

How to Install SCCM Reporting Services Point | ConfigMgr SSRS

This article is a step-by-step guide to install SCCM reporting services point role. I will show you how to install and configure the ConfigMgr SSRS reporting services point and enable reports.
To access reports in Configuration Manager, you need a reporting services point. When you run the reports in ConfigMgr, the Reporting Services connects to the Configuration Manager site database to retrieve data that is returned when you run reports.
If you are thinking of how do I enable reporting in SCCM, it involves a series of steps before you can use the reports in Configuration Manager. This guide shows every step that you require to install and configure reports in SCCM.
Like SCCM log files , there are many reports that come preinstalled with ConfigMgr. Configuration Manager supplies 470+ built-in reports, covering many of the reporting tasks that you might want to do. You can also use the SQL statements in these reports to help you write your own reports.
If you are looking to repair SSRS or reinstall the reporting services point, refer to the following guide on SCCM reinstall reporting services point .
What is Reporting in SCCM?
Reporting in Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager provides a set of tools and resources that help you use the advanced reporting capabilities of SQL Server Reporting Services. SCCM Reporting helps you gather, organize, and present information about users, hardware and software inventory, software updates, applications, site status, and other Configuration Manager operations in your organization.
Reporting provides you with a number of predefined reports that you can use as is or modify to meet your needs, as well as the ability to create custom reports. Configuration Manager includes over 450 report definitions in over 50 report folders, which are copied to the root report folder in SQL Server Reporting Services during the reporting services point installation process.
The reports are organized in subfolders based on the report category and displayed in the Configuration Manager console. Reports are not propagated up or down the Configuration Manager hierarchy; they run only against the database of the site in which they are created.
You can run the reports in Configuration Manager console by using Report Viewer , or you can run reports from a browser by using Report Manager. To run reports in the Configuration Manager console, you must have the Read right for the Site permission and the permissions configured for specific objects. The user account will need Modify right for the Site permission to modify the reports.
What is Reporting Services Point in SCCM?
SCCM’s reporting services point connects with SSRS in order to copy SCCM reports to a defined report folder. SCCM will establish the general and security settings for the reporting service. When you run reports, Reporting Services connects to the SCCM site DB to retrieve the returned data.
A Reporting Services Point role can be installed on a central administration site, primary sites, and on multiple site systems at a site and at other sites in the hierarchy. The reporting services point is not supported on Configuration Manager secondary sites .
By definition, the reporting services point is a site system role that is installed on a server that is running Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services. The reporting services point performs the following tasks:
- Reporting Services receives a copy of the Configuration Manager report definitions.
- Report folders are created depending on report categories.
- Configures the security policy for report folders and reports. These policies are based on Configuration Manager administrative users’ role-based rights. If you alter the security policy, the reporting services point connects to Reporting Services every 10 minutes to reapply it.
Prerequisites for Reporting Services Point
When you plan to install the reporting services point role in SCCM, the following prerequisites are required.
- .NET Framework for the Reporting Services Point. Use .NET Framework 4.8 and above.
- SQL Server Reporting Services for RSP
- SQL Server Native Client for the Reporting Services Point
- SQL Server 2017, SQL Server 2022 or later.
SQL Server Installation for Configuration Manager
One of the prerequisites for installing the Configuration Manager is SQL Server. The Configuration Manager stores its entire data in a dedicated database on SQL server. Each Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager site requires a supported SQL Server version and configuration to host the site database. Hence, you must install the supported SQL Server version for Configuration Manager .
The latest versions of Configuration Manager current branch support SQL Server 2017, SQL Server 2019 and later. You can install any of these versions of SQL Server for Configuration Manager. This guide assumes that you have already installed SQL Server for ConfigMgr. If you are planning to install the SQL Server for SCCM, refer to the following guides:
- Install SQL Server 2017 for Configuration Manager
- Install SQL Server 2019 for SCCM | ConfigMgr
- Upgrade SQL Server 2014 to SQL Server 2017
Create SSRS Connection Account
When you install SCCM reporting services point, you use a dedicated account which is nothing but the SSRS connection account. When you create this account in AD, provide it NO further domain access. Please do not make it a domain administrator. All it requires are regular, low rights. Make it a local administrator on SQL Server or the SSRS server at all costs. SCCM handles granting the rights required by SQL Server and SSRS.
Download SQL Server Reporting Services for SCCM
You can download the latest version of SQL Server Reporting Services from the Microsoft Download center . Older versions of SQL Server would install the SQL server and the reporting services. However, with SQL Server version 2017 and later, you must download the SSRS installer separately and install it.
Install SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)
SQL Server Reporting Services is a server-based reporting platform that provides comprehensive reporting functionality. Reporting Services offers the following features:
- Paginated reports optimized for document generation and printing.
- Mobile reports optimized for mobile devices, with responsive layout that adapts to different devices and the different ways you hold them.
- A modern web portal you can view in any modern web browser.
To install SSRS for SCCM, you will require the .NET Framework 4.7 or later and SQL Server Database Engine (2012 SP4 or later) , to store the report server database.
In this example, I will be installing SQL Server 2019 Reporting Services for Configuration Manager. Run the SQLServerReportingServices.msi installer to start the installation.
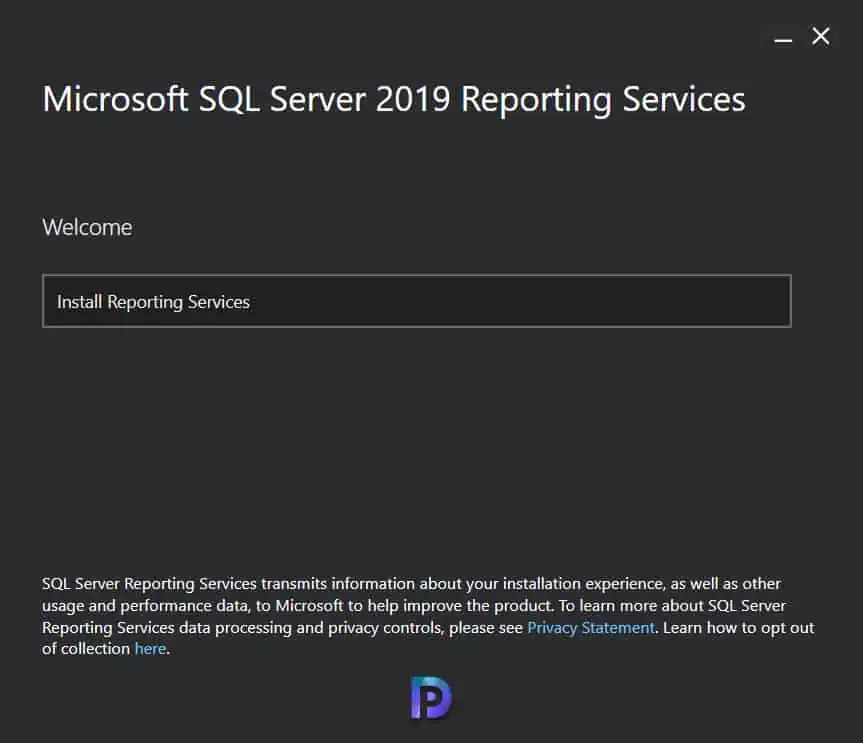
On the Choose an edition to install scree, there are two options:
- Choose a free edition – Evaluation (180 days), Developer, Express.
- Enter the product key.
Select the second option and enter the product key for SQL Server Reporting Services.
Tip : When you install the SQL server for Configuration Manager, the product key is displayed on one of the initial setup screens. You must use the same key while installing the SSRS.
Click Next .
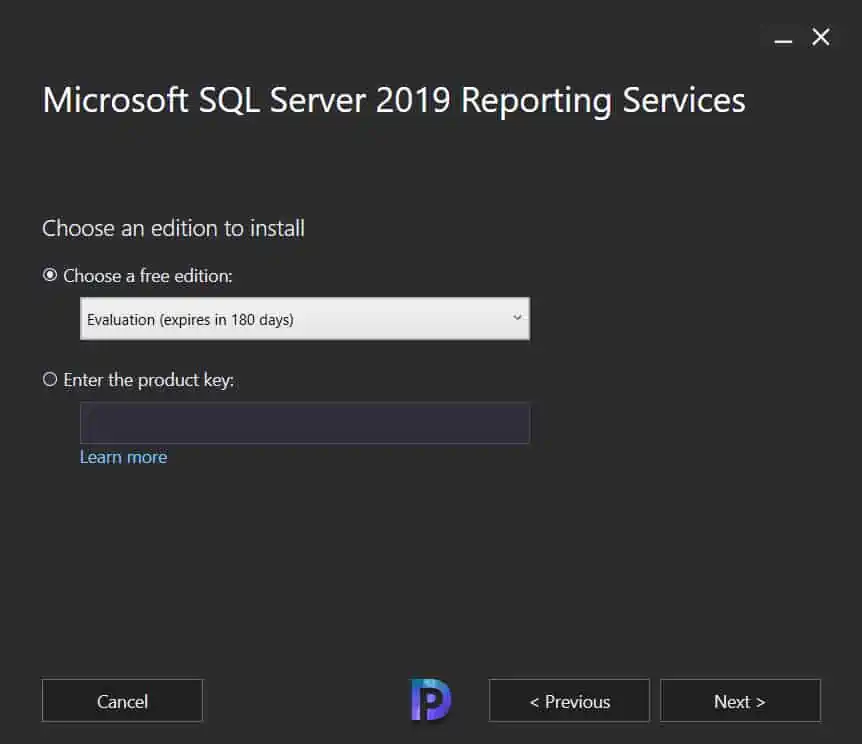
Click I accept the license terms and then click Next .
As mentioned earlier, you’ll need an instance of SQL Server Database engine to store the report server database. This option was enabled during the SQL Server installation. Select Install Reporting Services only and click Next .
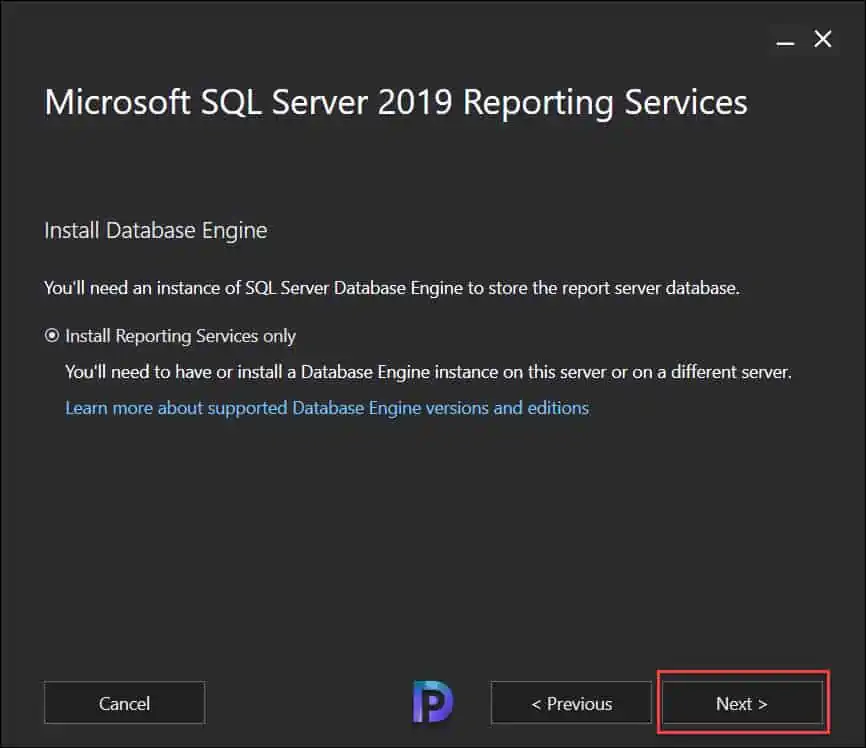
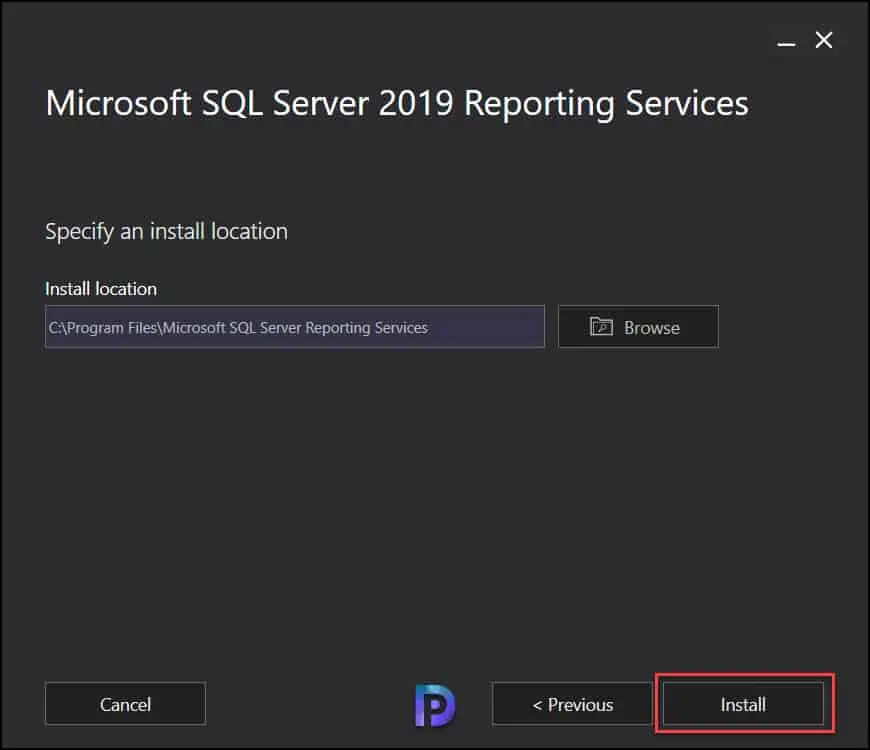
I am going to leave the install location to default, click Install . This begins the installation of Reporting Services. In the next section, we will look at the steps to configure the reporting services.
To launch the SQL Server Reporting Services, click Start and type “ Report Server “. From the list of search results, click “ Report Server Configuration Manager.”
Configure Reporting Server Configuration Manager
In this step, we will configure the reporting services for Configuration Manager. In the completion window of SQL Server 2019 Reporting Services, select Configure manually and customize settings and click Configure Report Server .
In the Report Server Configuration Manager window, select the report server instance as SSRS and click Connect .
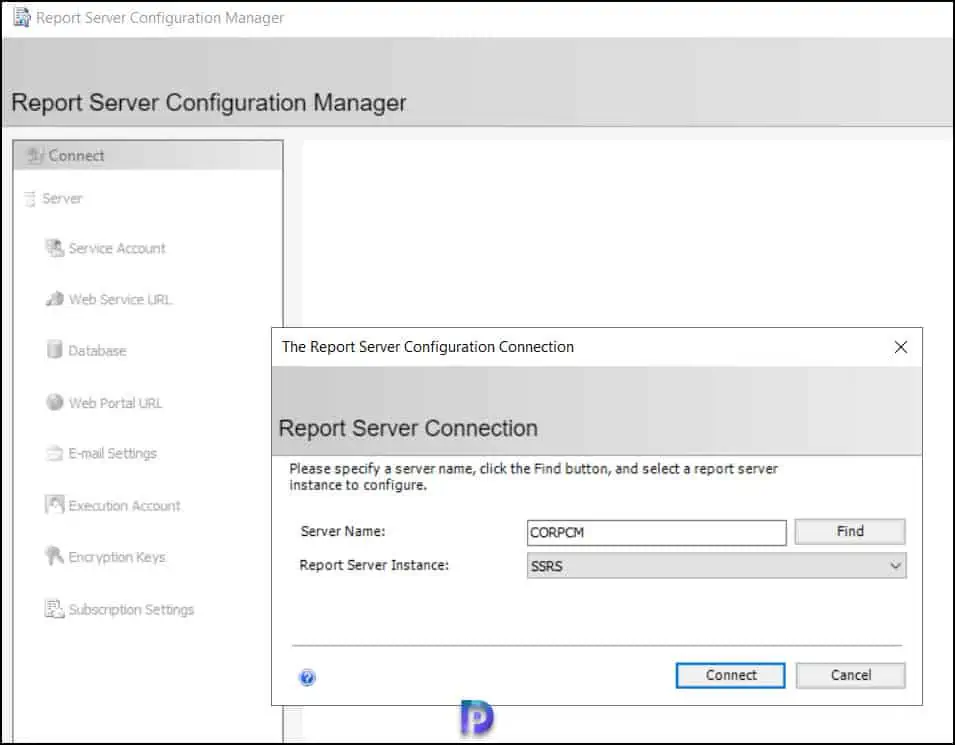
Select the Database tab and here we see the current report server database is empty. This means there is a report server database that has been created before. To create a new report server database for SCCM, select Change Database .
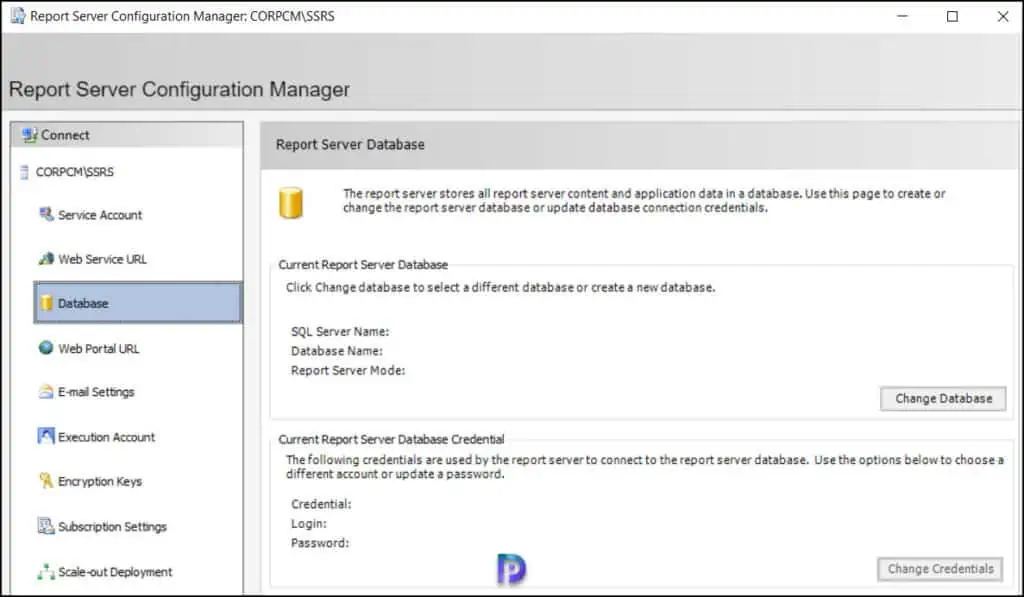
On the Action window, select Create a new report server database . Click Next .
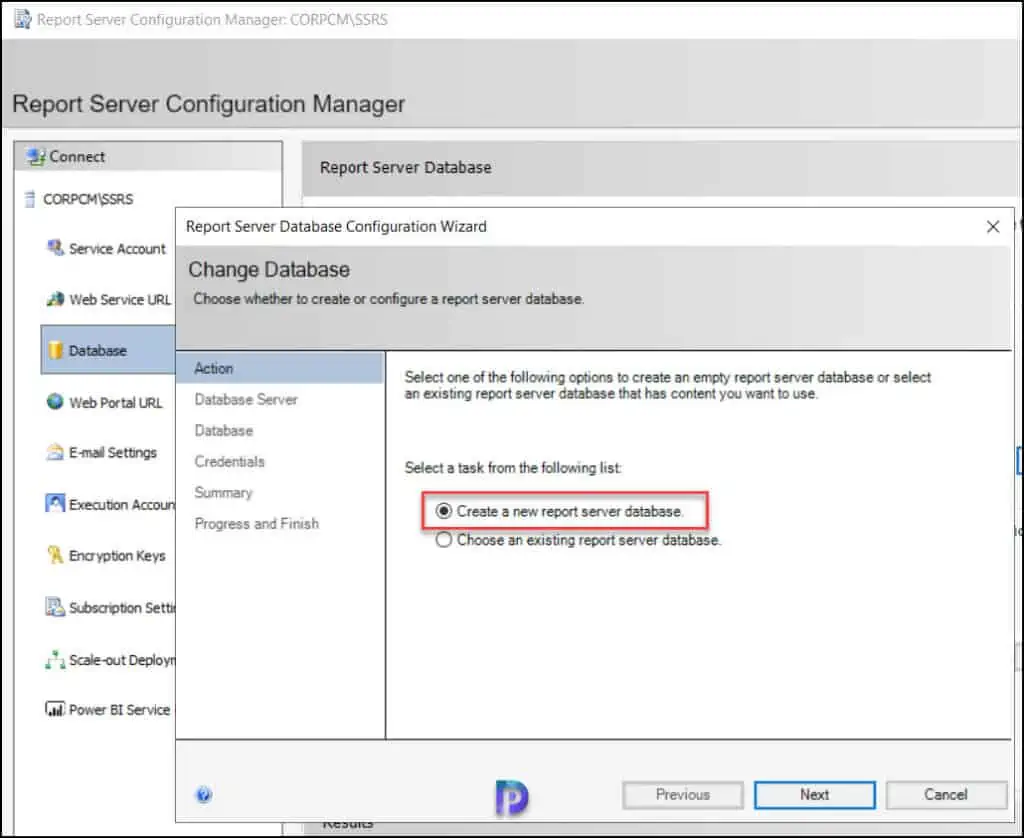
Test the credentials that you use to connect to the database server. If you see “ Test connection succeeded “, it means the credentials are valid, and you can proceed.
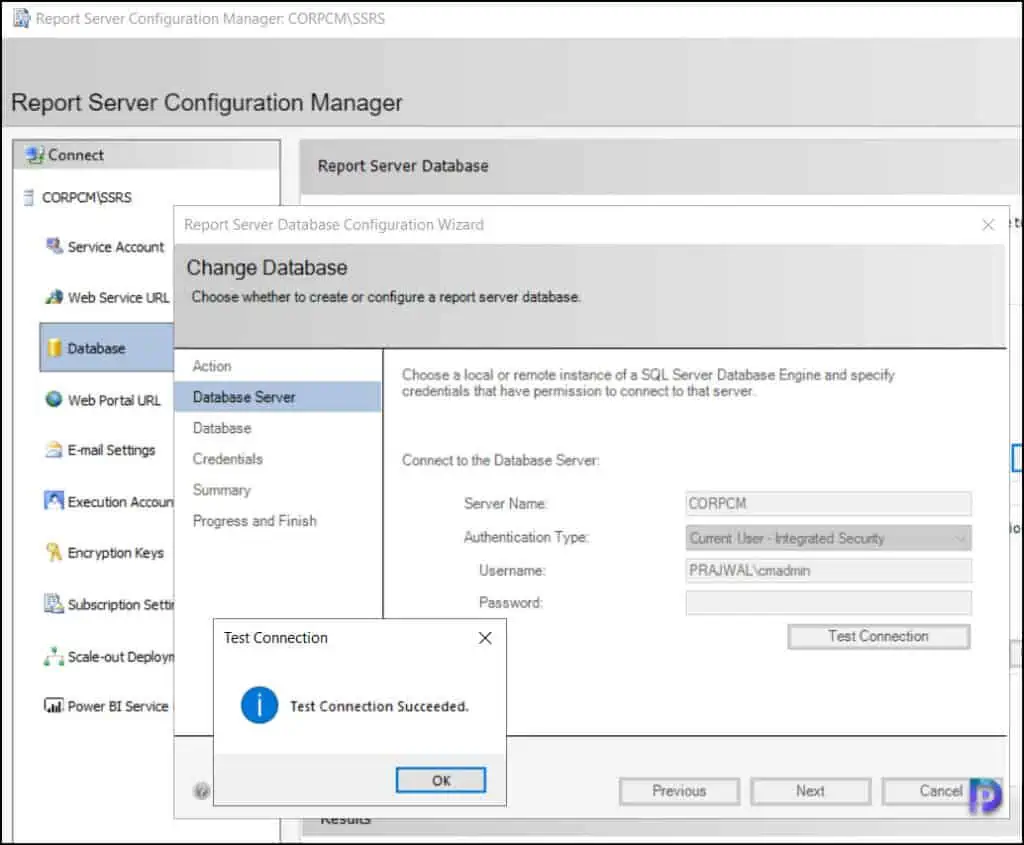
On the Database page of the Report Server Database configuration wizard, choose the Database Name , which is by default set as ReportServer . Select the database language, for example, English (United States) . The report server mode is set to native, which works fine for Configuration Manager. Click Next .
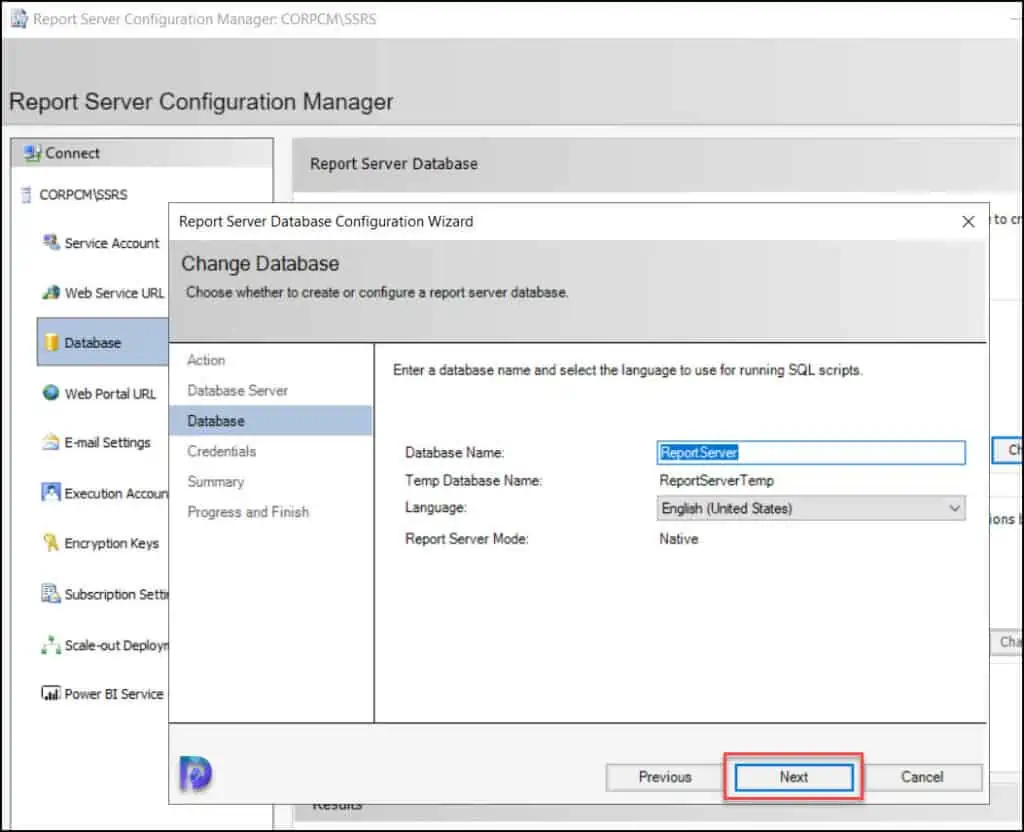
Specify the credentials of an existing account that the report server will use to connect to the report server database. Permission to access the report server database will be automatically granted to the account you specify. Select the Authentication type as Windows Credentials and specify the account name and password. Click Next .
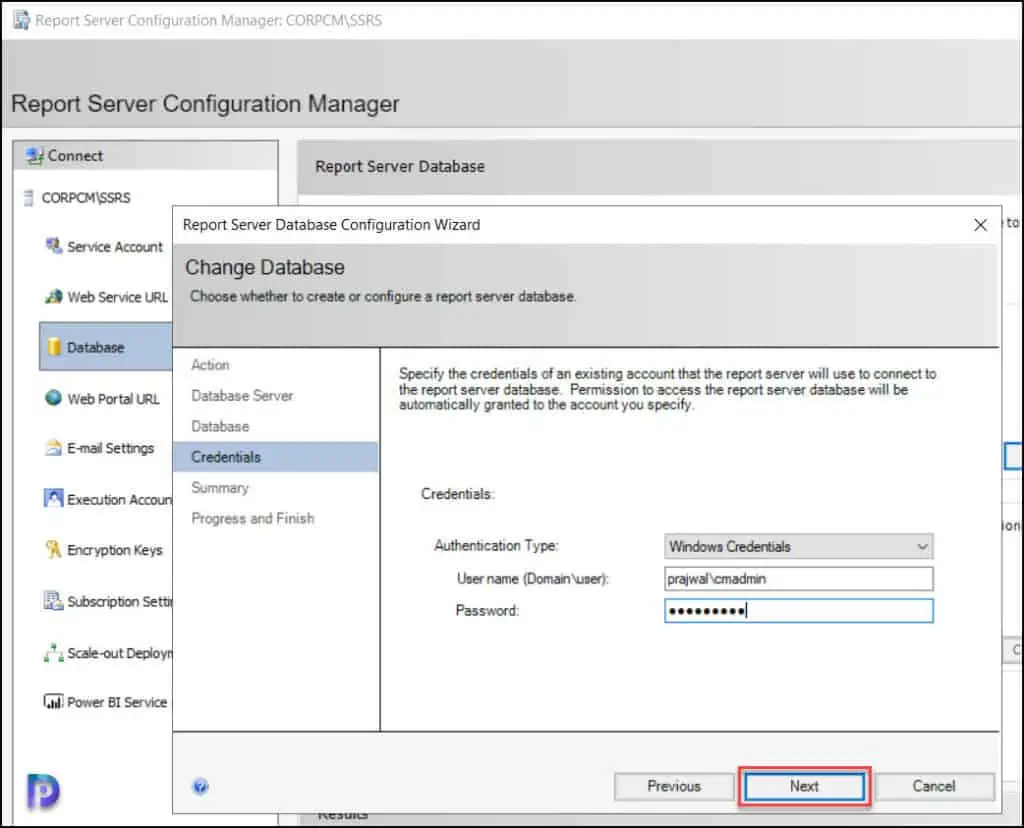
This begins the report server database creation now, and on the Progress and Finish page, ensure all the steps show as Success . Click Finish to close the report server database configuration wizard.
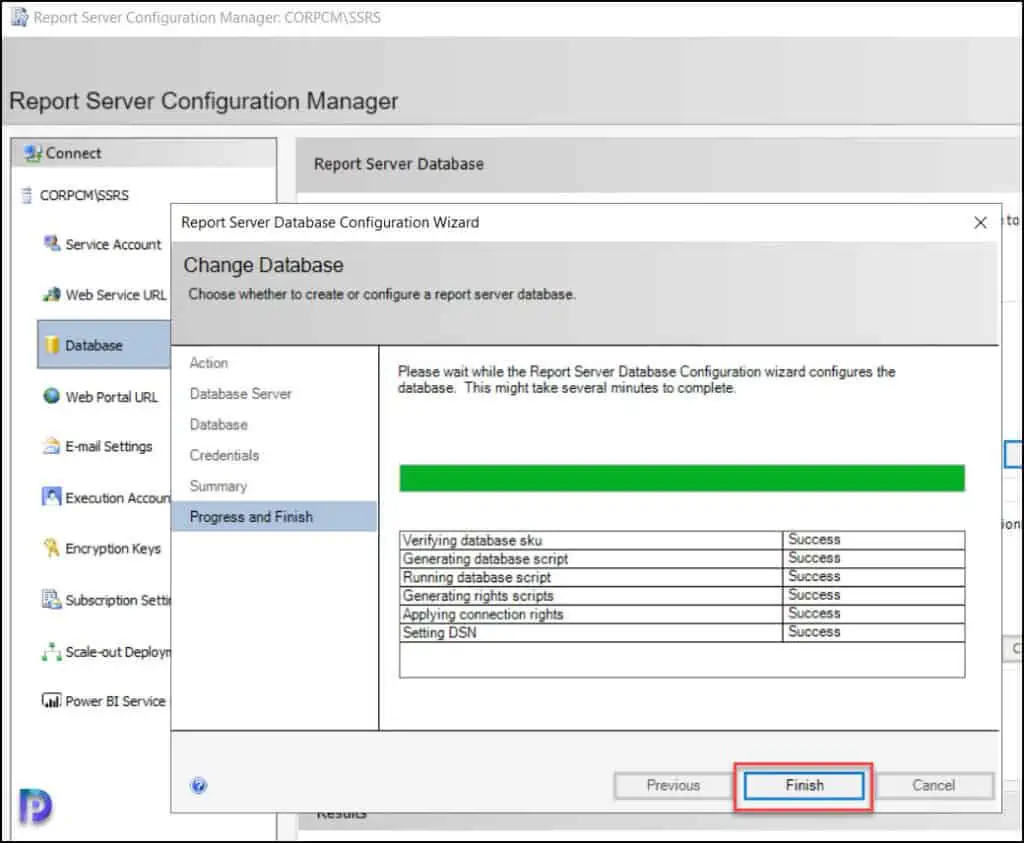
On the Database tab, we see the tasks have been completed successfully. If you don’t see them, you can click on the “ Apply ” button.
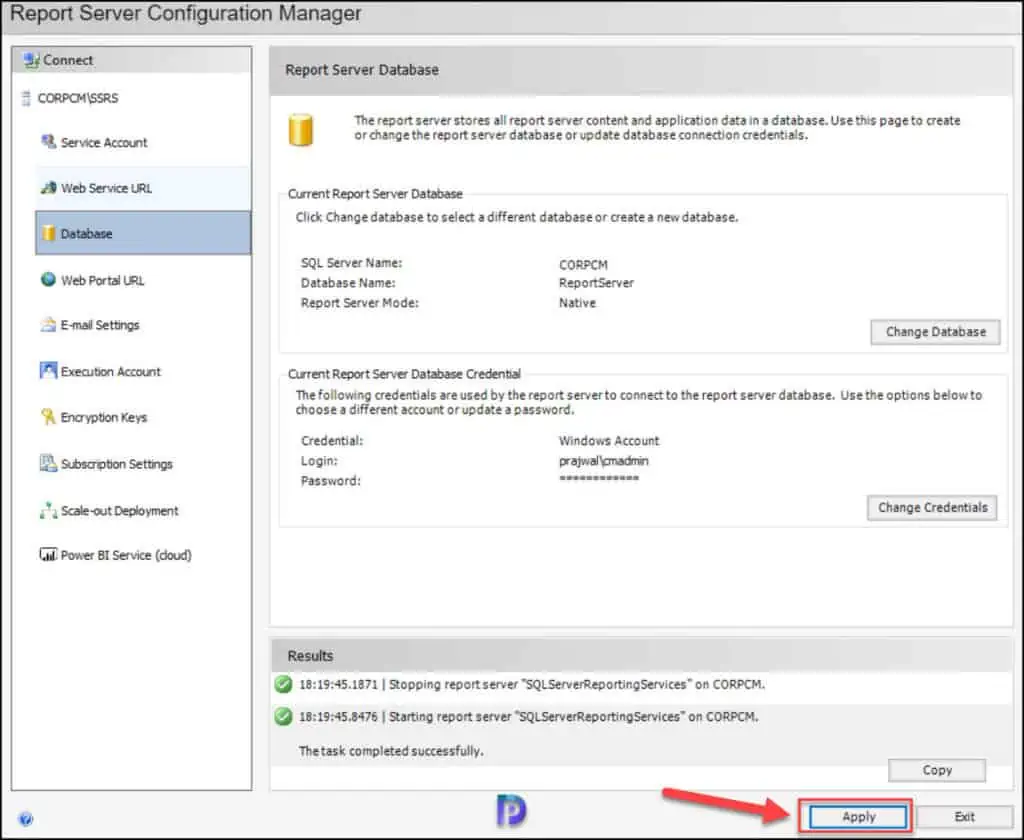
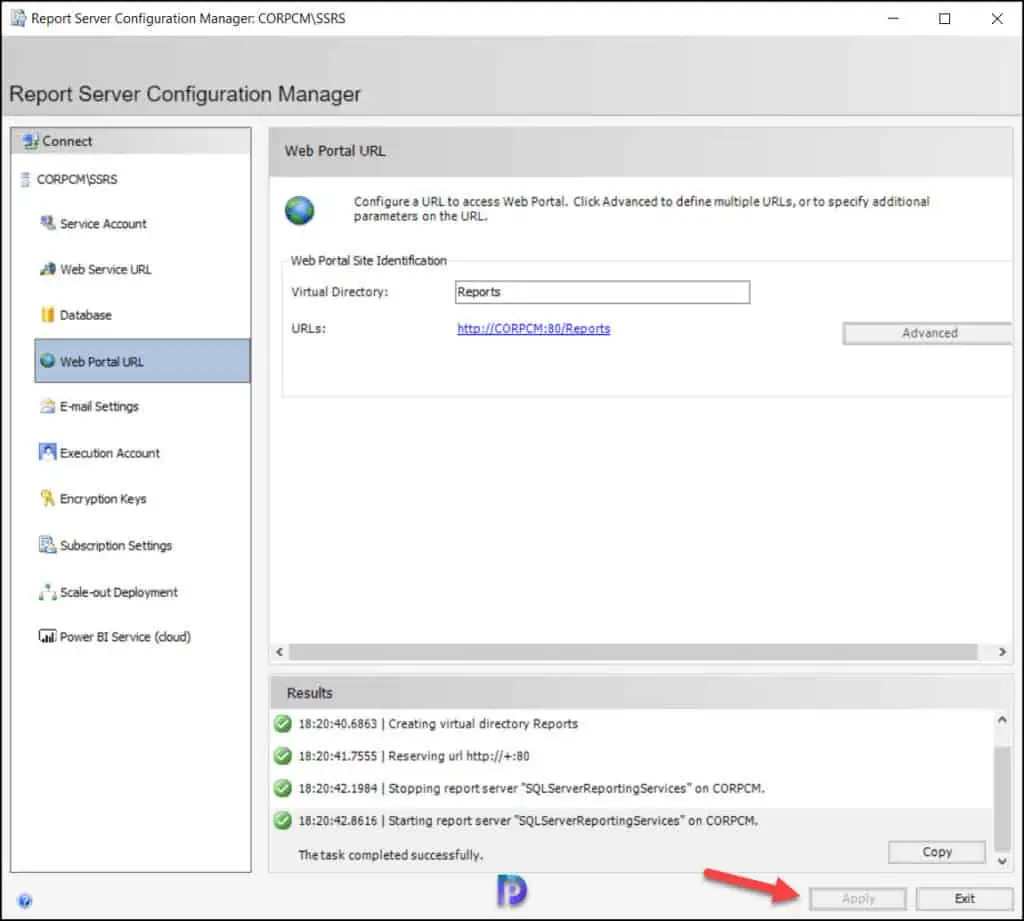
Configure the Web Service URL and Web Portal URL
In this step, we will configure a URL that is used to access the Report Server. You can define multiple URLs for a single report server instance and even specify additional parameters on the URL.
In the Report Server Configuration Manager tool, select the Web Server URL tab, and at the bottom, click the Apply button. This will configure the web service URL for reports.
Similarly, click the Web portal URL and click Apply . This will configure a dedicated URL to access the web portal. Click the Exit button to close the report server configuration manager wizard.
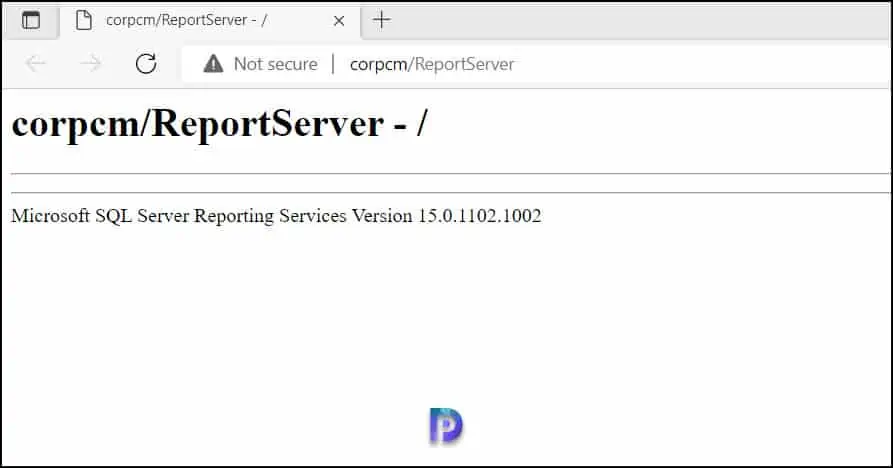
On the Web Service URL page , click the URL in Report Service Web Service URLs to test the connection to the report folder. The Windows Security dialog box might open and prompt you for security credentials. By default, your user account is displayed. Enter your password and click OK . Verify that the webpage opens successfully. Close the browser window.
At this point, no Configuration Manager reports are visible because we are yet to install SCCM reporting services point role. Once you install the reporting services point role, the reports will be visible in Configuration Manager console and web URL.
Install SCCM Reporting Services Point Role | ConfigMgr
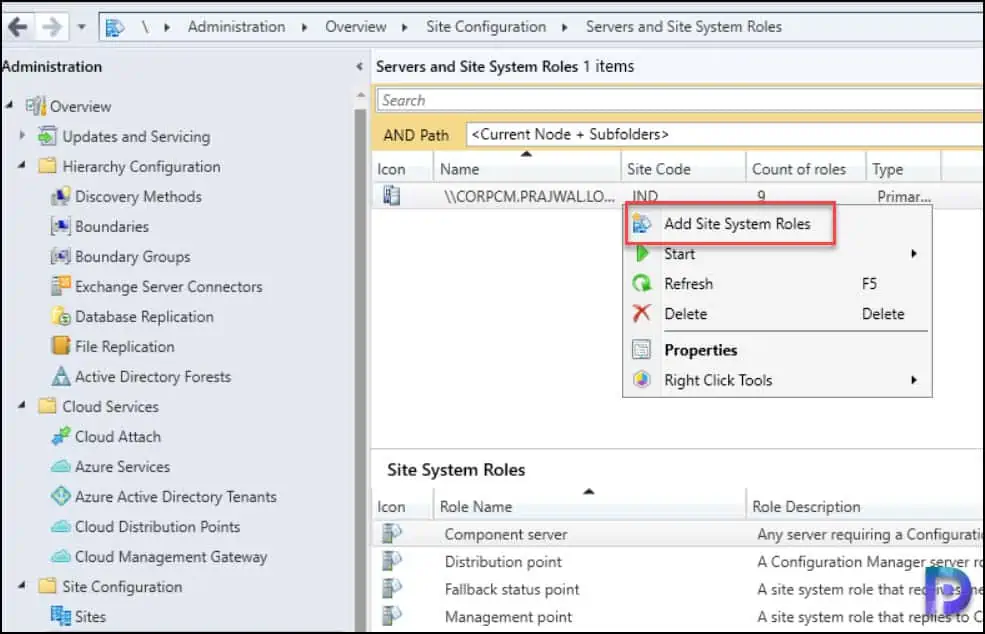
Follow the below steps to install a new reporting services point role using SCCM console:
- Launch the SCCM console.
- Click Administration > Site Configuration . Right click Servers and Site System Roles .
- Right-click SQL Server on which you plan to install reporting services point role and select Add Site System Roles .
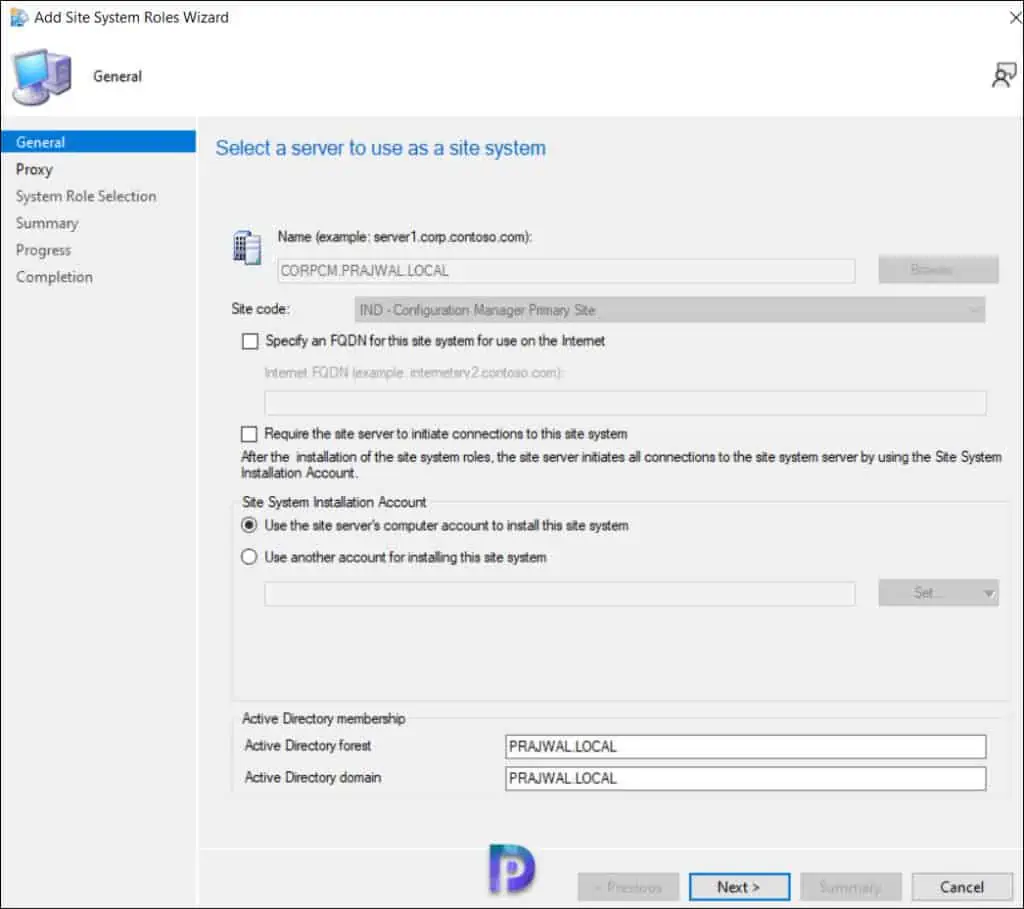
On the General window of Add Site System Roles wizard , you have two options for specifying the site system installation account.
- Use the site servers computer account to install this site system : Select this option to install the site system if both the site server and site system servers are in the same domain. Furthermore, the site server account should be added to the local administrators group on the remote site system server.
- Use another account for installing this site system : Use this option if the site server and site system servers are in a different domain and there is no two-way trust.
Typically, the first option is preferred in most cases while deploying the reporting services point role in an organization. Verify the Active Directory Forest and Active Directory Domain names and click Next .
If your organization uses Internet Proxy server, specify it on the Proxy page otherwise click Next .

On the System Role Selection page, from the list of roles, select Reporting Services Point and click Next .
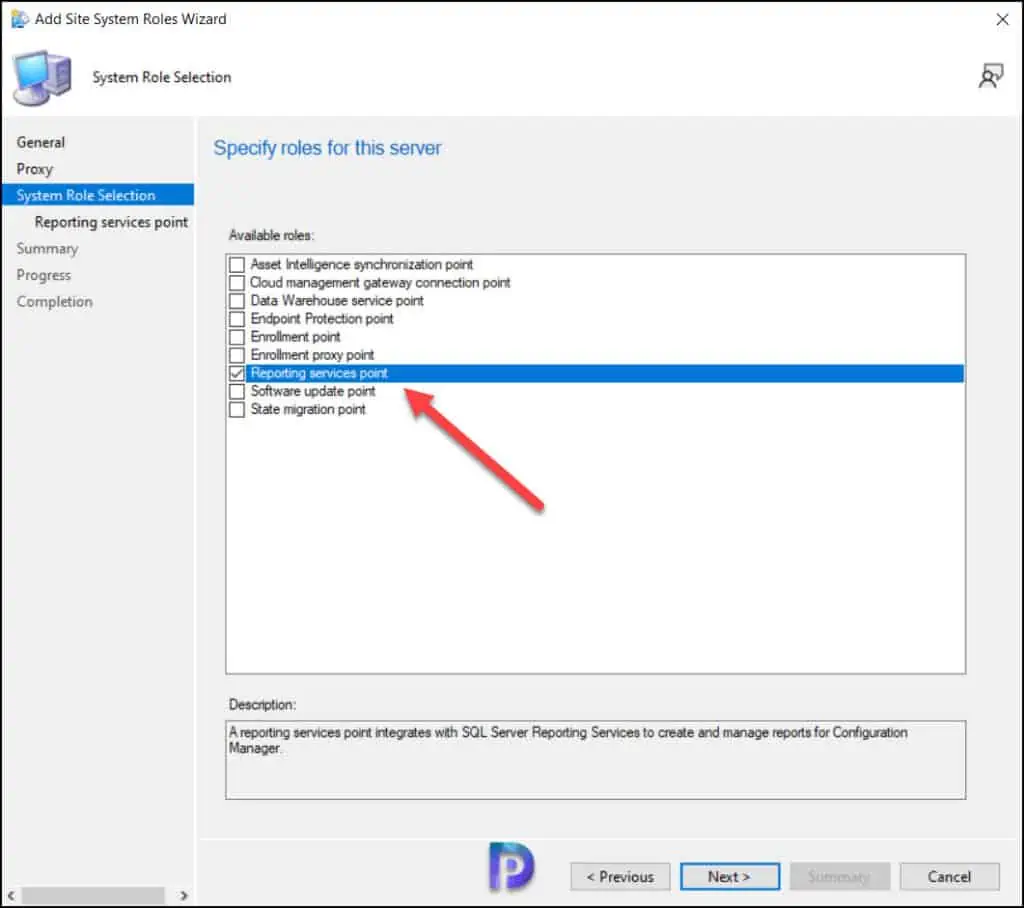
On the Reporting Services point page, you configure the settings for Reporting Services. This step is critical because the majority of errors such as reporting services server instance blank, is observed here.
If you have installed and configured the reporting services correctly and if the report server database is successfully created, this step should be easy for you. Ideally, the Reporting Services server instance should be automatically populated to SSRS. If the reporting services server instance is blank, you might need to verify the account permissions and perform additional troubleshooting steps .
In the below example, we see the Site Database server name, Database name, Folder Name, and Reporting services server instance are automatically populated.
Specify the credentials that SQL Reporting Services will use when connecting to the Configuration Manager site database and click on Verify . The pop-up window “ Successfully Verified ” confirms the reporting services point account permissions are correct. Click Next .
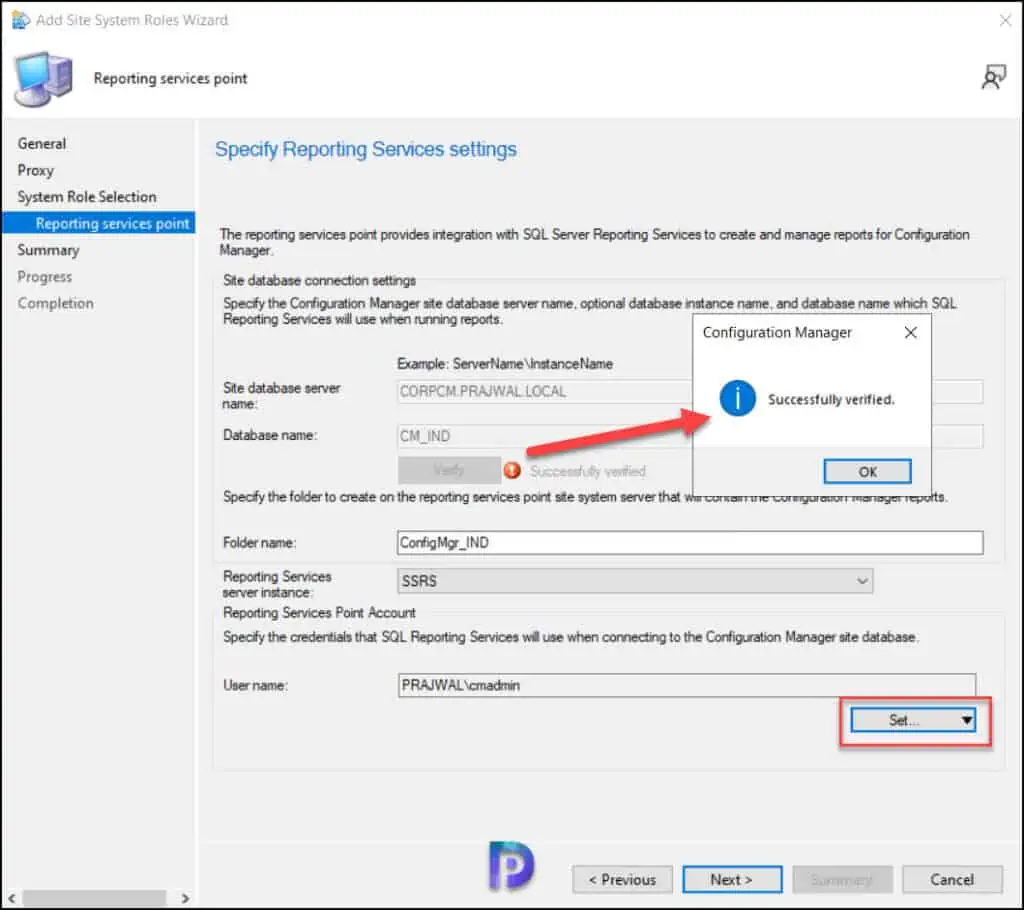
Review the reporting services point role configuration on Summary page and click Next . On the Completion window, click Close . This completes the reporting services point sccm installation steps.
SCCM Reporting Services Point Log Files
When you install a new reporting services point for SCCM, you can use the following log files to troubleshoot the SSRS installation errors. The log files are located in C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\Logs .
The following table lists the Configuration Manager log files that contain information related to reporting services point in SCCM.
Take a look at the full list of all the important Configuration Manager log files and their locations .
Verify Reporting Services Point Role Installation
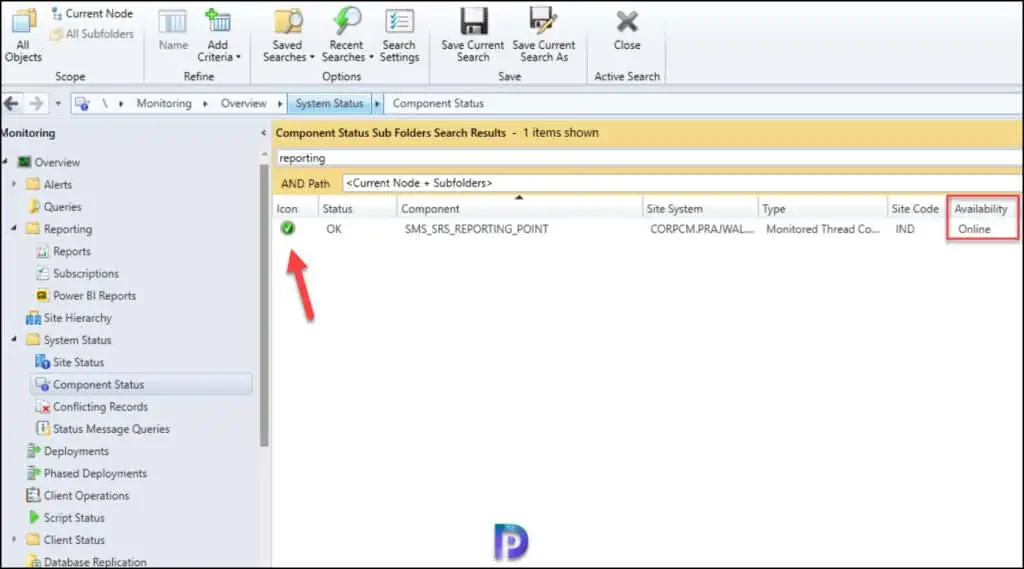
To verify that the Reporting Services point role has been installed, launch the SCCM console, click on Monitoring , expand System Sta tus , select Component Status, and look for SMS_SRS_REPORTING_POINT .
From the below screenshot, we see the SMS_SRS_REPORTING_POINT component is online. The green icon indicates the reporting point is healthy and there are no errors.
Let’s review the log file named srsrp.log and find out . The log file srsrp.log is located on the site server in the following path: C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\Logs .
The below two lines from the srsrp.log file confirm the successful installation of ConfigMgr SSRS reporting services point.
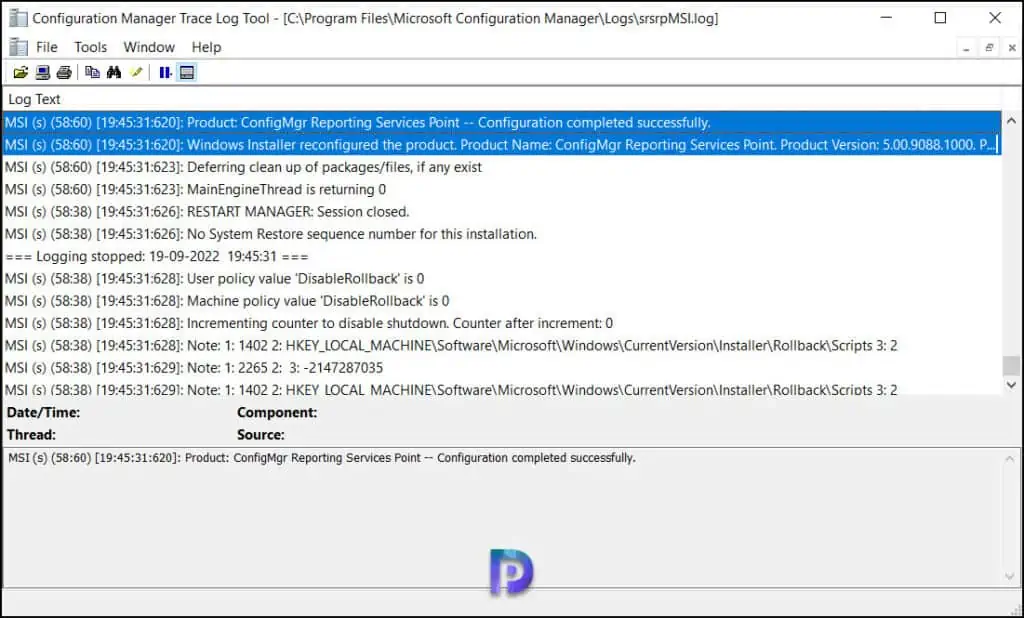
In the srsrp.log file, we see the Configuration Manager reports are deployed successfully. Each of these reports are created in a separate folder. Learn how to add SCCM Reports as favorites .
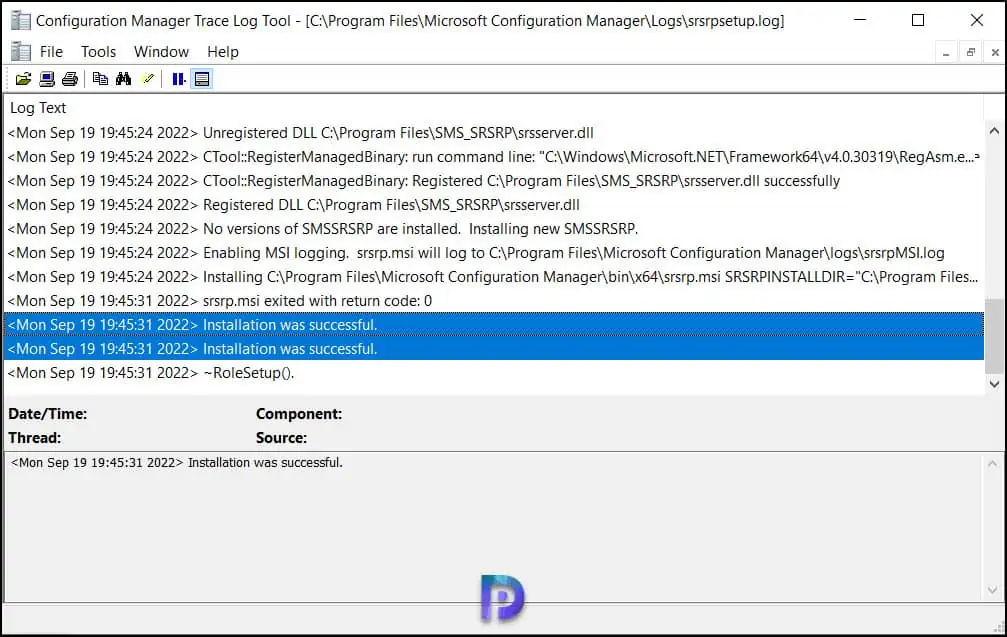
In the srsrpsetup.log , we see the ConfigMgr SSRS role installation was successful.
Please let us know if you found this article to be useful in the comments section below. Gratitude for reading!
Sign Up For Newsletter
Join our newsletter to stay updated and receive all the top articles published on the site get the latest articles delivered straight to your inbox..
Thank you for the instructions. The only question I still have is what server to install the Reporting Service Role. According to Microsoft, the Reporting Service Role CAN be installed on the CAS, Primary, AND other Site server in the MECM hierarchy. It doesn’t say …Primary OR other Site server, which makes me think it has to stay on our Primary Site server. We want to move the Reporting Service Role & SSRS to the SQL server. Is that acceptable, or must it remain on the Primary Site server?
Good afternoon, is there a way to reporting services on a separate server to that of the Config Manager DB?
Thanks for the post, a nice walkthrough.
Hi Prajwal,
I installed report services on my sccm server, and it works as usual except that the report account start to register Audit Failure log (4625) ASAP I added the service to SCCM, and every time i open SCCM console. I’m using WS2022, SQL 2019, SSRS 2019. I have few environment which has the same configuration, and there are no problem at all. Do you have any idea?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
PatchMyPC Sponsored AD

Recast Sponsored AD

Popular Articles

SCCM 2012 R2 Step by Step Guide

How To Deploy Software Updates Using SCCM ConfigMgr

How to Install WSUS for SCCM | SUP Role | ConfigMgr

Fix Skype for Business Recording Shows Pending Status
Recent articles.

