You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

- Workplace Training
- Professional Practice Credentials
- Soft Skills
- Technical Skills
- Leadership Skills
- View all skills
- Articles and News
- White Papers
- Deakin University

POWERING WORKPLACE PERFORMANCE
20 december, 2022, why problem solving skills matter in the workplace.

Whether you’re an artist, a software developer or a CEO of a multinational conglomerate, problem solving skills are a critical asset in any professional setting.
Closely linked to other cognitive competencies including self-management and critical thinking, problem solving is a key workplace skill that empowers employees to manage change, communicate effectively and bring a fresh perspective to old problems. But to harness the benefits of logical and adaptive thinking in the workplace, organisations must take concerted action to foster problem solving skills in their employees.
What do problem solving skills in the workplace look like?
Workplace problem solving has several prominent distinctions when compared to problem solving in other contexts. This includes the formal and goal-oriented structure of the problem, as well as the critical role of teamwork in reaching a solution. An individual who shows competence in problem solving outside the workplace may not necessarily thrive when confronting a workplace issue.
A lack of problem solving skills in the workplace can be detrimental to businesses. Problem solving skills enable employees to evaluate and effectively resolve daily challenges. Every job role within a business will face challenges and unexpected situations. Problem solving skills provide employees with the ability to recognise and analyse problems, identify and evaluate a range of potential solutions and then decide on and implement the most effective solution.
A workforce equipped with problem solving skills will be adaptive and ready to face the challenges of the constantly evolving modern workplace. Its employees will demonstrate an ability to:
- Listen actively
- Think analytically and creatively
- Come up with innovative solutions
- Communicate effectively
- Make decisions confidently based on evidence
- Work together as a team
The importance of problem solving skills in the workplace
Problem solving is a vital skill in the workplace. The ability to think logically and creatively empowers individuals to tackle challenges and seize opportunities in all levels of business. This in turn helps to achieve the following benefits of problem solving skills in the workplace:
Time and resources are used efficiently
All businesses have limited time and resources. This means that when a problem arises, it must be resolved as quickly as possible leveraging available resources. One of the major benefits of problem solving skills in the workplace is that employees can utilise their innovative thinking to prioritise tasks and focus on pressing challenges facing the business. This will result in them providing effective solutions that utilise available resources within the time frame available.
Improved problem solving skills also lead to improved time management as employees learn to make quick and effective decisions. Problem solving skills become even more critical where employees are expected to provide solutions to complex or urgent problems.
The business can better respond to changing client needs
One of the primary purposes of a business is to deliver reliable and excellent service to their clients. Satisfied clients buy more goods or services, create positive advertising by word-of-mouth and generate referrals. But businesses operate in a changing world, which leads to changing client needs that must be anticipated as early as possible.
Employees must be able to take the initiative to respond to those changing needs. A workforce equipped with problem solving skills can quickly reposition itself to better meet shifts in client needs and developments in the environment in which those clients operate.
The business stays ahead of the curve
To stay ahead of the curve, a business must be proactive across all levels. Change in the modern workplace is constant and businesses must come up with fast solutions to problems and be prepared to take advantage of new opportunities as they arise. Employees must be confident to continually challenge the norm and swiftly adapt to changes in the business and the market.
A team that can confidently solve problems will see problems as an opportunity to initiate change and growth, which will help to keep the business ahead of competitors.
The business can anticipate risk
Employees equipped with problem solving skills can handle difficult situations that arise in the workplace. They can expertly deal with challenges that create risk for the business.
A successful business must be able to assess the probability of something going wrong and be able to anticipate the negative consequences if it does. Problem solving skills assist employees to foresee the likely sources of risk to the business and to make considered decisions as to the best way to manage those risks. These skills also play a key role in refining an organisation’s internal talent pipeline.
Strategies for developing problem solving in employees
When developing problem solving in the workplace, it is critical to take a flexible approach that addresses the needs of both current and future employees.
Emphasise problem solving in recruitment and assessment
Whether they are entry level, managers or senior executives, problem solving is a crucial skill for all your employees. Skills that indicate a strong problem solving ability are listening skills, analytical thinking skills, creative thinking skills and communication skills. These skills should be sought out and encouraged in both recruitment and assessment.
One way to identify problem solving skills in interviews is by giving candidates problems that they must solve on the spot within a limited time frame. Interviewers can then assess both the solution that the candidate came up with as well as how they responded to the unexpected challenge.
Self management, not micromanagement
Micromanagement can impede a business’ ability to reach its goals. Instead of raising productivity, micromanagement is more likely to lower the morale of your employees, stifle creativity and damage trust. Employees must have the ability and be given the opportunity to manage their own workflow and productivity without constantly relying on a supervisor.
Problem solving skills will help equip your employees with the ability to self manage their tasks and projects. Through purposeful self management , they will be able to take initiative to solve both the straightforward and complex problems faced in their role.
Give employees goals rather than instructions
Giving employees step-by-step instructions as to how to complete each aspect of their job will not result in an agile and innovative workforce. Rather, it will restrict their ability to seek out new methods and evaluate current contexts.
By providing employees with goals rather than limiting instructions, businesses can increase employee engagement and productivity. This in turn can help empower employees to contribute meaningfully to larger business objectives.
Promote a culture of innovation and collaboration
A successful and resilient business supports its employees with a culture that promotes innovation and collaboration. Problem solving skills will allow your employees to build relationships and excel at daily decision making processes.
Good problem solvers possess good communication skills and can collaborate effectively with their team. They can also think laterally and creatively to find innovative solutions to problems and find opportunities for business development.
Ensure employees have the resources to solve problems
In order to identify issues and discover impactful solutions, employees must have access to relevant tools that provide them with in-depth insights into internal and external contexts. Even the most innovative thinker will struggle to fully capitalise on their problem solving skills without the right resources to support them.
Of course, the nature of these resources will depend on the employee’s role and the context in which they work. Resources may include software, subscriptions, technological equipment and specific communication channels. For all of their differences, these resources will ideally assist the employee to integrate root cause analysis into day-to-day processes.
Provide training
Despite common misconception, problem solving skills are not necessarily innate. Rather, analytical and creative thinking skills can be fostered through purposeful training that provides individuals with a toolkit of problem solving techniques. It also offers an open space for employees to build on existing skill sets through hypothetical scenarios that will test their ability to extempromise, communicate proactively and think creatively.
Start building problem solving skills today
All businesses have the power to create proficient problem solvers within their existing and future workforce. Contact our team today to find out how a bespoke DeakinCo. learning solution could help your employees build on their problem solving skill sets through purposeful, relevant training.
Looks like you’re in India. Would you like to go to your local site?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

What is problem-solving? And why is it important in the workplace?
September 28, 2023 by MindManager Blog
If there’s one thing you can count on as a business professional, it’s that you’ll never run short of new problems to solve. Thankfully, whether it includes handling difficult or unexpected situations in the workplace, or resolving complex organizational challenges, we all have the capacity to develop our business problem-solving skills.
The best way to get better at tackling problems productively is to start at the beginning. After all, the better you understand what problem-solving is – and the significant role it plays in every organization – the easier you’ll find it to improve on problem-solving skills in the workplace.
Let’s dive in!
What is problem-solving?
Problem-solving refers to the act of find solutions to difficult or complex issues.
A good problem-solving definition might be finding solutions to difficult or complex issues . In practice, however, solving problems in the workplace is a little more immersive than that.
In the workplace, problem-solving includes a variety of tools, resources, and techniques to:
- Identify what’s not working.
- Figure out why it’s broken.
- Determine the best course of action to fix it.
Whether you know them as obstacles, glitches, or setbacks, problems are a part of our everyday lives. The good news is that our brains excel at reasoning out intricate scenarios and making calculations in situations we’ve never experienced before. That means every one of us is hard-wired to be an adept problem-solver.
The trick is to learn how to take that innate ability and apply it in a deliberate and practiced way.
However, one thing is certain: successfully resolving business and workplace issues is essential.
Not only does effective problem-solving create value that encourages growth, it goes hand-in-hand with impactful decision making.
What are the benefits of problem-solving in business?
Practically speaking, problem-solving provides a golden opportunity to improve your processes, products, and systems – especially when you work through those challenges with others.
Learning to face difficulties calmly, and deal with them intentionally, can also:
- Ramp up your confidence.
- Increase your resilience.
- Help you develop valuable critical thinking skills.
Applying problem-solving skills in the face of an obstacle that seems insurmountable trains you to shift your perspective and look at potential hurdles in a different way.
It also gets you used to examining multiple options for dealing with a problem, which can help you feel more confident in the direction you take.
Solving problems as a team
Business problem solving as a team offers an even wider range of benefits since active collaboration tends to make good things happen at both the individual and group level.
For example:
- Team-based problem-solving is akin to having a built-in sounding board when you explore new approaches and ideas.
- As each team member’s critical thinking skills evolve, they bring fresh insights to the collective problem-solving process, bearing out the old adage that many heads are better than one.
- Solving problems as a team also reduces the feeling of personal risk and exposure that’s common when one person is tasked with solving a puzzle. When that same problem is shared, the sense of risk gets dispersed, and individual team members are less likely to feel singled out.
Not only is there less chance of arriving at an unreasonable or biased solution when you problem-solve as a group, team members assigned to carry that solution out will feel more invested in its success.
Examples of problem solving skills in the workplace
Improving on your problem-solving skills helps you make the most of your brain’s natural capacity to analyze and reason things out.
There are dozens of problem-solving skills that play out in the average workplace – all of which can contribute to your ability to correct oversights, resolve conflict , and work around unexpected obstructions.
Here are a few common examples of problem-solving skills in the workplace, and tips on how to improve them.
1. Data gathering
Figuring out the cause of a problem hinges on collecting relevant data. Consulting efficiently with colleagues, conducting online research, and brainstorming with your team are all valuable data gathering skills.
2. Active listening
As opposed to listening in a purely supportive or empathetic way, active listening involves concentrating fully on what the other person is saying so you can understand the content, respond accordingly, and remember what was said later.
3. Troubleshooting
The ability to analyze and troubleshoot a situation with the help of any data and human input you’ve gathered is essential for drilling down into the core of a problem, and scrutinizing potential solutions.
4. Brainstorming
Brainstorming has become synonymous with creative thinking, innovative idea generation, and problem-solving. The more productive your brainstorming sessions, the more likely you and your group are to put together a list of quality, workable solutions.
It’s interesting to note that effective decision making is both a contributor to, and a by-product of, effective problem-solving.
For example, honing your analytical abilities and other problem-solving skills will inevitably help you make better decisions. The more efficient your decision-making process becomes, meanwhile, the better you’ll get at uncovering and acting on the most promising solution to any dilemma.
A simple problem-solving scenario
It’s clear that we can all benefit from getting more comfortable with problem-solving in the workplace.
Examples of situations where your problem-solving skills will come in handy aren’t difficult to find, and might include:
- Fixing a technical issue for your customer.
- Improving your student’s test performance.
- Reducing the theft of your in-store merchandise.
- Bumping up your marketing reach.
But, here’s the interesting thing. While it’s evident in each of these situations that there’s a problem to be solved, the exact nature of that problem isn’t so obvious.
In the student’s case, for example, you’d need additional input to help you figure out why they’re performing poorly. Only then would you be able to take steps to find the best-fit solution and achieve the desired learning outcome.
Here’s a simple scenario to help demonstrate that idea:
Bringing new customers onboard in a timely manner is an important part of your client relations strategy. Since hiring Alex a few weeks ago, however, your onboarding process has been taking longer than it should and team members are beginning to complain.
While you can see that the problem in this scenario is the fact that your team isn’t meeting their client onboarding goals, the key is to get clear on exactly what’s causing the hold-up.
You could jump to the conclusion that Alex has time management issues and that it’s time to start looking for a replacement. But, since one of the most common mistakes in business problem-solving is attempting to seize on a solution right away, that might cause you to waste time and resources on a remedy that ultimately proves unnecessary, or that doesn’t provide a viable fix.
Instead, it’s time to put your problem-solving skills to work.
Using data gathering and troubleshooting to pinpoint and clarify the bottleneck in your onboarding process – and active listening to interpret the situation from Alex’s perspective – you soon determine that the real cause of the problem is not what you thought.
In truth, an administrative oversight during the hiring process (yet another problem to be solved!) left Alex unaware of, and without access to, the business process map that’s so vital to efficiently onboarding new customers. Once you provide the necessary resources, it doesn’t take Alex long to get up to speed – and your client onboarding process to revert back to the well-oiled machine that it was.
Even with a team of eager problem-solvers by your side, the truth is that it’s often necessary to have the right problem-solving tools in place to achieve your desired results. That’s where versatile mind mapping software can help.
Not only does MindManager® provide a visual framework that fully supports the problem-solving process, it improves comprehension, inspires more creative solutions, and boosts your ability to make the best possible decisions.
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
Why are problem solving skills in the workplace so important? Subskills, benefits, scenarios
Test your candidates' problem-solving skills with testgorilla.

The importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace can’t be overstated. Every business and job role has its problems. From entry-level hires to senior staffers, every one of your employees will face challenges that don’t can’t be answered by doing a quick Google search – or asking ChatGPT to come up with solutions.
That’s why employers must hire people with excellent problem-solving skills, especially for roles that require dealing with complex business challenges, tight deadlines, and changing variables – for example, when recruiting leaders .
But what are problem-solving skills? What role do they play in the workplace?
And, most importantly, how can you evaluate candidates’ skills before you hire them?
Table of contents
What are problem solving skills, the benefits of problem solving skills: why are problem solving skills important , examples of problems at the workplace – and how problem solving skills can help, how to assess problem solving skills, evaluate problem solving skills and hire candidates who can think for themselves.
To fully understand the importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace, it’s important first to understand the broad skill set that we commonly refer to as “problem solving skills”.
Generally, problem-solving refers to a person’s ability to successfully manage and find solutions for complex and unexpected situations.
Candidates with great problem-solving skills have a combination of analytical and creative thinking. They’re comfortable with making decisions and confident enough to rise to challenges in the workplace.
These candidates possess a combination of analytical, creative, and critical-thinking skills – and a high level of attention to detail . As a result, they will quickly identify problems when they arise and identify the most effective solutions.
They’ll also identify the factors and forces that might have caused the problem and instigate changes to mitigate future challenges.
There are six key problem-solving skills that you should look for when assessing job candidates:

1. Listening skills
Active listeners are generally great problem solvers.
They can listen to those around them to gather the information needed to solve the problem at hand. They also recognize the importance of valuing others’ opinions and experiences to help understand why the problem occurred and define the best course of action to remedy it.
2. Analytical thinking skills
Analytical thinkers can identify the logical reasons why a problem occurred, what the long-term effects of the issue could be, and identify how effective different solutions might be to select the most practical one.
That’s why it’s essential to assess analytical thinking skills during recruitment.
3. Creative thinking skills
Creative thinkers can balance their analytical skills with creative approaches to challenges. Creative thinking skills enable individuals to uncover innovative and progressive solutions to problems.
In this way, they’re able to provide new perspectives and provide imaginative and experimental solutions to all kinds of problems.
4. Communication skills
Problem solvers should also possess great communication skills . The ability to effectively relay complex information thoroughly yet succinctly is a huge benefit for employers working in fast-paced environments.
5. Decision-making skills
Those with problem-solving skills will also possess the ability to make decisions and be confident in them. This is important, because most problem-solving involves making firm decisions to reach a successful outcome.
6. Teamwork
Although problem-solvers need to be independent thinkers, it’s also vital for them to work well as part of a team .
Determining the best solution often requires collaboration, so it’s important that candidates can demonstrate how they can motivate others to come up with the best solutions and work with them to help develop and implement solutions.
Problem-solving skills enable you to find candidates who are cognitively equipped to handle anything their jobs throw at them.
Problem solvers can observe, judge, and act quickly when difficulties arise when they inevitably do. Moreover, they are not afraid of the unknown, which is invaluable to employers who rely on their employees to identify and solve problems.

