

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving

Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.

StrategyPunk
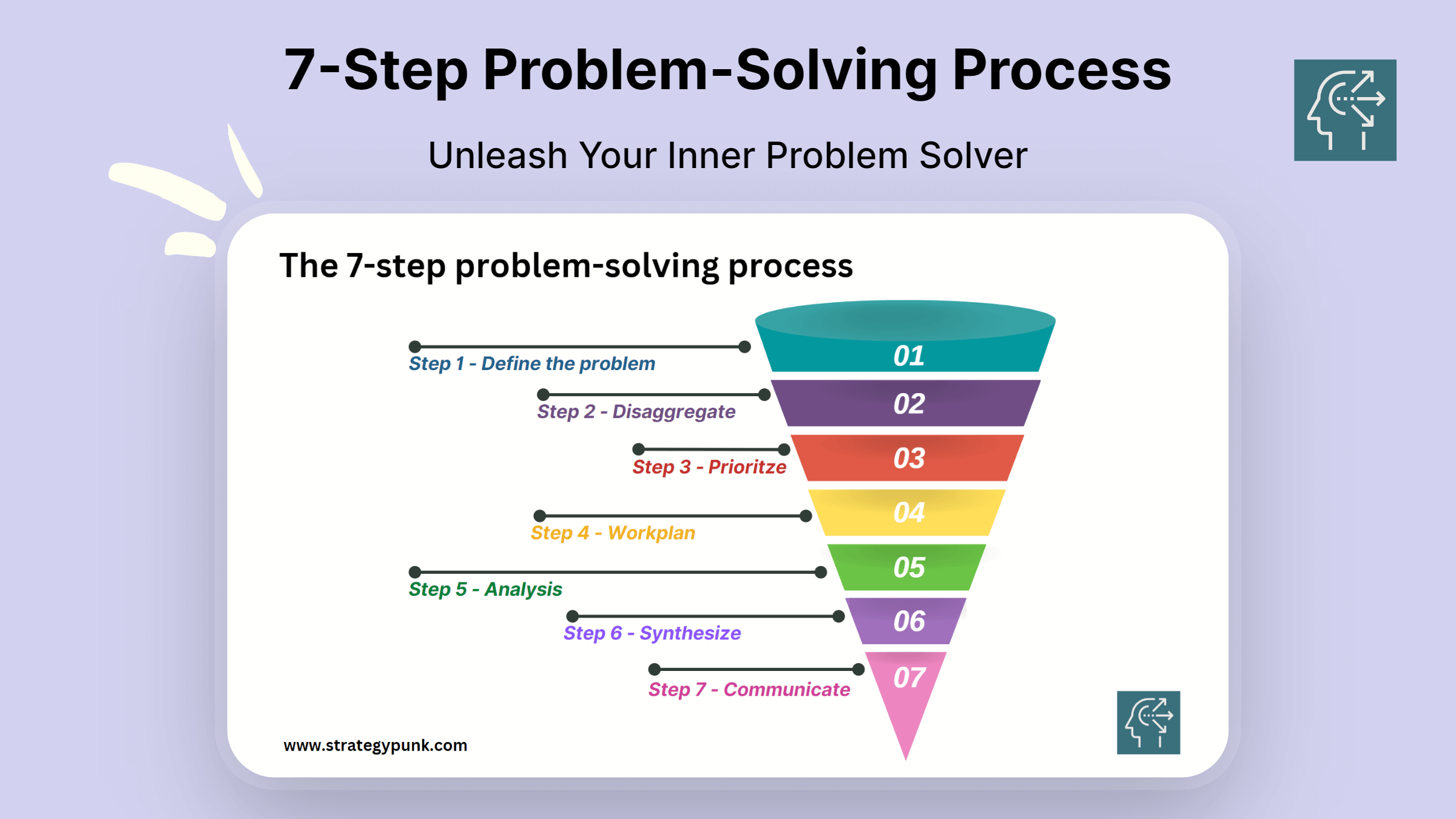
Introduction
Mastering the art of problem-solving is crucial for making better decisions. Whether you're a student, a business owner, or an employee, problem-solving skills can help you tackle complex issues and find practical solutions. The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a proven method that can help you approach problems systematically and efficiently.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
By following this process, you can avoid jumping to conclusions, overlooking important details, or making hasty decisions. Instead, you can approach problems with a clear and structured mindset, which can help you make better decisions and achieve better outcomes.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. At the end of the blog post, you can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates .
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable.
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Another critical aspect of defining the problem is identifying the stakeholders. Who is affected by it? Who has a stake in finding a solution? Identifying the stakeholders can help ensure that the problem is defined in a way that considers the needs and concerns of all those affected.
Once the problem is defined, it is essential to communicate the definition to all stakeholders. This helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that there is a shared understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation can be achieved by breaking down the problem into sub-problems, identifying the contributing factors, and analyzing the relationships between these factors. This step helps identify the most critical factors that must be addressed to solve the problem.
A tree or fishbone diagram is one effective way to disaggregate a problem. These diagrams help identify the different factors contributing to the problem and how they are related. Another way is to use a table to list the other factors contributing to the situation and their corresponding impact on the issue.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
After defining the problem and disaggregating it into smaller parts, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is prioritizing the issues that need addressing. Prioritizing helps to focus on the most pressing issues and allocate resources more effectively.
There are several ways to prioritize issues, including:
- Urgency: Prioritize issues based on their urgency. Problems that require immediate attention should be addressed first.
- Impact: Prioritize issues based on their impact on the organization or stakeholders. Problems with a high impact should be given priority.
- Resources: Prioritize issues based on the resources required to address them. Problems that require fewer resources should be dealt with first.
It is important to involve stakeholders in the prioritization process, considering their concerns and needs. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of engagement.
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Prioritizing issues is a critical step in problem-solving. By focusing on the most pressing problems, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and make better decisions.
Step 4: Workplan
After defining the problem, disaggregating, and prioritizing the issues, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to develop a work plan. This step involves creating a roadmap that outlines the steps needed to solve the problem.
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Creating a work plan can help keep the team on track and ensure everyone is working towards the same goal. It can also help to identify potential roadblocks or challenges that may arise during the problem-solving process and develop contingency plans to address them.
