- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Computer Networking
- Wireless Networking

How to Fix Your Internet Connection: Troubleshoot Common Issues
Methods for improving and repairing your connection
Last Updated: September 27, 2023 Fact Checked
Slow or Inconsistent Wi-Fi Connections
Simple fixes for connection issues, advanced fixes for connection issues.
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Kyle Smith . Kyle Smith is a wikiHow Technology Writer, learning and sharing information about the latest technology. He has presented his research at multiple engineering conferences and is the writer and editor of hundreds of online electronics repair guides. Kyle received a BS in Industrial Engineering from Cal Poly, San Luis Obispo. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 818,289 times. Learn more...
While some network issues can only be addressed from your Internet Service Provider's (ISP's) side, there are plenty of simple steps that you can take to resolve minor to moderate network issues at home! From repositioning your router to resetting the network, there are a few things you can try to get things working. This wikiHow will show you how to fix your internet connection, from handling slow Wi-Fi networks to troubleshooting problems on your PC or Mac.
Things You Should Know
- For slow internet, move your router so there are as few obstacles as possible between it and your device.
- Restart your router and modem to resolve common internet connection issues.
- If your problem persists, try updating your router firmware by navigating to its router login page.

- If you’re having connection issues on a different floor of your home, try different antenna angles for better coverage.

- The best way to ensure a consistent Internet connection is by minimizing the number of obstacles between your Internet device and the router.

- Make sure to check what speed your router is rated for. This is typically labeled AC####, where the four numbers represent the speed in megabits per second (mbps). Get a router that matches or exceeds your internet plan’s mbps.

- If your computer is able to connect to the Internet while connected directly to the router, your computer's wireless reception is most likely the problem.
- If your computer is able to connect to the Internet while connected directly to the modem, then the issue is likely cause by your router.
- If you cannot connect to the internet while connected directly to your modem, there is something wrong with the modem or with your internet service in general. You'll need to get in touch with your internet service provider's technical support line to fix modem-related issues.

- To stay relatively up-to-date, consider clearing your browser's cache once per month.

- Internet Explorer

- Restarting your computer will often also turn back on your Internet adapter if it was off.

- You may have to hold the Fn button in order to be able to press the Wi-Fi button.
- The Wi-Fi button usually looks like three curved lines increasing in size.
- Skip this step on a desktop computer.

- Many modems can also be soft-reset in this manner.
- In some cases, you can soft-reset your network by opening your router's page and clicking a Reset button in the "Advanced" or "Power" options.

- In most cases, the "reset" button is a recessed button on the back of the modem and router, meaning that you'll need to use a pen or a paperclip (or similar tool) to press the button.

- Clearing the DNS cache will resolve issues such as websites failing to load, especially if you can view the website in one browser but not another.
- To clear the DNS cache on a mobile item such as a smartphone or a tablet, simply restart the item.

- Windows - Press ⊞ Win + R > type in ncpa.cpl > click OK > right-click your network adapter > click Diagnose > follow any on-screen prompts.

- Add a second router to extend the range .
- Increase your computer's Wi-Fi reception .
- Make your own directional "cantenna" for your wireless adapter .

- Remember to be as calm and polite as possible, and do not take out your frustration on the company.
Community Q&A
- Most ISPs will perform network diagnoses and fixes for free if you're renting a modem/router from them. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1

- Resetting your network should be a last-ditch attempt to fix the network. While it will fix most of your potential network problems, it's very inconvenient to have to set back up all of your Internet-connected items. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 5
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://osxdaily.com/2016/09/22/fix-wi-fi-problems-macos-sierra/
About This Article

1. Restart your computer. 2. Make sure your wireless adapter is enabled. 3. Restart your modem and router. 4. Try a hard network reset. 5. Move closer to the router. 6. Try using Ethernet. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Feb 15, 2017
Is this article up to date?
Jul 7, 2017
Bobert Jones
Jul 18, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Keep up with tech in just 5 minutes a week!

8 Easy-to-Do Ways to Troubleshoot Network Connection
You'll be up and running in no time
A faulty Wi-Fi connection doesn’t have to ruin your day. There are plenty of ways you can restore a lost internet connection. Follow these network troubleshooting tips and you’ll be up and running in no time.
1. Check Your Settings
First, check your Wi-Fi settings. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . Switch Wi-Fi to the On position.
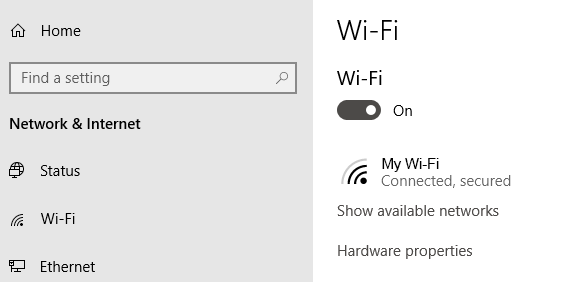
Phones and tablets also have settings that turn Wi-Fi on and off. Make sure that it is turned on so you can connect to the network.
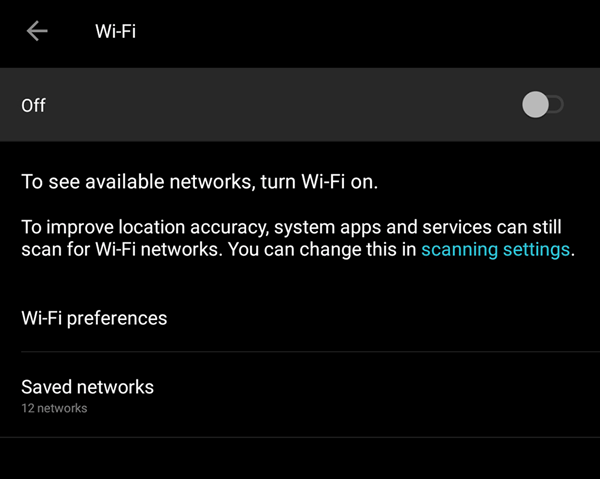
You also want to check if Airplane Mode is turned on.
2. Check Your Access Points
Check your WAN (wide area network) and LAN (local area network) connections. In layman’s terms, these are the Ethernet cables that go to and from your router.

