

Creative Writing Genre Guide – The Many Genres of Writing in The Creative Arts

Written by Scott Wilson

Like the hiss of a jagged sword slicing past your ear or the roar of a spacecraft entering the atmosphere of a strange planet, genre echos through every piece of creative writing.
Whether or not the author chooses consciously to conform to an existing genre or decides to break new ground, genre will attach to whatever they create. Even so-called non-genre, or literary, fiction is itself a sort of genre. Genre is a tool that is used by:
- Writers , to guide story and expectations
- Critics , to categorize and analyze creative works
- Publishers and Booksellers , to stock and market books to their target audiences
- Readers , to find and read works that align with their aesthetic preferences
Understanding and mastering genre is not optional for creative writers. But it’s not easy, either.
How Genre Defines Your Creative Writing Work

Genre is a hot topic in the world of creative writing. You won’t get far in the average creative writing program before you get into some kind of argument over how to classify some piece of work.
That’s because genre is necessarily subjective. There is no centralized Genre Board that puts a stamp inside the front cover of each new book that is released. The American Literature Association does not maintain an official list of genres that authors are required to choose from among before beginning their next story.
The reality of a serious writer is a reality of many voices, some of them belonging to the writer, some of them belonging to the world of readers at large. ~ Aberjhani
Our literary genres today are simply social conventions, conventions that evolve over time with community expectations and tropes. It’s impossible to come up with a genre writing definition that will satisfy everyone. At the same time, genre is descriptive enough to be indispensable for readers and writers alike.
Genre is so difficult to get a grip on because it is effectively a kind of rolling consensus.
Genre is defined by the authors themselves, by critics who seek to interpret works, by readers deciding what they like to read, and by publishers looking to market those works.
And those definitions change all the time.
The Rapid Evolution of Genre in Writing
Take the ancient and well-established genre of fantasy, for example. Myth and legend may be the oldest genres of fiction, stretching back to our earliest recorded works. The Epic of Gilgamesh and Beowulf both fall into the realm of fantasy.
But fantasy has evolved as its readers and writers have.
Fantasy writing today is nothing like what it was prior to Tolkien’s tales of Middle Earth reaching and shaping the expectations of readers. Epic works like The Lord of the Rings and the Chronicles of Narnia set a standard for their writing genre, and subsequent tales are inevitably judged by those standards.
With the pace of publishing increasing rapidly and the ease of finding literature to taste getting easier and easier, genre is evolving at a lightning pace.
Writing Sub-Genres Have Become Ever More Niche With the Internet

That kind of specificity comes with very distinctive expectations, however. Niche works are often expected by readers to follow a very specific formula—hit a certain set of plot points, come in at a particular word-count, feature a distinctive type of characters. If you’re aiming for success in the Highlander romance niche, you had better have an evil Englishman somewhere in the story—and heaven help you if there’s not a shirtless man in a kilt on the cover.
While this kind of narrow, formulaic approach is seen as a constraint by some authors, it represents a kind of feedback loop that allows writers to reach very specific audiences. If you plan to make a career out of creative writing, understanding and selling to the market is door you’ll need to open. Genre expectations give you the key.
The genre of writing you pick for any given story you choose to tell will define how it is viewed and what readers expect before you even put down the first word. So understanding how genres in writing work and how to use them in your own pieces is a key part of being a creative writer today.
Picking a Writing Genre Can Be Empowering for Creative Writers
Understanding what genre is and how genres are defined is the only way that you can understand how your own work will be perceived. And developing that kind of knowledge allows your writing to grow and operate on multiple levels as your stories unfold. Genre offers subtext to your stories. Adding a new entry to the catalog of any particular genre expands what the field has to say.
The many types of genres in writing offer an avenue for every writer to explore and expand their craft.
Equally important for some writers is the sense of context that genre creates for their writing. Not only can it help shape creative works by offering standards to aim at, but it also provides a set of expectations that can be subverted to critical effect. For example, The Red Badge of Courage by Stephen Crane would not have had the effect on readers that it did without a long tradition of glorious war stories from a genre that it mimicked, then up-ended with the hero’s cowardice.
Pure formless creativity and invention are wild and dangerous things. To develop a coherent story and a world that is true enough for readers to believe is a tricky business. Having a set of general rules to follow and expectations to meet brings focus.
Beyond that, the very act of channeling your imagination into a defined form and to tell your own story within those rules is a challenge that rewards the creative spirit. Finishing a novel can feel very much like clicking the last piece into place on a jigsaw puzzle. The picture on that puzzle is the genre. When everything lines up to match, your sense of satisfaction and accomplishment is immense.
Writing Genres Give Readers the Stories They Are Looking For

Those stores, and the publishers who print novels and magazines, live and die by genre sales. Some publishers either specialize in or dedicate certain of their imprints to particular genres. Editors, illustrators, and agents may also specialize by genre. Critics, industry awards, and writing groups are often dedicated to different genres. Even creative writing programs offer specializations or concentrations in certain writing genres.
Ultimately, however, genre in writing persists and is needed for the reader. The evolution of genres in writing has largely been in the hands of publishers and book sellers, all seeking to match works with groups of readers who will find them appealing.
Genre in Writing May Be Determined in Different Ways
Genres in writing are not absolutes. Any given work can fall into many different genres depending on how the term is being applied. For example, the two big categories of writing are the genres of poetry and prose. Every work will fall into one of those, as well as others.
The most common ways of categorizing genre are:
- By literary technique and style
- By setting or character type
Each of these different genres of writing will share certain characteristics, but may diverge through other categories. For example, there are works that have a common science fiction theme, but use technique and style more common to literary fiction. The Handmaid’s Tale , by Margaret Atwood, is one example… set in a dystopian future, it nonetheless develops characters and explores deep themes common to other classic works of literature.

In addition to crossing genres, creative writing works also may fall into sub-genres. The most writing genres evolve branches over time. In fact, science fiction, one of the biggest and most popular genre examples in writing today, is simply a sub-genre of the larger category of speculative fiction.
Sub-Genres Sprout From Pop-Culture in Unexpected Ways to Offer Something Uniquely Tailored to Every Audience

To give just one example of this process, consider the evolution of the genre of steampunk.
Steampunk is a sub-genre of cyberpunk, which already lies at the bottom of a long list of other sub-genres of fiction:
In addition, steampunk works almost all fall into the addition speculative fiction category of alternate history, since they imagine a historical era not as it was, but as it might have been. Some can be called Westerns; others are post-apocalyptic, taking another bite out of the dystopian genre apple.
The first proto-steampunk works were published in the ’70s and ‘80s by authors such as Tim Powers and James Blaylock, but it was 1990’s The Difference Engine , by William Gibson and Bruce Sterling that really kicked off steampunk as a genre—probably because Gibson and Sterling were also two of the prime movers in cyberpunk itself.
As steampunk caught on and became more popular, not only did newer works emerge to expand the genre (including its own sub-genres), but older novels that included or inspired the same elements were sometimes described as steampunk. Seminal works like H.G Wells’ The Time Machine and Jules Verne’s Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea are sometimes found in lists of steampunk works.
Why not just do away with genre, and consider each piece on its own merits? Ultimately, many scholars and creative writing professionals are able to do just that.
In the same way that a rock musician can understand, appreciate, and adapt techniques from the classical world, good writers recognize and respect good writing craft, regardless of genre.
But genre is also a part of artistic judgement. A creative work can be assessed by how well or poorly it conforms to the expectations of the genre it is aimed at.
How To Succeed as a Creative Writer in Different Types of Writing Genres
To be clear, you don’t need to pick a genre lane if you don’t want to. Iain Banks had no problem at all jumping back and forth between epic sci-fi novels, psychologically complex literary fiction, rollicking travelogues, and even poetry. All of it earned critical acclaim.
When J.K. Rowling decided she needed a break from fantasy, she picked up the pen name of Robert Galbraith and popped over into crime fiction instead.
But most creative writers aren’t made of the same stuff as Banks or Rowling. It may be that a particular genre is what inspires you to write in the first place. Perhaps it’s a fascination with the subject matter that draws you in to a particular kind of world. Or maybe it’s just a raw commercial calculation, playing to the market and what is most publishable.
In any case, deciding the genre or genres you are interested in writing in is only one part of the process. Each genre has its own unique path to success.
The Many Genres of Writing in English Literature
To help you get started, we’ve got a whole list of writing genre guides that take you step-by-step through the process of becoming a successful writer in that field.

Literary Fiction
Literary fiction is the non-genre genre of creative writing. It includes works that are too non-traditional to fit cleanly in existing genres or that focuses on characterization and exploration of deep truths over conventional plot or narrative structures. Much of the pantheon of great novels and works that are used in teaching creative writing fall into the literary fiction genre.
Fantasy authors excel in creating imaginary worlds where fantastic creatures roam, magic and the supernatural shape character’s lives, and medieval settings call classic mythology to mind. Fantasy is one of the oldest of genres in both Eastern and Western writing traditions, and its popularity continues to ensure steady careers for well-trained fantasy writers.
There is a fascination with the macabre and surreal that keeps horror novels on the top-seller lists year after year. From Anne Rice to Stephen King, some of the most commercially successful modern authors have chosen this genre. And with classics from Shelley and Poe as part of the enduring tradition of literature, a career in horror offers creative writers a shot at both fortune and fame.

Mystery, or crime, fiction embraces a whole spectrum of entertaining works from Agatha Christie’s classic detective novels to the hard-boiled works of Dennis Lehane. Writers who have the talent to deliver an intricate plot and keep readers engaged with a steady stream of clues, but still make the reveal and resolution a rewarding surprise, have a bright future in the mystery genre.
The Western genre is both relatively new and distinctively American in nature. Following in the footsteps of Louis L’Amour and Max Brand is no easy task, but there is plenty of life in the humble Western, as works by Cormac McCarthy and Larry McMurtry have shown. Western writers may or may not need a ten-gallon hat, but the definitely need story-telling skills and a strong set of research skills.
Young Adult
Young adult works often combine other genres into stories that deal particularly with the interests and concerns of teenagers. Whether it’s a mix of fantasy and school, like Harry Potter , or pure works that explore contemporary problems and challenges like the classic The Outsiders , young adult novels can shape the perspectives and growth of a generation. Young adult writers have to develop not only a knack for telling stories cleanly and understandably, but also for tapping into the zeitgeist of their target audience.

Science Fiction (Sci Fi)
Science fiction uses the prism of technology and time to explore both exciting theoretical science and social mores and consequences of humanity today. Science fiction is a genre that has a robust demand and strong traditions. Although it can be tough to break into sci-fi, studying creative writing offers the kind of analytical tools and techniques that can make it happen.
Short Story
The genre of short story is one rooted in length rather than subject. A short story can be told in almost any of the other genres listed here, but it is a form that requires its own set of skills and sensibilities. Creative writing degrees are one of the best places for writers to polish up their ability to deliver the crisp, clear, meaningful prose that is needed to build a successful short story.
Making people laugh is a rare skill in any kind of artistic endeavor. Comedic writing has a long and honorable history in the world of dramatic literature, serving as one of the first genres recognized by the Greeks. Comedy often crosses other genre boundaries, with tendrils in horror, science fiction, and crime. But pure comedies in the form of satire and parody serve important roles in social commentary as well as entertainment.
Historical Fiction
Writing historical fiction comes with a set of guard rails that play directly to the strengths of creative writers: research offers a glimpse of the world as it once was, and imagination fills out the humanity of those times. While the historical setting can be one grounded firmly in reality, like Hilary Mantel’s acclaimed Wolf Hall , it can also serve as a portal to the fantastical, as in Susanna Clarke’s incredible Jonathan Strange & Mr. Norrell .

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)

What is Creative Writing? A Key Piece of the Writer’s Toolbox
Not all writing is the same and there’s a type of writing that has the ability to transport, teach, and inspire others like no other.
Creative writing stands out due to its unique approach and focus on imagination. Here’s how to get started and grow as you explore the broad and beautiful world of creative writing!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way.
Creative writing can take on various forms such as:
- short stories
- screenplays
It’s a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way . It’s about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing
Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression:
1. Imagination and Creativity: Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work. It allows writers to explore different scenarios, characters, and worlds that may not exist in reality.
2. Emotional Engagement: Creative writing often evokes strong emotions in the reader. It aims to make the reader feel something — whether it’s happiness, sorrow, excitement, or fear.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It’s about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional.
4. Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner.
5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a piece that’s not just interesting to read, but also beautiful to hear when read aloud.
Remember, creative writing is not just about producing a work of art. It’s also a means of self-expression and a way to share your perspective with the world. Whether you’re considering it as a hobby or contemplating a career in it, understanding the nature and characteristics of creative writing can help you hone your skills and create more engaging pieces .
For more insights into creative writing, check out our articles on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree and is a degree in creative writing worth it .
Styles of Creative Writing
To fully understand creative writing , you must be aware of the various styles involved. Creative writing explores a multitude of genres, each with its own unique characteristics and techniques.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses expressive language to evoke emotions and ideas. Poets often employ rhythm, rhyme, and other poetic devices to create pieces that are deeply personal and impactful. Poems can vary greatly in length, style, and subject matter, making this a versatile and dynamic form of creative writing.
Short Stories
Short stories are another common style of creative writing. These are brief narratives that typically revolve around a single event or idea. Despite their length, short stories can provide a powerful punch, using precise language and tight narrative structures to convey a complete story in a limited space.
Novels represent a longer form of narrative creative writing. They usually involve complex plots, multiple characters, and various themes. Writing a novel requires a significant investment of time and effort; however, the result can be a rich and immersive reading experience.
Screenplays
Screenplays are written works intended for the screen, be it television, film, or online platforms. They require a specific format, incorporating dialogue and visual descriptions to guide the production process. Screenwriters must also consider the practical aspects of filmmaking, making this an intricate and specialized form of creative writing.
If you’re interested in this style, understanding creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree can provide useful insights.
Writing for the theater is another specialized form of creative writing. Plays, like screenplays, combine dialogue and action, but they also require an understanding of the unique dynamics of the theatrical stage. Playwrights must think about the live audience and the physical space of the theater when crafting their works.
Each of these styles offers unique opportunities for creativity and expression. Whether you’re drawn to the concise power of poetry, the detailed storytelling of novels, or the visual language of screenplays and plays, there’s a form of creative writing that will suit your artistic voice. The key is to explore, experiment, and find the style that resonates with you.
For those looking to spark their creativity, our article on creative writing prompts offers a wealth of ideas to get you started.
Importance of Creative Writing
Understanding what is creative writing involves recognizing its value and significance. Engaging in creative writing can provide numerous benefits – let’s take a closer look.
Developing Creativity and Imagination
Creative writing serves as a fertile ground for nurturing creativity and imagination. It encourages you to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and create unique and original content. This leads to improved problem-solving skills and a broader worldview , both of which can be beneficial in various aspects of life.
Through creative writing, one can build entire worlds, create characters, and weave complex narratives, all of which are products of a creative mind and vivid imagination. This can be especially beneficial for those seeking creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Enhancing Communication Skills
Creative writing can also play a crucial role in honing communication skills. It demands clarity, precision, and a strong command of language. This helps to improve your vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas effectively .
Moreover, creative writing encourages empathy as you often need to portray a variety of characters from different backgrounds and perspectives. This leads to a better understanding of people and improved interpersonal communication skills.
Exploring Emotions and Ideas
One of the most profound aspects of creative writing is its ability to provide a safe space for exploring emotions and ideas. It serves as an outlet for thoughts and feelings , allowing you to express yourself in ways that might not be possible in everyday conversation.
Writing can be therapeutic, helping you process complex emotions, navigate difficult life events, and gain insight into your own experiences and perceptions. It can also be a means of self-discovery , helping you to understand yourself and the world around you better.
So, whether you’re a seasoned writer or just starting out, the benefits of creative writing are vast and varied. For those interested in developing their creative writing skills, check out our articles on creative writing prompts and how to teach creative writing . If you’re considering a career in this field, you might find our article on is a degree in creative writing worth it helpful.
4 Steps to Start Creative Writing
Creative writing can seem daunting to beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start their journey into this creative field. Here are some steps to help you start creative writing .
1. Finding Inspiration
The first step in creative writing is finding inspiration . Inspiration can come from anywhere and anything. Observe the world around you, listen to conversations, explore different cultures, and delve into various topics of interest.
Reading widely can also be a significant source of inspiration. Read different types of books, articles, and blogs. Discover what resonates with you and sparks your imagination.
For structured creative prompts, visit our list of creative writing prompts to get your creative juices flowing.
Editor’s Note : When something excites or interests you, stop and take note – it could be the inspiration for your next creative writing piece.
2. Planning Your Piece
Once you have an idea, the next step is to plan your piece . Start by outlining:
- the main points
Remember, this can serve as a roadmap to guide your writing process. A plan doesn’t have to be rigid. It’s a flexible guideline that can be adjusted as you delve deeper into your writing. The primary purpose is to provide direction and prevent writer’s block.
3. Writing Your First Draft
After planning your piece, you can start writing your first draft . This is where you give life to your ideas and breathe life into your characters.
Don’t worry about making it perfect in the first go. The first draft is about getting your ideas down on paper . You can always refine and polish your work later. And if you don’t have a great place to write that first draft, consider a journal for writing .
4. Editing and Revising Your Work
The final step in the creative writing process is editing and revising your work . This is where you fine-tune your piece, correct grammatical errors, and improve sentence structure and flow.
Editing is also an opportunity to enhance your storytelling . You can add more descriptive details, develop your characters further, and make sure your plot is engaging and coherent.
Remember, writing is a craft that improves with practice . Don’t be discouraged if your first few pieces don’t meet your expectations. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, enjoy the creative process.
For more insights on creative writing, check out our articles on how to teach creative writing or creative writing activities for kids.
Tips to Improve Creative Writing Skills
Understanding what is creative writing is the first step. But how can one improve their creative writing skills? Here are some tips that can help.
Read Widely
Reading is a vital part of becoming a better writer. By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques . Different authors have unique voices and methods of telling stories, which can serve as inspiration for your own work. So, read widely and frequently!
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creative writing improves with practice. Consistently writing — whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly — helps develop your writing style and voice . Using creative writing prompts can be a fun way to stimulate your imagination and get the words flowing.
Attend Writing Workshops and Courses
Formal education such as workshops and courses can offer structured learning and expert guidance. These can provide invaluable insights into the world of creative writing, from understanding plot development to character creation. If you’re wondering is a degree in creative writing worth it, these classes can also give you a taste of what studying creative writing at a higher level might look like .
Joining Writing Groups and Communities
Being part of a writing community can provide motivation, constructive feedback, and a sense of camaraderie. These groups often hold regular meetings where members share their work and give each other feedback. Plus, it’s a great way to connect with others who share your passion for writing.
Seeking Feedback on Your Work
Feedback is a crucial part of improving as a writer. It offers a fresh perspective on your work, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. Whether it’s from a writing group, a mentor, or even friends and family, constructive criticism can help refine your writing .
Start Creative Writing Today!
Remember, becoming a proficient writer takes time and patience. So, don’t be discouraged by initial challenges. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the process. Who knows, your passion for creative writing might even lead to creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Happy writing!
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
You may also like, a guide to gratitude and mindfulness journaling + 25 prompts.
Planner Review: Anecdote 2024 Planner
Can creativity be taught or are people born with it, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals

14 Types of Creative Writing
by Melissa Donovan | Apr 6, 2021 | Creative Writing | 20 comments

Which types of creative writing have you tried?
When we talk about creative writing, fiction and poetry often take the spotlight, but there are many other types of creative writing that we can explore.
Most writers develop a preference for one form (and genre) above all others. This can be a good thing, because you can specialize in your form and genre and become quite proficient. However, occasionally working with other types of writing is beneficial. It prevents your work from becoming stale and overladen with form- or genre-specific clichés, and it’s a good way to acquire a variety of techniques that are uncommon in your preferred form and genre but that can be used to enhance it.
Types of Creative Writing
Free writing: Open a notebook or an electronic document and just start writing. Allow strange words and images to find their way to the page. Anything goes! Also called stream-of-consciousness writing, free writing is the pinnacle of creative writing.
Journals: A journal is any written log. You could keep a gratitude journal, a memory journal, a dream journal, or a goals journal. Many writers keep idea journals or all-purpose omni-journals that can be used for everything from daily free writes to brainstorming and project planning.
Diaries: A diary is a type of journal in which you write about your daily life. Some diaries are written in letter format (“Dear Diary…”). If you ever want to write a memoir, then it’s a good idea to start keeping a diary.
Letters: Because the ability to communicate effectively is increasingly valuable, letter writing is a useful skill. There is a long tradition of publishing letters, so take extra care with those emails you’re shooting off to friends, family, and business associates. Hot tip: one way to get published if you don’t have a lot of clips and credits is to write letters to the editor of a news publication.
Memoir: A genre of creative nonfiction , memoirs are books that contain personal accounts (or stories) that focus on specific experiences. For example, one might write a travel memoir.
Essays. Essays are often associated with academic writing, but there are many types of essays, including personal essays, descriptive essays, and persuasive essays, all of which can be quite creative (and not especially academic).
Journalism: Some forms of journalism are more creative than others. Traditionally, journalism was objective reporting on facts, people, and events. Today, journalists often infuse their writing with opinion and storytelling to make their pieces more compelling or convincing.
Poetry: Poetry is a popular but under-appreciated type of writing, and it’s easily the most artistic form of writing. You can write form poetry, free-form poetry, and prose poetry.
Song Lyrics: Song lyrics combine the craft of writing with the artistry of music. Composing lyrics is similar to writing poetry, and this is an ideal type of writing for anyone who can play a musical instrument.
Scripts: Hit the screen or the stage by writing scripts for film, television, theater, or video games. Beware: film is a director’s medium, not a writer’s medium, but movies have the potential to reach a non-reading audience.
Storytelling: Storytelling is the most popular form of creative writing and is found in the realms of both fiction and nonfiction writing. Popular forms of fiction include flash fiction, short stories, novellas, and full-length novels; and there are tons of genres to choose from. True stories, which are usually firsthand or secondhand accounts of real people and events, can be found in essays, diaries, memoirs, speeches, and more. Storytelling is a tremendously valuable skill, as it can be found in all other forms of writing, from poetry to speech writing.
Speeches: Whether persuasive, inspirational, or informative, speech writing can lead to interesting career opportunities in almost any field or industry. Also, speech-writing skills will come in handy if you’re ever asked to write and deliver a speech at an important event, such as a graduation, wedding, or award ceremony.
Vignettes: A vignette is defined as “a brief evocative description, account, or episode.” Vignettes can be poems, stories, descriptions, personal accounts…anything goes really. The key is that a vignette is extremely short — just a quick snippet.
Honorable Mention: Blogs. A blog is not a type of writing; it’s a publishing platform — a piece of technology that displays web-based content on an electronic device. A blog can be used to publish any type of writing. Most blogs feature articles and essays, but you can also find blogs that contain diaries or journals, poetry, fiction, journalism, and more.
Which of these types of creative writing have you tried? Are there any forms of writing on this list that you’d like to experiment with? Can you think of any other types of creative writing to add to this list? Share your thoughts by leaving a comment, and keep writing.

20 Comments
What is “flash” writing or stories.
Flash fiction refers to super short stories, a few hundred words or fewer.
its very helpful especially to those students like me who wasn’t capable or good in doing a creative writing
I’m glad you found this post helpful, Elena.
I also found this to be very helpful, especially because I don’t do very well at writing.
Thanks for letting me know you found this helpful. Like anything else, writing improves with practice.
Thank you Melissa. It’s very helpful!
You’re welcome!
Over all good list. Yes blogs can be publishing platforms but only if something is written first. I read what you wrote on a blog.
Thanks a lot Good job
Are these types of creaitve writing the same or different if I need to teach children’s creative writing? Can you recommend a website to teach these?
Hi Marie. Thanks for your question. I’ve come across many websites for teaching children’s creative writing. I recommend a search on Google, which will lead you to a ton of resources.
these are very helpful when it comes to getting in college or essays or just to improve my writing
Thanks, Donte. I’m glad you found this helpful.
Free writing really helps me get going. For some reason my prose are much better when I am not beholden to an overall plot or narrative with specific defined characters. I like to free writer “excerpts” on theprose.com. It allows me to practice writing and receive feedback at the same time. I am also trying to blog about writing my first novel, both for writing practice and to keep myself accountable. It really helps!
I feel the same way. Free writing is always a fun and creative experience for me.
Was trying to give an inservice on writing skills and the different types of writing.
Your wok here really helped. Thanks.
You’re welcome.
Hi, Melissa can you assist me ? I’m trying to improve my writing skills as quickly as possible. Plz send me some more tips and trick to improve my writing and communication skills.
You are welcome to peruse this website, which is packed with tips for improving your writing. I’d recommend focusing on the categories Better Writing and Writing Tips for writing improvement. You can also subscribe to get new articles send directly to your email. Thanks!
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- 23 Calming Hobbies to Restore Your Energy | NunziaDreams - […] You can do a lot with creative writing. […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- Poetry Prompts for Language Lovers
- Fiction Writing Exercise: The Internal and External Struggles of Your Characters
- 12 Character Writing Tips for Fiction Writers
- What is Free-Verse Poetry?
- Grammar Rules: Lay or Lie
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest
VIDEO COURSE
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Sign up now to watch a free lesson!
Learn How to Write a Novel
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Enroll now for daily lessons, weekly critique, and live events. Your first lesson is free!

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Feb 14, 2023
10 Types of Creative Writing (with Examples You’ll Love)
A lot falls under the term ‘creative writing’: poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is , it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at examples that demonstrate the sheer range of styles and genres under its vast umbrella.
To that end, we’ve collected a non-exhaustive list of works across multiple formats that have inspired the writers here at Reedsy. With 20 different works to explore, we hope they will inspire you, too.
People have been writing creatively for almost as long as we have been able to hold pens. Just think of long-form epic poems like The Odyssey or, later, the Cantar de Mio Cid — some of the earliest recorded writings of their kind.
Poetry is also a great place to start if you want to dip your own pen into the inkwell of creative writing. It can be as short or long as you want (you don’t have to write an epic of Homeric proportions), encourages you to build your observation skills, and often speaks from a single point of view .
Here are a few examples:
“Ozymandias” by Percy Bysshe Shelley
Nothing beside remains. Round the decay Of that colossal Wreck, boundless and bare The lone and level sands stretch far away.

This classic poem by Romantic poet Percy Shelley (also known as Mary Shelley’s husband) is all about legacy. What do we leave behind? How will we be remembered? The great king Ozymandias built himself a massive statue, proclaiming his might, but the irony is that his statue doesn’t survive the ravages of time. By framing this poem as told to him by a “traveller from an antique land,” Shelley effectively turns this into a story. Along with the careful use of juxtaposition to create irony, this poem accomplishes a lot in just a few lines.
“Trying to Raise the Dead” by Dorianne Laux
A direction. An object. My love, it needs a place to rest. Say anything. I’m listening. I’m ready to believe. Even lies, I don’t care.
Poetry is cherished for its ability to evoke strong emotions from the reader using very few words which is exactly what Dorianne Laux does in “ Trying to Raise the Dead .” With vivid imagery that underscores the painful yearning of the narrator, she transports us to a private nighttime scene as the narrator sneaks away from a party to pray to someone they’ve lost. We ache for their loss and how badly they want their lost loved one to acknowledge them in some way. It’s truly a masterclass on how writing can be used to portray emotions.
If you find yourself inspired to try out some poetry — and maybe even get it published — check out these poetry layouts that can elevate your verse!
Song Lyrics
Poetry’s closely related cousin, song lyrics are another great way to flex your creative writing muscles. You not only have to find the perfect rhyme scheme but also match it to the rhythm of the music. This can be a great challenge for an experienced poet or the musically inclined.
To see how music can add something extra to your poetry, check out these two examples:
“Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
You say I took the name in vain I don't even know the name But if I did, well, really, what's it to ya? There's a blaze of light in every word It doesn't matter which you heard The holy or the broken Hallelujah
Metaphors are commonplace in almost every kind of creative writing, but will often take center stage in shorter works like poetry and songs. At the slightest mention, they invite the listener to bring their emotional or cultural experience to the piece, allowing the writer to express more with fewer words while also giving it a deeper meaning. If a whole song is couched in metaphor, you might even be able to find multiple meanings to it, like in Leonard Cohen’s “ Hallelujah .” While Cohen’s Biblical references create a song that, on the surface, seems like it’s about a struggle with religion, the ambiguity of the lyrics has allowed it to be seen as a song about a complicated romantic relationship.
“I Will Follow You into the Dark” by Death Cab for Cutie
If Heaven and Hell decide that they both are satisfied Illuminate the no's on their vacancy signs If there's no one beside you when your soul embarks Then I'll follow you into the dark

You can think of song lyrics as poetry set to music. They manage to do many of the same things their literary counterparts do — including tugging on your heartstrings. Death Cab for Cutie’s incredibly popular indie rock ballad is about the singer’s deep devotion to his lover. While some might find the song a bit too dark and macabre, its melancholy tune and poignant lyrics remind us that love can endure beyond death.
Plays and Screenplays
From the short form of poetry, we move into the world of drama — also known as the play. This form is as old as the poem, stretching back to the works of ancient Greek playwrights like Sophocles, who adapted the myths of their day into dramatic form. The stage play (and the more modern screenplay) gives the words on the page a literal human voice, bringing life to a story and its characters entirely through dialogue.
Interested to see what that looks like? Take a look at these examples:
All My Sons by Arthur Miller
“I know you're no worse than most men but I thought you were better. I never saw you as a man. I saw you as my father.”
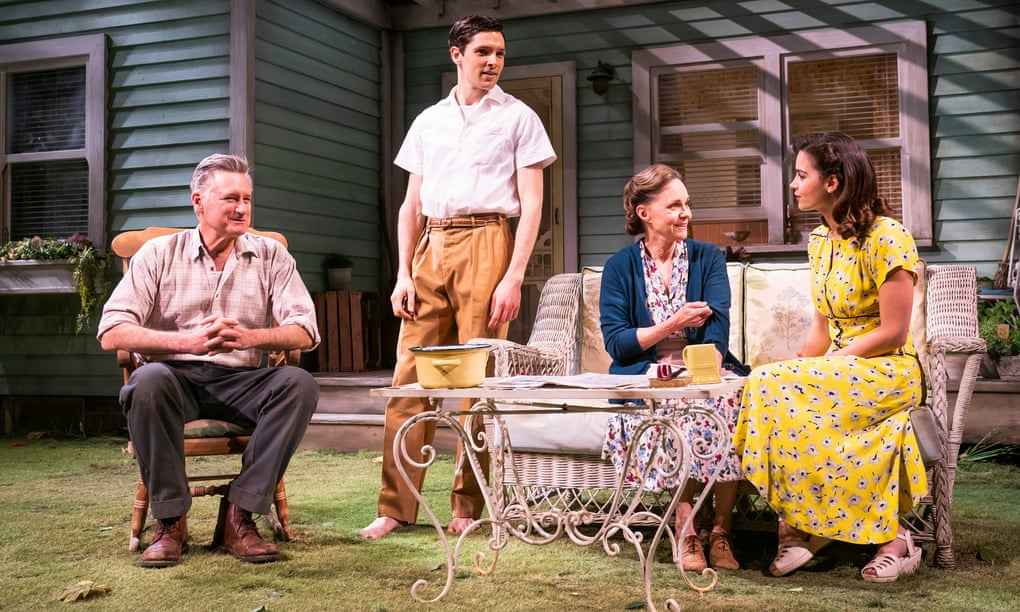

