- Food & Dining
- Coronavirus
- Real Estate
- Seattle History
- PNW Politics

Woodcock-Johnson Math Reasoning Questions
- Standardized Tests
Related Articles
Rice math strategies for third grade, four processes of algebra, differences between toefl & toeic.
- Classroom Assessment Tools for Elementary Students
- Cognitive Testing vs. Achievement Testing
The Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Achievement III (WJ-III) is a norm-referenced, standardized battery of tests utilized to assess school-aged students' academic abilities in the areas of: reading, oral language, math, written language, and academic knowledge. According to the test manual, the entire test can be administered in 60-70 minutes with each subtest taking about 5 minutes. This test is used to identify the student's current academic strengths and areas of need along with determining eligibility for additional support services such as special education.
Calculations
The calculation sub-test measures the student's ability to complete math computations. This is a paper and pencil test. These computations include addition, subtraction, multiplication and division along with a combination of these math operations. As the test increases in difficulty, calculations will include algebra, geometry, trigonometry and calculus. Simple test items would ask the student to write the numbers 1 to 10. More complex items might be to solve the following equation: 2 x 3 + 4 x 2 − x + 8 = 0
Math Fluency
This sub-test is a paper and pencil task which focuses on assessing the speed and accuracy of math facts. The student is given a response booklet which consists of 160 single- and double-digit addition, subtraction, multiplication and division problems. The student needs to solve as many problems as she can within three minutes.
Applied Problems
The applied problems sub-test addresses the student's ability to analyze and solve word problems. The student is provided with paper and pencil for computation. The test is given orally and as the problems become more complex, the student is provided with the written information to read with the examiner. The student is required to analyze the information, determine the correct operation and numerical information before solving the problem. An example might be: Susan has 11 dolls. Giselle has 10 dolls and gives 3 to Gabrielle. How many dolls does Giselle have now?
Quantitative Concepts
The quantitative concepts section consists of two sub-tests and measures the student's knowledge of math symbols, vocabulary, and concepts. Concepts, the first sub-test, is completed orally. This sub-test measures the student's understanding of counting, number identification, shapes, symbols, math terms and formulas. An example might be: What does the symbol x mean? The second sub-test, Number Series, requires that the student analyze a series of numbers, determine the pattern and identify the missing number. For example, the student would be asked to complete this pattern: 3, 6, 9, __, 15.
- Brewer Testing Services: Woodcock-Johnson Subtest Explanations
Susan Henrichon has more than 25 years of experience in education. She has taught special education and possesses administrative experience in the public school setting. She holds a Master of Education in special education from Westfield State University and a Certificate of Advanced Graduate Study in educational administration from the University of Massachusetts.
Topics Covered on the PCAT
What is covered on the dat exam, sat math vs. high school math, student learning objectives for the ged, examples of formal reading assessment tools, task analysis for math problems, where do i start to learn the math on ged tests, how similar is the gre to the sat, types of assessment used by middle school math teachers, most popular.
- 1 Topics Covered on the PCAT
- 2 What Is Covered on the DAT Exam?
- 3 SAT Math Vs. High School Math
- 4 Student Learning Objectives for the GED

Want to learn more about Riverside? hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(7083436, '0d51a9ef-7472-46c4-b0d6-ef4d2328ff08', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Take your analysis to the next level with the wj iv.

