Globalization: Case Studies
Learning objectives.
- Students will analyze how technological advancements have led to increased globalization.
- Students will create presentations that inform about ways in which globalization impacts daily life.
- Students will complete Parts 1 and 2 of the guided reading handout.
- (5 Minutes) Debrief Homework: Ask students to share key takeaways from homework. Highlight that 1) technological advances have increased globalization and 2) globalization has a direct impact on their daily lives in the food they eat. This sets the stage for a deeper look at the impact of globalization through case studies.
- Group 1: A Global Semiconductor Shortage
- Group 2: Big in China: The Global Market for Hollywood Movies
- Group 3: Human Trafficking in the Global Era
- A Global Semiconductor Shortage = data related to backorders, map of supply chain, chips used in a car visual, bullet points of what CHIPS Act does
- Big in China = data on box office sales, images related to censored movies, etc.
- Human Trafficking = data about numbers of people affected, visuals of common industries where trafficking is common, visuals about products tied to human trafficking.
Students should complete the Impact of Globalization Infographic/ Presentation. They will share at the beginning of the next class meeting. If possible, their infographics should be displayed or shared with the larger school audience (i.e: submitted to the school newspaper).
withholding of information, typically by a government or an authoritative body.
cable, made out of strands of glass as thin as hair, used to quickly transmit large volumes of internet traffic between locations all over the globe.
disease outbreak that has reached at least several countries, affecting a large group of people.
supreme or absolute authority over a territory.
a network—consisting of individual producers, companies, transportation, information, and more—that extracts a raw material, transforms it into a finished product, and delivers it to a consumer.
an international institution created in 1995 that regulates trade between nations. A replacement for the 1947 General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), the WTO manages the rules of international trade and attempts to ensure fair and equitable treatment for its 164 members. It does this by conducting negotiations, lowering trade barriers, and settling disputes. As of 2018, the WTO had 164 members.
- Sign into My Research
- Create My Research Account
- Company Website
- Our Products
- About Dissertations
- Español (España)
- Support Center

Find your institution
Examples: State University, [email protected]
Other access options
- More options
Select language
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
Welcome to My Research!
You may have access to the free features available through My Research. You can save searches, save documents, create alerts and more. Please log in through your library or institution to check if you have access.

Translate this article into 20 different languages!
If you log in through your library or institution you might have access to this article in multiple languages.

Get access to 20+ different citations styles
Styles include MLA, APA, Chicago and many more. This feature may be available for free if you log in through your library or institution.

Looking for a PDF of this document?
You may have access to it for free by logging in through your library or institution.

Want to save this document?
You may have access to different export options including Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive and citation management tools like RefWorks and EasyBib. Try logging in through your library or institution to get access to these tools.

- More like this
- Preview Available
- Scholarly Journal

McDonald's: A Case Study in Glocalization
No items selected.
Please select one or more items.
You might have access to the full article...
Try and log in through your institution to see if they have access to the full text.
Content area
The purpose of this research report was to assess McDonald's globalization strategy. We examined McDonald's strategy across six dimensions: menu, promotion, trademarks, restaurants, employees, and service. We also compared the company's performance across these six dimensions in 10 different countries: Saudi Arabia, France, the United Kingdom, Greece, Brazil, Indonesia, India, China, Japan, and New Zealand to measure McDonald's success in capitalizing on globalization and localization. As discussed in this report, McDonald's is a global brand through its worldwide standards and training operations, but the company is also local, with its franchising to local entrepreneurs, locally sourcing food, and targeting specific local consumer market demands. McDonald's is an excellent example of blending global with local - an organization that has glocalized very successfully.
Introduction and Purpose
McDonald's has been serving fast food to America since 1955 and has grown into one of the world's leading fast food giants. Today, McDonald's is the leading global foodservice retailer with 1.7 million employees and more than 34,000 restaurants in 119 countries serving nearly 69 million people each day (McDonald's, Annual Report, 2012).
Not too long ago people believed McDonald's would become "a lumbering cash cow in a mature market" (Serwer & Wyatt, 1994). However, its success abroad has offset the maturing market in America. In fact, 65% of McDonald's sales came from international revenues (McDonald's, Annual Report, 2012.) Its worldwide operation concentrates its global strategy, "Plan to Win," and on customer experience, which includes people, products, place, price, and promotion.
This paper will compare McDonald's marketing strategy to determine how well it capitalizes on both globalization and localization. It will look at this strategy by examining ten different countries: Saudi Arabia, France, the United Kingdom, Greece, Brazil, Indonesia, India, China, Japan, and New Zealand, across six different dimensions: menu, promotion, trademarks, restaurants, employees, and service.
McDonald's: The American Standard
The McDonald's American model focuses on fast and convenient service with high purchasing turnover. Its recognizable bright red and yellow colors with the iconic golden arches reaching into the sky offer Americans a piece of the familiar in a foreign country. "Our goal is to become customers' favorite place and way to eat and drink by serving core favorites such as our World Famous Fries, Big Mac,...
You have requested "on-the-fly" machine translation of selected content from our databases. This functionality is provided solely for your convenience and is in no way intended to replace human translation. Show full disclaimer
Neither ProQuest nor its licensors make any representations or warranties with respect to the translations. The translations are automatically generated "AS IS" and "AS AVAILABLE" and are not retained in our systems. PROQUEST AND ITS LICENSORS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIM ANY AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTIES FOR AVAILABILITY, ACCURACY, TIMELINESS, COMPLETENESS, NON-INFRINGMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Your use of the translations is subject to all use restrictions contained in your Electronic Products License Agreement and by using the translation functionality you agree to forgo any and all claims against ProQuest or its licensors for your use of the translation functionality and any output derived there from. Hide full disclaimer
Suggested sources
- About ProQuest
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Skip to content
- Skip to main navigation
- Skip to 1st column
- Skip to 2nd column
Global Policy Forum
- Board Members
- Support GPF
- GPF Partners
- Annual Reports and Statutes (GPF Europe)
- Contact and Disclaimer
- Publications
- Publications in German
- Upcoming Events
- Past Events
- Events in Germany
- General Information on Internships
- Internship Application
A Closer Look: Cases of Globalization

