Math Solver
Geogebra math solver.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills!



Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
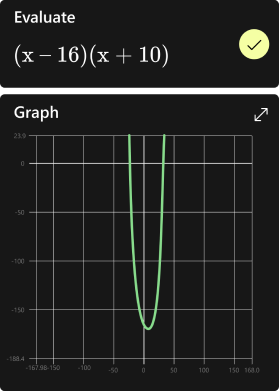
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Mathematics
How to Solve Math Problems
Last Updated: April 15, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Daron Cam . Daron Cam is an Academic Tutor and the Founder of Bay Area Tutors, Inc., a San Francisco Bay Area-based tutoring service that provides tutoring in mathematics, science, and overall academic confidence building. Daron has over eight years of teaching math in classrooms and over nine years of one-on-one tutoring experience. He teaches all levels of math including calculus, pre-algebra, algebra I, geometry, and SAT/ACT math prep. Daron holds a BA from the University of California, Berkeley and a math teaching credential from St. Mary's College. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 591,153 times.
Although math problems may be solved in different ways, there is a general method of visualizing, approaching and solving math problems that may help you to solve even the most difficult problem. Using these strategies can also help you to improve your math skills overall. Keep reading to learn about some of these math problem solving strategies.
Understanding the Problem

- Draw a Venn diagram. A Venn diagram shows the relationships among the numbers in your problem. Venn diagrams can be especially helpful with word problems.
- Draw a graph or chart.
- Arrange the components of the problem on a line.
- Draw simple shapes to represent more complex features of the problem.

Developing a Plan

Solving the Problem

Joseph Meyer
When doing practice problems, promptly check to see if your answers are correct. Use worksheets that provide answer keys for instant feedback. Discuss answers with a classmate or find explanations online. Immediate feedback will help you correct your mistakes, avoid bad habits, and advance your learning more quickly.
Expert Q&A

- Seek help from your teacher or a math tutor if you get stuck or if you have tried multiple strategies without success. Your teacher or a math tutor may be able to easily identify what is wrong and help you to understand how to correct it. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Keep practicing sums and diagrams. Go through the concept your class notes regularly. Write down your understanding of the methods and utilize it. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Daron Cam. Math Tutor. Expert Interview. 29 May 2020.
- ↑ http://www.interventioncentral.org/academic-interventions/math/math-problem-solving-combining-cognitive-metacognitive-strategies
- ↑ http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/Extras/StudyMath/ProblemSolving.aspx
- ↑ https://math.berkeley.edu/~gmelvin/polya.pdf
About This Article

To solve a math problem, try rewriting the problem in your own words so it's easier to solve. You can also make a drawing of the problem to help you figure out what it's asking you to do. If you're still completely stuck, try solving a different problem that's similar but easier and then use the same steps to solve the harder problem. Even if you can't figure out how to solve it, try to make an educated guess instead of leaving the question blank. To learn how to come up with a solid plan to use to help you solve a math problem, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Thakgalo Mokalapa
Feb 16, 2018
Did this article help you?
Offor Chukwuemeka
May 17, 2018
Jan 21, 2017
May 3, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
The algebra section of QuickMath allows you to manipulate mathematical expressions in all sorts of useful ways. At the moment, QuickMath can expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression, cancel common factors within fractions, split fractions up into smaller ('partial') fractions and join two or more fractions together into a single fraction. More specialized commands are on the way.
What is algebra?
Algebra is the branch of elementary mathematics which uses symbols to stand for unknown quantities. In a more basic sense, it consists of solving equations or manipulating expressions which contain symbols (usually letters, like x, y or z) as well as numbers and functions. Although solving equations is really a part of algebra, it is such a big area that it has its own section in QuickMath.
This part of QuickMath deals only with algebraic expressions. These are mathematical statements which contain letters, numbers and functions, but no equals signs. Here are a few examples of simple algebraic expressions :
The expand command is used mainly to rewrite polynomials with all brackets and whole number powers multiplied out and all like terms collected together. In the advanced section, you also have the option of expanding trigonometric functions, expanding modulo any integer and leaving certain parts of the expression untouched whilst expanding the rest.
Go to the Expand page
The factor command will try to rewrite an expression as a product of smaller expressions. It takes care of such things as taking out common factors, factoring by pairs, quadratic trinomials, differences of two squares, sums and differences of two cubes, and a whole lot more. The advanced section includes options for factoring trigonometric functions, factoring modulo any integer, factoring over the field of Gaussian integers (just the thing for those tricky sums of squares), and even extending the field over which factoring occurs with your own custom extensions.
Go to the Factor page
Simplifying is perhaps the most difficult of all the commands to describe. The way simplification is performed in QuickMath involves looking at many different combinations of transformations of an expression and choosing the one which has the smallest number of parts. Amongst other things, the Simplify command will take care of canceling common factors from the top and bottom of a fraction and collecting like terms. The advanced options allow you to simplify trigonometric functions or to instruct QuickMath to try harder to find a simplified expression.
Go to the Simplify page
The cancel command allows you to cancel out common factors in the denominator and numerator of any fraction appearing in an expression. This command works by canceling the greatest common divisor of the denominator and numerator.
Go to the Cancel page
Partial Fractions
The partial fractions command allows you to split a rational function into a sum or difference of fractions. A rational function is simply a quotient of two polynomials. Any rational function can be written as a sum of fractions, where the denominators of the fractions are powers of the factors of the denominator of the original expression. This command is especially useful if you need to integrate a rational function. By splitting it into partial fractions first, the integration can often be made much simpler.
Go to the Partial Fractions page
Join Fractions
The join fractions command essentially does the reverse of the partial fractions command. It will rewrite a number of fractions which are added or subtracted as a single fraction. The denominator of this single fraction will usually be the lowest common multiple of the denominators of all the fractions being added or subtracted. Any common factors in the numerator and denominator of the answer will automatically be cancelled out.
Go to the Join Fractions page
Introduction to Algebraic Functions
The notion of correspondence is encountered frequently in everyday life. For example, to each book in a library there corresponds the number of pages in the book. As another example, to each human being there corresponds a birth date. To cite a third example, if the temperature of the air is recorded throughout a day, then at each instant of time there is a corresponding temperature.
The examples of correspondences we have given involve two sets X and Y. In our first example, X denotes the set of books in a library and Y the set of positive integers. For each book x in X there corresponds a positive integer y, namely the number of pages in the book. In the second example, if we let X denote the set of all human beings and Y the set of all possible dates, then to each person x in X there corresponds a birth date y.
We sometimes represent correspondences by diagrams of the type shown in Figure 1.17, where the sets X and Y are represented by points within regions in a plane. The curved arrow indicates that the element y of Y corresponds to the element x of X. We have pictured X and Y as different sets. However, X and Y may have elements in common. As a matter of fact, we often have X = Y.

A function f from a set X to a set Y is a correspondence that assigns to each element x of X a unique element y of Y. The element y is called the image of x under f and is denoted by f(x). The set X is called the domain of the function. The range of the function consists of all images of elements of X.
Earlier, we introduced the notation f(x) for the element of Y which corresponds to x. This is usually read "f of x." We also call f(x) the value of f at x. In terms of the pictorial representation given earlier, we may now sketch a diagram as in Figure 1.18. The curved arrows indicate that the elements f(x), f(w), f(z), and f(a) of Y correspond to the elements x, y, z and a of X. Let us repeat the important fact that to each x in X there is assigned precisely one image f(x) in Y; however, different elements of X such as w and z in Figure 1.18 may have the same image in Y.

Solution As in Example 1, finding images under f is simply a matter of substituting the appropriate number for x in the expression for f(x). Thus:

Many formulas which occur in mathematics and the sciences determine functions. As an illustration, the formula A = pi*r 2 for the area A of a circle of radius r assigns to each positive real number r a unique value of A. This determines a function f, where f(r) = pi*r 2 , and we may write A= f(r). The letter r, which represents an arbitrary number from the domain off, is often called an independent variable. The letter A, which represents a number from the range off, is called a dependent variable, since its value depends on the number assigned tor. When two variables r and A are related in this manner, it is customary to use the phrase A is a function of r. To cite another example, if an automobile travels at a uniform rate of 50 miles per hour, then the distance d (miles) traveled in time t (hours) is given by d = 50t and hence the distance d is a function of time t.
We have seen that different elements in the domain of a function may have the same image. If images are always different, then, as in the next definition, the function is called one-to-one.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
20 Effective Math Strategies To Approach Problem-Solving
Katie Keeton
Math strategies for problem-solving help students use a range of approaches to solve many different types of problems. It involves identifying the problem and carrying out a plan of action to find the answer to mathematical problems.
Problem-solving skills are essential to math in the general classroom and real-life. They require logical reasoning and critical thinking skills. Students must be equipped with strategies to help them find solutions to problems.
This article explores mathematical problem solving strategies, logical reasoning and critical thinking skills to help learners with solving math word problems independently in real-life situations.
What are problem-solving strategies?
Problem-solving strategies in math are methods students can use to figure out solutions to math problems. Some problem-solving strategies:
- Draw a model
- Use different approaches
- Check the inverse to make sure the answer is correct
Students need to have a toolkit of math problem-solving strategies at their disposal to provide different ways to approach math problems. This makes it easier to find solutions and understand math better.
Strategies can help guide students to the solution when it is difficult ot know when to start.

