Li, K.A.; Hung, L.P.; Trappey, C.V. Patent landscape and key technology interaction roadmap using graph convolutional network–Case of mobile communication technologies beyond 5G. J. Inf. 2023 , 17 , 101354. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Pa, R.J.; Chen, N.K.; Huang, A.Z.; Li, K.A.; Hung, L.P. Digital transformation of technological IP portfolio analysis for complex domain of satellite communication innovations. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023 , 55 , 101879. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trappey, C.V.; Wu, H.Y.; Taghaboni-Dutta, F.; Trappey, A.J. Using patent data for technology forecasting: China RFID patent analysis. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2011 , 25 , 53–64. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Arcan, M.; Manjunath, S.; Robin, C.; Verma, G.; Pillai, D.; Sarkar, S.; Dutta, S.; Assem, H.; McCrae, J.P.; Buitelaar, P. Intent Classification by the Use of Automatically Generated Knowledge Graphs. Information 2023 , 14 , 288. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zafeiropoulos, N.; Bitilis, P.; Tsekouras, G.E.; Kotis, K. Evaluating Ontology-Based PD Monitoring and Alerting in Personal Health Knowledge Graphs and Graph Neural Networks. Information 2024 , 15 , 100. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Trappey, C.V.; Chang, A.C. Intelligent extraction of a knowledge ontology from global patents: The case of smart retailing technology mining. Int. J. Semantic Web Inf. Syst. 2020 , 16 , 61–80. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Liang, C.P.; Lin, H.J. Using machine learning language models to generate innovation knowledge graphs for patent mining. Appl. Sci. 2022 , 12 , 9818. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Chen, P.P.; Trappey, C.V.; Ma, L. A machine learning approach for solar power technology review and patent evolution analysis. Appl. Sci. 2019 , 9 , 1478. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Trappey, C.V.; Liang, C.P.; Lin, H.J. IP Analytics and Machine Learning Applied to Create Process Visualization Graphs for Chemical Utility Patents. Processes 2021 , 9 , 1342. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bharti, S.K.; Babu, K.S. Automatic keyword extraction for text summarization: A survey. arXiv 2017 , arXiv:1704.03242. [ Google Scholar ]
- Khan, M.Q.; Shahid, A.; Uddin, M.I.; Roman, M.; Alharbi, A.; Alosaimi, W.; Almalki, J.; Alshahrani, S.M. Impact analysis of keyword extraction using contextual word embedding. PeerJ 2022 , 8 , e967. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Trappey, C.V.; Trappey, A.J.; Lin, H.J.; Chang, A.C. Comparative Analysis of Food Related Sustainable Development Goals in the North Asia Pacific Region. Food Ethics 2023 , 8 , 21. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Petrus, J. Soft and Hard Clustering for Abstract Scientific Paper in Indonesian. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS), Jakarta, Indonesia, 24–25 October 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 131–136. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bock, H.H. Clustering methods: A history of k-means algorithms. In Selected Contributions in Data Analysis and Classification ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 161–172. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Chang, A.C.; Trappey, C.V.; Chien, J.Y.C. Intelligent RFQ summarization using natural language processing, text mining, and machine learning techniques. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2022 , 30 , 1–26. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Blei, D.; Lafferty, J. Correlated topic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2006 , 18 , 147. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003 , 3 , 993–1022. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trappey, A.J.; Trappey, C.V.; Govindarajan, U.H.; Jhuang, A.C. Construction and validation of an ontology-based technology function matrix: Technology mining of cyber physical system patent portfolios. World Pat. Inf. 2018 , 55 , 19–24. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gallagher, R.J.; Reing, K.; Kale, D.; Ver Steeg, G. Anchored correlation explanation: Topic modeling with minimal domain knowledge. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguistics 2017 , 5 , 529–542. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ounacer, S.; Mhamdi, D.; Ardchir, S.; Daif, A.; Azzouazi, M. Customer Sentiment Analysis in Hotel Reviews Through Natural Language Processing Techniques. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023 , 14 , 569–579. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Adamuthe, A.C.; Thampi, G.T. Forecasting Technology Maturity Curve of Cloud Computing with its Enabler Technologies. J. Sci. Res. 2020 , 64 , 239–246. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kotler, P. Marketing Management , 11th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coccia, M.; Roshani, S. Technological Phases of Quantum Technologies Driving Long-Term Development. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2942054/v1 (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Ampah, J.D.; Jin, C.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Appiah-Otoo, I.; Afrane, S.; Geng, Z.; Yusuf, A.A.; Li, T.; Mahlia, T.I.; Liu, H. Investigating the evolutionary trends and key enablers of hydrogen production technologies: A patent-life cycle and econometric analysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023 , 48 , 37674–37707. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Zou, F.; Jiang, L.; Porter, A.L.; Zhang, L. Technology life cycle analysis: From the dynamic perspective of patent citation networks. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022 , 181 , 121760. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hoosain, M.S.; Paul, B.S.; Kass, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Tools towards the sustainability and circularity of data centers. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2023 , 3 , 173–197. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, F.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Liu, Z. Green data centers: A survey, perspectives, and future directions. arXiv 2016 , arXiv:1608.00687. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, T.; Neng, J.; Wen, Y. Data Center Sustainability: Revisits and Outlooks. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2024 , 9 , 236–248. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kuncoro, I.W.; Pambudi, N.A.; Biddinika, M.K.; Widiastuti, I.; Hijriawan, M.; Wibowo, K.M. Immersion Cooling as the Next Technology for Data Center Cooling: A Review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019 , 1402 , 044057. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cutler, B.; Fowers, S.; Kramer, J.; Peterson, E. Dunking the data center. IEEE Spectr. 2017 , 54 , 26–31. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kanbur, B.B.; Wu, C.; Fan, S.; Duan, F. System-level experimental investigations of the direct immersion cooling data center units with thermodynamic and thermoeconomic assessments. Energy 2017 , 217 , 119373. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gözcü, O.; Özada, B.; Carfi, M.U.; Erden, H.S. Worldwide Energy Analysis of Major Free Cooling Methods for Data Centers. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th IEEE Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (ITherm), Orlando, FL, USA, 30 May–2 June 2017; pp. 968–976. [ Google Scholar ]
- Milad, M.; Darwish, M. UPS System: How Can Future Technology and Topology Improve the Energy Efficiency in Data Centers? In Proceedings of the 2014 49th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 1–4. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Krein, P.T. Data center challenges and their power electronics. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2017 , 2 , 39–46. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pelley, S.; Meisner, D.; Zandevakili, P.; Wenisch, T.F.; Underwood, J. Power routing: Dynamic power provisioning in the data center. ACM SIGPLAN Not. 2017 , 38 , 231–242. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shoukourian, H.; Wilde, T.; Auweter, A.; Bode, A. Monitoring power data: A first step towards a unified energy efficiency evaluation toolset for HPC data centers. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014 , 56 , 13–26. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mytton, D. Data centre water consumption. Clean Water 2014 , 4 , 11. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liang, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Study on the Construction of Big Data and Valorization Services of Intelligent Water. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 11th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2021; pp. 145–149. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ebrahimi, K.; Jones, G.F.; Fleischer, A.S. A review of data center cooling technology, operating conditions and the corresponding low-grade waste heat recovery opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014 , 31 , 622–638. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sharma, R.K.; Bash, C.E.; Patel, C.D.; Friedrich, R.J.; Chase, J.S. Balance of power: Dynamic thermal management for internet data centers. IEEE Internet Comput. 2005 , 9 , 42–49. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, Y.; Shan, K.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Research and Technologies for next-generation high-temperature data centers–State-of-the-arts and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023 , 171 , 112991. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ran, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y. Deepee: Joint Optimization of Job Scheduling and Cooling Control for Data Center Energy Efficiency Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Dallas, TX, USA, 7–10 July 2019; pp. 645–655. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bose, R.; Roy, S.; Mondal, H.; Chowdhury, D.R.; Chakraborty, S. Energy-efficient approach to lower the carbon emissions of data centers. Computing 2021 , 103 , 1703–1721. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lykou, G.; Mentzelioti, D.; Gritzalis, D. A new methodology toward effectively assessing data center sustainability. Comput. Secur. 2018 , 76 , 327–340. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ren, S.; He, Y. COCA: Online Distributed Resource Management for Cost Minimization and Carbon Neutrality in Data Centers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Denver, CO, USA, 7–22 November 2013; pp. 1–12. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wen, Y. Toward a Systematic Survey for Carbon Neutral Data Centers. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022 , 24 , 895–936. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shaw, R.; Howley, E.; Barrett, E. Applying reinforcement learning towards automating energy efficient virtual machine consolidation in cloud data centers. Inf. Syst. 2022 , 107 , 101722. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yao, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, D. A weighted pagerank-based algorithm for virtual machine placement in cloud computing. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 176369–176381. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Scioscia, F.; Bilenchi, I.; Ruta, M.; Gramegna, F.; Loconte, D. A multiplatform energy-aware OWL reasoner benchmarking framework. J. Web Semant. 2022 , 72 , 100694. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Reddy, K.H.K.; Luhach, A.K.; Kumar, V.V.; Pratihar, S.; Kumar, D.; Roy, D.S. Towards energy efficient Smart city services: A software defined resource management scheme for data centers. Sustain. Comput. Informatics Syst. 2022 , 35 , 100776. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Imamura, S.; Yoshida, E.; Oe, K. Reducing CPU Power Consumption with Device Utilization-Aware DVFS for Low-Latency SSDs. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2019 , 102 , 1740–1749. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chou, J.C.Y.; Lai, T.H.; Kim, J.; Rotem, D. Exploiting replication for energy-aware scheduling in disk storage systems. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2014 , 26 , 2734–2749. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jhuang, A.C.; Sun, J.J.; Trappey, A.J.; Trappey, C.V.; Govindarajan, U.H. Computer Supported Technology Function Matrix Construction for Patent Data Analytics. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 21st International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Wellington, New Zealand, 26–28 April 2017; pp. 457–462. [ Google Scholar ]
- Urbina-Suarez, N.A.; Angel-Ospina, A.C.; Lopez-Barrera, G.L.; Barajas-Solano, A.F.; Machuca-Martínez, F. S-curve and landscape maps for the analysis of trends on industrial textile wastewater treatment. Environ. Adv. 2024 , 15 , 100491. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zahoor, A.; Kun, R.; Mao, G.; Farkas, F.; Sápi, A.; Kónya, Z. Urgent Needs for Second Life Using and Recycling Design of Wasted E-car Lithium-ion Battery: A Scientometric Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024; ahead of print . [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, G. Comparative analysis of intelligent connected vehicle industry in China, United States and European Union from technology lifecycle perspective. Kybernetes , 2023; ahead of print . [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huang, L.; Hou, Z.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, T. Evolution of CCUS Technologies Using LDA Topic Model and Derwent Patent Data. Energies 2023 , 16 , 2556. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sossa, J.W.Z.; Marro, F.P.; Alzate, B.A.; Salazar, F.M.V.; Patiño, A.F.A. S-Curve analysis and technology life cycle. Application in series of data of articles and patents. Espacios 2016 , 37 , 19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clement, S.; Burdett, K.; Rteil, N.; Wynne, A.; Kenny, R. Is Hot IT a False Economy? An Analysis of Server and Data Center Energy Efficiency as Temperatures Rise. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2024 , 9 , 482–493. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zakarya, M.; Khan, A.A.; Qazani, M.R.C.; Ali, H.; Al-Bahri, M.; Khan, A.U.R.; Ali, A.; Khan, R. Sustainable computing across datacenters: A review of enabling models and techniques. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2024 , 52 , 100620. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jihad, N.J.; Abd Almuhsan, M.A. Future trends in optical wireless communications systems. Tech. Rom. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2023 , 13 , 53–67. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xu, J.; Fortes, J.A. Multi-objective Virtual Machine Placement in Virtualized Data Center Environments. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/ACM Int’l Conference on Green Computing and Communications & Int’l Conference on Cyber, Physical and Social Computing, Washington, DC, USA, 18–20 December 2010; pp. 179–188. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dutreilh, X.; Moreau, A.; Malenfant, J.; Rivierre, N.; Truck, I. From Data Center Resource Allocation to Control Theory and Back. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cloud Computing, Miami, FL, USA, 5–10 July 2010; pp. 410–417. [ Google Scholar ]
- Youssef, A.E. Exploring cloud computing services and applications. J. Emerg. Trends Comp. Inf. Sci. 2012 , 3 , 838–847. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ye, K.; Huang, D.; Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, S. Virtual Machine-based Energy-efficient Data Center Architecture for Cloud Computing: A Performance Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/ACM Int’l Conference on Green Computing and Communications & Int’l Conference on Cyber, Physical and Social Computing, Washington, DC, USA, 18–20 December 2010; pp. 171–178. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bitar, N.; Gringeri, S.; Xia, T.J. Technologies and protocols for data center and cloud networking. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2023 , 51 , 24–31. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bari, M.F.; Boutaba, R.; Esteves, R.; Granville, L.Z.; Podlesny, M.; Rabbani, M.G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhani, M.F. Data center network virtualization: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012 , 15 , 909–928. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lam, C.F.; Liu, H.; Koley, B.; Zhao, X.; Kamalov, V.; Gill, V. Fiber optic communication technologies: What’s needed for datacenter network operations. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2010 , 48 , 32–39. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sato, K.I.; Matsuura, H.; Konoike, R.; Suzuki, K.; Ikeda, K.; Namiki, S. Prospects and challenges of optical switching technologies for intra data center networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2022 , 14 , 903–915. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cheng, T.Y. A new method of creating technology/function matrix for systematic innovation without expert. J. Technol. Manag. 2012 , 7 , 118–127. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Skyquest. Available online: https://www.skyquestt.com/sample-request/data-center-cooling-market (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Marketsandmarkets. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/data-center-cooling (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- GMI. Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/data-center-cooling-market (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Newswire. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/data-center-rack-market-size-to-grow-by-usd-1628-53-million-belden-inc-black-box-corp-chatsworth-products-inc-and-more-among-the-key-companies-in-the-market-technavio-302090327.html (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Technavio. Available online: https://www.technavio.com/report/data-center-it-equipment-market-analysis (accessed on 25 March 2023).
