Year 6 writing at greater depth (GDS): quick wins, guidance and helpful materials
Note: This website works best with Javascript enabled. With Javascript disabled some parts of the website may not work as expected.

This is not an ideal time for a blog about end of KS2 statutory writing assessment. It’s the week after SATs for one thing. So, this blog is deliberately geared towards the immediate weeks ahead. It’s clear from so many conversations, across so many schools, that quick win advice might go down well right now. For some, addressing gaps caused by pandemic disruptions remained a priority up until recently. It’s hardly surprising that talk has been of expected drops in the numbers achieving GDS standard in writing. Still, there have been a number of requests for support in identifying writing opportunities that might be helpful in the final stretch of the assessment window.
This blog aims to provide some guidance along those lines. It does not reflect our wider views and approaches to developing reader-writers. It’s a deliberately short term and strategic look at primary writing with a particular aim in mind. It’s also an attempt to take some of the weight from our year 6 colleagues’ shoulders in what has been another challenging year. Under 'normal' circumstances, this time of year for the Year 6 teacher, especially the new-to-year-6 teacher, is seared into my own teaching memory. It can feel lonelier than it should, no matter how many times you might be told “You’ve got this”, no matter how healthy an outlook we might have on the place and nature of statutory KS2 assessments.
So, without any apologies, I’ll crack on with some targeted advice and helpful links.
The blog has three sections:
- section 1 looks at examples of pupil’s writing from the STA and highlights a broader view of what might constitute GDS writing. I think this might be most useful in relation to nudging possible borderline cases, and for some quick win writing opportunities in the run up to the close of the assessment window
- section 2 offers links to four evergreen, hugely helpful blogs from our Assessment Team (@HertsAssessment) colleagues, offering practical guidance related to writing moderation and the TAFs
- section 3 gathers links to my earlier blogs on the topic of GDS writing for those that have joined Twitter/become familiar with our blogs more recently. These offer further writing opportunities

1. In search of a benchmark: widening writing exemplifications
1a. core exemplifications.
Just briefly, let’s remember Frankie in all this. Frankie the ‘epitome’ of GDS .
Frankie stands as the one-and-only STA exemplification of writing judged to be representative of GDS for writing. My relationship with Frankie’s writing efforts rivals some of my friendships in terms of how often we get to interact. In recent weeks, we’ve become aware of newer teachers/year 6 returners that are not familiar with this bank of work.
For those not familiar, it’s essential reading under the current system. If you haven’t before, read the work and the associated commentaries, focusing on the most useful, perhaps less florid parts. This will give you a common reference point with year 6 teachers across the country. You can find it here:
Gov.UK: Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at greater depth within the expected standard, Frankie .
Keep in mind this statement from the opening of the exemplification files:
"Exemplification materials illustrate only how 'pupil can' statements in the frameworks might be met. They do not dictate a particular method of teaching, or the evidence expected from the classroom, which will vary from school to school. "
The word 'might' is important here – Frankie is one manifestation of the standard, not a definitive model. This is good news. Otherwise, we’d all best enrol our children in ballet classes at the earliest opportunity.
Reading each piece and considering the most useful parts of the commentaries can help us to keep in mind aspects of writing that we might want to draw attention to when working with the most assured writers. Exemplification banks, without the commentaries, can also offer some useful opportunities for focused reading for our children to see the work of others and consider what they like/dislike and how they would have gone about a similar task. This can add further layers to awareness of the limitless networks of choices that writers have at their disposal.
I used the plural ‘exemplification banks’ deliberately. Turning to one of the EXS exemplifications might help Frankie seem a little less lonely.
Meet Leigh , handily remembered as Near-Leigh GDS Leigh. My former colleague Clare Hodgson, our then moderation lead, wrote about Leigh’s work and how it might offer more helpful hints in an earlier blog for the assessment team.
Take a read of this helpful snippet in which Clare flags some learning relating to bullet 3 of the GDS statements. I’d thoroughly recommend reading the whole of this immensely popular blog .