Deploy Android Enterprise System Apps with Intune

How to Remove a device from your Microsoft account

Fix: A Requested Power Operation is Already in Progress

Manage Diagnostics Collection for Autopilot failure in Intune

Subscribe Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter to get our newest articles instantly!
- SQL Server training
- Write for us!

How to configure reporting services (SSRS) for Native mode
In SQL Server Reporting Services Native mode, a report server has a role of a standalone application server, that provides all viewing, processing, delivery, and management of reports and report models. This is the default mode for SSRS instances.
To set up SSRS Native mode on your local machine follow the instructions below:
First, go to the following location:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\<your MSRS>\Reporting Services\ReportServer\
Then find the file rsreportserver.config XML file and open it. In that file find the <AuthenticationTypes> section and ensure that <RSWindowsBasic/> element exists. If it doesn’t, add it manually and save the file.

Next, open Windows features , make sure Internet Information Services and Internet Information Services Hostable Web Core are turned on, click OK and wait for the changes to be applied.

Then open Computer Management , go to Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager and double click the Server Certificates option.

Once opened, a new menu will appear. Click the Create Self-Signed Certificate option in the Actions pane on the left.

Specify a friendly name for your certificate, select a certificate store for the new certificate, and click OK.

Afterwards it will be visible it in the list below:

Open Reporting Services Configuration Manager and connect to your Reporting Services Server instance.

Once connected select Web Service URL tab, change the SSL Certificate to the certificate you created in step 5 and click the Advanced button. If you are using Reporting Services Configuration Manager for SQL Server 2016 this option will be shown as HTTPS Certificate .

When that is clicked, a new menu will appear where you have to add a new SSL binding . Now click the Add button, like in the picture below.

Now add a IPv4 address with your created certificate and click OK.

And also add a IPv6 address with your certificate, by repeating step 9 and selecting the All IPv6 option.

After you’ve added both bindings, they should be visible in a grid below. Now click OK.

Now wait out certificate binding process and when it’s complete, you should get the following results.

Now select the Report Manager URL tab and click Advanced . If you are using Reporting Services Configuration Manager for SQL Server 2016 this tab will be visible as Web Portal URL .

Then, another menu will appear where you have to repeat step 10 and 11 to add SSL bindings and click OK.

Open a browser which supports SSRS Native service, as administrator and paste or click the second link from Report Manager URL tab. This could take a few minutes to load.

When the page is successfully loaded, click Folder Settings and another page will open.

Now, click the Edit option like in the picture below and then you will edit the role assignment options.

Check all desired roles which you want to assign to a group or a user and click the Apply button.

Now click New Role Assignment option.

Enter a new Group or user name , check all desired roles and click OK.

Now click the Site Settings link, on the upper right corner of the page, then go to the Security tab and repeat steps 18, 19, 20, and 21 (edit Admin user and check all roles, then create a New Role Assignment , create new user, check all roles and confirm).

Now you can open the link from step 16 or click the Home link and create or add your SSRS items to Native web service.

Once you have uploaded some SSRS items they will be visible in the filed below and you can manage them with the Details View option.

Troubleshooting:
If you are having trouble connecting to the SSRS Native service through the web browser because the message says that the service is unavailable, there are a few troubleshooting options, you should try:
Open your web browser with administrator privileges
Once the browser is open, click the Internet options setting.
Go to the Security tab, click Trusted sites and then click the Sites button like in the picture below:

Once the Sites button is clicked, paste the second link from Report Manager URL tab to the filed shown below and then click the Add button. Once that is set up, paste the link again to the browser press Enter.

Open Reporting Services Configuration Manager , go to the Encryption keys tab and click the Delete button for the Delete Encrypted Content option.

Go the server tab, stop the SSRS service and start it again. Then paste the link from the Report Manager URL again to the browser press Enter.

Useful resources
- Install Reporting Services native mode report server
- Verify a Reporting Services Installation
- Report Server Content Management (SSRS Native Mode)
- Recent Posts
- What is a SQL Server Data Dictionary and why would I want to create one? - December 26, 2016
- How to configure reporting services (SSRS) for Native mode - September 21, 2016
Related posts:
- What’s new in SQL Server 2016 Reporting Services (SSRS)
- What’s New in Reporting Services (SSRS) 2017
- How to create a SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) report
- Load testing for SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)
- How to administer SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) subscriptions using PowerShell
- Latest Articles
- Top Articles
- Posting/Update Guidelines
- Article Help Forum
- View Unanswered Questions
- View All Questions
- View C# questions
- View C++ questions
- View Javascript questions
- View Visual Basic questions
- View Python questions
- CodeProject.AI Server
- All Message Boards...
- Running a Business
- Sales / Marketing
- Collaboration / Beta Testing
- Work Issues
- Design and Architecture
- Artificial Intelligence
- Internet of Things
- ATL / WTL / STL
- Managed C++/CLI
- Objective-C and Swift
- System Admin
- Hosting and Servers
- Linux Programming
- .NET (Core and Framework)
- Visual Basic
- Web Development
- Site Bugs / Suggestions
- Spam and Abuse Watch
- Competitions
- The Insider Newsletter
- The Daily Build Newsletter
- Newsletter archive
- CodeProject Stuff
- Most Valuable Professionals
- The Lounge
- The CodeProject Blog
- Where I Am: Member Photos
- The Insider News
- The Weird & The Wonderful
- What is 'CodeProject'?
- General FAQ
- Ask a Question
- Bugs and Suggestions
Install and Configure SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)

What is SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)?
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) provides a set of on-premises tools and services that create, deploy, and manage reports. You can design reports using data, tables, graphs, charts, and images. You can easily deploy reports on the local or remote server.
Pre-requisites
- Microsoft SQL Server installed on the machine (please check my article to install SQL Server here ).
- Configure Named Pipe and TCP/IP Settings if your SQL Server Database Engine Instance is hosted on another machine (please check my article here ).
Install SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)
Let us install and configure SQL Server Reporting Services on the local machine.
Let us first download installation media for SSRS. To download compatible installation media, first run SQL Server Setup as shown in this article . Go to the Install SQL Server 2019 Developer Edition section of the article and follow steps 1 and 2. You will see the below screen. Now click on the Install SQL Server Reporting Services link and it will launch a download page for SSRS. Download installation media for SSRS report from that page.
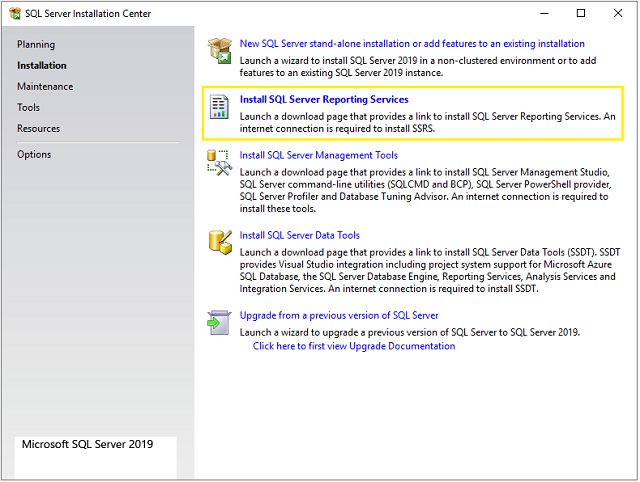
Now double click and run the downloaded installation media. You will see the below screen. Click on the Install Reporting Services button.
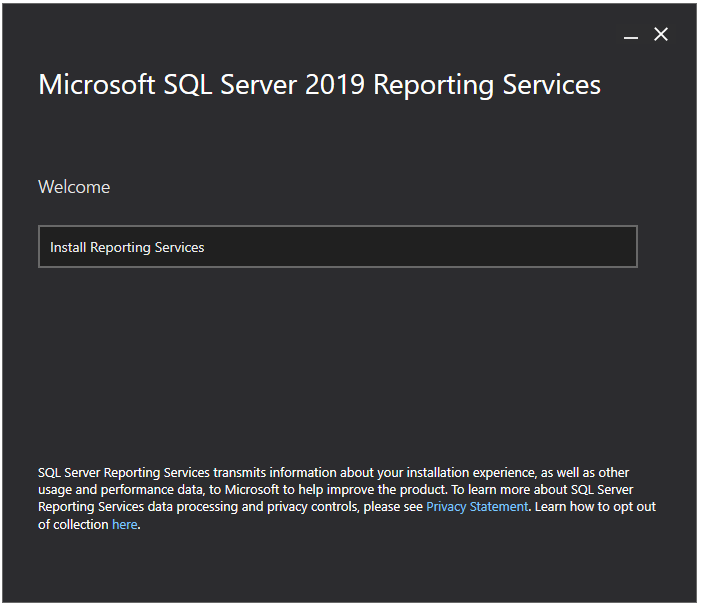
Next, you will see the below screen. Choose Express or Developer edition from Choose a free edition dropdown and click on the Next button.
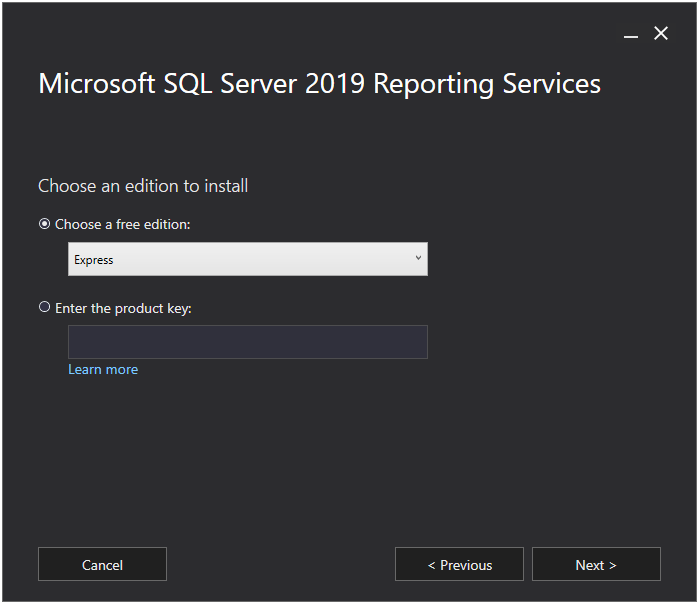
On the next screen, simply accept the license terms and click on the Next button.
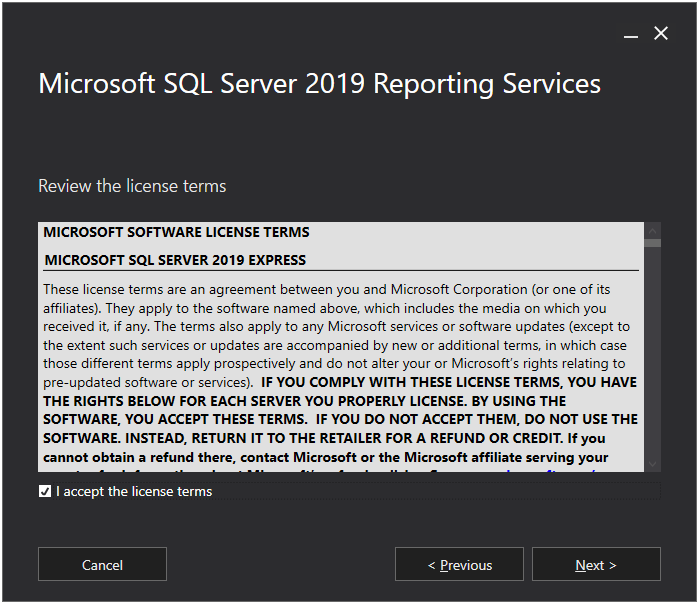
Now Install Reporting Services only option is already selected so just click on the Next button.
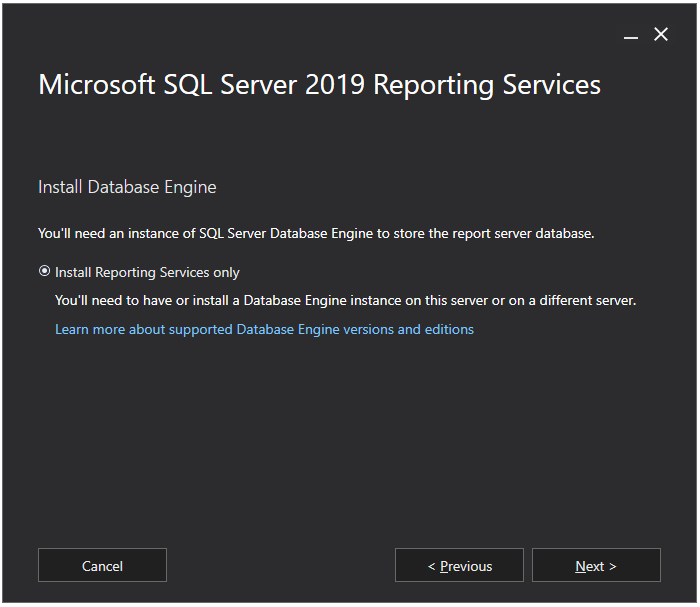
Choose the installation location of your choice. I will go with the default location. Click on the Install button.
It will start the installation of SSRS which will take some time.
Once the installation is finished, click on the Configure report server button, or if you want to install it later, simply click on the Close button.
Great! We have successfully installed SQL Server Reporting Services. I recommend restarting your machine before configuring it.
Configure SQL Server Reporting Services
Now that you have installed SQL Server Reporting Services, let us configure it.
Open Report Server Configuration Manager from the Start menu.

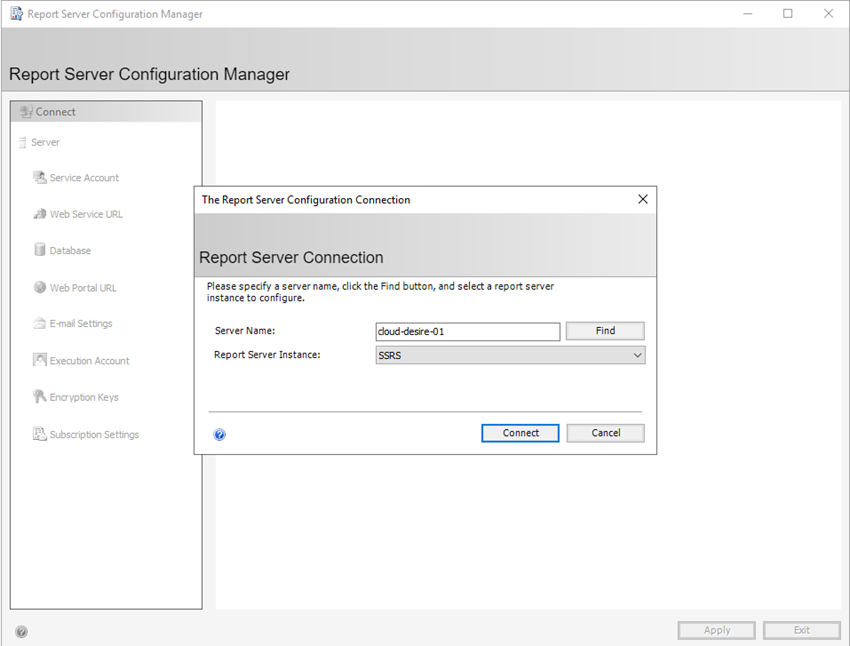
Next, you will see the configuration wizard. First, you need to connect an SQL server instance for which you want to configure SSRS. Select an instance and click on the Connect button.
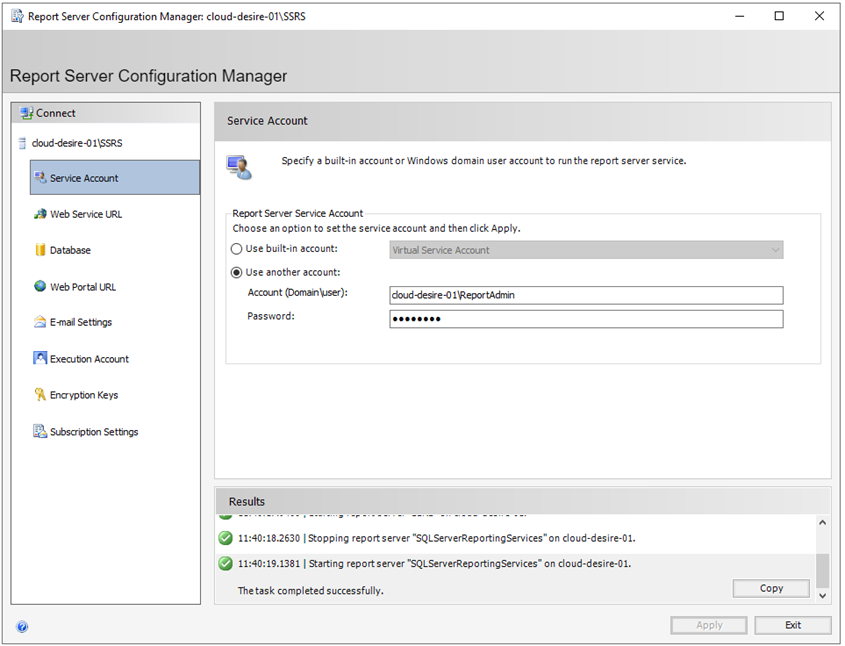
Next click on the Service Account tab from the left panel. You will see the service account configuration window. Specify windows account to run the report server service. I recommend creating a new dedicated user with administrator privileges for this. I have created one with the name ReportAdmin . Enter your account and password and click on Apply button. It will configure the service account.
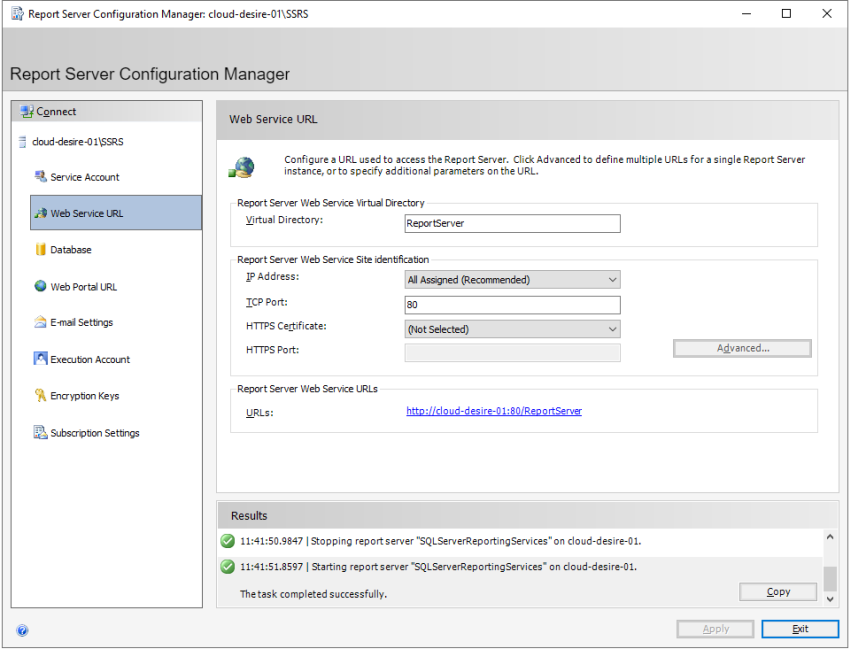
Next click on the Web Service URL tab from the left panel. Here, you can configure the report server URL. We will use this URL to deploy SSRS reports on the report server. You can also configure ports (80 or 443 (SSL)) on which the report server will host. It will preview URLs in the bottom section. I will go with default settings. Click on the Apply button and it will configure the report server web service URL.
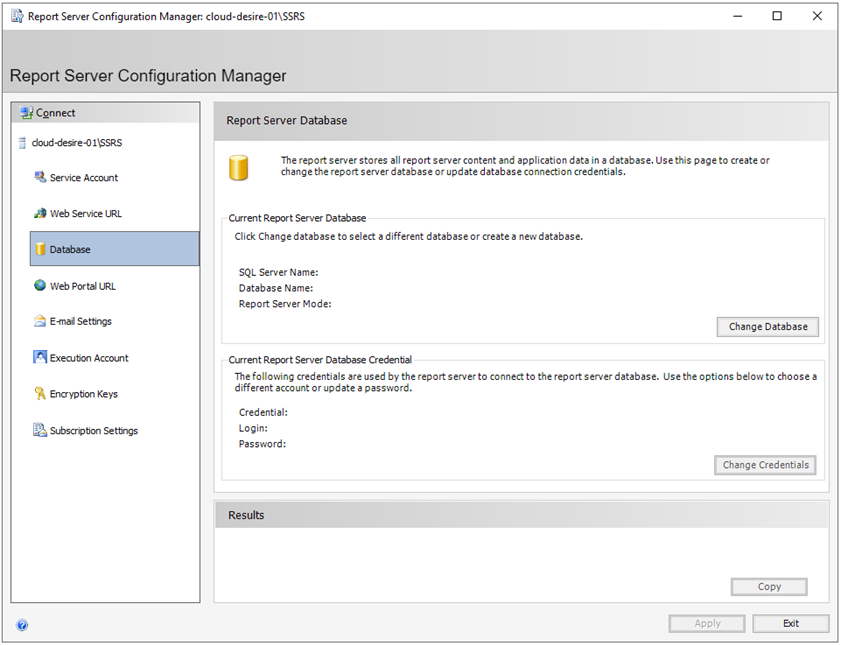
Next click on the Database tab from the left panel. Here, we will configure the database for the report server. Click on the Change Database button.
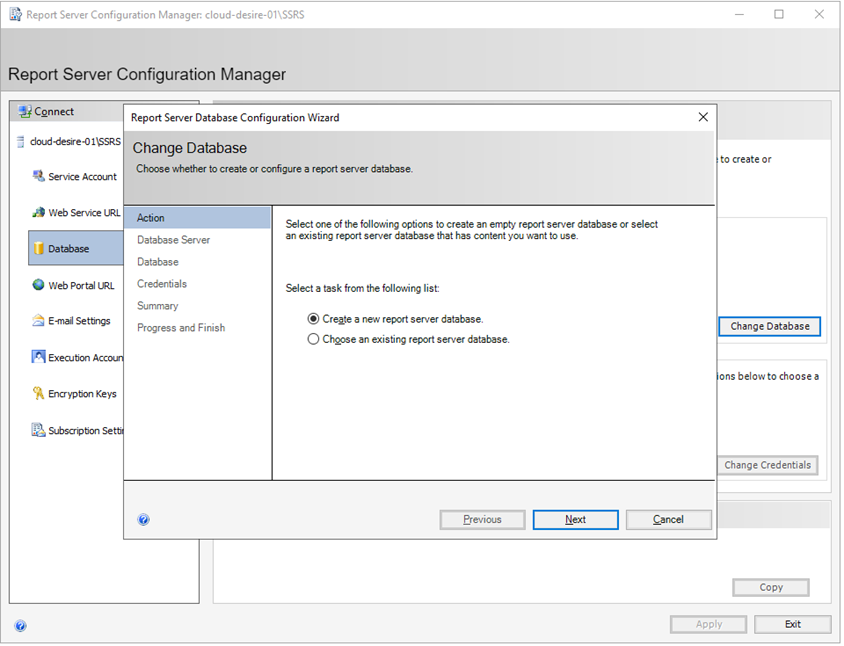
You will see Report Server Database Configuration Wizard . We are going to create a new database but if you have already an existing database for the report server, you can also configure it. For now, I will create a new report server database. Select the first option and click Next .
Now specify details to connect SQL Server Instance on which you want to create report server database. I will go with my local instance and use SQL Server Account authentication. Click the Test Connection button. If the connection is successful, click on Next .
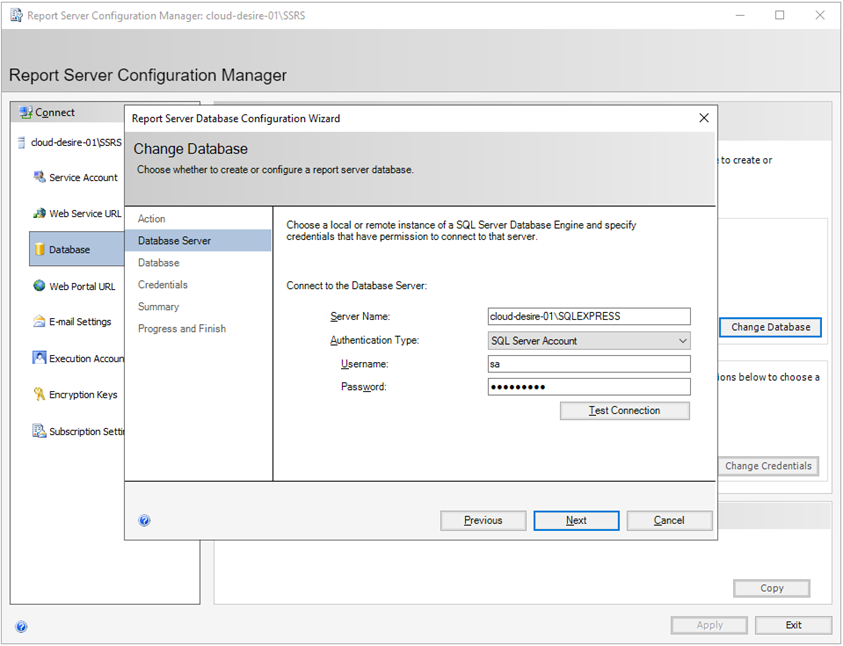
Now specify the database name and click Next .
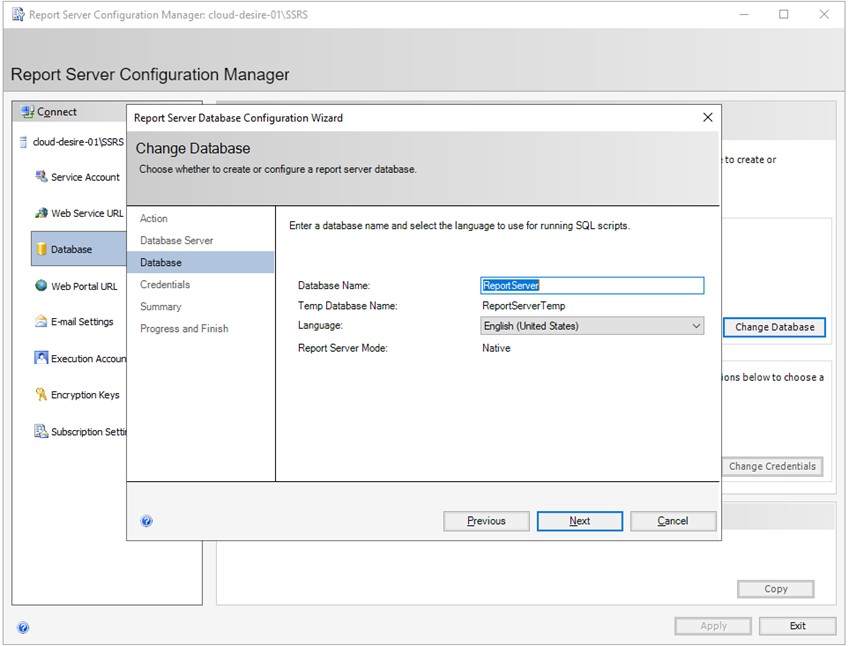
Now specify the credentials to connect to the report server database. I will again use SQL Server authentication. Click Next .
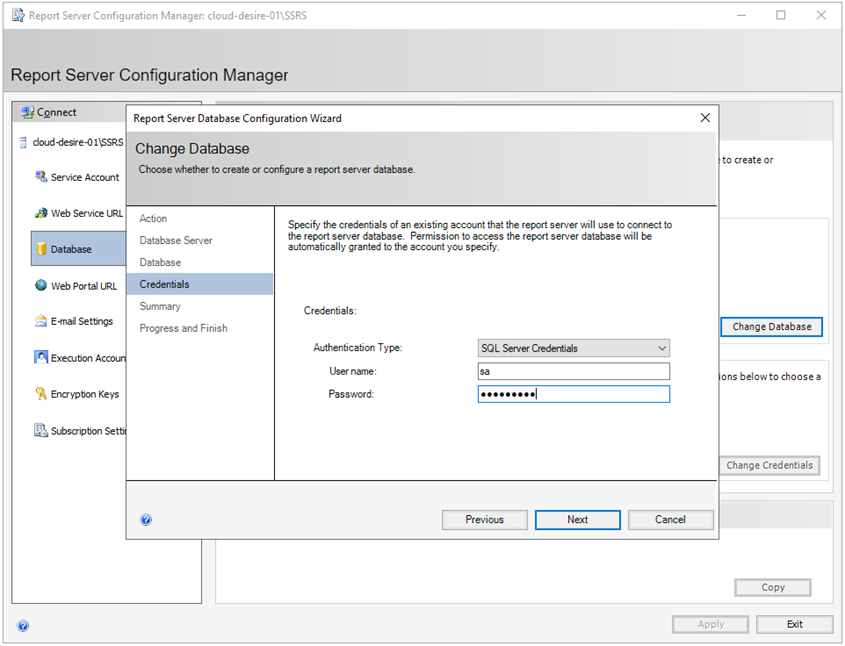
Next, you will see a summary of your selected settings. Verify and click on Next .
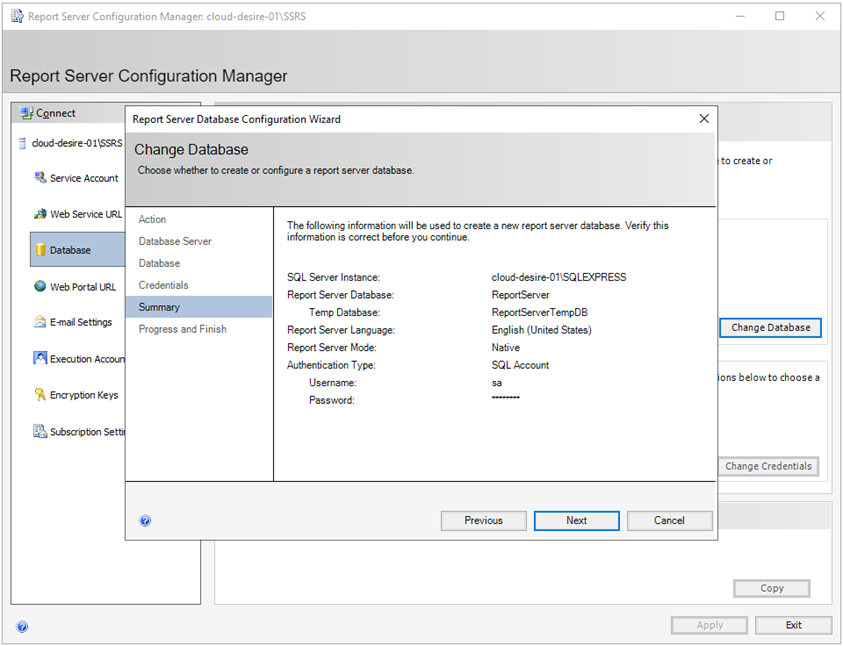
It will configure the report server database. After all the steps are executed successfully, click Finish .
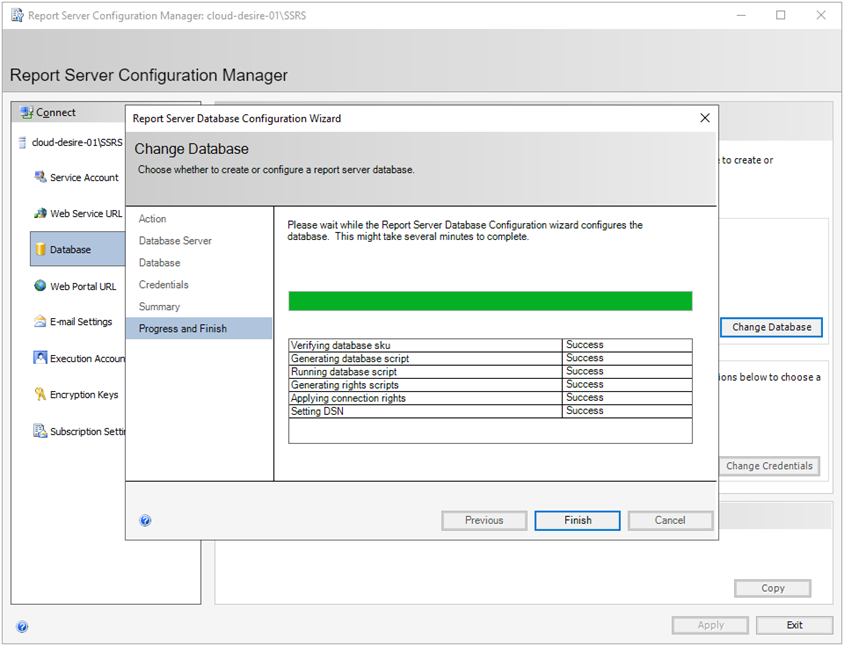
Click on the Apply button to finalize the Database configurations.
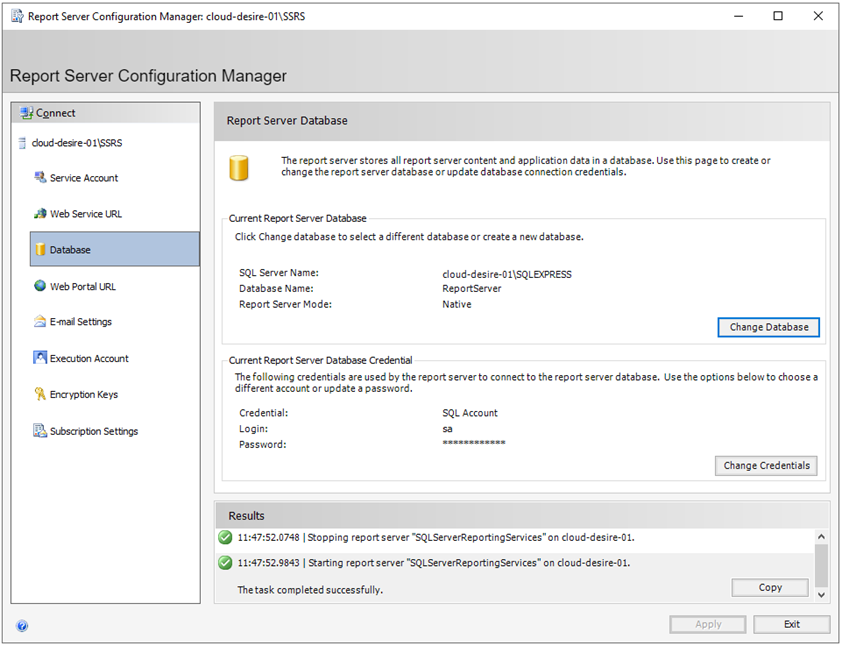
Next click on the Web Portal URL tab from the left panel. Here you can configure the web portal URL. We will use this URL to manage SSRS reports, data sources, report parameters, etc. It will preview URLs in the bottom section. I will go with default settings. Click on the Apply button and it will configure the report server web portal URL.
Now open the browser and enter the URL you configured in the Web Service URL section in step 4 (in my case http://cloud-desire-01/ReportServer). You should see the below web page which shows the report server name and SSRS version information.
Now open another browser window and enter the URL you configured in the Web Portal URL section in step 13 (in my case http://cloud-desire-01/Reports). You should see below web page which shows the web portal for SSRS.
Excellent! We have successfully configured SQL Server Reporting Services. Now you can deploy reports and data sources using Visual Studio or Report Builder tool.
As you can see, it is very easy to configure SQL Server Reporting Services if you follow the above steps accurately.
- 30 th October, 2021: Initial version
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed under The Code Project Open License (CPOL)

Comments and Discussions
SSRS 2022 Install, Setup and Configuration
By: Joe Gavin | Updated: 2024-02-21 | Comments (3) | Related: > Reporting Services Installation
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) is still one of the major components of the Microsoft Business Intelligence (MSBI) stack used to generate interactive and automated reports. It's part of Microsoft SQL Server services, along with SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) and SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS).
SSRS 2022 includes enhanced Windows Narrator support, security enhancements, browser performance improvements, and accessibility bug fixes.
The SSRS installation process has changed slightly since it was first released in 2004 as an add-on to SQL Server 2000. We saw in a previous tip: SSRS Install, Setup and Configuration , where the SSRS installation used to be part of the SQL Server installer up through SQL Server 2016. As of SQL Server 2017, the installation now has its own downloadable installer. There are only some minor differences between installing SSRS 2019 and SSRS 2022, but knowing where to get the installer and what to expect before you go through the installation process is helpful. This tip will walk through the various screens and options for the installation process.
We'll look at the minimum hardware and software requirements, see where to get the installer, and walk through each step of installing and configuring a new installation of SSRS 2022. The installation documented here was done on a SQL Server 2022 running on Windows Server 2022.
SSRS 2022 Requirements
You'll likely have more resources than this, but the following are the minimum requirements for installing SSRS 2022:
- 6 GB of available hard drive space
- 512 MB (1 GB is recommended)
- 1 GB (4 GB recommended)
- X64: AMD Opteron, AMD Athlon 64, Intel Xeon with Intel EM64T support, Intel Pentium IV with EM64T support
- 1.4 GHz (2 GHz recommended)
- Windows Server 2016/2019/2022, Windows 10 / 11
- SQL Server Database Engine 2014 SP3 or later
- .NET Framework 4.8 or later
SSRS 2022 Installation
Download the installer.
Go to Microsoft SQL Server 2022 Reporting Services Installer Download
- Click Download .
Retrieve and Run Installer
- Run SQLServerReportingServices.exe from your Download folder.
Welcome Screen
The installer opens, and you're presented with one option on the Welcome screen.
- Install Reporting Services.
Choose Edition and Install
There are four edition options for SSRS. The first three do not require a Product Key:
- Evaluation Edition – Full edition that is good for 180 days.
- Developer Edition – Full edition that can be used for non-production, e.g., test, development, training, or demonstration purposes.
- Express Edition – Limited edition with fewer features than the full edition.
- Paid Edition - The fourth option requires a product key. Click Learn more , which will take you to Find the product key for SQL Server Reporting Services .
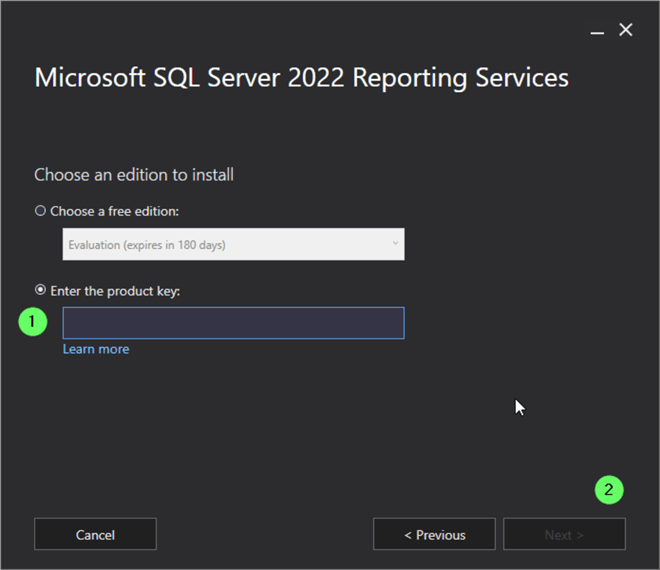
Install Paid Edition
- Click the Enter the product key radio button and enter the key in the box.
- Click Next .
Review Licensing Terms
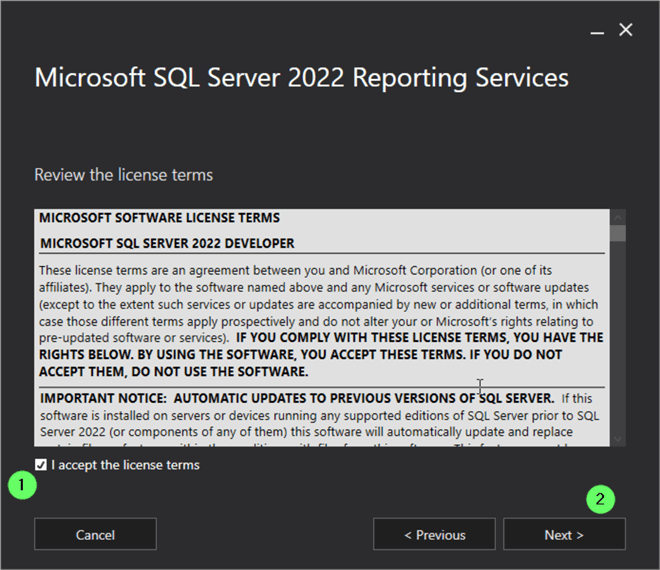
- Read and accept license terms by checking the 'I accept the license terms' checkbox.
Install Database Engine
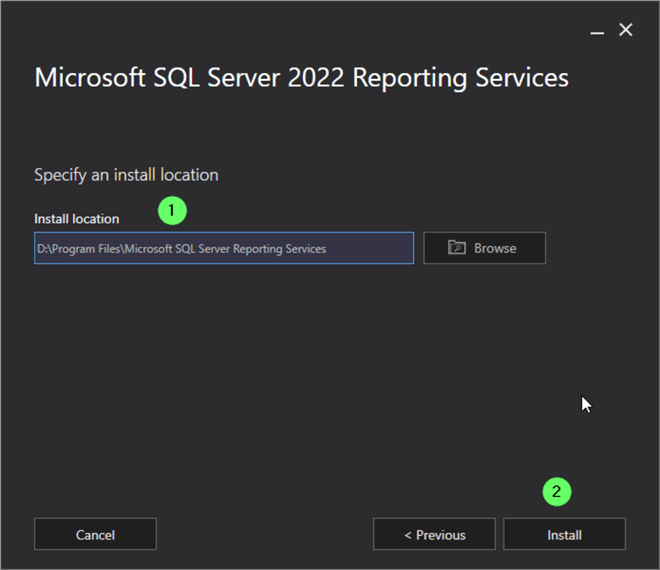
Specify Install Location
- Choose the drive and directory to install SSRS.
- Click Install .
The SSRS application has been installed, and now it's time to configure it.
Configure SSRS
- Click Configure report server , which runs RSConfigTool.exe to open the Report Server Configuration Manager.
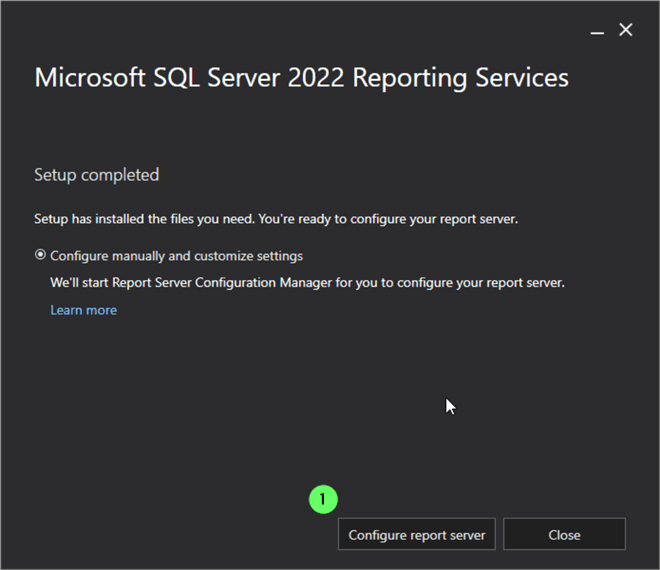
Connect to the SSRS Server
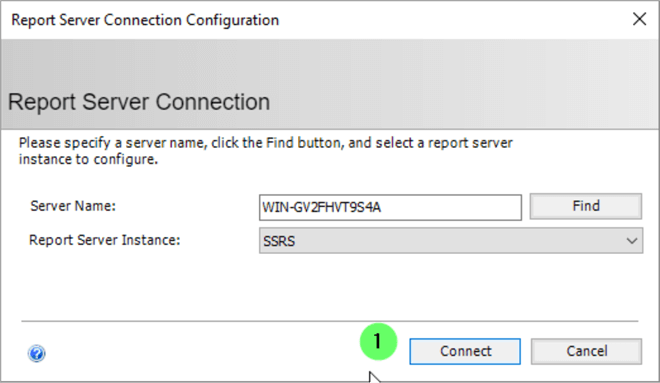
- Click Connect .
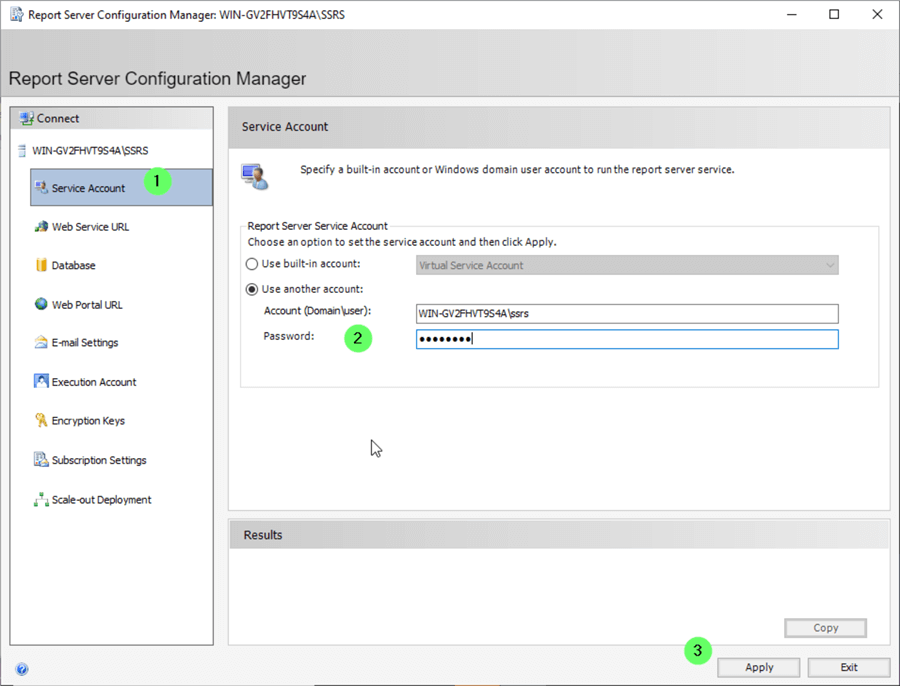
Configure Service Account
If the SSRS server requires access to remote servers, a Windows domain account can be specified to run the SSRS service.
- Click on Service Account in the Report Server Configuration Manager.
- Select the 'Use another account' radio button. Enter the domain account information and password.
- Click Apply .
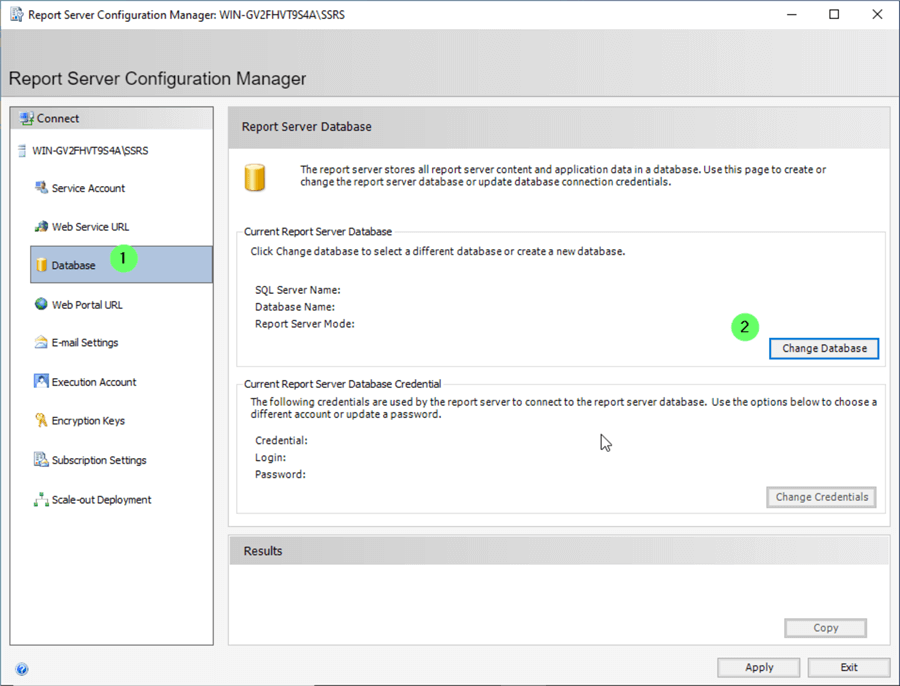
Configure SSRS Databases
Here, we configure the SSRS databases.
- Click Database in the Report Server Configuration Manager.
- Click Change Database .
Create New Database
The new SSRS installation can be pointed to an existing set of SSRS databases. However, since this is a new installation, the default 'Create a new report server database' is left selected, and the installer will create the new databases.
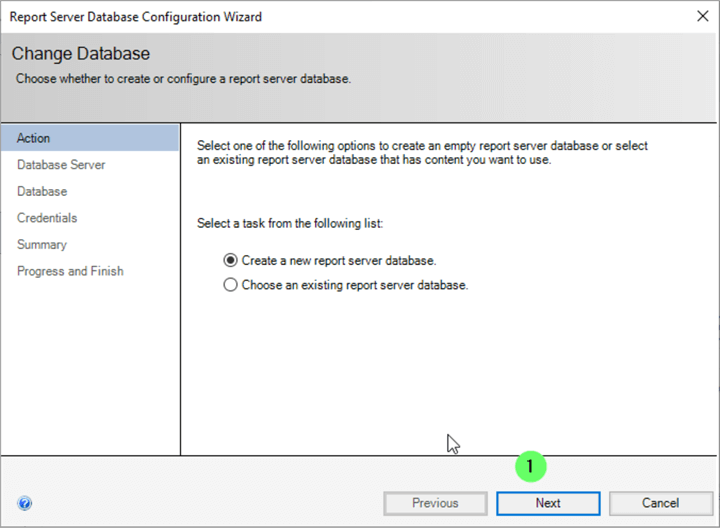
Test the Connection
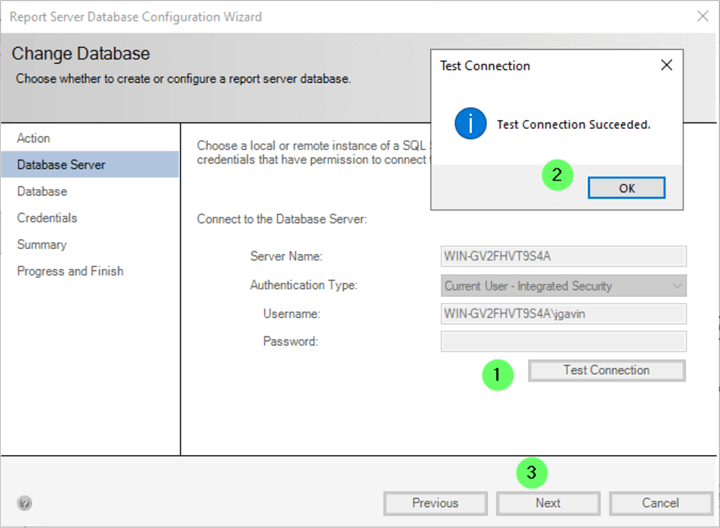
We must test the connection to the SQL Server to ensure connectivity before attempting to create the SSRS databases.
- Click Test Connection .
- If the connection is successful, click OK .
If the connection is unsuccessful, verify that the SQL Server service is running and accepting connections, and then run the test again.
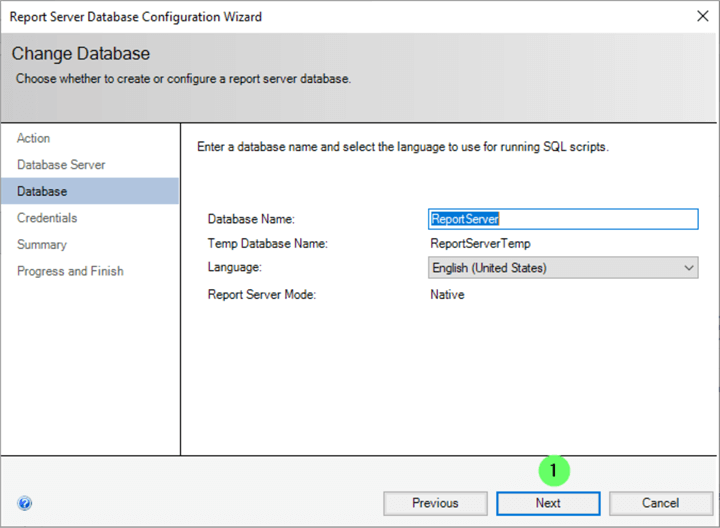
Name the Database
Unless a name other than the default database names must be used, leave the defaults as ReportServer and ReportServerTemp.
Specify Credentials
Review Summary
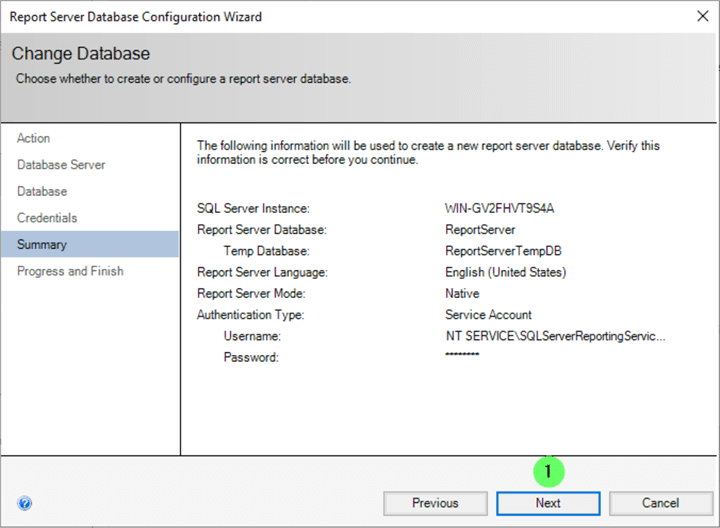
Review the install configuration on the Summary screen.
- Click Next if all information is correct.
Progress and Finish
Verify all tasks completed successfully.
- If all tasks are successful, click Finish .
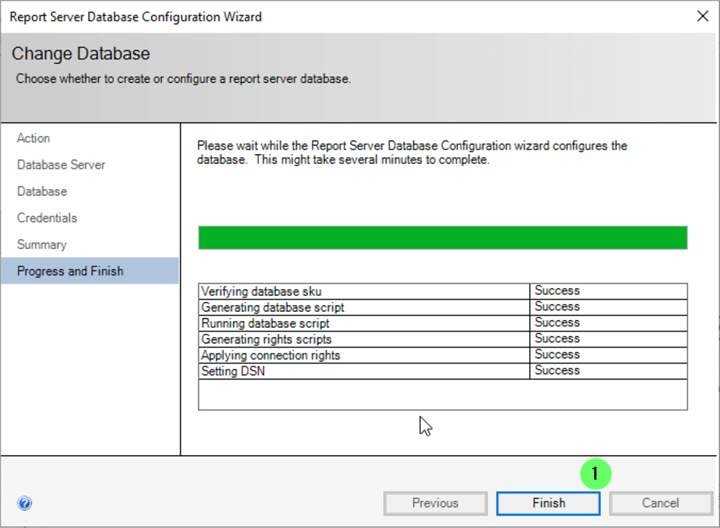
At this point, we have the SSRS service installed and databases created.
It's time to create the Web Service and the Web Portal.
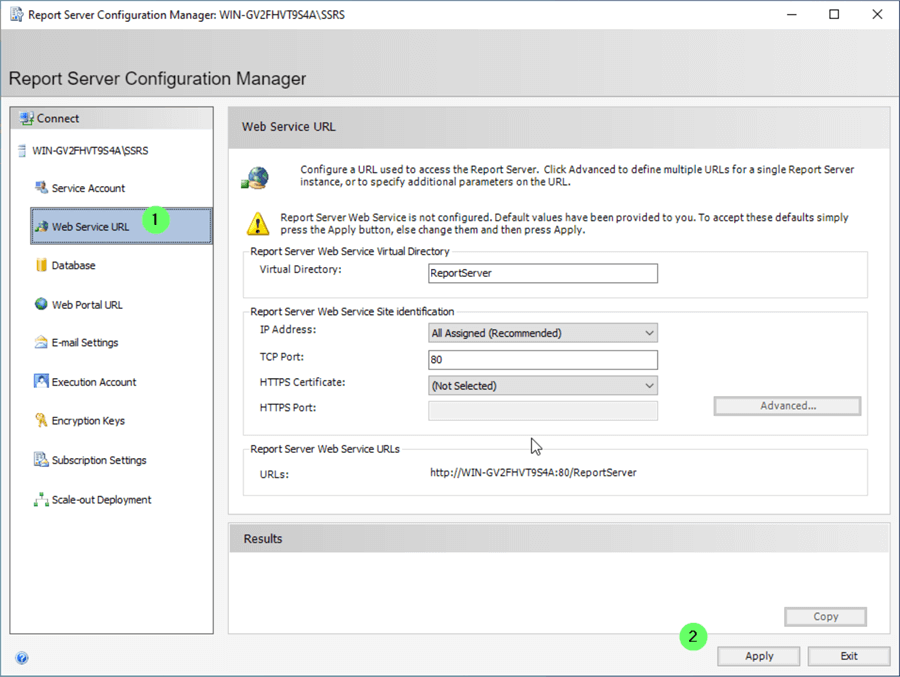
Create the SSRS Web Service
- Click on Web Service URL .
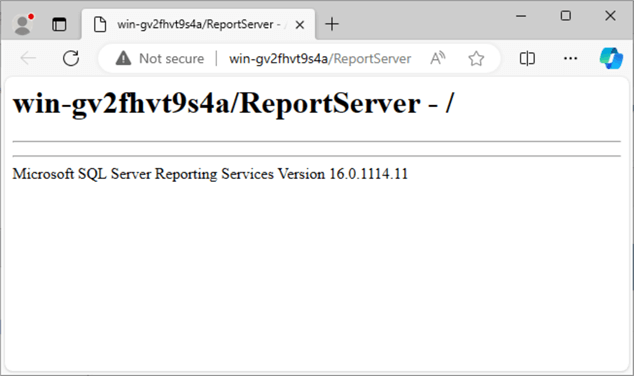
Validate Web Service
Open the Report Server Web Service URL to validate. There are no folders shown because no reports have been deployed yet.
Create Web Portal
- Click Web Portal URL .
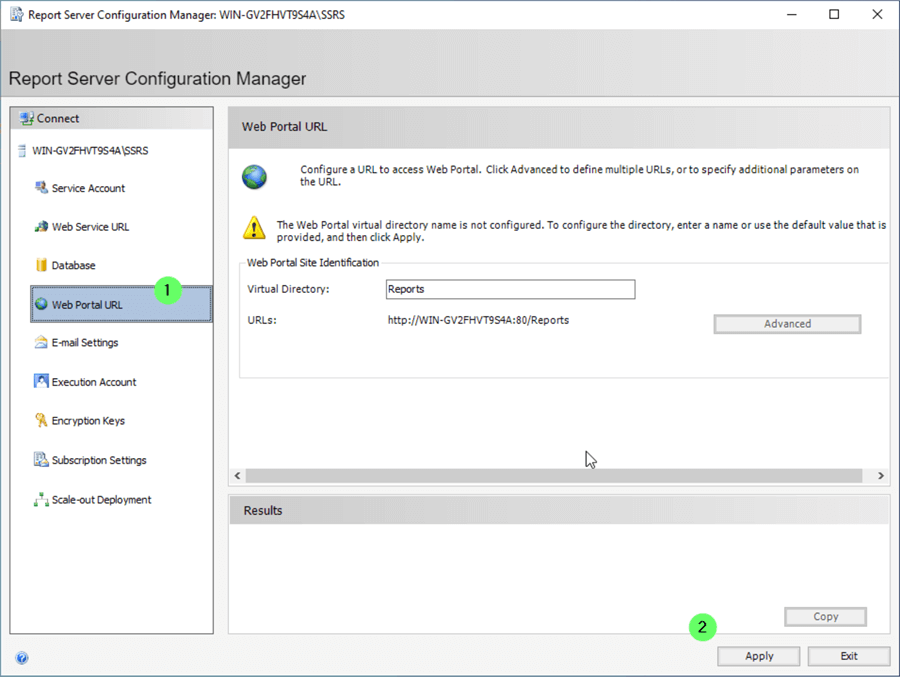
Validate Web Portal
To validate, open the Report Server Web Portal URL. Again, the root folder is empty because no reports have been deployed yet.
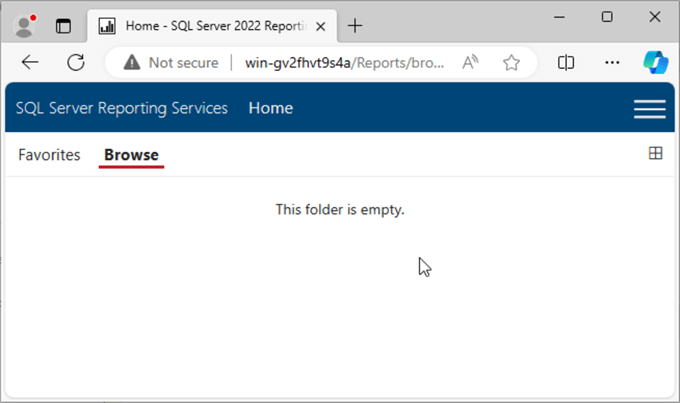
We now have a fully functioning SSRS server that's ready for reports to be deployed to it.
Email Settings
If Subscriptions to email reports will be created, we'll need to configure the email settings.
- Click E-mail Settings .
- Enter a Sender Address in the form of [email protected] .
- Enter the SMTP Server name.
- Select the Authentication dropdown menu to enter the account and password information if your SMTP server requires authentication.
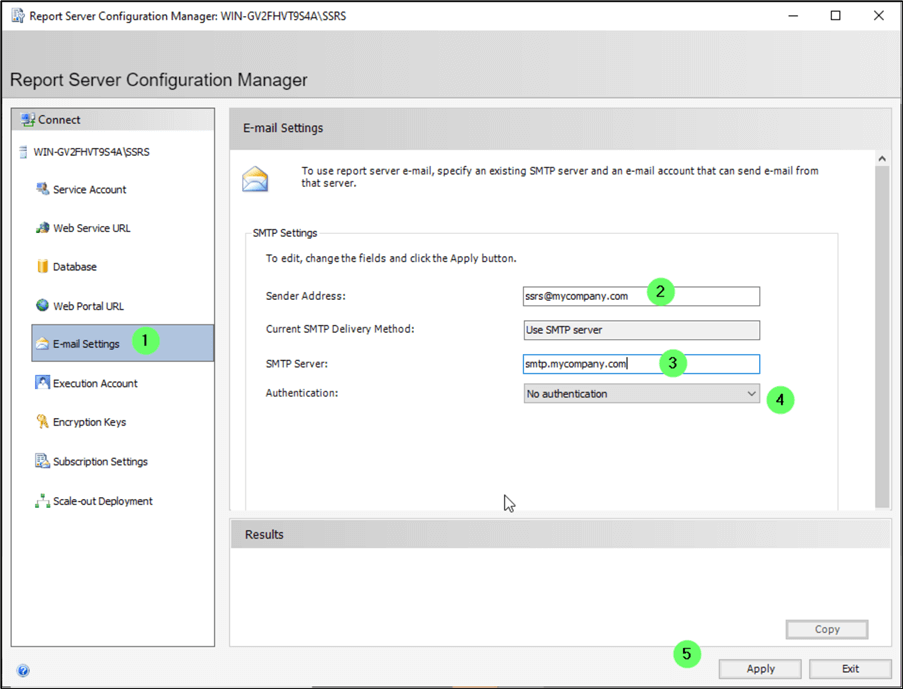
Email has been configured.
- Click Exit .
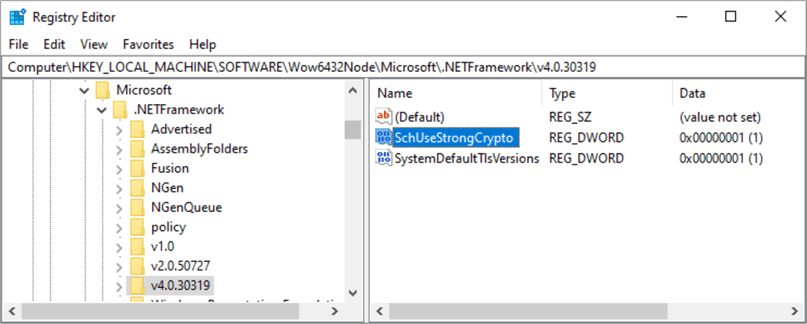
You may run into failures, sometimes sporadically, related to TLS 1.2, where subscriptions are not sending emails and generating errors like this:
ERROR: Error sending email. Exception: System.Net.Mail.SmtpException: Failure sending mail. ---> System.IO.IOException: Authentication failed because the remote party has closed the transport stream.
Adding the following registry keys will force TLS 1.2:
The following links have more information on SQL Server Reporting Services:
SSRS Install, Setup and Configuration
- SQL Server Reporting Services 2017 Installation and Configuration
- Install SSRS ReportServer Databases on Azure SQL Managed Instance
Installing SQL Server Reporting Services 2017
SQL Server Reporting Services Standalone Installation
- How to Add SSRS to Existing SQL Server Clustered Instance
- PowerShell Commands for SQL Server Reporting Services
- Visual Studio 2019 Install and Configure for the SQL Server DBA
- How to Install and Configure SSRS with Amazon RDS SQL Server
- Side by Side SSRS Install and Upgrade to Minimize Downtime