| Source: wikipedia.org/Ken Banks |
Globalization expands and accelerates the movement and exchange of ideas and commodities over vast distances. It is common to discuss the phenomenon from an abstract, global perspective, but in fact globalization's most important impacts are often highly localized. This page explores the various manifestations of interconnectedness in the world, noting how globalization affects real people and places.
Articles and Documents
Chinese imports and contraband make bolivia's textile trade a casualty of globalization (july 6, 2012).
Domestic manufacturing in Bolivia has been crushed by the influx of cheap foreign goods, mainly from China. Bolivian products cannot compete in the global market because of the small scale production, the strict labor law which keeps labor cost high, and the frequent political unrest which hurt competitiveness by raising costs. The Bolivian economy is reliant on raw material extraction, and its trade deficit keeps widening. Although the government is making an effort to raise tariffs and create state-owned companies to save jobs, globalization seems to have caused more bad than good in Bolivia. (Associated Press)
Is France on Course to Bid Adieu to Globalization? (July 21, 2011)
Many in France are blaming globalization for causing high youth unemployment and a stagnated, post recessionary economy. With the 2012 presidential election approaching, the theme of “deglobalization” appears to be growing in popularity due to its nationalistic appeal. Left-wing candidates, including member of Parliament Arnaud Montebourg, are advocating European-based protectionism, and saying that “globalization” has caused France’s high rates of youth unemployment, destroyed natural resources, and made France vulnerable to the fluctuations of interconnected financial markets. While Montebourg is not a likely front-runner for the presidency, his surprising popularity has highlighted the French peoples’ disillusionment and has prompted a discussion of globalization. Ideally, this will “force politicians to work harder on their answers”, and they will work to improve France’s economic recovery plans and their role in a globalized system. (YaleGlobal Online)
350 Movement Video from Bolivia's Climate Summit (April 22, 2010)
Immigrants now see better prospects back home (december 8, 2009), the human effect of globalization (august 30, 2009), following the trail of toxic trash (august 17, 2009), will the crisis reverse global migration (july 17, 2009), in many business schools, the bottom line is in english (april 10, 2007), globalization and child labor: the cause can also be a cure (march 13, 2007), landless workers movement: the difficult construction of a new world (september 29, 2006), for african cotton farmers, more crops equal less pay (august 15, 2006), meet the losers of globalization (march 8, 2006), thanks to corporations instead of democracy we get baywatch (september 13, 2005), global health priorities – priorities of the wealthy (april 22, 2005), guatemala: supermarket giants crush farmers (december 28, 2004).
This article looks at the effects of economic liberalization in Latin America's food retailing system and identifies small scale farmers as the "losers of globalization." Corporate transformations of the regional food sector and its failed trickle-down economics have not generated wealth but rather increased the social inequalities in the region, forcing smaller growers to migrate. ( New York Times )
Campesinos vs Oil Industry: Bolivia Takes On Goliath of Globalization (December 5, 2004)
Privatizations: the end of a cycle of plundering (november 1, 2004), globalization: europe's wary embrace (november 1, 2004), latin american indigenous movements in the context of globalization (october 11, 2004), mixed blessings of the megacities (september 24, 2004), dominican republic: us trade pact fails pregnant women - cafta fails to protect against rampant job discrimination (april 22, 2004), workers face uphill battle on road to globalization (january 27, 2004), money for nothing and calls for free (february 17, 2004), the next great wall (january 19, 2004).
This article examines the growth of geographical, physical and, increasingly, digital immigration barriers to the free movement of people between rich and poor countries. ( TomDispatch.com )
Areas of Work
Special Topics
Archived Sections
More from gpf.
FAIR USE NOTICE : This page contains copyrighted material the use of which has not been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. Global Policy Forum distributes this material without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. We believe this constitutes a fair use of any such copyrighted material as provided for in 17 U.S.C § 107. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond fair use, you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The State of Globalization in 2023
- Steven A. Altman
- Caroline R. Bastian

Data disproves the notion that the world has become more regionalized in recent years.
Plummeting flows of trade, capital, and people at the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic prompted a wave of speculation about the end of globalization, and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine brought even more predictions of a retreat toward national self-sufficiency. But, according to research for the latest DHL Global Connectedness Index, international flows show no signs of a sustained downturn. The data shows a broad pattern of decoupling between the U.S. and China, but the flows of countries that are geopolitically aligned with the U.S. and China do not — at least yet — indicate a broader split between rival blocs. Nor is there evidence that globalization is giving way to regionalization. While companies do need to adjust for heightened geopolitical tensions, they should not abandon global strategies. Corporate deglobalization, in fact, could be a riskier path than making focused adjustments to mitigate geopolitical risks.
Three key questions lie at the heart of debates about whether global crises and escalating geopolitical tensions have begun to reverse globalization: Has the growth of cross-border trade, capital, information and people flows gone into reverse? Are geopolitical tensions fracturing the world economy into rival blocs? And is globalization giving way to regionalization? The answer to all three questions — despite evidence of U.S.-China decoupling — is still “no.”
- Steven A. Altman is a senior research scholar, adjunct assistant professor, and director of the DHL Initiative on Globalization at the NYU Stern Center for the Future of Management .
- CB Caroline R. Bastian is a research scholar at the DHL Initiative on Globalization.
Partner Center

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.

A changing nation: the effects of globalisation on China
China is rapidly becoming the new champion of economic cooperation, trade and globalisation. As others retreat from the forefront, Chinese businesses are looking to expand and grow into all corners of the world.
China and globalisation are no strangers
The process has been happening for a long time, and it is essential that any business looking to break into China combines a global strategy combined with a market specific approach.
As the global economy shifts its focus towards China, new opportunities for businesses to enter the Chinese market are emerging. In other words, the impact of globalisation on China’s economic growth is already being felt. China is rapidly becoming the new champion of economic cooperation, trade and globalisation. As others retreat from the forefront, Chinese businesses are looking to expand and grow into all corners of the world.
A Chinese globalisation case study worth following is the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), devised by China’s premier Xi Jinping, which focuses on connecting the vast array of countries that sit within the region. It’s one of the reasons for the growth of globalisation on China, and this Chinese led trade network enables large, medium and small enterprises to realise their potential and trade more simply and expansively around Asia.
While businesses are eager to take to the world stage and reap the benefits of globalisation on China, they remain cautious of outsiders. Ensuring you are culturally sensitive will offset some of this reticence and businesses of any size must appreciate that Chinese business culture does not follow Western norms.
Businesses that wish to be successful in China need to not only consider the business culture, but also how regulations and political policies are shaped by that culture.
The shift towards protectionist attitudes that we have seen in some key markets are examples of Western politics negatively affecting the global ambitions of Chinese businesses. It is actually in spite of this that the outlook is still positive and demonstrates the resilience of Chinese businesses. Another good globalisation case study for China is Huawei, which shows this resilience and continues to expand its global market share.
Businesses that wish to be successful in China need to not only consider the business culture, but also how regulations and political policies are shaped by that culture. Building trust is key, as is working with local partners who understand the local landscape. It is imperative in Chinese business to show you are trying to work towards a mutually beneficial outcome.
Protectionism may bring short-term benefits but the global economy would suffer if the flow of capital and business were less dynamic. One should not react by shutting out outsiders. As the ideas of reciprocity and benevolence indicate, cooperation is a better way to succeed. As businesses large and small continue to look abroad for growth, it has become more important than ever to realise the power of diversity.
So, with all these considerations in mind, how has globalisation affected China?
The answer might be that while globalisation has boosted expansion and interaction within political, economic and cultural terms, it has also brought friction and conflict – which foreign businesses can help to assuage through understanding working practices in China.
Crucially, businesses must keep in mind that China is seeing a divergence between its generations. The young are more aware of the outside world and often more tolerant of different people and values. On the other hand, the older generations in China do not have much experience of the rest of the world, but they appreciate people who try to become more informed and understand Chinese culture. At the same time, as the younger Chinese look outwards, so does the government, and it is this shift in perceptions that presents the greatest opportunity for businesses to work in partnership with the Chinese. To become a global business player, one needs to be a global thinker first.
With this in mind, the Chinese way of conducting business is likely to become even more relevant, particularly as the previous instigators of global cooperation opt to retreat from the forefront of an increasingly connected world. Thus, while it is still not clear what direction China and globalisation are taking in respect of each other, and it remains unclear what shape plans such as the BRI will take, we are in a position where understanding the Chinese way of doing business is crucial not only for being successful in China, but also the wider world.
Finding Opportunity in Change - article 6
Key strategies for business leaders in the changing global economy.
Read the sixth article in the series >>
Finding Opportunity in Change homepage >>

