
- Become Involved |
- Give to the Library |
- Staff Directory |
- UNF Library
- Thomas G. Carpenter Library

Citation Styles: A Brief Guide to APA, MLA and Turabian
Sample bibliography: mla.
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Government Publications
- Other Materials
- In Text Citations
- Sample Bibliography: APA
- Sample Bibliography: Turabian
- Creating an Annotated Bibliography This link opens in a new window
The basic format for a book citation requires listing the author's name, the title of the book, the publisher's name, and the date of publication. Edited books, when cited in full, will list the editor's name instead of an author’s name.
Works Cited
Black Hearts Bleed Red . Directed by Jeri Cain Rossi. Mary Magdalene Films, 1992.
Desmond, John. "Flannery O'Connor's Misfit and the Mystery of Evil." Renascence: Essays on Values in Literature, vol. 56, no. 2, 2004, pp. 129-37. Literature Online.
Dowell, B. "The Moment of Grace in the Fiction of Flannery O'Connor." College English, vol. 27, 1965, pp. 235-9.
Evans, Robert C. "Poe, O'Connor, and the Mystery of the Misfit." Flannery O'Connor Bulletin, vol. 25, 1997, pp. 1-12.
Fike, Matthew. "The Timothy Allusion in 'A Good Man is Hard to Find'." Renascence: Essays on Values in Literature , vol. 52, no. 4, 2000, pp. 311-9. Literature Online.
Gentry, Marshall Bruce. "He Would Have Been a Good Man: Compassion and Meanness in Truman Capote and Flannery O'Connor." Flannery O'Connor's Radical Reality . Eds. Jan Nordby Gretlund and Karl-Heinz Westarp. U of South Carolina P, 2006, pp. 42-55.
A Good Man is Hard to Find and Other Stories . Recording for the Blind & Dyslexic, 2008.
Hewitt, Avis. "'Someone to Shoot Her Every Minute of Her Life': Maternity and Violent Death in Helena María Viramontes and Flannery O'Connor." Flannery O'Connor Review, vol. 4, 2006, pp. 12-26.
Keetley, Dawn. "'I Forgot What I Done': Repressed Anger and Violent Fantasy in 'A Good Man is Hard to Find'." 'On the Subject of the Feminist Business': Re-Reading Flannery O'Connor, edited by Teresa Caruso. Peter Lang, 2004, pp. 74-93.
Link, Alex. "Means, Meaning, and Mediated Space in 'A Good Man is Hard to Find'." Southern Quarterly: A Journal of the Arts in the South , vol. 44, no. 4, 2007, pp. 125-38.
Shinn, T. J. "Flannery O'Connor and the Violence of Grace." Contemporary Literature, 1968, pp. 58-73.
Sloan, Gary. "Mystery, Magic, and Malice: O'Connor and the Misfit." Journal of the Short Story in English , vol. 30, 1998, pp. 73-83.
Tsai, Hsiu-chih. "Violence as the Road to Transformation: O'Connor's 'A Good Man is Hard to Find'." NTU Studies in Language and Literature, vol. 13, 2004, pp. 59-98.
- << Previous: Sample Bibliography: APA
- Next: Sample Bibliography: Turabian >>
- Last Updated: Feb 22, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.unf.edu/citationguide
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA Annotated Bibliography Format
MLA Annotated Bibliography Format
The mla style center provides the following guidance for formatting an mla annotated bibliography:.
- Title your reference page as “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Include annotations after the full, listed reference.
- Annotations should typically not exceed a single paragraph.
- If you do exceed one paragraph, indent each new paragraph but do not add extra space between them.
- For more information on writing an annotation, visit the general annotated bibliography guide.
Here’s a run-through of everything this page includes:
Book example
Website example.
- Using-the-EasyBib-annotation-tool
Troubleshooting
Here are general mla bibliography format guidelines that also apply:.
- Organize sources alphabetically by author or title, by the publication date, or by subject. Ask your instructor how they would like this organized if they haven’t provided specific guidance.
- The entire bibliography MLA page or pages should be double-spaced.
- Have 1-inch margins around the page.
If you don’t need to include annotations with your citations, this guide on creating a regular MLA works cited page can help!
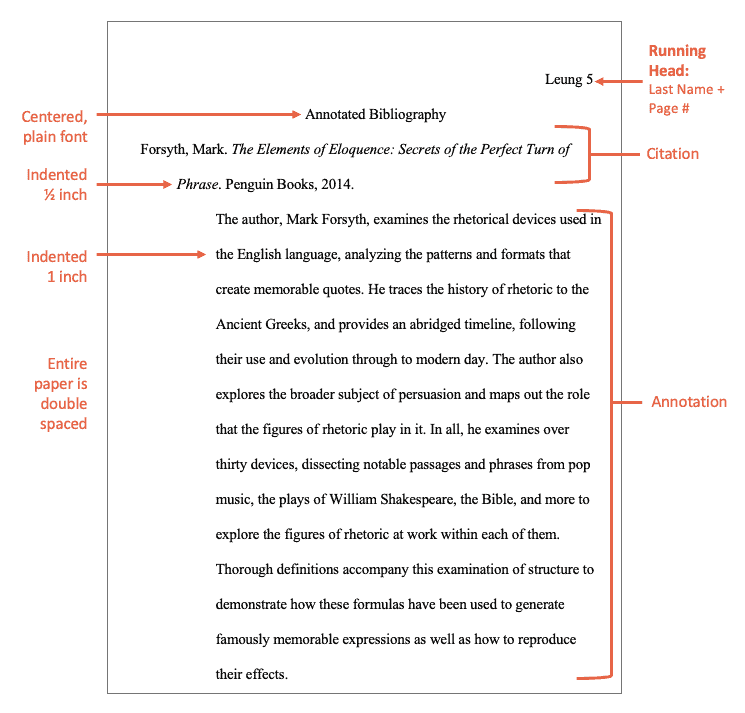
Forsyth, Mark. The Elements of Eloquence: Secrets of the Perfect Turn of Phrase . Penguin Books, 2014.
The author, Mark Forsyth, examines the rhetorical devices used in the English language, analyzing the patterns and formats that create memorable quotes. He traces the history of rhetoric to the Ancient Greeks, and provides an abridged timeline, following their use and evolution through to modern day. The author also explores the broader subject of persuasion and maps out the role that the figures of rhetoric play in it. In all, he examines over thirty devices, dissecting notable passages and phrases from pop music, the plays of William Shakespeare, the Bible, and more to explore the figures of rhetoric at work within each of them. Thorough definitions accompany this examination of structure to demonstrate how these formulas have been used to generate famously memorable expressions as well as how to reproduce their effects.
Here is another annotated bibliography example in MLA for an article on the MLA website.
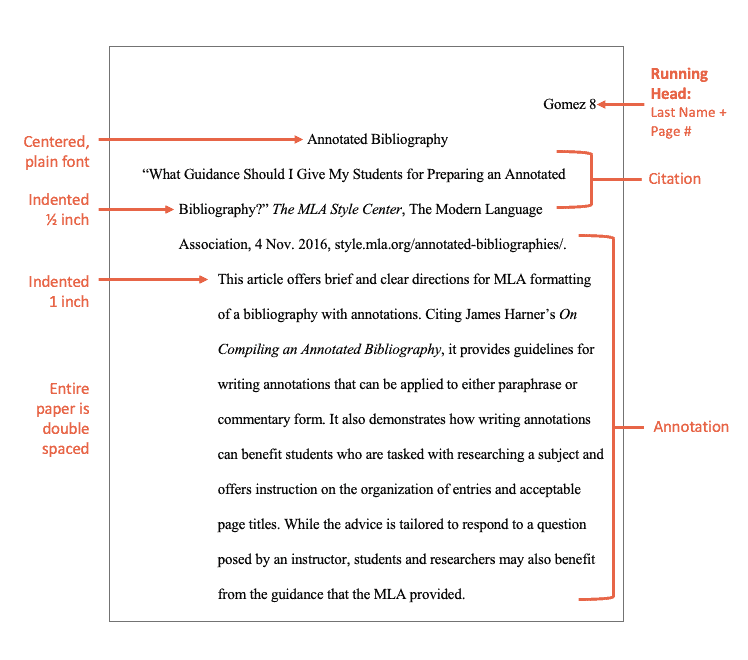
Citation with annotation:
“What Guidance Should I Give My Students for Preparing an Annotated Bibliography?” The MLA Style Center , The Modern Language Association, 4 Nov. 2016, style.mla.org/annotated-bibliographies/.
This article offers brief and clear directions for MLA formatting of a bibliography with annotations. Citing James Harner’s On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography , it provides guidelines for writing annotations that can be applied to either paraphrase or commentary form. It also demonstrates how writing annotations can benefit students who are tasked with researching a subject and offers instruction on the organization of entries and acceptable page titles. While the advice is tailored to respond to a question posed by an instructor, students and researchers may also benefit from the guidance that the MLA provided.
Citation without annotation:
The following is an example MLA format Works Cited citation for an article on the MLA website. This MLA bibliography example shows what the entry will look like without an annotation:
“What Guidance Should I Give My Students for Preparing an Annotated Bibliography?” The MLA Style Center, Modern Language Association, 4 Nov. 2016, style.mla.org/annotated-bibliographies/
Note that this MLA bibliography does not contain an introductory paragraph. If you are including a prefatory section, it should reside between the page title and the initial entry.
The MLA follows the rules set forth in James L. Harner’s On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography , 2nd edition, which they published in 2000. Harner submits that the typical organization for this type of work “…consists of three parts: prefatory matter, entries, and an index” (7). Following this, he adds, however, that “an electronic bibliography rarely includes an index” (7).
The “prefatory matter” functions similarly to an introduction, and “typically consists of an introduction, an explanation of editorial procedures, acknowledgements, and separate lists of abbreviations, major reference sources searched, and the subject author’s works” (7). He expands on this, “You must explain – and, if necessary, offer a rationale for – the taxonomy, the kinds of works included and excluded, and the chronological span (especially terminal date) of scholarship covered” (7).
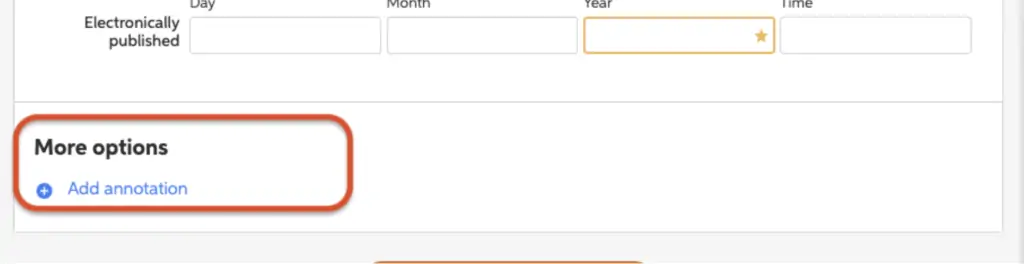
Using the EasyBib annotation tool
If you create your citations using the EasyBib citation generator, then you can also access the annotation tool!
When you create a new or edit an existing citation, you’ll review a citation form that lists every piece of information for the citation. At the bottom of this form is a section called “More options.” In this section, simply click the “Add annotation” text to open the tool. Copy and paste your annotation here, complete your citation, and both the citation and annotation will be automatically formatted together!
Always consult your instructor
Your instructor or school may have additional or different requirements for how you format and organize this page. If your teacher or professor requires an introduction, they may identify specific points to include or exclude which deviate from Harner’s definition, so it’s essential that you verify your understanding of the assignment before beginning.
If you are required to share your references in a manner other than in MLA bibliography format, there is also a guide on APA annotated bibliographies .
Solution #1: How do I annotate a source that is an image or video?
To annotate a visual source like an image or video, describe the important elements of your visual source to your reader as you would with a textual source.
If it is a painting, for example, you do not need to describe every color you see or the mood of the painting, but it may be important to include the artistic movement of which it is a part of, the style of painting, the subject, the culture of origin, or any information about the artist.
Keep in mind the style of annotation you are using for your works-cited annotations, whether you are providing more commentary on sources or simply summarizing them. Maintain the style of annotation consistent for all your annotations. Commentary will include more information about why a source is relevant to your paper, whereas a summary will more plainly describe the source.
van Gogh, Vincent. The Starry Night . 1889, Museum of Modern Art, New York City.
MoMA.org , https://www.moma.org/learn/moma_learning/vincent-van-gogh
-the-starry-night-1889/
Vincent van Gogh’s The Starry Night is a depiction of the night sky seen above the Saint-Paul mental asylum in Saint-Remy, France, where van Gogh received care as his mental health waned. van Gogh was born in Holland, but spent significant time in France. The influence of contemporaneous artistic styles such as Impressionism, Pointilism, and Neo-Impressionism can be seen in The Starry Night . The Starry Night combines the observable world with the world of van Gogh’s emotion, memory, and imagination.
Solution #2: How do I annotate a source that is an audio recording, song, or interview?
Annotate your works-cited MLA citation for an audio recording the same way you would for a textual source.
Keep the style of your annotations consistent, whether you are commenting on sources or simply summarizing sources.
Important elements of your audio source to consider in your annotation may include the following elements: the speaker(s) in the recording, where and when the recording was taken, the important members of the band or musicians of a song, or, if it is a clip, the context of the complete recording.
Describe your audio source as best you can in about 4-5 sentences for your annotation.
For example:
Tavernise, Sabrina. “Why Do So Many Traffic Stops Go Wrong?” The Daily , The New York Times,
1 Nov. 2021. Spotify app.
David D. Kirkpatrick, a national correspondent for the New York Times , breaks down years’ worth of investigative journalism from the NYT. Their journalism focused on casualties due to routine traffic stops performed by police nationwide. The NYT’s reporting suggested that many cities and municipalities may rely heavily on revenue generated from traffic tickets, and that officers may be encouraged to make more, even unnecessary, traffic stops. Kirkpatrick also suggested that training may encourage police to use unnecessary force and escalate encounters during traffic stops, as misleading data has been used to teach officers that traffic stops are disproportionately deadly for police.
Solution #3: How long should my annotation be?
An annotation for an MLA works-cited citation should be about a paragraph long. It shouldn’t be a few words or just one sentence.
If your annotation definitely needs to be longer than 4-5 sentences, make a new paragraph and indent it, but do not add any additional space or line breaks between the paragraphs of your annotation.
- Works Cited
Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography. 2nd ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2000.
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An annotated bibliography is a list containing complete information of sources (such as journals, books, and reports) cited in the text, along with a note or annotation for each source. It provides a brief description of each source in about 100–150 words. Below is an example of an annotated bibliography:
Annotated bibliography example:
Morritt, Robert D. Beringia: Archaic Migrations into North America . Cambridge Scholars Pub, 2011.
The author studies the migration of cultures from Asia to North America. The connection between the North American Athabaskan language family and Siberia is presented, together with comparisons and examinations of the implications of linguistics from anthropological, archaeological, and folklore perspectives. This book explores the origins of the earliest people in the Americas, including Siberian, Dene, and Navajo Creation myths; linguistic comparisons between Siberian Ket Navajo and Western Apache; and comparisons between indigenous groups that appear to share the same origin.
Ehrenreich, Barbara. Bright-Sided: How the Relentless Promotion of Positive Thinking has Undermined America . Metropolitan Books, 2009.
In this book, Barbara Ehrenreich shows how harmful the positive thinking movement is, how it means self-blame, victim-blaming, and national denial, inviting disaster. She shows that it wrecks efforts for education, skills, and reforms. The book analyzes how the school of mindless optimism was born, fed the subprime scandal, and has come to infect mainstream corporate management thinking.
An annotated bibliography, which contains a source and a description or an evaluation of a source, is always double-spaced.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
- powered by chegg, all of our writing tools, none of the ads, your ultimate mla format guide & generator, what is mla.
MLA stands for the Modern Language Association , an organization that focuses on language and literature.
Depending on which subject area your class or research focuses on, your professor may ask you to cite your sources in MLA style. This is a specific way to cite, following the Modern Language Association's guidelines. There are other styles, such as APA format and Chicago citation style , but MLA format is often used for literature, language, liberal arts, and other humanities subjects. This guide extensively covers this format but is not associated with the organization.
What is MLA Citing?
The Modern Language Association Handbook is in its 9th edition and standardizes the way scholars document their sources and format their papers. When everyone documents their sources and papers in the same way, it is simple to recognize and understand the types of sources used for a project. Readers of your work will look at your citations not only to understand them but possibly to explore them as well.
When you're borrowing information from a source and placing it in your research or assignment, it’s important to give credit to the original author. This is done by creating an MLA citation. Depending on the type of information you're including in your work, you may place citations in the body of your project and in a works-cited list at the end of your project.