Arthur Miller acts as a bridge between the classic and the new, creating 20th century tragedies that take place in living rooms and backyard instead of royal courts, so we had to include his breakout hit on this list. Set in the backyard of an all-American family in the summer of 1946, this tragedy manages to communicate family tensions in an unimaginable scale, building up to an intense climax reminiscent of classical drama.
💡 Read more about Arthur Miller and classical influences in our breakdown of Freytag’s pyramid .
“Everything is Fine” by Michael Schur ( The Good Place )
“Well, then this system sucks. What...one in a million gets to live in paradise and everyone else is tortured for eternity? Come on! I mean, I wasn't freaking Gandhi, but I was okay. I was a medium person. I should get to spend eternity in a medium place! Like Cincinnati. Everyone who wasn't perfect but wasn't terrible should get to spend eternity in Cincinnati.”
A screenplay, especially a TV pilot, is like a mini-play, but with the extra job of convincing an audience that they want to watch a hundred more episodes of the show. Blending moral philosophy with comedy, The Good Place is a fun hang-out show set in the afterlife that asks some big questions about what it means to be good.
It follows Eleanor Shellstrop, an incredibly imperfect woman from Arizona who wakes up in ‘The Good Place’ and realizes that there’s been a cosmic mixup. Determined not to lose her place in paradise, she recruits her “soulmate,” a former ethics professor, to teach her philosophy with the hope that she can learn to be a good person and keep up her charade of being an upstanding citizen. The pilot does a superb job of setting up the stakes, the story, and the characters, while smuggling in deep philosophical ideas.
Personal essays
Our first foray into nonfiction on this list is the personal essay. As its name suggests, these stories are in some way autobiographical — concerned with the author’s life and experiences. But don’t be fooled by the realistic component. These essays can take any shape or form, from comics to diary entries to recipes and anything else you can imagine. Typically zeroing in on a single issue, they allow you to explore your life and prove that the personal can be universal.
Here are a couple of fantastic examples:
“On Selling Your First Novel After 11 Years” by Min Jin Lee (Literary Hub)
There was so much to learn and practice, but I began to see the prose in verse and the verse in prose. Patterns surfaced in poems, stories, and plays. There was music in sentences and paragraphs. I could hear the silences in a sentence. All this schooling was like getting x-ray vision and animal-like hearing.

This deeply honest personal essay by Pachinko author Min Jin Lee is an account of her eleven-year struggle to publish her first novel . Like all good writing, it is intensely focused on personal emotional details. While grounded in the specifics of the author's personal journey, it embodies an experience that is absolutely universal: that of difficulty and adversity met by eventual success.
“A Cyclist on the English Landscape” by Roff Smith (New York Times)
These images, though, aren’t meant to be about me. They’re meant to represent a cyclist on the landscape, anybody — you, perhaps.
Roff Smith’s gorgeous photo essay for the NYT is a testament to the power of creatively combining visuals with text. Here, photographs of Smith atop a bike are far from simply ornamental. They’re integral to the ruminative mood of the essay, as essential as the writing. Though Smith places his work at the crosscurrents of various aesthetic influences (such as the painter Edward Hopper), what stands out the most in this taciturn, thoughtful piece of writing is his use of the second person to address the reader directly. Suddenly, the writer steps out of the body of the essay and makes eye contact with the reader. The reader is now part of the story as a second character, finally entering the picture.
Short Fiction
The short story is the happy medium of fiction writing. These bite-sized narratives can be devoured in a single sitting and still leave you reeling. Sometimes viewed as a stepping stone to novel writing, that couldn’t be further from the truth. Short story writing is an art all its own. The limited length means every word counts and there’s no better way to see that than with these two examples:
“An MFA Story” by Paul Dalla Rosa (Electric Literature)
At Starbucks, I remembered a reading Zhen had given, a reading organized by the program’s faculty. I had not wanted to go but did. In the bar, he read, "I wrote this in a Starbucks in Shanghai. On the bank of the Huangpu." It wasn’t an aside or introduction. It was two lines of the poem. I was in a Starbucks and I wasn’t writing any poems. I wasn’t writing anything.

This short story is a delightfully metafictional tale about the struggles of being a writer in New York. From paying the bills to facing criticism in a writing workshop and envying more productive writers, Paul Dalla Rosa’s story is a clever satire of the tribulations involved in the writing profession, and all the contradictions embodied by systemic creativity (as famously laid out in Mark McGurl’s The Program Era ). What’s more, this story is an excellent example of something that often happens in creative writing: a writer casting light on the private thoughts or moments of doubt we don’t admit to or openly talk about.
“Flowering Walrus” by Scott Skinner (Reedsy)
I tell him they’d been there a month at least, and he looks concerned. He has my tongue on a tissue paper and is gripping its sides with his pointer and thumb. My tongue has never spent much time outside of my mouth, and I imagine it as a walrus basking in the rays of the dental light. My walrus is not well.
A winner of Reedsy’s weekly Prompts writing contest, ‘ Flowering Walrus ’ is a story that balances the trivial and the serious well. In the pauses between its excellent, natural dialogue , the story manages to scatter the fear and sadness of bad medical news, as the protagonist hides his worries from his wife and daughter. Rich in subtext, these silences grow and resonate with the readers.
Want to give short story writing a go? Give our free course a go!

FREE COURSE
How to Craft a Killer Short Story
From pacing to character development, master the elements of short fiction.
Perhaps the thing that first comes to mind when talking about creative writing, novels are a form of fiction that many people know and love but writers sometimes find intimidating. The good news is that novels are nothing but one word put after another, like any other piece of writing, but expanded and put into a flowing narrative. Piece of cake, right?
To get an idea of the format’s breadth of scope, take a look at these two (very different) satirical novels:
Convenience Store Woman by Sayaka Murata
I wished I was back in the convenience store where I was valued as a working member of staff and things weren’t as complicated as this. Once we donned our uniforms, we were all equals regardless of gender, age, or nationality — all simply store workers.

Keiko, a thirty-six-year-old convenience store employee, finds comfort and happiness in the strict, uneventful routine of the shop’s daily operations. A funny, satirical, but simultaneously unnerving examination of the social structures we take for granted, Sayaka Murata’s Convenience Store Woman is deeply original and lingers with the reader long after they’ve put it down.
Erasure by Percival Everett
The hard, gritty truth of the matter is that I hardly ever think about race. Those times when I did think about it a lot I did so because of my guilt for not thinking about it.
Erasure is a truly accomplished satire of the publishing industry’s tendency to essentialize African American authors and their writing. Everett’s protagonist is a writer whose work doesn’t fit with what publishers expect from him — work that describes the “African American experience” — so he writes a parody novel about life in the ghetto. The publishers go crazy for it and, to the protagonist’s horror, it becomes the next big thing. This sophisticated novel is both ironic and tender, leaving its readers with much food for thought.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction is pretty broad: it applies to anything that does not claim to be fictional (although the rise of autofiction has definitely blurred the boundaries between fiction and nonfiction). It encompasses everything from personal essays and memoirs to humor writing, and they range in length from blog posts to full-length books. The defining characteristic of this massive genre is that it takes the world or the author’s experience and turns it into a narrative that a reader can follow along with.
Here, we want to focus on novel-length works that dig deep into their respective topics. While very different, these two examples truly show the breadth and depth of possibility of creative nonfiction:
Men We Reaped by Jesmyn Ward
Men’s bodies litter my family history. The pain of the women they left behind pulls them from the beyond, makes them appear as ghosts. In death, they transcend the circumstances of this place that I love and hate all at once and become supernatural.
Writer Jesmyn Ward recounts the deaths of five men from her rural Mississippi community in as many years. In her award-winning memoir , she delves into the lives of the friends and family she lost and tries to find some sense among the tragedy. Working backwards across five years, she questions why this had to happen over and over again, and slowly unveils the long history of racism and poverty that rules rural Black communities. Moving and emotionally raw, Men We Reaped is an indictment of a cruel system and the story of a woman's grief and rage as she tries to navigate it.
Cork Dork by Bianca Bosker
He believed that wine could reshape someone’s life. That’s why he preferred buying bottles to splurging on sweaters. Sweaters were things. Bottles of wine, said Morgan, “are ways that my humanity will be changed.”
In this work of immersive journalism , Bianca Bosker leaves behind her life as a tech journalist to explore the world of wine. Becoming a “cork dork” takes her everywhere from New York’s most refined restaurants to science labs while she learns what it takes to be a sommelier and a true wine obsessive. This funny and entertaining trip through the past and present of wine-making and tasting is sure to leave you better informed and wishing you, too, could leave your life behind for one devoted to wine.
Illustrated Narratives (Comics, graphic novels)
Once relegated to the “funny pages”, the past forty years of comics history have proven it to be a serious medium. Comics have transformed from the early days of Jack Kirby’s superheroes into a medium where almost every genre is represented. Humorous one-shots in the Sunday papers stand alongside illustrated memoirs, horror, fantasy, and just about anything else you can imagine. This type of visual storytelling lets the writer and artist get creative with perspective, tone, and so much more. For two very different, though equally entertaining, examples, check these out:
Calvin & Hobbes by Bill Watterson
"Life is like topography, Hobbes. There are summits of happiness and success, flat stretches of boring routine and valleys of frustration and failure."
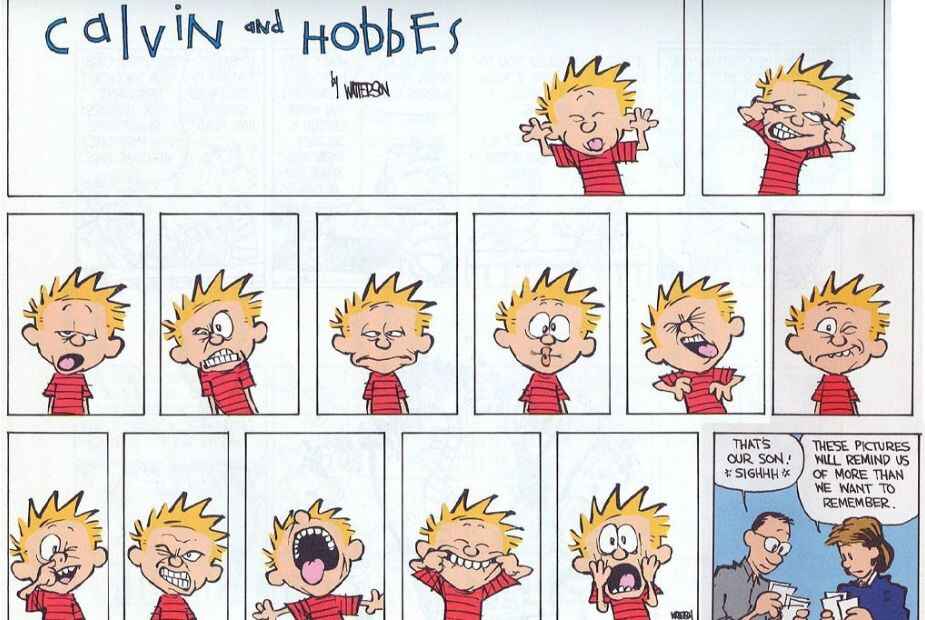

This beloved comic strip follows Calvin, a rambunctious six-year-old boy, and his stuffed tiger/imaginary friend, Hobbes. They get into all kinds of hijinks at school and at home, and muse on the world in the way only a six-year-old and an anthropomorphic tiger can. As laugh-out-loud funny as it is, Calvin & Hobbes ’ popularity persists as much for its whimsy as its use of humor to comment on life, childhood, adulthood, and everything in between.
From Hell by Alan Moore and Eddie Campbell
"I shall tell you where we are. We're in the most extreme and utter region of the human mind. A dim, subconscious underworld. A radiant abyss where men meet themselves. Hell, Netley. We're in Hell."
Comics aren't just the realm of superheroes and one-joke strips, as Alan Moore proves in this serialized graphic novel released between 1989 and 1998. A meticulously researched alternative history of Victorian London’s Ripper killings, this macabre story pulls no punches. Fact and fiction blend into a world where the Royal Family is involved in a dark conspiracy and Freemasons lurk on the sidelines. It’s a surreal mad-cap adventure that’s unsettling in the best way possible.
Video Games and RPGs
Probably the least expected entry on this list, we thought that video games and RPGs also deserved a mention — and some well-earned recognition for the intricate storytelling that goes into creating them.
Essentially gamified adventure stories, without attention to plot, characters, and a narrative arc, these games would lose a lot of their charm, so let’s look at two examples where the creative writing really shines through:
80 Days by inkle studios
"It was a triumph of invention over nature, and will almost certainly disappear into the dust once more in the next fifty years."

Named Time Magazine ’s game of the year in 2014, this narrative adventure is based on Around the World in 80 Days by Jules Verne. The player is cast as the novel’s narrator, Passpartout, and tasked with circumnavigating the globe in service of their employer, Phileas Fogg. Set in an alternate steampunk Victorian era, the game uses its globe-trotting to comment on the colonialist fantasies inherent in the original novel and its time period. On a storytelling level, the choose-your-own-adventure style means no two players’ journeys will be the same. This innovative approach to a classic novel shows the potential of video games as a storytelling medium, truly making the player part of the story.
What Remains of Edith Finch by Giant Sparrow
"If we lived forever, maybe we'd have time to understand things. But as it is, I think the best we can do is try to open our eyes, and appreciate how strange and brief all of this is."
This video game casts the player as 17-year-old Edith Finch. Returning to her family’s home on an island in the Pacific northwest, Edith explores the vast house and tries to figure out why she’s the only one of her family left alive. The story of each family member is revealed as you make your way through the house, slowly unpacking the tragic fate of the Finches. Eerie and immersive, this first-person exploration game uses the medium to tell a series of truly unique tales.
Fun and breezy on the surface, humor is often recognized as one of the trickiest forms of creative writing. After all, while you can see the artistic value in a piece of prose that you don’t necessarily enjoy, if a joke isn’t funny, you could say that it’s objectively failed.
With that said, it’s far from an impossible task, and many have succeeded in bringing smiles to their readers’ faces through their writing. Here are two examples:
‘How You Hope Your Extended Family Will React When You Explain Your Job to Them’ by Mike Lacher (McSweeney’s Internet Tendency)
“Is it true you don’t have desks?” your grandmother will ask. You will nod again and crack open a can of Country Time Lemonade. “My stars,” she will say, “it must be so wonderful to not have a traditional office and instead share a bistro-esque coworking space.”

