Module 6: Reports
How to write a formal report, learning outcomes.
- Discuss how to write a formal report
Writing formal reports, like informal report, and that of any other writing task follows the same three steps. First is the planning. Second is the writing. Third is the revising.


Planning Your Formal Report
In all business writing, the first step is to check and see whether there is a prescribed structure for the document that is about to be created. If so, follow that. Many formal reports have specific formats that must be followed exactly. For example, some sales proposal requests and responses become part of a contract; therefore, you should ensure documents such as these have a legal review both in the planning of the document and as a part of the final review step.
Other steps in preparation of a formal report follow in the same way as those for an informal report. In an informal report, however, it is less likely there will be multiple writers. With a formal report, there may be many contributors. If so, it is important to meet as a group to divide the work, talk about style, and plan how the final document will be assembled and edited to ensure a common voice or tone throughout. You may wish to consider some of the strategies discussed in Module 12: Collaboration in and Across Teams.
Next you’ll complete any data gathering needed. A formal report likely requires extensive planning and data gathering: some proposals may require weeks or months in researching and preparing. For example, think about a proposal for the next three years of new store locations or construction. The author (likely a team of authors) will need primary and secondary research, which takes a great deal of time to gather and analyze.
You will use knowledge of that data to create the report’s outline. In constructing that outline, again consider the depth of understanding of the reader and the likelihood the reader’s views align with that of the report’s determination.
With group writing, there may be several coordination meetings at each stage of the document’s creation.
Writing Your Formal Report
Writing the formal report is a much easier task once you have created a detailed outline in the planning process. This outline is what helps the writing move along, as you already know exactly what is to be provided where and when. When writing a formal report as a team, a carefully constructed outline facilitates assigning sections of the report to different authors from the team. The writer or writers can then focus on paragraph structure, wording, and phrasing using the lessons found in Module 2: Writing in Business.
With a formal report, it is extremely rare to see the casual phrasing that might be found in a short message or informal report. Formal reports rarely use personal pronouns, contractions, or passive verb structures. However, this does not mean the language should be stilted or use excessively long words. You’ll continue to use the same clarity of wording as in all business communications.
Formatting Your Report
Formal reports implement many of the formatting skills you learned earlier. Usually formal reports are single spaced with double spaces between paragraphs. Usually paragraphs are not indented, but this may vary from organization to organization. The right hand side of paragraphs are left ragged.
Section headings are always provided in a formal report. It is acceptable to use labels to match the section’s purpose (e.g., Introduction, Findings, Research Methods). The headings may also use terms directly related to the report’s purpose such as “Fruit Spoilage Problem,” “Facts about Fruit Spoilage,” “Suggestions to Improve Fruit Freshness.” You may also have specific subheadings within more general section titles.
Formal reports of all types use page numbers.The pages may be numbered in a format such as 1–50, or they may be numbered by the section, such as Methods 1–Methods 50. The material in the front part of a report is generally numbered in lowercase roman numerals (i–ix).
Revising Your Formal Report
Because of the length and possible subject complexity of formal reports, the final review takes more time than you might expect and involves more people. As mentioned in the start of this section, some reports may require additional legal review.
The most effective way to ensure a professional document is to have a team of individuals independently read the document, marking changes, corrections, and questions as they go. This team then meets as a group with one individual charged with collecting all corrections. This person ensures continuity across the entire document. If such a formal process cannot be completed, then you should work to ensure there are at least two reviewers who review work they themselves did not write.
As mentioned before, the final revision must consider both grammar and style issues as well as revisiting the primary purpose of the document.
Practice Question
- Plan, Write, Revise Formal Report. Authored by : Susan Kendall. License : CC BY: Attribution


How to Write a Formal Business Report (Template and Examples)
Formal business reports are official documents that guide and inform stakeholders. These reports are valuable tools when solving company problems or making decisions.
You should be clear and include all relevant information to make your report useful in decision-making and problem-solving.
Here are five steps for writing a formal business report:
- Define the purpose and intended audience
- Gather and analyze data
- Create an outline
- Draft the business report
- Revise and format your report
Keep reading to get valuable details under every step and learn to segment your report.
But first, let’s delve deep into formal business reports, the different types, and what differentiates them. We’ll also discuss the elements of a business report and cover valuable tips to perfect your writing skills.
Let’s get started!
Understanding formal business reports
Business reports provide an analysis of the current performance of a business and offer recommended actions to improve operations. A formal business report should include detailed data, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations.
What is a formal and informal business report?
A formal business report is a detailed and organized document that provides information about a specific topic, like research findings, market trends, or a financial situation. It usually includes conclusions based on data collected during the research process.
Formal business reports can present complicated topics in an easy-to-understand format, allowing company executives to make informed decisions. A formal report typically includes an introduction, a body of information, and a conclusion. It should consist of accurate data and reliable sources and be written formally with proper grammar and spelling.
An informal business report does not follow traditional, formal reports’ formal structure and layout. Instead, it is written in an easy-to-understand language and typically includes summaries of key points, along with recommendations or suggestions for further action.
Unlike formal reports, informal business reports do not need to be approved by higher management and can be sent directly to the intended recipient. Businesses often use informal reports to quickly provide updates or summaries of projects, data, or other important information. They are also commonly used when sharing ideas, solutions, or findings that don’t necessarily require a formal response from the receiver.
While informal reports may need more depth and detail than formal reports, they can still communicate important information concisely and clearly.
Types of formal business reports
Formal business reports include different types that may be used to present data, analyze performance, or make recommendations. Examples of formal business reports include annual, research, feasibility, and marketing research reports.
Feasibility Reports
A feasibility report is an analytical document that outlines whether an activity or project has the potential to be successful. It includes cost estimates, expected outcomes, and other factors affecting the project’s success.
Business Plans
A business plan is a formal outline of a company’s objectives and strategies for achieving them. It is used to obtain financing, attract investors, and set goals for the company.
Business plans typically include sections on market analysis, organizational structure, competitive analysis, product or service description, financial projections, marketing strategies, and tactics.
Progress Reports
A progress report is a document that details the current status of a project or activity. It outlines the progress made, challenges encountered, and a timeline for when the project should be completed.
Financial Reports
Financial reports provide information about the company’s financial performance over some time. They include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
A proposal is a document that outlines how an organization, company, or individual intends to complete a project. It usually includes information such as the purpose of the project, expected outcomes, methods, and associated costs. For example, businesses may use proposals to solicit funding from investors or government agencies.
Market Research Reports
A market research report is a document that provides information about customer needs and competitor activities to develop strategies for the organization. They typically include data on consumer preferences, product demand, market trends, and other relevant factors.
Risk Reports
A risk report is a document that details the potential risks associated with a specific activity or investment. It outlines possible losses and considers how they could affect an organization’s operations. Risk reports may also include measures the organization can take to mitigate losses and recommendations for further actions.
Technical Reports
Technical reports are documents that explain the results of a technical project or investigation in detail. They are used to document the findings of a project and provide a record that can be used as reference material.
Technical reports typically include sections on research methods, results, conclusions, recommendations, and implementation plans.
What are the key differences between writing a business report and writing an academic report?
Business reports inform a decision or provide direction in the form of recommendations. They may include factual data and analysis but are often practical and focus on the actionable steps needed to achieve a goal.
Academic reports take a more analytical approach, emphasizing research and thought-provoking discussions that examine different points of view.
Sources used
When writing business reports, only use real-world sources such as government reports. But when writing academic reports, you may cite theoretical works .
Conciseness
When writing business reports, use concise points with stakeholders in mind . As for academic reports, you may use technical terms and lengthy explanations to support a point.
Academic reports are often longer and more detailed than business reports and may also include recommendations but with a focus on developing new strategies or ideas.
When writing a business report, adhere to the following structure: cover page, table of contents, list of figures, executive summary, introduction, body, conclusion, and recommendations.
But when writing an academic report, follow the structure: introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
The purpose of both types of reports is to provide information that is useful and relevant to the target audience. So keep the audience in mind when writing a report; what information do they need to know? How will it help them make decisions or understand a concept better?
Elements of a formal business report
An excellent formal business report organizes information into these sections:
- Table of contents
- List of Figures
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Recommendation
1. Title page
The title page indicates the company name (and logo), the author’s and readers’ names and positions, and the date.
2. Table of contents
The table of contents lists the sections of a report with their page number and helps jump to a specific title.

3. List of Figures
The list mentions every chart or diagram included in the report and its page number for easy navigation.

4. Executive summary
The executive summary briefly overviews the report’s key points, findings, and conclusions. It helps readers to understand the report’s data without reading the entire document. Therefore, this section should be the last to write since the facts in the report will form the executive summary.

5. Introduction
The introduction outlines the research objectives and methods used to generate data for analysis. It sets the stage for what follows. Unlike the executive summary, it does not mention any conclusion or recommendation.

The body contains an in-depth review of the research results and their implications. It may include an analysis of trends, correlations, pictorial evidence, and other data supporting the report’s conclusions.
7. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the data discussed in the body . It is a brief sentence that takes around three to six sentences.
8. Recommendation
The recommendation suggests an action based on the facts presented in the report. It outlines steps or policy changes necessary to solve a problem.
9. Appendix
The appendix contains information that supports your report but would be distracting if you included it in the body. This information may consist of raw data, charts, transcripts, and surveys used for analysis or any additional resources used in the research process. You may also include acronyms used in the report.

10. References/Bibliography
This section consists of all references you used in your report. Citations protect you from plagiarism and give credit to your sources. You can write citations in APA, MLA, and Chicago styles , depending on the style of your formal report.
11. Glossary
The glossary is where you define all technical terms used in the report. Use an asterisk next to words you will describe in the glossary to indicate that the reader should check the glossary for a definition.

How to write a formal business report step-by-step
When writing a formal business report, start by defining the purpose of the report and the intended audience. You then gather data and analyze it before writing the report. Finally, write the report and revise it accordingly.
1. Define the purpose and intended audience
Why are you writing the report? Consider what information you need to include and who will read the report. This will help you structure your document correctly and provide relevant information.
Defining your target audience will help you tailor the language used and choose relevant information to include in the report.
2. Gather and analyze the data
Collect all data relevant to achieving the goal of your report. This should include quantitative and qualitative data, such as customer satisfaction surveys, case studies, performance metrics, or feedback from stakeholders.
Once you have collected all of your data, analyze it and identify any trends or patterns that may be useful in writing the report. You can use various tools and techniques like statistical analysis , gap analysis , or cause-and-effect diagrams .
3. Create an outline
An outline will help you organize your research data, stay on topic, and avoid including unrelated information under a particular title. Besides having a section of each formal business report element above, outline your key points, headings, and subheadings.
Use self-explanatory headings, for example, “ Impact of expanding market share. ”
3. Draft the report
Organize the data you collected during research into the draft report. Start by introducing the topic, providing background information, and the report’s objectives. Then include each of the main points you want to discuss, supported by evidence from the research data.
Have the relevant elements mentioned above and write adequate information under each section. The draft does not have to be perfect; you just need to organize the data roughly.
4. Revise and format your report
After completing your draft, proofread and edit it to remove irrelevant data or add forgotten information. Make sure everything looks good, including the formatting. It also helps to share the business report with someone who can review it and propose necessary changes. Once everything is settled, share the report with your intended audience.
Tips for writing a formal business report
When writing a formal report, use data and evidence to support your argument, add visuals, use consistent fonts and headings, and highlight important information. You should also use clear language that is easy to understand, considering the audience’s background knowledge.
1. Only use credible sources
Credible sources strengthen your report because they are factual, unbiased, and reliable. To identify a credible source, look out for the following markers.
- The source’s author should be an expert in their field.
- The information in the source should be up-to-date.
- The source should include evidence. The author should not have their opinions or speculations.
- A credible source is peer-reviewed by other experts in the field.
2. Use diagrams in formal business reports
Use diagrams like graphs and charts to illustrate relationships between ideas. They are more engaging, easier to understand, and they capture your audience’s attention.
Mind that you don’t clutter your diagrams with too much information. Excess detail will confuse your readers.
Achieve simplicity by:
- Removing backgrounds that cause distractions.
- Removing or lightening gridlines. Gridlines clutter diagrams.
- Reduce the number of colors you use. Only use color on crucial data in the diagram.
- Instead of adding every tiny detail, use symbols and have a key. The key explains what each symbol, figure, or line represents.
3. Use a consistent format
A consistent format makes it easy to follow your report. Keep the format headings and subheadings uniform throughout your report. And make your page margins and font styles consistent.
4. Use bold fonts to highlight
Bold fonts stand out against regular text to draw focus on essential data and make it easier to skim through the report. Use bolding sparingly; otherwise, the effect of highlighting will not work.
Formal business report template
A formal business report template will save both time and energy by providing a framework that simplifies the process of assembling data into a comprehensive document.
Check out this collection of editable business report templates to find one that works for you.
Final Thoughts: Formal Business Report
Formal business reports are essential tools for any business. An excellent report drives company decisions and recommends solutions to company problems. Writing one may be challenging, but this guide gives you a clear pathway to ease the process.
Remember to use visual aids and credible sources to fortify your report. Organize data into the above sections, and use the discussed tips to write your business report like a pro!
You may also like:
- How to Write a Resignation Letter for a Better Opportunity [Samples + Template Included]
- Bullet Form Examples: How to Use Bullet Points Effectively
- How to Write a Subject Line for Job Applications [+Samples]
Stop Stressing, Start Writing
Join over 540,000+ happy users writing smarter with WriterBuddy. Try WriterBuddy for Free!
Advanced AI writing tool trained to write better content faster.
- Sentence Rewriter Tool
- Instagram hashtag generator
- LinkedIn headline generator
- Acronym generator
- Title generator
- Business name generator
- Slogan generator
- Blog ideas generator
- Job Description Generator
- Brand Style Guide
- Affiliate Program
- Paraphrasing tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Content Detector
- Character Counter
- Word Counter
Copyright © 2024 WriterBuddy. All rights reserved.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Formal Reports
While you may write much shorter, more casual reports, it’s helpful to go into a bit of detail about formal reports. Formal reports are modular, which means that they have many pieces. Most audience members will not read every piece, so these pieces should stand on their own. That means that you will often repeat yourself. That’s okay. Your audience should be able to find exactly what they need in a particular section, even if that information has been repeated elsewhere.
While it’s fine to copy and paste between sections, you will likely need to edit your work to ensure that the tone, level of detail and organization meet the needs of that section. For example, the Executive Summary is aimed at managers. It’s a short, persuasive overview of everything in the report. The Introduction may contain very similar information, but it focuses on giving a short, technical overview of everything in the report. Its goal is to inform, not to persuade.
Let’s take a look at some of the parts of the report in greater detail.
The title page provides the audience with the:
- This should appear 2 inches from the top margin in uppercase letters.
- Type “Prepared for” on one line, followed by two separate lines that provide the receiving organization’s name and then the city and state. Some reports may include an additional line that presents the name of a specific person.
- Type “prepared by” on one line, followed by the name(s) of the author(s) and their organization, all on separate lines.
- This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
The items on the title page should be equally spaced apart from each other.
A note on page numbers:
The title page should not include a page number, but this page is counted as page “i.” Use software features to create two sections for your report. You can then utilize two different types of numbering schemes. When numbering the pages (i.e., i, ii, iii, etc.) for a formal report, use lowercase roman numerals for all front matter components. Utilize arabic numbers for the other pages that follow. Additionally, if you intend to bind the report on the left, move the left margin and center 0.25 inches to the right.
Letter of Transmittal
A letter of transmittal announces the report topic to the recipient(s).
If applicable, the first paragraph should identify who authorized the report and why the report is significant. Provide the purpose of the report in the first paragraph as well. The next paragraph should briefly identify, categorize, and describe the primary and secondary research of the report. Use the concluding paragraph to offer to discuss the report; it is also customary to conclude by thanking the reader for their time and consideration.
The letter of transmittal should be formatted as a business letter . Some report writers prefer to send a memo of transmittal instead.
When considering your audience for the letter or memo of transmittal, make sure that you use a level of formality appropriate for your relationship with the reader. While all letters should contain professional and respectful language, a letter to someone you do not know should pay closer attention to the formality of the word choice and tone.
Table of Contents
The table of contents page features the headings and secondary headings of the report and their page numbers, enabling audience members to quickly locate specific parts of the report. Leaders (i.e. spaced or unspaced dots) are used to guide the reader’s eye from the headings to their page numbers.
The words “TABLE OF CONTENTS” should appear at the top of the page in all uppercase and bolded letters. Type the titles of major report parts in all uppercase letters as well, double spacing between them. Secondary headings should be indented and single spaced, using a combination of upper- and lowercase letters.
Executive Summary
An executive summary presents an overview of the report that can be used as a time-saving device by recipients who do not have time to read the entire report.
The executive summary should include a:
- Summary of purpose
- Overview of key findings
- Identification of conclusions
- Overview of recommendations
To begin, type “EXECUTIVE SUMMARY” in all uppercase letters and centered. Follow this functional head with paragraphs that include the above information, but do not use first-level headings to separate each item. Each paragraph of information should be single-spaced with double spacing between paragraphs. Everything except for the title should be left-aligned.
An executive summary is usually ten percent of the length of the report. For example, a ten-page report should offer a one-page summary. A 100-page report should feature a summary that is approximately ten pages.
The executive summary is usually seen as the most important part of the report, and it should be written last. When you’re writing the executive summary, imagine that you’re sitting across from your most important audience member. If you only have a few minutes to talk to them, what do you want them to know? What would be most persuasive?
Introduction
The body of a formal report begins with an introduction. The introduction sets the stage for the report, clarifies what need(s) motivated it, and helps the reader understand what structure the report will follow.
Most report introductions address the following elements: background information, problem or purpose, significance, scope, methods, organization, and sources. As you may have noticed, some parts of a formal report fulfill similar purposes. Information from the letter of transmittal and the executive summary may be repeated in the introduction. Reword the information in order to avoid sounding repetitive.
To begin this section, type “BACKGROUND” or “INTRODUCTION” in all uppercase letters. This functional head should be followed by the information specified above (i.e., background information, problem or purpose, etc.). You do not need to utilize any first-level headings in this section.Because this section includes background information, it would be the appropriate place to address the needs of audiences that may need additional knowledge about the topic. Provide definitions of technical terms and instruction about the overall project if necessary. If you are uncertain if your audience needs a particular piece of information, go ahead and include it; it’s better to give your reader a little bit too much background than not enough.
Discussion of Findings
The Discussion of Findings section presents the evidence for your conclusions.
This key section should be carefully organized to enhance readability.
Useful organizational patterns for report findings include but are not limited to:
- Best Case/Worst Case
- Compare/Contrast
- Journalism Pattern
Use a Best Case/Worst Case organizational pattern when you think that the audience may lack interest in the topic. When examining a topic with clear alternatives to your proposed solution, consider using a Compare/Contrast pattern. Geographical patterns work effectively for topics that are discussed by location.
When describing the organization of the report in the first paragraph, broadly identify how the material in the report is organized rather than state that the report uses a specific pattern (e.g. Chronology, Geography). For example, write, “The research findings address curriculum trends in three provinces: (a) British Columbia, (b) Alberta, and (c) Ontario,” not, “This report uses a geographical organizational pattern.”
Follow the first paragraph with a first-level heading. Use first-level headings for all other major parts of this section. First-level headings should appear in bold, uppercase letters. Center first-level headings, but align any second-level headings with the left margin. Type any second-level headings in bold, upper- and lowercase letters.
As you present, interpret, and analyze evidence, consider using both text and graphics. Take into account what will be easiest for your audience to understand.
Include citations for all quoted or paraphrased material from sources as well; check with your organization as to whether they prefer parenthetical citations or footnotes.
Integrating Graphics
Formal report authors use graphics to present data in different forms. Paragraphs of text and complex or numerical data tend to bog readers down, making graphics a beneficial enhancement. Graphics also make data easier to understand, so they sometimes make a stronger impact on the audience.
Knowing when—and how—to effectively employ graphics is the key to successfully integrating them. Keeping the audience in mind is also critical. You will learn more about creating charts and graphs in the chapter on Visual Communication Strategies .
Conclusions and Recommendations
The conclusions and recommendations section conveys the key results from the analysis in the discussion of findings section. Up to this point, readers have carefully reviewed the data in the report; they are now logically prepared to read the report’s conclusions and recommendations.
Type “CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS” in all uppercase letters. Follow this functional head with the conclusions of the report. The conclusions should answer any research questions that were posed earlier in the report. Present the conclusions in an enumerated or bulleted list to enhance readability.
Recommendations offer a course of action, and they should answer any problem or research questions as well. Think back to the expectations of your audience. Have all of their requirements been addressed?
Works Cited
All formal reports should include a works cited page; his page documents the sources cited within the report. The recipient(s) of the report can also refer to this page to locate sources for further research.
It is acceptable to follow MLA (Modern Language Association), CMS (Chicago Manual of Style), or APA (American Psychological Association) documentation style for entries on this page. Arrange all sources alphabetically. Refer to the latest edition of the appropriate style handbook for more information about how to format entries for print and electronic sources on the Works Cited page
While some of the formatting rules may seem tedious at first, they are necessary in order for your audience to better understand the report. Using a regulated format allows for a more universal organization that everyone will understand. Being aware of your audience’s needs and expectations will allow for a strong report that will satisfy your employee and demonstrate your competence in your field.
Test Your Knowledge
Understanding the parts of the report can be challenging, so test your knowledge by dragging the part of the report to its definition.
Image Description
Figure 11.1 image description: This is a diagram of a report title page. Leave 2 inches between the top and the title of the report (which should be in uppercase letters), then write in the middle of the page who the report was prepared for. 3/4 of the way down the page, say who the report was prepared for. Then write the date submitted. [Return to Figure 11.1]
Figure 11.2 image description: A sample table of contents and List of Figures. Use uppercase letters for major parts and use leaders to guide the reader’s eye to the page numbers. The list of figures should be separate from the table of contents. [Return to Figure 11.2]
Figure 11.3 image description: A sample body page of an introduction. This one is separated into ‘PROBLEM’ (all in uppercase letters, bold, and in the center) and BACKGROUND. Each paragraph is single spaced with double spacing between paragraphs. [Return to Figure 11.3]
Business Writing For Everyone Copyright © 2021 by Arley Cruthers is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
How to Write a Report (2023 Guide & Free Templates)