Meet Sarah, Jacob and Janine.
Get comfortable with wj iv test analysis using these fictional student test scenarios..
The Woodcock Johnson ® Fourth Edition (WJ IV™) is a comprehensive suite of co-normed assessments that includes three batteries: Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Achievement (WJ IV ACH); Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities (WJ IV COG); and the Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Oral Language (WJ IV OL), each designed to provide powerful insights into learning and behavior throughout the lifespan. The WJ IV provides a means to analyze the presence and significance of strengths and weaknesses among an examinee’s cognitive, achievement, and linguistic abilities.
What are Variations?
Variation procedures allow an examiner to compare a student’s performances within an administered test battery. They require, at minimum, the administration of a WJ IV battery’s core tests. The core tests include WJ IV ACH: Tests 1–6; WJ IV COG: Tests 1–7; and WJ IV OL: Tests 1–4. Each core test measures a distinct ability; for instance, each core test of the WJ IV COG measures a specific Broad CHC Ability.
Variations can be computed using Riverside Score , the online scoring and reporting platform, after the core tests of a WJ IV battery have been administered. Variation procedures use a specific subset of core tests to calculate a student’s predicted performance. A student’s predicted test/cluster performance is determined by averaging their standard scores across a specific subset of core tests 1 . The difference between a student’s actual and expected standard score is then computed, and the magnitude of that difference is assigned discrepancy percentile rank 2 and discrepancy standard deviation 3 scores. These scores offer interpretive value when reviewing your examinee’s profile.
1 The subset of core tests used to determine predicted performance depends on the test/cluster being targeted. For example, if we are targeting WJ IV COG Test 1: Oral Vocabulary, the predicted score would be based on the average standard score of the remaining WJ IV COG core tests (Tests 2-7). 2 The discrepancy percentile rank is the percentage of peers, with the same predicted test/cluster performance, that had a difference score of the same magnitude or smaller than your examinee. The discrepancy percentile rank can be thought of as a base rate . Base rates provide an estimate regarding how common or rare a score difference was among other children who had a similar level of ability (i.e., similar predicted score) in the WJ IV normative sample. The utility of base rates is in their ability to tell you whether a difference is clinically significant . 3 The discrepancy standard deviation indicates the distance of your examinee’s difference score from the mean difference score of peers who had the similar performance expectations for a given test/cluster. This score can be thought of as a critical value. Critical values serve as a reference point indicating whether a difference between two scores occurred by chance. Differences in scores that meet or each the critical value are unlikely to have occurred by chance, and are considered to be statistically significant.
Each case scenario below highlights how examiners can use the WJ IV’s variation procedures to easily interpret a student’s personal strengths, and areas that may warrant intervention.
WJ IV ACH Variations: Sarah & Math
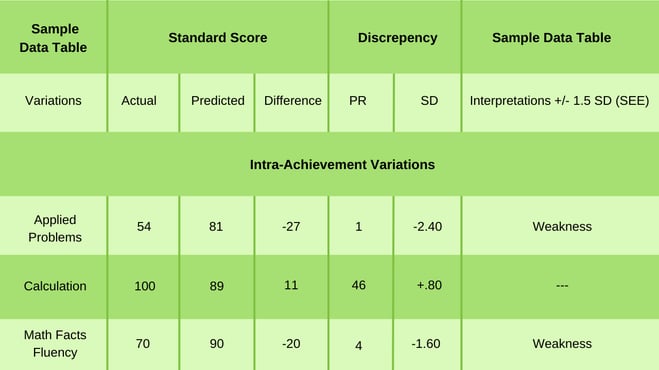
As part of the evaluation, a private psychologist administers the core tests of the WJ IV ACH (Tests 1–6) in addition to the math tests that make up the Broad Mathematics Cluster of the WJ IV ACH, including Test 2: Applied Problems, Test 5: Calculation, and Test 10: Math Facts Fluency. Administration of the WJ IV ACH’s core tests allows the psychologist to obtain a profile of Sarah’s academic strengths and weaknesses through the intra-achievement variation procedures.
Based on the above data, the psychologist finds that Sarah has two significant intra-achievement variations in Applied Problems and Math Facts Fluency.
Applied Problems Interpretation : Sarah’s actual math problem-solving skills were found to be more than two standard deviations below expectations, based on her performance across other areas of achievement. Moreover, the difference between her actual and expected performance on Applied Problems is only observed in 1% of her age-peers. The psychologist interprets this to mean that Sarah performed well below expected levels, and that the observed difference is quite rare when compared to her age-peers.
Calculation Interpretation : Using these data, the psychologist also determines that Sarah’s performance on an untimed measure of mathematical operations was approximately .80 standard deviations above expectations. The psychologist surmises that this is likely in response to Sarah’s participation in supplementary instruction that targets her calculation skills.
Math Facts Fluency Interpretation : Sarah’s actual math fluency skills were also lower than expected, by more than 1.5 standard deviations. In terms of frequency, the difference between her actual and predicted performance on Math Facts Fluency would only occur approximately 4 out of 100 times among her same-age peers. Given the magnitude and rarity of this difference, Sarah’s performance on Math Facts Fluency is deemed an area in need of improvement.
Considering these findings, the psychologist recommends further assessment in the domains of Fluid Reasoning and Cognitive Processing Speed, using the WJ IV COG. The psychologist explains that Fluid Reasoning and Cognitive Processing Speed are predictive of performance in applied problem-solving and fluency tasks, respectively. By administering these domains, the psychologist can compare Sarah’s cognitive functioning to these identified weaknesses in academic achievement. Sarah’s mother agrees to further testing. The psychologist also recommends that Sarah’s school shift Sarah’s supplementary math instruction to target her problem-solving and fluency skills, as her calculation skills were found to be almost one standard deviation above expected levels.
*These data are completely fictional and are solely provided for illustrative purposes.
WJ IV COG Variations: Jacob & Memory
.png?width=657&height=370&name=Copy%20of%20Copy%20of%20WMLS%20III%20Scoring%20%26%20Reporting%20(1).png)
As part of the evaluation the neuropsychologist administers the core tests of the WJ IV COG (Tests 1–7) in addition to the remaining tests needed to derive the Short-Term Working Memory (Tests 10 & 16) and Long-Term Retrieval (Test 13) Clusters.
Based on the above data, the neuropsychologist finds that Jacob has three significant intra-cognitive variations in Verbal Attention, Object-Number Sequencing, and Story Recall.
Verbal Attention Interpretation : Jacob’s ability to hold and manipulate information in his immediate awareness, while honing his attention, tested approximately -1.6 standard deviations below expectations. He struggled when asked to listen to a string of animals and digits and answer a specific question about the sequence. The magnitude of the negative difference between Jacob’s actual and predicted Verbal Attention score is rare, as it is only observed in 5% of those his same age.
Object-Number Sequencing Interpretation : Jacob’s actual working memory capacity also tested lower than expected. His observed performance fell approximately 1.89 SD’s below expected levels when he was asked to listen to a series of objects and digits, separate the information into two groups (e.g., objects and numbers), and then repeat information from each group in sequential order.
Story Recall Interpretation : Jacob faced the most challenges when asked to recall details from orated stories. During this task, Jacob’s ability to use his meaningful memory fell approximately -1.95 SD’s below expected levels.
The neuropsychologist explains that short-term working memory is needed to hold information, such as directions, long enough in mind for it to be processed, and share that Verbal Attention and Object-Number Sequencing, two tests tapping this broad ability, were found to be weaknesses in his profile. The neuropsychologist further shares that Jacob’s meaningful memory was found to be particularly underdeveloped based on expectations set by his performances in other cognitive domains. They express that meaningful memory what we use to remember contextualized verbal information, such as data gathered through informal conversations and classroom lessons. These data are validating to Jacob, who was seeking an explanation for his struggles.
Considering these findings, the neuropsychologist recommends a comprehensive measure of memory, to determine a more detailed profile of Jacob’s learning, and immediate, delayed, and recognition memory capabilities. They also suggest additional testing focused on measuring Jacob’s ability to engage in verbal and visual tasks of sustained attention, as weaknesses in honing attention can impact his ability to effectively store information in his short-term working memory.
WJ IV OL Variations: Janine
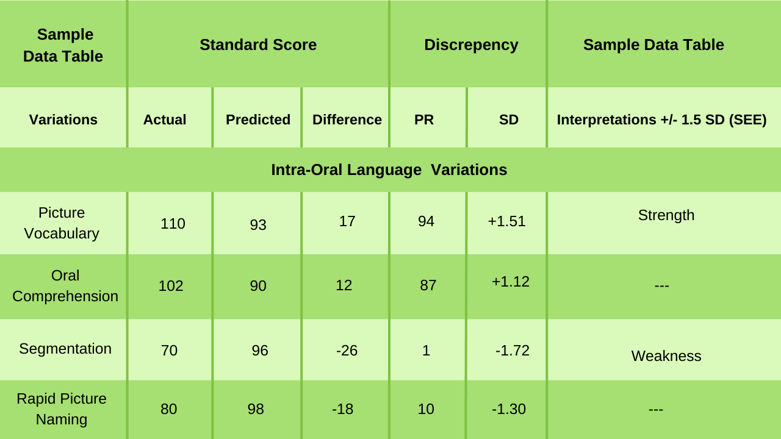
Based on the above data, the speech and language pathologist discovered that Janine has two significant intra-oral language variations in Picture Vocabulary and Segmentation.
Picture Vocabulary : Janine’s ability to identify and name pictures tested significantly above expectations when compared to the average of her performances across the other core WJ IV OL tests (SD = +1.51). The magnitude of the difference between Janine’s actual and predicted Picture Vocabulary score is rare, and it is only observed in no more than 6% of those her same age in the normative sample.
Segmentation : In contrast, Janine had trouble when asked to break apart real words into their constituent speech sounds (i.e., phonemes). When compared to same-age peers, the magnitude of her Segmentation difference score is rare, only occurring in 1% of the normative sample. This signals to the speech and language pathologist that this difference is clinically significant. Furthermore, Janine’s Segmentation difference score fell approximately 1.72 SD’s below expected levels, which meets the threshold for statistical significance.
Because of the clinical and statistical significance of Janine’s Segmentation standard score, when compared to her other WJ IV OL performances, the speech and language pathologist decides to conduct additional testing to gain a better understanding of Janine’s phonetic coding skills. They decide to administer both Test 7: Sound Blending, and Test 9: Sound Awareness.
Administering Test 7 allows the speech and language pathologist to determine if Janine’s ability to put speech sounds together (i.e., blend phonemes) may also warrant support. Test 9: Sound Awareness was administered considering, Janine’s performance on Test 3: Segmentation, as the skills tapped by Test 9 (i.e., rhyming and deletion) are lower-order/prerequisite skills needed to engage in more advanced phonetic coding tasks (e.g., segmentation and sound blending).

Recommended Articles:
New partnership to keep schools safe through modern student wellness.