Satire and parody make up a whole subgenre of creative writing, and websites like McSweeney’s Internet Tendency and The Onion consistently hit the mark with their parodies of magazine publishing and news media. This particular example finds humor in the divide between traditional family expectations and contemporary, ‘trendy’ work cultures. Playing on the inherent silliness of today’s tech-forward middle-class jobs, this witty piece imagines a scenario where the writer’s family fully understands what they do — and are enthralled to hear more. “‘Now is it true,’ your uncle will whisper, ‘that you’ve got a potential investment from one of the founders of I Can Haz Cheezburger?’”
‘Not a Foodie’ by Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell (Electric Literature)
I’m not a foodie, I never have been, and I know, in my heart, I never will be.
Highlighting what she sees as an unbearable social obsession with food , in this comic Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell takes a hilarious stand against the importance of food. From the writer’s courageous thesis (“I think there are more exciting things to talk about, and focus on in life, than what’s for dinner”) to the amusing appearance of family members and the narrator’s partner, ‘Not a Foodie’ demonstrates that even a seemingly mundane pet peeve can be approached creatively — and even reveal something profound about life.
We hope this list inspires you with your own writing. If there’s one thing you take away from this post, let it be that there is no limit to what you can write about or how you can write about it.
In the next part of this guide, we'll drill down into the fascinating world of creative nonfiction.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
Types of Creative Writing: A Detailed Explanantion
Read the blog and discover different Types of Creative Writing offering insights and examples to help you navigate the world of literary creativity. Explore various forms such as poetry, fiction, non-fiction, and scriptwriting. Discover how each style offers unique ways to express creativity, tell stories, and engage audiences.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Report Writing Course
- Communication and Influencing skill Training
- Effective Communication Skills
- Speed Writing Course
- E-mail Etiquette Training

Creative Writing is a diverse and exciting art that demands Writers to look into their imagination and express their thoughts in unique ways. From short stories to poetry, different Types of Creative Writing which cater to different styles and preferences. In this blog, we will delve into the different Types of Creative Writing, offering insights and examples to help you navigate the world of literary creativity.
Table of Contents
1) What are the various Types of Creative Writing?
a) Fiction writing
b) Poetry
c) Song lyrics
d) Journals and diaries
e) Drama and playwriting
f) Screenwriting
g) Experimental writing
h) Novels
2) Techniques used in Creative Writing
3) Conclusion
What are the various Types of Creative Writing?
Let’s discuss the various Types of Creative Writing:

Fiction writing
Fiction writing is one of the captivating Types of Creative Writing that transports readers into imaginary worlds, introduces them to memorable characters, and explores numerous emotions and themes. Within fiction, there are several distinct forms that Writers can explore to weave intricate tales. These forms include:
Fiction writing is a captivating part of Creative Writing that transports readers into imaginary worlds, introduces them to memorable characters, and explores an array of emotions and themes. Within fiction, there are several distinct forms that Writers can explore to weave intricate tales:
a) Short stories:
Short stories are concise yet potent narratives that distil the essence of a single plot, theme, or character arc. Writers craft short stories to deliver a powerful impact within a limited word count. The brevity of the format challenges Authors to make every word count, focusing on evoking emotions, building tension, and delivering a satisfying resolution in a short span of time.
Novels offer the canvas for Writers to embark on extended journeys of storytelling. With ample space to develop complex characters, intricate plotlines, and detailed settings, novels invite readers to immerse themselves in the fictional world fully. Writers can explore a myriad of themes, emotions, and conflicts, delving deep into the psyche of their characters and creating a lasting impact on the reader.
c) Flash fiction:
Flash fiction is the art of storytelling distilled into its most concise form. Writers embrace the challenge of telling a complete story within just a few hundred words. This form demands precision and creativity, forcing Writers to capture the essence of a narrative in a condensed space.
d) Fan fiction:
Fan fiction is a fascinating genre that allows Writers to extend and reimagine existing fictional universes. Writers create new stories, scenarios, and adventures featuring beloved characters from books, movies, TV shows, or video games. By building upon established foundations, Writers engage in a creative dialogue with the original creators and fellow fans.
d) Historical fiction:

Poetry
Poetry is the language of emotions, a lyrical form of expression that transcends conventional prose. It's one of the most interesting and beautiful Types of Creative Writing that condenses thoughts, feelings, and imagery into evocative verses.
It invites readers to experience the world through a different lens. Within the realm of poetry, various forms and styles allow poets to experiment with rhythm, sound, and language, resulting in a rich tapestry of literary artistry that involves the following:
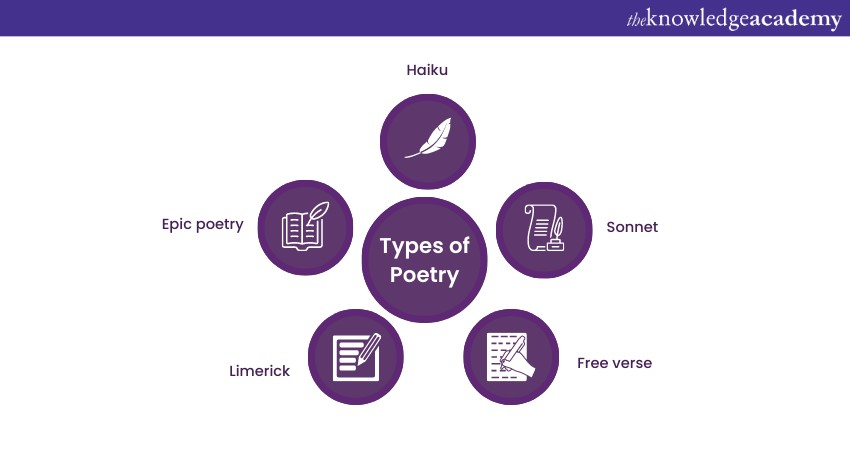
Haiku, originating from Japan, is a minimalist form of poetry that captures the essence of a moment in just three lines. With a syllable structure of 5-7-5, haikus distil nature's beauty and human experiences into concise verses. They often focus on capturing fleeting moments, seasons, and emotions, inviting readers to pause and reflect on the subtleties of life.
The sonnet is a structured and elegant poetic form dating back to the Renaissance. Typically composed of 14 lines, sonnets follow specific rhyme schemes, such as the Shakespearean (ABABCDCDEFEFGG) or the Petrarchan (ABBAABBACDCDCD). Sonnets explore themes of love, beauty, mortality, and the complexities of human emotion.
c) Free verse:
Free verse poetry breaks away from traditional rhyme and meter patterns, allowing poets to experiment with line breaks, rhythm, and imagery. This form gives poets the freedom to let their thoughts flow naturally, creating unique and organic rhythms that reflect the pace of modern life.
d) Limerick:
Limericks are playful and humorous five-line poems with a distinct AABBA rhyme scheme. These witty verses often feature light-hearted language and unexpected twists, making them a favourite for conveying amusing anecdotes and quirky observations.
e) Epic poetry:
Epic poems tell grand narratives of heroes, gods, and legendary quests. With their lengthy verses and intricate storytelling, epic poems like Homer's "The Iliad" and "The Odyssey" have shaped cultures and inspired countless works of literature. These narratives delve into themes of heroism, fate, and the human condition, offering readers an immersive journey through time and imagination.
Unlock your potential in report writing with our Report Writing Training – sign up now for enhanced personal and professional development!
Song lyrics
If you like writing poetry or you think that it can be your forte as a Creative Writer, then you can also try your hand at writing song lyrics. Song lyrics are another one of the most popular Types of Creative Writing.
Practising writing song lyrics is one of the best ways to bring out your creativity, especially if you have a knack for music. Although it sounds interesting and fun, matching the lines in a song lyric can be a challenging task.
You need to think about maintaining not only the intent of the song but also the kind of audience you’ll be approaching. Your song lyrics need to be tangible and understandable, and most importantly, they need to carry out a story and song at the same time.
If you don’t have any proper knowledge of music, then you can try getting help from your friends or peers who have a good knowledge of music and see if your lyrics are going well with the music.
Journals and diaries
Practicing journaling is a good way of regulating someone’s emotions and understand their feelings. If you are unsure what Type of Creative Writing you want to pursue, you can simply start by jotting down the events of your day.
Understanding what you go through every day, not only helps you in your personal development, but also help you to become a good Creative Writer. You can even publish your works as we have seen so many famous people publishing their diary entries. If you want to know where to start, there are several journal entries by famous people, whose works can inspire you to start Writing.
Keeping a journal or diary, is crucial for your mental health, as it helps you to express your feelings in a constructive manner. This also gives you another boost to your writing skills, if you are a budding Writer
Drama and playwriting
Drama and playwriting are artistic forms of Creative Writing that bring narratives to life through the dynamics of performance. These forms of creative expression explore the intricacies of human interaction, emotion, and conflict within the context of staged productions. Let's delve into the world of drama and playwriting, where characters come alive on the stage:
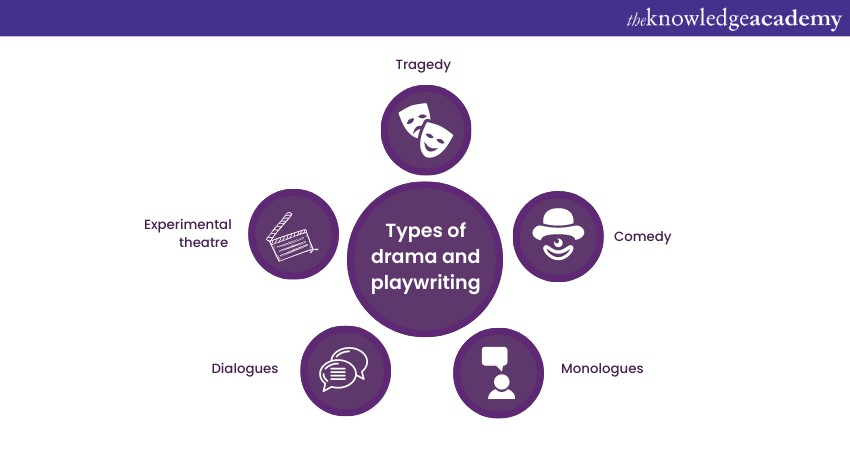
a) Tragedy:
Tragedy is a dramatic genre that delves into the darker aspects of human nature and the inevitability of suffering. Tragic plays often revolve around protagonists who face moral dilemmas, internal struggles, and external forces that ultimately lead to their downfall. Tragedies offer audiences a cathartic experience, allowing them to confront and process complex emotions while reflecting on the human condition.
Comedy is the art of entertainment through humour and light-heartedness. Comedic plays explore the absurdities of human behaviour, social conventions, and misunderstandings. These works aim to amuse and uplift audiences, often featuring witty dialogue, situational comedy, and humorous characters. From slapstick to sattire, comedies provide a diverse range of comedic experiences.
c) Monologues:
Monologues are powerful soliloquies delivered by a single character on stage. They offer insight into the character's thoughts, emotions, and motivations, allowing the audience to connect deeply with their inner world. Monologues provide actors with opportunities to showcase their talent and capture the essence of a character's complexity.
d) Dialogues:
Dialogues are the heart of dramatic interaction. They reveal the relationships between characters, advance the plot, and convey emotions and conflicts. Well-crafted dialogues create tension, build connections, and propel the narrative forward, immersing the audience in the unfolding drama.
e) Experimental theatre:
Experimental theatre pushes the boundaries of traditional forms and conventions. This genre encourages innovative approaches to staging, narrative structure, and performance. Playwrights and directors experiment with non-linear narratives, multimedia elements, immersive environments, and audience interaction to challenge perceptions and evoke thought-provoking responses.
Screenwriting
Screenwriting is the art of crafting stories specifically for the visual medium of film or television. It's a dynamic and collaborative form of writing that serves as the foundation for the creation of compelling on-screen narratives. Here are some key elements of screenwriting:
a) Writing for film:
Film screenwriting involves creating scripts that serve as blueprints for movies. ScreenWriters translate their ideas into a structured format that includes scenes, dialogues, actions, and descriptions. They must balance engaging storytelling with the technical aspects of filmmaking, considering camera angles, pacing, and visual cues.
b) Television scripts:
Television scripts are tailored to episodic formats, such as TV series or miniseries. Writers develop characters, story arcs, and dialogue that span multiple episodes, allowing for character development and plot progression over time. Each episode contributes to the overarching narrative while maintaining its own distinct identity.
c) Adaptation:
Adaptation involves transforming existing source material, such as books, plays, or real-life events, into screenplay format. Writers must distil the essence of the original work while making necessary changes to suit the visual medium and the constraints of time.
d) Dialogue and action:
Effective screenwriting places a strong emphasis on dialogue and action. Dialogue conveys characters' personalities, motivations, and conflicts, while action descriptions provide visual cues for directors, actors, and crew. Both elements work together to create a seamless and engaging on-screen experience.
Unlock your storytelling potential with our Creative Writing Training – embark on a journey of literary discovery today!
Experimental writing
Experimental writing defies traditional conventions, pushing the boundaries of language and structure to create innovative literary works. It challenges readers to engage with unconventional formats, fragmented narratives, and abstract concepts.
Through a stream of consciousness, collage writing, and visual poetry, experimental writing offers a fresh perspective, inviting readers to explore new realms of thought and emotion. It's a playground of creative freedom where Writers experiment with words as artists do with colours, producing compositions that evoke intrigue, reflection, and a deeper understanding of the limitless possibilities of language.
It is often said that good Writers are voracious readers. Well, if we take that into consideration, then there have many times where you might have loved reading novels. All the novels that you have read, or you know of, are one of the premium examples of Creative Writing.
They may vary in length, depending on the subject or genre that you choose to write on. If you are writing a long form novel, then they are divided into number of chapters. If you have a big idea waiting to be broken down into many chapters, then novels are for you.
Techniques used in Creative Writing
If you are wondering how to begin Creative Writing, you can start by following these techniques:
1) Narrative
Determining the narrative of your story is extremely important. If you control the narrative in your story, you can hold your audience’s attention for a long time, whether you are writing novels, novellas, or even short stories. In general, you should remember that whether you are doing Creative Writing or Non-fiction Writing, deciding on a narrative and then maintaining that throughout is crucial.
2) Characterisation
Characterisation is vital in building your story. If you don’t provide the details of your characters and describe their physical features, background, past, etc., you cannot help your reader imagine the situation. It is a crucial step in Creative Writing, enabling you to drive the plot forward and allow your story to build more layers.
Before you build your story, you need to have a solid plot to make your story upon. It is a blueprint to help you establish your story's theme agenda. It can also be referred to as a series of events that will help you build up the narrative. The plot has five parts: exposition or introduction, complications or rising action, climax, slow revelations and then the conclusion. The more solid your plot will be, the more you can create beautiful stories.
From the whimsical realms of children's literature to the thought-provoking depths of creative non-fiction, this blog about the different Types of Creative Writing has unveiled a world of literary possibilities. As pens meet paper and imaginations take flight, we hope this blog will guide you on your journey to weave tales that leave an indelible mark on hearts and minds.
Unlock your potential with our Personal Development Training and embark on a journey of self-discovery and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Incorporating Creative Writing skills will help you in your professional growth. Creative Writing helps in effective communication, improved problem-solving abilities, increased empathy, improved mental health, and enhanced creativity.
The factors which influence the organisational structure in various types of Creative Writing are genre, style, narrative, expectations from the audience, length, point of view, cultural and historical context, character development, and more.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development courses , including Organisational skills training, Emotional Intelligence Training, and Report Writing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Journalism .
Our Business Skills blogs covers a range of topics related to Sports Journalism, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Creative Writing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 30th Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
What are the Genres of Creative Writing?

The Black Bear Review boasts about accepting work in all four literary genres, but what does that mean? In simplest terms, genres are used to organize, categorize, and classify literature. The four primary genres of creative writing are fiction, creative non-fiction, poetry, and drama.
Fiction: The fiction genre includes all works conceived primarily out of the writer’s imagination. Although fiction may include some elements of reality (names of real-life towns or natural phenomena), it relies on make-believe events to drive plots that often parallel, rather than recite, real-life circumstances. Some examples of fiction form are the novel, short story, or novella.
Creative Non-Fiction: Writers of creative non-fiction develop stories based on true to life events but often infuse their own personal views and experiences in their work. Creative non-fiction pieces go beyond fact to appeal to readers through story, experience, and imagery. Some examples of creative non-fiction forms are personal essays, book reviews, memoirs, interviews, and cultural criticisms.
Poetry: Poetry includes writing meant to be heard out loud as well as read on the page. Although poetry can take many forms, its foundation is built on a balance of rhythm, imagery, metaphor, and other techniques used to communicate abstract ideas to readers. Poems may be structured (haikus, and sonnets), unstructured (free verse), or even appear to read as a narrative (prose poems).
Drama: The genre of drama can include both the fictitious and the fact. In a drama, the story is primarily conveyed through dialogue between characters. It may reference sound and movement, but much is left to reader’s imaginations. Drama includes movie scripts, ten-minute plays, screenplays, and written stage productions.
* Much of the information in this article has been taken from “Imaginative Writing: The Elements of Craft” by Janet Burroway and “Write Moves” by Nancy Pagh. We recommend looking into these books for yourself. They’re excellent resources to add to any writer’s toolbox!