There are several important benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace. Below, we’ll go through five of the most significant ones that all problem solvers can bring to their roles and workplaces:
1. Ability to organize their time intelligently
Time management skills can often be underlooked as one of the benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace.
However, those with problem-solving abilities also typically possess stellar time-management skills. The ability to manage their time wisely and laser-focus on what’s important to the business will lead to better decision-making and business impact.
2. Ability to prioritize, plan, and execute strategies
Problem solvers have no issue with carefully assessing customer and business needs and deciding how to prioritize, plan, and execute strategies to meet them. They can manage all moving parts and strategize to meet multiple unique demands.
3. Ability to think outside the box
Problem solvers can often identify hidden opportunities in problems. Thinking outside of the box is an important problem-solving skill in the workplace, because it can often lead to better outcomes than the originally expected ones.
4. Ability to work under pressure
This is often one of the most important benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace. Problem solvers often work well under pressure, for example when dealing with short deadlines and changing project requirements.
Depending on your workplace culture, you might prefer someone who can deliver quick solutions or someone who takes their time to identify the next steps. Both are valid and important problem solving qualities.
5. Ability to address risk
Planning is an important problem-solving skill. Problem solvers are not just equipped to deal with the problem at hand but are also able to anticipate problems that will arise in the future based on trends, patterns, experience, and current events.
Let’s now look at some specific examples of problems that could arise at the workplace – at any workplace, really – and how employees’ problem solving skills can help address each issue.
Below, you’ll find five typical scenarios where problem solving skills are essential.
Conflict between team members
Poor team dynamics or lack of a collaborative spirit might result in frequent workplace conflicts – especially within larger teams.
For example, members of cross-functional teams might disagree on the way they should address a particular issue or even on the priority they should give to it.
How problem solving skills can help:
Teamwork is essential when solving conflict – and a cornerstone of effective cross-functional team leadership .
For this, coworkers need to share a common understanding of the team’s goals and also be willing to work towards achieving them, even when they disagree on the specific approaches to each goal. The ability to understand others’ perspectives, analyze information critically, and come up with a few different solutions is key to finding a common ground and making progress on the team’s objectives.
Inefficient processes
Outdated, inefficient processes can reduce productivity and frustrate employees.
Multi-step approval processes are a typical example of this. Having multiple layers of approval for routine decisions can significantly slow down team progress and lead to missed opportunities.
Analytical thinking skills are key in identifying inefficiencies and building better procedures. Employees or team leads can build flowcharts that speed up decision making without having to ask a supervisor’s permission at every step of the process.
Book a free live demo with us and learn how quick and easy it is to create an online skills assessment

Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings and lack of clarity and direction – which, in turn, can be detrimental to team performance.
For example, if you’re a remote-first company, maintaining clear and effective remote communication can be challenging.
The over-reliance on emails and messaging apps might make it feel like teams are communicating effectively and are always connected. However, the lack of non-verbal cues and face-to-face interactions might make it more difficult to build rapport and a positive workplace culture .
Listening skills are essential to solving communication issues – and good listeners are often excellent at solving problems by recognizing, understanding, and acknowledging others’ points of view.
One-on-one meetings enable people to communicate more freely and effectively and solve challenges together, so consider encouraging team members to hop on a call each time they encounter a difficult challenge.
Additionally, you can help employees bond with each other with some remote team building activities to improve team cohesion. Plus, problem solving challenges can be excellent team building exercises.
Technological disruptions
New technologies often disrupt the usual ways of doing things – and sometimes, this can be disruptive for entire teams’ work.
For example, generative AI and automation technologies have revolutionized numerous types of work, including data analysis, marketing, customer service, and even content creation.
Creative thinking and cognitive flexibility are among the top 10 most important skills of the future , according to the World Economic Forum. Both are essential for adopting new technologies successfully – and finding ways to make the most out of each new tool to improve productivity.
Insufficient onboarding resources
Team members may struggle to do their best work if they haven't received proper training or resources.
For example, start-ups that experience rapid growth might hire a few employees at once – or even entire teams.
If they fail to allocate sufficient time and resources to onboarding new hires, this might lead to lost productivity, a lacking sense of belonging, or increased turnover. That’s true not only for junior employees but also for newly hired senior leaders , as the Harvard Business Review points out.
Your leadership team’s analytical and decision-making skills are crucial in enabling them to distribute limited resources in a way that would give their teams the best chances of success.
To build a solid onboarding process , you need leaders who are able to take ownership of it – and who have the right problem-solving skills.
Many organizations use problem-solving interview questions to identify the right candidates for their job openings. However, the most effective way to assess problem-solving skills is with pre-employment skills assessments .
That’s because skills tests provide an objective way to quantify a candidate’s problem-solving skills in a way that isn’t possible during an interview.
How problem solving skills tests work
Tests like TestGorilla’s problem-solving skills test assist organizations in finding candidates who are able to quickly identify the key elements of the problem and work through the problem at speed without making mistakes.
By presenting candidates with a wide range of questions related to typical problem-solving scenarios, hiring teams can rank their candidates based on an intensive assessment of each candidate’s skill level.
The test specifically evaluates whether a candidate can perform problem-solving tasks like:
Creating and adjust schedules
Prioritizing items based on a given set of rules
Interpreting data and applying logic to make decisions
Analyzing textual and numerical information to draw conclusions
As you can see, even the best interviewer would have trouble assessing each of these skill areas while still covering all the other questions that they need to ask.
If you’re convinced of the importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace and want to build a team of employees that can think independently and solve their own problems without constant supervision, assess problem-solving skills during the hiring process.
Problem-solving skills tests like ours are an excellent way to achieve this – especially if you combine them with other skills tests. Check out our extensive test library for other tests you can use in your talent assessment process to hire the best talent.
Sign up for our free plan to start building your first assessment – or schedule a demo with one of our experts to see how to evaluate applicants’ problem solving skills quickly, efficiently, and without bias.
Related posts

TestGorilla vs. Talview

TestGorilla vs. Central Test

TestGorilla vs. Prevue Assessments
Hire the best candidates with TestGorilla
Create pre-employment assessments in minutes to screen candidates, save time, and hire the best talent.

Latest posts

The best advice in pre-employment testing, in your inbox.
No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Hire the best. No bias. No stress.
Our screening tests identify the best candidates and make your hiring decisions faster, easier, and bias-free.
Free resources

This checklist covers key features you should look for when choosing a skills testing platform

This resource will help you develop an onboarding checklist for new hires.

How to assess your candidates' attention to detail.

Learn how to get human resources certified through HRCI or SHRM.

Learn how you can improve the level of talent at your company.

Learn how CapitalT reduced hiring bias with online skills assessments.

Learn how to make the resume process more efficient and more effective.

Improve your hiring strategy with these 7 critical recruitment metrics.

Learn how Sukhi decreased time spent reviewing resumes by 83%!

Hire more efficiently with these hacks that 99% of recruiters aren't using.

Make a business case for diversity and inclusion initiatives with this data.

Culture Development
Workplace problem-solving examples: real scenarios, practical solutions.
- March 11, 2024
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing work environment, problems are inevitable. From conflicts among employees to high levels of stress, workplace problems can significantly impact productivity and overall well-being. However, by developing the art of problem-solving and implementing practical solutions, organizations can effectively tackle these challenges and foster a positive work culture. In this article, we will delve into various workplace problem scenarios and explore strategies for resolution. By understanding common workplace problems and acquiring essential problem-solving skills, individuals and organizations can navigate these challenges with confidence and success.

Understanding Workplace Problems
Before we can effectively solve workplace problems , it is essential to gain a clear understanding of the issues at hand. Identifying common workplace problems is the first step toward finding practical solutions. By recognizing these challenges, organizations can develop targeted strategies and initiatives to address them.
Identifying Common Workplace Problems
One of the most common workplace problems is conflict. Whether it stems from differences in opinions, miscommunication, or personality clashes, conflict can disrupt collaboration and hinder productivity. It is important to note that conflict is a natural part of any workplace, as individuals with different backgrounds and perspectives come together to work towards a common goal. However, when conflict is not managed effectively, it can escalate and create a toxic work environment.
In addition to conflict, workplace stress and burnout pose significant challenges. High workloads, tight deadlines, and a lack of work-life balance can all contribute to employee stress and dissatisfaction. When employees are overwhelmed and exhausted, their performance and overall well-being are compromised. This not only affects the individuals directly, but it also has a ripple effect on the entire organization.
Another common workplace problem is poor communication. Ineffective communication can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and errors. It can also create a sense of confusion and frustration among employees. Clear and open communication is vital for successful collaboration and the smooth functioning of any organization.
The Impact of Workplace Problems on Productivity
Workplace problems can have a detrimental effect on productivity levels. When conflicts are left unresolved, they can create a tense work environment, leading to decreased employee motivation and engagement. The negative energy generated by unresolved conflicts can spread throughout the organization, affecting team dynamics and overall performance.
Similarly, high levels of stress and burnout can result in decreased productivity, as individuals may struggle to focus and perform optimally. When employees are constantly under pressure and overwhelmed, their ability to think creatively and problem-solve diminishes. This can lead to a decline in the quality of work produced and an increase in errors and inefficiencies.
Poor communication also hampers productivity. When information is not effectively shared or understood, it can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and rework. This not only wastes time and resources but also creates frustration and demotivation among employees.
Furthermore, workplace problems can negatively impact employee morale and job satisfaction. When individuals are constantly dealing with conflicts, stress, and poor communication, their overall job satisfaction and engagement suffer. This can result in higher turnover rates, as employees seek a healthier and more supportive work environment.
In conclusion, workplace problems such as conflict, stress, burnout, and poor communication can significantly hinder productivity and employee well-being. Organizations must address these issues promptly and proactively to create a positive and productive work atmosphere. By fostering open communication, providing support for stress management, and promoting conflict resolution strategies, organizations can create a work environment that encourages collaboration, innovation, and employee satisfaction.

The Art of Problem Solving in the Workplace
Now that we have a clear understanding of workplace problems, let’s explore the essential skills necessary for effective problem-solving in the workplace. By developing these skills and adopting a proactive approach, individuals can tackle problems head-on and find practical solutions.
Problem-solving in the workplace is a complex and multifaceted skill that requires a combination of analytical thinking, creativity, and effective communication. It goes beyond simply identifying problems and extends to finding innovative solutions that address the root causes.
Essential Problem-Solving Skills for the Workplace
To effectively solve workplace problems, individuals should possess a range of skills. These include strong analytical and critical thinking abilities, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, the ability to collaborate and work well in a team, and the capacity to adapt to change. By honing these skills, individuals can approach workplace problems with confidence and creativity.
Analytical and critical thinking skills are essential for problem-solving in the workplace. They involve the ability to gather and analyze relevant information, identify patterns and trends, and make logical connections. These skills enable individuals to break down complex problems into manageable components and develop effective strategies to solve them.
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are also crucial for problem-solving in the workplace. These skills enable individuals to clearly articulate their thoughts and ideas, actively listen to others, and collaborate effectively with colleagues. By fostering open and honest communication channels, individuals can better understand the root causes of problems and work towards finding practical solutions.
Collaboration and teamwork are essential for problem-solving in the workplace. By working together, individuals can leverage their diverse skills, knowledge, and perspectives to generate innovative solutions. Collaboration fosters a supportive and inclusive environment where everyone’s ideas are valued, leading to more effective problem-solving outcomes.
The ability to adapt to change is another important skill for problem-solving in the workplace. In today’s fast-paced and dynamic work environment, problems often arise due to changes in technology, processes, or market conditions. Individuals who can embrace change and adapt quickly are better equipped to find solutions that address the evolving needs of the organization.
The Role of Communication in Problem Solving
Communication is a key component of effective problem-solving in the workplace. By fostering open and honest communication channels, individuals can better understand the root causes of problems and work towards finding practical solutions. Active listening, clear and concise articulation of thoughts and ideas, and the ability to empathize are all valuable communication skills that facilitate problem-solving.
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker, paying attention to both verbal and non-verbal cues, and seeking clarification when necessary. By actively listening, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the problem at hand and the perspectives of others involved. This understanding is crucial for developing comprehensive and effective solutions.
Clear and concise articulation of thoughts and ideas is essential for effective problem-solving communication. By expressing oneself clearly, individuals can ensure that their ideas are understood by others. This clarity helps to avoid misunderstandings and promotes effective collaboration.
Empathy is a valuable communication skill that plays a significant role in problem-solving. By putting oneself in the shoes of others and understanding their emotions and perspectives, individuals can build trust and rapport. This empathetic connection fosters a supportive and collaborative environment where everyone feels valued and motivated to contribute to finding solutions.
In conclusion, problem-solving in the workplace requires a combination of essential skills such as analytical thinking, effective communication, collaboration, and adaptability. By honing these skills and fostering open communication channels, individuals can approach workplace problems with confidence and creativity, leading to practical and innovative solutions.
Real Scenarios of Workplace Problems
Now, let’s explore some real scenarios of workplace problems and delve into strategies for resolution. By examining these practical examples, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of how to approach and solve workplace problems.
Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
Imagine a scenario where two team members have conflicting ideas on how to approach a project. The disagreement becomes heated, leading to a tense work environment. To resolve this conflict, it is crucial to encourage open dialogue between the team members. Facilitating a calm and respectful conversation can help uncover underlying concerns and find common ground. Collaboration and compromise are key in reaching a resolution that satisfies all parties involved.
In this particular scenario, let’s dive deeper into the dynamics between the team members. One team member, let’s call her Sarah, strongly believes that a more conservative and traditional approach is necessary for the project’s success. On the other hand, her colleague, John, advocates for a more innovative and out-of-the-box strategy. The clash between their perspectives arises from their different backgrounds and experiences.
As the conflict escalates, it is essential for a neutral party, such as a team leader or a mediator, to step in and facilitate the conversation. This person should create a safe space for both Sarah and John to express their ideas and concerns without fear of judgment or retribution. By actively listening to each other, they can gain a better understanding of the underlying motivations behind their respective approaches.
During the conversation, it may become apparent that Sarah’s conservative approach stems from a fear of taking risks and a desire for stability. On the other hand, John’s innovative mindset is driven by a passion for pushing boundaries and finding creative solutions. Recognizing these underlying motivations can help foster empathy and create a foundation for collaboration.
As the dialogue progresses, Sarah and John can begin to identify areas of overlap and potential compromise. They may realize that while Sarah’s conservative approach provides stability, John’s innovative ideas can inject fresh perspectives into the project. By combining their strengths and finding a middle ground, they can develop a hybrid strategy that incorporates both stability and innovation.
Ultimately, conflict resolution in the workplace requires effective communication, active listening, empathy, and a willingness to find common ground. By addressing conflicts head-on and fostering a collaborative environment, teams can overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
Dealing with Workplace Stress and Burnout
Workplace stress and burnout can be debilitating for individuals and organizations alike. In this scenario, an employee is consistently overwhelmed by their workload and experiencing signs of burnout. To address this issue, organizations should promote a healthy work-life balance and provide resources to manage stress effectively. Encouraging employees to take breaks, providing access to mental health support, and fostering a supportive work culture are all practical solutions to alleviate workplace stress.
In this particular scenario, let’s imagine that the employee facing stress and burnout is named Alex. Alex has been working long hours, often sacrificing personal time and rest to meet tight deadlines and demanding expectations. As a result, Alex is experiencing physical and mental exhaustion, reduced productivity, and a sense of detachment from work.
Recognizing the signs of burnout, Alex’s organization takes proactive measures to address the issue. They understand that employee well-being is crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive workforce. To promote a healthy work-life balance, the organization encourages employees to take regular breaks and prioritize self-care. They emphasize the importance of disconnecting from work during non-working hours and encourage employees to engage in activities that promote relaxation and rejuvenation.
Additionally, the organization provides access to mental health support services, such as counseling or therapy sessions. They recognize that stress and burnout can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental well-being and offer resources to help employees manage their stress effectively. By destigmatizing mental health and providing confidential support, the organization creates an environment where employees feel comfortable seeking help when needed.
Furthermore, the organization fosters a supportive work culture by promoting open communication and empathy. They encourage managers and colleagues to check in with each other regularly, offering support and understanding. Team members are encouraged to collaborate and share the workload, ensuring that no one person is overwhelmed with excessive responsibilities.
By implementing these strategies, Alex’s organization aims to alleviate workplace stress and prevent burnout. They understand that a healthy and balanced workforce is more likely to be engaged, productive, and satisfied. Through a combination of promoting work-life balance, providing mental health support, and fostering a supportive work culture, organizations can effectively address workplace stress and create an environment conducive to employee well-being.
Practical Solutions to Workplace Problems
Now that we have explored real scenarios, let’s discuss practical solutions that organizations can implement to address workplace problems. By adopting proactive strategies and establishing effective policies, organizations can create a positive work environment conducive to problem-solving and productivity.
Implementing Effective Policies for Problem Resolution
Organizations should have clear and well-defined policies in place to address workplace problems. These policies should outline procedures for conflict resolution, channels for reporting problems, and accountability measures. By ensuring that employees are aware of these policies and have easy access to them, organizations can facilitate problem-solving and prevent issues from escalating.
Promoting a Positive Workplace Culture
A positive workplace culture is vital for problem-solving. By fostering an environment of respect, collaboration, and open communication, organizations can create a space where individuals feel empowered to address and solve problems. Encouraging teamwork, recognizing and appreciating employees’ contributions, and promoting a healthy work-life balance are all ways to cultivate a positive workplace culture.
The Role of Leadership in Problem Solving
Leadership plays a crucial role in facilitating effective problem-solving within organizations. Different leadership styles can impact how problems are approached and resolved.
Leadership Styles and Their Impact on Problem-Solving
Leaders who adopt an autocratic leadership style may make decisions independently, potentially leaving their team members feeling excluded and undervalued. On the other hand, leaders who adopt a democratic leadership style involve their team members in the problem-solving process, fostering a sense of ownership and empowerment. By encouraging employee participation, organizations can leverage the diverse perspectives and expertise of their workforce to find innovative solutions to workplace problems.
Encouraging Employee Participation in Problem Solving
To harness the collective problem-solving abilities of an organization, it is crucial to encourage employee participation. Leaders can create opportunities for employees to contribute their ideas and perspectives through brainstorming sessions, team meetings, and collaborative projects. By valuing employee input and involving them in decision-making processes, organizations can foster a culture of inclusivity and drive innovative problem-solving efforts.
In today’s dynamic work environment, workplace problems are unavoidable. However, by understanding common workplace problems, developing essential problem-solving skills, and implementing practical solutions, individuals and organizations can navigate these challenges effectively. By fostering a positive work culture, implementing effective policies, and encouraging employee participation, organizations can create an environment conducive to problem-solving and productivity. With proactive problem-solving strategies in place, organizations can thrive and overcome obstacles, ensuring long-term success and growth.
Related Stories
- June 17, 2024
What is Team Morale and How to Boost It
Navigating through the maze: understanding types of organizational change, transform your business with a top change management consultant, what can we help you find.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Problem-Solving Skills Are Essential for Leaders in Any Industry