The ultimate guide to problem solving techniques
Download these ready-to-go problem solving techniques that every student should know. Includes printable tasks for students including challenges, short explanations for teachers with questioning prompts.
20 Math Strategies For Problem-Solving
Different problem-solving math strategies are required for different parts of the problem. It is unlikely that students will use the same strategy to understand and solve the problem.
Here are 20 strategies to help students develop their problem-solving skills.
Strategies to understand the problem
Strategies that help students understand the problem before solving it helps ensure they understand:
- The context
- What the key information is
- How to form a plan to solve it
Following these steps leads students to the correct solution and makes the math word problem easier .
Here are five strategies to help students understand the content of the problem and identify key information.
1. Read the problem aloud
Read a word problem aloud to help understand it. Hearing the words engages auditory processing. This can make it easier to process and comprehend the context of the situation.
2. Highlight keywords
When keywords are highlighted in a word problem, it helps the student focus on the essential information needed to solve it. Some important keywords help determine which operation is needed. For example, if the word problem asks how many are left, the problem likely requires subtraction. Ensure students highlight the keywords carefully and do not highlight every number or keyword. There is likely irrelevant information in the word problem.
3. Summarize the information
Read the problem aloud, highlight the key information and then summarize the information. Students can do this in their heads or write down a quick summary. Summaries should include only the important information and be in simple terms that help contextualize the problem.
4. Determine the unknown
A common problem that students have when solving a word problem is misunderstanding what they are solving. Determine what the unknown information is before finding the answer. Often, a word problem contains a question where you can find the unknown information you need to solve. For example, in the question ‘How many apples are left?’ students need to find the number of apples left over.
5. Make a plan
Once students understand the context of the word problem, have dentified the important information and determined the unknown, they can make a plan to solve it. The plan will depend on the type of problem. Some problems involve more than one step to solve them as some require more than one answer. Encourage students to make a list of each step they need to take to solve the problem before getting started.
Strategies for solving the problem
1. draw a model or diagram.
Students may find it useful to draw a model, picture, diagram, or other visual aid to help with the problem solving process. It can help to visualize the problem to understand the relationships between the numbers in the problem. In turn, this helps students see the solution.
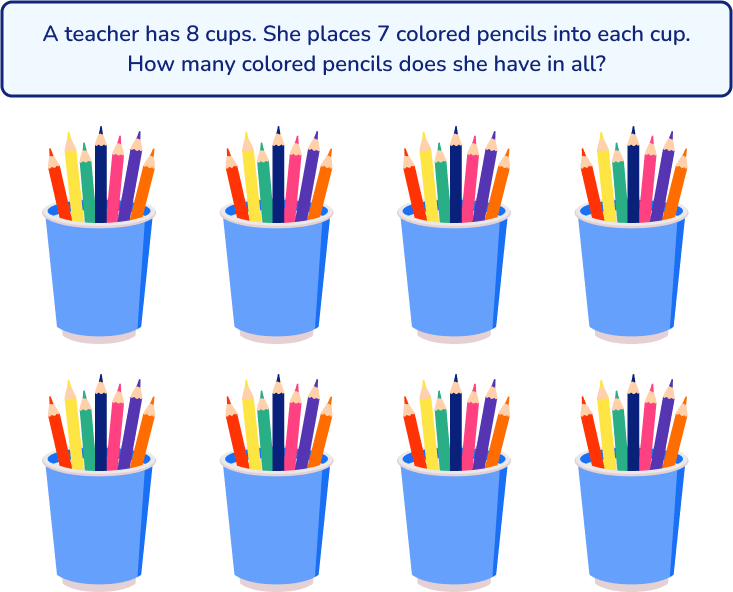
Similarly, you could draw a model to represent the objects in the problem:
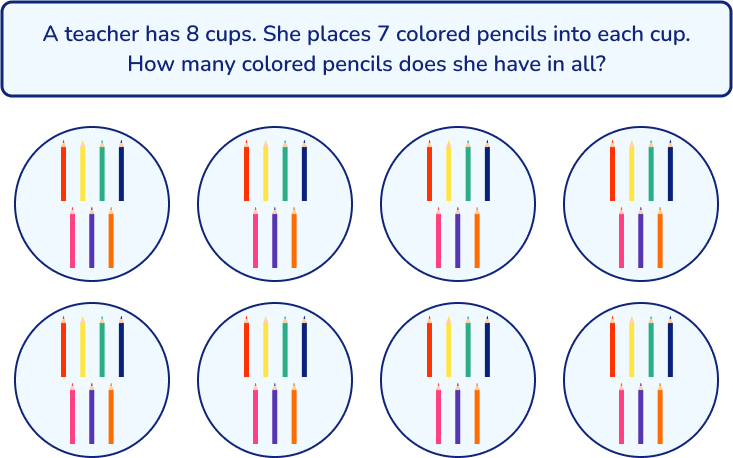
2. Act it out
This particular strategy is applicable at any grade level but is especially helpful in math investigation in elementary school . It involves a physical demonstration or students acting out the problem using movements, concrete resources and math manipulatives . When students act out a problem, they can visualize and contectualize the word problem in another way and secure an understanding of the math concepts. The examples below show how 1st-grade students could “act out” an addition and subtraction problem:
3. Work backwards
Working backwards is a popular problem-solving strategy. It involves starting with a possible solution and deciding what steps to take to arrive at that solution. This strategy can be particularly helpful when students solve math word problems involving multiple steps. They can start at the end and think carefully about each step taken as opposed to jumping to the end of the problem and missing steps in between.
For example,

To solve this problem working backwards, start with the final condition, which is Sam’s grandmother’s age (71) and work backwards to find Sam’s age. Subtract 20 from the grandmother’s age, which is 71. Then, divide the result by 3 to get Sam’s age. 71 – 20 = 51 51 ÷ 3 = 17 Sam is 17 years old.
4. Write a number sentence
When faced with a word problem, encourage students to write a number sentence based on the information. This helps translate the information in the word problem into a math equation or expression, which is more easily solved. It is important to fully understand the context of the word problem and what students need to solve before writing an equation to represent it.
5. Use a formula
Specific formulas help solve many math problems. For example, if a problem asks students to find the area of a rug, they would use the area formula (area = length × width) to solve. Make sure students know the important mathematical formulas they will need in tests and real-life. It can help to display these around the classroom or, for those who need more support, on students’ desks.
Strategies for checking the solution
Once the problem is solved using an appropriate strategy, it is equally important to check the solution to ensure it is correct and makes sense.
There are many strategies to check the solution. The strategy for a specific problem is dependent on the problem type and math content involved.
Here are five strategies to help students check their solutions.
1. Use the Inverse Operation
For simpler problems, a quick and easy problem solving strategy is to use the inverse operation. For example, if the operation to solve a word problem is 56 ÷ 8 = 7 students can check the answer is correct by multiplying 8 × 7. As good practice, encourage students to use the inverse operation routinely to check their work.
2. Estimate to check for reasonableness
Once students reach an answer, they can use estimation or rounding to see if the answer is reasonable. Round each number in the equation to a number that’s close and easy to work with, usually a multiple of ten. For example, if the question was 216 ÷ 18 and the quotient was 12, students might round 216 to 200 and round 18 to 20. Then use mental math to solve 200 ÷ 20, which is 10. When the estimate is clear the two numbers are close. This means your answer is reasonable.
3. Plug-In Method
This method is particularly useful for algebraic equations. Specifically when working with variables. To use the plug-in method, students solve the problem as asked and arrive at an answer. They can then plug the answer into the original equation to see if it works. If it does, the answer is correct.