About the author

Comments For This Article

Related Content
How to add Reporting Services to an existing SQL Server Clustered Instance
Adding Reporting Services to an existing SQL Server 2005 installation
Install SQL Server Reporting Services 32 bit on a 64 bit Windows Server
Install and Configure SQL Server Reporting Services 2012 SP1 and 2014 in SharePoint Integrated Mode Part 1
SQL Reference Guide
Power BI Training
Related Categories
Reporting Services Administration
Reporting Services Best Practices
Reporting Services Configuration
Reporting Services Installation
Reporting Services Migration
Reporting Services Monitoring
Reporting Services Network Load Balancing
Reporting Services Performance
Reporting Services Security
Development
Date Functions
System Functions
JOIN Tables
SQL Server Management Studio
Database Administration
Performance
Performance Tuning
Locking and Blocking
Data Analytics \ ETL
Microsoft Fabric
Azure Data Factory
Integration Services
Popular Articles
Date and Time Conversions Using SQL Server
Format SQL Server Dates with FORMAT Function
SQL Server CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY
SQL Server Cursor Example
SQL CASE Statement in Where Clause to Filter Based on a Condition or Expression
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Examples for SQL Server
SQL Convert Date to YYYYMMDD
Rolling up multiple rows into a single row and column for SQL Server data
SQL NOT IN Operator
Resolving could not open a connection to SQL Server errors
Format numbers in SQL Server
SQL Server PIVOT and UNPIVOT Examples
Script to retrieve SQL Server database backup history and no backups
How to install SQL Server 2022 step by step
An Introduction to SQL Triggers
Using MERGE in SQL Server to insert, update and delete at the same time
How to monitor backup and restore progress in SQL Server
List SQL Server Login and User Permissions with fn_my_permissions
SQL Server Loop through Table Rows without Cursor
SQL Server Database Stuck in Restoring State

Install and Configure SSRS step by step
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) is a server-based report generating software system from Microsoft. It is part of a suite of Microsoft SQL Server services, including SSAS (SQL Server Analysis Services) and SSIS (SQL Server Integration Services).
In this article, we will learn How to install and configure SSRS Native Mode step by step .
- 1.1 Install and configure SSRS Perquisites
- 1.2 Install SQL Server Reporting Services
- 1.3 Configure SQL Server Reporting Services
You might also like to read Install and Configure Power BI Report Server Step by Step
Applies To:
- SQL Server Reporting Services SSRS 2016.
- SQL Server Reporting Services SSRS 2014
- SQL Server Reporting Services SSRS 2012.
- SQL Server Reporting Services SSRS 2008.
How to Install and configure SSRS?
In this post, we considered that you have already installed SQL Server as mentioned at How to Install SQL Server 2012 Step by Step and How to install SQL Server 2019 Developer Edition .
Install and configure SSRS Perquisites
Before we getting started to Install and configure SSRS, you should prepare the following Prerequisites:
- Make sure that you have the same SQL Server version installation media that was used when the SQL Server is being installed.
- Create a new service account for Reporting Service. (Microsoft recommends to specify and use a separate account for each SQL Server service)
- Specify the authentication type and the account that has permission to connect to the database server. (Will be used during configuring the Report Server DB)
- Specify the authentication type and the account that the report server will use to connect to the report server database. (Will be used during configuring the Report Server DB)
- For the production environment, Don’t install SSRS on the database server, instead, you should create a new server for SSRS.
Install SQL Server Reporting Services
- Mount your SQL Server Media ISO/CD > Run SQL Server Installation file > From SQL Server Installation Center > Click on Installation.
- Click on New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.
- Click OK after the Setup Support Rules have been passed.
- Check Product Updates and click Next.
- Again, Check Setup Support Rules and click Next.
- From Installation Types > Check Perform a new installation.
- From Setup Role > Select SQL Server Feature Installation.
- Select Database Engine Services .
- Select Reporting Service -Native > Click Next.
- Configure instance by setting the instance name or leave default.
- Check Disk Space Requirement > Next.
- In Server Configuration > Set SSRS Service Account > Next.
- In Reporting Service Configuration > Check Install only .
- In Error Reporting > Click Next.
- Once the Installation Configuration Rules have been passed > Click Next.
- In Ready to install > Click on Install.
- Complete the installation wizard and click Finish.
You might also like to read Install and configure SSRS 2016
Configure SQL Server Reporting Services
- Open Reporting Service Configuration Manager.
- Click Find and select the existing instance that has been selected to add SSRS feature > Click on Connect.
- The Report Server Status should be shown with the current report server status and basic information about report server.
- Go to Service Account section to check the service account that has been set during the installation, you can also change the current service account through this section based on your requirement.
- Go to the Web Service URL section to configure the URL and port number for Report Service Web Service > Click On Apply to generate it.
- Got to Database section > Click on Change Database.
- Follow the Change Database wizard > Check Create a new report server database > Next.
- Select Authentication Type “SQL Server Account” > Set the Username and Password for the account that should have permission to connect to SQL server.
- Click on Test Connection > Next.
- Type your Database Name or leave it as default > Next.
- Again set the credential for the user that should have permission to access the Report Server Database.
- Review the Summary > Next.
- Wait until the Report Server Database Configuration wizard complete > Click on Finish.
- The Database section should show the current Report Server Database.
- Go to Report Manager section to configure the URL that will be used to access Report Manager. > Click on Apply.
- Try to navigate to the Report Manager URL to open Report Manager.
Note: in case you got any permission issue to open report Manager, please check
- SSRS Permission Issue: User does not have required permissions. Verify that sufficient permissions have been granted and Windows User Account Control (UAC) restrictions have been addressed.
- SSRS 2016: You are not allowed to view this folder. Contact your administrator to obtain the necessary permissions.
- Click on Report Builder to build your report.
- Click on Run.
- Great, the report builder is ready now to create your first report.
- Go now to Encryption Keys to take a backup of the symmetric key that used to encrypt sensitive data in the report server database like connection strings, credentials …etc.
Note: the symmetric key backup is very important especially in case of migrating or moving the report server installation to another server. you can restore this symmetric key to be able to access the encrypted content.
In conclusion, we have learned
- What’re the prerequisites to Install and Configure SSRS?
- How to Install and Configure SSRS step by step?
- Install and Configure SSRS 2016 step by step.
- How to Scale Out SQL Reporting Service (SSRS) to work with two Database Server (Always-on)?
- SSRS: Manage Permissions in Reporting Service .
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
5 thoughts on “Install and Configure SSRS step by step”
Pingback: Supported SQL Server Version for SharePoint 2016 | SPGeeks
Pingback: SSRS: SharePoint List does not exist | SP Geeks
very useful, thanks
Thanks for your feedback 🙂
great article
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Aenean massa feugiat imperdiet a scelerisque et morbi tempus massa tincidunt vitae libero aenean tincidunt molestie.

Kevin Holman's Blog
SCOM and anything else I find interesting
SCOM 2019 – QuickStart Deployment Guide
There is already a very good deployment guide posted on Microsoft Docs here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/scom/deploy-overview
The following article will cover a basic install of System Center Operations Manager 2019. The concept is to perform a limited deployment of OpsMgr, only utilizing as few servers as possible, but enough to demonstrate the roles and capabilities in SCOM. For this reason, this document will cover a deployment on 3 servers. A dedicated SQL server, and two management servers will be deployed. This will allow us to show the benefits of high availability for agent failover, and the highly available resource pool concepts. This is to be used as a template only, for a customer to implement as their own pilot or POC, or customized deployment guide. It is intended to be general in nature and will require the customer to modify it to suit their specific data and processes.
This also happens to be a very typical scenario for small environments for a production deployment. This is not a detailed architecture guide nor intended to displace the need for a complete and thorough design guide.
Server Names\Roles:
- OMMS2 Management Server Role, Web Console Role, Console
Windows Server 2019 will be installed as the base OS for all platforms. All servers will be a member of the AD domain.
SQL 2019 CU11 will be the base standard for all database and SQL reporting services.
High Level Deployment Process:
1. In AD, create the following accounts and groups, according to your naming convention:
- DOMAIN\OMAdmins OM Administrators security group
2. Add the OMAA , OMDAS accounts to the “ OMAdmins ” global group.
3. Add the domain user accounts for yourself and your team to the “ OMAdmins ” group.
4. Install Windows Server 2019 to all server role servers.
5. Install Prerequisites and SQL 2019 CU11 .
6. Install the Management Server and Database Components
7. Install the Reporting components.
8. Deploy Agents
9. Import Management packs
10. Set up security (roles and run-as accounts)
Prerequisites:
1. Install Windows Server 2019 to all Servers.
2. Join all servers to domain .
3. Install the Report Viewer controls to any server that will receive a SCOM console. Install them from here: DOWNLOAD . There is a prereq for the Report Viewer controls which is the “Microsoft System CLR Types for SQL Server 2014” ( ENU\x64\SQLSysClrTypes.msi ) available here: DOWNLOAD
4. OPTIONAL : If your organization enforces TLS 1.2 , you must ensure the prerequisites for TLS 1.2 have been met on all Management Servers. TLS 1.2 Blog Post
5. Install all available Windows Updates to ensure the servers are patched and secure.
6. Add the “ OMAdmins ” domain global group to the Local Administrators group on each server.
7. Install IIS on any management server that will also host a web console :
Open PowerShell ( as an administrator ) and run the following: Add-WindowsFeature NET-WCF-HTTP-Activation45,Web-Static-Content,Web-Default-Doc,Web-Dir-Browsing,Web-Http-Errors,Web-Http-Logging,Web-Request-Monitor,Web-Filtering,Web-Stat-Compression,Web-Mgmt-Console,Web-Metabase,Web-Asp-Net, Web-Windows-Auth –Restart Note: The server needs to be restarted at this point, even if you are not prompted to do so. If you do not reboot, you will get false failures about prerequisites missing for ISAPI/CGI/ASP.net registration.
8. Install SQL 2019 CU11 to OMSQL1
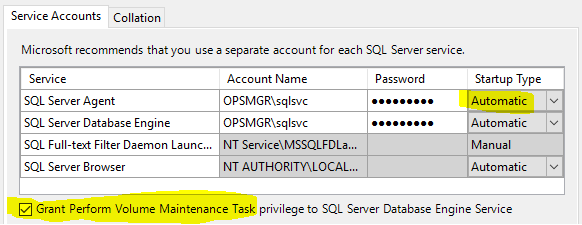
- Run setup, choose Installation > New SQL Server stand-alone installation…

- Full-Text and Semantic Extractions for Search

- Check the box to grant Volume Maintenance Task to the service account for the DB engine. This will help performance when auto-grow is needed.
- When you complete the installation – you might consider also downloading and installing SQL Server Management Studio Tools from: DOWNLOAD SQL Management Studio
9. Apply SQL 2019 CU11 (or whatever the latest Cumulative update available is). SCOM 2019 only supports SQL 2019 with CU8 or later and we STRONGLY recommend CU11 or later. At the time of this article being written, CU11 was the latest. Always install the latest Cumulative Update for SQL.
- REBOOT the SQL server.
SCOM Step by step deployment guide:
1. Install the Management Server role on OMMS1.
- Web Console
- The Management Server will be very busy (CPU) for several minutes after the installation completes. Before continuing it is best to give the Management Server time to complete all post install processes, complete discoveries, database sync and configuration, etc. 10 minutes is typically sufficient .
2. ( Optional ) Install the second Management Server on OMMS2 .
- Close when complete.
3. Install SCOM Reporting Role on the OMSQL1 .
- Choose “ Configure report server ”. You must immediately configure the Report Server.
- Now that configuration is done, click Exit
- You MUST see a “ Home ” screen before continuing to install SCOM reporting role.
- Add “ *.* ” to the end of the list of allowed extensions.
You have a fully deployed SCOM Management group at this point.
Open/Reopen the SCOM consoles, ensure you have a Reporting tab now, and within an hour you should see reports populated in the console.
Look for any health issues or alerts, and review the OpsMgr event logs on both management servers for errors or warnings.

Known / Common issues:
1. Management Server installation fails when TLS 1.0 is disabled, and prerequisites for TLS 1.2 are missing.
- On the first management server being installed, the UI will return a failure, and in the OpsMgrSetupWizard.log (found at C:\Users\< username >\AppData\Local\SCOM\LOGS), you see the following:
[09:41:56]: Info: :Info:GetLocalizedAdminGroupName: Administrators Group Name is: BUILTIN\Administrators [09:42:12]: Error: : PopulateUserRoles: failed : Threw Exception.Type: System.ArgumentException, Exception Error Code: 0x80070057
- This is caused by having TLS 1.0 disabled on the SCOM management server or SQL server. If TLS 1.2 is enforced or TLS 1.0 disabled, you must FIRST install the software prerequisites for TLS 1.2 for SCOM.
2. When using SSRS 2017 or SSRS 2019, you might see errors on a management server for event ID 31567 with description “ Failed to deploy reporting component to the SQL Server Reporting Services server ” and “ extension is not allowed ”. This is apparently because of a new security restriction in later builds of SSRS 2017. The workaround is to open SQL Management Studio , connect to your Reporting Services instance, open the Properties of the instance, Advanced , and add *.* to the list for “ AllowedResourceExtensionsForUpload ”
3. When using a scoped user profile, you might see a “ 500 – Internal server error ” when using a state view in the Web Console. You also might see an error in state views may for: Incorrect syntax near the keyword ‘CREATE’. This issue was first resolved in SCOM 2019 UR1 .

What’s next?
Once you have SCOM up and running, these are some good next steps to consider for getting some use out of it and keep it running smoothly:
1. Configure SCOM Security
- Add your OMAdmins Global Group to the SCOM Administrators User Role. Ensure you, your team, and the SCOM DAS and Action accounts are members of this group FIRST. Then, r emove BUILTIN\Administrators from the Operations Manager Administrators – User Role, to secure your SCOM installation.
2. Apply the latest Update Rollup.
- UR3 for SCOM 2019 – Step by Step – Kevin Holman’s Blog
3. Set SCOM License .
- https://kevinholman.com/2017/06/29/dont-forget-to-license-your-scom-2016-deployments/
4. Optimize SQL Server for growth and performance
- If you have a SQL Always On scenario – the secondary replicas need a SQL script run on them: https://kevinholman.com/2017/08/27/scom-2016-event-18054-errors-in-the-sql-application-log/
5. Set up SQL maintenance jobs .
- https://kevinholman.com/2017/08/03/what-sql-maintenance-should-i-perform-on-my-scom-2016-databases/
6. Configure Data Warehouse Retention .
- https://kevinholman.com/2010/01/05/understanding-and-modifying-data-warehouse-retention-and-grooming/
7. Optimize your management servers registry
- https://kevinholman.com/2017/03/08/recommended-registry-tweaks-for-scom-2016-management-servers/
8. Enable Agent Proxy as a default setting
- https://kevinholman.com/2017/03/10/enable-proxy-as-a-default-setting-in-scom-2016/
9. Configure Administration Settings per your requirements:
- Manual Agent Installs (Reject, Review, or Accept)
10. Backup Unsealed Management packs
- https://kevinholman.com/2017/07/07/scom-2012-and-2016-unsealed-mp-backup/
11. Deploy an agent to the SQL DB server.
- You could also deploy any additional agents at this point.
12. Import management packs .
- Import the Base OS and SQL MP’s at a minimum.
13. Configure Notifications :
- https://kevinholman.com/2012/04/27/opsmgr-2012-configure-notifications/
14. Deploy Unix and Linux Agents
- https://kevinholman.com/2016/11/11/monitoring-unix-linux-with-opsmgr-2016/
15. Configure Network Monitoring
- https://kevinholman.com/2011/07/20/opsmgr-2012-discovering-a-network-device/
16. Configure SQL MP RunAs Security :
- https://kevinholman.com/2016/08/25/sql-mp-run-as-accounts-no-longer-required/
17. Continue with optional activities from the Quick Reference guide:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/scom/manage-quick-reference
18. (Optional) Configure your management group to support APM monitoring.
- Import supporting management packs for IIS 8, and 10, and APM Web for IIS 8, and 10.
19. (Optional) Deploy Audit Collection Services
- My initial filter for lab use is: adtadmin /setquery /query:”SELECT * FROM AdtsEvent WHERE NOT (EventId=4768 OR EventId=4769 OR EventId=4624 OR EventId=4634 OR EventId=4672 OR EventId=4776)”
- You will need to grant NETWORK SERVICE full control to the AdtServer registry key to set a filter at the command line: http://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/operationsmanagerreporting/thread/ab22685e-36a1-49a9-b90e-d39ead31901f
20. Learn MP authoring.
- Download MPAuthor: http://www.silect.com/mp-author/
143 Comments
Will other System Center products need to be updated before I can move to SCOM 2019, or could I potentially update right away?
The recommended upgrade order is posted in the online product documentation.
But could it be, that SCOM 2019 supported agent platform is only Windows Server 2016 and above? What about Windows Server 2008 – 2012 R2, are they going to be left out for SCOM 2019?
Windows 2012R2 is supported as an agent. We are updating documentation. I am trying to get clear confirmation if Windows Server 2012 (non-R2) is truly unsupported or a documentation oversight. As to Windows Server 2008 and 2008R2, those are not supported with a SCOM 2019 agent. Those OS versions will fall out of Extended Support by Microsoft in Jan 2020, so they were not included in this release.
Server 2008R2 is not supported with a SCOM 2019 agent, but is it supported with the current 2012 MMA connected to a SCOM 2019 management group? If I recall Server 2003 was supported in a SCOM 2012R2 management group with the old agent version, but not on the new (at the time) MMA.
We don’t have any support statements for connecting 2008R2 to a SCOM 2019 management group, with any MMA. So the assumption is, that is something is not clearly defined as supported, then it isnt. This is similar to SCOM 2016 dropping support for 2003. You could still connect 2003 servers to SCOM 2016 using a SCOM 2012R2 agent, but it wasn’t a “supported configuration” according to our documentation. It worked fine. We just didn’t test/support it, because WS 2003 extended support expired, and we generally do not test or develop new products to work with unsupported products. I think the heartache is that WS2008/2008R2 is not expired yet, although it will expire soon, in Jan 2020. Why they dropped WS2012 OS, I don’t have a good answer, and we are pushing them to change on that one. The challenge with all of this, is that the Log Analytics MMA supports WS2008R2 and later, AND supports connecting to SCOM 2012 SP1 UR6 and later.
Hello, I want to update Audit Collection Services for UNIX/Linux, but after removing old version (1807) I can’t install new. Setup is stuck at Prerequisite Check Did Not Pass: Operations Manager is required to be installed prior to the installation of this product. SCOM 2019 is installed and running on this machine, and also Audit collection services for Windows.
Ugh. This is a bug. To work around this – change the reg key at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft Operations Manager\3.0\Setup\CurrentVersion TEMPORARILY from “10.19.10050.0” to “7.2.11719.0” Then run setup. This should work around the installer prereq check. Make sure you change this value back after you install this.
Setup went OK. But I still get alert: Event Description: Loading managed module type in assembly “Microsoft.SystemCenter.CrossPlatform.ACS” with type name “Microsoft.SystemCenter.CrossPlatform.ACS.ACSWriteAction” failed with error “The module assembly “Microsoft.SystemCenter.CrossPlatform.ACS” could not be loaded. The exception was: \nCould not load file or assembly ‘Microsoft.SystemCenter.CrossPlatform.ACS’ or one of its dependencies. The system cannot find the file specified..”. This may be because the type or assembly could not be found or the type does not have the MonitoringModuleAttribute. Workflow: Microsoft.ACS.Linux.RHEL.6.Su.Failed
Is this because support for RHEL 6 was removed? This alert has 50 repeats.
It is not supported, but it does work. I moved was able to somehow setup 2008 Servers in my SCOM 2019 POC environment. It does throw some alerts once it checks in with the 2019 MG, but I dont have that information and the POC environment has since been torn down. We eliminated over 250 2008 Servers in the past 8 months we are now only 2012 R2 and above. I think I will be keeping the legacy environment around for a bit and migrate our 2016 and 2019 servers over to the new and start validating 2012 R2 before I tear that down as well.
Hi Kevin, as usual very good post. Do you know if Microsoft has the intention to fix the xSCOM dsc resource so that we can use it to deploy SCOM 2019 ? https://www.powershellgallery.com/packages/xSCOM/1.3.3.0
As that has not been updated since 2015, and I have not heard anything about that – I seriously doubt it. That project was open sourced, regardless: https://github.com/PowerShell/xSCOM
You dont need xSCOM DSC resource. You can easily use PackageManagement instead
Hi Kevin, do you know when Microsoft is going to release the updated Linux/Unix management packs ? https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=29696 still only has the 1807 packs and we are eagerly waiting for the SuSE 12 PPC support.
My bad… I should have thought twice before posting 🙂 Of course they are in the installation folder of SCOM 2019 All good now 🙂
Kevin, again an excellent piece of work! Run into an issue with SQL 2017 reporting services. Everything is working fine except http://localhost/reports/ gives a HTTP 500 Internal Server Error after installing. Seems more people run into this issue.
Yes – this is a known issue. It did not repro with the early builds of SSRS 2017, but it evolved in newer versions. The PG is looking into resolving this.
I just installed SCOM 2019 with SQL/SSRS 2017 and ran into this issue. Is there anything new from the product group on this? Is there an estimated resolution date for it?
The most recent SSRS updated build 14.0.600.1274 at https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=55252 resolves the HTTP 500 error when browsing the /Reports URL.
I also ran into the HTTP 500 error problem on installing the SSRS 2017 and SCOM Reporting on a Windows Server 2019. The quick fix was removing SSRS 2017 and install SSRS 2016, which worked fine. Later, trying to reproduce this problem I saw that SSRS 2017 is working fine on Windows Server 2016. So it seems to me that the combination SSRS 2017 and Server 2019 is causing the HTTP 500 error.
Discovery Wizard SCOM 1902 show strange.. Now showing entire tabs (Computer select etc…)
We face an issue that once install SCOM(2019) web service in the same server with the SQL(2016) service, the web service can’t access properly. Not sure is SCOM, SQL or IIS issue, any idea to fix ? Thanks.
I never install IIS and SQL SSRS on the same server – this is likely your issue. I install the SCOM web console role on management servers. However, if you want to do this, see: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/reporting-services/install-windows/install-reporting-and-internet-information-services-side-by-side?view=sql-server-2017
If I am upgrading the SCOM management servers from 1807 to 2019 in a distributed environment, do I have to repeat this pre-upgrade task on each management server or just on the first MS? “7.Stop the Microsoft Monitoring Agent, System Center Data Access Service, System Center Configuration Management, and Microsoft Monitoring Agent services on all management servers except the one being upgraded.” Any plans on posting a guide for the upgrade process? Thanks!
So, to prepare for upgrading our 1807 deployment to SCOM 2019, I had our DBAs restore the OpMgr and DW DBs from our LAB MG to a new SQL 2017 server (from current SQL 2014). The DBA migrated all permissions as well, and afaik, they are identical and meet all documented requirements. After following all the MS steps to edit the registry keys and configservice.config file on each MS, and editing the listed tables on the DB server for both the OpsMgr and DW DBs, SCOM appears to be running, all MS are talking to SQL, with a fairly robust amount of data being exchanged for our LAB MG, but I can’t launch a console on any MS. Data Access Service fails, with Application Log Errors 1000 and 1026, System Log Error 7034 (OMSDK keeps restarting and failing) , and OpsManager Errors 26340 and 26380. If I restore the previous registry keys values and old configservice.config values, Management servers have no problem talking to the old DB. Any ideas? I’ve Googled for two days and found nothing, even looking at SCSM stuff.
This is typically a rights or TLS issue. Is the new SQL 2017 server using same ports, and configured the same?
Any other ideas for solution or diagnostics? Thanks.
Two of my DBAs swear up and down that logins, perms, ports (default on both old and new servers), firewall, etc. are all configured the same. And the management servers and SQL are talking. Traffic on all of them, and OpsMgr log files show that agents are available. Just no console and the DAS keeps failing, restarting, failing, etc. I notice that in Microsoft’s “How to configure Operations Manager to communicate with SQL Server” page, the database edits specify using (computer\instance,portNumber). On the old server, only SQL server name is used. Since we’re using default ports, my DBAs don’t think this should be an issue, but did this maybe change in SQL 2017? Grasping at straws here (at least it’s in the lab MG). Thanks.
Hi Kevin,Is Windows 2012 R2 supported (will still work) as a gateway role on SCOM 2019? I read the Software requirement for SCOM 2019 and it only covers from win2016. ( https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/scom/system-requirements?view=sc-om-2019 ).
Thanks, Nirmal
For SCOM server roles (such as a GW) only what is documented is supported.
Hi, Kevin if I try to discover a Windows computer (Advanced discovery, Browse for) it doesn’t function. SCOM tries to discover it but it never ends. And it doesn’t matter if I use the Action Account or the other account with the admin rights. Any idea?
Thanks, Casimir
I cover this here: https://kevinholman.com/2019/03/14/security-changes-in-scom-2019-log-on-as-a-service/
Hi Kevin, one thing more: the discover never ends and I see the info that the Discovery is the SQL Broker necessary.
I was wondering how much SCOM will complain if I do not install the reporting role ? We never really used the reporting in the past and I’m ok if we do not have this piece. However, I suspect I will have tons of msg in the logs about it.
None at all. It is completely optional. The DW is mandatory, and created during setup. However, there is zero requirement for a reporting role if you dont want it.
Note: if you upgrade the management servers to UR1 than you will have problems installing the SCOM Reporting server. I worked with MS tech support for several days and it couldn’t be installed. I ended up having to re-provision my new SCOM 2019 servers and re-install everything. then install UR1.
Hi Karen – I have addressed this and provided a simple solution in my UR1 and UR2 posts.
BTW, you are missing that .net 3.5 framework is required on the Web Console.
I’ve run the 2019 upgrade on two 1807 management servers so far and in both cases the old and new versions of SCOM are shown in appwiz.cpl . In “operations manager products” the consoles on the management servers are detected as 10.19.10050.0 and the management servers are still detected as 7.3.13142.0 – is this expected/a known issue or is it something specific to my environment do you think?
Morning, could you please verify if the URL used to download mgmt packs/updates from within the SCOM console is the same for SCOM 2012R2, 2016 and 2019? https://www.microsoft.com/mpdownload/ManagementPackCatalogWebService.asmx ports 80, 443 Our environment has very tight firewall rule controls so I need to get this correct. Thank you, Tony
I cannot. The reason is – I do not recommend every using that for downloading MP’s. I consider that a worst practice, as I recommend downloading each MP, extracting it – saving it into a repository, testing it in your lab/test environments, then migrating it to production. Sucking in MP’s from the web breaks that change control process, and removes your ability for a proper disaster recovery and rollback capability, in my opinion. I’m sure someone knows the answer to your question, however, but it isnt something I use with my customers.
Afternoon, I understand your position and generally agree. I want to enable it for the feature “show updates for currently installed management packs” since it also provides version info. I do follow the process you recommend, I think it is the safest route to go. We have a good change management process that requires us to document that updates have been tested and properly configured in “lower tiers” prior to migrating/moving on. Thanks as always, for your time and assistance. Regards, Tony
As far as I know – the link you posted is the one we use for MP downloads and updates.
This is a great guide!
After installing SSRS 2017, you mention “Browse to http://localhost/reports/ “. Did you mean “http://localhost/reportserver”?
I’m asking because “http://localhost/reports/” does not appear to work. It gives me “HTTP 404 Not Found”.
Navigating to “http://localhost/reportserver” shows “servername/ReportServer – /, Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services Version 14.0.600.1109”
I’m staging a POC of SCOM 2019 on Server 2016.
Ignore this.. I missed a step and am able to navigate to the URL “http://localhost/reports/”.
Would like to mention that the web console is not being installed as it’s not required.
After running the SCOM Reporting role on the SQL server, it fails and rolls back.
Kevin- Thanks so much for this! I’m getting the following error in the Application log in Event Viewer on some of my my test SCCM servers (source is Perflib): “Windows cannot open the 64-bit extensible counter DLL MOMConnector in a 32-bit environment.” Any ideas? It’s puzzling as they are 64 bit scom agents and 64 bit OS systems..
Is there a current .inf file for requesting certificates for SCOM communications?
I’m finding older ones, but I’m not sure if these are the best choice for settings, for TLS 1.2, etc… for best security.
Thanks for a great guide Kevin
I have installed SCOM2019 with a new management group and shall now remove the old one from Active Directory. When but I receive this error executing ” .\MomADAdmin.exe -d SKANDIKON SKANDIKON” with my domain admin user.
MomADAdmin failed to delete the container for SKANDIKON with the following exception: Access is denied. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070005 (E_ACCESSDENIED))
Can I delete the old management group under OU OperationsManager manually from Active Directory?
I have upgraded 2 Win2016 MS from v1807 to 2019 and everything seems to be reporting the correctly upgraded version except the database and data warehouse (7.3.13142.0). The SQL server is SQL 2016 Std. on Win2016 as well, is this normal and if not what might I have done to not have this update correctly?
Thanks for your time
Hi Kevin, thank you so much for your blog. It is very useful!!
We have installed everything and we are suffering the “Known Issues number 2”: We can browse reports ever but not Reports. We have updated the SQL from 17 to 17 with CU14. But the problem persists.
Do you know which version we need to solve the issue? Or do we need to change the SQL version?
Thank you again!
The SQL team should be releasing an update for SSRS which will address this soon.
Thank you Kevin. it works properly!
HI Kevin, We were able to install the 2019 SCOM Management Server using a remote instance of SQL.. When trying to install Reporting Services I am not able to select a remote instance on the “SQL Server instance for Reporting Services”. It’s grayed out and I am not able to type in the box.. We went back to the “Select Features to install” page and noticed at the bottom of the page under Requires: “This Feature requires a local SQL Reporting Services instance to be installed. Refer to the Operations Manager Supported Configuration document for the full list of system requirements”. Is there a way to install 2019 SCOM reporting services with a remote SQL instance or does it truly have to have SQL installed locally for reporting services?
SCOM Reporting Role must be installed on a local SQL Reporting Server. It has always been this way. The SCOM Reporting role is very minimal. Most customers just install this role and SSRS on their Data Warehouse server, or in larger environments, they install SSRS and the SCOM Reporting role on a dedicated server.
Some more back ground… We have a remote SQL server. I have installed a separate instance of SQL and reporting services on the remote instances specifically for reporting services. The ReportServer and ReportServerTempDB exist.. I used the Report Server Configuration manager on the Scom server and have connected to the database and web service url and web portal url by modifying the url’s and pointing to the the sql server and SSRS instance. While I can’t find anywhere that specifically states that says the SSRS instance must be local to the SCOM server it seems this needs to be the case. I’m looking for a confirmation.
You replied as I was typing up my follow up note. This is my first go around with SCOM.. I think I get it now..
Just wanted to check on the Power Settings. Is High Performance Power only needed for the SQL Server, or does this also apply to all Management Servers?
In a past company, which was very large…8 management groups… we were advised about this during a PS case, and at that time it was implied that it was all MS’s too, which we did, and we did see improvements. However, whilst implementing this elsewhere it was queried and I see that on this article, it is only mentioned within the SQL section.
So, I guess I am asking is it really necessary/safe to apply this to the Management Servers, or could there be another issue lurking.
My understanding is that this setting has no effect on VM’s at the guest level, so it really doesnt matter, since management servers are always VM’s in my experience. It matters much more when SQL servers are deployed on physical hardware.
How about upgrading the other SCOM management servers in a distributed environment. The first one did the upgrade with success from 1807, but the other three management servers will not be upgraded. How can I force that process? By the way, that are 2016 Core servers. Setup program is not supported on a Server Core installation.
What does “will not be upgraded” mean? Does it fail? If so – look in the log to see where it s failing.
On server core – you need to use the command line. I have never tested using server core and doing a SCOM version upgrade.
Thx Kevin for your quick response.
I’ve got also OpsMgr Management Configuration events:29112 ‘Service failed to execute bootstrap work item ‘ . So a bootstrap upgrade procedure will start at the other management servers, but fail with ‘Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ManagementConfiguration.DataAccessLayer.DataAccessException: Service binaries (cscmdbops.dll) version of 7.3.13142.0 is lower than minimum required Cmdb support version of 10.19.10050.0 recorded in Cmdb. Service binaries must be updated to version no lower than version of the Cmdb support objects. Alternatively Cmdb support objects may be rebuilt to match the version of binaries at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ManagementConfiguration.CmdbOperations.StoreInitializationOperataion.StoreVersionObtained(Object sender, DataAccessOperationCompletedEventArgs args)’
Our Management Configuration Service runs with the same Log On account as the Data Access Service
(SOLVED) This command will do the job:
Start-Process -FilePath “C:\Temp\SCOM2019\setup.exe” -ArgumentList ‘/Upgrade /InstallPath:”D:\Program Files\Microsoft System Center\Operations Manager” /components:OMServer /ManagementGroupName:XXXX /SqlServerInstance:XXXX /DatabaseName:OperationsManager /DWSqlServerInstance:XXXX /DWDatabaseName:OperationsManagerDW /ActionAccountUser:Domain\XXXX /ActionAccountPassword:******* /DASAccountUser:Domain\XXXXX /DASAccountPassword:****** /EnableErrorReporting:Never /SendCEIPReports:0 /UseMicrosoftUpdate:0 /AcceptEndUserLicenseAgreement:1 /silent’
Hello Kevin. Until SCOM 1807 Solaris 11 x86 was supported ( https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/scom/plan-supported-crossplat-os-1807?view=sc-om-1807 ) On the SCOM 2019 page I only see Solaris 11 SPARC Version, not x86 anymore. Do you know if this is an error or if it is correct (“by Design”)? https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/scom/plan-supported-crossplat-os?view=sc-om-2019 Indeed, if I try to add a Solaris 11 x86 System that worked with SCOM 2012R2, in SCOM 2019 I get a Message “not supported”. I’m just wondering why?
Great question. I don’t know. My guess would be lack of customer adoption of Solaris 11 on x86…. but I’m not sure the criteria used by the product group to choose which UNIX/Linux versions got support moving forward and which didn’t.
Hi, in the MP guide both, x86 and SPARC, are listed as supported. Still, the kit for Solaris 11 i386 is missing… Anyone found anything on that? Cheers, Patrick
Thanks for a great article. I have deployed many OPS managers from 2007 to 2016, but this is the first 2019, and no matter how many times i have re-installed this installation ( i thing i have installed it 6-7 times now – no matter what installation guide i follow ore have installede like i used to do) and for some reason i keep getting the same error and can’t figure out why. Maby you know why our can guide me in the right direction?
Data Warehouse failed to deploy reports for a management pack to SQL Reporting Services Server
Data Warehouse failed to deploy reports for a management pack to SQL Reporting Services Server. Failed to deploy reporting component to the SQL Server Reporting Services server. The operation will be retried. Exception ‘DeploymentException’: Failed to deploy reports for management pack with version dependent id ’84a5e876-f9eb-a3b1-e566-b7f7c2fe9dcf’. Uploading or saving files with .Settings extension is not allowed. Contact your administrator if you have any questions. —> Microsoft.ReportingServices.Diagnostics.Utilities.ResourceFileFormatNotAllowedException: Uploading or saving files with .Settings extension is not allowed. Contact your administrator if you have any questions.
One or more workflows were affected by this.
Workflow name: Microsoft.SystemCenter.DataWarehouse.Deployment.Report
Instance name: Data Warehouse Synchronization Service
Instance ID: {2D8188D5-F0F4-6A12-FD7F-0FCDD6E6B445}
Management group: XXXXXXXXXXXX
That’s #3 in the KNOWN ISSUES section of this guide.
Thanks a million! 🙂 Don’t know how I could miss that one…
In fairness – I only added it a few days ago. 🙂
Hi Kevin as always an excellent article ? is there a description how to install a gateway on a core server? Thanks Bruno
Finally I found, in short:
certutil -importpfx certificate.pfx Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.GatewayApprovalTool /managementServerName=MS-FQN /GatewayName=GW-FQN /Action=Create msiexec.exe /i MOMGateway.msi momcertimport64.exe
SCOM 2019 Linux discovery is failing with below error, could you please advise any workaround for this. The Winrm service is running.
Unexpected DiscoveryResult.ErrorData type. Please file bug report. ErrorData: System.ArgumentNullException Value cannot be null. Parameter name: lhs at System.Activities.WorkflowApplication.Invoke(Activity activity, IDictionary`2 inputs, WorkflowInstanceExtensionManager extensions, TimeSpan timeout) at System.Activities.WorkflowInvoker.Invoke(Activity workflow, IDictionary`2 inputs, TimeSpan timeout, WorkflowInstanceExtensionManager extensions) at Microsoft.SystemCenter.CrossPlatform.ClientActions.DefaultDiscovery.InvokeWorkflow(IManagedObject managementActionPoint, DiscoveryTargetEndpoint criteria, IInstallableAgents installableAgents)
When we run Winrm below error is comming
WSManFault Message = The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: “winrm quickconfig”.
Error number: -2144108526 0x80338012 The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: “winrm quickconfig”.
Regards, Kiran Kumar Reddy
I solved this problem by deleting old SCOM agents from the directory on all SCOM Management Servers and SCOM Gateways. When deleted I only needed 4 files “scx-1.6.4-7…..” for my environment. C:\Program Files\Microsoft System Center 2016\Operations Manager\Server\AgentManagement\UnixAgents\DownloadedKits And then discovery worked instantly.
SCOM 2019 / Windows Server 2019 / SQL Server 2017 Std / SSRS 2017 on DW server. Installing Scom reporting service role on Datawarehouse server fails always. Installation fails when Operations Manager Setup is configuring security extensions. After that SSRS Reporting services http://localhost/Reports is also broken.
Is this “known issue” or should I open ticket for MS for this case?
Not a known issue. Reporting should install fine if SSRS is properly installed and working prior to the SCOM reporting install.
Hi Jukka-Pekka Grohn, could you fix the error? Seams i run in the same. Everything i try runs in the same error. Would nice to hear from you. Thank you
Hi Everyone,
This is a Permissions issue with the account being used to do the Reporting install. I recommend validating the account being used has Admin rights to the database and all SCOM Servers. As a side note you might even ensure the SCOM Read account has SysAdmin rights on the database just for the install.
Has anyone had issues with the webconsole in 2019, i have tried everything i can think of but its not loading correctly i don’t get the side navigation and get the central dashboard squeezed in to where the navigation should be and the rest of the screen is just blue.
Afternoon, I am at a total loss. Followed the document to a tee and I get the 0x80070057 error, everything fails. did line for line of the instructions. sql server 2016,sp2 windows server 2016, 2 mgmt servers windows server 2016, one for mgmt server and console, other for web and reporting. did not make it past installing for the first mgmt server!! so frustrating with something that should be so simple! all prereqs met, passed all the screens to proceed. do I not need to do the tls 1.2 since windows server is 1.2 compliant? do I need tls 1.0 also????? thanks for your time and assistance. TS
If TLS 1.0 is disabled, you just need to apply the TLS prerequisites FIRST, before attempting an install. SCOM 2019 will install on a TLS 1.2 enforced environment, but not without the TLS 1.2 prerequisites first.
I have installed SCOM 2019, running is OK. I just want to allow another user (Windows guy) to monitor or administrator only windows devices. In this case I have allowed a separate user under ‘Securtiy > User Roles’. Whatever tutorial I followed, it seems that the user find access to everything as the SCOM administrator find !! have logged in web console each time. Its been 3 days, no single clue I have been able to identify !
In the ‘Group Scope’ and ‘Dashboards and Views’ I selected only Windows items. Very much appreciable your kind response in this regards.
By default, any local administrator of a SCOM server OS is all SCOM admin by inheritance. This is the first thing I tell people to change in my guides.
Hi Kevin, Thank you a lot. Another question.
is it possible to allow a specific Network departmemt’s user to install agent on their rest of network devices? Where the user can see only network devices only.
Allowing the network user in User Roles with ‘Profile: Advance Operator’ can’t see any option/wizard to install agent on Linux Machine!! Or if you tell how to do this would be much helpful.
Is this has any mandatory option to login from desktop console with that user instead of Web Console?
Appreciate your tremendous help/answer.
Hi Kevin. I downloaded SCOM 2019 from VLSC and it also offered me SQL Server 2019 Standard Edition under the same section that the SCOM 2019 key was (as was SQL Server 2017 Standard Edition). I thought I’d test SQL Server 2019 considering it was offered in the same section, however it fails to install when it tries to import the Management Packs.
Totally appreciate that SQL Server 2019 doesn’t appear to be supported yet, but thought it was worth a crack considering it was offered to me to download in the same section; under System Center 2019 – Operations Manager Server.
Do you know if this is definitely not supported yet? Perhaps they put it there as it will be later and maybe only for an upgrade from SQL Server 2017 from an existing install?
SQL 2019 is not supported for SCOM 2019. SQL 2019 just shipped, 11/4/2019. It was not available at the time SCOM was shipped. SCOM 2019 may add support for SQL 2019, but that will be some time in the future.
My System Center Datacenter comes with SQL 2019 — are you saying that MS is ship a product with incompatible components?
The System Center 2019 Datacenter licensing comes with usage rights for SQL standard edition, that much is true. However, I am not aware that we state SQL 2019 anywhere. We do state that it includes SQL server standard edition runtime to support System Center deployments. You still must ensure you are using a supported version of SQL server for the System Center product.
Thanks Kevin, thought so. Just odd that it was offered with the VL version of SCOM 2019 on the VLSC site.
“You also will see the same bug that was in SCOM 2016 UR6 where state views may throw an error: Incorrect syntax near the keyword ‘CREATE’. This bug was fixed in SCOM 2016 UR7 and is scheduled to be resolved for SCOM 2019 in SCOM 2019 UR1.”
There is a fix for this: https://support.microsoft.com/en-my/help/4506518/system-center-operations-manager-hotfix-for-scoped-group-users
I’ve been breaking my head about installation issue of SCOM for a day now, everytime I disabled the firewall on my SQL server it would continue to next step, when it was disabled it did not continue although I was 100% sure the appropiate firewall rules were setup (1433 was working and accessible).
Perhaps a good side-note for your readers and perhaps even worthwhile putting it in your steps. For SCOM to access the SQL server you not only need the SQL port open but also “Windows Management” also known as “WMI-In” in the firewall. If you enable this together with the SQL port it will work.
Thanks for your how to quickstart, I have it bookmarked to make my life easier as probably a lot of people do 🙂
Hi Kevin, FYI step # 11 above is pointing to a broken link (404) https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/om/manage/managing-discovery-and-agents?redirectedfrom=MSDN
Trying to install a new group. I’m not getting the step: “On the specify an installation screen – choose to create the first management server in a new management group.” It immediately asks for a group to connect to.
Kevin, i have a question about SCOM 2019 and it’s SQL Server Collation Requirements. I’m running up a test 2019 system and what it to reside on a SQL 2016 Always ON cluster. This SQL 2016 Always ON cluster has been configured with a different SQL Server Collation that the one required for SCOM 2019. As a result my installation fails at the database check – saying the SQL Server Collation is incorrect. My question is – does the SQL Server Collation need to be system wide for SCOM to function correctly (as i know it can be set per DB). Could i for example install my test SCOM db onto a different instance of SQL 2016 (that has the correct SQL Server Collation) and then move my SCOM db’s to the SQL 2016 Always ON cluster, that has the wrong SQL Server Collation, the SQL Server Collation can be per database, so my SCOM db’s should have the correct collation. but will the system collation settings of the SQL 2016 Always ON cluster break my SCOM db’s / install. thanks in advance and sorry for the longwinded explanation. karl
No – that would not be supported, because we have issues when the tempDB’s are a different collation. SCOM is not a simple database application, we tightly integrate with the SQL instances and leverage multiple services, like CLR, fulltext search, broker, custom messaging in the master database, and TempDB. The SCOM databases and the SQL instances themselves must use the supported collation.
Thanks Kevin, just what i thought. Now i have to break it to my SQL dba’s!
Hey, thanks for all your guides. We ran into an issue with installing the Reporting Server. The services are correct installed and i can run the homescreen. When i install the report server feature we stuck at specify a management server with: Unable to connect to the Data Access service for this management server. Ensure the Data Sccess service is running and the service, the management groupm and setup are all the same version.
telnet scom dw DB –> scom mgmt server 5723/5724 is open. Data access service is running
Anyone facing the same error? Thanks and kind regards,
Hello Kevin, Today I have install SCOM 2019 with SQL DB 2019. While scom agent installation my agent is not coming under “agent Managed” since I have click “Automatically approve new manually installed agent”.
1. I have tried manual agent installation ..no luck 2. I have tried push agent installation .no luck (stuck in pending management – only “Reject” option is enable
SQL Version : Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (RTM-CU8) (KB4577194) – 15.0.4073.23 (X64) Sep 23 2020 16:03:08 Copyright (C) 2019 Microsoft Corporation Standard Edition (64-bit) on Windows Server 2019 Standard 10.0
I had received below error but I have resolved this issue with your post on TLS 1.2 blog:
OleDb Module encountered a failure 0x80004005 during execution and will post it as output data item. Unspecified error : [DBNETLIB][ConnectionOpen (SECCreateCredentials()).]SSL Security error.
Workflow name: Microsoft.SystemCenter.SqlBrokerAvailabilityMonitorForPool
Instance name: All Management Servers Resource Pool
Instance ID: {4932D8F0-C8E2-2F4B-288E-3ED98A340B9F}
Requesting your help…
Hi i have this problem on install :
FW disabled, using only omaa account is in administrator and sysaadmin on SQL.
[00:05:38]: Always: :ImportManagementPack: Loading management pack D:\NEW\Install\SCOM\Setup\AMD64\..\..\ManagementPacks\System.Library.mp. 00:05:38 [00:05:43]: Error: :ImportManagementPack: Error: Unable to load management pack D:\NEW\Install\SCOM\Setup\AMD64\..\..\ManagementPacks\System.Library.mp [00:05:43]: Error: :: Database error. MPInfra_p_ManagementPackInstall failed with exception: Database error. MPInfra_p_ManagementPackInstall failed with exception: Maximum stored procedure, function, trigger, or view nesting level exceeded (limit 32). [00:05:43]: Error: :ImportManagementPack: Unknown Error. System.ArgumentException : The requested management pack is not valid. See inner exception for details. Parameter name: managementPack [00:05:43]: Always: :FirstManagementServer: Failed to load MP D:\NEW\Install\SCOM\Setup\AMD64\..\..\ManagementPacks\System.Library.mp. We will retry. [00:05:43]: Always: :ImportManagementPack: Loading management pack D:\NEW\Install\SCOM\Setup\AMD64\..\..\ManagementPacks\System.Library.mp. 00:05:43
OK this is problem with SQL 2019 need min CU8
Hi Kevin, Thanks for this and all that you post, invaluable. I’m fairly new to SCOM and have been tasked with doing a side-by-side migration/upgrade from SCOM 2012R2 to 2019. The plan being to have both environments stood up and slowly migrate existing gateways and agents by multi-homing them so they are reporting to both. Once I’ve seen them reporting ok to the new env for a while disconnect them from the old environment. My question, in order to accomplish this, the new environment, new servers that I will install SCOM 2019 fresh on, the Management group name should be new and different from the existing one correct? Thanks and kindest regards Rich
Yes absolutely! The MG name must be different or you cannot multi-home. MG name is not relevant – so just make it short, generic, easy to type, and unique. I like things like MON1, MON2, MON3 etc. Or DEV, PROD, PROD1, PROD2, etc. People typing out these long Management Group names like there is some kind of naming standard to apply, are ridiculous. KISS.
Every time I try and install SCOM2019 with SQL19 I get operational database configuration failed any help would be great first time I installed SCOM Very new to it all.
Thanks Russell
Did you first apply CU8 or later to all your SQL 2019 servers being used for SCOM?
I didnt but when i did it worked thanks for the Reply Kevin 🙂
I created this SCOM 2019 AutomatedLab to deploy an Hyper-V SCOM Environment from scratch, with one script.
Check it out if you are looking to get a lab set up quickly: https://github.com/v-bldrum/SCOM-Scripts-and-SQL/tree/master/AutomatedLab
Hi Kevin, Two more questions although they can be very naíf… 1) Are there any restrictions on the name of SCOM DBs? Our db Admin have rules for naming and I’m sure if SCOM supports anything other than OperationsManager or OperatinsManagerDW. 2) Are there any restrictions for creating DBs in shared SQL instances? For now, the installation is in a non-productive environment. Thanks once again for your time and support.
No restrictions on the DB names that I know of.
We do not mandate dedicated instances. But keep in mind: 1. The SCOM installer needs Sysadmin and Local Admin rights to get through the install. 2. The DB’s need to be created by the installer Setup routine. 3. We modify permissions, master DB, and MSDB in the instance. 4. All our sizing assumes a dedicated instance. You might see performance issues in a shared instance depending on the size of your SCOM deployment.
For Linux monitoring, is domain account required or user account having access on Linux machines as well, will do?
Getting this error while inux installation with a user account that has access on Linux machine. Please assist how to resolve.
Unexpected DiscoveryResult.ErrorData type. Please file bug report. ErrorData: Microsoft.SystemCenter.CrossPlatform.ClientLibrary.Common.SDKAbstraction.TaskInvocationException Task invocation failed with error code -2130771961. Error message was: Creation of module with CLSID “{}” failed with error “Illegal operation attempted on a registry key that has been marked for deletion.” in rule “Microsoft.Unix.WSMan.Discovery.Task” running for instance “UNIX/LINUX monitoring Resource Pool” with id:”{}” in management group “”.
at System.Activities.WorkflowApplication.Invoke(Activity activity, IDictionary`2 inputs, WorkflowInstanceExtensionManager extensions, TimeSpan timeout) at System.Activities.WorkflowInvoker.Invoke(Activity workflow, IDictionary`2 inputs,
Once you apply UR1, you cannot install, or re-install SCOM reporting Role.
You will see an error in the setup UI (when you supply a management server name) that states “Unable to connect to the Data Access service for this management server. Ensure the Data Access service is running and that the service, the management group, and setup are all the same version.”
Apply the following workaround to install/reinstall SCOM Reporting role:
QUERY the OPERATIONSMANAGER database, and record the VERSION number that is returned. You will need this value later. You need to change the PrincipalName to your SCOM Management server that you point the reporting install to. — 10.19.10050.0 – 2019 RTM — 10.19.10311.0 – 2019 UR1 — 10.19.10349.0 – 2019 UR1 with post UR1 Hotfix USE OperationsManager SELECT PrincipalName, Version FROM MTV_HealthService WHERE IsManagementServer = 1 AND PrincipalName = ‘OMMS1.opsmgr.net’
UPDATE the VERSION entry in the OpsDB to match the RTM version number which is 10.19.10050.0 just for this management server.
UPDATE MTV_HealthService SET Version = ‘10.19.10050.0’ — 2019 RTM WHERE PrincipalName = ‘OMMS1.opsmgr.net’
Install SCOM 2019 Reporting, and choose this same Management Server. Reporting install will work now. REVERT the VERSION entry in the OpsDB to match the original value you recorded
UPDATE MTV_HealthService SET Version = ‘10.19.10311.0’ — 2019 UR1 WHERE PrincipalName = ‘OMMS1.opsmgr.net’
Hello Kevin,
We have installed SCOM 2016 in our environment and have 4 Management servers (All VMs) and two separate database servers (both high end physical servers with RAID 1+0 configured) each for OpSDB and Data Warehouse. We need to configure AEM for roughly 1,00,000 clients with 25000 clients reporting to each management server. We have enabled created a group policy in AD with object level targeting where each Server’s entry is directed to corresponding SCOM AEM Workstations AD group. Currently, we are managing around 20K clients. We sometimes face issues of high memory on any of the Management Server randomly. Going forward we will add more clients for monitoring but before that i have some queries.
1. What is the right/any alternate method of monitoring these much clients on multiple management servers using group policy ? 2. Is Virtualization (only Management Servers) supported for monitoring 1,00,000 AEM clients ? 3. How to find out clients reporting to which server from SCOM end or any other tool.? (Client doesn’t show up where they are reporting to in console)
Is this SCOM management group dedicated to AEM only, or is it also managing Windows Agents?
I do not recommend mixing AEM monitoring with server monitoring at this kind of scale (which your AEM numbers are our maximum)
Yes Kevin. This setup is purely dedicated to AEM only. What are your thoughts on the 3 points I have mentioned above as I can see there is very less information is available on internet for SCOM AEM.
thanks for the information, a question because when updating the packages and restarting it no longer allows the connection to the scom indicating that the port is busy and that the data access is stopped
Thanks for having this platform. I am having issues deploying agents to Linux (RHEL 7 and 8). Push from OpsMan fails with:
Agent verification failed. Error detail: The server certificate on the destination computer (lmgllvtinf5001.zzzz.com:1270) has the following errors: Encountered an internal error in the SSL library. It is possible that: 1. The destination certificate is signed by another certificate authority not trusted by the management server. 2. The destination has an invalid certificate, e.g., its common name (CN) does not match the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) used for the connection. The FQDN used for the connection is: lmgllvtinf5001.zzz.com. 3. The servers in the resource pool have not been configured to trust certificates signed by other servers in the pool.
The server certificate on the destination computer (lmgllvtinf5001.zzzzzzz.com:1270) has the following errors: Encountered an internal error in the SSL library. It is possible that: 1. The destination certificate is signed by another certificate authority not trusted by the management server. 2. The destination has an invalid certificate, e.g., its common name (CN) does not match the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) used for the connection. The FQDN used for the connection is: lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local. 3. The servers in the resource pool have not been configured to trust certificates signed by other servers in the pool.
I am running SCOM 2019 with a Linux Resource Pool with 2 MGMT servers and followed cert exports/imports per your KB’s. Seems to be cipher related but cannot be certain. I get the same failure running WinRM Enumerate to the Linux Server in question:
WSManFault Message = The server certificate on the destination computer (lmgllvtinf5001.zzzzzz.com:1270) has the following errors: Encountered an internal error in the SSL library.
Error number: -2147012721 0x80072F8F
Here is the output from the Linux server with verifying the cert:
sysops1@lmgllvtinf5001:/etc/opt/omi/ssl # openssl s_client -connect localhost:1270 CONNECTED(00000003) depth=0 CN = lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local, CN = lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local verify error:num=20:unable to get local issuer certificate verify return:1 depth=0 CN = lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local, CN = lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local verify error:num=21:unable to verify the first certificate verify return:1 — Certificate chain 0 s:/CN=lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local/CN=lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local i:/CN=SCX-Certificate/title=SCX55a8126f-c88a-4701-9754-8625324426ff/DC=LMGLWVCMGT4002 — Server certificate —–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—– MIIDRTCCAi0CAQEwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAwbDEYMBYGA1UEAxMPU0NYLUNlcnRp ZmljYXRlMTAwLgYDVQQMEydTQ1g1NWE4MTI2Zi1jODhhLTQ3MDEtOTc1NC04NjI1 MzI0NDI2ZmYxHjAcBgoJkiaJk/IsZAEZFg5MTUdMV1ZDTUdUNDAwMjAeFw0yMTAy MTIwMDUyMjJaFw0zMjAyMTIwMTExNDFaMEwxJDAiBgNVBAMMG2xtZ2xsdnRpbmY1 MDAxLmhjcGxhYi5sb2NhbDEkMCIGA1UEAwwbbG1nbGx2dGluZjUwMDEuaGNwbGFi LmxvY2FsMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAztH94mfSyPTH CNTWtD/6xTsh3QP/VwFj+Tk56UjQLfSA7i8rmf99vNDEDEqYu37dFFb4iSrOwpgP XCF2sVdgbEBGDrn5Ac+RImgY9XQDRB9RULVS5qDPpmjV3G6Zx6G6yM9WhP9lx3vH ee59r9eYbj8QifrntpsDMWVr+d2XjSD7mVLzAXB3Jh3yO+lpVyy2fvlUYca2q+BD MtLeCamS8OJMOy28oBLDwAfMMwkUo+FoOQ1nj9IBVPWlNmOGYubhDcx6Ih/IYFQs YgXTmkqcOlGLzamNjwWSCHzMcPAbUZlhWHNPZdz1zBRu2mi1IGyMHvj4t0ALTU4C QsuoR+jcZQIDAQABoxcwFTATBgNVHSUEDDAKBggrBgEFBQcDATANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQsFAAOCAQEADXwPzPKySe1KvCaFhEwuO7eqJHJnk+4E3pgZbNX5imjo3ldmpHkc vJ1yn/Aix/chaD3B/fTe07KWrjsGmlyzDruCLMCn3SzAiP++2fjHtypPdd/APGDK uJTjZxfcUaPs4Oi8C0ZXgiSLUDCgWIkJbIVXL45u7yE6xiQikOXZBzbLbirjhwzr tPVpVvr/50FWWVYzXmRTv29vF1Yi/WVokh1W3UnKsLUwkN3odyQJtMUqMWleNQYW tPK1v7qHWiiPZTQ/lMxSp09DIL1J9k2hDJ01dU6bTq8oqUDtkGKLJCq7fvmWVrMd oepylTL07wwMeMm94DH6yFM3tA9soIrNgg== —–END CERTIFICATE—– subject=/CN=lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local/CN=lmgllvtinf5001.hcplab.local issuer=/CN=SCX-Certificate/title=SCX55a8126f-c88a-4701-9754-8625324426ff/DC=LMGLWVCMGT4002 — No client certificate CA names sent — SSL handshake has read 1154 bytes and written 607 bytes — New, TLSv1/SSLv3, Cipher is AES256-GCM-SHA384 Server public key is 2048 bit Secure Renegotiation IS supported Compression: NONE Expansion: NONE No ALPN negotiated SSL-Session: Protocol : TLSv1.2 Cipher : AES256-GCM-SHA384 Session-ID: 6FB3880342F3670DE7970F27FBA5C31B3C10DC1C834922C0DB6863B0A9409DB7 Session-ID-ctx: Master-Key: 27EB40E69E555D01C7C7B7B3B392A2FA9C002F802554213DB5ADA7B7C964AA87B289663E8052B331C5215F7B865C829D Key-Arg : None Krb5 Principal: None PSK identity: None PSK identity hint: None TLS session ticket lifetime hint: 300 (seconds) TLS session ticket: 0000 – 87 fe 53 a7 40 3a 55 e8-fb d1 a2 87 47 63 24 07 ..S.@:U…..Gc$. 0010 – a2 b6 03 40 a3 36 c4 92-d6 55 85 e0 bf eb 8d 00 …@.6…U…… 0020 – 3a 27 40 88 c9 92 25 21-0d ae 8a a1 00 bf 68 b0 :’@…%!……h. 0030 – 09 f3 b8 e4 26 57 25 2d-b7 a7 26 ab ad 8e 0a 13 ….&W%-..&….. 0040 – 32 e1 1b 78 f1 df e4 27-49 3c 34 52 0e 02 09 69 2..x…’I<4R…i 0050 – 77 a4 a4 26 9e 26 98 6f-6e 11 4c f1 0b 79 72 a0 w..&.&.on.L..yr. 0060 – 99 26 9e ef 25 53 da 43-33 1e 03 b5 89 ff a7 1a .&..%S.C3……. 0070 – 9f 74 45 26 8e 82 0b 80-dd 5c bc f9 07 c5 d9 c0 .tE&…..\…… 0080 – 47 40 db 61 e4 69 0d 85-49 16 8b 55 54 60 69 26 [email protected]`i& 0090 – 11 91 79 65 87 1b e4 8d-f7 ff e6 66 fc 57 51 bc ..ye…….f.WQ.
Start Time: 1644631874 Timeout : 300 (sec) Verify return code: 21 (unable to verify the first certificate)
Before i open a ticket with MS is there anything stunning I am missing?
I’d open a support call.
We do have similar issue. Do we have any solution?
Is SQL 2019 CU15 officially supported for SCOM 2019 ?
Sushanth S K
We do not comment on specific CU’s unless it is listed in the product documentation as a minimum requirement. For any supported version of SQL, SCOM always supports whatever the currently released CU is.
im getting the “Error: :PopulateUserRoles: failed” on my scom 2019 install and i have already confirmed that the tls 1.2 prereqs are installed per this link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/scom/plan-security-tls12-config?view=sc-om-2019
i decided to turn on verbose logging on the schannel and i am seeing the below at the time the :PopulateUserRoles errors out:
The certificate received from the remote server was issued by an untrusted certificate authority. Because of this, none of the data contained in the certificate can be validated. The TLS connection request has failed. The attached data contains the server certificate.
A fatal alert was generated and sent to the remote endpoint. This may result in termination of the connection. The TLS protocol defined fatal alert code is 48. The TLS alert registry can be found at http://www.iana.org/assignments/tls-parameters/tls-parameters.xhtml#tls-parameters-6
the iana link says alert code 48 is “unknown ca” but im not quite sure what certificate is being referenced either on the mgmt server or the db server.
I have not seen TLS 1.2 fail when the prereqs are there. What version did you install? The previous versions are still available for download.
on my MS i have MSOLEDB 19.0 and MSOLEDB 18.3 both installed. and they are also both installed on my DB and DW boxes as well. in addition i also have MS SQL Server 2012 Native Client 11.4 on all 3 servers. the OS is 2019 and the SQL server vrs is 2019
SCOM 2019 did not support MSOLEDB at install.
https://kevinholman.com/2018/05/06/implementing-tls-1-2-enforcement-with-scom/
One caveat – SQL Native Client is deprecated. SNAC11 and ODBC11/13 are the minimum drivers to support TLS 1.2. However, we generally recommend the latest MSOLEDBSQL which is actually supported by SQL. Our current documentation does not specify that we support MSOLEDBSQL in SCOM 2019, but I believe we started supporting it in SCOM 2019 UR2.
My general recommendation is to go with what works – For SCOM 2019 new deployments – install SNAC11 + ODBC13, then install SCOM 2019, then install the latest Update Rollup, then install MSOLEDBSQL
i removed all versions of MSOLEDB and ODBC from my mgmt server and only left SNAC 11.4 and ODBC 13.0. kicked off another install and now the MS, DB, DW are installed/configured. i appreciate ur time as always man!
I always use a UDL file on the desktop to test and validate TLS being the issue: https://mohammaddarab.com/how-to-test-connection-to-sql-server-using-udl-file/
Hi Kevin, We updated our company SCOM2019 Mgmt server and Agents, progressively from RTM to UR3. All SCOM Mgmt servers and the Agents were updated successfully and we can see the UR3 versions inside the SCOM Mgmt server console.
Mgmt server version = 10.19.10505.0 Agents version = 10.19.10177.0 .
However; once you open the monitored server registry, the SCOM Agent is still displaying RTM version = 10.19.10014.0.
We uninstall and re-install the SCOM Agent manually and updated it progressively from RTM to UR3, we can see the SCOM Agent version update itself progressively in the SCOM Mgmt server but does not update its version in the monitored registry it stay on the RTM version = 10.19.10014.0
Why do you think the registry should change? Which key?
Hi Kevin, Its not the Licence key, its the SCOM Agent Version # in the monitored server registry and the control panel program, that stays on # 10.19.10014.0 even if we update manually or automatically.
it does show the correct version in SCOM Mgmt server
(Get-ItemProperty “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft Operations Manager\3.0\setup”) (Get-ItemProperty “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft Operations Manager\3.0\setup”).AgentVersion
I believe once we update the SCOM Agent to UR3 it must change from RTM version = 10.19.10014.0.to Agents version = 10.19.10177.0.
It does show the correct agent version (10.19.10177.0.) in the SCOM2019 Mgmt server conrol panel but inside the monitored server the SCOM Agent remains on RTM version = 10.19.10014.0
Is it possible for our SCOM service accounts will be manage GMSA (Group Managed Service Accounts – https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/security/group-managed-service-accounts/group-managed-service-accounts-overview )? The AD team is implementing every 100 days, password will automatically change and this will impact our SCOM environment. RunAs accounts are also affected is also affected. Does SCOM 2019 and SCOM 2016 have this capability for the GMSA? Additionally, we still have SCOM 2012 R2 and migrating the agents to 2019. 🙂
Thanks and more power.
I am doing a side by side migration of SCOM 2012R2 to SCOM 2019. Is it possible for me to apply SCOM 2019 UR4 Console/Agent update to my already deployed SCOM 2012 R2 Consoles and Agents so they can be upgraded to SCOM 2019 UR4 version? I have about 40 SCOM 2012 R2 consoles installed on 40 computers and about 500 2012 R2 SCOM Agents deployed to servers all on the same domain.
We use SCCM to deploy Consoles and Agents to servers/workstations, so I was thinking of having SCCM uninstall the SCOM 2012 R2 agents and consoles, then have SCCM reinstall the SCOM agents and consoles with the SCOM 2019 UR4 updates including the Console hotfix. I just didnt know if upgrading was a possibility for the already installed 2012 R2 consoles/agents via SCCM or if I would have to do the uninstall and re-install route?
Thanks in advance, Kevin! Your website has helped me out a ton.
Any help here.. getting below error while discovery linux device from scom 2022.
WinRM cannot process the request. The following error occurred while using Kerberos authentication: The computer xxx.xxx.xxx is unknown to Kerberos. Verify that the computer exists on the network, that the name provided is spelled correctly, and that the Kerberos configuration for accessing the computer is correct. The most common Kerberos configuration issue is that an SPN with the format HTTP/xxx.xxx.xxx is not configured for the target. If Kerberos is not required, specify the Negotiate authentication mechanism and resubmit the operation
We’ve completed an in-place upgrade of a 2016 management group to 2019. The environment consists of two management servers on Windows 2016 server, and SQL 2016 for our DBs.
As far as I’m aware, we followed the step by step guide to the letter. There were no errors during the upgrade on either management server.
Following the upgrade, both management servers are in an offline state (grey ticks in console). The second management server to be upgraded is now displaying an alert the same as the one described by John in this thread:
“Management configuration service failed to complete bootstrap procedure”. This alert is NOT present on the first mgmt server.
The body of the same alert reports that the version of cscmdbops.dll is lower than the expected version of 10.19.10050.0.
However when I check the .dll version on each mgmt server it is actually version 10.19.10050.0, not the version 7.x .dll that the alert is complaining about.
Grateful for any advice. We’re trying to avoid a side by side upgrade, but can roll back to snap shots for this environment if required.
Update: The grey state of the management servers was resolved by giving the SCOM action and Datawarehouse write accounts the local “logon as a service” right on each management server. I missed this requirement in the security matrix spreadsheet.
The bootstrap error persists. Will probably rollback the upgrade and try again with above permissions in place.
Good morning Kevin,
Will using Local System as the action and SDK account cause any issues? My current org would like to use the least amount of accounts for SCOM. We used to have four (One for AA, SDK, DReader, DWriter), but now we want to use LocalSystem for SDK/AA and one account for DReader/DWriter. Is that possible?
In a large environment, you end up with a lot of SQL logins when doing that (for each management server Computer Account) but that’s the biggest hurdle I know of. Why not just use a single account for all of SCOM? I am heading in that direction. I have never understood why we separate into 4 distinct accounts, and nobody has ever provided a good reason for continuing that beyond the “separation of duties with minimal rights” debate. Seems like a lot of extra garbage to keep up with for very little purpose.
Our environment is only 2 Management Servers and we will be managing about 200 or less agents. So it will be a small environment. We are going to convert our SCOM accounts to GMSA today, so I will ask to see if we can just use one account for everything instead of using local system for AA/SDK.
On another note, I think I would have to use at least 1 account for everything. Im going through the steps to switch to GMSA accounts and each account requires different roles within the databases. Im not too savvy with SQL, but If Im using local system as the AA and SDK account, thats gonna be a problem adding roles isnt it? With using one account, I should be able to apply all those roles to that one account and be good to go (I think)
You can use a single GMSA for everything *except* the SSRS report server execution account.
I just had a customer do this. When you add the SQL login, you grant the specific role level requirements as documented here: https://kevinholman.com/2020/07/23/scom-2019-security-account-matrix/ https://kevinholman.com/2022/09/26/scom-2022-security-account-matrix/
You simply add those specific rights for the single account, based on the 4 individual account/role requirements. No problemo.
It worked like a charm. We are actually using the AA/SDK as local system and the Data Reader/Writer accounts as 1 GMSA. So far no errors in events log or anything abnormal.
What will happen if we remove the SCOM service accounts from local admin groups? Our Security is asking us to remove the service accounts from admin group. Appreciate your response
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Our Services
- Free products
Subscription
Complete SCCM / MECM Installation Guide and Configuration
Founder of System Center Dudes. Based in Montreal, Canada, Senior Microsoft SCCM Consultant, 8 times Enterprise Mobility MVP. Working in the industry since 1999. His specialization is designing, deploying and configuring SCCM, mass deployment of Windows operating systems, Office 365 and Intune deployments.
Benoit Lecours
Table of Content
Sccm hardware requirements, sccm installation guide.
- Operating System
Active Directory schema extension
Create the system management container, sccm accounts.
- Network Configuration
Firewall Configuration
No_sms_on_drive.sms, windows server features, roles and features, report viewer, adk for windows 10, active directory, local admin accounts, sccm client, windows updates, install sql server management studio (ssms), install sql reporting services.
- Apply SQL 2017 CU2 or higher
SPN Creation
Sql configuration, database sizing, create database.
- Review the Site Database properties
TempDB sizing
- Review the TempDB properties
SQL Communications
Prerequisite check, new sccm installation, system center 2012 r2 configuration manager toolkit, sccm current branch installation extra information, sccm current branch upgrade, sccm current branch configuration, role description, site system role placement in hierarchy, prerequisites.
- SCCM Application Catalog Installation
Verification and Logs files
Url redirection, client settings, role description, aisp installation, verification, enable inventory reporting classes, maintenance tasks.
- CRP Installation
Configuration Manager Policy Module
Introduction, pre-requisites, distribution point server configuration.
- Windows Server configuration – Roles and Features
Remote Differential Compression
Windows deployment service.
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable
Powershell 3.0
Distribution point site server installation.
- Add new distribution point server to the SCCM console – Site System
Replicate content
Distribution point monitoring, requirements.
- EPP Installation
SUP Configuration
- SCCM Enrollment Point Installation
FSP Installation
Configure clients, sccm management point installation, configure reporting services, add reporting services point role in sccm, recovery model, web browser.
- WSUS Installation
- Software Update Point Installation
- SCCM State Migration Point Installation
Create the USMT Package
Sccm system health validator point installation, configure client settings, sccm service connection point installation, planning for sccm boundaries and boundary groups, overlapping boundaries, real world scenario.
- Create Boundary Group
- Create Site Assignment Boundary Group
Create Content Location Boundary Group
How to create custom client device settings, set the client settings priority, how to deploy a client settings, how to apply, how to verify your client settings, what is sccm discovery methods, active directory system discovery, active directory group discovery, active directory user discovery, active directory forest discovery, heartbeat discovery, network discovery.
- Part 22 – Configure Maintenance Tasks
To enable the site backup maintenance task
Verify that the backup site server maintenance task is running, more sccm ressources.