- 17 Jan 2023
Any organization offering a product or service is in the business of solving problems.
Whether providing medical care to address health issues or quick convenience to those hungry for dinner, a business’s purpose is to satisfy customer needs .
In addition to solving customers’ problems, you’ll undoubtedly encounter challenges within your organization as it evolves to meet customer needs. You’re likely to experience growing pains in the form of missed targets, unattained goals, and team disagreements.
Yet, the ubiquity of problems doesn’t have to be discouraging; with the right frameworks and tools, you can build the skills to solve consumers' and your organization’s most challenging issues.
Here’s a primer on problem-solving in business, why it’s important, the skills you need, and how to build them.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving is the process of systematically removing barriers that prevent you or others from reaching goals.
Your business removes obstacles in customers’ lives through its products or services, just as you can remove obstacles that keep your team from achieving business goals.
Design Thinking
Design thinking , as described by Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , is a human-centered , solutions-based approach to problem-solving and innovation. Originally created for product design, design thinking’s use case has evolved . It’s now used to solve internal business problems, too.
The design thinking process has four stages :

- Clarify: Clarify a problem through research and feedback from those impacted.
- Ideate: Armed with new insights, generate as many solutions as possible.
- Develop: Combine and cull your ideas into a short list of viable, feasible, and desirable options before building prototypes (if making physical products) and creating a plan of action (if solving an intangible problem).
- Implement: Execute the strongest idea, ensuring clear communication with all stakeholders about its potential value and deliberate reasoning.
Using this framework, you can generate innovative ideas that wouldn’t have surfaced otherwise.
Creative Problem-Solving
Another, less structured approach to challenges is creative problem-solving , which employs a series of exercises to explore open-ended solutions and develop new perspectives. This is especially useful when a problem’s root cause has yet to be defined.
You can use creative problem-solving tools in design thinking’s “ideate” stage, which include:
- Brainstorming: Instruct everyone to develop as many ideas as possible in an allotted time frame without passing judgment.
- Divergent thinking exercises: Rather than arriving at the same conclusion (convergent thinking), instruct everyone to come up with a unique idea for a given prompt (divergent thinking). This type of exercise helps avoid the tendency to agree with others’ ideas without considering alternatives.
- Alternate worlds: Ask your team to consider how various personas would manage the problem. For instance, how would a pilot approach it? What about a young child? What about a seasoned engineer?
It can be tempting to fall back on how problems have been solved before, especially if they worked well. However, if you’re striving for innovation, relying on existing systems can stunt your company’s growth.
Related: How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips
Why Is Problem-Solving Important for Leaders?
While obstacles’ specifics vary between industries, strong problem-solving skills are crucial for leaders in any field.
Whether building a new product or dealing with internal issues, you’re bound to come up against challenges. Having frameworks and tools at your disposal when they arise can turn issues into opportunities.
As a leader, it’s rarely your responsibility to solve a problem single-handedly, so it’s crucial to know how to empower employees to work together to find the best solution.
Your job is to guide them through each step of the framework and set the parameters and prompts within which they can be creative. Then, you can develop a list of ideas together, test the best ones, and implement the chosen solution.
Related: 5 Design Thinking Skills for Business Professionals
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need
1. problem framing.
One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you’re trying to solve.
“Before you begin to generate solutions for your problem, you must always think hard about how you’re going to frame that problem,” Datar says in the course.
For instance, imagine you work for a company that sells children’s sneakers, and sales have plummeted. When framing the problem, consider:
- What is the children’s sneaker market like right now?
- Should we improve the quality of our sneakers?
- Should we assess all children’s footwear?
- Is this a marketing issue for children’s sneakers specifically?
- Is this a bigger issue that impacts how we should market or produce all footwear?
While there’s no one right way to frame a problem, how you do can impact the solutions you generate. It’s imperative to accurately frame problems to align with organizational priorities and ensure your team generates useful ideas for your firm.
To solve a problem, you need to empathize with those impacted by it. Empathy is the ability to understand others’ emotions and experiences. While many believe empathy is a fixed trait, it’s a skill you can strengthen through practice.
When confronted with a problem, consider whom it impacts. Returning to the children’s sneaker example, think of who’s affected:
- Your organization’s employees, because sales are down
- The customers who typically buy your sneakers
- The children who typically wear your sneakers
Empathy is required to get to the problem’s root and consider each group’s perspective. Assuming someone’s perspective often isn’t accurate, so the best way to get that information is by collecting user feedback.
For instance, if you asked customers who typically buy your children’s sneakers why they’ve stopped, they could say, “A new brand of children’s sneakers came onto the market that have soles with more traction. I want my child to be as safe as possible, so I bought those instead.”
When someone shares their feelings and experiences, you have an opportunity to empathize with them. This can yield solutions to their problem that directly address its root and shows you care. In this case, you may design a new line of children’s sneakers with extremely grippy soles for added safety, knowing that’s what your customers care most about.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Breaking Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind in which you examine situations through the lens of past experiences. This locks you into one mindset rather than allowing you to consider alternative possibilities.
For instance, your cognitive fixedness may make you think rubber is the only material for sneaker treads. What else could you use? Is there a grippier alternative you haven’t considered?
Problem-solving is all about overcoming cognitive fixedness. You not only need to foster this skill in yourself but among your team.
4. Creating a Psychologically Safe Environment
As a leader, it’s your job to create an environment conducive to problem-solving. In a psychologically safe environment, all team members feel comfortable bringing ideas to the table, which are likely influenced by their personal opinions and experiences.
If employees are penalized for “bad” ideas or chastised for questioning long-held procedures and systems, innovation has no place to take root.
By employing the design thinking framework and creative problem-solving exercises, you can foster a setting in which your team feels comfortable sharing ideas and new, innovative solutions can grow.

How to Build Problem-Solving Skills
The most obvious answer to how to build your problem-solving skills is perhaps the most intimidating: You must practice.
Again and again, you’ll encounter challenges, use creative problem-solving tools and design thinking frameworks, and assess results to learn what to do differently next time.
While most of your practice will occur within your organization, you can learn in a lower-stakes setting by taking an online course, such as Design Thinking and Innovation . Datar guides you through each tool and framework, presenting real-world business examples to help you envision how you would approach the same types of problems in your organization.
Are you interested in uncovering innovative solutions for your organization’s business problems? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation —one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses —to learn how to leverage proven frameworks and tools to solve challenges. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author

The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills in the Workplace

The ability to solve problems, both simple and complex, is valuable in all workplaces. More than 60% of employers look for evidence of problem-solving ability when evaluating candidates for roles in their organization. Problem-solving in the workplace draws on many different skills, often in collaboration, from analytical thinking and creativity to confident decision-making in critical situations. Modern employees who know how to problem solve and don’t panic when a problem arises can be trusted to work independently and contribute towards an organization’s success.
Some people are natural problem solvers - they see a challenge and they start to suggest solutions without even blinking. For others, problem-solving in the workplace doesn’t come as naturally, but they can develop skills and strategies to help them in the long term.
The role of problem-solving in the workplace
Let’s take a more specific look at problem-solving in the workplace and start to understand just why it’s such a valuable trait.
To begin with, good problem solvers tend to be good decision-makers. When solving a problem, people may be required to make several smaller decisions to reach a complete solution so an ability to quickly make decisions is essential for fast and effective outcomes. If your team lacks this capability, then any challenges thrown their way will cause them to stall and fall behind. They may even make poor decisions if their ability to problem solve isn’t well-rounded and well-informed.
Strong problem-solving skills also contribute to innovation. This is useful for providing our organizations with a competitive edge but also for finding creative solutions to obstacles. Good problem-solving relies upon the ability to find a solution to the issue as it exists here and now, and not rely on using an approach that worked previously. This is why innovation as a facet of problem-solving in the workplace is key.
Problem-solving in the workplace often involves a lot of teamwork. Collaborating on a problem is a great way for a team to bond and learn more about each other’s strengths. In this way, problem-solving contributes towards team unity and purpose. There are even games you can present to your team to have fun and bond while improving their ability to problem solve.
Identifying problem-solving skills in employees
Many people may answer yes when asked if they’re good problem solvers, but we don’t have to rely on self-reporting (although it’s a useful measure). Instead, we can look out for certain behaviors and traits that indicate someone is good at solving problems. Key indicators of problem-solving capability include taking a proactive approach to challenges and asking insightful questions, as this shows both an understanding of a situation and the ability to think further outside it.
Hiring Managers often need to assess an applicant’s problem-solving abilities during the recruitment process. They can do this by asking situational questions about hypothetical problems and scenarios, and assessing how they would draw upon their skills and experience to tackle a problem. Recruiters can also use abstract reasoning tests to get an understanding of someone’s problem-solving abilities, seeing how they combine logic, fluid intelligence, and lateral thinking to find solutions.
HR teams and managers may also want to assess the problem-solving skills of their existing team members. They can do this with performance reviews, discussing examples that have occurred in the workplace and how the individual tackled an issue, and with feedback sessions utilizing 360-degree feedback from fellow employees. Managers can also consciously observe how their employees solve problems on a day-to-day basis, reviewing whether someone attempts to take on challenges independently or turns to others for help.
Developing problem-solving skills in your team
Just because someone struggles to solve problems now doesn’t mean they can’t be coached to take a more confident approach in the future. Training and development programs focused on critical thinking, creative problem-solving, and decision-making strategies provide people with the skills and confidence to take on problems by giving them practice scenarios and examples to work from. This can be done at an individual and team level - it’s useful for a team that works closely together to understand how they can divide tasks and decision-making when it comes to problem-solving, and team bonding games provide a light-hearted way to learn this.
It’s easier to suggest solutions to problems in the workplace when you know it’s ok to experiment and make mistakes. If they want to benefit from problem-solving employees, leadership teams and managers should foster a supportive work environment where employees are encouraged to propose and test new ideas without fear of failure. They can do this through their approach to problem-solving in the workplace, and by being empathetic should errors occur in attempts to tackle problems.
Team leaders should also recognize the value of diverse perspectives when it comes to problem-solving. They shouldn’t always turn to the same people when a new problem presents itself but should encourage input from all parties. Varied viewpoints can lead to more innovative solutions or improvements on pre-existing solutions.
Leveraging Thomas’ expertise
For extra support in understanding your employees’ problem-solving abilities, you can turn to Thomas. Our assessments can help identify individuals with strong problem-solving capabilities or areas where employees need development. We can also provide tailored development solutions based on your assessment results with workshops designed to enhance problem-solving skills at a leadership and employee level.
The impact of strong problem-solving skills on business success
Businesses made up of individuals with strong problem-solving skills set themselves up for success. When we recruit problem solvers and develop the problem-solving skills of our existing employees, we contribute to organizational growth by fostering innovation and improving how our teams collaborate.
There’s a very real return on investment to be made when companies spend time and effort on developing these skills. They create more agile, innovative individuals who give their organizations a competitive advantage versus organizations who overlook this crucial area.
Problem-solving in the workplace shouldn't be overlooked. Speak to an expert at Thomas today and see how we can enhance the problem-solving capabilities of your teams and set them up for success.
Please select which Thomas product you would like to sign in to