You have a report due in a few days, but you’re still procrastinating like a pro.
Sounds familiar?
If you’ve been staring at a blank page, wondering how to write a report the best way possible, you’re not alone. For many, writing a report, especially for the first time, can feel like rolling a giant boulder uphill.
The good news is that from a first draft to creating reports that people love to read is a skill you can develop and polish over time.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or someone who wants to up their report-writing game, keep reading for a 2023 guide and step-by-step instructions on how to write a report. Plus, learn about the basic report format.
You’ll also get access to report templates that you can edit and customize immediately and learn about a tool to make reports online (no need to download software!). You can also jump right into customizing templates by creating a free account .
What is report writing?
Report writing is a way of communicating information, data, insight, or analysis. It’s an essential skill that will come in handy in various settings, from academic research or diving into historical events to business meetings.
But creating a report can be a bit intimidating at first.
In its simplest form, report writing starts with researching and gathering all the information, analyzing your findings, and presenting it in a way that’s easy for your audience to understand.
Sounds easy enough, right?
Well, there’s a bit more to it than that. We’ll guide you through every step of the process to write an entire report from a rough draft and data in the next section.
But first, let’s get to know the different types of reports.
Types of reports
Reports come in all shapes and sizes, and the type of report you write will depend on your specific goals and audience. Each type of report has its unique purpose, format, and style.

The most common types of reports are:
- Academic report – These include school reports, book reports, thesis reports, or analytical reports between two opposing ideas.
- Business report – Business reports range from annual reports to SWOT analyses . The goal of business reports is to communicate ideas, information, or insights in a business setting.
- Research report – Research reports are often more scientific or methodological in nature. They can take the form of case studies or research papers.
Learn more : 20 Types of Reports and When to Use Them (Plus Templates)
How to write a report without feeling overwhelmed
Breaking down the report writing process into three stages can make it much more manageable for you, especially if it’s your first time to create one.
These three stages are:
- Pre-writing stage
- Writing stage
- Post-writing stage
Let’s take a look at the steps for each stage and how to write a good report in 2023 that you can be proud of.
Stage 1: Pre-writing
The pre-writing stage is all about preparation. Take some time to gather your thoughts and organize your main idea. Write a summary first.
Here are important steps to help you deal with the overwhelm of creating an insightful report.
Understand the purpose of your report
Knowing your purpose will help you focus and stay on track throughout the process. Dig into the why of your report through these questions:
- Who is your intended reader? Are you familiar with your audience’s language and how they think?
- What are you trying to achieve with your report? Are you trying to inform, persuade, or recommend a course of action to the reader?
Research your topic
It’s time to gather as much information as you can about your topic. This might involve reading books, articles, and other reports. You might also need to conduct interviews with subject matter experts.
Pro tip on how to write a report : Pick reputable sources like research papers, recently-published books, and case studies by trustworthy authors.
Make a report outline
An outline is a roadmap for your report. It covers your title, introduction, thesis statement, main points, and conclusion. Organizing your thoughts this way will help you keep focus and ensure you cover all the necessary information.
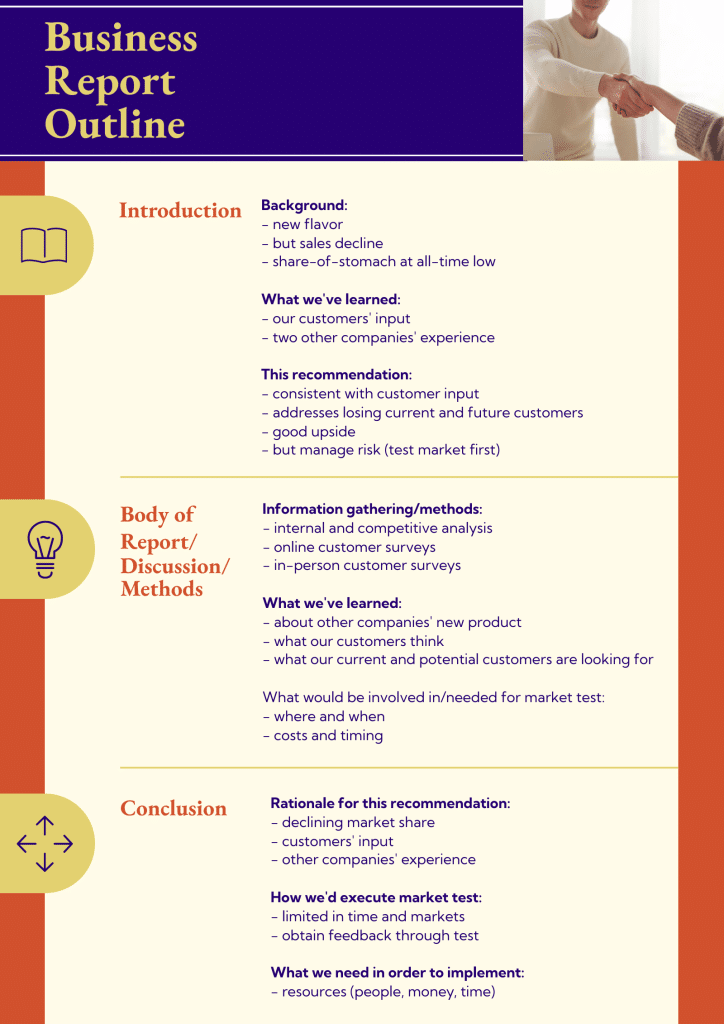
While you can create a report without creating an outline, you could write a better report with an outline. An outline helps you organize your facts and important points on paper.
Stage 2: Writing
Once you have completed the pre-writing stage, it’s time to write your report.
Follow the proper report writing format
You will feel a lot of resistance at this point because this is where most of the tedious work of report writing happens. However, the process can be a breeze if you follow a proper structure and report writing format.
The structure of your report can vary depending on the type of report you’re creating, but the report writing format below can serve as a guide for anyone.
- Title page. This is the first page of your report and should include the report’s title, the author’s name, the date of presentation or submission, and any other relevant information, such as your name or the organization’s name.
- Table of Contents (TOC ). This section contains subsections of your report and their corresponding page numbering. A well-written TOC will help readers navigate your report easily and find the information they need.
- Brief summary . This part provides an overview of the report’s particular purpose, subject, methodology, key findings, and recommendations. This section is often called the executive summary in corporate reports.
- Introduction . The introduction should provide background information about the topic and explain why the report was written. It should also state the aims and objectives of your report and give an overview of the methodology used to gather and analyze the data. Make sure you include a powerful topic sentence.
- Main body. The main body of the report should be divided into subsections, each dealing with a specific aspect of the topic. These sections should be clearly labeled and organized in a logical order. In most reports, this is also the part where you explain and present your findings, analysis, and recommendations.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points of your report and provide a final summary, thought, or suggestions. Review your thesis statement. The conclusion also includes any limitations of the study and areas for further research or future action.
- References . This section should include a list of all the sources cited in the report, like books, journal articles, websites, and any other sources used to gather information on your subject.
- Appendices . In the appendices section, you should include any additional information relevant to the report but not in the article’s main body. This might consist of raw data, event details, graphs, charts, or tables.
With all these key report elements, your readers can look forward to an informative, well-organized, and easy-to-read report.
Pro tips: Remember to use clear and concise language in your essay. It is also required to follow a specific type of formatting set by your organization or instructor.
Plus, use the active voice when you can because it helps improve clarity. To write a report essay in a passive voice makes it sound less concise.
Reports should usually be written in the third person.
Edit and proofread the article
Once you have completed your first essay draft, take some time to edit and proofread your work. Look for spelling mistakes and grammar errors, as well as any areas where the flow of your article could be improved. Review your topic sentence.
If hiring a professional editor isn’t possible, have a colleague or someone else read your rough draft and provide feedback. You can also use tools like Grammarly and the Hemingway App .
Stage 3: Post-writing
You’re almost there! This stage is about finalizing your report and ensuring it is ready to be shared.
Format your report
Ensure your report is formatted correctly, with clear and easy-to-read fonts, headings, and subheadings.
Incorporate visuals
Adding visuals to your report article is another great way to help your audience understand complex information more easily.
From charts to illustrations, the right visual can help highlight and explain key points, events, trends, and patterns in your data, making it easier for the reader to interpret the information.

Want to check out more templates? Get access to the template gallery today .
However, it’s important to use visuals sparingly and ensure they are relevant and effectively support the texts. You will learn more about effectively incorporating visuals into your report as you scroll down below to the next sections.
Share your report
Once your report is complete, share it with your audience. This might involve submitting it to your boss, presenting it to a group, or sharing it online.
A final note for this section: Remember to take your time, stay organized, and most importantly, have fun! Writing a report can be a rewarding experience, especially if you get positive feedback when you present.
How to add visuals to your report
Adding visuals to your report is more than just putting a graph or chart for every piece of information.
There are no hard and fast rules but use the pointers below as guidelines:
- Each visual in your report should have a purpose. Don’t just add a pie chart or bar graph for the sake of adding one. Your visual of choice should offer clarity to readers that’s impossible to achieve with words alone. Piktochart’s report maker lets you search for free stock images and illustrations to add to any page with drag and drop.
- Add captions, legends, or arrows to your visuals when possible. For more technical reports, graphics are either Tables or Figures. Number them in order of appearance (Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, etc.) and give each a descriptive title.
- Place the visual close to the relevant text on the page.
- Document the source of the visual, citing it in both the caption and references section if necessary.
- Make the graphic stand out with colors, borders, boxes, spacing, and frames.
Learn more : How to Improve Your Data Visualization Design in 6 Steps
Write reports like a pro with Piktochart’s easy-to-edit report templates
Creating reports from scratch can be time-consuming. The great news is you don’t have to make reports from scratch like how it used to be in the 90s and early 2000s. Organizations of all shapes and sizes now understand that you can also create the perfect report with the help of templates.
For example, Piktochart offers a variety of fully customizable templates, allowing you to easily add your branding, colors, and text within the online editor. You can visualize your thesis statement and first draft in less than an hour. It’s also possible to start writing directly in the tool, adding graphics page by page.
These templates range from reports for school presentations to sales reports. By editing them, you can create professional-looking reports without the hassle of formatting and design.
Here are some examples of Piktochart’s professionally-designed templates. If you can’t pick one that matches your report writing format and needs, create a free Piktochart account to get access to more templates.
Survey report template
This survey report template includes clear visualizations, making your report findings easier to understand. From customer surveys to employee satisfaction reports, this template is quite versatile.
Research report template
This research report template is perfect for anyone looking to create a thorough and professional research report. The template includes all the necessary sections to help you easily organize your research and present your findings in a concise document.

Corporate report template
Looking for a corporate report template example with an editable table of contents and foreword? This template is the perfect fit!
Whether you’re presenting to investors or sharing information with your team, this corporate report template will help you create a polished and informative executive summary for any corporate organization.

Case study report template
Whether you’re conducting a business case study or an academic case study, this case study report template can help you earn your readers’ trust. This template is specifically designed with fashion as its main theme, but you can edit the photos and details to make it more on-brand with your niche.

Marketing report template
Use this template to create comprehensive marketing reports. The template includes editable sections for social media, data from search engines, email marketing, and paid ads.

Financial report template
With this customizable finance report template, you don’t need to make a financial report from scratch. Once you’ve written your content, save your report in PDF or PNG formats.
Annual report template
This annual report template is the right template for creating a professional and informative executive summary of your organization’s performance over the past year. This template was designed for HR annual reports, but you can also repurpose it for other types of yearly reports.

See more report templates by creating a free Piktochart account .
Quick checklist for better report writing
Before you submit or present your report, use the quick checklist below to help ensure that your report is well-structured, accurate, clear, and properly cited. Most of all, you must ensure that your report meets your audience’s expectations and has all the information and details they need.
Purpose and audience
- Does the report address its purpose and meet the needs of the intended audience?
Structure and organization
- Is the material appropriately arranged in sections?
- Have irrelevant details been removed?
Accuracy and analysis
- Has all the material been checked for accuracy?
- Are graphs and tables clearly labeled? Check the page numbers too.
- Is the data in graphs or tables analyzed and explained in words?
- Does the discussion or conclusion show how the results relate to the objectives mentioned in the introduction?
- Have the results been compared with existing research from the literature survey?
Writing style and clarity
- Is the report written in a tone that’s indicated in the brand style guide (for corporate reports)? Does it avoid colloquialisms or contractions?
- Does it follow the organization’s specific guidelines for writing style?
- Is it jargon-free and clearly written? Have you translated technical terms into simpler words?
- Use the active voice when you can because it helps improve clarity. A written report in a passive voice may make it sound less concise.
Acknowledgment and citation
- Have all ideas and event data taken from or inspired by someone else’s work been acknowledged with a reference?
- Have all illustrations and figures taken from someone else’s work been cited correctly?
Proofreading
- Has the report been carefully proofread for typos, spelling errors, and grammatical mistakes?
Make engaging and effective reports quickly with Piktochart
Writing a report is a must-have skill for anyone looking to communicate more effectively in their personal and professional lives.
With the steps we’ve provided in this guide, anyone can learn how to write a report that is informative, engaging, and comprehensive.
Plus, the free templates we highlighted are valuable for individuals looking to create reports quickly and efficiently. They can also be used to transform a longer report filled with texts into something more engaging and easy to digest.
Sign up for a free Piktochart account today, and look forward to writing reports with its library of modern, customizable report templates.
Piktochart offers professionally designed templates for all your visual communication needs. It is your one-stop shop for presentations , posters , logos , email signatures , infographics , and more. Customize all templates according to your brand assets in seconds. Get started for free today.