Obviously, writing such as 'Frankies' clearly meets this statement - but how 'assured and conscious' do our Y6 writers need to be? Here it is worth turning to the 'Leigh' exemplification file as a benchmark as Leigh only narrowly misses the greater depth standard. There is one piece - piece B - where Leigh is able to meet the 'assured and conscious control' statement. The annotations on the remaining pieces show where Leigh has been less consistent and hence why the award remains at expected standard.
Reflect too, as you read the collection, on the purpose and audience for each piece in the collection. Are there enough opportunities for Leigh to write formally? Could more opportunities for formal writing have helped? Does the recount provide any evidence for Greater depth? (No!) Additionally, has Leigh been given adequate time to re-draft some sections of his/her work to consider precision of language, or tidy up punctuation? The implications are that greater depth writers may need longer to craft their writing, as well as more exposure to a range of reading material and a range of tasks that have clearly defined purpose and audience.
Leigh’s writing is offered as one of two banks that exemplify writing demonstrating sufficient evidence of the requirements for a judgement of EXS, but was evaluated as stronger than their fellow EXS-achiever Morgan. Towards the end of each bank there is a tick-grid showing which pieces meet which bullet point in each standard. Here’s Leigh’s tally sheet for the EXS statements. If it was a game of bingo, you’d be getting excited:

It's almost a clean sweep. Bullet two and three relate to narrative features and are demonstrated sufficiently well in two pieces to secure an overall nod of approval for those two statements, as shown by the tick in the final column. Piece A did not offer evidence of the EXS spelling list statement, but given that every other piece does, it’s no wonder that that statement is also judged to be fully met.
Nice work Leigh. So let’s give the GDS bullets a quick once-over.

Back to our imagined game of bingo. It’s far from a full house but Leigh does manage to get a complete line of ticks for Piece B (third column) and a close-to-complete line for piece E (sixth column).
It’s by looking at these pieces that we can begin to broaden our view of the nature of writing that might support a judgement of GDS. Frankie is a very particular, ballet-obsessed writer who may well skew judgements towards a very secure bank of evidence demonstrating the standard. Leigh is a very particular, different kind of writer, offering pieces that might draw closer parallels with the writing produced by your children. In piece B, we have something that we might fairly characterise as 'very recognisably primary school writing'. It’s writing that with the right inputs, we might see from confident Year 4 writers. Here its labelled as procedural; for our purposes I am going to call it Very Fancy Instructions. Take a look, read the piece, read the commentaries, and consider how you might apply some of those pointers to writing from your own curriculum. It’s a style of writing that is likely very familiar to your young writers. Might Piece B offer some inspiration for some instructional writing based on rich, well-known content?
Piece E, a retelling of Jack and the Beanstalk in something like the Star Wars universe, meets all but bullet 3 (as discussed by Clare above). Once again the commentaries are instructive and acknowledge some strengths in the manipulation of grammar, and some indications of why it doesn’t quite hit the spot. Might this be useful in revisiting earlier narrative writing with a view to some targeted editing with that bullet point in mind? Further developing the literary language used in a piece, moving beyond structures more typical of day-to-day speech will likely pay dividends. Giving children the chance to revisit earlier writing with a more mature eye can make all the difference and is a perfectly legitimate writing activity. Writers revisit old work; writers put down a project and pick it up later, with fresh, or older, wiser eyes. Your writers shouldn’t be any different – and that really can be a very quick win. It’s also immensely gratifying for children to appreciate for themselves their own progress and growth as writers in their time with you. Revising earlier pieces will provide an opportunity for this, as well as a further lesson that writing is something to be crafted over time, not just within the context of a single lesson or unit.
1b. Lessons from moderation materials

Besides Leigh’s writing, there are further samples to draw from in the collections used in Lead moderator/moderator standardisation exercises. These can be found in various locations, but our friends at Babcock offer up a beautifully well-organised webpage gathering them all together for very easy access. Thank you Babcock – this has been so useful in terms of its clear layout.
Please do me a quick favour, to help with orientation, if this is new to you:
- follow this link - Devon County Council: KS2 Pupil Writing Collections (previously Babcock)
- scroll down slowly enough to count the number of collections judged at GDS
I make it nine. Nine is better than one. Include Leigh here and we have nine-and-a-bit. Frankie is no longer the singular star in a GDS solar system. We’ve got a galaxy of pointers, all with commentaries and some really nice pieces to broaden the horizons of all three standards.