Total with VAT: {{CartWithDetails.cartMaster.total_after_vat}} {{currency}}
Your cart is empty.
Problem-Solving Skills in the Workplace: Types, Benefits, And How To Improve
Written By : Bakkah
21 Jun 2024
Table of Content
What are Problem-Solving Skills?
Benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace, how to improve problem-solving skills in the workplace, how to assess problem-solving skills, types of problem-solving skills in the workplace with examples, popular articles.
PRINCE2 Methodology - 2024 Full Guide About Advantages and Disadvantages
Prosci Methodology - Change Management Methodology
Application of PMO in government entities in Saudi Arabia
In the modern workplace, problem-solving skills are indispensable for both individual and organizational success. These skills enable employees to navigate challenges, innovate solutions, and make informed decisions that drive progress.
Developing robust problem-solving abilities can enhance productivity, foster a positive work environment, and contribute significantly to achieving business objectives.
Here is an in-depth exploration of problem-solving skills, their benefits, types, and how to improve and assess them in the workplace.
Problem-solving skills are the abilities and techniques individuals use to identify, analyze, and resolve challenges or obstacles efficiently and effectively. These skills encompass a range of cognitive processes including critical thinking, creativity, analytical thinking, and decision-making.
They involve understanding the root cause of a problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating these solutions, and implementing the best one while continuously monitoring and adjusting as necessary.
These skills are essential across various aspects of life, from personal issues to professional tasks. In a workplace setting, strong problem-solving skills can enhance productivity, foster innovation, and improve decision-making processes.
They enable individuals to handle unexpected situations, work collaboratively with others, and contribute to the achievement of organizational goals.
Overall, problem-solving skills are fundamental for navigating complex situations and achieving successful outcomes in diverse contexts.
Problem-solving skills in the workplace offer numerous benefits, including enhanced productivity, increased innovation, improved decision-making, better collaboration, and greater adaptability.
These skills enable employees to address challenges efficiently, contribute to organizational goals, and maintain a positive work environment.
Here is a detailed discussion of the benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace:
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Problem-solving skills enable employees to tackle challenges and obstacles efficiently, leading to faster and more effective project completion.
This boost in productivity helps maintain smooth operations and reduces delays, ensuring that tasks are completed on time and to a high standard.
By anticipating and addressing potential issues proactively, employees can minimize disruptions and keep workflows streamlined.
2. Enhanced Employee Confidence and Independence
Employees with strong problem-solving skills are more confident and self-reliant. They can handle unexpected situations with ease, reducing the need for constant supervision.
This empowerment fosters a sense of accountability and ownership over their work, leading to increased job satisfaction and morale.
3. Improved Collaboration and Teamwork
Problem-solving often involves collaboration and the sharing of diverse perspectives. When employees work together to brainstorm and implement solutions, it strengthens teamwork and encourages a cooperative work environment.
This collective approach not only enhances problem-solving outcomes but also builds a more cohesive and supportive team dynamic.
4. Fostering Innovation and Creativity
Strong problem-solving skills drive innovative thinking and creativity within the workplace. Employees are more likely to think outside the box and develop unique solutions to complex issues.
This culture of innovation helps the organization stay competitive and adaptable in a rapidly changing market, promoting continuous improvement and long-term success.
5. Better Risk Management
Employees with strong problem-solving skills are adept at assessing risks and identifying potential issues before they become significant problems.
This proactive approach to risk management helps the organization mitigate potential threats and reduce the likelihood of costly disruptions. Effective problem solvers can also develop contingency plans to address unforeseen events, enhancing the organization's resilience.
6. Enhanced Decision-Making
Problem-solving skills are closely tied to effective decision-making. Employees who excel in problem-solving are better at evaluating options, weighing pros and cons, and making informed decisions that benefit the organization.
That leads to more strategic and thoughtful decision-making processes, ensuring the best possible outcomes are achieved.
Overall, the development and application of problem-solving skills in the workplace yield significant advantages.
From enhancing productivity and fostering a positive work environment to driving innovation and ensuring organizational resilience, these skills are indispensable for achieving sustained success in any professional setting.
Improving problem-solving skills in the workplace is essential for enhancing productivity, fostering innovation, and ensuring organizational success.
By focusing on key strategies and practices, employees can develop and refine their problem-solving abilities, leading to more effective and efficient resolution of challenges.
Here are several strategies to help improve problem-solving skills in the workplace:
1. Encourage Continuous Learning
Promote a culture of continuous learning by offering regular training and professional development opportunities focused on problem-solving techniques and critical thinking skills.
Encourage employees to attend workshops, seminars, and courses that enhance their ability to analyze and address problems effectively.
2. Foster a Collaborative Environment
Create an environment that encourages collaboration and open communication. Encourage team members to share their perspectives and brainstorm solutions together.
That leads to more diverse and innovative solutions, strengthens teamwork, and builds a supportive work culture.
3. Practice Problem-Solving Scenarios
Regularly engage employees in problem-solving scenarios and exercises. That could include case studies, role-playing, or simulated challenges relevant to their work.
These activities help employees practice their skills in a controlled setting, making them more adept at handling real-world problems.
4. Utilize Tools and Techniques
Introduce and train employees on various problem-solving tools and techniques, such as the 5 Whys, SWOT analysis, and mind mapping. Familiarity with these methods can help employees systematically approach and dissect problems, leading to more effective solutions.
5. Promote Critical Thinking
Encourage employees to question assumptions, analyze data, and consider multiple perspectives before arriving at a solution. Fostering a mindset of critical thinking helps employees evaluate problems more thoroughly and develop well-rounded, effective solutions.
6. Provide Constructive Feedback
Offer regular, constructive feedback on employees' problem-solving efforts. Highlight their strengths and suggest areas for improvement. Constructive feedback helps employees refine their skills and apply lessons learned to future challenges.
7. Encourage a Growth Mindset
Cultivate a growth mindset within the organization, where challenges are viewed as opportunities for learning and development. Encourage employees to embrace mistakes as part of the learning process and to persist in finding solutions despite setbacks.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their employees' problem-solving skills. That not only improves individual performance but also contributes to the overall success and resilience of the organization.
Assessing problem-solving skills in the workplace is crucial for identifying employees' strengths and areas for improvement. Effective assessment methods provide valuable insights into an individual's ability to tackle challenges and contribute to organizational success.
By employing various evaluation techniques, employers can ensure they have a capable and adept workforce.
Here is a breakdown of how to assess problem-solving skills:
1. Use Real-World Scenarios
Evaluate problem-solving skills by presenting employees with real-world scenarios relevant to their roles. This can be done through case studies, simulations, or practical exercises.
Observing how employees approach and resolve these scenarios provides a clear indication of their problem-solving abilities.
2. Conduct Behavioral Interviews
Incorporate behavioral interview questions that focus on past experiences with problem-solving. Ask candidates to describe specific instances where they successfully resolved a difficult situation.
That helps assess their thought processes, strategies, and effectiveness in addressing problems.
3. Implement Performance Reviews
Include problem-solving as a key criterion in regular performance reviews. Assess employees' ability to identify issues, develop solutions, and implement them effectively.
Providing specific examples and feedback during reviews helps employees understand their performance and areas for growth.
4. Use Assessment Tests
Administer standardized problem-solving assessment tests to evaluate employees' skills objectively. These tests can measure various aspects of problem-solving, including critical thinking, analytical abilities, and decision-making.
Results from these tests can be used to identify strengths and areas needing improvement.
5. Observe On-the-Job Performance
Monitor employees' problem-solving abilities in their day-to-day tasks. Pay attention to how they handle unexpected challenges, their approach to finding solutions, and their effectiveness in resolving issues.
Direct observation provides real-time insights into their practical problem-solving skills.
6. Gather Peer Feedback
Collect feedback from colleagues and team members regarding an employee's problem-solving capabilities.
Peer feedback can offer valuable perspectives on how well an individual collaborates, communicates, and contributes to solving team problems. This holistic view helps in assessing their overall effectiveness.
7. Conduct Self-Assessments
Encourage employees to conduct self-assessments of their problem-solving skills.
Provide them with reflective questions or self-evaluation forms to assess their strengths and identify areas for improvement. Self-assessments promote self-awareness and personal development.
8. Utilize 360-Degree Feedback
Implement a 360-degree feedback process, where employees receive feedback from supervisors, peers, subordinates, and other stakeholders. This comprehensive approach provides a well-rounded view of an employee's problem-solving abilities and areas for development.
By utilizing these assessment methods, organizations can effectively evaluate and enhance their employees' problem-solving skills. That helps identify talent and areas for growth and contributes to building a more capable and resilient workforce.
Problem-solving skills are essential for navigating challenges and driving success in the workplace. They encompass a range of abilities that enable employees to identify issues, develop solutions, and implement effective strategies.
Here are several types of problem-solving skills critical in the workplace with examples:
1. Analytical Thinking
Analytical skills involve the ability to collect and analyze information, see patterns, and derive meaningful insights. Employees with strong analytical skills can break down complex problems into manageable parts, making it easier to understand and address the root cause.
Analytical thinking helps in interpreting data accurately and making data-driven decisions. It also involves identifying relationships between different variables and forecasting potential outcomes based on existing data.
Example: Using data analysis software to identify trends in sales performance and determine the underlying factors affecting revenue.
By examining sales data over time, an employee might discover that certain product features are more popular during specific seasons, leading to strategic adjustments in inventory and marketing efforts.
2. Creativity
Creativity in problem-solving is about thinking outside the box and coming up with innovative solutions. It involves brainstorming new ideas and approaches that are not immediately obvious.
Creative problem solvers can find unique and effective ways to address challenges, often leading to groundbreaking solutions that can provide a competitive edge.
Creativity also involves the ability to see connections between seemingly unrelated concepts and to envision multiple possibilities.
Example: Developing a new marketing campaign that uses unconventional channels to reach a target audience. For instance, leveraging viral social media trends or creating interactive online experiences that engage users in novel ways.
3. Research Skills
Research skills involve the ability to gather relevant information from various sources, evaluate its credibility, and apply it to solve problems. Good research skills help employees find evidence-based solutions and stay informed about best practices and industry trends.
Effective researchers are thorough and systematic in their approach, ensuring they gather comprehensive and accurate data.
Example: Conducting market research to understand customer preferences and inform product development strategies. That might involve surveys, focus groups, and analyzing competitor products to identify gaps and opportunities in the market.)
4. Decision-Making Skills
Decision-making skills are crucial for choosing the best course of action among several alternatives. Effective decision-makers weigh the pros and cons, consider the implications of each option, and select the most appropriate solution based on the available information.
Good decision-making also involves being decisive and confident while remaining open to new information that might affect the choice.
Example: Choosing the best software vendor after comparing features, costs, and customer reviews.
This process includes conducting thorough research, consulting with team members who will use the software, and considering the long-term support and scalability offered by the vendor.
5. Communication Skills
Effective communication is essential for problem-solving as it involves clearly explaining the problem, proposing solutions, and collaborating with others to implement them.
Good communicators can articulate their ideas, listen to feedback, and ensure everyone is on the same page. Communication skills also encompass the ability to present complex information clearly and concisely, both verbally and in writing.
Example: Leading a team meeting to discuss a project issue and collaboratively developing a plan to address it. That includes facilitating open discussions, ensuring all voices are heard, and summarizing the agreed-upon action steps.
6. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves evaluating information and arguments, identifying logical connections, and making reasoned decisions. It requires questioning assumptions, considering multiple perspectives, and assessing the validity of different solutions.
Critical thinkers can dissect complex issues, understand the underlying principles, and develop well-supported conclusions. This skill is crucial for avoiding biases and making sound judgments based on objective analysis.
Example: Assessing the potential impact of a new policy by considering various stakeholders’ viewpoints and potential outcomes.
That might involve analyzing how the policy affects different departments, forecasting long-term implications, and ensuring that the decision aligns with the company's strategic goals.
7. Teamwork Skills
Teamwork skills are vital for solving problems that require input and collaboration from multiple people. Employees who excel in teamwork can work effectively with others, leveraging diverse skills and perspectives to find comprehensive solutions.
Successful teamwork involves clear communication, mutual respect, and the ability to manage conflicts constructively.
Example: Collaborating with a cross-functional team to develop a new product that meets technical and customer requirements.
That might involve engineers, marketers, and customer service representatives working together to ensure the product is innovative and user-friendly.
8. Adaptability
Adaptability is the ability to remain flexible and adjust to new information or changing circumstances. Adaptable problem solvers can pivot their strategies when faced with unexpected challenges and continue to find effective solutions.
This skill is increasingly important in today's fast-paced work environments, where change is constant.
Example: Quickly adjusting a project plan in response to a sudden change in client requirements or market conditions. This might involve reallocating resources, updating timelines, and modifying deliverables to meet the new specifications.
9. Time Management
Time management skills are crucial for solving problems efficiently and meeting deadlines. Effective time managers can prioritize tasks, allocate resources appropriately, and avoid procrastination, ensuring that solutions are implemented promptly on time.
Good time management also involves setting realistic goals, breaking tasks into manageable steps, and using tools to track progress.
Example: Creating a detailed project timeline to ensure all steps of a problem-solving process are completed on schedule. That includes setting milestones, deadlines, and contingency plans to address potential delays.
10. Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence (EI) involves the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others. High EI helps in problem-solving by facilitating better teamwork, communication, and conflict resolution.
Employees with strong EI can navigate stressful situations calmly and empathize with others' perspectives, leading to more harmonious and effective collaboration.
Example: Managing a team conflict by mediating discussions and helping team members understand each other's viewpoints. That might involve active listening, validating emotions, and finding a compromise that satisfies all parties involved.
These examples demonstrate how various problem-solving skills can be applied in different workplace scenarios, leading to effective and innovative solutions.
By developing and honing these problem-solving skills, employees can navigate workplace challenges more effectively, contribute to the success of their teams, and drive organizational growth.
Investing in these skills not only enhances individual performance but also strengthens the overall resilience and adaptability of the organization.
Master Problem-Solving Skills in the Workplace with Bakkah Courses!
Unlock your potential and enhance your problem-solving skills in the workplace with Bakkah’s comprehensive range of professional courses.
Our Project Management Professional (PMP) Course and Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) Course introduce foundational and advanced problem-solving methodologies for effective project management.
For those managing multiple projects, the Program Management Professional (PgMP) Certification and PRINCE2 Agile Certification blend Agile flexibility with PRINCE2 structure, providing dynamic problem-solving techniques.
For risk management, the Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Course and Management of Risk (MoR) Certification focus on identifying and mitigating risks effectively.
Additionally, the Lean Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt Courses delve into process improvement and sophisticated problem-solving skills using Lean Six Sigma methodologies.
Whether you’re managing projects, handling risks, or improving operational efficiency, our courses are designed to equip you with the skills needed to tackle challenges effectively and drive success.
Invest in your future today and become a master problem solver in the workplace. Enroll now and take the first step towards professional excellence with Bakkah!
Developing robust problem-solving skills is vital for both individual and organizational success in the workplace. These skills encompass a wide range of cognitive abilities, from analytical thinking and creativity to communication and emotional intelligence.
By honing these skills, employees can tackle challenges more effectively, contribute to a positive and productive work environment, and drive innovation and growth within their organizations.
Related Courses
Our learning programs are delivered through a tested and professionally designed methodology.
Live Online

3,191.25 SAR

3,832.95 SAR
Exam is included

Your experience on this site will be improved by allowing cookies.
Added to Cart
{{ convertjson(lastcartitem.course.title) }}, features with this course, total with vat, {{ parsefloat(totalfeatures(lastcartitem)) }} {{currency}}.