Click here to enlarge figure
| Keyword Extraction Methods | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple statistical methods | In the absence of considering linguistic features of the text, attention is focused on extracting statistical data from the text, including word position, word frequency, and inverse document frequency, to generate a list of keywords. | N-gram TF–IDF PAT-tree |
| Linguistic methods | Requires a thorough understanding of grammar and semantic structures between words. It involves techniques such as syntactic role identification, parsing, and morphological analysis to determine keyword relationships. | WordNet EDR Tree Tagger |
| Machine learning methods | Using machine learning algorithms, keywords are identified based on training data, can better handle context and semantics, and typically yield higher accuracy. | SVM NB Bagging KeyBERT |
| Cluster | Cluster Meaning (Number of Patents for Each Cluster) | Keyword Extraction Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Processor and related hardware (631) | CPU, board, processor, server |
| 2 | Power supply and management equipment (291) | transformers, power supplies, capacitors, grids, power equipment |
| 3 | Cooling technology and heat recovery (570) | coolants, cool, cooling racks, refrigeration, fluidical |
| thermoelectric, ventilator, refrigerate, HVAC, heating | ||
| 4 | Network and communication technologies (309) | ethernet, cloud, protocol, transport, IP |
| Topic | Meaning of Topic | Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heat recovery | heat, liquid, heat exchanger, refrigeration, evaporator, coolant |
| 2 | Cooling technology | cool, air, cold, fluid, temperature, cooling, cool air, flow, air flow |
| 3 | Virtualization, resource management and performance optimization | virtual, resource management, performance optimization, virtual machine, resource allocation |
| 4 | Cloud services and resource allocation | virtual, execute, cloud, virtual machine, host, computing, virtualize, workload, instance, program, cloud computing |
| 5 | Power supply and distribution | power, power distribution, power supply, power device, power comprise |
| 6 | Rack and equipment installation | rack, assembly, frame, cabinet, housing, enclosure, electronic rack |
| 7 | Network communication and data transfer | network, network switch, network involve, network traffic, optical |
| 8 | Optical communications and fiber technology | optical, fiber, cable, connector, optical signal |
| 9 | Energy efficiency and conservation measures | reduce, efficiency, energy, energy consumption, energy saving |
| 10 | Storage technology, inspection and measurement technology | drawing, detect, diagram, schematic, drawing schematic |
| F1 Energy Efficiency | F2 Environmental and Sustainability | F3 Energy Efficient Operations | F4 Reliability | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | Cooling and heat recovery | 343 | 71 | 241 | 31 | 686 |
| T2 | Energy saving technology | 301 | 70 | 230 | 36 | 637 |
| T3 | Computing systems and HPC | 280 | 41 | 186 | 28 | 535 |
| T4 | Cloud and virtualization | 286 | 40 | 195 | 29 | 550 |
| Sum | 1210 | 222 | 852 | 124 | 2408 | |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Trappey, A.J.C.; Lin, G.-B.; Hung, L.-P. Intelligent Text Mining for Ontological Knowledge Graph Refinement and Patent Portfolio Analysis—Case Study of Net-Zero Data Center Innovation Management. Information 2024 , 15 , 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15070374
Trappey AJC, Lin G-B, Hung L-P. Intelligent Text Mining for Ontological Knowledge Graph Refinement and Patent Portfolio Analysis—Case Study of Net-Zero Data Center Innovation Management. Information . 2024; 15(7):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15070374
Trappey, Amy J. C., Ging-Bin Lin, and Li-Ping Hung. 2024. "Intelligent Text Mining for Ontological Knowledge Graph Refinement and Patent Portfolio Analysis—Case Study of Net-Zero Data Center Innovation Management" Information 15, no. 7: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15070374
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
PRINCE2 Case Studies: Real-World Project Management Examples
This blog delves into several compelling PRINCE2 Case Studies where PRINCE2 has been instrumental in driving project success across various industries. PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a broadly recognised project management methodology that provides a structured approach to managing projects.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- PRINCE2® Foundation
- PRINCE2® Practitioner
- PRINCE2® Foundation Exam Resit

This blog gives insights on prominent PRINCE2 Case Studies. The examples are from different organisations. They illustrate how these organisations have successfully applied this methodology to achieve their project goals. We will have a careful look at each of these examples and analyse them. Each example will guide you through the issues that you may face while doing your projects.
Table of Contents
1) PRINCE2 Case Studies
a) Australian Department of Parliamentary Services
b) Environment Canada
c) Transpower
d) University of Western Australia Library
e) VocaLink
2) Conclusion
PRINCE2 Case Studies
The following case studies showcase the application of PRINCE2 in diverse sectors. They highlight the benefits and outcomes of using this robust project management framework.
Australian Department of Parliamentary Services Case Study
The Australian Department of Parliamentary Services (DPS) undertook a major IT infrastructure project. The goal was to upgrade their parliamentary network services. This complex project required careful planning. Coordination and execution were also important to avoid disruptions to critical parliamentary activities.
Application of PRINCE2:
1) Project Initiation: The project began with a clear project brief and a detailed Project Initiation Document (PID). This helped define the project scope and clarified the objectives and deliverables.
2) Roles and Responsibilities: PRINCE2's role-based structure ensured that everyone involved had a clear understanding of responsibilities. This ranged from the project board to the project team.
3) Stages and Plans: The project was divided into manageable stages. Each stage had its plan and review process. This approach allowed for continuous monitoring. Adjustments were made as needed.
4) Risk Management: A comprehensive Risk Management strategy was implemented. It identified potential risks and developed mitigation plans.
Outcomes:
The use of PRINCE2 enabled DPS to complete project on time and within budget. There were minimal disruptions. The structured approach facilitated effective communication. It also supported decision-making. This led to a successful upgrade of the IT infrastructure.