Copyright © 2020 Black Bear Review

Elements of Creative Writing
J.D. Schraffenberger, University of Northern Iowa
Rachel Morgan, University of Northern Iowa
Grant Tracey, University of Northern Iowa
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780915996179
Publisher: University of Northern Iowa
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Robert Moreira, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 3/21/24
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, content is accurate, error free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book is relevant and up-to-date.
Clarity rating: 5
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I would agree that the text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
Text is modular, yes, but I would like to see the addition of a section on dramatic writing.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Topics are presented in logical, clear fashion.
Interface rating: 5
Navigation is good.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical issues that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I'd like to see more diverse creative writing examples.
As I stated above, textbook is good except that it does not include a section on dramatic writing.

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter One: One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- Chapter Two: Plotting
- Chapter Three: Counterpointed Plotting
- Chapter Four: Show and Tell
- Chapter Five: Characterization and Method Writing
- Chapter Six: Character and Dialouge
- Chapter Seven: Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- Chapter Eight: Point of View
- Chapter Nine: Learning the Unwritten Rules
- Chapter One: A Poetry State of Mind
- Chapter Two: The Architecture of a Poem
- Chapter Three: Sound
- Chapter Four: Inspiration and Risk
- Chapter Five: Endings and Beginnings
- Chapter Six: Figurative Language
- Chapter Seven: Forms, Forms, Forms
- Chapter Eight: Go to the Image
- Chapter Nine: The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
Creative Nonfiction
- Chapter One: Creative Nonfiction and the Essay
- Chapter Two: Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- Chapter Three: Research and History
- Chapter Four: Writing Environments
- Chapter Five: Notes on Style
- Chapter Seven: Imagery and the Senses
- Chapter Eight: Writing the Body
- Chapter Nine: Forms
Back Matter
- Contributors
- North American Review Staff
Ancillary Material
- University of Northern Iowa
About the Book
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They’ve selected nearly all of the readings and examples (more than 60) from writing that has appeared in NAR pages over the years. Because they had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, their perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, they hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of the magazine as they analyze and discuss some reasons this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable. This project was supported by NAR staff and funded via the UNI Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
About the Contributors
J.D. Schraffenberger is a professor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. He is the author of two books of poems, Saint Joe's Passion and The Waxen Poor , and co-author with Martín Espada and Lauren Schmidt of The Necessary Poetics of Atheism . His other work has appeared in Best of Brevity , Best Creative Nonfiction , Notre Dame Review , Poetry East , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Rachel Morgan is an instructor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. She is the author of the chapbook Honey & Blood , Blood & Honey . Her work is included in the anthology Fracture: Essays, Poems, and Stories on Fracking in American and has appeared in the Journal of American Medical Association , Boulevard , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Grant Tracey author of three novels in the Hayden Fuller Mysteries ; the chapbook Winsome featuring cab driver Eddie Sands; and the story collection Final Stanzas , is fiction editor of the North American Review and an English professor at the University of Northern Iowa, where he teaches film, modern drama, and creative writing. Nominated four times for a Pushcart Prize, he has published nearly fifty short stories and three previous collections. He has acted in over forty community theater productions and has published critical work on Samuel Fuller and James Cagney. He lives in Cedar Falls, Iowa.
Contribute to this Page
Genres of Writing: Definition, Examples, and 12 Types
What is the definition of Genre?
Genre is a label that tells audience members what to expect from our stories.
It is a clear framework to catalog all stories and helps writers give audience members what they are hoping for—and more. The genres of writing choices are the most important ones we need to make.
When people use the term genre, they often refer to different story elements at different times. They might mean the content of the story, the medium through which the story is presented, or even its sales category.
Without clear definitions, these labels don’t help us deliver what readers want when they choose to read, watch, or listen to a particular story .
In the Story Grid Universe, we break genre into five clear categories to help us identify, meet, and innovate story requirements. Understanding genre helps us delight audiences by meeting their expectations in unexpected ways.

Download Our In-depth Guide to Genre
This 99-page book written by Story Grid founder Shawn Coyne, walks you step-by-step through each of the twelve genres and what you need in your story to make it work.
Genre Categories: Introducing the Story Grid Genre 5-Leaf Clover
The Story Grid Genre 5-Leaf Clover is the tool we use to define the genres of writing in our stories. Each of the five leaves helps us determine a different element of a story’s experience. It helps to think of the five categories visually, so we present them as a five-leaf clover.

The goal of the Genre Five-Leaf Clover is to help us think about how each element or leaf comes together to form the global story. We can check our stories to make sure we are using the best combination possible to deliver a satisfying story experience.
By defining the specific genres and their conventions, we can start to look for each element within masterworks and study to understand ways of meeting these expectations within our own stories.
1. What is the Time Genre?
The TIME GENRE indicates how the reader experiences the time it takes to go from the beginning to the end of our stories. It answers how long the story will take to consume.
There are three categories of the Time Genre our stories can fall into: Short, Medium, and Long form.
Read more about the Time Genre .
2. What is the Structure Genre?
The STRUCTURE GENRE indicates to our reader who or what the change of the story will affect. It addresses whether the change will occur for a single AVATAR or throughout the whole system or context.
There are three categories of the Structure Genre our stories can fall into: Archplot, Miniplot, and Antiplot.
Read more about the Structure Genre .
3. What is the Style Genre?
The STYLE GENRE sets the tone for what the audience will experience during the story. It puts constraints on what we include in the story to keep a consistent feel so the audience does not get confused.
This genre leaf is divided into two broad categories and several mediums. The broad categories are Drama and Comedy. The mediums include Documentary, Musical, Dance, Literary, Theatrical, Cinematic, Epistolary, and Animation.
Read more about the Style Genre .
4. What is the Reality Genre?
The REALITY GENRE constrains the way the ALTERNATE WORLD of our story operates by establishing codes, laws, and norms. It dictates how much readers must suspend disbelief when building the worlds of our stories in their minds.
There are four categories of the Reality Genre our stories can fall into: Absurdism, Factualism, Realism, and Fantasy.
Read more about the Reality Genre .
5. What is the Content Genre?
The CONTENT GENRE defines what is contained in a story and specifically determines the need and VALUE at stake. It sets expectations for the reader using the FOUR CORE FRAMEWORK , CONVENTIONS , and OBLIGATORY MOMENTS . The Content Genre is divided into two sections: external and internal.
The external content genres of writing are:
Action Genre
An external story in the Action genre focuses on the protagonist’s sacrifice for positive movement along the death / life VALUE spectrum while generating feelings of excitement in the reader.
In Action stories, readers see the lengths the protagonist will go to protect themselves and/or other potential victims.
Read our in-depth article on the Action Genre .
An external story in the War genre focuses on the self-actualization of the protagonist through the expression of the gifts of love and self-sacrifice. Each AVATAR can act heroically by defending fellow warriors honorably in the face of horrific pain and loss.
Read our in-depth article on the War Genre .
Horror Genre
An external story in the Horror genre focuses on the ability of a protagonist to self-actualize through the expression of the gift of courage and selflessness in the face of fear. The Horror genre pits a single victim (even though there may be multiple AVATARS) against impossible odds and a supernatural, scientifically explainable or ambiguous monster possessed by evil and intent on annihilation.
Read our in-depth article on the Horror Genre.
Crime Genre
An external story in the Crime genre focuses on the Justice / Injustice spectrum while generating feelings in the reader of intrigue (solving the puzzle) and security or personal safety when the perpetrator is exposed.
Read our in-depth article on the Crime Genre .
Thriller Genre
An external story in the Thriller genre focuses on the protagonist’s need for safety. This leads the reader to identify with the protagonist, who seeks to defeat an antagonist that personifies evil.
Thriller stories blend elements of three other genres as the powerful individual protagonist from the ACTION genre faces the embodiment of evil (the monster) from the HORROR genre in a story about unmasking an antagonist who has committed a crime against society, as in the CRIME genre. The protagonist ends up as a victim and faces damnation if they fail to identify and defeat the villain.
Read our in-depth article on the Thriller Genre .
Western/Eastern Genre
An external story in the Western or Eastern genres focuses on the conflict between the individual and society. It turns on the subjugation / freedom spectrum while generating feelings of intrigue in the reader.
Read our in-depth article on the Western/Eastern Genre .
An external story in the Love genre focuses on the need for connection in a variety of forms, including desire, commitment, and intimacy, allowing readers to identify with the lovers as protagonists and respond to the fulfillment of the couple’s fate on the hate-love spectrum with a feeling of romance.
Read our in-depth article on the Love Genre .
Performance Genre
An external story in the Performance genre focuses on the outward expression of the protagonist’s internal gifts and need for approval. It turns on the shame / respect spectrum while generating feelings of triumph in the reader.
Read our in-depth article on the Performance Genre .
Society Genre
An external story in the Society genre focuses the protagonist’s need for recognition in a disenfranchised group. It turns on the impotence / power spectrum while generating feelings of triumph or righteous indignation depending on whether the Revolution succeeds or fails.
Read our in-depth article on the Society Genre .
The internal content genres of writing are:
An internal story in the Status genre focuses on the protagonist’s need for respect. These stories turn on the failure / success spectrum while generating feelings of admiration or pity in the reader, depending on the outcome.
Read our in-depth article on the Status Genre .
An internal story in the Morality genre focuses on the choice to act on behalf of ourselves or others and the consequences of that choice. It turns on the selfishness / altruism spectrum while providing feelings in the reader of satisfaction or contempt.
Read our in-depth article on the Morality Genre .
An internal story, Worldview genres focus on the lens through which we view the world and the consequences of those lens choices. It turns on the naivete/sophistication spectrum, while providing readers with feelings of relief at the protagonist’s emerging whole from a threat to their internal status quo, or pity for a less fortunate avatar.
Read our in-depth article on the Worldview Genre .
Additional Resources for Genres of Writing:
- Story Grid 101: The First Five Principles of the Story Grid Methodology by Shawn Coyne
- The Four Core Framework: Needs, Life Values, Emotions and Events in Storytelling by Shawn Coyne
Share this Article:
🟢 Twitter — 🔵 Facebook — 🔴 Pinterest
Sign up below and we'll immediately send you a coupon code to get any Story Grid title - print, ebook or audiobook - for free.
Level Up Your Craft Newsletter

Ebooks, Publishing, and Everything in Between
- Downloads & Pricing
- Advertising
Exploring the Different Types of Creative Writing
- on Sep 26, 2022
- in Writing Tips
- Last update: November 16th, 2023
Writing comes in all forms and sizes. But in order for a work to be considered creative writing, it must come from a place of imagination and emotion.
This is something many people pursuing a creative writing degree online at first struggle to get a handle on. Take for example what Franz Kafa said about creative writing, “Don’t bend; don’t water it down; don’t try to make it logical; don’t edit your own soul according to the fashion. Rather, follow your most intense obsessions mercilessly.”
Many authors who choose to follow Kafka’s advice—to write “mercilessly” and from the soul—find it comforting that their writing doesn’t have to conform to one style. But this variety of types and forms might leave some writers a bit confused.
That’s why, in this article, we are going to walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, with some great examples from authors who absolutely rocked their respective forms.

In this article:
- Creative Writing Definition
- Creative Writing Techniques
- Free Writing
- Journal Diaries
- Personal Essays
- Short Fiction
- Novels/Novellas
What Is Creative Writing?
Think of creative writing as a form of artistic expression. Authors bring this expression to life using their imagination, personal writing style, and personality.
Creative writing is also different from straightforward academic or technical writing. For instance, an economics book like Khalid Ikram’s The Political Economy of Reforms in Egypt is an academic monograph. This means that readers would rightfully expect it to contain analytic rather than creative writing.
So what are some elements that make a written piece more creative than analytic?
Popular Techniques Used in Creative Writing
Despite the fact that creative writing can be “freer” and less traditional than academic writing, it is likely to contain one or more of the following six elements:
1. Literary Devices
Many creative writers use literary devices to convey the meaning and themes of their work. Some common literary devices are allegories , metaphors and similes , foreshadowing , and imagery . These all serve to make the writing more vivid and descriptive .
2. Narrative
Authors often use this technique to engage readers through storytelling. Narrative isn’t limited to novels and short stories; poems, autobiographies, and essays can be considered narratives if they tell a story. This can be fiction (as in novels) or nonfiction (as in memoirs and essays).
3. Point of View
All creative writing must have a point of view; that’s what makes it imaginative and original. The point of view is the perspective from which the author writes a particular piece. Depending on the type of work, the point of view can be first person, third person omniscient, third person limited , mixed (using third- and first-person writing), or—very rarely—second person.
4. Characterization
Characterization is the process by which authors bring their characters to life by assigning them physical descriptions, personality traits, points of view, background and history, and actions. Characterization is key in creative writing because it helps drive the plot forward.
5. Dialogue
An important element used in many creative writing works is dialogue . Assigning
dialogue to characters is a way for authors to show their characters’ different traits without explicitly listing them.
Dialogue also immerses readers in the narrative’s action by highlighting the emotions and tensions between characters. Like characterization, it also helps drive the plot forward.
6. Plot
The plot is the sequence of events that make up a narrative and establish the themes and conflicts of a work . Plots will usually include an exp osi tion (the introduction), rising action (the complications), climax (the peak in action and excitement), falling action (the revelations and slowing down of events), and denouement (the conclusion).