Riverside Insights and CAI Founders to Host Virtual Conference on SLD Identification
Navigating the challenges of identifying sld and id, subscribe to our newsletter.
We hate spam. You’ll only receive essential emails.
Submit a Comment
Click here to subscribe
Stay up to date
At Riverside Insights, we share your commitment to helping individuals elevate their learning potential-from early childhood through their academic journeys, and for the rest of their lives.
Popular Post
Recent posts.

The trusted classic, completely reimagined.
The woodcock-johnson v (wj v) system is structured to offer customized, efficient, and flexible assessments that examiners need to accurately evaluate learning problems in children and adults. the wj v is designed to measure intellectual abilities, academic achievement, and oral language abilities..

Eliminates the need to manage physical test materials. Evaluations are easily accessible and web-based.

Examinee profiles and reporting can be shared and sent to those with proper permissions, facilitating a multidisciplinary team approach to assessment.

New Tests and Clusters
Designed to help examiners better assess comprehension, processing speed, executive functioning, working memory, spelling, phoneme-grapheme knowledge, and more.

Automated Scoring Accuracy
Basal and ceiling rules are automatically implemented by the platform, ranging from 4-6, expediting the testing experience without sacrificing accuracy.

Streamlined Administration
Preloaded tests help avoid any pause or delay in testing. Additionally, some introduction tasks are presented in video format, ensuring that each examinee has an identical opportunity to understand the expectations of the test.
New Features
Some of these new offerings will be released throughout 2025.
- Introducing a new voice capture feature which will improve scoring accuracy, particularly on time retrieval tasks
- The introduction to tasks on several tests are in a video format, allowing a standardized presentation.
- Users can select the reason for referral and recommended clusters are automatically created , reducing time spent on test preparation. This feature will not be available at publication, but later in 2025.
Not all new tests will be available at launch, and some names may change.
- Verbal Analogies
- Visual Working Memory
- Story Comprehension
- Symbol Inhibition
- Math Problem Identification
- Magnitude Comparison
- Academic Vocabulary
- Rapid Letter Naming
- Rapid Phoneme Naming
- Rapid Number Naming
- Rapid Quantity Naming
- Paragraph Reading
- Comprehension
- Letter Writing Fluency
- Number Sense
- Language Expression
- Sentence Writing Accuracy
- Phonemic Word Retrieval
New Clusters
Not all new clusters will be available at launch, and some names may change.
- Inductive Reasoning
- New Learning Efficiency
- Retrieval Fluency
- Working Memory-Attention Control
- Perceptual Speed-Search
- Cognitive Efficiency-Extended
- Basic Reading Skills- Extended
- Expressive Language
- Reading Fluency- Extended
- Spelling Skills
- Number Concepts
- Math Problem Solving- Extended
- Phonemic Awareness
- Phonemic Awareness- Extended
- Phonemic Manipulation
- Phonemic Manipulation- Extended
- Retrieval Fluency- Extended
- Phonemic Retrieval Fluency
- RAN- Reading
- Auditory Working Memory- Extended
- Auditory Memory Span- Extended
Woodcock-Johnson IV
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 08 April 2017
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Kelly L. Hoover 4 &
- Andrew S. Davis 4
214 Accesses
WJ IV ; Woodcock-Johnson IV
Description
The Woodcock-Johnson IV (WJ IV; Schrank et al. 2014b ) is the most recent iteration of the well-known Woodcock-Johnson battery of tests. Unlike previous versions which included a cognitive battery and an achievement battery, the WJ IV consists of three co-normed assessment batteries: the Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Cognitive Abilities (WJ IV COG; Schrank et al. 2014a ), the Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Achievement (WJ IV ACH; Schrank et al. 2014c ), and the Woodcock-Johnson Test of Oral Language (WJ IV OL; Schrank et al. 2014d ). Each of these assessment batteries can be used independently or in combination with one or both of the other batteries.
The norming sample for the WJ IV is comprised of 7,416 participants ranging from age 2 to 90 who were demographically representative of the United States population (Mather and Wendling 2014b ; McGrew et al. 2014 ). An online scoring system is used to convert raw scores to standard scores, percentiles,...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
References and Readings
Carroll, J. B. (1993). Human cognitive abilities: A survey of factor-analytic studies . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Carroll, J. B. (2005). The three-stratum theory of cognitive abilities. In D. P. Flanagan & P. L. Harrison (Eds.), Contemporary intellectual assessment: Theories, tests, and issues (2nd ed., pp. 69–76). New York: Guilford Press.
Google Scholar
Horn, J. L. (1991). Measurement of intellectual capabilities: A review of theory. In K. S. McGrew, J. K. Werder, & R. W. Woodcock (Eds.), WJ-R technical manual (pp. 197–232). Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Horn, J. L., & Noll, J. (1997). Human cognitive capabilities: Gf-Gc theory. In D. P. Flanagan, J. L. Genshaft, & P. L. Harrison (Eds.), Contemporary intellectual assessment: Theories, tests, and issues (pp. 53–91). New York: Guilford Press.
Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N. L. (2004). Kaufman assessment battery for children (2nd ed.). San Antonio: Pearson.
Mather, N., & Wendling, B. J. (2014a). Examiner’s manual: Woodcock-Johnson IV tests of achievement . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Mather, N., & Wendling, B. J. (2014b). Examiner’s manual: Woodcock-Johnson IV tests of cognitive abilities . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
McGrew, K. S. (2005). The Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory of cognitive abilities: Past, present, and future. In D. P. Flanagan & P. L. Harrison (Eds.), Contemporary intellectual assessment: Theories, tests, and issues (pp. 136–181). New York: Guilford Press.
McGrew, K. S. (2009). CHC theory and the human cognitive abilities project: Standing on the shoulders of the giants of psychometric intelligence research. Intelligence, 37 , 1–10.
Article Google Scholar
McGrew, K. S., LaForte, E. M., & Schrank, F. A. (2014). Technical manual: Woodcock-Johnson IV . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Roid, G. H. (2003). Stanford Binet intelligence scales (5th ed.). Austin: PRO-ED.
Schrank, F. A., & Dailey, D. (2014). Woodcock-Johnson online scoring and reporting [Online format] . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Schrank, F. A., McGrew, K. S., & Mather, N. (2014a). Woodcock -Johnson IV tests of cognitive abilities . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Schrank, F. A., Mather, N., & McGrew, K. S. (2014b). Woodcock -Johnson IV . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Schrank, F. A., Mather, N., & McGrew, K. S. (2014c). Woodcock -Johnson IV tests of achievement . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Schrank, F. A., Mather, N., & McGrew, K. S. (2014d). Woodcock -Johnson IV tests of oral language . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Wechsler, D. (2002). Wechsler intelligence scale for children (4th ed.). San Antonio: Pearson.
Wechsler, D. (2008). Wechsler adult intelligence scale (4th ed.). San Antonio: Pearson.
Woodcock, R. W., & Johnson, M. B. (1977). Woodcock-Johnsonpsycho-educational battery . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Woodcock, R. W., & Johnson, M. B. (1989). Woodcock-Johnsonpsycho-educational battery – Revised . Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Woodcock, R. W., McGrew, K. S., & Mather, N. (2001, 2007). Woodcock-Johnson III. Rolling Meadows: Riverside.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Psychology, Ball State University, Teachers College Room 505, Muncie, IN, 47306, USA
Kelly L. Hoover & Andrew S. Davis
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kelly L. Hoover .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Richmond, Virgin Islands, USA
Jeffrey Kreutzer
Kessler Foundation , West Orange, New Jersey, USA
John DeLuca
Suite 200 , Wynnewood, Pennsylvania, USA
Bruce Caplan