Let me direct you to 2019 KS2 standardisation exercise 2 and take a look at Pupil C’s work, judged as meeting GDS. This one gave a number of moderators pause for thought. It has many nice touches, but it has its shaky moments. Here’s a top tip: if you are ever unsure whether a bank represents achievement at EXS or GDS, read it out loud. It really helps. Try reading some of Pupil C out loud. You’ll pick up on some less confident stretches, minor lapses, and moments where they seem to become somewhat locked into a groove, unsure of where to go next.
This writing is officially judged to have indicated a higher achievement than Leigh’s but I also think it offers a less intimidating vision of what GDS might look like. Some evidence banks scream GDS almost instantly. They are just plainly, obviously GDS through and through. That's arguably less useful in terms of mapping out the standard, and certainly not so useful in helping us make a call on borderline cases.
From this bank, and again like Leigh, take a look at the pieces that stand out as fairly common primary writing tasks, for example Piece B, the science investigation . Familiarity is helpful. What do they do there that makes that piece contribute to the overall judgement? Might your children do better? For instance, I think the investigation loses sight of its purpose once it gets to the second page, and there are real lapses in clarity. A sharper, scaled down version of the evaluations would have helped me maintain a better understanding of the learning from this investigation. Might this present an opportunity to revisit some similar work from across the year?
Then there’s Piece C, an information text on a ‘newly discovered, genetically engineered hybrid animal’ drawing upon research of two distinct species:

For our purposes here, let’s just note some especially helpful aspects of this piece:
- it legitimately offers scope to make use of more formal language structures (bullet 3) and as such achieves a suitably authoritative and expert register (bullet 2)
- each section is very short – generally around the 50-60 word mark. Writing in chunks or bursts on distinct aspects of the topic should generally be less demanding than a task that builds in additional challenges from text level conventions or requirements. I can picture my children taking a section in turn (perhaps on differently coloured paper to reinforce their distinctness - don't ask me why, it just seems to help keep things in their rightful place) and working in a very focused, deliberate way for each domain
- the range of conjunctive language is relatively limited but is used effectively to link ideas (and when, where, despite, because, before, also)
- perhaps most importantly, the familiarity and friendliness of the form – this type of text is a a staple in non-fiction reading across the primary phase, and will have likely had a place in writing lessons in multiple year groups, across the phases
- finally, keep in mind the availability of books that provide a rich bank of language/language features as helpful incidental models of this kind of writing, for example Norman Messenger’s The Land of Neverbelieve as well as online entries describing the features of real animals just waiting to try a new kind of coupling
In terms of quick wins, you might want to think about those tasks that are most obviously aligned to generic primary writing: Leigh’s procedural/instructions writing based on a taught topic; the science write up; the information text; the narrative sequences/episodes (as opposed to full short stories). They may well prove useful as targeted reading, close to the act of writing. Discuss with children what they like and what sort of friendly critique they might offer the authors. Try and divorce these pieces from their statutory assessment context and any sense of 'teaching to the test' and instead foster a notion that we are simply looking at, and evaluating, some work from peers in a wider community of writers. Take note of features that they find especially effective and begin to consider how this might influence their own writing, whether in fresh composition or in revisiting and revising older work.
2. Guidance related to writing moderation/TAFs
This section provides a series of links to blogs from our colleagues in the Assessment Team ( @HertsAssessment ). Each provides helpful and accessible insights from previous rounds of moderation based on the current TAF.
'Write away!' and other lessons derived from the 2018 KS2 Writing Moderations
Clare Hodgson, my former co-presenter of our Y6 GDS writing course, wrote this extremely helpful blog drawing upon her experiences as a lead moderator, and those of the moderation team she worked with. This blog was written in October of that year, so keep in mind that much of the advice is geared towards the rest of that academic year. That said, it contains an extremely helpful checklist for downloading that should prove helpful at this late stage of the year. Clare offers five, easily-digested ‘lessons’, that will also serve as a very helpful primer for next year – especially for those new to year 6, or new to the Year 6 writing framework.