June 5, 2021
Case study on globalisation.
INTRODUCTION
Globalisation has created more competitive environment in India. Knowing the need of this modern era most of our companies are prepared their strategy to face &enjoy global market. Viraj Co. one of major Steel Co. located in Tarapur MIDC (Tal. & Dist. Palghar) in the year 1991 and presently enjoying good success in global market. This research paper with the study of positive and negative impact of globalization and challenges of globalization also conducted case study of Viraj Profile Co. for studying how this company is facing Challenges of Globalisation.
OBJECTIVE OF THE CASE STUDY
1) To study positive & negative impact of Globalisation on Indian economy.
2) To find out the Challenges created by Globalisation.
3) To study whether Indian Companies are in position to face challenge of globalization.
Positive Impact of Globalisation
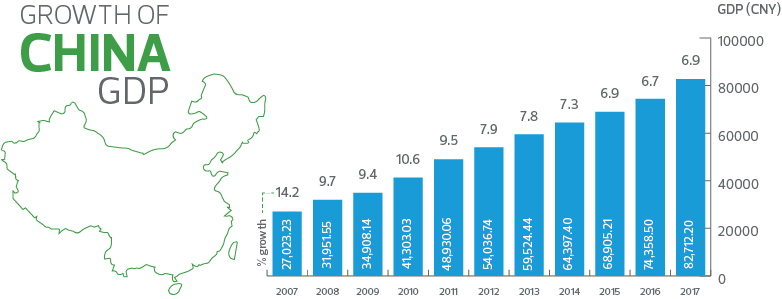
1) The rate of growth of the Gross Domestic Product of India has been on the increase from 5.6 % during 1980-90 to 7% in the 1993-2001 periods. In the last four years, the annual growth rate of the GDP was impressive at 7.5 % (2003-04), 8.5 % (2004-05), 9% (2005-06) and 9.2 % (2006-07).
2) The foreign exchange reserves (as at the end of the financial year) were $ 39 billion (2000-01), $ 107 billion (2003-04), $ 145 billion (2005-06) and $ 180 billion (in February 2007). It is expected that India will cross the $ 200 billion.
3) The cumulative FDI inflows from 1991 to September 2006 were Rs.1, 81,566 cr. (US $ 43.29 billion)., etc. In the inflow of FDI, India has surpassed South Korea to become the fourth largest recipient.
4) India controls at the present 45 % of the global outsourcing market with an estimated income of $ 50 billion.
5) As per the Forbes list for 2007, the number of billionaires of India has risen to 40 (from 36 last year) more than those of Japan (24), China (17), France (14) and Italy (14) this year.
6) The services sector acts as the engine of growth of the economy with a contribution of more than 60 % of GDP. India is ranked 18th among the world’s leading exporters of services with a share of 1.3% in world exports. (Source: Economic Survey 2000& 2005).
Negative Impact of Globalisation
• Exploitation of Underdeveloped Countries: Multinational Corporations (MNCs), based in developed countries, purchase at lower rates the raw materials from backward countries, process them in their own countries and sell the manufactured goods with big profit in backward countries.
• Increase in Unemployment: The MNCs employ machines to reduce the number of employees: they are capital intensive rather labor. Widening of Rich-poor Gap: Globalisation brings benefits to the rich who are small in number and keeps the vast majority of people in poverty.
• Harmful Effects on Small Industries and Small Business: In the free economy, the big fish has got license to eat the small fish. Small-scale and cottage industries cannot grow in competition with big ones. Destruction of Environment: Globalisation would destroy environment. In the name of economic development, environment is getting affected.
Case study of Viraj Profiles Limited
Viraj Profiles Limited founded by Mr Neeraj Raja Kochher
( Chairman & Managing Director) in the year 1991 in Tarapur MIDC (Tal. & Dist. Palghar).It was started as a small induction furnace to manufacture utensil grade steel for domestic markets with employee strength of 150 people. Over the years the company expanded its operations across the globe, increased its product portfolio and today the company boasts of employee strength of 9000. Under the leadership of Mr. Neeraj Kochher , Viraj has expanded its foot prints across 6 continents, more than 90 countries and is currently serving to more than 1300 satisfied customers.
Now it is the second largest manufacturer of stainless steel long products in the world and is ranked number one in stainless steel flanges. Fundamental in ensuring the continuous growth of the organisation, Mr Neeraj Raja Kochhar has transformed the company into, one of the fastest growing business houses in India, is currently a major player in the global stainless steel market with a capacity of 528,000 tonnes per annum and with an annual turnover of over US $ 1.5 billion. Over the last 20 years the Co. has achieved over 90 product certifications and approvals in the petrochemical, food and beverage, construction, pharmaceutical, defence and marine industries.
Mission of the Company:
• To be one stop shop for stainless steel engineering products.
• To be the first preference of the global market leaders.
• Up gradation and adaption of latest technology.
• Product and market development for maximizing value.
• Delivering operational excellence.
• Continual growth through customer service, innovation, quality& commitment.
• Plough back income to diversify into stainless steel projects.
• To be a responsible & abiding Corporate Citizen.
• Committed for a greener environment.
• To be the organization of choice & a great place to work.
• Openness to backward & forward integration to sharpen.
CHALLENGES OF GLOBALISATION
1) To ensure that the benefits of globalisation extend to all countries.
2) To ensure that the benefits of globalisation extend to all parts of the country.
3) To tackle the increased global competition.
4) To protect labour rights, employment practices, and the environment.
In this challenging environment Viraj Profile Co. is continuously making growth because of some following reasons:-
Its performance oriented culture, qualified and experienced HR professionals, aims to encourage employees to perform beyond their roles and responsibilities,upgradation and adaption of latest technology, product and market development for maximizing value , Delivering operational excellence, Continual growth through customer service, innovation, quality and commitment . Their safety and wellbeing facilities for employees such as Medical Insurance, Pick up and Drop facility, periodic health camps, Doctor on campus, hostel facilities etc , Professional Growth , Adequate well trained and motivated manpower, Adequate container/cargo handling equipment, M&R Facility, World Class Fire Fighting equipments etc.
Suggestions to make Globalisation successful
1) The globalisation has brought exceptional opportunities for human development for all, in developing as well as developed countries. Under the commercial marketing forces, globalisation has to be used more to promote economic growth to yield profits.
2) India should pay immediate attention to ensure rapid development in education, health, water and sanitation, labor and employment so that under time-bound programes the targets are completed without delay.
3) A strong foundation of human development of all people is essential for the social, political and economic development of the country.
4) Initiative by government for training to small scale entrepreneurs.
5) The government should take immediate steps to increase and create additional employment opportunities in the rural parts, to reduce the growing inequality.
6) There should perfect strategy for a sustainable and productive growth.
7) Mere growth of the GDP and others at the macro level in billions does not solve the chronic (unending) poverty and backward level of living norms of the people at the micro level. The growth should be sustainable with human development and decent employment potential. The welfare of a country does not percolate from the top, but should be built upon development from the bottom.
Aishwarya Says:
I have always been against Glorifying Over Work and therefore, in the year 2021, I have decided to launch this campaign “Balancing Life”and talk about this wrong practice, that we have been following since last few years. I will be talking to and interviewing around 1 lakh people in the coming 2021 and publish their interview regarding their opinion on glamourising Over Work.
If you are interested in participating in the same, do let me know.
Do follow me on Facebook , Twitter Youtube and Instagram .
The copyright of this Article belongs exclusively to Ms. Aishwarya Sandeep. Reproduction of the same, without permission will amount to Copyright Infringement. Appropriate Legal Action under the Indian Laws will be taken.
If you would also like to contribute to my website, then do share your articles or poems at [email protected]
We also have a Facebook Group Restarter Moms for Mothers or Women who would like to rejoin their careers post a career break or women who are enterpreneurs.
You may also like to read:
Misuse of Section 295A as a weapon against the content on OTT Platforms – 1 – Aishwarya Sandeep
Insanity as a Defense under IPC 3 – Aishwarya Sandeep
Over Population – Aishwarya Sandeep
Featured articles
Basic intellectual property rights for digital content creators, the doctrine of preemptive defense: legal implications and controversies, sebi regulatory framework for ipos in india, debentures – a brief on alternative source of capital, a study on the principle of separate legal entity and its exception, a comparative analysis between sole proprietorship and one person company, related articles.
This article has been written by Dr Tamanna Khosla, a first year student of Lloyd college. Every war when it…
The Nuremberg Trials and the Establishment of the Legal Principles for War Crimes
This article has been written by Shikha Jain, a 1st year student of Maharashtra National Law University, Mumbai. Abstract…
Live in relationship and inheritance of property – current scenario
This article is written by Ms. Akriti Gauri 2nd year law student Lloyd Law College, Greater Noida. ABSTRACT: A live-in…
Child custody and guardianship: a legal complexities
This article is written by Ms. Akriti Gauri 2nd year law student Lloyd Law College, Greater Noida. ABSTRACT:- The article…
Definition of state jurisdiction in International Law
This Article has been written by A. Taibah Fathima, a 5th year BA.,LLB student from Government Law College, Villupuram, Tamil…
Defining and regulating state immunity in International legal practice
Legal implications of the india – taiwan bilateral relations.
This article is written by HARSHIT SINGH SOLANKI of semester 3 from S.S.Jain Subodh Law college. ABSTRACT The article explores…
The case concerning the legality of the use of force (Serbia and Montenegro vs United Kingdom ) (2004) use of force and State responsibility.
This article has been written by Mr. Suryansh Katoch a 1st year student of Army Law College, Pune, Maharashtra. …
The Case Concerning the Legal Consequences of the Construction of a Wall in the Occupied Palestinian Territory (2004): Human Rights and State Responsibility
This article has been written by Mr. Omkar Tamhane, a first-year student at Maharashtra National Law University, Mumbai. ABSTRACT…
The Montevideo convention on the rights and duties of states: statehood criteria and historical context
This Article is written by Ms. Sreya Saloni 2nd year law student from Lloyd Law College Greater Noida. Abstract: The…
Probate process navigating inheritance challenges in India
This article has been written by Ms. Gargi Lad, a third-year student at NMIMS, School of Law, Bangalore. INTRODUCTION…
Indian’s compliance with the International Convention for the regulation of whaling
This article has been written by Ms Anna Kapur a 2nd year student of Bharti Vidya Peeth New Law College,…
WhatsApp us
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
Breadcrumbs Section. Click here to navigate to respective pages.