Other Posts
10 Best Sales Report Templates for Tracking Revenue, KPIs & Growth

10 Types of HR Reports (With Templates and Examples)

7 Captivating Report Design Ideas And Tips (With Templates and Examples)

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Writing a Formal Report
Report organization.
Reports vary by size, format, and function. You need to be flexible and adjust your report to the needs of the audience. Reports are typically organized around six key elements:
- Who the report is about and/or prepared for
- What was done, what problems were addressed, and the results, including conclusions and/or recommendations
- Where the subject studied occurred
- When the subject studied occurred
- Why the report was written (function), including under what authority, for what reason, or by whose request
- How the subject operated, functioned, or was used
Pay attention to these essential elements when you consider your stakeholders. That may include the person(s) the report is about, whom it is for, and the larger audience of the organization. Ask yourself who the key decision-makers are, who the experts will be, and how your words and images may be interpreted.
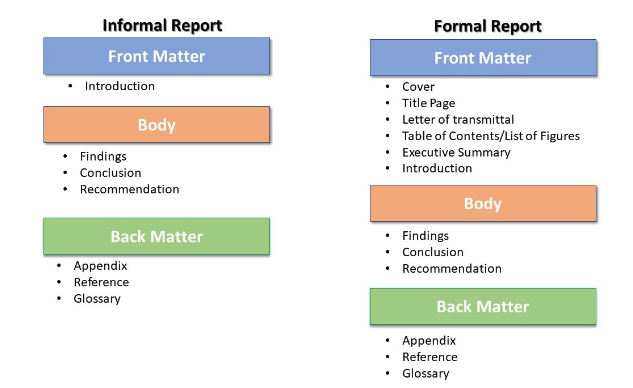
While there is no universal format for a report, there is a common order to the information. Each element supports the main purpose or function, playing an important role in the transmission of information. There are several different organizational patterns that may be used for formal reports, but all formal reports contain front matter (prefatory) material, a body, and back matter (supplementary) items. The prefatory material is therefore critical to providing the audience with an overview and roadmap of the report. The body of a formal report discusses the findings that lead to the recommendations. The back matter provides additional information. Some common elements in a report are shown in Activity 11.1 below.
Activity 11.1 | Report Cover and Letter of Transmittal Binding Cover and Letter of Transmittal
Front Matter
Front matter includes all the information preceding the body of the report.
The title page provides the audience with the:
- This should appear 2 inches from the top margin in uppercase letters.
- Type “Prepared for” on one line, followed by two separate lines that provide the receiving organization’s name. Some reports may include an additional line that presents the name of a specific person.
- Type “prepared by” on one line, followed by the name(s) of the author(s) and their organization, all on separate lines.
- This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
The items on the title page should be equally spaced apart from each other.
A note on page numbers: The title page should not include a page number, but this page is counted as page “i.” Use software features to create two sections for your report. You can then utilize two different types of numbering schemes. When numbering the pages (i.e., i, ii, iii, etc.) for a formal report, use lowercase Roman numerals for all front matter components. Utilize Arabic numbers for the other pages that follow. Additionally, if you intend to bind the report on the left, move the left margin and center 0.25 inches to the right.
A note on font: If there is no specific preference for serif vs. sans serif font, choose one and use it consistently throughout the report. Do not utilize anything besides a traditional serif (e.g., Times New Roman) or sans serif (e.g., Arial or Calibri) font.
Letter or Memo of Transmittal
A letter or memo of transmittal announces the report topic to the recipient(s).
If applicable, the first paragraph should identify who authorized the report and why the report is significant. Provide the purpose of the report in the first paragraph as well. The next paragraph should briefly identify, categorize, and describe the primary and secondary research of the report. Use the concluding paragraph to offer to discuss the report; it is also customary to conclude by thanking the reader for their time and consideration.
A letter of transmittal should be formatted as a business letter. Some report writers prefer to send a memo of transmittal instead. When considering your audience for the letter or memo of transmittal, make sure that you use a level of formality appropriate for your relationship with the reader. While all letters should contain professional and respectful language, you should pay closer attention to the formality of the word choice and tone in a letter to someone you do not know. Figure 11.1 illustrates a report with a letter of transmittal.
Table of Contents
The table of contents page features the headings and secondary headings of the report and their page numbers, enabling audience members to quickly locate specific parts of the report. Leaders (i.e. spaced or unspaced dots) are used to guide the reader’s eye from the headings to their page numbers.
The words “TABLE OF CONTENTS” should appear at the top of the page in all uppercase and bolded letters. Type the titles of major report parts in all uppercase letters as well, double spacing between them. Secondary headings should be indented and single-spaced, using a combination of upper and lowercase letters. Figure 11.2 demonstrates the organization of a typical table of contents and executive summary for a report.
List of Figures and Tables
The list of figures has many of the same design considerations as the table of contents. Readers use the list of figures to find the illustrations, diagrams, tables, and charts in your report. Complications arise when you have both tables and figures. Strictly speaking, figures are illustrations, drawings, photographs, graphs, and charts. Tables are rows and columns of words and numbers; they are not considered figures. For longer reports that contain dozens of figures and tables each, create separate lists of figures and tables. Put them together on the same page if they fit. You can combine the two lists under the heading, “List of Figures and Tables,” and identify the items as figure or table as is done in Figure 11.2.
Executive Summary
An executive summary presents an overview of the report that can be used as a time-saving device by recipients who do not have time to read the entire report.
The executive summary should include a:
- Summary of purpose
- Overview of key findings
- Identification of conclusions
- Overview of recommendations
If the executive summary, introduction, and transmittal letter strike you as repetitive, remember that readers don’t necessarily start at the beginning of a report and read page by page to the end. They skip around; they may scan the table of contents and they usually skim the executive summary for key facts and conclusions. They may read carefully only a section or two from the body of the report, and then skip the rest. For these reasons, reports are designed with some duplication so that readers will be sure to see the important information no matter where they dip into the report.
To organize this section, type “EXECUTIVE SUMMARY” in all uppercase letters and centred. Follow this functional head with paragraphs that include the above information, but do not use first-level headings to separate each item. Each paragraph of information should be single-spaced with double spacing between paragraphs. Everything except for the title should be left-aligned.
An executive summary is usually ten percent of the length of the report. For example, a ten-page report should offer a one-page summary. A 100-page report should feature a summary that is approximately ten pages.
The body is the main section of the report and includes the introduction, discussion or findings, conclusion (and recommendations, if appropriate).
Introduction
The body of a formal report begins with an introduction. The introduction sets the stage for the report, clarifies what need(s) motivated it, and orients the reader to its structure. Most report introductions address the following elements: background information, problem or purpose, significance, scope, methods, organization, and sources. As you may have noticed, some parts of a formal report fulfill similar purposes. Information from the letter of transmittal and the executive summary may be repeated in the introduction. Reword the information in order to avoid sounding repetitive.
To begin this section, type “BACKGROUND” or “INTRODUCTION” in all uppercase letters. This functional head should be followed by the information specified above (i.e., background information, problem or purpose, etc.). You do not need to utilize any first-level headings in this section.
Because this section includes background information, it would be the appropriate place to address the needs of audiences that may need additional knowledge about the topic. Provide definitions of technical terms and instructions about the overall project if necessary. If you are uncertain if your audience needs a particular piece of information, go ahead and include it; it’s better to give your reader a little bit too much background than not enough. The organization of a typical introduction is illustrated in Figure 11.3.
Discussion of Findings
The Discussion of Findings section presents the evidence for your conclusions. This key section should be carefully organized to enhance readability.
To begin, type “DISCUSSION OF FINDINGS” in all uppercase letters. Center this and all other functional heads. Follow “DISCUSSION OF FINDINGS” with a brief paragraph that previews the organization of the report.
Useful organizational patterns for report findings include but are not limited to:
- Best Case/Worst Case
- Compare/Contrast
- Journalism Pattern
Use a Best Case/Worst Case organizational pattern when you think that the audience may lack interest in the topic. When examining a topic with clear alternatives to your proposed solution, consider using a Compare/Contrast pattern. Geographical patterns work effectively for topics that are discussed by location. When describing the organization of the report in the first paragraph, broadly identify how the material in the report is organized rather than state that the report uses a specific pattern (e.g. Chronology, Geography). For example, write, “The research findings address curriculum trends in three provinces: (a) British Columbia, (b) Alberta, and (c) Ontario,” not, “This report uses a geographical organizational pattern.”
Follow the first paragraph with a first-level heading. Use first-level headings for all other major parts of this section. First-level headings should appear in bold, uppercase letters. Center first-level headings, but align any second-level headings with the left margin. Type any second-level headings in bold, upper- and lowercase letters.
As you present, interpret, and analyze evidence, consider using both text and graphics. Take into account what will be easiest for your audience to understand. Include citations for all quoted or paraphrased material from sources as well; check with your organization as to whether they prefer parenthetical citations or footnotes.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The conclusions and recommendations section conveys the key results from the analysis in the discussion of findings section. Up to this point, readers have reviewed the data in the report; they are now logically prepared to read the report’s conclusions and recommendations. Type “CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS” in all uppercase letters. Follow this functional head with the conclusions of the report. The conclusions should answer any research questions that were posed earlier in the report. Present the conclusions in an enumerated or bulleted list to enhance readability. Recommendations offer a course of action, and they should answer any problem or research questions as well. Think back to the expectations of your audience. Have all of their requirements been addressed?
The difference between the conclusions and recommendation section is detailed in Chapter 12: Recommendation Report . All reports will contain a conclusion section, but not all reports will have a recommendation section. Whether a recommendation section is included or not depends on the type and purpose of the report.
Back Matters
Back matters contain all the supplementary materials and can include works cited, appendices, a glossary and an index.
Works Cited
All formal reports should include a works cited page; this page documents the sources cited within the report. Documenting your information sources is all about establishing, maintaining, and protecting your credibility in the profession. You must cite (“document”) borrowed information regardless of the shape or form in which you present it. Whether you directly quote, paraphrase, or summarize it—it’s still borrowed information. Whether it comes from a book, article, a diagram, a table, a web page, a product brochure, an expert whom you interview in person—it’s still borrowed information. Use the documentation style appropriate to your industry (e.g. APA, MLA, Chicago).
Appendices are those extra sections following the conclusion. What do you put in an appendix?—anything that does not comfortably fit in the main part of the report but cannot be left out of the report altogether. The appendix is commonly used for large tables of data, big chunks of sample code, fold-out maps, background that is too basic or too advanced for the body of the report, or large illustrations that just do not fit in the body of the report. Anything that you feel is too large for the main part of the report or that you think would be distracting and interrupt the flow of the report is a good candidate for an appendix. Notice that each one is given a letter (A, B, C, and so on).
Fundamentals of Business Communication Revised (2022) Copyright © 2022 by Venecia Williams & Nia Sonja is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write a Business Report: A Step By Step Guide with Examples

Table of contents

To see what Databox can do for you, including how it helps you track and visualize your performance data in real-time, check out our home page. Click here .
With so much experience under your belt, you already know a lot about business reporting.
So, we don’t want to waste your time pointing out the obvious because we know what you need.
Secrets. Tricks. Best practices.sales rep drilldown business report
The answer to how to write a mind-blowing business report that you don’t need to spend hours and days writing.
A business report that will immediately allow you to identify your strengths and weaknesses.
A report that’ll help you learn more about your business and do more accurate forecasting and planning for the future.
We believe we have just that right here.
With this comprehensive guide, you’ll create effective sales, analytical, and informative business reports (and business dashboards ) that will help you improve your strategies, achieve your goals, and grow your business.
So, let’s dive in.
What Is a Business Report?
Importance of creating business reports, types of business reports, what should be included in a business report, how to write a business report: an 11-step guide.
- Business Report Examples
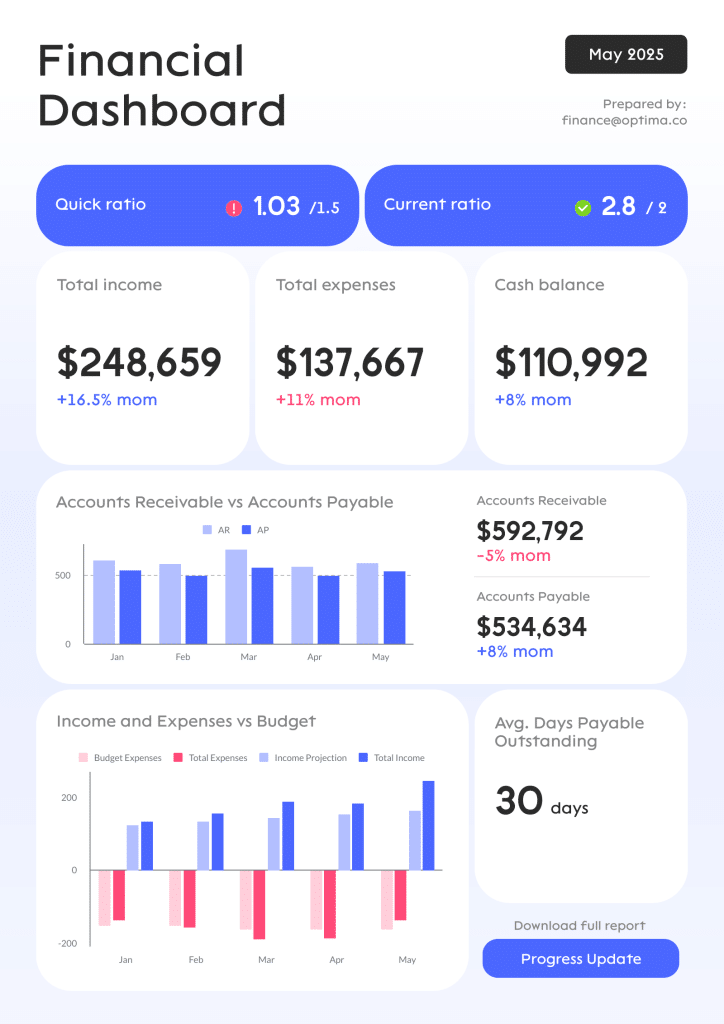
Although there’s a variety of business reports that differ in many aspects, in short, a business report definition would be the following:
A business report is an informative document that contains important data such as facts, analyses, research findings, and statistics about a business with the goal to make this information accessible to people within a company.
Their main purpose is to facilitate the decision-making process related to the future of the business, as well as to maintain effective communication between people who create the reports and those they report to.
A good business report is concise and well-organized, looks professional, and displays the relevant data you can act on. The point is to reflect upon what you’ve achieved so far (typically, over the past month, quarter or year) and to use the data to create a new strategy or adjust the current one to reach even more business goals.
Business reports should be objective and based on the data. When stating the facts, people rely on numbers rather than giving descriptions. For instance, instead of saying “our conversion rate skyrocketed”, you would display the exact percentages that back up that claim.
Business reporting matters for several reasons, among which the most important ones are:
Recognizing Opportunities to Grow
Detecting issues and solving them quickly, evaluating a potential partner, having a paper trail, keeping things transparent for the stakeholders, setting new company goals.
In fact, over half of the companies that contributed to Databox’s state of business reporting research confirmed that regular monitoring and reporting brought them significant concrete benefits.
If you never look back at what you’ve achieved, you can’t figure out what you’ve done well and what you can leverage in the future for even better results.
When you analyze a specific aspect of your business over a specific time period and present the data you gathered in a report, you can detect an opportunity to grow more easily because you have all the information in one place and organized neatly.
Is it time to introduce new products or services? Is there a way to enhance your marketing strategy? Prepare a report. Can you optimize your finances? Write a financial business report . Whatever decision you need to make, it’s easier when you base it on a report.
Reports are essential for crisis management because they can introduce a sense of calmness into your team. Putting everything on paper makes it easier to encompass all the relevant information and when you know all the facts, you can make a more accurate and effective decision about what to do next.
Writing business reports regularly will also help you identify potential issues or risks and act timely to prevent damage and stop it from escalating. That’s why monthly reporting is better than doing it only once a year.
Having an insight into your finances , operations and other business aspects more regularly allows you to have better control over them and mitigate potential risks more effectively.
Different types of business reports may be accessible to the general public. And if they’re not, specific situations may require a company to send them over to the person requesting them. That may happen if you’re considering a partnership with another company. Before making the final decision, you should learn about their financial health as every partnership poses a certain risk for your finances and/or reputation. Will this decision be profitable?
Having an insight into a company’s business report helps you establish vital business relationships. And it goes the other way around – any potential partner can request that you pull a business report for them to see, so writing business reports can help you prove you’re a suitable business partner.
In business, and especially in large companies, it’s easy to misplace information when it’s communicated verbally. Having a written report about any aspect of your business doesn’t only prevent you from losing important data, but it also helps you keep records so you can return to them at any given moment and use them in the future.
That’s why it’s always good to have a paper trail of anything important you want to share with colleagues, managers, clients, or investors. Nowadays, of course, it doesn’t have to literally be a paper trail, since we keep the data in electronic form.
Writing business reports helps you keep things transparent for the stakeholders, which is the foundation of efficient communication between these two sides.
You typically need to report to different people – sometimes they’re your managers, sometimes they’re a client. But your company’s stakeholders will also require an insight into the performance of your business, and relying on reports will help you maintain favorable business relationships. A business report shows you clearly how your company is performing and there isn’t room for manipulation.
Once you set business goals and the KPIs that help you track your progress towards them, you should remember they’re not set in stone. From time to time, you’ll need to revisit your goals and critical metrics and determine whether they’re still relevant.
When you write a business report and go through it with your team members or managers, you have a chance to do just that and determine if you’re efficient in reaching your goals. Sometimes, new insights will come up while writing these reports and help you identify new objectives that may have emerged.
Depending on your goals and needs, you’ll be writing different types of business reports. Here are five basic types of business reports .
Informational Report
Analytical report, research report, explanatory report, progress report.
Informational reports provide you with strictly objective data without getting into the details, such as explaining why something happened or what the result may be – just pure facts.
An example of this type of business report is a statement where you describe a department within your company: the report contains the list of people working in this department, what their titles are, and what they’re responsible for.
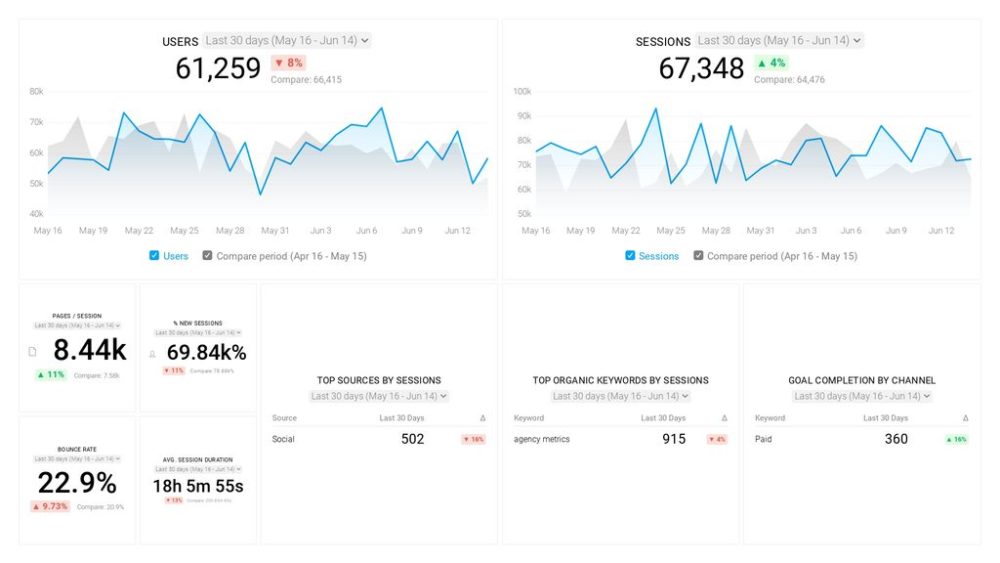
Another example related to a company’s website could look like this Google Analytics website traffic engagement report . As we explained above, this report shows objective data without getting too much into the details, so in this case, just the most important website engagement metrics such as average session duration, bounce rate, sessions, sessions by channel, and so on. Overall, you can use this report to monitor your website traffic, see which keywords are most successful, or how many returning users you have, but without further, in-depth analysis.
Analytical reports help you understand the data you’ve collected and plan for the future based on these insights. You can’t make business decisions based on facts only, so analytical reports are crucial for the decision-making process.
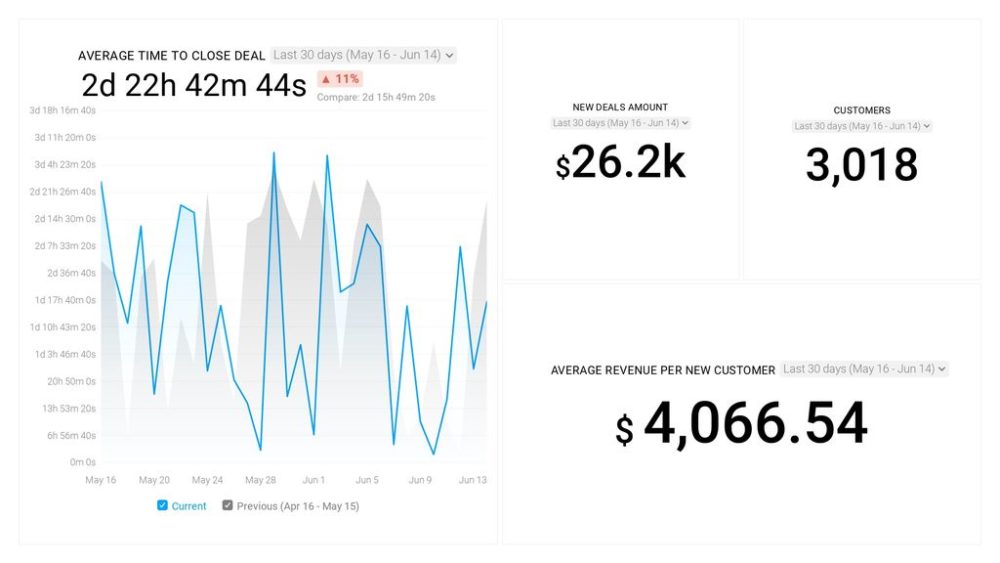
This type of business report is commonly used for sales forecasting. For instance, if you write a report where you identify a drop or an increase in sales, you’ll want to find out why it happened. This HubSpot’s sales analytics report is a good example of what metrics should be included in such a report, like average revenue per new client or average time to close the deal. You can find more web analytics dashboard examples here.
From these business reports, you can find out if you will reach your goals by implementing your current strategy or if you need to make adjustments.
Research is critical when you’re about to introduce a change to your business. Whether it’s a new strategy or a new partner, you need an extensive report to have an overview of all important details. These reports usually analyze new target markets and competition, and contain a lot of statistical data.
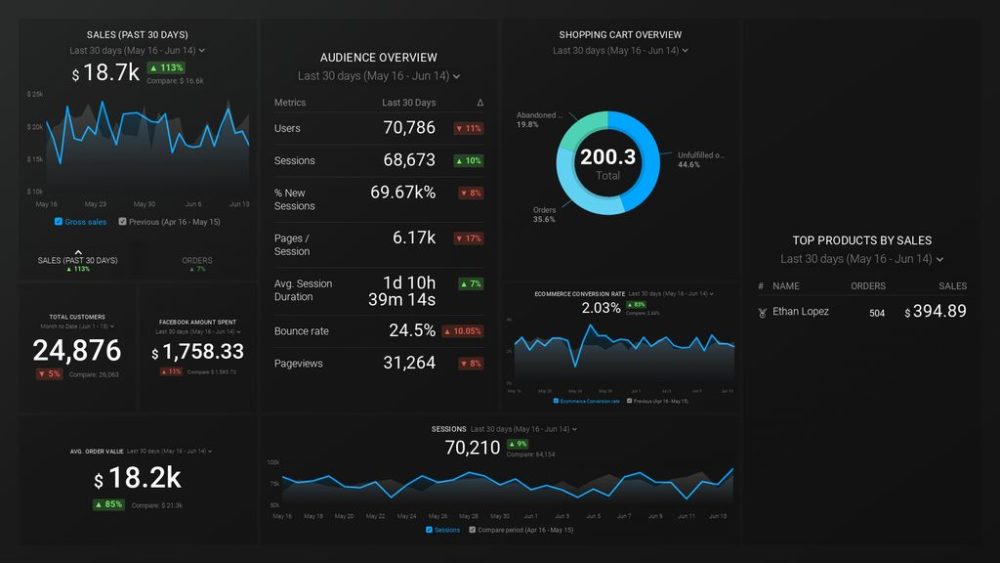
While not the same, here is an example of an ecommerce dashboard that could help track each part of a campaign in detail, no matter whether you are launching a new product, testing a new strategy, and similar. Similar to a research report, it contains key data on your audience (target market), shows your top-selling products, conversion rate and more. If you are an online store owner who is using paid ads, you can rely on this report to monitor key online sales stats in line with Facebook Ads and Google Analytics. See more ecommerce dashboards here.
As you might guess from its name, you write the explanatory report when it’s necessary for you to explain a specific situation or a project you’ve done to your team members. It’s important to write this report in a way that everyone will be able to understand.
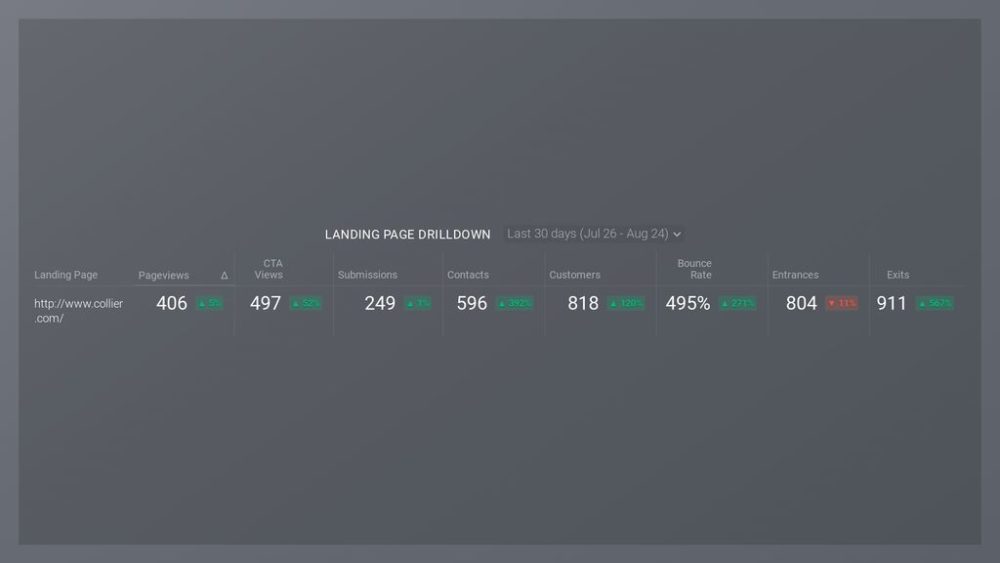
Explanatory reports include elements like research results, reasons and goals of the research, facts, methodology, and more. While not exactly an explanatory report, this example of a HubSpot marketing drilldown report is the closest thing to it, as it helps marketers drill into an individual landing page performance, and identify how good their best landing pages are at converting, or which ones have the best performance.
A progress report is actually an update for your manager or client – it informs them about where you stand at the moment and how things are going. It’s like a checkpoint on your way towards your goal.
These reports may be the least demanding to write since you don’t need to do comprehensive research before submitting them. You just need to sum up your progress up to the point when the report was requested. This business report may include your current results, the strategy you’re implementing, the obstacles you’ve come across, etc. If this is a marketing progress report you can use marketing report templates to provide a more comprehensive overview.
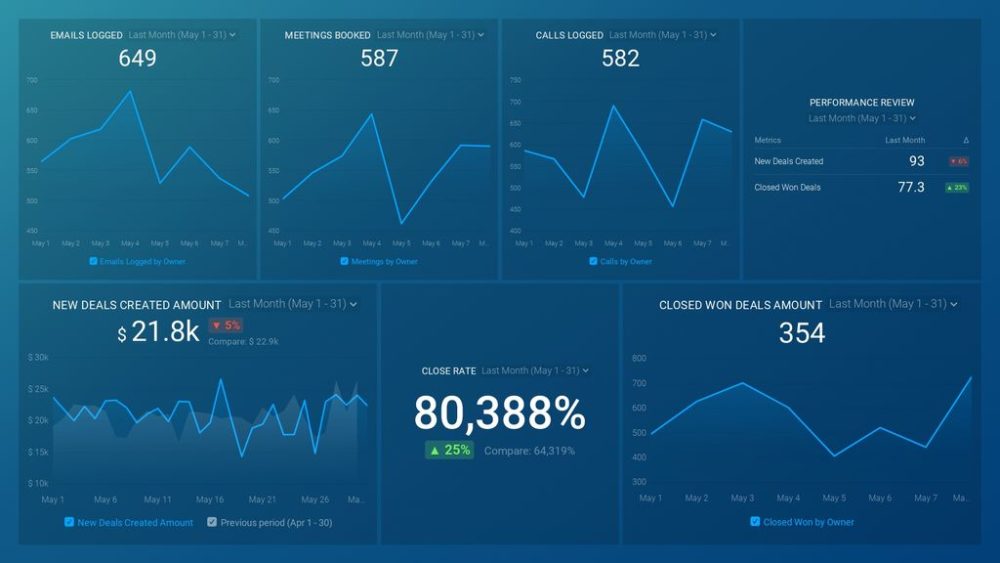
In many companies, progress reports are done on a weekly or even daily basis. Here is an example of a daily sales report from Databox. HubSpot users can rely on this sales rep drilldown business report to see how individual each sales rep is performing and measure performance against goals. Browse through all our KPI dashboards here.
What does a great business report look like? If you’re not sure what sections your report should have, you’ll learn what to include in the following lines.
Business Report Formatting
Different types of reports require different lengths and structures, so your business report format may depend on what elements your report needs to have. For example, progress reports are typically pretty simple, while analytical or explanatory reports are a different story.
However, most reports will start with a title and a table of contents, so the person reading the report knows what to expect. Then, add a summary and move on to the introduction. After you’ve written the body and the conclusion, don’t forget to include suggestions based on your findings that will help your team create an actionable plan as you move forward.
After that, list the references you used while creating the report, and attach any additional documents or images that can help the person reading the report understand it better.
This outline may vary depending on what kind of report you’re writing. Short business reports may not need a table of contents, and informative reports won’t contain any analyses. Also, less formal reports don’t need to follow a strict structure in every situation.
Business Report Contents
When it comes to the contents of your report, keep in mind the person who’s going to read it and try to balance between including all the relevant information, but not overwhelming the reader with too many details.
- The introduction to the report should state the reason why you’re writing it, and what its main goal is. Also, mention what methodology and reporting software you’ve used, if applicable.
- The body of the report is where you’ll expose all your key findings, explain your methodology, share the important data and statistics, and present your results and conclusion.
- The conclusion , similarly to the summary you’ll add at the beginning of the report, briefly singles out the most important points and findings of the report.
If you decide to include more sections like recommendations, this is where you’ll suggest the next steps your team or the company may want to take to improve the results or take advantage of them if they’re favorable.
PRO TIP: Are You Tracking the Right Metrics for Your SaaS Company?
As a SaaS business leader, there’s no shortage of metrics you could be monitoring, but the real question is, which metrics should you be paying most attention to? To monitor the health of your SaaS business, you want to identify any obstacles to growth and determine which elements of your growth strategy require improvements. To do that, you can track the following key metrics in a convenient dashboard with data from Profitwell:
- Recurring Revenue. See the portion of your company’s revenue that is expected to grow month-over-month.
- MRR overview. View the different contributions to and losses from MRR from different kinds of customer engagements.
- Customer overview . View the total number of clients your company has at any given point in time and the gains and losses from different customer transactions.
- Growth Overview . Summarize all of the different kinds of customer transactions and their impact on revenue growth.
- Churn overview. Measure the number and percentage of customers or subscribers you lost during a given time period.
If you want to track these in ProfitWell, you can do it easily by building a plug-and-play dashboard that takes your customer data from ProfitWell and automatically visualizes the right metrics to allow you to monitor your SaaS revenue performance at a glance.
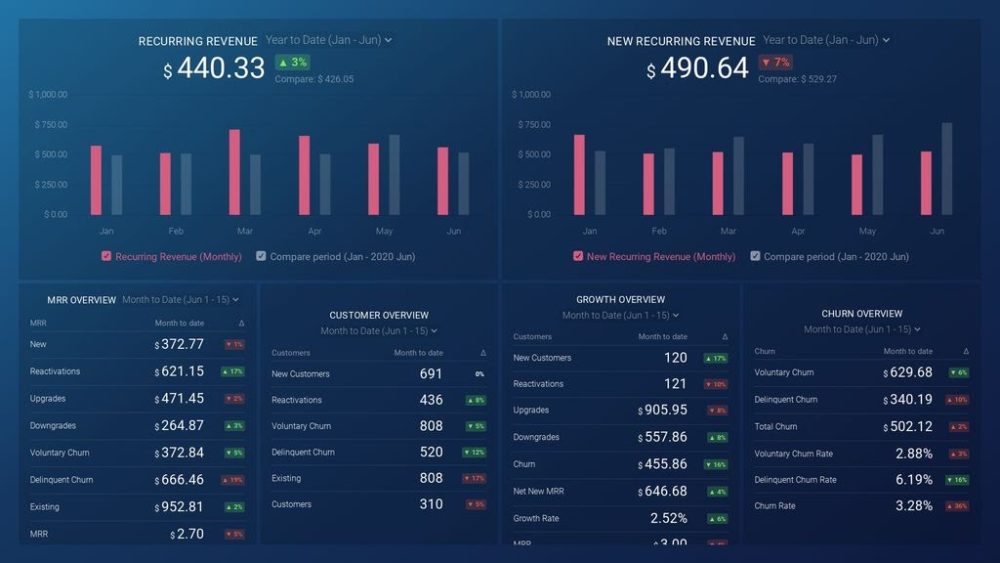
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your Profitwell account with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Note : Other than text, make sure you include images, graphs, charts, and tables. These elements will make your report more readable and illustrate your points.
Whether you’re writing a specific type of business report for the first time or you simply want to improve the quality of your reports, make sure you follow this comprehensive guide to writing an effective business report.
- Do Your Research
- Create an Outline
- Determine Formatting Guidelines
- Think of an Engaging Title
- Write the Introduction
- Divide the Body of the Report into Sections
- Choose Illustrations
- Conclude Effectively
- Gather Additional Documentation
- Add a Summary
- Proofread Your Work
Step 1: Do Your Research
A well-planned report is a job half done. That means you need to do research before you start writing: you need to know who you’re writing for and how much they know about the topic of your report. You need to explore the best business dashboard software and templates you can use for your report.
Also, if you believe you will need additional resources and documents to add in the appendix, you should do it during this phase of report writing.
Step 2: Create an Outline
Once you’ve gathered the resources, it’s time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don’t have a clear plan.
Moreover, the report shouldn’t be complicated to read, so sticking to a plan will allow you to keep it concise and clear, without straying from the topic.
Step 3: Determine Formatting Guidelines
Most companies have their in-house formatting that every official document has to follow. If you’re not sure if such rules exist in your company, it’s time you checked with your managers.
If there arent’ any guidelines regarding formatting, make sure you set your own rules to make the report look professional. Choose a simple and readable format and make sure it supports all the symbols you may need to use in the report. Set up proper headings, spacing, and all the other elements you may need in Word or Google Docs.
Pro tip: Google Docs may be easier to share with people who are supposed to read your business report.
Step 4: Think of an Engaging Title
Even if you’re writing a formal business report, the title should be clear and engaging. Reports are typically considered dull as they’re a part of official business documentation, but there’s no reason why you can’t make them interesting to read. Your title should suit the report topic and be in different font size so the reader can recognize it’s a title. Underneath the title, you should add the name of the author of the report.
Step 5: Write the Introduction
A good introductory paragraph for a business report should explain to the reader why you’ve written the report. Use the introduction to provide a bit of background on the report’s topic and mention the past results if there’s been a significant improvement since your last report.
Step 6: Divide the Body of the Report into Sections
As this will be the most comprehensive part of your report, make sure you separate the data into logical sections. Your report is supposed to tell a story about your business, and these sections (such as methodology, hypothesis, survey, findings, and more) will help the data look well-organized and easy to read.
Step 7: Choose Illustrations
Of course, each of these sections should be followed with charts, graphs, tables, or other illustrations that help you make a point. Survey results are typically best displayed in pie charts and graphs, and these enable the reader to visualize the data better. From the formatting point of view, breaking the long text sections with illustrations makes the report more readable.
Pro tip: Using centralized dashboard solutions like Databox can bring your reporting game to the next level. Sign up for a forever-free trial now to see how you can use Databox to track and visualize performance easier than ever before .
Step 8: Conclude Effectively
Finish your report with a to-the-point conclusion that will highlight all the main data from the report. Make sure it’s not too long, as it’s supposed to be a summary of the body of the report. In case you don’t want to add a specific section for recommendations, this is where you can include them, along with your assessments.
Step 9: Gather Additional Documentation
If you’ve determined what additional documents, images, surveys, or other attachments you may need for your report, now is the time to collect them. Request access to those you may not be able to get on time, so you have everything you need by the deadline. Copy the documents you can use in the original form, and scan the documents you need in electronic format.
Step 10: Add a Summary
The summary is usually at the top of the report, but it’s actually something you should write after your report is completed. Only then will you know exactly what your most relevant information and findings are, so you can include them in this brief paragraph that summarizes your report’s main points.
The summary should tell the reader about the objective of the report, the methodology used, and even mention some of the key findings and conclusions.
Step 11: Proofread Your Work
It may seem like common sense, but this final step of the process is often overlooked. Proofreading your work is how you make sure your report will look professional because errors can ruin the overall impression the reader will form about your work, no matter how great the report is.
Look for any spelling or grammatical mistakes you can fix, and if you’re not sure about specific expressions or terminology, use Google to double-check it. Make sure your writing is to-the-point and clear, especially if you’re writing for people who may not know the industry so well. Also, double-check the facts and numbers you’ve included in the report before you send it out or start your reporting meeting.
Business Report Examples (with Ready-to-Use Templates)
Here, we’re sharing a few business reporting examples that you can copy, along with ready-to-use and free-to-download templates. If you don’t know where to start and what to include in different types of business reports, these business report examples are a great way to get started or at least get some inspiration to create yours.
Activity Report Example
Annual report example, project status report example, financial report example, sales report example, marketing report example.
Note : Each of the business report templates shared below can be customized to fit your individual needs with our DIY Dashboard Designer . No coding or design skills are necessary.
For reporting on sales activity, HubSpot users can rely this streamlined sales activity report that includes key sales metrics, such as calls, meetings, or emails logged by owner. This way, you can easily track the number of calls, meetings, and emails for each sales rep and identify potential leaks in your sales funnel. Check all our sales team activity dashboards here. Or if you are looking for dashboards that track general sales performance, browse through all Databox sales dashboards here.