The Main Types of Creative Writing (With Examples)
What’s great about creative writing is that there are so many types to choose from. In this section, we’ll walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, along with some examples.
Type 1: Free writing
Free writing, also known as stream-of-consciousness writing, is a technique that allows words and images to spill onto the page without giving thought to logic, sequence, or grammar. Although authors often use it as an exercise to get rid of the infamous writer’s block , free writing is also useful within a larger work.
For instance, let’s take a look at this excerpt from Toni Morrison’s novel Beloved.
Beloved by Toni Morrison [an excerpt]
the air is heavy I am not dead I am not there is a house there is what she whispered to me I am where she told me I am not dead I sit the sun closes my eyes when I open them I see the face I lost Sethe’s is the face that left me Sethe sees me see her and I see the smile her smiling face is the place for me it is the face I lost she is my face smiling at me
Note how the author uses free writing to convey the character’s disjointed and agitated thoughts. Even punctuation has been set aside here, adding to the rush of the character’s fear and confusion. The imagery is powerful (“the sun closes my eyes”; “her smiling face is the place for me”) and relies on repetitions like “I am not dead” and “I see” to immerse the readers in the character’s disturbed mental state.
Type 2: Journals and Diaries
A journal is a written account of an author’s experiences, activities, and feelings. A diary is an example of a journal, in which an author documents his/her life frequently.
Journals and diaries can be considered creative writing, particularly if they offer more than just a log of events. For instance, if a diary entry discusses how the writer ran into an old friend, it might include details of the writer’s emotions and probably use literary devices to convey these feelings.
It’s almost impossible to read the word “diary” and not think of Anne Frank. Let’s look at this excerpt from her work The Diary of a Young Girl .
Anne Frank: The Diary of a Young Girl [an excerpt]
Saturday, 20 June, 1942: I haven’t written for a few days, because I wanted first of all to think about my diary. It’s an odd idea for someone like me to keep a diary; not only because I have never done so before, but because it seems to me that neither I—nor for that matter anyone else—will be interested in the unbosomings of a thirteen-year-old schoolgirl. Still, what does that matter? I want to write, but more than that, I want to bring out all kinds of things that lie buried deep in my heart.
In the extract above, Anne adopts a reflective tone. She uses the rhetorical question “what does that matter?” to illustrate how she arrived at the conclusion that this diary will help bring out what is “buried deep in her heart.”
In this way, the diary serves as a log of events that happened in Anne’s life, but also as a space for Anne to reflect on them, and to explore her resulting emotions.
Type 3: Memoir
Although they might seem similar at first, memoirs and diaries are two different creative writing types. While diaries offer a log of events recorded at frequent intervals, memoirs allow the writer to select key moments and scenes that help shed light on the writer’s life.
Let’s examine this excerpt from the memoir of Roxanne Gay, author of Bad Feminist .
Hunger: A Memoir of (My) Body by Roxanne Gay:
I ate and ate and ate in the hopes that if I made myself big, my body would be safe. I buried the girl I was because she ran into all kinds of trouble. I tried to erase every memory of her, but she is still there, somewhere . . . I was trapped in my body, one that I barely recognized or understood, but at least I was safe.
Roxanne Gay offers readers a powerful work on anxiety, food, and body image by taking them on a journey through her past . Using evocative imagery in the excerpt above (“I buried the girl I was”; “I was trapped in my body”) the author shares her psychological trauma and resulting tumultuous relationship with food.
As with most memoirs—and diaries—this one is intimate, allowing readers into the dark crevices of the author’s mind. However, unlike a diary, this memoir does not provide an account of the writer’s day-to-day life, but rather focuses on certain events—big and small—that the author feels made her who she is today.
Type 4: Letters
Unlike diary and journal entries—which usually don’t have a specific recipient—letters address one target reader. Many famous authors have had collections of their letters published, revealing a side of them that isn’t visible in other works.
Letter writing uncovers the nature of the relationship between sender and recipient, and can include elements of creative writing such as imagery, opinion, humor, and feeling.
Here is an excerpt from a letter by Truman Capote, author of Breakfast at Tiffany’s and In Cold Blood .
Too Brief a Treat: The Letters of Truman Capote , edited by Gerald Clarke
Dear Bob; Have come, am here, am slowly freezing to death; my fingers are pencils of ice. But really, all told, I think this is quite a place, at least so far. The company is fairly good… I have a bedroom in the mansion (there are bats circulating in some of the rooms, and Leo keeps his light on all night, for the wind blows eerily, doors creak, and the faint cheep cheep of the bats cry in the towers above: no kidding.
In his letter to editor and friend Robert “Bob” Linscott, Truman paints a scene of his new setting . He uses hyperbole (“freezing to death”) and a powerful metaphor (“my fingers are pencils of ice”) to convey the discomforting cold weather. Truman also uses sound imagery (“doors creak”; “wind blows eerily”; “cheep cheep of the bats”) to communicate the creepy, sinister mood to his reader.
Type 5: Personal Essays
Many of us don’t normally think of essays as creative writing, but that’s probably because our minds go to academic research essays. However, there are many types of essays that require creative rather than analytic writing, including discursive essays, descriptive essays, and personal essays.
A personal essay, also known as a narrative essay, is a piece of nonfiction work that offers readers a story drawn from the author’s personal experience. This is different from a memoir, in which the primary focus is on the author and their multiple experiences.
A personal essay, on the other hand, focuses on a message or theme , and the author’s personal experience is there to communicate that theme using memorable characters and setting , as well as engaging events . These, of course, all have to be true, otherwise the personal essay would turn into a fictional short story.
Here is an excerpt from a personal essay by writers Chantha Nguon and Kim Green.
The Gradual Extinction of Softness by Chantha Nguon and Kim Green
In 1975, the Khmer Rouge informed the Cambodian people that we had no history, but we knew it was a lie. Cambodia has a rich past, a mosaic of flavors from near and far: South Indian traders gave us Buddhism and spicy curries; China brought rice noodles and astrology; and French colonizers passed on a love of strong coffee, flan, and a light, crusty baguette. We lifted the best tastes from everywhere and added our own.
The opening of this paragraph establishes the author’s strong and unwavering opinion : “we knew it was a lie.” Instead of providing a history of Cambodia, she demonstrates the country’s rich past by discussing its diverse “flavors”: “spicy curries”; “strong coffee”; “light, crusty baguette”, etc.
Using gustatory imagery , which conveys a sense of taste , the authors reveal their personal version of what makes Cambodia wonderful. The writer communicates the essay’s theme of food and memories through a story of her childhood.
Type 6: Poetry
Robert Frost once wrote: “Poetry is when an emotion has found its thought and the thought has found words.” Good poetry is effective because it uses the power of imagery to convey what it is to be human. Every word in a poem counts, and the best poems are those that evoke the reader’s emotions without unpacking too much.
As one of the most diverse types of creative writing, poetry can come in many forms. Some poets prefer to write in the more traditional forms such as sonnets , villanelles , and haikus , where you have particular structures, rhyme, and rhythm to follow. And others prefer the freedom of free verse and blackout poetry .
Let’s take a look at this excerpt from Maya Angelou’s powerful lyric poem , “Still I Rise.”
“Still I Rise” from And Still I Rise: A Book of Poems by Maya Angelou
Out of the huts of history’s shame I rise Up from a past that’s rooted in pain I rise I’m a black ocean, leaping and wide, Welling and swelling I bear in the tide. Leaving behind nights of terror and fear I rise Into a daybreak that’s wondrously clear I rise Bringing the gifts that my ancestors gave, I am the dream and the hope of the slave. I rise I rise I rise.
Packed with powerful language, this excerpt from Angelou’s poem gives us absolute
chills! The refrain “I rise” is repeated 7 times in these two verses alone,
hammering home the idea that the speaker cannot be defeated.
The imagery, repetition, and rhyme scheme all work together to convey the emotions of pride and resilience. Both verses also rely heavily on metaphors (“I’m a black ocean”; “I am the dream and the hope of the slave”) to convey the speaker’s power. She is not like an ocean or a dream; she is both, and she is unstoppable.
Type 7: Song Lyrics
Song lyrics are in many ways similar to poems, except that lyrics are meant to be sung . They are a form of creative writing that allows writers to surpass the rules of grammar and punctuation in favor of creating rhyme and rhythm . This means that the creativity of a song lyricist is free from the traditional restrictions of language.
Type 8: Scripts
Scriptwriting is a form of creative writing that relies heavily on character dialogue , stage directions , and setting . Scripts are written for films and TV shows (known as screenplays and teleplays), stage plays, commercials, and radio and podcast programs.
Like song lyrics, scripts are written with the intention of reaching a non-reading audience. In other words, scriptwriters must bear in mind how their writing will be 1) interpreted by other storytellers , such as directors, designers, etc., and 2) performed by actors.
Let’s examine the iconic opening scene from the screenplay of the film Forrest Gump .
Forrest Gump , screenplay by Eric Roth [an excerpt]
THE MAN Hello, I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump. She nods, not much interested. He takes an old candy kiss out of his pocket. Offering it to her: FORREST (cont’d) Do you want a chocolate? She shakes “no.” He unwraps it, popping it in his mouth. FORREST (cont’d) I could eat about a million and a half of these. Mama said, “Life was just a box of chocolates. You never know what you gonna get.”
From the dialogue and stage directions in this opening scene, the audience can see that there is something innocent, kind-hearted, and simple about the character Forrest Gump. This is conveyed through the way he introduces himself with a slight repetition (“I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump.”) to a complete stranger, and the way he quotes his mother to her.
Moreover, the action of Forrest “popping” the candy in his mouth is almost childlike , and that the stranger is reluctant to communicate with him foreshadows the fact that the people Forrest meets are initially suspicious of him and his innocence. Thus, the pauses and silences in the scene are just as important to the work as what is explicitly said.
Type 9: Short Fiction
Short fiction is a form of creative fiction writing that typically falls between 5,000 to 10,000 words ; however, there is definitely room to go lower than 5,000 words, depending on the topic.
For instance, flash fiction is a form of short fiction that can be 1,000 words or less. In the case of flash fiction, the author unpacks the “skeleton” of a story in as few words as possible. For instance, legend has it that Ernest Hemingway wrote a 6-word “story”:
For sale: baby shoes, never worn.
In just six words, the reader is led to understand that this is a story of death and loss.
Nevertheless, the average short story is usually structured around the following elements: characterization , setting , plot , and conflict . Many fiction authors start out writing short fiction because it enables them to nail all the essential elements, which they can then expand upon in longer works.
Let’s look at an excerpt from Janet Frame’s short story, “The Bath”
“The Bath” by Janet Frame [an excerpt]
She leaned forward, feeling the pain in her back and shoulder. She grasped the rim of the bath but her fingers slithered from it almost at once. She would not pancic, she told herself; she would try gradually, carefully, to get out. Again she leaned forward; again her grip loosened as if iron hands had deliberately uncurled her stiffened blue fingers from their trembling hold. Her heart began to beat faster, her breath came more quickly, her mouth was dry. She moistened her lips. If I shout for help, she thought, no-one will hear me. No-one in the world will hear me. No-one will know I’m in the bath and can’t get out.
In this paragraph, there is an image of a frail, old woman, physically unable to get out of her bathtub. The diction , or word choice, serves to convey the woman’s sense of fear and helplessness. For instance, words like “grasped,” “slithered,” “uncurled,” and “stiffened,” demonstrate the immense effort it takes for her to try to get out.
The image of her “moistening” her lips illustrates that fear has turned her mouth dry. And the repetition of “no-one” in the last few sentences highlights the woman’s loneliness and entrapment —two of the story’s main themes. Indeed, the bath symbolizes the unavoidable obstacles brought about by old age.
Type 10: Novellas / Novels
Novels are one of the most popular forms of creative writing. Though they vary in length, depending on the subject, they’re generally considered a long form of fiction , typically divided into chapters .
Novellas, on the other hand, are shorter than novels but longer than short stories. Like short stories, novels, and novellas contain characters , plot , dialogue , and setting ; however, their longer forms allow writers a chance to delve much deeper into those elements.
Type 11: Speeches
Speeches are a form of writing similar to essays in that both forms are non-fiction , and both usually entail a discussion of the writer’s personal experiences and include engaging events and a particular theme.
However, speeches differ from essays in that the former are meant to be recited (usually in front of an audience), and tend to be persuasive and inspirational. For instance, think of the purpose of graduation speeches and political speeches: they aim to inspire and move listeners.
One of the most well-known speeches from the 20th century is Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream”. Let’s examine the excerpt below:
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King [an excerpt]
Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy. Now is the time to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice. Now is the time to lift our nation from the quicksands of racial injustice to the solid rock of brotherhood. Now is the time to make justice a reality for all of God’s children.
What immediately catches the eye (and ear) in this paragraph is the speaker’s usage of anaphora : the repetition of the phrase “now is the time” serves to emphasize the urgency of the matter being discussed (i.e. the prevalence of racial injustice).
The speaker’s repetition of the pronoun “our” is an appeal to his audience’s emotions and their sense of unity. Both he and they are in this together, and thus he is motivating them to take on the challenge as one.
Moreover, the use of figurative language is abundant here and can be found in similar inspirational and motivational styles of creative writing. The imagery created by the metaphor and alliteration in “the d ark and d esolate valley of segregation,” and its juxtaposition with “sunlit path of racial justice,” together aim to convey the speaker’s main message. Segregation has brought nothing but darkness and ruin to American society, but there is hope and light on the path toward racial equality.
Final Thoughts
Creative writing acts as a medium for artistic expression. It can come in a variety of forms, from screenplays and speeches to poetry and flash fiction. But what groups all of these different types of creative writing under the “creative” umbrella, regardless of form, is their display of a writer’s imagination, creativity, and linguistic prowess.
How to Write the Best Book Introduction
Making Use of Humor in Writing
4 Different Types of Writing You Need to Understand
I appreciate you offering such a thought-provoking perspective. It should be useful for academic writing in addition to creative writing, in my opinion. Each method you listed is pertinent and appropriate.
You’re absolutely right! Many of these writing methods can be applied to both creative and academic writing, enhancing the depth and effectiveness of communication.
Robert smith enago
Thank you for sharing this enlightening blog post on the various types of creative writing. Your exploration of different writing methods and styles provides an inspiring perspective on the boundless possibilities within the realm of creativity.
It is remarkable to see how creative writing encompasses an array of forms, each with its unique allure and artistic essence. From poetry, fiction, and drama to screenwriting, creative nonfiction, and even songwriting, each avenue offers writers a chance to express their thoughts, emotions, and imagination in captivating ways.
We truly appreciate your kind words! Creative writing is indeed a vast and fascinating world with endless opportunities for self-expression 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.

Kotobee is the complete end-to-end ebook solution for you and your business. Export multiple formats. Deliver securely.
Create, publish, and sell ebooks with ease
Kotobee es la solución completa de ebooks de extremo a extremo para usted y su empresa.
Cree, publique y venda libros electrónicos con facilidad

Recent Posts
- The Different Types of Characters in a Story Explained
- LMS Integration: Types, Examples, and Best Practices
- How to Edit a Book for Publishing: Tips & Best Practices
- Book Royalties: What They Are and How to Earn the Best Rates
- Game-Based Learning: What It Is, and How to Apply It
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
Types of Writing Genres: A Short Guide