If students use the equation 20m+80=300 to solve this problem and find that m = 11, they can plug that value back into the equation to see if it is correct. 20m + 80 = 300 20 (11) + 80 = 300 220 + 80 = 300 300 = 300 ✓
4. Peer Review
Peer review is a great tool to use at any grade level as it promotes critical thinking and collaboration between students. The reviewers can look at the problem from a different view as they check to see if the problem was solved correctly. Problem solvers receive immediate feedback and the opportunity to discuss their thinking with their peers. This strategy is effective with mixed-ability partners or similar-ability partners. In mixed-ability groups, the partner with stronger skills provides guidance and support to the partner with weaker skills, while reinforcing their own understanding of the content and communication skills. If partners have comparable ability levels and problem-solving skills, they may find that they approach problems differently or have unique insights to offer each other about the problem-solving process.
5. Use a Calculator
A calculator can be introduced at any grade level but may be best for older students who already have a foundational understanding of basic math operations. Provide students with a calculator to allow them to check their solutions independently, accurately, and quickly. Since calculators are so readily available on smartphones and tablets, they allow students to develop practical skills that apply to real-world situations.
Step-by-step problem-solving processes for your classroom
In his book, How to Solve It , published in 1945, mathematician George Polya introduced a 4-step process to solve problems.
Polya’s 4 steps include:
- Understand the problem
- Devise a plan
- Carry out the plan
Today, in the style of George Polya, many problem-solving strategies use various acronyms and steps to help students recall.
Many teachers create posters and anchor charts of their chosen process to display in their classrooms. They can be implemented in any elementary, middle school or high school classroom.
Here are 5 problem-solving strategies to introduce to students and use in the classroom.
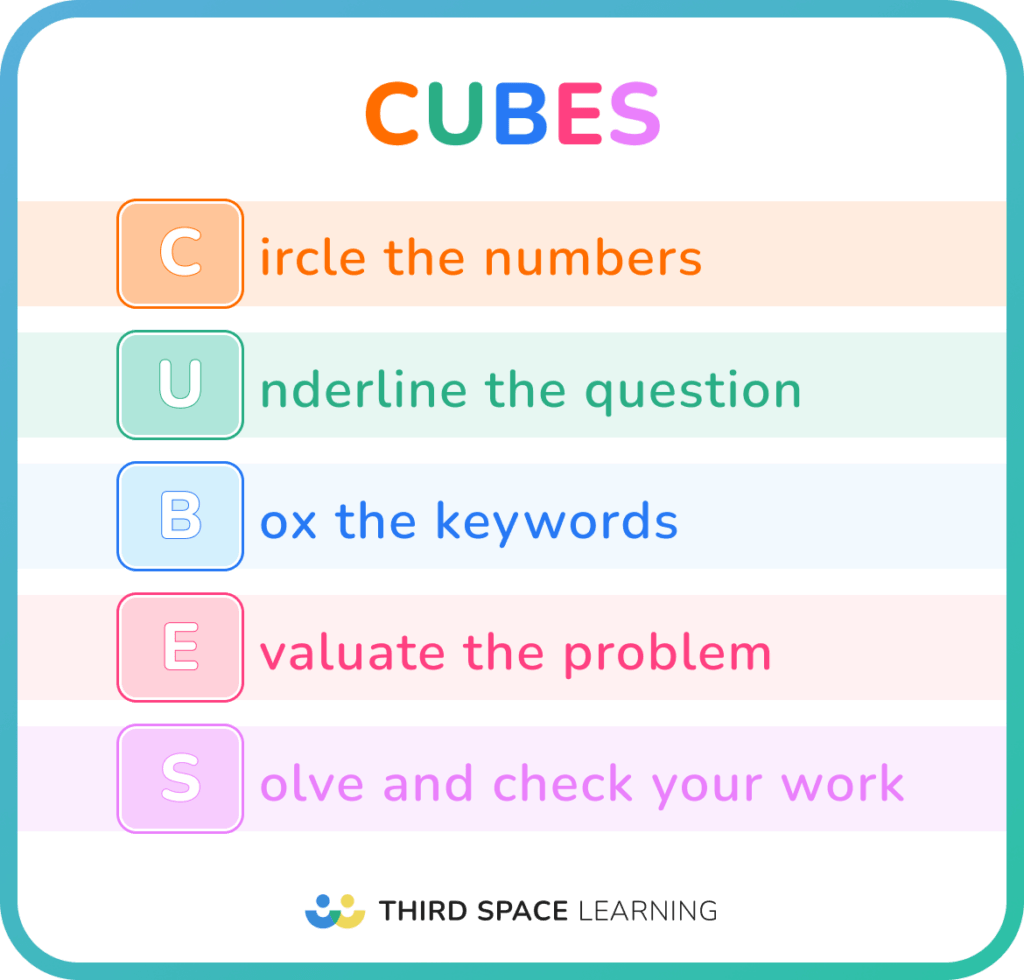
How Third Space Learning improves problem-solving
Resources .
Third Space Learning offers a free resource library is filled with hundreds of high-quality resources. A team of experienced math experts carefully created each resource to develop students mental arithmetic, problem solving and critical thinking.
Explore the range of problem solving resources for 2nd to 8th grade students.
One-on-one tutoring
Third Space Learning offers one-on-one math tutoring to help students improve their math skills. Highly qualified tutors deliver high-quality lessons aligned to state standards.
Former teachers and math experts write all of Third Space Learning’s tutoring lessons. Expertly designed lessons follow a “my turn, follow me, your turn” pedagogy to help students move from guided instruction and problem-solving to independent practice.
Throughout each lesson, tutors ask higher-level thinking questions to promote critical thinking and ensure students are developing a deep understanding of the content and problem-solving skills.
Problem-solving
Educators can use many different strategies to teach problem-solving and help students develop and carry out a plan when solving math problems. Incorporate these math strategies into any math program and use them with a variety of math concepts, from whole numbers and fractions to algebra.
Teaching students how to choose and implement problem-solving strategies helps them develop mathematical reasoning skills and critical thinking they can apply to real-life problem-solving.
READ MORE : 8 Common Core math examples
There are many different strategies for problem-solving; Here are 5 problem-solving strategies: • draw a model • act it out • work backwards • write a number sentence • use a formula
Here are 10 strategies of problem-solving: • Read the problem aloud • Highlight keywords • Summarize the information • Determine the unknown • Make a plan • Draw a model • Act it out • Work backwards • Write a number sentence • Use a formula
1. Understand the problem 2. Devise a plan 3. Carry out the plan 4. Look back
Some strategies you can use to solve challenging math problems are: breaking the problem into smaller parts, using diagrams or models, applying logical reasoning, and trying different approaches.
Related articles

Why Student Centered Learning Is Important: A Guide For Educators

13 Effective Learning Strategies: A Guide to Using them in your Math Classroom

Differentiated Instruction: 9 Differentiated Curriculum And Instruction Strategies For Teachers

5 Math Mastery Strategies To Incorporate Into Your 4th and 5th Grade Classrooms
Ultimate Guide to Metacognition [FREE]
Looking for a summary on metacognition in relation to math teaching and learning?
Check out this guide featuring practical examples, tips and strategies to successfully embed metacognition across your school to accelerate math growth.
Privacy Overview

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.6: Problem Solving Strategies
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 132869

- Michelle Manes
- University of Hawaii
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Think back to the first problem in this chapter, the ABC Problem. What did you do to solve it? Even if you did not figure it out completely by yourself, you probably worked towards a solution and figured out some things that did not work.
Unlike exercises, there is never a simple recipe for solving a problem. You can get better and better at solving problems, both by building up your background knowledge and by simply practicing. As you solve more problems (and learn how other people solve them), you learn strategies and techniques that can be useful. But no single strategy works every time.
How to Solve It
George Pólya was a great champion in the field of teaching effective problem solving skills. He was born in Hungary in 1887, received his Ph.D. at the University of Budapest, and was a professor at Stanford University (among other universities). He wrote many mathematical papers along with three books, most famously, How to Solve it . Pólya died at the age 98 in 1985. [1]