Several tools and techniques can be used to develop a work plan, including Gantt charts, flowcharts, and mind maps. These tools can help to visualize the steps needed to solve the problem and identify dependencies between tasks.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Once the problem has been defined and disaggregated, the next step is to analyze the information gathered. This step involves examining the data, identifying patterns, and determining the root cause of the problem.
Several methods can be used during the analysis phase, including:
- Root cause analysis
- Pareto analysis
- SWOT analysis
Root cause analysis is a popular method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem. This method involves asking a series of "why" questions to get to the root cause of the issue.
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Finally, SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for analyzing the internal and external factors that may impact the problem. This method involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the issue.
Overall, the analysis phase is critical for identifying the root cause of the problem and developing practical solutions. By using a combination of methods, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the issue and make informed decisions.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
One way to synthesize the information is to use a decision matrix. This involves creating a table that lists the potential solutions and the essential criteria for making a decision. Each answer is then rated against each standard, and the scores are tallied to arrive at a final decision.
Another approach to synthesizing the information is to use a mind map. This involves creating a visual representation of the problem and the potential solutions. The mind map can identify the relationships between the different pieces of information and help prioritize the solutions.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure everyone's perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Communicate
After synthesizing the information, the next step is communicating the findings to the relevant stakeholders. This is a crucial step because it helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the decision-making process is transparent.
One effective way to communicate the findings is through a well-organized report. The report should include the problem statement, the analysis, the synthesis, and the recommended solution. It should be clear, concise, and easy to understand.
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
During the presentation, it is essential to be open to feedback and questions from the audience. This helps ensure everyone agrees with the recommended solution and addresses concerns or objections.
Effective communication is vital to ensuring the decision-making process is successful. Stakeholders can make informed decisions and work towards a common goal by communicating the findings clearly and concisely.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
Through disaggregation, individuals can break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. By prioritizing potential solutions, individuals can focus their efforts on the most impactful actions. The work step allows individuals to develop a clear action plan, while the analysis step provides a framework for evaluating possible solutions.
The synthesis step combines all the information gathered to develop a comprehensive solution. Finally, the communication step allows individuals to share their answers with others and gather feedback.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
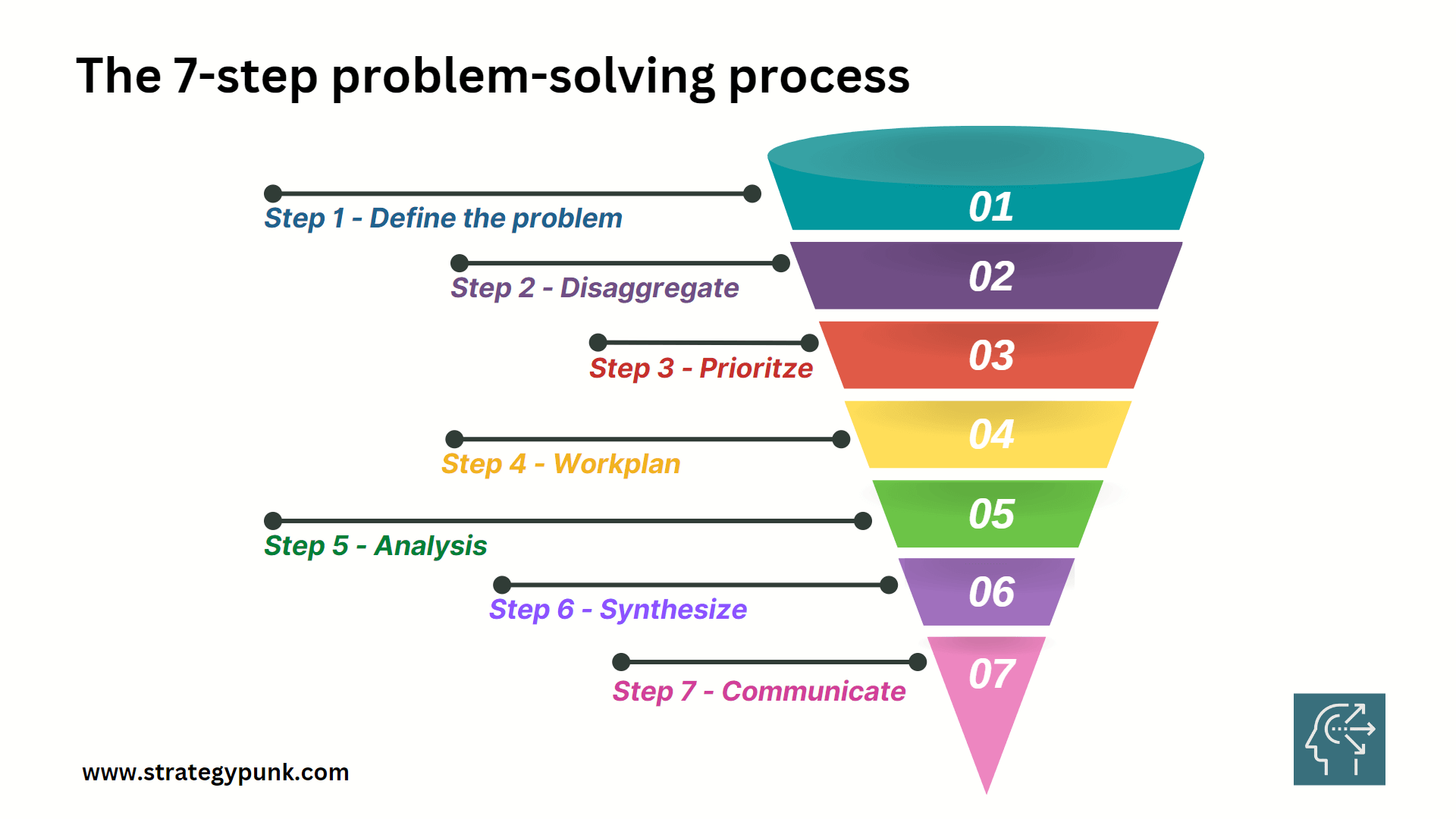
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts, prioritizing the issues, creating a work plan, analyzing the data, synthesizing the information, and communicating the findings.
By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, break it down into manageable components, and prioritize the most impactful actions. The work plan, analysis, and synthesis steps provide a framework for developing comprehensive solutions, while the communication step ensures transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.