If you suspect that the cables are the culprit, try swapping them out with new ones.
3. Go Around Obstacles
Walls, furniture, and other obstructions can be the reason why you’re unable to go online. Moving closer to the router can re-establish the connection. If moving closer to the router does not solve the issue, then at least we can remove it from the list of suspects.
4. Restart the Router
Sometimes restarting the router can help fix connectivity issues. This is even truer in cases where the router has not been turned off in a while. A quick restart can jolt the router back into working like it used to.
If that doesn’t work, you might also consider resetting the router. But only do so if you’re okay with it being restored to its factory settings. You will have to reconfigure everything including the SSID and password.
5. Check the Wi-Fi Name and Password
Check the network name (otherwise known as SSID) and password of the network connection. If you’re used to connecting automatically when in range of a router but are no longer able to, changes may have been made to the network while you’re away.
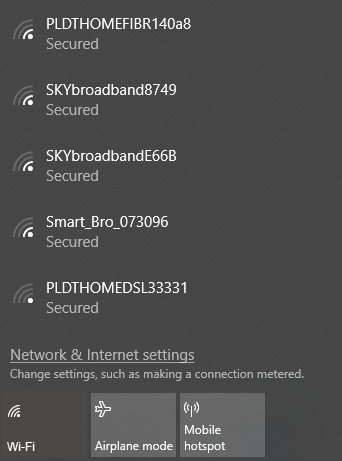
It could be as simple as administrators updating the password or the SSID could have been changed to a different one.
6. Check DHCP Settings
Routers are usually set up as DHCP servers. This setting lets computers join a network automatically. With DHCP turned on, users will no longer have to mess with IP Address and DNS Server settings manually.
To edit your DHCP settings, go to Windows Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . Under Wi-Fi , click Manage Known Networks . Select a network and click Properties .
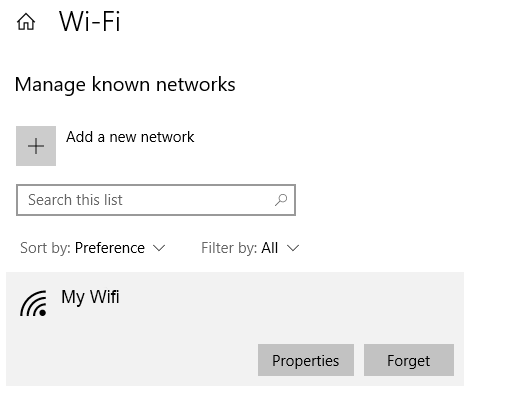
Under IP Settings , click Edit . From the drop-down menu, select Automatic (DHCP) .
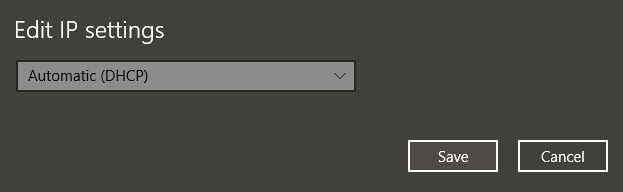
Note: Selecting Manual will let you set your DNS Server Address and IP Address settings manually.
7. Update Windows
Your network problems could be caused by your system. If that is the case, Windows could have possibly released a fix. Try updating your Windows machine to the latest release.
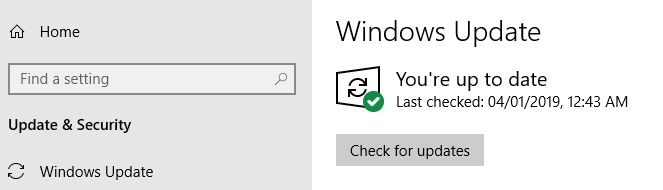
Go to Windows Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update . Click Check for Updates . If there are updates available, Windows will download and install them.
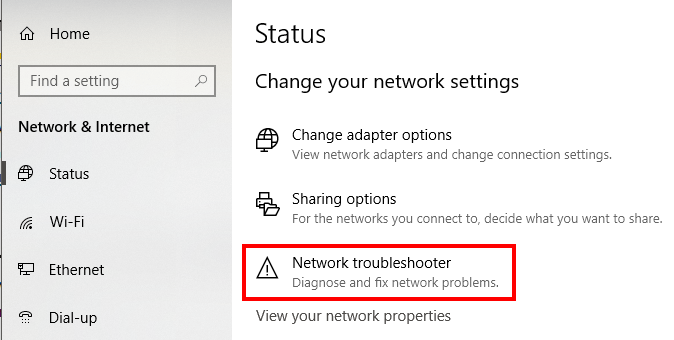
8. Open Windows Network Diagnostics
Windows has a tool called Windows Network Diagnostics that lets users troubleshoot connection issues.
Go to Windows Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Under Change Your Network Settings , click Network Troubleshooter .
Windows Network Diagnostics will run a couple of tests to see what’s possibly causing your Wi-Fi issues.
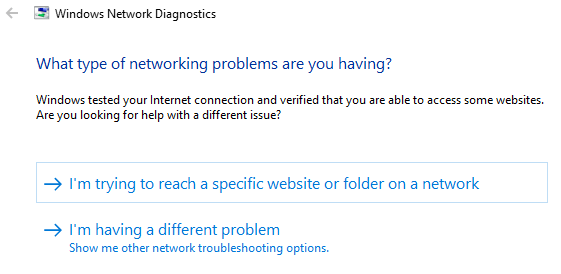
Windows will let you know if it does not find any issue. Otherwise, you will be given a list of possible actions to take to resolve the problem.
This tool, or a version of it, should be available in Windows 7 to Windows 10.
Christopher Jan Benitez is a freelance writer for hire who provides actionable and useful web content to small businesses and startups. In his spare time, he religiously watches professional wrestling and finds solace in listening to '80s speed metal. Read Christopher's Full Bio
Read More Posts:
The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting Home WiFi and Router Issues
- Tyler Cooper
- Restarting your router is the simplest way to solve Wi-Fi issues.
- Learning your router’s icons will help you diagnose any problems.
- Placing your router in a centralized and open area is essential for the best connection speed and stability.
- Speed tests and other diagnostic programs are useful tools for assessing your network connection.
- The best mesh Wi-Fi networks offer extensive coverage and the quickest speeds for your home.
Ninety-nine percent of home Wi-Fi issues can be fixed by unplugging the router, waiting five seconds, then plugging it back in. This resets the device and frequently improves the speed. But if that doesn’t fix your problem, this guide will provide you a to-the-point reference for dealing with some of the most common home Wi-Fi issues, such as the Wi-Fi not working, slowing down, disappearing, or not connecting with devices.
Keep reading to find out what to do if your connection is running slower than usual, as well as how to troubleshoot a network that won’t connect at all. We’ll also take a look at several tools you can use to help troubleshoot your connection no matter what problems crop up.
Table of Contents
Home wi-fi quick fix, understanding your router’s icons, how to troubleshoot wi-fi, tools for wi-fi troubleshooting, ways to boost your speeds or wi-fi reach, why does my computer keep disconnecting from wi-fi.
- If All Else Fails, Contact Your Service Provider
If your wireless connection suddenly stops working, restart your router before trying anything else. Here’s the process:
- Unplug or power off your router.
- Wait two to five minutes before plugging it back in.
- Wait five more minutes and retry the connection.
In most cases, this should fix your issue and allow you to get back online. If you go through these steps and something still isn’t working, you may need to contact your internet service provider for assistance.
Most routers have a series of icons that illuminate to convey different status messages at a glance. Though these can vary from brand to brand, most manufacturer’s include at least three primary status indicators:
Interpreting the Colors of Your Router’s Lights
Important note : In order to be clear on what your specific device is communicating to you, refer to the user manual for a more detailed explanation.
Pro tip: You can usually find a digital copy of your router’s manual by typing your device model number followed by “user manual” into Google.
If you’ve tried the quick fix above to no success, there are still several other ways you may be able to troubleshoot your Wi-Fi connection. In order to identify the technique most likely to actually help you, let’s break down some common issues:
“I’m experiencing slower-than-normal network speeds.”
Try this: Plug an ethernet cable directly into your router and test your internet speeds using our speed test tool . Next, test your speeds on the Wi-Fi connection. If they’re both slow, the issue is likely with your service provider and not your equipment. Give them a call.
If the hardwired connection is much faster than the wireless one, however, there may be more you can do to optimize your network. Wired connections will usually always be faster than wireless in some capacity, but the difference shouldn’t be so vast that your Wi-Fi is unusable. First, try moving your router to a more central location in your home. If that’s not an option, it may be worth exploring how to extend your Wi-Fi connection to all areas of your home.
Also, you might be encountering interference from networks adjacent to yours. If you think this may be the case, you can try changing the channel your router is broadcasting on. For starters, you’ll want to use the 5 GHz band whenever possible, if your router supports it. These tend to be less congested and therefore better performing than their 2.4 GHz counterparts.
“I have no internet connection at all.”
Try this: Plug an ethernet cable into your router and see if you’re able to get a signal on a desktop or laptop. If you can’t, your access has been cut and you should contact your ISP.
If you’re able to load web pages through a hardwired connection, there’s definitely something wrong with your Wi-Fi network. If restarting the router didn’t fix the issue, you may need to set it up again completely. Most routers have a small “reset” button that needs to be held down with a paperclip or other small object. Doing this will restore the device to factory settings and you’ll be able to go through the first-time setup once again.
If you’ve been through this process and still can’t get connected, you’ll likely need to contact your ISP for help. You could have an unpaid balance that has caused the company to suspend your account, or there might simply be an outage in your area.
“My Wi-Fi network disappeared completely.”
Try this: Check to see where your router is positioned. If it’s somewhere cramped, such as behind a couch or crammed into a storage closet, it might’ve overheated and shut down automatically to prevent any damage.
If you’re able to move your router to a place with more airflow, you should be able to solve the overheating issue. If you feel that your router is positioned in a good location and that overheating isn’t the problem, there are a few other things that could be happening.
For one, your network may have reset itself due to an update. Take a look at the default network name (usually printed somewhere on the router itself) and see if you recognize that network when looking for a connection.
“My phone/laptop/tablet won’t connect even though my other devices are fine.”
Try this: Turn off the offending device and turn it back on. You can also try turning the Wi-Fi off and on again in the settings of your device, just to be thorough.
If this doesn’t help, you may need to delete your network from the device entirely. On an iOS or Android device, you can simply click on the network name and hit “Forget This Network.” This means you’ll have to find the network again and put the password in like you did the first time you set it up, but it should solve any remaining connection issues in the process.
Our speed test tool allows you to see how your current network is performing in terms of both upload and download speeds. You can use this at any time to test the quality of your connection, and if you’re having any issues, you can use it to gauge your progress on getting them resolved. You can also use Speed Test periodically to see if you’re really getting the speeds that you’re paying for (look at your bill for payment info). Just remember that using Wi-Fi will always slow things down a little bit.
You can also run speed tests on different devices and from different locations. If the speed is sluggish on one device or in one location but not the others, that indicates an issue specific to the device or location.
Wireless Diagnostics (Mac)
The network diagnostics tool is a robust program that allows you to get a clear picture of your network health, as well as troubleshoot any issues you may be experiencing. You can find this program by hitting “command” plus “spacebar” and typing “Wireless Diagnostics” into the search bar.
When you first open the program, it will scan your immediate area for any available Wi-Fi networks. Once this is done, you’ll be presented with two options: monitor my Wi-Fi connection and continue to summary. Choose neither of these. Instead, at the top of your screen, select “Scan” from the Window drop-down menu. You will see a list of networks. Select “Scan Now.”
The service will then show you a full list of connections around you, including what channel they are operating on. The program will also show you the best channels for both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands based on network congestion. In order to actually change the channels your router is operating on, you’ll need to Google search the brand of the device followed by “IP address.” You will then type this in just like you would any regular website.
NirSoft (Windows)
NirSoft functions very similarly to the wireless diagnostics tools for Mac, scanning your Wi-Fi environment and displaying all available networks, as well as a number of useful statistics for each. You’ll still need to log into your router’s control panel to actually change its configuration.
NetSpot (Mac & Windows)
NetSpot is a fantastic alternative to both options above and even features some additional tools that intermediate users may find valuable. Above and beyond being able to view detailed information about your network, NetSpot also allows you to visualize its footprint in your home, showing you any dead zones and weak points that need to be patched up. Available as a free download, you’d be hard-pressed to find a more feature-complete troubleshooting program.
A little more speed or reach makes a big difference. To inject more oomph into your internet, try boosting your Wi-Fi signal and speeds with the following methods:
If your router is in a corner, closet, drawer, or non-central location, move it to a more open, central spot in the home (not the kitchen though. There is too much potential for liquid messes and signal interference from metal appliances). WiFi signals are stronger when they don’t have to travel through walls or floors, and a central location means better access to more devices. If your home is three floors, the central location is the middle of the second floor. Alternatively, adjust the angle of the antenna on your router, and see if that helps. Use compressed air to get gunk off your router, too. For more speed with heavy usage devices such as online gaming consoles and video-streaming laptops, keep them as close as possible to the router.
This method also gives you an idea whether neighbors, visitors, hackers, and others are connected to your network. The main step to see connected devices is to access your router’s admin panel. Another guide we wrote covers how to get into the admin panel. It’s easier than it may seem! Here are some other links that may help:
- Netgear login tutorial
- Linksys login tutorial
- Asus login tutorial
- TP-Link login tutorial
You may see a lot of devices connected to your WiFi, whether they’re on the 2.4GHz or 5GHz band. Smart speakers, smart thermostats, security cameras, and other smart home-type devices tend to be a better fit for 2.4GHz. PCs, laptops, gaming consoles for online gaming, and smart TVs that stream a lot of video should usually go on 5GHz.
2.4GHz band: This band has better range, works well through walls, and tends to be slower than 5GHz. It may slow down noticeably if “cluttered” with too many baby monitors, Bluetooth devices, garage door openers, smart home devices, holiday lights, etc. More than 20 of these devices might be too much, although some WiFi networks can have 200+ devices connected to them and perform just fine. If too many smart devices is an issue for your system:
- Reduce video/picture resolution on doorbell cameras and video devices to speed up the WiFi.
- Use a smart home hub to take traffic off WiFi and Bluetooth, which helps with congestion and speeds.
Routers tend to choose bands automatically depending on how far away the device is when you connect to the network. Reallocating devices to different bands depends on your router. With some routers, you do it through software. Others, you flip a switch on the router. A few, especially some mesh systems, aren’t super user-friendly in this regard. “Trickery” might be necessary. For instance, devices tend to connect to 5GHz as the default. If you want them on the other band and they’re portable (say, a group of smart light bulbs), you could go to the edges of your WiFi coverage, where they “flip” over to 2.4GHz since the range is better. Finish setting up there, then put the devices where they are supposed to be. They will stay on the 2.4GHz band. If the devices are not portable, then temporarily unplug the router closest to the device or separate the router and device as much as you can. These tricks often force the 2.4GHz band to be used.
Wi-Fi extenders work similarly to boosters and repeaters. Basically, they extend or amplify the main Wi-Fi network and create a second network. They’re useful if the main Wi-Fi signal is weak and you have just one dead zone (a mesh system may work better if the home has multiple dead zones). Extenders plug into outlets and resemble air fresheners. Extenders do create second networks, some with different names. It’s not always convenient to connect to two networks from the same house, so look for extenders that use the same network name when rebroadcasting. Also, while extenders extend the reach of your network, speeds may slow a bit. A mesh network enhances range without sacrificing speed and changing network names, so we touch on that in a bit.
It could be time for a change if you lived in a small apartment and took your router along to your new, much larger home. Bigger homes might need mesh routers or routers that can pair with repeaters/extenders to help WiFi signals reach farther. Before upgrading, though, especially if the space to cover has not changed, try moving the router if it’s in a closed location, and blast any dust buildup with compressed air.