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Hoover, K.L., Davis, A.S. (2017). Woodcock-Johnson IV. In: Kreutzer, J., DeLuca, J., Caplan, B. (eds) Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56782-2_1501-3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56782-2_1501-3
Received : 25 January 2017
Accepted : 22 March 2017
Published : 08 April 2017
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-56782-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-56782-2
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Woodcock–Johnson Test
Developed in 1977 by Richard Woodcock and Mary E. Bonner Johnson, the Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities is one of the most popular IQ tests available today. Most recently updated in 2014 (referred to as the WJ IV), the Woodcock-Johnson test is an intelligence test that can be used on participants from the age of 2 all the way to people in their 90s. The test is similar in nature, and can often be used in place of, the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) for an educational diagnosis of children. The test is used primarily to measure ability for academic achievement, oral language, scholastic aptitude, and overall cognitive skills.
What are the Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities?
The Woodcock-Johnson test is a multiple choice intelligence test that can be administered by schools, psychologists, and testing centers. The test includes what are known as the Standard Battery and Extended Battery of tests. Previously, the Woodcock-Johnson III test ( also known as the WJ-III test) was used to develop intelligence index scores for the General Intellectual Ability (GIA) and Brief Intellectual Ability (BIA). With the introduction of the WJ IV test, there are now three test batteries, which can be used independently or in combination. Those batteries are:
- The WJ IV Tests of Cognitive Abilities. This test is used to identify learning problems and individual strengths and weaknesses. This is similar to other intelligence tests such as the Stanford-Binet and Wechsler Intelligence tests .
- The WJ IV Tests of Achievement. This test battery is used to measure math and reading proficiency and compare academic achievement in relation to the subject’s academic knowledge.
- The WJ IV Tests of Oral Language. This test battery is used to assess language proficiency.
The WJ IV Tests of Cognitive Abilities
The Cognitive Abilities portion of the Woodcock-Johnson test consists of the following tests.
Standard Battery
- Oral Vocabulary
- Number Series
- Verbal Attention
- Letter-Pattern Matching
- Phonological Processing
- Story Recall Test
- Visualization
- General Information
- Concept Formation :
Extended Battery
- Numbers Reverse
- Number-Pattern Matching
- Nonword Repetition
- Visual-Auditory Learning
- Picture Recognition
- Analysis-Synthesis
- Object-Number Sequencing
- Pair Cancellation
- Memory for Words
From these tests the following intelligence clusters are scored.
- Short-Term Working Memory-Extended
- Brief Intellectual Ability
- Gf-Gc Composite
- Cognitive Processing Speed (Gs)
- Number Facility (N)
- Perceptual Speed (P)
- General Intellectual Ability
- Auditory Processing (Ga)
- Comprehension-Knowledge (Gc)
- Auditory Memory Span (MS)
- Comprehension-Knowledge-Extended
- Long-Term Retrieval (Glr)
- Fluid Reasoning (Gf)
- Visual Processing (Gv)
- Fluid Reasoning-Extended
- Cognitive Efficiency
- Short-Term Working Memory (Gwm)
- Cognitive Efficiency-Extended Clusters
The WJ IV Tests of Achievement
The Woodcock Johnson Tests of Achievement portion of the test consists of the following tests:
- Letter-Word Identification
- Applied Problems
- Passage Comprehension
- Calculation
- Writing Samples
- Word Attack
- Oral Reading
- Sentence Reading Fluency
- Math Facts Fluency
- Writing Fluency
- Reading Recall
- Number Matrices
- Word Reading Fluency
- Spelling of Sounds
- Reading Vocabulary
- Social Studies
- Brief Achievement
- Broad Achievement
- Broad Mathematics
- Written Language
- Math Calculation Skills
- Reading Fluency
- Broad Written Language
- Reading Rate
- Basic Writing Skills
- Mathematics
- Written Expression
- Math Problem Solving
- Academic Skills
- Reading Comprehension-Extended
- Academic Applications
- Reading Comprehension
- Academic Fluency
- Broad Reading
- Academic Knowledge
- Basic Reading Skills
- Phoneme-Grapheme Knowledge
The WJ IV Tests of Oral Language
The Achievement portion of the Woodcock-Johnson test consists of the following tests.
- Picture Vocabulary
- Oral Comprehension
- Segmentation
- Rapid Picture Naming
- Sentence Repetition
- Understanding Directions
- Sound Blending
- Retrieval Fluency
- Sound Awareness
- Vocabulario sobre dibujos
- Comprensión oral
- Comprensión de indicaciones
- Listening Comprehension (Spanish)
- Broad Oral Language (Spanish)
- Oral Language (Spanish)
- Speed of Lexical Access
- Phonetic Coding
- Oral Language
- Broad Oral Language
- Oral Expression
- Listening Comprehension
Woodcock-Johnson IV Scoring
Like many other intelligence tests, Woodcock Johnson scoring has some complexities. T here are several different scores generated upon completing the Woodcock-Johnson test. The three types of WJ IV scoring ranges that are provided upon completing the exam are the level of development, comparison with peers and degree of proficiency scores.
Level of development scores are designed to explain the scores in terms of age equivalents and grade equivalents. Thus, these scores explain a child’s score against people of their same age or grade to determine if their scores index at, above, or below their current age and grade.
Comparison with peers scores test takers against a standard score like other IQ tests (where the average score is 100 and the standard deviation is 15). This also offers a percentile rank which quantifies where the score falls within the total testing population and a range classification which assigns a label to a range of scores. The table below shows how all three relate.
Degree of proficiency scores are metrics which show how a child performs on a functional level versus tasks that typical children in their same age group or grade would perform at a 90% level of efficiency. Scores can range from 100/90 to 0/90. The table below shows a detailed view of RPI scores, perceived functionality, and the score’s implication for the child’s academic achievement.
WJ III vs. WJ IV
In 2014 The fourth edition of the test replaced the Woodcock-Johnson III Tests of Cognitive Abilities. There were quite a few changes as the test moved from version three to four, with some of the more notable changes listed below:
- The Woodcock-Johnson III Tests of Achievement had fourteen more extended battery clusters between Parallel Forms, Standard Battery Academic Tests, Extended Battery Academic Tests, Standard BAttery Academic Clusters, and Extended Battery Academic Clusters.
- The Tests of Achievement Story Recall, Understanding Directions, Picture Vocabulary and Oral Comprehension tests in the WJ III were replaced with the WJ IV Cognitive Battery, WJ IV Oral Language Battery, WJ IV Oral Language Battery, and WJ IV Oral Language Battery.
- The Academic Knowledge Cluster was replaced by a long selection of new tests including: Oral Reading Test, Reading Test, Reading Recall Test, Number Matrices Test, Word Reading Fluency Test, Science Test, Social Studies Test, Humanities Test, and a new Reading Cluster.
- The Woodcock-Johnson III Tests of Cognitive Abilities included five new tests within the standard battery including Verbal Attention, Letter Pattern Matching, Phonological Processing, Story Recall, and Visualization
- Another key change in the Cognitive Abilities test was the inclusion of tests for diagnostics, which were previously only included as a supplement to the WJ III tests.
- Scoring differences on the Cognitive Abilities test was also quite significant, as the WJ III tested a variety of new clusters of intelligence. As an example, Phonemic Awareness, Working Memory and Delayed Recall were replaced by Comprehension Knowledge, Fluid Reasoning, and Short-term Working Memory.
Blog Topics
- IQ Test (59)
Recent Posts
- Free Aptitude Test
- Batman IQ Score
- Spiderman IQ Score
- Donald Trump’s IQ Score
- Steve Jobs IQ Score
- Emma Watson IQ Score
- Tony Stark’s IQ Score
- Eminem IQ Score
- Robin Williams IQ Score
- Joe Biden’s IQ Score
- Katherine Johnson IQ Score
- Bill Gates IQ Score
- Alex Trebek IQ Score
- Minimum IQ For The Military
- Bobby Fischer IQ Score