7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template.

Lidl SWOT Analysis: Free PPT Template and In-Depth Insights
Discover Lidl's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with our free PowerPoint template. This in-depth SWOT analysis provides valuable insights to help you understand Lidl's market position and strategic direction.

Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Download our free PPT template for in-depth PESTLE insights into Nestlé's global strategy. Learn more today!

PESTLE Analysis: Decoding Reddit's Landscape (Free PPT)
Decode Reddit's global influence with our free PowerPoint PESTLE Analysis. Explore the hub of vibrant discussions and ideas.

Navigating the Terrain: A PESTLE Analysis of Lululemon (Free PowerPoint)
Explore Lululemon's business terrain with our free PESTLE analysis PowerPoint. Instant access!

7 Steps to an Effective Problem-Solving Process
September 1, 2016 | Leadership Articles

An effective problem-solving process is one of the key attributes that separate great leaders from average ones.
Being a successful leader doesn’t mean that you don’t have any problems. Rather, it means that you know how to solve problems effectively as they arise. If you never had to deal with any problems, chances are pretty high that your company doesn’t really need you. They could hire an entry-level person to do your job!
Unfortunately, there are many examples of leaders out there who have been promoted to management or leadership positions because they are competent and excel in the technical skills needed to do the work. These people find themselves suddenly needing to “think on their feet” and solve problems that are far more high-level and complicated than they’ve ever really had to deal with before. Are there tools available to these people to help them solve the problem correctly and effectively? Absolutely!
Today, I am going to introduce you to the Seven Steps of Effective Problem Solving that Bullet Proof® Managers are learning about, developing, and implementing in their teams.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
What are things like when they are the way we want them to be?
This question helps you find the standard against which we’re going to measure where we are now. If things were going the way we want them to go, what does that look like? If this person were doing the job we want him or her to do, what would they be doing?
And then ask this important question: How much variation from the norm is tolerable?
Therein lies the problem. From an engineering perspective, you might have very little tolerance. From a behavioral perspective, you might have more tolerance. You might say it’s okay with me when this person doesn’t do it exactly as I say because I’m okay with them taking some liberty with this. Some other issue you may need 100% compliance.
Step 2: Analyze the Problem
At what stage is this problem? This helps you identify the urgency of the problem, and there are generally three stages.
The emergent stage is where the problem is just beginning to happen. It does not cause an immediate threat to the way business operates every day. It is just beginning to happen and you have time on your side to be able to correct it without it causing much damage to the processes it is affecting. The mature stage is where this problem is causing more than just minor damage. Some amount of damage has been done, and you need to jump on it immediately to fix it before it becomes a problem where the consequences may be greater, deeper, and more expensive if we don’t solve this problem fast.
The third stage is the crisis stage, when the problem is so serious it must be corrected immediately. At this stage, real damage has been done to company processes, reputation, finances, etc. that will have potentially long-term effects on your ability to do business.
Step 3: Describe the Problem
You should be able to describe a problem by writing it in the form of a statement and you should do it in 12 words or less, assuming it’s not a complicated, scientific problem. This way, you have clarity exactly what the issue is. Then, perhaps try distributing it to your team to ensure they agree that this is the root of the problem, that it makes sense, and everyone that is working toward a solution is working toward the same goal.
The most important question of all, when describing your problem: Is your premise correct?
Let me give you an example of what I mean. We’ve all heard – or read – the story of the engineer’s take on the old “half empty, half full” question. A speaker holds up the glass of water and asks if the glass is half empty or half full, a discussion within the group ensues, and you generally expect some sort of lesson in optimism, etc. from it. In this version, an engineer is in the room and answers, “I see this glass of water as being twice the size it needs to be.”
You see, sometimes when you are the one in charge of the problem, you tend to set the premise of the problem from your own perspective. But, that premise may not be accurate, or it may just need an alternate perspective from which to see it. If your premise is not correct, or at least incomplete, you are not fully understanding the problem and considering all the best options for a solution.
Step 4: Look for Root Causes
This step involves asking and answering a lot of questions. Ask questions like: What caused this problem? Who is responsible for this problem? When did this problem first emerge? Why did this happen? How did this variance from the standard come to be? Where does it hurt us the most? How do we go about resolving this problem?
Also, ask the most important question: Can we solve this problem for good so it will never occur again? Because an important aspect to leadership is coming up with solutions that people can use for a long-term benefit, rather than having to deal with the same problems over and over and over.
Step 5: Develop Alternate Solutions
Just about any problem you have to deal with has more solutions to it than the one that you think of first. So, it is best to develop a list of alternate solutions that you and your team can assess and decide which one will be the best for the particular problem. I often use the ⅓ + 1 Rule to create consensus around one – or the top two or three solutions – that will be best for everyone involved.
Then rank those solutions based on efficiency, cost, long-term value, what resources you have and that you can commit to the solution of the problem. Then, look at every one of those solutions carefully and decide what you believe to be the best solution to this problem at this time.
Step 6: Implement the Solution
Implementing the solution you decide on can include creating an implementation plan. It could also include planning on what happens next if something goes wrong with the solution if it doesn’t work out the way you thought it would. Implementation means that everyone on your team knows and understands their part in making the solution work, that there are timelines for execution, and also that you have a system in place to track whether or not the solution has corrected the problem.
Step 7: Measure the Results
From your implementation plan in step 6, make sure you track and measure the results so you can answer questions such as: Did it work? Was this a good solution? Did we learn something here in the implementation that we could apply to other potential problems?
These seven simple steps will help you become a more effective, efficient problem solver in your organization. As you practice this process and develop the skills, these steps will become more natural to you until the point that you are using them without noticing!
About Crestcom International, LLC.
Crestcom International, LLC is an international leadership development organization, training more than one million leaders for 25,000 businesses in over 60 countries across the globe. Crestcom achieves this through a blend of live-facilitated multimedia video, interactive exercises, and shared learning experiences. Crestcom implements action plans and coaching accountability sessions to ensure measured development in key leadership competency areas. For more information, please contact your local Crestcom representative found here .
Interested in a free Leadership Skills Workshop with your team?
- Address instantly fixable issues that impact customer perceptions and employee morale.
- Learn and practice a habit that will raise employee performance.
- Set actions with specific and measurable steps that they'll gladly be accountable to achieve.
- Case Studies
- Leadership Articles
- Multi-Generational Leadership
- Owning a franchise
- Press Releases
Latest Posts

Stay Updated
Browse by topic.
[st-tag-cloud]
Privacy Overview

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

7 Steps To Problem-Solving
The 7 steps to problem-solving is a disciplined and methodical approach to identifying and then addressing the root cause of problems. Instead, a more robust approach involves working through a problem using the hypothesis-driven framework of the scientific method. Each viable hypothesis is tested using a range of specific diagnostics and then recommendations are made.
Table of Contents
Understanding the 7 steps to problem-solving
The core argument of this approach is that the most obvious solutions to a problem are often not the best solutions.
Good problem-solving in business is a skill that must be learned. Businesses that are adept at problem-solving take responsibility for their own decisions and have courage and confidence in their convictions. Ultimately, this removes doubt which can impede the growth of businesses and indeed employees alike.
Moving through the 7 steps to problem-solving
Although many versions of the 7-step approach exist, the McKinsey approach is the most widely used in business settings. Here is how decision makers can move through each of the steps systematically.
Step 1 – Define the problem
First, the scope and extent of the problem must be identified. Actions and behaviors of individuals must be the focus – instead of a focus on the individuals themselves. Whatever the case, the problem must be clearly defined and be universally accepted by all relevant parties.
Step 2 – Disaggregate the problem
In the second step, break down the problem (challenge) into smaller parts using logic trees and develop an early hypothesis. Here, economic and scientific principles can be useful in brainstorming potential solutions. Avoid cognitive biases, such as deciding that a previous solution should be used again because it worked last time.
Step 3 – Prioritize issues
Which constituent parts could be key driving factors of the problem? Prioritize each according to those which have the biggest impact on the problem. Eliminate parts that have negligible impact. This step helps businesses use their resources wisely.