- Post author By admin
- October 11, 2022
In this blog, we will discuss the different types of writing genres. Every genre of writing has its mindset and set of expectations. Genres are the tool for creativity and provide various perspectives to tell your story in different ways.
As a writer, your work will fit into a certain genre whether you want it or not, and that is purely based on what you are creating. On one side, some work may fit into one Genre. On the other hand, some may have different genres.
There are three different types of writing genres that we will take a look at in this blog. We have separated writing genres like Professional Writing, Literary Writing, and, lastly, Academic Writing.
If you’re wondering which one is right for you then this is the right place for you.
Here we will discover different writing genres that you need to know!
So, without further ado, let’s dive into it!
Table of Contents
What is the Need for Types of Writing Genres?
They Help Writers Sort Out Their Ideas and Feelings : When writers know what kind of writing they are doing, they can use the rules of that kind of writing to help them organize their writing. This can speed up the writing process and help writers make work simpler and more sense.
They Help People Know What to Expect From a Piece of Writing : When a reader knows the genre of a piece of writing, they can guess what they know about it to guess what the piece is about. This can help people read faster and better understand what they are reading.
They Help Writers Connect With the People Who Read Their Work : When writers choose the right type for their readers, their writing is easier to understand and more interesting to read. This can help writers connect with their readers and reach their goals for dialogue.
Aside From These General Benefits: there are other reasons to use different types of writing. For example, expository writing can help writers explain complicated ideas clearly, while descriptive writing can help writers paint detailed pictures in the minds of their readers. Narrative writing can help writers tell stories that entertain and teach, while persuasive writing can help writers persuade readers to do something.
They Can Help a Writer Find His or Her Voice : By trying different types of writing, writers can find the type that fits their style and attitude the best. This can help writers find their style, which will help them connect with their readers.
They Can Help Writers Come Up With Better Ideas : Writers can stretch their creative skills and develop new ideas if they try to write in different styles. This can make writers more creative and help them develop more original ideas.
They Can Help Writers Get Better at What They Do : Writers can improve their skills by learning the rules of different types of writing. This can help writers write better and make their work look more polished.
In the end, there are different types of writing because they are used for different things. If writers know the rules for each type, they can choose the right one for their purpose and audience. This will help them write in a clear, powerful, and interesting way.
What are Writing Genres?
The writing Genre is mostly called the name of Literary Genre. It is a type of narrative that can be used or written. Mostly, it is used for one purpose only to share emotions, ideas, and news with other people. Writing Genre is used to tell the story interestingly.
Writing within each Genre will reflect a whole new story and share several features like rhyme, image, and stylistic devices. The main focus of each Genre is to describe the events, theory, and several ideas in certain ways. In other words, the aim of each writing genre is how the elements are conveyed and described.
What are the Different Types of Writing Genres?
Three main types of Writing Genres are as follows:
- Professional Writing.
- Literary Writing.
- Academic Writing.
Professional Writing Genre (Types of Writing Genres)
Social media .
Social Media is a growing genre in business communication. The level of discussion in social media may vary depending on the topic and audience. Well-considered successful post on social media to help understand how it’s used to reach a wider target audience.
Business Letters
It can be both formal and informal. A perfectly written business letter shows the reader why it is important. If you want successful communication, then a structured approach is very important.
Memos
Well, Memos provide a clear summary, and the most crucial information is given at the beginning, but Paper Memos are no longer used nowadays. A positive tone is used to help the reader understand what the author is trying to say, making it appropriate for the users.
In the past, memos were considered the best business correspondence. The Main Guideline of the memo still exists, even if the median of the paper memo has been changed.
Meeting Minutes
Meeting Minutes include dates, times, attendees, and location. This is the standard format of Meeting Minutes. It is also important to record the most crucial details to avoid any misunderstanding later.
As a result, there are many ways involved in recording meeting minutes. The minutes should be uniform with the location and names. Unnecessary information should be avoided so that it can not cause any difficulty later.
This is the end of the Professional writing genre. Now we move to the Literary writing genre, and lastly, we will continue with the Academic Genre.
Literary Writing Genre (Types of Writing Genres)
Mystery .
This Genre is mostly associated with crime, mainly murder, but it does have to be. Any story which involves the unraveling of a secret or mystery would be considered within this Genre.
This Genre often describes a criminal investigation or legal case. Well, the most popular novel is The Sherlock Holmes Story. Mystery novels are a genre that typically has a problem to solve.
Category of Mystery Genre:
- Locked-room mysteries.
- Historical mysteries.
- Police procedural whodunit. ( A story about a murder in which the identity of the murderer is hidden at the end )
Literary nonfiction
Literary nonfiction is all about real events and people. Nonfiction can be found in magazines like The Atlantic, The New York, and Harper’s Magazine.
This type of Genre is associated with creating feelings of fear and dread. Some of you might think of this Genre as full of “blood and gore”. Anything which creates negative feelings about something will come under the category of Horror.
Horror is the genre of film, literature, and TV shows. The main aim of the horror genre is to create fear.
Gothic novels are an example of ancient horror literature. On the other hand, Stephen King is considered the father of modern horror literature. Well, nowadays, new writers have pushed the boundaries of horror stories. Writers include John Langan, Stephen Graham Jones, and many more.
In the Historical Genre, the story takes place in the past. Sometimes real people are included to interact with the fictional character to create a sense of realism.
Romance
This Genre deals with the love stories between two people. The element of romance can be found in many types of literature. Romance has been there since ancient times, but time travels so fast, and the paranormal romances have become more popular nowadays.
Science Fiction
As the name suggests, Science Fiction is the genre that deals with science and technology in society. Science fiction is a special type of Genre that includes elements of time travel, futuristic societies, and space. People often call Science Fiction ( Sci-Fi ) .
Magical realism
Magical realism is a type of literature in which the real world is depicted with an influence of magic and fantasy. In magical realism, the stories may occur in the real world but with some supernatural elements. Magical realism has close ties with Latin American Authors. Magical realism is used by literature from around the globe.
Fantasy novels are fiction stories that are set in imaginary universes. This Genre is inspired by folklore and mythology that is enjoyed by both children and adults
Dystopian novels are about futuristic and oppressive societies. In other words, the Dystopian novel features some political and social unrest. It can help us examine real types of fear like mass surveillance by the government.
Graphic Fiction
Graphic Fiction is the category of Graphic Novels and Comic Books.
Short Stories
Well, this type of Genre may fit into any number of genres. In Short stories, there is only one plot to it, no subplot in this Genre.
Tall Tales stories are not realistic or don’t try to become realistic.
Academic Writing Genre (Types of Writing Genres)
Analytical writing.
In Analytical writing, the author has a chance to include persuasive writing. A common layout uses the structure of methods, results, introduction, summary, and discussion.
Professional Writing
Professional Writing is a wide category that includes emails, studies, reports, business letters, and summaries. If you are writing for a client, then it is beneficial for you to follow the style rule of the company.
Argumentative Writing
Argumentative writing is a type of academic essay. In this, the writer breaks down an idea into its parts and then offers evidence for each part. This writing is mostly based on understanding and reading fiction or nonfiction texts.
Argumentative writing has three sections:
- Evidence or supporting point.
- Conclusion.
Most Common Types of Writing Genres That You Should Know
Descriptive writing .
In Descriptive writing, the author writes about every aspect of the person, place, or event and describes all aspects in detail.
Example of Descriptive Writing:
- Narrative Nonfiction.
- Fictional Stories.
Expository Writing
Expository writing is used to educate the reader. So the main goal of expository writing is to teach the reader rather than entertainment.
Example of Expository Writing:
- Technical Writing.
- Recipes writing.
Narrative Writing
Narrative Writing is used to tell people what happens somewhere or with someone. Narrative Writing includes Fiction and nonfiction. Whereas nonfiction is based on real events, and fiction writing is completely made up.
Example of Narrative Writing:
- Short-story.
- Presentations
- Speeches, and many more.
Persuasive Writing
Persuasive writing is used to convince the reader about something. This type of writing is written when the author has a strong opinion on something. It is used to encourage people to take action regarding any issue.
Example of Persuasive Writing:
- An opinion piece in the newspaper.
- Sales writing.
Read more about writing styles: Different Types Of Writing Styles
Now you know the different types of writing genres and their most used forms. So which Genre or form is close to you, and which one do you use the most. In this blog, we provide you with a short guide to types of writing genres, with the most common Genre that you should know.
I hope you like it!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1.what are the seven styles of writing.
The seven most common types of essay writing Narrative Descriptive Expository Persuasive Compare Reflective Personal
Q2. What are the three main genres of literature?
The three major genres are: Drama Poetry Prose
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (278)
- General (75)
- How To (16)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts
Genres of Writing
Writing in the Disciplines (Various Genres)
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines from Harvard University – Includes downloadable writing guides for History , Philosophy , English , and Psychology
- Genres of Writing from Duke University – Offers guides for the many genres you may encounter while writing in college, including annotated bibliographies , creative writing , ethnography , summaries , academic email , cover letters , and personal statements
Critique Writing
- Critique Writing from The University of Arizona – Explains each part of a typical summary-critique paper of an academic article, and includes a sample paper with notes
Literature Reviews
- Writing a Literature Review from Boston College Libraries – Describes the different phases of writing a Literature Review
- Literature Reviews from UNC Chapel Hill – Provides strategies and helpful tips for writing a Literature Review
Job and Fellowship Applications
- Navigating the Application Process from Carleton’s Career Center – Guides and advice on writing resumes and cover letters, asking for references, preparing writing samples, and even writing a thank you note
Research Writing
- Designing a Research Question from advanced authentic Research – Walks through the process of crafting a research question, with a focus on STEM
Science Writing
- Writing Lab Reports from Indiana University Bloomington – Provides explanations of each section of a typical lab report
Writing for the Web
- Writing for the Web from Carleton’s Office of Accessibility Resources (OAR) – Explains how to write effectively for online readers
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Finding Your Footing: Sub-genres in Creative Nonfiction

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Memoir is perhaps the “flagship” of creative nonfiction, the sub-genre most familiar to those outside of literary and academic circles. Most human beings lead interesting lives filled with struggle, conflict, drama, decisions, turning points, etc.; but not all of these stories translate into successful memoir. The success of the memoir depends on the writer’s ability to sequence events, to tell a story, and to describe characters in believable ways, among other things. Writer Carol Spindel reminds us that in the mid-2000s a scandal surrounding writer James Frey’s A Million Little Pieces erupted after he was forced to admit that large sections of his “memoir” were “fictionalized:” he’d embellished, made things up. A memoir that strays from the truth is not far removed from lying, because regardless of the writer’s intention, the story deceives the reader. Spindel writes that, unlike in novels, “The knowledge expressed in the memoir has the legitimacy acquired through first-hand experience.” Good memoir also provides reflection on the events that have happened to the writer, so it “can give readers insights into society, and even into the larger meaning of life itself” (Spindel).
The Braided Essay
The braided essay is a good tool for introducing writers—especially student writers—to the CNF genre. In a braided essay, the writer has multiple “threads” or “through-lines” of material, each on a different subject. The essay is broken into sections using medial white space, lines of white space on a page where there are no words (much like stanzas in poetry), and each time there is a section break, the writer moves from one “thread” to another. Braided essays take their name from this alternating of storylines, as well as from the threads the story contains; there are usually three, though to have four or two is also possible. Though there is not a strict formula for success, the form usually contains at least one thread that is very personal and based on memory, and at least one thread that is heavily researched. Often, the threads seem very disparate at first, but by the climax of the essay, the threads being to blend together; connections are revealed.
Topical Writing
Perhaps the genre closest to an essay or a blog post, topical writing is an author’s take on a given topic of specific interest to the reader. For example, nature writing and travel writing have been popular for centuries, while food writing is gathering steam via cooking blogs. Nature writing involves exploring the writer’s experience in a beautiful and thoroughly rendered natural setting, such as a cabin on a mountaintop. Travel Writing, as the name implies, details the writer’s experiences while traveling, whether by choice on a vacation or out of necessity due to business or serving in the military. Finally, contemporary food writing explores the writer’s connection to cooking and enjoying food of any variety. All three will occasionally step into the writer’s personal experiences via memories, but these episodes are always related to the topic driving the essay.
Whatever form a creative nonfiction piece takes, it must remain based in the author’s actual lived experiences and perceptions. Like academic writing, the piece must be accurately researched and the sources must be documented. Finally, the author must also always leave room to reflect on how their experiences have shaped them into the person they are now. It’s the reflection that makes the reader feel satisfied: it offers something to the reader that they can carry with them, a way of seeing the world.
Creative Writing Program Marks Three Decades of Growth, Diversity

By Luisa A. Igloria
2024: a milestone year which marks the 30 th anniversary of Old Dominion University’s MFA Creative Writing Program. Its origins can be said to go back to April 1978, when the English Department’s (now Professor Emeritus, retired) Phil Raisor organized the first “Poetry Jam,” in collaboration with Pulitzer prize-winning poet W.D. Snodgrass (then a visiting poet at ODU). Raisor describes this period as “ a heady time .” Not many realize that from 1978 to 1994, ODU was also the home of AWP (the Association of Writers and Writing Programs) until it moved to George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia.
The two-day celebration that was “Poetry Jam” has evolved into the annual ODU Literary Festival, a week-long affair at the beginning of October bringing writers of local, national, and international reputation to campus. The ODU Literary Festival is among the longest continuously running literary festivals nationwide. It has featured Rita Dove, Maxine Hong Kingston, Susan Sontag, Edward Albee, John McPhee, Tim O’Brien, Joy Harjo, Dorothy Allison, Billy Collins, Naomi Shihab Nye, Sabina Murray, Jane Hirshfield, Brian Turner, S.A. Cosby, Nicole Sealey, Franny Choi, Ross Gay, Adrian Matejka, Aimee Nezhukumatathil, Ilya Kaminsky, Marcelo Hernandez Castillo, Jose Olivarez, and Ocean Vuong, among a roster of other luminaries. MFA alumni who have gone on to publish books have also regularly been invited to read.
From an initial cohort of 12 students and three creative writing professors, ODU’s MFA Creative Writing Program has grown to anywhere between 25 to 33 talented students per year. Currently they work with a five-member core faculty (Kent Wascom, John McManus, and Jane Alberdeston in fiction; and Luisa A. Igloria and Marianne L. Chan in poetry). Award-winning writers who made up part of original teaching faculty along with Raisor (but are now also either retired or relocated) are legends in their own right—Toi Derricotte, Tony Ardizzone, Janet Peery, Scott Cairns, Sheri Reynolds, Tim Seibles, and Michael Pearson. Other faculty that ODU’s MFA Creative Writing Program was privileged to briefly have in its ranks include Molly McCully Brown and Benjamín Naka-Hasebe Kingsley.
"What we’ve also found to be consistently true is how collegial this program is — with a lively and supportive cohort, and friendships that last beyond time spent here." — Luisa A. Igloria, Louis I. Jaffe Endowed Professor & University Professor of English and Creative Writing at Old Dominion University
Our student body is diverse — from all over the country as well as from closer by. Over the last ten years, we’ve also seen an increase in the number of international students who are drawn to what our program has to offer: an exciting three-year curriculum of workshops, literature, literary publishing, and critical studies; as well as opportunities to teach in the classroom, tutor in the University’s Writing Center, coordinate the student reading series and the Writers in Community outreach program, and produce the student-led literary journal Barely South Review . The third year gives our students more time to immerse themselves in the completion of a book-ready creative thesis. And our students’ successes have been nothing but amazing. They’ve published with some of the best (many while still in the program), won important prizes, moved into tenured academic positions, and been published in global languages. What we’ve also found to be consistently true is how collegial this program is — with a lively and supportive cohort, and friendships that last beyond time spent here.
Our themed studio workshops are now offered as hybrid/cross genre experiences. My colleagues teach workshops in horror, speculative and experimental fiction, poetry of place, poetry and the archive — these give our students so many more options for honing their skills. And we continue to explore ways to collaborate with other programs and units of the university. One of my cornerstone projects during my term as 20 th Poet Laureate of the Commonwealth was the creation of a Virginia Poets Database, which is not only supported by the University through the Perry Library’s Digital Commons, but also by the MFA Program in the form of an assistantship for one of our students. With the awareness of ODU’s new integration with Eastern Virginia Medical School (EVMS) and its impact on other programs, I was inspired to design and pilot a new 700-level seminar on “Writing the Body Fantastic: Exploring Metaphors of Human Corporeality.” In the fall of 2024, I look forward to a themed graduate workshop on “Writing (in) the Anthropocene,” where my students and I will explore the subject of climate precarity and how we can respond in our own work.
Even as the University and wider community go through shifts and change through time, the MFA program has grown with resilience and grace. Once, during the six years (2009-15) that I directed the MFA Program, a State Council of Higher Education for Virginia (SCHEV) university-wide review amended the guidelines for what kind of graduate student would be allowed to teach classes (only those who had already earned 18 or more graduate credits). Thus, two of our first-year MFA students at that time had to be given another assignment for their Teaching Assistantships. I thought of AWP’s hallmarks of an effective MFA program , which lists the provision of editorial and publishing experience to its students through an affiliated magazine or press — and immediately sought department and upper administration support for creating a literary journal. This is what led to the creation of our biannual Barely South Review in 2009.
In 2010, HuffPost and Poets & Writers listed us among “ The Top 25 Underrated Creative Writing MFA Programs ” (better underrated than overrated, right?) — and while our MFA Creative Writing Program might be smaller than others, we do grow good writers here. When I joined the faculty in 1998, I was excited by the high caliber of both faculty and students. Twenty-five years later, I remain just as if not more excited, and look forward to all the that awaits us in our continued growth.
This essay was originally published in the Spring 2024 edition of Barely South Review , ODU’s student-led literary journal. The University’s growing MFA in Creative Writing program connects students with a seven-member creative writing faculty in fiction, poetry, and nonfiction.
Enhance your college career by gaining relevant experience with the skills and knowledge needed for your future career. Discover our experiential learning opportunities.
Picture yourself in the classroom, speak with professors in your major, and meet current students.
From sports games to concerts and lectures, join the ODU community at a variety of campus events.