Declaration of Independence
As the title suggests, this blog looks at the notion of independence and independent writing. If any questions remain in relation to this aspect of the statutory requirements, here’s a good place to head.
With sincere thanks to our colleagues on the Assessment Team.
3. Earlier blogs on GDS
I’d just like to bring this blog to a close by flagging some further pieces that I put together between 2017 and 2021. Between them they offer a range of guidance and suggestions designed to support the achievement of GDS but situated within the context of whole class teaching. Please note that the earliest blogs reflect the Interim Teacher Assessment Frameworks (2016 and 2017). Expectations have changed – and if you didn’t teach under those, well, that’s something to be thankful for. Three of those blogs, the In Search of…series, explicitly address the challenges around expectations for formal and informal writing. Please note, the infamous requirement to shift between levels of formality, like some kind of language-based Hokey Cokey, no longer applies. And that is a very good thing indeed. Nonetheless, the wider points about voice, register and levels of formality should still be useful. Each link has a summary so that you can target your reading according to your needs.
The long and the short of GDS in Year 6 writing
An introduction to the current framework, with a brief exploration of each of the four bullets.
GDS and writing in year 6: keeping things focused now time is short
This blog built on the one directly above it. It looks at the role that reading might play in developing writing and offers some suggestions around particular approaches to instruction that might prove especially helpful when time is running short. As such, it offers further quick win suggestions, in addition to those given in Section 1.
Martin Galway

- HFL Education Board of Directors
- HFL members information
- Corporate social responsibility
- HFL Education Executive
- Education Services team
- Business Services team
- Anti-racism statement
- Gender, ethnicity and disability pay gap
- Latest news
- HFL Education podcast
- Press and media
- Contract services - academies
- Contract services - maintained schools
- Key Stage 1 (KS1) Reading Fluency Project
- Key Stage 2 (KS2) Reading Fluency Project
- Key Stage 3 (KS3) Reading Fluency Project
- Key Stage 4 (KS4) Reading Fluency Project
- Collaboration with the Education Endowment Foundation (EEF)
- KS2 Reading Fluency Project: Education Endowment Foundation (EEF) funded trial
- Early Years advisory and consultancy support for schools
- Early Years expert keynote speakers and trainers
- Early Years PVI services
- Early Years PVI and schools training
- Early Years Quality Standards (EYQS)
- Evaluate the Effectiveness of your Early Years Provision (EEEYP)
- Safeguarding Audit for the Early Years
- Supporting Smooth Transitions
- Foundation subjects and curriculum design
- Secondary school effectiveness
- GCSE English, maths and science and maths 'A'-level remote revision support
- Anti-bullying
- Behaviour and attitudes to learning
- Herts Voices
- HFL Education Wellbeing Quality Mark
- Online safety
- Race equity and anti-racism
- Relationships Education, including RSE, RSHE and PSHE
- SEND support for mainstream schools
- Eastern Partnership UK (SEND)
- Special Schools and Educational Support Centres
- Leadership and management support
- Small Schools' Programme
- The Great School Framework
- Curriculum Modelling and Timetable Service
- Business management services
- Financial services for academies
- Financial services for maintained schools
- Supporting governing boards
- Clerking services
- Governance consultancy services
- Governor training
- Modern Governor
- Governors in Hertfordshire
- GDPR Data Protection Officer and Toolkit Service
- GDPR Health Check
- Leadership recruitment
- Teach in Herts
- HFL Supply Framework
- HR Advisory Service
- HR Business Partner Service
- HR Consultancy
- Mediation Service
- Investigation Service
- Restructure and Organisation Design Service
- TUPE Support Service
- 360-Degree Feedback Service
- Insights Discovery
- HR Training and L&D
- Staff Absence Insurance
- Financial Planning and Support for Staff
- Managed Payroll Service
- Occupational Health Service and Employee Assistance Programme
- Create and implement a digital strategy
- EdTech in schools
- HFL Broadband
- HFL MIS Framework
- Making the most of your MIS
- Technology in Schools Service Desk
- HFL Education Hub
- HFL Education Annual Mathematics Challenge
- All resources
- Early Years
- Mathematics
- Religious education
- Equality and diversity
- HR and recruitment
- School business management
- Technology and MIS
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Education, training and skills
- School curriculum
- Primary curriculum, key stage 2
- Tests and assessments (key stage 2)
Teacher assessment exemplification: KS2 English writing
Examples of pupils' work to support teachers' assessment of English writing at the end of key stage 2.