Step 4 – Plan the analyses
Before testing each hypothesis, develop a work and process plan for each. Staff should be assigned to analytical tasks with unique output and completion dates. Hypothesis testing should also be reviewed at regular intervals to measure viability and adjust strategies accordingly.
Step 5 – Conduct the analyses
In step five, gather the critical data required to accept or reject each hypothesis. Data analysis methods will vary according to the nature of the project, but each business must understand the reasons for implementing specific methods. In question-based problem solving, the Five Whys or Fishbone method may be used. More complicated problems may require the use of statistical analysis . In any case, this is often the longest and most complex step of the process.
Step 6 – Synthesise the results
Once the results have been determined, they must be synthesized in such a way that they can be tested for validity and logic. In a business context, assess the implications of the findings for a business moving forward. Does it solve the problem?
Step 7 – Communicate
In the final step, the business must present the solutions in such a way that they link back to the original problem statement. When presenting to clients, this is vital. It shows that the business understands the problem and has a solution supported by facts or hard data. Above all, the data should be woven into a convincing story that ends with recommendations for future action.
Key takeaways
- 7 steps to problem-solving is a methodical approach to problem-solving based on the scientific method.
- Although a somewhat rigorous approach, the strategy can be learned by any business willing to devote the time and resources.
- Fundamentally, the 7 steps to problem-solving method involves formulating and then testing hypotheses. Through the process of elimination, a business can narrow its focus to the likely root cause of a problem.
Key Highlights
- Definition : The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is a structured methodology rooted in the scientific method. It emphasizes systematic hypothesis testing and data analysis to identify and address the root cause of problems, avoiding surface-level solutions.
- Problem-Solving Skill : Effective problem-solving is a learned skill that fosters responsible decision-making, boosts confidence, and supports business growth .
- Define the Problem : Clearly outline the problem’s scope and impact, focusing on actions and behaviors rather than individuals.
- Disaggregate the Problem : Break down the problem into smaller parts using logic trees and form early hypotheses. Avoid biases from past solutions.
- Prioritize Issues : Identify key driving factors of the problem and prioritize them by impact. Eliminate parts with minimal impact to allocate resources efficiently.
- Plan the Analyses : Develop work and process plans for hypothesis testing, assigning staff and setting completion dates. Regularly review and adjust strategies.
- Conduct the Analyses : Gather critical data to accept or reject hypotheses. Use methods like Five Whys, Fishbone diagrams, or statistical analysis .
- Synthesize the Results : Combine and analyze results to determine their validity and implications for the business . Assess if the problem is solved.
- Communicate : Present solutions that link back to the original problem statement, supported by facts. Create a compelling story ending with recommendations.
- The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is based on the scientific method.
- It requires a structured approach to formulating and testing hypotheses.
- Businesses willing to invest time and resources can learn and apply this method effectively.
Connected Decision-Making Frameworks
Cynefin Framework

SWOT Analysis

Personal SWOT Analysis

Pareto Analysis

Failure Mode And Effects Analysis

Blindspot Analysis

Comparable Company Analysis

Cost-Benefit Analysis

Agile Business Analysis

SOAR Analysis

STEEPLE Analysis

Pestel Analysis

DESTEP Analysis

Paired Comparison Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy , Marketing Strategy , Business Models , Tech Business Models , Jobs-To-Be Done , Design Thinking , Lean Startup Canvas , Value Chain , Value Proposition Canvas , Balanced Scorecard , Business Model Canvas , SWOT Analysis , Growth Hacking , Bundling , Unbundling , Bootstrapping , Venture Capital , Porter’s Five Forces , Porter’s Generic Strategies , Porter’s Five Forces , PESTEL Analysis , SWOT , Porter’s Diamond Model , Ansoff , Technology Adoption Curve , TOWS , SOAR , Balanced
Read Next: Mental Models , Biases , Bounded Rationality , Mandela Effect , Dunning-Kruger Effect , Lindy Effect , Crowding Out Effect , Bandwagon Effect , Decision-Making Matrix .
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Business Model Innovation
- Platform Business Models
- Network Effects In A Nutshell
- Digital Business Models
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
A guide to problem-solving techniques, steps, and skills

You might associate problem-solving with the math exercises that a seven-year-old would do at school. But problem-solving isn’t just about math — it’s a crucial skill that helps everyone make better decisions in everyday life or work.