Schedule Testing Today!
Smoky mountain academic resources & training, woodcock-johnson iv, tests of achievement (wj iv) grade k - adult.
Primarily orally-administered
One on one testing environment
Provides parents with a 'snapshot' of their child's academic achievement
Includes consultation with parents to discuss test results and observations during testing
Also includes WJ IV Interpretation & Instructional Interventions Program (WIIIP®), which provides a detailed interpretation of student performance offering research-based interventions and strategies based on an examinee’s scores.
If this is your student’s first time taking the Woodcock-Johnson Test IV, then it is highly recommended (but not required) that the Broad Oral Language Cluster should be added to the Basic Test . This gives the Test Administrator more information and helps get a good baseline or the “big” picture of where a student performs academically.
The Basic Test: $110 (10 sub-tests, ~2 hrs.) Inquire about discounts during off-peak testing times
Meets North Carolina state home-schooling requirements
Meets Florida state home-schooling requirements
Qualifies for Duke Talent Identification Program with 95th percentile score
13 interpretive clusters: Broad Achievement, Brief Achievement, Academic Skills, Academic Fluency, Academic Applications, Reading, Broad Reading, Mathematics, Broad Mathematics, Math Calculation Skills, Written Language, Broad Written Language, Written Expression
The Basic test includes the following Subtests:
Passage Comprehension - Application Test
Letter/Word Identification - Skill Test
Sentence Reading Fluency - Speed Test
Word Reading Fluency - Speed Test (Tester may substitute Word Attack, a phonics skill test for beginning readers)
Spelling - Skill Test
Writing Fluency - Speed Test
Writing Samples - Application Test
Calculation - Skill Test
Math Fluency - Speed Test
Applied Problems - Application Test
Optional Testing Add-ons
+ $70 Broad Oral Language (6 additional sub-tests, ~1.25 hr) Highly recommended having administered the first time Especially useful if your child is struggling in several areas. This Test can Help determine if your child is struggling with Oral Language or Auditory Processing. (No Reading, Writing or Academic Knowledge required in this test) Includes 5 interpretive clusters: Oral Language, Broad Oral Language, Listening Comprehension, Oral Expression, Speed of Lexical Access
+ $90 Dyslexia Screening Cluster (10 additional subtests ~2hr) Includes Broad Oral Language and Additional Reading Clusters. Gives you a detailed Report in Screening for Dyslexia and Reading Disabilities. Does not Officially Diagnose Dyslexia, but will give you information about your child’s tendencies towards dyslexia. Can be scheduled at a separate time from basic test, if needed. Please communicate this with your testing associate.
+ $30 Processing / Speed Cluster (2 additional sub-test, ~.5 hr) Useful for helping determine if you child may struggle with processing information for academic tasks. Helpful if you are noticing your child has trouble finishing work and/or struggles with timed tasks. 1 interpretive cluster: Speed of Lexical Access
+ $25 Specific Reading Cluster (4 additional sub-tests, ~.5 hr) More Detailed Report Concerning Your Child’s Reading Level and to gain insight what particular areas of reading they may be struggling with. 4 additional interpretive clusters: Basic Reading Skills, Reading Fluency, Reading Rate, Phoneme-Grapheme Knowledge
+ $25 Reading Comprehension Cluster (2 additional sub-tests, ~.5 hr) More detailed report concerning your child’s Reading Comprehension Level. 1 additional interpretive cluster: Reading Comprehension
+ $30 Phonics Cluster (2 additional sub-tests, ~.5 hr) More Detailed Report Concerning your child’s ability to read and decode words Phonetically 1 interpretive cluster: Phonetic Coding
+ $10 Specific Math Cluster (1 additional sub-test, ~.25 hr) More Detailed Report concerning your Child’s Math Problem Solving Ability. 1 additional interpretive cluster: Math Problem Solving
+ $10 Specific Basic Writing / Editing Cluster (1 additional sub-test, ~.25 hr) More Detailed Report concerning your Child’s Basic Writing Ability. 1 additional interpretive cluster: Basic Writing Skills
+ $25 Academic Knowledge Cluster (3 add'l sub-tests, ~.5 hr) Report Concerning your Child’s General Academic Knowledge Science, Social Studies, Humanities
Tests administered outside the SMART associate's home testing area will be subject to a travel fee. Please contact an Associate to arrange a date and then complete the Registration Form below.
Click here for tips on how to prepare for your test session.
S.M.A.R.T. is an approved NCSEAA Provider. You may use your ESA+ class wallet account for students with disabilities to pay for Woodcock-Johnson Test Session.

How to Prepare for your Woodcock-Johnson IV Test Session with S.M.A.R.T.
There is no need to study or prepare for your session in any certain way. These tests are intended to show you what your child can do academically without assistance or prompting and what they have stored in their long-term memory.
If you would like to prepare your students for the types of questions that they will see during their Woodcock-Johnson IV evaluation, some things you can do are as follows:
Younger students may review basic addition and subtraction concepts. (Also they can review simple multiplication and division if they have learned it)
Practice basic mixed math facts with a timer. (Students are asked to do as many problems as they are able within the time limit. There is no pressure to complete all the problems.)
Review basic calculation skills such as multi-digit addition and subtraction, multi-digit multiplication, long division and fractions without the use of a calculator, with older students that have learned these skills previously.
Review applied math skills such as counting money, reading an analog clock, and solving basic word problems with students who have learned these skills previously.
Review basic sentence writing skills with students who have previously learned to write sentences.
Review basic spelling skills or letter writing skills.
Read simple sentences or words and answer questions with a timer. (Students are asked to do as many questions as they are able within the time limit. There is no pressure to complete all the questions.)
Practice how to fill in a missing word in short sentences or passages.

The Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Achievement is a very student friendly, low stress, and gentle assessment. All S.M.A.R.T. Testing associates will work with your child to make sure they have a pleasant testing experience.
The basic test consists of 10 subtests that measure students’ ability levels in reading, mathematics, and written expression. These assessments do not follow any particular curriculum, course of study, or state standards. It is a nationally-normed standardized test that gives a snapshot of your child’s ability to independently use the skills that they have learned in reading, writing, and math.
We recommend that you encourage your child that the evaluation is a chance for them to show what they know. Make sure your child understands that they will not be able to answer every question on the test and encourage them to try their best. The scores on a Woodcock-Johnson test are for your information to help you know how you can continue to educate your child.

Start now with 100 FREE practice questions!
Privacy Protected - We do not sell or share your information with anyone. By submitting you agree to TestingMom.com's terms of use and privacy policy .
Woodcock Johnson Tests
What is the Woodcock Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities?
The Woodcock Johnson IV test, or Woodcock Johnson Fourth Edition, was recently released as the newest and most recent version of the Woodcock Johnson test. The Fourth Edition serves to replace the Woodcock Johnson III, or Third Edition. This older version was used for some time until replaced by this newest version.
Historically, the Woodcock Johnson test has been used for a broad range of ages from young children to elderly individuals. For kids, the test is often used to determine whether they are eligible for entry into a gifted or advanced program. As a result, doing well on the test can be important for the child’s educational future.
The Woodcock Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities contain the greatest breadth of cognitive abilities of any standardized body of tests. These tests help to identify learning problems. It helps to measure aspects of seven different broad CHC abilities (Cattell–Horn–Carroll theory , commonly abbreviated to CHC , is a prominent psychological theory on the structure of human cognitive abilities). Finally, it offers a new Gf-Gc Composite [This measures intellectual level (or intellectual development) from Fluid Reasoning ( Gf ) and Comprehension-Knowledge ( Gc ) tests alone] for comparison with other cognitive abilities, oral language, and achievement.
Privacy Protected - We do not sell or share your information with anyone.By submitting you agree to TestingMom.com's terms of use .
Understanding relative strengths and weaknesses in comparison to the Gf-Gc Composite can lead to individualized instruction designed to target identified learning needs. The examiners can use the Cognitive Abilities tests alone, but if combined with the Oral and Achievement tests, it will increase diagnostic capability and sensitivity, providing greater insight into your child’s abilities and needs.
When students are given the Woodcock Johnson Tests of Achievement, the examiner may administer the Standard Battery questions or the Extended Battery, depending on what the school district requires. Subtests in the Extended Battery are often given if the district wants to evaluate a child’s reading, math, writing, language or other skills. The test also contains new domain-specific scholastic aptitude CLUSTERS that allow for efficient and valid predictions of academic achievement, providing even more feedback for specific help that can be given for your child. The tests of achievement help compare your child’s levels of achievement to academic knowledge.
Prepare your child to tackle both the Standard and Extended Batteries of the Woodcock Johnson Tests with ease. TestingMom.com can help build your child’s confidence! We offer access to 3,000+ practice questions that cover the skills found on the 11 Standard Battery and 9 Extended Battery tests.
Plus, we offer parent resources to help you navigate the testing process, access to 30+ games from top educational publishers, a Student Success Team who’s standing by to help with your questions, and more!
Want to try us out? Sign up for a free account today and get 100 free practice questions.
Skill Assessment
The skills tested on the Woodcock Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities are:
- Comprehension-Knowledge
- Long-Term Retrieval
- Visual-Spatial Thinking
- Auditory Processing
- Fluid Reasoning
- Processing Speed
- Short-Term Memory
- Quantitative Knowledge
- Reading-Writing Ability
Breakdown for Woodcock Johnson
The following tests are included in the Woodcock Johnson IV Tests of Achievement Standard Battery:
- Test 1 : Letter-Word Identification
- Test 2: Applied Problems
- Test 3: Spelling
- Test 4: Passage Comprehension
- Test 5: Calculation
- Test 6: Writing Samples
- Test 7: Word Attack
- Test 8: Oral Reading – NEW
- Test 9: Sentence Reading Fluency
- Test 10: Math Facts Fluency
- Test 11: Writing Fluency
The following tests are included in the Woodcock Johnson IV Tests of Achievement Extended Battery:
- Test 12: Reading Recall – NEW
- Test 13: Number Matrices- NEW
- Test 14: Editing
- Test 15: Word Reading Fluency – NEW
- Test 16: Spelling of Sounds
- Test 17: Reading Vocabulary
- Test 18: Science
- Test 19: Social Studies
- Test 20: Humanities
The following tests are included in the Woodcock Johnson IV Tests of Achievement CLUSTERS:
- Brief Achievement
- Written Language
- Reading Fluency
- Reading Rate
- Mathematics
- Math Problem Solving
- Reading Comprehension Extended
- Reading Comprehension
- Broad Reading
- Basic Reading
- Broad Achievement
- Broad Mathematics
- Math Calculation Skills
- Broad Written Language
- Basic Writing Skills
- Written Expression
- Academic Skills
- Academic Applications
- Academic Fluency
- Academic Knowledge
- Phoneme – Grapheme Knowledge
The following tests are included in the Woodcock Johnson IV Tests of Oral Language Standard Battery:
- Test 1 : Picture Vocabulary
- Test 2: Oral Comprehension
- Test 3: Segmentation – NEW
- Test 4: Rapid Picture Naming
- Test 5: Sentence Repetition
- Test 6: Understanding Directions
- Test 7: Sound Blending
- Test 8: Retrieval Fluency
- Test 9: Sound Awareness
The following tests are included in the Woodcock Johnson IV Tests of Oral Language CLUSTERS:
- Listening Comprehension (Spanish) – NEW
- Broad Oral Language (Spanish) – NEW
- Oral Language (Spanish) – NEW
- Speed of Lexical Access – NEW
- Phonetic Coding – NEW
- Vocabulary* – NEW
- Oral Language
- Broad Oral Language
- Oral Expression
- Listening Comprehension
* Obtained when used with the WJ IV Tests of Cognitive Abilities
Want to help your children build the confidence and familiarity they need to score higher on the Woodcock Johnson Tests? Join TestingMom.com! In addition to thousands of practice questions, we’ve also got lessons for parents so you understand the best way to help your child prep for Test Day.
We’ll get you started with 100 free gifted and talented practice questions. Just sign up for a free account below to try us out!
Looking for more resources to help your child approach the Woodcock Johnson Tests with confidence? TestingMom.com can help with:
- 3,000+ Woodcock Johnson practice questions that cover both the Standard and Extended Batteries to help your child build confidence and familiarity for Test Day.
- A customizable program , based on your child’s grade level and upcoming tests, so you can target your child’s prep for maximum improvement.
- Interactive practice with 30+ games from top educational publishers to strengthen your child’s overall skills like math, language arts, science, social studies and more.
- A Student Success Team to help you if you need a little advice or if you get stuck.
- Over 100,000 practice questions for the most popular tests for Pre-K to 8th Grade, including gifted and talented, private school admissions, state tests and more—all for one low price.
- Parent resources to help you easily navigate your child’s testing process.
Tell us about your experiences
36 Responses
Dear Sir/Madame, I am a senior student from China, and I would like to do a research to investigate the factors that related to math achievement of students in primary school in Shanghai, China. I find that many researches use Woodcock Johnson III to test the math achievement of children. However, I could not find the manual for this text, could you please tell me how can I get access to it?
That edition of the test is old and outdated. You will have a difficult time finding the manual. I would encourage you and any other researcher/examiner to use the latest and most updated version of the Woodcock Johnson which is the Woodcock Johnson -IV. It has math, reading, writing and so much more to offer in the area of assessment.
TestingMom.com
We do have practice materials for our members for the Woodcock Johnson-IV. Once you log-in, you can go here: https://members.testingmom.com/test-prep/wj-iv/practice-questions