The handbook explains how to create MLA citations. This page summarizes the information in the handbook’s 9th edition.
There is also a section below on a recommended way to create an MLA header. These headers appear at the top of your assignment’s pages. Check with your instructor on whether they prefer a certain MLA format for the header.
What is MLA Format?
The 9th edition is the most recent and updated version for MLA citations. Released in April 2021, the citation format differs slightly from previous versions. This update follows the 2016 update for the 8th edition that contained many significant changes from previous editions.
For the 8th edition, the biggest difference and most exciting update was the use of one standard format for all source types. In previous versions, scholars were required to locate the citation format for the specific source that they used. There were different formats for books, websites, periodicals, and so on. After 2016, using one universal MLA citation format allowed scholars to spend less time trying to locate the proper format to document their sources and focus more on their research .
Other updates included the addition of “containers.” A container provides details on a work contained within a larger work. For example, books contain chapters, albums contain songs, and journals contain journal articles. The source is the larger work, such as a website, while the container is a smaller work within that source, such as a short story on the website.
MLA now encourages you to add DOIs or URLs to citations. Use a DOI instead of a URL when it’s available. According to the MLA 9th edition, you can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx).
Social media pseudonyms and usernames can replace the real name of the author. Volume and issue numbers are now abbreviated as “vol.” and “no.” Cities of publication and the source’s medium (such as print or web) are no longer included in citations. For academic presses/publishers, with the words “university” or “press,” shorten “university” to “U”, and “press” to “P” (Cambridge UP). Lowercase seasons when using them in the date field of a citation (spring 2021 not Spring 2021).
Bibliography vs. Works Cited - What's the Difference?
You may have heard the two terms, "Bibliography" and "Works Cited" thrown around interchangeably. The truth is that they are two different words with two completely different meanings.
A bibliography is a list of sources that the writer recommends for further reading. A works-cited list is a list of sources that were included in the author's writing.
Want to suggest some books and websites to your reader? Create an MLA format bibliography by creating a list of full citations and label the page as "Bibliography."
Did you use any quotes or place any paraphrases in your writing? Create in-text citations and place them in the body of your work. Then, create a list of full citations and place them at the end of the project. Label the page as "Works Cited."
The good news is that references in MLA bibliography format and regular works-cited lists are structured the exact same way.
Citing Basics
When adding information to your project from another source, you are required to add an MLA citation. There are two types of MLA format citations: in-text citations and full citations.
Full Citation Basics:
All sources used for a project are found on the MLA format “Works Cited” page, which is generally the last portion of a project.
MLA citing format often includes the following pieces of information, in this order:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Source." Title of Container , Other contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication Date, Location.
For more information about each individual element and for proper formatting rules, see the sections below on author names, titles, containers, names of other contributors, source versions, numbers, publishers, publication dates, and locations.
Find more in-depth rules regarding the works-cited list in MLA format on the page down below, along with a sample page.
Don't forget, our BibMe MLA citation generator is an MLA formatter that helps you create your citations quickly and easily!
Citation Components
The author's name is generally the first item in a citation (unless the source does not have an author). The author's name is followed by a period.
If the source has one author , place the last name first, add a comma, and then the first name.
MLA format:
Lee, Harper.
Fitzgerald, F. Scott.
If your source has two authors , place them in the same order they're shown on the source. The first author is in reverse order, add a comma and the word "and", then place the second author in standard form. Follow their names with a period.
Monsen, Avery, and Jory John.
For three or more authors , only include the first listed author's name. Place the first author's name in reverse order (Last name, First name) place a comma afterwards, and then add the Latin phrase "et al."
Borokhovic, Kenneth A., et al.
For social media posts, it's acceptable to use a screen name or username in place of the author's name. Start the citation with the user's handle.
@TheOnion. "Experts Warn Number of Retirees Will Completely Overwhelm Scenic Railway Industry by 2030." Twitter , 9 Oct. 2017, 9:50 a.m., twitter.com/TheOnion/status/917386689500340225.
No author listed? If there isn't an author, start the citation with the title and skip the author section completely.
Citations do not need to always start with the name of the author. When your research focuses on a specific individual that is someone other than the author, it is appropriate for readers to see that individual's name at the beginning of the citation. Directors, actors, translators, editors, and illustrators are common individuals to list at the beginning. Again, only include their name in place of the author if your research focuses on that specific individual.
To include someone other than the author at the beginning of the citation, place their name in reverse order, add a comma afterwards, and then the role of that individual followed by a period.
Fimmel, Travis, performer. Vikings . Created by Michael Hirst, History Channel, 2013-2016.
Gage, John T., editor. The Promise of Reason: Studies in the New Rhetoric . SIU Press, 2011.
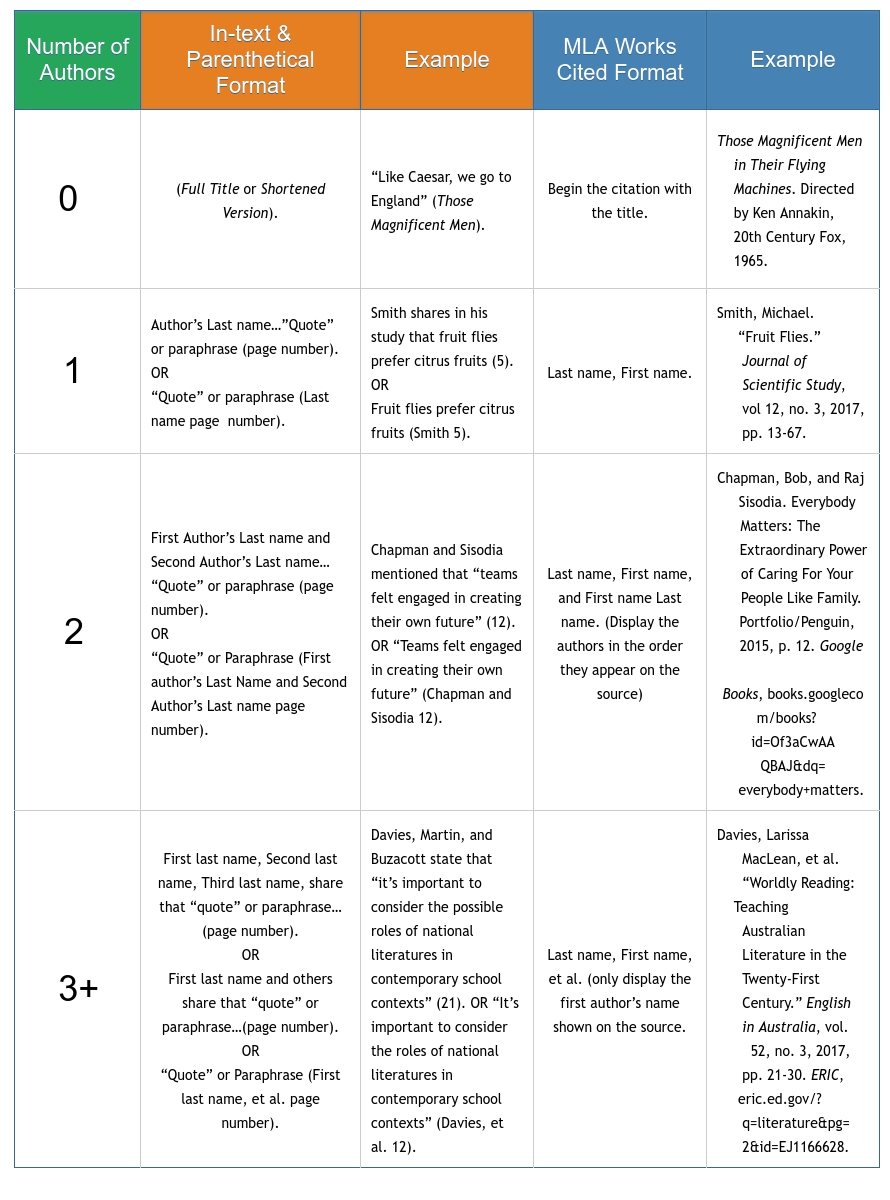
Here's a helpful table to refer to when structuring author names:
Titles and Containers:
Titles follow the name of the author and are written in title capitalization form.
If you're citing a source in its entirety, such as a full book, a movie, or a music album, then place the title in italics.
Franzen, Jonathan. The Corrections . Farrar, Straus, and Giroux, 2001.
Rufus Du Sol. Bloom . Sweat It Out! 2016.
If you're citing a source, such as a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a journal or website, then place the title of the piece in quotations and add a period afterwards. Follow it with the title of the full source, in italics, and then add a comma. This second portion is called the container . Containers house smaller works, such as songs, in larger comprehensive works, such as albums.
Examples with containers:
| Song | Album | "Song." , | Beyonce. "Single Ladies (Put a Ring on It)." , Sony, 2008, track 2. |
| Chapter | Book | "Chapter." , | Aku, Hanjat. "I'm Drifting." , edited by Burton Raffel, State University of New York Albany, 1964. |
| Article | Website or Periodical | "Article Title." , | Vance, Erik, and Erika Larsen. "Mind Over Matter." , Dec. 2016, pp. 30-55. |
| Web page | Website | "Web page." | Becker, Mikkel. "6 Common Dog Behavior Myths Get Busted." , 19 July 2016, www.vetstreet.com/our-pet-experts/6-common-dog-behavior-myths-get-busted. |
Wondering what to do with subtitles? Place a colon in between the title and subtitle. Write both parts in title capitalization form.
Nasar, Sylvia. A Beautiful Mind: The Life of Mathematical Genius and Nobel Laureate John Nash . Simon and Schuster, 2001.
If the source does not have a title , give a brief description and do not use quotation marks or italics.
Israel, Aaron. Brooklyn rooftop acrylic painting. 2012, 12 W 9th Street, New York City.
For a tweet , the full text of the tweet is placed where the title sits.
@LOCMaps. "#DYK the first public zoo to open in the US was the #Philadelphia Zoo? #50States." Twitter , 9 Feb. 2017, 3:14 p.m., twitter.com/LOCMaps/status/829785441549185024.
For email messages, the subject of the email is the title. Place this information in quotation marks.
Rabe, Leor. "Fwd: Japan Itinerary." Received by Raphael Rabe, 11 Feb 2017.
Citations with Two Containers:
It is possible for a source to sit in a second or larger container. A journal article sits in its first container, which is the journal itself, but it can also sit in a larger container, such as a database. A song can sit in its first container, which is the album it's found on. Then it can sit in its next container, which could be Spotify or iTunes.
It is important to include the second container because the content on one container may differ from content from another container.
MLA citing with two containers should be formatted like this:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Source." Title of Container , Other Contributors, Version, Numbers, Publisher, Publication Date, Location. Title of Second Container , Other Contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication Date, Location.
In most cases, for the second container, only the title of the second container and the location is needed. Why? For readers to locate the source themselves, they'll most likely use the majority of the information found in the first part of the citation.
Examples of Citations with 2 Containers:
Sallis, James, et al. "Physical Education's Role in Public Health: Steps Forward and Backward Over 20 Years and Hope for the Future." Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport , vol. 83, no. 2, Jun. 2012, pp. 125-135. ProQuest , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=http://search.proquest.com/docview/1023317255?accountid=35635.
Baker, Martha. "Fashion: Isaac in Wonderland." New York Magazine , vol. 24, no. 3, 21 Jan. 1991, pp. 50-54. Google Books , books.google.com/books?id=PukCAAAAMBAJ&lpg=PP1&dq=magazine&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=magazine&f=false.
Remember, BibMe has an MLA works-cited generator that creates citations for you quickly and easily!
Format for Other Contributors:
In MLA citing, when there are other individuals (besides the author) who play a significant role in your research, include them in this section of the citation. Other contributors can also be added to help individuals locate the source themselves. You can add as many other contributors as you like.
Start this part of the citation with the individual's role, followed by the word "by". Notice that when adding other contributors after a period, you capitalize the first letter of the individual's role. When adding other contributors after a comma, you lowercase the first letter of the individual’s role.
Gaitskill, Mary. "Twilight of the Superheroes." The Scribner Anthology of Contemporary Short Fiction: 50 North American Stories Since 1970, edited by Lex Williford and Michael Martone, Simon and Schuster, 2012, pp. 228-238.
The Incredibles . Directed by Brad Bird, produced by John Walker, Pixar, 2004.
Gospodinov, Georgi. The Physics of Sorrow . Translated by Angela Rodel, Open Letter, 2015.
Format for Versions:
Sources can come in different versions. There are numerous bible versions; books can come in versions (such as numbered editions), and even movies and songs can have special versions.
When a source indicates that it is different than other versions, include this information in the citation. This will help readers locate the exact source that you used for your project.
The Bible . Lexham English Version, Logos, 2011, lexhamenglishbible.com.
Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion . 2nd ed., Clarendon, 1979.
Afrojack. "Take Over Control." Beatport , performance by Eva Simons, extended version, 2011, www.beatport.com/track/take-over-control-feat-eva-simons-extended/1621534.
Format for Numbers:
Any numbers related to a source that isn't the publication date, page range, or version number should be placed in the numbers position of the citation. This includes volume and issue numbers for journal articles, volume or series numbers for books, comic book numbers, and television episode numbers, to name a few.
When including volume and issue numbers, use the abbreviation “vol.” for volume and “no.” for number.
Zhai, Xiaojuan, and Jingjing Wang. "Improving Relations Between Users and Libraries: A Survey of Chinese Academic Libraries." The Electronic Library , vol. 34, no. 4, 2016, pp. 597-616. ProQuest Research Library , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=http://search.proquest.com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/1841764839?accountid=35635.
"Chestnut." Westworld , directed by Richard J. Lewis, season 1, episode 2, Warner Bros., 2016.
Publishers:
The publisher produces the source. In the citation, place the publisher before the date of publication. Include the publisher for any source type except websites when the name of the publisher is the same as the name of the website. Also, it’s not necessary to include the name of publishers for newspapers, magazines, or journal articles, since the name of the publisher is generally insignificant.
When sources have more than one publisher that share responsibility for the production of the source, place a slash between the names of the publishers.
Use the abbreviation “UP” when the name of the publisher includes the words “University Press.”
Cambridge UP
Publication Dates:
When including the date that the source was published, display the amount of information that is found on the source, whether it's the full date, the month and year, or just the year.
If the date includes a season rather than a month, make sure to lowercase the season (spring 2021 not Spring 2021). Do not capitalize the season.
2 Nov. 2016 or Nov. 2, 2016
When multiple dates are shown on the source, include the date that is most relevant to your work and research.
Abbreviate months longer than 4 letters.
The location refers to the place where the source can be found. This can be in the form of a URL, page number, disc number, or physical place.
When citing websites in MLA, include DOIs or URLs. Copy the DOI or URL directly from the address bar or link in your browser window. If a DOI number is present, use it in place of a URL. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx.
For page numbers, use the abbreviation “p.” when referring to only one page, and “pp.” for a range of pages.
In-Text & Parenthetical Citation Basics:
When using a direct quote or paraphrasing information from a source, add an in-text or parenthetical citation into the body of your work. Direct quotes are word-for-word quotes pulled from a source and added to your project. A paraphrase is when you take a section of information from a source and put it in your own words. Both direct quotes and paraphrases require an in-text or parenthetical citation to follow it.