Growth Tactics

How to Improve Problem Solving Skills in the Workplace
Jump To Section
In a career spanning over two decades in leadership and management, I’ve found myself at the epicenter of problem solving in the workplace more times than I can count. The nature of managing teams and leading projects means that each day comes with its own set of challenges, each presenting a new “fire” to extinguish.
This relentless demand for solutions has served not as a setback, but as a rigorous training ground for honing my problem solving skills. I’ve come to realize that the capability to effectively solve problems is not just an asset but a necessity in the fast-paced and ever-evolving workplace. The journey of refining these skills is continuous, demanding both dedication and a willingness to adapt.
This article aims to share insights and strategies on how to enhance problem solving skills in the workplace, drawing from lessons learned through firsthand experiences. Here, we’ll explore why cultivating strong problem solving abilities is crucial for professional growth and organizational success, and how you can systematically improve these skills to navigate the complex challenges of today’s work environment. Let’s dive in, and uncover the means to turn problems into opportunities for innovation and advancement.
Understanding the Importance of Problem Solving
In the modern workplace, the ability to tackle difficulties effectively is not a luxury, it is an absolute necessity. Problems can arise from a variety of sources: internal challenges, market competition, technological advancements, or unforeseen global events. Employees and leaders alike who excel in problem solving become invaluable assets to their organizations. But what makes problem-solving skills so crucial? Let’s unpack this.
Value in the Workplace
First and foremost, problem solving is directly linked to productivity and efficiency. A workforce adept in identifying issues quickly and proposing viable solutions can save a company from costly downtime and resource wastage. It is the oil that keeps the organizational machinery running smoothly.
Beyond the immediacy of resolving specific issues, problem-solving skills foster a proactive mindset. Rather than waiting for directives, employees who are skilled problem solvers take ownership and initiative. They are the ones who anticipate potential roadblocks and ward them off before they impact workflow.
Innovation and Adaptation
The constant push to find better, faster, and more cost-effective methods gives rise to innovation. When employees approach problems with a creative mindset, they often discover new ways of doing things that significantly improve operations. This adaptive quality ensures that a company is not just reacting to change but is staying ahead of it, prepared to pivot and embrace new opportunities.
Team Dynamics and Morale
A culture that values and develops problem-solving skills is also conducive to stronger team collaboration. When everyone brings their problem-solving ‘A-game’, it creates a synergistic effect where the sum is greater than its parts. Moreover, teams that solve problems together experience heightened morale and job satisfaction. Overcoming hurdles collectively strengthens workplace harmony and builds a sense of camaraderie and trust.
Risk Management
The strategic side of problem solving involves risk management—identifying potential issues before they become actual ones. Effective problem solvers are able to extract lessons from every challenge and apply them to future scenarios. This makes the business more resilient and able to handle adverse situations with more agility.
Measure of Leadership
Finally, for anyone in or aspiring to leadership, being a competent problem solver is a defining characteristic. Leaders are often judged by their capacity to navigate through crises and lead their teams to success. It’s not simply about extinguishing fires; it’s about doing so in a way that instills confidence and maintains or even boosts momentum.
Essential Problem-Solving Skills to Develop
To flourish in today’s complex business environment, mastering a set of core problem-solving skills is imperative. These skills serve as the toolkit for dismantling difficulties and turning them into opportunities. Here are some crucial abilities that professionals should foster:
Analytical Skills
The bedrock of problem solving is the ability to break down complex information into manageable parts. Analytical thinkers can dissect a problem and understand its components, which makes finding a solution more straightforward. Developing sharp analytical skills allows you to evaluate data methodically, recognize patterns, and isolate the variables that influence outcomes.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking goes hand-in-hand with analytical capabilities. It involves questioning assumptions, evaluating arguments, and considering the validity and reliability of data before making decisions. By honing critical thinking, you reinforce your judgment and decision-making processes, ensuring that your solutions are well-founded and not just spur-of-the-moment guesses.
Creative Thinking
While analytical and critical skills are important, sometimes the best solutions come from outside the proverbial box. Creative thinking unlocks innovative solutions to problems that may not be apparent using traditional methods. Cultivating creativity isn’t just for artistic pursuits; it’s about looking at challenges from fresh angles and being open to unconventional ideas that can lead to breakthroughs.
Emotional Intelligence
Problem solving is not solely an intellectual exercise; it often involves managing emotions and interpersonal relations. Emotional intelligence (EQ) empowers you to understand and manage your own emotions and those of others. High EQ leads to better communication and collaboration, which is essential when you’re working through problems in a team setting.
Decision-Making Skills
All the analysis, critical thought, and creativity ultimately aim at making decisions. Timely and decisive action is often required to resolve issues before they balloon. Training yourself to weigh the pros and cons and then confidently make choices is an essential component of effective problem solving.
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is about seeing the big picture . Those skilled in strategy are able to formulate step-by-step plans that lead to solutions, considering both short-term results and long-term implications. This forward-thinking approach is invaluable for moving from problem identification to successful execution of solutions.
Adaptability and Flexibility
In a world where change is the only constant, being adaptable and flexible is key. Problems often don’t follow a script, and you need to be able to pivot and adjust your plans as new information or variables come into play.
Persistence
Finally, an often-overlooked aspect of problem solving is the persistence to follow through. Some problems are more complex and stubborn than others, requiring sustained effort and the resilience to face setbacks.
By intentionally cultivating these skills, you will become better equipped to face the multitude of challenges that the workplace can throw at you. Strengthening these capabilities is not an overnight affair but rather a continuous journey of personal and professional development to become a good problem solver. As you advance these essential problem-solving skills, you’ll find yourself becoming a go-to source for solutions in your workplace, deepening your value and effectiveness in your role.
Strategies to Enhance Problem Solving Skills
Developing effective problem-solving skills is a dynamic and continuous process. To better navigate the complexities of the workplace and personal challenges, it’s beneficial to adopt certain strategies that can enhance these skills over time. Below are some effective strategies to consider incorporating into your personal development plan :
Continuous Learning
Keeping abreast of industry trends, technological advancements, and professional knowledge is essential. Engaging in continuous learning through courses, workshops, and reading can expose you to new ideas and methodologies that enhance your problem-solving skills.
Practice Critical Analysis
Like any other skill, problem-solving abilities improve with practice. Try to tackle diverse problems, even if they’re hypothetical. Games and puzzles that require strategic thinking can also sharpen your problem-solving skills.
Reflect on Past Experiences
Maintaining a journal where you document thechallenges you’ve faced, the approaches you took, and the outcomes can help you analyze your growth. This reflection can provide insights into how your approaches can be improved or adapted for future issues.
Foster Creativity
Regular brainstorming sessions, either solo or in a group, can help you think outside the box and generate creative solutions. Don’t judge ideas as they come; the goal is to open up as many possibilities as you can, and then evaluate them later for viability.
Seek Diverse Perspectives
Different perspectives can lead to unique solutions. By networking with others and collaborating, you can experience different problem-solving styles and learn new techniques. This can be particularly useful in complex scenarios where interdisciplinary approaches might be beneficial.
Develop Emotional Intelligence
Since problem-solving often involves other people, understanding emotional dynamics can lead to better outcomes. Work on emotional intelligence by practicing empathy and self-awareness. Knowing how your emotions influence your decisions can help you manage them more effectively.
Implement Structured Problem-Solving Methods
Familiarize yourself with structured problem-solving techniques such as SWOT Analysis, Root Cause Analysis, or the Five Whys. These frameworks can provide a systematic approach to dissecting and addressing problems more effectively.
Embrace Mistakes as Learning Opportunities
Every problem-solving process offers a lesson. Embrace mistakes and analyze them to understand what went wrong and why. This analysis can turn failures into valuable learning opportunities, preventing similar mistakes in the future.
Prioritize Problems
Not all problems need to be solved immediately, and not all require the same amount of resources. Learning to prioritize problems based on their impact and urgency can enhance your effectiveness.
By incorporating these strategies into your regular practices, you can sharpen your problem-solving skills and become more adept at navigating the challenges of both your professional and personal life. Enhancing these skills not only makes you a more competent individual but also a valuable team player and leader in any organizational setting.
Training and Resources for Skill Enhancement
Developing and enhancing problem-solving skills is a journey that involves continual learning and growth. Thankfully, in today’s digital world, there are abundant resources and training opportunities available that cater to varying levels of expertise and professional fields. Utilizing these resources can significantly boost your ability to tackle complex problems effectively. Here’s a guide to some of the most valuable types and sources of training and resources available:
Online Courses and Workshops
Platforms like Coursera, edX, and LinkedIn Learning offer courses taught by industry professionals and university professors. These platforms cover a wide range of topics from analytical thinking, critical reasoning, and creative problem-solving, to specialized courses tailored to specific industries. Interactive workshops can also simulate real-life problem-solving scenarios, offering hands-on experience.
Books and eBooks
A wealth of knowledge exists in books focused on enhancing problem-solving skills. Titles such as “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman, and “The Art of Problem Solving” by Russell L. Ackoff provide insights into human cognition and practical strategies for effective problem-solving. eBooks available on platforms like Amazon Kindle allow easy access to the latest titles as well as classic texts.
Professional Development Seminars
Industry-specific seminars hosted by professional bodies or trade associations can be invaluable. These seminars often address current challenges in the field and offer problem-solving techniques that are immediately applicable to your work. Attending these events also provides networking opportunities with peers who may have faced similar challenges.
Mentorship Programs
Finding a mentor in your field can provide personalized guidance on navigating professional challenges. Mentors can share their experiences, offer advice on developing problem-solving strategies, and provide feedback on your approach to different situations.
Group Discussion Forums and Online Communities
Platforms like Reddit, Quora, and specific professional networks (e.g., Stack Overflow for tech professionals) can be excellent resources for sharing and receiving advice on problem-solving. Engaging with these communities allows you to discuss real-world problems, explore multiple perspectives, and learn from the experiences of others.
Simulation Games
Strategic and simulation games (e.g., chess, SimCity, or even escape rooms) can be fun and effective ways to sharpen your strategic thinking and decision-making skills. These games challenge you to think ahead, anticipate problems, and devise solutions within constraints, mirroring real-life problem-solving situations.
YouTube Channels and TED Talks
Educational YouTube channels (such as TED-Ed or CrashCourse) and TED Talks offer free access to engaging content that can broaden your perspective and inspire innovative thinking. They cover a vast range of subjects, including psychology, business strategies, and science—all of which can enhance your problem-solving skills.
E-learning Apps
Mobile apps designed for learning new skills can be highly convenient. Apps like Lumosity, which offers brain-training exercises, or Brilliant.org , which focuses on problem-solving and critical thinking, allow you to practice and improve your skills on the go.
By leveraging these diverse training and resources, you can effectively enhance your problem-solving skills and apply them to your professional and personal life. Remember, the key to improvement is consistency and the willingness to step out of your comfort zone to tackle new challenges.
Practical Ways to Apply Problem Solving in Everyday Work
Incorporating problem-solving techniques into daily work routines can transform the way challenges are approached, making processes more efficient and outcomes more effective. Here are practical ways to apply problem-solving skills in everyday work:
Start with Clear Problem Definition
The first step in solving any problem is accurately defining it. Spend time understanding the issue at hand. Ask questions like, “What exactly is the problem?”, “Why is it a problem?”, and “What are the consequences of this problem?” A clear, concise problem statement paves the way for focused and effective solutions.
Break Down the Problem
Large or complex problems can seem daunting at first. Break them down into smaller, more manageable components. This approach makes it easier to tackle each part of the problem systematically, without feeling overwhelmed. Analyzing smaller pieces of the puzzle often reveals insights that apply to the problem at large.
Implement the 5 Whys Technique
Originating from lean manufacturing practices, the 5 Whys technique is about asking “Why?” a minimum of five times to drill down into the root cause of a problem. This method encourages deeper investigation beyond surface-level issues and can uncover underlying problems that, once solved, prevent future occurrences.
Leverage Diverse Perspectives
Collaboration can bring diverse perspectives to the table, shedding new light on the problem. Encourage team members to share their insights, experiences, and potential solutions. Sometimes, a fresh pair of eyes can see a solution that may not be apparent from a single viewpoint.
Apply Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves analyzing facts to understand a problem or topic objectively. It requires distancing yourself from emotional responses to evaluate data and evidence logically. In the context of problem-solving, this means looking at all angles of a problem, questioning assumptions, and considering various outcomes before deciding on a course of action.
Experiment with Brainstorming and Mind Mapping
Brainstorming sessions can generate a multitude of solutions in a short amount of time, making them invaluable for problem-solving. Mind mapping, on the other hand, can help visually organize thoughts, ideas, and potential solutions, making the relationships between different aspects of the problem and its possible solutions clearer.
Prioritize Solutions
Once potential solutions have been identified, evaluate and prioritize them based on criteria like feasibility, impact, and resource requirements. This step ensures that effort is invested in implementing solutions that are most likely to resolve the problem effectively.
Develop an Action Plan
An actionable plan outlines the steps needed to implement the chosen solution. This plan should include tasks, timelines, responsible individuals, and resources needed. Breaking the solution down into manageable steps ensures progress can be tracked, and adjustments can be made as needed.
Reflect and Learn from Outcomes
After implementing a solution, it’s crucial to assess its effectiveness. Did it solve the problem? What worked well, and what didn’t? Reflecting on these questions and learning from the outcomes is a critical part of the problem-solving process. It not only helps in refining current solutions but also enhances problem-solving skills for future challenges.
By integrating these practical strategies into everyday work, individuals and teams can foster a proactive problem-solving culture. This approach not only addresses issues more efficiently but also contributes to continuous improvement and innovation within the workplace.
Incorporating Problem Solving into Team Collaboration
Bringing problem-solving to the forefront of team collaboration not only enhances productivity but also drives innovation and team cohesion. Here are several strategies for effectively incorporating problem-solving into the fabric of team collaboration :
Foster Open Communication
Establish a communication-rich environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and ideas. Encourage active listening and ensure that all voices are heard without judgment. This openness facilitates the free flow of information, which is critical for identifying issues and brainstorming solutions collaboratively.
Define Roles Clearly
Clearly defining roles within the team helps in streamlining the problem-solving process. Assign a facilitator to guide discussions, a scribe to document the process, and various roles based on team members’ unique skills and expertise. When everyone understands their responsibilities, the team can tackle problems more efficiently.
Utilize Group Problem-Solving Models
Adopt structured problem-solving models such as the PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) or the Six Thinking Hats technique to give a clear framework to the collaborative process. These models help organize thoughts, manage the flow of ideas, and assess solutions systematically.
Create a Safe Space for Creativity
Innovative solutions often arise from creative thinking. Create a team culture where creativity is valued and nurtured. Establish an environment where it’s safe to take risks and where unconventional ideas are explored, not immediately dismissed.
Encourage Collaborative Tools
Leverage technology to facilitate collaboration. Use project management tools, shared documents, and digital whiteboards to allow team members to contribute ideas, organize thoughts, and track progress in real-time, even when working remotely.
Value Diverse Perspectives
Diversity within teams brings a range of perspectives to problem-solving, which can lead to more comprehensive and robust solutions. Encourage team members with different backgrounds, skills, and experiences to contribute their viewpoints. Recognize the value of diversity as a strength in the problem-solving process.
Implement Regular Group Reflection Sessions
After completing a project or resolving an issue, reconvene the team for reflection sessions. What was learned? What could have been done better? Reviewing the problem-solving process and the outcomes can offer valuable learning experiences that improve the teams’ ability to handle future issues collectively.
Establish a Clear Process for Decision Making
While consensus may be ideal, it’s not always practical. Establish a decision-making process that is transparent and fair, such as voting or taking turns to make final decisions. Having a process in place can help avoid conflict and ensure that decisions are made in a timely manner.
Empower Team Members
Empower individuals within the team to take initiative and make decisions within their scope. This empowerment can lead to faster problem resolution and encourages a sense of ownership and accountability within the team.
Celebrate Successes and Learn from Failures
Acknowledge when the team successfully solves a problem and celebrate the achievement, no matter how small. This positive reinforcement motivates team members for future problem-solving endeavors. Similarly, view failures not as setbacks but as learning opportunities, providing valuable insights for improvement.
Incorporating problem-solving into team collaboration isn’t just about fixing issues; it’s about building a dynamic, resilient, and innovative team capable of confronting any challenge that comes their way with confidence and collective expertise.
Measuring the Impact of Improved Problem-Solving Skills
As organizations and teams focus on enhancing problem-solving abilities, it becomes essential to measure the impact of these improvements. Evaluating the outcomes not only validates the effort invested in developing these skills but also guides future training and development initiatives. Here are approaches to quantitatively and qualitatively measure the impact of enhanced problem-solving skills within a team or organization:
Benchmarking Performance Metrics
Before and after implementing problem-solving training or initiatives, benchmark key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the organization’s goals. Metrics such as customer satisfaction scores, product defect rates, service delivery times, and employee efficiency can provide tangible evidence of the impact of improved problem-solving skills. Monitoring these metrics over time helps in assessing the long-term effects on operational efficiency and productivity.
Employee Feedback and Self-Assessment
Gather feedback from team members about their confidence and competence in solving problems before and after training or initiatives. Surveys, interviews, and self-assessment tools can be used to measure perceived improvements in problem-solving abilities. Employees’ reflections on their growth and challenges provide invaluable insights into the effectiveness of development efforts and areas for further improvement.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Document specific instances where enhanced problem-solving skills led to significant positive outcomes—for example, a complex project delivered successfully, a critical issue resolved efficiently, or a notable innovation developed. These case studies serve as qualitative evidence of the impact and can be incredibly motivating for individuals and teams, illustrating the real-world applications and benefits of effective problem-solving.
Turnaround Time for Issue Resolution
Measure the time taken to identify, address, and resolve issues before and after applying focused problem-solving strategies. A reduction in the turnaround time indicates a more efficient problem-solving process. This metric can be particularly revealing in high-pressure environments where rapid response to challenges is crucial.
Innovation and Idea Implementation
Track the number of new ideas, innovations, and continuous improvement projects generated and implemented within a specific timeframe. Improved problem-solving skills often lead to a more innovative mindset and a higher rate of actionable ideas that can drive the organization forward.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculate the return on investment for training and development initiatives aimed at enhancing problem-solving skills. This can involve comparing the costs associated with these initiatives against the tangible benefits obtained, such as cost savings from efficiencies, increased sales from innovative products, or reduced waste and rework. Demonstrating a strong ROI is compelling evidence of the value of investing in problem-solving capabilities.
Employee Retention and Engagement
Examine trends in employee retention and engagement levels. Organizations that focus on developing problem-solving skills often see improvements in these areas because employees feel more empowered, valued, and capable. Higher engagement and lower turnover rates indirectly reflect the positive impact of a problem-solving culture.