- Literature & Fiction
- History & Criticism

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Buy new: .savingPriceOverride { color:#CC0C39!important; font-weight: 300!important; } .reinventMobileHeaderPrice { font-weight: 400; } #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPriceSavingsPercentageMargin, #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPricePriceToPayMargin { margin-right: 4px; } -25% $135.17 $ 135 . 17 FREE delivery Monday, June 3 Ships from: Amazon.com Sold by: Amazon.com
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Save with Used - Acceptable .savingPriceOverride { color:#CC0C39!important; font-weight: 300!important; } .reinventMobileHeaderPrice { font-weight: 400; } #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPriceSavingsPercentageMargin, #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPricePriceToPayMargin { margin-right: 4px; } $54.17 $ 54 . 17 FREE delivery Monday, June 3 Ships from: Amazon Sold by: Perpetual Textbooks

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Follow the author

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Three Genres: The Writing of Literary Prose, Poems and Plays 9th Edition
Purchase options and add-ons.
- ISBN-10 0205012752
- ISBN-13 978-0205012756
- Edition 9th
- Publisher Pearson
- Publication date January 27, 2011
- Language English
- Dimensions 1.1 x 5.9 x 8.9 inches
- Print length 472 pages
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Customers who viewed this item also viewed

Editorial Reviews
From the back cover.
Stephen Minot’s THREE GENRES provides creative writers with a
solid foundation to understand and study fiction, nonfiction, poetry, and
drama. Full of expert advice and complete works as examples, this classic
book is the ultimate guide for creative writers at all levels. Each section is
comprehensive, and draws on Professor Minot’s many years of experience
as a teacher and professional writer to supply creative writers with the skills
necessary to produce their own works. Professor Minot eagerly encourages
creative writers to write on their own because “there is no better way to
increase your understanding of poetry, literary prose, or drama than to
write them.”
About the Author
About Stephen Minot
Stephen Minot, Professor Emeritus of the Creative Writing Department at the University of California, Riverside, has taught creative writing for over thirty years. Over the span of his very successful career, Professor Minot authored three novels, two collections of short stories, and three textbooks including Reading Fiction and Literary Nonfiction, The Fourth Genre . His short stories have appeared in a variety of magazines and literary quarterlies including The Atlantic, Harpers, The Kenyon Review, The Virginia Quarterly Review, and the Sewanee Review , just to name a few. Professor Minot’s work has also appeared in the O. Henry Prize Stories collection and The Best American Short Stories . He is also the recipient of the Atlantic First Award, the Saxton Memorial Fellowship, and the National Endowment for the Arts Fellowship for writing. Professor Minot and Virginia, his wife, split their time between California and Maine.
About Diane Thiel
Diane Thiel is the author of eight books of poetry, nonfiction and creative writing pedagogy, including Echolocations , Resistance Fantasies, Winding Roads: Exercises in Writing Creative Nonfiction, Cross Roads: Creative Writing in Four Genres, and Open Roads: Exercises in Writing Poetry. Thiel’s translation of Alexis Stamatis’s novel, American Fugue , received an NEA Award. Her work appears in many journals, is re-printed in over fifty anthologies, and has been translated widely. She has received numerous awards, such as the PEN Translation, Robert Frost, and Robinson Jeffers Awards, and was a Fulbright Scholar. Thiel has taught creative writing for twenty years and is a Professor at the University of New Mexico.
Product details
- Publisher : Pearson; 9th edition (January 27, 2011)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 472 pages
- ISBN-10 : 0205012752
- ISBN-13 : 978-0205012756
- Reading age : 1 year and up
- Item Weight : 1.32 pounds
- Dimensions : 1.1 x 5.9 x 8.9 inches
- #294 in Drama Literary Criticism
- #1,150 in Authorship Reference
- #2,664 in Fiction Writing Reference (Books)
About the author
Stephen minot.
Discover more of the author’s books, see similar authors, read author blogs and more
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
Reviews with images

- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
No products in the cart.

Four Wonderful Ways to Courageously Develop and Grow as a Writer
Post by Ali Luke.
When it comes to your writing, do you sometimes feel like you have the brakes on?
You might want to move forward … but something’s holding you back.
I’ve seen so many writers blame themselves for procrastinating. They feel guilty that they can’t seem to “just get on with it.” Sometimes, they worry that they’re simply lazy or not cut out for the writing life.
But I don’t believe that procrastination is usually about laziness or about not being suited to writing. Instead, procrastination is often a symptom of a lack of confidence.
If you feel that you’re not writing as much as you want, or you’re writing but it’s as though you’re spinning your wheels and not really making bigger-picture progress in your writing career, then I hope I can give you some encouragement and some practical steps to move forward and grow as a writer.
Because you can’t think yourself into being more confident. You need to take action.
Here are some wonderful ways to nurture your creative growth and development as a writer.
#1: Create a Physical Space for Your Writing
Just like anything important to you, your writing needs space within your life.
Here, I’m not talking about space on your calendar—though of course that’s important too.
Your writing needs actual physical space.
Plenty of people dedicate a serious amount of space in their homes to an interest or hobby. Some people have entire craft rooms stocked with yarns and fabrics. Others have a garage jam-packed with sports equipment. Some have kitchen cupboards full of cake pans and baking accessories.
Your writing might well take place on a computer ( or even on your phone ) … but you still need more than just virtual space.
You need a quiet place in your home where you can write. You might also want to have notebooks, pens, inspiring photos, or useful books to hand. You’ll need a chair you can sit on comfortably while you’re writing.
It’s also important to choose a space where you feel as safe as possible . I hate to be overlooked when I’m writing—so I write with my back to the wall, facing into the room. I thought this was just my own weird quirk, but I’ve since learned that it’s a very normal psychological need .
#2: Build a Consistent Writing Habit
Whatever type of writing you do, it’s going to be hard to build the momentum you need in order to develop as a writer if you aren’t writing regularly. That means you need to develop a writing habit .
To start with, you don’t necessarily need to commit to a big project. In fact, even if you have a big project on the go, you may want to build a writing habit that also incorporates practice and experimentation.
For instance, you might decide to spend 5-10 minutes each day simply writing anything that comes to mind. This can get you into the habit of writing, without the pressure that comes with setting goals like “I’ll write eight chapters a month” or “I’ll publish a blog post every week.”
You could use creative writing prompts or journal prompts for your daily writing (if you’re not keen on traditional writing prompts, there are some great alternative suggestions here ). If you want to stretch yourself with something bigger, you could gradually build up a longer piece, paragraph by paragraph, day after day.
#3: Try Out a New Genre or Style of Writing
If you’ve been writing consistently, perhaps for years, you may feel that you’ve ended up in a bit of a writing rut. Perhaps you only ever write in one genre, for instance. Maybe you use the same familiar tropes or character archetypes in almost all your novels, or your short stories are all structured in the same way.
Growth is about trying new things. Even if you try a new genre or style and decide it’s not for you, you’ll still have learned something in the process.
You could experiment with:
- Writing in a different genre. Perhaps you’ve only written speculative fiction so far, but you’d like to try your hand at romance … or vice versa.
- Writing in a different style . Maybe you love fast-moving action, but you want to have a go writing something much more slow-paced, centering on a character’s thoughts and emotions.
- Writing using a different viewpoint and/or tense . If you normally use, say, third-person past tense, you could switch to first-person present tense.
- Using a different structure. If all your stories so far have involved a single first-person narrator, how about splitting your narrative between two narrators?
Short stories are a great place to try something new. I particularly like short story competitions for this: using an unusual style or format for your piece can help you stand out, and even if your experiment doesn’t quite work, you’ve only committed a relatively small amount of writing time to it.
#4: Ask for Feedback on Your Writing
Receiving feedback on your writing is such an important way to develop as a writer … though I know how daunting it can be. The first time I read out a piece of my writing in front of a writers’ group, my knees were shaking.
Direct feedback on your work will help you to gain a better understanding of your craft, both on a big-picture and detailed level. You can get this kind of feedback within a writing workshop group or writers’ club , from a beta reader , or via a paid critique .
On the big picture level, you might get feedback about things like these:
- A character who readers find unsympathetic or who seems one-dimensional.
- Plot events that don’t quite hang together.
- Scenes where your pacing is too fast or too slow.
On a detailed level, beta readers and fellow writers can help with things like these:
- Overly wordy or clunky-sounding sentences.
- Using the same word too often (without intending to).
- Dialogue that doesn’t quite fit with your character’s voice (or your setting).
How can you take your next steps to grow as a writer—even if you feel stuck and scared?
This is such a common struggle that I wrote a short ebook about it called The Courageous Writer: How to Grow in Confidence and Nurture Your Creativity .
When I talk to writers, a lack of confidence is the one thing that helps many of them back from the growth and development they want to achieve.
One of the things I talk about in that ebook is breaking challenging (or scary!) writing tasks into small pieces.
Perhaps one of the ideas above, such as entering a short story competition sounds overwhelming right now.
Here’s how you could take little, manageable steps toward it:
- Look up a list of short story competitions you could enter (no commitment!)
- Choose one competition with a topic or structure that appeals to you.
- Spend 10 minutes using that competition idea as a brainstorming prompt. What ideas arise from it? What stories could you tell? (Again, no commitment!)
- Pick one story idea to develop further. What characters could come into the story? Is there a little snippet of dialogue or action already in your head? Write it down.
… and so on.
Step by step, you can build your way up to a finished story. Each small step might feel a bit daunting at first, but if any step feels too daunting, just break it down even more.
Soon, you’ll have reached a new milestone on your writing journey—and you’ll be ready to tackle the next one.
With each step along the way, you’ll grow as a writer and developing your skills.

Ali Luke writes at Aliventures.com about making the most of your writing time, with tips on staying focused, motivated, and on track. For practical ways to become more confident and creative, download her free mini-ebook The Courageous Writer: How to Grow in Confidence and Nurture Your Creativity .
Featured Photo by Daniel Öberg on Unsplash
Search Posts Here
Subscribe to my blog, similar posts.

Revealing Yourself: Divulging Personal Information in Your Writing
Today’s post is by Bailey Belmont. Deciding how much personal information to share in your writing is something that every…

Print on Demand–While You Wait, Here and Now
Imagine this future. You’ve ordered your double latte, and while you’re waiting for the barista to make your drink, you…

Juries: How They Work, How They’re Chosen, and What Lawyers Handle Them Best
Today’s guest post is by Karen A. Wyle: Want to write legal thrillers? Or put a courtroom scene in your…

Personal Coaching for Fiction Writers
NEW! Personal Coaching! Writing a novel is complex and requires a deep understanding of scene and novel structure. It always requires…

The ABCs of Becoming a Super-Productive Writer
Productivity is often considered evidence of success. A person who is productive appears organized, proficient in his craft or skill….

How to Finally Finish That Novel
Today’s guest post is by multipublished author and writing instructor Cathy Yardley: Are you a closet fiction writer? Have you…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
[related_books]
Next Steps for Your Manuscript

Free Amazon Email Course

Guest Blogging

Get your Free Ebook!
Subscribe to my email blasts to level up your writing and be notified of upcoming events and offers!
Review Cart

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Genre is a tool that is used by: Writers, to guide story and expectations. Critics, to categorize and analyze creative works. Publishers and Booksellers, to stock and market books to their target audiences. Readers, to find and read works that align with their aesthetic preferences.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It's about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional. 4. ... By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques. Different authors have unique voices and ...
Scripts: Hit the screen or the stage by writing scripts for film, television, theater, or video games. Beware: film is a director's medium, not a writer's medium, but movies have the potential to reach a non-reading audience. Storytelling: Storytelling is the most popular form of creative writing and is found in the realms of both fiction ...
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Read the blog and discover different Types of Creative Writing offering insights and examples to help you navigate the world of literary creativity. Explore various forms such as poetry, fiction, non-fiction, and scriptwriting. Discover how each style offers unique ways to express creativity, tell stories, and engage audiences.
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
The four primary genres of creative writing are fiction, creative non-fiction, poetry, and drama. Fiction: The fiction genre includes all works conceived primarily out of the writer's imagination. Although fiction may include some elements of reality (names of real-life towns or natural phenomena), it relies on make-believe events to drive ...
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
Literary techniques you develop with writing plays and screenplays can include satire, motif, dramatic irony, allusion, and diction. 5. Personal essays. Focusing on the author's life and experiences, a personal essay is a form of creative non-fiction that almost acts as an autobiography.
Genre Categories: Introducing the Story Grid Genre 5-Leaf Clover. The Story Grid Genre 5-Leaf Clover is the tool we use to define the genres of writing in our stories. Each of the five leaves helps us determine a different element of a story's experience. It helps to think of the five categories visually, so we present them as a five-leaf clover.
Type 3: Memoir. Although they might seem similar at first, memoirs and diaries are two different creative writing types. While diaries offer a log of events recorded at frequent intervals, memoirs allow the writer to select key moments and scenes that help shed light on the writer's life.
Creative writing is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics.Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to ...
On one side, some work may fit into one Genre. On the other hand, some may have different genres. There are three different types of writing genres that we will take a look at in this blog. We have separated writing genres like Professional Writing, Literary Writing, and, lastly, Academic Writing. If you're wondering which one is right for ...
Genres of Writing from Duke University - Offers guides for the many genres you may encounter while writing in college, including annotated bibliographies, creative writing, ethnography, summaries, academic email, cover letters, and personal statements. Critique Writing.
A Guide to 14 Literary Genres. Fiction refers to a story that comes from a writer's imagination, as opposed to one based strictly on fact or a true story. In the literary world, a work of fiction can refer to a short story, novella, and novel, which is the longest form of literary prose. Every work of fiction falls into a sub-genre, each with ...
Memoir. Memoir is perhaps the "flagship" of creative nonfiction, the sub-genre most familiar to those outside of literary and academic circles. Most human beings lead interesting lives filled with struggle, conflict, drama, decisions, turning points, etc.; but not all of these stories translate into successful memoir.
Free Resources for Writing Instruction. 3 Genres of Writing: Narrative, Creative Writing and Poetry. We have finally settled into another school year! Give yourself a pat on the back! Now that our routines are a bit more established, we can really dive in and start incorporating different genres of writing into our classrooms!
List of writing genres. Writing genres (more commonly known as literary genres) are categories that distinguish literature (including works of prose, poetry, drama, hybrid forms, etc.) based on some set of stylistic criteria. Sharing literary conventions, they typically consist of similarities in theme/topic, style, tropes, and storytelling ...
Stephen Minot: Three Genres 8/e: Back Cover Copy. Stephen Minot's Three Genres provides creative writers with a solid foundation to understand the worlds of fiction, nonfiction, poetry, and drama. Chock full of expert advice and complete works as examples, this text is the ultimate guide for creative writers everywhere.
Three Genres gives students a basic introduction to fiction/ literary nonfiction, poetry, and drama and helps them to develop their creative skills in each area. Each genre section is self-contained and includes complete works as examples along with helpful advice about how to draw on the variety of techniques they use.
From an initial cohort of 12 students and three creative writing professors, ODU's MFA Creative Writing Program has grown to anywhere between 25 to 33 talented students per year. ... Our themed studio workshops are now offered as hybrid/cross genre experiences. My colleagues teach workshops in horror, speculative and experimental fiction ...
Three Genres gives students a basic introduction to fiction/ literary nonfiction, poetry, and drama and helps them to develop their creative skills in each area. Each genre section is self-contained and includes complete works as examples along with helpful advice about how to draw on the variety of techniques they use.
Here are some wonderful ways to nurture your creative growth and development as a writer. #1: Create a Physical Space for Your Writing. Just like anything important to you, your writing needs space within your life. ... #3: Try Out a New Genre or Style of Writing. If you've been writing consistently, perhaps for years, you may feel that you ...