Format your parenthetical or in-text citation in MLA as follows:
"Direct quote" or paraphrase (Author's last name and page number).
Author's last name said that "Direct Quote" or paraphrase (page number).
*See the comprehensive section below on MLA in-text citations for further clarification and instructions.
MLA In-Text and Parenthetical Citations
What is an in-text citation or parenthetical citation.
You used information from websites, articles, books, and other sources for your paper, right? Hopefully, you did, because the best research and writing projects validate claims using information from other sources.
The purpose of an in-text citation is to give the reader a brief idea about where you found the information used in your writing.
When you place a line of text, word for word (called a direct quote), or an idea (called a paraphrase) from another source into your writing, you, the writer, must display:
- who created that information (the original author's name)
- the page number you found it on
Check out this example:
"A main clause has to have a finite verb " (Cameron 94).
No author? No problem! Include the title, and if it's lengthy, shorten it.
The major thing to keep in mind is that whichever information you include in the in-text or parenthetical citation, whether it's the author's name or the title, it needs to match the first word in the full citation. The full citation is found on the “Works Cited” page in MLA.
Format your parenthetical and MLA in-text citation as follows:
"Direct quote" or Paraphrase (Author's last name and page number). This is an MLA parenthetical citation as the author's name is in parentheses.
Author's Last Name states, "Direct Quote" or paraphrase (page number). This is an MLA citation in prose as the author's name is in the prose of your sentence.
"Jim never got back with a bucket of water under an hour—and even then somebody generally had to go after him" (Twain 8).
Twain went on to say, “Jim never got back with a bucket of water under an hour—and even then somebody generally had to go after him” (8).
Other things to keep in mind:
If your in-text citation comes from a website or another source that does not have page numbers, use the following abbreviations:
- If the source has designated paragraph numbers, use par. or pars.
- If the source has designated sections, use sec. or secs.
- If the source has designated chapters, use ch. or chs.
- If the source has designated lines, use line or lines.
Example in MLA formatting:
Gregor's sister is quite persuasive, especially when she states to her parents, "It'll be the death of both of you, I can see it coming. We can't all work as hard as we have to and then come home to be tortured like this, we can't endure it" (Kafka, ch. 3).
- If there aren't page, paragraph, section, or chapter numbers, only include the author's name in the in-text or parenthetical citation.
- If the original source is an audio or video recording, after the author's name or title, place a timestamp.
The girl's affection towards Marley is clear when she blushes upon his arrival and shares that she would like to accompany him to the theater ( Tales of Times Ago 12:45).
- Two authors : place both names in the reference.
Malcolm and Knowles state... (12).
The smaller the class size, the more attention a student receives, which greatly impacts learning (Malcolm and Knowles 12).
- Three or more authors : place all three names in the in-text citation. It's also acceptable to use the phrase, "and others," or another cohesive term. For parenthetical citations, use the abbreviation et al.
Smith, Baker, and Klein share that.... (78). OR Smith and others share that.... (78).
Many lizards, including the Carolina anole, only eat when they're hungry. They'll ignore food until their body sends a signal to eat (Smith et al. 78).
- Authors with the same last name : Include the first initial of the author’s first name in the in-text or parenthetical citation.
One study shows that the average time spent on homework is 52 minutes (R. Brown 17). However, a more recent study, released in 2018, found that the average student spends 42 minutes completing homework (S. Brown 966).
- Quoted text : Share in the text that the quote comes from another individual.
Lawrence shares his insight by stating that “instructions need to be shared, not assumed” (Young 55).
Common Examples:
Citations for books:.
The basic entry for a book consists of the author's name, the book title, the publisher, and the year published.
Author's Last name, First name. Book Title . Publisher, Year Published.
MLA book citation example:
Shelley, Mary. Frankenstein . Lackington, Hughes, Harding, Mavor & Jones, 1818.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears on the title page.
For a book written by two authors:
- List them in order as they appear on the cover or title page.
- Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the second author's name is written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the second author's name.
Smith, John, and Bob Anderson. The Sample Book . Books For Us, 2017.
- For books with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by a comma and the abbreviation "et al."
Campbell, Megan, et al. The Best Noun Book . Books For Us, 2017.
The full title of the book, including any subtitles, should be italicized and followed by a period. If the book has a subtitle, the main title should be followed by a colon (unless the main title ends with a question mark or exclamation point).
The Best Books for Kids: A Complete Anthology.
Publication information can generally be found on the title page of a book. If it is not available there, it may also be found on the copyright page. State the name of the publisher.
If you are citing a specific page range from the book, include the page(s) at the end of the citation.
Smith, John, and Bob Anderson. The Sample Book . Books For Us, 2017, pp. 5-12.
When a book has no edition number/name present, it is generally a first edition. If you have to cite a specific edition of a book later than the first, see the section below on citing edited books.
Citations for Translated Books:
If the translation is the focus of your project, include the translator's name at the beginning of the citation, like this:
Translator's Last name, First name, translator. Title . By Original Author's First name Last name, Publisher, Year published.
If it's not the actual translation that is the focus, but the text itself, include the translator's name in the "other contributors" position, like this:
Original Author's Last name, First name. Title . Translated by First Name Last name. Publisher, Year published.
Citations for E-Books:
E-books are formatted differently than print books. Why? Some e-books have different, or extra, information than print books. In addition, e-book pages are often numbered differently. Since the content and format may differ from print books, e-book citations are structured differently. When citing an e-book from a website, format the e-book citation with the website title and URL. When citing an e-book in a digital book format, which lacks a URL or that requires software on an e-reader device, include “e-book ed.” for the Version element of the citation. If you know that the e-book file format (EPUB, MOBI, etc.) varies depending on the e-book publication, you may also include the file format as a supplemental element at the end of the entry.
Format for an e-book found on the Internet:
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-Book . Publisher, Year Published. Title of Website , URL.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . Duke UP, 2010. Google Books , books.google.com/books?id=syqTarqO5XEC&lpg=PP1&dq=electronic%20music&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=electronic%20music&f=false.
Format for an e-book found on an e-reader:
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-book. . E-Book ed., Publisher, Year Published.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . E-book ed., Duke UP, 2010. EPUB.
Author's Last name, First name. Title of E-book. E-Book ed., Publisher, Year Published. File Format.
Rodgers, Tara. Pink Noises: Women on Electronic Music and Sound . E-Book ed., Duke UP, 2010. EPUB.
Citations for Chapters in Books:
Individual chapters are cited when a writer uses a book filled with many chapters, each written by different authors. When citing a specific chapter in a book or an anthology, structure the citation like this:
Last name, First name of Chapter's Author. "Title of Chapter." Title of Book , Other Contributors and their roles, Version (if there's a specific edition), Publisher, Year Published, Page or Page Range.
Levi-Strauss, Claude. "The Structural Study of Myth." Literary Adverb Theory: An Anthology , edited by Julie Rivkin and Michael Ryan, 3rd ed., Wiley Blackwell, 2017, pp. 178-195.
Citations for Edited Books:
If your book is not a first edition, you should note this in the citation. If the book is a revised edition or an edition that includes substantial new content, include the number, name, or year of the edition and the abbreviation "ed." after the book title. "Revised edition" should be abbreviated as "Revised ed." and "Abridged edition" should be "Abridged ed." The edition can usually be found on the title page, as well the copyright page, along with the edition's date.
Author's Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book . Numbered ed., Publisher, Year Published.
Ferraro, Gary, and Susan Andreatta, editors. Cultural Anthropology: An Applied Perspective . 10th ed., Cengage Learning, 2014.
Smith, John. The MLA Sample Paper Book . Revised ed., Books For Us, 2017.
If your edited book has more than one author, refer to the directions above under the heading "Authors."
Also, BibMe.org helps you create your citations with more than one author quickly and easily! Try our MLA formatter!
Citations for Websites:
Wondering how to cite a website in MLA? The most basic entry for an MLA website citation consists of the author name(s), page title, website title, sponsoring institution/publisher, date published, and the DOI or URL.
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Individual Web Page." Title of Website , Publisher, Date, DOI or URL.
Fosslien, Liz, and Mollie West. "3 Ways to Hack Your Environment to Help You Create." Huffpost Preposition Endeavor , Huffington Post, Dec. 7, 2016, www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/3-ways-to-hack-your-environment-to-help-you-create us 580f758be4b02444efa569bc.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears on the website.
For a page with two or more authors, list them in the order they appear on the website. Only the first author's name should be reversed, with the others written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the last author's name. For pages with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by the abbreviation "et al."
If no author is available, begin the citation with the page title.
The page title should be placed within quotation marks. Place a period after the page title within the quotation marks. The page title is followed by the name of the website, which is italicized, followed by a comma.
After the website title, include the sponsoring institution or publisher followed by a comma. The sponsoring institution/publisher can usually be found at the bottom of the website, in the footer. If the name of the publisher is the same as the name as the website, do not include the publisher information in your citation. In MLA format, it is not recommended to include duplicate information for a website.
Next, state the publication date of the page.In some cases, a specific date might not be available, and the date published may only be specific to a month or even a year. Provide whatever date information is available.
End the citation with the URL. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. End the entire citation with a period.
Looking for an MLA formatter to create your website citations quickly and easily? Check out the BibMe MLA citation machine! Our MLA format website creates your citations in just a few clicks.
Citations for Online Journal Articles:
The most basic entry for a journal consists of the author name(s), article title, journal name, volume number, issue number, year published, page numbers, name of website or database where the article was found, and URL or Direct Object Identifier (DOI).
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Journal Article." Title of Journal , vol. number, issue no., Date, Page Range. Database or Website Name , URL or DOI.
Snyder, Vivian. "The Effect Course-Based Reading Strategy Training on the Reading Comprehension Skills of Developmental College Students." Research and Teaching in Developmental Education , vol. 18, no. 2, spring 2002, pp. 37-41. *JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/42802532.
*According to MLA 9th edition, lowercase seasons (spring 2002 not Spring 2002). Do not capitalize seasons.
Most online journal articles have two containers. The first is the journal that the article is in, and the second is the website or database the journal is in.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears in the journal.
For an article written by two authors, list them in the order they appear in the journal. Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the second is written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the second author's name.
Krispeth, Klein, and Stewart Jacobs.
For articles with three or more authors, include the name of the first author in the citation, followed by a comma and the abbreviation "et al."
Jones, Langston, et al.
The article title should be placed within quotation marks. Place a period after the article title within the quotation marks, unless the article title ends with a question mark or exclamation mark. The article title is followed by the name of the journal, which is italicized.
Include the volume number of the journal, but use the abbreviation "vol." You may also need to include the issue number, depending on the journal. Use the abbreviation "no." before the journal's issue number.
Jones, Robert, et al. "Librarianship in the Future." Libraries Today , vol. 5, no. 2, Mar. 2017, pp. 89-103. Database Life , www.dbl.com/6854.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. If the article has a DOI, use the DOI instead of the URL.
Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs)
Simply put, a Digital Object Identifier (usually abbreviated as “DOI”) is an identification number or source link for a document or file. It’s a system that is widely used by journals today. The DOI is comprised of symbols, numbers, and letters.
Example: https://doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1805-z.
This unique number system is very beneficial to readers and authors since it can be used to immediately locate an exact document, even if a host web page or database has altered an article’s URL.
How do I find an article’s DOI?
In print or PDF form, the first place to check is the front page of the article. If it is an online article, look for the DOI near the top of the article, at the very end of the article, or wherever citation information is located. Here are a few examples:
Here is an example from The New England Journal of Medicine:

Here is an example from the bottom of a Nature article:
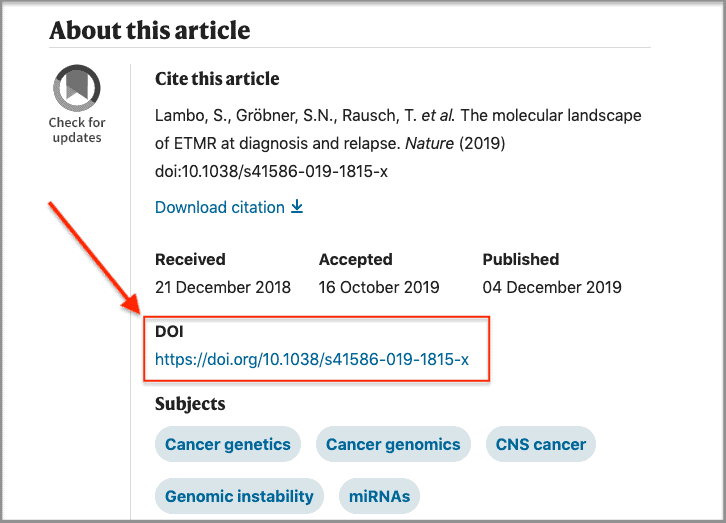
Where in a citation is the DOI included?
If a DOI for an article exists, place it at the end of the citation. Here’s an example for the New England Journal of Medicine article previously shown:
Thomas, Cristina, et al. “Facing Uncertainty.” New England Journal of Medicine , vol. 381, no. 23, 2019, pp. 2253–2259, https://doi:10.1056/nejmcps1906037.
Citations for Blogs:
Blogs can be good sources to use for research papers and projects since many are regularly updated and written by influencers and experts.
Blogs can belong to a single individual, a group of people, or a company. Most entries for a blog include a title for that day’s entry, the date it was posted, and the information.
To cite a blog, you’ll need the following pieces of information: * The author’s name(s) or the name of the company who posted the blog * The title of the individual blog post * The title of the blog * The name of the publisher (if it differs from the name of the author(s) or title of the blog) * The date the blog post was posted * The website address (URL) for the blog post
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Blog Post.” Title of Blog , Publisher, Date Published, URL.
BibMe. “How to Spell in English: British vs. American.” BibMe Blog, www.bibme.org/blog/writing-tips/how-to-spell-in-english-british-vs-american/.
Notice in the above example, the date is missing. If there is no date shown on the blog post, omit it from the full citation.
Williams, Lindsay. “How to Get the Most from Your Online Language Lessons with a Tutor.” Lindsay Does Languages , 2019 Feb. 12, www.lindsaydoeslanguages.com/how-to-get-the-most-from-your-online-language-lessons-with-a-tutor/.
Cite a blog post in the text of the paper using this format:
(Author’s Last name) OR Author’s Last name...
Since there isn’t a page number, only use the author’s last name.
Citations for Newspapers:
The most basic entry for a newspaper consists of the author name(s), article title, newspaper name, publication date, page numbers, and sometimes a URL if found online. Omit volume numbers, issue numbers, and the names of publishers from newspaper citations.
Format if found on a website:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Article." Title of Newspaper's Website , Publication Date, URL.
Format if found on a database:
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Article." Title of Newspaper , Publication Date, Page or Page Range (if available). Title of Database , URL.
MLA format example:
This example is for a print newspaper:
Hageman, William. "Program Brings Together Veterans, Neglected Dogs." Chicago Tribune , 4 Jan. 2015, p. 10.
The full article title should be placed within quotations. Next, state the name of the newspaper in italics.
Towards the end of the citation, include the page numbers on which the article appears with a period. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
Don't forget, the BibMe citation generator in MLA creates citations for you quickly and easily! Also, check out BibMe Plus paper checker, which scans your paper for correct usage of language elements. Have a determiner out of place in your writing? A pronoun spelled incorrectly? An overused adjective ? No worries, BibMe Plus has you covered!
Citations for Photographs:
The most basic entry for a photograph consists of the photographer's name, the title of the photograph, the title of the book, website, or collection where the photograph can be located, the publisher of the photograph or publication where the image was located, the date the photograph was posted or taken, and the page number, location of the museum (such as a city and state), or URL if found online.
Photographer's Last name, First name. "Title of the Photograph." Title of the Book, Website, Collection, or other type of publication where the photograph was found , Date photograph was taken, Page Number (if applicable), Location (such as a city and state if necessary) where the photograph can be found, or URL.
Begin with the name of the photographer or main contributor (if available). This person's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (and any middle name).
For a photograph taken from a publication or website, include the title of the photograph in quotation marks followed by a period. If the photograph does not have a formal title, create a description. If you make your own description, only include a capital at the beginning of the description and at the beginning of any proper nouns. Do not place the description in italics or quotation marks.
Place the title of the publication in italics immediately following the description, followed by a comma.
Digital Image/Photograph found online:
Photograph of the Hudson Area Public Library. JMS Collective , 19 Apr. 2016, www.jmscollective.com/hudson-ny-3/historic-hudson-armory-now-public-\ library/.
*Note that the above photograph does not have a formal title, so the photograph citation contains a description instead.
Photograph or Image viewed in a museum:
Vishniac, Roman. "Red Spotted Purple." Roman Vishniac's Science Work , early 1950s - late 1960s, International Center of Photography at Mana, New Jersey.
Photograph or Image found in a book:
Barnard, Edwin. Photograph of Murray Street, Hobart. Exiled: The Port Arthur Convict Photographs , National Library of Australia, 2010, p. 20.
Citing Social Media in MLA Format:
It's not uncommon to see social media posts included in research projects and papers. Most social media citations use the following structure:
@Username (First name Last name, if known, and differs from handle). "Text of post." Social Media Platform , Date posted, URL.
If the post is a photo or image instead of text, include a description of the image. Only capitalize the first letter in the description and the first letter for any proper nouns. Do not place the description in quotation marks.
If the post is long or includes emojis or links, it is acceptable to include only the beginning of the tweet with an ellipsis at the end of the included portion.
Citing a Twee:
@BibMe. "Need help with MLA essay format? Here are 6 steps to getting it done..." Twitter , 3 Dec. 2018, twitter.com/bibme/status/1069682724716204032.
Citing a Facebook Post:
DeGeneres, Ellen. "Holiday party goals..." Facebook , 21 Dec. 2018, www.facebook.com/ellentv/photos/a.182755292239/10157188088077240/?type=3&theater.
Citing an Instagram Post:
@dualipa. "A lil Hollywood glam brunch! Thank you @variety for by Breakthrough Artist of the Year award and thank you for your continuous support...." Instagram , 2 Dec. 2018, www.instagram.com/p/Bq33SC2BAsr/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link.
Citations for Music:
Citing a Song from the Internet:
To cite this type of source, structure the reference as follows:
Singer's Last Name, First name OR Band Name. "Title of Song." Title of Website or Service , Other Contributors and their roles (if applicable), Version, Date Published, URL.
Lopez, Jennifer. "Us." Spotify , 2 Feb. 2018, open.spotify.com/track/2MMvonKGALz6YOJwaKDO3q.
Citing a song from an album or downloaded:
Singer's Last name, First name OR Band Name. "Title of Song." Title of Album , Other Contributors and their roles (if applicable), Version, Publisher, Date Published or Released.
Lopez, Jennifer. "On the Floor." LOVE? , performance by Pitbull, Island, 2011.
Citations for Films:
The most basic entry for a film consists of the title, director, publisher, and year of release. You may also choose to include the names of the writer(s), performer(s), and the producer(s), depending on who your research focuses on. You can also include certain individuals to help readers locate the exact source themselves.
Example of a common way to cite a film:
Film Title . Directed by First name Last name, performance by First Name Last Name, Publisher, Year.
BibMe: The Movie . Directed by John Smith, performance by Jane Doe, New York Stories, 2017.
If your research focuses on a specific individual, you can begin the citation with that individual's name (in reverse order) and their role. Format it the same way as you would an author's name.
Doe, Jane, performer. BibMe: The Movie . Directed by John Smith, New York Stories, 2017.
If the film is dubbed in English or does not have an English title, use the foreign language title in the citation, followed by a square bracket that includes the translated title.
Citas gobiernan el mundo [ Citations Rule the World ]. Directed by Sara Paul, Showcase Films, 2017.
If the film was found online, such as YouTube or another site, include the name of the website and the URL.
Last name, First name of Individual who posted the video OR Account name. "Film Title." Website Title , other individuals and their roles (if applicable), Publisher, Year Published, URL.
The New York Public Library. "2018 National Book Awards Finalists at NYPL." YouTube , 15 Nov. 2018, youtu.be/edJqg3NuF2Q.
*Note that the New York Public Library was not listed as the publisher of the video. Adding "The New York Public Library" in the citation twice is not necessary.
Since the citation has two titles included (the title of the film and the title of the website), the title of the film is placed in quotation marks and the title of the website is in italics.
Citations for TV/Radio:
The most basic MLA format citation for a radio/TV program consists of the individuals responsible for the creation of the episode (if they're important to your research), the episode title, program/series name, broadcasting network or publisher, the original broadcast date, and the URL.
"The Highlights of 100." Seinfeld , NBC, 2 Feb. 1995.
If your research focuses on a specific individual from a TV or radio broadcast, include their name at the beginning of the citation in the author position.
If relevant, you may also choose to include the names of personnel involved with the program. Depending if the personnel are relevant to the specific episode or the series as a whole, place the personnel names after the program/series name. You may cite narrator(s) preceded by "narrated by", writer(s) preceded by "written by", directors preceded by "directed by", performer(s) preceded by "performance by", and/or producer(s) preceded by "produced by" and then the individual names. Include as many individuals as you like. Write these personnel names in normal order --- do not reverse the first and last names.
"The Highlights of 100." Seinfeld , directed by Andy Ackerman, written by Peter Mehlman, NBC, 2 Feb. 1995.
Also include the name of the network on which the program was broadcasted, followed by a comma.
State the date on which your program was originally broadcasted, followed by a period. When including the URL, follow the date with a comma and place the URL at the end, followed by a period to end the citation. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them.
Citations for Lectures:
The most basic entry for a lecture consists of the speaker's name, presentation title, date conducted, and the name and location of the venue.
Speaker's Last name, First name. Title of Lecture . Date Conducted, Venue, Location.
Pausch, Randy. Really Achieving Your Childhood Dreams . 18 Sept. 2007, McConomy Auditorium, Pittsburgh.
Begin the citation with the name of the speaker. This person's name should be reversed. If the lecture has a title, place it in the citation in italics, followed by a period. State the date on which the lecture was conducted, followed by a comma. Conclude your citation with the location/venue name and the city in which it occurred, separated by a comma.
Citations for Encyclopedias
The most basic entry for an encyclopedia consists of the author name(s), article title, encyclopedia name, publisher, and year published.
Last Name, First Name. "Article Title." Encyclopedia Name , Publisher, Year Published.
Smith, John. "Internet." Encyclopedia Britannica , 2012.
Notice that the name of the publisher was not included in the example above. Only include the name of the publisher if it differs from the name of the encyclopedia. Encyclopedia Britannica is the name of the encyclopedia AND the name of the publisher. It is not necessary to include Encyclopedia Britannica twice in the citation.
If there are no authors for the article, begin the citation with the article title instead.
"Media." World Book Encyclopedia , 2010.
If the encyclopedia arranges articles alphabetically, do not cite the page number(s) or number of volumes. If articles are not arranged alphabetically, you may want to include page number(s) and/or volume number, which is preceded by the abbreviation "vol." The volume should be cited after the encyclopedia name (or any edition), and before any publication information. After the publication year, include the page numbers on which the article appears, along with a period. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
Saunders, Bill. "Treasure." Encyclopedia Britannica , vol. 18, 2012, p. 56.
If the encyclopedia entry is found on a website, use the following structure:
Last name, First name. "Encyclopedia Entry." Title of Encyclopedia Website , Publisher, Year published, URL.
Citations for Magazines:
The most basic entry for a magazine consists of the author name(s), article title, magazine name, the volume and issue numbers (if available), publication date, page numbers, and URL if found online.
Last name, First name. "Article Title." Magazine Name , vol. number, issue no., Publication Date, Page Numbers or URL.
Print example:
Pratt, Sybil. "A Feast of Tradition." BookPage , Oct. 2017, p. 8.
Online example:
Geagan, Kate. "Sweeter Swaps: How to Choose Sustainable Sweeteners." Clean Eating , no. 83, Nov./Dec. 2018, pp. 36-37. Flipster , cleaneating.eoncontent.ebscohost.com/1927216#&pageSet=19.
The first author's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name). The name should not be abbreviated and should be written exactly as it appears in the magazine.
For an article written by two or more authors, list them in the order as they appear on the title page. Only the first author's name should be reversed, while the others are written in normal order. Separate author names by a comma, and place the word "and" before the last author's name. For articles with three or more authors, only include the first author, followed by the abbreviation "et al."
The full article title should be placed within quotations. Unless there is punctuation that ends the article title, place a period after the title within the quotations. Next, state the name of the magazine in italics.
If volume and issue numbers are available, include them in the citation. Use the abbreviations “vol.” and “no.” before the volume number and issue number.
Example: vol. 6, no. 1
The date the magazine was published comes directly after the volume and issue number. Use whichever date the magazine includes, whether it's a complete date, a period spanning two months, a season (lowercased), or just a month and year. Follow this information with a comma.
Include the page number(s) on which the article appears. Cite all inclusive page numbers --- if the article spans pages that are not consecutive, cite only the first page, followed by a plus sign.
If the magazine article was found online, include the DOI or URL. Use a DOI instead of a URL when it is available. You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx. End the citation with a period.
Citations for Interviews:
Begin your citation with the name of the person interviewed. This person's name should be reversed, with a comma placed after the last name and a period after the first name (or any middle name).
For an interview that has been broadcast or published, if there is a title, include it after the name of the person interviewed.
Jolie, Angelina. "Being a Mother." Interview conducted by Steve Kroft, 60 Minutes , CBS, 3 Feb. 2009.
If there is no title, use the word "Interview" in place of a title and do not use quotation marks or italics. If the interviewer's name is known, add it, preceded by "Conducted by", after the word "Interview". Do not reverse the interviewer's name.
Jenkins, Lila. Interview. Conducted by Jessica Grossman. 5 Mar. 2017.
For published interviews found online, include the title of the website after the title of the interview. In addition, add the URL at the end of the citation.
Michaels, Jamye. "Fighting to Survive." Women's Magazine of Life , 2 Nov. 2016, www.womensmagazine.com/fightingtosurvive.com.
Citations for Dissertations and Theses:
In order to obtain a degree, most colleges and universities require students to submit a dissertation or thesis towards the end of their academic track. Dissertations and theses are lengthy essays or in-depth research projects that relate to the scope of the student’s learning.
For example, if a student is close to obtaining their Master’s in Library Science, the student could study and write about the Internet searching habits of elderly individuals, or perhaps focus on the research skills of economically disadvantaged adults.
Upon completion, this individual assignment is often presented to the main directors, committee members, or professors at the school for approval.
A dissertation is generally assigned to students who are completing their doctorate degree, and many graduate schools require students to hand in a thesis to obtain a master’s degree.
Since so much research and work went into these scholarly projects, and new ideas and conclusions are often produced, many colleges and universities publish the completed papers. You can find these projects on many school websites and databases.
Here’s one way you can reference a dissertation or thesis:
Author’s Last Name, First name. Title of Dissertation or Thesis . Year Completed. University or College, Degree Abbr. Database , DOI or URL.
Kim, Kee Han. Development of an Improved Methodology for Analyzing Existing Single-Family Residential Energy Use . 2014. Texas A & M U, PhD. ProQuest , https://ezproxy.nypl.org/socabs/docview/1665251619/abstract/E9D36166E31040AEPQ/1?accountid=35635.
Fletcher, Marissa. Influences of Nutrition and Pathogenicity from a Microbial Diet on Immunity and Longevity in Caenorhabditis Elegans . 2012. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, PhD. DSpace@MIT , https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/120633.
Using Visuals
Including a visual in your project is a great way to make information come to life, as visuals can complement written work and enhance understanding.
Photographs, maps, charts, graphs, line drawings, musical scores, and tables are images that can be included in a project.
Follow these directions to add an image to your research paper:
- Images should be placed close to where they’re mentioned in the text.
- Provide a brief explanation about the image in the written portion of the paper, but do not write out all data shown in the image. Doing so would make the image unnecessary. (See the visual “Table example” at the end of this section.)
Correct example: Table 1 shows commonly used words in Shakespeare’s plays and their English translation.
Incorrect example: Table 1 shows commonly used words in Shakespeare’s plays and their English translation. Brave translates to handsome , character means a letter or word , egal means equal , fancy is a term for desire , and honest translates to pure .
- Tables are titled Table X, figures are Fig. X, and examples are Ex. X.
- Any type of image that includes an illustration is considered a “Figure”.
- Musical scores or sheet music are considered “Examples”.
- If the information below the image contains all of the source information, a full reference on the “Works Cited” page is not necessary.
- Double space everything.
- The image should have the same 1-inch margins as the rest of the paper.
Check out the examples below to see how tables, figures, and musical scores are arranged.
Table Example:
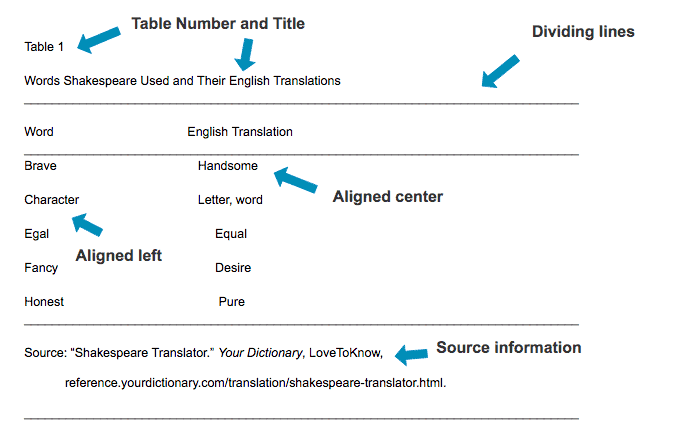
Figure Example:
Musical score example:
Your “Works Cited” Page
An MLA "Works Cited" or MLA "Work Cited" page contains all of the citations for a project.
- This page sits on its own and is found at the end of a project.
- If there is only one citation on the page, title the page: Work Cited. While it might seem silly to have a full page dedicated to one citation, a “Work Cited” page in MLA is still necessary. If there are multiple citations on the page, title the page: Works Cited.
- Double space the entire list of works cited.
- Include the writer's last name and the page number, at the top right corner of the page.
- Every in-text or parenthetical citation in the body of the project should correspond with its full citation listed on the MLA “Works Cited” or “Work Cited” page.
- All full citations in MLA formatting have a hanging indent. This means that the first line of the citation sits flush against the left margin. The second line, and any subsequent lines, are indented in another half inch. If you need a visual, all full citations on this page have a hanging indent.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first letter found in the citation.
- If there are multiple sources by the same author, only include the author's name in the first citation. For each citation afterwards, MLA formatting requires you to include three dashes and a period. Organize the citations by the title.
Example of a Works-Cited List with Multiple Works by Same Author:
Riggs, Ransom. Miss Peregrine's Home for Peculiar Children . Quirk, 2011.
---. Tales of the Peculiar . Dutton, 2016.
- When alphabetizing by titles, ignore “A,” “An,” and “The,” and use the next part of the title.
- If the title starts with a number, place the title where it would belong if the number was spelled out.
MLA formatting example:
1492: The Year Our World Began would be alphabetized under F (for fourteen)
Sample Works Cited:

Formatting Your Header:
The first page of your MLA format paper should include a header. An MLA cover page, or MLA title page, that sits on its own isn't necessary or recommended.
MLA heading format includes the following pieces of information, styled like this, in this order:
Your professor or teacher's name
The class and/or course number
Date of submission
- Double space everything on the page.
- In the top right corner, include your last name and the page number.
- The title should be centered in the middle of the page.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read for the entire paper.
- MLA paper format requires 12-point font, or another size close to it.
Sample MLA Header:

Using BibMe.org to Create Citations for your MLA Works Cited Page or MLA Bibliography
Wondering how to use MLA format? The BibMe automatic MLA format generator formats your citations for you. Enter a title, web address, ISBN number, or other identifying information into the MLA format template to automatically cite your sources. If you need help with BibMe.org or our citation machine in MLA, click here on more styles .
Try This Out:
The BibMe service is an extremely helpful resource that helps you create your citations for your project, but there's more. The BibMe service also has a feature that will help to proofread your entire MLA format essay. The BibMe Plus paper checker scans for proper spelling, punctuation, language elements, and syntax. It will tell you if a language element, such as a preposition , conjunction , or interjection , is a bit off. It also has a built-in plagiarism checker , which scans papers for instances of accidental plagiarism. Try it out now!
More Information:
Here's more information on the previous handbooks. There's further good information here , including MLA format examples and examples of MLA in-text citations.
Background Information and History:
The Modern Language Association was developed in 1883 and was created to strengthen the study and teaching of languages and literature. With over 25,000 current members worldwide, the Modern Language Association continuously strives to keep its members up-to-date on the best practices, methods, and trends related to language and literature. The Modern Language Association boasts an annual conference, journal, an online communication platform, numerous area-focused committees, and one of its most popular publications, the MLA Handbook, now in its 9th edition.
Updated June 25, 2021
Edited and written by Elise Barbeau and Michele Kirschenbaum. Elise is a citation expert and has her master’s degree in public history/library science. She has experience in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing. Michele is a certified library media specialist who loves citations and teaching. She’s been writing about citing sources since 2014.
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: MLA Annotated Bibliography
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
Annotated Bibliography
- Updated MLA Ninth Edition Annotated Bibliography Template
This template includes a space to add your topic and thesis statement as this is preferred for the annotated bibliography assignments in ENC courses taught at IRSC. Always follow your professor's instructions over any instructions on this LibGuide or inside the MLA Handbook.
Your professor may ask that you create an annotated bibliography in MLA style. An annotated bibliography is similar to the Works Cited page found at the end of a paper. The paper formatting is the same but instead of following a full research paper, the student will write a brief annotation for each source which will directly follow the source's Works Cited entry. The annotations contain descriptive or evaluative comments about your sources. Annotations should be short, typically no longer than one paragraph. Indent the annotation an inch from the start of the entry. Each citation should adhere to MLA guidelines. The title might be 'Annotated Bibliography' or 'Annotated List of Works Cited'.
Below is an example of an annotated bibliography in MLA style. You are welcome to use the template linked above to get you started with the correct formatting.

- << Previous: Formatting Your Works Cited List
- Next: MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 5:26 PM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla
- ENC Learning Commons
Annotated Bibliography
- Sample MLA Annotation
- URL: https://libguides.enc.edu/writing_basics/annotatedbib
- Definition and Descriptions
- Evaluation Tools
- Parts of an Annotation
- Sample APA Annotation
- Sample ASA Annotation
- Sample Chicago Annotation
Research Tools
Modern Language Association (MLA) Annotations
Creating an annotated bibliography in MLA style
The MLA Handbook is on reserve at the IRC desk on the Ground Floor.
General guidelines
Some anno tatio ns are merely descriptive , summarizing the authors' qualifications, research methods, and arguments. Your professor might also ask you to identify the authors' theoretical frameworks .
Many annotations evaluate the quality of scholarship in a book or article. You might want to consider the logic of authors' arguments, and the quality of their evidence. Your findings can be positive, negative, or mixed.
Your professor might also want you to explain why the source is relevant to your assignment.
Sample Page: MLA-formatted annotated bibliography
Battle, Ken. “Child Poverty: The Evolution and Impact of Child Benefits.” A Question of Commitment: Children's Rights in Canada . Ed. Katherine Covell and R.Brian Howe. Waterloo, ON: Wilfrid Laurier University Press. 2007. 21-44.
Ken Battle draws on a close study of government documents, as well as his own research as an extensively-published policy analyst, to explain Canadian child benefit programs. He outlines some fundamental assumptions supporting the belief that all society members should contribute to the upbringing of children. His comparison of child poverty rates in a number of countries is a useful wake-up to anyone assuming Canadian society is doing a good job of protecting children. Battle pays particular attention to the National Child Benefit (NCB), arguing that it did not deserve to be criticized by politicians and journalists. He outlines the NCB’s development, costs, and benefits, and laments that the Conservative government scaled it back in favour of the inferior Universal Child Care Benefit (UCCB). However, he relies too heavily on his own work; he is the sole or primary author of almost half the sources in his bibliography. He could make this work stronger by drawing from others' perspectives and analyses. However, Battle does offer a valuable source for this essay, because the chapter provides a concise overview of government-funded assistance currently available to parents. This offers context for analyzing the scope and financial reality of child poverty in Canada.
Kerr, Don and Roderic Beaujot. “Child Poverty and Family Structure in Canada, 1981-1997.” Journal of Comparative Family Studies 34.3 (2003): 321-335.
Sociology professors Kerr and Beaujot analyze the demographics of impoverished families. Drawing on data from Canada’s annual Survey of Consumer Finances, the authors consider whether each family had one or two parents, the age of single parents, and the number of children in each household. They analyze child poverty rates in light of both these demographic factors and larger economic issues. Kerr and Beaujot use this data to argue that
Rules! rules! rules!
The MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers states the following formatting rules:
- The text and the works cited list should be double-spaced.
- Number your pages at the top right of the page.
- Reference list entries must have a hanging indent (to do this in Microsoft Word 2003, select the citation, click Format, then Paragraph, then Special, and choose Hanging).
- There should be 1 inch (2.54 cm) margins all around (top, bottom, left, and right) on each page.
- Use Times Roman font, or a similar serif font.
- Capitalize each important word (noun or verb) in a book or article title
- Each paragraph should be indented.
More Sample Annotations
Cornell University Library offers these instructions on preparing an annotated bibliography.
- << Previous: Sample Chicago Annotation
- Last Updated: Nov 7, 2023 8:23 AM

MLA Citation Guide (9th edition) : Works Cited and Sample Papers
- Getting Started
- How do I Cite?
- In-Text Citations
- Works Cited and Sample Papers
- Additional Resources
Header Image

Quick Rules for an MLA Works Cited List
Your research paper ends with a list of all the sources cited in your paper. Here are some quick rules for this Works Cited list:
- Begin the works cited list on a new page after the text.
- Name it "Works Cited," and center the section label in bold at the top of the page.
- Order the reference list alphabetically by author's last name.
- Double-space the entire list (both within and between entries).
- Apply a hanging indent of 0.5 in. to each entry. This means that the first line of the reference is flush left and subsequent lines are indented 0.5 in. from the left margin.
Sample Paper with Works Cited List
The Modern Language Association (MLA) has compiled several sample papers that include explanations of the elements and formatting in MLA 9th edition.
MLA Title Pages
MLA Title Page: Format and Template This resource discusses the correct format for title pages in MLA style and includes examples.
- << Previous: In-Text Citations
- Next: Additional Resources >>
- Last Updated: Jun 24, 2022 12:43 PM
- URL: https://paperpile.libguides.com/mla
Using MLA Format

Document Sources
Works cited quick guide.
Learn how to use the MLA format template.
Digital Citation Tool
Build citations with our interactive template.
In-Text Citations
Get help with in-text citations.
Endnotes and Footnotes
Read our guide about using notes in MLA style.

Set Up Your Paper
Setting up a research paper.
Get our guidelines for setting up academic research papers.
Formatting Captions
Learn how to format captions.
Sample Papers
Read sample papers written in MLA style.
Annotated Bibliographies
Learn how to set up an annotated bibliography.

Get Writing and Teaching Tips
Ask the mla.
Browse answers and ask MLA editors questions.
Writing Tips
Improve your writing with these suggestions.
Teaching Resources and Advice
Get teaching advice, lesson plans, and activities.
Test your knowledge with these fun quizzes.
Recent questions from Ask the MLA
How do i alphabetize irish surnames in the works-cited list.
This post explains how to alphabetize Irish surnames Read More
How do I alphabetize a works-cited-list entry that begins with a hashtag or another symbol?
The MLA recommends that writers should “ignore symbols when alphabetizing” (“How”). This includes hashtags. Thus, if an entry begins with a hashtag or another symbol,… Read More
How do I cite a work accessed through Wayback Machine ?
Wayback Machine is an archive of websites that lives on the Internet Archive ’s site, so you would treat the Internet Archive as the container of… Read More
How do I style the title of a fairy tale?
Fairy tales are typically enclosed in quotation marks, in the style of other short-form works. Some people may not know that Disney’s 1989 film The … Read More
How do I cite an anonymously translated poem?
If a translator’s name is not provided in the source, then skip that element in your works-cited-list entry. Follow the MLA template of core elements,… Read More
How do I cite a work that has incorrect citation information on its cover sheet?
Some works, especially works contained in databases, may list citation information for the work on a cover sheet or in a footer. If that citation… Read More
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- A complete guide to MLA in-text citations
MLA In-text Citations | A Complete Guide (9th Edition)
Published on July 9, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024.
An MLA in-text citation provides the author’s last name and a page number in parentheses.
If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by “ et al. ”
If the part you’re citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range. If you want to cite multiple non-consecutive pages at the same time, separate the page numbers with commas.
| Number of authors | Example |
|---|---|
| 1 author | (Moore 37) |
| 2 authors | (Moore and Patel 48–50) |
| 3+ authors | (Moore et al. 59, 34) |
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Where to include an mla in-text citation, citing sources with no author, citing sources with no page numbers, citing different sources with the same author name, citing sources indirectly, frequently asked questions about mla in-text citations.
Place the parenthetical citation directly after the relevant quote or paraphrase , and before the period or other punctuation mark (except with block quotes , where the citation comes after the period).
If you have already named the author in the sentence, add only the page number in parentheses. When mentioning a source with three or more authors outside of parentheses, use “and others” or “and colleagues” in place of “et al.”
- MLA is the second most popular citation style (Smith and Morrison 17–19) .
- According to Smith and Morrison , MLA is the second most popular citation style (17–19) .
- APA is by far “the most used citation style in the US” (Moore et al. 74) , but it is less dominant in the UK (Smith 16) .
- Moore and colleagues state that APA is more popular in the US than elsewhere (74) .

Combining citations
If a sentence is supported by more than one source, you can combine the citations in a single set of parentheses. Separate the two sources with a semicolon .
Livestock farming is one of the biggest global contributors to climate change (Garcia 64; Davies 14) .
Consecutive citations of the same source
If you cite the same source repeatedly within a paragraph, you can include the full citation the first time you cite it, then just the page number for subsequent citations.
MLA is the second most popular citation style (Smith and Morrison 17–19) . It is more popular than Chicago style, but less popular than APA (21) .
You can do this as long as it remains clear what source you’re citing. If you cite something else in between or start a new paragraph, reintroduce the full citation again to avoid ambiguity.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
For sources with no named author , the in-text citation must match the first element of the Works Cited entry. This may be the name of an organization, or the title of the source.
If the source title or organization name is longer than four words, shorten it to the first word or phrase in the in-text citation, excluding any articles ( a, an, and the ). The shortened title or organization name should begin with the word the source is alphabetized by in the Works Cited.
Follow the general MLA rules for formatting titles : If the source is a self-contained work (e.g. a whole website or an entire book ), put the title in italics; if the source is contained within a larger whole (e.g. a page on a website or a chapter of a book), put the title in quotation marks.
| Full source title or organization name | In-text citation |
|---|---|
| ( 187) | |
| “Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions” | (“Sources”) |
| “A Quick Guide to Proofreading” | (“Quick Guide”) |
| National Academy of Sciences and the Royal Academy | (National Academy 24) |
If a source does not have page numbers but is divided into numbered parts (e.g. chapters, sections, scenes, Bible books and verses, Articles of the Constitution , or timestamps), use these numbers to locate the relevant passage.
If the source does not use any numbering system, include only the author’s name in the in-text citation. Don’t include paragraph numbers unless they are explicitly numbered in the source.
| Source type | What to do | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Source divided into numbered parts | Add a comma after the author and give a paragraph, section, or chapter number with a relevant abbreviation. | (Luxemburg, ch. 26) |
| with numbered lines | Include the act, scene, and line numbers, separated by periods, instead of a page number. | ( 1.2.95) |
| Audiovisual source | Include the time range as displayed in the media player. | (Wynn 10:23–45) |
| Source with no numbered divisions | Include only the author’s name (or, if there is no author, the shortened title). | (Rajaram) |
Note that if there are no numbered divisions and you have already named the author in your sentence, then no parenthetical citation is necessary.
If your Works Cited page includes more than one entry under the same last name, you need to distinguish between these sources in your in-text citations.
Multiple sources by the same author
If you cite more than one work by the same author, add a shortened title to signal which source you are referring to.
In this example, the first source is a whole book, so the title appears in italics; the second is an article published in a journal, so the title appears in quotation marks.
Different authors with the same last name
To distinguish between different authors with the same last name, use the authors’ initials (or, if the initials are the same, full first names) in your in-text citations:
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Sometimes you might want to cite something that you found quoted in a secondary source . If possible, always seek out the original source and cite it directly.
If you can’t access the original source, make sure to name both the original author and the author of the source that you accessed . Use the abbreviation “qtd. in” (short for “quoted in”) to indicate where you found the quotation.
In these cases, only the source you accessed directly is included in the Works Cited list.
You must include an MLA in-text citation every time you quote or paraphrase from a source (e.g. a book , movie , website , or article ).
Some source types, such as books and journal articles , may contain footnotes (or endnotes) with additional information. The following rules apply when citing information from a note in an MLA in-text citation :
- To cite information from a single numbered note, write “n” after the page number, and then write the note number, e.g. (Smith 105n2)
- To cite information from multiple numbered notes, write “nn” and include a range, e.g. (Smith 77nn1–2)
- To cite information from an unnumbered note, write “un” after the page number, with a space in between, e.g. (Jones 250 un)
If a source has two authors, name both authors in your MLA in-text citation and Works Cited entry. If there are three or more authors, name only the first author, followed by et al.
| Number of authors | In-text citation | Works Cited entry |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | (Moore 37) | Moore, Jason W. |
| 2 authors | (Moore and Patel 37) | Moore, Jason W., and Raj Patel. |
| 3+ authors | (Moore et al. 37) | Moore, Jason W., et al. |
If a source has no author, start the MLA Works Cited entry with the source title . Use a shortened version of the title in your MLA in-text citation .
If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g. a chapter number, or a timestamp for a video or audio source) to identify the relevant passage in your in-text citation. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only the author’s name (or the title).
If you already named the author or title in your sentence, and there is no locator available, you don’t need a parenthetical citation:
- Rajaram argues that representations of migration are shaped by “cultural, political, and ideological interests.”
- The homepage of The Correspondent describes it as “a movement for radically different news.”
Yes. MLA style uses title case, which means that all principal words (nouns, pronouns , verbs, adjectives , adverbs , and some conjunctions ) are capitalized.
This applies to titles of sources as well as the title of, and subheadings in, your paper. Use MLA capitalization style even when the original source title uses different capitalization .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). MLA In-text Citations | A Complete Guide (9th Edition). Scribbr. Retrieved July 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/in-text-citations/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to format your mla works cited page, block quoting in mla style, how to cite a book in mla, what is your plagiarism score.