Get the latest insights and exclusive content delivered to your inbox
This blog post is a completely revised Step-by-step SCCM Installation Guide. It covers every aspect of the SCCM Installation. From the server prerequisites to the SQL installation, the SCCM installation and all configuration and site server installation. Following this guide, you should have a functional SCCM server in a few hours.
We already did a guide in the past when SCCM 1511 was released, but it was time for a 2020 refresh.
Since our first guide, more than 12 SCCM versions have been released… and the product even changed its name to Microsoft Endpoint Manager. (MEM or MEMCM).
SCCM installation has never been easy, and the product can be complex for inexperienced administrators. With this blog post, we aim to bring it a bit further, explaining concepts and best practices rather than just guiding the user through the installation process.
If you’re unfamiliar with SCCM’s Current Branch Features, you can visit this Microsoft Docs article , which covers everything.
Stop reading this guide if you’re still running SCCM 2012 (!) and plan to migrate. You do not need to do a completely new installation. See our blog post on upgrading to the SCCM Current Branch instead.
We hope this guide brings all the necessary information and that you’ll appreciate administering it.
Part 1 – Design Recommendation and Installation Prerequisites
In the first part, we will cover SCCM installation prerequisites, precisely hardware requirements, design recommendations, and server prerequisites.
The hardware requirements for a Primary Site server largely depend on the enabled features and how each component is utilized. When the number of clients grows and changes, the server hardware requirements change accordingly. For the initial deployment, hardware requirements can be estimated for each server by determining:
- The overall need for each component (Will you do Operating System Deployment ? How many daily software deployments ? Is Inventory and reporting necessary for your organization? Will you manage Internet Clients?)
- The number of clients planned to be installed
- The load on each of the installed SCCM components
In general, medium environments (a couple thousand clients) should consider the following recommendations when planning hardware:
- SCCM and SQL Server communicate constantly. We recommend installing the SCCM database and SQL Server on the Primary site server. This is debatable, and we understand that some organizations try to standardize their SQL distribution. Performance is simply better using a local installation when appropriately configured.
- Neither the SCCM site nor the SQL database should share their disks with other applications.
- Configure the SQL Server databases and logs to run on a disk different from where the SCCM database is located.
Another issue to consider when determining hardware requirements for a site server is the total amount of data that will be stored in the database. An approximate figure of 5Mb to 10Mb per client is typically used to estimate the required database size for a single site.
In our setup, we will install a single primary site with the roles of management point, reporting point, distribution point, PXE service point, state migration point, fallback status point, and software update point. SQL Reporting Services will be used to provide consolidated reporting for the hierarchy. This role will also be installed on the SCCM Server. Running reports can impact server CPU and memory utilization, particularly if large, poorly structured queries are executed as part of the report generation.
Consider placing a client-facing role (Distribution Point, Reporting Point) on a separate server to reduce load on your Primary server.
Here’s our recommended reading about hardware requirements:
- Design a hierarchy of sites
- Recommended hardware
- Supported configurations
- Plan for the site database
- Plan for site system servers and site system roles
We strongly recommend that you understand SQL Server before installing SCCM. Talk to and have a good relationship with your DBA if you have one in your organization.
Here’s our recommended reading about SQL :
- Storage Top 10 Best Practice
- SQL Server Best Practices Article
- Disk Partition Alignment Best Practices for SQL Server
O perating System
Our servers run Windows 2019 with the latest security patches for this post.
Make sure that your OS is supported; see the SCCM Current Branch Technet Documentation
Disk IOs are the most critical aspect of SCCM performance. We recommend configuring the disks following SQL Best practices. Split the load on different drives. When formatting SQL drives, NTFS’s cluster size (block size) must be 64KB instead of the default 4K. See the previously recommended reading to achieve this.
Primary Site server prerequisites
Once your hardware is carefully planned, we can now prepare our environment and server before SCCM Installation.
You need to extend the Active Directory Schema only if you didn’t have a previous installation of SCCM in your domain. If you have SCCM 2007 already installed and are planning a migration, skip this step.
- Login to a server with an account that is a member of the Schema Admins security group
- From SCCM ISO run .\SMSSETUP\BIN\X64\extadsch.exe
- Check the schema extension result, and open Extadsch.log located in the root of the system drive.
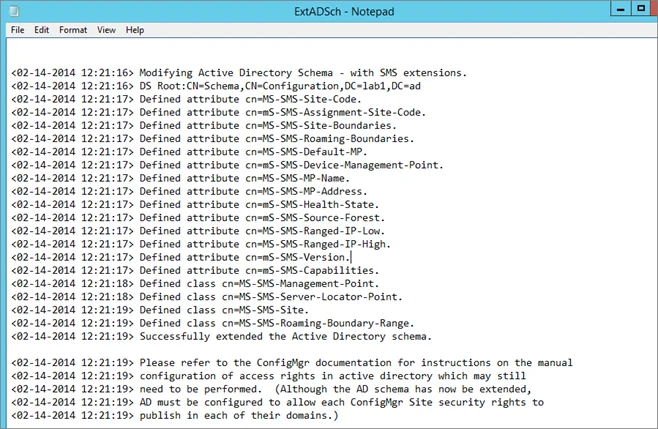
Configuration Manager does not automatically create the System Management container in Active Directory Domain Services when the schema is extended. The container must be created once for each domain, including a Configuration Manager primary or secondary site server that publishes site information to Active Directory Domain Services.
- Start ADSIEdit , go to the System container and create a new Object
- Select Container
- Enter System Management
Set security permission
- Open properties of the container System Management created previously
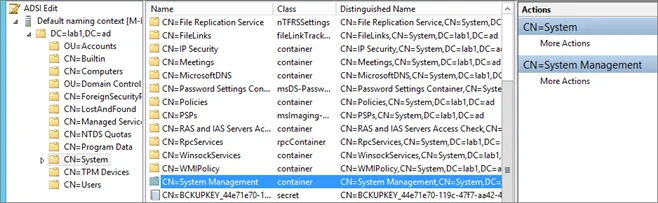
- In the Security tab, add the site server computer account and Grant Full Control permissions
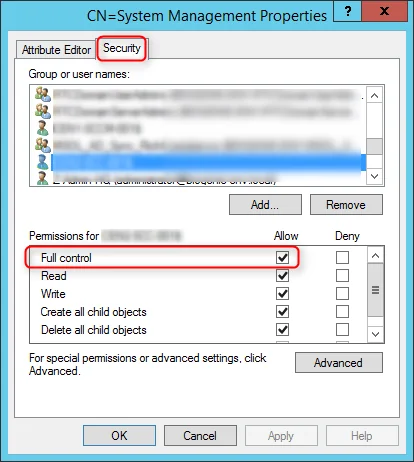
- Click Advanced, select the site server’s computer account, and then click Edit
- In the Applies to list, select This object and all descendant objects
- Click OK and close the ADSIEdit console
Create the necessary accounts and groups created before installation. You can use a different name, but I’ll refer to these names throughout the guide.
- SQL server services account – SCCM-SQLService
- SCCM Network Access Account – SCCM-NAA
- Domain user account for use SCCM client push install – SCCM-ClientPush
- Domain user account for use with reporting services User – SCCM-SQLReporting
- Domain account used to join machine to the domain during OSD – SCCM-DomainJoin
- Domain group containing all SCCM Admins Group – SCCM-Admins
- Domain group containing all SCCM servers in the hierarchy Group – SCCM-SiteServers
Network Configuration
- Make sure that the server has a fixed IP and that the internet connection is up
- Make sure the firewall service is ON
Run this script in an elevated command prompt to open the ports needed for SCCM.
** If you are using custom ports, change the values before running the script. **
@echo ========= SQL Server Ports =================== @echo Enabling SQLServer default instance port 1433 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Server” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=1433 @echo Enabling Dedicated Admin Connection port 1434 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Admin Connection” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=1434 @echo Enabling conventional SQL Server Service Broker port 4022 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Service Broker” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=4022 @echo Enabling Transact-SQL Debugger/RPC port 135 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Debugger/RPC” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=135 @echo ========= Analysis Services Ports ============== @echo Enabling SSAS Default Instance port 2383 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”Analysis Services” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=2383 @echo Enabling SQL Server Browser Service port 2382 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Browser” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=2382 @echo ========= Misc Applications ============== @echo Enabling HTTP port 80 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”HTTP” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=80 @echo Enabling SSL port 443 netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SSL” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=443 @echo Enabling port for SQL Server Browser Service’s ‘Browse’ Button netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Browser” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=1434 @echo Allowing Ping command netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”ICMP Allow incoming V4 echo request” protocol=icmpv4:8,any dir=in action=allow
Place a file name no_sms_on_drive.sms on the root drive of each drive you don’t want SCCM to put content on.
The following components must be installed on the Primary site server before SCCM installation. We’ll install all these components using a PowerShell script.
- .Net Framework 3.51 SP1
- .Net Framework 4
- BITS Server Extension
- WSUS 3.0 SP2
- ADK for Windows 8.1
On the Site Server computer, open a PowerShell command prompt as an administrator and type the following commands. This will install the required features without using the Windows 2012 GUI.
Get-Module servermanager Install-WindowsFeature Web-Windows-Auth Install-WindowsFeature Web-ISAPI-Ext Install-WindowsFeature Web-Metabase Install-WindowsFeature Web-WMI Install-WindowsFeature BITS Install-WindowsFeature RDC Install-WindowsFeature NET-Framework-Features -source \yournetwork\yourshare\sxs Install-WindowsFeature Web-Asp-Net Install-WindowsFeature Web-Asp-Net45 Install-WindowsFeature NET-HTTP-Activation Install-WindowsFeature NET-Non-HTTP-Activ
Ensure that all components are showing as SUCCESS as an EXIT Code. It’s normal to have Windows Update warnings at this point.
Download and install – here
- Select the default path
- Do not join CEIP
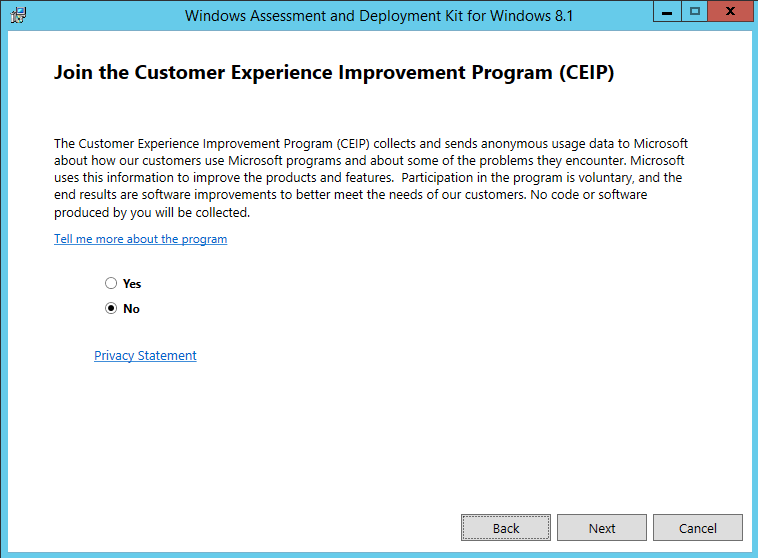
- Accept the License Agreement
- Deployment Tools
- Windows Pre-installation Environment
- User state Migration tool
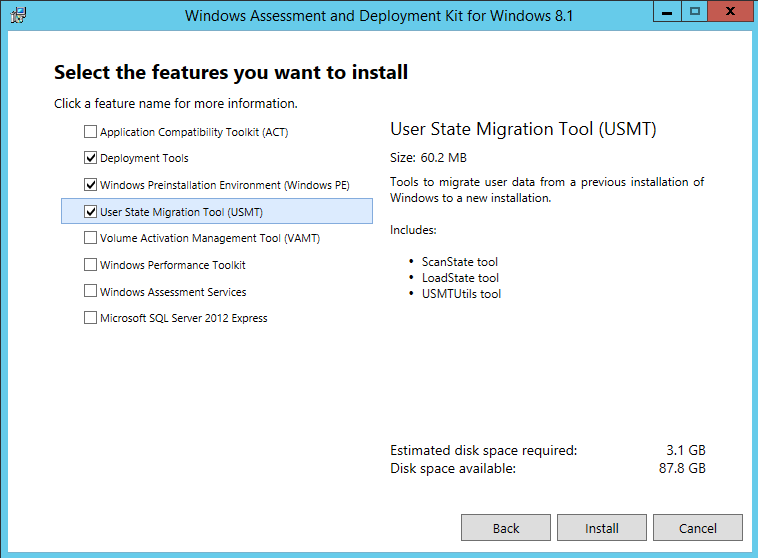
- Add the computer account of all your site servers in the SCCM-SiteServers AD group.
- Ensure that the group has Full Control of the SYSTEM Container in the Active Directory.
Add both the SCCM computer account and the SCCM Admin account to the local administrator group on the site server.
- SCCM-Admins
- SCCM-SiteServers
If applicable, uninstall the SCCM 2007 client and FEP if present on the server before the installation. The 2012 SCCM Management Point installation will fail if the client is present.
Run Windows update and patch your server to the highest level
Your server is now ready for the SQL installation.
Part 2 – SCCM SQL 2017 Installation
We will go through the complete SCCM SQL 2017 Install Guide to install and configure SQL before installing SCCM Current Branch 1806 or higher.
This post is our updated version of our SQL install guide for version 2017 and higher. If you are planning on installing an older version of SQL, please follow our previous post here .
Click the following link to see all supported SQL versions . For our post, we will install SQL 2017 locally on the same server where the Primary Site will be installed.
- Execute Setup.exe from the SQL installation media, select New SQL server stand-alone installation.
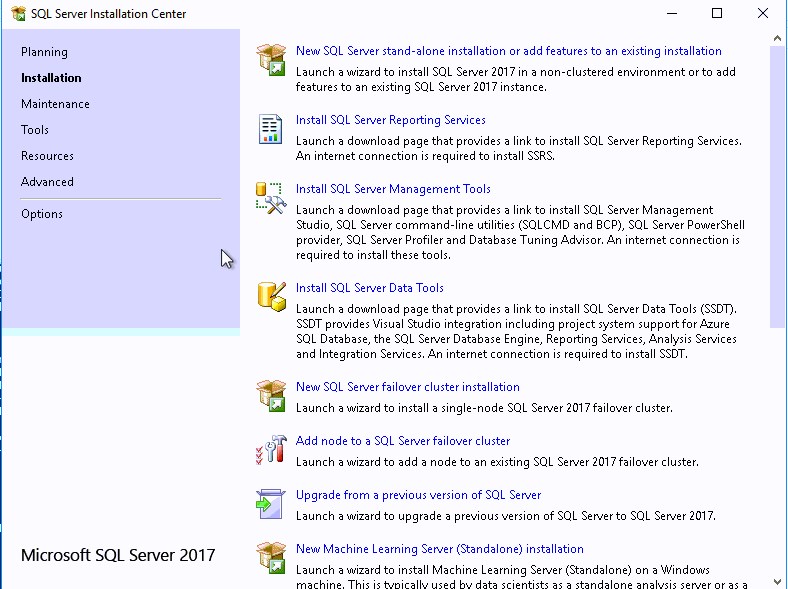
- Provide the product key and click N ext
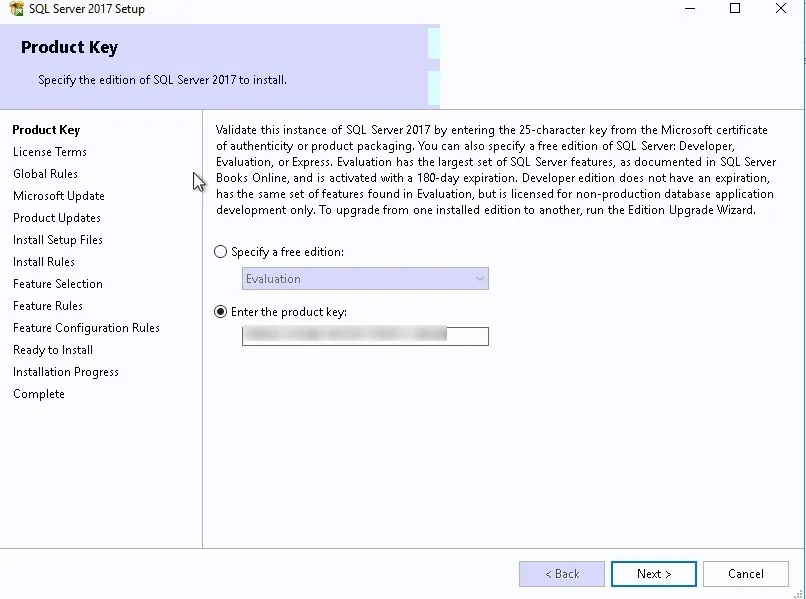
- Review and Click Next
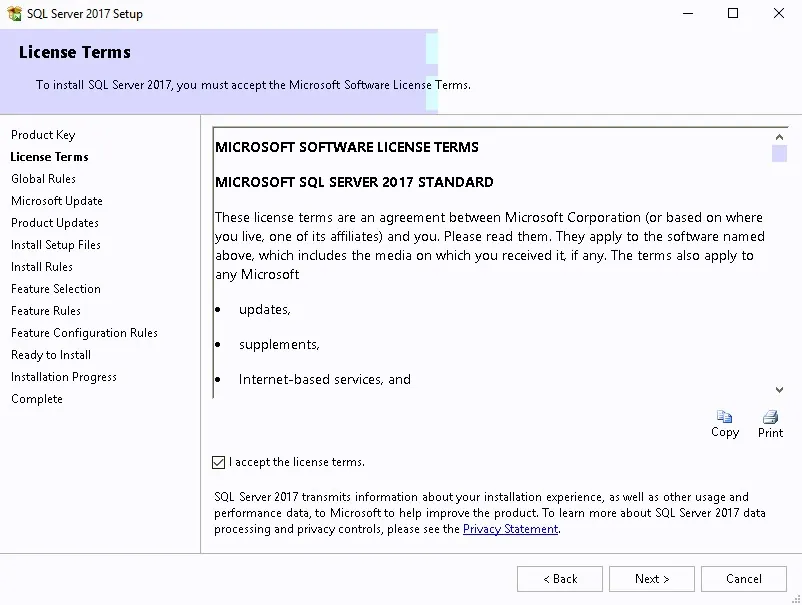
- Check Use Microsoft Update to check for updates and click Next
- Select SQL Server Feature I nstallation
Note that some steps in the wizard are automatically skipped when no action is required. For example, product updates, Install setup Files and Install Rules might be skipped.
- Select the Database Engine feature and specify the SQL installation directory. This is the directory for the program files and shared features.
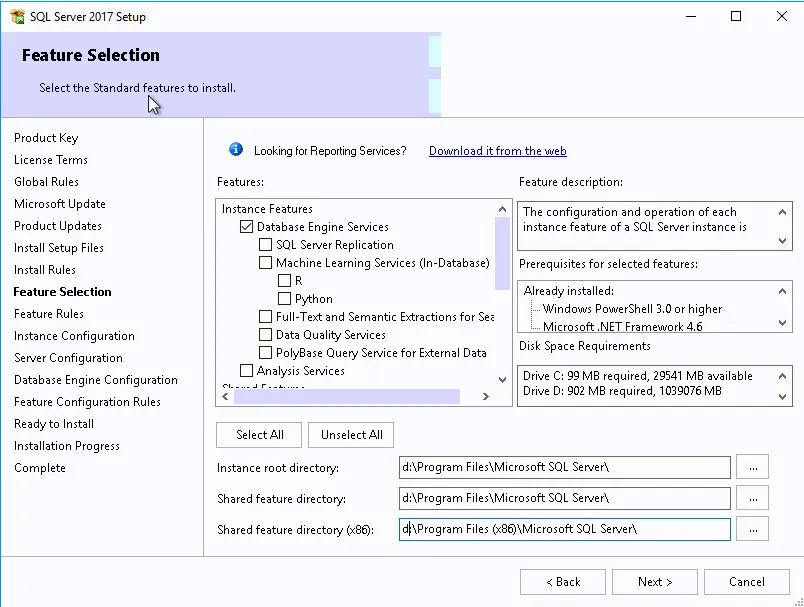
- Select Default instance and ensure that your instance is created on the SQL Volume.
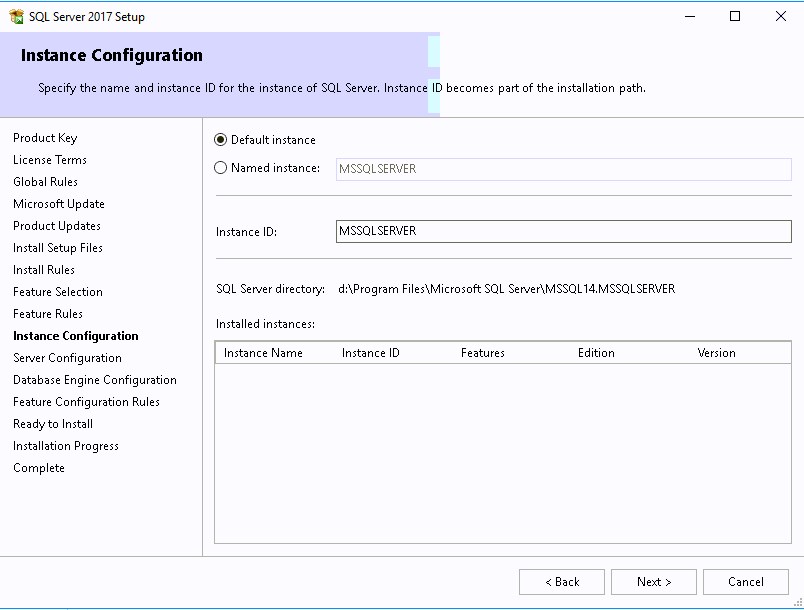
- Set all services to run as the SQL domain account that you created previously and set the services startup type to Automatic.
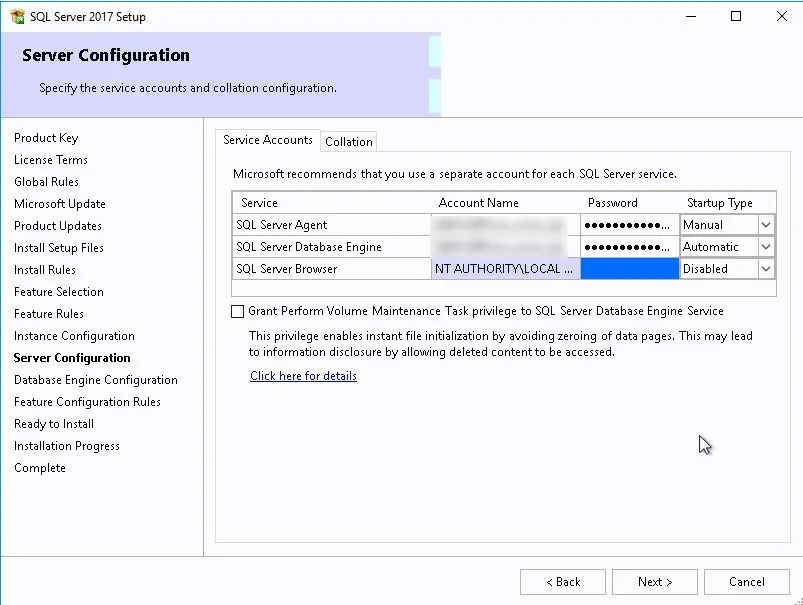
- On the Collation tab, set the Database Engine to use SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS.
- In the Server Configuration tab, set the authentication mode to Windows Authentication and in the SQL Server Administrators, add your SCCM Admins group.
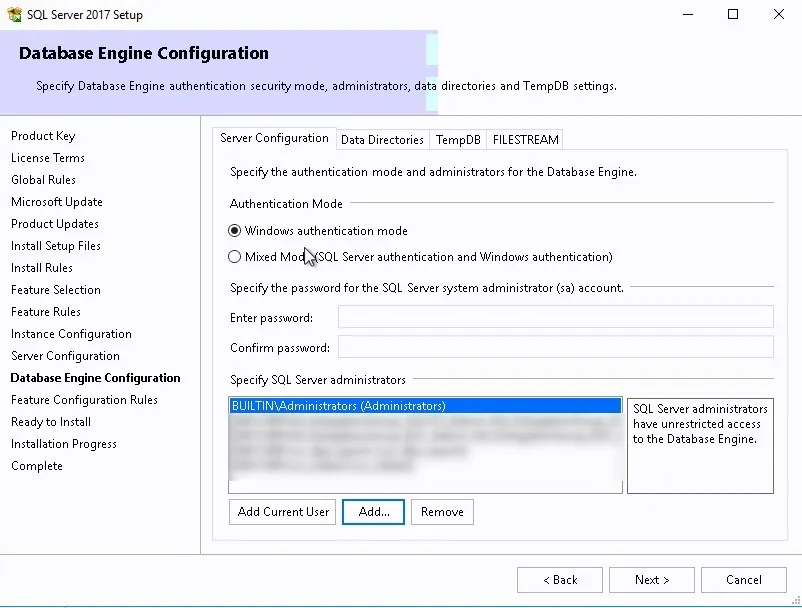
- In the Data Directories tab, set your drive letters correctly for your SQL databases , Logs , TempDB , and backup .
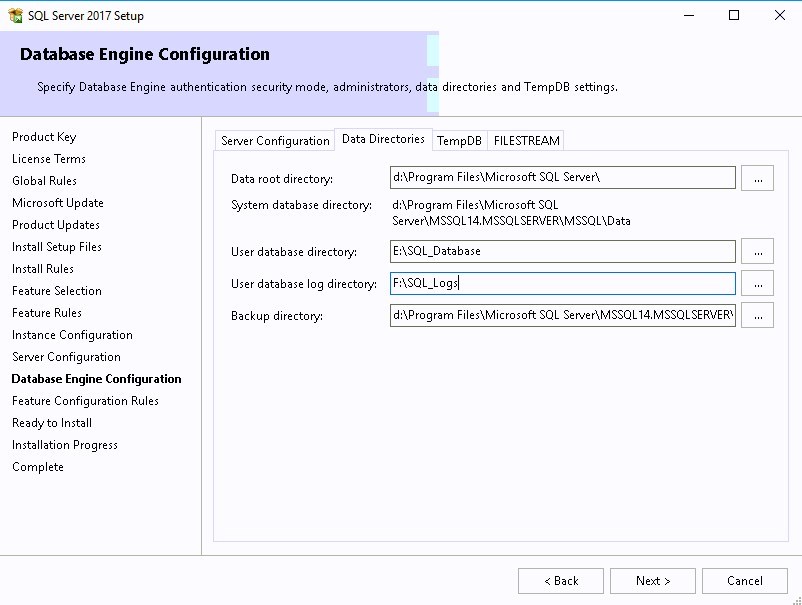
- On the TempDB , complete the various information based on the Database sizing section below.
- Click Install
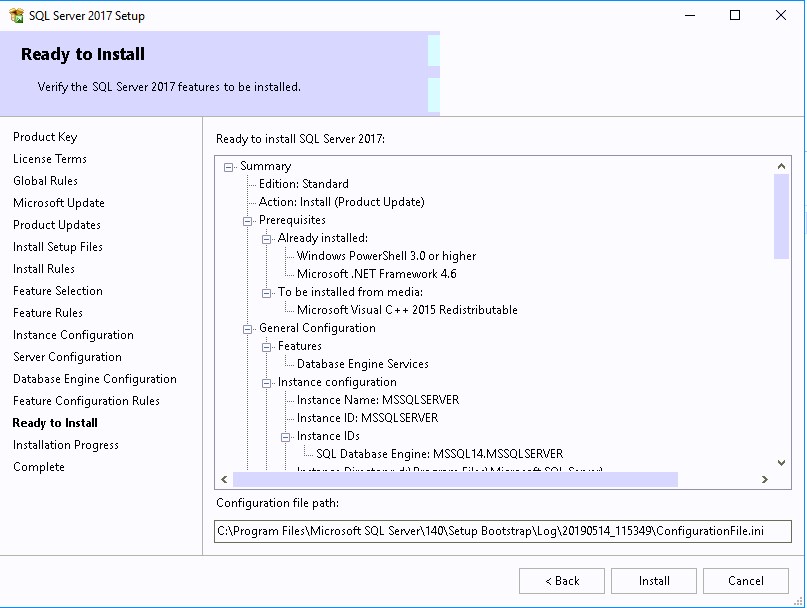
- Complete the installation by clicking Close
- Back in the SQL Server Installation Center, click on Install SQL Server Management tools.
- This will redirect you to the Download page of SQL Server Management Studio. SSMS is no longer tied to the SQL server installation in terms of version.