Environment Canada Case Study
Environment Canada launched a project to develop and implement new environmental monitoring system. The objective was to enhance the accuracy. It also aimed to improve the efficiency of data collection. An analysis for environmental protection and policymaking was a key goal.
Application of PRINCE2:
1) Business Case: A strong business case was developed. It outlined the need for the new system and expected benefits. This document was crucial for securing stakeholder buy-in and funding.
2) Quality Management: PRINCE2's focus on quality ensured project deliverables met the required standards. Regular quality reviews were conducted. Audits were performed throughout the project lifecycle.
3) Change Control: The project adopted a rigorous change control process. This was necessary to manage any changes to the project scope or requirements. It helped maintain project stability and control costs.
Environment Canada successfully implemented a new environmental monitoring system, which has significantly improved data accuracy and efficiency. The project was completed within the set timelines. And it stayed on budget. This was thanks to the disciplined application of PRINCE2 principles.
Transpower Case Study
Transpower New Zealand's state-owned electricity transmission company, embarked on project to upgrade its national grid infrastructure. The project aimed to enhance the reliability. It also sought to increase the capacity of the electricity transmission network.
1) Tailoring PRINCE2: Transpower tailored the PRINCE2 methodology to fit the specific needs of the project. This ensured flexibility while maintaining the core principles.
2) Stakeholder Engagement: Active stakeholder engagement was key focus. Regular communication and updates were provided to all interested parties. This helped manage expectations. It also secured ongoing support.
3) Issue Management: A structured issue management process was in place to address any problems that arose during the project. This ensured issues were resolved promptly and effectively.
The project resulted in a more robust and reliable national grid. It met the growing demand for electricity. The use of PRINCE2 enabled Transpower. They managed project complexities. They delivered the desired outcomes.
Enhance your understanding of the core principles of PRINCE2® Foundation & Practitioner Training – Register now!
University of Western Australia Library Case Study
The University of Western Australia (UWA) Library initiated project to digitise its extensive collection of rare and valuable documents. The goal was to preserve these documents. Also make them accessible to a wider audience.
1) Project Planning: Detailed project plans were developed. These plans outlined the steps required to digitise the documents. Steps included scanning, cataloguing, and storage.
2) Resource Management: PRINCE2's resource management framework helped ensure that necessary resources were available when needed. This included staff, equipment and budget.
3) Progress Monitoring: Regular progress reports and reviews were conducted. These tracked the project's progress and allowed necessary adjustments.
The digitisations project was a success. Thousands of documents were preserved. They were made accessible online. The structured approach of PRINCE2 facilitated efficient project execution. The strategy ensured high-quality results.
VocaLink Case Study
VocaLink a leading payment systems provider took on project to develop a new real-time payment platform. The objective was to provide faster. It also aimed to deliver more efficient payment processing services.
1) Detailed Planning: A comprehensive project plan was formulated. It details each phase of platform development, from the initial design to the final implementation.
2) Risk Management: A proactive Risk Management strategy employed to identify potential risks early. Mitigation plans were developed to address them.
3) Customer Focus: The project maintained strong focus on customer needs, ensuring the final platform met user requirements. It delivered high-quality User Experience (UX).
The new real-time payment platform was successfully launched. It provides VocaLink's customers with faster. More reliable payment services. The application of PRINCE2 principles ensured that project was provided on time and met all Key Performance Indicators (KPI).
Attain in-depth knowledge about PRINCE2® principles, themes, and processes with our PRINCE2® Foundation Course .
Conclusion
PRINCE 2 Case Studies highlight the effectiveness of the PRINCE2 methodology in managing diverse projects across various sectors. By providing a structured framework for planning, executing, and monitoring, PRINCE2 helps organisations achieve their objectives, manage risks, and deliver high-quality outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
A successful PRINCE2 project example is the construction of Heathrow Airport Terminal 5. It applied PRINCE2 methodology effectively in planning, execution, and delivery, incorporating regular reviews and clear roles, leading to its completion within budget and on time.
Deciding between PRINCE2 and Agile should be based on project needs and personal career goals. PRINCE2 is ideal for structured environments requiring clear governance, while Agile suits dynamic projects with frequent changes. For a blend of both, PRINCE2 Agile offers structure with flexibility to adapt to changes.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Project Management Courses , including the PRINCE2® Foundation & Practitioner Training and PRINCE2 Agile® Practitioner Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Agile Roles and Responsibilities .
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to PRINCE2®, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Sat 6th Jul 2024, Sun 7th Jul 2024
Mon 8th Jul 2024
Mon 15th Jul 2024
Sat 20th Jul 2024, Sun 21st Jul 2024
Mon 22nd Jul 2024
Mon 29th Jul 2024
Sat 3rd Aug 2024, Sun 4th Aug 2024
Mon 5th Aug 2024
Mon 12th Aug 2024
Sat 17th Aug 2024, Sun 18th Aug 2024
Mon 19th Aug 2024
Tue 27th Aug 2024
Sat 31st Aug 2024, Sun 1st Sep 2024
Mon 2nd Sep 2024
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Sat 14th Sep 2024, Sun 15th Sep 2024
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Sat 28th Sep 2024, Sun 29th Sep 2024
Mon 30th Sep 2024
Mon 7th Oct 2024
Sat 12th Oct 2024, Sun 13th Oct 2024
Mon 14th Oct 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024
Sat 26th Oct 2024, Sun 27th Oct 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Mon 4th Nov 2024
Sat 9th Nov 2024, Sun 10th Nov 2024
Mon 11th Nov 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Sat 23rd Nov 2024, Sun 24th Nov 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Sat 7th Dec 2024, Sun 8th Dec 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
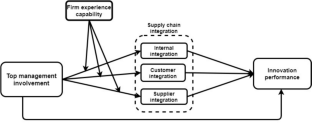
The Role of Top Management Involvement and Supply Chain Integration on Smes’ Innovation Performance: Moderation Impact of Firm Experience Capability
- Published: 28 June 2024
Cite this article

- Timothy Amoako ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6669-6344 1 ,
- Hao Chen 1 ,
- Stephen Abiam Danso 1 &
- Edem Segbefia 1
21 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Top management involvement (MVV) is acknowledged to be a critical factor in enhancing firm performance. As a result, we evaluated the mediation role of supply chain integration (SCI) in the relationship between MVV and innovation performance. Again, the study evaluated the moderation role of firm experience capability (FEXCAP) in the association between MVV and SCI (internal, customer, and supplier). To this end, we conducted a quantitative empirical study in Ghana enterprise agency. Data was gathered from 685 manufacturing and service small and medium enterprises’ top managers and analyzed using the Analysis of Moment Structures (Amos) and Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 26 software. The results revealed that SCI (internal, customer, and supplier) partially mediated the relationship between MVV and innovation performance.