Serving the Community College of Vermont & Vermont State University
How To Do Research

MLA 9th Edition Citation Style
Pause or complete the video before closing. Otherwise it will keep playing.
MLA (Modern Language Association) format is most commonly used to cite sources in the humanities. The following examples use MLA 9th edition.
Parenthetical Citation
MLA format uses a parenthetical citation, which is a brief mention in the text of your paper that leads the reader to the complete information about that reference. It usually appears at the end of a sentence. A parenthetical citation involves placing relevant source information in parentheses after a quote or a paraphrase. The author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your works cited page.
Seed says of Dracula “in short, he is a combination of Gothic villain, Regency rake, and monster” (62).
Dracula, “…is a combination of Gothic villain, Regency rake, and monster” (Seed 62).
Seed believes that Dracula is a mix of scoundrel, ogre, and devilish man (62).
Reference List
Parenthetical citations will refer your reader to the full list of sources you used. This list is at the end of your paper.
- Works Cited : A list of sources that are directly quoted, summarized or paraphrased in the writing.
- Bibliography : A list of sources that were used in the background research, development of ideas, and any other research that contributed to the writing.
For both a works cited page and bibliography, references are listed in alphabetical order by author’s last name. Each reference citation is made up of the same elements that always appear in the same order. Leave out any that aren't available for or don't apply to a source.
- One author: Last Name, First Name.
- Two authors: Author 1 Last Name, First Name, and Author 2 First Name Last Name.
- Three or more authors: Author 1 Last Name, First Name, et al.
- Title: The title or description of the work.
- Title of container: The title or description of the larger work this source is part of, such as a journal, an anthology, or a podcast series.
- Other contributors : This can include editors, translators, and others. Include the contributor's role in addition to their name (for example, "Edited by Ana Jones").
- Version: The edition, revision, or other version of the work. Not included for first editions.
- Number: Where the work appears if it is part of a sequence, such as the volume, issue, or episode number.
- Publisher: Included unless the work is self-published, a journal, or a website whose site name and publisher are very similar.
- Publication date: If no formal publication date exists, provide the most exact date available.
- Location : Where the work appears within its container, such as the page range for a chapter in a book. For online works, this is the DOI or URL.
MLA Style | Reference List Citation Format Examples
- Generative AI
Electronic articles
Seed, David. "The Narrative Method of Dracula." Nineteenth-Century Fiction , vol. 41, no. 1, 1985, pp. 61-75. JSTOR , https://doi.org/10.2307/3044836.
Electronic articles with no DOI
Caesar, Terry Paul. “Slavery and Motherhood in Toni Morrison’s ‘Beloved.’” Revista de Letras , vol. 34, 1994, pp. 111–20. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/27666617.
Print articles
Smith, Jane. "Student Search Strategies." College Research Quarterly, vol. 79, no.23, 2010, pp. 42-49.
Hopkins, Lisa. Bram Stoker: A Literary Life. Palgrave Macmillan, 2007.
Books with no author
New Concise World Atlas . Oxford University Press, 2001.
eBooks in library databases
Collins, Wilkie, and Steve Farmer. Moonstone. Broadview Press, 1999. EBSCO eBook Collection , search.ebscohost.com.hrt-proxy.libraries.vsc.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,cookie&db=nlebk&AN=313817&site=eds-live&scope=site&profile=eds-ccv.
(If a DOI is present, use that instead of the URL.)
Kindle eBook
Rowley, Hazel. Franklin and Eleanor: An Extraordinary Marriage. Kindle ed., Farrar, 2010.
eBook from Google Books or an eBook website
Wallace, Mike. Greater Gotham: A History of New York City from 1898 to 1919. Oxford University Press, 2017, Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=AnUzDwAAQBAJ&lpg=PP1&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false.
Page from a Website
Gaiman, Neil. "The Neil Story (With Additional Footnote)." Neil Gaiman , May 17, 2017. journal.neilgaiman.com/2017/05/the-neil-story-with-additional-footnote.html.
Page from a Website with No Author
"Well-Being Concepts". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , May 31, 2016, www.cdc.gov/hrqol/wellbeing.htm. Accessed 11 Nov. 2022.
Note : Date of access is not required but is recommended, especially if access or the content is likely to change.
Video From a Library Database
I Am Not Your Negro: James Baldwin and Race in America . Directed by Raoul Peck, Kino Lorber, 2016. Kanopy , www.kanopy.com/en/castleton/video/542400.
If emphasizing a specific performer or director, you can list them as the author.
Sennott, Rachel, performer. Shiva Baby . Directed by Emma Seligman. Utopia, 2020. Kanopy , www.kanopy.com/en/castleton/video/11394284.
YouTube Video
MrsBoschert. “Hellenistic Art.” YouTube , 23 Feb. 2010, https://youtu.be/hvryEuuTtNY.
Online works of art, photographs, maps, or charts
Bearden, Romare. The Train . 1975. MOMA, www.moma.org/collection/works/65232?locale=en.
- << Previous: Citing Sources
- Next: APA Style >>
Additional Resources
- MLA Official Site The official site of the MLA Style Guide
- MLA Interactive Practice Template This template is a tool for teaching and learning MLA style, not a citation generator. To verify that your entry is correct, consult the MLA Handbook.
- MLA Format (OWL Purdue Univ.)
- MLA Sample Works Cited (OWL, Purdue Univ.)
- How do I cite generative AI in MLA style? - Ask the MLA
Printable Cheat Sheet
- MLA Cheat Sheet
- Tutorial: MLA 9th Edition Citation Style
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 5:17 PM
- URL: https://libraries.vsc.edu/research

Generative Artificial Intelligence
- A Very Brief Introduction to Generative AI
- Information Discovery with AI
Citation and Attribution with AI Tools
Chicago style.
- Copyright and Scholarly Communication
If you choose to use generative AI tools for course assignments, academic work, or other forms of published writing, you should give special attention to how you acknowledge and cite the output of those tools in your work. You should always check with your instructor before using AI for coursework.
As with all things related to AI, the norms and conventions for citing AI-generated content are likely to evolve over the next few years. For now, some of the major style guides have released preliminary guidelines. Individual publishers may have their own guidance on citing AI-generated content.
Here are some fundamental ideas that hold true for citing AI generated content, no matter which citation style you're using:
- Do cite or acknowledge the outputs of generative AI tools when you use them in your work. This includes direct quotations and paraphrasing, as well as using the tool for tasks like editing, translating, idea generation, and data processing.
- Generative AI tools can create fake citations.
- These tools may cite a real piece of writing, but the cited content may be inaccurate.
Be flexible in your approach to citing AI-generated content, because emerging guidelines will always lag behind the current state of technology, and the way that technology is applied. If you are unsure of how to cite something, include a note in your text that describes how you used a certain tool.
When in doubt, remember that we cite sources for two primary purposes: first, to give credit to the author or creator; and second, to help others locate the sources you used in your research. Use these two concepts to help make decisions about using and citing AI-generated content.
- APA: How to Cite ChatGPT Released April 7, 2023
When you cite AI-generated content using APA style, you should treat that content as the output of an algorithm , with the author of the content being the company or organization that created the model. For example, when citing ChatGPT, the author would be OpenAI, the company that created ChatGPT.
Here are some guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in APA style:
- When you reference this content directly in your text, you should include an in-text citation, and an associated entry in your reference list.
- If you have used AI tools for some part of your research, you should describe that use in your introduction or methods section, and include the prompts that you used.
When referencing shorter passages of text, you can include that text directly in your paper. You might also include an appendix or link to an online supplement that includes the full text of long responses from a generative AI tool.
Author. (Date). Name of tool (Version of tool) [Large language model]. URL
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
In-Text Citation Example:
(OpenAI, 2023)
- Chicago Manual of Style, Citing Content Developed or Generated by Artificial Intelligence Released in spring 2023
Chicago style requires that you cite AI-generated content in your work by including either a note or a parenthetical citation, but advises you not to include that source in your bibliography or reference list. The reason given for this is that, because you cannot provide a link to the conversation or session with the AI tool, you should tread that content as you would a phone call or private conversation. However, AI tools are starting to introduce functionality that does allow a user to generate a sharable link to a chat conversation, so this guidance from the Chicago Manual of Style may change.
Here are some general guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in Chicago style:
- Treat the AI tool as the author of the content.
- If possible, describe the prompt used to generate the content in the text, but if that approach doesn't work, you can include that information in a footnote or endnote.
- The date used in your citation will be the date the content was generated.
Format: 1. Author, Title, Publisher, Date, url for the tool.
Example (if information about the prompt has been included within the text of your paper):
1. Text generated by ChatGPT, OpenAI, March 7, 2023, https://chat.openai.com/chat.
Example (including information about the prompt):
1. ChatGPT, response to "Explain how to make pizza dough from common household ingredients," OpenAI, March 7, 2023, https://chat.openai.com/chat.
- How Do I Cite Generative AI in MLA Style? Released March 17, 2023
MLA style is generally more flexible that either APA or Chicago style, so while they provide specific examples for citing commonly used AI tools, they encourage writers to adapt those guidelines to fit the situation.
Hare are some other guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in MLA style:
- Cite the AI tool when you incorporate its output into your work. This includes direct quotations, images, and data, as well as paraphrased content.
- If you use an AI tool for some other purpose, such as translating, editing, or generating an outline, include a note about this somewhere in your paper.
- The MLA views AI-generated content as a source with no author, so you'll use the title of the source in your in-text citations, and in your reference list. The title you choose should be a brief description of the AI-generated content, such as an abbreviated version of the prompt you used.
- If you create a shareable link to the chat transcript, include that instead of the tool's URL.
Format: "Description of chat" prompt. Name of AI tool, version of AI tool, Company, Date of chat, URL.
Example:
"Examples of harm reduction initiatives" prompt. ChatGPT, 23 Mar. version, OpenAI, 4 Mar. 2023, chat.openai.com/chat.
("Examples of harm reduction")
- << Previous: Information Discovery with AI
- Next: Copyright and Scholarly Communication >>
- Last Updated: Jan 29, 2024 8:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.brown.edu/AI
Brown University Library | Providence, RI 02912 | (401) 863-2165 | Contact | Comments | Library Feedback | Site Map
Library Intranet
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual . Both books provide extensive examples, so it's a good idea to consult them if you want to become even more familiar with MLA guidelines or if you have a particular reference question.
Basic in-text citation rules
In MLA Style, referring to the works of others in your text is done using parenthetical citations . This method involves providing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way to do this is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as the examples below will illustrate, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- The source information required in a parenthetical citation depends (1) upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD) and (2) upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page.
In-text citations: Author-page style
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
In-text citations for print sources by a corporate author
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
In-text citations for sources with non-standard labeling systems
If a source uses a labeling or numbering system other than page numbers, such as a script or poetry, precede the citation with said label. When citing a poem, for instance, the parenthetical would begin with the word “line”, and then the line number or range. For example, the examination of William Blake’s poem “The Tyger” would be cited as such:
The speaker makes an ardent call for the exploration of the connection between the violence of nature and the divinity of creation. “In what distant deeps or skies. / Burnt the fire of thine eyes," they ask in reference to the tiger as they attempt to reconcile their intimidation with their relationship to creationism (lines 5-6).
Longer labels, such as chapters (ch.) and scenes (sc.), should be abbreviated.
In-text citations for print sources with no known author
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article) or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
"The Impact of Global Warming in North America." Global Warming: Early Signs . 1999. www.climatehotmap.org/. Accessed 23 Mar. 2009.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Parenthetical citations and Works Cited pages, used in conjunction, allow readers to know which sources you consulted in writing your essay, so that they can either verify your interpretation of the sources or use them in their own scholarly work.
Author-page citation for classic and literary works with multiple editions
Page numbers are always required, but additional citation information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto . In such cases, give the page number of your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:
Author-page citation for works in an anthology, periodical, or collection
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
See also our page on documenting periodicals in the Works Cited .
Citing authors with same last names
Sometimes more information is necessary to identify the source from which a quotation is taken. For instance, if two or more authors have the same last name, provide both authors' first initials (or even the authors' full name if different authors share initials) in your citation. For example:
Citing a work by multiple authors
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
Corresponding Works Cited entry:
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR, doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al.
Franck, Caroline, et al. “Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic.” American Journal of Preventative Medicine , vol. 45, no. 3, Sept. 2013, pp. 327-333.
Citing multiple works by the same author
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author :
Citing two books by the same author :
Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
Citing multivolume works
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
Citing the Bible
In your first parenthetical citation, you want to make clear which Bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
If future references employ the same edition of the Bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
Citing indirect sources
Sometimes you may have to use an indirect source. An indirect source is a source cited within another source. For such indirect quotations, use "qtd. in" to indicate the source you actually consulted. For example:
Note that, in most cases, a responsible researcher will attempt to find the original source, rather than citing an indirect source.
Citing transcripts, plays, or screenplays
Sources that take the form of a dialogue involving two or more participants have special guidelines for their quotation and citation. Each line of dialogue should begin with the speaker's name written in all capitals and indented half an inch. A period follows the name (e.g., JAMES.) . After the period, write the dialogue. Each successive line after the first should receive an additional indentation. When another person begins speaking, start a new line with that person's name indented only half an inch. Repeat this pattern each time the speaker changes. You can include stage directions in the quote if they appear in the original source.
Conclude with a parenthetical that explains where to find the excerpt in the source. Usually, the author and title of the source can be given in a signal phrase before quoting the excerpt, so the concluding parenthetical will often just contain location information like page numbers or act/scene indicators.
Here is an example from O'Neill's The Iceman Cometh.
WILLIE. (Pleadingly) Give me a drink, Rocky. Harry said it was all right. God, I need a drink.
ROCKY. Den grab it. It's right under your nose.
WILLIE. (Avidly) Thanks. (He takes the bottle with both twitching hands and tilts it to his lips and gulps down the whiskey in big swallows.) (1.1)
Citing non-print or sources from the Internet
With more and more scholarly work published on the Internet, you may have to cite sources you found in digital environments. While many sources on the Internet should not be used for scholarly work (reference the OWL's Evaluating Sources of Information resource), some Web sources are perfectly acceptable for research. When creating in-text citations for electronic, film, or Internet sources, remember that your citation must reference the source on your Works Cited page.
Sometimes writers are confused with how to craft parenthetical citations for electronic sources because of the absence of page numbers. However, these sorts of entries often do not require a page number in the parenthetical citation. For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
Miscellaneous non-print sources
Two types of non-print sources you may encounter are films and lectures/presentations:
In the two examples above “Herzog” (a film’s director) and “Yates” (a presentor) lead the reader to the first item in each citation’s respective entry on the Works Cited page:
Herzog, Werner, dir. Fitzcarraldo . Perf. Klaus Kinski. Filmverlag der Autoren, 1982.
Yates, Jane. "Invention in Rhetoric and Composition." Gaps Addressed: Future Work in Rhetoric and Composition, CCCC, Palmer House Hilton, 2002. Address.
Electronic sources
Electronic sources may include web pages and online news or magazine articles:
In the first example (an online magazine article), the writer has chosen not to include the author name in-text; however, two entries from the same author appear in the Works Cited. Thus, the writer includes both the author’s last name and the article title in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader to the appropriate entry on the Works Cited page (see below).
In the second example (a web page), a parenthetical citation is not necessary because the page does not list an author, and the title of the article, “MLA Formatting and Style Guide,” is used as a signal phrase within the sentence. If the title of the article was not named in the sentence, an abbreviated version would appear in a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence. Both corresponding Works Cited entries are as follows:
Taylor, Rumsey. "Fitzcarraldo." Slant , 13 Jun. 2003, www.slantmagazine.com/film/review/fitzcarraldo/. Accessed 29 Sep. 2009.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL , 2 Aug. 2016, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Multiple citations
To cite multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the citations by a semi-colon:
Time-based media sources
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
When a citation is not needed
Common sense and ethics should determine your need for documenting sources. You do not need to give sources for familiar proverbs, well-known quotations, or common knowledge (For example, it is expected that U.S. citizens know that George Washington was the first President.). Remember that citing sources is a rhetorical task, and, as such, can vary based on your audience. If you’re writing for an expert audience of a scholarly journal, for example, you may need to deal with expectations of what constitutes “common knowledge” that differ from common norms.
Other Sources
The MLA Handbook describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the handbook does not describe, making the best way to proceed can be unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of MLA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard MLA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source. For example, Norquest College provides guidelines for citing Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers —an author category that does not appear in the MLA Handbook . In cases like this, however, it's a good idea to ask your instructor or supervisor whether using third-party citation guidelines might present problems.