Problem-solving involves finding effective solutions to address complex challenges, in any context they may arise.
Unfortunately, structured and systematic problem-solving methods aren’t commonly taught. Instead, when solving a problem, PMs tend to rely heavily on intuition. While for simple issues this might work well, solving a complex problem with a straightforward solution is often ineffective and can even create more problems.
In this article, you’ll learn a framework for approaching problem-solving, alongside how you can improve your problem-solving skills.
The 7 steps to problem-solving
When it comes to problem-solving there are seven key steps that you should follow: define the problem, disaggregate, prioritize problem branches, create an analysis plan, conduct analysis, synthesis, and communication.
1. Define the problem
Problem-solving begins with a clear understanding of the issue at hand. Without a well-defined problem statement, confusion and misunderstandings can hinder progress. It’s crucial to ensure that the problem statement is outcome-focused, specific, measurable whenever possible, and time-bound.
Additionally, aligning the problem definition with relevant stakeholders and decision-makers is essential to ensure efforts are directed towards addressing the actual problem rather than side issues.
2. Disaggregate
Complex issues often require deeper analysis. Instead of tackling the entire problem at once, the next step is to break it down into smaller, more manageable components.
Various types of logic trees (also known as issue trees or decision trees) can be used to break down the problem. At each stage where new branches are created, it’s important for them to be “MECE” – mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive. This process of breaking down continues until manageable components are identified, allowing for individual examination.
The decomposition of the problem demands looking at the problem from various perspectives. That is why collaboration within a team often yields more valuable results, as diverse viewpoints lead to a richer pool of ideas and solutions.
3. Prioritize problem branches
The next step involves prioritization. Not all branches of the problem tree have the same impact, so it’s important to understand the significance of each and focus attention on the most impactful areas. Prioritizing helps streamline efforts and minimize the time required to solve the problem.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
4. Create an analysis plan
For prioritized components, you may need to conduct in-depth analysis. Before proceeding, a work plan is created for data gathering and analysis. If work is conducted within a team, having a plan provides guidance on what needs to be achieved, who is responsible for which tasks, and the timelines involved.
5. Conduct analysis
Data gathering and analysis are central to the problem-solving process. It’s a good practice to set time limits for this phase to prevent excessive time spent on perfecting details. You can employ heuristics and rule-of-thumb reasoning to improve efficiency and direct efforts towards the most impactful work.
6. Synthesis
After each individual branch component has been researched, the problem isn’t solved yet. The next step is synthesizing the data logically to address the initial question. The synthesis process and the logical relationship between the individual branch results depend on the logic tree used.
7. Communication
The last step is communicating the story and the solution of the problem to the stakeholders and decision-makers. Clear effective communication is necessary to build trust in the solution and facilitates understanding among all parties involved. It ensures that stakeholders grasp the intricacies of the problem and the proposed solution, leading to informed decision-making.
Exploring problem-solving in various contexts
While problem-solving has traditionally been associated with fields like engineering and science, today it has become a fundamental skill for individuals across all professions. In fact, problem-solving consistently ranks as one of the top skills required by employers.
Problem-solving techniques can be applied in diverse contexts:
- Individuals — What career path should I choose? Where should I live? These are examples of simple and common personal challenges that require effective problem-solving skills
- Organizations — Businesses also face many decisions that are not trivial to answer. Should we expand into new markets this year? How can we enhance the quality of our product development? Will our office accommodate the upcoming year’s growth in terms of capacity?
- Societal issues — The biggest world challenges are also complex problems that can be addressed with the same technique. How can we minimize the impact of climate change? How do we fight cancer?
Despite the variation in domains and contexts, the fundamental approach to solving these questions remains the same. It starts with gaining a clear understanding of the problem, followed by decomposition, conducting analysis of the decomposed branches, and synthesizing it into a result that answers the initial problem.
