

Technical Writing vs. Literary Writing: Key Differences
Technical Writing vs Literary Writing
Technical and literary writing are two distinct writing styles used by authors depending on the subject matter, audience, and purpose of writing. Writing serves as a form of communication; however, often a piece is written to appeal to a specific category of readers rather than a broad cross section of readers. When a text is about a scientific subject and requires the use of technical specifications and jargon, it will have a different content and style than a piece written by a storyteller. This distinction represents the primary difference between technical writing and literary writing. Let’s examine each style more closely.
Technical Writing
Technical writing is a style chosen by scientists and experts in technical subjects to describe subject matter containing technical words. This style is intended for readers with specific interests in technical subjects. However, technical writing is not limited to technical or scientific subjects; a writer can choose to write on any topic technically. The primary goal of this writing style is to inform as much as possible, and it is often persuasive, as if urging the reader to take some action.
For example, if a writer presents an essay on global warming, including all scientific facts and figures, their intention is to make the reader think about the severe situation of climate change and global warming. The essay will be full of scientific details, with a formal tone. The text is factual, and the writer tries to be as straightforward as possible, with the length of the text only as long as necessary. Technical writing is restricted by standard formats, limiting the writer’s freedom of expression.
Key Takeaways
- Technical writing is primarily informative and persuasive, while literary writing is more focused on entertainment and emotional arousal.
- Technical writing is bound by standard formats and has limited freedom of expression, while literary writing allows for more flexibility and creativity.
- The intended audience for technical writing is usually experts and academics, while literary writing targets a general audience.
Literary Writing
Certain texts are not necessary to read, but we read them because they entertain or educate us in a writing style that is flowing and full of figures of speech. Literary writing also aims to educate, but writers have more freedom to evoke readers’ emotions.
Literary writing can be personal and informal at times. The text is often lyrical or prosaic, with a lot of flexibility available to the writer. Literary writing has an aesthetic appeal, and writers take care to make it enjoyable for readers. There is no word limit for literary writing, and this style has a long history.
Differences Between Technical Writing and Literary Writing
• The content and writing style of technical writing differ from literary writing due to vastly different subject matter. • The intended audiences for technical writing are academics and experts, while literary writing is for general readers. • The main purpose of technical writing is to inform and prompt action from readers, whereas the primary purpose of literary writing is to entertain and evoke emotions. • Technical writing is straightforward and to the point, while literary writing makes use of figures of speech. • Technical writing is non-fiction, whereas literary writing is mostly fiction. • Logic and reasoning dominate technical writing, while humanism is the main characteristic of literary writing.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles
Difference between power & authority, distinguishing could of & could have, distinguishing pixie & bob haircuts, distinguishing between debate & discussion, distinguishing between dialogue & conversation, distinguishing between a present & a gift, distinguishing between will & can, distinguishing between up & upon.

Home » Language » Difference Between Technical Writing and Literary Writing
Difference Between Technical Writing and Literary Writing
Main difference – technical writing vs literary writing.
Technical writing and Literary writing are two important writing styles used by writers depending on the subject matter, purpose and intended audience. The main difference between technical writing and literary writing is that, literary language is the writing style used in literary work while technical writing is a style used in writing for a particular field. Let us first briefly analyze theses two styles separately before discussing the difference between technical writing and literary writing.
What is Literary Writing
Literary writing is a style of writing that is used in creative and literary work; this is the style of writing that is used in fiction . Examples for literary writing includes poems, novels, short stories, dramas etc. The most significant difference between literary writing and other styles of writing is that the language used in literary writing uses many literary figures . Observe the below-given stanza to observe this feature.
“I wandered lonely as a cloud
That floats on high o’er vales and hills,
When all at once I saw a crowd,
A host, of golden daffodils;
Beside the lake, beneath the trees,
Fluttering and dancing in the breeze.”
(First stanza from William Wordsworth’s “I wandered Lonely As a Cloud”)

A Novel, an example for literary writing
What is Technical Writing
Technical writing is a style of writing used in delivering technical information regarding a particular subject. Here, the intended audience should have a certain knowledge about the subject in order to understand the technical jargon and the meaning of the text. Technical writing is the style of writing that is mostly observed in Non-fiction. Examples for technical writing include essays , manuals, reports etc. This style of writing is direct and simple. If we were to express the idea conveyed in the above poem in technical writing, we’d simply say. “The narrator was walking alone, when he saw a patch of daffodils near the lake.”

A Manual, an example for Technical Writing
Let us now look at the differences between technical writing and literary writing,
Definition:
Technical writing: Technical writing is a process of managing technical information in a way that allow people to take actions.
Literary writing: Literary writing is a creating innovative, creative work, such as poems or novels, and compilations or volumes of creative work.
Technical Writing: Written to inform, instruct readers about a certain thing.
Literary Writing: Written to entertain, amuse readers.
Technical Writing: The language used in technical writing is direct, factua l, and straightforward.
Literary Writing: The language used in literary writing is creative, imaginative and uses literary techniques like hyperbole, personification, similes, metaphors, etc.
Technical Writing: Technical Writing appeals to the mind.
Literary Writing: Literary Writing appeals to emotions.
Technical Writing: Technical writing has technical vocabulary, simple sentences, impersonal, objective tone .
Literary Writing: Literary writing might have complex sentence structure and linguistic aspects like dialects, ambiguity, etc.
Technical Writing: Technical writing is written for those who are knowledgeable about that particular subject area.
Literary Writing: Literary writing is written for general readers.
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
General Writing vs. Technical Writing
What's the difference.
General writing and technical writing are two distinct forms of written communication. General writing is more creative and expressive, often used in literature, journalism, or personal communication. It focuses on engaging the reader's emotions and imagination, using descriptive language and storytelling techniques. On the other hand, technical writing is more objective and precise, used in fields such as science, engineering, or technology. It aims to convey complex information in a clear and concise manner, using specialized terminology and logical organization. While general writing appeals to a broader audience, technical writing targets specific readers who require accurate and detailed instructions or explanations.
Further Detail
Introduction.
Writing is a fundamental skill that plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives. Whether it is for personal expression, academic pursuits, or professional communication, the way we write can greatly impact the effectiveness and clarity of our message. Two prominent forms of writing that often come up in discussions are general writing and technical writing. While both share the goal of conveying information, they differ significantly in terms of purpose, audience, style, and structure. In this article, we will explore the attributes of general writing and technical writing, highlighting their unique characteristics and the contexts in which they are commonly employed.
General writing encompasses a broad range of writing styles and purposes. It is primarily used for creative expression, storytelling, opinion sharing, or persuasive communication. The purpose of general writing is often to entertain, inform, or evoke emotions in the reader. It allows for more freedom in terms of language choice, tone, and narrative techniques. On the other hand, technical writing is focused on providing clear and concise instructions, explanations, or documentation about a specific subject matter. Its primary purpose is to convey complex information in a straightforward manner, ensuring that the reader can understand and follow the instructions or grasp the technical concepts being presented.
The intended audience is another crucial factor that distinguishes general writing from technical writing. General writing is typically aimed at a broader audience, ranging from the general public to specific interest groups. The language used in general writing is often more accessible, employing everyday vocabulary and avoiding technical jargon. It aims to engage and captivate readers of various backgrounds and interests. In contrast, technical writing targets a specific audience with a particular knowledge base or expertise in the subject matter. The language used in technical writing is more specialized, utilizing industry-specific terminology and concepts that are familiar to the intended readers. The goal is to provide precise and accurate information to those who require it for professional or educational purposes.
Style and Tone
The style and tone of writing also differ significantly between general writing and technical writing. General writing allows for more creativity and personal expression. It often employs descriptive language, figurative expressions, and narrative techniques to engage the reader's imagination and emotions. The tone can vary depending on the purpose of the piece, ranging from formal to informal, conversational, or even poetic. In contrast, technical writing adopts a more objective and formal style. It focuses on clarity, precision, and accuracy, avoiding ambiguity or subjective language. The tone is typically neutral and professional, aiming to convey information in a straightforward and unbiased manner.
The structure of general writing and technical writing also exhibits notable differences. General writing allows for more flexibility in terms of structure, often following a narrative or essay format. It may include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, with the content flowing in a logical and coherent manner. The structure can vary depending on the genre or purpose of the piece, allowing for creative experimentation. On the other hand, technical writing follows a more standardized and structured approach. It often employs headings, subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists to organize information systematically. Technical documents may also include tables, diagrams, or illustrations to enhance clarity and understanding.
To further illustrate the differences between general writing and technical writing, let's consider a couple of examples. In general writing, imagine a short story that aims to captivate the reader's emotions and imagination. The author may use vivid descriptions, engaging dialogue, and narrative techniques to create a compelling narrative. On the other hand, in technical writing, consider a user manual for a new smartphone. The document would provide step-by-step instructions on how to set up and use the device, using clear and concise language, accompanied by diagrams or screenshots to aid understanding.
In conclusion, general writing and technical writing are two distinct forms of writing that serve different purposes and cater to specific audiences. General writing allows for creativity, personal expression, and emotional engagement, while technical writing focuses on clarity, precision, and conveying complex information effectively. Understanding the attributes of each form of writing is essential for selecting the appropriate style, tone, and structure to effectively communicate with the intended audience. Whether you are crafting a captivating story or providing clear instructions, honing your writing skills in both general and technical writing can greatly enhance your ability to convey your message with impact and clarity.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
Technical vs. Academic, Creative, Business, and Literary Writing: What Is the Difference?
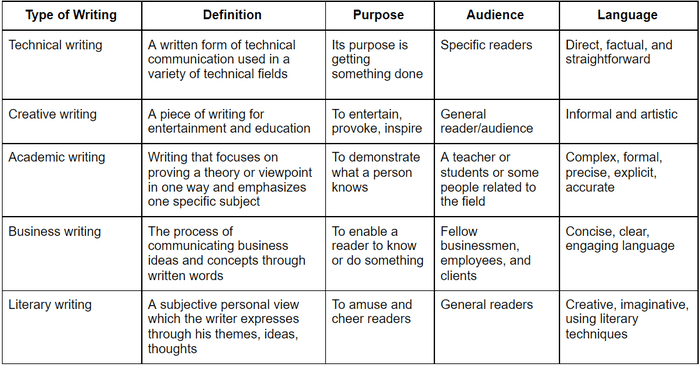
Technical writing is all about the content that focuses on providing detailed and clear information on the product or service. It contains a factual and straightforward message. Technical writers convert complex technical information into useful and easy-to-understand language. You should know that there are different types of technical writing , for example, online tutorials , instruction manuals, API documentation, and so on.
The main idea of all types of technical writing is to help the end-user understand any technical aspect of the product or service.
In addition to technical writing, there are many types of other writings, such as creative, business, and literary writing. All of them have distinctive features. Let’s compare these writings to technical writing and see what they have in common and what makes them different.
Technical Writing vs. Academic Writing
Some people might think these two types of writing are similar. The truth is that these are two completely different categories. It may seem that academic writing should be more complicated since it is focused on some specific and narrow discipline. Indeed, this type of writing may describe very complex concepts and provide specialized knowledge.
Technical writing is intended to describe technical information. It may vary depending on the specifics of a particular industry.
Academic writing is aimed to present a certain point of view on a particular subject. Academic papers show results of research and demonstrate someone’s knowledge. In turn, technical writing explains something to readers and informs them. Technical papers often explain how to use a particular product or service. Technical documents can also describe procedures used by the manufacturer to perform certain tasks. What technical and academic writing have in common is that both types may contain jargon.
Academic and technical writing target different audiences. Academic papers are usually intended for fellow scholars. However, there are also academic pieces of writing intended for a broad audience. Technical writing is intended for people who use a product or service.
Technical Writing vs. Creative Writing
Creative writing is a piece of writing for entertainment and education. It focuses on imaginative and symbolic content, and creative papers are published to entertain, provoke, inspire the user. Technical writing, on the other hand, is not done to amuse its reader. It is used to inform someone. Some technical articles are sometimes made to trigger the reader to take action.
There is no such specific reader who prefers creative papers. Anyone can read the creative paper if they want to, and it gives readers a theme, message, moral, or lesson which is helpful in their real lives or provides temporary entertainment to the reader.
Creative writing has many genres and subgenres. If you want to write creatively, you should have talent. Of course, talent alone is not enough - practice is everything here.
It doesn’t mean that creativity can’t be used in technical writing. Technical articles contain so many facts and data that they can bore and overwhelm readers. This is where creativity in technical writing might come in handy. A tech writer should be creative to encourage their readers to continue reading the document.

Technical Writing vs. Business Writing
Business writing is just about any kind of writing people do at work, if we are not talking about journalism or creative writing. Business writing includes reports, emails, proposals, white papers, minutes, business cases, letters, copywriting, bids, and tenders.
However, many reports, bids, and proposals contain technical data and specifications. So business writers may find themselves editing technical content, and technical writers may be called upon to write persuasive documents for a non-technical audience.
The main objective for both these writings is to inform, be useful, build something or operate the equipment.
The language needs to be clear, concise, and accurate. Wordiness, repetition, and unfamiliar words that the audience may not understand do not belong in either business or technical writing.
Of course, you can use technical jargon in documents where the audience has the same technical background. But too much jargon tends to be a huge problem. So, if in doubt, avoid jargon or explain it.
Some business documents need to be persuasive, whereas technical documents tend to be neutral and objective.
However, there are differences in the content, language, and style of technical and business writing. More on technical writing in business is in our article What Value Technical Writers Bring to Business?
Technical Writing vs. Literary Writing
The main difference between technical writing and literary writing is that literary language is used in literary work while technical writing is used in writing for a particular field. Literary writing is used in fiction. Examples of literary writing include poems, novels, short stories, dramas, etc. The language used in literary writing is creative, imaginative and uses literary techniques like hyperbole, personification, similes, metaphors, etc.
Technical writing is the style of writing that is mostly observed in non-fiction. The language used in technical writing is direct, factual, and straightforward.
Literary writing appeals to emotions. Technical writing appeals to the mind.
Technical writing is aimed at people who have knowledge about a particular subject area. Literary writing is written for general readers.

Every writing style is important in its own way. They are used by writers depending on the subject matter, purpose, language, and target audience. Below is the table that summarizes what you found out about the types of writing mentioned in this article:
It doesn’t matter what you write: essays, business materials, fiction, letters, or just notes in your journal, your writing will be at its best if you stay focused on your purpose and target audience.
Good luck with your technical writing! ClickHelp Team Author, host and deliver documentation across platforms and devices
Give it a Try!
Mind if we email you once a month?
Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Technical and literary writing: what’s the difference « dekonztruktschon.
In an advanced new media class, I’m introducing technical writing to some excellent students. When I asked for a technical report, I got a lot of very well-written essays. It’s a media production studio, not a writing class, so I haven’t made the specifications of the technical report genre very central to the instruction, but they’ll be writing several more of these reports as the semester progresses, so I’m taking advantage of this well-written resource.
Technical writers are different from poets or authors of literary works in terms of their interest, purpose and style of writing. They both have writing expertise to be appreciated by their readers, but they are limited in their style as dictated by the nature of the material they create. Technical writers also need some creativity to go with their logic and knowledge expertise about technical subjects. Technical writing in the surface is non-fiction writing. But not all non-fiction manuscripts are considered technical documents. Literature has in its genres both fiction and non-fiction. Unlike the wide circulation of literary fiction that caters to general readers, technical writing targets specific audience. The readers of technical writing are those mostly interested on technical subjects. They include experts, professionals, field practitioners and the academics. via Technical and Literary Writing: What’s the difference? « Dekonztruktschon .
Related Posts
Related posts.

I’m still teaching journalism and my usual courses, but after 21 years I’ve stepped aside as faculty adviser to the Setonian. The student voice of the hill (founded in 1919) will continue to evolve.

So I’m starting a thing. Wish me luck. #blender3d #medieval #york #mysteryplay #corpuschristi

Yesterday my stack of unmarked assignments was about 120, so this is not bad.
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
What Are The Differences Between Technical Writing And Creative Writing
By: Author Paul Jenkins
Posted on Published: June 7, 2023 - Last updated: July 31, 2023
Categories Writing
You’ve always had a passion for writing, but now you’re faced with choosing between two distinct paths: technical writing or creative writing. As an aspiring writer, it’s essential to understand the differences between these two forms of written communication, as each has its nuances and unique requirements that can make all the difference in which path leads to your career success.
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between technical and creative writing – from their purpose and goals to target audience and essential skill sets – so you can confidently decide which path is right for you.
By understanding these distinctions, you’ll be better equipped to unleash your creativity while maintaining clarity and precision in your work. It’s time to break free from confusion and let your talent shine within the realm that truly resonates with you.
Key Takeaways
- Technical writing focuses on explaining complex concepts accurately, while creative writing aims for audience engagement through storytelling.
- Technical writing creates documentation such as user manuals, tutorials, FAQs, and white papers, while creative writing allows more freedom in style and content.
- Technical writing adopts a neutral, objective voice, uses precise terminology, avoids colloquial language, and follows a specific structure for clear communication of complex information. In contrast, creative writing often employs a unique voice that reflects the author’s or characters’ personality within the story and has more latitude regarding word choice, including slang or poetic expressions.
- Technical writing requires thorough research and fact-checking, ensures document consistency, and prioritizes clarity and accuracy. In contrast, creative writing adds depth to characters and stories through research, lends credibility to the fictional world through fact-checking, and incorporates emotional appeal to keep readers hooked.
Defining Technical Writing
You’ll find that technical writing focuses on clearly explaining complex concepts, processes, or procedures precisely and accurately. This type of writing often involves breaking down technical jargon into simpler terms to make the information accessible to a broader audience.
Technical writers create documentation types such as user manuals, tutorials, FAQs, and white papers to ensure that users can understand how products or systems work. Their main goal is to inform and engage readers who might feel overwhelmed by intricate details.
To satisfy your subconscious desire for freedom while still being concise and clear, technical writing aims at telling engaging stories in an easy-to-grasp language. Using active voice and contractions like ‘it’s’ instead of ‘it is,’ the text becomes more approachable without sacrificing accuracy.
The key here is finding the right balance between providing correct information and keeping the reader captivated throughout the piece. Remember that it’s essential to cater your writing style according to your audience’s needs so they can efficiently grasp new concepts or learn about new tools without feeling bogged down by overly complicated wording or explanations.
Defining Creative Writing
Creative writing is just a breeze compared to technical writing – you let your imagination run wild and create worlds filled with fascinating characters and stories!
With creative inspiration at your fingertips, you can explore the depths of your imagination and express emotions that resonate with readers. The freedom in creative writing allows you to break away from the confines of structured formats and rigid guidelines, allowing you to paint vibrant pictures using words as your brush.
However, don’t be fooled into thinking that creative writing doesn’t require discipline or skill. Developing a unique voice and style that captivates an audience’s subconscious desire for freedom takes practice and dedication.
Imagination exploration may come naturally to some, but honing it into a well-crafted piece of literature is an art form. Whether you’re penning poetry or spinning tales of intrigue, remember that clarity and engagement are crucial in making your work truly memorable.
Purpose and Goals
Understanding the purpose and goals of creative writing is essential, as this helps you craft captivating stories that truly resonate with readers.
The primary aim of creative writing is audience engagement through storytelling, which allows readers to lose themselves in the world of your creation. This type of writing encourages imaginatively expressing ideas, emotions, and experiences while emphasizing content focus.
By honing your skills as a creative writer, you’ll be able to effectively transport your audience into new worlds and evoke powerful emotions within them.
To achieve this level of engagement, it’s crucial for you as a writer to tap into your subconscious desire for freedom and exploration. Creative writing provides an outlet for both the author and reader to break free from the confines of everyday life and experience something entirely different.
By carefully choosing your words, building vivid imagery, and creating dynamic characters, you will captivate and inspire those who read your work.
Ultimately, the purpose and goals of creative writing are rooted in connecting with readers on a deep emotional level while providing an escape from reality that fosters creativity within everyone who engages with it.
Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial in crafting a story that resonates with them and evokes an emotional connection. In technical writing, your primary focus is to inform and educate the reader about a specific subject or topic.
This means you’ll need to present accurate information clearly and concisely, making it easy for the reader to understand complex concepts. Audience engagement is essential here, ensuring they can grasp the material without feeling overwhelmed or confused.
On the other hand, creative writing aims to entertain and captivate its audience by creating vivid mental images and thought-provoking narratives. Content personalization plays a significant role in this process, as tailoring your style and tone to your target audience’s preferences will help foster their subconscious desire for freedom through immersive storytelling experiences.
By understanding who you’re writing for and what they want from your work, you’ll be better equipped to create engaging content that speaks directly to their hearts, minds, and imaginations.
Writing Style and Tone
Mastering the appropriate writing style and tone is key to effectively connecting with your audience, whether you’re aiming to inform or entertain them. In technical writing, the focus is on accuracy and clarity, while creative writing allows more freedom in style and content.
Understanding the differences between these two types of writing will help you tailor your approach to best suit your audience’s needs.
- Writing Voice: Technical writing typically adopts a neutral, objective voice conveying information without personal bias or opinion. On the other hand, creative writing often employs a unique voice that reflects the author’s or characters’ personality within the story.
- Tone Variations: The tone in technical writing remains consistent throughout – informative and straightforward – whereas creative writing may employ various tones such as humorous, suspenseful, or emotional to engage readers and evoke different feelings.
- Structure and Organization: Technical documents follow a specific structure for clear communication of complex information; creative pieces can have more flexible organization depending on artistic intent.
- Language Choice: Technical writers use precise terminology and avoid colloquial language; creative writers have more latitude regarding word choice, including slang or poetic expressions.
By being aware of these distinctions in style and tone between technical and creative writing, you’ll be better equipped to craft engaging content that appeals to your audience’s subconscious desire for freedom while ensuring accurate information presentation.
Remember that mastering this balance is an ongoing process and worth pursuing as it improves your skills as a writer and enhances your ability to connect with readers from various backgrounds.
Structure and Format
Navigating the world of structure and format can be intriguing and challenging, as it’ll help you craft pieces that captivate your audience while maintaining a clear message. In technical writing, structure and format are crucial for presenting information in an organized, easy-to-understand manner.
This often involves using headings, subheadings, bullet points, numbered lists, tables, and charts to break down complex concepts into digestible chunks.
On the other hand, creative writing allows for more structural adaptability and format variations to suit the story or idea being conveyed.
As you explore different writing projects, remember that your choice of structure and format should always serve your intended purpose.
Whether creating a detailed user manual or penning a captivating short story, remember that your audience’s subconscious desire for freedom can be met through engaging storytelling combined with accurate information presentation.
By striking the right balance between these elements, you’ll create works that resonate with readers while effectively conveying your message.
Use of Language
As you delve into written expression, you’ll quickly find that how you wield your words can either enchant or inform your audience, depending on your goal.
In creative writing, language evolution and cultural influences significantly shape a story’s tone, style, and atmosphere. Writers often use rich vocabulary and diverse sentence structures to create vivid images and evoke emotions in their readers.
They may experiment with literary devices like similes, metaphors, and symbolism to convey deeper meanings beneath the surface of their narrative.
On the other hand, technical writing prioritizes clarity and accuracy above all else. The focus is on concisely presenting information while still maintaining an engaging storytelling approach. This means using straightforward language with minimal jargon or ambiguity – something that can be easily understood by a wide range of audiences regardless of their background knowledge or expertise.
While there might not be as much room for artistic flair as in creative writing, effective technical writers still need to consider factors such as audience needs and cultural influences when crafting content that speaks to their subconscious desire for freedom – freedom from confusion or misunderstanding when trying to grasp complex concepts or procedures.

Research and Fact-Checking
In your pursuit of crafting compelling content, thorough research and meticulous fact-checking become indispensable tools to ensure credibility and accuracy in both creative and technical writing. While these two forms of writing might differ in their objectives, structure, and style, the importance of research techniques and fact-checking methods cannot be overstated.
In creative writing, research helps you create well-developed characters, vivid settings, and engaging stories that resonate with readers. Employing proper fact-checking methods allows you to maintain a certain level of authenticity in the world you have created.
For instance, if your novel is set during a specific period or revolves around a particular topic or profession, it’s crucial for you as an author to have a good grasp of the historical context or relevant details.
On the other hand, technical writing demands precision and consistency; thus, using sound research techniques provides accurate information that your target audience can rely on.
Whether creating user manuals for software or composing scientific articles for publications, ensuring that each piece of information is correct builds trust with your readership while fostering professionalism within your work.
Imagery and Descriptive Language
You’ll find that mastering the art of imagery and descriptive language can truly elevate your writing, immersing readers in vivid scenes and stirring emotions with just a few carefully chosen words.
Visual storytelling is essential for both technical and creative writers, but it plays a more prominent role in the latter.
In creative writing, you can explore sensory appeal, using rich descriptions to evoke feelings, sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and tactile sensations that transport your audience into the world you’ve created.
In technical writing, imagery might be used sparingly to clarify complex concepts or make information more relatable; however, it’s important not to get carried away with descriptive language.
Instead of focusing on sensory appeal to engage your reader emotionally or transport them somewhere else mentally (which is often desirable in creative writing), concentrate on presenting information clearly and concisely.
This way, you’ll focus on helping your audience understand the material at hand while providing enough detail to keep them engaged and interested in what they’re learning.
Emotional Appeal
Emotional appeal plays a significant role in keeping your readers hooked, whether it’s through creative or technical writing. By tapping into the emotional impact of your content, you can create a powerful reader connection that keeps them engaged and invested in your work.
In creative writing, this often means creating relatable characters and evoking emotions through vivid imagery and storytelling. Meanwhile, an emotional appeal can be achieved in technical writing by presenting information that resonates with the reader’s experiences and needs.
When you focus on appealing to your audience’s subconscious desire for freedom, you ignite their curiosity and encourage them to explore new ideas.
This could involve crafting stories that inspire readers to question societal norms or break free from restrictive patterns in creative writing.
For technical writers, this might mean making complex concepts more accessible so that readers feel empowered to apply newfound knowledge in their personal or professional lives.
By incorporating emotional appeal into both forms of writing, you can foster deeper connections with your readers and leave a lasting impact on their hearts and minds.
Real-life Applications
By harnessing the power of emotional appeal, you’ll find that both your creative and technical writing endeavors can soar to new heights, opening doors in your readers’ minds like a master key unlocking hidden chambers.
Real-life applications of these two distinct writing styles are abundant, with practical implementation serving as an essential component for success in various fields.
Creative Writing:
- Can foster interdisciplinary collaboration by uniting professionals from different backgrounds to solve complex problems
- Helps convey abstract concepts through engaging storytelling, sparking curiosity, and inspiring innovation
Technical Writing:
- Facilitates clear communication between team members in diverse industries, ensuring accurate information presentation
- Streamlines processes and procedures by providing concise instructions, contributing to overall efficiency
Incorporating emotional appeal into your work will captivate your audience and grant them a subconscious desire for freedom – freedom to explore ideas beyond their current understanding or perspective.
Whether you’re weaving intricate tales filled with vivid imagery or breaking down complex technical jargon into digestible pieces, the ability to resonate emotionally with your reader is a vital tool that can greatly impact the effectiveness of your message.
As a writer who understands this power, you’ll be poised to influence change across many domains through interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative thinking.
Employment Opportunities
Mastering the art of emotional appeal in creative and technical writing can unlock many employment opportunities. It allows you to shape worlds with your words and guide readers on an unforgettable journey through innovative ideas.
As job market trends evolve, there is an increasing demand for skilled writers. Employers seek those who can engage audiences with compelling storytelling while presenting accurate and concise information.
From drafting engaging blog posts, creating captivating stories, or developing comprehensive technical documents, your expertise in these two distinct writing styles will make you highly sought by employers.
In addition to traditional full-time positions, numerous freelancing options offer the freedom and flexibility many crave. With platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and Freelancer.com readily available, offering your writing services globally has never been easier and connecting with potential clients from diverse industries.
By honing your creative and technical writing skills, you’ll be able to tap into this ever-expanding market. You can embark on a fulfilling career path that allows you financial stability and the opportunity to quench your subconscious desire for freedom.
Educational Requirements
Regarding educational requirements, you’ll find a wide range of options for pursuing a career in creative and technical writing.
Industry demands are constantly evolving, so staying updated with the latest trends and advancements in your chosen field is essential.
Some common educational paths for these careers include:
- Bachelor’s or Master’s degrees in English, journalism, communications, or related fields .
- Specialized certification programs focused on specific areas, such as technical communication or copywriting.
- Workshops, conferences, and online courses to enhance your skills and knowledge .
Although formal education can help you establish a strong foundation in writing principles and techniques, hands-on experience is just as valuable. You can build an impressive portfolio by participating in internships or freelance projects, demonstrating your ability to adapt to various styles and formats.
In addition, networking with other professionals can open doors for job opportunities while providing insights into their experiences navigating the world of creative and technical writing.
Essential Skill Sets
It’s crucial to hone various skills to excel as a creative or technical writer, as both fields require unique abilities and aptitudes. Skill development is an ongoing process that involves practicing techniques, learning new methods, and staying updated with industry trends.
For a creative writer, essential skills include developing compelling storylines, crafting engaging characters, maintaining consistency in style and tone, and effectively using literary devices.
In contrast, a technical writer must be adept at breaking down complex information into easy-to-understand language, designing user-friendly documentation formats, incorporating visuals when necessary, and ensuring accuracy in every detail.
Collaboration importance cannot be stressed enough for both types of writers. Creative writers often work closely with editors who provide feedback on their work while coordinating with other professionals like designers and marketers during the publishing process.
This requires strong communication skills and the ability to adapt one’s vision based on input from others.
Similarly, technical writers collaborate with subject matter experts (SMEs), engineers, project managers, and other stakeholders to ensure that their content accurately reflects the intended message while remaining accessible to the target audience.
Embrace your subconscious desire for freedom by honing these diverse skill sets; doing so will allow you to flourish in either realm of writing while maintaining versatility within your career options.
Tips for Success in Each Domain
To thrive in either domain, you’ll need to employ specific strategies tailored to the unique demands of each field while leveraging your core writing skills. Whether you’re pursuing technical or creative writing, professional development is crucial for staying ahead and overcoming writing challenges. Here are some tips for success in each domain:
For technical writing:
- Stay updated with industry trends and technology advancements
- Regularly attend workshops or conferences related to your niche
- Focus on clarity and precision in language
- Develop strong research skills to establish credibility
- Learn various documentation styles and formats
For creative writing:
- Experiment with different genres and styles to find your voice .
- Join a writers’ group or take creative writing classes for feedback and support .
- Read widely to expose yourself to diverse perspectives and ideas .
- Balance self-expression with audience engagement by considering their desires, emotions, and needs .
- Embrace vulnerability through an honest exploration of themes that resonate with readers.
In both fields, seeking continuous growth is essential. When engaging in technical writing, I strive for accuracy without losing sight of the importance of engaging storytelling.
Don’t be afraid to push boundaries in creative endeavors – remember that your audience has a subconscious desire for freedom.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can a writer successfully transition from technical writing to creative writing, or vice versa.
Unleash your creative adaptations, finding writing balance in the transition. Embrace both worlds, blending concise language with engaging storytelling. Master accurate information presentation while satisfying your audience’s subconscious desire for freedom.
Are any specific software or tools recommended for technical writers and creative writers to enhance their work?
Explore software comparisons and tool adaptations to enhance your writing. Technical writers often use programs like Adobe FrameMaker, while creative writers benefit from tools like Scrivener.
Can someone excel in technical and creative writing, or is it better to focus on one area to build expertise?
You’re at a crossroads: balancing expertise or embracing skill versatility. Excelling in both technical and creative writing is possible, but focusing on one area might deepen your mastery.
How do the revision and editing processes differ between technical writing and creative writing? Are there any specific strategies or techniques that should be employed for each?
In revising creative writing, focus on storytelling and emotional impact. For technical writing, prioritize clarity and accuracy. Employ editing strategies to ensure consistency in style, tone, and formatting for each genre.
Are there any notable examples of individuals who have succeeded in both technical and creative writing, and what lessons can be learned from their careers?
You can achieve notable dual success in technical and creative writing, like Kurt Vonnegut and Samuel R. Delany. Career lessons to learn: adapt your style, embrace versatility, and keep an open mind for growth.
So, you see how different technical and creative writing can be? Coincidentally, mastering one might even improve your skills in the other.
Keep exploring both worlds to sharpen your writing prowess.
Remember, the key lies in understanding their unique purposes and styles. Who knows? Maybe you’ll end up excelling at both!
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Technical Writing Process

Related Papers
Cutilioux Rukhshan
dheya al-othmany
This paper has focused on technical writing as a skill for engineers. It has sought to define technical writing and throw light on the content and technique of writing the various components of successful technical reports (for example, articles, papers, or research reports, such as theses and dissertations). Then, it has highlighted other special features and principles of effective technical writing. The material in this paper is divided into seven major parts. Part 1 (Technical writing for engineers) stresses that a successful engineering career requires strong writing skills. Part 2 (How to write the major sections or elements of a report) describes the techniques of writing the abstract, introduction, literature review, procedure/methods & materials, results, discussion, conclusion, and recommendations. Part 3 (Special features of technical writing) brings into focus some of the special features of technical writing such as tables & graphs in the text, graphics in instructions, team writing, ethics (plagiarism), document sources, three citation styles and IEEE reference style. Part 4 (Technical usage) deals with writing abbreviations, initialisms and acronyms, numbers, units of measurement, and equations. Part 5 (Technical style) highlights the imperative writing style and other features of technical writing such as the use of active and passive voices, plain vs. complex syntax, avoiding redundant or superfluous expressions, and vague generalities, using words or expressions with visual impact, the past tense to describe experimental work, the present tense to describe hypotheses, principles, theories and truths, and breaking up the text of the report into short sections. Part 6 (Document specifications) emphasizes the technical writer's need to conform to such document specifications as word count, format, font, number of words per line of text imposed. Finally, part 7 (Reader-friendly technical writing) suggests choosing the varied writing modes (- atterns of organization of information) to suit the technical writing task, checking for technical accuracy and following three levels of editing to help increase the readability of a technical text.
George Tchobanoglous
Tchobanoglous, G., Leverenz, H. (2013), A Guidance Manual on the Preparation of Technical Reports, Papers, and Presentations, University of California, Davis, Davis, CA
Sina Khatami
Jordi Pique
Norman Fenton
This document describes the basic principles of good writing. It is primarily targeted at students and researchers writing technical and business reports, but the principles are relevant to any form of writing, including letters and memos. Therefore, the document contains valuable lessons for anybody wishing to improve their writing skills. The ideas described here are, apart from fairly minor exceptions, not original. They are drawn from a range of excellent books and have also been influenced by various outstanding authors I have worked with. Thus, the approach represents a kind of modern consensus. This approach is very different to the style that was promoted by the traditional English schools ’ system, which encouraged students to write in an unnecessarily complex and formal way. The approach described here emphasises simplicity (‘plain English’) and informality. For example, it encourages shorter sentences and use of the simplest words and phrases possible. It explains how you...
Ekong Nancy
the paper tried to examine the nature of technical writing and the role it plays in communication.
Hayden Coombs
Technical writing is used in many technical and professional fields. Its goal is to accurately and concisely convey direction, explanation, or instruction to specific audiences of varying levels of technical knowledge so that each reader clearly understands the information they need. Objectives In an increasingly complex world, good technical writing is increasingly important. This course will teach you how to create and design quality communication for the professional environment. After the successful completion of the course, students will be able to: 1. Communicate using Markel's Eight Measures of Excellence: honesty, clarity, accuracy, comprehensiveness, accessibility, conciseness, professional appearance, and correctness. 2. Evaluate the communication situation: audience, purpose, and context. 3. Create effective professional memos, proposals, technical definitions, and reports. 4. Integrate visual items in technical documents, 5. Understand how to analyze, incorporate, and attribute data from research. 6. Use a cover letter, résumé, and LinkedIn profile in an effective job search. 7. Continue developing lifelong learning and self-editing skills. 8. Continue developing as a professional and leader. 9. Use Word effectively in document design. Required Course Materials • Practical Strategies for Technical Communication Mike Markel, ISBN: 978-1319261023 • Red pen • Printing funds • Internet access Class Policies: 1. Attendance-This is a face-to-face class for a reason: It is essential that all students attend class. Attendance will be taken at the beginning of every class. Written documentation for a universitysanctioned absence must be provided. Arrangements concerning absences are entirely at my discretion.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Jan A Kozák
『現代思想』vol. 52-1(特集:ビッグ・クエスチョン)
Yasushi Hirai
Energy engineering and control systems
Fedir Matiko
Letters in Mathematical Physics
Shigeaki Nagamachi
BMC Women's Health
ariel revel
Bernard Kamau
Limnologica
Maria Auxiliadora Nascimento Ferreira
Naturwissenschaften
John P. Sean Kent
Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research
Luis Muscolo
Journal of biological physics
Acta Tropica
Tonglin Zhang
Sustainability
Willard Mbewe
Journal of Hypertension
Pierre Clerson
IEEE Access
Nattapong Hatchavanich
Journal of Materials Science
Carl Zweben
Revista Colombiana de Gastroenterología
Orlando Ricaurte
José Manuel Bustos Gisbert
Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures
Ishaq ahmad
Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece
G. Vougioukalakis
Revista vínculos
Shayther Diaz44
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

TECHNICAL WRITING vs. ACADEMIC WRITING
Sep 02, 2014
1.21k likes | 4.1k Views
TECHNICAL WRITING vs. ACADEMIC WRITING. TYPES of WRITING. PERSONAL ACADEMIC PROFESSIONAL. PERSONAL WRITING. Purpose/Objective : to entertain to inform Evaluation : desired emotional response informed. PERSONAL WRITING. Graphics : emoticons text-messaging lingo Formats : e-mail
Share Presentation
- urpose objective
- limited public speaking opportunities

Presentation Transcript
TECHNICAL WRITINGvs.ACADEMIC WRITING
TYPES of WRITING PERSONAL ACADEMIC PROFESSIONAL
PERSONAL WRITING • Purpose/Objective: • to entertain • to inform • Evaluation: • desired emotional response • informed
PERSONAL WRITING • Graphics: • emoticons • text-messaging lingo • Formats: • e-mail • letters • journals • text messages
PERSONAL WRITING • Audience: • equal knowledge • friends • colleagues • Informality
*AUDIENCES* Specific Audiences boss supervisor team committee politicians bank officers general public General Audience generic reader teacher perhaps fellow students TW AW
*AUDIENCES* 1 Document = Many Readers: (Many Readers = Many Needs) “food chain” boss, supervisor team engineers workers politicians bank officers general public 1 Document = 1 Reader: (1 Reader = 1 Need) teacher TW AW
PURPOSES • Purpose = • Writing Situation • Objective • Why was the document written?
PURPOSES Situation-Oriented see a need — address a need internal motivation professional motivation outcome-oriented: to get something accomplished Assignment-Oriented passive (vs. active) given a topic, test given an assignment external motivation scholastic motivation grade-oriented grade, g.p.a., degree TW AW
EVALUATION CRITERIA Success satisfaction of the needs of all readers something was done informed persuaded Success correct answer right information unity, coherence support, detail grammar TW AW
APPLICATIONS Real-World Applications case studies illustrative scenarios operations management for a job for a raise or promotion for a bid practical College Application “academic” writing essays essay exams for academics for grade for degree “show what you know” demonstrative TW AW
DISCIPLINES Across Disciplines “interdisciplinary” computer sciences psychology mixture of: history math science technology Single Discipline “discipline-specific” literary data for an English paper historical information on a history paper psychological ideas on a psychology test rarely a mixture TW AW
*PAGE DESIGN* Paragraphs 6-10 lines vary lengths for visual White Space Columns Headings Lists Graphics Varying Fonts Use of Color Relative Spacing Relative Margins Relative Justification Paragraphs Minimum of 3-5 sentences No maximum length NO White Space Columns Headings Lists Graphics Varying Fonts Use of Color Double Spacing Equal Margins Left Justification TW AW
COMPONENTS Oral, Visual, Written produce documents present documents write to be read write to be seen write to be heard Written infrequent oral and visual components predominant written component write to be read by teacher write to be graded not to be seen or heard TW AW
GRAPHICS tables charts graphs diagrams photographs maps blue prints uncommon photographs TW AW
FORMATS memos e-mails letters cover letters resumes proposals manuals portfolio abstracts reports formal informal essay questions essays based on the rhetorical strategies Description Narration Illustration Process-Analysis Division-Classification Comparison-Contrast Definition Cause-Effect Pro-Con Argument TW AW
GRAMMAR Grammar-less visual-oriented grammar = less important fragments = permissible active voice descriptive writing concise sentences spelling! proofread! Grammar-full written-oriented grammar = key sentence errors = avoided active voice descriptive writing concise sentences spelling! proofread! TW AW
CONCLUSIONS • Technical Communication: • Practicality in the employment world • Real-World application • Academic Writing: • Demonstration of knowledge • Limited to academia
CONCLUSIONS • Technical Communication: • By an informed writer • Conveying necessary information • Both visually & verbally • To a lesser-informed reader • (writer = teacher) • Academic Writing: • By a student-learner for an expert reader
CONCLUSIONS • Technical Communication: • Read by many, • To satisfy the needs of many • Academic Writing: • Read by one, • To appease the criteria of one
CONCLUSIONS • Technical Communication: • “Information Retrieval” • organization & format = designed • to help readers quickly & easily locate information • Academic Writing: • “Information Retrieval” • little concern beyond a logical organization
CONCLUSIONS • Technical Communication: • Public Speaking component — • formal conference speeches • informal meeting speeches • Academic Writing: • Limited Public Speaking opportunities • conferences or rare class projects • Public Speaking courses
DEFINITION Technical Communication: • Encompasses a wide range • of writing and speaking responsibilities • required to communicate your ideas • on the job.
SIMILARITIES • Grammar: • active voice • descriptive writing • concise sentences • spelling! • proofread!
SIMILARITIES • Writing as a Process: • Planning • Drafting • Revising
EDUCATIONAL PHILOSOPHIES writing: process & product HEURISTIC: process reader-focused how-to analyze-and-compose process PRESCRIPTIVE: product writer-focused models/forms of writing writing: product Prescriptive/regulatory teach from models Rhetorical/abstract strategies writer-focused TW AW
ACADEMIC WRITING Purpose/Objective: to demonstrate knowledge to “show what you know” Audience: superior knowledge teachers, perhaps peer editors Evaluation: correct information unity, coherence, depth, clarity, grammar Graphics: limited to explain or persuade/convince
ACADEMIC WRITING Formats: Description Narration Illustration Process-Analysis Division-Classification (Rhetorical Strategies or Writing Models) Comparison-Contrast Definition Cause-Effect Pro-Con Argument-Persuasion
TECHNICAL WRITING Purpose/Objective: to entertain to inform Audience: equal knowledge friends, colleagues Evaluation: desired emotional response informed Graphics: emoticons text-messaging lingo Formats: e-mail letters journals text messages
- More by User

680 views • 31 slides

Academic Writing
Academic Writing . Liv Jonassen Elizabeth Tomchak. Outcomes. Understand what is expected at Masters level at University. Know how to use an appropriate academic writing style. Know the differences between an essay and a report. Know the different sections within a report. Activity.
1.05k views • 58 slides

Academic writing
Academic writing. Create a message your readers will remember. Academic writing is… …created by scholars for other scholars …focused on issues that matter to other scholars …offer a balanced point of view (“What is,” 2004). What are the steps in becoming a good academic writer?.
513 views • 29 slides

Technical & Academic Writing
Technical & Academic Writing. These slides are available at www.eng.odu.edu/edservices.htm. Materials, Hand-outs, and Assignments related to this Presentation are available at www.eng.odu.edu/edservices.htm. Rhetoric. HOW WRITING WORKS. Rhetoric = Symbolic Action.
753 views • 55 slides

Academic Writing. Values and Commentary. Purpose. To explain the values of academic writing (i.e. what the academy likes to see in writing Historicize these values so the answer to why is not “that’s just the way it is” Show what’s missing (offer critique). Main premise.
664 views • 28 slides

Academic Writing. Peter S. Cahn, PhD Associate Provost for Academic Affairs MGH Institute of Health Professions [email protected]. Learning objectives. Overcome barriers to getting started on writing projects. Present scientific ideas clearly. Edit manuscripts to refine the argument.
582 views • 20 slides

Academic writing. Identify the object. You have been given What is this? Define, list, label. Identify . This is a round chocolate cake. It has been cut into 10 slices, is covered with chocolate icing and decorated with chocolate florets. Describe. F eatures or properties Composition
462 views • 24 slides

Academic Writing. Lesson 14 June 11, 2013 Lynn Mallory. Learning Targets. To make strong conclusions about a topic using correct grammar. To explain the purposes and parts of an abstract. To analyze an abstract and give advice to the author. Review -- Parts of the Conclusion.
331 views • 16 slides

ACADEMIC WRITING
ACADEMIC WRITING. October 30 , 2013. ALL GOOD WRITING. Is well-organized, with main ideas introduced early on and defended, complicated, and refined throughout Is coherent and unified Explores and explains worthwhile content Is aware of its audience
556 views • 40 slides

Academic Writing. Lesson 13 June 8, 2013 Lynn Mallory. Learning Targets. 1 . To analyze the conclusion section of a research paper and give advice to the author. 2 . To practice making sentences with modal verbs. 3 . To make strong conclusions about a topic using correct grammar.
260 views • 11 slides

Mustwrite1.weebly.com. Academic Writing. Lesson 5 May 16, 2013 Lynn Mallory. Learning Targets. To analyze the introductions of scientific research papers and suggest improvements to the authors. To write an introduction to a research paper.
412 views • 18 slides

Technical vs. Creative Writing
Technical vs. Creative Writing. Technical. Conveys specific information about a technical subject to a specific audience or specific purpose. creative. Is fiction – poetry, short stories, plays, and novels – and is most different from technical writing. Proper technical writing practice.
2.11k views • 14 slides

Academic writing. March 8 th 2012. Basics of writing 1. The units of writing can be arranged as follows: Your mind your hand letters words _________ __________ ___________ books. Basics of writing 1. For this class: Sentences Paragraphs Essays. Today. Sentences
402 views • 16 slides

Academic Writing. Learning Development Service Student Guidance Centre. What attracts good marks?. Lowest marks Weak structure Shows little research Mostly descriptive Considers only one point of view Better marks Evidence of background learning Answers the question
724 views • 28 slides

Academic Writing. Instructor: Zhu Yaoyun @ Shandong University. 1. Abstract writing. 2. Notes and bibliographies. 3. Paper writing. Contents. The IMRaD article (Weissberg and Buker 1990). Abstract Introduction Materials and Methods Results Discussion.
477 views • 27 slides

Technical writing/Business writing
Technical writing/Business writing. Technical & General writing: Difference Technical writing- (a) a means to some other end. (b) Purely practical motives. (c) It informs and educates. (d) Involves intellect and facts. (e) Precise and direct. (f) Always impersonal.
2.31k views • 25 slides

TOMSK POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY. ACADEMIC WRITING. Made by Matukhin D.L. Associate Prof. EEI TPU. CONTENTS. SUMMARY ABSTRACT ANNOTATION. WHAT’S S UMMARY?. Pick out the key issues in a written paper; Link the ideas up in your own text. SUMMARY IN NUMBERS. 1/3 of the original paper;
355 views • 13 slides

Academic Writing. Peer Review & Visuals and Formatting (Chapters 5-6). Peer Review. How to conduct Peer Review Sample draft: p 33 Use p 31 to respond See sample 75-77 afterward How did it improve?. Peer Review. How to conduct Peer Review Sample student draft Use p 31 to respond.
384 views • 20 slides

Academic Writing. Objectives. Identify why academic writing is important Recognise a report format Discuss narration perspective Demonstrate writing in third person. Science Communication Is Important!. “If I have seen further it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants.” (Newton)
543 views • 22 slides

Academic Writing. Planning Your Work. You need to know. PART II – Wiki Due November 23 rd @ 5pm Individual profile page Topic page Comments on 2 other pages PART III – Research Paper DUE 11 th January 2013 @ 5 pm Email to lecturer No penalty for early submission.
358 views • 15 slides

There are several reasons that you wish to know that how to create a website, varying from your personal or your hobby pages, for creating affiliate marketing websites, through the full-fledged business sites.
185 views • 4 slides

Academic Writing. Mrs. Stutz emilyannemulder@gmail Moodle: AW - Stutz, access code: letmein (registration closes in three weeks). Prescribed Text . Bailey, Stephen . Academic Writing: A Handbook for International Students . Third Edition. Oxford : Routledge , 2011. ISBN 978-0415595810
423 views • 14 slides
- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Software Development Life Cycle
- Waterfall Model
- Software Requirements
- Software Measurement and Metrics
- Software Design Process
- System configuration management
- Software Maintenance
- Software Development Tutorial
- Software Testing Tutorial
- Product Management Tutorial
- Project Management Tutorial
- Agile Methodology
- Selenium Basics
Difference between Technical Writing and General Writing
- Difference between Technical Writing and Academic Writing
- Difference between Technical Writing and Creative Writing
- Difference between Academic Writing and General Writing
- Difference between Transactive Writing and Personal Essay
- Difference between Texting and Email
- Difference between Academic Writing and Non Academic Writing
- Difference between Generalization and Specialization in DBMS
- Difference between Texting and Messaging
- Difference Between Programming, Scripting, and Markup Languages
- Difference between General Management and Project Management
- Difference between Paper and Article for Scientific Writings
- Difference between Plotter and Printer
- Difference between Flow and TypeScript
- Difference Between Presentation and Representation
- Difference between Paragrah and Essay
- Difference between write() and writelines() function in Python
- Difference between Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Difference between Graphic Design and Illustration
- Difference between Formal and Informal Letter
1. Technical Writing : Technical writing is a piece of writing which focuses on factual and straight forward content and technical papers are published to inform and instruct and educate the user about some specific topic. There exists specific readers who prefers technical papers. It gives readers information about some technical topics or it gives directions on how to do something.
For example writing any articles on GeeksforGeeks related to computer science field comes under technical writing.
2. General Writing : General writing refers to any piece of writing which focuses in general subjects of writing and general papers are published for amusement of the reader. But sometimes many general topics also gives life lessons, moral, inspiration etc. There is not such specific set of audience or readers like technical writing. It is written on subjective tone and purely personal style.
For example writing any prose or story which will be published in a local magazine comes under general writing.
Difference between Technical Writing and General Writing :
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Difference Between
- Software Engineering
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Technical Writing vs. Creative Writing: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, structure and form, audience engagement, technical writing and creative writing definitions, technical writing, creative writing, is jargon typically used in technical writing, what is the fundamental aim of creative writing, is creative writing often associated with storytelling, can creative writing be structured or formal, can creative writing be non-fictional, is imaginative thinking a vital component of creative writing, are accuracy and precision critical in technical writing, can technical writing be performed by industry non-experts, how important is the reader’s emotional journey in creative writing, what is the primary purpose of technical writing, does creative writing allow for exploration of emotional depth, what types of documents are common in technical writing, how is symbolism utilized in creative writing, who is the intended audience for technical writing, can technical writing include visuals, how is simplicity valued in technical writing, can creative writing be used for professional or business purposes, can technical writing be creative, is objectivity crucial in technical writing, can creative writing encompass various literary forms.

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mar 17, 2010 • Download as PPT, PDF •. 4 likes • 7,167 views. muhammad ilyas. Education Business. difference between literary and technical writing. 1. Presentation TECHNICAL WRITING ( LEISURE ) 2. 3.
Literary writing targets a broader audience, including general readers, while technical writing targets a specific audience with specialized knowledge or interests. Another notable difference is the use of language. Literary writing often employs figurative language, such as metaphors and similes, to create imagery and convey emotions.
8. While technical writing and literary writing both value precision and effective communication, they utilize language and structure in distinctly different ways. Technical writing extracts and simplifies, prioritizing directness, while literary writing embellishes and explores, offering multifaceted explorations of themes and emotions. 5.
The distinction between technical writing and literary writing lies in the fact that while the former involves conveying complex technical information in a clear, concise, and well-structured manner, the latter entails using creative, imaginative language to express emotions, tell stories, and captivate readers. Learn the difference here.
Technical Vs. Literary Writing Comparison Definitions Group Members Technical Writing is a field that focuses on providing information to users who need assistance to accomplish a defined goal or task. Literary Writing is basically creating original writing rather than analyzing ... Turn your last-minute presentation into a winning momentum ...
It can be a personal and very informal as the text is often lyrical or prosaic with a lot of flexibility at the disposal of the writer. Literary writing has an aesthetic appeal, and the writer takes care to make it enjoyable for the readers. There is no limitation of words in the case of literary writing, and this style of writing is very old.
The main difference between technical writing and literary writing is that, literary language is the writing style used in literary work while technical writing is a style used in writing for a particular field. Let us first briefly analyze theses two styles separately before discussing the difference between technical writing and literary writing.
The style and tone of writing also differ significantly between general writing and technical writing. General writing allows for more creativity and personal expression. It often employs descriptive language, figurative expressions, and narrative techniques to engage the reader's imagination and emotions.
The main difference between technical writing and literary writing is that literary language is used in literary work while technical writing is used in writing for a particular field. Literary writing is used in fiction. Examples of literary writing include poems, novels, short stories, dramas, etc. The language used in literary writing is ...
But not all non-fiction manuscripts are considered technical documents. Literature has in its genres both fiction and non-fiction. Unlike the wide circulation of literary fiction that caters to general readers, technical writing targets specific audience. The readers of technical writing are those mostly interested on technical subjects.
Technical writing relies on visuals for clarity; creative writing focuses on text-based storytelling. Uses headings & subheadings. May use unconventional formatting. Technical writing organizes content with a clear hierarchy; creative writing may play with the layout for effect. Often includes tables & charts.
Lecture 1-technical-writing. Technical writing focuses on precise and unemotional language to communicate complex information to a specific audience. It employs formats and styles suited to its purpose of informing or instructing readers. Common types of technical writing include reports, manuals, specifications, proposals, and graphics to aid ...
Know your stuff; do not read slides; time yourself and be ready to skip slides if time is short. Dress for success; speak clearly, loud enough and not too quickly; maintain eye contact with audience. Ask questions and stimulate thinking. Presentation is a story telling; be positive and keep it simple.
The material in this paper is divided into seven major parts. Part 1 (Technical writing for engineers) stresses that a successful engineering career requires strong writing skills. Part 2 (How to write the major sections or elements of a report) describes the techniques of writing the abstract, introduction, literature review, procedure/methods ...
Technical vs. Creative Writing. Technical vs. Creative Writing. Technical. Conveys specific information about a technical subject to a specific audience or specific purpose. creative. Is fiction - poetry, short stories, plays, and novels - and is most different from technical writing. Proper technical writing practice. 2.11k views • 14 slides
Abstract. This article proposes a means of characterizing the difference between technical and literary writing, involving a theory of representation in which these distinct writing types are comparable to distinct types of visual representation. Any difference is only intelligible relative to a background of similarlity, but recent discussions ...
Technical writing is a form of writing that implies writing technical documentation, help topics, user manuals, articles and the like that helps people understand how to use an app or device. A ...
09. Technical writing is archival. General writing is non-archival. 10. It is accurate and more precise in manner. It is decorative and bombastic in manner. 11. Technical writing is related to any specific area or domain. General domain is related to any life in general.
"The Definition of Technical Writing and the Differences Between Academic Writing and Technical Writing," PowerPoint Presentation is the sole property of Dr. Elizabeth Lohman. This PowerPoint presentation cannot be copied or duplicated in any way or presented in any way without the written consent of Dr. Elizabeth Lohman.
Creative writing, contrastingly, is an art form that seeks to entertain, provoke thought, or express emotions and ideas through various literary mediums like stories, poems, and scripts. 14. Technical writing adheres to stringent guidelines and prefers clarity over style. Its language is straightforward, sentences are precise, and the purpose ...
The document discusses the key differences between technical writing and other types of writing such as creative, expressive, expository, and persuasive writing. Technical writing conveys specific information about a technical subject to a specific audience for a specific purpose, whereas creative writing is fiction. The document also provides examples of imagery, symbolism, and diction to ...