George Pólya, circa 1973
- Image of Pólya by Thane Plambeck from Palo Alto, California (Flickr) [CC BY 2.0 ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 )], via Wikimedia Commons ↵
In 1945, Pólya published the short book How to Solve It , which gave a four-step method for solving mathematical problems:
- First, you have to understand the problem.
- After understanding, then make a plan.
- Carry out the plan.
- Look back on your work. How could it be better?
This is all well and good, but how do you actually do these steps?!?! Steps 1. and 2. are particularly mysterious! How do you “make a plan?” That is where you need some tools in your toolbox, and some experience to draw upon.
Much has been written since 1945 to explain these steps in more detail, but the truth is that they are more art than science. This is where math becomes a creative endeavor (and where it becomes so much fun). We will articulate some useful problem solving strategies, but no such list will ever be complete. This is really just a start to help you on your way. The best way to become a skilled problem solver is to learn the background material well, and then to solve a lot of problems!
We have already seen one problem solving strategy, which we call “Wishful Thinking.” Do not be afraid to change the problem! Ask yourself “what if” questions:
- What if the picture was different?
- What if the numbers were simpler?
- What if I just made up some numbers?
You need to be sure to go back to the original problem at the end, but wishful thinking can be a powerful strategy for getting started.
This brings us to the most important problem solving strategy of all:
A Problem Solving Strategy: Try Something!
If you are really trying to solve a problem, the whole point is that you do not know what to do right out of the starting gate. You need to just try something! Put pencil to paper (or stylus to screen or chalk to board or whatever!) and try something. This is often an important step in understanding the problem; just mess around with it a bit to understand the situation and figure out what is going on.
Note that being "good at mathematics" is not about doing things right the first time. It is about figuring things out. Practice being okay with having done something incorrectly. Try to avoid using an eraser and just lightly cross out incorrect work (do not black out the entire thing). This way if it turns out that you did something useful, you still have that work to reference! If what you tried first does not work, try something else! Play around with the problem until you have a feel for what is going on.
Last week, Alex borrowed money from several of his friends. He finally got paid at work, so he brought cash to school to pay back his debts. First he saw Brianna, and he gave her 1/4 of the money he had brought to school. Then Alex saw Chris and gave him 1/3 of what was left after paying Brianna. Finally, Alex saw David and gave him 1/2 of the remaining money. Who got the most money from Alex?
Think/Pair/Share
After you have worked on the problem on your own for a while, talk through your ideas with a partner if possible (even if you have not solved it). What did you try? What did you figure out about the problem? This problem lends itself to two particular strategies. Did you try either of these as you worked on the problem? If not, read about the strategy and then try it out before watching the solution.
A Problem Solving Strategy: Draw a Picture
Some problems are obviously about a geometric situation, and it is clear you want to draw a picture and mark down all of the given information before you try to solve it. But even for a problem that is not geometric, like this one, thinking visually can help! Can you represent something in the situation by a picture?
Draw a square to represent all of Alex’s money. Then shade 1/4 of the square — that’s what he gave away to Brianna. How can the picture help you finish the problem?
After you have worked on the problem yourself using this strategy (or if you are completely stuck), you can watch someone else’s solution.
A Problem Solving Strategy: Make Up Numbers
Part of what makes this problem difficult is that it is about money, but there are no numbers given. That means the numbers must not be important. So just make them up!
Try this: Assume (that is, pretend) Alex had some specific amount of money when he showed up at school, say $100. Then figure out how much he gives to each person.
Or try working backward: suppose Alex has some specific amount left at the end, say $10. Since he gave David half of what he had before seeing David, that means he had $20 before running into David. Now, work backwards and figure out how much each person got.
Watch the solution only after you tried this strategy for yourself.
If you use the “Make Up Numbers” strategy, it is really important to remember what the original problem was asking! You do not want to answer something like “Everyone got $10.” That is not true in the original problem; that is an artifact of the numbers you made up. So after you work everything out, be sure to re-read the problem and answer what was asked!

(Squares on a Chess Board)
How many squares, of any possible size, are on a 8 × 8 chess board? (The answer is not 64... It’s a lot bigger!)
Remember Pólya’s first step is to understand the problem. If you are not sure what is being asked, or why the answer is not just 64, be sure to ask someone!
Think / Pair / Share
After you have worked on the problem on your own for a while, talk through your ideas with a partner if possible (even if you have not solved it). What did you try? What did you figure out about the problem, even if you have not solved it completely?
Most people want to draw a picture for this problem, but even with the picture it can be hard to know if you have found the correct answer. The numbers get big, and it can be hard to keep track of your work. Your goal at the end is to be absolutely positive that you found the right answer. Instead of asking the teacher, “Is this right?”, you should be ready to justify it and say, “Here’s my answer, and here is how I got it.”
A Problem Solving Strategy: Try a Simpler Problem
Pólya suggested this strategy: “If you can’t solve a problem, then there is an easier problem you can solve: find it.” He also said, “If you cannot solve the proposed problem, try to solve first some related problem. Could you imagine a more accessible related problem?” In this case, an 8 × 8 chess board is pretty big. Can you solve the problem for smaller boards? Like 1 × 1? 2 × 2? 3 × 3?
The ultimate goal is to solve the original problem. But working with smaller boards might give you some insight and help you devise your plan (that is Pólya’s step (2)).
A Problem Solving Strategy: Work Systematically
If you are working on simpler problems, it is useful to keep track of what you have figured out and what changes as the problem gets more complicated.
For example, in this problem you might keep track of how many 1 × 1 squares are on each board, how many 2 × 2 squares on are each board, how many 3 × 3 squares are on each board, and so on. You could keep track of the information in a table:
A Problem Solving Strategy: Use Manipulatives to Help You Investigate
Sometimes even drawing a picture may not be enough to help you investigate a problem. Having actual materials that you move around can sometimes help a lot!
For example, in this problem it can be difficult to keep track of which squares you have already counted. You might want to cut out 1 × 1 squares, 2 × 2 squares, 3 × 3 squares, and so on. You can actually move the smaller squares across the chess board in a systematic way, making sure that you count everything once and do not count anything twice.
A Problem Solving Strategy: Look for and Explain Patterns
Sometimes the numbers in a problem are so big, there is no way you will actually count everything up by hand. For example, if the problem in this section were about a 100 × 100 chess board, you would not want to go through counting all the squares by hand! It would be much more appealing to find a pattern in the smaller boards and then extend that pattern to solve the problem for a 100 × 100 chess board just with a calculation.
If you have not done so already, extend the table above all the way to an 8 × 8 chess board, filling in all the rows and columns. Use your table to find the total number of squares in an 8 × 8 chess board. Then:
- Describe all of the patterns you see in the table. If possible, actually describe these to a friend.
- Explain and justify any of the patterns you see (if possible, actually do this with a friend). If you don't have a partner to work with, imagine they asked you, "How can you be sure the patterns will continue?"
- Expand this to find what calculation(s) you would perform to find the total number of squares on a 100 × 100 chess board.
(We will come back to this question soon. So if you are not sure right now how to explain and justify the patterns you found, that is OK.)
(Broken Clock)
This clock has been broken into three pieces. If you add the numbers in each piece, the sums are consecutive numbers. ( Consecutive numbers are whole numbers that appear one after the other, such as 1, 2, 3, 4 or 13, 14, 15.)