Harvard Style
- Position of the citation
- Secondary Referencing
- Date of Publication
- Page numbers
- Paraphrasing and Summarising
- Examples of References in Harvard style
- Quick A-Z Examples of References
- Citation Tools and Software

There are many tools available to create references for you automatically. Citing and organising your materials can be made simpler with the help of these tools and you can choose from a variety of citation formats.
Reference Management Software
Reference management software enables you to:
- collect references
- store references and notes
- organise references
- format references in a required referencing style to create a Reference list
- insert in-text citations into a document as you type. This will also generate a reference list or bibliography at the end of your document, based on those citations.
When writing the literature review phase of your thesis or article, having software to make bibliographies and add in-text citations will make the process much simpler and free up your time to work on other research-related tasks. In addition, you can change the citation style in seconds in your document which is convenient for different publishing requirements.
Examples of different packages are:
|
is the online, cloud based free version to store all your references and ATU library provides full support, library guides and training on this for individuals and groups. We have access to the expanded free version of EndNote Online through our subscription to Clarivate's and users are encouraged to log into this resource to access EndNote Online.
EndNote Online allows you to:
Along with the over 4800 citation styles available with EndNote Online, ATU library has developed a customised style template for use with Harvard ( ). Check out our for more details. | |
|
Zotero is a free citation tool that helps store and format bibliographic information. Zotero allows you to easily save citations that you find online, share your citations with others, and create bibliographies. You can use it online and download free software for your computer.
More information on Zotero can be found on their website at and in the ATU guide below.
| |
|
|
Mendeley is a free, easy to use application to help collect, organise, cite and share references. Features of Mendeley include:
More information on Mendeley can be found on their website at
|
Other Citation and Referencing Tools
| Cite Them Right is an online platform designed to advise students on how to reference correctly across eight referencing styles. It is based on the book of the same name in its 12th edition, by Richard Pears and Graham Shields.
There are examples to copy and a ' ' box so you can build your reference on screen and paste it into your assignment in the Reference list.
ATU Library has an institutional subscription to this service making it freely available to all our staff and students in all campuses. | |
|
| Microsoft Word comes with a very useful tool to aid you in referencing various sources of information correctly. It allows you to:
This will be done based on the reference information you provide for the document. You do this by using the ‘References’ tab on its toolbar. |
| MyBib.com is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes references for you to copy straight into your academic assignments in the Reference List.
MyBib can format webpages, books, journals, PDFs, and 30 other sources in over 9,000 different citation styles, including APA 7, Chicago, Harvard and MLA 9. This includes the Cite them Right 12 edition Harvard style which ATU library supports.
You can set up a free account or just use it to create a one-off Reference list. You can copy your generated citations directly into your assignment, or save them to your bibliography for later. You can export them into other citation managers like Zotero or Mendeley, print them directly, or store them in your Google Drive.
Special features:
|
ATU Referencing Tool Guides

- << Previous: Tables
- Next: Contact Us >>
- Last Updated: Jul 4, 2024 9:31 AM
- URL: https://atlantictu.libguides.com/harvard

AI Generator
Footnotes are essential in academic writing, providing readers with additional information, sources, or explanations without disrupting the main text. Footnote Format varies depending on the citation style used. In the Chicago Style , footnotes provide full bibliographic details the first time a source is cited, and a shortened version for subsequent citations. In contrast, MLA Bibliography uses parenthetical in-text citations with a comprehensive bibliography at the end, but can include footnotes for supplementary information.
What are Footnotes?
Footnotes are notes placed at the bottom of a page in a document that provide additional information or citations for the main text. They are indicated by a superscript number within the text and correspond to the matching note at the page’s footer.
Examples of Footnotes
- Brown, John. History of Medieval Europe. (New York: Academic Press, 2010), 45.
- Smith, Jane. “The Renaissance Era.” Journal of European History 23, no. 2 (2012): 78-80.
- Taylor, Lisa. Art in the 19th Century. (London: Art World Publishing, 2005), 123.
- Doe, Mary. Modern Literature. (Chicago: Literary House, 2015), 89.
- Johnson, Mark. “The Industrial Revolution.” History Today 15, no. 4 (2011): 150-152.
- Clark, Susan. Ancient Civilizations. (Boston: History Press, 2008), 66.
- “Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture.” Environmental Studies Journal 30, no. 3 (2019): 110.
- Roberts, Anna. Women in the Workforce. (Philadelphia: Social Science Publishing, 2013), 47.
- “Global Economic Trends.” Economics Review 18, no. 1 (2020): 25.
- Baker, Tom. The Evolution of Technology. (San Francisco: Tech Books, 2011), 77.
- Williams, Paul. Philosophy in the 21st Century. (Austin: Academic House, 2017), 132.
- Nelson, Kevin. “Political Changes in the 20th Century.” Political Science Quarterly 22, no. 2 (2018): 99-101.
- White, Emma. Cultural Shifts in America. (Miami: Culture Press, 2014), 105.
- “Renewable Energy Sources.” Green Technology Journal 27, no. 4 (2021): 210.
- Green, Michelle. Global Health Issues. (Washington: Health World Publishing, 2019), 85.
- Anderson, David. “Advancements in Biotechnology.” Science Today 33, no. 1 (2022): 58.
- Lee, Robert. Urban Development. (Seattle: City Press, 2009), 94.
- Harris, Rachel. Education Reforms. (Denver: Education World, 2012), 74.
- “The Digital Revolution.” Tech Innovations Journal 29, no. 2 (2023): 115.
- Martinez, Laura. Immigration Policies. (Los Angeles: Policy Press, 2016), 120.
OSCOLA Footnotes Examples
- John Smith, Constitutional Law (Oxford University Press 2015) 45.
- Jane Doe, ‘Judicial Review in the Modern Era’ (2018) 23 Oxford Journal of Legal Studies 78.
- Mary Johnson, ‘Corporate Governance Reforms’ [2020] Law Quarterly Review 123.
- David Brown, ‘Human Rights in International Law’ (2005) 12(3) European Journal of International Law 345.
- John Taylor, Criminal Law: Theory and Doctrine (3rd edn, Hart Publishing 2013) 89.
- Anna White, Family Law (Sweet & Maxwell 2010) 66.
- Michael Green, ‘Environmental Regulations and Compliance’ (2017) 9(2) Journal of Environmental Law 110.
- Susan Clark, Land Law (2nd edn, Palgrave Macmillan 2011) 47.
- Kevin Roberts, ‘Commercial Law in the Digital Age’ [2019] Business Law Review 25.
- Emma Harris, Tort Law (Oxford University Press 2008) 132.
Footnotes Examples in Research
- John Smith, The Impact of Climate Change on Coastal Ecosystems (Springer 2019), 45.
- Jane Doe, “Renewable Energy Adoption in Urban Areas,” Energy Policy 34, no. 2 (2020): 112-115.
- Mark Johnson, Advanced Microbiology (3rd ed., Wiley 2015), 89.
- Susan Clark, “Genetic Modifications in Agriculture,” Journal of Agricultural Science 42, no. 1 (2018): 75-80.
- Paul Taylor, History of Medieval Europe (Routledge 2014), 123.
- Mary White, “The Renaissance Art Movement,” Art History Review 27, no. 3 (2016): 198-200.
- Kevin Roberts, Economic Theories and Policies (Oxford University Press 2017), 66.
- Lisa Harris, “The Role of Women in World War II,” Historical Journal 22, no. 4 (2019): 150-152.
- Robert Brown, Environmental Science: An Introduction (Pearson 2021), 77.
- Emily Davis, “Social Media’s Influence on Teenagers,” Journal of Social Research 19, no. 2 (2017): 58-61.
Footnotes in Word
Place the Cursor : First, place your cursor at the point in the text where you want to add the footnote.
Insert Footnote : Go to the “References” tab on the ribbon, Click on “Insert Footnote.”
Type the Footnote Text : After clicking “Insert Footnote,” Word will automatically place a superscript number at the cursor point and move the cursor to the bottom of the page. Type the text of your footnote here.
Format Footnotes : You can format the footnote text just like any other text in Word. Change the font, size, or style to match your document’s formatting.
Manage Footnotes : Word automatically numbers footnotes consecutively. If you need to delete a footnote, simply delete the superscript number in the main text, and Word will renumber the remaining footnotes.
How to Write a Footnote
- Inserting a Footnote: In Microsoft Word, place your cursor where you want the footnote, go to the “References” tab, and click “Insert Footnote.” In Google Docs, place your cursor where you want the footnote, then go to “Insert” > “Footnote.”
- Formatting the Footnote Text: Follow the required citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) for academic texts. For general texts, provide additional information or comments succinctly.
What is Chicago-Style Footnotes?
The Chicago Manual of Style (CMS) is widely used in academic writing, particularly in the humanities and social sciences. It provides a standard method for documenting sources, ensuring consistency and clarity in scholarly work.
Examples of Chicago-Style Footnotes
- 10 Examples of Chicago-Style Footnotes
- John Smith, History of Medieval Europe (New York: Academic Press, 2010), 45.
- Jane Doe, “The Renaissance Era,” Journal of European History 23, no. 2 (2012): 78.
- Mary Johnson, Modern Literature (Chicago: Literary House, 2015), 89.
- Mark Johnson, “The Industrial Revolution,” History Today 15, no. 4 (2011): 150.
- Lisa Taylor, Art in the 19th Century (London: Art World Publishing, 2005), 123.
- Anna White, Women in the Workforce (Philadelphia: Social Science Publishing, 2013), 47.
- David Brown, The Evolution of Technology (San Francisco: Tech Books, 2011), 77.
- Paul Williams, Philosophy in the 21st Century (Austin: Academic House, 2017), 132.
- Robert Nelson, “Political Changes in the 20th Century,” Political Science Quarterly 22, no. 2 (2018): 99.
- Emma Harris, Cultural Shifts in America (Miami: Culture Press, 2014), 105.
What is APA Style Footnotes?
APA (American Psychological Association) style primarily uses in-text citations and a reference list for documentation. However, footnotes can still be used in APA style to provide additional content or clarification that would otherwise disrupt the flow of the text.
Examples of APA Style Footnotes
- Smith, J. (2010). History of Medieval Europe. New York, NY: Academic Press.
- Doe, J. (2012). The Renaissance Era. Journal of European History, 23(2), 78-80.
- Taylor, L. (2005). Art in the 19th Century. London, England: Art World Publishing.
- Doe, M. (2015). Modern Literature. Chicago Style , IL: Literary House.
- Johnson, M. (2011). The Industrial Revolution. History Today, 15(4), 150-152.
- Clark, S. (2008). Ancient Civilizations. Boston, MA: History Press.
- Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture. (2019). Environmental Studies Journal, 30 (3), 110.
- Roberts, A. (2013). Women in the Workforce. Philadelphia, PA: Social Science Publishing.
- Global Economic Trends. (2020). Economics Review, 18(1), 25.
- Baker, T. (2011). The Evolution of Technology. San Francisco, CA: Tech Books.
What is MLA Style Footnotes?
MLA (Modern Language Association) style footnotes are used to provide additional information or citations for sources within academic writing, following the MLA Style Handbook guidelines.
Examples of MLA Style Footnotes
- John Smith, The Art of Literature (New York: Harper Collins, 2016) 45.
- Jane Doe, “The Renaissance Era,” Journal of Historical Studies, vol. 23, no. 2, 2012, pp. 78-80.
- Lisa Taylor, Art in the 19th Century (London: Art World Publishing, 2005) 123.
- Mary Doe, Modern Literature (Chicago: Literary House, 2015) 89.
- Mark Johnson, “The Industrial Revolution,” History Today, vol. 15, no. 4, 2011, pp. 150-152.
- Susan Clark, Ancient Civilizations (Boston: History Press, 2008) 66.
- “Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture,” Environmental Studies Journal, vol. 30, no. 3, 2019, p. 110.
- Anna Roberts, Women in the Workforce (Philadelphia: Social Science Publishing, 2013) 47.
- “Global Economic Trends,” Economics Review , vol. 18, no. 1, 2020, p. 25.
- Tom Baker, The Evolution of Technology (San Francisco: Tech Books, 2011) 77.
What is the Difference Between Footnotes and Endnotes?
| Feature | Footnotes | Endnotes |
|---|---|---|
| At the bottom of the page where the reference appears. | At the end of the document or a section. | |
| Easily accessible for quick reference while reading. | Requires flipping to the end of the document, which can interrupt reading flow. | |
| Typically numbered consecutively throughout each page. | Typically numbered consecutively throughout the entire document or section. | |
| Commonly used for detailed, immediate reference needs. | Used when references are less critical to immediate understanding. | |
| Can clutter the bottom of pages with extensive notes. | Keeps the main text cleaner but can create a long section. | |
| Preferred for providing instant context without leaving the page. | Preferred for a cleaner page layout, less distraction from main text. | |
| Often preferred in humanities and social sciences. | Sometimes preferred in scientific and technical writing. | |
| More practical for shorter documents with fewer citations. | More practical for longer documents with extensive citations. |
Importance of Using Footnotes
Provides Credibility: Footnotes allow you to cite sources accurately, giving your work credibility and demonstrating that your research is based on reliable information. Enhances Readability: By placing additional information or citations at the bottom of the page, footnotes keep the main text clear and focused, making it easier for readers to follow your argument. Supports Academic Integrity: Properly using footnotes helps avoid plagiarism by giving proper credit to the original authors of the sources you used in your research. Organizes Sources: Footnotes help organize and keep track of the sources you have referenced, making it easier to compile a bibliography or reference list at the end of your document. Facilitates Verification: By providing detailed citations, footnotes make it easier for readers to verify the information and consult the original sources for more in-depth study.
Tips for Writing Footnotes
- Author Names : Use the author’s full name in the footnote. For multiple authors, list them in the order they appear in the source.
- Titles : Italicize book and journal titles. Use quotation marks for article and webpage titles.
- Publication Details : Include the city of publication, publisher, and year. For journal articles, include the volume, issue number, and date.
What are footnotes used for?
Footnotes provide additional information, citations, or explanations without interrupting the main text.
How do you format footnotes?
Footnotes are formatted with a superscript number in the text and corresponding note at the page’s bottom.
When should I use footnotes?
Use footnotes to cite sources, provide additional data, or clarify points made in the text.
How are footnotes numbered?
Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout the document or chapter.
Can footnotes include images or tables?
Yes, footnotes can include images or tables if they provide relevant supplementary information.
How do I cite a book in a footnote?
Include the author’s name, book title, publication details, and page number.
What styles use footnotes?
Footnotes are used in various citation styles, including Chicago, Turabian, and sometimes MLA.
Can I use footnotes in MLA style?
While MLA typically uses in-text citations, footnotes can be used for additional commentary or references.
What is a Chicago Citation footnote example?
A Chicago citation footnote might look like this: John Smith, The Art of Literature (New York: Harper Collins, 2016), 45.
Can footnotes be used in digital documents?
Yes, footnotes can be used in digital documents and are often interactive for easy navigation.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- How it works
- Pay for essays
- Do my homework
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Do my assignment
- Coursework help
- Our Writers