If you’re preparing for annual reporting, you will benefit from choosing this HubSpot annual performance report . It contains all the relevant metrics, such as email and landing page performance, new contacts, top blog posts by page views, and more. See all our performance dashboard templates here.
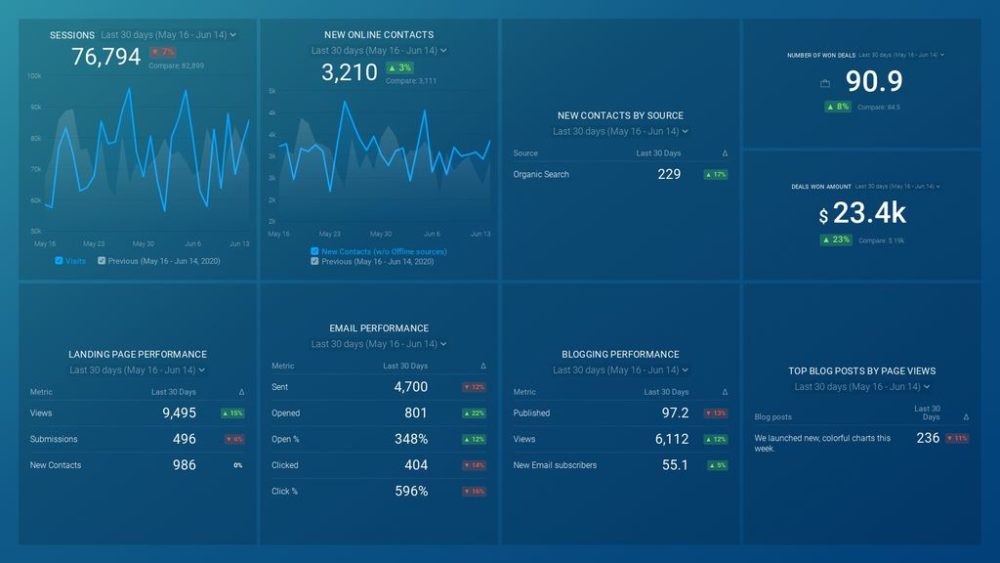
Project status reports can be very similar to progress reports. If you’re in need of one of those, here’s an example of a Project overview dashboard from Harvest that shows that can help you create simple, but well-organized report based on metrics that matter: hours tracked, billable hours, billable amount split by team members., and more. Check out more project management dashboard templates we offer here.
Are you creating a financial report? You will find this QuickBooks + HubSpot integration a great choice for a financial performance dashboard that makes creating a report simple. This dashboard focuses on the essential financial report
ting metrics and answers all your revenue-related questions. See all Databox financial dashboards here.
If you’re tracking your sales team’s monthly performance, this sales report template will help you prepare an outstanding report. Check out all the vital productivity KPIs, track your progress towards your goals, and understand well how your current sales pipeline is performing. See all sales performance dashboards we have available here.
Marketing reports can be easily prepared by using this monthly marketing report template . With HubSpot’s reporting, you can determine where your website traffic is coming from, how your landing pages and specific blog posts are performing, and how successful your email campaigns are. Browse all Databox marketing dashboards or marketing report examples here.
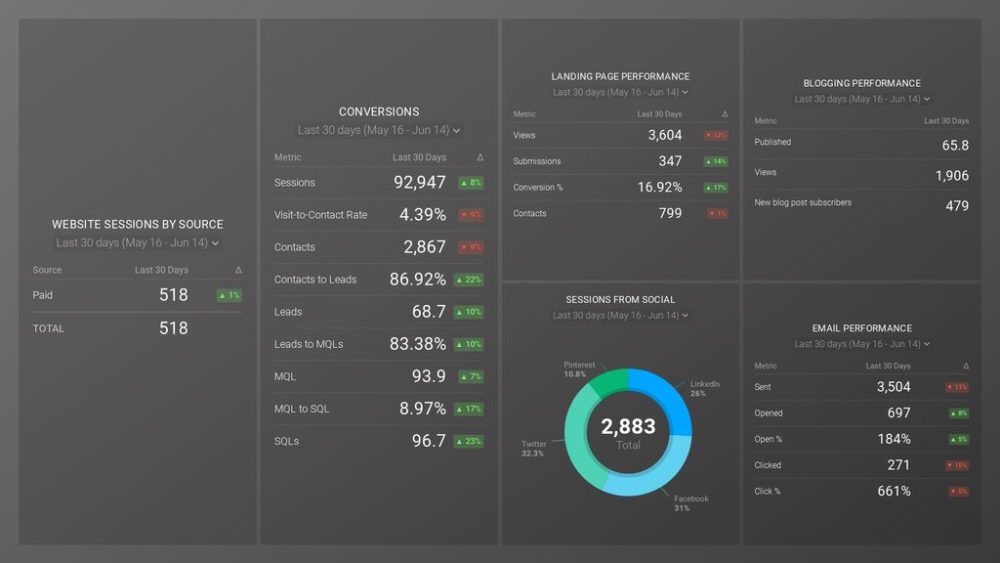
Create a Professional Business Report in No Time with Databox
Does creating a business report still sound like a daunting task? It doesn’t have to be with Databox.
In times when we’re all trying to save our time and energy for things that matter rather than scattering valuable resources on tedious, repetitive tasks, it’s critical to optimize your business process. And we want to help you do just that.
Using a business reporting dashboard enables you to track data from all the different tools you’re using – but in one place. With Databox, you can monitor and report on performance in a single dashboard that is optimized for all your favorite devices and you can create streamlined and beautiful dashboards even if you are not that tech-savvy. (no coding or design skills are required).
Automating business reporting has never been easier. And with Databox, you can do exactly that in just a few clicks. Sign up now and get your first 3 business dashboards for free.
- Databox Benchmarks
- Future Value Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Return On Ads Calculator
- Percentage Growth Rate Calculator
- Report Automation
- Client Reporting
- What is a KPI?
- Google Sheets KPIs
- Sales Analysis Report
- Shopify Reports
- Data Analysis Report
- Google Sheets Dashboard
- Best Dashboard Examples
- Analysing Data
- Marketing Agency KPIs
- Automate Agency Google Ads Report
- Marketing Research Report
- Social Media Dashboard Examples
- Ecom Dashboard Examples

Does Your Performance Stack Up?
Are you maximizing your business potential? Stop guessing and start comparing with companies like yours.