After 34 years as a LDTC in Piscataway I recently became an independent Learning Consultant and need to order my own copy of the Woodcock Johnson Test of Achievement. I haven’t been able to find where I can order this test
the Woodcock Johnson Tests
Hi Hao –
We do provide a section for the Woodcock Johnson Tests of Achievement with a paid subscription to TestingMom.com.
All the best,
Who is allowed to administer the Woodcock Johnson tests? I have a MSE in Education with a specialty in Reading. Would I qualify to administer the tests?
Hi Linda –
The Woodcock-Johnson is an IQ Test and must be administered by a psychologist.
This test can also be administered by an educational specialist (Special Ed teacher or RSP teacher) as well it is used to assess the strengths and weaknesses in cognitive, academic, and linguistic abilities.
Can the WJ-iv be administered more than one time per year?
Hi Beth –
This would be a question best answered by your child’s school district.
my son has learning disabilities and was tested when he was 7 his scores were very low, my question is, do they test when they get older or do they go by that test the rest of their life?
Hi Marilyn –
We would certainly recommend speaking to your son’s teacher. This test can be given again, but it is left to the discretion of the school.
I am trying to interpret my child’s scores on the Woodcock Johnson Teat Of Achievement Form A. Please tell me what the SSPR stands for in the sixth column of his Woodcock Johnson IV Score report. I am looking for his Percentile rank. Thank you in advance for any help you can give.
Hi Larry, please email our Parent Success Team at [email protected] and we can help you out with the Woodcock Johnson results.
Tracey Miller
Hi there I would like to have my child tested for Dyslexia if possible , could you tell me what the cost of this would be please he is 13 years old , Thank you
I was supposed to free questions upon signing up, however, when I clicked where it told me to nothing happed. I’m extremely unhappy and will not be paying to sign up for anything on your site!
My child was a given an IEP assessment with this test. Particularly my concern for my child is the section Reading Clusters. In 4 categories he rated as Low Average, 1 category rated as low, and 2 categories rated as average. This was exactly why I requested the IEP assessment but they say that he is doing “fine” or “average”. This doesn’t make any sense to me as I see there is a clear problem. Help.
Hi Regina, if you’ll email us at [email protected] and we can research more on the Woodcock Johnson scoring for your child.
What do the test scores mean, where are the number/scores ranges for indication of impairment.
Hi Shelley, that’s a great question about the scoring on the Woodcock Johnson! Please email us at [email protected] and provide us more information.
Rose Anderson
Please send more information
For more information, please email us at [email protected].
Is the Woodcock-Johnson III still used, or can people only administer version IV now?
Great question! Here’s what we know about the updated version. The Woodcock-Johnson tests are a series of individually administered tests of cognitive abilities, academic achievement, and oral language. The Woodcock-Johnson III (WJ III) was the third edition of this series of tests, while the Woodcock-Johnson IV (WJ IV) is the fourth edition.
Although the WJ IV was released in 2014, the WJ III is still used by some practitioners and researchers. However, it is important to note that the WJ III has been superseded by the WJ IV, which is the current version of the test. The WJ IV is an updated and improved version of the WJ III, and it includes new features such as expanded age ranges, updated norms, and new subtests.
While the WJ III may still be used in some settings, it is generally recommended that practitioners and researchers use the most current version of the Woodcock-Johnson tests, which is the WJ IV.
By providing practice questions aren’t you invalidating the test, especially for diagnostic purposes? You are not doing your children any favors by teaching the test.
Our materials provide the underlying skills needed for a child to do well on the Woodcock Johnson test. Providing practice questions for the Woodcock Johnson and preparing a child for a test can be beneficial in many ways. It is important to strike a balance between familiarizing a child with the testing process with focus on process of elimation, pacing through questions, etc.
Firstly, practice questions can help alleviate test anxiety, which is a common issue faced by many students. By familiarizing them with the format and types of questions they will encounter, we can empower them to feel more confident and comfortable in a testing environment.
Secondly, exposing children to practice questions allows them to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are valuable assets not only for taking tests but also for their overall education and future success. It is essential to clarify that teaching the test is not the goal; rather, it is to foster these skills through exposure to various types of problems.
My child was administered the Woodcock Johnson by an independent neuropsychologist. The same test was re-administered in less than three months by a teacher at the school my son attends. The school states that the performance on this test are relatively similar to prior testing results. My son has been diagnosed with a specific learning disability in written expression and reading fluency but the district states that they don’t observe that, and in their interpretation my child is above average, and it doesn’t meet their criteria for a SLD. How re-administering the test in less than 3 months affect my child? Is the test valid?
We, at Testing Mom, can appreciate your concerns and it’s clear you are an engaged and dedicated parent. Let’s unpack the situation with the Woodcock Johnson test that your son has undergone twice in less than three months.
The Woodcock Johnson test is a well-respected and widely-used tool for measuring various cognitive abilities and academic skills. It’s especially useful in diagnosing specific learning disabilities, like the one you mentioned your son has been diagnosed with.
However, regarding the re-administration of the test in less than three months, there are certain factors to consider. While it’s not inherently problematic to re-administer the test within this timeframe, the scores might not necessarily reflect significant changes in your child’s abilities or skills over such a short period.
In terms of the validity of the test, the Woodcock Johnson is a well-validated measure. Nevertheless, the interpretation of the results can sometimes be subjective and depend on the professional administering and evaluating the test. If the school and the neuropsychologist have different interpretations of your son’s performance, it might be beneficial to have a conversation with both parties to understand the reasons behind their conclusions.
Moreover, eligibility for special services often requires that a child’s learning disability significantly impacts their academic performance. If your son’s scores are interpreted as “above average,” this could be why the school is stating that he does not meet their criteria for a Specific Learning Disability (SLD), even though he has a diagnosis. Please talk to the neuropsychologist or other medical professional for their advice on this matter since they will have more knowledge of the specifics of your son’s situation.
Keep advocating for your son, Elizabeth. Your involvement in his education will make a significant difference for the years to come!
Marwa Saeed Abd Elmaksoud
I am Marwa Saeed , Pediatric Neurologist from Egypt. I need to ask about the possibility to conduct a Reserch on Woodcock Johnson Tests through translation and validation on Egyptian children with learning disabilities Is this possible?! How can we get it and practice on?! Thanks I’m advance
Hello Marwa, please email us at [email protected] for more info. Thanks
Hello . I am a psychologist and I want to learn Woodcock Johnson Can you give me details about the test ? Thank you in advance
Hi Iman, we have information on these two pages that outlines in detail about the Woodcock Johnson tests:
How is the Woodcock-Johnson Scored?
Is there a difference between the achievement battery in the Woodcock Johnson selection, the third edition, and the achievement battery in the fourth edition?… If so, what is it?
The Woodcock-Johnson IV is the updated and redesigned edition of one of the most widely used batteries of individually administered psycho-educational tests. This latest version places emphasis on the most important and diagnostically useful measures of academic achievement, oral language, and cognitive abilities. The design of three independent and co-normed batteries facilitates the evaluation of strengths and weaknesses within—and among—measures of academic performance, oral language competence, and cognitive abilities.
See if TestingMom.com supports your child’s test by your school district. If you don't see your child's school district listed, check with us! We have practice for other tests as well.