Customer Feedback and Retention
Monitor changes in customer feedback and retention rates. Improvements in problem-solving can enhance product quality, customer service, and overall satisfaction, leading to positive feedback and higher retention. Changes in these metrics can provide insight into how enhanced problem-solving skills are perceived from the customer’s perspective.
By employing a combination of these quantitative and qualitative measures, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact of improved problem-solving skills. This evaluative approach enables continuous improvement, helping to cultivate a culture of problem-solving that drives success and innovation.
Improving problem-solving skills in the workplace is crucial for any organization aiming to enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and maintain competitiveness. By encouraging a collaborative environment, providing ongoing training, implementing structured problem-solving frameworks, and promoting a culture of continuous improvement, teams can develop stronger analytical and creative thinking capabilities.
It’s essential for these efforts to be supported by managers and integrated into the core values of the organization to ensure their effectiveness and sustainability. As businesses work on refining these skills among their employees, they not only solve immediate challenges more effectively but also equip their workforce with the tools needed for future success. Thus, investing in and nurturing problem-solving skills becomes a pivotal strategy for organizational growth and resilience.

How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills (and Show Them Off in Your Job Hunt)

Problem-solving skills are critical for any career path—no matter where you work or what job you have, you’ll face problems big and small all the time. If you want to succeed in your career, being able to effectively navigate (and solve!) those problems is a must. And if you’re on the job hunt, showcasing your problem-solving skills can help you land your dream gig.
But what, exactly, are problem-solving skills? What can you do to improve them? And if you’re looking for a new position, how can you show off your problem-solving skills during your job search to help you land an awesome job?
Consider this your guide to all things problem-solving. Let’s get started.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills and Why Are They Important?
“Problem-solving skills are skills that allow you to identify and define a situation that needs changing,” says Doug Noll , an attorney and adjunct faculty member at the Straus Institute of Dispute Resolution at Pepperdine University’s Caruso School of Law, where he teaches graduate-level classes in decision-making and problem-solving. Once you identify what needs changing, problem-solving skills also enable you to “identify the best outcomes, define potential processes for achieving the best outcomes, and evaluate how the process achieved (or failed to achieve) the desired outcome,” he says. “Every job imaginable involves problem-solving.”
Being able to effectively solve problems can help you succeed and impress, regardless of what kind of job you have or career you plan to pursue. “A person who sorts out problems and makes decisions—or at least brings potential solutions to the table—is seen as someone who can get things done,” says organizational consultant Irial O’Farrell , author of the upcoming book The Manager’s Dilemma: How to Empower Your Team’s Problem Solving . “This makes managers’ lives easier—and managers notice people who make their lives easier, who get things done, and who don’t have to be told [what to do] the whole time. In turn, opportunities are put their way, enhancing their career.”
And the further you progress in your career, the more important those skills become, Noll says. “As you rise in an organization, the problems become more complex, ambiguous, uncertain, and risky. Only people able to solve these types of problems are promoted.” So as you hone your problem-solving skills, you become more valuable to any organization—and will be able to climb the ladder more easily as a result.
The 6 Steps of Problem-Solving—and the Skills You Need for Each One
Problem-solving is a process. And, like any process, there are certain steps you need to take in order to get to the finish line:
Step #1: Identify and Assess the Problem
You can’t solve a problem if you don’t know what the problem is. So “the first step is to recognize that an issue—or potential issue—exists,” O’Farrell says. In order to do that, you’ll need “a certain amount of knowledge or awareness of what should be happening as compared to what is actually happening.”
Once you recognize there’s a problem, you’ll need to evaluate its potential impact. “Is this going to affect three people or 203 people? Is this going to cost us $10 or $100,000? How material is this issue?” O’Farrell says. “Being able to evaluate the size, impact, and costs [of a problem] is a key skill here.”
When you understand the scope of the problem, you’ll have a better idea of what you’re dealing with—and will be able to come up with appropriate, relevant solutions as a result.
Skills needed during this step of the problem-solving process include:
- Attention to detail
- Data collection
- Forecasting
Step #2: Get to the Source of the Problem
Once you know what the problem is (and what its potential impact might be), it’s time to figure out where the problem is coming from or why it’s happening—as identifying the source of the problem will give you key insights into how to fix it.
“Often we notice a problem because of its symptoms, rather than its root cause. As a result, it is common to focus on resolving the symptoms, rather than what is causing the symptoms,” O’Farrell says. But “by understanding the root causes, a better, longer-term solution can be identified.”
There are a variety of techniques to help you dig deeper and understand what’s causing the problem at hand. For example, a 5 Whys analysis could help you uncover the root cause of a problem by having you ask “Why?” five times in a row, with each “Why?” building off the previous answer. Or you might try the fishbone diagram —also known as a cause-and-effect analysis—which encourages looking at the different categories that could be causing a problem and brainstorming potential root causes within each of those categories.
During this stage of the problem-solving process, curiosity is key; you’ll need it to explore all the different factors that could be contributing to the problem.
- Analysis (including root-cause analysis)
- Brainstorming
- Critical thinking
Step #3: Brainstorm Potential Solutions
Once you’ve identified the problem (and the root of the problem), “the next step is to brainstorm potential options that will resolve it,” O’Farrell says.
How much brainstorming you’ll need to do will depend on the problem you’re dealing with. “If it’s a fairly small, straightforward issue, then identifying a few options might be sufficient,” O’Farrell says. Especially for a bigger issue, “Taking some time to think beyond the obvious might lead to a better and longer-term solution.”
The size and scope of the problem will also determine who needs to be involved in this step. In some cases, you may be able to brainstorm solutions yourself. But if you’re dealing with a larger, more complex issue, getting more people involved (and choosing the right people, i.e. those best equipped to handle the problem) is important. You’ll need to be able to judge what kind of problem it is and who to bring in to help and lead a productive brainstorming session.
One of the most important skills you’ll draw on at this stage is creativity. The more creative you are during your brainstorm, the more (and better) potential solutions you’ll be able to come up with—and the more likely one of those solutions will be the solution you’re looking for.
Skills you might need during this step of the problem-solving process include:
- Communication
- Meeting facilitation
Step #4: Evaluate Solutions
Once you have a list of potential solutions from your brainstorming session, the next step is to examine each one carefully and narrow down your list so only the best solutions remain.
In order to succeed during this stage of the problem-solving process, you’ll need to be able to dig into each potential solution and evaluate how viable it is. You may make a pros and cons list for each potential solution, talk through the benefits and drawbacks with your team, and then narrow down your options to the solutions that have the most potential upsides.
All the work you put into the problem-solving process up to this point will also come in handy as you’re evaluating which of your potential solutions might ultimately be the most effective. “Having a strong understanding of what the issue is, why it’s an issue, and what is causing it helps in being able to determine if each of the solutions will sort the issue out,” O’Farrell says.
- Fact-checking
- Prioritization
Step #5: Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of potential solutions—and weighed the pros and cons of each—it’s time for you (or your supervisor or another decision-maker) to choose one.
“Depending on the type and impact of the issue and your role and authority, you may be the one making the decision or you may be presenting the issue and potential solutions to your boss,” O’Farrell says.
Knowing who should make the call is a key part of this step; if the problem is complex or will have a major impact on your organization that goes beyond your level of responsibility, it’s probably best to bring potential solutions to your boss and/or other stakeholders—and give them the final say.
- Decision-making
- Public speaking
Step #6: Implement the Decision and Reflect on the Outcome
Choosing a solution in and of itself doesn’t fix anything. You need to actually implement that solution—and do it well. That means developing a plan and coordinating with other key players in your organization to put that plan into action—which requires a host of skills (such as communication, collaboration, and project management).
Before you can hang up your problem-solving hat, you’ll also need to “go back and evaluate if the solution sorted out the issue” or if it caused any unintended consequences, O’Farrell says.
For example, let’s say your organization has a problem with taking too long to address customer service requests—and you rolled out a new ticket management system in order to deal with the issue. Once you implement that new system, you’ll want to follow up to make sure it’s allowing your customer service reps to deal with requests faster and hasn’t caused any new, different, or unexpected issues (for example, tickets getting lost in the queue or customers being less satisfied with the quality of support they received).
- Adaptability
- Collaboration
- Data analysis
- Goal setting
- Organization
- Project management
- Project planning
- Time management
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
Clearly, solving problems is a complex process—and it’s a process you need to nail if you want to grow in your career. But how can you improve your problem-solving skills so they can help you thrive in your career?
- Put on your student hat. One of the best ways to improve here is to study how to effectively solve problems. “Read case studies of complex problems,” Noll says. (For example, if you want to land a marketing job, you might search for case studies on how other companies were able to increase their qualified leads or drive more traffic to their website.) Noll also suggests reading books about different problem-solving techniques—or, if you really want to level up your skills, investing in a general course in critical thinking and problem-solving. “A good course should teach you how to think,” he says—and critical thinking plays a huge role in problem-solving.
- Try different brainstorming techniques. If you want to be a better problem solver, try pushing yourself to think outside of the box. “Learning some brainstorming techniques and expanding your thinking beyond the obvious solutions is also a way to make your problem-solving skills stand out,” O’Farrell says. Brainstorming techniques like brainwriting (a nonverbal brainstorming technique for teams) or rapid ideation (which pushes you to come up with as many ideas as possible in a short time frame) can help spark creative thinking—and help you become a more creative problem solver in the process.
- Ask expert problem-solvers how they solve problems. People in your professional (or personal!) life who excel at solving problems can be a great resource for leveling up your own problem-solving skills. “Talk to senior mentors about how they approached complex problems,” Noll says. “Get them to talk about their failures and mistakes,” he says, not just their successes. Seeing how other people solve problems and what they’ve learned from their experiences can help you approach problems in a different way and can make you a more versatile problem solver.
- Practice, practice, practice. Like with anything else, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, you need to practice solving problems. “Most people jump to the easy, intuitive answer rather than [carefully thinking] through the problem,” O’Farrell says. So next time you’re confronted with a problem, rather than jump to a hasty solution, take your time to go through the entire problem-solving process. And if you don’t have any real problems to deal with? Attempting to solve hypothetical problems can be just as helpful.
How to Show Off Your Problem-Solving Skills During the Job Search
Recruiters and hiring managers are looking for people with problem-solving skills who can help them, their team, and their company achieve their goals even in the face of obstacles and setbacks. So if you want to stand out, nail the interview, and score the job, you’ll need to showcase your problem-solving skills throughout your job search.
Here are a few ways to show off your problem-solving skills:
On a Resume
You can show potential employers that you’re a problem solver right on your resume. As you write your bullets for each past job and other experiences, “Incorporate one main challenge that you had to overcome, and give a brief synopsis of how you approached it, what the solution was and, most importantly, what the positive outcome was,” O’Farrell says.
For example, let’s say you’re a marketing manager and you had to figure out a way to launch a new product with a minimal budget. Under your current role, you might include a bullet point that says:
- Launched new sunscreen line across digital and traditional channels with <$10,000 budget by exploring up-and-coming distribution channels and negotiating wide-scale distribution agreements, bringing in $60,000 in new product sales within 90 days of launch
O’Farrell also recommends using action verbs (like “ analyze,” “evaluate,” or “identify”) to call out your problem-solving skills on a resume.
In a Cover Letter
In your cover letter, you’ll have more room and flexibility to showcase your problem-solving skills—and you should definitely take advantage of the opportunity.
Noll suggests using your cover letter to tell a quick story (think two to three sentences) about when and how you’ve solved a relevant problem. In your story, you want to include:
- What the problem was
- How you approached it/came to a solution
- What the outcomes of your problem-solving were
- What lessons you learned
Another strategy is to highlight how you would use your problem-solving skills within the context of the role you’re applying for. “I’d recommend reviewing the job description and identifying what types of problems you might have to deal with in the role,” O’Farrell says. Then you can speak directly to how you might approach them.
For example, let’s say you’re applying for an executive assistant position that requires extensive scheduling and calendar management for an exec who is often traveling for business. In that situation, you might explain how you’d solve the problem of scheduling while the exec is out of office (for example, by developing an appointment approval system that allows the exec to approve all appointment requests remotely, with a plan for how to notify the exec of appointment requests that need immediate attention).
During Interviews
The interview process offers the best opportunity for your problem-solving skills to shine, so you’ll want to come prepared.
“In preparation for the interview, select two to three situations where you used your problem-solving skills,” O’Farrell says. That way, when the interviewer asks you for examples of problems you’ve faced in your career—and how you solved them—you’ll have relevant stories ready. If you’re not sure how to tell your story effectively, the STAR method (which breaks down your story into four parts: S ituation, T ask, A ction, and R esult) can be helpful.
As a potential candidate, it’s also important to ask how you’ll need to use your skills on the job, Noll says. So you might ask the interviewers to share some of the issues or problems they’re hoping to solve by filling this position.
And if they turn around and ask you how you’d solve those problems? Don’t panic! If you have a story of a similar problem you’ve solved in the past, this is a great opportunity to share it. Otherwise, just talk through how you would approach it. Remember, the interviewers don’t expect you to come up with detailed solutions for problems their company is facing on the spot; they just want to get a sense of how you would begin to think about those problems if you were hired.
More From Forbes
Stumped five ways to hone your problem-solving skills.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Respect the worth of other people's insights
Problems continuously arise in organizational life, making problem-solving an essential skill for leaders. Leaders who are good at tackling conundrums are likely to be more effective at overcoming obstacles and guiding their teams to achieve their goals. So, what’s the secret to better problem-solving skills?
1. Understand the root cause of the problem
“Too often, people fail because they haven’t correctly defined what the problem is,” says David Ross, an international strategist, founder of consultancy Phoenix Strategic Management and author of Confronting the Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in the Age of Uncertainty .
Ross explains that as teams grapple with “wicked” problems – those where there can be several root causes for why a problem exists – there can often be disagreement on the initial assumptions made. As a result, their chances of successfully solving the problem are low.
“Before commencing the process of solving the problem, it is worthwhile identifying who your key stakeholders are and talking to them about the issue,” Ross recommends. “Who could be affected by the issue? What is the problem – and why? How are people affected?”
He argues that if leaders treat people with dignity, respecting the worth of their insights, they are more likely to successfully solve problems.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, 2. unfocus the mind.
“To solve problems, we need to commit to making time to face a problem in its full complexity, which also requires that we take back control of our thinking,” says Chris Griffiths, an expert on creativity and innovative thinking skills, founder and CEO of software provider OpenGenius, and co-author of The Focus Fix: Finding Clarity, Creativity and Resilience in an Overwhelming World .
To do this, it’s necessary to harness the power of the unfocused mind, according to Griffiths. “It might sound oxymoronic, but just like our devices, our brain needs time to recharge,” he says. “ A plethora of research has shown that daydreaming allows us to make creative connections and see abstract solutions that are not obvious when we’re engaged in direct work.”
To make use of the unfocused mind in problem solving, you must begin by getting to know the problem from all angles. “At this stage, don’t worry about actually solving the problem,” says Griffiths. “You’re simply giving your subconscious mind the information it needs to get creative with when you zone out. From here, pick a monotonous or rhythmic activity that will help you to activate the daydreaming state – that might be a walk, some doodling, or even some chores.”
Do this regularly, argues Griffiths, and you’ll soon find that flashes of inspiration and novel solutions naturally present themselves while you’re ostensibly thinking of other things. He says: “By allowing you to access the fullest creative potential of your own brain, daydreaming acts as a skeleton key for a wide range of problems.”
3. Be comfortable making judgment calls
“Admitting to not knowing the future takes courage,” says Professor Stephen Wyatt, founder and lead consultant at consultancy Corporate Rebirth and author of Antidote to the Crisis of Leadership: Opportunity in Complexity . “Leaders are worried our teams won’t respect us and our boards will lose faith in us, but what doesn’t work is drawing up plans and forecasts and holding yourself or others rigidly to them.”
Wyatt advises leaders to heighten their situational awareness – to look broadly, integrate more perspectives and be able to connect the dots. “We need to be comfortable in making judgment calls as the future is unknown,” he says. “There is no data on it. But equally, very few initiatives cannot be adjusted, refined or reviewed while in motion.”
Leaders need to stay vigilant, according to Wyatt, create the capacity of the enterprise to adapt and maintain the support of stakeholders. “The concept of the infallible leader needs to be updated,” he concludes.
4. Be prepared to fail and learn
“Organisations, and arguably society more widely, are obsessed with problems and the notion of problems,” says Steve Hearsum, founder of organizational change consultancy Edge + Stretch and author of No Silver Bullet: Bursting the Bubble of the Organisational Quick Fix .
Hearsum argues that this tendency is complicated by the myth of fixability, namely the idea that all problems, however complex, have a solution. “Our need for certainty, to minimize and dampen the anxiety of ‘not knowing,’ leads us to oversimplify and ignore or filter out anything that challenges the idea that there is a solution,” he says.
Leaders need to shift their mindset to cultivate their comfort with not knowing and couple that with being OK with being wrong, sometimes, notes Hearsum. He adds: “That means developing reflexivity to understand your own beliefs and judgments, and what influences these, asking questions and experimenting.”
5. Unleash the power of empathy
Leaders must be able to communicate problems in order to find solutions to them. But they should avoid bombarding their teams with complex, technical details since these can overwhelm their people’s cognitive load, says Dr Jessica Barker MBE , author of Hacked: The Secrets Behind Cyber Attacks .
Instead, she recommends that leaders frame their messages in ways that cut through jargon and ensure that their advice is relevant, accessible and actionable. “An essential leadership skill for this is empathy,” Barker explains. “When you’re trying to build a positive culture, it is crucial to understand why people are not practicing the behaviors you want rather than trying to force that behavioral change with fear, uncertainty and doubt.”