Real-world examples of problem-solving
Let’s now explore some examples where we can apply the problem solving framework.
Problem: In the production of electronic devices, you observe an increasing number of defects. How can you reduce the error rate and improve the quality?
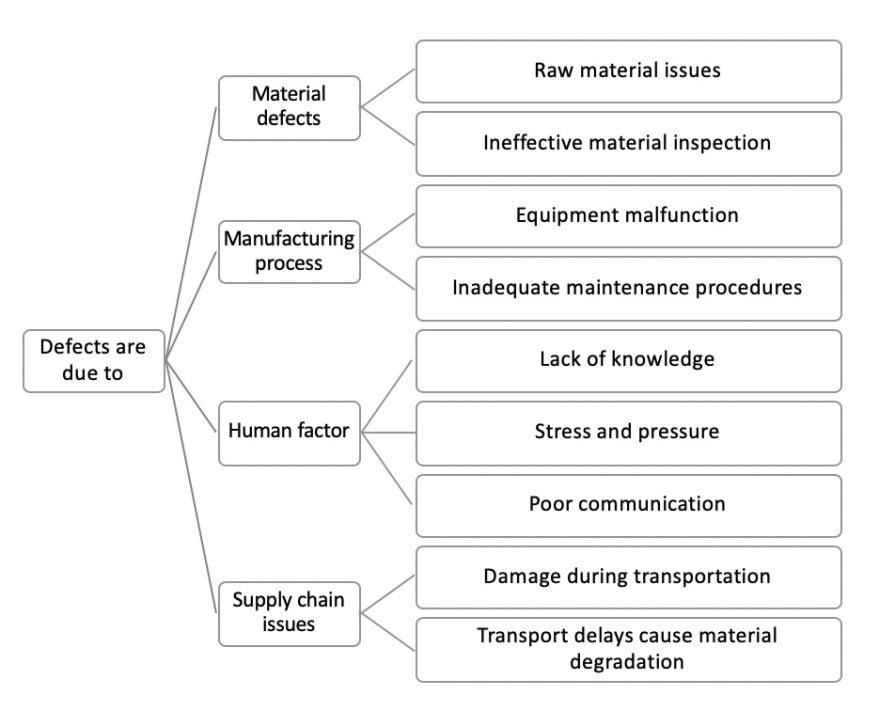
Before delving into analysis, you can deprioritize branches that you already have information for or ones you deem less important. For instance, while transportation delays may occur, the resulting material degradation is likely negligible. For other branches, additional research and data gathering may be necessary.
Once results are obtained, synthesis is crucial to address the core question: How can you decrease the defect rate?
While all factors listed may play a role, their significance varies. Your task is to prioritize effectively. Through data analysis, you may discover that altering the equipment would bring the most substantial positive outcome. However, executing a solution isn’t always straightforward. In prioritizing, you should consider both the potential impact and the level of effort needed for implementation.
By evaluating impact and effort, you can systematically prioritize areas for improvement, focusing on those with high impact and requiring minimal effort to address. This approach ensures efficient allocation of resources towards improvements that offer the greatest return on investment.
Problem : What should be my next job role?
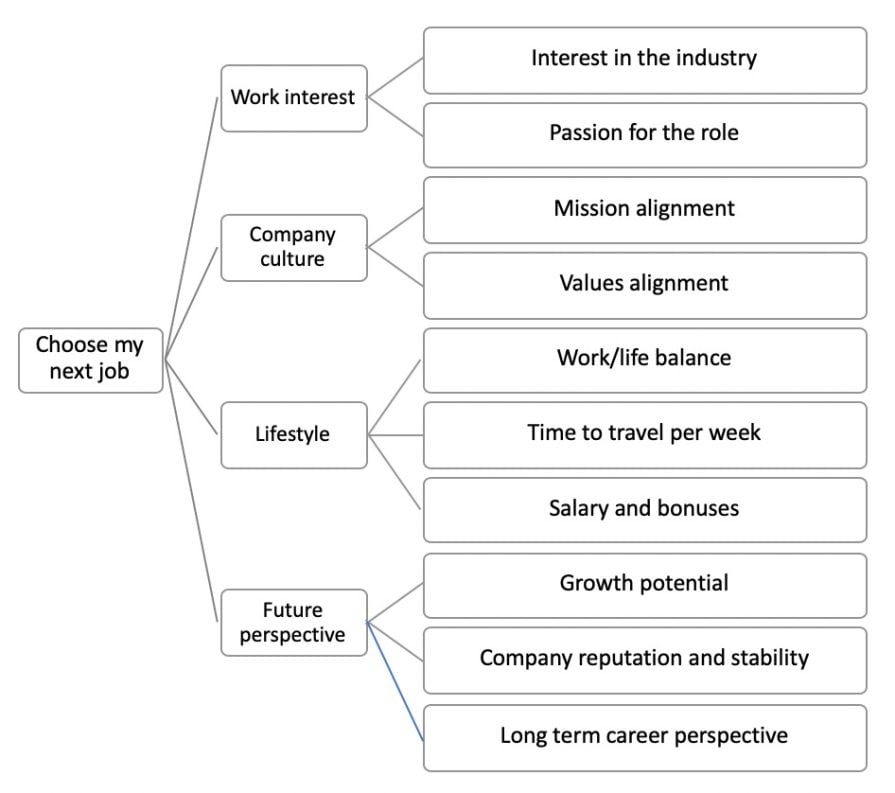
When breaking down this problem, you need to consider various factors that are important for your future happiness in the role. This includes aspects like the company culture, our interest in the work itself, and the lifestyle that you can afford with the role.
However, not all factors carry the same weight for us. To make sense of the results, we can assign a weight factor to each branch. For instance, passion for the job role may have a weight factor of 1, while interest in the industry may have a weight factor of 0.5, because that is less important for you.
By applying these weights to a specific role and summing the values, you can have an estimate of how suitable that role is for you. Moreover, you can compare two roles and make an informed decision based on these weighted indicators.
Key problem-solving skills
This framework provides the foundation and guidance needed to effectively solve problems. However, successfully applying this framework requires the following:
- Creativity — During the decomposition phase, it’s essential to approach the problem from various perspectives and think outside the box to generate innovative ideas for breaking down the problem tree
- Decision-making — Throughout the process, decisions must be made, even when full confidence is lacking. Employing rules of thumb to simplify analysis or selecting one tree cut over another requires decisiveness and comfort with choices made
- Analytical skills — Analytical and research skills are necessary for the phase following decomposition, involving data gathering and analysis on selected tree branches
- Teamwork — Collaboration and teamwork are crucial when working within a team setting. Solving problems effectively often requires collective effort and shared responsibility
- Communication — Clear and structured communication is essential to convey the problem solution to stakeholders and decision-makers and build trust
How to enhance your problem-solving skills
Problem-solving requires practice and a certain mindset. The more you practice, the easier it becomes. Here are some strategies to enhance your skills:
- Practice structured thinking in your daily life — Break down problems or questions into manageable parts. You don’t need to go through the entire problem-solving process and conduct detailed analysis. When conveying a message, simplify the conversation by breaking the message into smaller, more understandable segments
- Regularly challenging yourself with games and puzzles — Solving puzzles, riddles, or strategy games can boost your problem-solving skills and cognitive agility.
- Engage with individuals from diverse backgrounds and viewpoints — Conversing with people who offer different perspectives provides fresh insights and alternative solutions to problems. This boosts creativity and helps in approaching challenges from new angles
Final thoughts
Problem-solving extends far beyond mathematics or scientific fields; it’s a critical skill for making informed decisions in every area of life and work. The seven-step framework presented here provides a systematic approach to problem-solving, relevant across various domains.
Now, consider this: What’s one question currently on your mind? Grab a piece of paper and try to apply the problem-solving framework. You might uncover fresh insights you hadn’t considered before.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #career development
- #tools and resources