Additionally, FEXCAP positively moderated the association between MVV and SCI (internal, customer, and supplier). The study is critical as it endorses the significant role of MVV in improving the effectiveness of SCI and FEXCAP in firm innovation performance. We evaluated our model in a small and medium context.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Artificial intelligence-driven innovation for enhancing supply chain resilience and performance under the effect of supply chain dynamism: an empirical investigation
Customer experience management: toward implementing an evolving marketing concept.
Competitiveness Through Development of Strategic Talent Management and Agile Management Ecosystems
Data availability.
The research data will be made available upon request.
Afshan, N., Mandal, P., & Gunasekaran, A. (2022). Mediating role of immediate performance outcomes between supply chain integration and firm performance. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 34 (4), 669–687. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-11-2020-0841
Article Google Scholar
Alfalla-Luque, R., Marin-Garcia, J. A., & Medina-Lopez, C. (2015). An analysis of the direct and mediated effects of employee commitment and supply chain integration on organisational performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 162 , 242–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.07.004
Amoako, T., Huai Sheng, Z., & Dogbe, C. S. K. (2022a). Effect of internal integration on SMEs’ performance: The role of external integration and ICT. International Journal of Productivity and PerformaNce Management, 71 (2), 643–665. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-03-2020-0120
Amoako, T., Sheng, Z. H., & Dogbe, C. S. K. (2022b). Assessing the moderation role of ICT in the relationship between supply chain integration and SME performance. Journal of Industrial Integration and Management, 7 (02), 203–233. https://doi.org/10.1142/S2424862221500160
Amoako-Gyampah, K., Meredith, J., & Loyd, K. W. (2018). Using a social capital lens to identify the mechanisms of top management commitment: A case study of a technology project. Project Management Journal, 49 (1), 79–95. https://doi.org/10.1177/875697281804900106
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103 (3), 411. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.103.3.411
Attrams, A. S., & Tshehla, M. (2022). Challenges of services sector SMEs in a developing country: A case of Ghana. Journal of the International Council for Small Business, 3 (3), 228–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/26437015.2021.1982369
Bagozzi, R. P., Yi, Y., & Phillips, L. W. (1991). Assessing construct validity in organizational research. Administrative science quarterly , 421–458. https://doi.org/10.2307/2393203
Balsmeier, B., & Czarnitzki, D. (2013). How important is industry-specific managerial experience for innovative firm performance? In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2013, No. 1, p. 12060). Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510: Academy of Management
Barney, J. B. (2012). Purchasing, supply chain management and sustained competitive advantage: The relevance of resource-based theory. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 48 (2), 3–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-493X.2012.03265.x
Barrales-Molina, V., Montes, F. J. L., & Gutierrez-Gutierrez, L. J. (2015). Dynamic capabilities, human resources, and operating routines: A new product development approach. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 115 (8), 1388–1411. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-02-2015-0058
Ben Slimane, S., Coeurderoy, R., & Mhenni, H. (2022). Digital transformation of small and medium enterprises: A systematic literature review and an integrative framework. International Studies of Management & Organization, 52 (2), 96–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/00208825.2022.2072067
Ben Slimane, S. (2021). Absorption–technological absorptive capacity and innovation: The primacy of knowledge. Innovation Economics, Engineering and Management Handbook 2: Special Themes , 43–49. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119832522.ch3
Bengtsson, M., Raza-Ullah, T., & Vanyushyn, V. (2016). The coopetition paradox and tension: The moderating role of coopetition capability. Industrial Marketing Management, 53 , 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.11.008
Boonstra, A. (2013). How do top managers support strategic information system projects and why do they sometimes withhold this support? International Journal of Project Management, 31 (4), 498–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2012.09.013
Brusset, X., & Teller, C. (2016). Supply Chain Capabilities, Risks, and Resilience. International Journal of Production Economic, 184 , 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.09.008
Campbell, D. T., & Fiske, D. W. (1959). Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychological Bulletin, 56 (2), 81. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0046016
Caroline, N., Harriet, K., & Anne, N. (2016). Top management commitment for successful small and medium enterprises (SMEs): a hoax or a reality? European Scientific Journal , 12(4). https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2016.v12n4p259
Chang, W., Ellinger, A. E., & Kim, K. K. (2016). Supply chain integration and firm financial performance: A meta-analysis of positional advantage mediation and moderating factors. European Management Journal, 34 (3), 282–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2015.11.008
Chen, H., Amoako, T., Quansah, C. E. Danso, S. A., & Jidda, D. J. (2023). Assessment of the impact of management commitment and supply chain integration on SMEs’ innovation performance: Moderation role of government support. Heliyon, 9(5). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15914
Chen, I. J., & Paulraj, A. (2004). Towards a theory of supply chain management: The constructs and measurements. Journal of Operations Management, 22 (2), 119–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2003.12.007
Colbert, B. A. (2004). The complex resource-based view: Implications for theory and practice in strategic human resource management. Academy of Management Review, 29 (3), 341–358. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.2004.13670987
Danese, P., Romano, P., & Formentini, M. (2013). The impact of supply chain integration on responsiveness: The moderating effect of using an international supplier network. Transportation Research Part e: Logistics and Transportation Review, 49 (1), 125–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2012.08.002
Dong, L. (2008). Exploring the impact of top management support of enterprise systems implementations outcomes: Two cases. Business Process Management Journal, 14 (2), 204–218. https://doi.org/10.1108/14637150810864934
Doty, D. H., & Glick, W. H. (1998). Common methods bias: Does common methods variance really bias results? Organizational Research Methods, 1 (4), 374–406. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428198140
Easterby-Smith, M., Lyles, M. A., & Peteraf, M. A. (2009). Dynamic capabilities: Current debates and future directions. British Journal of Management, 20 , S1–S8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8551.2008.00609.x
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Martin, J. A. (2000). Dynamic capabilities: What are they? Strategic Management Journal, 21 (10–11), 1105–1121. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0266(200010/11)21:10/11%3c1105::AID-SMJ133%3e3.0.CO;2-E
Farzaneh, M., Ghasemzadeh, P., & Nazari, J. A. (2021). Contributory role of dynamic capabilities in the relationship between organizational learning and innovation performance. European Journal of Innovation Management, 24 (3), 655–676. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-12-2019-0355
Fawcett, S. E., & Magnan, G. M. (2002). The rhetoric and reality of supply chain integration. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 32 (5), 339–361. https://doi.org/10.1108/09600030210436222
Flynn, B. B., & Huo, & B., Zhao, X. (2010). The impact of supply chain integration on performance: A contingency and configuration approach. Journal of Operations Management, 28 (1), 58–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2009.06.001
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics . Sage Publications Sage CA. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224378101800313
Book Google Scholar
Frohlich, M. T., & Westbrook, R. (2001). Arcs of integration: An international study of supply chain strategies. Journal of Operations Management, 19 (2), 185–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-6963(00)00055-3
Gaskin, J., & Lim, J. (2016). Master Validity Tool, AMOS Plugin: Gaskination's StatWiki.