COMMENTS
Examiners using the WJ IV ACH can derive several mathematics clusters of interest in the evaluation of Dyscalculia. These include Mathematics, Broad Mathematics, Math Calculation Skills, and Math Problem Solving. The breakdown of these clusters is listed within the WJ-IV Selective Testing Table (Mather & Wendling, 2014, p. 14).
Woodcock-Johnson ® IV Tests of Achievement ... Mathematics Test 2: Applied Problems Test 13: Number Matrices ... Basic Math Skills Test 10: Math Facts Fluency Math Problem Solving Written Language (Grw) Written Language Test 3: Spelling Test 14: Editing Broad Written Language Test 6: Writing Samples Test 16: Spelling of Sounds
The Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Achievement III (WJ-III) is a norm-referenced, standardized battery of tests utilized to assess school-aged students' academic abilities in the areas of: reading, oral language, math, written language, and academic knowledge. According to the test manual, the entire test can be administered in 60-70 minutes with ...
The Woodcock-Johnson IV (WJ IV) system includes comprehensive, co-normed cognitive, ... Broad Reading Basic Reading Skills Reading Comprehension Reading Fluency Reading Rate Mathematics Broad Mathematics Math Calculation Skills Math Problem Solving Written Language Broad Written Language Basic Writing Skills Written Expression Academic Skills ...
The Riverside Insights Assessment Management System is our new name for the WJ IV Online Scoring and Reporting system. Accessible Accessible for free with a test record purchase, this platform allows examiners to easily enter raw scores, assessment data, and test session observations for any test in the WJ IV suite of assessments— all within ...
The Woodcock Johnson ... Applied Problems Interpretation: Sarah's actual math problem-solving skills were found to be more than two standard deviations below expectations, based on her performance across other areas of achievement. Moreover, the difference between her actual and expected performance on Applied Problems is only observed in 1% ...
Woodcock-Johnson III Tests of Cognitive Abilities: Clusters/Tests Score Form ... Math achievement including problem solving, number facility, automaticity with facts, and reasoning Math Calculation Skills Computational skills and automaticity with math facts
The WJ IV ACH is a revised and expanded version of the Woodcock-Johnson III Tests of Achievement (WJ III ACH; Woodcock ... This cluster includes Test 5: Calculation and Test 10: Math Facts Fluency. The Math Problem Solving cluster yields a measure of mathematical knowledge and reasoning. Tasks on this cluster require examinees to problem ...
Woodcock-Johnson ® IV Preview • Winter, 2014, Vol. 1 The IDEA emphasizes the importance of assessing problem-solving abilities in mathematics, and the WJ IV ACH includes a new Math Problem Solving cluster consisting of math problem-solving skills with story problems and quantitative reasoning with number matrices.
The Woodcock Johnson, Fourth Edition (WJ-IV) is a comprehensive set of tests to assess intellectual ability, academic achievement, and oral language ability. The WJ-IV includes three batteries: (1) the WJ-IV Tests of Cognitive Abilities (WJ-IV Cog; Schrank et al. 2014d ), which assess overall intellectual ability and specific cognitive ...
Woodcock-Johnson ® III Assessment Service Bulletin Number 5 ... Comprehension Comprehension Written Expression Math Problem Solving Applied Problems Capitalization Listening Spelling Writing Samples Punctuation Comprehension Writing Composition Spelling Oral Expression Contextual Language Story Construction Math Reasoning
The trusted classic, completely. reimagined. The Woodcock-Johnson V (WJ V) system is structured to offer customized, efficient, and flexible assessments that examiners need to accurately evaluate learning problems in children and adults. The WJ V is designed to measure intellectual abilities, academic achievement, and oral language abilities.
Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities Sample Question #7. Solve the following calculation problem. 18% of 140 = If you're interested in more Woodcock-Johnson practice questions from TestingMom.com, visit the following: 100 Free Practice Questions. Get Your Questions.
The Woodcock-Johnson IV (WJ IV; Schrank et al. 2014b) is the most recent iteration of the well-known Woodcock-Johnson battery of tests. Unlike previous versions which included a cognitive battery and an achievement battery, the WJ IV consists of three co-normed assessment batteries: the Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Cognitive Abilities (WJ IV ...
The Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Achievement (WJ IV ACH; Schrank, Mather, & McGrew, 2014) is an individually-administered, norm-referenced instrument that is useful for screening, diagnosing, and monitoring progress in reading, writing, and mathematics achievement areas for persons ages 2-90+ years. Basic skills, fluency, and application are ...
The primary focus of the chapter is on the instructional implications that can be derived from the Woodcock-Johnson IV (WJ IV) Tests of Achievement. ... For students with weaknesses in math problem solving, it is important to determine whether language or reading problems are contributing to a mathematics problem, or if the difficulty stems ...
The Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Achievement (WJ IV ACH; Schrank, Mather, & McGrew, 2014a) is an individually administered measure containing tests of reading, mathematics, written. language, and ...
Reviews the test Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Achievement by F. A. Schrank, N. Mather, & K. S. McGrew (2014). The Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Achievement is an individually administered measure containing tests of reading, mathematics, written language, and academic knowledge. Despite relatively minor limitations, the WJ IV ACH is a strong test and meets its stated purpose.
Developed in 1977 by Richard Woodcock and Mary E. Bonner Johnson, the Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities is one of the most popular IQ tests available today. Most recently updated in 2014 (referred to as the WJ IV), the Woodcock-Johnson test is an intelligence test that can be used on participants from the age of 2 all the way to ...
The Woodcock-Johnson IV Tests of Achievement is a very student friendly, low stress, and gentle assessment. All S.M.A.R.T. Testing associates will work with your child to make sure they have a pleasant testing experience. The basic test consists of 10 subtests that measure students' ability levels in reading, mathematics, and written expression.
The Most Trusted, In-Depth Measure of Strengths and Weaknesses. The Woodcock-Johnson IV (WJ IV) is the only assessment that offers three co-normed batteries that can be administered individually or in combination to produce actionable insights for specific referral concerns. Shop the WJ IV Now!
The Woodcock Johnson Tests were revised most recently in 2014 and this latest version is commonly called the WJ IV test. The Woodcock Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities can be given to children from the age of 2 through adulthood. The Woodcock Johnson tests cover a wide range of cognitive skills. Woodcock Johnson Test Overview - TestingMom.com.