Economic consequences of globalisation: case study of Thailand
DOI link for Economic consequences of globalisation: case study of Thailand
Click here to navigate to parent product.
The paper reviews empirical works examining the effect of globalisation in Thailand, beginning with a discussion of its integration into the economy. Three drivers of economic globalisation are emphasised: international trade, foreign direct investment, and cross-border labour mobility. The finding points to globalisation’s potential to create a favourable economic impact. Opening up to international trade could promote productivity and drive economic growth. Large FDI inflows enticed by export-oriented industrialisation are likely to generate horizontal technological spillovers within a given industry; vertical spillovers through the linkages were not a robust result. There is no evidence that employing foreign workers retards firm productivity; rather, the opposite is the case. It is the well-performing firms that are in a position to attract foreign workers and maintain production capacity. Global production sharing (GPS) does not necessarily mean the participating countries are trapped into the low end of the quality ladder. The Thai experience supports for further globalising its economy. Any possible side effects to globalisation can be mitigated by other policies such as strengthening the social safety net.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Taylor & Francis Online
- Taylor & Francis Group
- Students/Researchers
- Librarians/Institutions
Connect with us
Registered in England & Wales No. 3099067 5 Howick Place | London | SW1P 1WG © 2024 Informa UK Limited
A Global version of Locals (a case study on globalization, media & the socio-cultural trends in Türkiye)
- Original Paper
- Published: 06 March 2023
- Volume 3 , article number 54 , ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- Eyad Trabulsi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5123-2897 1
148 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Globalization creates opportunities to local communities if it is addressed via an organized process and by well-structured institutions. Economy has played a key role in promoting globalization, thus, other aspects/dimensions of globalization (i.e. Socio-Cultural, Communicative, and Political) might be more essential for globalization in order to influence local communities. The paper explores the context of trends captured in the Turkish urban & national plans, their potential consequences (opportunities and challenges), and taking into consideration ‘ globalization ’ impact within their broader dimensions (e.g. Socio-Cultural); in order to achieve this mission, and to identify the future trends, the paper conducts: Text /discourse analysis, capturing the most frequently used words in 2 of the main Turkish urban /national plans; Keywords relevance measure. The paper also draws future scenarios, based on the captured trends, forecasting the future potentials and risks.The paper question is: How globalization trends residing in Turkish urban & national plans influence the Future Scenarios of Türkiye? The study is important in order to draw attention to the significance of Socio-Cultural dimension of globalization in shaping the future of nations, and to the profound consequences of its impact. It demonstrates how powerful is Socio-Cultural aspect of urban /national planning in preparing the ground for better future, in light of the significant challenges of globalization on local communities /states.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Understanding urban sustainability through newspaper discourse: a look at Germany