Understanding MLA research proposal format: a comprehensive guide

A historian and political analyst by training, Jay Brines offers six years of experience in academic writing. His in-depth understanding of political theories and historical contexts brings a rich perspective to his papers, making them a valuable resource for students in these fields. You can always count on this paper writer.
How to write a research paper MLA format? It's a common question among students and researchers who are preparing papers in the humanities. A research paper proposal outlines the objective, scope, and direction of your academic endeavor. Academic proposals are essential because they allow researchers to explain their study's purpose and request comments or financing. Formatting this text in MLA style follows humanities field standards and makes it organized and readable. This introduction to MLA style paper will explain why writing guidelines are essential for academic achievement and how they help you write a clear, professional, and convincing MLA research proposal format.
Coherent and well-structured proposals are crucial. They prepare the basis for the study and provide a clear path for it, ensuring all project issues are examined and adequately expressed. When drafting such proposals, it's beneficial to understand "What is MLA format?" as this style guide can help organize your documentation and citations effectively, ensuring clarity and consistency throughout the academic writing process. Using the right proposal structure helps you communicate your work's research significance and persuade others to do the study. This introductory section emphasizes the importance of MLA proposal formatting in academic writing and research preparation before diving into the details.
Mastering the essentials of MLA style for crafting research proposals
Modern Language Association (MLA) style is popular in language and literary writing. It's essential to familiarize yourself with the specific guidelines that govern this style. Understanding MLA rules helps research proposals sound professional and scholarly. MLA style paper format organizes proposals, making research aims obvious to reviewers and researchers. MLA proposal format, citations, and organization are crucial for academic legitimacy. The style basics will be covered in this part to help you write a solid MLA research proposal.
The crucial role of following MLA guidelines in writing
Following MLA formatting basics while writing an academic paper is essential to scholarly communication. These standards organize material simply and consistently, making the text easier to read. Researchers should follow MLA formatting principles to guarantee that their work is regarded seriously and evaluated on its merits rather than formatting problems.
Understanding and using MLA style paper format in a study proposal helps generate a professional tone and structure, which is crucial to convincing review panels of its viability and need. It shows attention to detail and adherence to "academic writing" norms, which are appreciated in scholarship. This section will explain MLA style paper format and how to use it to write a research proposal, covering citation styles and formatting a research paper.
Developing a compelling title and abstract
The title page for research proposal writings generally makes the initial impression. A brief title summarizes your study and engages readers. It should be concise, informative, and reflect your idea. Meanwhile, the abstract, much like you might find in a research proposal sample MLA format, condenses your study goals, methods, and consequences. Well-written abstracts instantly convey the scope and relevance of your study, inspiring additional investigation. Title and abstract efficiency can greatly affect study publicity and accessibility.
Crafting a compelling abstract: a quick guide for 100-200 words
Any study project needs an abstract writing to summarize its aims, methodologies, and implications. Effective abstract tips include beginning with a clear problem or purpose, a quick summary of the research methodology used, and a picture of the expected outcomes.
This section of the proposal frequently decides the reader's interest in reading the whole thing. It is the first substantive description of your work viewed by an external scholar, and a well-written abstract may greatly improve its reception. Thus, abstract writing is essential for researchers who want their proposal to stand out. Writing services can help you learn how to start a paper effectively, ensuring your abstract catches the reader's attention immediately. Moreover, services such as write my paper for me can provide guidance on structuring and refining your abstract, making it a powerful introduction to your proposal.
Strategies and insights for crafting engaging titles and abstracts
The title of your MLA research proposal format sets the tone and identifies the subject. A short, detailed, and informative title structure should convey the study's substance and entice the reader to learn more. A strong title quickly tells the reader about the study topic, which is vital in academic writing that prioritizes clarity and accuracy.
To write a good title and abstract, be clear when reading the research proposal example MLA and avoid unclear terminology. Additionally, connecting the title and abstract with the primary research challenges and approaches helps give a comprehensive preview of the proposal's content and persuasively argues for the research's necessity and relevance.
Organizing your research proposal: a strategic approach
Effectively communicating your research proposal sample MLA strategy requires a well-structured research proposal. This section helps you organize your proposal to include all important elements. Your study topic, technique, and projected results should flow together to make a cohesive paper. A logical MLA proposal format helps your proposal flow and emphasizes the importance and viability of your research idea.
Blueprint for organizing your proposal with defined sections
A well-organized proposal organization is crucial to a clear document. A well-organized proposal helps the reviewer identify crucial material and evaluate the study's feasibility and relevance. The parts should be organized from topic introduction to research methodology approaches, expected results implications, and conclusions.
The introduction proposal example, literature review, methodology, expected outcomes, and conclusion should be clearly divided. Each part should explain the research's goals, importance, and methodology and add to the proposal's narrative. This systematic technique helps deliver material effectively and shows the researcher's extensive planning and comprehension of the academic project's needs.
Guidelines for numbering and formatting subsections to enhance clarity and coherence
Effective structuring extends to the detailed organization of your content. Numbering and MLA formatting sub-sections enhance the readability and navigability of your proposal. Here are key practices to consider:
- Consistent sub-section headings: Use uniform styles for headings and subheadings to maintain a coherent MLA structure.
- Sequential numbering: Number sections and sub-sections in a sequential manner to guide the reader through your proposal.
- Logical flow: Arrange sections in a logical order, starting with the introduction proposal example and proceeding through methods, results, and conclusions.
- Visual distinction: Make use of bold or italicized fonts sparingly to emphasize important points without distracting from the main text.
Crafting the introduction and conducting the literature review
The beginning of your MLA research proposal example should set the stage for your investigation. It presents the study issue, emphasizes its relevance, and specifies your research goals. You must demonstrate your understanding of existing research and its relevance to your subject in the literature review after the introduction. This part places your research in the existing scholarly conversation and highlights gaps your study seeks to fill.
Advice for crafting a powerful introduction to frame your research
Introduction writing in a research proposal sample MLA includes background information, the research topic, and study goals. A good beginning sets the stage for the subject, engages the reader, and persuades them that it is important. The study scope and desired contributions to knowledge must be clearly defined.
A good introduction should flow into a Literature review that critically evaluates pertinent research. Literature review guidelines recommend that this part show a deep awareness of the academic environment around the research issue and identify gaps that the present study will fill.
Best practices for performing a literature review in MLA-style research proposals
When conducting a literature review for an MLA research proposal, consider the following MLA guidelines for essay projects:
- Relevant sources: Focus on recent and pertinent literature to support your research context.
- Citation consistency: Adhere strictly to MLA citation guidelines to maintain uniformity and avoid plagiarism.
- Critical analysis: Evaluate and synthesize the literature; don't just summarize. Highlight debates, major themes, and gaps in the research.
- Integration with proposal: Clearly link the literature review to your research questions and objectives, demonstrating its direct relevance.
Formulating the research methodology and anticipating outcomes
Define your research methodology by detailing data collection and analysis methods. The research design, data-collecting techniques, and analytic procedures should be clearly stated in this section to support the study's goals. Describe methodology limitations to honestly examine your approach's flaws and display critical thinking and problem-solving.
Outlining expected results predicts what the research seeks and what it may mean in the area. This indicates the study's direction, likely influence, and relevance. This section addresses research challenges to prepare the proposal for skepticism and scrutiny by showing that the researcher has examined and planned for probable hurdles.
A conclusion of your MLA research proposal is a conclusion summary of the article's main elements. This section revisits key topics like the structured approach to proposal development, MLA formatting, and strategic considerations for each section — from writing an impactful title to writing a clear and concise abstract. The conclusion summarizes these essential elements to help the reader comprehend the MLA structure and substance.
How should I format the title page in an MLA research proposal?
MLA research proposal does not need a title page; instead, write your name, instructor's name, course name, and date in the upper left corner of the first page and the title centered on the following line.
Can I use bullet points in an MLA research proposal?
Bullet points can assist in clarifying procedures or list topics in the methodology section, even though MLA style prioritizes paragraph form.
How do I cite sources within the proposal?
Use parenthetical citations with the author's last name and page number, and list all books cited at the conclusion of your proposal.
Related posts

How to Write an Exemplification Essay | A Guide from WritePaperFor.Me

How to Create a Dissertation Outline. Writing Tips and Free Template

How to Write a Dissertation: Helpful Tips and Impressive Ideas
What are you waiting for?
You are a couple of clicks away from tranquility at an affordable price!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
An Update on Current Trend in Sample Preparation Automation in Bioanalysis: strategies, Challenges and Future Direction
Affiliation.
- 1 National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research-Ahmedabad (NIPER-A), An Institute of National Importance, Government of India, Opp. Airforce Station, Palaj, Gandhinagar 382355, Gujarat, India.
- PMID: 38949910
- DOI: 10.1080/10408347.2024.2362707
Automation in sample preparation improves accuracy, productivity, and precision in bioanalysis. Moreover, it reduces resource consumption for repetitive procedures. Automated sample analysis allows uninterrupted handling of large volumes of biological samples originating from preclinical and clinical studies. Automation significantly helps in management of complex testing methods where generation of large volumes of data is required for process monitoring. Compared to traditional sample preparation processes, automated procedures reduce associated expenses and manual error, facilitate laboratory transfers, enhance data quality, and better protect the health of analysts. Automated sample preparation techniques based on robotics potentially increase the throughput of bioanalytical laboratories. Robotic liquid handler, an automated sample preparation system built on a robotic technique ensures optimal laboratory output while saving expensive solvents, manpower, and time. Nowadays, most of the traditional extraction processes are being automated using several formats of online techniques. This review covered most of the automated sample preparation techniques reported till date, which accelerated and simplified the sample preparation procedure for bioanalytical sample analysis. This article critically analyzed different developmental aspects of automated sample preparation techniques based on robotics as well as conventional sample preparation methods that are accelerated using automated technologies.
Keywords: automation in sample preparation; bioanalysis.
PubMed Disclaimer
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
Related information
Linkout - more resources, full text sources.
- Taylor & Francis
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
MLA 8 th edition vs MLA 9 th edition. The 9 th edition of the MLA handbook re-introduces guidelines regarding paper formatting (which were not present in the 8 th edition). The guidance in the 9 th addition is consistent with the guidance in previous editions and expands on the formatting of tables, figures/illustrations, and lists. The 9 th edition also offers new guidance in areas like ...
The basic format for a book citation requires listing the author's name, the title of the book, the publisher's name, and the date of publication. Edited books, when cited in full, will list the editor's name instead of an author's name. Works Cited. Black Hearts Bleed Red. Directed by Jeri Cain Rossi. Mary Magdalene Films, 1992. Desmond, John.
MLA provides guidelines for writing and formatting your annotated bibliography. An example of a typical annotation is shown below. Example of an MLA source annotation. Kenny, Anthony. A New History of Western Philosophy: In Four Parts. Oxford UP, 2010. Broad history of Western philosophy from the ancient Greeks to the present day.
Here's an MLA example: Lark knows how to handle life on the river: "I try to count the seconds before I hear the thunder, so I know how far the storm is, but I'm too rattled" (Wingate 12). Check out the full EasyBib MLA in-text & parenthetical citations guide to learn more about styling these types of references.
MLA format is a widely used citation style for academic papers. Learn how to format your title page, header, and Works Cited page with our free template and examples. Watch our 3-minute video to see how easy it is to apply MLA rules to your document.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
The nine core elements of MLA citations. 1. Author. Begin each source entry with the name of the author (s) or creator (s). The name of the first author is always inverted (Last name, First name). When a source has two authors, the second author's name is shown in the normal order (First name Last name).
The MLA Style Center provides the following guidance for formatting an MLA annotated bibliography: Title your reference page as "Annotated Bibliography" or "Annotated List of Works Cited.". Include annotations after the full, listed reference. Annotations should typically not exceed a single paragraph.
Step 2: Create the MLA Annotations. Creating the annotation is the pivotal part. This is an annotated bibliography, after all. The first thing to think about is whether this is a summary annotation or evaluative annotation. Per the names, the summary annotation provides a summary while an evaluative annotation evaluates the work.
The good news is that references in MLA bibliography format and regular works-cited lists are structured the exact same way. Citing Basics . When adding information to your project from another source, you are required to add an MLA citation. There are two types of MLA format citations: in-text citations and full citations. Full Citation Basics:
MLA Sample Paper. This resource contains a sample MLA paper that adheres to the 2016 updates. To download the MLA sample paper, click this link.
Author's last name, first name. "Article title." Periodical title Volume # Date: inclusive pages. Note: If an edition is named on the masthead, add a comma after the date and specify the edition. Examples: Hall, Trish. "IQ Scores Are Up, and Psychologists Wonder Why." New York Times 24 Feb. 1998, late ed.: F1+.
Your professor may ask that you create an annotated bibliography in MLA style. An annotated bibliography is similar to the Works Cited page found at the end of a paper. The paper formatting is the same but instead of following a full research paper, the student will write a brief annotation for each source which will directly follow the source ...
Citations by Format. Entries in the works-cited list are created using the MLA template of core elements—facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date. To use the template, evaluate the work you're citing to see which elements apply to the source. Then, list each element relevant to your source in the order given on ...
Rules! rules! rules! The MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers states the following formatting rules:. The text and the works cited list should be double-spaced. Number your pages at the top right of the page. Reference list entries must have a hanging indent (to do this in Microsoft Word 2003, select the citation, click Format, then Paragraph, then Special, and choose Hanging).
Cambridge UP, 2003. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Begin the works cited list on a new page after the text. Name it "Works Cited," and center the section label in bold at the top of the page. Order the reference list alphabetically by author's last name. Double-space the entire list (both within and between entries). Apply a hanging indent of 0.5 in. to each entry.
The MLA guidelines call for the bibliography to be called Works Cited. Science Buddies has summarized some of the most common MLA formats for your use: MLA Format Examples . The APA guidelines call for the bibliography to be called the Reference List.
Get started with MLA style. Learn how to document sources, set up your paper, and improve your teaching and writing. Document Sources Works Cited Quick Guide Learn how to use the MLA format template. Digital Citation Tool Build citations with our interactive template. In-Text Citations Get help with in-text citations. Endnotes and Footnotes Read our …
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA ...
Sample Bibliography: MLA Works Cited Format. Google Classroom. Made possible with support from: "Battery." Encyclopedia Britannica. 1990. "Best Batteries." Consumer Reports Magazine 32 Dec. 1994: 71-72. Booth, Steven A. "High-Drain Alkaline AA-Batteries." Popular Electronics 62 Jan. 1999: 58.
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
The following examples use MLA 9th edition. Parenthetical Citation. MLA format uses a parenthetical citation, which is a brief mention in the text of your paper that leads the reader to the complete information about that reference. It usually appears at the end of a sentence. A parenthetical citation involves placing relevant source ...
MLA style is generally more flexible that either APA or Chicago style, so while they provide specific examples for citing commonly used AI tools, they encourage writers to adapt those guidelines to fit the situation.. Hare are some other guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in MLA style: Cite the AI tool when you incorporate its output into your work.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
MyBib.com is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes references for you to copy straight into your academic assignments in the Reference List. MyBib can format webpages, books, journals, PDFs, and 30 other sources in over 9,000 different citation styles, including APA 7, Chicago, Harvard and MLA 9.
Footnotes are essential in academic writing, providing additional information, citations, and explanations at the bottom of a page. Learn about footnote formats, including Chicago Style and MLA Bibliography, to enhance your research and writing skills.
MLA proposal format, citations, and organization are crucial for academic legitimacy. The style basics will be covered in this part to help you write a solid MLA research proposal. The crucial role of following MLA guidelines in writing. Following MLA formatting basics while writing an academic paper is essential to scholarly communication.
Automation in sample preparation improves accuracy, productivity, and precision in bioanalysis. Moreover, it reduces resource consumption for repetitive procedures. Automated sample analysis allows uninterrupted handling of large volumes of biological samples originating from preclinical and clinica …