>> Related Reading: The Best Wi-Fi Routers, Tested and Reviewed
Upgrading to mesh makes sense if your Wi-Fi connection is strong in some places but weak or dead in others. You may need mesh for coverage in large homes, multistory homes, and garages that are not close to the router. In a mesh network, a primary router and satellite nodes or modules coordinate to deliver speedy, efficient Wi-Fi. You put the nodes in different areas throughout your house, and each node is capable of broadcasting Wi-Fi. Mesh systems have become much more affordable, but you may be disappointed if you go entry-level. Plan to spend about $400 for impressive results. Look for two main features:
- Triband (three bands instead of two): The third band is another 5GHz band, and it’ll speed up communications between the primary router and the satellites.
- Wi-Fi 6: Wi-Fi 6 is more secure, efficient, and speedy compared with Wi-Fi 5. Wi-Fi 6 also handles traffic and congestion better. It has been available for a few years, but nowadays more and more devices support it. There’s also Wi-Fi 6E, which is even newer and stronger. Fewer devices support it, so don’t get your hopes up too much for that just yet (If you’re an avid online gamer, 6E can make a big difference and is worth further investigation).
If you live with a bunch of roommates or relatives who love streaming and gaming, all of you may need to agree on some guidelines or take turns using the internet connection. Of course, first try suggestions such as restarting the router, moving it to a central place, running speed tests, and using an extender for a dead zone. Do avoid putting your router in the kitchen, as microwaves and metal appliances can mess with the signal. So can liquids and food that get spilled on the router. Otherwise, here are ideas for Wi-Fi sharing and communication:
- Limit certain activities to certain times (perhaps downloading online games during the wee hours when everyone is asleep). Be aware that torrenting (while also being illegal) is a huge bandwidth hog.
- Give a heads up before hopping onto Zoom or any high bandwidth activity so that everyone else in the home doesn’t try to Zoom, FaceTime, and livestream classes all at once.
- If you live in a multi-family residence, ask your housemates to not share your Wi-Fi passwords with others in the building.
- Agree to dial back the graphics, for instance, by streaming in standard definition instead of 4K or Ultra HD.
- Pay a bit more money per resident for more bandwidth..
(more common if you’re in an apartment building and experiencing frequent Wi-Fi disconnects or out of range or weak Wi-Fi signals). By default, U.S. routers tend to be automatically set to channels 1, 6, and 11, especially 6. Assume that everyone else in the building is on these channels. Manually adjust your router so it is on channel 1, and retest your WiFi until you find a channel it works well on. Or, use a third-party app that shows the channels around you and helps find a less crowded channel.
If your internet plan has certain limits, then you are unlikely to get more. Say that you’ve been content with web surfing and some video streaming here and there at 25 Mbps max for the past few years. You’ve recently gotten into online gaming, and your new partner and stepchildren, all of whom love streaming movies, moved in. You may need a new plan that can support both online gaming and streaming in 4K, giving you speeds of 50 Mbps to 100 Mbps. Now, if you’re doing a lot of live streaming all of the sudden, perhaps taking online classes live every day or doing Twitch broadcasting, you might need speeds up to 150 Mbps or even 200 Mbps. However, if you cannot afford to upgrade your plan, you may still be able to improve your internet speeds. “If budget is a limiting factor, it’s best to call the service provider to see if there are faster plans that you can upgrade to,” said Mark Chen, founder and CEO of GetBillSmart. “Sometimes you’re stuck on a legacy plan that they can easily upgrade you to. You can also threaten to cancel to get a better deal and use those savings to get faster speeds.”
Once you’ve resolved the issue by following one of the above steps, make sure to secure your wireless home network to prevent hackers or neighbors from accessing your Wi-Fi.
If you find that you are consistently getting booted from your Wi-Fi network, there are a few things that could be happening. We recommend looking for any patterns in the service disruptions. Do they only happen at a certain time of the evening? Maybe it even drops when you pop something into the microwave? Believe it or not, there are many signals from Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, and smart lights constantly flowing through your home that can disrupt your internet connection.
If you’ve ruled out network interference using the tools listed above, you may need to try updating your router’s firmware. This is essentially the device’s “operating system,” and like any other piece of software, it needs to be updated from time to time to keep functioning properly.
If you’ve updated your firmware and are still getting disconnects, you may need to consider replacing the router outright, especially if it’s more than a few years old. Routers are computers, and computers unfortunately do tend to fail after a few years. If you’ve been renting a modem and router from your ISP, it might be better to invest in your own equipment since ISPs tend to rent out old hardware.
Firmware Updates by Brand
How to log into your router’s control panel.
Click on your router’s brand below to see in-depth instructions on how to log in to its configuration area, where you can adjust network passwords and names, as well as change the channels they are operating on.
- NETGEAR login tutorial
If All Else Fails, Contact Your Service Provider.
Though technical support from many companies can be a hit or miss experience, if you’ve tried everything above and nothing seems to be working, it might be best to simply reach out to request a tech to come to your home and sort the issue out directly. This may entail a service fee of some kind, but if it gets you back online, it’ll be worthwhile in the end.
Tech Support Phone Numbers for Common ISPs:
- AT&T Internet tech support: (800) 288-2020
- CenturyLink tech support: (888) 723-8010
- Cox tech support: (800) 234-3993
- Frontier tech support: (888) 884-0504
- Hughesnet tech support: (866) 347-3292
- Mediacom Cable tech support: (800) 883-0145
- Rise Broadband tech support: (877) 910-6207
- Spectrum tech support: (855) 757-7328
- Suddenlink Communications tech support: (877) 794-2724
- TDS tech support: (866) 571-6662
- Verizon Fios tech support: (800) 837-4966
- Viasat tech support: (855) 463-9333
- Windstream tech support: (800) 347-1991
- WOW! tech support: (855) 496-9929
- XFINITY tech support: (800) 934-6489
- The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting Home Wi-Fi and Router Issues
Offer Detail
- I Tried Both: Apple Watch 9 vs Fitbit Charge 6
- Best Places to Print Photos Online
Can't Connect to the Internet? Try These Tips
Finding and fixing internet connection problems
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- University of Illinois
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/jonfishersquare-93eb80e77a004035887f56816d3623c5.jpg)
- Wichita Technical Institute
In This Article
Jump to a Section
- Why the Internet Isn't Working
- Solutions to Try
- Frequently Asked Questions
When you suddenly can't connect to the internet, any of several things could be wrong. Use the suggestions in this list to find and solve common internet connection problems.
Reasons Why Your Internet Isn't Working
There could be any number of reasons you can't reach the internet: The firewall might be malfunctioning, the wireless signal might be blocked or too weak to use, the router might be experiencing issues, there could be IP address conflicts . . . the list goes on.
The good news is that there are 10 key steps you can take that will solve most connection issues. We're listed them here, in order of easiest to hardest, so start with the first step and keep going until your connection is back up and running the way you like.
How to Fix Internet Connection Problems
When you experience trouble with your internet connection, it's best to start your troubleshooting with simple solutions first and move on to more advanced fixes as needed.
Confirm your wired or wireless network hardware is switched on and plugged in . Unplugged or loose network cables, routers, and modems are easy to miss. Yet, these devices are a common reason you might be unable to connect to the internet. If you're on a wireless network, another reason is that the device's Wi-Fi radio has been shut off.
Before assuming your internet connection is faulty, visit several websites rather than just one . What may seem to be a network problem connecting to the internet may be a website or server that is temporarily offline.
Avoid IP Address conflicts . If your computer and another device on the network have the same IP address, the IP address conflict between them prevents either from working properly online. To resolve this conflict, release and renew your IP address . If your network uses static IP addresses , manually change your IP to a different number.
Check for computer firewall malfunctions . Firewall software prevents unwanted network traffic from disrupting its operation. These software firewalls can malfunction and block valid internet traffic. When two software firewalls, such as Windows Firewall and a third-party product, are installed on the same computer, contention between the two can also incorrectly block traffic.
If you recently installed or upgraded a software firewall on your computer, temporarily disable it to determine whether it may be the cause of your internet connection problem.
Make sure you're within wireless signal range . The performance of Wi-Fi network connections depends on the distance between the device and the wireless access point. The farther away from a Wi-Fi device, the slower the local connection. Wireless signal interference in the area can also limit the range of a Wi-Fi connection.
If you can't reach the access point and can't connect to the internet, measure your Wi-Fi signal strength and then boost your Wi-Fi signal .
Check your wireless network configuration . Wi-Fi networks with encryption options like WPA or WEP require computers to use matching security keys when connecting. If someone changes the encryption key or passphrase on the access point, devices that worked before can't establish sessions and internet connections. Likewise (though less likely), if the access point settings are changed to require a specific Wi-Fi channel number, some computers may be unable to discover it.
In this case, try these potential solutions:
- Confirm the Wi-Fi channel number and encryption keys on your router have not recently changed (check with the network administrator if necessary).
- If the password was changed and you don't remember the new one, change the password again and then update your devices so that they use the same password. You can do this by logging in to the router .
- When using a hotspot, carefully follow the provider's instructions.
Check for broadband router or access point malfunctions . Home networks that use broadband routers are easier to manage than those without one, but technical glitches with the router can prevent computers from connecting to the internet. Router failures are caused by overheating, excessive traffic, or an older unit going bad. Typical symptoms of a bad router include computers on the network not being able to obtain IP addresses or the router console not responding to requests.
When this happens:
- Check the router's lights and console, if possible, to ensure it is running and responding properly.
- Check if you need to update your router's firmware . Outdated firmware can cause problems for new devices trying to connect. Keeping the firmware up to date removes glitches and software hiccups.
- If that's not the problem, reset the router .
Contact your ISP if you suspect your account has been blocked . Internet service providers (ISPs) can block access to your account if you fail to make a payment or violate the provider's Terms of Service. When using paid hotspots that charge by the hour or day, people might forget to keep their subscriptions updated. Other common reasons an ISP might block your account include exceeding bandwidth caps, sending spam emails, and downloading illegal or inappropriate content.
Look for computer glitches . Although uncommon, a computer's network adapter hardware might fail due to overheating or age. Failures in the operating system software that control the adapter, on the other hand, can frequently occur, especially with computers that are used heavily. Viruses and worms also may disable or block a computer's network interfaces from functioning properly. Finally, if you use a laptop or other mobile device, transporting it from one location to another can corrupt the state of its network.
Here's how to find computer problems:
- Scan your computer for malware and remove any found.
- On Windows computers, reset the network connection .
- Reboot the computer.
Contact your internet provider to verify whether it is experiencing an outage . If you use satellite internet service, you may notice you can't connect to the internet during periods of extreme weather. Providers (including cellular internet carriers) in dense urban areas may be unable to support peaks in network traffic that cause sporadic outages for some customers.
If you subscribe to newer or more complex forms of internet services (such as fixed wireless broadband ), you may experience more downtime than others as providers encounter more issues with relatively less mature equipment.
Some providers give advice on troubleshooting problems connecting to their network (sometimes for a fee).
If you get a network connection error on Steam , check the Steam server status, disable your firewall, close background apps, and update the Steam client. If you still have trouble, troubleshoot your internet connection
If your PlayStation won't connect to the internet , check the status of the PlayStation Network, restart your network equipment, then fully power down the console and turn it back on. If you still have problems, move your PlayStation closer to the wireless router or use a wired connection.
If your Nintendo Switch won't connect to the internet , the Nintendo Switch Online service could be down, or a firewall could be preventing the Switch from accessing your network. If possible, move your Switch closer to the router, or use an Ethernet connection.
If your Xbox won't connect to the internet , double-check your Wi-Fi settings, then power cycle your network hardware and game console. If the Xbox network is down, all you can do is wait until it's fixed.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- What to Do When Windows 11 Can't Connect to a Network
- How to Fix Netflix Error Code NW-2-5 on Any Device
- How to Fix It When There's No Internet Connection
- How to Fix Amazon Error Code 1060
- How to Fix it When a Chromebook Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Set up a Home Wi-Fi Network
- How to Fix a Vizio TV That Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Connect Two Routers on a Home Network
- How to Connect to Your Home Router as an Administrator
- What to Do When Windows 10 Can't Connect to a Network
- Is X (formerly Twitter) Down...Or Is It Just You?
- How to Measure Your Wi-Fi Signal Strength
- How to Fix Common Xbox 360 Wireless Networking Problems
- How to Fix an Xbox That Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Fix it When Your Wi-Fi Network Is Not Showing Up
- How to Fix the PS4 'Cannot Connect to the Wi-Fi Network' Error
- CenturyLink
- Verizon Fios
- 5G Internet
- Best Internet Deals
- Best Internet Providers
- Cable Internet
- Cheap Internet
- Fiber Internet
- High Speed Internet
- No Contract Internet
- Prepaid Internet
- Satellite Internet
- Los Angeles
- New York City
- Philadelphia
- How to set up internet
- Router Guide
- Tips to fix slow internet
- What is a good internet speed
- Wifi Connection Problems
Home Internet
Wi-Fi is not working? Here’s how to fix your internet connection