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Techniques for running customer behavior analysis
Customer behavior analysis (CBA) is the study of how individual customers, groups, or segments act when interacting with your product.

How to use — but not abuse — frameworks
While frameworks have clear benefits, it’s important to understand how and when to use them, as they are often overused or used in the wrong context or setting.

Key lessons from failed products
All the metrics, data, and analysis you made will make a difference, but success isn’t always directly proportional to the effort you put in.

Leader Spotlight: Aligning to a ‘healthy days’ North Star, with Nupur Srivastava
Nupur Srivastava, COO of Included Health, talks about using the number of days a member considers themselves healthy as a North Star.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply

- Decision Making
- Goal Setting
- Managing Performance
- Managing Projects and Change
- Managing Through Covid
- Personal Development
- Problem Solving
- Time Management
- Workplace Well-being
- Free Downloads
Seven Step Problem Solving Technique
What's the problem?
Our seven step problem solving technique provides a structured basis to help deliver outcomes and solutions to your problems. (But if you’re in hurry, click here for our “manage in a minute” tip: 7 Problem Solving Steps ).
Ever heard people say (or perhaps said yourself) things like :
“I wished we hadn’t jumped to that solution so quickly.”
“I think we may have solved the wrong problem.”
“It was only at the end that I realised we had acted too quickly with too little information.”
“The solution we went ahead with turned out to be impractical and too expensive.”
A structured process helps ensure you stay on track with what you really need to do, to solve a problem.
The seven step problem solving technique covers:
- Finding the right problem to solve
- Defining the problem
- Analysing the problem
- Developing possibilities
- Selecting the best solution
- Implementing
- Evaluating and learning
You’ll find a brief explanation of these points below. Once you’ve read these, you can find more details, in our comprehensive guide to problem solving: What’s the Problem (with a tool for each or our problem solving steps).
1 Find the Right Problems to Solve
Surprised to start with this step? Not many problem solving processes include this step, yet it is absolutely crucial. Think how often we spend time and resources on problems which don’t necessarily demand such attention. Ask yourself “Is it the right problem to solve?”. This is also one of the most important stages in our seven step problem solving technique. Why?
Well too often our approach to problem solving is reactive, we wait for the problems to arise. So firstly in our seven step problem solving process, we advocate taking a proactive approach, go and find problems to solve; important and valuable problems. The real starting point then for any problem solving process is to find the right problem to solve.
How do you go about finding the right problems to solve?
That’s what we set to answer in our problem solving skill article: “Finding the Right problems to Solve”. You will find useful management tips in this activity to start the problem solving process by looking firstly at the possibilities in your current issues and then secondly looking to the future.
2 Define the Problem
It is very tempting to gloss over this step and move to analysis and solutions. However, like the first step, it is one of the secrets of effective problem solving and helps to differentiate our seven step problem solving technique. Combining problems that are valuable to solve, with defining exactly what you are trying to solve, can dramatically improve the effectiveness of the problem solving process. The secret to defining the problem, is really about attitude. Try to see every problem as an opportunity.
This is the crucial attitude which will then help you define the problem in a way which focuses on the potential and opportunity in the situation. Peter Drucker advocates that we should starve problems and start feeding opportunities. Perhaps because we don’t see the right problems to solve or the opportunity in solving them. Essentially Drucker suggests that we should move from a problem focus to an opportunity focus.
Define your problem as an opportunity! Our problem solving activity tool does just that, providing a process to frame your problem as an opportunity and a question checklist to help you define what exactly the problem is, and why it is worth your while solving it. The question checklist also leads you through a structured set of questions to start the analysis of the problem. Which is the next step in the seven step problem solving technique.
3 Analyse the Problem
Analysis is a process of discovery of the facts, finding out what you know about the situation. The problem solving activity question checklist leads you through a set of questions to identify the nature of the problem and to analyse what it is and what it isn’t.
One of the most important aspects of analysing any situation is involving the right people.
In “ the best management tools ever: a good question ” we suggest using Reg Revans approach of asking three questions:
- Who knows? – about the situation/opportunity, or who has the information we need to solve it/realise it
- Who cares? – that something is done about it
- Who can? – do something about the solution
These questions are fundamental management tips. They help us to identify the people who need to come together, in order to take appropriate action to solve an issue or realise an opportunity.
Analysis often requires a detailed examination of the situation. This is an important element in seven step problem solving.
An excellent approach to detailed examination is adopted in our structured problem solving technique which uses four steps to improve processes in your organisation. This management tool firstly helps you define the current situation, then challenges all aspects of that current process. The third and fourth steps are to develop options and then seek an optimal solution. The tool leads us from analysis to the next two stages in our seven step problem solving technique, that is developing options and selecting a solution.
4 Develop Possibilities
The previous steps will have already revealed plenty of possibilities for solving the problem and realising the opportunities. At this stage it is important to give time and space for creative solutions. Placing a high value on the ideas of others is a crucial leadership concept and facilitator skill when generating ideas to solve problems.
We have already suggested that for effective problem solving you need to ensure that you find the right problems to solve and then ask yourself what opportunities are created by solving this problem. But how do you focus on opportunities?
We have developed a tool, the power of positive thinking , which helps you to focus on those opportunities, using 5 questions that create opportunities. A group process is recommended to help get possible solutions from a wide range of people – solutions which can create significant opportunities for the organisation.
A second resource provides a great process to explore new possibilities and potential. In “ the best management tools ever: a good question ” there is a tool which groups questions to help you:
- focus collective attention on the situation
- connect ideas and deeper insight
- create forward momentum and move to action
A rich range of possible solutions opens up the opportunities. When you consider you have plenty of ideas with potential it’s time to make a decision.
5 Select the Best Solution
The next phase in our seven step problem solving technique is to consider the number of solutions found. It’s likely that more than one will be viable so how do you decide which solution to select? There will be constraints restricting what you can do, issues about whether solutions fit within what is currently done, and various stakeholders views to consider. Solutions therefore need to be evaluated. A powerful way to do this has been proposed by Peter Drucker. In our business planning tool, “ business goal setting “, we suggest using Drucker’s three criteria as a filter to select ideas to take forward. To screen your ideas apply the three filter tests:
- Operational validity – Can you take action on this idea, or can you only talk about it? Can you really do something right away to bring about the kind of future you desire?
- Economic validity – Will the idea produce economic result? What would be the early indicators that it was working?
- Personal commitment – Do you really believe in the idea? Do you really want to be that kind of people, do that kind of work, and run that kind of business?
Take you time answering these questions. You may well find that many of the other stages in our business goal setting article can help in the problem solving process. Especially if the problem is of organisational significance and its solution could impact the direction the business or unit takes.
6 Implement
Implementing the seven step problem solving technique moves to a project implementation process. But before putting your decision into effect check that you have:
- carefully defined the problem, and the desired outcome
- analysed the problem at length
- collected every available item of information about it
- explored all possible avenues, and generated every conceivable option
- chosen the best alternative after considerable deliberation.
To implement first make sure that you follow project management guidelines , particularly to be clear on the outcomes, ask yourself what will be different when you solve the problem and realise the opportunity.
Secondly what are the objectives, these should clearly demonstrate how you will get to the outcomes. Gaining clarity on these, and acceptance from the various stakeholders is crucial to succeeding.
The implementation process can then effectively follow a project management model of:
- Do it – carry out activities to implement
- Deliver it – test and ensure it has met the outcomes
Make sure that the three “who’s” are with you!
During the seven step problem solving process you should build the commitment of those:
- who care – they want to see a solution,
- who can – they are able to make it happen
- who know – they can help you implement effectively.
7 Evaluate and Learn from the seven step problem solving technique
You will have done some things really well by applying this seven step problem solving technique. It would be all too easy to forget them in rushing to solve the next problem, or to implement the solution. You should evaluate at least two areas:
- How you carried out the seven step problem solving process
- The effectiveness of the solution you implemented. Did it deliver the outcomes you expected?
You should also ask what you are now able to do, or what you could do next, now that you have improved things by solving the problem. What further opportunities can you now realise that you weren’t able to before?
This seven step problem solving technique ensures you follow a systematic process but it also emphasises two secrets of effective problem solving:
- Use your problem solving skills to ask: “is it the right problem to solve?”
- Then ensure that any problem solving activity asks the question: “what opportunities are created by this problem?”
The eighth problem solving step

- Tool 1: When you don’t know what to do
- Tool 2: Defining questions for problem solving
- Tool 3: Finding the right problems to solve
- Tool 4: Problem solving check-list
- Tool 4a: Using the question check-list with your team
- Tool 5: Problem analysis in 4 steps
- Tool 5a: Using 4 Step problem analysis with your team
- Tool 6: Questions that create possibilities
- Tool 6a: Using the 5 questions with your team
- Tool 6b: Putting creativity to work – 5 alternate questions
- Tool 6c: Workshop outline
- Tool 7: Evaluating alternatives
- Tool 8: Creative thinking techniques A-Z
- Tool 9: The 5 Whys technique
Further Reading
>> return to problem solving hub, looking for more resources.
Try our great value e-guides

Making Better Decisions

Managing Performance Bundle

Goal Setting Bundle
I love your e-guides.
I’m teaching team leaders and team members 7 Step Problem Solving and found your site very enlightening and useful for my classes!!!
Kenneth - United States

Grab a Freebie
Sign up to our newsletter and receive "How to be a Happy Manager"