- Adjust the installation path if needed, then click Install
- Click on Install SQL Reporting Services in the SQL Serv er Installation Center.
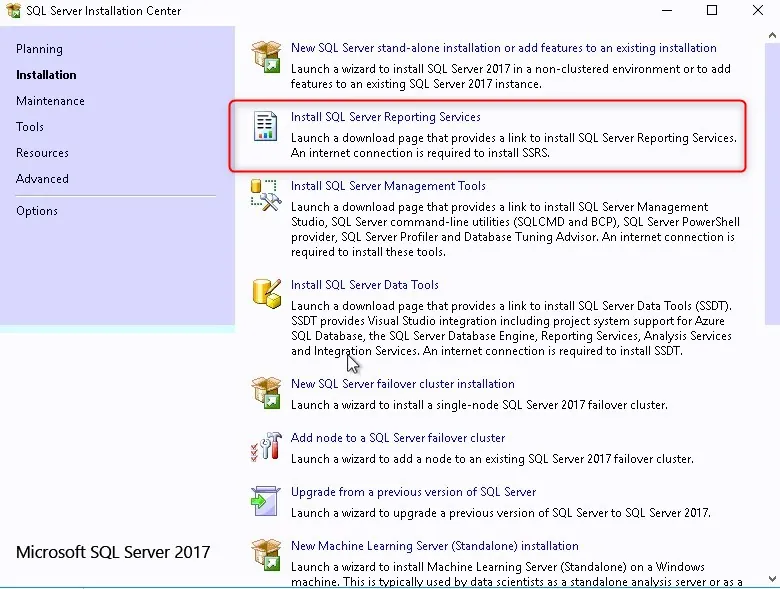
- The SQL reporting services are just like the Management console; they require a separate download .
- Click on Install Reporting Services
- Provide the Product key
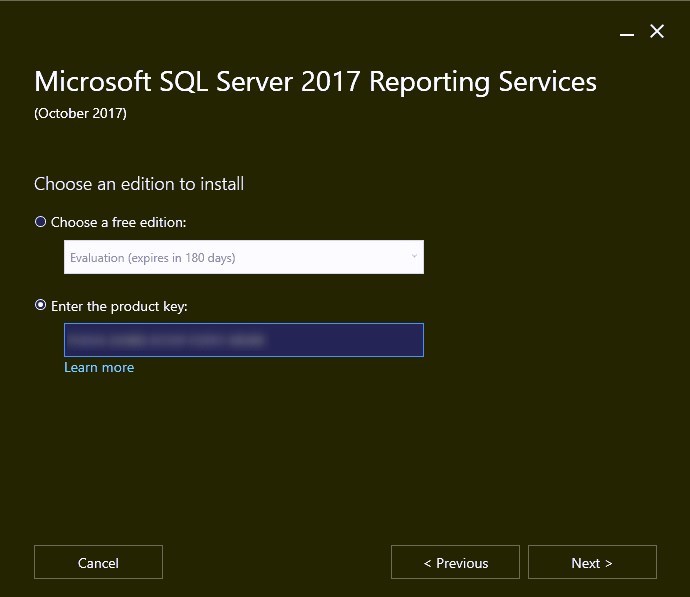
- Accept License terms
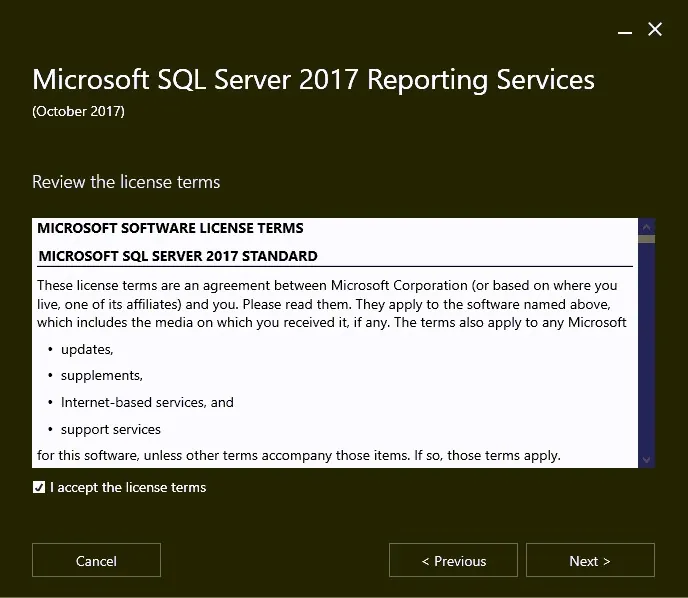
- Select the installation path, click Install
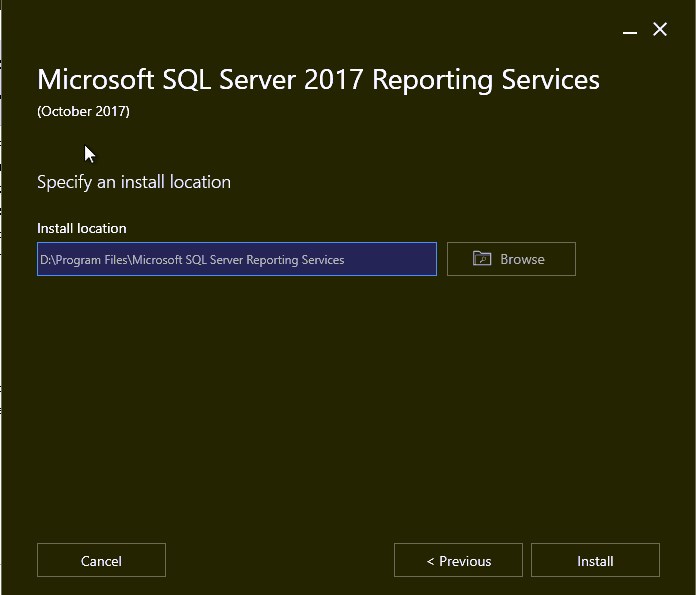
- A reboot is required after the installation
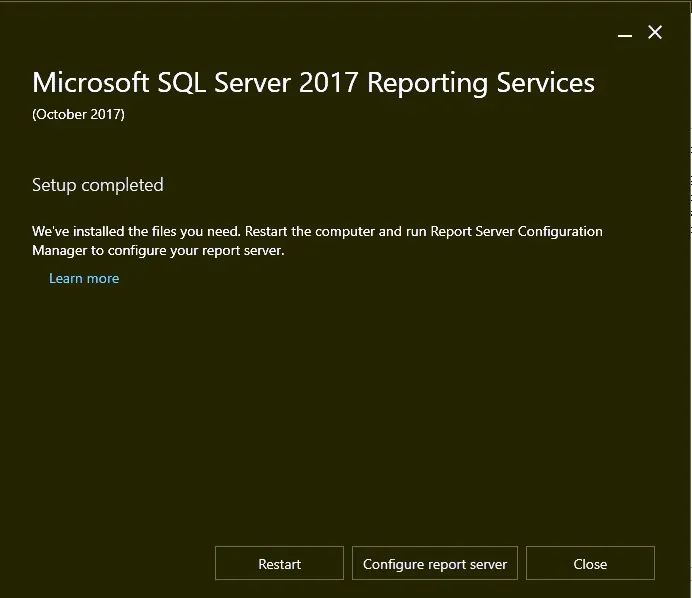
Apply SQL 2017 CU 2 or higher
At the time of this writing, the latest SQL Cumulative Update is CU17 . We will install it to have an updated SQL Installation. Note that CU2 is the minimum requirement.
- Download and execute SQL 2017 CU17
- Accept the license terms and click Next
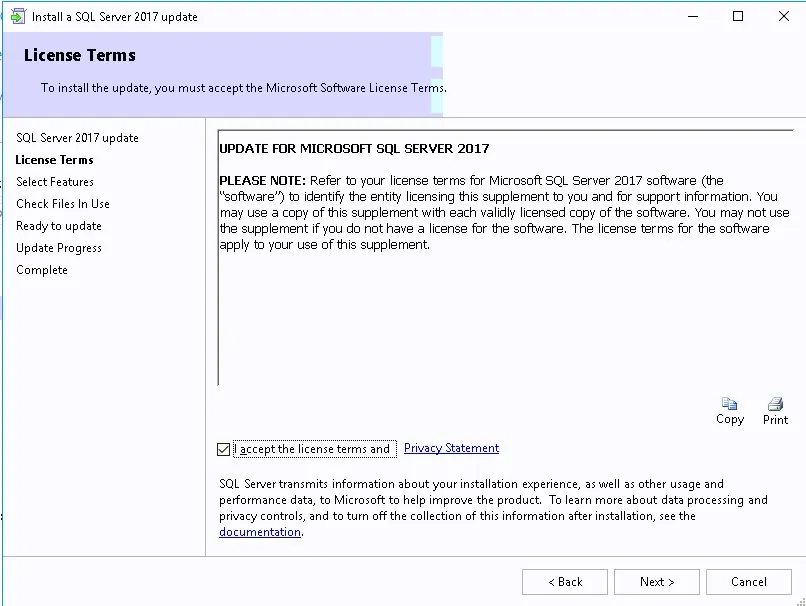
- Leave default values, click Next
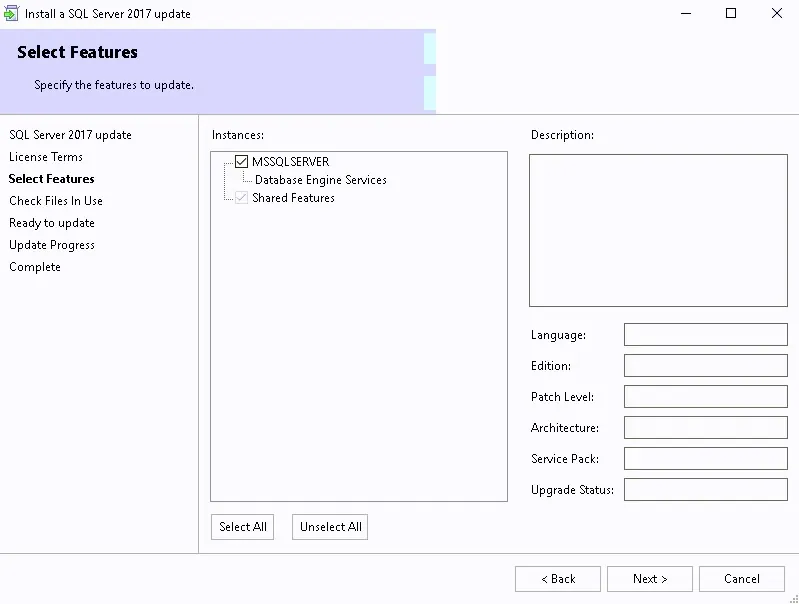
- Wait for Check File in Use and click Next
- Click Update
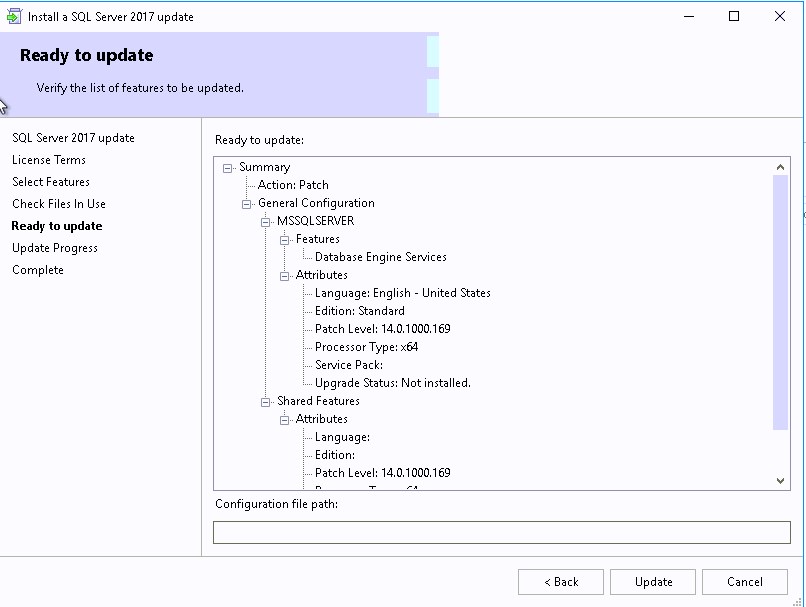
- Update completed; might require a reboot.
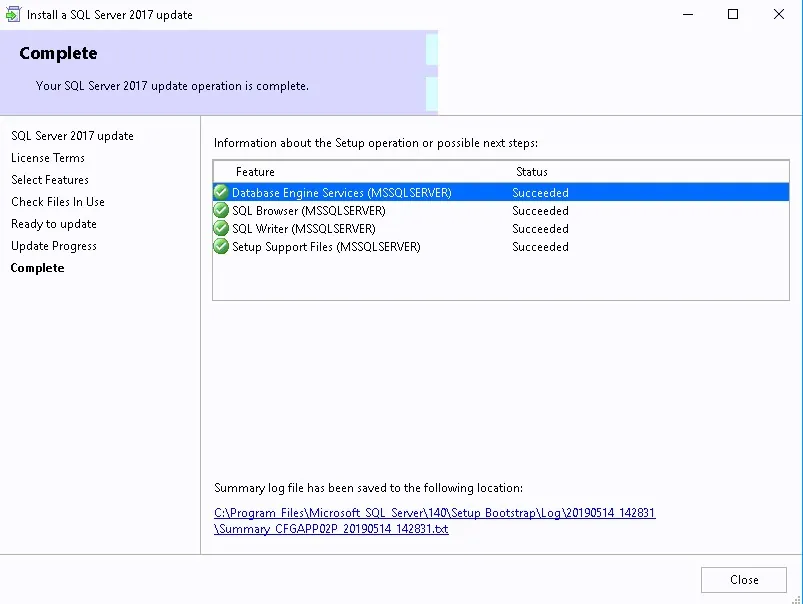
When you configure SQL Server to use the local system account, a Service Principal Name (SPN) for the account is automatically created in Active Directory Domain Services. When the local system account is unused, you must manually register the SPN for the SQL Server service account.
Since we are using a domain account, we must run the Setspn tool on a computer that resides in the domain of the SQL Server. It must use Domain Administrator credentials to run.
Run both commands to create the SPN, Change the server name and account name in each commands.
- setspn -A MSSQLSvc/yourservername:1433 yourdomain\SQLSA
- setspn -A MSSQLSvc/yourserver.fullfqdn.com:1433 yourdomain\SQLSA
To verify the domain user SPN is correctly registered, use the Setspn -L command
- setspn –L yourdomain\SQLSA
SCCM setup verifies that SQL Server reserves a minimum of 8 GB of memory for the primary site. To avoid the warning, we’ll set the SQL Server memory limits to 8GB-12GB (80% of available RAM).
- Open SQL Server Management Studio
- Right-click the top SQL Server instance node.
- Select Properties
- Minimum 8192
- Maximum 12288
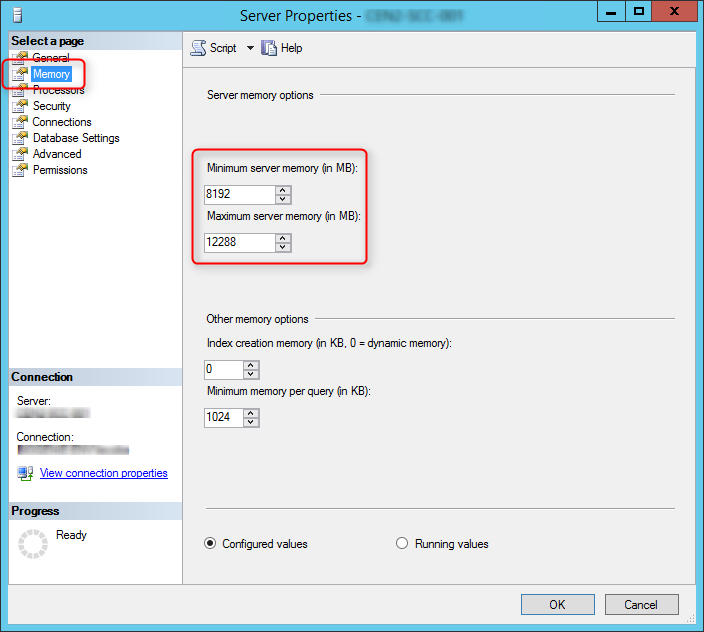
We always recommend creating the SCCM database before the setup. This is not mandatory, SCCM will create the database for you during setup but will not create it the optimal way. We strongly recommend watching The Top Ten Lessons Learned in Managing SQL session from MMS2013 which covers it all.
We follow the guide made by MVP, Kent Agerlund to estimate my DB sizing need. Visit his blog post and download the provided Excel file. Input your values in the blue cells and keep it for the next part. We’ll create the DB using those values using a script in the next section.
For this blog post, We’ve created a Database for 2000 clients, 2 processors, 2 cores and 16GB RAM.
To create the database, you can use Kent’s script and input your values (as returned previously in the Excel file) OR use the following one which is really simple:
The Name value will become your Site Code during the SCCM installation. Be sure to select a unique Site Code.
- **Replace all XXX value with your 3 character Site Code**
- **Change the values of the Filename, Size, MaxSize and FileGrowth. Change the location of the file to your SQL and Logs drives**
USE master CREATE DATABASE CM_XXX ON ( NAME = CM_XXX_1,FILENAME = ‘E:\SCCMDB\CM_XXX_1.mdf’,SIZE = 7560, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 2495) LOG ON ( NAME = XXX_log, FILENAME = ‘G:\SCCMLogs\CM_XXX.ldf’, SIZE = 4990, MAXSIZE = 4990, FILEGROWTH = 512) ALTER DATABASE CM_XXX ADD FILE ( NAME = CM_XXX_2, FILENAME = ‘E:\SCCMDB\CM_XXX_2.mdf’, SIZE = 7560, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 2495)
Review the Site Database properties
- Open SQL Management Studio
- Right-click your DB, Select Properties
- In the General tab, verify that the SQL collation name is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
- In the File tab, verify that your database files has been created with the script value
- Verify that the file is located on your SQL Volume
- Change the database owner to SA. By default the owner will be the account that created the database.
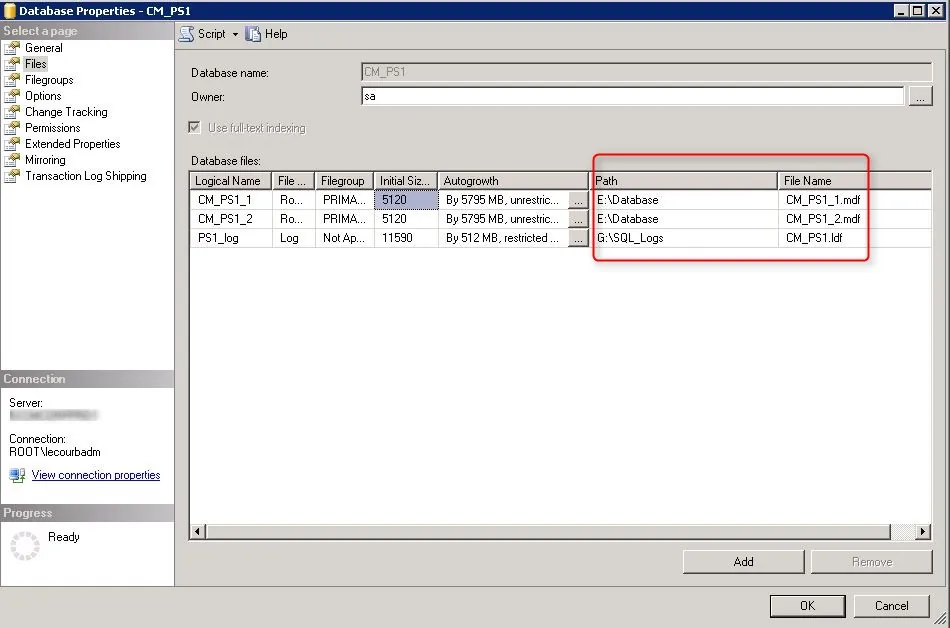
If you find out that you made an error, you can safely delete the Database using SQL Management Studio and rerun the script.
- Right-click your DB, Select Delete
This section is left here for reference to help configure the TempDB in the installation wizard.
Run the following scripts to size the TempDB. (using the value returned by the Excel file)
**Change the values of Filename, Size, MaxSize and FileGrowth. Change the location of the file to your TempDB drives**
use master go alter database tempdb modify file (name=’tempdev’, filename=’F:\SCCMTempDB\tempDB.MDF’, SIZE= 4536, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 512) go alter database tempdb modify file (name=’templog’, filename=’G:\SCCMLogs\templog.LDF’, SIZE= 2268, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 512) go
Review the TempDB properties
- In System Database, Right click the TempDB, select Properties
- In the File Tab, verify that your database files has been created with the script value
- Ensure that the TempDB and log are on the TempDB volume
To ensure proper SQL communication, verify that settings are set accordingly in SQL Network configuration
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Go to SQL Server Network Configuration / Protocols for MSSQLServer
- On the Right Pane, right-click TCP/IP and select Properties
- Enable: YES
- Listen All : NO
- In the IP Addresses tab
- Active : YES
- Enabled : YES
- Enabled : NO
- TCP Dynamic Ports : Blank value
- TCP Port : 1433
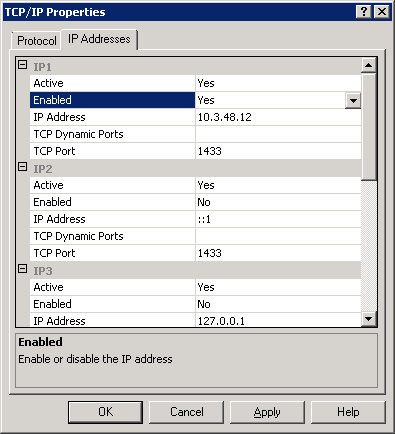
Once the modification has been made, restart the SQL Server Service.
The server is now ready for the SCCM installation. We will now run the prerequisite checker and proceed to the complete SCCM Installation. We will install a stand-alone Primary site.
Part 3 – SCCM Current Branch Installation
Before launching the SCCM installation, we recommend launching the Prereqchk tool in order to verify if all components are configured correctly. The SCCM installation wizard will also run this check but if you’re missing a requirement, you’ll have to go through the whole installation wizard again after fixing it. We prefer to use the standalone tool before running the setup.
To start the prerequisite check tool :
- Open an Administrator command prompt
- Browse to .\SMSSETUP\BIN\X64
- Run the following command: Prereqchk.exe /AdminUI
If you follow the prerequisite guide correctly you’ll have this result :
Refer to this Technet article to see the list of all checks done by the tool.
If you have any warning or error refer to this Technet article in order to resolve it, or go thought part 1 and part 2 of this guide.
We are finally ready to launch the setup. First, reboot the server. This will make sure that the machine is not in a Reboot pending state.
- Mount and open the SCCM ISO that was previously downloaded from the Microsoft Volume Licensing Site
- Run Splash.hta
- Select Install
- On the first screen, Click Next
- On the Getting Started screen, Select Install a Configuration Manager Primary Site and click Next
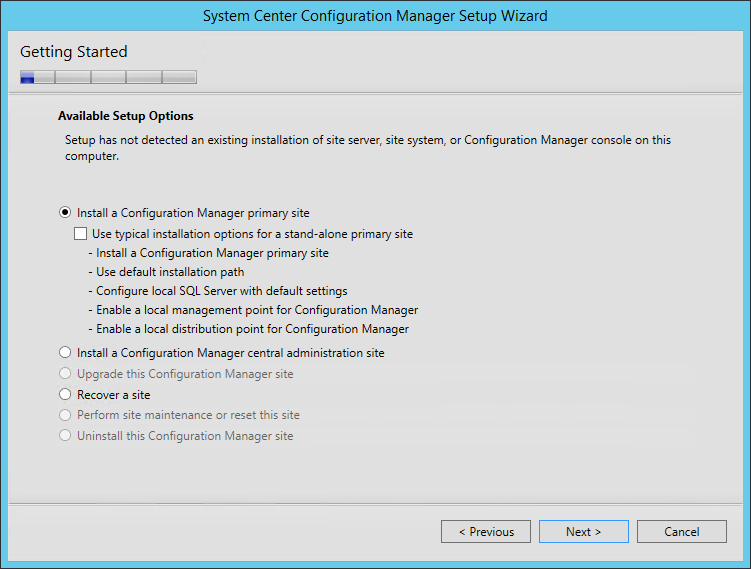
- On the Product Key screen, enter it and click Next
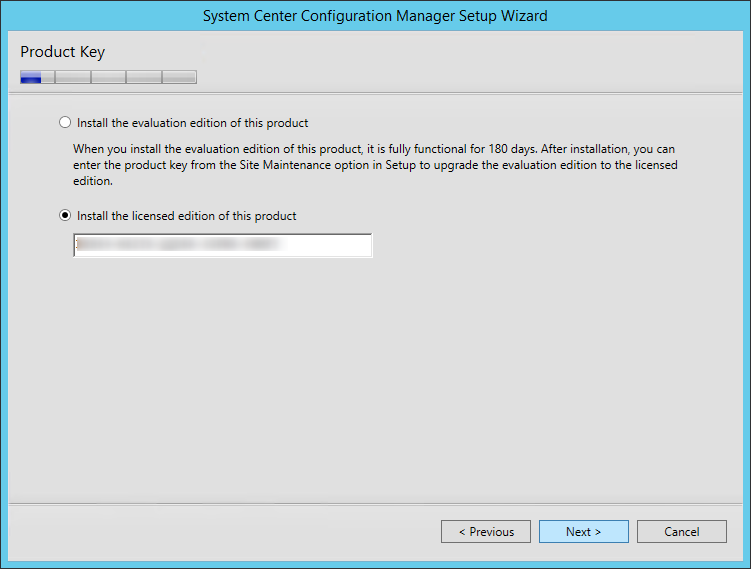
- On the Microsoft Software License Terms screen, accept the terms and click Next
- On the Product License Terms screen, accept the License Terms and click Next

- On the Prerequisite Downloads screen, specify a location to download the prerequisite file. This folder can be deleted after setup
- On the Server Language Selection screen, select the language you want to display in the SCCM Console and Reports. You can modify language later by running setup again and select the Site Maintenance option
- On the Client Language Selection screen, select the Client language to support. You can modify languages later by running setup again and select the Site Maintenance option
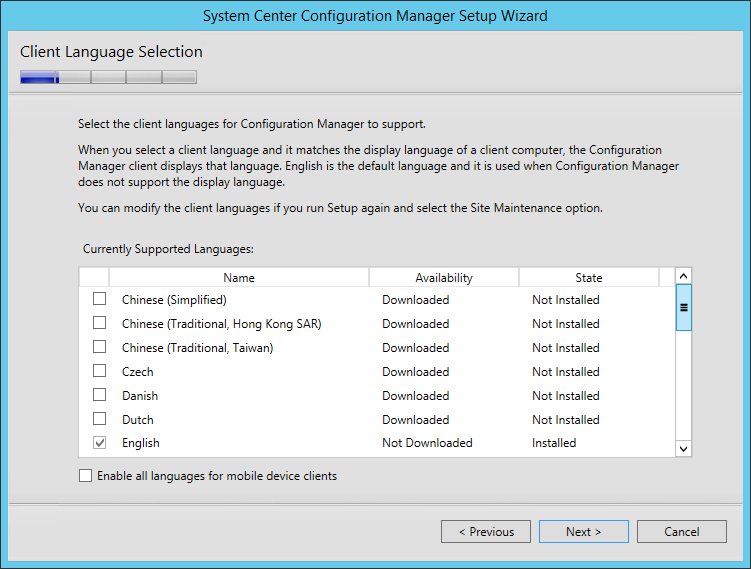
- Note : Site codes cannot be used more than one time in a Configuration Manager hierarchy for a central administration site or primary sites. If you reuse a site code, you run the risk of having object ID conflicts in your Configuration Manager hierarchy. This applies also if you’re doing a migration from an earlier version.
- Enter your Site Name. This name will appear in the console so choose accordingly
- On the Primary Site Installation screen, select Install the primary site as a stand-alone site. If you have a Central Administration site , this is where you would join the Primary Site to the existing hierarchy
- On the warning, click Yes
- On the Database Information screen
- Enter your SQL Server Name . In our case the SQL server is the same box as SCCM
- Leave the Instance Blank
- Enter your Database name . Once again, this must match the previously created Database in part 2
- Leave the Service Broker Port to 4022
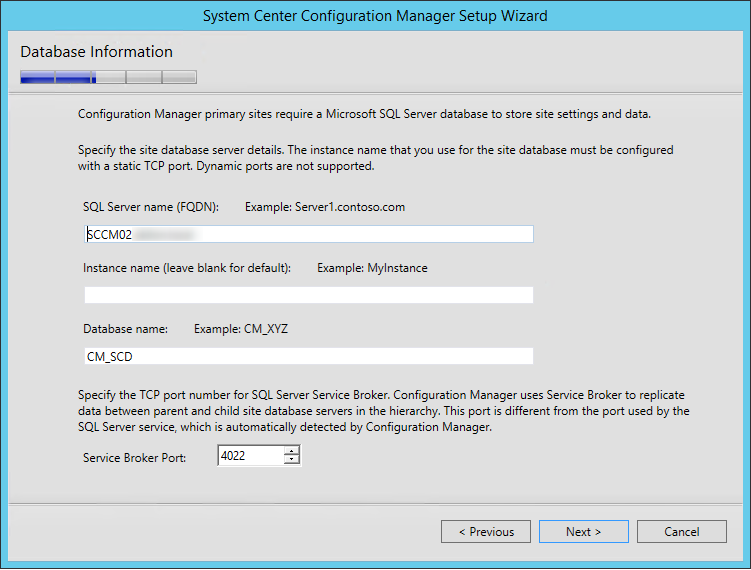
- Enter the path to the SQL Server data file. Locate this on the SQL Volume
- Enter the path to the SQL Server log file. Locate this on the SQL Logs Volume.
- I like to use the same directory where I created my database and logs (E:\SCCMDB, G:\SCCMLogs)
- On the SMS Provider Settings screen, leave the SMS Provider to the default value which is the local server. Refer to the following Technet article to read about the SMS Provider.
- On the Client Computer Communication Settings screen, select Configure the communication method on each site system role. This is where you select to have HTTPS or not on your initial Management Point and Distribution Point. This setting can be changed later
- On the Site System Roles screen :
- Check Install a Management Point
- Check Install a Distribution Point
- The Client connection drop-down is unavailable due to our previous selection
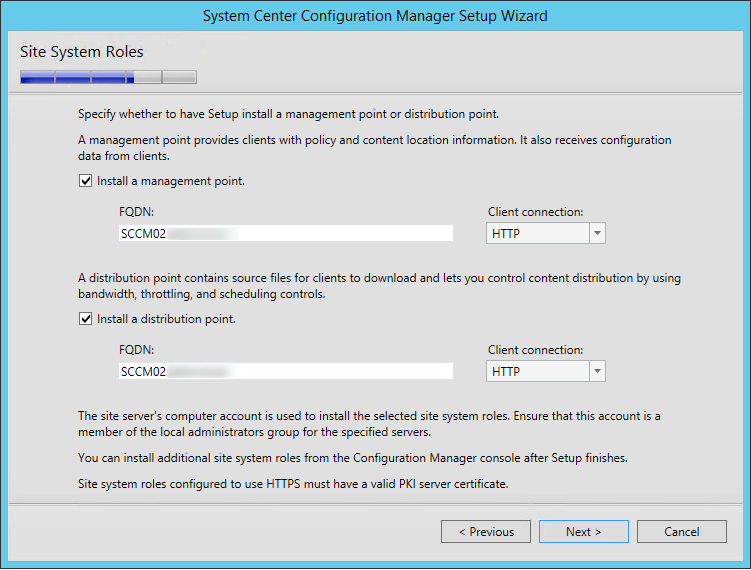
- On the Usage Data screen, click Next. This new screen basically tells that you accept that you will send some telemetry data to Microsoft
- On the Service Connection Point screen, click Next. This new role enables your deployment to download updates and new features
- On the Settings Summary Screen, review your options and click Next
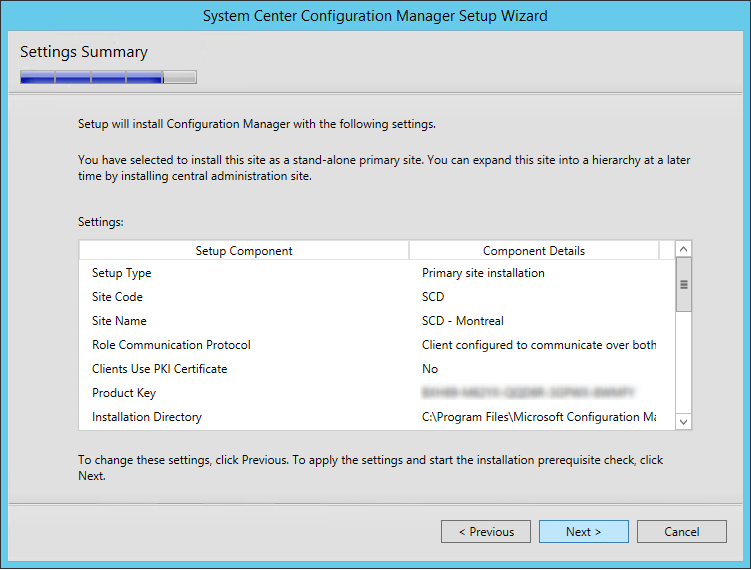
- On the Prerequisite Check screen, you should have no error since you’ve run it before setup, click Next
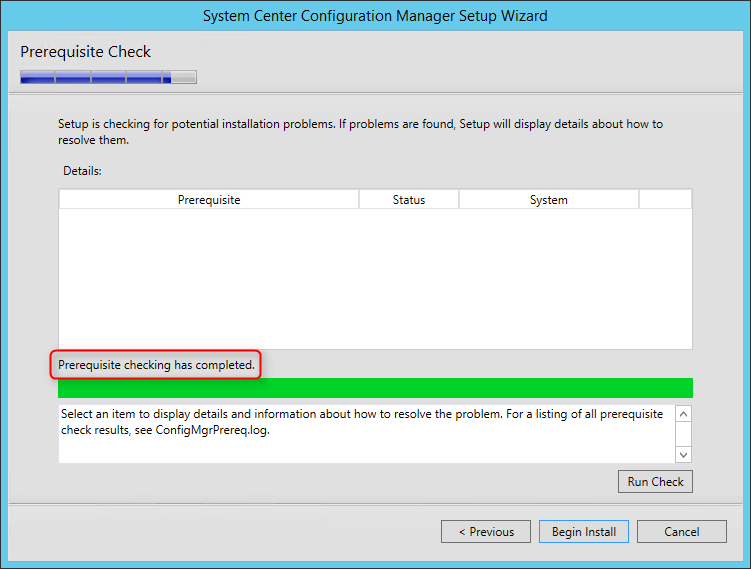
- The installation is in progress. You can count between 15 and 30 minutes depending of your server specifications
- You can follow the progress by clicking the View Log button or open the ConfigMgrSetup.log file on the C: drive
- Wait for Core setup has completed and close the wizard
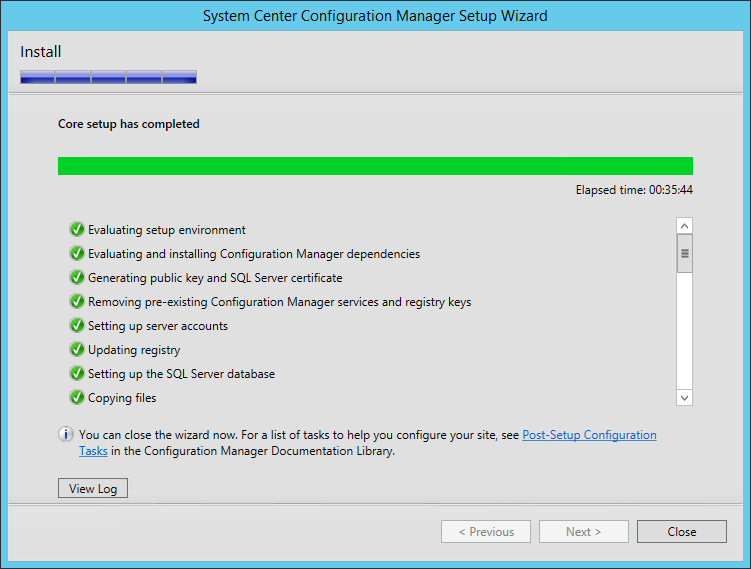
We’re still not done yet ! Before opening the SCCM console, we suggest to install the following tools :
CMTrace will become your best friend when reading log files.
- Open the SCCM ISO
- Browse to .SMSSETUPTOOLS
- Click on CMTrace.exe
- Click on YES to set is as your default log viewer
Additionally, you can read our blog post :
- How to use CMTrace like a Pro Part 1
- How to use CMTrace like a Pro Part 2
The SCCM 2012 R2 toolkit is compatible with SCCM Current Branch and contains fifteen downloadable tools to help you manage and troubleshoot SCCM.
Download and install it here
You can also refer to our blog post about Useful Resources to help you begin with SCCM. If you need further help to understand and configure various SCCM site components, consult our Step-by-Step SCCM 1511 Installation Guide blog series. It covers all you need to know.
The first task we like to do after a new SCCM installation is to upgrade it to the latest version. If you’re not familiar with this, Microsoft releases a Baseline version that you can install from scratch and then, you must upgrade to the latest version. We have a bunch of guides for each version. For reference, at the time of this blog post, the baseline is 1902 and the latest version is SCCM 1910. Just follow our latest upgrade guide and you’ll be at the latest available version.
The next sections will be for configuring the various site server roles in your newly installed SCCM server. Role installation order is not important, you can install roles independently of others.
Part 4 – Application Catalog web service point
This part will describe how to install the SCCM Application Catalog web service point and the Application Catalog website point. Both of these roles are now unsupported . We do not recommend adding this role to your hierarchy.
The application catalogue’s Silverlight user experience isn’t supported as of current branch version 1806. Starting in version 1906, updated clients automatically use the management point for user-available application deployments. You also can’t install new application catalogue roles. Support ends for the application catalogue roles with version 1910 .
The Application Catalog web service point provides software information to the Application Catalog website from the Software Library.
The Application Catalog website point provides users with a list of available software.
This is not a mandatory site system but you need both the Application Catalog website point and the Application Catalog web service point if you want to provide your user with a Self-Service application catalog (web portal).
The Application Catalog web service point and the Application Catalog website point are hierarchy-wide options. It’s supported to install those roles on a stand-alone Primary site or child Primary site. It’s not supported to install it on a Central Administration site or Seconday site. The Application Catalog web service point must reside in the same forest as the site database.
If you’re having less than 10,000 users in your company, co-locating the Application Catalog web service and Application Catalog website roles on the same server should be ok. The web service role connects directly to the SCCM SQL database so ensure that the network connectivity between the SQL server and the Application Catalog web service servers is robust.
If you have more geographically distributed users, consider deploying additional application catalogs to keep responsiveness high and user satisfaction up. Use client settings to configure collections of computers to use different Application Catalog servers.
Read more on how to provide a great application catalog experience to your user in this Technet blog article .
If your client needs HTTPS connections, you must first deploy a web server certificate to the site system. If you need to allow Internet clients to access the application catalog, you also need to deploy a web server certificate to the Management Point configured to support Internet clients . When supporting Internet clients, Microsoft recommends that you install the Application Catalog website point in a perimeter network, and the Application Catalog web service point on the intranet. For more information about certificates see the following Technet article .
Using Windows Server 2012, the following features must be installed before the role installation:
Application Catalog web service point
- .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 and 4.0
WCF activation:
- HTTP Activation
- Non-HTTP Activation
IIS Configuration:
- ASP.NET (and automatically selected options)
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
Application Catalog website point
- .NET Framework 4.0
- Static Content
- Default Document
- Windows Authentication
SCCM Application Catalog Installation
For this post, we will be installing both roles on our stand-alone Primary site using HTTP connections. If you split the roles between different machines, do the installation section twice, once for the first site system (selecting Application Catalog web service point during role selection)and a second time on the other site system (selecting Application Catalog website point during role selection).
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select Application Catalog web service point and Application Catalog website point, click Next
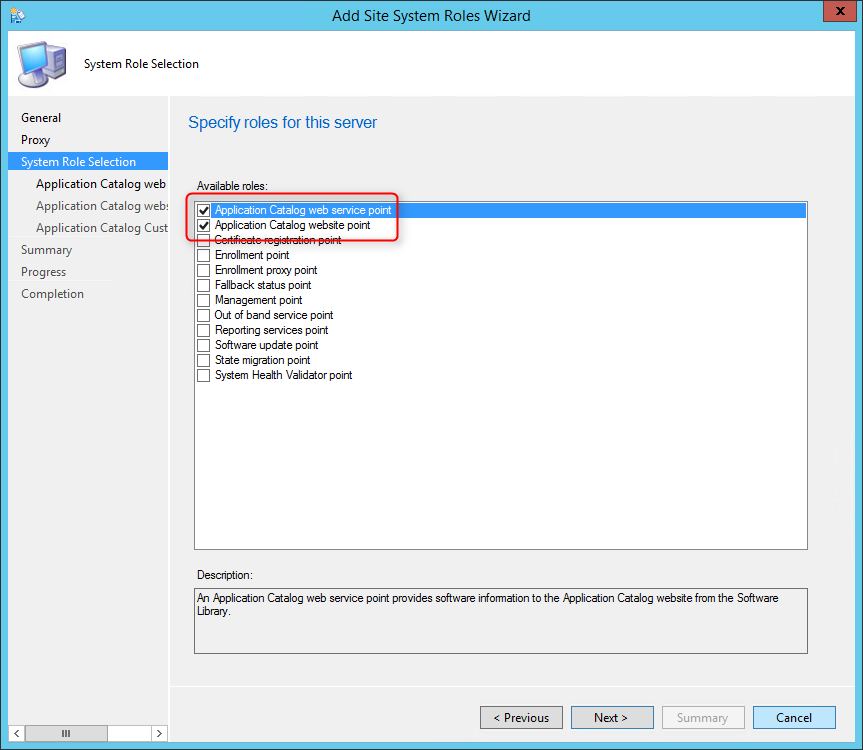
- In the IIS Website and Web application name fields,leave both to the default values
- This is just the name that you’ll see in IIS after the installation (see next screenshot). It has nothing to do with your user facing portal
- Enter the port and protocol that you want to use
- In the IIS Website keep the default value
- In Web application name, enter the name that you want for your Application Catalog. This is the URL that will be published to your users
- On the Application Catalog Customizations tab, enter your organization name and the desired colour for your website
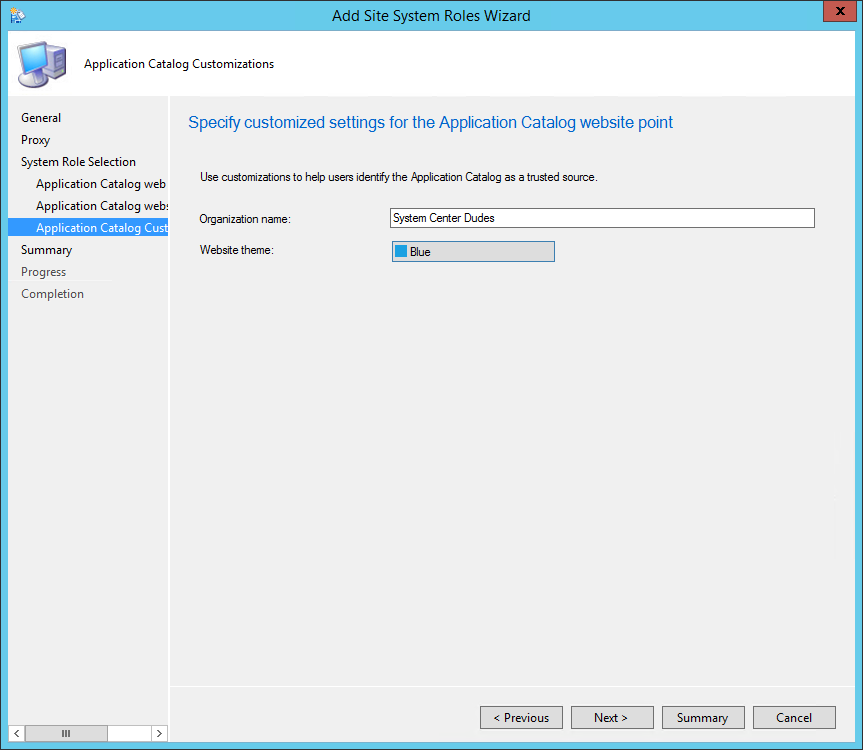
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next and complete the wizard
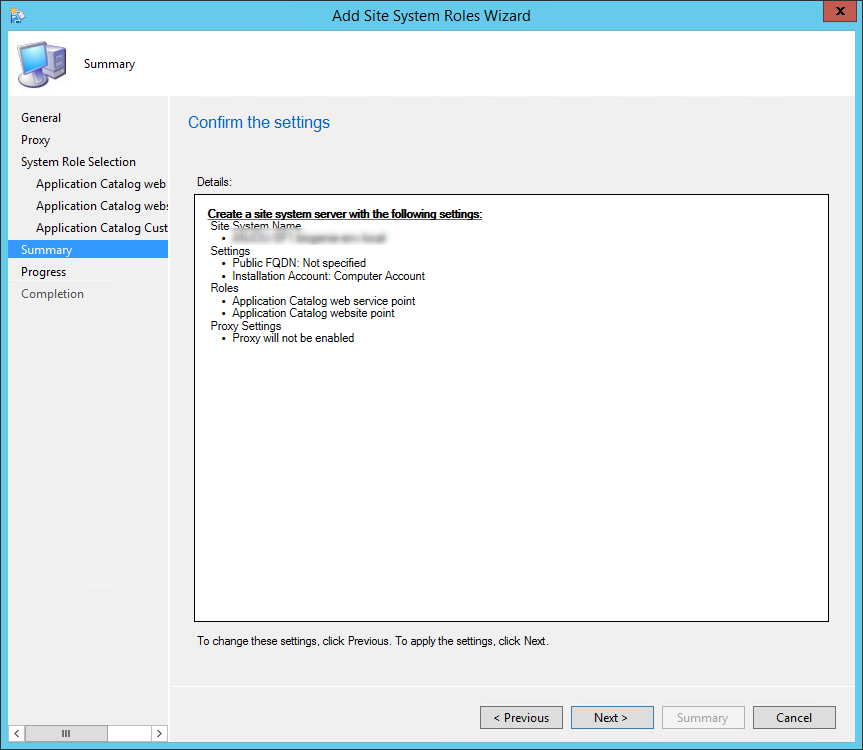
You can verify the role installation in the following logs:
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ SMSAWEBSVCSetup.log and awebsvcMSI.log – Records details of about the Application Catalog Web Service Point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ SMSPORTALWEBSetup.log and portlwebMSI.log – Records details of about the Application Catalog Website Point installation
In the console :
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Monitoring / System Status / Component Status
- See status of the components SMS_PORTALWEB_CONTROL_MANAGER and SMS_AWEBSVC_CONTROL_MANAGER