A Message From Our CEO
At Databox, we’re obsessed with helping companies more easily monitor, analyze, and report their results. Whether it’s the resources we put into building and maintaining integrations with 100+ popular marketing tools, enabling customizability of charts, dashboards, and reports, or building functionality to make analysis, benchmarking, and forecasting easier, we’re constantly trying to find ways to help our customers save time and deliver better results.
Do you want an All-in-One Analytics Platform?
Hey, we’re Databox. Our mission is to help businesses save time and grow faster. Click here to see our platform in action.
Stefana Zarić is a freelance writer & content marketer. Other than writing for SaaS and fintech clients, she educates future writers who want to build a career in marketing. When not working, Stefana loves to read books, play with her kid, travel, and dance.
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business
What is kpi reporting kpi report examples, tips, and best practices.
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- 5 Strategies for Call-Based Lead Generation & Management (Based on 110+ Expert Respondents) June 27, 2024
- SaaS Growth Marketing Challenges and Wins in 2024 June 20, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
How To Write a Report: A Detailed Guide [+AI Method]
![how to write the formal report How To Write a Report: A Detailed Guide [+AI Method]](https://cdn.prod.website-files.com/5f7ece8a7da656e8a25402bc/645b8df737dcc500780779ca_How%20to%20Draft%20a%20Winning%20Report.jpg)
- Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writers often wonder how to stand out from the crowd when writing a professional report.
Unlike articles or blogs, the informative, formal nature of reports can make them feel stiff and boring. And whether you want a top grade or to make an impact on your audience, another dull report probably won’t help.

In my career I’ve written a range of reports for both internal and external audiences—and regularly read reports from industry leaders, too. Top reports are informative and educational, summarizing key information quickly so it’s easy to digest. But the best examples also use high-quality research and concise but compelling language to bring the subject matter to life.
In this article, I’ll focus on general thematic reports, the kind you may be asked to write at college or work. I’ll give you the lowdown on how to write an effective report that still packs in the facts.
Types of reports
The term “report” comprises a wide genre of documents. If you’re used to other kinds of academic writing, it will help to understand the key qualities that reports share.
What sets reports apart
Reports are similar to other kinds of academic writing in many ways: you’ll still need strong research in the background, clear citations, and a formal language style , for example.
But several details set reports apart from other forms. Reports:
- Stick to the facts rather than veering into personal opinion or argument
- Save interpretation and recommendations for the end of the piece
- Use clear organizational techniques like bullet points, heading and subheadings, and charts or graphics
- Use concise, clear language that can be easily skimmed
Common types of reports
Reports are used in a wide range of contexts, so make sure you’re writing the right kind of report for your purposes. Here’s an overview of some common types.

Pre-writing steps
Before you set pen to paper, it’s important to do your research and plan your report carefully. Giving yourself plenty of time for this stage will make the actual writing quicker and less rambling.
1. Define the audience and purpose of the report
If you haven’t already been given a purpose for the report, be sure to define this before you begin. This can help you decide on the type of research you need to do and check if your report is fulfilling its goals while you draft.
Examples of common report aims:
- To demonstrate your understanding of an academic topic or text
- To improve understanding of the work your department is doing, so other departments in the same organization can build on your success
- To raise awareness of a particular problem that your organization can solve
On top of this, ask yourself who your audience is and what is their level of prior knowledge relative to yours. Within a hierarchy, such as a company or school, the audience may be more senior than you (vertical reporting), or at the same level as you (lateral reporting). This can affect what information is relevant to include.
Additionally, note whether it’s an internal or external publication and what your audience might do with the information they learn from your report.

Read the full article: Use AI to better define your audience
2. establish goals and objectives.
If you are writing your report for school or university, check the assessment guidelines for the report before you begin. You’ll need to include all the required elements.
If you are writing for professional purposes, however, the goals and objectives may be up to you or your department to define. An objective for your report should ideally be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-Bound).
For example, a lead-generating report can be used for the aim of securing meetings with interested buyers by highlighting a problem that your company can solve, and the impact of your report can be measured by the number of downloads and subsequent meetings within a certain time period.
An internal report could be used to inform a strategy meeting, and the impact could be measured in how many strategic recommendations are made as a result.
Read the full article: Develop your strategy and goals
3. research and gather information.
A report needs to be based on factual evidence, so the research stage is absolutely key to producing an informative piece. Firstly, you should review the major literature on the topic to make sure you can define and explain key terms and set out any needed context.
For academic reports, your professor or institution may be able to provide a recommended reading list. Use your college library and make sure you find out which academic journals your institution subscribes to. You can often access these online using sites like JSTOR and Google Scholar .
You may also want to include primary sources to add originality to your report and make it more appealing to your audience. These could include:
- Original research such as interviews
- Statistics you’ve compiled
- Details of experiments, tests, or observations you’ve made
It’s really helpful to keep organized notes during your research. Note any key quotations with page numbers, plus publication and author details for each text you reference or read. This will make it much easier to create your citations and bibliography later on.
You could do this on paper or using flexible software like Notion or Evernote or specialist software like Mendeley or Zotero .
Read the full article: 8 Must-Have Tools for Researchers in 2023 (Including AI)
4. outline your report structure.
Creating an outline before you begin writing is key to successfully drafting a report.
Start by noting down a skeleton framework, i.e. the main points you want to cover, which you will then develop as you write. In some cases, if you’re clear on what you might include in your report, this step might come before you start researching; alternatively, your main points might change during your research phase.
Although the exact layout of your report will depend on your objectives, a report should include the following sections:
- Introduction
- Summary of context
- Summary of your main topic or text
- Bibliography
Additional sections that you may want to include, depending on context:
- An abstract — used in academic contexts.
- A summary of your findings — useful if you include your own original research (such as interviews or statistics)
- Recommendations for further action or research
Read the full article: How to Properly Write an Outline Using AI
5. write the draft of your report.
Your first draft is your chance to develop the ideas you noted down during outlining. You might need to continue researching as you go, especially if you find that certain areas need more evidence or explanation.
Write your title and abstract
The title of your report should clearly and concisely state what it is about. Your audience may need to quickly select it from a list of other publications, so make sure to use keywords to make your work easy to identify. Remember that this is also your audience’s first impression of your writing!
You may also need to create an abstract for your work: a short summary of your research and findings, giving a quick statement about the problem and/or potential solution, a concise explanation of what you did to investigate it, and your findings in brief. You will probably want to write your abstract after finishing the rest of the report.
Create a table of contents
The table of contents should direct readers to each section of the report with page numbers. You may want to include hyperlinks to relevant sections if you are presenting your document electronically.
Prepare your sections
Developing each section in full will form the bulk of your drafting work. Make sure each section is adding value to your report.

Balance analysis with facts
Report writing should be factual. There will be times when you need to draw conclusions and make recommendations. However, this analysis should not overwhelm the factual content of your report. Remember, this is not a persuasive opinion piece. Make sure your analysis is grounded in evidence, and keep your recommendations concise.
Use clear language
A report should clearly inform the audience about the topic at hand. Keep your language precise and easy to understand. Keep sentences and paragraphs at a sensible length. If you use technical terms your audience might not know, include definitions. Try to avoid emotive language that can make the report sound like a persuasive essay.
Sometimes it can be difficult to achieve all this while writing the first draft, so feel free to come back to improve on it in later drafts.
Use visuals to keep it interesting
Many reports use visuals like graphs, charts, photographs, or infographics. These can convey information quickly and engage your audience by breaking up the text.
Simple graphs and charts can usually be made in spreadsheet software, but you may want to call on the skills of a graphic designer if your organization has the resources. Make sure to caption and number your graphics.
Cite your sources
Your institution or organization may stipulate a citation model, so double-check what is required before you begin. In general, quotations or anything else taken from another source should be properly cited, including the author’s name, title, and page number, plus other information, depending on format. Citations may be in-text or footnotes.
It’s a good idea to add citations as you write, because going back and putting them in afterwards can be very fiddly and time-consuming.
At the end of your report you will also need to provide a bibliography, which lists the texts you have cited. Citation software like Zotero or a bibliography generator like MyBib can make this easier.
Follow an appropriate format
Make sure to check the style guidelines provided by your academic institution or work organization. These might determine the page formatting you need to use (e.g. page numbering, page size, use of images, etc.). If no such guidelines exist, look at other reports from your field to determine what will be clear and useful for your audience.
Read the full article: Essay writing guide
6. edit, review and revise.
Reviewing and revising your work is one of the most important parts of the writing process, so make sure you give yourself plenty of time for this part and avoid rushing to meet a deadline. Review your content first, checking that each section has enough evidence and development, before moving on to editing for clarity and technical accuracy.
Using a reading and writing assistant like Wordtune can make editing at the phrase, sentence, or word level quicker and easier. Wordtune not only finds spelling, punctuation, and grammar errors, but it can also suggest changes to your vocabulary and sentence structure that make your work clearer and more compelling. You can even specify whether you want a more formal or casual tone — most reports should be formal in nature.
Read the full article: The complete editing guide
Writing a report using an ai prompt (chatgpt + wordtune).
You can use this prompt to generate a useful report:
Please generate a comprehensive report on the topic "[Your Specific Topic Here]". Ensure the report adheres to the following structure and guidelines: Title: Craft a concise and descriptive title that encapsulates the essence of the report. Abstract: Provide a succinct summary (100-150 words) that encapsulates the main objectives, methodology, findings, and significance of the report. Table of Contents: List all the sections and relevant sub-sections of the report for easy navigation. Introduction: Introduce the topic, its background, relevance in today's context, and the primary objectives of this report. Body: Dive deep into the topic. This should include: Background/History: A brief history or background of the topic. Current Scenario: Present relevant data, facts, and figures. Analysis/Discussion: Discuss the implications of the data, any patterns observed, and their significance. Conclusion: Summarize the main findings, discuss their implications, and suggest recommendations or potential future research directions. Additionally, ensure that the content is: - Well-researched and cites reputable sources. - Coherent and logically structured. - Free from jargon, unless necessary, and is accessible to a general audience.
Make sure your next report has an impact
Whether your report is for academic or business purposes, you need to make sure it is well-researched, clearly expressed, and conveys the main points quickly and concisely to your audience. Careful planning and organization can make this process much easier, as well as leaving time to review and revise your work, either manually or with the help of software like Wordtune. Following these tips, your first report is sure to make an impact — and the more you write, the easier it will get.
Share This Article:

Grammarly Alternatives: Which Writing Assistant is the Best Choice for You?

The Dos and Don’ts of Using AI to Study
.webp)
How to Use Modal Verbs for Clear Communication
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
How to Write a Report Properly and Effectively

Written by: Chloe West

If you’re looking for the best way to document information or share your findings in a professional and well thought out manner, a report might be the best way to go. But if you don’t know how to write a report, where should you start?
Report writing is different from many other types of writing, which is why it’s a good idea to do your due diligence before you get started.
What do you need to include in your report? How should you flesh out each section?
There are different report formats based on your specific needs, but the structure tends to remain similar for each.
Let’s go over our steps for how to write a report properly so you can effectively communicate your findings.
Here’s a short selection of 8 easy-to-edit report templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

1 Determine Your Objective
First and foremost, why are you writing this report? What is the point or goal? Is this an academic report or is it business-related? Perhaps you need to put together an annual report , sales report or financial report.
Also consider who your audience is. Your report might be internal for company use only, or it might be external to present to investors, customers and more.
Is this a periodic report that you’re going to have to revisit every month, quarter or year? Is it for people above you in the company or is it for your department?
Understanding your objective is important to know what your content will contain and where you’ll need to go to pull your information.
2 Put Together an Outline
Never start writing anything without putting together an outline first. This will help you to structure your report, understand what resources you need in order to find all of your results and materials and more.
This outline doesn’t need to be too in depth, but it does give you a starting point for your full report. You can then refer back to this outline throughout your report writing process .
Start with the purpose or objective of your report, then list out your main points and a few bullets underneath that you want to make sure you cover in the contents of your report.
Your outline might look something like this:

3 Gather Your Research
Start searching around your topic and gather the research you need to put together your report. This might be online sources, journals, experiments or just analytics and numbers from your company CRM or sales software .
Add all of the research to your outline so that you know which numbers and information pertains to each of your main points.
Once you’ve finished gathering everything you need to complete your report, you can get started writing.
You might need to go back and find more information and do more research throughout, and that’s okay. But once you feel like you have a grasp of the material you need to cover, you can move onto the next step and get started with a report generator .
Hey marketers! Need to create scroll-stopping visual content fast?
- Transform your visual content with Visme’s easy-to-use content creation platform
- Produce beautiful, effective marketing content quickly even without an extensive design skillset
- Inspire your sales team to create their own content with branded templates for easy customization
Sign up. It’s free.

4 How to Write a Report Cover Page
Now we’re ready to get started on your report cover page! When you’re first working on your cover page, it’s a good idea to start with a template .
This helps you to spice up your report design and make it more than a black and white word document. It can also help you design your title page in an aesthetically pleasing way so it stands out to your audience.
Check out this Visme report template cover page below.

Customize this report template and make it your own! Edit and Download
When determining how to write a report cover page, there are up to five things you will want to include, the most important of which is naturally your report’s title.
Others include who the report is for, who the report was prepared by (you!), the date or your department within your company.
Having this information right on the report cover page is the best way to let your reader know at a glance exactly what is inside of the report and who it’s for.
5 How to Write a Report Table of Contents
The next part of your report will be your table of contents. While you might not know exactly how your report will be laid out yet, your outline will help you get started here.
As you write your report – or even when you finish writing it – you can come back and update the table of contents to match your headings and subheadings.
Because you want to make it easy to navigate, ensure that all of your page titles and subheadings correlate exactly with what you place in your table of contents.
Take a look at the table of contents in the below report template.

See how they have obvious dividers so it’s easy to determine which section begins on which page? You want to make sure you emulate something similar.
There are many different ways to do this.
For one, you can right align your table of contents so the titles are directly next to the page numbers, like in the example below that was designed right in Visme.

Or you can have a dotted line or other visual flow element that guides the reader’s eye across the table straight to the page number.
Just make sure there’s no confusion in locating the correct page number for each section.
6 How to Write a Report Introduction
The first section you start writing in your report is always a summary or introduction . This should stretch across just one or two pages to give your reader a brief glimpse into what your results or findings are.
Talk about the methodology used to gather the material you cover within your report, whether it was research, an experiment, gathering analytics, looking through CRM data , calculating revenue and more.
You also want to include visuals to help tell your story. This could be anything from photography to icons or graphics. You might even include shapes to help with your design.
Here’s an example of a proposal report introduction with a nice page design and black and white photo to offset the text.

7 How to Write a Report Body
Now we’re getting into the meat of your report. You’ve already put together your outline, gathered your research and created your cover page, table of contents and introduction.
This means you should know exactly what the main part of your report is going to contain, making it easier for you to dive into the body.
While reports can vary greatly in length, with shorter reports containing 7-15 pages and longer reports ranging anywhere from 30-50 pages or more, the length tends to depend on your topic. Shorter reports focus on one single topic with longer reports covering multiple.
Take these steps to properly write an effective report body or get assignment writing help .

Split the body into sections.
Although you’ll have each of your main headers in your table of contents – i.e., your introduction, body and conclusion – you’ll also want to include your subheadings.
And you’ll want to divide your report body into various sections based on what it covers.
If you’re creating an annual report, you might divide this up by different months. If you’re creating a financial report, perhaps you’ll divide it up based on various stats and numbers.
There are many different ways to divide your report body into sections, but just like we’ve broken this article up into different subheadings, it’s important to do so. This helps make it easier for your reader to digest each of the different sections.
Take a look at how this report template has broken up the body into bite-sized chunks.

Dive into your results and findings.
This is where you’ll really get into all of the research you gathered and talk about your topic. Over the course of the subheadings you’ve previously laid out, flesh each one out with the results you’ve discovered.
Reports tend to be more formal in nature, so keep that in mind as you write. Veer away from a more conversational tone, avoid the use of contractions and properly cite all of your sources and results.
Make sure you cover every aspect of your report’s topics, including the most relevant statistics, up-to-date research and more.
Use data visualizations and graphic organizers.
Don’t fill your report to the brim with just text. Including images, icons, graphics, charts and graphic organizers is a great way to further visualize your content and make your point.
If you’re creating a financial report or sales report, data visualizations are key to showcasing your numbers and statistics in an easily digestible way.
Here’s an example of one of our templates that includes charts and graphs within the report pages to make it even easier to understand.

Learning how to tell a story with data is essential to creating a good report. But you don’t want to stop at just data visualization tools within your report.
Incorporating photos and graphics into your report design is another great way to represent your text and engage your reader. Reports get a bad rap for being boring walls of text, but we encourage you to think outside the box.
Use stock photography and vector icons to help convey your point.
Take a look at the template page below and how it creatively brings in various types of visuals to add more to the page.