Can you break another clock into a different number of pieces so that the sums are consecutive numbers? Assume that each piece has at least two numbers and that no number is damaged (e.g. 12 isn’t split into two digits 1 and 2).
Remember that your first step is to understand the problem. Work out what is going on here. What are the sums of the numbers on each piece? Are they consecutive?
After you have worked on the problem on your own for a while, talk through your ideas with a partner if possible (even if you have not solved it). What did you try? What progress have you made?
A Problem Solving Strategy: Find the Math, Remove the Context
Sometimes the problem has a lot of details in it that are unimportant, or at least unimportant for getting started. The goal is to find the underlying math problem, then come back to the original question and see if you can solve it using the math.
In this case, worrying about the clock and exactly how the pieces break is less important than worrying about finding consecutive numbers that sum to the correct total. Ask yourself:
- What is the sum of all the numbers on the clock’s face?
- Can I find two consecutive numbers that give the correct sum? Or four consecutive numbers? Or some other amount?
- How do I know when I am done? When should I stop looking?
Of course, solving the question about consecutive numbers is not the same as solving the original problem. You have to go back and see if the clock can actually break apart so that each piece gives you one of those consecutive numbers. Maybe you can solve the math problem, but it does not translate into solving the clock problem.
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- One-Step Addition
- One-Step Subtraction
- One-Step Multiplication
- One-Step Division
- One-Step Decimals
- Two-Step Integers
- Two-Step Add/Subtract
- Two-Step Multiply/Divide
- Two-Step Fractions
- Two-Step Decimals
- Multi-Step Integers
- Multi-Step with Parentheses
- Multi-Step Rational
- Multi-Step Fractions
- Multi-Step Decimals
- Solve by Factoring
- Completing the Square
- Quadratic Formula
- Biquadratic
- Logarithmic
- Exponential
- Rational Roots
- Floor/Ceiling
- Equation Given Roots
- Newton Raphson
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Cramer's Rule
- Gaussian Elimination
- System of Inequalities
- Perfect Squares
- Difference of Squares
- Difference of Cubes
- Sum of Cubes
- Polynomials
- Distributive Property
- FOIL method
- Perfect Cubes
- Binomial Expansion
- Negative Rule
- Product Rule
- Quotient Rule
- Expand Power Rule
- Fraction Exponent
- Exponent Rules
- Exponential Form
- Logarithmic Form
- Absolute Value
- Rational Number
- Powers of i
- Complex Form
- Partial Fractions
- Is Polynomial
- Leading Coefficient
- Leading Term
- Standard Form
- Complete the Square
- Synthetic Division
- Linear Factors
- Rationalize Denominator
- Rationalize Numerator
- Identify Type
- Convergence
- Interval Notation
- Pi (Product) Notation
- Boolean Algebra
- Truth Table
- Mutual Exclusive
- Cardinality
- Caretesian Product
- Age Problems
- Distance Problems
- Cost Problems
- Investment Problems
- Number Problems
- Percent Problems
- Addition/Subtraction
- Multiplication/Division
- Dice Problems
- Coin Problems
- Card Problems
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- \mathrm{Lauren's\:age\:is\:half\:of\:Joe's\:age.\:Emma\:is\:four\:years\:older\:than\:Joe.\:The\:sum\:of\:Lauren,\:Emma,\:and\:Joe's\:age\:is\:54.\:How\:old\:is\:Joe?}
- \mathrm{Kira\:went\:for\:a\:drive\:in\:her\:new\:car.\:She\:drove\:for\:142.5\:miles\:at\:a\:speed\:of\:57\:mph.\:For\:how\:many\:hours\:did\:she\:drive?}
- \mathrm{The\:sum\:of\:two\:numbers\:is\:249\:.\:Twice\:the\:larger\:number\:plus\:three\:times\:the\:smaller\:number\:is\:591\:.\:Find\:the\:numbers.}
- \mathrm{If\:2\:tacos\:and\:3\:drinks\:cost\:12\:and\:3\:tacos\:and\:2\:drinks\:cost\:13\:how\:much\:does\:a\:taco\:cost?}
- \mathrm{You\:deposit\:3000\:in\:an\:account\:earning\:2\%\:interest\:compounded\:monthly.\:How\:much\:will\:you\:have\:in\:the\:account\:in\:15\:years?}
- How do you solve word problems?
- To solve word problems start by reading the problem carefully and understanding what it's asking. Try underlining or highlighting key information, such as numbers and key words that indicate what operation is needed to perform. Translate the problem into mathematical expressions or equations, and use the information and equations generated to solve for the answer.
- How do you identify word problems in math?
- Word problems in math can be identified by the use of language that describes a situation or scenario. Word problems often use words and phrases which indicate that performing calculations is needed to find a solution. Additionally, word problems will often include specific information such as numbers, measurements, and units that needed to be used to solve the problem.
- Is there a calculator that can solve word problems?
- Symbolab is the best calculator for solving a wide range of word problems, including age problems, distance problems, cost problems, investments problems, number problems, and percent problems.
- What is an age problem?
- An age problem is a type of word problem in math that involves calculating the age of one or more people at a specific point in time. These problems often use phrases such as 'x years ago,' 'in y years,' or 'y years later,' which indicate that the problem is related to time and age.
word-problems-calculator
- Middle School Math Solutions – Simultaneous Equations Calculator Solving simultaneous equations is one small algebra step further on from simple equations. Symbolab math solutions...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
LAST STRETCH!

You can still support your source of education news this teacher appreciation week.
The Hechinger Report
Covering Innovation & Inequality in Education
Kindergarten math is often too basic. Here’s why that’s a problem
Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)

The Hechinger Report is a national nonprofit newsroom that reports on one topic: education. Sign up for our weekly newsletters to get stories like this delivered directly to your inbox. Consider supporting our stories and becoming a member today.
ASTON, Pa.— In Jodie Murphy’s kindergarten class, math lessons go beyond the basics of counting and recognizing numbers.

On a recent morning, the children used plastic red and yellow dots for a counting exercise: One student tossed the coin-sized dots onto a cookie sheet while another hid her eyes. The second student then opened her eyes, counted up the dots and picked the corresponding number from a stack of cards.
The dots showed up again a few minutes later in a more complex task. Murphy set a two-minute timer, and students counted as many dot arrays as they could, adding or taking away dots to match a corresponding written number. Four dots next to a printed number 6, for example, meant that students had to draw in two extra dots — an important precursor to learning addition.
Kindergarten may be math’s most important year — it lays the groundwork for understanding the relationship between number and quantity and helps develop “number sense,” or how numbers relate to each other, experts and researchers say.

But too often teachers spend that crucial year reinforcing basic information students may already know. Research shows that many kindergarteners learn early on how to count and recognize basic shapes — two areas that make up the majority of kindergarten math content. Though basic math content is crucial for students who begin school with little math knowledge, a growing body of research argues more comprehensive kindergarten math instruction that moves beyond counting could help more students become successful in math later on.
Stories that inspire
Sign up now to receive our deeply reported education coverage in your inbox.
Because so many students nationally are struggling in math — a longstanding challenge made worse by remote schooling during the pandemic — experts and educators say more emphasis needs to be put on foundational, early childhood math. But for a variety of reasons, kindergarten often misses the mark: Math takes a backseat to literacy, teachers are often unprepared to teach it, and appropriate curriculum, if it exists at all, can be scattershot, overly repetitive — or both.
Manipulating numbers in different ways, part of a supplemental math curriculum for Murphy’s whole class at Hilltop Elementary in this suburb of Philadelphia, is an attempt to address those problems. In an effort to improve math achievement district-wide, all elementary students in the Chichester School District get an extra 30-minute daily dose of math. In kindergarten, the extra time is spent on foundational skills like understanding numbers and quantity, but also the basics of addition and subtraction, said Diana Hanobeck, the district’s director of curriculum and instruction.
Related: You probably don’t have your preschooler thinking about math enough
Chichester district leaders say implementing the intervention, called SpringMath , along with other steps that include hiring a math specialist for each school, has brought urgent attention to students’ math achievement by bringing more students to mastery — and a lot of that has to do with how much students are learning in kindergarten. Student math achievement, which dropped to a low of 13.5 percent of students proficient or advanced during the pandemic, has more than doubled across grades since the intervention began, although still below the state average. Last spring, 47 percent of the district’s fourth graders were proficient or advanced in math on the Pennsylvania System of School Assessment test.
“The intervention is very targeted by skill and gives teachers data for each student,” said Hanobeck. “We are seeing it close gaps for students, and they are more able to access elementary school math.”
Murphy, the kindergarten teacher, said that while some students arrive at school able to do “rote counting,” others arrive with no prior knowledge or a very limited understanding of numbers and counting. The interventions have improved all students’ accuracy and fluency in more complex tasks, such as being able to count up or down from a number like 16 or 20, and adding and subtracting numbers up to 5.
“It used to take all year for some students to count on from different starting points, that’s actually really hard for kids to do,” Murphy said. “Students are meeting their goals far faster now. We are moving on, but also moving deeper.”

That deep thought is important, even in the earliest grades. Kindergarten math proficiency is especially predictive of future academic success in all subjects including reading, research has shown. In one study, students’ number competence in kindergarten — which includes the ability to understand number quantities, their relationships to each other, and the ability to join and separate sets of numbers, like 4 and 2 making 6 — presaged mathematical achievement in third grade, with greater number competence leading to higher math achievement.
It’s also the time when learning gaps between students are at their smallest, and it’s easier to put all students on equal footing. “Kindergarten is crucial,” said University of Oregon math education researcher Ben Clarke. “It’s well-documented in the research literature that gaps start early, grow over time and essentially become codified and very hard to remediate.”
But the math content commonly found in kindergarten — such as counting the days on a calendar — is often embedded within a curriculum “in which the teaching of mathematics is secondary to other learning goals,” according to a report from the National Academies of Science. “Learning experiences in which mathematics is a supplementary activity rather than the primary focus are less effective” in building student math skills than if math is the main goal, researchers wrote.
Related: Teachers conquering their math anxiety
The math students are taught in kindergarten often progresses no further than basic counting and shapes. In a 2013 study , researcher and University of Colorado Boulder associate professor Mimi Engel found that students who spent more time on the advanced concepts in kindergarten learned more math. Engel hypothesizes that exposure to more advanced content in kindergarten may help students in later grades when content grows more complex.
“We want some amount of repetition across grades in content,” Engel said. “There’s variation in kids’ skill sets when they start kindergarten, and, as a teacher, there are a number of reasons why you want to start with the basics, and scaffold instruction. But what I’m interested in is: when does repetition become redundancy?”
According to researcher Amanda VanDerHeyden, founder of SpringMath, breaking numbers apart and putting them back together and understanding how numbers relate to each other does more to help develop kindergarteners’ mathematical thinking than counting alone. Students should move from using concrete objects to model problems, to using representations of those objects and then to numbers in the abstract — like understanding that the number 3 is a symbol for three objects.
To improve students’ math skills, some schools and districts have recently upgraded the math curriculum and materials teachers use, so they are able to build increasingly complex skills in an organized, orderly way.
Kindergarteners in Hailey Lang’s classroom at Dr. William Burrus Elementary School in Hendersonville, Tennessee, were recently counting penguins — a digital whiteboard showed a photo of a mother penguin with seven fuzzy babies in tow.
“Can we make a math drawing about this picture? No details, you can just use little circles,” Lang said. Students drew one big circle and seven smaller circles on their papers to represent the penguins. Then they translated the circles into a number sentence: 1 (big circle) + 7 (small circles) = 8.