Web browser
Verify that the Application Catalog is accessible :
- Open a web browser
- Replace YourServerName with the server name on which you installed the Application Catalog Website Point
- Replace CMApplicationCatalog with the name that you give your Application Catalog. (Default is CMApplicationCatalog)
If everything is set up correctly, you’ll see a web page like this :
The default URL to access the Application Catalog is not really intuitive for your users.
It’s possible to create a DNS entry to redirect it to something easier (ex: http://ApplicationCatalog) The following Coretech article describe how to achieve that.
Ensure that the client settings for your clients are set correctly to access the Application Catalog
- Go to Administration / Client Settings
- Right-click your client settings and select Properties
- On the left pane, select Computer Agent
- Click the Set Website button and select your Application Catalog (the name will be automatically populated if your Application Catalog is installed)
- Select Yes on both Add Default Application Catalog website to Internet Explorer trusted site zone and Allow Silverlight application to run in elevated trust mode
- Enter your organisation name in Organisation name displayed in Software Center
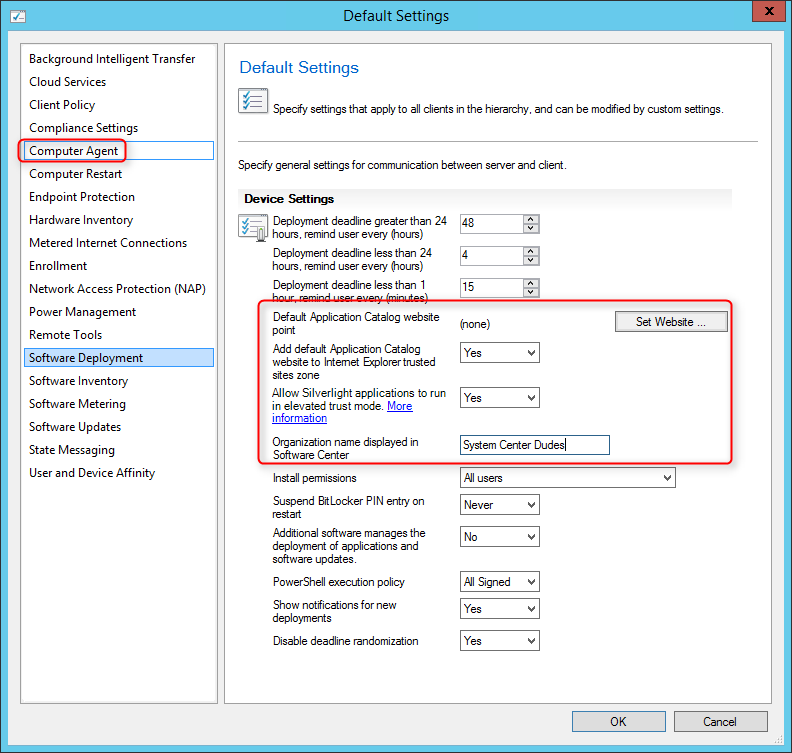
That’s it, you’ve installed your SCCM Application Catalog, publish the link to your user and start publishing your applications.
Part 6 – Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point
This part will describe the Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point (AISP).
The AISP is used to connects to Microsoft in order to download Asset Intelligence catalog information and upload uncategorized titles. For more information about planning for Asset Intelligence, see Prerequisites for Asset Intelligence in Configuration Manager .
This is not a mandatory Site System but we recommend to install the AISP if you are planning to use Asset Intelligence. Read our blog post on Why should you use Asset Intelligence in SCCM .
The AISP is a hierarchy-wide option. SCCM supports a single instance of this site system role in a hierarchy and only at the top-level site. Install it on your Central Administration Site or stand-alone Primary Site depending of your design.
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and site System Roles
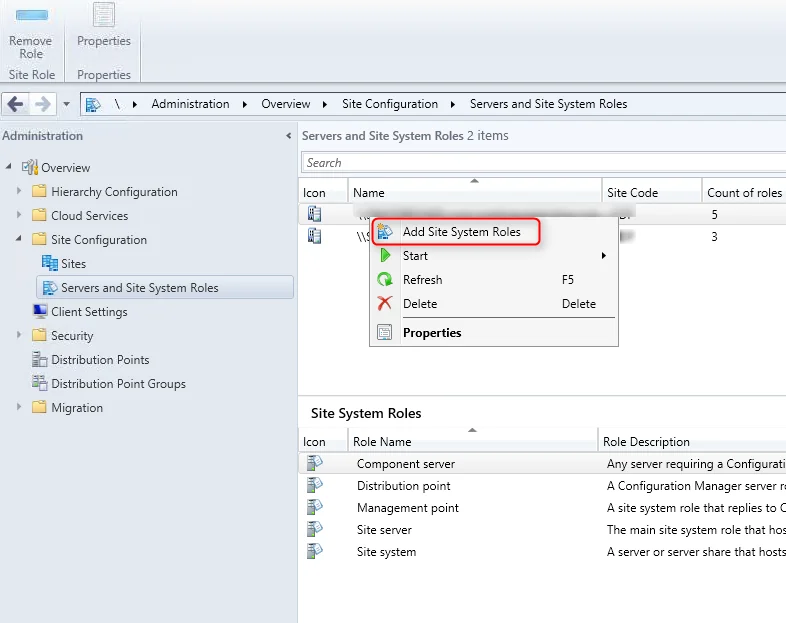
- On the Proxy tab, enter your Proxy server information if needed and click Next
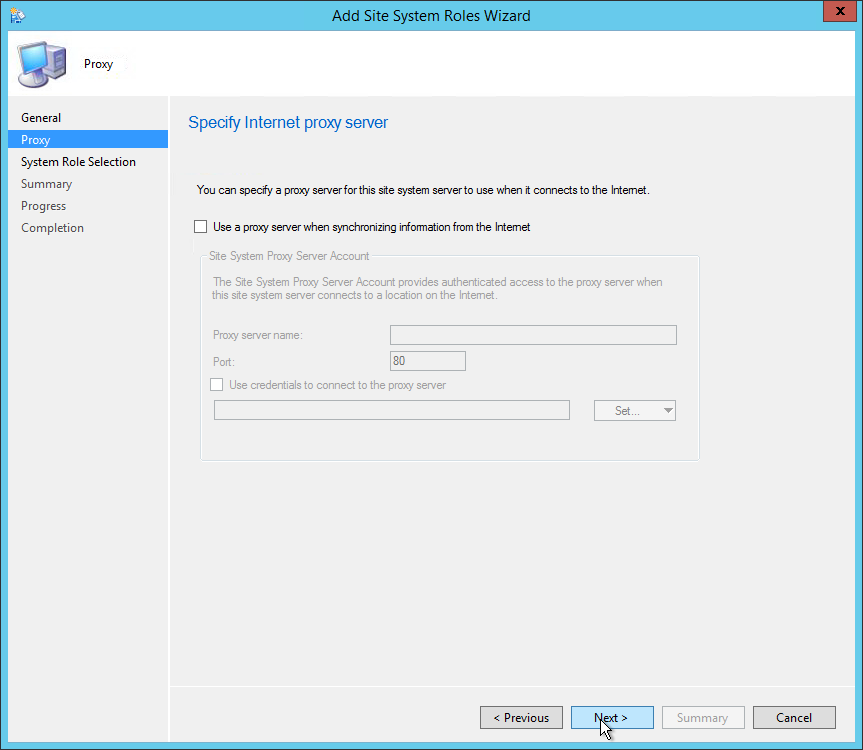
- On the Site System Role Selection tab, select Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point , click Next
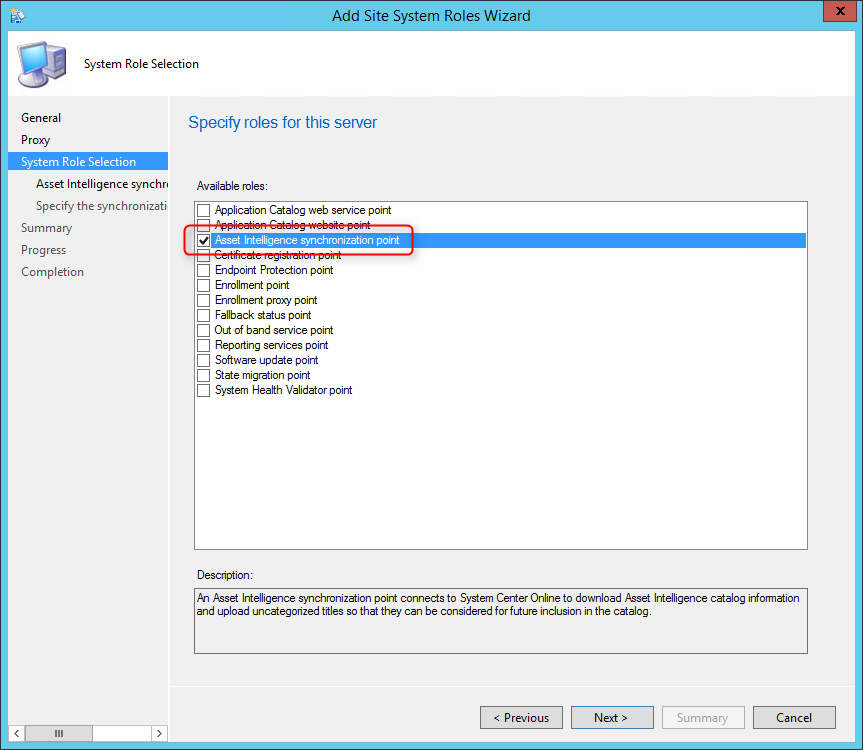
- By default, the Use this Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point setting is selected and cannot be configured on this page. System Center Online accepts network traffic only over TCP port 443, therefore the SSL port number setting cannot be configured on this page of the wizard
- You can specify a path to the System Center Online authentication certificate (.pfx) file. Typically, you do not specify a path for the certificate because the connection certificate is automatically provisioned during site role installation
- Specify the desired catalog Synchronization Schedule , click Next
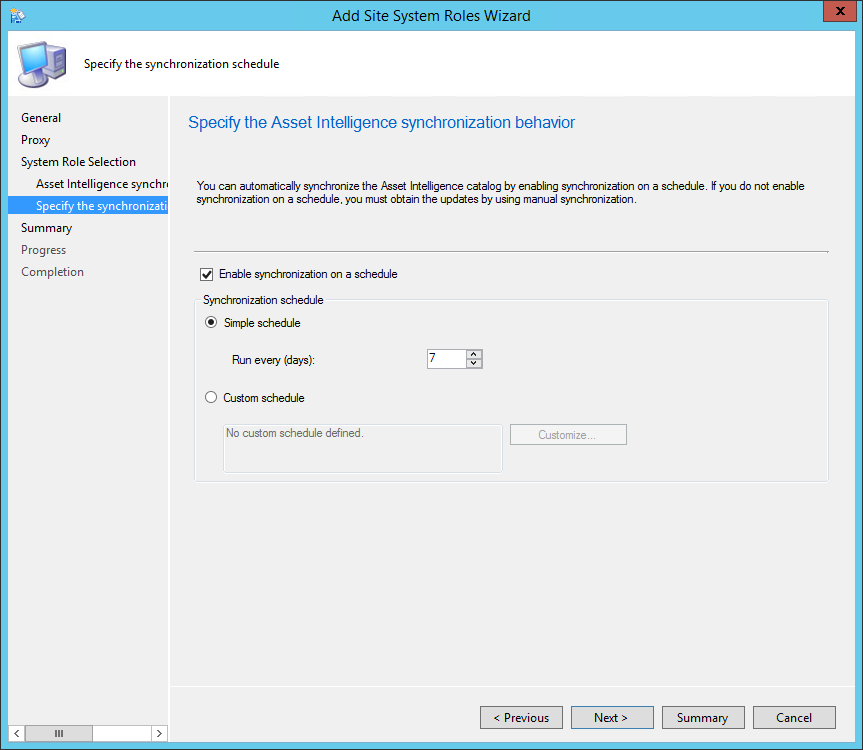
- On the Summary tab, review your setting and click Next
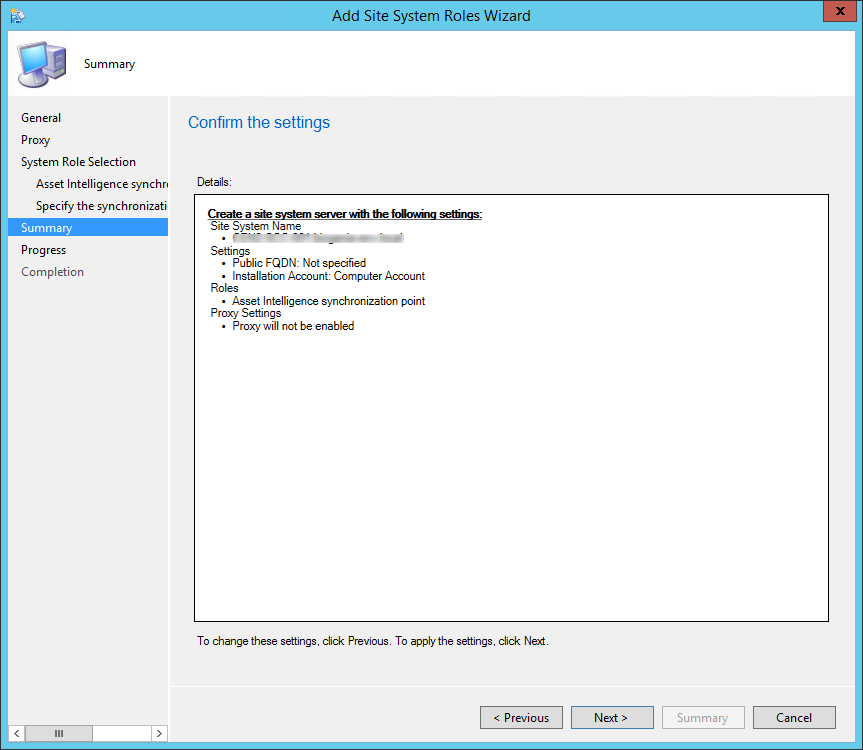
- Wait for the setup to complete and close the wizard
- AIUSSetup.log – Information about the installation of the Asset Intelligence catalog synchronization point site system role
- AIUpdateSvc.log – Information about the Asset Intelligence catalog synchronization service
- Aikbmgr.log – Information about the Asset Intelligence catalog manager service
- Verify that the role installation is completed in AIUSSetup.log
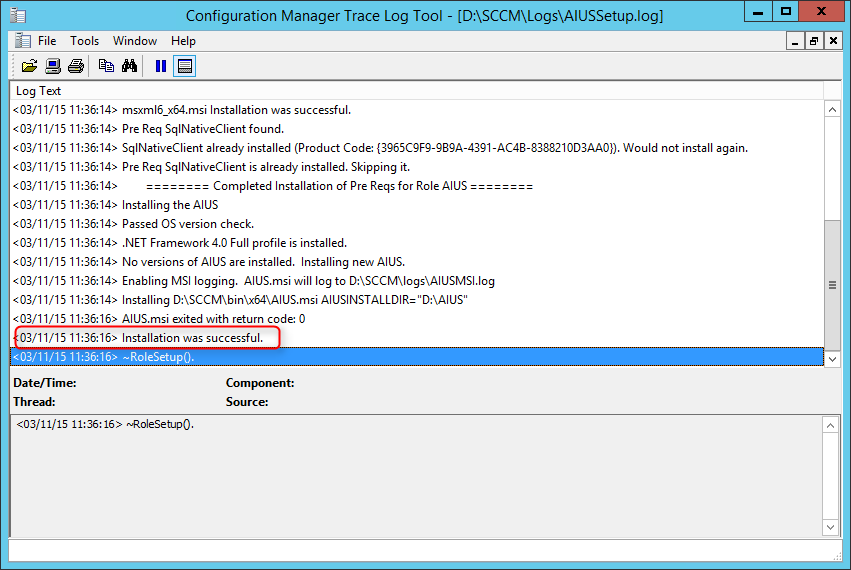
- Navigate to Assets and Compliance / Overview / Asset Intelligence
- Verify that the Sync is Enabled and Successful
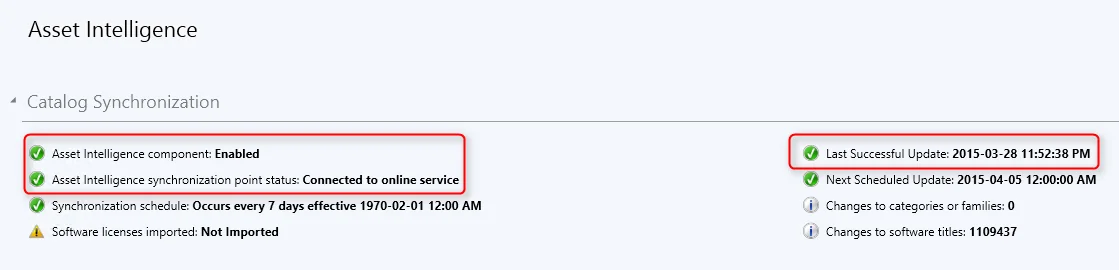
In order to have inventory data, first ensure that Hardware Inventory is enabled in your Client Settings.
- Navigate to Administration / Client Settings
- Right-click your Client Settings and choose Properties
- On the Hardware Inventory Tab
- Ensure that your hardware inventory is Enabled
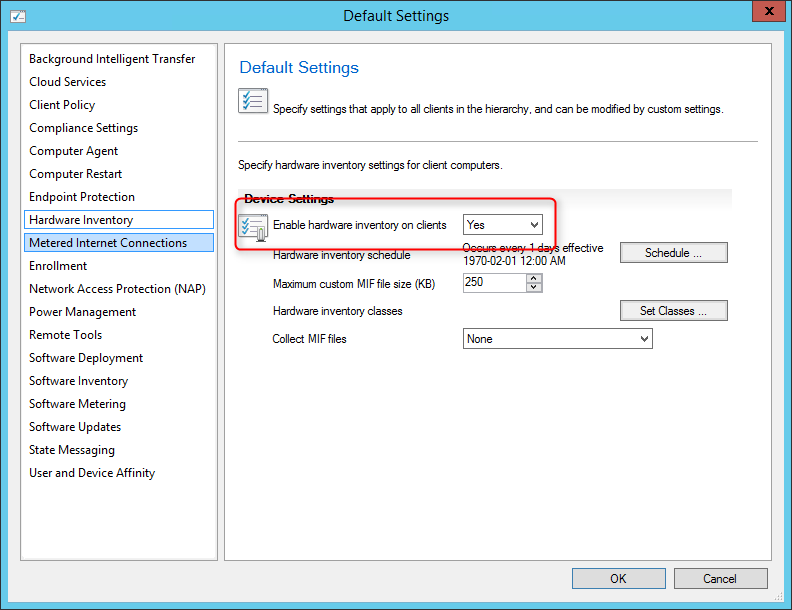
Once confirmed, enable inventory reporting classes :
- Navigate to Assets and Compliance / Asset Intelligence
- Right-click Asset Intelligence and select Edit Inventory Classes
- Select Enable only the selected Asset Intelligence reporting classes
- See the following Technet article to see dependencies between hardware and reporting class
2 maintenance tasks are available for Asset Intelligence :
- This maintenance task checks that the software title that is reported in software inventory is reconciled with the software title in the Asset Intelligence catalog.
- This maintenance task provides the information that is displayed in the Assets and Compliance workspace. When the task runs, Configuration Manager gathers a count for all inventoried software titles at the primary site.
To set the maintenance tasks :
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Sites
- Select Site Maintenance on the top ribbon
- Select the desired schedule for both tasks
You’re now done installing the AISP.
Part 7 – Certificate Registration Point
We will describe how to install SCCM Certificate Registration Point (CRP).
Using SCCM and Intune, the CRP communicates with a server that runs the Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) to provision device certificate requests.
This is not a mandatory Site System but we recommend to install a CRP if you need to provision client certificates to your devices (like VPN or WIFI).
Before the CRP can be installed, dependencies outside SCCM is required. I won’t cover the prerequisite configuration in details as they are well documented on this Technet article and it goes beyond SCCM. Here’s an overview of what needs to be done :
- Install the NDES role on a Windows 2012 R2 Server
- Modify the security permissions for the certificate templates that the NDES is using
- Deploy a PKI certificate that supports client authentication
- Locate and export the Root CA certificate that the client authentication certificate chains to
- Increase the IIS default URL size limit
- Modify the request-filtering settings in IIS
On the machine that will receive the CRP role, install the following using Windows server role and features:
- ASP .NET 3.5
- ASP .NET 4.5
- WCF HTTP Activation
If you are installing CRP on a remote machine from the site server, you will need to add the machine account of the site server to the local administrator’s group on the CRP machine.
The Certificate Registration Point must not be installed on the same server that runs the Network Device Enrollment Service. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration Site, child Primary Site or stand-alone Primary Site but it’s not supported on a Secondary Site.
CRP Installation
- Right click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
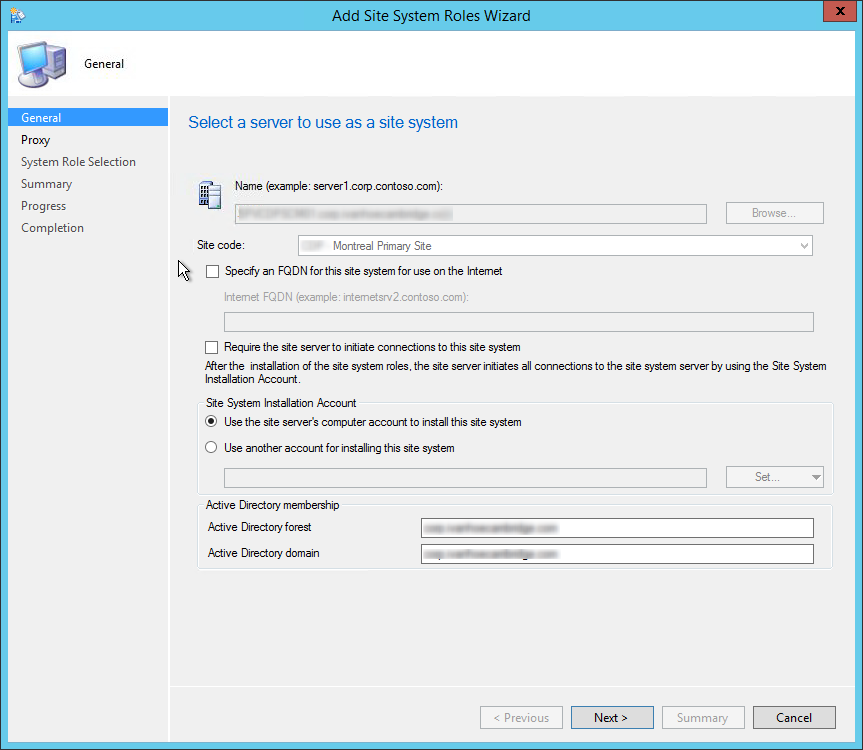
- On the Site System Role tab, select Certificate Registration Point, click Next
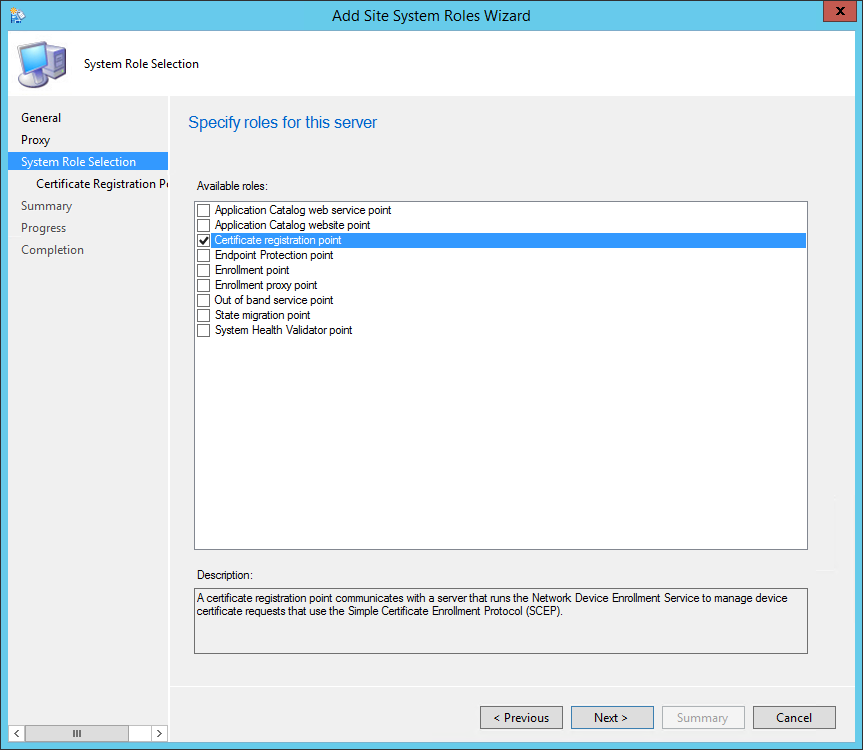
- On the Certificate Registration Point Properties, leave the default website name and virtual application name. Take note of your Virtual Application Name, you will need it later.
- Click on Add
- This URL will be part of the profile send to the devices. The device will needs to access this URL from the internet
- Example : https://ndes.systemcenterdudes.com/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll
- Enter the path to your exported Root CA Certificate (.cer file)
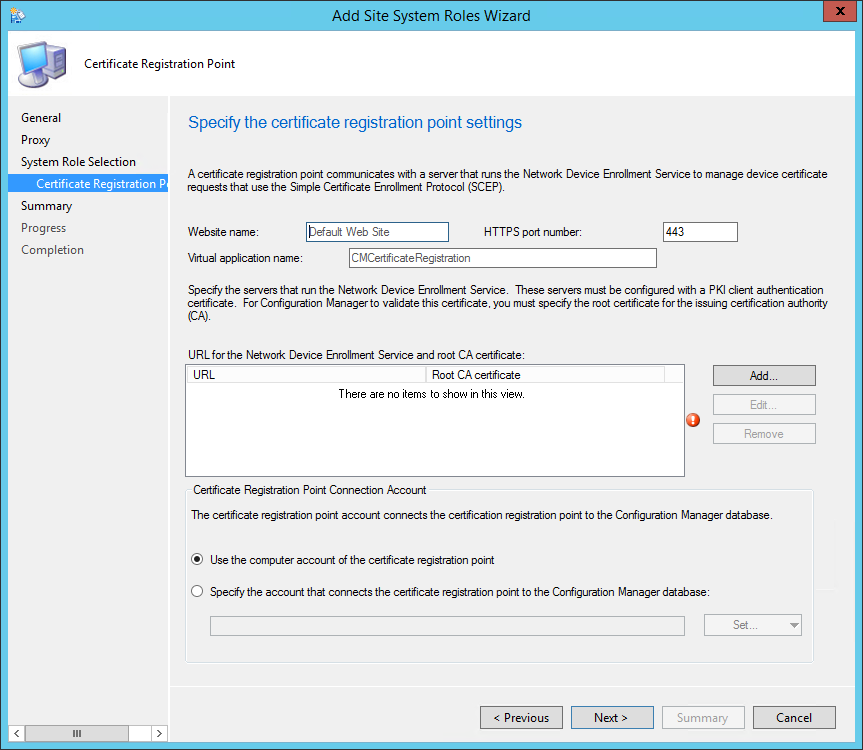
- Once completed, click on Next , review the Summary and close the wizard
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath\Logs\crpmsi.log – Detailed CRP Installation status
- HTTP Error 403 is ok. If you have a 404 error or 500 error, look at the logs file before continuing
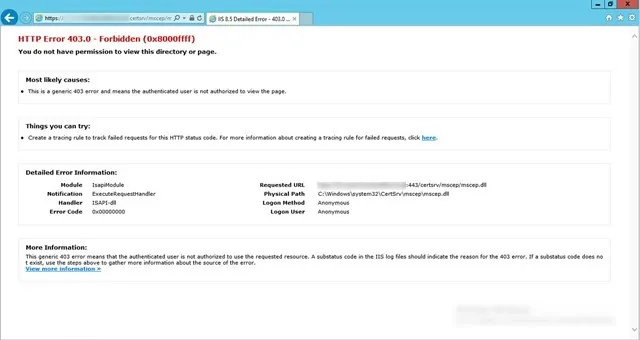
- After the CRP is installed, the system will export the certificate that will be used for NDES plugin to the certmgr.box folder. It may take up to 1 hour to appear.
- Save this .cer file on the NDES server as we will need it in the next section.
Now that the Certificate Registration Point has been installed, we must install a plug-in on the NDES server to establish the connection with SCCM.
On the server that runs the Network Device Enrollment Service :
- Copy the \SMSSETUP\POLICYMODULE\X64 folder from the the Configuration Manager installation media to a temporary folder
- From the temporary folder, run PolicyModuleSetup.exe
- Click Next, accept the license terms and click Next
- On the Installation Folder page, accept the default installation folder click Next
- On the Certificate Registration Point page, specify the URL of the Certificate Registration Point. This is the Virtual Application Name created during the SCCM role installation (Example : https://crp.systemcenterdudes.com/CMCertificateRegistration )
- Accept the default port of 443, click Next
- On the Client Certificate for the Policy Module page , browse to and specify the client authentication certificate. This is the same certificate you used in the CRP Installation wizard in SCCM
- On the Certificate Registration Point Certificate page , click Browse to select the exported certificate file (the one exported from \inboxes\certmgr.box )
- Click Next and complete the wizard
- Open the registry editor and browse to HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\MSCEP
- Make sure that the values of EncryptionTemplate, GeneralPurposeTemplate and SignatureTemplate match the names of the template on your CA
- Open Internet Explorer on the NDES server and browse to https://ndes.systemcenterdudes.com/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll , you will no longer see the web page but instead you should see an error 403, this is expected
Once all the above has been configured and verified, you are ready to create your certificate profile in SCCM.
Here are my favourites articles covering the subject :
- Technet Article
- Configuration Team Blog article
- Pieter Wigleven’s installation (Technical Solution Professional at Microsoft)
- Peter van der Woude’s key configuration steps
Part 8 – Distribution Point Installation
In this part, we will describe how to perform an SCCM distribution point installation.
I saw a lot of posts recently on the Technet forum which leads me to think that there’s a lack of documentation explaining this.
Several distribution points can provide better access to available software, updates, and operation systems. A local Distribution Point also prevents the installation thought the WAN.
- Functional SCCM hierarchy
- SCCM Admin console access
- RDP access on the Distribution Point server
- The required level of security in the SCCM console
Prevent package from replication on the wrong drive
- Logon locally on the target machine with remote desktop
- Create an empty file called NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS on the root of each drive where SCCM should NOT write. (If any)
Local Administrator group
On the DP, add a group that contains your site system computer account in the Administrators group.
I like to create a SCCM system groups that contain all my distribution points.
- Open Server Manager
- Expand Local Users and Groups
- Click on Groups
- Double-click on “Administrators”
- Add the security groups that contain the SCCM computer account
Windows Server configuration – Roles and Features
Configuration Manager requires some roles and features to be installed on the server prior to the DP installation
- Open Server Manager, on the Features node, starts the Add Features Wizard .
- On the Select Features page, select Remote Differential Compression
IIS needs to be installed on the server but it will automatically be installed using the site installation wizard.
Make sure that these roles are installed on your server prior to the installation :
- IIS WMI Compatibility tool
- IIS Scripting Tool
For Windows Server 2012+, WDS is installed and configured automatically when you configure a distribution point to support PXE or Multicast.
For Windows Server 2003, you must install and configure WDS manually.
The distribution point site system role does not require Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS). When BITS is configured on the distribution point computer, BITS on the distribution point computer is not used to facilitate the download of content by clients that use BITS
Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable
You can run the Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable Setup from the Configuration Manager installation at: <ConfigMgrInstallationFolder>\Client\x64\vcredist_x64.exe
For Configuration Manager SP1, vcredist_x64.exe is installed automatically when you configure a distribution point to support PXE.
For Windows 2012 only, you need to enable Powershell 3.0 (or further) before installing the distribution point.
Ensure that your firewall is set correctly. 2 ports need to be opened.

Reboot your server to avoid the case where your server is in “Reboot pending State” which will result in unexpected reboot during distribution point installation.
Now that the Distribution point server is ready to receive a new role, we need to add the server to the site server list
Add new distribution point server to the SCCM console – Site System
- In the Configuration Manager console, click Administration
- In the Administration workspace, expand Site Configuration , and then right click Servers and Site System Roles .
- Select Create Site System Server . The Create Site System Server Wizard opens.
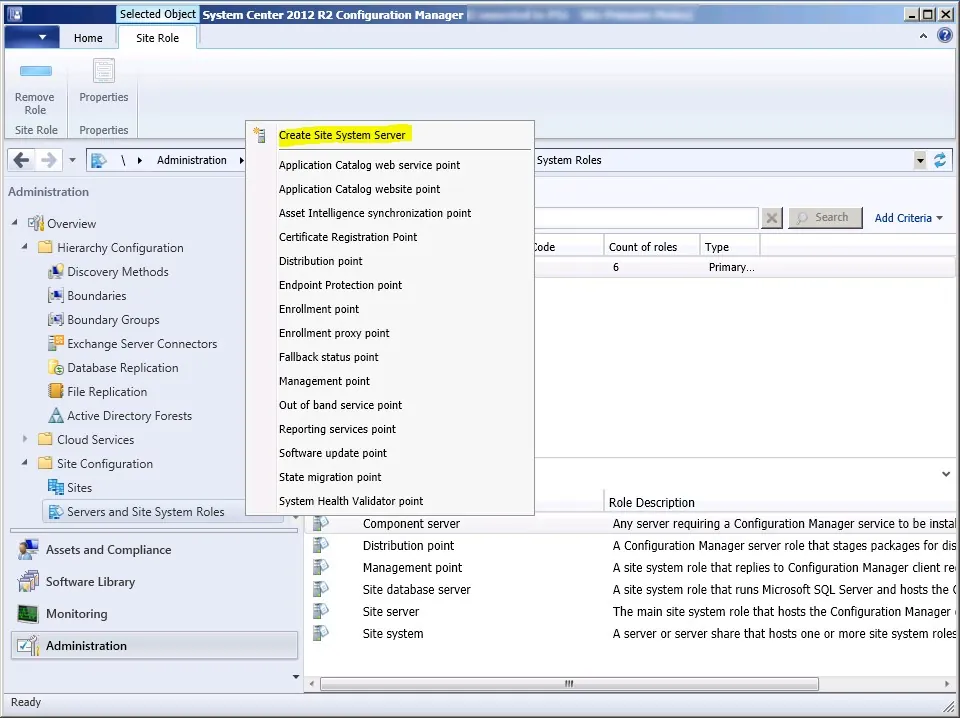
- On the General page , specify the Name for the site system server
- Select the Site Code and Click Next
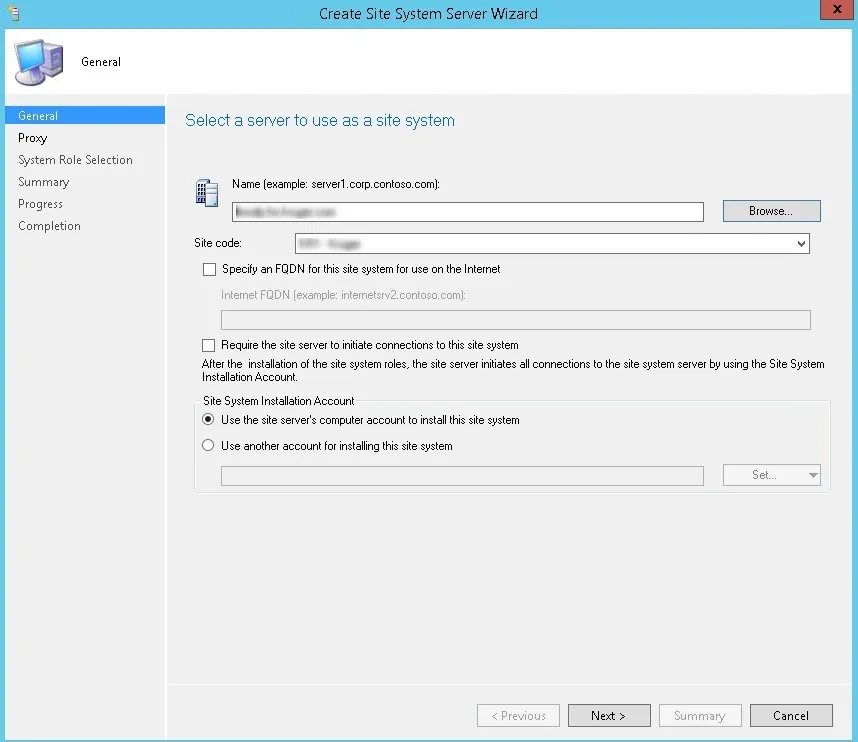
- Do not specify a proxy server, click Next
- Select Distribution point in the role selection screen, click Next
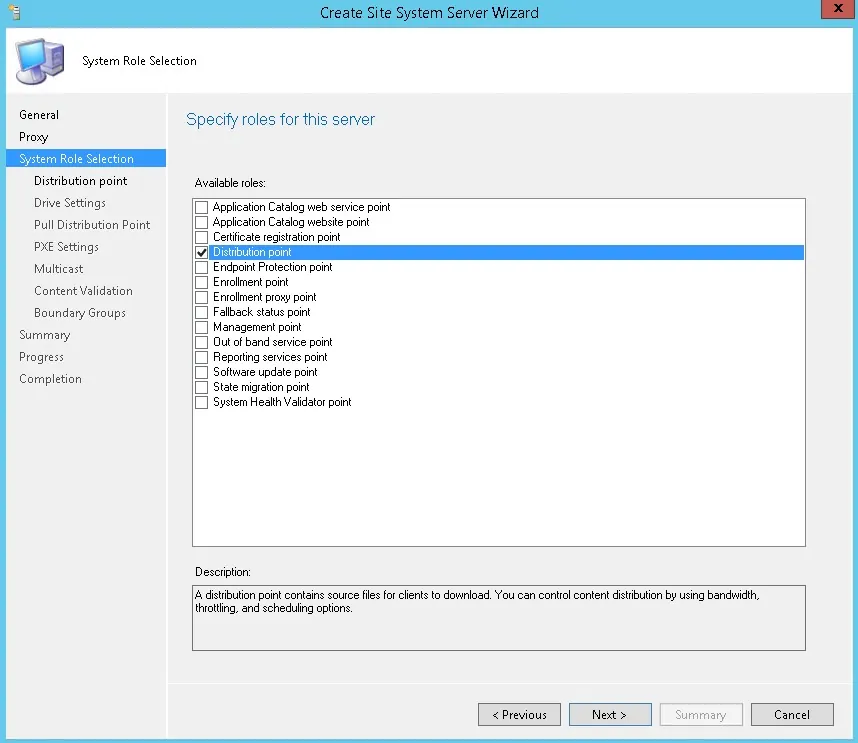
- Check Install and configure IIS if required by CM
- Add a description if needed
- Select HTTP
- Select Create self-signed certificate, click Next
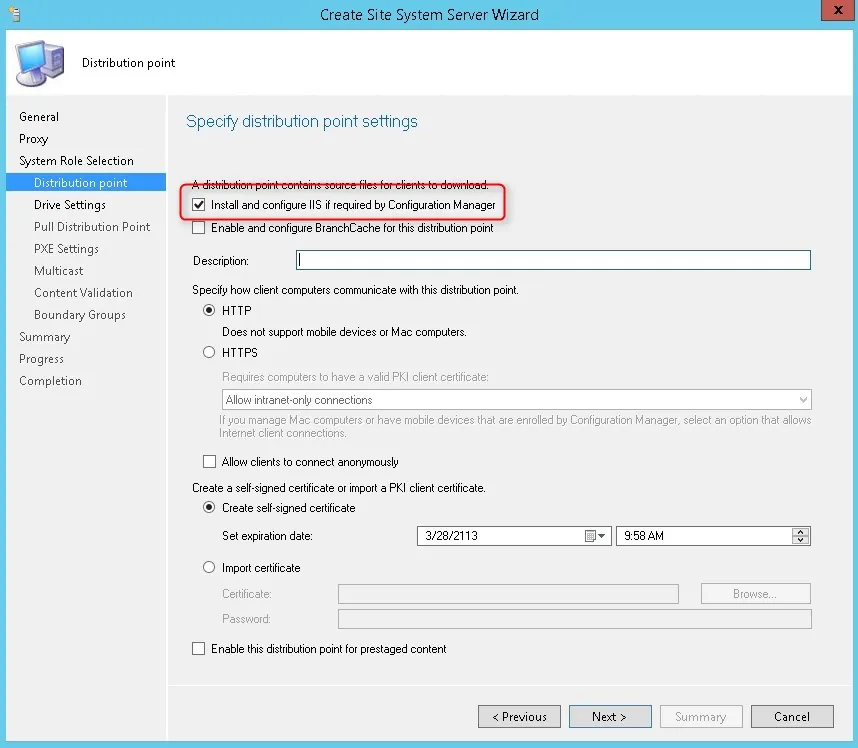
- Set drive configuration to your needs. This is where the SCCMContentLib will be created so select a drive with enough storage space, click Next
- Do not configure a pull distribution point, click Next
- Do not configure PXE for now, click Next
- Do not enable multicast for now, click Next
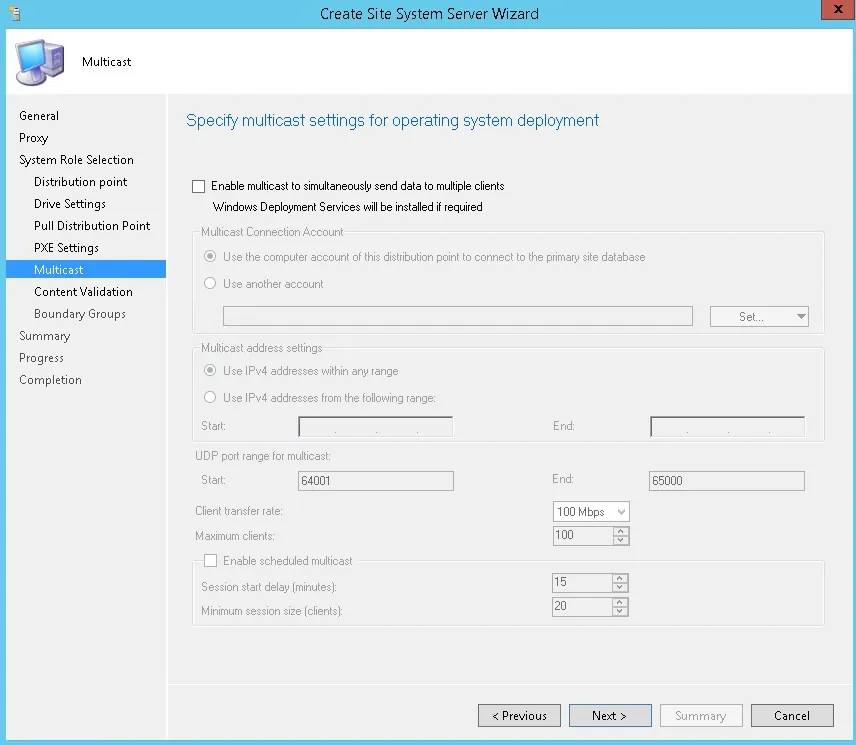
- Enable content validation to occur where it fits your environment, click Next
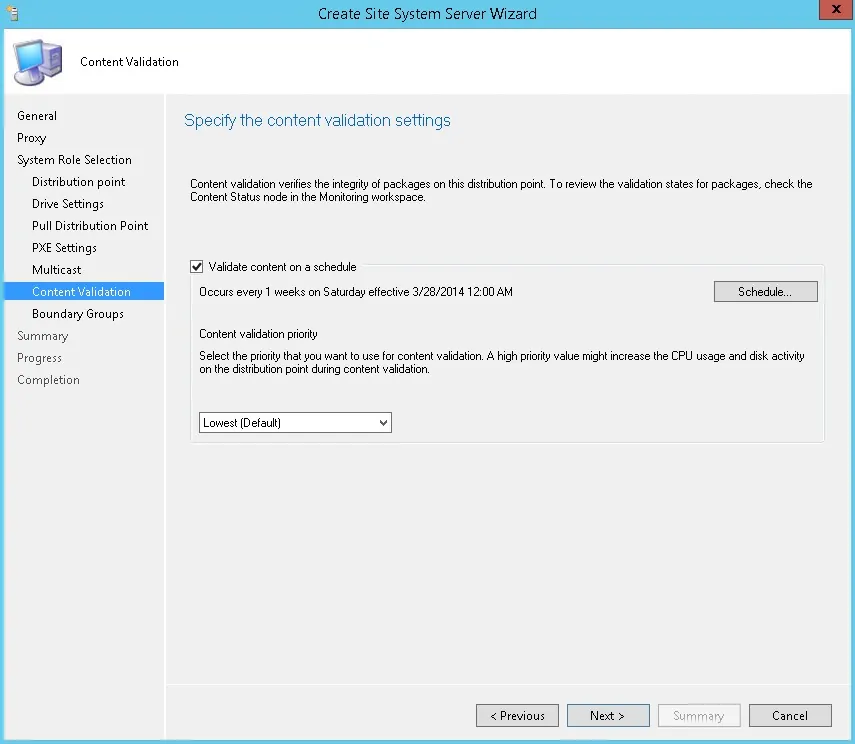
- Add the boundary group that needs to be associated with this DP and Uncheck the Allow fallback source location for content , click Next
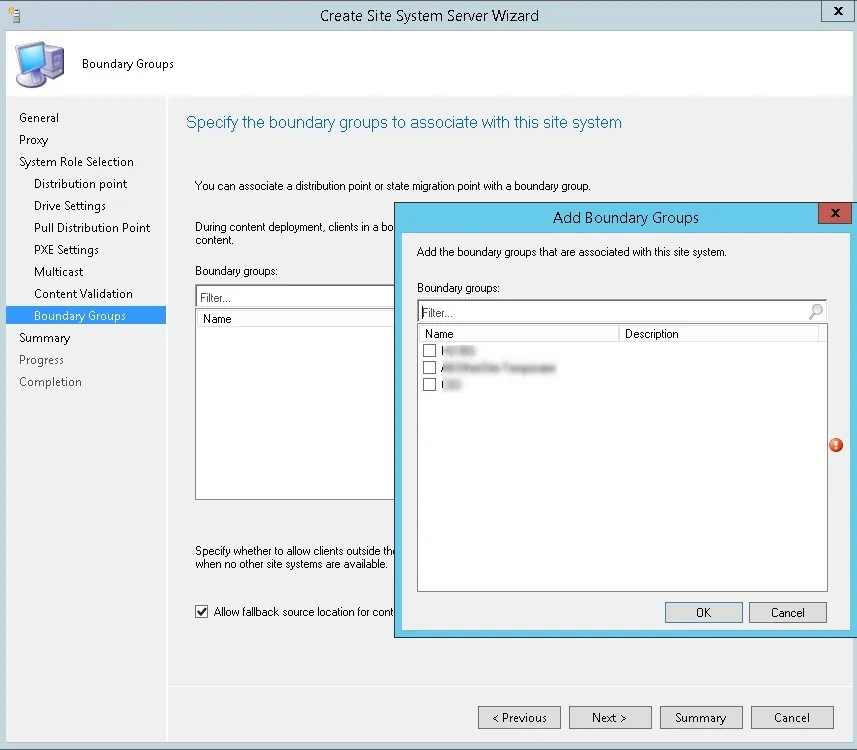
- Review the summary page and complete the installation, click Next
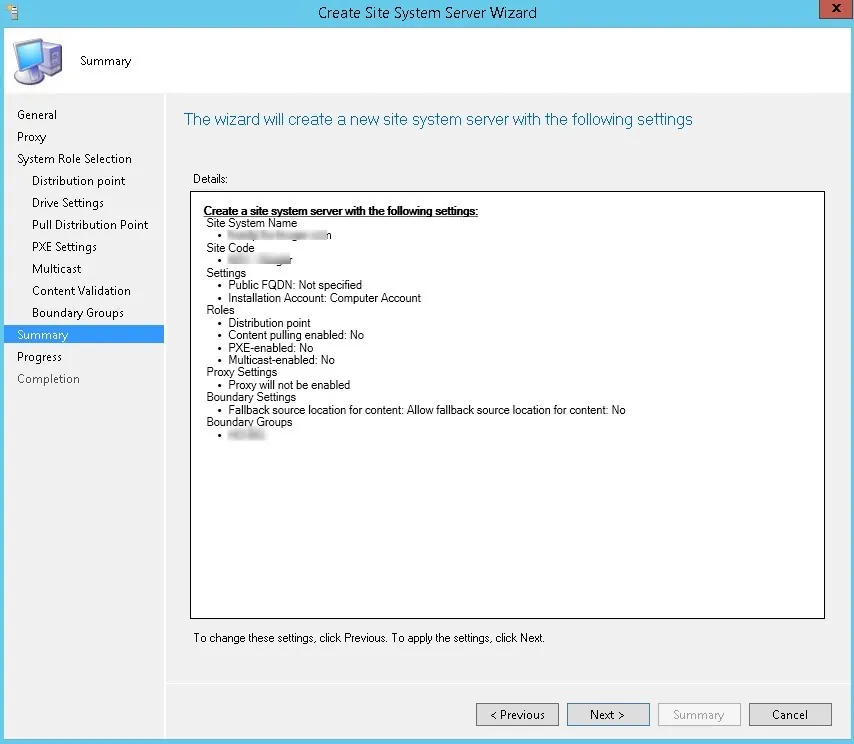
WARNING Your remote server may reboot if there’s a missing requirement
At this point, the major part of installation a distribution point server is completed.
You can track the installation progress in 2 logs:
- Distmgr.log on the site server
- Smsdpprov.log on the distribution point. ( InstallationDrive \SMS_DP$\SMS\Logs)
Windows Explorer
At this point, you will the SCCM file structure created on the site server.
You can also track the installation progress in the SCCM console under Monitoring / Distribution Status / Distribution Point Configuration Status
- Click on your DP
- Click the detail tab on the bottom
- Check for green check mark on all components
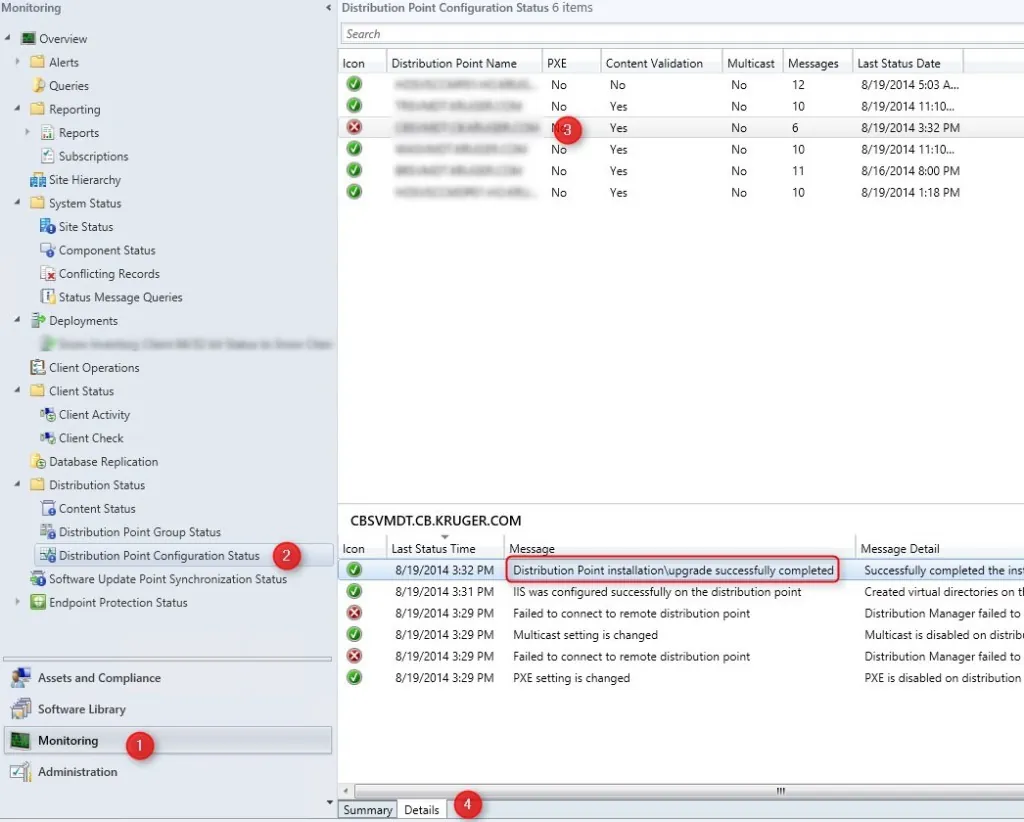
Note: Error on the IIS Virtual directory is normal at the start of the process. SCCM is making a check as if IIS is installed at the start of the process even if you tell SCCM to enable you IIS for you. That results in errors but be patient and the installation should succeed anyway
- Verify the status of your new DP in Administration / System Status / Site Status
You can now replicate your content to your newly created DP. Replicate manually all your content or add your DP in an existing DP group.
Replicate a package or Application to your newly created site system
Verify that the content is well replicated in the SCCM Console. (or check distmgr.log )
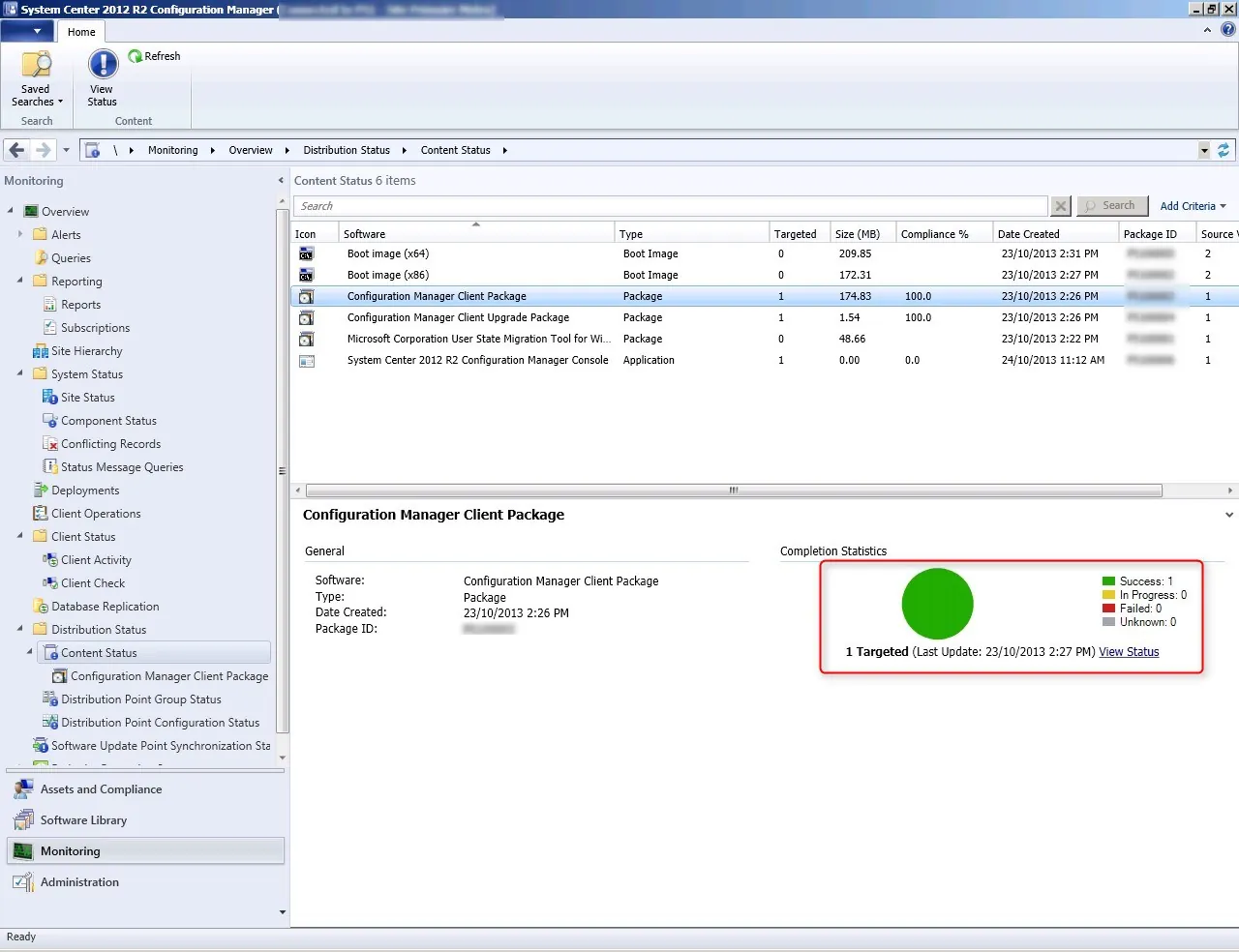
That’s it ! You’re done creating your DP.
If you have multiple Distribution Points, I suggest you read our post on 8 ways to monitor your distribution points. This post explains in detail the various options to make sure that your DP is healthy.
You can also check our custom report about Distribution Point Monitoring to display all your DP status using a single click.
Part 9 – Endpoint protection point
In this part, we will describe how to install SCCM Endpoint Protection Point (EPP).
The Endpoint Protection Point provides the default settings for all antimalware policies and installs the Endpoint Protection client on the Site System server to provide a data source from which the SCCM database resolves malware IDs to names. When you install this Site System Role, you must accept the license terms for System Center 2012 R2 Endpoint Protection.
This is not a mandatory Site System but you need to install a EPP if you’re planning to use SCCM as your anti-virus management solution (using Endpoint Protection).
This Site System is a hierarchy-wide option. SCCM supports a single instance of this site system role in a hierarchy and only at the top-level site in the hierarchy. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration Site or stand-alone Primary Site.
Before installing the EP role, you must have a Software Update Point installed and configured.
EPP Installation
- On the Site System Role tab, select Endpoint Protection Point, click Next
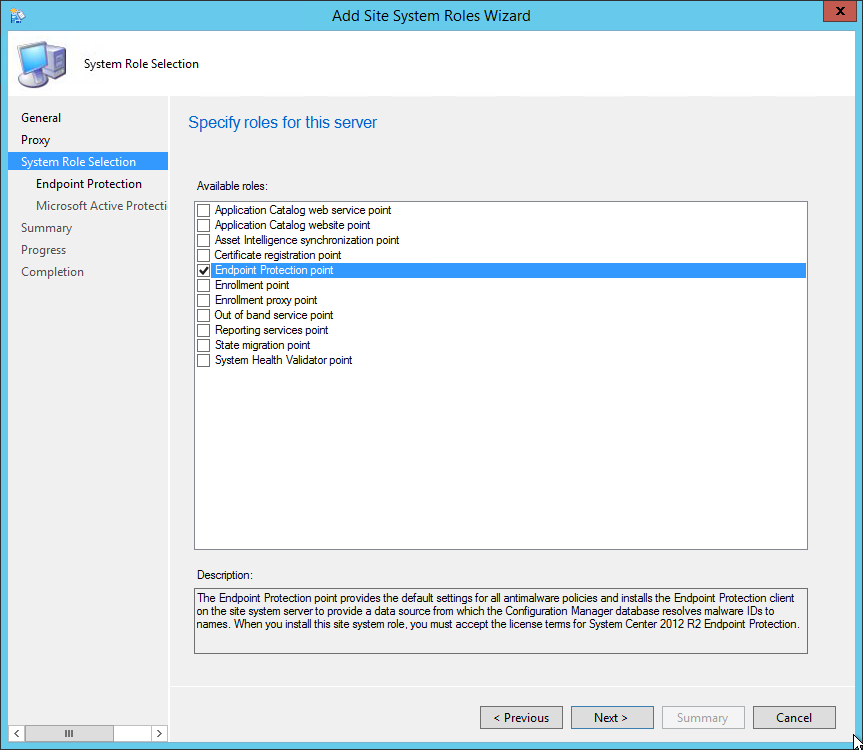
- Accept the License Terms and click Next
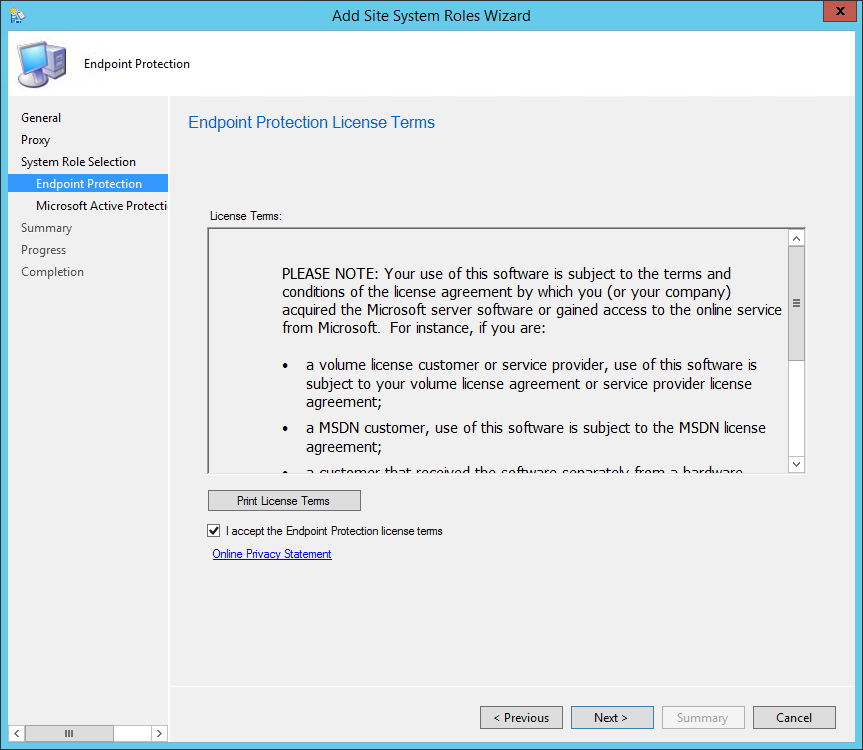
- Select Do not join MAPS , click NEXT
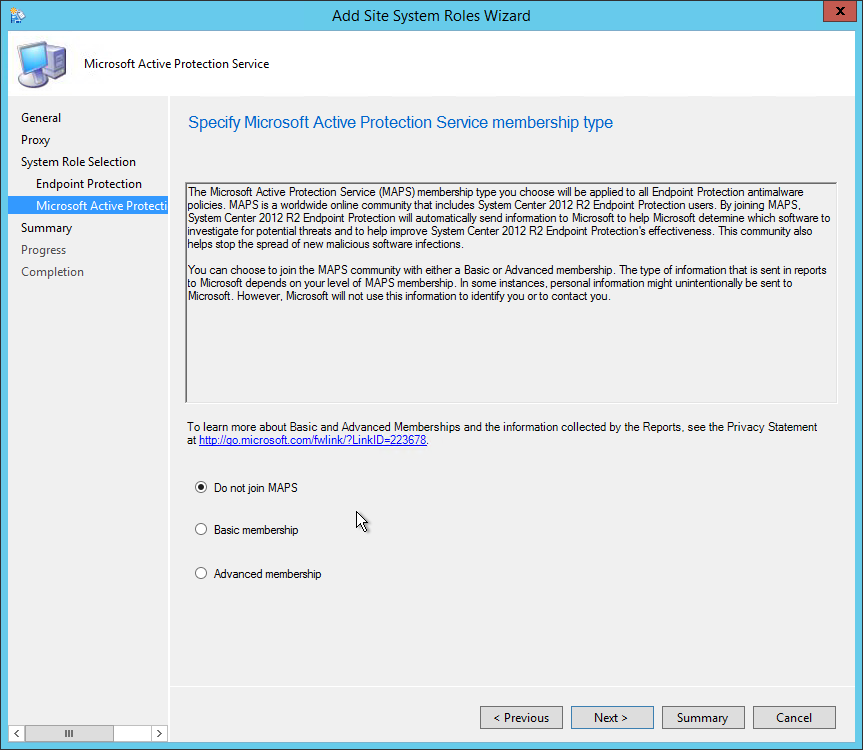
• On the Summary tab, review your settings and click Next
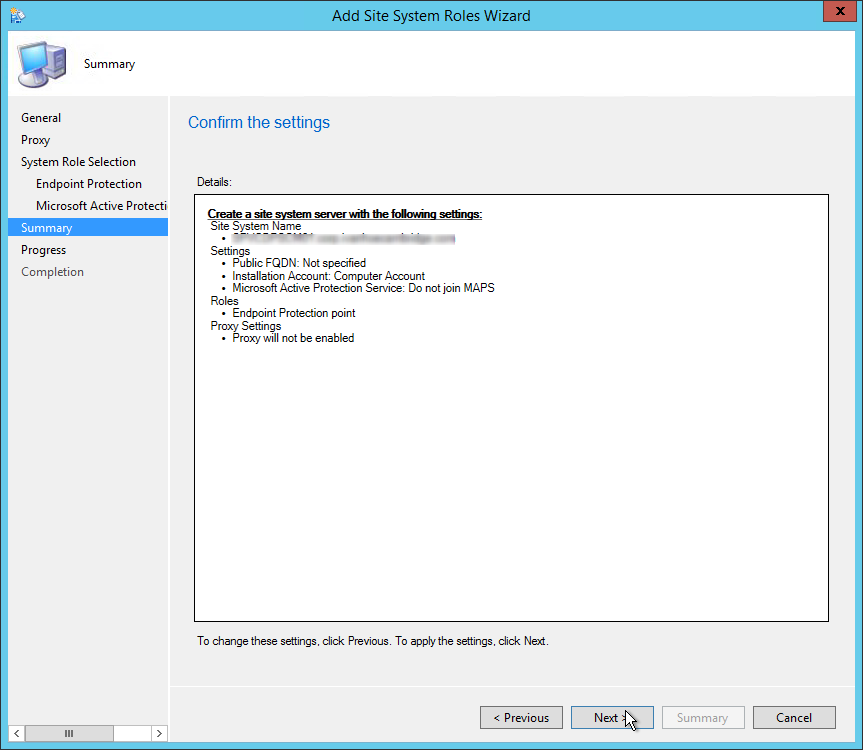
- Wait for the setup to complete and click Close
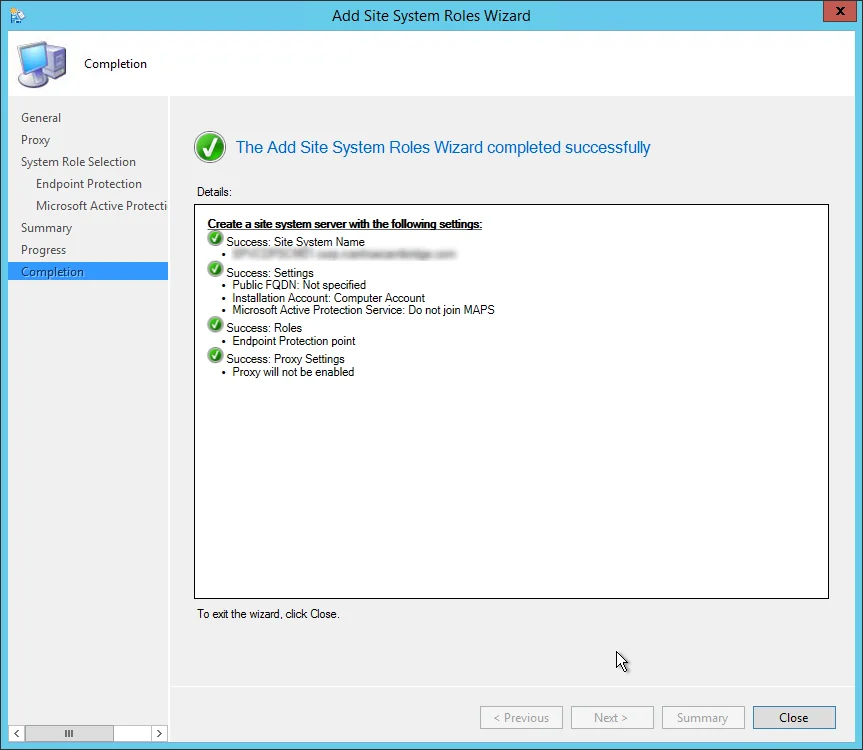
After the installation, you must add Endpoint Protection definition files in your Software Update Point.
- Click the Configure Site Components button and select Software Update Point
- On the Product tabs, check Forefront Endpoint Protection 2010 and click Ok
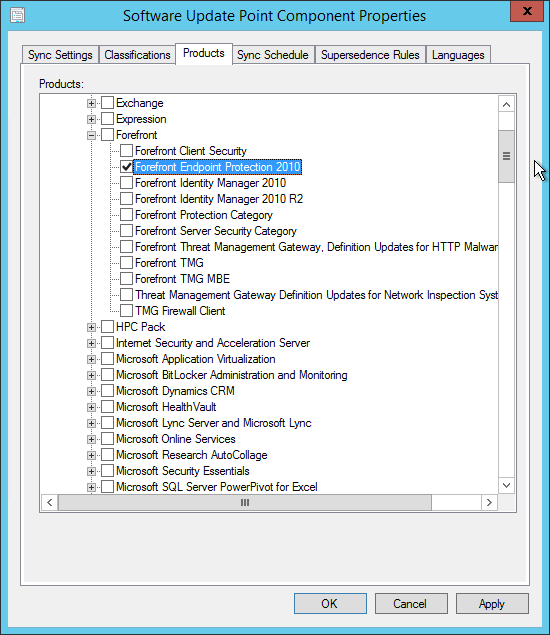
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath\Logs\EPSetup.log – Detailed EP Installation status
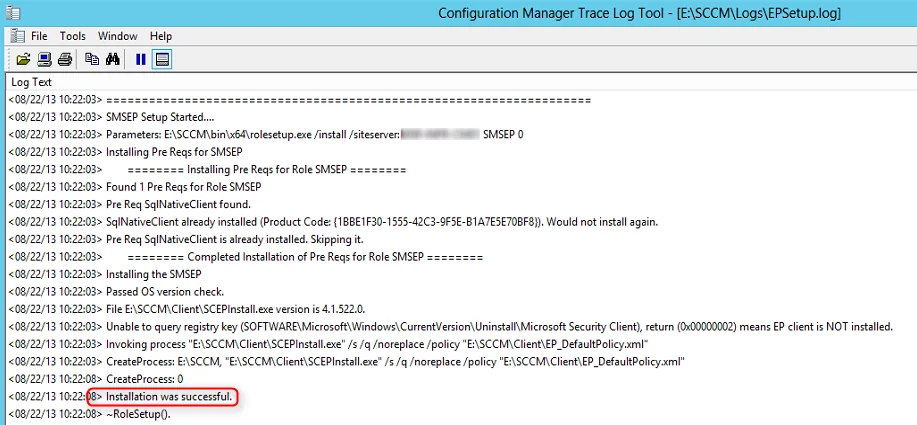
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath\Logs\Wsyncmgr.log – SUP Synchronization status
You are now ready to manage EndPoint Protection using SCCM. We have a complete guide to managing endpoint protection. You can download it from our product page .
Part 10 – Enrollment Point Installation
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point site system roles.
The Enrollment Point uses PKI certificates for Configuration Manager to enroll mobile devices, Mac computers and to provision Intel AMT-based computers.
The Enrollment Proxy Point manages Configuration Manager enrollment requests from mobile devices and Mac computers.
This is not a mandatory site system but you need both Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point if you want to enroll legacy mobile devices, Mac computers and to provision Intel AMT-based computers. Since modern mobile devices are mostly managed using Windows Intune , this post will focus mainly on Mac computer enrollment.
The SCCM Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point are site-wide options. It’s supported to install those roles on a stand-alone or child Primary site. It’s not supported to install it on a Central Administration site or Secondary site.
You must install an SCCM Enrollment Point in the user’s forest so that the user can be authenticated if a user enrolls mobile devices by using SCCM and their Active Directory account is in a forest that is untrusted by the site server’s forest.
When you support mobile devices on the Internet, as a security best practice, install the Enrollment Proxy Point in a perimeter network and the Enrollment Point on the intranet.
Beginning with System Center 2012 Configuration Manager SP2, the computer that hosts the SCCM Enrollment Point or Enrollment Proxy Point site system role must have a minimum of 5% of the computers available memory free to enable the site system role to process requests. When those site system role are co-located with another site system role that has this same requirement, this memory requirement for the computer does not increase, but remains at a minimum of 5%.
Enrollment Point
- .NET Framework 3.5
- HTTP Activation (and automatically selected options)
- ASP.NET 4.5
- ASP.NET 3.5 (and automatically selected options)
- .NET Extensibility 3.5
- ASP.NET 4.5 (and automatically selected options)
- .NET Extensibility 4.5
Enrollment Proxy Point
SCCM Enrollment Point Installation
For this post we will be installing both roles on a stand-alone Primary site using HTTPS connections. If you split the roles between different machine, do the installation section twice, once for the first site system (selecting Enrollment Point during role selection)and a second time on the other site system (selecting Enrollment Proxy Point during role selection).
- On the Site System Role tab, select Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point , click Next
- This is the names that you’ll see in IIS after the installation
- Enter the port number you want to use. The HTTPS setting is automatically selected and requires a PKI certificate on the server for server authentication to the Enrollment Proxy Point and for encryption of data over SSL. For more information about the certificate requirements, see PKI Certificate Requirements for Configuration Manager .
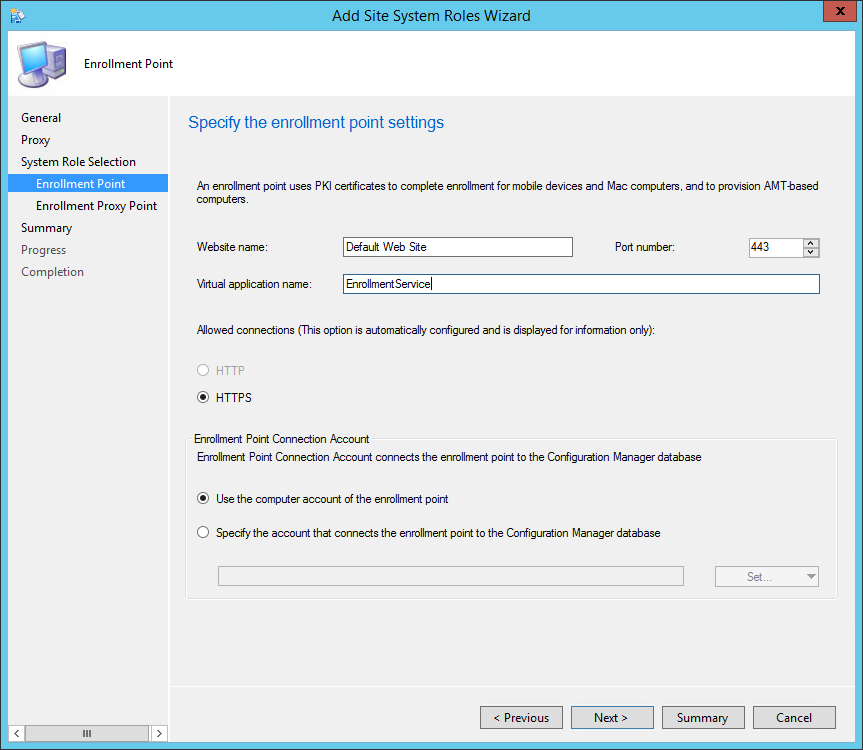
- The Enrollment point will be populated by default and can’t be changed
- Keep the Website name to it’s default value
- The Virtual application name can’t be changed. This will be used for client installation (https://servername/ EnrollmentServer )
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ enrollsrvMSI.log and enrollmentservice.log – Records details of about the Enrollment Point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ enrollwebMSI.log – Records details of about the Enrollment Proxy Point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ enrollmentweb.log – Records communication between mobile devices and the Enrollment Proxy Point
That’s it, you’ve installed your SCCM Enrollment Point, follow this Technet Guide if you want to proceed to next steps for Mac computers enrollment
Part 12 – Fallback Status Point
We will describe how to install SCCM Fallback Status Point (FSP).
The FSP helps monitor client installation and identify unmanaged clients that cannot communicate with their management point.
This is not a mandatory Site System but we recommend to install a FSP for better client management and monitoring. This is the Site System that receive State Message related to client installation, client site assignment, and clients unable to communicate with their HTTPS Management Point.
If the FSP is not configured properly you’ll end up having A fallback status point has not been specified errors in your logs.
This Site System is a hierarchy-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a child Primary Site or stand-alone Primary Site but it’s not supported on a Central Administration site nor Secondary Site.