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working towards the expected standard, Dani
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-852-1, STA/18/8104/e
PDF , 2.13 MB , 30 pages
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at the expected standard
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-850-7, STA/18/8102/e
PDF , 1.97 MB , 44 pages
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at the expected standard, Leigh
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-849-1, STA/18/8101/e
PDF , 3.14 MB , 44 pages
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at greater depth within the expected standard, Frankie
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-851-4, STA/18/8103/e
PDF , 2.01 MB , 36 pages
These exemplification materials provide examples of pupils’ work to support teachers in making judgements against the new statutory teacher assessment frameworks for English writing at the end of key stage 2. They are for use from the 2018/2019 academic year onwards.
They illustrate how the ‘pupil can’ statements in the frameworks might be met. They do not dictate a particular method of teaching, or the evidence expected from the classroom, which will vary from school to school.
If teachers are confident in their judgements they may choose not to refer to these materials. These exemplification materials are provided to help teachers make their judgements where they want additional guidance.
Local authorities may also find the materials useful to support external moderation visits.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .


3. Try some real-world writing
Writing at home can be a great way of practising writing, including using grammar and punctuation to create particular effects. Here are some ideas to encourage regular writing:
- Create a story about a space adventurer with strange planetary systems to explore. Every week or month, your child could write about a new chapter about a different planet. Before long, the chapters will have built into a book they can be really proud of.
- Write an A-to-Z. It could be based on anything your child is interested in – animals, space, dinosaurs, fairies, even their favourite TV programme. A page for each letter of the alphabet gives you 26 short pieces of writing spread over the year that build into one big project.
- Produce a version of a book for a younger child. For example, they could write The Rhino Who Came to Tea or The Very Hungry Angler Fish . Books with a distinctive format such as The Day the Crayons Quit or The Last Polar Bears are perfect for this.
- Write the book of a film or TV programme. If children have watched something they’ve really enjoyed, they could try and tell the same story in writing. Watching the story on screen can give them a useful frame to hang their own writing on.
- While writing using a pen and pencil is useful practice, writing on the computer counts too. You might want to turn the spelling and grammar check off to help children to learn to confidently use their own knowledge. The grammar check can be wrong, too, so this can be confusing for children.
4. Tell stories aloud
Giving your child the opportunity to tell stories orally is a great way to get them used to structuring their ideas and using adventurous language. If they’re not sure where to start, see if they can retell a story that they already know well. Our Traditional tale titles activity sheet has some fun ideas for retelling old stories.
If your child finds it useful to plan out their story first, try our free Story mountain to make a great plot with a beginning, middle, and end. Your child might also enjoy reciting poetry – see if your child can memorise and perform ‘Who has seen the wind?’ with our Perform a poem activity sheet .
Activity: Story mountain

Activity: Perform a poem

Read the poem, talk about what it means, and perform it to an audience.
5. Find story inspiration
You can find fun story ideas anywhere! Why not raid your kitchen cupboards or hunt through the attic to find lost treasures? Anything from an old hat to a telescope will do the trick. What could the object be used for? Who might be looking for it? What secrets could it hold? Suggest different genres such as mystery or science fiction and discuss how the item might be used in this kind of story.
Real-world facts can also be a great source of inspiration. For example, did you know a jumping flea can accelerate faster than a space rocket taking off into orbit? What crazy story can your child make out of this fact? Newspapers and news websites can be great for finding these sorts of ideas.
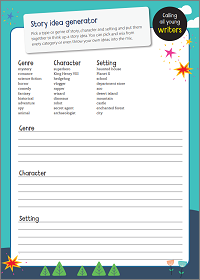
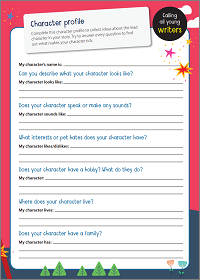
For more storytelling ideas, download our free Story idea generator or our Character profile activity sheet .