The lesson is new to students this year since they adopted the Eureka Math curriculum. It’s what Sumner County Superintendent Scott Langford calls “high-quality” instructional material, with lessons that move students beyond simply counting objects like penguins. Students look at penguins in a picture, translate them into representational circle drawings, then finally move on to their abstract number quantities.
Sumner County elementary coordinator Karen Medana said she appreciates the fact that the curriculum offers explicit guidance for teachers and builds on a sequence of skills.
One reason for redundancy in kindergarten math may be that classrooms lack cohesive materials that progress students through skills in an orderly way. A 2023 report from the Center for Education Market Dynamics showed that only 36 percent of elementary schools use high-quality instructional materials, as defined by EdReports, a nonprofit organization that evaluates curricula for rigor, coherence and usability. Eureka Math is one of several math programs that meet EdReports’ standards.
Related: How to boost math skills in the early grades
Often teachers are left to gather their own math materials outside the school’s curriculum. The Brookings Institution reports that large numbers of teachers use a district-approved curriculum as “one resource among many.” Nearly all teachers say they gather resources from the internet and sites like Teachers Pay Teachers — meaning what students learn varies widely, not only from district to district, but from classroom to classroom.
What students learn might not even be aligned from one grade to another. In a new, unpublished paper still in revision, researcher Engel found “notable inconsistencies” between pre-K and kindergarten classroom math content and how it is taught in New York City schools. Engel said results suggest that in many classrooms, kindergarten math might be poorly aligned with both pre-K and elementary school.
When teachers have access to well-aligned materials, students may learn more. At Marcus Hook Elementary, a Title I elementary school in the Chichester District, kindergarten teacher Danielle Adler’s students were deep into first grade addition, using numbers up to 12. They had already completed all the SpringMath kindergarten math skills in March, so she let them keep going.
“In the past we did focus more on counting, recognizing numbers and counting numbers,” Adler said, “But over the last three years I’ve seen the kids’ skills grow tremendously. Not only what they’re expected to do, but what they’re capable of doing has grown.”
What kindergarteners are expected to do at school has changed dramatically over the last 30 years, including more time spent on academic content. Adler and other kindergarten teachers agree that they hold higher expectations for today’s students, spend more time on teacher-directed instruction and substantially less time on “art, music, science and child-selected activities.”
Some worry that increasing time spent on academic subjects like math, and pushing kindergarten students beyond the basics of numbers and counting, will be viewed as unpleasant “work” that takes away from play-based learning and is just not appropriate for 5- and 6-year-olds, some of whom are still learning how to hold a pencil.
Engel said kindergarteners can be taught more advanced content and are ready to learn it. But it should be taught using practices shown to work for young children, including small group work, hands-on work with objects such as blocks that illustrate math concepts, and learning through play.
Related: How can you help your kids get better at math?
Mathematician John Mighton, the founder of the curriculum JUMP Math, said it’s a mistake to believe that evidence-based instructional practices must be laborious and dull to be effective. He has called on adults to think more like children to make more engaging math lessons.
“Children love repetition, exploring small variations on a theme and incrementally harder challenges much more than adults do,” he wrote — all practices supported by evidence to increase learning.
Simple lessons, when done well, can teach complex ideas and get children excited.
“People say kids don’t have the attention,” to learn more advanced concepts, he said, but he strongly believes that children have more math ability than adults give them credit for. Getting students working together, successfully tackling a series of challenges that build on each other, can create a kind of collective effervescence — a feeling of mutual energy and harmony that occurs when people work toward a common goal.
That energy overflowed in Adler’s classroom, for example, as students excitedly colored in graphs showing how many addition problems they got correct, and proudly showed off how the number correct had grown over time.
VanDerHeyden pointed out that, for young kids, much of a math intervention should look and feel like a game.
It’s often harder than it looks to advance kindergarten skills while keeping the fun — elementary teachers often say they have low confidence in their own abilities to do math or to teach it. Research suggests that teachers who are less confident in math might not pay enough attention to how students are learning, or even spend less time on math in class.
Teachers like Murphy have made some tweaks geared to engaging students. In class she calls SpringMath “math games,” and refers to timed fluency tests as “math races.” She even turned choosing a partner into a game, by spinning a wheel to see who students will get.
“We can do all these little things so they’re having fun while they’re learning,” Murphy said.
This story about kindergarten math was produced by The Hechinger Report , a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Hechinger’s newsletter
Related articles
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
Letters to the Editor
At The Hechinger Report, we publish thoughtful letters from readers that contribute to the ongoing discussion about the education topics we cover. Please read our guidelines for more information. We will not consider letters that do not contain a full name and valid email address. You may submit news tips or ideas here without a full name, but not letters.
By submitting your name, you grant us permission to publish it with your letter. We will never publish your email address. You must fill out all fields to submit a letter.
I did not see the word pattern in this long disappointing article. The great mathematician and math educator Lynn Steen said “Mathematics is the science of patterns”. Patterns are the building blocks of mathematics. We need to start there in our curriculum, with our students, and for PK-3 teachers. The most important math we can teach kids is to look for and see patterns!
As an elderly retired kindergarten teacher, I truly appreciated your article regarding math in kdgn. I used the program called “Math Their Way,” which taught many areas of math, and the children enjoyed patterns, estimating, etc., all hands on activities.
Since 2008, California’s preschool and TK programs are supposed to adhere to “California Preschool Learning Foundations.” Regardless of the style of the school, anything from a play-based, Reggio, Montessori, Waldorf, authoritarian, religious, etc. graduates should know shapes, numbers, ordering, and simple addition and subtraction. It was wonderful, integrated through daily play and learning about each other through conflict resolution. They arrived at school ready to learn. In our elementary school, the kids who went to preschool, or had parents who worked through preschool material, represented about 2/3 of the class. They also knew the alphabet, a few were readers, had some social skills, and general interacted well with adults. The rest of the class seemed to have none of these skills and occupied most of the teacher’s time. Meanwhile, many of the other students and parents became frustrated because their children were “ahead,” started teaching them at home because they were in fact bored, and by the next year, the single year gap became 2-3, and the next year for a handfuls of kids it was 3-4. I watched this happen over and over again.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Submit a letter
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Teens who discovered new way to prove Pythagoras’s theorem uncover even more proofs
As high school students, Calcea Johnson and Ne’Kiya Jackson worked to find valid new proof for the 2,000-year-old theorem
Two college freshmen who, during their final year of high school, found a new way to prove Pythagoras’s theorem by using trigonometry – which mathematicians for generations thought was impossible – have since uncovered multiple more such proofs, they revealed in a national interview on Sunday.
“We found five, and then we found a general format that could potentially produce at least five additional proofs,” Calcea Johnson said on CBS’s 60 Minutes, a little more than a year after she and Ne’Kiya Jackson collaborated on an accomplishment that earned them international recognition.
Nonetheless, in comments that stunned their interviewer, Bill Whitaker, the two graduates of St Mary’s Academy in New Orleans denied seeing themselves as math geniuses and dismissed any interest in pursuing careers in mathematics.
“People might expect too much out of me if I become a mathematician,” Jackson said, shaking her head. Johnson, for her part, added: “I may take up a minor in math, but I don’t want that to be my job job.”
Sunday’s conversation on CBS’s popular Sunday evening news magazine were perhaps their most extensive, widely broadcast remarks to date on the new ground that they broke with respect to the Pythagorean theorem.
The 2,000-year-old theorem established that the sum of the squares of a right triangle’s two shorter sides equals the square of the hypotenuse – the third, longest side opposite the shape’s right angle. Countless schoolchildren taking geometry have memorized the notation summarizing the theorem: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 .
For 2,000 years, mathematicians maintained that any alleged proof of the Pythagorean theorem that was based in trigonometry would constitute a logical fallacy known as circular reason – in essence, trying to validate an idea with the idea itself.
But the bonus question on a math contest that Johnson and Jackson took home to complete during the Christmas break of their final year at St Mary’s served as the impetus for them to plot out a new way to demonstrate that one could indeed use trigonometry to prove Pythagoras’s theorem.
Their work was so compelling that the pair went to a regional meeting of the American Mathematical Society in Atlanta in March 2023 to outline their findings. At the organization’s recommendation, Jackson and Johnson have submitted their discoveries for final peer review and publication – as well as working on additional proofs while that process is pending, as 60 Minutes noted.
The 60 Minutes interview gave Johnson and Jackson occasion to reflect on the intense reaction caused by initial media reports on their innovative work at St Mary’s, a Catholic high school that has been dedicated to educating Black girls since its founding shortly after the US civil war.
Some of it was negative. Some in the math community smarted at claims in a press release issued by St Mary’s that asserted Jackson and Johnson’s research was “unprecedented”. And they flocked to social media demanding that a 2009 trigonometry-based proof for Pythagoras’s theorem get its due.
Yet a lot of the reaction to Johnson and Jackson was positive, especially as mathematicians who picked apart their work confirmed that – by all indications – they had arrived at a valid new proof, a celebration-worthy accomplishment.
Michelle Obama wrote a post on social media that linked to a story about Johnson and Jackson, adding the text: “I just love this story. … Way to go, Ne’Kiya and Calcea! I’m rooting for you and can’t wait to see what you all do next.”
They also received a commendation from Louisiana’s then governor as well as symbolic keys to the city of New Orleans .
Asked on 60 Minutes why they thought people were so impressed with what they had done, Jackson said she thought the public was surprised young Black women could author such a feat.
“I’d like to be celebrated for what it is,” Jackson said. “Like – it’s a great mathematical achievement.”
Jackson is now attending New Orleans’ Xavier University and enrolled in its pharmacy department. Meanwhile, Johnson – who graduated from St Mary’s as its valedictorian – is now an environmental engineering student at Louisiana State University in Baton Rouge.
- New Orleans
- Mathematics
Most viewed
Watch CBS News
Teens surprise math world with Pythagorean Theorem trigonometry proof | 60 Minutes