Test out each of Visme’s data visualization tools, stock photo library, vector icon selection and more to help your report stand out from the crowd.
Cover the materials used.
Make sure you include which materials were used to find your results and each of your sources. Sometimes this section will be short and sweet, by simply mentioning your CRM software or other tools that you used to pull numbers. Others will be longer.
Whether you used your company’s data or determined your results using an experiment or a third-party source, be sure to include each and every resource used within your report.
Take advantage of Visme's Dynamic Fields to ensure your personal and company data is accurate and consistent throughout your reports.
Summarize each section.
Not every section in your report body will be long enough to need a summary, but if you have a section that includes a lot of information or stretches across a couple of pages, it’s a good idea to summarize it at the end.
This will help your reader make sure they retained all of the information and allow them to skim through your report at a later date by reading your section summaries.
8 How to Write a Report Conclusion
You’re almost done! Now it’s time to write your conclusion and finalize your report.
First, start by summarizing your points. Yes, you wrote small summaries for each section in the body, but now you’re going to give an overall summary of your report’s contents.
Refer to your findings and discuss what they mean. While your body was more for demonstrating your results, you can use the conclusion to talk about their context in the real world, or what they mean for your business.
Then you’ll want to talk about next steps. If your results weren’t as positive as you were hoping, write about what the plan is to make sure they improve for the next time around. Lay out your goals and strategies for using these findings.
And make sure you’re not introducing any new information. While you may be talking about the information in a different way, you should still be exclusively referring to data and content that is already found in your report.
Looking to create a stand-out visual report?
- Choose from dozens of professionally designed templates
- Create animated charts and creatively visualize stats and figures
- Customize anything to fit your brand image and content needs
9 Include Your Sources
You covered your materials and resources used in a section of your report body, but the end of each report should include an entire bibliography that lists each one of your sources in alphabetical order so the reader can easily access more information.
You can also include acknowledgements, giving thanks to particular organizations or people that helped you put together your report contents.
And depending on the purpose of your report, you might also want to include a glossary at the end to help define industry terms for external readers who might not fully understand.
Ready to get started on your next report? Visme makes it easy with premade report templates that allow you to plug in your information and send your report off to its audience!
Learn how to write a report that stands out by following the steps laid out in this article and inputting into a stunning template. Sign up for your Visme account to get started today.
Plus, learn how to design beautiful documents like your next report by watching our quick 5-minute tutorial video.
Design beautiful visual content you can be proud of.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Chloe West is the content marketing manager at Visme. Her experience in digital marketing includes everything from social media, blogging, email marketing to graphic design, strategy creation and implementation, and more. During her spare time, she enjoys exploring her home city of Charleston with her son.
Report Writing Format, Tips, Samples and Examples
Pankaj dhiman.
- Created on December 11, 2023
How to Write a Report: A Complete Guide (Format, Tips, Common Mistakes, Samples and Examples of Report Writing)
Struggling to write clear, concise reports that impress? Fear not! This blog is your one-stop guide to mastering report writing . Learn the essential format, uncover impactful tips, avoid common pitfalls, and get inspired by real-world examples.
Whether you’re a student, professional, or simply seeking to communicate effectively, this blog empowers you to craft compelling reports that leave a lasting impression.
Must Read: Notice Writing: How to write, Format, Examples
What is Report Writing ?
Report Writing – Writing reports is an organized method of communicating ideas, analysis, and conclusions to a target audience for a predetermined goal. It entails the methodical presentation of information, statistics, and suggestions, frequently drawn from study or inquiry.
Its main goal is to inform, convince, or suggest actions, which makes it a crucial ability in a variety of professional domains.
A well-written report usually has a concise conclusion, a well-thought-out analysis, a clear introduction, a thorough methodology, and a presentation of the findings.
It doesn’t matter what format is used as long as information is delivered in a logical manner, supports decision-making, and fosters understanding among stakeholders.
Must Read : Article Writing Format, Objective, Common Mistakes, and Samples
Format of Report Writing
- Title Page:
- Title of the report.
- Author’s name.
- Date of submission.
- Any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Abstract/Summary:
- A brief overview of the report’s key points.
- Summarizes the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions.
- Table of Contents:
- Lists all sections and subsections with corresponding page numbers.
Introduction:
- Provides background information on the subject.
- Clearly states the purpose and objectives of the report.
- Methodology:
- Details how the information was gathered or the experiment conducted.
- Includes any relevant procedures, tools, or techniques used.
- Findings/Results:
- Presents the main outcomes, data, or observations.
- Often includes visual aids such as charts, graphs, or tables.
- Discussion:
- Analyzes and interprets the results.
- Provides context and explanations for the findings.
Conclusion:
- Summarizes the key points.
- May include recommendations or implications.
Must Read: Directed Writing: Format, Benefits, Topics, Common Mistakes and Examples
Report Writing Examples – Solved Questions from previous papers
Example 1: historical event report.
Question : Write a report on the historical significance of the “ Battle of Willow Creek ” based on the research of Sarah Turner. Analyze the key events, outcomes, and the lasting impact on the region.
Solved Report:
Title: Historical Event Report – The “Battle of Willow Creek” by Sarah Turner
This report delves into the historical significance of the “Battle of Willow Creek” based on the research of Sarah Turner. Examining key events, outcomes, and the lasting impact on the region, it sheds light on a pivotal moment in our local history.
Sarah Turner’s extensive research on the “Battle of Willow Creek” provides a unique opportunity to explore a critical chapter in our local history. This report aims to unravel the intricacies of this historical event.
Key Events:
The Battle of Willow Creek unfolded on [date] between [opposing forces]. Sarah Turner’s research meticulously outlines the sequence of events leading to the conflict, including the political climate, disputes over resources, and the strategies employed by both sides.
Through Turner’s insights, we gain a nuanced understanding of the immediate outcomes of the battle, such as changes in territorial control and the impact on the local population. The report highlights the consequences that rippled through subsequent years.
Lasting Impact:
Sarah Turner’s research underscores the enduring impact of the Battle of Willow Creek on the region’s development, cultural identity, and socio-political landscape. The report examines how the event shaped the community we know today.
The “Battle of Willow Creek,” as explored by Sarah Turner, emerges as a significant historical event with far-reaching consequences. Understanding its intricacies enriches our appreciation of local history and its role in shaping our community.
Access the Learning Platform
Report writing Samples
book review report.
Title: Book Review – “The Lost City” by Emily Rodriguez
“The Lost City” by Emily Rodriguez is an enthralling adventure novel that takes readers on a captivating journey through uncharted territories. The author weaves a tale of mystery, discovery, and self-realization that keeps the reader engaged from beginning to end.
Themes and Characters:
Rodriguez skillfully explores themes of resilience, friendship, and the pursuit of the unknown. The characters are well-developed, each contributing uniquely to the narrative. The protagonist’s transformation throughout the story adds depth to the overall theme of self-discovery.
Plot and Pacing:
The plot is intricately crafted, with twists and turns that maintain suspense and intrigue. Rodriguez’s ability to balance action scenes with moments of introspection contributes to the novel’s well-paced narrative.
Writing Style:
The author’s writing style is engaging and descriptive, allowing readers to vividly envision the settings and empathize with the characters. Dialogue flows naturally, enhancing the overall readability of the book.
“The Lost City” is a commendable work by Emily Rodriguez, showcasing her storytelling prowess and ability to create a captivating narrative. This novel is recommended for readers who enjoy adventure, mystery, and character-driven stories.
Must Read: What is Descriptive Writing? Learn how to write, Examples and Secret Tips
Report Writing Tips
Recognise your audience:
Take into account your target audience’s expectations and degree of knowledge. Adjust the content, tone, and language to the readers’ needs.
Precision and succinctness:
To communicate your point, use language that is simple and unambiguous. Steer clear of convoluted sentences or needless jargon that could confuse the reader.
Logical Structure:
Organize your report with a clear and logical structure, including sections like introduction, methodology, findings, discussion, and conclusion.
Use headings and subheadings to improve readability.
Introduction with Purpose:
Clearly state the purpose, objectives, and scope of the report in the introduction.
Provide context to help readers understand the importance of the information presented.
Methodology Details:
Clearly explain the methods or processes used to gather information.
Include details that would allow others to replicate the study or experiment.
Presentation of Findings:
Give a well-organized and structured presentation of your findings.
Employ graphics (tables, graphs, and charts) to support the text and improve comprehension.
Talk and Interpretation:
Examine the findings and talk about the ramifications.
Explain the significance of the results and how they relate to the main goal.
Brief Conclusion:
Recap the main ideas in the conclusion.
Indicate in detail any suggestions or actions that should be implemented in light of the results.
Explore the Access Platform
Common mistakes for Report Writing
Insufficient defining:.
Error: Employing ambiguous or imprecise wording that could cause misunderstandings.
Impact: It’s possible that readers won’t grasp the content, which could cause misunderstandings and confusion.
Solution: Explain difficult concepts, use clear language, and express ideas clearly.
Inadequate Coordination:
Error: Not adhering to a coherent and systematic format for the report.
Impact: The report’s overall effectiveness may be lowered by readers finding it difficult to follow the information’s flow due to the report’s lack of structure.
Solution: Make sure the sections are arranged clearly and sequentially, each of which adds to the report’s overall coherence.
Inadequate Research:
Error: Conducting insufficient research or relying on incomplete data.
Impact: Inaccuracies in data or lack of comprehensive information can weaken the report’s credibility and reliability.
Solution: Thoroughly research the topic, use reliable sources, and gather comprehensive data to support your findings.
Inconsistent Formatting:
Error: Using inconsistent formatting for headings, fonts, or spacing throughout the report.
Impact: Inconsistent formatting can make the report look unprofessional and distract from the content.
Solution: Maintain a uniform format for headings, fonts, and spacing to enhance the visual appeal and professionalism of the report.
Unsubstantiated Conclusions:
Error: Drawing conclusions that are not adequately supported by the evidence or findings presented.
Impact: Unsubstantiated conclusions can undermine the report’s credibility and weaken the overall argument.
Solution: Ensure that your conclusions are directly derived from the results and are logically connected to your research objectives, providing sufficient evidence to support your claims.
To sum up, proficient report writing necessitates precision, organization, and clarity. Making impactful reports requires avoiding common errors like ambiguous wording, shoddy organization, inadequate research, inconsistent formatting, and conclusions that are not supported by evidence.
One can improve the caliber and legitimacy of their reports by following a logical format, carrying out extensive research, staying clear, and providing conclusions that are supported by evidence.
Aiming for linguistic accuracy and meticulousness guarantees that the desired meaning is communicated successfully, promoting a deeper comprehension of the topic among readers.
About The Author
See author's posts
Recent Posts
- Effective Homeschooling: Laws, Curriculum, Tips and Strategies
- When should you start talking to your child about financial management?
- 7 Misconceptions About Homeschooling in Singapore Debunked
- Summertopiya 2024: Online Summer Learning for Kids & Teens
- Transformative Teaching: Aaysha Sufran’s Journey at Tutopiya
- Join Tutopiya: Be a Top IGCSE Tutor Globally Today!
- 50 Fun Indoor and Outdoor Activities for Kids This Summer
- Mastering the IGCSE: How Mock Exams Transform Study Habits and Techniques
- Summer Fun And Learning: Explore, Create, Make Friends at Summertopiya 2024!
- Beyond Grades: The True Purpose of Education and Mock Assessments Explained
Get Started
Learner guide
Tutor guide
Curriculums
IGCSE Tuition
PSLE Tuition
SIngapore O Level Tuition
Singapore A Level Tuition
SAT Tuition
Math Tuition
Additional Math Tuition
English Tuition
English Literature Tuition
Science Tuition
Physics Tuition
Chemistry Tuition
Biology Tuition
Economics Tuition
Business Studies Tuition
French Tuition
Spanish Tuition
Chinese Tuition
Computer Science Tuition
Geography Tuition
History Tuition
TOK Tuition
Privacy policy
22 Changi Business Park Central 2, #02-08, Singapore, 486032
All rights reserved
©2022 tutopiya

How to Write a Report - Tips and Sample

What is a Report
A report is a written document that presents findings from an investigation, project, or study. It analyzes specific issues or data in detail. This type of writing is common in sciences, social sciences, and business, making it a valuable skill across different fields. Reports have a clear purpose and target audience. Like all academic writing, they emphasize clarity and brevity. Before starting, understand any guidelines in your brief and use headings to organize your report effectively.
Key parts of a report typically include:
- Detailed summaries of events or activities
- Analysis of their impact
- Evaluation of facts and data
- Predictions for future developments
- Recommendations for next steps
Reports differ from essays. While both use factual information, essays include personal opinions and arguments. Reports focus on facts, with interpretations mainly in the conclusion. They are highly structured, often with tables of contents, headings, and subheadings, which help readers quickly locate information. Essays, in contrast, are usually read straight through without needing to jump between sections.
Jobs that Use Written Reports
Many professions rely on written reports to communicate findings, make decisions, and guide future actions. Some of these jobs include:
- Scientists and Researchers : They use reports to document experiments, present research findings, and analyze data. These reports are crucial for advancing knowledge in their fields.
- Healthcare Professionals : Doctors, nurses, and medical researchers write reports to track patient progress, document clinical trials, and share medical research results.
- Business Analysts and Managers : They create reports to analyze market trends, assess financial performance, and propose business strategies. These reports help companies make informed decisions.
- Engineers and Technicians : Reports are used to document project progress, troubleshoot problems, and provide technical evaluations. They are essential for ensuring projects stay on track and meet specifications.
- Law Enforcement and Legal Professionals : Police officers, detectives, and lawyers write reports to document incidents, investigations, and legal proceedings. These reports are vital for building cases and ensuring justice.
- Academics and Educators : Professors, teachers, and educational researchers write reports to present research findings, assess educational methods, and evaluate student performance.
- Environmental Scientists and Conservationists : They use reports to document environmental studies, assess the impact of human activities on ecosystems, and propose conservation strategies.
- Journalists and Writers : They create investigative reports, feature stories, and analysis pieces to inform the public about current events, trends, and important issues.
- Government Officials and Policy Makers : They write reports to analyze policy impacts, assess program effectiveness, and provide recommendations for legislative actions.
- Financial Advisors and Accountants : Reports are used to analyze financial data, evaluate investment options, and provide clients with detailed financial assessments and plans.
Writing Reports Are Not Your Thing?
Our professional writers will get you any report type meeting your requirements in no time
Guide on How to Write a Report
Writing a report can seem challenging, but with clear steps, it becomes manageable. This section will simplify the process, helping you create well-structured and informative reports. Whether you need to write for work, school, or personal projects, following this guide will ensure your report is effective and easy to read. Let's start by breaking down the essential parts and understanding the purpose of each section.
If you want to save time, you can always buy essays online .
.webp)
Understand the Brief
Before you begin writing your report, you must first understand the brief. This step ensures that you know exactly what is required and expected. Here's how to do it:
- Read the Brief Carefully: Make sure you read the assignment or project brief thoroughly. Look for key details such as the purpose of the report, the target audience, and any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Identify the Main Objectives: Determine what the report aims to achieve. Is it to inform, analyze, recommend, or persuade? Knowing the objective helps shape your content and approach.
- Clarify Doubts: If anything is unclear, don't hesitate to ask for clarification. It's better to ask questions upfront than to guess and risk misunderstanding the task.
- Take Notes: Jot down important points from the brief. Highlight deadlines, required sections, and any specific data or information you need to include
Gather Information
Not every piece of information will fit in your report, so choose the ones that directly relate to your topic and support your main points. Finding all the information needed for your report will involve talking to people, reading articles and books, or looking at data like charts and graphs.
Once you have everything, take a moment to organize it. Is there information about the background, the main points, or any conclusions? Think of categories to group similar things together.
Meanwhile, If you want to further advance your writing skills, read our article about how to write a cover letter for essay .
Organize and Analyze Material
Now that you've sorted your information pieces, it's time to see how they fit together. Look for patterns and relationships between the information. Do some pieces contradict each other? Are there different perspectives on the same topic?
Once you see connections, group related pieces together. Think of headings or labels for each group that capture the main idea of that section. This will be the framework for your report's structure.
It is also important to not just describe the information but dig deeper. What does it all mean? Are there trends or underlying causes you can identify? Use your analysis to support your report's arguments or conclusions.
Write the First Draft
Now that you've gathered and organized your information, it's time to build your report. This is where you write your first draft. Start with a strong foundation:
- Grab your reader's attention and introduce the topic of your report. Briefly explain what you'll be covering and why it's important.
- In the body section, use organized information to build your case. Each paragraph should focus on one main point and use evidence from your research (facts, figures, quotes) to support it.
- Some reports may benefit from additional sections like a methodology (how you gathered information) or a limitations section (acknowledging any constraints of your study). Review your report's purpose and see if these sections are necessary.
This is a first draft, so focus on getting your ideas down on paper. Don't get bogged down in perfect grammar or style – you can polish that later. Just make sure you write in a clear way and use everyday language your target audience can understand. Don't be afraid to write freely and rearrange sections later. It's easier to work with a complete draft than a collection of disconnected thoughts.
Review and Redraft
Congratulations, you've conquered the first draft! Now comes the crucial stage of reviewing, editing, and redrafting. This is where you transform your rough draft into a polished and professional report.
Put your report aside for a day or two. This allows you to come back with fresh eyes and a more objective perspective. After, read your report aloud. Does it make sense? Does it flow smoothly from one point to the next? Are there any confusing sections that need clarification?
To edit with a keen eye, follow these tips:
- Grammar and mechanics: This is where you hunt down typos, grammatical errors, and punctuation mistakes. Use a spellchecker, but don't rely solely on it.
- Sentence structure and style: Can you improve the flow of your sentences? Are they concise and easy to understand? Avoid jargon and overly complex sentence structures.
- Strengthen your arguments: Review your evidence. Does it adequately support your claims? Are there any gaps that need to be filled?
- Conciseness is key: Look for opportunities to tighten your writing without sacrificing clarity. Eliminate unnecessary words and redundancy.
- Tailoring your tone: Is your report written in an appropriate tone for your audience? You might need to adjust the formality depending on whether you're writing for a manager, a client, or a scientific journal.
Report Structure Checklist
| Section 📝 | Description 📄 |
|---|---|
| Title Page | |
| Terms of Reference | |
| Summary | |
| Table of Contents | |
| Introduction | |
| Methodology | |
| Results | |
| Discussion | |
| Conclusion | |
| Appendices | |
| Bibliography |
Report Types
There are different types of report papers. Even though they are very formal, academic reports are only one of many people will come across in their lifetime. Some reports concentrate on the annual performance of a company, some on a project's progress, and others on scientific findings.
.webp)
Academic Reports
An academic report represents supported data and information about a particular subject. This could be a historical event, a book, or a scientific finding. The credibility of such academic writing is very important as it, in the future, could be used as a backup for dissertations, essays, and other academic work.
Students are often assigned to write reports to test their understanding of a topic. They also provide evidence of the student's ability to critically analyze and synthesize information. It also demonstrates the student's writing skills and ability to simply convey complex findings and ideas.
Project Reports
Every project has numerous stakeholders who like to keep an eye on how things are going. This can be challenging if the number of people who need to be kept in the loop is high. One way to ensure everyone is updated and on the same page is periodic project reports.
Project managers are often assigned to make a report for people that affect the project's fate. It is a detailed document that summarizes the work done during the project and the work that needs to be completed. It informs about deadlines and helps form coherent expectations. Previous reports can be used as a reference point as the project progresses.
Sales Reports
Sales reports are excellent ways to keep your team updated on your sales strategies. It provides significant information to stakeholders, including managers, investors, and executives, so they can make informed decisions about the direction of their business.
A sales report usually provides information about a company's sales performance over a precise period. These reports include information about the revenue generated, the total number of units sold, and other metrics that help the company define the success of sales performance.
Sales report preparation is a meticulous job. To communicate information engagingly, you can put together graphs showing various information, including engagement increase, profit margins, and more.
Business Reports
If you were assigned a business report, something tells us you are wondering how to write a report for work. Let us tell you that the strategy is not much different from writing an academic report. A Strong thesis statement, compelling storytelling, credible sources, and correct format are all that matter.
Business reports can take many forms, such as marketing reports, operational reports, market research reports, feasible studies, and more. The purpose of such report writing is to provide analysis and recommendations to support decision-making and help shape a company's future strategy.
Most business reports include charts, graphs, and other visual aids that help illustrate key points and make complex information easy to digest.
Scientific Reports
Scientific reports present the results of scientific research or investigation to a specific audience. Unlike book reports, a scientific report is always reviewed by other experts in the field for its accuracy, quality, and relevance.
If you are a scientist or a science student, you can't escape writing a lab report. You will need to provide background information on the research topic and explain the study's purpose. A scientific report includes a discussion part where the researcher interprets the results and significance of the study.
Whether you are assigned to write medical reports or make a report about new findings in the field of physics, your writing should always have an introduction, methodology, results, conclusion, and references. These are the foundation of a well-written report.
Annual Reports
An annual report is a comprehensive piece of writing that provides information about a company's performance over a year. In its nature, it might remind us of extended financial reports.
Annual reports represent types of longer reports. They usually include an overview of a company's activities, a financial summary, detailed product and service information, and market conditions. But it's not just a report of the company's performance in the sales market, but also an overview of its social responsibility programs and sustainability activities.
The format of annual report writing depends on the company's specific requirements, the needs of its stakeholder, and the regulation of the country it's based.
Student Research Report Sample
Here is a sample report that uses the format and tips we discussed in the article. Remember, this is just an example. Feel free to adjust the content to match your own research findings and analysis.
Meanwhile, if you need an expert to help with your physics homework, our physics helper is ready to take on the job!
The Bottom Line
By following the steps and tips outlined in this guide, you can create a clear, concise, and effective report. Remember to:
- Understand the brief thoroughly before you start.
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your report logically.
- Keep your writing clear, focusing on facts and analysis.
- Tailor your content to your audience and purpose.
- Proofread carefully to ensure clarity and accuracy.
And if you're short on time for other assignments, just say, ' write my argumentative essay ,' and our expert writers will gladly help you out.
Are You Looking for Help with Your Writing?
Our expert writers will provide top-notch assistance with any writing project
How to Write a Short Report?
What is the format of a report, what is the structure of a report.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Added new sections like defining reports, jobs that use reports, checklist, etc
- Added a new sample, FAQs and a checklist
- Updated writing guidelines
- REPORT WRITING TOP TIP Writing the report: where do I start? TOP TIP Understand the brief . (n.d.). https://www.ucc.ie/en/media/support/skillscentre/pdfx27sampbookmarks/ReportWriting.pdf
- EAP Writing Reports . (n.d.). Www.uefap.com. Retrieved June 26, 2024, from https://www.uefap.com/writing/genre/report.htm
.webp)