Gaskin, J., James, M., & Lim, J. (2020). Indirect Effects, AMOS Plugin. Gaskination's StatWiki.
GEA. (2020). Ghana Enterprise Agency. Available: https://gea.gov.gh/ , 2020.
Gounaris, S., & Tzempelikos, N. (2012). Conceptualization and measurement of key account management orientation. JBM-Journal of Business Market Management, 5(3): 173–194. https://hdl.handle.net/10419/66011
Hair, J. F., William, C. B., Babin, B. J., et al. (2010). Multivariate Data Analysis . Prentice Hall.
Google Scholar
Harmancioglu, N., Grinstein, A., & Goldman, A. (2010). Innovation and performance outcomes of market information collection efforts: The role of top management team involvement. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 27 (1), 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2009.09.005
Helfat, C. E. (2007). Stylized facts, empirical research, and theory development in management. Strategic organization, 5 (2), 185–192. https://doi.org/10.1177/1476127007077559
Hermano, V., & Martín-Cruz, N. (2016). The role of top management involvement in firms performing projects: A dynamic capabilities approach. Journal of Business Research, 69 (9), 3447–3458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.01.041
Hooshangi, M., Sadaghiani, J. S., & Astaneh, M. R. (2017). The mediation role of supply chain integration in the relationship between employee commitment with organisational performance. International Journal of Business Information Systems, 24 (2), 210–226. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIS.2017.081447
Horn, P., Scheffler, P., & Schiele, H. (2014). Internal integration as a pre-condition for external integration in global sourcing: A social capital perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 153 , 54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.03.020
Hsu, L. C., & Wang, C. H. (2012). Clarifying the effect of intellectual capital on performance: The mediating role of dynamic capability. British Journal of Management, 23 (2), 179–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8551.2010.00718.x
Huang, M. C., Yen, G. F., & Liu, T. C. (2014). Reexamining supply chain integration and the supplier's performance relationships under uncertainty. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 19 (1), 64–78. https://doi.org/10.1108/SCM-04-2013-0114 .
Huo, B. (2012). The impact of supply chain integration on company performance: An organizational capability perspective. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 17 (6), 596–610. https://doi.org/10.1108/13598541211269210
Huo, B., Ye, Y., & Zhao, X. (2016). The impact of human capital on supply chain integration and competitive performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 178 , 132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.05.009
Jajja, M. S. S., Chatha, K. A., & Farooq, S. (2018). Impact of supply chain risk on agility performance: Mediating role of supply chain integration. International Journal of Production Economics, 205 , 118–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.08.032
Kline, P. (2015). A handbook of test construction (psychology revivals): introduction to psychometric design. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315695990
Kozlenkova, I. V., Samaha, S. A., & Palmatier, R. W. (2014). Resource-based theory in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 42 , 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-013-0336-7
Kwon, I. W. G., & Suh, T. (2004). Factors affecting the level of trust and commitment in supply chain relationships. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 40 (1), 4–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-493X.2004.tb00165.x
Lee, H. L., & Whang, S. (2000). Information sharing in a supply chain. International Journal of Manufacturing Technology and Management, 1 (1), 79–93. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMTM.2000.001329
Leuschner, R., Rogers, D. S., & Charvet, F. F. (2013). A meta-analysis of supply chain integration and firm performance. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 49 (2), 34–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/jscm.12013
MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, P. M. (2012). Common method bias in marketing: Causes, mechanisms, and procedural remedies. Journal of Retailing, 88 (4), 542–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretai.2012.08.001
Marchet, G., Melacini, M., & Perotti, S. (2018). Business logistics models in omni-channel: A classification framework and empirical analysis. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 48 (4), 439–464. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPDLM-09-2016-0273
Menguc, B., Auh, S., & Yannopoulos, P. (2014). Customer and supplier involvement in design: The moderating role of incremental and radical innovation capability. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31 (2), 313–328. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12097
Merrilees, B., Rundle-Thiele, S., & Lye, A. (2011). Marketing Capabilities: Antecedents and implications for B2B SME performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 40 (3), 368–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2010.08.005
Napolitano, L. (1997). Customer-supplier partnering: A strategy whose time has come. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 17 (4), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/08853134.1997.10754105
Naranjo-Gil, D. (2009). Management information systems and strategic performances: The role of top team composition. International Journal of Information Management, 29 (2), 104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2008.05.009
Narasimhan, R., & Kim, S. W. (2002). Effect of supply chain integration on the relationship between diversification and performance: Evidence from Japanese and Korean firms. Journal of Operations Management, 20 (3), 303–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-6963(02)00008-6
Nunnally, J. C. (1978). An overview of psychological measurement. Clinical diagnosis of mental disorders: A handbook , 97–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-2490-4_4
Ouakouak, M. L., Ouedraogo, N., & Mbengue, A. (2014). The mediating role of organizational capabilities in the relationship between middle managers’ involvement and firm performance: A European study. European Management Journal, 32 (2), 305–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2013.03.002
Pakurár, M., Haddad, H., & Nagy, J. (2019). The impact of supply chain integration and internal control on financial performance in the Jordanian banking sector. Sustainability, 11 (5), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051248
Petit, Y. (2012). Project portfolios in dynamic environments: Organizing for uncertainty. International Journal of Project Management, 30 (5), 539–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2011.11.007
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Lee, J.-Y. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88 (5), 879. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Ponsignon, F., Smith, J. S., & Smart, A. (2020). Development and validation of a measurement scale for the experience capability construct. Journal of Service Managemen, t, 32 (3), 315–345. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOSM-11-2019-0353
Robertson, J., Caruana, A., & Ferreira, C. (2021). Innovation performance: The effect of knowledge-based dynamic capabilities in cross-country innovation ecosystems. International Business Review . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101866.101866
Rodríguez, N. G., Pérez, M. J. S., & Gutiérrez, J. A. T. (2008). Can a good organizational climate compensate for a lack of top management commitment to new product development? Journal of Business Research, 61 (2), 118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2007.06.011
Ruel, S., El Baz, J., Ivanov, D. & Das, A. (2021). Supply chain viability: Conceptualization, measurement, and nomological validation. Annals of Operations Research , 335 , 1107–1136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-03974-9
Schoenherr, T., & Swink, M. (2012). Revisiting the arcs of integration: Cross-validations and extensions. Journal of Operations Management, 30 (1–2), 99–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2011.09.001
Shou, Y., Li, Y., & Park, Y. (2018). Supply chain integration and operational performance: The contingency effects of production systems. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 24 (4), 352–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pursup.2017.11.004
Siagian, H., & Tarigan, Z. J. H. (2021). The impact of top management commitment, green purchasing, and supply chain management practices on operational performance (Doctoral dissertation: Petra Christian University). https://repository.petra.ac.id/id/eprint/19181
Song, G., & Song, S. (2021). Fostering supply chain integration in omni-channel retailing through human resource factors: Empirical study in China’s market. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 24 (1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/13675567.2020.1713305
Sood, A., James, G. M., & Tellis, G. J. (2012). Predicting the path of technological innovation: SAW vs. Moore, Bass, Gompertz, and Kryder. Marketing Science, 31 (6): 964–979. https://doi.org/10.1287/mksc.1120.0739
Staeh, L. (2010). Understanding the role of managerial agency in achieving business benefits from ERP systems. Information Systems Journal, 20 (3), 213–238. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2575.2008.00316.x
Swink, M. (2000). Technological innovativeness as a moderator of new product design integration and top management support. Journal of Product Innovation Management: An International Publication of the Product Development & Management Association, 17 (3), 208–220. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-5885.1730208
Takase, M., Maude, P., & Manias, E. (2005). Nurses’ job dissatisfaction and turnover intention: Methodological myths and an alternative approach. Nursing & Health Sciences, 7 (3), 209–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2018.2005.00232.x
Teece, D. J. (2007). Explicating dynamic capabilities: The nature and microfoundations of (sustainable) enterprise performance. Strategic Management Journal, 28 (13), 1319–1350. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.640
Teece, D. J. (2019). A capability theory of the firm: An economics and (strategic) management perspective. New Zealand Economic Papers, 53 (1), 1–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/00779954.2017.1371208
Teece, D. J., Pisano, G., & Shuen, A. (1990). Firm capabilities, resources and the concept of strategy,. Economic analysis and policy working paper EAP 38, University of California .
Teece, D. J., Pisano, G., & Shuen, A. (1997). Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strategic Management , 18(7): 509-533. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0266(199708)18:7%3C509::AID-SMJ882%3E3.0.CO;2-Z
Teece, D. J. (2017). Dynamic capabilities and (digital) platform lifecycles. Entrepreneurship, innovation, and platforms . Emerald Publishing Limited, pp.211–225. https://doi.org/10.1108/S0742-332220170000037008
Thanh Nhon, H., Van Phuong, N., & Quang Trung, N. (2020). Exploring the mediating role of dynamic capabilities in the relationship between intellectual capital and performance of information and communications technology firms. Cogent Business & Management, 7 (1), 1831724. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2020.1831724
Thun, J. H., & Müller, A. (2010). An empirical analysis of green supply chain management in the German automotive industry. Business Strategy and the Environment, 19 (2), 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.642
Tian, H., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Pomegbe, W. W. K. (2021a). Organizational learning ambidexterity and openness, as determinants of SMEs’ innovation performance. European Journal of Innovation Management, 24 (2), 414–438. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-05-2019-0140
Tian, H., Otchere, S. K., & Coffie, C. P. (2021b). Supply chain integration, interfirm value co-creation and firm performance nexus in Ghanaian SMEs: Mediating roles of stakeholder pressure and innovation capability. Sustainability, 13 (4), 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042351
Tzempelikos, N. (2015). Top management commitment and involvement and their link to key account management effectiveness. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 30 (1), 32–44. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-12-2012-0238
Visamitanan, K., & Assarut, N. (2021). Impact of green supply chain management practices on employee engagement and organizational commitment: Mediating role of firm performance. Global Business Review., 10 (1177/09721509211018569), 09721509211018569. https://doi.org/10.1177/09721509211018569
Wong, C. Y., Boon-Itt, S., & Wong, C. W. (2011). The contingency effects of environmental uncertainty on the relationship between supply chain integration and operational performance. Journal of Operations Management, 29 (6), 604–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2011.01.003
Wu, L., Chuang, C.-H., & Hsu, C.-H. (2014). Information sharing and collaborative behaviors in enabling supply chain performance: A social exchange perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 148 , 122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.09.016
Ye, X., Ren, S., & Li, X. (2020). The mediating role of psychological capital between perceived management commitment and safety behavior. Journal of Safety Research, 72 , 29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsr.2019.12.004
Yen, H. R., & Niehoff, B. P. (2004). Organizational citizenship behaviors and organizational effectiveness: Examining relationships in Taiwanese banks. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 34 (8), 1617–1637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2004.tb02790.x
Young, R., & Poon, S. (2013). Top management support—almost always necessary and sometimes sufficient for success: Findings from a fuzzy set analysis. International Journal of Project Management, 31 (7), 943–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2012.11.013
Yu, Y., & Huo, B. (2018). Supply chain quality integration: Relational antecedents and operational consequences. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 23 (3), 188–206. https://doi.org/10.1108/SCM-08-2017-0280
Zhang, M., Guo, H., & Huo, B. (2019). Linking supply chain quality integration with mass customization and product modularity. International Journal of Production Economics, 207 , 227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.01.011
Zhao, X., Huo, B., & Flynn, B. B. (2008). The impact of power and relationship commitment on the integration between manufacturers and customers in a supply chain. Journal of Operations Management, 26 (3), 368–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2007.08.002
Zhao, X., Huo, B., & Selen, W. (2011). The impact of internal integration and relationship commitment on external integration. Journal of Operations Management, 29 (1–2), 17–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2010.04.004
Zhu, Y., Quansah, P. E., & Obeng, A. F. (2022). High-performance work systems and safety performance in the mining sector: exploring the mediating influence of workforce agility and the moderating effect of safety locus of control. Current Psychology, 42, 25100–25126 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03606-w
Download references
The research was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (NSSFC;18BGL255).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Jiangsu University, School of Management, Zhenjiang, China
Timothy Amoako, Hao Chen, Stephen Abiam Danso & Edem Segbefia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Timothy Amoako .
Ethics declarations
Conflicting interests.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Amoako, T., Chen, H., Danso, S.A. et al. The Role of Top Management Involvement and Supply Chain Integration on Smes’ Innovation Performance: Moderation Impact of Firm Experience Capability. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-02166-7
Download citation
Received : 15 April 2024
Accepted : 14 June 2024
Published : 28 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-02166-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Top management involvement
- Supply chain integration
- Firm experience capability
- Innovation performance
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. Sumario: The cases described here provide detailed examples focus on information-technology-based tools for KM, these cases pay close attention to people management and organisational ...