Published 10:19 am ET Jan 12
Editorial note: This post may contain links to offers and services from which Allconnect receives a commission. The partners and associated compensation do not affect our editorial integrity. Read more about our advertising policy .

IsiMS, Getty Images
Wi-Fi connection issues can occur for various reasons, from equipment problems to internet outages. If you can’t connect to your home Wi-Fi , read on to learn how to troubleshoot the causes and fix your internet connection. Get your internet working again with these helpful tips, or shop for new internet providers near you by entering your address on this page.
Why is your Wi-Fi not connecting?
It can be frustrating if you’ve recently set up internet but, for some reason, can’t connect to Wi-Fi. Wireless service that is not working can be caused by:
Modem and router problems
- Cable connection issues
Device malfunctions
- Bad weather
Internet disruptions or power outages
Before you call your ISP or pay for a technician visit, find out how to get your Wi-Fi working again with these solutions. If you have high-speed internet but are getting slow Wi-Fi, check out tips for getting a faster internet speed . However, ongoing connectivity troubles could be an issue with your internet provider. Consider upgrading or switching your internet service if you have repeated outages. Find internet deals at your location when you enter your address on this page.
When your Wi-Fi is not working, a common culprit is your equipment. You may have a separate modem and router , or a gateway that combines both units into one device. Examining your internet hardware is a good place to start troubleshooting. Devices can cause problems if they are not connected properly, are outdated or incompatible with your internet connection.
How to fix modem and router problems
Try these methods in order until you find one that works.
- Reboot your equipment. Unplug your modem and router and plug it back in after 60 seconds. This technique will clear the router cache and improve your internet speed as well.
- Reset your Wi-Fi. Figuring out how to reset Wi-Fi is different from rebooting your router. Your router has a reset button that will wipe the router history and revert your device to its factory settings. Pressing this button on your router will reset your Wi-Fi. You may need to use a paperclip since the button may be slightly indented.
- Get new equipment. Updating your equipment might fix your Wi-Fi troubles, especially if your modem and router are over five years old. Routers have a three- to five-year lifespan. Also, check to make sure that your equipment is suitable for your internet connection type. For example, a cable modem will not work if you have fiber internet .
Internet connection issues
Loose or incorrectly placed internet cables are another frequent problem that can affect your Wi-Fi connection. Ethernet cables, power cords, surge protectors, power strips and extension cords can interrupt your internet signal if not secured correctly.
How to fix cable connection issues
- Double-check all your cables and cords to ensure they are properly fastened.
- Confirm that all Ethernet cables “click” into the port when attached.
- Make sure all power cords are plugged in. Check each plug to eliminate an inoperative outlet as the source of the problem.
- Verify that power strips are switched on if you use a surge protector strip.
- Avoid using extension cords when possible to remove additional breakage points.
Your wireless devices could be the reason you’re not getting an internet connection. If your device is broken or disconnected from the Wi-Fi network, it could seem as if your Wi-Fi is down. Use the process of elimination to determine if your connectivity issues are a result of faulty devices.
How to fix device malfunctions
- If your laptop won’t connect to Wi-Fi, check that the Wi-Fi is turned on in your settings and that you are connected to the correct Wi-Fi network. Restart your laptop and run an antivirus program to make sure malware isn’t preventing your device from connecting to your home Wi-Fi.
- For cell phones that are not picking up the internet signal, try moving closer to the router and restarting your device. Double-check your Wi-Fi network and password and make sure your phone is not on Airplane mode.
Bad weather
Some internet connections are vulnerable to inclement weather conditions. Satellite , fixed wireless and 5G internet are not hard-wired services, meaning obstructions like storms, ice and fog can interfere with the signals from the radio tower or satellite dish.
How to deal with bad weather
In most cases, you will need to wait until bad weather passes. Fixed wireless and 5G services might be restored by moving your gateway to a new location. Try plugging in your modem and router in a different part of your house, such as near a window, and at a higher position, like the second floor of your home.
A power outage or an outage with your specific internet provider can be the source of your Wi-Fi connection problem. Contact your power company or internet provider’s customer support to get an estimate of when service will be restored in your area.
How to deal with internet disruptions or power outages
When your home internet is down, you can use a hotspot to connect laptops and tablets to the internet through your cell phone provider. Use cellular data on your phone instead of your home Wi-Fi connection. Have a backup battery or portable charger available to recharge your devices during longer outages.
Cyber attacks or hacking
Cyber attacks and hacking can affect your modem, router or devices. Malware like viruses and spyware can delay or suspend your internet connection and put your personal data at risk.
How to deal with cyber attacks or hacking
Preventative measures are the best way to ward off digital attacks. Use these methods to deal with cyber attacks before they happen:
- Install antivirus software on your computer, tablets and cell phones.
- Change your passwords on your devices and your home wireless network occasionally (a couple of times a year is fine), or immediately if you suspect any unusual activity on your accounts.
- Activate the firewall on your router. Most ISPs have a free app to manage your router, and the firewall feature can usually be found in the Settings tab. For example, AT&T internet offers free network protection called ActiveArmor, but you must activate it from the AT&T Smart Home Manager app.
Wi-Fi connection problems FAQs
Why is my wi-fi suddenly not working.
If your Wi-Fi unexpectedly stops working, it could just be a temporary system irregularity. Try rebooting your modem and router as well as your device.
Why is my Wi-Fi connected, but I don’t have internet?
If your Wi-Fi is connected but you cannot access the internet, you likely have an issue with your modem. Try restarting your modem and check that all cables are securely attached.
Why is my phone not connecting to Wi-Fi?
Your phone might not connect to Wi-Fi if you do not have your Wi-Fi enabled. On your phone, go to Settings and make sure your Wi-Fi is on and you are connected to the correct network.
Why is my Wi-Fi router not working?
Reasons your Wi-Fi router is not working can include a loose cable or a bad location. Put your router in a central area of your home. Try to keep it away from microwaves and Bluetooth devices that could cause signal interference. Ensure all cables are fastened and reset your Wi-Fi device.
Why is my TV not connecting to Wi-Fi?
Your TV may not connect to Wi-Fi if it is too far from the Wi-Fi signal or if your TV Wi-Fi is not set up correctly. Verify that the network and password are entered accurately in the TV settings. Move your router closer to the TV if possible and reboot your modem, router and TV.
This content is produced through an alliance between USA TODAY and Allconnect.com. Under the alliance, Allconnect publishes articles about broadband-related topics upholding strict editorial integrity standards in line with USA TODAY’s Principles of Ethical Conduct . The opinions, analyses, reviews and recommendations expressed are those of the Allconnect editorial staff alone. The information is believed to be accurate as of the publish date, but always check the provider’s website for the most current information. Read more about our Allconnect Advertising Disclosure.