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.4: Writing Formal Reports
While you may write much shorter, more casual reports, it’s helpful to go into a bit of detail about formal reports. Formal reports are modular, which means that they have many pieces. Most audience members will not read every piece, so these pieces should stand on their own. That means that you will sometimes repeat yourself. That’s okay. Your audience should be able to find exactly what they need in a particular section, even if that information has already been introduced elsewhere.
For example, the Executive Summary is aimed at managers. It’s a short, persuasive overview of everything in the report. The Introduction may contain very similar information, but it focuses on giving a short, technical overview of everything in the report. Its goal is to inform, not to persuade.
Let’s take a look at some of the parts of the report in greater detail.
The title page may be formatted in different ways depending on company-specific requirements, but it generally provides the audience with the following information:
- This should appear 2 inches from the top margin in uppercase letters.
- Type “Prepared for” on one line, followed by two separate lines that provide the receiving organization’s name and then the city and state. Some reports may include an additional line that presents the name of a specific person.
- Type “prepared by” on one line, followed by the name(s) of the author(s) and their organization, all on separate lines.
- This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
The items on the title page should be equally spaced apart from each other.
A Note on Page Numbers:
The title page should not include a page number, but this page is counted as page “i.” Use software features to create two sections for your report. You can then utilize two different types of numbering schemes. When numbering the pages (i.e., i, ii, iii, etc.) for a formal report, use lowercase roman numerals for all front matter components. Use arabic numbers for the other pages that follow. Additionally, if you intend to bind the report on the left, move the left margin and center 0.25 inches to the right.
Letter of Transmittal
A letter of transmittal announces the report topic to the recipient(s).
If applicable, the first paragraph should identify who authorized the report and why the report is significant. Provide the purpose of the report in the first paragraph as well. The next paragraph should briefly identify, categorize, and describe the primary and secondary research of the report. Use the concluding paragraph to offer to discuss the report; it is also customary to conclude by thanking the reader for their time and consideration.
The letter of transmittal should be formatted as a business letter ( please see 4.3: Writing Business Letters for more details ). Some report writers prefer to send a memo of transmittal instead.
When considering your audience for the letter or memo of transmittal, make sure that you use a level of formality appropriate for your relationship with the reader. While all letters should contain professional and respectful language, a letter to someone you do not know should pay closer attention to the formality of the word choice and tone.
Table of Contents
The table of contents page features the headings and secondary headings of the report and their page numbers, enabling audience members to quickly locate specific parts of the report. Leaders (i.e. spaced or unspaced dots) are used to guide the reader’s eye from the headings to their page numbers.
The words “TABLE OF CONTENTS” should appear at the top of the page in all uppercase and bolded letters. You can type the titles of major report parts in all uppercase letters as well, double spacing between them. Secondary headings should be indented and single spaced, using a combination of upper- and lowercase letters.
Executive Summary
An executive summary presents an overview of the report that can be used as a time-saving device by recipients who do not have time to read the entire report.
The executive summary should include a:
- Summary of purpose
- Overview of key findings
- Identification of conclusions
- Overview of recommendations
To begin, type “EXECUTIVE SUMMARY” in all uppercase letters and centered. Follow this functional head with paragraphs that include the above information, but do not use first-level headings to separate each item. Each paragraph of information should be single-spaced with double spacing between paragraphs. Everything except for the title should be left-aligned.
An executive summary is usually ten percent of the length of the report. For example, a ten-page report should offer a one-page summary. A 100-page report should feature a summary that is approximately ten pages.
The executive summary is usually seen as the most important part of the report, and it should be written last. When you’re writing the executive summary, imagine sitting across from your most important audience members. If you have just a few minutes to talk to them, what do you want them to know? What would be most persuasive?
Introduction
The main text of a formal report begins with an introduction. The introduction sets the stage for the report, clarifies what need(s) motivated it, and helps the reader understand what structure the report will follow.
Most report introductions address the following elements: background information, problem or purpose, significance, scope, methods, organization, and sources. As you may have noticed, some parts of a formal report fulfill similar purposes. Information from the letter of transmittal and the executive summary may be repeated in the introduction. Reword the information in order to avoid sounding repetitive.
To begin this section, type “BACKGROUND” or “INTRODUCTION” in all uppercase letters. This functional head should be followed by the information specified above (i.e., background information, problem or purpose, etc.). You do not need to utilize any first-level headings in this section. Because this section includes background information, it would be the appropriate place to provide information for audiences that may need additional knowledge about the topic. Provide definitions of technical terms and instruction about the overall project if necessary. If you are uncertain if your audience needs a particular piece of information, go ahead and include it; it’s better to give your reader too much background than not enough.
Discussion of Findings
The Discussion of Findings section presents the evidence for your conclusions.
This key section should be carefully organized to enhance readability.
Useful organizational patterns for report findings include but are not limited to:
- Best Case/Worst Case
- Compare/Contrast
- Journalistic Pattern
Use a Best Case/Worst Case organizational pattern when you think that the audience may lack interest in the topic. When examining a topic with clear alternatives to your proposed solution, consider using a Compare/Contrast pattern. Geographical patterns work effectively for topics that are discussed by location.
When describing the organization of the report in the first paragraph, broadly identify how the material in the report is organized rather than state that the report uses a specific pattern (e.g. Chronology, Geography). For example, write, “The research findings address curriculum trends in three provinces: (a) British Columbia, (b) Alberta, and (c) Ontario,” not, “This report uses a geographical organizational pattern.”
Follow the first paragraph with a first-level heading. Use first-level headings for all other major parts of this section. First-level headings should appear in bold font. Center first-level headings, but align any second-level headings with the left margin. Type any second-level headings in bold, upper- and lowercase letters.
Using numbers to distinguish between first-level and second-level headings might be a good idea if you have a lot of sections (example: 1.First-level Heading vs. 1.1. Second-level Heading).
As you present, interpret, and analyze evidence, consider using both text and graphics. Take into account what will be easiest for your audience to understand.
Include citations for all quoted or paraphrased material from sources as well; check with your organization as to whether they prefer parenthetical citations or footnotes.
Integrating Graphics
Formal report authors use graphics to present data in different forms. Paragraphs of text and complex or numerical data tend to bog readers down, making graphics a beneficial enhancement. Graphics also make data easier to understand, so they sometimes make a stronger impact on the audience.
Knowing when—and how—to effectively employ graphics is key to successfully integrating them. Keeping the audience in mind is also critical ( for more information about creating charts and graphs, see 2.3: Effective Document Design and Appendix A: Visual Communication .)
Conclusions and Recommendations
The conclusions and recommendations section conveys the key results from the analysis in the discussion of findings section. Up to this point, readers have carefully reviewed the data in the report; they are now logically prepared to read the report’s conclusions and recommendations.
Type “CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS” in all uppercase letters. Follow this functional heading with the conclusions of the report. The conclusions should answer any research questions that were posed earlier in the report. Present the conclusions in an enumerated or bulleted list to enhance readability.
Recommendations offer a course of action, and they should answer any problem or research questions as well. Think back to the expectations of your audience. Have all of their requirements been addressed?
Works Cited/ Reference Page
All formal reports should include a works cited page; his page documents the sources cited within the report. The recipient(s) of the report can also refer to this page to locate sources for further research.
It is acceptable to follow MLA ( Modern Language Association ), CMS ( Chicago Manual of Style ), or APA (American Psychological Association) documentation style for entries on this page. Arrange all sources alphabetically. Refer to the latest edition of the appropriate style handbook for more information about how to format entries for print and electronic sources.
While some formatting rules may seem tedious at first, they are necessary in order for your audience to better understand the report and to be able to locate and examine your sources if needed. Using a regulated format allows for an organization and citation style that everyone can follow. Being aware of your audience’s needs and expectations will allow for a strong report that will satisfy your employee and demonstrate your competence in your field.
9.4: Writing Formal Reports Copyright © 2021 by Melissa Ashman; Arley Cruthers; eCampusOntario; Ontario Business Faculty; and University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Formal Report
Report generator.

Reports give information in a capsulized form. They let you discuss a specific topic or subject which is typically presented to a particular audience for a certain purpose. There are two basic ways of delivering reports: written report and oral. Each of which is effective in disseminating information to the audience.
18+ Formal Report Examples
Formal report example.

- Google Docs
Size: A4, US
Download this well-made formal report template as it will make your daily business operations smooth and hassle-free. As it is ready-made, it is easy to edit and customize any content that you want to be replaced. Once you have downloaded this template, you may open it on any software device in any file format.
Business Report Sample

Business reports are commonly used in the business industry, which is why it is always a good idea to make use of the above-shown ready-made report template. This document can help you create a report in no time. Just enter your business details in the desired places of the report and get it printed. It is convenient to use as it can be opened in various file formats.
Corporate Report Example

Submit corporate reports to the top management by using this formally written and professionally designed corporate report template. This template comes with an easy-to-edit document outline with report sections so that you can easily prepare your report. Download this business report template now on your PC or mobile device in any file format of your choice.
Collection Report Example

Easily track and document information relating to payments of your business with the help of this “Collection Report” template. As it is highly customizable in nature, you can make changes to it however you want. Download now, and open on any software device of your choosing!
Training Report Template Example

- Apple Pages
Size: 39 KB
Professional Report Template Example

Size: 41 KB
Event Report Template Example

Size: 37 KB
Consulting Report Template Example

Size: 36 KB
Monthly Report Template Example

Size: 31 KB
Formal Laboratory Report Example

Size: 319 KB
Formal Business Report

Size: 104 KB
Formal Investigation Report

Formal Audit and Review Report Sample

Size: 180 KB
Formal Incident Report

Size: 17 KB
Formal Analytical Report Sample

Size: 14 KB
Formal Recommendation Report

Size: 94 KB
Formal Accident Sample Report
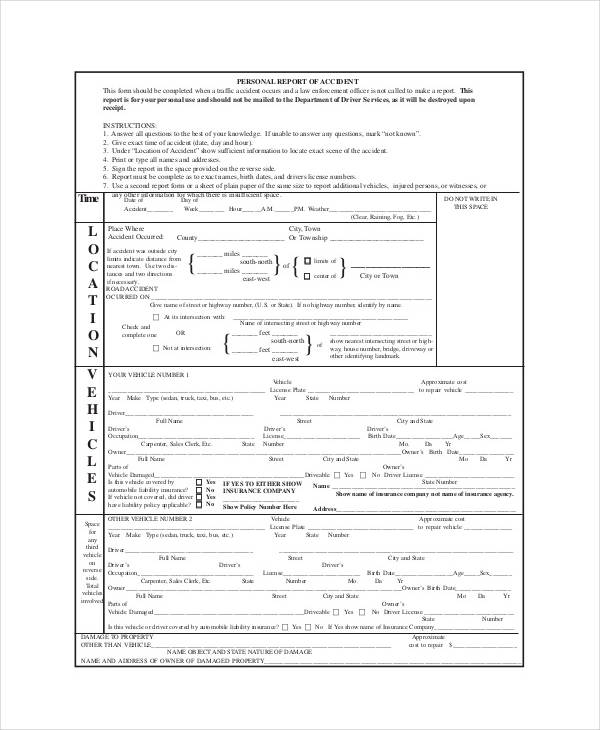
Size: 19 KB
Formal Progress Report

Size: 73 KB
Short Formal Report Example

Size: 102 KB
A free report does not only present facts on specific topics but also evidence and accounts (both written and oral) which typically supports such a report. Different reports provide different information.
What Is a Formal Report?
In business, a formal report is considered an important report which includes a detailed presentation of different pieces of information necessary for business operations and the decision-making process. A formal report typically carries information obtained from the research, formal analysis , and observations conducted during a specific period of time.
Formal reports may either be informative or analytical and they discuss a certain problem in-depth. They also come up with a solution to address such a problem.
How to Write a Formal Report
The rules, as well as the terms of writing a formal report, may differ from one organization to another. Still, the research reports are written in order to communicate with a specific audience.
In order to write a formal report, one must first be familiar with the rules and terms for writing a formal report. Of course, one needs to observe the correctness and accuracy of the information being provided, while at the same time providing the necessary evidence to prove the collection of such information.
Another thing the writer needs to consider is the readers—whether or not they would be able to understand the information presented. Because a report is a summarized form of the whole project report , the author needs to carefully think as to what information to include, and whether or not such information is important enough to be included in the report.
Components of a Formal Report
The elements present in a formal report tend to vary depending on the standard format set by each company or organization. Such components are the divisions that make a formal report easy to comprehend. Here are the basic components that are typically found in a formal report.
- Cover page.
- Letter of transmittal. This section contains a brief description of the report or the project presented on the report, which typically ends with an assignment or instruction for its readers.
- Title page. This section includes the name of the report (or the topic of the report), the name of the authors (with the necessary descriptions), the name of recipients (e.g. panels, judges, etc.) including titles (or designations) and name of the organization where they belong.
- Table of contents. It contains section headings and page numbers where each section begins.
- List of tables and figures. Contains a list of figure and table names, including pages where each figure and table are found.
- Abstract or executive summary. Summarizes what the whole report is all about, and the details of the subject being tackled in the report.
- Introduction, body, and conclusion. These sections discuss the structure of the report in full detail.
- Appendices. Supporting details and information not found on the preceding pages.
- References. Works cited, written in a specific format.
General FAQs
1. what do you mean by a formal report.
A formal report is an official document that contains detailed information relating to a certain subject or problem. It helps make business decisions and is written for a specific audience.
2. What is the Format of a Formal Report?
The format of a formal report is as follows:
- Cover letter
- Table of contents
- Abstract page
- Introduction
- Conclusion and Recommendations
3. What is the Importance of Writing a Formal Report?
A formal report is crucial for every company as it helps them keep records of the work that has been done during a specific period. It lets them describe problems and evaluate their importance.
4. What is the Main Difference Between a Formal and Informal Report?
A formal report follows a detailed structure and is often used in academic papers or when there is a need to present a lengthy overview of development within a business. An informal report, however, can be structured in anyway and is typically used for shorter documents.
5. What Are Some Examples of Formal Reports?
Here are some examples of formal reports:
- Inspection Report
- Safety Report
- Compliance Report
- Incident Report
- Annual Report
- Research reports
- Feasibility reports
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, formal reports.
- © 2023 by Angela Eward-Mangione - Hillsborough Community College , Katherine McGee
Formal Reports are a common genre of discourse in business and academic settings . Formal Reports are fancy. They aren’t one-offs. They tend to written by teams of people, often distributed teams. And they often report results from substantive textual research and empirical research . Corporations invest substantial sums to produce formal reports.
Formal Reports tend to share these organizational characteristics:
- front matter (prefatory) material
- back matter (supplementary) items.
Key Words: Organizational Schema
Many business professionals need to write a formal report at some point during their career, and some professionals write them on a regular basis. Knowledge Workers in business, education, and government use formal reports to make important decisions.
The purposes for Formal Reports vary across occasions , professions, disciplinary communities . They tend to be high stakes documents. Common types of formal reports include
- Personnel Evaluation Reports
- Feasibility Reports
- Recommendation Reports
Analyze Your Audience
As with any genre of writing, when writing formal business reports, it is necessary to know your audience . For example, if your audience is familiar with the background information related to your project, you don’t want to bombard them with details; instead, you will want to inform your audience about the aspects of your topic that they’re unfamiliar with or have limited knowledge of. In contrast, if your audience does not already know anything about your project, you will want to give them all of the necessary information for them to understand. Age and educational level are also important to consider when you write. You don’t want to use technical jargon when writing to an audience of non-specialists. These are just a couple of examples of different audience needs you will want to consider as you write your report. There are several aspects of your audience that you want to take into account: their gender and race/ethnicity, age/educational level, subject knowledge, and expectations–what they expect to learn from your report.
Gender and Race/Ethnicity
You don’t want to make assumptions about the gender, race, or beliefs of your audience. Use gender neutral language such as “he or she” rather than simply “he” or use “they” and pluralize the nouns (e.g. Writers need to think about audience). Don’t say anything that implies your reader has a certain gender, race, cultural identity, or belief system. One important way to avoid doing this is to avoid using the word “you.” Writers always need to think about the implied meanings of their words.
Educational Level and Subject Knowledge
While age may not necessarily be an issue in the business world—your audience will almost all be adults—educational level and knowledge of your subject are important to consider when writing your report. If you are writing for someone outside of your specific field, you will either need to exclude technical jargon or provide in-text reminders or indications of what specific terms mean or items are. For example, if you work for an automotive company, and you are writing on behalf of mechanical engineers but for an audience of business professionals, you don’t want to assume that your audience knows the names of all of the parts that make up an engine; you will have to use terms they will recognize. In some cases, a glossary of terms may be appropriate.
Expectations and Research
What does your audience expect to get out of reading your report? What is its purpose? Make sure that you have specifically responded to the expectations of your boss, manager, or client. If your audience expects you to have research, make sure you know what type of research they expect. Do they want research from scholarly journal articles? Do they want you to conduct your own research? No matter what type of research you do, make sure that it is properly documented using whatever format the audience prefers (MLA, APA, and Chicago Manual of Style are some of the most commonly-used formats). You also want to establish a strong ethos in your report. Use confident language that shows that you have done your research and present them with the research.
Here are some questions to consider about your audience as you write:
- What does your audience expect to learn from your report?
- What type of ethos should you establish?
- How much research does your audience expect you to have?
- How current does your research need to be?
- What types of sources does your audience expect you to have?
- What is the age of your audience?
- What is the educational level of your audience?
- How much background information does your audience need?
- What technical terms will your audience need defined? What terms will they already be familiar with?
- What is the cultural background of your audience?
[ Audience | Audience Analysis for Technical Documents | Diplomacy, Tone, and Emphasis in Business Writing ]
Stylistic Conventions for Formal Reports
Not surprisingly, Formal Reports employ a technical, professional writing style . Yet what is perhaps surprising is the preponderance of the passive voice in Formal Reports.
Contrary to what is expected in other types of writing, in business reports, passive voice is sometimes preferred. If the action is more important than the person doing it, use passive rather than active voice.
A few phrases you might use include:
- The data analyzed in this report shows . . .
- This study was designed to analyze . . .
- The data was collected . . .
- The 500 students were surveyed
[ When is Passive Voice Preferable to the Active Voice? | You-Centered Business Style ]
Conventions for Organizaing Formal Reports
There are several different organizational strategies that may be used for formal reports, but all formal reports contain front matter (prefatory) material, a body, and back matter (supplementary) items. The body of a formal report discusses the findings that lead to the recommendations. The prefatory material is therefore critical to providing the audience with an overview and roadmap of the report. The following section will explain how to write a formal report with an audience in mind.
Front Matter Components
The title page provides the audience with the:
- This should appear 2 inches from the top margin in uppercase letters.
- Type “Prepared for” on one line, followed by two separate lines that provide the receiving organization’s name and then the city and state. Some reports may include an additional line that presents the name of a specific person.
- Type “prepared by” on one line, followed by the name(s) of the author(s) and their organization, all on separate lines.
- This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
The items on the title page should be equally spaced apart from each other.
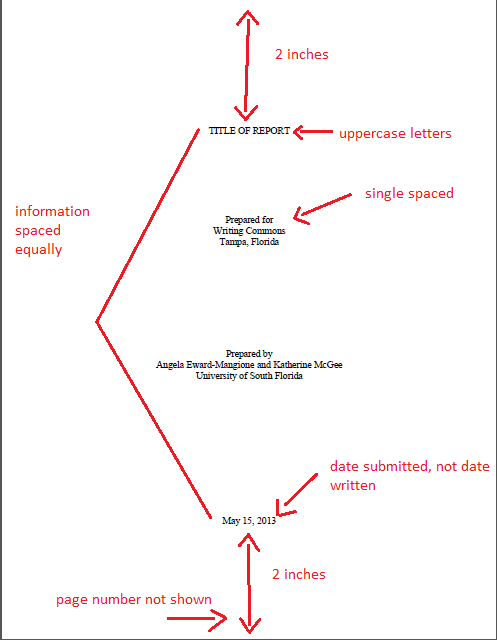
A note on page numbers:
The title page should not include a page number, but this page is counted as page “i.” Use software features to create two sections for your report. You can then utilize two different types of numbering schemes. When numbering the pages (i.e., i, ii, iii, etc.) for a formal report, use lowercase roman numerals for all front matter components. Utilize arabic numbers for the other pages that follow. Additionally, if you intend to bind the report on the left, move the left margin and center 0.25 inches to the right.
A note on font:
If there is no specific preference for serif vs. sans serif font, choose one and use it consistently throughout the report. Do not utilize anything besides a traditional serif (e.g., Times New Roman) or sans serif (e.g., Arial or Calibri) font.
Letter of Transmittal
A letter of transmittal announces the report topic to the recipient(s).
If applicable, the first paragraph should identify who authorized the report and why the report is significant. Provide the purpose of the report in the first paragraph as well. The next paragraph should briefly identify, categorize, and describe the primary and secondary research of the report. Use the concluding paragraph to offer to discuss the report; it is also customary to conclude by thanking the reader for their time and consideration.
The letter of transmittal should be formatted as a business letter. Some report writers prefer to send a memo of transmittal instead.
When considering your audience for the letter or memo of transmittal, make sure that you use a level of formality appropriate for your relationship with the reader. While all letters should contain professional and respectful language, a letter to someone you do not know should pay closer attention to the formality of the word choice and tone.
The table of contents page features the headings and secondary headings of the report and their page numbers, enabling audience members to quickly locate specific parts of the report. Leaders (i.e. spaced or unspaced dots) are used to guide the reader’s eye from the headings to their page numbers.

The words “TABLE OF CONTENTS” should appear at the top of the page in all uppercase and bolded letters. Type the titles of major report parts in all uppercase letters as well, double spacing between them. Secondary headings should be indented and single spaced, using a combination of upper- and lowercase letters.
Executive Summary
An executive summary presents an overview of the report that can be used as a time-saving device by recipients who do not have time to read the entire report.
The executive summary should include a:
- Summary of purpose
- Overview of key findings
- Identification of conclusions
- Overview of recommendations
To begin, type “EXECUTIVE SUMMARY” in all uppercase letters and centered. Follow this functional head with paragraphs that include the above information, but do not use first-level headings to separate each item. Each paragraph of information should be single-spaced with double spacing between paragraphs. Everything except for the title should be left-aligned.
An executive summary is usually ten percent of the length of the report. For example, a ten-page report should offer a one-page summary. A 100-page report should feature a summary that is approximately ten pages.
Body of Report
The body of a formal report begins with an introduction. The introduction sets the stage for the report, clarifies what need(s) motivated it, and orients the reader to its structure.
Most report introductions address the following elements: background information, problem or purpose, significance, scope, methods, organization, and sources. As you may have noticed, some parts of a formal report fulfill similar purposes. Information from the letter of transmittal and the executive summary may be repeated in the introduction. Reword the information in order to avoid sounding repetitive.