- On the Site System Role tab, select Fallback Status Point, click Next
- On the Fallback Status Point tab, specify the number of state messages to process. We recommend to leave the default value, click Next
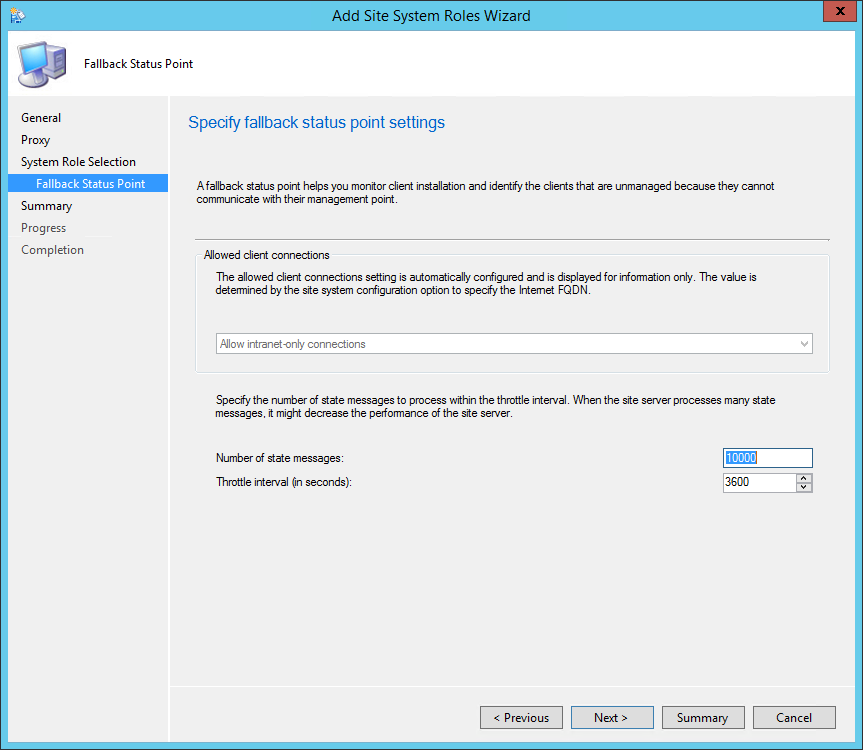
- Smsfspsetup.log – DetailedFSP Installation status
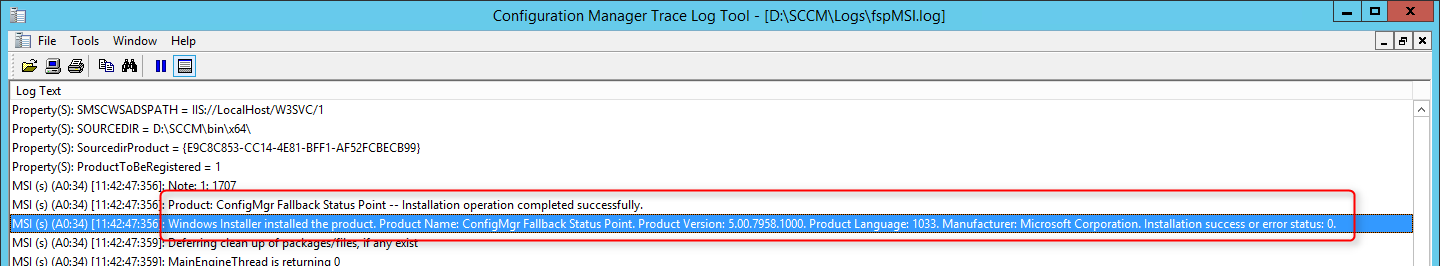
- Fspmgr.log – Verify whether clients are successfully sending state messages to the FSP
You can also check if reports that depend on the FSP are populated with data. See the full list of reports that rely on the FSP here .
Use the FSP client properties to point your clients to your newly created FSP
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Site
- Click the Client Installation Setting icon on the ribbon
- Select Client Push Installation
- On the Installation Properties tab
- Enter your server FQDN in the FSP properties
Part 13 – Management Point Installation
We will describe how to install an SCCM Management Point (MP).
Every SCCM hierarchy must have a Management Point to enable client communication. The Management Point is the primary point of contact between Configuration Manager clients and the site server. Management Points can provide clients with installation prerequisites, configuration details, advertisements and software distribution package source file locations. Additionally, Management Points receive inventory data, software metering information and state messages from clients.
Multiple Management Points are used for load-balancing traffic and for clients to continue receiving their policy after Management Point failure. Read about SCCM High-Availability options in this Technet article .
Prior to SCCM 2012 R2 SP1, it was not possible to assign client directly to a specific Management Point. It’s now possible using the new Preferred Management Point feature . Read about how clients choose their Management Point in this Technet article .
The Management Point is a site-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a stand-alone Primary site, child Primary site or Seconday site. It’s not supported to install a Management Point on a Central Administration site.
Each primary site can support up to 10 Management Points.
By default, when you install a Secondary site, a Management Point is installed on the Secondary site server. Secondary sites do not support more than one Management Point and this Management Point cannot support mobile devices that are enrolled by Configuration Manager.
See the full Supported Configuration in the following Technet article .
On Windows 2012, the following features must be installed before the Management Point Installation:
- .NET Framework 4.5
- BITS Server Extensions or Background Intelligent Transfer Services (BITS)
- ISAPI Extensions
- IIS 6 WMI Compatibility
- On the Site System Role tab, select Management Point, click Next
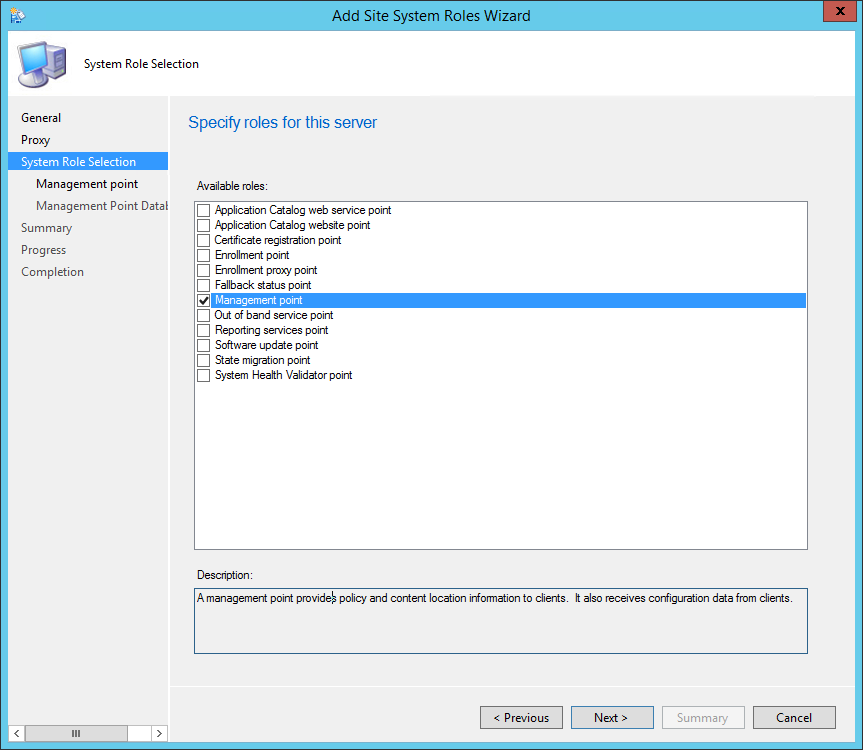
- On the Management Point tab
- Select the desired client connections methods. HTTPS required to have a valid PKI certificate for client authentication
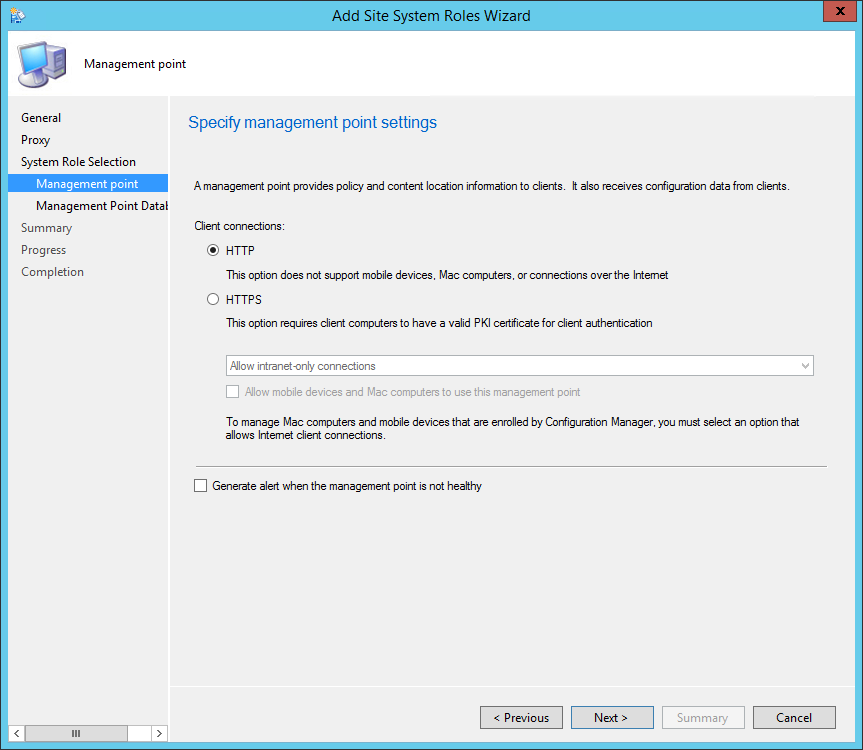
- On the Management Point Database tab, specify if you want to use the site database or a database replica. Read about database replica here
- Specify if you want to use the computer account of the Management Point to connect to the database or a specified account
You can verify the installation in the following logs:
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ mpMSI.log – Records details of about the management point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ MPSetup.log.log – Records the management point installation wrapper process
Part 14 – Reporting Point Installation
We will describe how to install a SCCM Current Branch reporting services point.
This role can be installed on a remote machine, the process is the same but the location of the logs is different.
Before you can install the reporting services point role you must configure SQL correctly.
We’ll be using SQL 2012 on this post. We are assuming that SQL is already installed and that your SCCM site is up and healthy.
During the initial SQL installation, you must select Reporting Services .
If you have installed SQL Server, but have not installed Reporting Services follow the following steps. If Reporting Services is already installed, skip to the “ Configure Reporting Services ” section.
- Launch the SQL Server 2012 installation from the media.
- Click the Installation link on the left to view the Installation options.
- Click the top link, New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.
- Follow the SQL Server Setup wizard until you get to the Installation Type screen.
- Select Add features to an existing instance of SQL Server 2012 .
- Click Next to move to the Feature Selection page.
- Select Reporting Services – Native
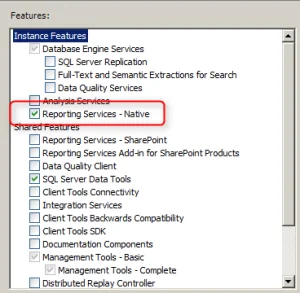
- At the Reporting Services Configuration page
- Select Install Only
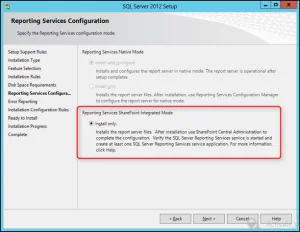
Continue through the wizard and reboot the computer at the end of the installation if instructed to do so.
Before configuring the reporting point, some configuration needs to be made on the SQL side. The virtual instance needs to be created for SCCM to connect and store its reports.
If you installed Reporting Services during the installation of the SQL Server instance, SSRS will be configured automatically for you. If you install SSRS later, then you will have to go back and configure it as a subsequent step.
To configure, Open Reporting Services Configuration Manager
- Click Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server > Configuration Tools > Reporting Services Configuration Manager