Activity: Story idea generator
Activity: Character profile
6. Draw your ideas first
If your child isn’t sure where to start with a story or even a piece of non-fiction, it can sometimes be helpful to sketch out their ideas first. For instance, can they draw a picture of a dastardly villain or a brave hero? How about a scary woodland or an enchanted castle?
Your child might also find it useful to draw maps or diagrams. What are all the different areas of their fantasy landscape called? How is the baddie’s base organised?
Some children might enjoy taking this idea a step further and drawing their own comics. This is great practice – it stretches your child’s creativity, gets them thinking about plot, character, and dialogue, and is a big confidence boost once they’ve finished and have an amazing story to look back on.
What your child will learn
In Year 6 (age 10–11), your child will be aiming to build upon the goals and expectations they were first set in Year 5. They will be expected to:
- Identifying the audience for and purpose of the writing
- Noting and developing initial ideas, drawing on reading and research where necessary.
- Selecting appropriate grammar and vocabulary, understanding how such choices can change and enhance meaning
- In narratives, describing settings, characters and atmosphere and integrating dialogue to convey character and advance the action
- Using a wide range of devices to build cohesion within and across paragraphs
- Using further organisational and presentational devices to structure text and to guide the reader (for example, headings, bullet points , and underlining).
- Assessing the effectiveness of their own and others’ writing
- Proposing changes to vocabulary, grammar and punctuation to enhance effects and clarify meaning
- Ensuring the consistent and correct use of tense throughout a piece of writing
- Ensuring correct subject and verb agreement when using singular and plural , distinguishing between the language of speech and writing and choosing the appropriate register.
- Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors.
Handwriting, spelling, grammar, and punctuation are all important aspects of writing too. You can find out more about them on our dedicated pages:

Handwriting in Year 6 (age 10-11)
Find out more about handwriting in Year 6 at Primary School.
Find out more

Spelling in Year 6 (age 10-11)
Find out more about spelling in Year 6 at Primary School.

Grammar and punctuation in Year 6 (age 10-11)
Find out more about grammar and punctuation in Year 6 at Primary School.
- Age 5–6 (Year 1)
- Age 6–7 (Year 2)
- Age 7–8 (Year 3)
- Age 8–9 (Year 4)
- Age 9–10 (Year 5)
- Age 10–11 (Year 6)
- Year 1 (age 5–6)
- Year 2 (age 6–7)
- Year 3 (age 7–8)
- Year 4 (age 8–9)
- Year 5 (age 9–10)
- Year 6 (age 10–11)
- Grammar glossary
- Grammar books
Having trouble logging in? Some users have reported difficulties following a site update. If this includes you, please email [email protected] so we can get you up and running.
Making great literacy lessons easy. Why join Plazoom?
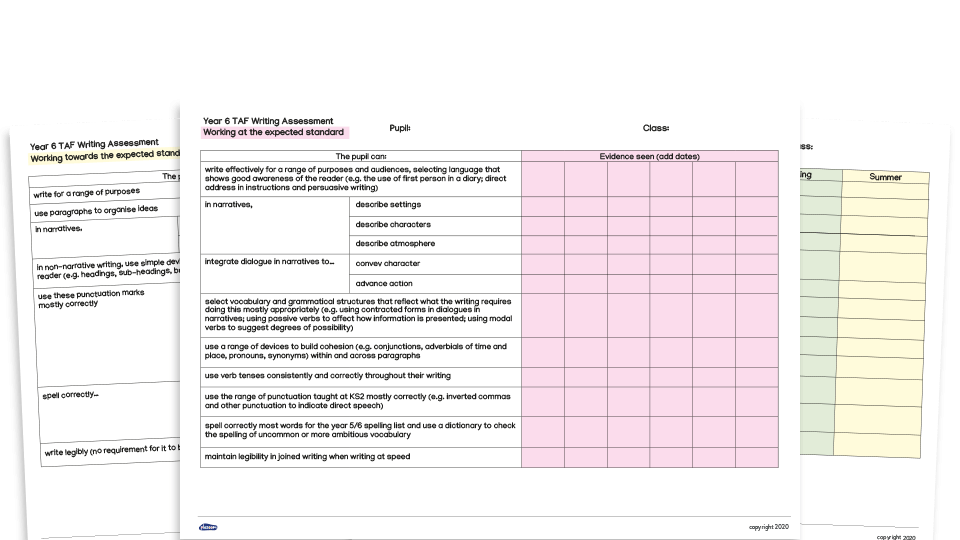
Year 6 Writing Assessment Framework Checklists
Resource Collection Plan, assess, review
Subscribe today and receive…
- Unlimited access to 1000s of resources
- 80+ CPD guides and 60+ training videos
- Access to THREE whole-school curriculums: - Real Writing - Real Comprehension - Real Grammar
- The complete Word Whosh vocabulary building programme
- Free subscription to Teach Reading & Writing magazine, and digital access to all back issues
- Exclusive, member-only resource collections
- New resources added every week
This Year 6 writing assessment pack contains a series of checklists that can be used to assess pupils against the End of KS2 Teacher Assessment Framework (TAF) for writing.