To begin this section, type “BACKGROUND” or “INTRODUCTION” in all uppercase letters. This functional head should be followed by the information specified above (i.e., background information, problem or purpose, etc.). You do not need to utilize any first-level headings in this section.
Because this section includes background information, it would be the appropriate place to address the needs of audiences that may need additional knowledge about the topic. Provide definitions of technical terms and instruction about the overall project if necessary. If you are uncertain if your audience needs a particular piece of information, go ahead and include it; it’s better to give your reader a little bit too much background than not enough.
Discussion of Findings
The Discussion of Findings section presents the evidence for your conclusions.
This key section should be carefully organized to enhance readability.
To begin, type “DISCUSSION OF FINDINGS” in all uppercase letters. Center this and all other functional heads. Follow “DISCUSSION OF FINDINGS” with a brief paragraph that previews the organization of the report.
Useful organizational patterns for report findings include but are not limited to:
- Best Case/Worst Case
- Compare/Contrast
- Journalism Pattern
Use a Best Case/Worst Case organizational pattern when you think that the audience may lack interest in the topic. When examining a topic with clear alternatives to your proposed solution, consider using a Compare/Contrast pattern. Geographical patterns work effectively for topics that are discussed by location.
When describing the organization of the report in the first paragraph, broadly identify how the material in the report is organized rather than state that the report uses a specific pattern (e.g. Chronology, Geography). For example, write, “The research findings address curriculum trends in three states: (a) Florida, (b) Georgia, and (c) North Carolina,” not, “This report uses a geographical organizational pattern.”
Follow the first paragraph with a first-level heading. Use first-level headings for all other major parts of this section. First-level headings should appear in bold, uppercase letters. Center first-level headings, but align any second-level headings with the left margin. Type any second-level headings in bold, upper- and lowercase letters.
As you present, interpret, and analyze evidence, consider using both text and graphics. Take into account what will be easiest for your audience to understand.
Include citations for all quoted or paraphrased material from sources as well; check with your organization as to whether they prefer parenthetical citations or footnotes.
Integrating Graphics
Formal report authors use graphics to present data in different forms. Paragraphs of text and complex or numerical data tend to bog readers down, making graphics a beneficial enhancement. Graphics also make data easier to understand, so they sometimes make a stronger impact on the audience.
Knowing when—and how—to effectively employ graphics is the key to successfully integrating them. Keeping the audience in mind is also critical.
Figure 1 summarizes uses and audience benefits for the most frequently employed types of graphics. The types of graphics are presented alphabetically to make them easier to remember.
| Graphic Type | USE This type . . . | BENEFITS The audience can . . . |
| Bar Chart | Represents data with the height or length of rectangular bars | Compare items Grasp a series of numbers |
| Flowchart | Illustrates a sequence of events with shapes connected by arrows | Grasp a series of steps |
| Line Chart | Shows changes in quantitative data over time or plots the relationship between two variables with one or more lines | Compare variables Visualize change over time |
| Map | Illustrates activities or trends on a map that represents geographically organized parts of a region, country, or the world | Compare geographical trends Grasp geographical relationships |
| Pie Chart | Depicts distribution of parts in a whole with wedges in a circle graph | Compare significance of parts and parts-to-whole relationship(s) |
| Table | Presents data or values in rows and columns | Compare data or values Grasp relationships between data or values |
Computers have made it easier for professionals to create effective graphics. Most of the graphics in Figure 1 can be created in Microsoft Office Word and Excel.
There may also be some occasions in which a formal report includes graphics from a particular print or online source. In these instances, it is critical to include a caption that presents the source of the graphic.
Back Matter Components
Conclusions and recommendations.
The conclusions and recommendations section conveys the key results from the analysis in the discussion of findings section. Up to this point, readers have carefully reviewed the data in the report; they are now logically prepared to read the report’s conclusions and recommendations.
Type “CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS” in all uppercase letters. Follow this functional head with the conclusions of the report. The conclusions should answer any research questions that were posed earlier in the report. Present the conclusions in an enumerated or bulleted list to enhance readability.
Recommendations offer a course of action, and they should answer any problem or research questions as well. Think back to the expectations of your audience. Have all of their requirements been addressed?
Works Cited
All formal reports should include a works cited page; his page documents the sources cited within the report. The recipient(s) of the report can also refer to this page to locate sources for further research.
It is acceptable to follow MLA (Modern Language Association), CMS (Chicago Manual of Style), or APA (American Psychological Association) documentation style for entries on this page. Arrange all sources alphabetically. Refer to the latest edition of the appropriate style handbook for more information about how to format entries for print and electronic sources on the Works Cited page
While some of the formatting rules may seem tedious at first, they are necessary in order for your audience to better understand the report. Using a regulated format allows for a more universal organization that everyone will understand. Being aware of your audience’s needs and expectations will allow for a strong report that will satisfy your employee and demonstrate your competence in your field.
Recommended Resources
- Recommendation Report Assignment

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

- Essay Editor
How to Write a Business Report With Example

One of the most effective ways to convey essential information is through a business report. This article will guide you through the purpose of a business report, provide valuable writing tips, outline how to format your business report correctly and offer an example for better understanding.
What is the Purpose of a Business Report?
A business report serves as a critical tool for decision-making within an organization. Its primary purpose is to analyze a particular situation or issue, evaluate the available options, and provide recommendations based on the findings. Business reports convey information in a structured and organized manner, making it easier for stakeholders to understand the implications and make informed decisions. They can address various aspects such as financial performance, market analysis, project evaluations, or operational efficiency.
Business Report Writing Tips
Writing a business report requires a methodical approach and attention to detail. Here are some essential tips to ensure your report is effective and professional:
- Understand the objective: Before you start writing, clearly understand the purpose of the report. Know what information is needed and why it is important.
- Know your audience: Tailor your report to your audience's needs. Consider their level of knowledge about the subject and what they are looking to gain from it.
- Be clear and concise: Use straightforward language and avoid jargon. Keep sentences and paragraphs short to maintain readability.
- Use evidence-based analysis: Support your findings and recommendations with data, statistics, and credible sources. This strengthens the validity of your report.
- Organize logically: Structure your report in a logical order. Start with the most critical information and follow with supporting details.
- Revise and proofread: Ensure your report is free from grammatical errors and typos. Review the content for clarity, coherence, and accuracy.
Determining Business Report Types
Different types of business reports serve different purposes. Determining the type of report you need to write before you begin is important. Common types include:
- Informational reports: Provide data without analysis or recommendations, such as monthly sales reports.
- Analytical reports: Include analysis and interpretation of data, along with recommendations, like market analysis reports.
- Research reports: Present research studies findings and may include data and analysis.
- Progress reports: Update stakeholders on the progress of a project, including achievements and any issues encountered.
- Financial reports: Offer detailed financial information and analysis, such as annual financial statements.
How to Format Your Business Report Correctly?
Formatting a business report correctly ensures it is professional and easy to navigate. Here's a breakdown of the essential components of a business report structure:
Table of Contents
The table of contents is crucial for guiding readers through your report. It should list all the sections and sub-sections along with their corresponding page numbers, allowing readers to quickly find the information they are looking for.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is a brief overview of the report. It should summarize the key points, including the purpose of the report, major findings, and recommendations. This section lets busy executives grasp the main insights without reading the entire document.
Body Paragraphs
The body of the report contains detailed content and is usually divided into several sections. Each section should have a clear heading and be organized logically. Here are some common sections found in business reports:
- Introduction: Explains the background, purpose, and scope of the report.
- Methodology: Describes how the data was collected and analyzed.
- Analysis: Presents the findings of the report in detail.
- Discussion: Interprets the findings and discusses their implications.
Findings & Recommendations
This section is critical as it presents the report's main findings and provides actionable recommendations based on them. Ensure that each recommendation is supported by the data and analysis provided in the report.
Conclusion Paragraph
The conclusion should briefly summarize the key findings and recommendations. It should restate the importance of the report's objectives and the value of the recommendations provided.
Example of a Business Report
Here is a brief written report example to help you understand how to apply these principles. This business report example for students outlines a market analysis for a new product launch.
Related articles
How to write a reaction paper nice and easy.
In the world of student home assignments there lives an interesting and creative project, a reaction essay, by name. It deals with the person's feedback on a movie, book, article, a piece of work, evoking thoughts and emotions. What is the essence of this paper? How to write a perfect one? Let's get acquainted with this issue. At first, imagine the situation when you've just watched a deep philosophical movie or read an article that cut you to the very heart. You feel like thunderstruck. You ne ...
Classification Essay Guide
A classification essay is a powerful tool in academic writing, enabling writers to break down broad topics into organized categories for better understanding. This guide will show you how to write a classification essay, from designing a perfect outline to selecting compelling topics. Continue reading to learn how to create a clear, insightful, and engaging classification essay. What is a Classification Essay? A Brief Overview A classification essay is a type of academic writing that involves ...
How to Write a Successful Letter of Motivation
Every person wishing to get to College or University faces a real challenge – writing a motivation letter. Through lack of knowledge, the process may seem quite stressful and backbreaking. But the devil is not so black as he is painted. Just calm down and let's start. Today we will: 1. discuss the structure of a motivation letter and its peculiarities in terms of sense and format; 2. accentuate the moments, colleges pay special attention to; and 3. give some tips on how to create a real suc ...
How to Write a Good Conclusion For a Lab Report
Writing a good conclusion for your science lab report can be the difference between a good grade and a great one. It's your last chance to show you understand the experiment and why it matters. This article will help you learn how to write a lab conclusion that sums up your work and shows your teacher that you understood what you did. What Should Be in Your Lab Report Conclusion? A good lab report conclusion wraps up your lab work in a neat package. When you're thinking about how to write a c ...
How to Write Recommendations in Research Paper
Every research paper should end with a conclusion and recommendations concerning the main topic. How to write a recommendation report? What should be added in this part, and what – shouldn't be? What is the structure of this section? Having answered these questions, a person may write this fragment of the project perfectly. Let's get into this issue together. Recommendations in a research paper: meaning and purpose What is the purpose of recommendations? Why are they so important? Generally, ...
Essay Format Tips from an English Teacher
Writing a solid and well-crafted essay is crucial for students and researchers, as it involves presenting arguments clearly and succinctly. Whether you are writing a paper for an assignment, a scientific journal, or a personal statement, understanding the correct essay format is pivotal. This meticulously collated guide covers key features of essay formatting and provides tips to refine your writing. What is an Essay Format? An essay format is a blueprint for shaping your written assignment, ...
How to Write Essay Introductions
When you acquaint two strangers, you introduce one person to another, right? The same thing concerns the text and any material you wish to present to your reader or listener. At that moment an introduction composed of letters comes onto the stage and plays its leading part. Being the first thing the audience is faced with, an essay introduction should catch a person's attention, give information about the topic and idea the author discusses, and prepare him for the following comprehension. How ...
Diagnostic Essay Writing Guide and Outline Sample
Imagine stepping into a classroom on the first day and being asked to write an essay. This exercise, commonly referred to as a diagnostic essay, is a common tool used by instructors to gauge their students' writing proficiency. Interestingly, in a study exploring the effectiveness of evaluation papers, over 70% of participants reported that these tasks significantly improved their understanding of their writing strengths and challenges. This finding underscores the assessment assignment's role i ...
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
4 takeaways from the first presidential debate

Domenico Montanaro

President Biden and former President Donald Trump participate in the first presidential debate of the 2024 elections at CNN's studios in Atlanta on June 27. Andrew Caballero-Reynolds/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
If some people who listened to the radio in 1960 thought Richard Nixon won the presidential debate with John F. Kennedy, then maybe people reading the transcript of Thursday night’s match-up would think President Biden won.
But elections aren’t won in transcripts. The reality is, fairly or not, debates are often about optics — how the candidates present themselves, defend their records and parry attacks.

Fact check: What did Biden and Trump claim about immigration in the debate?
And that’s why so many Democrats are ringing the fire alarms after the first general-election presidential debate of 2024. The Biden campaign said the president had a cold to explain why he sounded so hoarse and weak. But Biden’s stumbles right from the beginning played into his biggest vulnerability — his age and whether the 81-year-old is up to the challenge of handling four more years in office.
There were issues for Trump, too, as he continued to spread falsehoods and bathe in the kinds of conspiratorial grievances that have turned off many voters.
Not much has changed the dynamics of this race; will anything that happened Thursday night make a difference either?
Here are four takeaways from the first Biden-Trump debate of this campaign:
1. First and foremost, let’s talk about the elephant in the room – Democrats have to be wondering if they’d be better off with someone else as their nominee.
Neither candidate is the official nominee yet. The national political conventions haven’t happened — but it’s next to impossible that Democrats would replace Biden.
Still, given he delivered the kind of performance Democrats feared, party leaders, strategists and many voters, frankly, had to be wondering during this debate what it would be like if any of a handful of other Democrats were standing on that stage.
Biden got a bit stronger as the debate went on, especially on foreign policy. He had some one-liners, like calling Trump a “whiner” when Trump wouldn’t definitively say that he would accept the results of the 2024 election. But Biden often wasn’t able to show vigor or consistently convey what he wanted to say. He simply couldn’t deliver the kinds of happy-warrior blows with that toothy smile audiences have seen from Biden in years past.
“Sometimes the spin don’t spin,” one Democratic strategist texted midway through the debate when asked for reaction.
2. If how Biden sounded wasn’t bad enough, the visuals might have been equally as bad.
An important rule of thumb for candidates — and moderators — in debates is to be conscious of how things look, of how you look, of what people are seeing at home. And what people saw — and this was predictable — was a split screen.

What to know about the key policies that got airtime in the presidential debate
Biden wasn’t able to use that to his advantage at all, even as Trump doled out falsehood after falsehood. Instead, he looked genuinely shocked and confused, which is never a good look.
Trump and his base might not care about late-night comedy, but this week’s monologues are going to sting Democratic voters.
3. The format — and hands-off moderators — benefited Trump.
The muting of the candidates was likely intended to make the debate calmer and not allow Trump to run roughshod over the moderators or his opponent. But it had the effect of making Trump seem more sedate than usual.
Trump employed rounds of verbal jujitsu, in which he threw back his own vulnerabilities and directed them toward Biden. He was even able at one point, during a strange exchange about golf handicaps, to say, “Let’s not act like children.”
The moderation, or lack thereof, also allowed Trump to spread falsehoods and hyperbole without being interrupted or corrected. CNN indicated before the debate that the moderators were not going to play a strong role in fact checking the candidates, and they lived up to that.
They left it to the candidates, essentially, and with Biden unable to deliver in real time and the moderators declining to, the audience was left with a salad bowl full of rotten eggs and moldy lettuce that passed for facts.
4. This debate might not move the needle much, if at all.
Despite Biden’s struggles, which will understandably get the headlines, Trump had some difficult moments, too, especially in the second half of the debate.
In addition to spreading myriad falsehoods, he did little to credibly defend his conduct on and before the Jan. 6 siege on the Capitol; he used the kind of hyperbolic and vituperative language that has long turned off swing voters; and showed why many are concerned about some of his positions on the issues, especially on abortion and how the U.S. should be represented on the world stage.
So despite Biden’s shortcomings, millions will still likely vote for Biden, anyway, because he’s not Trump.
The bottom line is: Americans have said they are unhappy with their choices, and, in this – the biggest moment of the 2024 presidential campaign yet — it was clear why.
Correction June 28, 2024
A previous version of this story referenced this week's live SNL episode but in fact the show is on its summer hiatus.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When writing a formal report as a team, a carefully constructed outline facilitates assigning sections of the report to different authors from the team. The writer or writers can then focus on paragraph structure, wording, and phrasing using the lessons found in Module 2: Writing in Business.
When writing a formal report, use data and evidence to support your argument, add visuals, use consistent fonts and headings, and highlight important information. You should also use clear language that is easy to understand, considering the audience's background knowledge. 1. Only use credible sources.
Name of the author and any necessary identifying information. Type "prepared by" on one line, followed by the name (s) of the author (s) and their organization, all on separate lines. Date of submission. This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
It should also state the aims and objectives of your report and give an overview of the methodology used to gather and analyze the data. Make sure you include a powerful topic sentence. Main body. The main body of the report should be divided into subsections, each dealing with a specific aspect of the topic.
A formal business report is an official document used to organize statistics, research, and data to help decision-makers analyze information. Formal reports can encompass several pages or many, depending on the topic presented. Related: Everything You Need to Know About Report Writing Example of a formal report An example of a formal report ...
Name of the author and any necessary identifying information. Type "prepared by" on one line, followed by the name (s) of the author (s) and their organization, all on separate lines. Date of submission. This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
Step 2: Create an Outline. Once you've gathered the resources, it's time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don't have a clear plan.
Knowing how to write a successful report can make you a valuable asset in your current workplace or an appealing candidate for new employers. Here are some steps to follow when writing a report: 1. Decide on terms of reference. Many formal reports include a section that details the document's "terms of reference" (or ToR).
This report format follows a formal writing style and dives into a topic related to the student's academic studies. Create your own Presentation Report with this easy-to-edit template! Edit and Download. For more report examples you can learn from, check out our guide on Report Examples With Sample Templates.
When writing a formal report as a team, a carefully constructed outline facilitates assigning sections of the report to different authors from the team. The writer or writers can then focus on paragraph structure, wording, and phrasing using the lessons found in Module 2: Writing in Business.
Pre-writing steps. Before you set pen to paper, it's important to do your research and plan your report carefully. Giving yourself plenty of time for this stage will make the actual writing quicker and less rambling. 1. Define the audience and purpose of the report.
Name of the author and any necessary identifying information. Type "prepared by" on one line, followed by the name (s) of the author (s) and their organization, all on separate lines. Date of submission. This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
Make sure the title is clear and visible at the beginning of the report. You should also add your name and the names of others who have worked on the report and the date you wrote it. 4. Write a table of contents. The table of contents page should follow the title and authors.
Formal reports should be clear and concise and written in a formal business tone, avoiding slang and the overuse of jargon. When writing a formal report, planning and rhetorical awareness ...
4 How to Write a Report Cover Page. Now we're ready to get started on your report cover page! When you're first working on your cover page, it's a good idea to start with a template.. This helps you to spice up your report design and make it more than a black and white word document. It can also help you design your title page in an aesthetically pleasing way so it stands out to your ...
4. Use concise and professional language. You should strive to use clear and concise language when writing your report. Try to get the point across as clearly and quickly as possible and use simple yet professional language. Avoid using "fluff" or wordy sentences when possible.
Must Read: Directed Writing: Format, Benefits, Topics, Common Mistakes and Examples . Report Writing Examples - Solved Questions from previous papers . Example 1: Historical Event Report . Question: Write a report on the historical significance of the "Battle of Willow Creek" based on the research of Sarah Turner. Analyze the key events ...
Title: You need a comprehensive but concise title to set the right tone and make a good impression. It should be reflective of the general themes in the report. Table of Contents: Your title page must be followed by a table of contents. We suggest writing an entire report first and creating a table of content later.
Title of the report. This should appear 2 inches from the top margin in uppercase letters. Name, title, and organization of the individual receiving the report. Type "Prepared for" on one line, followed by two separate lines that provide the receiving organization's name and then the city and state.
How to Write a Formal Report. The rules, as well as the terms of writing a formal report, may differ from one organization to another. Still, the research reports are written in order to communicate with a specific audience. In order to write a formal report, one must first be familiar with the rules and terms for writing a formal report.
Many business professionals need to write a formal report at some point during their career, and some professionals write them on a regular basis. Key decision makers in business, education, and government use formal reports to make important decisions. As opposed to informational reports that offer facts and information without analysis, formal reports provide the end product of a thorough ...
Determining the type of report you need to write before you begin is important. Common types include: Informational reports: Provide data without analysis or recommendations, such as monthly sales reports. Analytical reports: Include analysis and interpretation of data, along with recommendations, like market analysis reports.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
The format — and hands-off moderators — benefited Trump. The muting of the candidates was likely intended to make the debate calmer and not allow Trump to run roughshod over the moderators or ...