Lisa Iscrupe is a senior writer helping readers understand the complexities of broadband, internet and other home services, including energy and renewable products. Her work appears on SaveOnEnergy.com and CNET.com, with national sources such as CNN, The Daily MBA and The Media Bulletin referencing her articles.

Hannah Whatley is an editor who enjoys collaborating with writers to offer readers the most relevant, accurate, and up-to-date information for their home purchases. She has previously edited for The Motley Fool, The Modest Wallet, Grammarly, JoinCake.com and SaveOnEnergy.com, gaining expertise in several industries. Hannah has a B.A. in English from Thomas Edison State University. When she isn’t editing, she enjoys studying linguistics and languages.
More Stories
Internet providers in fresno, ca.
From visiting the bustling Tower District to setting out for the Sierra Nevadas or Yosemite National Park, locals have plenty to keep them busy in
Internet providers in Omaha, NE
The most populous city in Nebraska. The origin of (and modern-day go-to for) the Reuben sandwich. The namesake of a famous ‘90s song and home to a
Internet providers in Pittsburgh, PA
Known for many famous sports figures, a plethora of bridges, and its beautiful skyline situated at the intersection of the Ohio, Monongahela, and A
Internet providers in Oklahoma City, OK
The state capital of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, is also its largest by population, with more than 1.4 million residents in the metro area. OKC is hom
Internet providers in Charleston, SC
Charleston, South Carolina, is one of the oldest cities in the nation. The Holy City was settled in 1670, dating its origins to more than a century
Internet providers in Greenville, SC
It may not be the largest city in South Carolina, but Greenville is a hub of culture and entertainment in the Palmetto State. With a metro area of
Starry internet plans: Fast, affordable fixed wireless
Starry Internet overview Starry Internet is a 5G fixed wireless provider that covers around 2% of the U.S. Starry fixed wireless internet speeds ra
Internet providers in Raleigh, NC
The capital of North Carolina is known for its natural beauty and sprawling parklands. Appropriately dubbed the City of Oaks for its oak-lined stre
- Meta Quest 4
- Google Pixel 9
- Google Pixel 8a
- Apple Vision Pro 2
- Nintendo Switch 2
- Samsung Galaxy Ring
- Yellowstone Season 6
- Recall an Email in Outlook
- Stranger Things Season 5
Digital Trends may earn a commission when you buy through links on our site. Why trust us?
Wi-Fi not working? How to fix the most common problems