The Symbolic Power of the Global: Interpreting Cultural and Ideological Change in Melbourne, Australia

Analysis of the Themes and Evolution Trends of Urban Renewal Policies in Hangzhou—Based on a Text Mining of the Policy Documents from 2002 to 2021
Data availability.
Data supporting the results reported in the article can be found (if applicable) via the provided references only at the end of the research.
Akhmetov Timur (2018) Strategic culture of Turkey. Gaziantep Univ J Soc Sci 17(453):470
Google Scholar
Altheide DL (2019) THE MASS MEDIA. In David RP, Altheide L (eds) The Media as Culture. ResearchGate (pp. 657–684)
Billard TJ, Gross L (2020) LGBTQ Politics in Media and Culture. OXFORD RESEARCH ENCYCLOPEDIA. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 1–19
Brenner N (2004) New State Spaces: Urban Governance and the Rescaling of Statehood. OUP Oxford, Oxford
Book Google Scholar
Cutler AC, Haufler V, Porter T (1999) Private Authority and International Affairs. Suny Press, New York
Duygu ÜNALAN ŞD (2019) Globalization and Media: Dissemination of Culture Through Media. In A. D. Gürhan TOPÇU, Communication Studies (pp. 1-24). Ankara: GENERAL DISTRIBUTION Akademisyen Kitabevi A.Ş
Hjelm OA (2022) Mass media logic and social media logic in news on Facebook. Malmo University, Malmo
Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality. (n.d.). Vision 2050 Istanbul. Retrieved June 1, 2021, from Vision 2050 Istanbul: https://vizyon2050.istanbul/en
MonkeyLearn. (n.d.). Monkey Learn | WordCloud. Retrieved June 22, 2021, from Monkey Learn: https://monkeylearn.com
Lambe Kayode Mustapha AA (2011). Globalization, Global Media and Homogenization of Global Culture: Implications for Islam and Muslims. National Seminar on New Media and Islamic Issues: Challenges and Opportunities (p. 35). ResearchGate.
Oran B (2002). Türk Dış Politikası. İletişim Yayıncılık.
Picciotto S (2006). Regulatory Networks and Global Governance. The retreat of the State: Challenges to Law and Lawyers . Institute of Advanced Legal Studies, University of London
Presidency of The Republic of Turkey. (2019). 100th Year Turkey Plan. the Eleventh Development Plan (2019–2023) . Ankara, Ankara, Turkey: Presidency of Strategy and Budget
Ramirez DG (2020) JOURNALISM IN THE ATTENTION ECONOMY:the relation between digital platforms and news organizations. Brazilian J Res 17(4):27
Rhydderch A (2017). Scenario Building: The 2x2 Matrix Technique. Futuribles International
Sassen S (1991) The Global City: New York, London. Princeton University Press, Tokyo
SDGs, U. (n.d.). SDGs. Retrieved June 14, 2021, from The 17 Goals | Sustainable Development: https://sdgs.un.org/goals
Statista.com. (2019). Penetration of leading social networks in Turkey as of 3rd quarter 2019, by platform. Retrieved June 25, 2021, from Statia: https://www.statista.com/statistics/284503/turkey-social-network-penetration/
Strokes M (1999) Sounding Out The Culture Industries and the Globalisation of Istanbul. In: Keyder Ç (ed) Between the Global and the Local. Rowman and Littlefield, Boulder CO, Lanham, pp 121–139
UNDP, G. C. (2018). Foresight Manual - UNDP. Retrieved June 22, 2021, from UNDP: https://www.undp.org
Weiss L (2003) States in the Global Economy. Cambridge Studies in International Relations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 245–270
Download references
Acknowledgements
There is no funding organizations, individuals, or entities that supported in any financial funds to this research whether partially or in full.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Urban & Regional Planning Department, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, Türkiye
Eyad Trabulsi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
There is only one author for this paper who prepared it and is submitting it for publishing.

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Eyad Trabulsi .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
No committee has approved this research, as it was prepared for the purpose of submitting a term paper at the Culture and Urban Space course at ITU; Confirmation that all research was performed in accordance with relevant guidelines/regulations applicable when human participants are involved (e.g. Declaration of Helsinki, or similar).
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (PDF 258 KB)
Supplementary file2 (docx 19 kb), rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Trabulsi, E. A Global version of Locals (a case study on globalization, media & the socio-cultural trends in Türkiye). SN Soc Sci 3 , 54 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-023-00635-5
Download citation
Received : 03 May 2022
Accepted : 05 February 2023
Published : 06 March 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-023-00635-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Globalization
- Urban Planning
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Fast and Pluribus: Impacts of a Globalizing McDonald’s
The expansion of McDonald’s in the twentieth century brought the fast food chain to more than 100 countries. But how well did it integrate into its new home(s)?

The connection between globalization and McDonald’s is a tale of scholarly metonymy. There’s no textual shortage of evidence that references the now-global fast food chain’s success in other countries , often linking it to themes of self-sufficiency, post-industrial stability, and democracy-formed capitalism.