History Daily
New Orleans teens solve 2,000-year-old math problem
Posted: May 11, 2024 | Last updated: May 11, 2024

Some ingenuity
Teacher Michelle Blouin Williams initiated a math competition with a bonus question tasking students to develop a new proof for the Pythagorean theorem using trigonometry, without anticipating that anyone would successfully tackle the challenge.
She said, “I was just looking for some ingenuity.”

Williams' expectations
Calcea Johnson and Ne’Kiya Jackson exceeded Williams' expectations by successfully solving the challenge in 2023.

St. Mary's Academy
These two teenagers, who were seniors at St. Mary's Academy in New Orleans, a renowned Catholic school for girls with impressive college acceptance and graduation rates, were featured on CBS News' "60 Minutes" to discuss their accomplishment.

$500 reward
Initially enticed by the math competition's $500 reward, their determination to complete the task intensified as they delved into the complex bonus question.

Over a period of two months, these high school seniors dedicated themselves to completing their proof.

Pages and pages
During an interview with "60 Minutes," CeCe Johnson, the mother of Calcea, said “It was pages and pages and pages of, like, over 20 or 30 pages for this one problem.”

The garbage can
Her father, Cal Johnson, added, “Yeah, the garbage can was full of papers, which she would, you know, work out the problems and — if that didn’t work she would ball it up, throw it in the trash.”

Upon completion
Upon completion, the teachers at St. Mary's Academy acknowledged the significance of Calcea and Ne'Kiya's achievement and submitted their proof to the American Mathematical Society for recognition at a conference in March 2023, where the students presented their findings.

The Pythagorean theorem
The Pythagorean theorem, at its core, states that knowing the lengths of two sides of a right triangle allows you to determine the length of the third side using the formula a² + b² = c².

While commonly attributed to the Greek mathematician Pythagoras, historical evidence suggests its existence in Babylon and Iron Age India. This theorem finds practical applications in construction, architecture, navigation, and surveying.

A mathematical proof
A mathematical proof is a logical argument that demonstrates the truth of a mathematical theorem. American mathematician Daniel Kane likens proofs to essays, but rooted in mathematical concepts.

Using trigonometry
As per the "60 Minutes" segment, “there had been more than 300 documented proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem using algebra and geometry, but for 2,000 years a proof using trigonometry was thought to be impossible.”

Mathematician Elisha Loomis
Back in 1927, mathematician Elisha Loomis made a statement in his book "The Pythagorean Proposition." Loomis contended that a trigonometric proof of the theorem was impossible as it would create a circular argument.

Stuart Anderson
Stuart Anderson, a retired mathematics professor from Texas A&M University-Commerce, mentioned to Scientific American, “A lot of the basic trig ‘identities’ are nothing more than Pythagoras’ theorem.”

Trigonometric functions
Loomis contended that attempting to use trigonometric functions to prove the Pythagorean theorem would result in a circular reasoning loop, as the functions themselves are built upon the theorem. This, according to Loomis, would constitute a fundamental mathematical mistake.

The law of sines
As reported by Scientific American, the teenagers challenged this notion during their presentation in 2023 and stated that “a trigonometric identity called the law of sines didn’t depend on the Pythagorean theorem and that they could use it to prove the theorem.”

Final peer review
Calcea and Ne'Kiya are now part of a select few who have achieved a similar milestone, such as mathematician Jason Zimba, who developed a new proof in 2009. They submitted their proof for the final peer review earlier this year and are actively working on crafting additional proofs.

In recognition
In recognition of their accomplishment, the teenagers were honored with the keys to the city of New Orleans and received commendations from the governor of Louisiana, along with other public acknowledgments.

Widespread recognition
Despite the widespread recognition of their accomplishment which “blew up,” as Ne'Kiya expressed it, the two students maintain their humility and even chuckled at being labeled as geniuses.

Surprised and skeptical
Upon the revelation of their achievement, there were individuals who appeared surprised and skeptical, dismissing the news as untrue, as mentioned by St. Mary's president Pamela Rogers during the interview.
African Americans
“They were saying, ‘Oh, they could not have done it. African Americans don’t have the brains to do it.’ ... People — have a vision of who can be successful. And — to some people, it is not always an African American female. And to us, it’s always an African American female.”

The significant reaction
When questioned by interviewer Bill Whitaker about their thoughts on the significant reaction, Ne’Kiya said, “Probably because we’re African American, one. And we’re also women. So I think — oh, and our age. Of course our ages probably played a big part.”

Great mathematical achievement
“I’d like to actually be celebrated for what it is. Like, it’s a great mathematical achievement,” she continued.
More for You
Where you can see northern lights Sunday night from another solar storm
Explosion Rips Through 10-Story Russian Apartment Building
'We're looking at a downsized America': Kevin O'Leary cautions any new house, car and lifestyle you acquire will be a lot 'smaller' — here's what he means and how you can prepare
I Asked 5 Chefs to Name Their Favorite Mayo, and They All Chose the Same Brand
The dog breed that has attacked the most people, based on data. Plus, see the rest of the top 20.
24-year-old earns $50,000 a year living in a town of 121—how she spends her time and money
Top 20 Things You Didn't Know About The Big Bang Theory
A Photo of Pedro Pascal and Dakota Johnson Kissing Passionately on the Street Has Gone Viral
15 Musicians Who Left a Void in The Music World
Broncos release former Super Bowl champion WR
11 Of The Most Popular Ice Cream Flavors In America
The best- and worst-paying college majors, 5 years after graduation
23 Weird Things People Think Only Their Families Did
11 Gender-Specific Lessons We Need to Stop Teaching Children in a Modern World
Putin Ally Threatens NATO Countries With 'Special Ammunition'
Saying goodbye to "Young Sheldon"
Westminster Dog Show crowns champions and sparks joy
The one-hit wonders every 1970s kid will remember
29-year-old ex-bartender now earns $100,000 working in AI without a college degree—here's how
These Are The Most Famous Dinosaurs From Jurassic Park
ernvisual: AI Homework Helper 4+
Ai math solver - scan & learn, designed for ipad.
- Offers In-App Purchases
Screenshots
Description.
ernvisual: AI Homework Helper simplifies learning with instant answers across math, history, coding, science, grammar, and more. Scan, solve, and succeed today! ernvisual: AI Homework Helper Are you tired of struggling with homework problems? Look no further than ernvisual: AI Homework Helper – your all-in-one academic assistant. With a powerful combination of cutting-edge technology and user-friendly design, Ernvisual is here to revolutionize the way you approach your studies. Scan Questions with Ease Forget about manual entry – simply snap a photo of any problem, whether it's from a textbook, worksheet, or handwritten notes. ernvisual's advanced scanning technology instantly digitizes the question, saving you valuable time and effort. Solve Problems Instantly Get ready to witness the magic of learning unfold before your eyes. With ernvisual, you'll receive step-by-step solutions to even the most challenging problems. From math and history to coding and science, our intelligent algorithms ensure accurate and reliable answers every time. Your Personal Study Helper Whether you're a student, educator, or lifelong learner, Ernvisual is your trusted companion for mastering academic subjects. With its intuitive interface and comprehensive features, ernvisual empowers users of all skill levels to tackle challenges with confidence. Comprehensive Homework Assistance ernvisual offers an array of tools beyond math, including history, geography, coding, grammar, science, and an Essay Assistant. Just upload your assignment or specific questions, and ernvisual will guide you through comprehensive explanations and answers. It's like having a tutor in your pocket! Unlock Academic Possibilities Experience the ultimate homework-solving solution without spending a dime. Download ernvisual and unlock a world of academic possibilities. With frequent updates and enhancements, you'll always have access to the latest tools and resources. Don't let academic challenges hold you back any longer. Embrace the future of learning with ernvisual – where solving homework is as easy as 1, 2, 3. Download now and discover the joy of academic mastery. Privacy Policy: https://happystudios.vercel.app/work Terms of Use: https://happystudios.vercel.app/blog
Version 1.1
Great News! We have added homework helper feature . Just try it out!
App Privacy
The developer, ERNBRANDS , indicated that the app’s privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see the developer’s privacy policy .
Data Not Collected
The developer does not collect any data from this app.
Privacy practices may vary, for example, based on the features you use or your age. Learn More
Information
- Unlock all features. $5.99
- Unlock all features $4.99
- Unlock all features. $39.99
- Unlock All Features. $9.99
- App Support
- Privacy Policy
More By This Developer
ernvisual - AI Video Generator
BrookerLab - Real Estate CRM
You Might Also Like
Math AI : Tutor & Math Helper
Math Solver: Homework AI Tutor
Algebra AI: Solve Math Problem
Math Ai Homework Helper Tutor
AI Math Solver Homework Help
AI HW Solvr
Letter from the Editor: The problem with math
- Updated: May. 12, 2024, 5:15 a.m. |
- Published: May. 12, 2024, 5:15 a.m.