Wi-Fi problems can strike anyone at any time, no matter how much networking experience you may have. But if you’ve not come across a particular Wi-Fi issue before, there’s no need to worry if you don’t know how to fix it. All you need are the right tools and a few tips, and you’ll be able to solve your Wi-Fi problem in no time.
Basic Wi-Fi troubleshooting checklist
Quick fixes for common problems, slow or no wi-fi or internet access in certain rooms, slow internet everywhere.
- One device can’t connect to the Wi-Fi
Nothing can connect to Wi-Fi
Connections drop at random times, wi-fi network disappears entirely, unknown devices on my wi-fi network, a recent update broke wi-fi.
- The satellite routers on my mesh network aren’t connecting
- My smart device isn’t connecting to Wi-Fi
- My console can’t connect to Wi-Fi
- Can’t connect to wireless printer
- Can’t connect to a guest Wi-Fi network that I set up
- Wi-Fi 6 or 6E isn’t working, even with a Wi-Fi 6 router
- Can’t find a router with Wi-Fi 7
Whether you’re experiencing problems with slow internet, Wi-Fi signal dropping, or you just can’t connect to Wi-Fi at all, here are some of the quickest and easiest fixes you can try. We’ll also cover some advanced advice on more troubling issues that would definitely result in your Wi-Fi not working at all, or at slower speeds.
If you have a non-specific problem with your Wi-Fi or don’t consider the problem serious enough to investigate more in-depth problems, consider the items on this list as a great way to start fixing your problem.
- Make sure your device’s Wi-Fi is on — Most laptops have a shortcut key that will turn off their Wi-Fi and it can be easy to press accidentally. Similarly, there is a quick toggle on most phones that will turn off the phone’s Wi-Fi capabilities.
- Restart your router — A quick restart of your router (achieved by unplugging it, waiting 30 seconds to 1 minute, and plugging it back in again) can fix many Wi-Fi difficulties.
- Check for an outage — Most ISP’s will have an outage map available on their website. Try using your phone’s data to check and see if an outage is reported in your area.
Forgot the Wi-Fi password
If you really can’t remember your Wi-Fi password, and there are no notes or cards with it written down somewhere, you’ll have to reset your router . Use a paperclip to press the hidden switch in the pinhole on the back of your router for 30 seconds. It should then default to factory settings.
- Best router deals: Save on mesh networks and Wi-Fi 6 routers
- The most common Windows 11 problems and how to fix them
- The most common GoTo Meeting problems and how to solve them
Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
Wi-Fi connection lost when logging back into the computer
This problem can crop up on Windows 10 due to an issue with Fast Startup. Fast Startup keeps certain processes running so you can log back in very quickly. However, this can sometimes cause a bug with the wireless driver that prevents it from reconnecting to Wi-Fi properly. In the short term, you can turn off Fast Startup to prevent this problem . Search for Power Option s in your Windows 10 or Windows 11 search bar and go to this section of the Control Panel. Select Choose What the Power Button Does on the left-side menu, and then look at the new section Shutdown Settings . Find the option to Turn On Fast Startup and make sure it is deselected.
In the long term, you may need to update the driver for your wireless network adapter to fix any bugs causing this issue. You can follow our guide on how to update Windows 10 drivers for more information.
The network connects, but there’s no internet access
It might sound like a tired tip, but try resetting your modem by unplugging it and plugging it back in. If that’s no good, you can connect a laptop or desktop to your router with an Ethernet cable ( these are the best ones ) to see if it’s the router or your Wi-Fi that’s not working. If this works, then your best bet to get Wi-Fi working again is to reset your router . If there’s still no internet, though, you may have an outage. Contact your ISP.
Router crashes regularly and only restarting it helps
If your router needs to be restarted regularly, you should give your router a full reset . On most routers, you’ll find a Reset button that you can hold down with a paperclip. Do so for 30 seconds, and the router should default from factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
If that doesn’t work, your router may be on its way out. Your only real option is to return it if it is within its warranty period or to buy a new one.
Wi-Fi is made up of radio waves, meaning your Wi-Fi router broadcasts in all directions from a central location. If your router is in a far corner of your house, then you’re covering a great deal of the outside world unnecessarily. If you can, move your router to a more centralized location. The closer you can put your router to the center of your coverage area, the better reception will be throughout your home.
If you have external antennas, you can try adjusting those, too. Alternating between fully vertical and fully horizontal positions can help it reach in multiple directions.
If you live in an apartment building, other routers might be interfering with yours. Free software, like NetSpot on Mac, Windows, and Android, or Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android, can show you every wireless network nearby and what channel they’re using. If your router overlaps with nearby networks in particular rooms, consider switching to a less congested channel. If you need help switching, here’s our guide on how to change your Wi-Fi channel .
If none of that helps, your home might be too much for one router to handle. Consider purchasing a wireless repeater or setting up an old router to serve as one to extend the range of your main router. Upgrading to a whole-home mesh wireless system can also help with dead spots in certain areas of your home. Either way, it might be time to go and buy a new router .
If your Wi-Fi speed is slow no matter where you are, try plugging a laptop into your router directly and test your internet speed using one of the best internet speed tests . If speeds are still down, the problem is likely with your internet connection, not your router. Try some of these ways to improve your internet speed and contact your ISP.
If that’s not the issue, it could be that your current wireless channel is overcrowded by your devices or by those of other nearby networks. Consider changing the channel on your router in your router settings, by accessing the admin settings .
If that doesn’t help, performing a factory reset on your router and setting it up again may help. On most routers, there’s a Reset button that you can hold down with a paperclip. Do so for 30 seconds, and the router should default to factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured, and see if that helps.
If none of that works and your internet is fine on a wired connection, your router might be dying. Consider buying a new one: Here are the best routers we’ve reviewed and why they’re great picks. If the router seems fine, then it might instead be your modem, which could suffer connectivity issues if it’s on its way out, too. If you’re looking to upgrade your modem as a fix, we also have a guide on some of the top modem-router combos . Upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E router can also help ease issues with congestion and support faster speeds, provided that your broadband plan is capable of these boosted speeds.
One device can’t connect to the Wi-Fi
Sometimes you run into a Wi-Fi issue with one particular device. It’s probably just a momentary network issue, which is an easy fix. Try turning off the Wi-Fi on your device, then re-enabling it — or unplugging and replugging your Wi-Fi dongle. If that doesn’t work, restart the device and try again. Then try restarting the router itself.
If that doesn’t help, or if the problem reoccurs, consider deleting your current network from the list of saved networks on your device, then reconnect again.
If you’re running Windows 10 or 11, search for “wifi troubleshooting” and open the result, which should be Identify and Repair Network Issues . That will go through a series of diagnostics that may restore connectivity. On MacOS, you can run Wireless Diagnostics . Hold the Options key and click the AirPort (Wi-Fi) icon on the menu bar. Find Open Wireless Diagnostics , and then follow the on-screen instructions.
If you can’t connect to your Wi-Fi at all, plug your laptop into the router directly using an Ethernet cable, and see if you can connect that way. The particular type of Ethernet cable doesn’t matter, but there are some Ethernet cables that are better than others . If that works, your Wi-Fi is the problem and you should try some of the other fixes listed here. If it doesn’t work, then your internet may be down altogether. Check your ISP’s webpage and social accounts, or give them a call to see if they are reporting problems. Sometimes providers can be a little slow to note issues, so you can also check with a monitoring site like Downdetector and see if other users in your region are reporting problems.
Resetting your router can fix a myriad of issues, too, and an inability to connect is one of them. Press the Reset button on the back of the router with a paperclip for 30 seconds, and the router should default to factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
If that’s no use, you may need to consider buying a new router.
Is there some sort of pattern? Do connections drop whenever you use the microwave? Have you just installed a fish tank? It may sound weird, but some routers have trouble with these and other home hardware. The 2.5GHz band is readily interfered with by other devices, and 5GHz and 6GHz are notorious for being interrupted by physical objects. It could also be that you’re experiencing interference from other networks or devices. If your neighbors are heavy Wi-Fi users at a particular time each day, this could be slowing you down.
Changing your router’s channel might help. You can use NetSpot on Mac and Windows and Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android to show you every wireless network nearby. If yours overlaps with nearby networks, switching to a less congested channel in your router settings can help. We have a guide that will walk you through changing the channel on your router .
You can also try moving your router to a more accessible location so that there’s less distance (and interfering devices) between you and the router.
If that doesn’t work, try performing a factory reset on your router by pressing a paperclip into the miniature hole on it and following the reset steps as outlined in your manual.
If you lose track of your Wi-Fi network on any device, it’s possible that your router reset itself. Do you see an unprotected network named after your brand of router? That might be yours. Connect a laptop or desktop to it via an Ethernet cable, then use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured again.
If you don’t see such a network, plug your laptop into the router with an Ethernet cable, and see if you get a connection. Use our guide to finding your router’s IP address and login information for more help. Also, if you don’t have a cable, check out our guide on how to choose the right Ethernet cable .
Log into your Wi-Fi app or administrator settings (which you can find by searching your IP address on your browser ). Look for a list of currently connected devices and pinpoint the ones you don’t recognize.
First, make sure these don’t represent connections you didn’t realize you had — each smart device will have its own connection, for example, and they can have some strange titles if you didn’t name them. Game consoles and TVs may also be connected, and if you’ve had friends and family over recently they may have connected with unfamiliar devices.
If you’ve ruled out all familiar devices and there’s still a connection or two you don’t recognize, it’s possible someone else is hijacking your Wi-Fi network. In this case, look in your settings for an option to block these devices on your Wi-Fi and ban their MAC addresses, if possible. Then change your Wi-Fi password, and reboot your router. This may not stop especially determined hackers, but it’s usually enough to kick unwanted guests off your network.
If you want to take more drastic action, here are some steps for how to deal with someone stealing your Wi-Fi .
This can happen with some operating system updates. Windows 10 updates in mid-2020 had bugs that stopped some users from connecting to their Wi-Fi networks or even seeing a Wi-Fi connection at all. Similar updates to iOS, Android, and other platforms also have created bugs in the past that disrupt Wi-Fi connections.
When something like this happens, it’s best to wait for a patch that fixes the problem. In the meantime, remove the update and roll back your system to an earlier version to help get your online connectivity back.
While routers can last for years without needing a replacement, keep in mind that some problems can develop with age — a router may start lacking support for new device updates and similar issues that prevent it from working properly (as seen when Apple discontinued the AirPort Extreme, for example). That’s a sign that it’s time to look for a new router.
The satellite routers on my mesh network aren’t connecting
Make sure that your satellite devices are powered up and turned on. If they are, try unplugging and replugging the problematic device and see if it will connect to your network then. If your router app allows you to restart a Wi-Fi point (Google’s Home app, for example, allows this), then reboot that point and see if this helps, too.
Google also allows you to run a test to make sure the network is set up properly. You can find Wifi points on the Home app, under Test mesh . If the test comes back with a weak or failed connection, you should try repositioning your satellite routers to be closer to your primary router. This also is a good tactic for any mesh system that keeps dropping its satellite points — they could be too far away from the primary point.
You can also double-check to make sure that your satellite router devices have a different SSID than your primary router. If they were accidentally all assigned the same SSID, then the mesh network may not be able to coordinate properly.
If your router still seems unable to connect, then make sure that nothing significant has changed for your network settings. For example, if your ISP WAN (wide-area network) type changed for some reason, you may have to go back into the settings for the router and make sure that the right WAN setting is chosen.
There are additional special cases where certain Wi-Fi technology can interfere with mesh networks, so it’s also a good idea to contact router support directly and explain your situation if nothing is working.
My smart device isn’t connecting to Wi-Fi
First, make sure that your smart device and your router are both updated. Then try resetting your router and rebooting your smart device. You can either unplug and plug in the smart device or check its app for a reboot option — the Google Home app, for example, has a Reboot tool under each device section that you can use.
If the device still isn’t connecting properly, try moving it next to the router and seeing if it connects then — distance and interference can make a difference, especially for smaller smart devices. You should also double-check to make sure that your smart device doesn’t need a Zigbee hub to operate , which is more common among older smart devices but a problem that still occasionally crops up.
If your smart device keeps dropping a Wi-Fi signal, especially during busy times of the day, check to see if your router supports automatic band switching for devices. If it does, try turning this feature off. Sometimes a router will try to switch a smart device to a different band, but the device isn’t ready for that, causing it to lose a connection. There may also be issues with connecting to a mesh router, and you may have to be very specific about your network connection to make smart devices work.
It’s also a good idea to check if your particular device is suffering from temporary bugs that make connecting to Wi-Fi difficult or impossible. Nest minis and HomePod minis have both encountered such errors in the past. In these cases, a fix is usually patched in before too long, so keep making sure that your device is updated. Sometimes operating system updates, like a new iOS patch , also can affect smart device performance.
There are a number of other router settings that may block smart devices, but they are manufacturer dependent. If you can’t find what’s wrong, contact your router manufacturer’s support and explain that you think your router is having trouble connecting.
My console can’t connect to Wi-Fi
Check social media and Downdetector to make sure nothing is wrong with your gaming platform — sometimes your Xbox or PlayStation can get online just fine, but Xbox Live or Playstation Network is down for any number of reasons, but they’re typically back up again after a short period.
If everything looks all right there, reboot both your router and your game console and see if they can successfully connect. This is also a good time to test your internet connection. Major systems like Xbox and PlayStation have an option in their Settings menu to test your internet connection. On PlayStation, head to Settings , then Network , then select Test Internet Connection . On Xbox, go to Profile & System , select Settings , and in the General section, select Network Settings , where you will find an option to Test Network Speed & Statistics . This can provide more information about what’s going wrong and even tips on what you may need to change.
If your console and router seem to be acting properly but Wi-Fi keeps dropping, you may want to try moving the two devices closer to each other to see if the Wi-Fi signal improves. Try to remove any material or objects between the console and router: Placing both in a high, clear location often brings the best results. You can also try reducing the number of other devices on the network, especially if they’re streaming.
Can’t connect to wireless printer
First, make sure you are trying to connect to your Wi-Fi and not via Wi-Fi Direct — they are two different technologies. We also highly suggest the traditional routine of turning everything off and back on again, especially if your printer has connected to Wi-Fi successfully in the past. If your printer is far away from your router and keeps running into Wi-Fi errors, try moving it to a closer position.
If it looks like your printer is connected to Wi-Fi but you can’t get it to work, head into your printer settings on your computer and make sure the correct default printer is selected. Microsoft also has some troubleshooters you can run to see if they pick up on anything obviously awry.
It’s also a good idea to check your router security, firewalls, and VPN security to see if any of them are identifying the printer as a strange device and refusing a wireless connection. You may need to disable certain firewalls or reconfigure security protocols to use your printer successfully. When all else fails, uninstall your printer drivers and reinstall the more recent versions to see if this makes a difference.
And if your printer isn’t wirelessly enabled, consider upgrading to one that is. We have some recommendations for the best printers , laser printers , and multifunction printers that can be used wirelessly and connect to your home network.
Can’t connect to a guest Wi-Fi network that I set up
Guest Wi-Fi networks allow you to share your Wi-Fi with others in a secure way that helps prevent security issues. You’ve probably seen it on business routers, but it can be set up on home routers, too. If someone is having trouble connecting to the guest network but otherwise the Wi-Fi seems to be working, there are a few things you can try.
First, if you just set up your guest network, wait a few minutes. It may take a little time for the network to show up. If the guest network is visible, take a minute to head into your router app and check settings. Settings like Public Wi-Fi Active and Allow Guests to Access My Local Network should always be enabled. If it’s still not working, reset your router and try again.
Keep in mind, some guest networks have a stricter limit on how many devices can use them. If you have over a dozen people already on the guest network, others may not be able to log on.
Wi-Fi 6 or 6E isn’t working, even with a Wi-Fi 6 router
Wi-Fi 6 offers a host of improvements from older Wi-Fi standards, including improved performance, less latency, and better security. But if you don’t think you’re getting Wi-Fi 6 features from a router that supports it, something could be wrong with your setup.
Do you have any extenders on your network? If those aren’t compatible with Wi-Fi 6, you won’t be able to enjoy Wi-Fi 6 speed and features. If your device has picked up the signal from an extender, Wi-Fi 6 benefits may not be making the trip.
Additionally, most devices will need at least partial support for Wi-Fi 6 features to be able to use them. Devices that are several years old may not be compatible with any Wi-Fi 6 changes. That includes your phone and laptop, as well as smart devices that you might be using.
Even desktop computers may struggle with this. Internal Wi-Fi adapters may struggle to pick up on Wi-Fi 6 benefits when you switch to a new router, even if they are technically compatible. You should update your Wi-Fi drivers to fix any potential issues.
Can’t find a router with Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi 7 is the next generation of wireless technology, and it’s technical name is 802.11be. It’s the successor to existing Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E routers, and will offer much greater performance, with up to 36 Gbps data transfer rates — that’s more than three times faster than Wi-Fi 6 speeds. It also lets devices use multiple frequencies simultaneously to better utilize available network bandwidth.
The only downside to this is that Wi-Fi 7 routers aren’t yet available at competitive prices. There are some Wi-Fi 7 routers, like the impressive TP-Link Deco BE85 , but that’s a $1,500 mesh router system and complete overkill for just about anyone.
You can expect to see more Wi-Fi 7 routers with more approachable price tags in the coming months.
Editors' Recommendations
- ChatGPT not working? The most common problems and fixes
- The most common Skype problems and how to fix them
- The most common Microsoft Teams problems and how to fix them
- The most common Zoom problems and how to fix them
- How to change your router’s Wi-Fi password
- Work From Home

Whether you're designing it yourself or getting a pre-built PC, it can be easy to get a computer and realize that it doesn't have a native Wi-Fi adapter. Or, maybe it does, but you're internet speeds are getting faster, game downloads are getting bigger, you've already upgraded your router and need an adapter to match your newfound power requirements. No matter the situation, an external Wi-Fi adapter that you can add to your PC setup or even laptop setup will be worth your time. Here, we investigate the best Wi-Fi adapters for PC use. Most are incredibly affordable and just snap into a free USB port and start working. The best Wi-Fi adapter for PC in 2024
Buy the for the overall best Wi-Fi adapter for most people. Buy the as a good runner-up. Buy the for a convenient USB stick adapter on the affordable side. Buy the if you're having trouble with reception. Buy the for a miniature USB Wi-Fi adapter plug on the cheap. (Great for laptops!)
If you use a desktop PC or laptop for long enough, chances are you're going to come across one of the common GPU problems that have plagued gamers and workers since the humble graphics card debuted for the first time. The question is, do you know how to fix them? If not, never fear. We're here to help.
Whether you're encountering poor performance, overheating, visual artifacts, or a dreaded black screen, we're going to help you diagnose and fix these common GPU problems.
Your computer’s motherboard is one of the most vital components in your PC’s chain of command. Think of it as the brain of your entire system, handling everything from processors and graphics cards to power distribution and local memory. If your computer’s been running slower than normal, and you’ve done everything you can to clear your cache, cookies, and other digital debris, then there’s a good chance your motherboard may be the culprit.
Fortunately, there’s a couple of methods you can use for getting your motherboard back in working order, and we’re going to walk you through each part of the process.