Among these chunks of research is a more endogenous angle that examines the impact McDonald’s has had within offshore cultures; namely, how the American fast food model has been diffused across different countries. Such case studies, which look at individual cultural phenomena and their direct applications to globalization activity, refines not only the framework of McDonald’s in theories, but overall globalization processes and strategies as well.
Japan’s stylish renditions of fast food practices, for one, existed long before McDonald’s came to the country. Given the existing popularity of convenient and on-the-go meals—including conveyor belt sushi and street vendor meals—American fast food chains were bound to succeed. Scholars John W. Traphagan and L. Keith Brown investigate this supposition by employing an ethnographic model of research, building the argument that Japan not only assimilated—but basically swallowed whole—the McDonald’s dining model , to the point that younger people especially believe McDonald’s is a Japanese company.
Traphagan and Brown emphasize that, rather than “styles of preparation or ingredients,” fast food is defined by “a style of selling food.” Essentially, McDonald’s brought no real paradigm shifts to Japan—but rather constructed a space in which already-formed Japanese cultural practices could continue.
Their case study contrasts with that of geographers Ray Oldakowski and John McEwen, who similarly investigate McDonald’s and its cultural assimilation—but in Ecuador. Their evidence shows that the integration of American fast food dining followed a different path , and McDonald’s remains an obviously foreign establishment in the cityscape. McDonald’s didn’t attempt to adapt to Japanese or Ecuadorian culture (for McDonald’s, “the strategy has been one of consistency, i.e. McDonald’s prefers not to change its way of doing business to adapt to foreign cultures, rather, it changes local cultures to meet its own needs,” they note), but Ecuadorians clearly viewed the fast food chain as a deviation from local tastes, unlike Japanese consumers.
“[A] comparison of exterior designs revealed that the McDonald’s in Guayaquil [Ecuador] were very similar to the typical McDonald’s restaurants in the United States,” write the authors. Moreover, the menus were also similar. Only 2 percent of those polled considered the food served at McDonald’s similar to Ecuadorian food. In contrast, very few interviewees considered Kentucky Fried Chicken—another American fast food establishment—different from Ecuadorian food. Eighty-four percent reported that KFC was the most similar to Ecuadorian food, and 68 percent said it was actually where they dined regularly.
Weekly Newsletter
Get your fix of JSTOR Daily’s best stories in your inbox each Thursday.
Privacy Policy Contact Us You may unsubscribe at any time by clicking on the provided link on any marketing message.
“Those results suggest that McDonald’s might gain new customers, and more visits from existing customers, if they also offered menu items more typical of Ecuadorian food,” conclude the authors.
In neither Japan nor Ecuador did McDonald’s actively work to adapt itself to the tastes of the host countries, but the depth of integration into local dining customs differed between the two nations. Such observations could prompt additional nation-specific analyses and possibly reveal additional adaptations to the “strategy of consistency” associated with McDonald’s. However, the study of the globalization of fast food from a micro-cultural angle requires challenging assumptive attitudes around American businesses and classical theories, with one of the most popular—and infamously controvertible—examples being the Golden Arches Theory of Conflict Prevention , built on tropes of democratic peace through development. Globalization and its effects could also be examined in light of McDonald’s cultural impacts on its origin country of America, opening a conversation on socio-economics and class .
Support JSTOR Daily! Join our new membership program on Patreon today.

JSTOR is a digital library for scholars, researchers, and students. JSTOR Daily readers can access the original research behind our articles for free on JSTOR.
Get Our Newsletter
More stories.

The Georgia Peach: A Labor History

Modern Piracy: Arbitration as Plunder

Islands in the Cash Stream

Why Call for Divestment?
Recent posts.
- The Barrier-Breaking Ozark Club of Great Falls, Montana
- Building the Olympic Games
- Windmills, Arabic, and an Environmental Victory
- The Stickiness of Teflon
- The “Mexican-Hindus” of Rural California
Support JSTOR Daily
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Reliable knowledge. Facts you can trust. Insights you can use.

Copyright Statement

The Case for Globalization
May 05, 2022
By Li Wei, Professor of Economics at Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business

The First Wave of Globalization
According to the American economist Frederic Mishkin, the period from 1870 to 1914 was the first wave of globalization. At that time, global trade grew at an average annual rate of 4%, and its share of global GDP increased from 10% in 1870 to 20% in 1914. International capital flows increased at an average annual rate of 4.8%, rising from 7% of global GDP in 1870 to 20% of GDP in 1914. In his famous book published in 1919, The Economic Consequences of Peace, John Maynard Keynes wrote fondly of this era:
“What an extraordinary episode in the economic progress of man that age was which came to an end in August, 1914!…An inhabitant of London could order by telephone, sipping his morning tea in bed, the various products of the whole earth, in such quantity as he might see fit, and reasonably expect their early delivery upon his doorstep; he could at the same moment and by the same means adventure his wealth in the natural resources and new enterprises of any quarter of the world, and share, without exertion or even trouble, in their prospective fruits and advantages; or he could decide to couple the security of his fortunes with the good faith of the townspeople of any substantial municipality in any continent that fancy or information might recommend.”
This first wave of globalization was accompanied by unprecedented economy prosperity. From 1870 to 1914, global GDP per capita grew at an annual rate of 1.3%; While from 1820 to 1870, it only grew by 0.53%.
Another benefit of globalization is that it accelerates the development of poorer countries. Japan is a prime example – since the 17 th century, Japan was closed to the outside world, but after the Perry Expedition arrived at the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1853 with their “black ships”, Japan had no choice but to trade with the United States, which led to Japan opening its border. This eventually led to the Meiji Restoration of 1868 and Japan’s full integration of the Japanese economy into the global economy. In 1870, Japan’s per capita income was less than 25% of Britain’s. But from 1870 to 1913, the gap between the two countries narrowed – Japan’s per capita income grew by 1.5%, while Britain’s only grew by 1.0%.
The opposite case happened in China. After the Opium War, although China gradually opened its doors, reform was slow. Unlike Japan, China was not fully integrated into the global economy – this caused the gap between China and more advanced countries to widen. In 1870, for example, China’s per capita income was equivalent to 24% of Britain’s, and by 1914, that had fallen to 13%.
The End of the First Wave of Globalization
Along with the economic prosperity brought by the first wave of globalization came the awakening of national consciousness in many countries, which ultimately contributed to the outbreak of World War I. As violence spread across the world, normal trade and investment activities were greatly disrupted, thus ending the first wave of globalization. Unfortunately, the postwar years were also full of turmoil – from 1914 to 1929, the average international trade-to-GDP ratio fell from 22% to 16%, and capital flows fell from 20% to 8%.
The worst was still yet to come. In 1929, the United States fell into an economic crisis, which soon spread to other countries and placed the global economy under enormous pressure. Unemployment in America was at 25%, and per capita income fell 30% by 1933, and was only slightly higher in 1939 than in 1929. To protect themselves, countries adopted beggar-thy-neighbor economic policies, such as the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act in the United States in 1930, which sharply increased tariffs on imported goods. Britain withdrew from the gold standard in 1931, causing the pound to fall, and thus winning more market share for its products globally. It also raised tariffs on imported goods. As some countries abandoned the gold standard and devalued their currencies, those countries that were still tied to the gold standard felt they were “getting the short end of the stick” and followed suit, devaluing their currencies and imposing import taxes. As a result, no one won in this zero-sum game. There was a period of breakdown in international trade and finance which was later described as a “currency war”. Towering tariffs caused the trade volume to plummet worldwide.
The economic crisis brought years of economic decline in the United States, historically known as the Great Depression. However, the situation was far worse in Germany and Italy. As their economy collapsed and social tensions intensified, democratic governments could not control the situation, which led to fascist governments rising to power. As soon as they came to power, they adopted a “guns before butter” model, vastly expanding military spending and preparing for war. Within a few years, World War II broke out, which was the largest war ever fought by mankind. Losses were also the greatest with at least 50 million people losing their lives from 1939 to 1945, more than half of them civilians.
Mishkin believed that the end of the first wave of globalization and the outbreak of two world wars taught us two lessons: one is that globalization is not an irreversible process; the second is that the consequences of rejecting globalization could be catastrophic.
China in the Globalized World
After World War II, in order to prevent another world war, capitalist countries led by the United States established the Bretton Woods system. The system was characterized by its “dual peg”, whereby the dollar was pegged to the gold (at the time the U.S set the price of gold at USD $35 an ounce), and other currencies were pegged to the dollar. The three institutions – the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank and the World Trade Organization (WTO) – were established at this time. Following this period was the development of a new wave of globalization.
In this new wave, Japan developed first, followed by the Four Asian Tigers (i.e. South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, and Hong Kong), and finally China. Before 1978, the atmosphere of the Cold War was still very apparent, and China’s top leaders were focused on war and revolution at the cost of economic development. However, after 1978, with Deng Xiaoping at the helm of a new generation of leaders, peace and economic development were brought to the forefront of policy in China. Fortunately, the leaders at that time did not adopt a closed-door policy, but chose to integrate into the global financial system, similar to the way Japan and the Four Asian Tigers had done. Since then, foreign investment flooded into China, bringing not only capital but advanced technology and ideas, which greatly boosted China’s economy. At the same time, China also joined global supply chains through foreign trade, and continually increased its production capabilities and market size.
After reform and opening up in 1978, China was lucky to catch on to a period when globalization was in full swing. Since China’s economy is deeply integrated into the global economy, it could be said that without globalization, China’s economy would not be where it is today.
It is clear from these examples that solitary development cannot exist in a modern economy. The modern economy is interconnected, and only by embracing globalization can a country achieve economic growth. Isolation from the global economic system will only lead to impoverishment and the weakening of an economy. Today, Russia is facing a very difficult situation because not only is it facing economic sanctions from governments in Western countries but is also facing a backlash from Western companies. Western corporations, such as Visa and Mastercard, have announced their withdrawal from the Russian market. Russia’s relations with the western world are now under a high state of uncertainty, and this poses a serious threat to globalization.
Globalization is China’s lifeline. Maintaining it will mean making difficult decisions. What China does next to preserve the global order will have implications that go beyond our lifetime.
Enjoying what you’re reading?
Professor profile.