An organization's captured (and codified) knowledge--white papers, case studies, documented processes--should help project teams perform better, but does it? Existing research has not answered the question, even as U.S. companies alone spend billions annually on knowledge management programs.
Journal of Education and Social Sciences, Vol. 6, Issue 2, (February) ISSN 2289-1552 2017 132 In the start of the existence of such a process Davenport (1994) made the following statement: "knowledge management is the process of capturing, distributing, and effectively using knowledge", being a clear and straightforward statement and point of view
This case is about the knowledge management (KM) practices at Whirlpool Corporation (Whirlpool). In 1999, the then CEO of Whirlpool, David R. Whitwam (Whitwam), launched a worldwide effort to embed innovation as a core competency across the organization. He felt that Whirlpool could gain sustainable competitive advantage by focusing on innovation.
Since researching and consulting on knowledge management from the mid-1990s, I have collected over 400 examples of knowledge management in practice in organizations large and small around the world. About 30 of these are in-depth case studies from our own research and interviews that have been published in our reports and books; around 50 are ...
Knowledge Management in Small and Micro Organisations: Case Study on Knowledge Retention in Arts Consultancy Number of pages and appendix pages 85 + 2 Knowledge management is a set of processes of acquiring, creating, sharing and using in-formation resources in an organisational context for the benefit of specific organisational objectives.
questions (Yin, 2018). A multiple case study was the most appropriate design for the study because it supports the exploration of how small retail business leaders use knowledge management strategies for achieving business sustainability. Research Question . The research question that guided this study was: What knowledge management
Fig. 2 shows the research publication trend in "knowledge management". The study begins with the year 2000, observing an increasing trend in publications yearly, with 28,548 publications cited 49,6339 times. ... Strategic management accounting in small and medium-sized enterprises in emerging countries and markets: A case study from China ...
Model for Knowledge Management in Small Companies Case Study. 011-0148. Model for Knowledge Management in Small Companies: Case Study. Ana Carolina Manfrinato Pimentel - UNESP - Bauru, SP, Brazil Av. Eng Luiz Edmundo C. Coube s/n, phone:55-14-3103-6000 [email protected].
Journal of Knowledge Management, 18(1), 121-136. Article Google Scholar Zieba, M., Bolisani, E., & Scarso, E. (2016). Emergent approach to knowledge management by small companies: Multiple case-study research. Journal of Knowledge Management, 20(2), 292-307. Article Google Scholar Download references
3. Discussion. With the growing importance of knowledge management in organization, facilitation of tacit knowledge sharing among individuals (which is usually centered on sharing experiences, skills, and know-how) had been a topic of interest for organizations (Taylor, Citation 2007).However, sharing and transfer of knowledge is a challenge because of the unstructured nature of the tacit ...
International Journal of Training and Development 5:3 ISSN 1360-3736. Problems in knowledge management: a case study of a knowledge-intensive company. SJ van Zolingen, JN Streumer and M Stooker. Knowledge management has become an important tool in staying ahead in the competition between companies. In this article five different phases of the ...
Abstract This chapter presents an action research-based case study of the development of pKADS (portable knowledge asset development system), an open source, desktopbased knowledge management (KM) tool, implemented in Java and targeted at government and nongovernment organizations. pKADS was a collaborative project involving Business Information Systems, University College Cork, Ireland and ...
In particular, after introducing the notion of emergent approach, the paper aims to examine if that notion is useful to properly describe the way small businesses approach their KM activities.,The study is based on the results of a qualitative survey involving 12 owners and managers of small companies belonging to the knowledge-intensive ...
Knowledge Management (KM) is presently experiencing a rebirth, with greater executive interest and organizational commitment. Driven by the post-Covid transition to hybrid and remote work, the employee churn during the great resignation, and the explosion of AI driven by knowledge graphs and large language models, the value that KM offers is better understood, and KM initiatives are being ...
Knowledge management systems (KMS) are a class of information systems that manage, store and distribute knowledge. The simplest KMS do this with explicit knowledge; advanced ones with tacit knowledge. Knowledge management systems have proliferated in practice. In turn, theoretical research on knowledge management and KMS multiplied.
All this means that companies need to approach knowledge management (KM) appropriately. This is crucial in the case of knowledge-intensive small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), where tangible resources are scarcer in comparison to the bigger companies, and more concerned with learning than accountability (Gronum et al., 2012)
This case study comprised three main stages: an analysis of the state of knowledge management in the firm, implementation of changes in knowledge management, and analysis of the obtained results ...
This study aims to examine the impact of knowledge management (KM) and total quality management (TQM) on employee effectiveness (EE) and supply chain performance (SCP) in emerging economies.
The literature falls short in examining talent management (TM) and knowledge management (KM) in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). In response to this research gap, a case study was motivated to explore how SMEs perform TM and KM activities. As this master thesis had the rare opportunity of conducting interviewees with
View PDF. Knowledge Management Analysis: A Case Study Mayur S. Desai, JHJ School of Business, Texas Sourhern University Houston, Texas 77004, (713) 313-7279 [email protected] Ezi I. Mecha, IBM Corporation, Fairfax, Virginia, 410-978-5063 (301) 866 -161, [email protected] Thomas C. Richards, BCIS Department, College of Business, The University ...
Knowledge management enablers: a case study - Author: Ying‐Jung Yeh, Sun‐Quae Lai, Chin‐Tsang Ho - To analyze the crucial role that enablers play in carrying out knowledge management within the enterprise., - This research uses the method of a case study and has directed the survey on Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Inc. (ASE) and ...
2009. Description. This casebook is an accompaniment to Knowledge Management: Facilitators' Guide, with case studies from Scotland and the UK as well as from APO members the ROC, Japan, Singapore, and Vietnam. It is meant to inspire and guide more SMEs to apply KM techniques. Download. ind-40-km_smes-2010.
Ontological knowledge graph (OKG) is a well-formed visual representation that depicts knowledge organization in formal elements (e.g., entities and attributes) and their interrelationships. OKG is crucial for innovation management analysis as it provides a clear boundary to understand complex knowledge domain in detail. In the patent analysis field, it facilitates the definition of a well ...
The Knowledge Academy offers various Project Management Courses, including the PRINCE2® Foundation & Practitioner Training and PRINCE2 Agile® Practitioner Course.These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Agile Roles and Responsibilities. Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to PRINCE2®, offering valuable resources, best ...
Journal of the Knowledge Economy - Top management involvement (MVV) is acknowledged to be a critical factor in enhancing firm performance. ... Table 1 demonstrates that most of the firms under study were small-sized and service firms, with 58.7% and 56.9%, respectively. The firms in the study had been in business for at least five years, with ...