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
We are offering inhouse programs to upskill your entire organization

The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills in the Workplace
November 10, 2022 - job & career, discover your own management 3.0 path: answer a few questions to get personalized recommendations.
Tell us a bit about yourself, and we’ll tailor our recommendations to match your interests. Just answer a few quick questions below to get started!
Our Recommendation Based on Your Answers
Build upon the foundation of your knowledge by delving deeper into the main principles and practices of Agile Leadership with our Agile Change Leadership Workshop .
Build upon the foundation of your knowledge by delving deeper into the main principles and practices of Agile Leadership with our Agile Co-Creation Leadership Workshop .
Build upon the foundation of your knowledge by delving deeper into the main principles and practices of Agile Leadership with our Agile Team Leadership Workshop .
Build upon the foundation of your knowledge by delving deeper into the main principles and practices of Agile Leadership with our Agile People Leadership Workshop .
If you are interested in other options we offer, please check our Learning Path .
The Foundation Workshop is where your Management 3.0 learning journey truly begins, and you will learn about the principles, pillars and popular practices you can use right away.
The Foundation Workshop is where your Management 3.0 learning journey truly begins, and you will learn about the principles, pillars and popular practices you can use right away. If you are interested in other options we offer, please check our Learning Path .
Agility in HR Workshop by Management 3.0 is the popular Management 3.0 Foundation Workshop with additional content and ICAgile accreditation targeted for people who work in or closely with human resources.
With our global team, we provide tailor-made programs to enhance mindsets and skills for entire organizations, ensuring your business is future-ready! Learn more about our Inhouse Training Programs .
Our Company License gives your learning team, transformation staff and leaders the ability to facilitate the Management 3.0 mindset, practices and official workshops yourselves.
You sound like a match for our global Facilitator community! Get your Management 3.0 Facilitator License now !
We have defined certain requirements that you must meet to become a licensed Management 3.0 Facilitator. We offer both workshop-based and practice-based approaches. Read more about the requirements .
In the Official Management 3.0 Community you can connect with curious and focused like-minded leaders from all over the world to practice, share, and grow!
Our practical, hands on and tangible tools and management games are the best way to foster transformational change within teams, companies and even on a personal level.
According to Management 3.0 Facilitator Ilija Popjanev , problem solving is essential for individuals and organizations as it enables us to control all aspects of our business environment. In this article, Ilija looks into problem-solving skills, how the problem-solving process works, and which tools help you to advance this skill set.
In this article you will learn about:
What is Problem Solving?
- Problem-Solving in Six Easy Steps
Why is Problem-Solving so Important for Leaders, Teams, and Organizations?
Problem-solving techniques in the workplace, better employee experience by using problem-solving tools from management 3.0, how do employees develop problem-solving skills, what skills make a good problem solver.
In the last few years, we have been living 100% in the VUCA world, with so many unpredictable and complex threats and challenges. As a result, organizations must create a sense of urgency to redesign their present business models and to rebuild the foundations for the future of work.
All companies now need effective problem-solving skills and tools at all levels, starting with individuals and teams, and finishing with their leaders and managers. This new reality enables growth and success only for those well-equipped and empowered by effective problem-solving skills and tools.
One of the behaviors of Management 1.0 style is to constantly look for ways to stop “fighting fires,”. Instead, the Management 3.0 style seeks to “find the root cause” of the problem, and then to refocus, improve, and plan a different way for fulfilling workplace tasks.
Management 3.0 provides effective tools and principles for building the system for effective problem solving. It provides us with techniques we can use to understand what is happening in our world, to identify things we want to change, and then apply everything that needs to be done to achieve the desired outcome. We live by the motto: fail fast, recover quickly, and learn from the failures.
The agile way of working does not mean being perfect, but instead it allows for failures and sees them as opportunities to learn, grow, and adapt . Perfection is useless if we do not provide value fast for our customers. That is why problem solving is the foundation for continuous improvement, learning, and collaboration, which leads to innovations and success in ever-changing economies and the new normal that we now live in.
The definition of problem solving according to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary is: “The process or act of finding a solution to a problem.” Similarly, the Oxford English Dictionary describes problem solving as: “The process of finding solutions to difficult or complex issues.”
For me, Problem-solving is a process of understanding and owning the problem, constant pursuit for solutions and improvements, and putting into action the best option for the desired outcome.
Understanding context and interacting with our teammates are the essence of effective problem-solving. We must clearly understand the complexity of our environment and the specifics of the context because things continuously change and evolve. Here, the Complexity Thinking Guidelines may help you to better understand what is happening and how to navigate complex environments more effectively.
We must have a lens through which to see problems as opportunities to improve, and regard our teams as sources of knowledge and experience. We have to connect people and opportunities in ways that can facilitate the best solutions for the problems that we are handling. Try using the Personal Maps , an excellent tool for bringing teams together and fostering diversity, respect, trust, and collaboration.
Today, all innovations and solved problems are team efforts because teams constantly improve their toolbox and competencies. Teams want to create something that was not there before, and which maximize their knowledge and resources.
To accomplish that, they need to build a process in a few easy steps:
- Be present, observe what is happening in your world, and define the problem.
- Review where you are now and what influences that state.
- Constantly improve and change things by using creative tools and tactics.
- Seek solutions and alternatives to make changes more effective.
- Make team decisions about which tools and solutions should be used.
- Implement improvements, monitor the process, and constantly adapt!
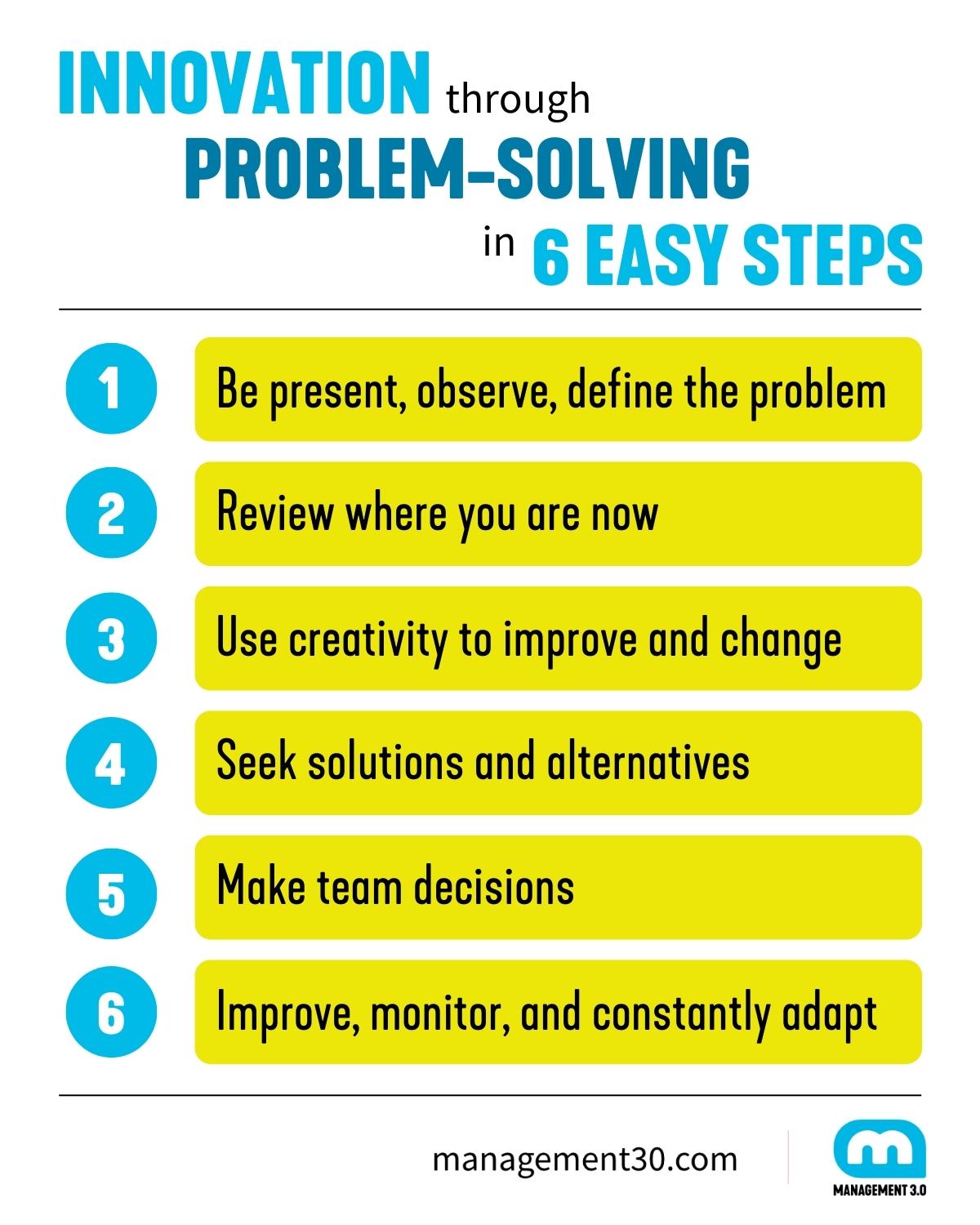
At this stage, by following the Management 3.0 principle of “Improving the system,” you can use the tools Celebration Grids , combined with Yay! Questions , to best engage the team in the problem-solving process, while keeping track of what is working well, what can be changed, and what new options exist.
Documenting everything is an integral part of the problem-solving process. By using Celebration Grids, you are gamifying the process and keeping the team flow and energy on a higher level.
Also read: What type of problem-solver are you?
Problem-solving is crucial for everyone: individuals, teams, leaders, organizations, and ultimately for all stakeholders because it empowers us to better control the environment and everything that is going on in our world. Try using Delegation Poker so that teams can become more empowered to solve problems both alongside leaders and within their organization.
Today, the speed of problem solving is important, and that is why organizations must give more power and authority on a team level , so employees can react quickly and even prevent problems. As a leading indicator, the Management 3.0 tool Problem Time can help you measure the time spent on uncompleted problem-solving tasks and activities; this is a valuable add-on to “lead and cycle time” lagging indicators, with which you measure the time taken on completed tasks.
Developing and refining problem-solving skills through constant practice and experimentation can refine the ability to solve problems and address issues with more complexities.
We may face various challenges in our daily work, and effective problem-solving can make a difference.
Make a Difference with Problem-Solving
- Problem-solving skills are important if you want to add more value . As an agilist, your objective is not to be perfect but to maximize the value you provide for all stakeholders. Start fast, deliver value early, manage failures and prioritize tasks by setting the urgency criteria.
- Problem-solving skills are important if you need to improve your results. You have to accept the complexity of success factors and better understand the need for changes and improvements in a continually uncertain environment. Results depend on your problem-solving skills!
- Problem-solving skills are important if you have to fix things that do not work. When your processes are not working as planned, problem solving will give you the structure and mechanisms to identify issues, figure out why things are broken, and take actions to fix them.
- Problem-solving skills are important when you have to address a risk. Sharpen your problem-solving skills to anticipate future events better and increase the awareness of cause-and-effect relationships. This enables you to take the right actions and influence the outcomes if issues do occur.
- Problem-solving skills are important if you work simultaneously on several projects. You should apply the same problem-solving techniques when you work on multiple projects, business functions, market segments, services, systems, processes, and teams. Standardize and scale!
- Problem-solving skills are important when you want to seize the day. Problem solving is all about innovation , building new things, and changing the system into a better one. This can help us to identify opportunities even in challenging times and prepare us for the future. You can visualize the process with the Meddles Game to better understand your ideas, solutions, and activities. It is a great way to engage your team as you can build the problem-solving concept and it is an effective tool for influencing all stakeholders affected by the problem.
Also read: Collaborative Leadership explained .
Solving complex problems may be difficult, but problems will be solved when we use the right tools. Besides the powerful Management 3.0 tools I already mentioned, as a big fan of Lean and Liberating structures, I think you can find lots of problem-solving techniques to use in your daily business.
Here is my short list of tools and techniques:
- 5 Whys – a great way to uncover the root cause is to understand the problem better.
- Fishbone analysis – for visual analysis of the root causes of a problem. Easy to combine with ‘5 Whys’ or ‘Mind mapping’ to brainstorm and determine the cause and effect of any problem.
- Silent brainstorming – gives everyone a chance to participate in idea generation as not only the loudest people, but also the quiet ones, will participate equally. Everyone’s opinion has the same weight.
- Mind maps – structured visual diagrams to share your ideas, concepts, and solutions the same way your brain does. You explain the problems quickly, then share fresh ideas, and finally come to a team consensus that can lead to an effective solution.
- Six thinking hats – enable your team to consider problems from different angles, focusing on facts, creative solutions, or why some solutions might not work.
- Agreement certainty matrix – another tremendous visual tool for brainstorming problems and challenges by sorting them into simple, complicated, complex, or chaotic domains to later agree on what approach should be used to solve the concrete problems affecting a team.
- Conversation café – enables the team to engage in productive conversations, with less arguing but more active listening, solving the problem in rounds of dialogues until reaching a consensus regarding the best problem-solving approach.
- Design thinking – when you are struggling for fresh ideas, the 5-step process will help you empathize with the problem, then begin defining and developing new ideas, before prototyping and testing them.
Edward Deming’s PDCA is the most known concept for continuous improvement and problem solving. You can gamify your events using the Change Management Game , a card game where PDCA will help you define the problem, take action, collect feedback, and adopt the new solution.
The “carrot and stick” approach, or in HR language, “pay for performance,” does not work anymore, especially for roles that require problem-solving, creativity, and innovative thinking. Creative people need a higher level of authority and empowerment to self-manage challenges and problem scenarios. When leaders and organizations create such systems, they foster intrinsic motivation and job satisfaction among these people. Creatives are seeking self-actualization through their careers.
This is one more case which calls for Management 3.0’s Delegation Poker to define the levels of authority in terms of problem-solving issues, as well as Moving Motivators to define key motivators for increasing productivity and employee satisfaction by changing behavior.
Improving Employee Experience with Problem-Solving
1. Use problem solving as a key motivator – have in mind Millennials and Gen Z creative workers ’ affinity towards tasks in which they feel challenged and have a sense of meaning. Provide them with big and tough problems to solve and use challenging tasks to keep them constantly engaged.
2. Continuous improvement can make a difference – creatives seek a sense of purpose and think outside of the box, so encouraging the ‘How can we execute this task better?’ mindset and problem solving become powerful tools for creating sustainable corporate culture.
3. Don’t connect solving problems with rewards – it can kill the perceived intrinsic value of the activity; it will disengage and dissatisfy employees. Autonomy, trust, respect, and gratitude will do the job.
4. Apply the seven rules for creative managers – unleash the power of diversity , and cooperation, rely on merits, optimize exploration, open boundaries, keep options open, and update your workplace.