Professor of Economics, Associate Dean for Asia and Oceania, Director of Case Center and Director of Big Data Economic Research Center, Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business (CKGSB) PhD, University of Michigan
Related Articles
The chinese economy is due a round of quantitative easing.

26 January 2024
Limitless Supply Economics

22 January 2024
Using ‘fusion’ to help generate new growth within an enterprise

16 November 2023
Mixing it up

03 April 2024
Driving change

02 April 2024
Meeting in the middle

Economic Refurbishment

01 April 2024
Our Programs

The Biotech Innovation Program
--> global unicorn program series -->.
This program equips CEOs and founders in the life sciences and biotechnology industry with the essential knowledge and connections needed to thrive in this rapidly evolving sector.
Location University of California, San Diego, USA
Date September 9-13, 2024
Language English

CKGSB-ESCP Global Unicorn Program in Luxury & Tech
Delivered collaboratively by ESCP and CKGSB, this immersive program is tailored for visionary global leaders seeking to navigate the intersection of luxury and technology.
Location ESCP Montparnasse Campus, Paris
Date September 23-26, 2024

CKGSB-ESMT Global Unicorn Program in Deep Tech
The program will provide practical business strategies to grow, scale, globalize, and potentially exit deep tech ventures and will touch upon the latest insights on deep tech advancements, such as AI, cutting-edge computing, and cybersecurity innovation.
Location Berlin
Date October 28-31, 2024

Global Unicorn Program: Scaling for Success in the Age of AI
In collaboration with the Stanford Center for Professional Development (SCPD), this CKGSB program equips entrepreneurs, intrapreneurs and key stakeholders with the tools, insights, and skills necessary to lead a new generation of unicorn companies.
Location Stanford University Campus, California, United States
Date Dec 09 - 13, 2024
Emerging Tech Management Week: Silicon Valley
This program offers insights into emerging technology developments and the skills required to innovate, grow, and transform your business strategy.
Location University of California, Berkeley, USA
Date November 3-8, 2024

Get China insights delivered directly to your inbox!
We use cookies to personalise content and ads, to provide social media features and to analyse our traffic. We also share information about your use of our site with our social media, advertising and analytics partners who may combine it with other information that you’ve provided to them or that they’ve collected from your use of their services.

Understand China from the inside
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter today!
- Upcoming Events
- CKGSB Knowledge Magazine
- China Insights
- CKGSB Newsletter
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Economic globalization in the 21st century: A case study of India
- Author & abstract
- 6 References
- Most related
- Related works & more
Corrections
(Assistant Professor, Christ (Deemed to be) University, NCR, India)
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher, references listed on ideas.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
Identifying shrinking cities from a physical city perspective and influencing factors: A case study of the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle in China
- Cao, Naigang
- Wen, Yanfang
- Wang, Jinghan
- Gao, Xiaotong
- Sun, Pingjun
Urban shrinkage, increasingly prevalent in fast-developing countries like China, is a complex phenomenon deeply influenced by globalization and localized factors. This study focuses on the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle, a high-growth region in China, to explore urban shrinkage and its driving factors. Adopting a physical city perspective and utilizing a two-step diagnostic method, the research precisely identifies shrinking cities within the circle and employs a geo-detector model for empirical analysis of influencing factors. Findings reveal a significant developmental imbalance within the circle, with sustainable and transitional growth cities located in core areas, whereas significantly shrinking and potential shrinking cities are found in peripheral zones. This pattern underscores the endogenous challenges of rapid urbanization. The study highlights that urban shrinkage results from interplay between demographic and economic changes, with fiscal autonomy, consumption levels, public service provision, per capita GDP, and industrial structure being key factors. Addressing urban shrinkage effectively requires a shift from traditional balanced development paradigms towards fostering regional coordinated growth, emphasizing the construction of a multi-core urban network and integrating small and medium-sized cities into the developmental process. This innovative approach not only enriches urban shrinkage research but also offers practical insights for sustainable urban governance.
- Shrinking cities;
- Physical city;
- Two-step diagnostic method;
- Influencing factors;
- Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The State of Globalization in 2022. Globalization Digital Article. Steven A. Altman. Caroline R. Bastian. Its collapse has been vastly overstated, according to an analysis of international flows ...
The State of Globalization in 2021. by. Steven A. Altman. and. Caroline R. Bastian. March 18, 2021. Suriyapong Thongsawang/Getty Images. Summary. As the coronavirus swept the world, closing ...
Highlight that 1) technological advances have increased globalization and 2) globalization has a direct impact on their daily lives in the food they eat. This sets the stage for a deeper look at the impact of globalization through case studies. (15 Minutes) Reading - The Impact of Globalization: Divide the class into three groups and assign ...
7 Pankaj Ghemawat and Jamie L. Matthews, "The Globalization of CEMEX," Harvard Business School Case No. 701-017. 8 Joel Podolny and John Roberts, "CEMEX, S.A. de C.V.: Global Competition in a Local Business," Stanford University Graduate School of Business, Case No. S-IB-17. 9 L. Hossie, "Remaking Mexico," The Globe and Mail, February 7 ...
The purpose of this research report was to assess McDonald's globalization strategy. We examined McDonald's strategy across six dimensions: menu, promotion, trademarks, restaurants, employees, and service. We also compared the company's performance across these six dimensions in 10 different countries: Saudi Arabia, France, the United Kingdom ...
Globalization expands and accelerates the movement and exchange of ideas and commodities over vast distances. It is common to discuss the phenomenon from an abstract, global perspective, but in fact globalization's most important impacts are often highly localized. ... Migration is a major factor in global society. A recent study shows how the ...
strong position to influence national (and international) law has long been The World Bank and Crimes of Globalization. 17. recognized (Passas, 1999: 401). In an increasingly globalized world, we need to adopt conceptions of crime that transcend limitations of traditional state-based law.
Edexcel GCSE PE 9-1 Paper 2. 104 terms. dolphin898. Preview. A Level Edexcel Geography Globalisation - Enquiry Q1-Q3. 73 terms. matty2604. Preview. Computing mark scheme 2.
The State of Globalization in 2023. by. Steven A. Altman. and. Caroline R. Bastian. July 11, 2023. Daniel Grizelj/Getty Images. Summary. Plummeting flows of trade, capital, and people at the ...
Abstract. Amazon's success depends on the access it enjoys to a single and global market. While this has been true for now, the firm's CEO wonders whether he and others have taken globalization for granted. The case reviews the evidence and discusses the extent to which globalization could go into reverse mode.
A Chinese globalisation case study worth following is the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), devised by China's premier Xi Jinping, which focuses on connecting the vast array of countries that sit within the region. It's one of the reasons for the growth of globalisation in China, and this Chinese led trade network enables large, medium and ...
McKinsey Global Survey results:Five forces reshaping the global economyThe core drivers of globalization are alive and well, but executives are still grappl. ng with how to seize the opportunities of an interlinked world economy.An ongoing shift in global economic activity from developed to developing economies, accompanied by growth in the ...
Currently, over 70% of Coca Cola's business income is generated from non-US sources (Coca-Cola Company, 2012). In over a century, Coca-Cola has grown the company into a multi-million dollar business. However, the road to success has not always been easy for Coca-Cola. Many countries have banned the use of Coca-Cola products, claiming that ...
Coca-Cola is a company globalization example that reveals how successful globalization can be when done effectively. The company started off in the late 1800s selling the original Coca-Cola drink ...
A Chinese globalisation case study worth following is the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), devised by China's premier Xi Jinping, which focuses on connecting the vast array of countries that sit within the region. It's one of the reasons for the growth of globalisation on China, and this Chinese led trade network enables large, medium and ...
This study aims to investigate the relation between globalisation, which includes foreign direct investment (FDI), exports, imports, foreign remittances and economic growth in India. To achieve the said objective, Autoregressive Distributed Lag bounds testing approach has been utilised.
OBJECTIVE OF THE CASE STUDY. 1) To study positive & negative impact of Globalisation on Indian economy. 2) To find out the Challenges created by Globalisation. 3) To study whether Indian Companies are in position to face challenge of globalization. Positive Impact of Globalisation.
Jonathan Köhler is a senior scientist at the Fraunhofer ISI (Institute for Systems and Innovation Research). He has a PhD on Bounded Rationality in Savings Decisions.From 2000 to 2005, he was Research Theme Manager at Integrating Frameworks, Tyndall Centre, responsible for development and coordination of the research theme on Integrated Assessment methodologies for climate change policy ...
The paper reviews empirical works examining the effect of globalisation in Thailand, beginning with a discussion of its integration into the economy. Three drivers of economic globalisation are emphasised: international trade, foreign direct investment, and cross-border labour mobility. The finding points to globalisation's potential to ...
Globalization creates opportunities to local communities if it is addressed via an organized process and by well-structured institutions. Economy has played a key role in promoting globalization, thus, other aspects/dimensions of globalization (i.e. Socio-Cultural, Communicative, and Political) might be more essential for globalization in order to influence local communities. The paper ...
The connection between globalization and McDonald's is a tale of scholarly metonymy. There's no textual shortage of evidence that references the now-global fast food chain's success in other countries, often linking it to themes of self-sufficiency, post-industrial stability, and democracy-formed capitalism.. Among these chunks of research is a more endogenous angle that examines the ...
The First Wave of Globalization. According to the American economist Frederic Mishkin, the period from 1870 to 1914 was the first wave of globalization. At that time, global trade grew at an average annual rate of 4%, and its share of global GDP increased from 10% in 1870 to 20% in 1914. International capital flows increased at an average ...
Economic globalization, is defined as increased interconnectedness through higher trade volumes and enhanced capital flows. Factors such as better transport and communication facilities, relaxation in government policies, and advancement in technology (digitally and physically) have led to rapid economic globalization.
The possibility of a significant reversal of globalization has emerged recently as a central political issue with potentially fundamental economic consequences, reversing the trends towards greater openness and liberalization that have characterized world business since the Second World War. Such a major break away from past trends could have enormous consequences for all firms and especially ...
A Cosmopolitan Case against World Government, by Ilya Somin explains why support for globalization and opposition to global government are not contradictory positions.
Urban shrinkage, increasingly prevalent in fast-developing countries like China, is a complex phenomenon deeply influenced by globalization and localized factors. This study focuses on the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle, a high-growth region in China, to explore urban shrinkage and its driving factors. Adopting a physical city perspective and utilizing a two-step diagnostic method, the ...