Grab a Freebie!
Sign up to our newsletter and receive a free copy of "How to be a Happy Manager"
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
The Happy Manager
- Testimonials
- Write For Us
- Terms & Conditions
Knowledge Hub
What's new.
- Why Your Business Location Has an Impact on Your Employees’ Happiness
- How Outplacement Services Can Benefit Your Employees and Your Business
- 5 Tips for Boosting Team Productivity
- Employee Happiness and Social Media: A Strategy for Business Success?
- Best Practices for Managing Large Engineering Projects
- Can Applicant Tracking Systems Improve the Selection Process?
© 2024 The Happy Manager. Part of Apex Leadership Ltd. Tel +44 (0)7572 797430
- Privacy Policy
Website by Limely
Click on the links to download your free tools
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn More
FIND A MEDIATOR QUICK LISTS
- Mediators Listed by State/City
- Mediators Listed by Practice Area
- Mediator Services
- Certification
- Mediate University
- Statewide Banner
- Online Meeting Room
- About Mediation
- Public Policy
Seven Steps for Effective Problem Solving in the Workplace
Problem-solving and decision-making. Ask anyone in the workplace if these activities are part of their day and they answer ‘Yes!’ But how many of us have had training in problem-solving? We know it’s a critical element of our work, but do we know how to do it effectively?
People tend to do three things when faced with a problem: they get afraid or uncomfortable and wish it would go away; they feel that they have to come up with an answer and it has to be the right answer; and they look for someone to blame. Being faced with a problem becomes a problem. And that’s a problem because, in fact, there are always going to be problems!
There are two reasons why we tend to see a problem as a problem: it has to be solved and we’re not sure how to find the best solution, and there will probably be conflicts about what the best solution is. Most of us tend to be “conflict-averse”. We don’t feel comfortable dealing with conflict and we tend to have the feeling that something bad is going to happen. The goal of a good problem-solving process is to make us and our organization more “conflict-friendly” and “conflict-competent”.
There are two important things to remember about problems and conflicts: they happen all the time and they are opportunities to improve the system and the relationships. They are actually providing us with information that we can use to fix what needs fixing and do a better job. Looked at in this way, we can almost begin to welcome problems! (Well, almost.)
Because people are born problem solvers, the biggest challenge is to overcome the tendency to immediately come up with a solution. Let me say that again. The most common mistake in problem solving is trying to find a solution right away. That’s a mistake because it tries to put the solution at the beginning of the process, when what we need is a solution at the end of the process.
Here are seven-steps for an effective problem-solving process.
1. Identify the issues.
- Be clear about what the problem is.
- Remember that different people might have different views of what the issues are.
- Separate the listing of issues from the identification of interests (that’s the next step!).
2. Understand everyone’s interests.
- This is a critical step that is usually missing.
- Interests are the needs that you want satisfied by any given solution. We often ignore our true interests as we become attached to one particular solution.
- The best solution is the one that satisfies everyone’s interests.
- This is the time for active listening. Put down your differences for awhile and listen to each other with the intention to understand.
- Separate the naming of interests from the listing of solutions.
3. List the possible solutions (options)
- This is the time to do some brainstorming. There may be lots of room for creativity.
- Separate the listing of options from the evaluation of the options.
4. Evaluate the options.
- What are the pluses and minuses? Honestly!
- Separate the evaluation of options from the selection of options.
5. Select an option or options.
- What’s the best option, in the balance?
- Is there a way to “bundle” a number of options together for a more satisfactory solution?
6. Document the agreement(s).
- Don’t rely on memory.
- Writing it down will help you think through all the details and implications.
7. Agree on contingencies, monitoring, and evaluation.
- Conditions may change. Make contingency agreements about foreseeable future circumstances (If-then!).
- How will you monitor compliance and follow-through?
- Create opportunities to evaluate the agreements and their implementation. (“Let’s try it this way for three months and then look at it.”)
Effective problem solving does take some time and attention more of the latter than the former. But less time and attention than is required by a problem not well solved. What it really takes is a willingness to slow down. A problem is like a curve in the road. Take it right and you’ll find yourself in good shape for the straightaway that follows. Take it too fast and you may not be in as good shape.
Working through this process is not always a strictly linear exercise. You may have to cycle back to an earlier step. For example, if you’re having trouble selecting an option, you may have to go back to thinking about the interests.
This process can be used in a large group, between two people, or by one person who is faced with a difficult decision. The more difficult and important the problem, the more helpful and necessary it is to use a disciplined process. If you’re just trying to decide where to go out for lunch, you probably don’t need to go through these seven steps!
Don’t worry if it feels a bit unfamiliar and uncomfortable at first. You’ll have lots of opportunities to practice!
Tim Hicks is a conflict management professional providing mediation, facilitation, training, coaching, and consulting to individuals and organizations. From 2006 to 2014 he led the Master’s degree program in Conflict and Dispute Resolution at the University of Oregon as its first director. He returned to private practice in 2015. Tim is… MORE >
Featured Members
Read these next, the road less traveled: a review of j. kim wright’s lawyers as peacemakers: practicing holistic, problem-solving law.
Published by the American Bar Association in April, 2010, Lawyers as Peacemakers was named an ABA Flagship Book and is a best-seller. It is excerpted here with permission of the...
The Role Of The Peacemaker: Adaptive Versus Technical Work
People often wonder what a peacemaker does. Is it mediation, or is it something different? What distinguishes peacemaking from other mediation processes? A successful peacemaking process consists of several principles....
Setting Up a New Zoom Account for Mediators
This video discusses Zoom settings for mediators, designed to establish rapport and confidentiality. Links to downloadable / embeddable video here. As dispute resolution offices around the world are switching to...

COMMENTS
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use ...
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the ...
Step 6: Implement the Solution. Implementing the solution you decide on can include creating an implementation plan. It could also include planning on what happens next if something goes wrong with the solution if it doesn’t work out the way you thought it would. Implementation means that everyone on your team knows and understands their part ...
Problem statements should commence with a question or a firm hypothesis. Be specific, actionable and focus on what the decision maker needs to move forward. Break a problem into component parts so that problems can be divided and allocated. The parts should be MECE. Do it as a team, share with Experts and client to get input and alignment.
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is a systematic approach used to address complex issues, make informed decisions, and find effective solutions to problems. These steps typically include: 1. Identifying the Problem: Clearly define the issue or challenge that needs to be resolved. 2.
The 7 steps to problem-solving. When it comes to problem-solving there are seven key steps that you should follow: define the problem, disaggregate, prioritize problem branches, create an analysis plan, conduct analysis, synthesis, and communication. 1. Define the problem. Problem-solving begins with a clear understanding of the issue at hand.
A comprehensive guide to problem solving, complete with these 9 essential tools: Tool 1: When you don’t know what to do. Tool 2: Defining questions for problem solving. Tool 3: Finding the right problems to solve. Tool 4: Problem solving check-list. Tool 4a: Using the question check-list with your team.
Here are seven-steps for an effective problem-solving process. 1. Identify the issues. Be clear about what the problem is. Remember that different people might have different views of what the issues are. Separate the listing of issues from the identification of interests (that’s the next step!). 2.