We start solving problems from a very early age (the alphabet, learning to eat, driving a bicycle etc.). Then, everyday activities sharpen our problem-solving skills and enable us to solve more complex issues.
As an adult, you can still develop your problem-solving skills by:
- Daily practicing of logic games, such as chess, and puzzles like Sudoku.
- Video games can teach you how to deal with failure and persist in achieving your goals.
- Keep an idea journal or blog as a collection of all your ideas, thoughts, and patterns.
- Think outside of the box – take a different perspective to understand the problem better.
- Practice brainstorming combined with mind mapping, working with your team.
- Put yourself in new situations – take on a challenging project at work.
- Start using the “what if” mindset in daily circumstances and test new approaches.
- Read more books on creativity and articles which cover your areas of interest.
I also believe coaching can help build creativity and problem-solving skills, encouraging people to take greater ownership of their work and commit to corporate goals. A coach can provide clear guidance as to what is important at the moment; they help people better, focus, and move into action. By asking powerful questions and challenging others to think outside of the box, the coach removes their barriers and lets them see the situation from a new perspective.
Coaching can provide structure so people develop their own expertise and insights to contribute better when problems arise and the pressure to succeed is growing.
The interview is an excellent opportunity to research a candidate’s problem-solving skills, and STAR questions should be related to their previous experience dealing with problems. A candidate with good problem-solving skills can quickly embed in the team and become a valuable asset for the company.
In my Agility in HR workshops , we regularly discuss interview questions. Some popular STAR questions are:
- “If you cannot find a solution to a problem, how do you deal with the situation?”
- “How do you react when faced with unexpected problems or challenges?”
- “Describe an occasion when you had to adapt at the last minute. How did you handle this?”
Problem-solving requires the ability to identify a problem, find the root cause, create solutions, and execute them. All these steps are essential for achieving the desired results.
Some of the skills that problem solvers must constantly sharpen are:
- Collaborative communication . Clear communication is essential when you explain the problem and the solution to your teammates. During brainstorming sessions, asking the right questions to determine the root cause , as well as synergic collaboration are needed.
- Active listening is important to prevent mistakes as you can absorb the details your colleagues tell you about the problem. Use open-ended questions for clarification, and always be open to feedback and views that differ from yours.
- Coachability. The willingness to accept feedback and the ability to improve. Learning from more experienced people, being curious to ask many questions, constructively using your ego, skipping excuses and blaming others, and accepting Feedback Wraps from your coach.
- Decision making . Problems cannot be solved without risk-taking and bringing important decisions (including relevant data, levels of delegation, alternative solutions etc.) to the forefront.
- Critical thinking . Be 100% objective when you try to find the cause of the problem. Skip ego trips and personal biases. Identify your mistakes in the thinking process and show personal accountability .
- Research and data analysis . Proper research allows you to diagnose the actual problem, not just the symptoms. If the cause of the problem is not immediately apparent, you can use the power of data to discover the issue’s history, some patterns, future trends, etc.
- Persistence . Trust in the problem-solving process you have designed and follow every step with patience and persistence; even when you fail repeatedly, do not give up. Keep moving and remember Thomas Edison’s quote: “I have not failed. I have just found 9,999 ways that do not work.”

In the new VUCA world we now live in, problem solving is a crucial soft skill, and employers are actively seeking people with this skill set because they can prepare for problems before they arise. Problem solvers better identify opportunities, understand their environment, create a solution, and generate ideas that lead to great results and success.
According to a study made by LinkedIn Learning in August 2022 , future skills are rapidly changing, and problem solving is among the top soft skills employers search for from their candidates, as well as communication and leadership skills.
Using all aforementioned tools and practices from Management 3.0, following the guides, and sharpening your skills, will help you not only to be effective in resolving the problems that may arise, but also to solve them with enthusiasm and passion. They will create a higher level of engagement and collaboration in the team and help unleash people’s creativity and innovation. A win-win for everyone!
Photo by Parabol on Unsplash
Have you already read these?
Four ways to find the first job you love, why valuing professional skills is so important, the challenges & opportunities of reentering the workforce post pandemic, 9 reasons why quitting your job could be good for you, privacy overview, sign up for our engaging newsletter.

Subscribe Here!
Wait a second!
Buy Meddlers Game
Buy Kudo Cards
Buy Change Management Game
Buy Moving Motivators Game
Buy Delegation Poker Cards
Why Problem Solving is Important in the Workplace

Ben is responsible for talent analytics at Test Partnership and is often who you will speak to if you book a demo .
What is problem solving?
What is an example of problem solving, why problem solving is important, how to improve problem solving, how to assess candidates on their problem solving, our recommended test partnership assessments for measuring problem solving.

Problem solving in the workplace refers to a person’s ability to handle difficult or unexpected situations and find solutions to complex business challenges. Employees with exceptional problem solving ability will carefully analyse the problem, identify a range of potential solutions, and correctly identify the most effective of the available solutions to remedy the situation. This ensures that employees in complex work who are relied upon to find effective solutions to key business issues are maximally equipped to deal with modern problems that face 21st century businesses.
Those with good problem solving ability will move the business forward more effectively.
Those lacking problem solving ability will inevitably recommend ineffective solutions to key business issues, solutions which will either fail to resolve the underlying issue or indeed exasperate it. For example, they may misinterpret the information presented to them, fail to identify effective solutions to problems, or provide solutions which are unsuitable or indeed counterproductive. Employees with poor problem solving ability cannot be relied upon when the unexpected happens, shifting the burden on other staff. As a result, problem solving ability is a common core competency when hiring professional, managerial, or technical roles, and highly prized by HR professionals and hiring managers.
Problem-solving refers to the ability to identify and resolve problems in an effective and efficient manner. An example of problem-solving can be seen in the role of a customer service representative. A customer service representative is responsible for handling customer complaints and issues, and finding a solution that will satisfy the customer.
Problem solving ability is essential to performance in any role where issues need to be dealt with quickly, or where the issues that employees face are particularly complex. Employees skilled in problem solving contribute to a more adaptable and productive work environment. It promotes teamwork, critical thinking, and strategic decision-making, leading to improved outcomes and organisational success.
Watch a video instead?
If you would prefer to watch a video, here Ben outlines why problem solving is important in the workplace:
For example, management consultants are expected to solve particularly complex issues that their clients may be facing, and within very specific time-frames. Should a consultant fail to provide a solution within the specified timeframe, this will inevitably look bad in the eyes of the client, sullying the relationship and potentially negatively impacting the consultancy’s reputation. However, a consultant with exceptional problem solving ability will most likely provide effective solutions to the client’s problems and provide them within the requisite time period.
"As a competency, problem solving is a common performance criterion for roles that require staff to solve urgent or complex problems." Ben Schwencke Consultant
As a competency, problem solving is a common performance criterion for roles that require staff to solve urgent or complex problems. These include, but are not limited to: management consultants, IT professionals, finance professionals, legal professionals, data scientists, managers, and executives. As a general rule, the more the role involves employees providing solutions to complex or urgent problems, the more important problem solving ability will be, and the more damage employees could potential cause if they lack those essential problem solving abilities in the workplace.
When a customer contacts a company with a problem, the customer service representative must first listen carefully to the customer's complaint and understand the issue. They then need to gather information and assess the situation to determine the cause of the problem.
They must evaluate different options and choose the best course of action to resolve the problem.
Next, they must evaluate different options and choose the best course of action to resolve the problem. Finally, they must implement the chosen solution and follow up to ensure that the problem has been fully resolved.
Problem solving as a psychological construct is underpinned predominantly by specific cognitive abilities. The ability to solve quantitative problems for example, is underpinned by a person’s level of numerical reasoning , and their ability to solve qualitative problems is underpinned by their verbal reasoning . Indeed, the academic research in this field suggests that the predictive validity of ability tests is largely attributable to problem solving abilities. Aptitude test questions are essentially just cognitive problems, and a candidate’s ability to solve them serves as a very useful proxy for their overall problem solving ability.
Other assessments may also measure problem solving to some degree, particularly certain assessment centre exercises, such as case study exercises. Here, candidates will be presented with a particular workplace relevant problem and told to generate solutions to that problem. Although this can be an effective method of assessing problem solving ability, assessment centre exercises are quite resource intensive, and are thus only suitable for the later stages of the recruitment process. Ability tests, however, can be used early in the recruitment process, ensuring that all subsequent candidate hold the requisite level of problem solving ability.
- Insights numerical reasoning
- Insights verbal reasoning
- Insights inductive reasoning
- Concepts critical thinking
- Concepts data analysis
- MindmetriQ Series of Gamified Assessments
Want to hire for problem-solving skills?
Discover why thousands of companies love our modern assessment platform. Fresh new assessments built with the latest science to ensure you hire for high levels of problem-solving.
Other articles you may be interested in

How to Measure Quality of Hire
Learn of our 5 great ways to measure quality of hire which makes organisations make informed decisions about future hires.

Candidate Selection: A Definitive Guide
Learn of candidate selection to improve your candidate selection process and build a high-performing workforce.

Skills Based Hiring: An Ultimate Guide
Learn what skills-based hiring is and why it's an important innovation.

What is a sten score?
Sten scores are standardised 1-10 scores commonly used in psychometric testing...
- Coach Portal

- Executive Coaching
- Leadership Training
- Executive Presence
- Manager Development
- Team Assessment & Alignment
- Executive Team Development
- New Leader Assimilation
- Presentation & Orals Coaching
- Change Strategy & Training
- Strategic Planning & Board Services
- Culture Assessment & Integration
- Organizational Design
- Employee Experience
- Succession & Workforce Planning
- Career Management
- Promote Diversity Equity & Inclusion
- Competency Modeling
- LEAD NOW! Model
- LEAD NOW! All Access
- Teaming For Success Model
- Assessments
- Certifications
- Facilitation
- Client Success Stories
- Clients & Partners
- Join Our Team
- Ask A Coach
- Blog Articles
- Leadership Lessons
- LEAD NOW! Videos
- White Papers
- Leadership Growth Hour
- LEAD NOW! Certifications
- Teaming For Success Certifications
- Connect With Us
- Assessment Center
7 Advantages of Team Problem-Solving
--> Team Performance ,--> Teaming ,--> Problem Solving -->