The checklists can be used as a record of where evidence can be found to show whether pupils are working towards, working at or greater depth in writing and could be used to finalise teacher judgements prior to writing moderations within a school or before external moderation. A selection of formats are included that could be used as assessment records by the teacher or could be placed inside pupils’ books to keep a running record of their achievements.
This resource is part of the Plan, assess, review collection. View more from this collection
- Teacher notes
- Y6 TAF writing assessment sheets - two versions
- Y6 TAF writing assessment pupil sheets - two versions
- Y6 'working towards' assessment sheet
- Y6 'working at' assessment sheet
- Y6 'greater depth' assessment sheet
Trending Today
Ks2 comprehension – classic literature…, ks1 and ks2 writing templates for…, year 1 home learning pack (1), year 6 spelling revision – ks2…, look inside.
Click through to see what this resource has to offer
More from this collection
Ks2 sats reading assessment practice pack - set c, year 4 sats reading assessment practice pack - set b, year 6 writing tasks – sats narrative writing taf evidence, ks2 sats reading assessment practice pack – set b, year 6 sats writing evidence: science write-up (circuits) – teacher assessment..., year 4 sats reading assessment practice pack - set c, ks1 teacher assessment framework - writing checklists, year 6 sats writing evidence: formal letter ks2 (complaint) – teacher assessment..., browse by year group, upgrade now.
Click 'Upgrade now' to activate your subscription. An invoice will appear on your accounts page and be sent by email. Once paid, the benefits of your full account will be unlocked within five days.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Free Year 6 Writing Checklist. In Childspeak. Supports Current TAF.
Subject: English
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
31 October 2021
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
samwhatling
Helpful for children when knowing what they need to include
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
teacheroftheyear
A good resource, but why pdf??
Superb resource - clear and user friendly thank you- time saver
thomasdwalker
Uneditable = unusable :(
Sophisticatx
The language is clear and engaging.
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Teachers must use these frameworks for the 2018/19 academic year onwards to make statutory teacher assessment judgements for pupils at the end of key stage 2 in English writing and science. The ...
This will give you a common reference point with year 6 teachers across the country. You can find it here: Gov.UK: Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at greater depth within the expected standard, Frankie. Keep in mind this statement from the opening of the exemplification files:
Examples of pupils' work to support teachers' assessment of English writing at the end of key stage 2. From: Standards and Testing Agency ... They are for use from the 2018/2019 academic year onwards.
You can use this helpful resource to make formative or summative assessments on Year 6 students' writing in line with Y6 requirements. Each checklist presents you with a form of writing moderation, alongside a space for you to tick whether your pupil meets each specific requirement. This is helpful for tracking individual student progress and identifying where pupils need more support. This ...
For the latest catalogue Fax 01772 01772 863158 866153 email: [email protected] Visit our Website at: www.topical-resources.co.uk. Year 6 - Independent Writing Activities. Introduction.
Notes for Y6 teachers regarding end of KS2 writing assessment the pupil can statements in the standard have or passive voice are utilised. For GDS, evidence of pupils punctuation used. GDS writers must To ensure that schools have adequately prepared for their statutory assessments of Year 6
Assess your students' writing abilities with this handy Year 6 Writing Assessment. This teacher-made resource is a handy exam to judge your students' writing skills on an individual level. This resource offers a narrative writing prompt and accompanying writing lines. It also includes a narative marking rubric that will help give you a clear view of your students' strengths and ...