Find the seven differences between the two panels, not six. Answers at bottom. King Features
- Therese Bottomly | The Oregonian/OregonLive
As we approach the May primary, now is a good time to revisit journalists’ love of math.
If you think there is a touch of sarcasm there, you are correct. We’re word people, I sometimes say, when a reader points out a numbers problem.
If you purchase a product or register for an account through a link on our site, we may receive compensation. By using this site, you consent to our User Agreement and agree that your clicks, interactions, and personal information may be collected, recorded, and/or stored by us and social media and other third-party partners in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- May 13, 2024 • 27:46 How Biden Adopted Trump’s Trade War With China
- May 10, 2024 • 27:42 Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
- May 9, 2024 • 34:42 One Strongman, One Billion Voters, and the Future of India
- May 8, 2024 • 28:28 A Plan to Remake the Middle East
- May 7, 2024 • 27:43 How Changing Ocean Temperatures Could Upend Life on Earth
- May 6, 2024 • 29:23 R.F.K. Jr.’s Battle to Get on the Ballot
- May 3, 2024 • 25:33 The Protesters and the President
- May 2, 2024 • 29:13 Biden Loosens Up on Weed
- May 1, 2024 • 35:16 The New Abortion Fight Before the Supreme Court
- April 30, 2024 • 27:40 The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
- April 29, 2024 • 47:53 Trump 2.0: What a Second Trump Presidency Would Bring
- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
The porn star testified for eight hours at donald trump’s hush-money trial. this is how it went..
Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Jonah E. Bromwich
Produced by Olivia Natt and Michael Simon Johnson
Edited by Lexie Diao
With Paige Cowett
Original music by Will Reid and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
This episode contains descriptions of an alleged sexual liaison.
What happened when Stormy Daniels took the stand for eight hours in the first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump?
Jonah Bromwich, one of the lead reporters covering the trial for The Times, was in the room.
On today’s episode

Jonah E. Bromwich , who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times.

Background reading
In a second day of cross-examination, Stormy Daniels resisted the implication she had tried to shake down Donald J. Trump by selling her story of a sexual liaison.
Here are six takeaways from Ms. Daniels’s earlier testimony.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Jonah E. Bromwich covers criminal justice in New York, with a focus on the Manhattan district attorney’s office and state criminal courts in Manhattan. More about Jonah E. Bromwich
Advertisement
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus.
About this app. arrow_forward. Mathway is the world's smartest math calculator for algebra, graphing, calculus and more! Mathway gives you unlimited access to math solutions that can help you understand complex concepts. Simply point your camera and snap a photo or type your math homework question for step-by-step answers.
Screenshots. With millions of users and billions of problems solved, Mathway is the world's #1 math problem solver. From basic algebra to complex calculus, Mathway instantly solves your most difficult math problems. Simply type your problem in (or point your camera and snap a pic!) to receive instant free answers.
Screenshots. Mathway is the world's smartest math calculator for algebra, graphing, calculus and more! Mathway gives you unlimited access to math solutions that can help you understand complex concepts. Simply point your camera and snap a photo or type your math homework question for step-by-step answers. If a premium subscription option is ...
Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now! Math Solver. GeoGebra Math Solver. Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills! About us Partners Help Center.
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,100 Mastery points! Start Unit test. There are lots of strategies we can use to solve equations. Let's explore some different ways to solve equations and inequalities. We'll also see what it takes for an equation to have no solution, or infinite solutions.
3. Work on an easier problem. If there is an easier problem available that is similar to the one you are trying to solve, work on the easier problem first. Solving an easier problem that requires some of the same steps and formulas will help you to tackle the more difficult problem. [8] [9] 4.
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
This part of QuickMath deals only with algebraic expressions. These are mathematical statements which contain letters, numbers and functions, but no equals signs. Here are a few examples of simple algebraic expressions : x 2 -1. x 2 -2x+1. ab 2 +3a 3 b-5ab. x 3 +1. 1. a + b.
Here are five strategies to help students check their solutions. 1. Use the Inverse Operation. For simpler problems, a quick and easy problem solving strategy is to use the inverse operation. For example, if the operation to solve a word problem is 56 ÷ 8 = 7 students can check the answer is correct by multiplying 8 × 7.
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
Step 1: Understanding the problem. We are given in the problem that there are 25 chickens and cows. All together there are 76 feet. Chickens have 2 feet and cows have 4 feet. We are trying to determine how many cows and how many chickens Mr. Jones has on his farm. Step 2: Devise a plan.
In 1945, Pólya published the short book How to Solve It, which gave a four-step method for solving mathematical problems: First, you have to understand the problem. After understanding, then make a plan. Carry out the plan. ... Sometimes the numbers in a problem are so big, there is no way you will actually count everything up by hand.
Algebra Calculator - get free step-by-step solutions for your algebra math problems
An age problem is a type of word problem in math that involves calculating the age of one or more people at a specific point in time. These problems often use phrases such as 'x years ago,' 'in y years,' or 'y years later,' which indicate that the problem is related to time and age. Show more
Set up a daily routine where you dedicate time to solve math problems. This can be through traditional problem sheets, online quizzes, or interactive platforms that offer immediate feedback. Regular practice helps reinforce learned concepts and discover areas needing improvement. Make use of diverse resources to challenge different aspects of ...
Manipulating numbers in different ways, part of a supplemental math curriculum for Murphy's whole class at Hilltop Elementary in this suburb of Philadelphia, is an attempt to address those problems. In an effort to improve math achievement district-wide, all elementary students in the Chichester School District get an extra 30-minute daily ...
A high school teacher didn't expect a solution when she set a 2,000-year-old Pythagorean Theorem problem in front of her students. Then Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson stepped up to the challenge.
As high school students, Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson worked to find valid new proof for the 2,000-year-old theorem Two college freshmen who, during their final year of high school, found ...
A high school teacher didn't expect a solution when she set a 2,000-year-old Pythagorean Theorem problem in front of her students. Then Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson stepped up to the ...
Some ingenuity. Teacher Michelle Blouin Williams initiated a math competition with a bonus question tasking students to develop a new proof for the Pythagorean theorem using trigonometry, without ...
Solve Problems Instantly Get ready to witness the magic of learning unfold before your eyes. With ernvisual, you'll receive step-by-step solutions to even the most challenging problems. From math and history to coding and science, our intelligent algorithms ensure accurate and reliable answers every time. Your Personal Study Helper
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon.
A: I reached out to one of the creators, Bob Weber Jr., and he complimented the sharp-eyed reader. "While working on this one, I decided at the last minute that it would be fun to add a mouse ...
Produced by Nina Feldman , Clare Toeniskoetter and Rikki Novetsky. Edited by Liz O. Baylen. Original music by Marion Lozano , Elisheba Ittoop and Dan Powell. Engineered by Alyssa Moxley. If and ...
On today's episode. Jonah E. Bromwich, who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times. Stormy Daniels leaving court on Thursday, after a second day of cross-examination in the ...
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus.