Review of Related Literature: Format, Example, & How to Make RRL
A review of related literature is a separate paper or a part of an article that collects and synthesizes discussion on a topic. Its purpose is to show the current state of research on the issue and highlight gaps in existing knowledge. A literature review can be included in a research paper or scholarly article, typically following the introduction and before the research methods section.

This article will clarify the definition, significance, and structure of a review of related literature. You’ll also learn how to organize your literature review and discover ideas for an RRL in different subjects.

🔤 What Is RRL?
- ❗ Significance of Literature Review
- 🔎 How to Search for Literature
- 🧩 Literature Review Structure
- 📋 Format of RRL — APA, MLA, & Others
- ✍️ How to Write an RRL
- 📚 Examples of RRL
🔗 References
A review of related literature (RRL) is a part of the research report that examines significant studies, theories, and concepts published in scholarly sources on a particular topic. An RRL includes 3 main components:
- A short overview and critique of the previous research.
- Similarities and differences between past studies and the current one.
- An explanation of the theoretical frameworks underpinning the research.
❗ Significance of Review of Related Literature
Although the goal of a review of related literature differs depending on the discipline and its intended use, its significance cannot be overstated. Here are some examples of how a review might be beneficial:
- It helps determine knowledge gaps .
- It saves from duplicating research that has already been conducted.
- It provides an overview of various research areas within the discipline.
- It demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the topic.
🔎 How to Perform a Literature Search
Including a description of your search strategy in the literature review section can significantly increase your grade. You can search sources with the following steps:
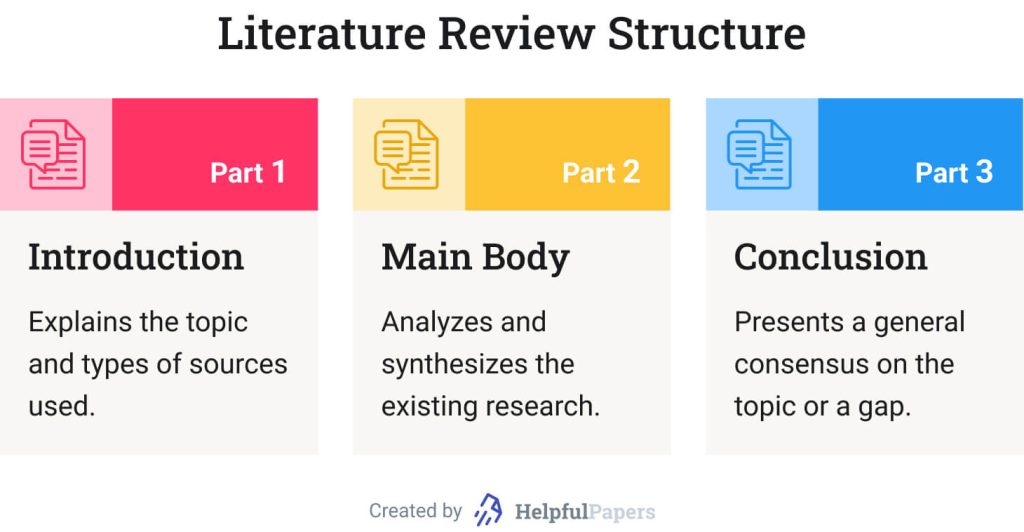
🧩 Literature Review Structure Example
The majority of literature reviews follow a standard introduction-body-conclusion structure. Let’s look at the RRL structure in detail.
Introduction of Review of Related Literature: Sample
An introduction should clarify the study topic and the depth of the information to be delivered. It should also explain the types of sources used. If your lit. review is part of a larger research proposal or project, you can combine its introductory paragraph with the introduction of your paper.
Here is a sample introduction to an RRL about cyberbullying:
Bullying has troubled people since the beginning of time. However, with modern technological advancements, especially social media, bullying has evolved into cyberbullying. As a result, nowadays, teenagers and adults cannot flee their bullies, which makes them feel lonely and helpless. This literature review will examine recent studies on cyberbullying.
Sample Review of Related Literature Thesis
A thesis statement should include the central idea of your literature review and the primary supporting elements you discovered in the literature. Thesis statements are typically put at the end of the introductory paragraph.
Look at a sample thesis of a review of related literature:
This literature review shows that scholars have recently covered the issues of bullies’ motivation, the impact of bullying on victims and aggressors, common cyberbullying techniques, and victims’ coping strategies. However, there is still no agreement on the best practices to address cyberbullying.
Literature Review Body Paragraph Example
The main body of a literature review should provide an overview of the existing research on the issue. Body paragraphs should not just summarize each source but analyze them. You can organize your paragraphs with these 3 elements:
- Claim . Start with a topic sentence linked to your literature review purpose.
- Evidence . Cite relevant information from your chosen sources.
- Discussion . Explain how the cited data supports your claim.
Here’s a literature review body paragraph example:
Scholars have examined the link between the aggressor and the victim. Beran et al. (2007) state that students bullied online often become cyberbullies themselves. Faucher et al. (2014) confirm this with their findings: they discovered that male and female students began engaging in cyberbullying after being subject to bullying. Hence, one can conclude that being a victim of bullying increases one’s likelihood of becoming a cyberbully.
Review of Related Literature: Conclusion
A conclusion presents a general consensus on the topic. Depending on your literature review purpose, it might include the following:
- Introduction to further research . If you write a literature review as part of a larger research project, you can present your research question in your conclusion .
- Overview of theories . You can summarize critical theories and concepts to help your reader understand the topic better.
- Discussion of the gap . If you identified a research gap in the reviewed literature, your conclusion could explain why that gap is significant.
Check out a conclusion example that discusses a research gap:
There is extensive research into bullies’ motivation, the consequences of bullying for victims and aggressors, strategies for bullying, and coping with it. Yet, scholars still have not reached a consensus on what to consider the best practices to combat cyberbullying. This question is of great importance because of the significant adverse effects of cyberbullying on victims and bullies.
📋 Format of RRL — APA, MLA, & Others
In this section, we will discuss how to format an RRL according to the most common citation styles: APA, Chicago, MLA, and Harvard.
Writing a literature review using the APA7 style requires the following text formatting:
- When using APA in-text citations , include the author’s last name and the year of publication in parentheses.
- For direct quotations , you must also add the page number. If you use sources without page numbers, such as websites or e-books, include a paragraph number instead.
- When referring to the author’s name in a sentence , you do not need to repeat it at the end of the sentence. Instead, include the year of publication inside the parentheses after their name.
- The reference list should be included at the end of your literature review. It is always alphabetized by the last name of the author (from A to Z), and the lines are indented one-half inch from the left margin of your paper. Do not forget to invert authors’ names (the last name should come first) and include the full titles of journals instead of their abbreviations. If you use an online source, add its URL.
The RRL format in the Chicago style is as follows:
- Author-date . You place your citations in brackets within the text, indicating the name of the author and the year of publication.
- Notes and bibliography . You place your citations in numbered footnotes or endnotes to connect the citation back to the source in the bibliography.
- The reference list, or bibliography , in Chicago style, is at the end of a literature review. The sources are arranged alphabetically and single-spaced. Each bibliography entry begins with the author’s name and the source’s title, followed by publication information, such as the city of publication, the publisher, and the year of publication.
Writing a literature review using the MLA style requires the following text formatting:
- In the MLA format, you can cite a source in the text by indicating the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the citation. If the cited information takes several pages, you need to include all the page numbers.
- The reference list in MLA style is titled “ Works Cited .” In this section, all sources used in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order. Each entry should contain the author, title of the source, title of the journal or a larger volume, other contributors, version, number, publisher, and publication date.
The Harvard style requires you to use the following text formatting for your RRL:
- In-text citations in the Harvard style include the author’s last name and the year of publication. If you are using a direct quote in your literature review, you need to add the page number as well.
- Arrange your list of references alphabetically. Each entry should contain the author’s last name, their initials, the year of publication, the title of the source, and other publication information, like the journal title and issue number or the publisher.
✍️ How to Write Review of Related Literature – Sample
Literature reviews can be organized in many ways depending on what you want to achieve with them. In this section, we will look at 3 examples of how you can write your RRL.

Thematic Literature Review
A thematic literature review is arranged around central themes or issues discussed in the sources. If you have identified some recurring themes in the literature, you can divide your RRL into sections that address various aspects of the topic. For example, if you examine studies on e-learning, you can distinguish such themes as the cost-effectiveness of online learning, the technologies used, and its effectiveness compared to traditional education.
Chronological Literature Review
A chronological literature review is a way to track the development of the topic over time. If you use this method, avoid merely listing and summarizing sources in chronological order. Instead, try to analyze the trends, turning moments, and critical debates that have shaped the field’s path. Also, you can give your interpretation of how and why specific advances occurred.
Methodological Literature Review
A methodological literature review differs from the preceding ones in that it usually doesn’t focus on the sources’ content. Instead, it is concerned with the research methods . So, if your references come from several disciplines or fields employing various research techniques, you can compare the findings and conclusions of different methodologies, for instance:
- empirical vs. theoretical studies;
- qualitative vs. quantitative research.
📚 Examples of Review of Related Literature and Studies
We have prepared a short example of RRL on climate change for you to see how everything works in practice!
Climate change is one of the most important issues nowadays. Based on a variety of facts, it is now clearer than ever that humans are altering the Earth's climate. The atmosphere and oceans have warmed, causing sea level rise, a significant loss of Arctic ice, and other climate-related changes. This literature review provides a thorough summary of research on climate change, focusing on climate change fingerprints and evidence of human influence on the Earth's climate system.
Physical Mechanisms and Evidence of Human Influence
Scientists are convinced that climate change is directly influenced by the emission of greenhouse gases. They have carefully analyzed various climate data and evidence, concluding that the majority of the observed global warming over the past 50 years cannot be explained by natural factors alone. Instead, there is compelling evidence pointing to a significant contribution of human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases (Walker, 2014). For example, based on simple physics calculations, doubled carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere can lead to a global temperature increase of approximately 1 degree Celsius. (Elderfield, 2022). In order to determine the human influence on climate, scientists still have to analyze a lot of natural changes that affect temperature, precipitation, and other components of climate on timeframes ranging from days to decades and beyond.
Fingerprinting Climate Change
Fingerprinting climate change is a useful tool to identify the causes of global warming because different factors leave unique marks on climate records. This is evident when scientists look beyond overall temperature changes and examine how warming is distributed geographically and over time (Watson, 2022). By investigating these climate patterns, scientists can obtain a more complex understanding of the connections between natural climate variability and climate variability caused by human activity.
Modeling Climate Change and Feedback
To accurately predict the consequences of feedback mechanisms, the rate of warming, and regional climate change, scientists can employ sophisticated mathematical models of the atmosphere, ocean, land, and ice (the cryosphere). These models are grounded in well-established physical laws and incorporate the latest scientific understanding of climate-related processes (Shuckburgh, 2013). Although different climate models produce slightly varying projections for future warming, they all will agree that feedback mechanisms play a significant role in amplifying the initial warming caused by greenhouse gas emissions. (Meehl, 2019).
In conclusion, the literature on global warming indicates that there are well-understood physical processes that link variations in greenhouse gas concentrations to climate change. In addition, it covers the scientific proof that the rates of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and continue to rise fast. According to the sources, the majority of this recent change is almost definitely caused by greenhouse gas emissions produced by human activities. Citizens and governments can alter their energy production methods and consumption patterns to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and, thus, the magnitude of climate change. By acting now, society can prevent the worst consequences of climate change and build a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.
Have you ever struggled with finding the topic for an RRL in different subjects? Read the following paragraphs to get some ideas!
Nursing Literature Review Example
Many topics in the nursing field require research. For example, you can write a review of literature related to dengue fever . Give a general overview of dengue virus infections, including its clinical symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and therapy.
Another good idea is to review related literature and studies about teenage pregnancy . This review can describe the effectiveness of specific programs for adolescent mothers and their children and summarize recommendations for preventing early pregnancy.
📝 Check out some more valuable examples below:
- Hospital Readmissions: Literature Review .
- Literature Review: Lower Sepsis Mortality Rates .
- Breast Cancer: Literature Review .
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Literature Review .
- PICO for Pressure Ulcers: Literature Review .
- COVID-19 Spread Prevention: Literature Review .
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Literature Review .
- Hypertension Treatment Adherence: Literature Review .
- Neonatal Sepsis Prevention: Literature Review .
- Healthcare-Associated Infections: Literature Review .
- Understaffing in Nursing: Literature Review .
Psychology Literature Review Example
If you look for an RRL topic in psychology , you can write a review of related literature about stress . Summarize scientific evidence about stress stages, side effects, types, or reduction strategies. Or you can write a review of related literature about computer game addiction . In this case, you may concentrate on the neural mechanisms underlying the internet gaming disorder, compare it to other addictions, or evaluate treatment strategies.
A review of related literature about cyberbullying is another interesting option. You can highlight the impact of cyberbullying on undergraduate students’ academic, social, and emotional development.
📝 Look at the examples that we have prepared for you to come up with some more ideas:
- Mindfulness in Counseling: A Literature Review .
- Team-Building Across Cultures: Literature Review .
- Anxiety and Decision Making: Literature Review .
- Literature Review on Depression .
- Literature Review on Narcissism .
- Effects of Depression Among Adolescents .
- Causes and Effects of Anxiety in Children .
Literature Review — Sociology Example
Sociological research poses critical questions about social structures and phenomena. For example, you can write a review of related literature about child labor , exploring cultural beliefs and social norms that normalize the exploitation of children. Or you can create a review of related literature about social media . It can investigate the impact of social media on relationships between adolescents or the role of social networks on immigrants’ acculturation .
📝 You can find some more ideas below!
- Single Mothers’ Experiences of Relationships with Their Adolescent Sons .
- Teachers and Students’ Gender-Based Interactions .
- Gender Identity: Biological Perspective and Social Cognitive Theory .
- Gender: Culturally-Prescribed Role or Biological Sex .
- The Influence of Opioid Misuse on Academic Achievement of Veteran Students .
- The Importance of Ethics in Research .
- The Role of Family and Social Network Support in Mental Health .
Education Literature Review Example
For your education studies , you can write a review of related literature about academic performance to determine factors that affect student achievement and highlight research gaps. One more idea is to create a review of related literature on study habits , considering their role in the student’s life and academic outcomes.
You can also evaluate a computerized grading system in a review of related literature to single out its advantages and barriers to implementation. Or you can complete a review of related literature on instructional materials to identify their most common types and effects on student achievement.
📝 Find some inspiration in the examples below:
- Literature Review on Online Learning Challenges From COVID-19 .
- Education, Leadership, and Management: Literature Review .
- Literature Review: Standardized Testing Bias .
- Bullying of Disabled Children in School .
- Interventions and Letter & Sound Recognition: A Literature Review .
- Social-Emotional Skills Program for Preschoolers .
- Effectiveness of Educational Leadership Management Skills .
Business Research Literature Review
If you’re a business student, you can focus on customer satisfaction in your review of related literature. Discuss specific customer satisfaction features and how it is affected by service quality and prices. You can also create a theoretical literature review about consumer buying behavior to evaluate theories that have significantly contributed to understanding how consumers make purchasing decisions.
📝 Look at the examples to get more exciting ideas:
- Leadership and Communication: Literature Review .
- Human Resource Development: Literature Review .
- Project Management. Literature Review .
- Strategic HRM: A Literature Review .
- Customer Relationship Management: Literature Review .
- Literature Review on International Financial Reporting Standards .
- Cultures of Management: Literature Review .
To conclude, a review of related literature is a significant genre of scholarly works that can be applied in various disciplines and for multiple goals. The sources examined in an RRL provide theoretical frameworks for future studies and help create original research questions and hypotheses.
When you finish your outstanding literature review, don’t forget to check whether it sounds logical and coherent. Our text-to-speech tool can help you with that!
- Literature Reviews | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Writing a Literature Review | Purdue Online Writing Lab
- Learn How to Write a Review of Literature | University of Wisconsin-Madison
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It | University of Toronto
- Writing a Literature Review | UC San Diego
- Conduct a Literature Review | The University of Arizona
- Methods for Literature Reviews | National Library of Medicine
- Literature Reviews: 5. Write the Review | Georgia State University
How to Write an Animal Testing Essay: Tips for Argumentative & Persuasive Papers
Descriptive essay topics: examples, outline, & more.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE: Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Review of Related Literature (RRL)
Ai generator.
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a crucial section in research that examines existing studies and publications related to a specific topic. It summarizes and synthesizes previous findings, identifies gaps, and provides context for the current research. RRL ensures the research is grounded in established knowledge, guiding the direction and focus of new studies.
What Is Review of Related Literature (RRL)?
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a detailed analysis of existing research relevant to a specific topic. It evaluates, synthesizes, and summarizes previous studies to identify trends, gaps, and conflicts in the literature. RRL provides a foundation for new research, ensuring it builds on established knowledge and addresses existing gaps.
Format of Review of Related Literature (RRL)
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a critical part of any research paper or thesis . It provides an overview of existing research on your topic and helps to establish the context for your study. Here is a typical format for an RRL:
1. Introduction
- Purpose : Explain the purpose of the review and its importance to your research.
- Scope : Define the scope of the literature reviewed, including the time frame, types of sources, and key themes.
2. Theoretical Framework
- Concepts and Theories : Present the main theories and concepts that underpin your research.
- Relevance : Explain how these theories relate to your study.
3. Review of Empirical Studies
- Sub-theme 1 : Summarize key studies, including methodologies, findings, and conclusions.
- Sub-theme 2 : Continue summarizing studies, focusing on different aspects or variables.
- Sub-theme 3 : Include any additional relevant studies.
4. Methodological Review
- Approaches : Discuss the various methodologies used in the reviewed studies.
- Strengths and Weaknesses : Highlight the strengths and weaknesses of these methodologies.
- Gaps : Identify gaps in the existing research that your study aims to address.
5. Synthesis and Critique
- Integration : Integrate findings from the reviewed studies to show the current state of knowledge.
- Critique : Critically evaluate the literature, discussing inconsistencies, limitations, and areas for further research.
6. Conclusion
- Summary : Summarize the main findings from the literature review.
- Research Gap : Clearly state the research gap your study will address.
- Contribution : Explain how your study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
7. References
- Citation Style : List all the sources cited in your literature review in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
Review of Related Literature (RRL) 1. Introduction This review examines research on social media’s impact on mental health, focusing on anxiety and depression across various demographics over the past ten years. 2. Theoretical Framework Anchored in Social Comparison Theory and Uses and Gratifications Theory, this review explores how individuals’ social media interactions affect their mental health. 3. Review of Empirical Studies Adolescents’ Mental Health Instagram & Body Image : Smith & Johnson (2017) found Instagram use linked to body image issues and lower self-esteem among 500 high school students. Facebook & Anxiety : Brown & Green (2016) showed Facebook use correlated with higher anxiety and depressive symptoms in a longitudinal study of 300 students. Young Adults’ Mental Health Twitter & Stress : Davis & Lee (2018) reported higher stress levels among heavy Twitter users in a survey of 400 university students. LinkedIn & Self-Esteem : Miller & White (2019) found LinkedIn use positively influenced professional self-esteem in 200 young professionals. Adult Mental Health General Social Media Use : Thompson & Evans (2020) found moderate social media use associated with better mental health outcomes, while excessive use correlated with higher anxiety and depression in 1,000 adults. 4. Methodological Review Studies used cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal designs, and mixed methods. Cross-sectional surveys provided large data sets but couldn’t infer causation. Longitudinal studies offered insights into long-term effects but were resource-intensive. Mixed methods enriched data through qualitative insights but required careful integration. 5. Synthesis and Critique The literature shows a complex relationship between social media and mental health, with platform-specific and demographic-specific effects. However, reliance on self-reported data introduces bias, and many cross-sectional studies limit causal inference. More longitudinal and experimental research is needed. 6. Conclusion Current research offers insights into social media’s mental health impact but leaves gaps, particularly regarding long-term effects and causation. This study aims to address these gaps through comprehensive longitudinal analysis. 7. References Brown, A., & Green, K. (2016). Facebook Use and Anxiety Among High School Students . Psychology in the Schools, 53(3), 257-264. Davis, R., & Lee, S. (2018). Twitter and Psychological Stress: A Study of University Students . Journal of College Student Development, 59(2), 120-135. Miller, P., & White, H. (2019). LinkedIn and Its Effect on Professional Self-Esteem . Journal of Applied Psychology, 104(1), 78-90. Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2017). The Impact of Instagram on Teen Body Image . Journal of Adolescent Health, 60(5), 555-560. Thompson, M., & Evans, D. (2020). The Relationship Between Social Media Use and Mental Health in Adults . Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 23(4), 201-208.
Review of Related Literature (RRL) Examples
Review of related literature in research, review of related literature in research paper, review of related literature qualitative research.

Review of Related Literature Quantitative Research

More Review of Related Literature (RRL) Examples
- Impact of E-learning on Student Performance
- Effectiveness of Mindfulness in Workplace
- Green Building and Energy Efficiency
- Impact of Technology on Healthcare Delivery
- Effects of Nutrition on Cognitive Development in Children
- Impact of Employee Training Programs on Productivity
- Effects of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Impact of Parental Involvement on Student Achievement
- Effects of Mobile Learning on Student Engagement
- Effects of Urban Green Spaces on Mental Health
Purpose of the Review of Related Literature (RRL)
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) serves several critical purposes in research:
- Establishing Context : It situates your research within the broader field, showing how your study relates to existing work.
- Identifying Gaps : It highlights gaps, inconsistencies, and areas needing further exploration in current knowledge, providing a clear rationale for your study.
- Avoiding Duplication : By reviewing what has already been done, it helps ensure your research is original and not a repetition of existing studies.
- Building on Existing Knowledge : It allows you to build on the findings of previous research, using established theories and methodologies to inform your work.
- Theoretical Foundation : It provides a theoretical basis for your research, grounding it in existing concepts and theories.
- Methodological Insights : It offers insights into the methods and approaches used in similar studies, helping you choose the most appropriate methods for your research.
- Establishing Credibility : It demonstrates your familiarity with the field, showing that you are well-informed and have a solid foundation for your research.
- Supporting Arguments : It provides evidence and support for your research questions, hypotheses, and objectives, strengthening the overall argument of your study.
How to Write Review of Related Literature (RRL)
Writing a Review of Related Literature (RRL) involves several key steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define the Scope and Objectives
- Determine the Scope : Decide on the breadth of the literature you will review, including specific themes, time frame, and types of sources.
- Set Objectives : Clearly define the purpose of the review. What do you aim to achieve? Identify gaps, establish context, or build on existing knowledge.
2. Search for Relevant Literature
- Identify Keywords : Use keywords and phrases related to your research topic.
- Use Databases : Search academic databases like Google Scholar, PubMed, JSTOR, etc., for relevant articles, books, and papers.
- Select Sources : Choose sources that are credible, recent, and relevant to your research.
3. Evaluate and Select the Literature
- Read Abstracts and Summaries : Quickly determine the relevance of each source.
- Assess Quality : Consider the methodology, credibility of the authors, and publication source.
- Select Key Studies : Choose studies that are most relevant to your research questions and objectives.
4. Organize the Literature
- Thematic Organization : Group studies by themes or topics.
- Chronological Organization : Arrange studies in the order they were published to show the development of ideas over time.
- Methodological Organization : Categorize studies by the methods they used.
5. Write the Review
- State the purpose and scope of the review.
- Explain the importance of the topic.
- Theoretical Framework : Present and discuss the main theories and concepts.
- Summarize key studies, including their methodologies, findings, and conclusions.
- Organize by themes or other chosen organizational methods.
- Methodological Review : Discuss the various methodologies used, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Synthesis and Critique : Integrate findings, critically evaluate the literature, and identify gaps or inconsistencies.
- Summarize the main findings from the literature review.
- Highlight the research gaps your study will address.
- State how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
6. Cite the Sources
- Use Appropriate Citation Style : Follow the required citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- List References : Provide a complete list of all sources cited in your review.
What is an RRL?
An RRL summarizes and synthesizes existing research on a specific topic to identify gaps and guide future studies.
Why is RRL important?
It provides context, highlights gaps, and ensures new research builds on existing knowledge.
How do you write an RRL?
Organize by themes, summarize studies, evaluate methodologies, identify gaps, and conclude with relevance to current research.
What sources are used in RRL?
Peer-reviewed journals, books, conference papers, and credible online resources.
How long should an RRL be?
Length varies; typically 10-20% of the total research paper.
What are common RRL mistakes?
Lack of organization, insufficient synthesis, over-reliance on outdated sources, and failure to identify gaps.
Can an RRL include non-scholarly sources?
Primarily scholarly, but reputable non-scholarly sources can be included for context.
What is the difference between RRL and bibliography?
RRL synthesizes and analyzes the literature, while a bibliography lists sources.
How often should an RRL be updated?
Regularly, especially when new relevant research is published.
Can an RRL influence research direction?
Yes, it identifies gaps and trends that shape the focus and methodology of new research.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods

Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES

Related Papers
Ana Liza Sigue
Motoky Hayakawa
Rene E Ofreneo
... Rene E. Ofreneo University of the Philippines School of Labor and Industrial Relations ... Erickson, Christopher L.; Kuruvilla, Sarosh ; Ofreneo, Rene E.; and Ortiz, Maria Asuncion , &quot;Recent Developments in Employment Relations in the Philippines&quot; (2001). ...
Lucita Lazo
This book begins by looking at the status of women in Filipino society and their place in the general socio-economic situation. It continues with sections on education and training in the Philippines and work and training. The next section reviews the constraints to women’s participation in training. In the summary the author gives a general overview of the situation of women and opportunities for work and training in the Philippines and offers some practical suggestions for the enhancement of women’s training and development.
EducationInvestor Global
Tony Mitchener
Rosalyn Eder
In this article, I examine the role of CHED and the Technical Panels (TPs) in the “production” of the globally competitive Filipina/o worker. For this paper, I draw on relevant literature on the topic and take nurse education, which is rooted in the colonial system established during the US-American occupation, as an example of how CHED and the TPs could be more linked to labor migration. I use the colonial difference - a space that offers critical insights and interpretation - to illustrate how coloniality remains hidden under the cloak of modernity. Link to the article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00131946.2016.1214913
Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Sustainable Development ISSN 2782-8557(Print)
Ryan O Tayco , Pio Supat
This study aims to determine the employability of the Negros Oriental State University graduates from 2016 to 2020. Employability is measured using different dimensions-from the graduates' side including the perspectives of the employers. A total of 1, 056 NORSU graduates and 68 employers locally and abroad answered the questionnaire through online and offline survey methods. Basic statistics were used and simple linear regression was also used to estimate the relationship between manifestations of respondents in NORSU VMGOs and the job performance as perceived by the employers. Most of the respondents in the study are presently employed and work locally. Many of them stay and accept the job because of the salaries and benefits they received, a career challenge, and related to the course they have taken in college. The study shows that the curriculum used and competencies learned by the NORSU graduates are relevant to their job. Competencies such as communication skills, human relations skills, critical thinking skills, and problem-solving skills are found to be useful by the respondents. It is found that the manifestation of the respondents is very high and homogenous. The same can be said with job performance as perceived by employers in terms of attitudes and values, skills and competencies, and knowledge. Furthermore, job performance and the manifestation of NORSU VMGOs have a significant relationship. That is, those respondents who have higher job performance in terms of attitude and values, skills and competencies, and knowledge have higher manifestations of NORSU VMGOs.
Annals of Tropical Research
Pedro Armenia
Ezekiel Succor
RELATED PAPERS
Renata Dantas
Journal of Management Info
patrick eke
Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering
Eunseob Kim
Urszula Krzych
Scientific Annals of the Danube Delta Institute
Madalina Sbarcea
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
hanjun zhao
Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice
Suzanne Cosh
Electric Power Systems Research
Afonso José do Prado
Journal of Applied Physics
Sylvain Laframboise
Chemical Biology & Drug Design
Kuldip Upadhyay
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology
Elena Lyakso
Anne-Marie Dubois
Oliver Krone
Molecular Psychiatry
Richard Ebstein
Limnology and Oceanography
Oscar Schofield
Davide Riccardi
Lucas Shuttleworth
Brain Research
Valeri Goncharuk
Pediatric Pulmonology
Yasemin Gokdemir
Revista gaúcha de enfermagem
Marli Terezinha Stein Backes
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Review of Related Literature
- First Online: 16 September 2017
Cite this chapter

- Sayed Hadi Sadeghi 3
Part of the book series: Studies in Systems, Decision and Control ((SSDC,volume 122))
1109 Accesses
1 Citations
This chapter presents a review of the literature and consists of three parts. The first part traces, via various studies, the historical background and rapid development of e-learning and presents some current definitions of the concept.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Quakers Hill, NSW, Australia
Sayed Hadi Sadeghi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sayed Hadi Sadeghi .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Sadeghi, S.H. (2018). Review of Related Literature. In: E-Learning Practice in Higher Education: A Mixed-Method Comparative Analysis. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, vol 122. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65939-8_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65939-8_2
Published : 16 September 2017
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-65938-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-65939-8
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
The effectiveness of digital twins in promoting precision health across the entire population: a systematic review
- Mei-di Shen 1 ,
- Si-bing Chen 2 &
- Xiang-dong Ding ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0001-1925-0654 2
npj Digital Medicine volume 7 , Article number: 145 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
38 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Public health
- Risk factors
- Signs and symptoms
Digital twins represent a promising technology within the domain of precision healthcare, offering significant prospects for individualized medical interventions. Existing systematic reviews, however, mainly focus on the technological dimensions of digital twins, with a limited exploration of their impact on health-related outcomes. Therefore, this systematic review aims to explore the efficacy of digital twins in improving precision healthcare at the population level. The literature search for this study encompassed PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, SinoMed, CNKI, and Wanfang Database to retrieve potentially relevant records. Patient health-related outcomes were synthesized employing quantitative content analysis, whereas the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) scales were used to evaluate the quality and potential bias inherent in each selected study. Following established inclusion and exclusion criteria, 12 studies were screened from an initial 1321 records for further analysis. These studies included patients with various conditions, including cancers, type 2 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, heart failure, qi deficiency, post-hepatectomy liver failure, and dental issues. The review coded three types of interventions: personalized health management, precision individual therapy effects, and predicting individual risk, leading to a total of 45 outcomes being measured. The collective effectiveness of these outcomes at the population level was calculated at 80% (36 out of 45). No studies exhibited unacceptable differences in quality. Overall, employing digital twins in precision health demonstrates practical advantages, warranting its expanded use to facilitate the transition from the development phase to broad application.
PROSPERO registry: CRD42024507256.
Similar content being viewed by others
Digital twins for health: a scoping review
Digital twins in medicine
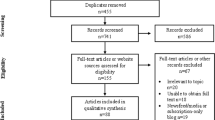
The health digital twin to tackle cardiovascular disease—a review of an emerging interdisciplinary field
Introduction.
Precision health represents a paradigm shift from the conventional “one size fits all” medical approach, focusing on specific diagnosis, treatment, and health management by incorporating individualized factors such as omics data, clinical information, and health outcomes 1 , 2 . This approach significantly impacts various diseases, potentially improving overall health while reducing healthcare costs 3 , 4 . Within this context, digital twins emerged as a promising technology 5 , creating digital replicas of the human body through two key steps: building mappings and enabling dynamic evolution 6 . Unlike traditional data mining methods, digital twins consider individual variability, providing continuous, dynamic recommendations for clinical practice 7 . This approach has gained significant attention among researchers, highlighting its potential applications in advancing precision health.
Several systematic reviews have explored the advancement of digital twins within the healthcare sector. One rapid review 8 identified four core functionalities of digital twins in healthcare management: safety management, information management, health management/well-being promotion, and operational control. Another systematic review 9 , through an analysis of 22 selected publications, summarized the diverse application scenarios of digital twins in healthcare, confirming their potential in continuous monitoring, personalized therapy, and hospital management. Furthermore, a quantitative review 10 assessed 94 high-quality articles published from 2018 to 2022, revealing a primary focus on technological advancements (such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things) and application scenarios (including personalized, precise, and real-time healthcare solutions), thus highlighting the pivotal role of digital twins technology in the field of precision health. Another systematic review 11 , incorporating 18 framework papers or reviews, underscored the need for ongoing research into digital twins’ healthcare applications, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, a systematic review 12 on the application of digital twins in cardiovascular diseases presented proof-of-concept and data-driven approaches, offering valuable insights for implementing digital twins in this specific medical area.
While the existing literature offers valuable insights into the technological aspects of digital twins in healthcare, these systematic reviews failed to thoroughly examine the actual impacts on population health. Despite the increasing interest and expanding body of research on digital twins in healthcare, the direct effects on patient health-related outcomes remain unclear. This knowledge gap highlights the need to investigate how digital twins promote and restore patient health, which is vital for advancing precision health technologies. Therefore, the objective of our systematic review is to assess the effectiveness of digital twins in improving health-related outcomes at the population level, providing a clearer understanding of their practical benefits in the context of precision health.
Search results
The selection process for the systematic review is outlined in the PRISMA flow chart (Fig. 1 ). Initially, 1321 records were identified. Of these, 446 duplicates (446/1321, 33.76%) were removed, leaving 875 records (875/1321, 66.24%) for title and abstract screening. Applying the pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria led to the exclusion of 858 records (858/875, 98.06%), leaving 17 records (17/875, 1.94%) for full-text review. Further scrutiny resulted in the exclusion of one study (1/17, 5.88%) lacking health-related outcomes and four studies (4/17, 23.53%) with overlapping data. Ultimately, 12 (12/17, 70.59%) original studies 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 were included in the systematic review. Supplementary Table 1 provides a summary of the reasons for exclusion at the full-text reading phase.
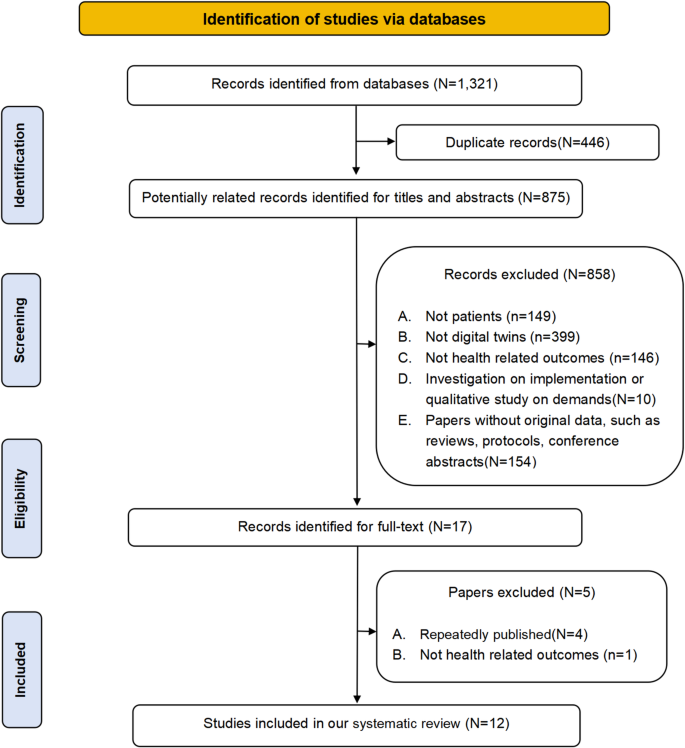
Flow chart of included studies in the systematic review.
Study characteristics
The studies included in this systematic review were published between 2021 (2/12, 16.67%) 23 , 24 and 2023 (8/12, 66.67%) 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 . Originating from diverse regions, 4/12 studies (33.33%) were from Asia 13 , 14 , 21 , 24 , 5/12 (41.67%) from America 15 , 17 , 19 , 20 , 22 , and 3/12 (25.00%) from Europe 16 , 18 , 23 . The review encompassed various study designs, including randomized controlled trials (1/12, 8.33%) 14 , quasi-experiments (6/12, 50.00%) 13 , 15 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 21 , and cohort studies (5/12, 41.67%) 17 , 20 , 22 , 23 , 24 . The sample sizes ranged from 15 13 to 3500 patients 19 . Five studies assessed the impact of digital twins on virtual patients 15 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 , while seven examined their effect on real-world patients 13 , 14 , 17 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 . These patients included had various diseases, including cancer (4/12, 33.33%) 15 , 16 , 19 , 22 , type 2 diabetes (2/12, 16.66%) 13 , 14 , multiple sclerosis (2/12, 16.66%) 17 , 18 , qi deficiency (1/12, 8.33%) 21 , heart failure (1/12, 8.33%) 20 , post-hepatectomy liver failure (1/12, 8.33%) 23 , and dental issues (1/12, 8.33%) 24 . This review coded interventions into three types: personalized health management (3/12, 25.00%) 13 , 14 , 21 , precision individual therapy effects (3/12, 25.00%) 15 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 22 , and predicting individual risk (3/12, 25.00%) 17 , 23 , 24 , with a total of 45 measured outcomes. Characteristics of the included studies are detailed in Table 1 .
Risk of bias assessment
The risk of bias for the studies included in this review is summarized in Fig. 2 . In the single RCT 14 assessed, 10 out of 13 items received positive responses. Limitations were observed due to incomplete reporting of baseline characteristics and issues with blinding. Among the six quasi-experimental studies evaluated, five (83.33%) 13 , 15 , 16 , 18 , 21 achieved at least six positive responses, indicating an acceptable quality, while one study (16.67%) 19 fell slightly below this threshold with five positive responses. The primary challenges in these quasi-experimental studies were due to the lack of control groups, inadequate baseline comparisons, and limited follow-up reporting. Four out of five (80.00%) 17 , 20 , 22 , 23 of the cohort studies met or exceeded the criterion with at least eight positive responses, demonstrating their acceptable quality. However, one study (20.00%) 24 had a lower score due to incomplete data regarding loss to follow-up and the specifics of the interventions applied. Table 1 elaborates on the specific reasons for these assessments. Despite these concerns, the overall quality of the included studies is considered a generally acceptable risk of bias.
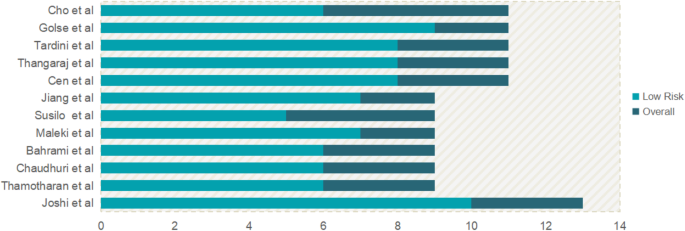
The summary of bias risk via the Joanna Briggs Institute assessment tools.
The impact of digital twins on health-related outcomes among patients
This review includes 12 studies that collectively assessed 45 outcomes, achieving an overall effectiveness rate of 80% (36 out of 45 outcomes), as depicted in Fig. 3a . The digital twins analyzed were coded into three functional categories: personalized health management, precision individual therapy effects, and predicting individual risks. A comprehensive analysis of the effectiveness of digital twins across these categories is provided, detailing the impact and outcomes associated with each function.
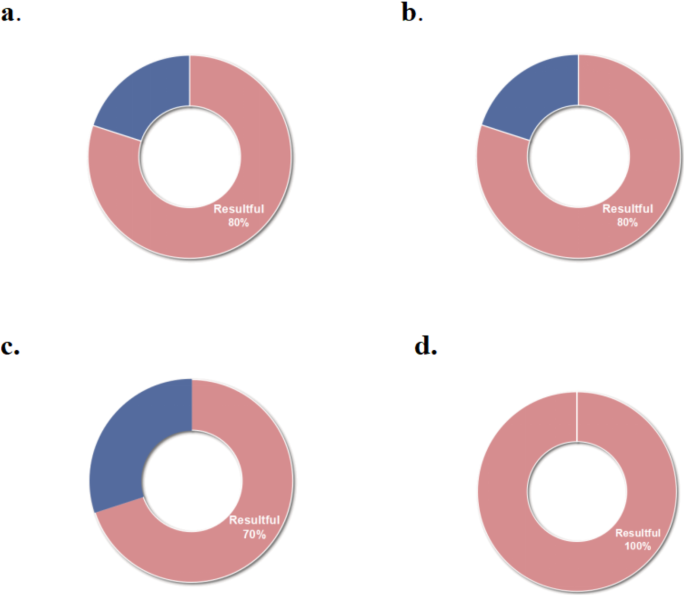
a The overall effectiveness of digital twins; b The effectiveness of personalized health management driven by digital twins; c The effectiveness of precision individualized therapy effects driven by digital twins; d The effectiveness of prediction of individual risk driven by digital twins.
The effectiveness of digital twins in personalized health management
In this review, three studies 13 , 14 , 21 employing digital twins for personalized health management reported an effectiveness of 80% (24 out of 30 outcomes), as shown in Fig. 3b . A self-control study 13 involving 15 elderly patients with diabetes, used virtual patient representations based on health information to guide individualized insulin infusion. Over 14 days, this approach improved the time in range (TIR) from 3–75% to 86–97%, decreased hypoglycemia duration from 0–22% to 0–9%, and reduced hyperglycemia time from 0–98% to 0–12%. A 1-year randomized controlled trial 14 with 319 type 2 diabetes patients, implemented personalized digital twins interventions based on nutrition, activity, and sleep. This trial demonstrated significant improvements in Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1C), Homeostatic Model Assessment 2 of Insulin Resistance (HOMA2-IR), Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Liver Fat Score (NAFLD-LFS), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Fibrosis Score (NAFLD-NFS), and other primary outcomes (all, P < 0.001; Table 2 ). However, no significant changes were observed in weight, Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Fibrosis-4 Score (FIB4), and AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) (all, P > 0.05). A non-randomized controlled trial 21 introduced a digital twin-based Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) health management platform for patients with qi deficiency. It was found to significantly improve blood pressure, main and secondary TCM symptoms, total TCM symptom scores, and quality of life (all, P < 0.05). Nonetheless, no significant improvements were observed in heart rate and BMI (all, P > 0.05; Table 2 ).
The effectiveness of digital twins in precision individual therapy effects
Six studies 15 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 22 focused on the precision of individual therapy effects using digital twins, demonstrating a 70% effectiveness rate (7 out of 10 outcomes), as detailed in Fig. 3c . In a self-control study 15 , a data-driven approach was employed to create digital twins, generating 100 virtual patients to predict the potential tumor biology outcomes of radiotherapy regimens with varying contents and doses. This study showed that personalized radiotherapy plans derived from digital twins could extend the median tumor progression time by approximately six days and reduce radiation doses by 16.7%. Bahrami et al. 16 created 3000 virtual patients experiencing cancer pain to administer precision dosing of fentanyl transdermal patch therapy. The intervention led to a 16% decrease in average pain intensity and an additional median pain-free duration of 23 hours, extending from 72 hours in cancer patients. Another quasi-experimental study 18 created 3000 virtual patients with multiple sclerosis to assess the impact of Ocrelizumab. Findings indicated Ocrelizumab can resulted in a reduction in relapses (0.191 [0.143, 0.239]) and lymphopenic adverse events (83.73% vs . 19.9%) compared to a placebo. American researchers 19 developed a quantitative systems pharmacology model using digital twins to identify the optimal dosing for aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients. This approach resulted in at least a 50% tumor size reduction by day 42 among 3500 virtual patients. A cohort study 20 assessed the 5-year composite cardiovascular outcomes in 2173 virtual patients who were treated with spironolactone or left untreated and indicated no statistically significant inter-group differences (0.85, [0.69–1.04]). Tardini et al. 22 employed digital twins to optimize multi-step treatment for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in 134 patients. The optimized treatment selection through digital twins predicted increased survival rates by 3.73 (−0.75, 8.96) and dysphagia rates by 0.75 (−4.48, 6.72) compared to clinician decisions, with no statistical significance.
The effectiveness of digital twins in predicting individual risk
Three studies 17 , 23 , 24 employing digital twins to predict individual patient risks demonstrated a 100% effectiveness rate (5 out of 5 outcomes), as shown in Fig. 3d . A cohort study 17 used digital twins to forecast the onset age for disease-specific brain atrophy in patients with multiple sclerosis. Findings indicated that the onset of progressive brain tissue loss, on average, preceded clinical symptoms by 5-6 years among the 519 patients ( P < 0.01). Another study 23 focused on predicting postoperative liver failure in 47 patients undergoing major hepatectomy through mathematical models of blood circulation. The study highlighted that elevated Postoperative Portal Vein pressure (PPV) and Portocaval Gradient (PCG) values above 17.5 mmHg and 13.5 mmHg, respectively, correlated with the measured values (all, P < 0.0001; Table 2 ). These indicators were effective in predicting post-hepatectomy liver failure, accurately identifying three out of four patients who experienced this complication. Cho et al. 24 created digital twins for 50 adult female patients using facial scans and cone-beam computed tomography images to evaluate the anteroposterior position of the maxillary central incisors and forehead inclination. The analysis demonstrated significant differences in the position of the maxillary central incisors ( P = 0.04) and forehead inclination ( P = 0.02) between the two groups.
This systematic review outlines the effectiveness of digital twins in improving health-related outcomes across various diseases, including cancers, type 2 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, qi deficiency, heart failure, post-hepatectomy liver failure, and dental issues, at the population level. Distinct from prior reviews that focused on the technological dimensions of digital twins, our analysis shows the practical applications of digital twins in healthcare. The applications have been categorized into three main areas: personalized health management, precision individual therapy effects, and predicting individual risks, encompassing a total of 45 outcomes. An overall effectiveness of 80% was observed across these outcomes. This review offers valuable insights into the application of digital twins in precision health and supports the transition of digital twins from construction to population-wide implementation.
Digital twins play a crucial role in achieving precision health 25 . They serve as virtual models of human organs, tissues, cells, or microenvironments, dynamically updating based on real-time data to offer feedback for interventions on their real counterparts 26 , 27 . Digital twins can solve complex problems in personalized health management 28 , 29 and enable comprehensive, proactive, and precise healthcare 30 . In the studies reviewed, researchers implemented digital twins by creating virtual patients based on personal health data and using simulations to generate personalized recommendations and predictions. It is worth noting that while certain indicators have not experienced significant improvement in personalized health management for patients with type 2 diabetes and Qi deficiency, it does not undermine the effectiveness of digital twins. Firstly, these studies have demonstrated significant improvements in primary outcome measures. Secondly, improving health-related outcomes in chronic diseases is an ongoing, complex process heavily influenced by changes in health behaviors 31 , 32 . While digital twins can provide personalized health guidance based on individual health data, their impact on actual behaviors warrants further investigation.
The dual nature of medications, providing benefits yet potentially leading to severe clinical outcomes like morbidity or mortality, must be carefully considered. The impact of therapy is subject to various factors, including the drug attributes and the specific disease characteristics 33 . Achieving accurate medication administration remains a significant challenge for healthcare providers 34 , underscoring the need for innovative methodologies like computational precise drug delivery 35 , 36 , a example highlighted in our review of digital twins. Regarding the prediction of individual therapy effects for conditions such as cancer, multiple sclerosis, and heart failure, six studies within this review have reported partly significant improvements in patient health-related outcomes. These advancements facilitate the tailored selection and dosing of therapy, underscoring the ability of digital twins to optimize patient-specific treatment plans effectively.
Furthermore, digital twins can enhance clinical understanding and personalize disease risk prediction 37 . It enables a quantitative understanding and prediction of individuals by continuously predicting and evaluating patient data in a virtual environment 38 . In patients with multiple sclerosis, digital twins have facilitated predictions regarding the onset of disease-specific brain atrophy, allowing for early intervention strategies. Similarly, digital twins assessed the risk of liver failure after liver resection, aiding healthcare professionals in making timely decisions. Moreover, the application of digital twins in the three-dimensional analysis of patients with dental problems has demonstrated highly effective clinical significance, underscoring its potential across various medical specialties. In summary, the adoption of digital twins has significantly contributed to advancing precision health and restoring patient well-being by creating virtual patients based on personal health data and using simulations to generate personalized recommendations and predictions.
Recent studies have introduced various digital twin systems, covering areas such as hospital management 8 , remote monitoring 9 , and diagnosing and treating various conditions 39 , 40 . Nevertheless, these systems were not included in this review due to the lack of detailed descriptions at the population health level, which constrains the broader application of this emerging technology. Our analysis underscores the reported effectiveness of digital twins, providing unique opportunities for dynamic prevention and precise intervention across different diseases. Multiple research methodologies and outcome measures poses a challenge for quantitative publication detection. This systematic review employed a comprehensive retrieval strategy across various databases for screening articles on the effectiveness of digital twins, to reduce the omission of negative results. And four repeated publications were excluded based on authors, affiliation, population, and other criteria to mitigate the bias of overestimating the digital twins effect due to repeated publication.
However, there are still limitations. Firstly, the limited published research on digital twins’ application at the population level hinders the ability to perform a quantitative meta-analysis, possibly limiting our findings’ interpretability. We encourage reporting additional high-quality randomized controlled trials on the applicability of digital twins to facilitate quantitative analysis of their effectiveness in precision health at the population level. Secondly, this review assessed the effectiveness of digital twins primarily through statistical significance ( P -value or 95% confidence interval). However, there are four quasi-experimental studies did not report statistical significance. One of the limitations of this study is the use of significant changes in author self-reports as a criterion in these four quasi-experimental studies for identifying effectiveness. In clinical practice, the author’s self-reported clinical significance can also provide the effectiveness of digital twins. Thirdly, by focusing solely on studies published in Chinese and English, this review may have omitted relevant research available in other languages, potentially limiting the scope of the analyzed literature. Lastly, our review primarily emphasized reporting statistical differences between groups. Future work should incorporate more application feedback from real patients to expose digital twins to the nuances of actual patient populations.
The application of digital twins is currently limited and primarily focused on precision health for individual patients. Expanding digital twins’ application from individual to group precision health is recommended to signify a more extensive integration in healthcare settings. This expansion involves sharing real-time data and integrating medical information across diverse medical institutions within a region, signifying the development of group precision health. Investigating both personalized medical care and collective health management has significant implications for improving medical diagnosis and treatment approaches, predicting disease risks, optimizing health management strategies, and reducing societal healthcare costs 41 .
Digital twins intervention encompasses various aspects such as health management, decision-making, and prediction, among others 9 . It represents a technological and conceptual innovation in traditional population health intervention. However, the current content design of the digital twins intervention is insufficient and suggests that it should be improved by incorporating more effective content strategies tailored to the characteristics of the target population. Findings from this study indicate that interventions did not differ significantly in our study is from digital twins driven by personalized health management, which means that compared with the other two function-driven digital twins, personalized health management needs to receive more attention to enhance its effect in population-level. For example, within the sphere of chronic disease management, integrating effective behavioral change strategies into digital twins is advisable to positively influence health-related indicators, such as weight and BMI. The effectiveness of such digital behavior change strategies has been reported in previous studies 42 , 43 . The consensus among researchers on the importance of combining effective content strategies with digital intervention technologies underscores the potential for this approach to improve patient health-related outcomes significantly.
The applications of digital twins in precision health are mainly focused on model establishment and prediction description, with limited implementation in multi-center settings. A more robust and detailed data foundation is recommended to improve clinical decision-making and reduce the likelihood of imprecise treatments. This requires continuous updating and capturing of dynamic information by digital twins in the future, as well as the improvement of the data platform that facilitates mapping, interaction, and iterative optimization. Integrating digital twins effectively into clinical workflows can support clinical interventions, assist physicians in making informed decisions, and increase the standard of patient care 6 .
The accessibility of health data is a significant challenge for the clinical implementation of digital twins. Although the internet and information technology have significantly enhanced health data availability, health data, including information systems and electronic health records, remain heterogeneous and are difficult to share 44 . Health data often contains confidential patient information, as well as unreliable information, posing challenges for implementing digital twins in healthcare settings. The primary technology utilized in digital twins, artificial intelligence algorithms, demands high-performance hardware devices and software platforms for data analysis 45 , necessitating healthcare organizations to allocate increased investment and budget for computing infrastructure supporting digital twins’ application. Therefore, future research should be focused on the technical aspects of digital twins to resolve these challenges. The automated processing of health data using a large language model and the rapid conversion of complex natural language texts into comprehensive knowledge texts are encouraged. The development of high-performance computing technology is essential for cost-effective computing requirements, which can facilitate the application of digital twins in clinical practice 46 .
Overall, this systematic review offers a comprehensive overview of digital twins in precision health, examining their impact at the population level. The findings indicate a significant overall effectiveness rate of 80% for the measured outcomes, highlighting digital twins’ pivotal role in advancing precision health. Future research should broaden the application of digital twins across various populations, integrate proven content strategies, and implement these approaches in various healthcare settings. Such efforts will maximize the benefits of digital technologies in healthcare, promoting more precise and efficacious strategies, thereby elevating patient outcomes and improving overall healthcare experiences. While digital twins offer great promise for precision health, their broad adoption and practical implementation are still in the early stages. Development, and application are essential to unlock the full potential of digital twins in revolutionizing healthcare delivery.
This systematic review was performed following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines 47 . The protocol for this systematic review was prospectively registered on PROSPERO, which can be accessed via the following link: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42024507256 . The registered protocol underwent an update, which included polishing the title of the article, modifying the limitation of the control group and language in the inclusion/exclusion criteria, and refining the process of data synthesis and analysis to enhance that clarity and readability of this systematic review. These modifications were updated in the revision notes section of the PROSPERO.
Literature search strategy
Literature searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, SinoMed, CNKI, and Wanfang Database, covering publications up to December 24, 2023. A comprehensive search strategy was developed using a combination of Medical Subject Headings terms and free-text terms, as detailed in Supplementary Table 2 . Furthermore, reference lists of articles and reviews meeting the inclusion criteria were reviewed for additional relevant studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria for this systematic review included: 1) Population: Patients diagnosed with any diseases or symptoms; 2) Intervention: Any interventions involving digital twins; 3) Controls: Non-digital twin groups, such as standard care or conventional therapy, as well as no control group; 4) Outcomes: Health-related outcomes as the primary outcomes of interest; 5) Study design: All study designs that measured patient health-related outcomes after digital twins were included, including intervention studies and predictive cohort studies.
Initially, duplicates were removed. Exclusion criteria included: 1) Papers lacking original data, such as reviews, protocols, and conference abstracts; 2) Studies not in English or Chinese; 3) Surveys focusing on implementation and qualitative studies related to requirements. In cases of data duplication, the most comprehensive data report was included.
Study selection and Data extraction
Following the automatic removal of duplicates, two independent reviewers (MD.SHEN and SB.CHEN) conducted initial screenings of titles and abstracts against the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria to identify potentially relevant studies. Afterward, the same reviewers examined the full texts of these shortlisted articles to confirm their suitability for inclusion. This process also involved checking the reference lists of these articles for any additional studies that might meet the criteria. Data from the included studies were systematically extracted using a pre-designed extraction form. Recorded information included the first author’s name, publication year, country of origin, type of study, sample size, study population, intervention, controls, measurements, and an appraisal of each study. Disagreements between the reviewers were resolved by consultation with a third senior reviewer (XD.DING), ensuring consensus.
Quality appraisal
The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) scales 48 were used to assess the quality and potential bias of each study included in the review, employing specific tools tailored to the type of study under evaluation. These tools feature response options of “yes,” “no,” “unclear,” or “not applicable” for each assessment item. For randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the JBI scale includes 13 items, with answering “yes” to at least six items indicating a high-quality study. Quasi-experimental studies were evaluated using a nine-item checklist, where five or more positive responses qualify the research as high quality. Cohort studies underwent evaluation through an 11-item checklist, with six or more affirmative responses indicating high quality. The assessment was independently carried out by two reviewers (MD.SHEN and SB.CHEN), and any disagreements were resolved through consultation with a third senior reviewer (XD.DING), ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the quality assessment.
Data synthesis and analysis
Given the heterogeneity in type of study and outcome measures, a meta-analysis was deemed unfeasible. Instead, a quantitative content analysis was employed to analyze all the selected studies 49 , 50 . Key information was extracted using a pre-designed standardized form, including the first author’s name, patient characteristics, intervention functional characteristics, measurements, results, effectiveness, and adverse events. Two reviewers (MD.SHEN and SB.CHEN) independently coded digital twin technology into three categories for descriptive analysis: personalized health management, precision individual therapy effects, and predicting individual risk, based on its functional characteristics. The Kappa statistic was applied to evaluate the inter-rater reliability during the coding process, yielding a value of 0.871, which signifies good agreement between the researchers 51 , 52 . The assessment of digital twins effectiveness was based on statistical significance ( P -value or 95% confidence interval). Outcomes with statistical significance were labeled as “resultful,” whereas those lacking statistical significance were deemed “resultless.” For quasi-experimental studies, significant changes in the authors’ self-reports were used to determine the effectiveness in the absence of reporting of statistical significance. The proportion of effectiveness was calculated as the number of “resultful” indicators divided by the total number of outcomes within each category.
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Code availability
Code sharing is not applicable to this article as no codes were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Fu, M. R. et al. Precision health: A nursing perspective. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 7 , 5–12 (2020).
PubMed Google Scholar
Naithani, N., Sinha, S., Misra, P., Vasudevan, B. & Sahu, R. Precision medicine: Concept and tools. Med. J., Armed Forces India 77 , 249–257 (2021).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Payne, K. & Gavan, S. P. Economics and precision medicine. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 280 , 263–281 (2023).
Ielapi, N. et al. Precision medicine and precision nursing: the era of biomarkers and precision health. Int. J. Gen. Med. 13 , 1705–1711 (2020).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Corral-Acero, J. et al. The ‘Digital Twin’ to enable the vision of precision cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 41 , 4556–4564 (2020).
Ferdousi, R., Laamarti, F., Hossain, M. A., Yang, C. S. & Saddik, A. E. Digital twins for well-being: an overview. Digital Twin 1 , 2022 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
Vallée, A. Digital twin for healthcare systems. Front. Digital health 5 , 1253050 (2023).
Elkefi, S. & Asan, O. Digital twins for managing health care systems: rapid literature review. J. Med. Internet Res. 24 , e37641 (2022).
Sun, T., He, X. & Li, Z. Digital twin in healthcare: Recent updates and challenges. Digital Health 9 , 20552076221149651 (2023).
Sheng, B. et al. Detecting latent topics and trends of digital twins in healthcare: A structural topic model-based systematic review. Digital Health 9 , 20552076231203672 (2023).
Khan, A. et al. A scoping review of digital twins in the context of the Covid-19 pandemic. Biomed. Eng. Comput. Biol. 13 , 11795972221102115 (2022).
Coorey, G. et al. The health digital twin to tackle cardiovascular disease-a review of an emerging interdisciplinary field. NPJ Digital Med. 5 , 126 (2022).
Thamotharan, P. et al. Human Digital Twin for Personalized Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Management. J. Clin. Med. 12 , https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062094 (2023).
Joshi, S. et al. Digital twin-enabled personalized nutrition improves metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes: results of a 1-year randomized controlled study. Endocr. Pract. : Off. J. Am. Coll. Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinologists 29 , 960–970 (2023).
Chaudhuri, A. et al. Predictive digital twin for optimizing patient-specific radiotherapy regimens under uncertainty in high-grade gliomas. Front. Artif. Intell. 6 , 1222612–1222612 (2023).
Bahrami, F., Rossi, R. M., De Nys, K. & Defraeye, T. An individualized digital twin of a patient for transdermal fentanyl therapy for chronic pain management. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 13 , 2272–2285 (2023).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cen, S., Gebregziabher, M., Moazami, S., Azevedo, C. J. & Pelletier, D. Toward precision medicine using a “digital twin” approach: modeling the onset of disease-specific brain atrophy in individuals with multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 13 , 16279 (2023).
Maleki, A. et al. Moving forward through the in silico modeling of multiple sclerosis: Treatment layer implementation and validation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 21 , 3081–3090 (2023).
Susilo, M. E. et al. Systems-based digital twins to help characterize clinical dose–response and propose predictive biomarkers in a Phase I study of bispecific antibody, mosunetuzumab, in NHL. Clin. Transl. Sci. 16 , 1134–1148 (2023).
Thangaraj, P. M., Vasisht Shankar, S., Oikonomou, E. K. & Khera, R. RCT-Twin-GAN Generates Digital Twins of Randomized Control Trials Adapted to Real-world Patients to Enhance their Inference and Application. medRxiv : the preprint server for health sciences , https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.06.23299464 (2023).
Jiang, J., Li, Q. & Yang, F. TCM Physical Health Management Training and Nursing Effect Evaluation Based on Digital Twin. Sci. Progr. 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3907481 (2022).
Tardini, E. et al. Optimal treatment selection in sequential systemic and locoregional therapy of oropharyngeal squamous carcinomas: deep Q-learning with a patient-physician digital twin dyad. J. Med. Int. Res. 24 , e29455 (2022).
Google Scholar
Golse, N. et al. Predicting the risk of post-hepatectomy portal hypertension using a digital twin: A clinical proof of concept. J. Hepatol. 74 , 661–669 (2021).
Cho, S.-W. et al. Sagittal relationship between the maxillary central incisors and the forehead in digital twins of korean adult females. J. Personal. Med. 11 , https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030203 (2021).
Imoto, S., Hasegawa, T. & Yamaguchi, R. Data science and precision health care. Nutr. Rev. 78 , 53–57 (2020).
Drummond, D. & Coulet, A. Technical, ethical, legal, and societal challenges with digital twin systems for the management of chronic diseases in children and young people. J. Med. Internet Res. 24 , e39698 (2022).
Bertezene, S. The digital twin in health: Organizational contributions and epistemological limits in a context of health crisis. Med. Sci. M/S 38 , 663–668 (2022).
Johnson, K. B. et al. Precision Medicine, AI, and the Future of Personalized Health Care. Clin. Transl. Sci. 14 , 86–93 (2021).
Powell, J. & Li, X. Integrated, data-driven health management: A step closer to personalized and predictive healthcare. Cell Syst. 13 , 201–203 (2022).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Delpierre, C. & Lefèvre, T. Precision and personalized medicine: What their current definition says and silences about the model of health they promote. Implication for the development of personalized health. Front. Sociol. 8 , 1112159 (2023).
Raiff, B. R., Burrows, C. & Dwyer, M. Behavior-analytic approaches to the management of diabetes mellitus: current status and future directions. Behav. Anal. Pract. 14 , 240–252 (2021).
Ahern, D. K. et al. Behavior-based diabetes management: impact on care, hospitalizations, and costs. Am. J. Managed care 27 , 96–102 (2021).
Tyson, R. J. et al. Precision dosing priority criteria: drug, disease, and patient population variables. Front. Pharmacol. 11 , 420 (2020).
Walton, R., Dovey, S., Harvey, E. & Freemantle, N. Computer support for determining drug dose: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clin. Res.) 318 , 984–990 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Friedrichs, M. & Shoshi, A. History and future of KALIS: Towards computer-assisted decision making in prescriptive medicine. J. Integr. Bioinform. 16 , https://doi.org/10.1515/jib-2019-0011 (2019).
Zhao, H. et al. Identifying the serious clinical outcomes of adverse reactions to drugs by a multi-task deep learning framework. Commun. Biol. 6 , 870 (2023).
Thiong’o, G. M. & Rutka, J. T. Digital twin technology: the future of predicting neurological complications of pediatric cancers and their treatment. Front. Oncol. 11 , 781499 (2021).
Sun, T., He, X., Song, X., Shu, L. & Li, Z. The digital twin in medicine: a key to the future of healthcare? Front. Med. 9 , 907066 (2022).
Sarp, S., Kuzlu, M., Zhao, Y. & Gueler, O. Digital twin in healthcare: a study for chronic wound management. IEEE J. Biomed. health Inform. 27 , 5634–5643 (2023).
Chu, Y., Li, S., Tang, J. & Wu, H. The potential of the Medical Digital Twin in diabetes management: a review. Front. Med. 10 , 1178912 (2023).
Barricelli, B. R., Casiraghi, E. & Fogli, D. A survey on digital twin: definitions, characteristics, applications, and design implications. IEEE Access 7 , 167653–167671 (2019).
Keller, R. et al. Digital behavior change interventions for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: systematic market analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 24 , e33348 (2022).
Priesterroth, L., Grammes, J., Holtz, K., Reinwarth, A. & Kubiak, T. Gamification and behavior change techniques in diabetes self-management apps. J. diabetes Sci. Technol. 13 , 954–958 (2019).
Venkatesh, K. P., Raza, M. M. & Kvedar, J. C. Health digital twins as tools for precision medicine: Considerations for computation, implementation, and regulation. NPJ digital Med. 5 , 150 (2022).
Venkatesh, K. P., Brito, G. & Kamel Boulos, M. N. Health digital twins in life science and health care innovation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 64 , 159–170 (2024).
Katsoulakis, E. et al. Digital twins for health: a scoping review. NPJ Digital Med. 7 , 77 (2024).
Page, M. J. et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin. Res. ed.) 372 , n71 (2021).
Barker, T. H. et al. Revising the JBI quantitative critical appraisal tools to improve their applicability: an overview of methods and the development process. JBI Evid. Synth. 21 , 478–493 (2023).
Manganello, J. & Blake, N. A study of quantitative content analysis of health messages in U.S. media from 1985 to 2005. Health Commun. 25 , 387–396 (2010).
Giannantonio, C. M. Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology, 2nd edition. Organ. Res. Methods 13 , 392–394 (2010).
Rigby, A. S. Statistical methods in epidemiology. v. Towards an understanding of the kappa coefficient. Disabil. Rehabilitation 22 , 339–344 (2000).
Lantz, C. A. & Nebenzahl, E. Behavior and interpretation of the kappa statistic: resolution of the two paradoxes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 49 , 431–434 (1996).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Nursing, Peking University, Beijing, China
Mei-di Shen
Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Microsurgery, China-Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China
Si-bing Chen & Xiang-dong Ding
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MD.SHEN contributed to the data collection, analysis and the manuscript writing. SB.CHEN contributed to the data collection and analysis. XD.DING contributed to the critical revision of the manuscript as well as the initial study conception. All authors read and approved the final manuscript, and jointly take responsibility for the decision to submit this work for publication.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiang-dong Ding .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary file, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shen, Md., Chen, Sb. & Ding, Xd. The effectiveness of digital twins in promoting precision health across the entire population: a systematic review. npj Digit. Med. 7 , 145 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-024-01146-0
Download citation
Received : 29 January 2024
Accepted : 22 May 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-024-01146-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
NTRS - NASA Technical Reports Server
Available downloads, related records.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

FHFA Statistics Measuring Price Effects from Disasters Using Public Data: A Case Study of Hurricane Ian
What happens to home values after a disaster? In a recent working paper , we address this question with a combination of readily available public data sources that track insurance claims and house prices. Focusing on a specific storm, Hurricane Ian, we use leading statistical estimation approaches, difference-in-differences (DiD) and synthetic control methods (SCM), to provide some insights. A key finding is that data limitations create problems for identifying precise price effects. This blogpost discusses the data, methodological choices, and basic findings.
As a preview, we find positive price effects for homes affected by the hurricane. However, our results should not be interpreted as causal, but more correlational. Several factors, including COVID-19 and measurement error, could have confounding influences which make it difficult to measure the effects of Ian’s damage on home prices. Still, the exercise is useful because it demonstrates how one might use public information and why it is useful to continue improving such data releases to support policy analyses.
Defining Damages from Hurricane Ian to Estimate Price Effects
Hurricane Ian struck southwest Florida on September 23, 2022, damaging homes across the state. According to the National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone Report, Hurricane Ian “was responsible for over 150 direct and indirect deaths and over $112 billion in damage, making it the costliest hurricane in Florida’s history and the third costliest in the United States history”. 1 Figure 1 shows that path of Ian through Florida. Real estate listings are shown with yellow dots (larger circles indicating counties with more properties for sale) and darker blue shading indicates places that had more claims filed for damages. The figure shows a large concentration of insurance claims in southwest Florida, which also has a large number of real estate listings. We focus on Lee County, which has the darkest shading and is located on the Gulf Coast side of the state where the storm first landed.
Figure 1: Hurricane Ian’s path through Florida in 2022
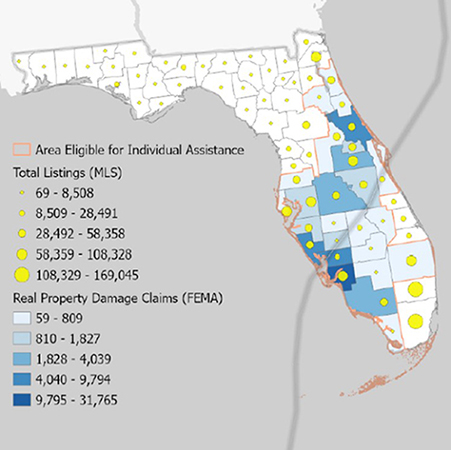
We estimate price effects by combining publicly available damages data with real estate listings data for southwest Florida between March 2015 and June 2023. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) determines real property damage to properties for claims with limited or no insurance as part of the Individuals and Households Program (IHP). This information is combined with real estate market activity from Multiple Listing Service (MLS) data sourced by CoreLogic.
The key challenge we face is that many damage-related reports rely on publicly available disaster data, which for privacy reasons typically only include coarse descriptions of location. As a result, individual properties must be assigned damages from an aggregate level (e.g., county or ZIP code), thus introducing measurement error. This is a problem because previous research has shown mismeasured “treatment” variables like damages to a home can create problems for estimating causal price effects. 2
After merging IHP and MLS data, treated areas are classified at the county or ZIP code levels and with each home in an area assigned the same treatment status. This occurs regardless of whether the home was damaged. We consider multiple ways to assign treatment at the county and ZIP code levels. While the full set of aggregate treatment definitions are shown in the paper, this blogpost only presents a preferred specification at the county level (with damages aggregated for all homes therein) where treatment indicates county damages exceed the median for other counties.
Preliminary Evidence
Real estate market measures are illustrated in two panels within Figure 2. While not shown here, the trends are similar between Lee County (the focus area) and the entire state of Florida. The left panel presents median list (solid navy line) and close prices (solid maroon line) for each month during our sample. Both price trends are noisy and lack a sharp change when the storm hit, which is denoted by the dashed vertical black line. The right panel shows a reduction in the number of new listings, suggesting that prices could have been propped up by a decrease in home supply. Alternatively, homes that sold after the storm could be disproportionately better quality and command a premium. We are agnostic about the correct channel at work here: more careful analysis is needed to identify the mechanism(s) operating to affect prices. Finally, a potential COVID-19 effect starts after 2020 with prices increasing more quickly in the left panel and greater listing volatility in the right panel.
The lack of a clear and sustained impact on home prices suggests a more rigorous empirical analysis is needed for prices. We emphasize that we do not claim to establish a causal relationship nor that a price adjustment mechanism is identified correctly. We simply aim to estimate any aggregate price effect while using public data and documenting the challenges even when using leading statistical approaches.
Figure 2: Real estate market activity in Lee County, Florida
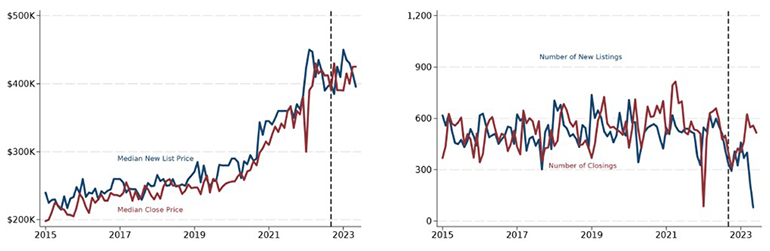
Difference-in-Differences Method for Price Effects
The most common approach used in the disaster literature for estimating price effects is a difference-in-differences (DiD) or event study approach. 3 In generalized terms, this means comparing price trends in affected (“treated”) areas with price trends in unaffected (“control”) areas.
Figure 3: Dynamic DiD for Lee County where Hurricane Ian made landfall
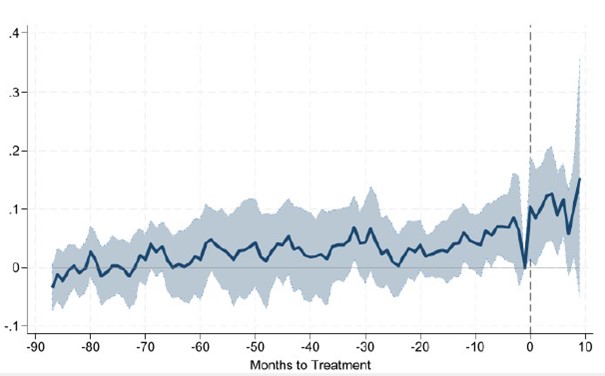
Figure 3 conveys the DiD results for a dynamic treatment (“event study”). The horizontal axis represents time relative to Ian, with the vertical dashed line indicating Ian’s landfall. The vertical axis shows an estimated parameter that is the difference in price trends between affected and unaffected areas at each time, with the shaded area representing the 95% confidence interval of the parameter. Higher prices are correlated with damages post-Ian. Where is this shown? By the price trend increasing above the zero line after the dashed vertical line.
However, the key assumption underlying DiD is the parallel trends assumption, which says that absent Hurricane Ian the areas affected and not affected would have had similar price trends. To test whether this assumption holds, researchers commonly conduct “pre-trends” tests, checking whether before Ian affected and not affected areas had similar price trends. In Figure 3, this corresponds to the difference in price trends being close to zero prior to the dashed line. As the figure shows, there is evidence that parallel trends does appear to be violated about 20 to 25 months prior to Ian’s arrival. What happened at that time? That was the early period of COVID. This is problematic statistically because the homes that saw prices increase during the early stages of the pandemic were the same homes that were damaged by Ian, making identification of the true Ian price effects challenging.
Synthetic Control Method for Price Effects
Another approach one can take is to construct a suitable control using the synthetic control method (SCM) at the aggregated level. The SCM determines an optimal weighted average of untreated counties (i.e. its synthetic control) to match the pre-Ian price trends of Lee County. Figure 4 below illustrates Lee County and its synthetic control. The figure suggests a time-varying price premium of at least five percent that peaks in the low double digits a few months after Ian, similar to the DiD finding. However, despite the apparent good fit in the figure with the blue and red lines appearing to be on top of each other until the dashed vertical line, more sensitive goodness of fit tests indicate these estimates lack statistical significance.
Figure 4: Synthetic control for Lee County
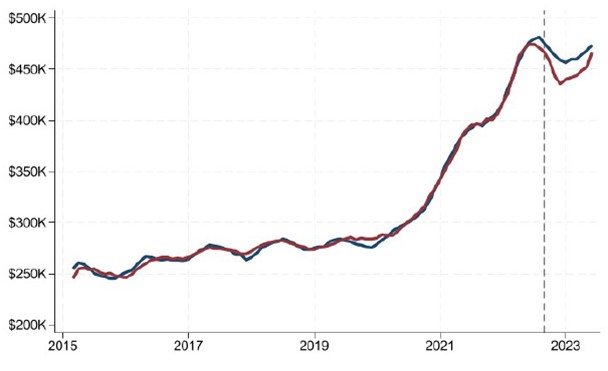
In summary, using publicly available data it may be difficult to estimate price effects even when employing leading empirical techniques. While we record some evidence for positive price effects for Ian, it is possible that declines across many markets but less so in the target county. Either way, these results should be viewed with some skepticism because of an inability to establishing actual property-level damages when using public data. Given the local nature of damages, when one is unable to precisely identify which units are treated or not, finding a suitable control group is extremely difficult. For those interested in working with such data, we offer several suggestions in the paper and encourage you to read further.
1 See https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/data/tcr/AL092022_Ian.pdf .
2 For recent academic research on this type of problem in a difference-in-differences setting, see Denteh Kedagni (2022) and Negi Negi (2022), for example. The problem is the mismeasurement of the treatment variable, often called a “misclassification” problem.
3 See another one of FHFA’s working papers, for a recent review of the applied disaster literature: Justin Contat, Carrie Hopkins, Luis Mejia, Matthew Suandi. 2024. “When Climate Meets Real Estate: A Survey of the Literature." Real Estate Economics. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-6229.12489 .
By:Justin Contat
Senior Economist
Division of Research and Statistics
By:Will Doerner
Supervisory Economist
By:Robert Renner
Senior Geographer
By:Malcolm Rogers
Tagged: FHFA Stats Blog; Source: FHFA; Natural Disasters; Natural Disaster Price Effects; hurricane; real estate valuation

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tips on how to write a review of related literature in research. Given that you will probably need to produce a number of these at some point, here are a few general tips on how to write an effective review of related literature 2. Define your topic, audience, and purpose: You will be spending a lot of time with this review, so choose a topic ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A review of related literature (RRL) is a part of the research report that examines significant studies, theories, and concepts published in scholarly sources on a particular topic. An RRL includes 3 main components: A short overview and critique of the previous research.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Understand how study background and literature review are different here: INFOGRAPHIC: 6 Differences between study background and literature review. 3. Shortlist a good reference management software: It is also recommended that you shortlist a good reference management software like Zotero to manage your bibliographic data and related research ...
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a crucial section in research that examines existing studies and publications related to a specific topic. It summarizes and synthesizes previous findings, identifies gaps, and provides context for the current research. RRL ensures the research is grounded in established knowledge, guiding the direction and focus of new studies.
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.. Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
What kinds of literature reviews are written? Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified.
Introduction. Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
The literature review provides a way for the novice researcher to convince the proposal the reviewers that she is knowledgeable about the related research and the "intellectual traditions" that support the proposed study. The literature review provides the researcher with an opportunity to identify any gaps that may exist in the body of ...
India. V [email protected]. REVIEW OF RELA TED LITERA TURE (RRL): A STUDY. By. Dr. V .Thangavel *. Abstract: Writing of review literature is the pre-qualification to undertake literature ...
Conducting a review of related literature (RRL) is a crucial step in the process of writing an MBA dissertation. To perform a thorough RRL, start by identifying key themes and concepts relevant to your dissertation topic. Utilize academic databases and journals to search for scholarly articles, books, and other sources that provide insights ...
A literature review is a critical analysis of existing literature in a research field. It evaluates the contribution made by other researchers in that field and highlights gaps in knowledge that need to be addressed. To begin with, you can read a lot of articles, books, and other published works on the topics of your interest.
A review of literature is a classification and evaluation of what accredited scholars and. researchers have written on a topic, organized according to a guiding concept such as a research ...
A Critical Paper: The Miseducation of the Filipinos. Ezekiel Succor. Download Free PDF. View PDF. CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES This chapter presents the related literature and studies after the thorough and in-depth search done by the researchers.
The literature and studies cited in this chapter tackle the different concept, understanding, and ideas, generalization or conclusions and different development related to study of the enrollment from the past up to the present and which serves as the researchers guide in developing the project. Those that were also included in this chapter ...
There are many types of literature reviews. The purposes of a literature review will vary, and the sources used in one will depend on the discipline and the review's topic. Literature reviews may have differences that include: Purpose: The reason or objective of the review. One review may be to see how much has been published on a topic (a ...
R.I.E., Bhopal. [email protected]. Introduction. "Review of related Literature" is mostly known as the second chapter in almost every. empirical thesis. But it is the very first step to ...
This chapter presents a review of the literature and consists of three parts. The first part traces, via various studies, the historical background and rapid development of e-learning and presents some current definitions of the concept. The second part investigates the literature in the e-learning field that focuses on cultural issues. An
evolved GT studies who actually advocate a priori reviews (Goldkuhl & Cronholm, 2010, Thornberg, 2012). The review of related literature is actually one of the most debated-about part of the GT methodology. This chapter includes both literature that were reviewed before the study commenced,
A review of related literature (RRL) is important for obtaining an overview of the current knowledge on the topic. It provides the investigator with a framework on which to build an appropriate hypothesis. Further, an RRL guides the researcher in the direction of adding something new to the field without duplicating previous efforts.
Related Literature In this part of the research study, the researchers will include all the related literature and studies, providing five (5) literatures and five (5) studies. Peperomia pellucida, locally known as "ulasimang-bato" or "pansit-pansitan", has long been used in Philippine traditional medicine for its analgesic, anti ...
Abstract. The Shiji (史記 or Records of the Grand Historian) is a treasure trove of Chinese language and culture with complex, multifaceted textual images that are truly difficult to completely recreate in translation, requiring translators to make tradeoffs.Burton Watson's 華茲生 translation of the Shiji clearly positions it as a literary text and he regards his main task as conveying ...
The impact of digital twins on health-related outcomes among patients. This review includes 12 studies that collectively assessed 45 outcomes, achieving an overall effectiveness rate of 80% (36 ...
Chapter 2. Review of Related Literature. This chapter is a discussion of the literatures and the. result of other related researches to which the present. study is related or has some bearing or ...
The current study, however, is limited in scope with a focus on the application of thermoplastic composites to aircraft structures. Further, the study does not provide a comprehensive assessment of the available literature but rather offers an overview of past and present research being conducted in the field of thermoplastic composites.
MCB301 1/23/24 Primary Literature Analysis 1- Van Der Goot Problem and/or Question: In this paper, Van Der Goot investigates tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenases (tdo-2) role in regulating age related protein toxicity and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. There is significance in understanding the molecular mechanisms involved in this process given it is crucial for organismal survival to perform ...
The key challenge we face is that many damage-related reports rely on publicly available disaster data, which for privacy reasons typically only include coarse descriptions of location. ... Florida Image Difference-in-Differences Method for Price Effects The most common approach used in the disaster literature for estimating price effects is a ...