This handy writing checklist is great for monitoring your Year 6 pupils' progress against the writing standards for KS2. Based on the 2016 DfE Exemplification Guidance and 2017 Interim Teacher Assessment Materials, this checklist is here to lend you a helping hand when tracking and recording how well your pupils are doing in their writing. The age-related expectations have been broken down ...
In Year 6 (age 10-11), your child will be aiming to build upon the goals and expectations they were first set in Year 5. They will be expected to: Plan their writing by: Identifying the audience for and purpose of the writing. Noting and developing initial ideas, drawing on reading and research where necessary. Draft and write by:
This Year 6 writing assessment pack contains a series of checklists that can be used to assess pupils against the End of KS2 Teacher Assessment Framework (TAF) for writing. The checklists can be used as a record of where evidence can be found to show whether pupils are working towards, working at or greater depth in writing and could be used to finalise teacher judgements prior to writing ...
Some children will be working towards their current year group expectations, others working within the expected level and some may even be exceeding the level expected. Also included in this document are the Year 6 Teacher Assessment Frameworks (TAFs) used for assessment. You can find more information on the English curriculum at:
Year 6 Writing Curriculum Coverage Checklist! Subject: English. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Assessment and revision. File previews. pdf, 249.2 KB. docx, 23.72 KB. This checklist provides an academic overview of the writing curriculum content to be covered in Year 6. I offered this to teachers, who marked it off as they covered individual ...
Use These Independent Writing Activities for Year 6 PDF Resources. Creative writing is an extremely important activity for children to do. It's an exercise that helps pupils to practise almost any aspect of English that's taught in school. Whether it's spelling and grammar, contractions, tenses or perspectives, independent writing helps ...
This great KS2 Sats Writing Assessment checklist is a fab way to help kids understand how their writing is being assessed, specific things they need to improve on, and the level they're currently working at. It's all in line with KS2 exemplification materials and the national curriculum. The resource outlines the expected standards for the KS2 SATs writing assessment for you to tick off as ...
What is this Writing Moderation Assessment checklist? You can use this helpful writing moderation Y6 checklist to make formative or summative assessments on Year 6 students' writing in line with writing moderation Y6 materials.Inside this resource, you will find a great writing assessment checklist that tracks progress from working towards the national standards, working at the expected ...
These checklists link to the '2017-2018 Teacher Assessment Framework for Key Stage 2 in writing. They are split into: ... Year 6 Writing Checklist Year 6 Writing Checklist Working at the expected standard: The pupil can write effectively for a range of purposes and audiences, selecting language that shows good awareness of the reader (e.g ...
Use These Independent Writing Activities for Year 6 PDF Resources. Creative writing is an extremely important activity for children to do. It's an exercise that helps pupils to practise almost any aspect of English that's taught in school. Whether it's spelling and grammar, contractions, tenses or perspectives, independent writing helps ...
Year 6 Writing Assessment Grid IMPORTANT : Please note that grammatical features should only be ticked when they add to the composition of a piece of writing, e.g. when they are used to add detail for the reader and are not just added because they are on a tick list. Date and genre of work: Working towards the expected standard in Y6
This resource provides an outline of the Year 6 Writing Assessment overview. These checklists are linked to the 2018-2019 National Curriculum teacher exemplification assessments for KS2 in writing. The checklists are split by the following three criteria:working towards the expected standardworking at the expected standardsworking at a greater depth within the expected standardThe text is ...
This resource provides an outline of the Year 6 Writing Assessment overview. These checklists are linked to the 2018-2019 National Curriculum teacher exemplification assessments for KS2 in writing. The checklists are split by the following three criteria:working towards the expected standardworking at the expected standardsworking at a greater depth within the expected standardThe text is ...
Supports Current TAF. Subject: English. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Lesson (complete) Videos. File previews. pdf, 253.87 KB. Give a copy to each child during extended writing so they can tick off objectives that they have included. You might choose to laminate checklists so they can be reused and ticked off with whiteboard pen.