- Click Connect to connect to the SQL instance
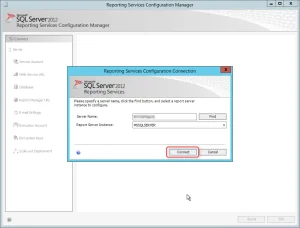
- On the left-hand side of the Reporting Services Configuration Manager, click Database .
- Click the Change Database button
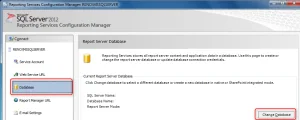
- Select Create a new report server database and click Next
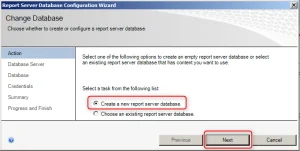
This wizard creates two databases: ReportServer , used to store report definitions and security, and ReportServerTempDB which is used as scratch space when preparing reports.
- Click the Web Service URL tab
- Click Apply
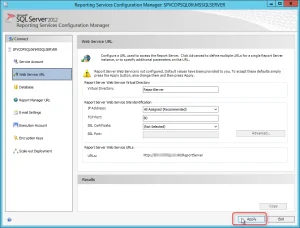
This step sets up the SSRS web service. The web service is the program that runs in the background that communicates between the web page, which you will set up next, and the databases.
- Select the Report Manager URL
- Accept the default settings and click Apply .
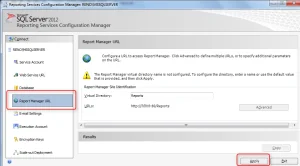
If the Apply button was already grayed out, this means the SSRS was already configured. This step sets up the Report Manager web site where you will publish reports
Exit Reporting Service Configuration Manager.
- Navigate to Administration/Site/Configuration/Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click on your Site Server and click Add system Roles
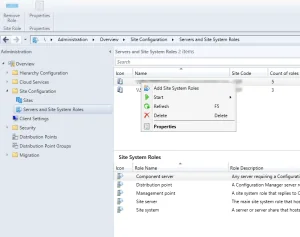
- On the General tab, click Next
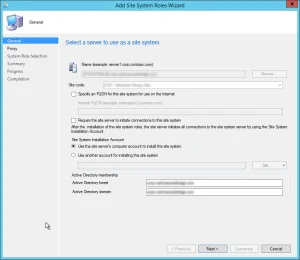
- On the Proxy tab, Click Next
- On the Site System Role, select Reporting Services Point , Click Next
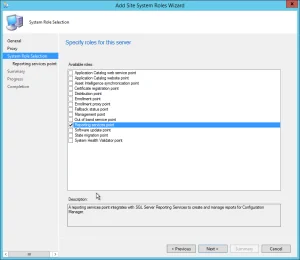
- On Rethe porting Services setting tab
- Click Verify
- At the bottom, Add an account to use for the reporting point. This account needs to have access to the SCCM DB
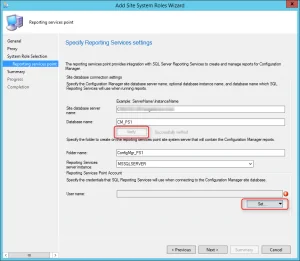
- Wait for the process to complete and close the wizard
Using the simple recovery model improves performance and saves your server hard drive and possibly a large transaction log file.
To change the Recovery Model of the ReportingDB to Simple
- Open SQL Management Studio
- Right-click on the ReportServer database and select Properties
- Go to the Options page
- Under Recovery model select Simple
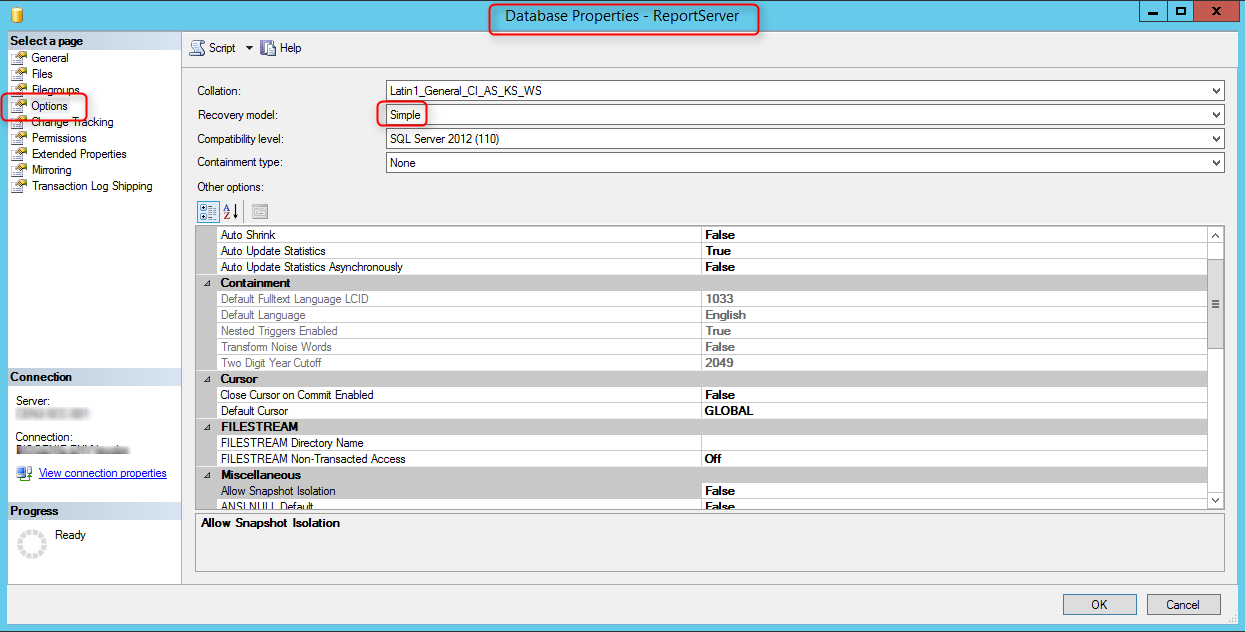
Check for the following logs for reporting point installation status. Both logs are under the SCCM logs file locations.
- Srspsetup.log
- Srsrpmsi.log
If your reporting point is installed on a remote server look for the logs in :
Drive: \SMS\Logs\
Open Monitor/Reporting/Reports node. Verify that your reports are listed
Open Internet Explorer, navigate to http://yourservername/Reports
If everything went well, you’ll have a folder Config_SiteCode containing your reports
If you check your SQL instance, you’ll see the 2 new database which were created by the installation.
- Locate ReportServer and ReportServerTempDB
Happy reporting! 🙂
Part 15 – Software Update Point Installation
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch Software Update Point (SUP).
The SUP integrates with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to provide software updates to Configuration Manager clients.
This is not a mandatory Site System but your need to install a SUP if you’re planning to use SCCM as your patch management platform.
This Site System is a site-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration Site, child Primary Site, stand-alone Primary Site and Secondary Site.
When your hierarchy contains a Central Administration Site, install a Software Update Point and synchronizes with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) before you install a SUP at any child’s Primary Site.
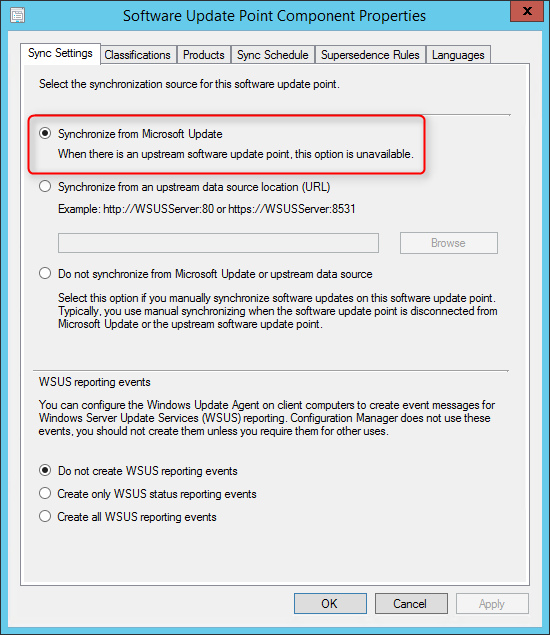
When you install a Software Update Point at a child Primary Site, configure it to synchronize with the SUP at the Central Administration Site.
Consider installing a SUP in Secondary Site when data transfer across the network is slow.
The WSUS Administration Console is required on the Configuration Manager site server when the software update point is on a remote site system server and WSUS is not already installed on the site server. The WSUS version on the site server must be the same as the WSUS version running on the software update points.
When using WSUS 3.0 (on server 2008, it was possible to install the console only). This has changed with 2012 and 2016. One way to do it is to add the Windows Software Update Services role and deselecting Database and WID Database. The problem is that will still cause some trouble with the post-install task.
The recommended way to do it :
- Start PowerShell Console (as Administrator)
- Run : Install-WindowsFeature -Name UpdateServices-Ui
This will install the console only and not run a post-install task.
WSUS Installation
Perform the following on the server that will host the SUP role.
- Open Server Manager / Add Roles and Features
- Select the Windows Server Update Services Role, click Next
- Select WSUS Services and Database, click Next
- Launch Windows Server Update Services from the Start Menu. You will be prompt with the following window :
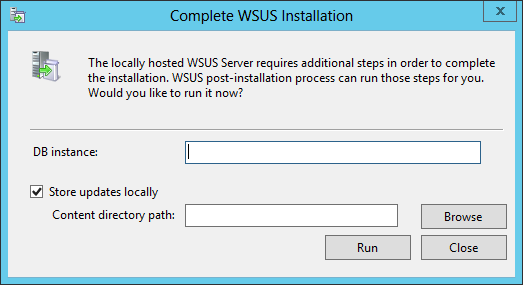
- On the DB instance , enter your server name
- On Content directory path , use a drive with enough drive space. This is where your WSUS will store updates
- When the WSUS Configuration Wizard starts, click Cancel
- Under Databases, Right-click SUSDB, select Properties and click Files
- Change Owner to SA
- Change the Autogrowth value to 512MB, click Ok and close SQL MS
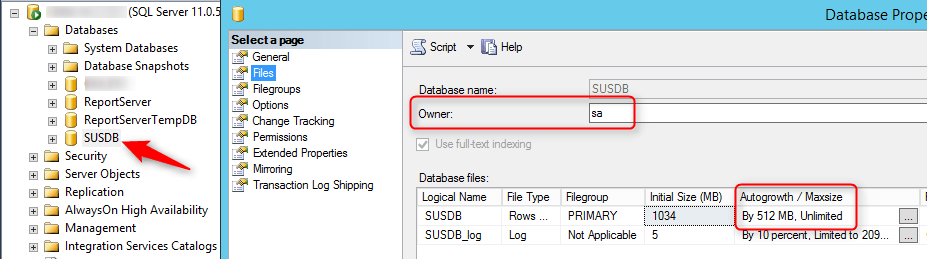
Software Update Point Installation
- On the Site System Role tab, select Software Update Point, click Next
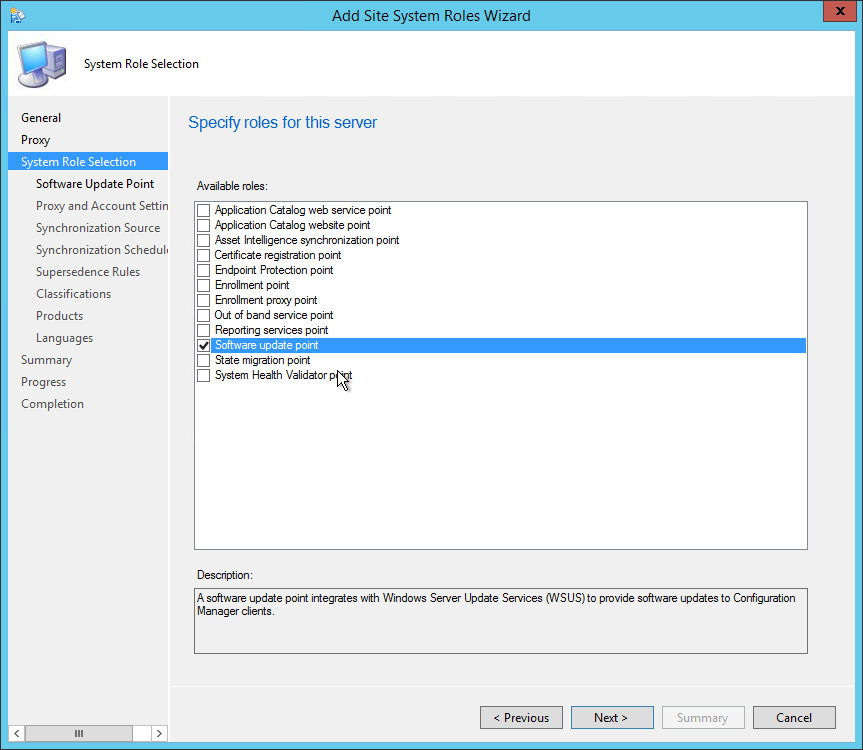
- On the Software Update Point tab, select WSUS is configured to use ports 8530 and 8531, click Next
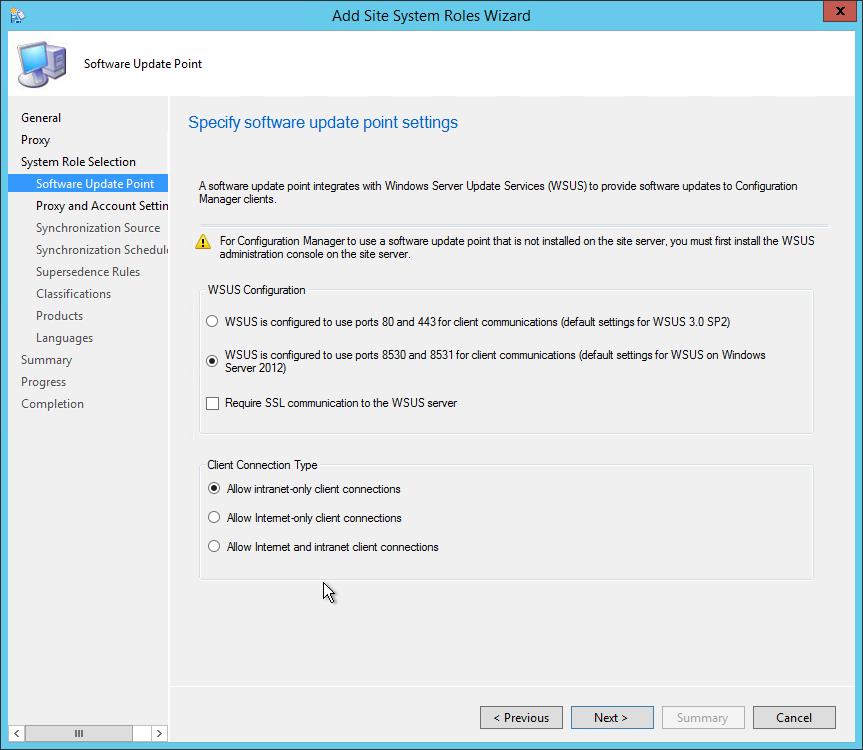
- On the Proxy and Account Settings tab, specify your credentials if necessary, click Next
- On the Synchronization Source tab, specify if you want to synchronize from Microsoft Update or an upstream source. Refer to the Site System Placement section if you’re unsure. For a stand-alone Primary Site, select Synchronize from Microsoft Update, click Next
- On the Synchronization Schedule tab, check the Enable synchronization on a schedule checkbox and select your desired schedule. 1 day is usually enough but it can be lowered if you’re synchronizing Endpoint Protection definition files, click Next
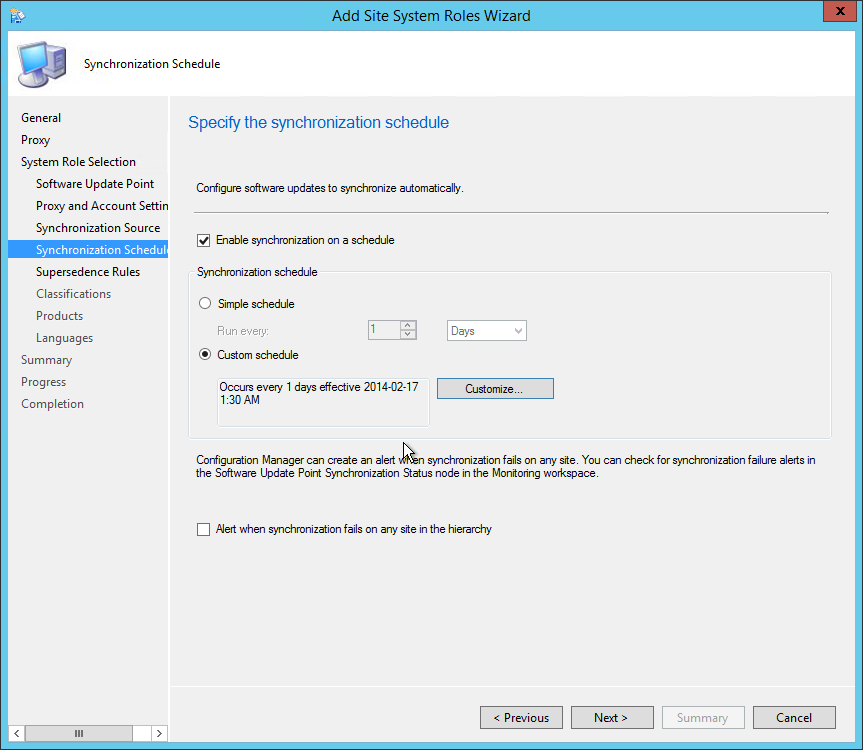
- On the Supersedence Rules tab, select Immediately expire a superseded software update, click Next
- Full description on this Microsoft Support Article
- On the Products tabs, select the products that you want to manage using SCCM, click Next
- On the Languages tab, select the desired language, click Next
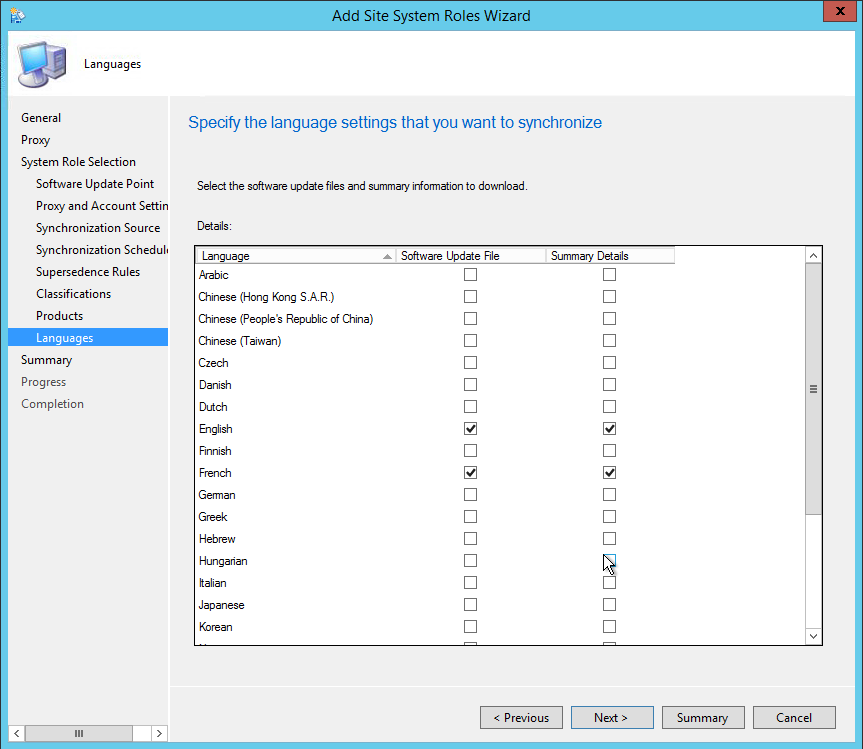
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next, wait for the setup to complete and click Close
- ConfigMgrSetup\Logs\SUPSetup.log -Provides information about the software update point installation. When the software update point installation completes, Installation was successful is written to this log file
- ConfigMgrSetup\Logs\WCM.log – Provides information about the software update point configuration and connecting to the WSUS server for subscribed update categories, classifications, and languages
- ConfigMgrSetup\Logs\WSUSCtrl.log – Provides information about the configuration, database connectivity, and health of the WSUS server for the site
- ConfigMgrSetup\Logs\Wsyncmgr.log – Provides information about the software updates synchronization process
Bonus link : I suggest that you read the excellent article written by Kent Agerlund on how to avoid what he calls the House of Cards
Part 16 – State Migration Point Installation
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch State Migration Point (SMP).
The State Migration Point stores user state data when a computer is migrated to a new operating system.
This is not a mandatory Site System but you need a State Migration Point if you plan to use the User State steps in your Task Sequence. These steps integrate with User State Migration Tools (USMT) to backup your user data before applying a new operating system to a computer.
The State Migration Point is a site-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a child Primary Site, stand-alone Primary Site or Seconday Site. It’s not supported to install it on a Central Administration site.
The State Migration Point can be installed on the site server computer or on a remote computer. It can be co-located on a server that has the distribution point role.
SCCM State Migration Point Installation
- On the Site System Role tab, select State Migration Point, click Next
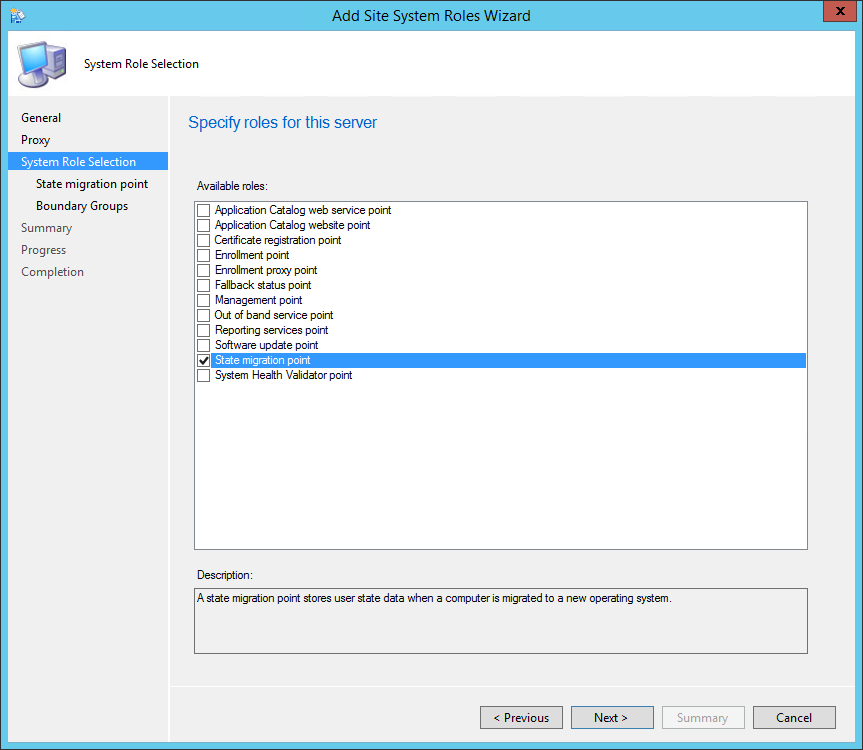
- Click the star icon, specify the folder where you want the data to be stored and how much space must be reserved on the drive
- Specify the Deletion Policy. This is the delay to keep the data after a successful restore.
- Enable Restore-Only mode if needed. Use this setting if you want your SMP to be in read-only mode. This is useful if you replace or decommission an existing SMP
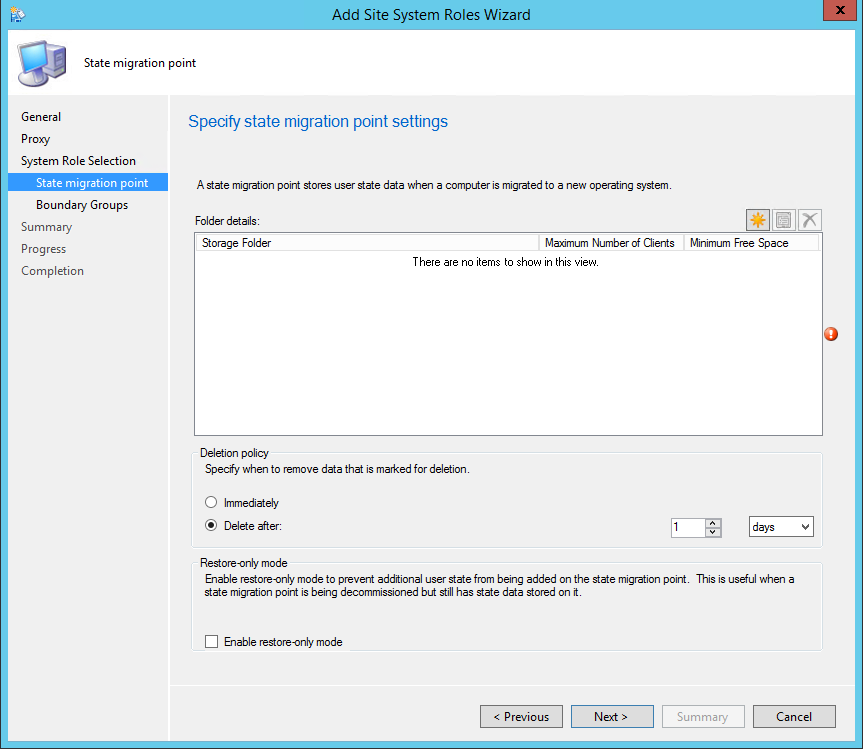
- On the Boundary Groups tab, add the boundary group that can access the State migration Point. If you add the role on a site system that already has the Distribution Point role, the boundary group of this DP will already be listed
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath\Logs\ Smssmpsetup.log – Detailed State Migration Point Installation status
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath\Logs\ Smpmsi.log – Provides information about the State Migration Point
If you have any error in the installation process refer to this post that explains the permission needed for the SMP to install correctly.
To store the user state data on a State Migration Point, you must create a package that contains the USMT source files. This package is specified when you add the Capture User State step to your task sequence.
- If you don’t have this folder, it’s because you haven’t installed the USMT (included in Windows ADK) during your SCCM Installation
- Copy the folder content in your Content Library (In my example D:\Sources\OSD\USMT )
- Go to Software Library / Application Management / Packages
- Right-click Packages and select Create a new package
- Enter the Name, Manufacturer, Language
- Check the This package contains source files check-box and specify your source folder ( D:\Sources\OSD\USMT)
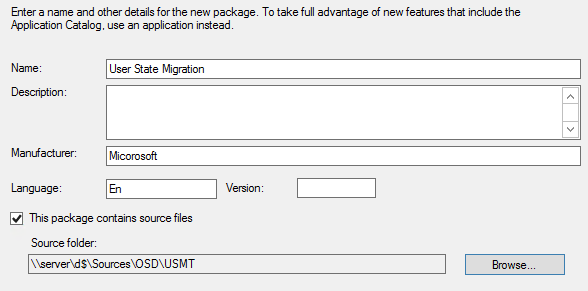
- On the Program Type tab, select Do not create a program and click Next
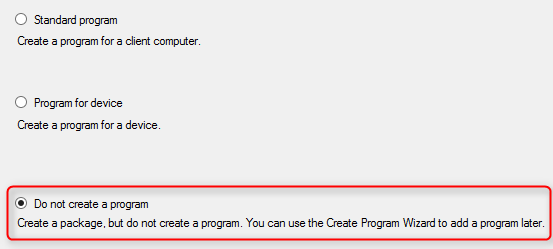
- Complete the Create Package wizard
The State Migration Point and the USMT package are now ready for use in an OSD Task Sequence using the Capture User State and Restore User State steps.
Part 17 – System Health Validator Point
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch System Health Validator Point (SHVP).
The System Health Validator Point validates Configuration Manager Network Access Protection (NAP) policies.
This is not a mandatory site system but you need a System Health Validator Point if you plan to use NAP evaluation in your software update deployments. This site system integrates with an existing NAP server in your infrastructure.
The System Health Validator Point is a hierarchy-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration site, stand-alone Primary site, child Primary site. It’s not supported to install it on a Seconday site. The System Health Validator Point must be installed on a NAP health policy server.
- On the Site System Role tab, select System Health Validator Point, click Next
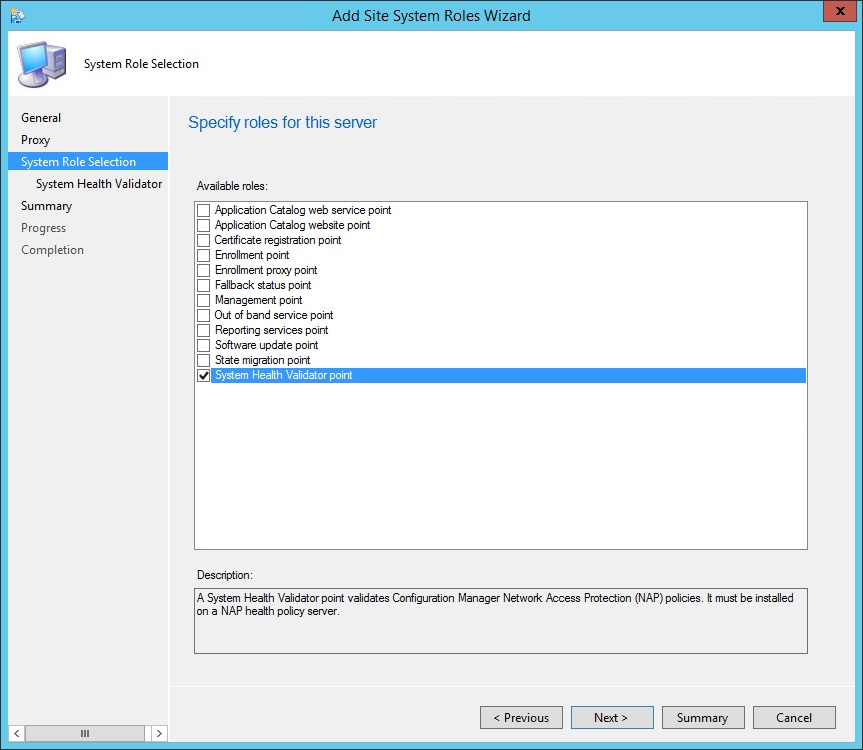
- There are no properties to configure for this site system role
- ConfigMgrInstallationPath \Logs\ SMSSHVSetup.log – Detailed System Health Validator Point installation status
In order to enable Network Access Protection on your clients, you must configure your client settings :
- Browse to Administration / Client Settings
- Create a new client settings, select Network Access Protection on the left and choose Yes under Enable Network Access Protection on clients
- Select the desired NAP re-evaluation schedule and click Ok
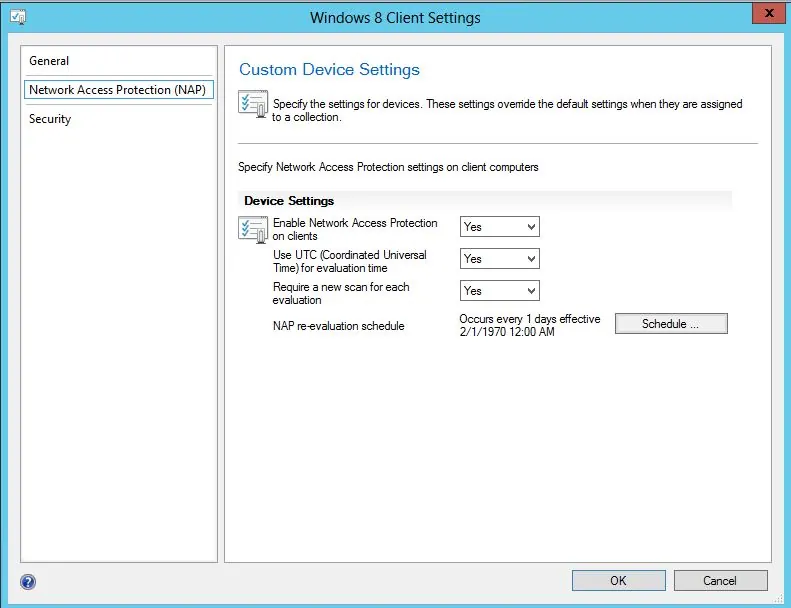
In case you’re used to NAP in SCCM 2007 and looking for a Network Access Protection node in the console, the 2012 version of NAP is slightly different.
From Technet :
The New Policies Wizard is no longer available to create a NAP policy for software updates: The Network Access Protection node in the Configuration Manager console and the New Policies Wizard are no longer available in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager. To create a NAP policy for software updates, you must select Enable NAP evaluation on the NAP Evaluation tab in software update properties.
Part 18 – Service Connection Point Installation
We will describe how to perform an SCCM Service Connection Point Installation. The Service Connection Point is a new site system role that serves several important functions for the SCCM hierarchy.
It might affect how you configure this site system role:
- Manage mobile devices with Microsoft Intune – This role replaces the Windows Intune connector used by previous versions of SCCM, and can be configured with your Intune subscription details
- Manage mobile devices with on-premises MDM – This role provides support for on-premises devices you manage that do not connect to the Internet
- Upload usage data from your Configuration Manager infrastructure – You can control the level or amount of detail you upload
- Download updates that apply to your Configuration Manager infrastructure – Only relevant updates for your infrastructure are made available, based on usage data you upload
Each hierarchy supports a single instance of this role . The site system role can only be installed at the top-tier site of your hierarchy (On a Central Administration Site or a stand-alone Primary Site).
The SCCM 1511 installation or upgrade wizard will ask to install the Service Connection Point. If you select to skip the role installation, you can manually add it to SCCM using the following steps.
- Go to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click the Site System you wish to add the role
- Click Add Site System Role in the Ribbon
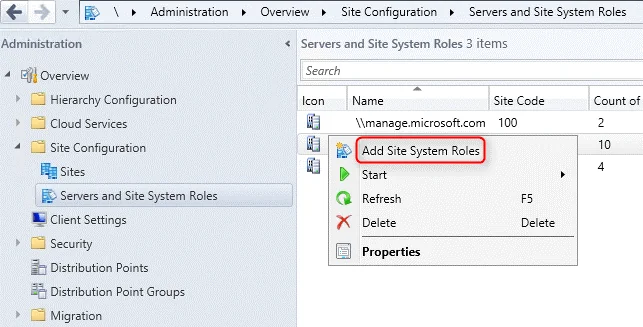
- On the General tab, click Next
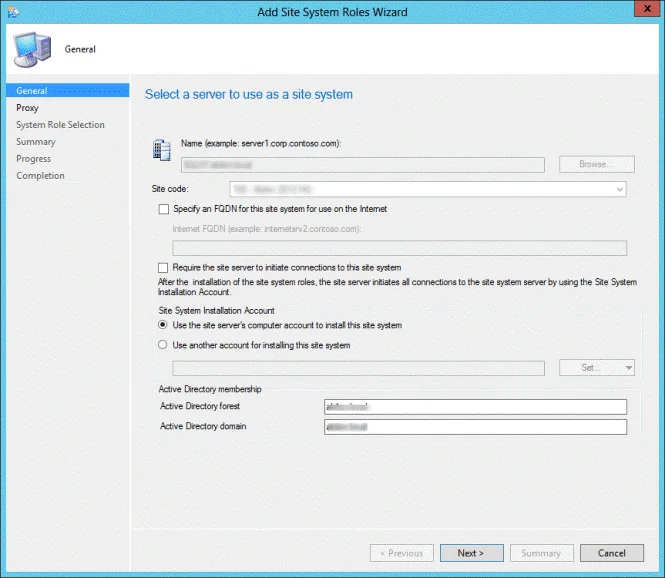
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select Service Connection Point and click Next
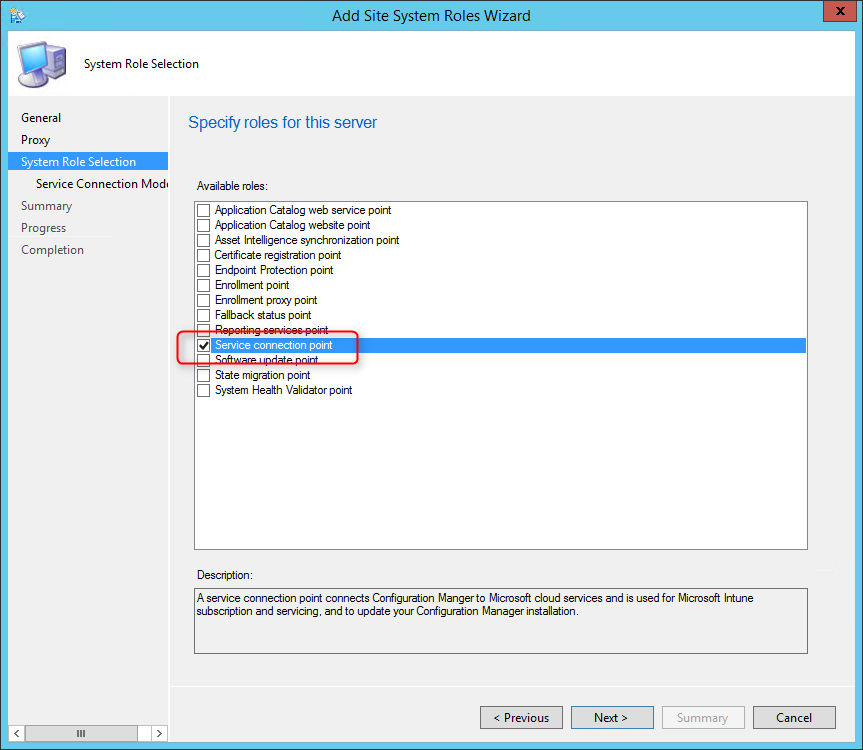
- In Online mode, the Service Connection Point automatically downloads updates that are available for your current infrastructure and product version, making them available in the SCCM console
- In Offline mode, the Service Connection Point does not connect to the Microsoft cloud service and you must manually use the service connection tool when your Service Connection Point is in Offline mode to import available updates
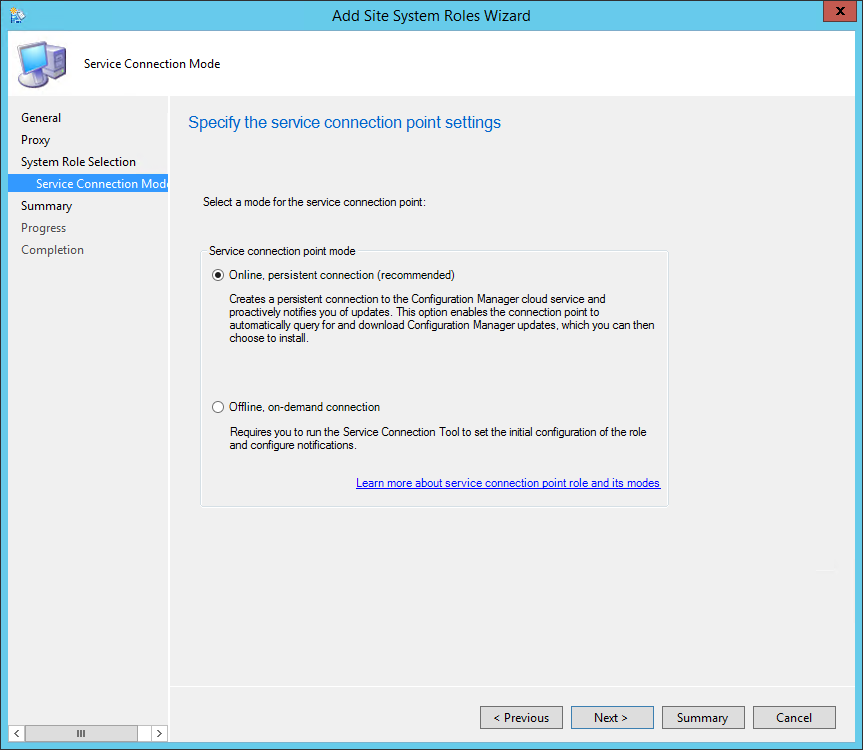
- On the Summary screen, wait for the setup to complete and close the wizard
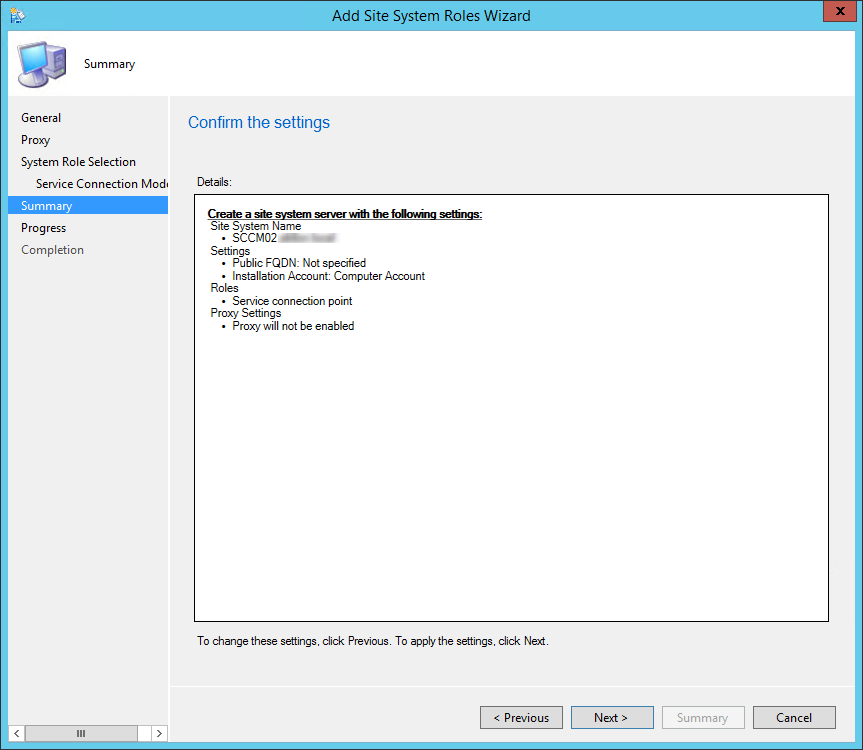
- ConnectorSetup.log – Information about role installation and that the Service Connection Point was created successfully
Now that all our site servers are installed, we are now ready to configure the various aspect of SCCM.
Part 19 – Plan and Configure Boundaries
We will start our configuration with the SCCM boundaries. First, let’s define what a boundary in SCCM is :
From Technet :
In MEMCM/SCCM, a boundary is a network location on the intranet that can contain one or more devices that you want to manage. Boundaries can be an IP subnet, Active Directory site name, IPv6 Prefix, or an IP address range, and the hierarchy can include any combination of these boundary types. To use a boundary, you must add the boundary to one or more boundary groups. Boundary groups are collections of boundaries. By using boundary groups, clients on the intranet can find an assigned site and locate content when they have to install software, such as applications, software updates, and operating system images. A boundary does not enable clients to be managed at the network location. To manage a client, the boundary must be a member of a boundary group. Simple Boundaries on do nothing, they must be added to one or more boundary groups in order to work.
A boundary group is self-explanatory, it’s a group of boundaries used for site assignment and for content location. Beginning with SCCM 2012 R2 SP1 , a boundary group can direct your clients to their Distribution Points for content, State Migration Point , Preferred Management Point and Software Update Point . Prior to R2 SP1, Content location is used by client to identify available Distribution Points or State Migration Point based on the client network location.
To resume :
- Site Assignment boundary group associates a resource to a site
- Content Location boundary group is used to retrieve its deployment content (applications, packages, images, etc)
Before designing your strategy, choose wisely on which boundary type to use.
If you’re unsure which boundary type to use, you can read Jason Sandys’s excellent post about why you shouldn’t use IP Subnet boundaries.
Microsoft recommends the following :
- When designing your boundary strategy, we recommend using boundaries based on Active Directory sites before using other boundary types. If boundaries based on Active Directory sites are not an option, use IP subnet or IPv6 boundaries. If none of these options are available to you, then leverage IP address range boundaries. This is because the site evaluates boundary members periodically, and the query required to assess members of an IP address range requires a substantially larger use of SQL Server resources than queries that assess members of other boundary types.
- It’s also recommended to split your Site Assignment and Content location group.
SCCM Current Branch supports overlapping boundary configurations for content location.
When a client requests content, and the client network location belongs to multiple boundary groups, Configuration Manager sends the client a list of all Distribution Points with the content.
This behaviour enables the client to select the nearest server from which to transfer the content or state migration information.
In our various SCCM installations, our clients are often confused about this topic. Let’s make an example to help you understand :
- Contoso has 1000 clients
- 1 Primary Site (Montreal)
- 3 remote offices with their local Distribution Point (New York, Chicago, Los Angeles)
- Active Directory Sites are based on their site subnets (MTL,NY,CHI,LA)
In that scenario, we need to create 4 Boundary, 1 for each office :
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Boundary
- Right-click Boundaries and select Create Boundary
- Tip: If you have multiple Active Directory Sites, IP Ranges or Subnets, you can enable Active Directory Forest Discovery which can create them automatically
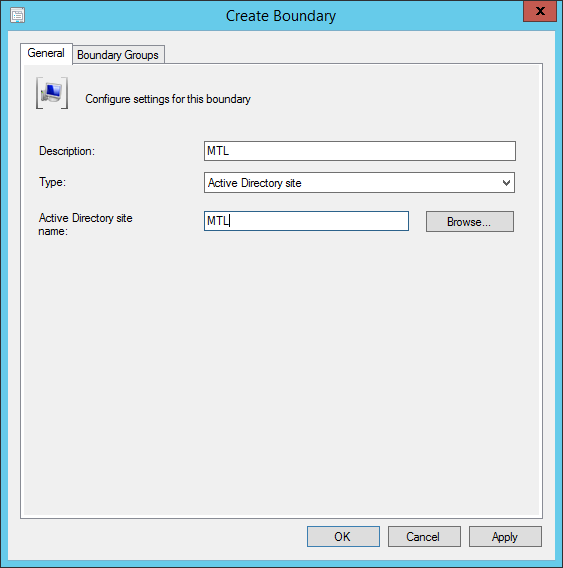
Create Boundary Group
Now, we’ll create a Site Assignment Boundary Group and add all those AD Site. That way, all my clients for my 4 locations will be assigned to my Montreal Primary Site. For Content Location, we want clients to get their content locally at their respective location. We will create 4 Content Boundary groups, add only their AD Site Boundary and assign their local Distribution Point.
Here’s how to make this happen in SCCM :
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Boundary Groups
- Right-click Boundary Groups and select Create Boundary Groups
Create Site Assignment Boundary Group
- We’ll start by creating a group for Site Assignment : SA – MTL
- Click the Add bouton on the bottom
- On the Add Boundaries screen , select all boundaries. This will direct all my clients to the Primary Site located in Montreal for Site Assignment
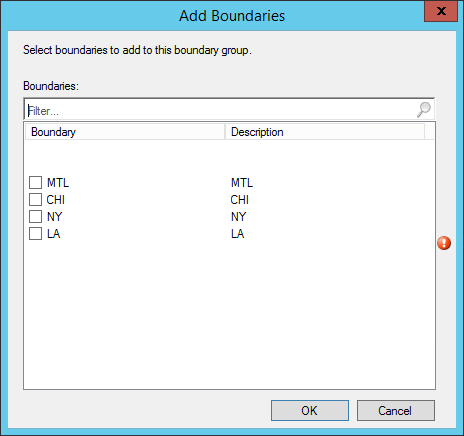
- On the References tab, check the Use this boundary group for site assignment box
- Select your assigned site. In my case : MTL
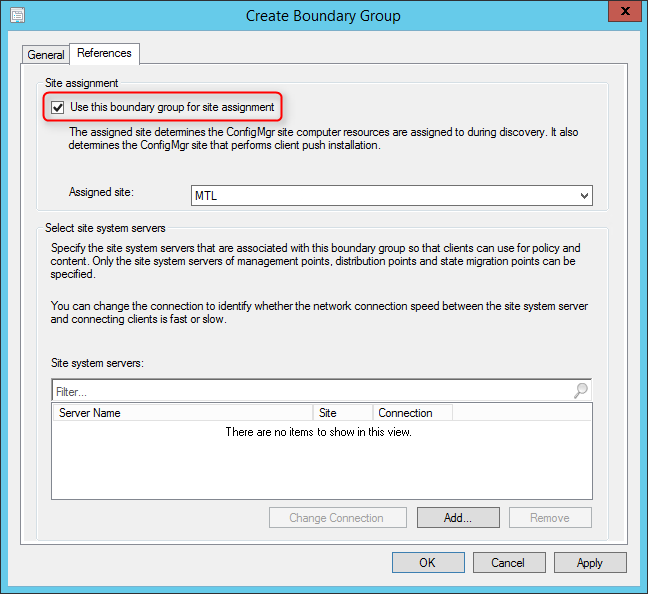
- We’ll name our group Content Location – MTL
- Select only the MTL boundary
- The MTL boundary will be listed
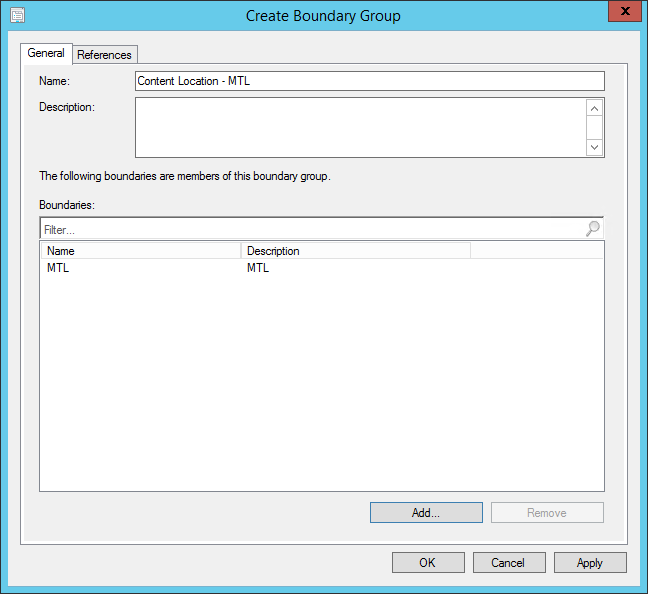
- On the References tab, uncheck the Use this boundary group for site assignment box
- Click on Add at the bottom
- Select the Site System that host the Distribution Point role for the Montreal site. For our example DPMTL01
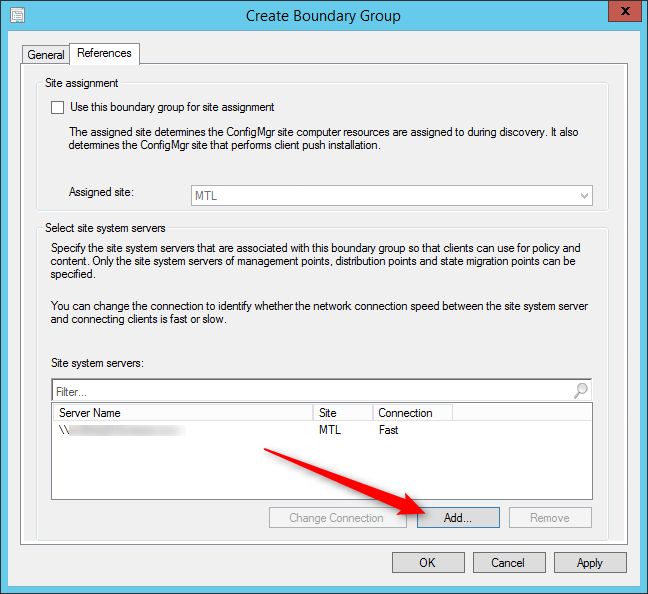
- Repeat the steps for the other sites (New York, Chicago, Los Angeles)
- Once completed our clients are assigned to their local respective Site Systems
This is a simple but typical scenario. You can have multiples boundaries and Site System in your Boundary Groups if needed.
Part 20 – Configure Client Settings
This part will explain how to create a custom SCCM client settings and how to deploy it.
Client settings are used to configure your deployed agents. This is where you decide any configuration like :
- Enabling hardware inventory agent
- Enabling power settings options
- Enable cloud services
- Set scan schedules
- BITS throttling
In previous versions of SCCM, client settings were specific to the site. You had 1 client settings that applied to all your hierarchy. In SCCM you can specify clients setting at the collection level. You can have different settings for specific collections, overlapping settings are set using a priority setting.
When you modify the Default Client Settings , the settings are applied to all clients in the hierarchy automatically. You do not need to deploy the Default Client Settings to apply it. By default, it has a 10000 priority value (This is the lower priority). All other custom client settings can have a priority value of 1 to 9999 which will always override the Default Client Settings . (The higher Priority is 1).
We won’t explain each client’s settings and their descriptions. The Technet documentation is pretty clear and many of the client settings are self-explanatory. We cannot make any recommendations either as each environment has its own needs and limitations. If you have any questions concerning a specific setting, use the comment section and we’ll try to help you so you can make the right decision for your organization.
When you deploy a custom client settings, they override the Default Client Settings .
Before you begin, ensure that you created a collection that contains the devices that require these custom client settings.
For our blog post, we will set the Client Policy polling interval to 15 minutes.
- Go to Administration / Client Settings
- On the top ribbon, click Create Custom Client Device Settings
- In the Create Custom Device Settings page, specify a name for the custom settings and description
- Select one or more of the available settings. We will select Client Policy
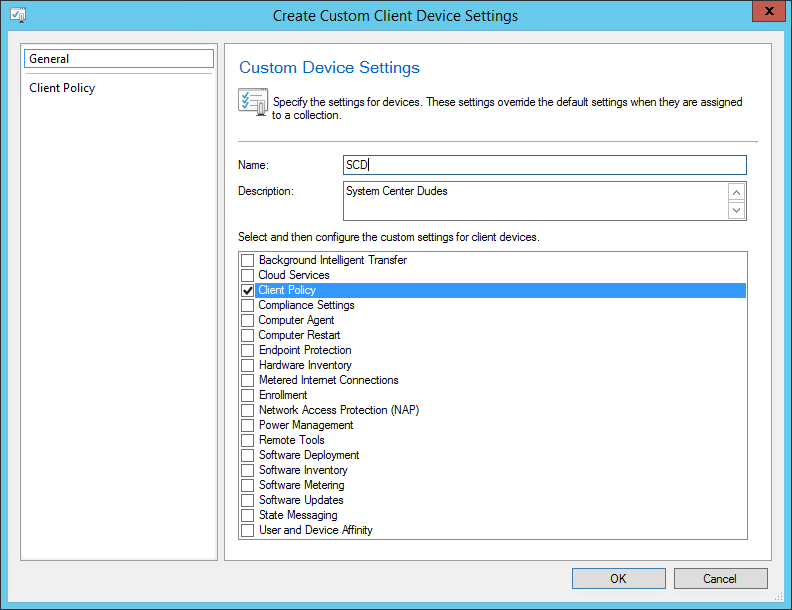
- On the left pane, Client Policy will be displayed, click on it
- We will set the Client Policy polling interval to 15 minutes
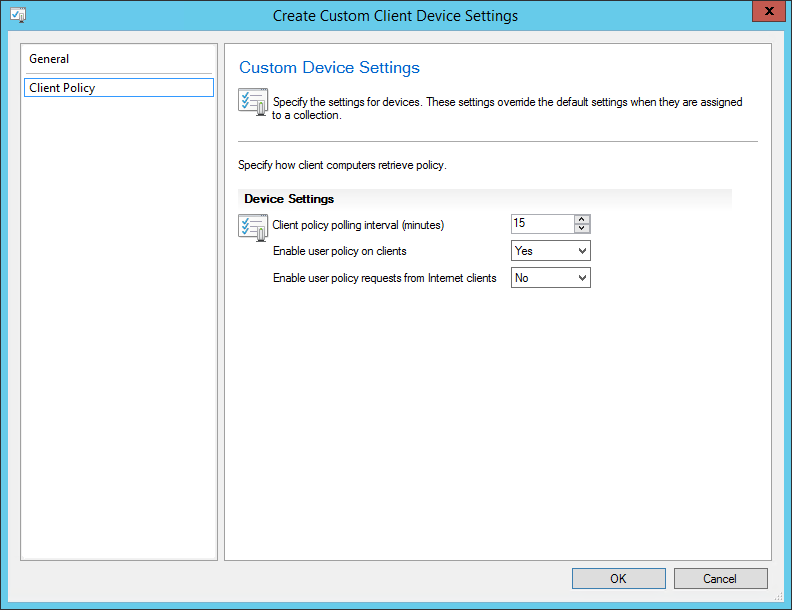
- Your newly created setting will be displayed in the console
When you create a new client setting, it automatically takes the next available priority. (Beginning with 1) Before deploying it, make sure that your priority is well set for your needs. A higher priority (1) will override any settings with a lower priority. (9999). Don’t get confused 1 is higher !
To change the priority number :
- On the top ribbon, select your client settings and click Increase Priority or Decrease Priority
- You can see each client settings priority and if they are deployed in the same section
Now that your client settings are created, you need to deploy it to a collection. This new client settings will apply to only this collection and depending on the priority, will override the settings.
- Select the custom client settings that you have just created
- On the top ribbon, click Deploy
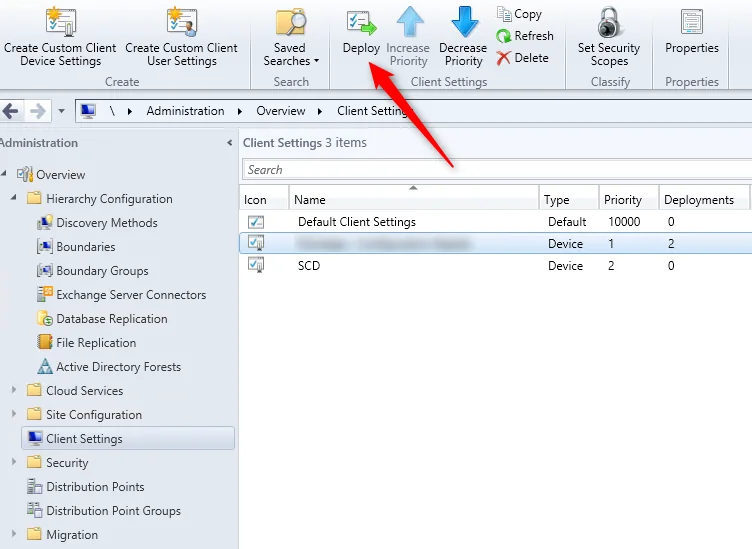
- In the Select Collection dialog box, select the collection that contains the devices to be configured with the custom settings, and then click Ok
- You can verify the selected collection if you click the Deployments tab on the bottom of the console
Client computers will apply your custom settings when they download their next client policy. You can trigger it manually to speed up the process.
Manually on the client
- In Control Panel , click on the Configuration Manager icon
- In the Action tab, select Machine Policy Retrieval & Evaluation Cycle
- Click Run now
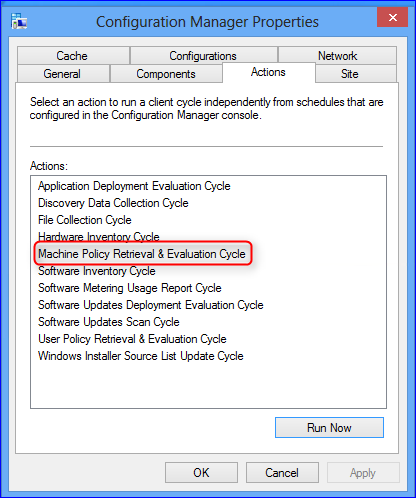
Using the SCCM Console
To initiate client policy retrieval by using client notification (Configuration Manager SP1+ only)
- In the SCCM console
- Go to Assets and Compliance / Device Collections
- Select the device collection containing the computers that you want to download policy
- Right-click a single device or the whole collection and select Client Notification and then Download Computer Policy
It’s possible to see which client settings are applied to a specific client. You must use the Resultant Client Settings function in the SCCM console.
We already cover this in a previous article .
Part 21 – Configure Discovery Methods
After you completed your SCCM installation, you certainly want to start managing some systems. The effective way to add them in SCCM is to configure SCCM discovery methods. This blog article will explain the various discovery methods and will describe how to configure it.
Here’s the official discovery methods definition from Technet :
SCCM discovery methods identifies computer and user resources that you can manage by using Configuration Manager. It can also discover the network infrastructure in your environment. Discovery creates a discovery data record (DDR) for each discovered object and stores this information in the Configuration Manager database.
When discovery of a resource is successful, discovery puts information about the resource in a file that is referred to as a discovery data record (DDR). DDRs are in turn processed by site servers and entered into the Configuration Manager database where they are then replicated by database-replication with all sites. The replication makes discovery data available at each site in the hierarchy, regardless of where it was discovered or processed. You can use discovery information to create custom queries and collections that logically group resources for management tasks such as the assignment of custom client settings and software deployments. Computers must be discovered before you can use client push installation to install the Configuration Manager client on devices.
In simple words, it means that SCCM needs to discover a device before it can manage them. It’s not mandatory to discover computers, if you manually install the client, it will appear in the console and it can be managed. The problem is that if you have a thousand computers, it can be a fastidious process. By using Active Directory System Discovery, all your computers will be shown on the console, from there you can choose to install the client using various SCCM methods . Of course, if you need information about your users and groups, you need to configure User and Group discovery, it’s the only way to bring this information in SCCM.
There are 5 Types of Discovery Methods that can be configured. Each one targets a specific object type (Computers, Users, Groups, Active Directory) :
Discovers computers in your organization from specified locations in Active Directory. In order to push the SCCM client to the computers, the resources must be discovered first. You can specify to discover only computers that have logged on to the domain in a given period of time. This option is useful to exclude obsolete computer accounts from Active Directory. You also have the option to fetch custom Active Directory Attributes. This is useful if your organization store custom information in AD. You can read our blog post concerning this topic.
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Discovery Methods
- Right-Click Active Directory System Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory System Discovery
- Click on the Star icon and select the Active Directory container that you want to include in the discovery process
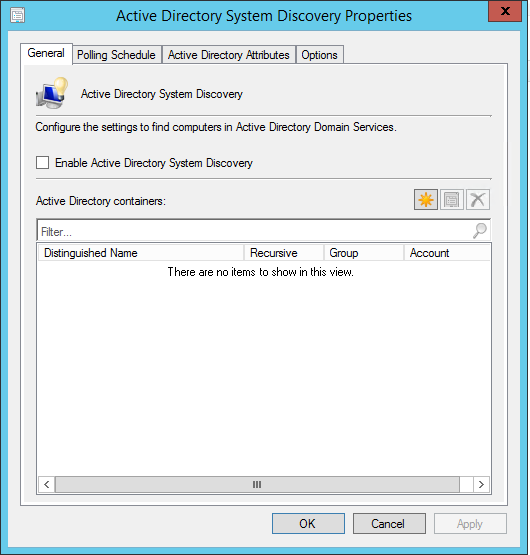
- A 7-day cycle with a 5 minutes delta interval is usually fine in most environment
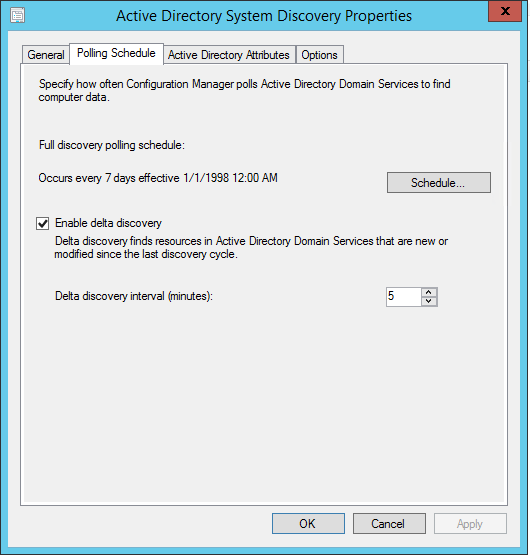
- This is useful if you have custom data in Active Directory that you want to use in SCCM
- This is useful if your Active Directory isn’t clean. Use this to discover only good records
Discovers groups from specified locations in Active Directory. The discovery process discovers local, global or universal security groups. When you configure the Group discovery you have the option to discover the membership of distribution groups. With the Active Directory Group Discovery, you can also discover the computers that have logged in to the domain in a given period of time. Once discovered, you can use group information for example to create deployment based on Active Directory groups.
Be careful when configuring this method: If you discover a group that contains a computer object that is NOT discovered in Active Directory System Discovery, the computer will be discovered. If the automatic client push is enabled, this could lead to unwanted clients’ computers.
To discover resources using this method:
- Right-Click Active Directory Group Discovery and select Properties
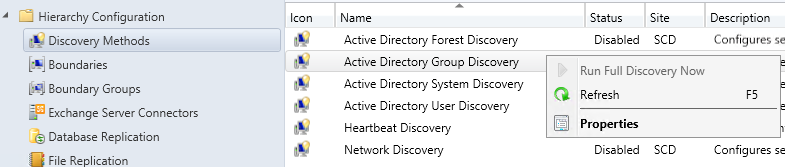
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory Group Discovery
- Remember : If you discover a group that contains a computer object that is NOT discovered in Active Directory System Discovery, the computer will be discovered.
The discovery process discovers user accounts from specified locations in Active Directory. You also have the option to fetch custom Active Directory Attributes. This is useful if your organization store custom information in AD about your users. Once discovered, you can use group information for example to create user-based deployment.
- Right-Click Active Directory User Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory User Discovery
- A 7-day cycle with a 5 minutes delta interval is usually fine in most environment.
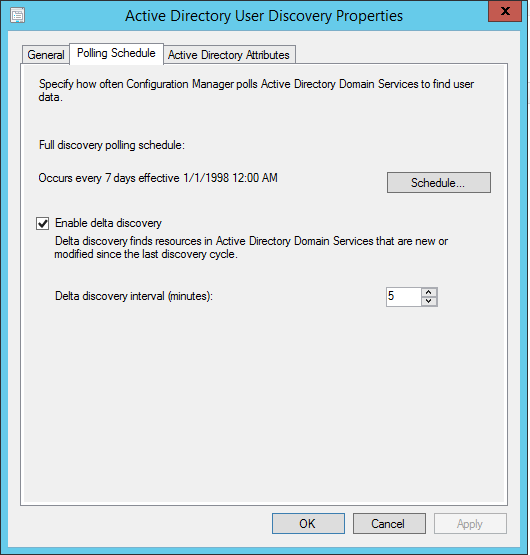
Discovers Active Directory sites and subnets, and creates Configuration Manager boundaries for each site and subnet from the forests which have been configured for discovery. Using this discovery method you can automatically create the Active Directory or IP subnet boundaries that are within the discovered Active Directory Forests. This is very useful if you have multiple AD Site and Subnet, instead of creating them manually, use this method to do the job for you.
- Right-Click Active Directory Forest Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory Forest Discovery
- Select the desired options
Heartbeat Discovery runs on every client and to update their discovery records in the database. The records (Discovery Data Records) are sent to the Management Point in a specified duration of time. Heartbeat Discovery can force the discovery of a computer as a new resource record, or can repopulate the database record of a computer that was deleted from the database.
HeartBeat Discovery is enabled by default and is scheduled to run every 7 days.
- Right-Click Heartbeat Discovery and select Properties
- Make sure that this setting is enabled and that the schedule run less frequently than the Clear Install Flag maintenance task.
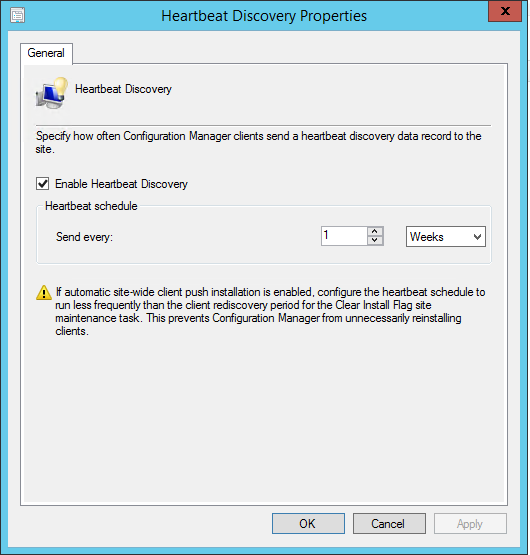
The Network Discovery searches your network infrastructure for network devices that have an IP address. It can search the domains, SNMP devices and DHCP servers to find the resources. It also discovers devices that might not be found by other discovery methods. This includes printers, routers, and bridges.
We won’t go into detail of this discovery method as it’s old and depreciated methods. We never saw any customers using this method in production.
Part 22 – Configure Maintenance Tasks
Each Configuration Manager site supports maintenance tasks that help maintain the operational efficiency of the site database. By default, several maintenance tasks are enabled in each site, and all tasks support independent schedules. Maintenance tasks are set up individually for each site and apply to the database at that site. However, some tasks, like Delete Aged Discovery Data , affect information that is available in all sites in a hierarchy.
To set up maintenance tasks for Configuration Manager :
- Go to Administration / Site Configuration / Sites
- On the Home tab, in the Settings group, choose Site Maintenance
- To set up the task, choose Edit , ensure the Enable this task checkbox is checked and set up a schedule for when the task runs.
To enable or disable the task without editing the task properties, choose the Enable or Disable button. The button label changes depending on the current configuration of the task.
When you are finished configuring the maintenance tasks, choose OK to finish the procedure.
This topic lists details for each of the SCCM site maintenance tasks :
Backup Site Server : Use this task to prepare for the recovery of critical data. You can create a backup of your critical information to restore a site and the Configuration Manager database. For more information, see our next section that covers it.
Check Application Title with Inventory Information : Use this task to maintain consistency between software titles that are reported in the software inventory and software titles in the Asset Intelligence catalog. Central administration site : Enabled
Clear Install Flag : Use this task to remove the installed flag for clients that don’t submit a Heartbeat Discovery record during the Client Rediscovery period. The installed flag prevents automatic client push installation to a computer that might have an active Configuration Manager client.
Delete Aged Application Request Data : Use this task to delete aged application requests from the database.
Delete Aged Client Download History : Use this task to delete historical data about the download source used by clients.
Delete Aged Client Operations : Use this task to delete all aged data for client operations from the site database. For example, this includes data for aged or expired client notifications (like download requests for machine or user policy), and for Endpoint Protection (like requests by an administrative user for clients to run a scan or download updated definitions).
Delete Aged Client Presence History : Use this task to delete history information about the online status of clients (recorded by client notification) that is older than the specified time.
Delete Aged Cloud Management Gateway Traffic Data : Use this task to delete all aged data about the traffic that passes through the cloud management gateway from the site database. For example, this includes data about the number of requests, total request bytes, total response bytes, number of failed requests, and a maximum number of concurrent requests.
Delete Aged Collected Files : Use this task to delete aged information about collected files from the database. This task also deletes the collected files from the site server folder structure at the selected site. By default, the five most-recent copies of collected files are stored on the site server in the Inboxes\sinv.box\FileCol directory.
Delete Aged Computer Association Data : Use this task to delete aged Operating System Deployment computer association data from the database. This information is used as part of completing user state restores.
Delete Aged Delete Detection Data : Use this task to delete aged data from the database that has been created by Extraction Views. By default, Extraction Views are disabled. You only enable them by using the Configuration Manager SDK. Unless Extraction Views are enabled, there is no data for this task to delete.
Delete Aged Device Wipe Record : Use this task to delete aged data about mobile device wipe actions from the database.
Delete Aged Devices Managed by the Exchange Server Connector : Use this task to delete aged data about mobile devices that are managed by using the Exchange Server connector. This data is deleted according to the interval that is configured for the Ignore mobile devices that are inactive for more than (days) option on the Discovery tab of the Exchange Server connector properties.
Delete Aged Discovery Data : Use this task to delete aged discovery data from the database. This data can include records that result from heartbeat discovery, network discovery, and Active Directory Domain Services discovery methods (System, User, and Group). This task will also remove aged devices marked as decommissioned. When this task runs at a site, data associated with that site is deleted, and those changes replicate to other sites.
Delete Aged Distribution Point Usage Data : Use this task to delete from the database aged data for distribution points that has been stored longer than a specified time.
Delete Aged Endpoint Protection Health Status History Data : Use this task to delete aged status information for Endpoint Protection from the database.
Delete Aged Enrolled Devices : Beginning with the update for 1602, this task is disabled by default. You can use this task to delete from the site database the aged data about mobile devices that haven’t reported any information to the site for a specified time.
Delete Aged Inventory History : Use this task to delete inventory data that has been stored longer than a specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Log Data : Use this task to delete aged log data that is used for troubleshooting from the database. This data isn’t related to Configuration Manager component operations.
Delete Aged Notification Task History : Use this task to delete information about client notification tasks from the site database when it hasn’t been updated for a specified time.
Delete Aged Replication Summary Data : Use this task to delete aged replication summary data from the site database when it hasn’t been updated for a specified time.
Delete Aged Passcode Records : Use this task at the top-level site of your hierarchy to delete aged Passcode Reset data for Android and Windows Phone devices. Passcode Reset data is encrypted, but does include the PIN for devices. By default, this task is enabled and deletes data that is older than one day.
Delete Aged Replication Tracking Data : Use this task to delete aged data about database replication between Configuration Manager sites from the database. When you change the configuration of this maintenance task, the configuration applies to each applicable site in the hierarchy.
Delete Aged Software Metering Data : Use this task to delete aged data for software metering that has been stored longer than a specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Software Metering Summary Data : Use this task to delete aged summary data for software metering that has been stored longer than a specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Status Messages : Use this task to delete aged status message data as configured in status filter rules from the database.
Delete Aged Threat Data : Use this task to delete aged Endpoint Protection threat data that has been stored longer than a specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Unknown Computers : Use this task to delete information about unknown computers from the site database when it hasn’t been updated for a specified time.
Delete Aged User Device Affinity Data : Use this task to delete aged User Device Affinity data from the database.
Delete Aged CMPivot Results : Use this task to delete from the site database aged information from clients in CMPivot queries .
Delete Aged Cloud Management Gateway Traffic Data : Use this task to delete from the site database all aged data about the traffic that passes through the cloud management gateway . This data includes:
- The number of requests
- Total request bytes
- Total response bytes
- Number of failed requests
- Maximum number of concurrent requests
Delete Expired MDM Bulk Enroll Package Records : Use this task to delete old Bulk Enrollment certificates and corresponding profiles after the enrollment certificate has expired.
Delete Inactive Client Discovery Data : Use this task to delete discovery data for inactive clients from the database. Clients are marked as inactive when the client is flagged as obsolete and by configurations that are made for client status.
This task operates only on resources that are Configuration Manager clients. It’s different than the Delete Aged Discovery Data task, which deletes any aged discovery data record. When this task runs at a site, it removes the data from the database at all sites in a hierarchy.
When it’s enabled, configure this task to run at an interval greater than the Heartbeat Discovery schedule. This enables active clients to send a Heartbeat Discovery record to mark their client record as active so this task doesn’t delete them.
Delete Obsolete Alerts : Use this task to delete expired alerts that have been stored longer than a specified time from the database.
Delete Obsolete Client Discovery Data : Use this task to delete obsolete client records from the database. A record that is marked as obsolete has usually been replaced by a newer record for the same client. The newer record becomes the client’s current record.
Delete Obsolete Forest Discovery Sites and Subnets : Use this task to delete data about Active Directory sites, subnets, and domains that haven’t been discovered by the Active Directory Forest Discovery method in the last 30 days. This removes the discovery data, but doesn’t affect boundaries that are created from this discovery data
Delete Orphaned Client Deployment State Records : Use this task to periodically purge the table that contains client deployment state information. This task will clean up records associated with obsolete or decommissioned devices.
Delete Unused Application Revisions : Use this task to delete application revisions that are no longer referenced.
Evaluate Collection Members : You configure the Collection Membership Evaluation as a site component.
Monitor Keys : Use this task to monitor the integrity of the Configuration Manager database primary keys. A primary key is a column (or a combination of columns) that uniquely identifies one row and distinguishes it from any other row in a Microsoft SQL Server database table.
Rebuild Indexes : Use this task to rebuild the Configuration Manager database indexes. An index is a database structure that is created on a database table to speed up data retrieval. For example, searching an indexed column is often much faster than searching a column that isn’t indexed.
Summarize Installed Software Data : Use this task to summarize the data for installed software from multiple records into one general record. Data summarization can compress the amount of data that is stored in the Configuration Manager database.
Summarize Software Metering File Usage Data : Use this task to summarize the data from multiple records for software metering file usage into one general record. Data summarization can compress the amount of data that is stored in the Configuration Manager database.
Summarize Software Metering Monthly Usage Data : Use this task to summarize the data from multiple records for software metering monthly usage into one general record. Data summarization can compress the amount of data that is stored in the Configuration Manager database.
Update Application Available Targeting : Use this task to have Configuration Manager recalculate the mapping of policy and application deployments to resources in collections. When you deploy policy or applications to a collection, Configuration Manager creates an initial mapping between the objects that you deploy and the collection members.
These mappings are stored in a table for quick reference. When a collections membership changes, these stored mappings are updated to reflect those changes. However, it’s possible for these mappings to fall out of sync. For example, if the site fails to properly process a notification file, that change might not be reflected in a change to the mappings. This task refreshes that mapping based on current collection membership.
Update Application Catalog Tables : Use this task to synchronize the Application Catalog website database cache with the latest application information. When you change the configuration of this maintenance task, the configuration applies to all primary sites in the hierarchy.
Part 23 – Backup your Server after SCCM Installation
In the last part of this SCCM Installation Guide, we will setup automation backup for Configuration Manager sites by scheduling the predefined Backup Site Server maintenance task. This task has the following features:
- Runs on a schedule
- Backs up the site database
- Backs up specific registry keys
- Backs up specific folders and files
- Backs up the CD.Latest folder
Plan to run the default site backup task at a minimum of every five days. This schedule is because Configuration Manager uses a SQL Server change tracking retention period of five days.
To simplify the backup process, you can create an AfterBackup.bat file. This script automatically runs post-backup actions after the backup task completes successfully. Use the AfterBackup.bat file to archive the backup snapshot to a secure location. You can also use the AfterBackup.bat file to copy files to your backup folder, or to start other backup tasks.
Site backup status information is written to the Smsbkup.log file. This file is created in the destination folder that you specify in the properties of the Backup Site Server maintenance task.
- Go to the Administration workspace, expand Site Configuration
- Click Site Maintenance Tasks in the ribbon.
- Select the Backup Site Server task, and click Edit .
- Select the option to Enable this task . Click Set Paths to specify the backup destination. You have the following options:
- Local drive on site server for site data and database : Specifies that the task stores the backup files for the site and site database in the specified path on the local disk drive of the site server. Create the local folder before the backup task runs. The Local System account on the site server must have Write NTFS file permissions to the local folder for the site server backup. The Local System account on the computer that’s running SQL Server must have Write NTFS permissions to the folder for the site database backup.
- Network path (UNC name) for site data and database : Specifies that the task stores the backup files for the site and site database in the specified network path. Create the share before the backup task runs. The computer account of the site server must have Write NTFS and share permissions to the shared network folder. If SQL Server is installed on another computer, the computer account of the SQL Server must have the same permissions.
- Local drives on site server and SQL Server : Specifies that the task stores the backup files for the site in the specified path on the local drive of the site server. The task stores the backup files for the site database in the specified path on the local drive of the site database server. Create the local folders before the backup task runs. The computer account of the site server must have Write NTFS permissions to the folder that you create on the site server. The computer account of the SQL Server must have Write NTFS permissions to the folder that you create on the site database server. This option is available only when the site database isn’t installed on the site server.
- Go to the Component Status node of the Monitoring workspace. Review the status messages for SMS_SITE_BACKUP . When site backup completes successfully, you see message ID 5035 . This message indicates that the site backup completed without any errors.
- When you configure the backup task to create an alert when it fails, look for backup failure alerts in the Alerts node of the Monitoring workspace.
- Open Windows Explorer on the site server and browse to <ConfigMgrInstallationFolder>\Logs . Review Smsbkup.log for warnings and errors. When site backup completes successfully, the log shows Backup completed with message ID STATMSG: ID=5035 .
It’s also possible to backup your SCCM server using SQL Maintenance task. The biggest advantage of this method is that it offers compression. Please read this blog post if you prefer this method. Be aware that this backup method doesn’t backup the CD.Latest folder which is important. You could also have both backup methods enabled if needed.
System Center Dudes offers numerous configurations guides and custom reports to ease your Configuration Manager day-to-day operations.
Consult our product page to see the complete list.
That conclude this SCCM Installation Guide, we hope that it was hepful. Feel free to leave your comment in the section below.
Only authorized users can leave comments
haverland389
Jonathan Lefebvre
Daniel Schindler
Two days ago, Microsoft had an outage affecting Intune AutoPilot Pre-Provisionning. Users...
SCCM can be used to deploy packages and applications on multiple computers. But as with any other...
Microsoft has released the first SCCM version for 2024 as the release cadence is now reduced to 2...
Please fill out the form, and one of our representatives will contact you in Less Than 24 Hours . We are open from Monday to Friday .
Consulting Services
Reports and Guides
I'm interested in working with you
Consulting services and time banks are used for generic requests. All others are fixed-price plans.
Thank you for your request. You will receive an email with more details. Take note that we normally work from Monday to Friday. We will get in touch with you as soon as possible.
Thank for your reply!
Something went wrong!
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Configure a report server database connection (Report Server Configuration Manager)
- 10 contributors
For content related to previous versions of SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS), see SQL Server 2014 Reporting Services .
Each report server instance requires a connection to the report server database that stores reports, shared data sources, resources, and metadata managed by the server. The initial connection can be created during a report server installation if you're installing the default configuration. In most cases, you use the Reporting Services Configuration tool to configure the connection after Setup is complete. You can modify the connection at any time to change the account type or reset credentials. For step-by-step instructions on how to create the database and configure the connection, see Create a Native mode report server database (Report Server Configuration Manager) .
You must configure a report server database connection in the following circumstances:
Configuring a report server for first use.
Configuring a report server to use a different report server database.
Changing the user account or password that is used for the database connection. You only need to update the database connection when the account information is stored in the RSReportServer.config file. If you're using the service account for the connection, which uses Windows integrated security as the credential type, the password isn't stored. This feature eliminates the need to update the connection information. For more information about changing accounts, see Configure the Report Server service account (Report Server Configuration Manager) .
Configuring a report server scale-out deployment. Configuring a scale-out deployment requires that you create multiple connections to a report server database. For more information about how to perform this multi-step operation, see Configure a Native mode report server scale-out deployment (Report Server Configuration Manager) .
How Reporting Services connects to the database engine
Report server access to a report server database depends on credentials and connection information. It also depends on encryption keys that are valid for the report server instance that uses that database. Having valid encryption keys is necessary for storing and retrieving sensitive data. Encryption keys are created automatically when you configure the database for the first time. After the keys are created, you must update them if you change the Report Server service identity. For more information about working with encryption keys, see Configure and manage encryption keys (Report Server Configuration Manager) .
The report server database is an internal component, accessed only by the report server. The credentials and connection information you specify for the report server database are used exclusively by the report server. Users who request reports don't require databases permissions or a database sign-in for the report server database.
Reporting Services uses System.Data.SqlClient to connect to the Database Engine that hosts the report server database. If you're using a local instance of the Database Engine, the report server establishes the connection using shared memory. If you're using a remote database server for the report server database, you might have to enable remote connections depending on the edition you're using. If you're using the Enterprise edition, remote connections are enabled for TCP/IP by default.
To verify that the instance accepts remote connections, select Start , choose All Programs , select Microsoft SQL Server , choose Configuration Tools , select SQL Server Configuration Manager , and then verify that the TCP/IP protocol is enabled for each service.
When you enable remote connections, the client and server protocols are also enabled. To verify the protocols are enabled, select Start , choose All Programs , select Microsoft SQL Server , choose Configuration Tools , select SQL Server Configuration Manager , choose SQL Server Network Configuration , and then select Protocols for MSSQLSERVER . For more information, see Enable or disable a server network protocol in SQL Server.
Define a report server database connection
To configure the connection, you must use the Reporting Services Configuration Manager tool or the rsconfig command line utility. A report server requires the following connection information:
Name of the Database Engine instance hosting the report server database.
Name of the report server database. When creating a connection for the first time, you can create a new report server database or select an existing database. For more information, see Create a report server database;Report Server Configuration Manager) .
Credential type. You can use the service accounts, a Windows domain account, or a SQL Server database sign-in.
User name and password (required only if you're using Windows domain account or a SQL Server sign-in).
The credentials that you provide must be granted access to the report server database. If you use the Reporting Services Configuration tool, this step is performed automatically. For more information about the permissions required to access the database, see the "Database Permissions" section in this article.
Store database connection information
Reporting Services stores and encrypts the connection information in the following RSreportserver.config settings. You must use the Reporting Services Configuration tool or rsconfig utility to create encrypted values for these settings.
Not all of the values are set for every type of connection. If you configure the connection using the default values (that is, using the service accounts to make the connection), < LogonUser >, < LogonDomain >, and < LogonCred > are empty, as follows:
If you configure the connection to use a specific Windows account or database sign-in, you must remember to update the stored values if you then change the account or sign in.
Choose a credential type
There are three types of credentials that can be used in a connection to a report server database:
Windows integrated security using the Report Server service account. Because the report server is implemented as a single service, only the account under which the service runs requires database access.
A Windows user account. If the report server and the report server database are installed on the same computer, you can use a local account. Otherwise, you must use a domain account.
A SQL Server sign-in.
A custom authentication extension cannot be used to connect to a report server database. Custom authentication extensions are used only to authenticate a principal to a report server. They do not affect connections to the report server database or to external data sources that provide content to reports.
If the instance of the Database Engine is configured for Windows Authentication and is in the same domain or a trusted domain with the report server computer, you can configure the connection to use the service account or a domain user account that you manage as a connection property through the Reporting Services Configuration tool. If the database server is in a different domain or if you're using workgroup security, you must configure the connection to use a SQL Server database sign-in. In this case, be sure to encrypt the connection.
When using Azure SQL Managed Instance to host report server databases, SQL Server authentication is the only supported credential type. In addition, please note that Managed Instance cannot host report server instance.
Use service accounts and integrated security
You can use Windows integrated security to connect through the Report Server service account. The account is granted sign-in rights to the report server database. This credential type is the default chosen by Setup if you install Reporting Services in the default configuration.
The service account is a trusted account that provides a low-maintenance approach to managing a report server database connection. Because the service account uses Windows integrated security to make the connection, the credentials don't have to be stored. However, if you then change the service account password or identity (for example, switching from a built-in account to a domain account), be sure to use the Reporting Services Configuration tool to make the change. The tool automatically updates the database permissions to use the revised account information. For more information, see Configure the Report Server service account (Report Server Configuration Manager) .
If you configure the database connection to use the service account, the account must have network permissions if the report server database is on a remote computer. Don't use the service account if the report server database is on a different domain, behind a firewall, or if you're using workgroup security instead of domain security. Use a SQL Server database user account instead.
Use a domain user account
You can specify a Windows user account for the report server connection to the report server database. If you use a local or domain account, you must update the report server database connection every time you change the password or the account. Always use the Reporting Services Configuration tool to update the connection.
Use a SQL Server sign-in
You can specify a single SQL Server sign-in to connect to the report server database. If you use SQL Server authentication and the report server database is on a remote computer, use IPSec to help secure the transmission of data between the servers. If you use a database sign-in, you must update the report server database connection every time you change the password or the account.
Database permissions
Accounts used to connect to the report server database are granted the following roles:
public and RSExecRole roles for the ReportServer database.
RSExecRole role for the master , msdb , and ReportServerTempDB databases.
When you use the Reporting Services Configuration tool to create or modify the connection, these permissions are granted automatically. If you use the rsconfig utility, and you're specifying a different account for the connection, you must update the SQL Server sign-in for that new account. You can create script files in the Reporting Services Configuration tool that update the SQL Server sign-in for the report server.
Verify the database name
Use the Reporting Services Configuration tool to determine which report server database is used by a particular report server instance. To find the name, connect to the report server instance and open the Database Setup page.
Use a different report server database or move a report server database
You can configure a report server instance to use a different report server database by changing the connection information. A common case for switching databases is when you deploy a production report server. Switching from a test report server database to a production report server database is typically how production servers are rolled out. You can also move a report server database to another computer. For more information, see Upgrade and migrate Reporting Services in SQL Server.
Configure multiple report servers to use the same report server database
You can configure multiple report servers to use the same report server database. This deployment configuration is called a scale-out deployment. This configuration is a prerequisite if you want to run multiple report servers in a server cluster. However, you can also use this configuration if you want to segment service applications. And you can use it to test the installation and settings of a new report server instance to compare it with an existing report server installation. For more information, see Configure a Native mode report server scale-out deployment (Report Server Configuration Manager) .
Related content
- Create a report server database
- Manage a Reporting Services Native mode report server
- Configure the report server service account
More questions? Try asking the Reporting Services forum .
Was this page helpful?
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to use the Reporting Services Configuration Manager to configure a Native Mode report server installation. Find out the scenarios, requirements, and steps to start the tool and connect to a local or remote report server instance.
Learn how to use the Report Server Configuration Manager tool to set up and manage your report server. Find articles about how to configure URLs, service account, database connection, email delivery, and more.
Learn how to customize and configure SQL Server Reporting Service parameters and settings using Report Server Configuration Manager tool. Find out how to change web service URL, database connection, e-mail settings, encryption keys, subscription settings and more.
Learn how to install and configure SQL Server Reporting Services and the reporting services point in your Configuration Manager hierarchy. Follow the step-by-step instructions and screenshots to set up reporting for your site database and reports.
Follow the below steps to install a new reporting services point role using SCCM console: Launch the SCCM console. Click Administration > Site Configuration. Right click Servers and Site System Roles. Right-click SQL Server on which you plan to install reporting services point role and select Add Site System Roles.
Learn how to install and configure SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) 2019 on Windows Server 2019. Follow the step-by-step guide with screenshots and tips for creating databases, web services, email settings and more.
Learn how to install and configure SSRS 2017, a reporting solution for SQL Server, using the Configuration Manager. Follow the steps to set up service account, report manager, databases, SMTP, execution account, encryption keys, Power BI integration and more.
Learn how to set up SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) in Native mode, a standalone application server for reports and report models. Follow the step-by-step instructions to create a self-signed certificate, configure SSL bindings, and manage roles and items.
Open Report Server Configuration Manager from the Start menu. Step 2. Next, you will see the configuration wizard. First, you need to connect an SQL server instance for which you want to configure SSRS. ... Step 6. You will see Report Server Database Configuration Wizard. We are going to create a new database but if you have already an existing ...
Setup SSRS SQL Server Reporting Services Configuration Manager. If you are using Windows 7, then go to All Programs, or If you are using Windows 8 or a later version, then go to installed applications. Next, click on the SSRS SQL Server Reporting Services Configuration Manager. Once click on it, It will open the SSRS Reporting Services ...
Click the Change Database button. This will launch the Report Server Database Configuration Wizard. From the wizard's initial screen, select the option to create a new Report Server database and ...
Open Report Server Configuration Manager from the Start menu. Step 2. Next, you will see the configuration wizard. First, you need to connect an SQL server instance for which you want to configure SSRS. ... Step 6. You will see Report Server Database Configuration Wizard. We are going to create a new database but if you have already an existing ...
Click on Service Account in the Report Server Configuration Manager. Select the 'Use another account' radio button. Enter the domain account information and password. Click Apply. ... How to install SQL Server 2022 step by step. An Introduction to SQL Triggers. Using MERGE in SQL Server to insert, update and delete at the same time ...
Learn how to install and configure Reporting Services on Windows Server. Follow the steps to download, install, and set up the report server, database, service, and URL reservations.
Steps to Setup Report Server Configuration Manager. Click on Connect and insert a Server Name and Select Report Server Instance as shown below, then click on Connect. Then, click on Service Account. Now you have to sign up for a Report Server Service Account. Here, you have two options, use a built-in account, or use another account.
In "Report Server Configuration Manager" , switch to the "Databases" tab. You will see there where your current report server databases are located: Using SSMS, connect to the SQL Server Instance and you will see the report server databases: Step 3: Take a backup of your report server databases directly to Azure
Double click on the downloaded file " PBIDesktopRS_x64.msi " to install the Power BI Desktop. Accept the terms, then click Next. Specify the installation folder, click "Next". Check create a desktop shortcut, then Click on "Install". Wait for a moment till the Power BI Desktop is installed.
The Report Server Status should be shown with the current report server status and basic information about report server. Go to Service Account section to check the service account that has been set during the installation, you can also change the current service account through this section based on your requirement.
As you learned in Chapter 2, you use the Reporting Services Configuration Manager to set the values required to run the report server.In that chapter, you configured the service account, the virtual directories and URLs for the Web service and Report Manager (if you're running Reporting Services in native mode), database connection information, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server ...
SCOM Step by step deployment guide: 1. Install the Management Server role on OMMS1. Log on using your personal domain user account that is a member of the OMAdmins group, and has "sysadmin" role level rights over the SQL instance. Run Setup.exe. Click Install.
Next Steps: Configure and administer a report server (SSRS Native Mode) and Report Server Configuration Manager (native mode). Web portal (native mode) Use Web portal (SSRS native mode) to set permissions, manage subscriptions and schedules, and work with reports.
Learn how to install and configure SCCM (Microsoft Endpoint Manager) from scratch. This guide covers hardware requirements, SQL Server, site roles, prerequisites, and more.
For step-by-step instructions on how to create the database and configure the connection, see Create a Native mode report server database (Report Server Configuration Manager). You must configure a report server database connection in the following circumstances: Configuring a report server for first use.
Let's have a quick look at the step-by-step guide to create a new database for SSRS reporting service. This activity could help to troubleshoot some of the SSRS issues.The SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) provides a set of on-premises tools and services that create, deploy, and manage mobile and paginated reports.