Fix network connection issues in Windows
Try these things to troubleshoot network connection issues in Windows 11.
Make sure Wi-Fi is on. Select Start > Settings > Network & internet , then turn on Wi-Fi . Next, select More options ( > ) next to Wi-Fi, then select Show available networks . If a network you expect to see appears in the list, select it, then select Connect . Open Wi-Fi settings
See if you can use the Wi-Fi network to get to websites from a different device. If you can’t, restart your modem, router, and device, and re-connect to the Wi-Fi.
Try turning Wi-Fi on and off. This can solve issues by restarting your connection.
If your Surface still isn't connecting, try the steps on Surface can't find my wireless network .
Get more help fixing network connection issues
Try these things to troubleshoot network connection issues in Windows 10.
Use the Network troubleshooter. Select Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Under Change your network settings , select Network troubleshooter . Open Status settings
Make sure Wi-Fi is on. Select Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . Next, select Show available networks , and if a network you expect to see appears in the list, select it, then select Connect . Open Wi-Fi settings
See if you can use the Wi-Fi to get to websites from a different device. If you can’t, restart your modem, router, and device, and re-connect to the Wi-Fi.

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
10 ways to troubleshoot and fix any Wi-Fi problems you're encountering
- When you encounter Wi-Fi problems, you can try troubleshooting your network or devices, check with your internet service provider, and more.
- Start by eliminating obvious problems and making sure you know whether it's related to the Wi-Fi network, internet connection, one device or all devices.
- Here are 10 ways to troubleshoot and solve Wi-Fi problems.
It can be hard to imagine or remember the days before Wi-Fi , when you had to run Ethernet cables throughout the house to connect computers to the internet and carry files around on CDs and portable hard drives (affectionately known as "sneakernet").
These days, we take Wi-Fi for granted – right up until it stops working and brings our modern connected household to a complete stop.
How to fix Wi-Fi problems
Here are 10 ways to troubleshoot and solve common Wi-Fi problems.
Basic check: Is the Wi-Fi router running?
It's not out of the question for the plug to have been accidentally pulled or the cat to have stepped on the power button. Make sure the Wi-Fi router's lights are on.
Is the issue related to one device or all devices?
Fixing computer problems like Wi-Fi connection issues often comes down to the process of elimination. That's why technical support technicians often start by asking silly and obvious questions like "is the computer plugged in?" Once you know the Wi-Fi is running, check to see if the problem happens on just one device or on all of them. If you can't connect on your laptop, for example, check your phone to see if you can see Wi-Fi signal strength bars.
Send a ping to Google
One other easy thing you can check for: is the connection problem related to your Wi-Fi network or to your internet service provider's internet signal? Your Wi-Fi network might be fine, for example, but the ISP's internet may be out. To find out, run a ping test using a computer.
1. On your PC, click the Start button search box and type "CMD," then press Enter.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type "ping Google.com."
3. Wait for the result.
If you see an error message, you might not have a working internet connection; continue troubleshooting in the next section. If you see a reply from Google, then you have a working internet connection and the problem lies elsewhere.
You can also log into your account for your internet service provider to check if there's an outage in your area. With many providers, a banner will appear at the top of your account page notifying you of an outage, or you can search for an outage map on the site.
Troubleshooting no service at all
This is unfortunately one of the more common problems people run into — the internet simply doesn't work at all. If none of the devices or computers on your Wi-Fi network can connect, reset both the internet router and Wi-Fi (this might be one device or two different ones). Unplug them, wait two minutes, and plug them back in. If your Wi-Fi doesn't start working again, the problem might be with your internet service provider — call customer service and let them troubleshoot.
Resolving slow or spotty internet in certain rooms
If your Wi-Fi drops out in certain parts of the house on a regular basis, the problem is almost certainly a "dead zone" caused by a router that can't reach everywhere. If possible, move the router to a more central location in the house. Alternatively, you can add a Wi-Fi extender to increase the range of your router.
Troubleshooting slow or spotty internet at certain times of day
If your connection problem isn't related to where you are in the house but is an intermittent problem at certain times of the day, the issue is likely related to a lack of bandwidth; too many devices are connected to the Wi-Fi network and using too much data. If three people are streaming Netflix on different devices at the same time, for example, there's your culprit. If possible, connect devices with an Ethernet cable so they aren't using Wi-Fi, or better yet, take one or more bandwidth hogs offline entirely.
Is your connection slow because of the Wi-Fi network or the ISP?
If you have a connection that's noticeably slow, it can also be helpful to figure out if your poor performance is being caused by a slow internet connection provided by your ISP or if the Wi-Fi network in your home is not working properly. You can do this by running an internet speed test . Run the test at speedtest.net in any browser (on a computer or mobile device). If the internet speed seems normal (at least 10Mbps, for example) the issue is related to your Wi-Fi network, not the internet. Read our detailed guide on how to check the strength of your Wi-Fi for more information.
How to resolve issues with your router
It can be challenging to know exactly what is causing a problem with your Wi-Fi connection, and the router itself has some settings and configurations that might be "breaking" your Wi-Fi network. If possible, check on and update your router's firmware. Most modern routers work with a simple mobile app you can use to check on the firmware and install any available updates. This can resolve issues with your connection reliability and speed. In addition, you can probably use the app to change the channels your router is using to broadcast on its various bands. If your connection is slow or intermittent, changing the channels might significantly improve your Wi-Fi service. For more information, read our article on how to boost your internet connection .
What to do if one device has trouble connecting
Make sure the device's software is up to date. And if your router is a dual-band or tri-band device, try connecting to one of the other Wi-Fi bands. There are any number of reasons why a laptop might connect more easily to one of the 5GHz radios rather than the other, for example.
What to do if your game console can't connect to Wi-Fi
Occasionally, consoles like the Xbox and PS4 can run into trouble connecting to Wi-Fi. Consoles can be affected by the same kind of glitches that affect PCs and mobile devices, but they generally only need to go to one internet location, so troubleshooting can be easier. Open a site like Downdetector in a web browser on your computer or a mobile device and use it to see if the Playstation Network or Xbox Live is down. If so, just wait for the site to come back up. Otherwise, reboot both the router and the console and move them closer together, if possible.

Related coverage from Tech Reference :
'why isn't my internet working': how to identify why you can't connect to the internet and troubleshoot accordingly, how to boost your internet speed at home in 8 ways, and make sure you're not being overcharged for low speeds, 'what is a good internet speed': the internet speeds you should aim for, based on how you use the internet, how to find out how fast your internet is using a free and accurate google speed test, 'why won't my pc connect to wi-fi': 6 ways to troubleshoot your windows computer's internet connection.
Watch: 10 inventions to fight your biggest fashion problems
- Main content
11 Tips to Troubleshoot Internet Connection Problems Win 10
Internet connection problems can be frustrating. This tutorial provides 11 tips with step-by-step guides to help you troubleshoot Internet connection problems on Windows 10, incl. WiFi connected but no Internet, router not connecting to Internet, Internet connected but not working, etc. MiniTool data recovery software also aids you to easily recover lost/deleted files on Windows 10 for free if you lost some data because of computer OS crash, etc.
Internet connection problems can sometimes occur, for instance, computer suddenly can’t connect to Internet, WiFi connected but no Internet Windows 10, etc. Don’t worry, the Internet connection issue is possible to fix.
Below are 11 tips to help you troubleshoot internet connection problems. Try the methods below to fix Internet connection issues like WiFi connected but no Internet connection, router not connecting to Internet, internet connected but not working, and so forth.

Learn how to download free Hola VPN for Chrome, Edge, PC, Mac, Android, iOS, etc. to use it to unblock and access worldwide content online with no limit.
Part 1. No Internet Connection – Troubleshoot Internet Connection Problems (Basic Tips)
If you can’t connect to your WiFi or Internet, you can try the 11 fixes below to troubleshoot Internet connection problems.
Fix 1. Restart Your Computer
Restarting computer can often fix many issues you are encountering. When your computer suddenly has no Internet connection, you can click Start -> Power -> Restart to reboot your computer.
Fix 2. Check Internet Connection with Another Device or Try to Access Other Websites
If you meet this site can’t be reached error when visiting a website, you can try to visit more websites to see if you can access them. You can also try another device to see if it can connect to the Internet. If the Internet connection problem only happens on one device, then you can focus on fixing no Internet connection problem on that specific machine. You can get some solutions in Part 2.
Fix 3. Restart Internet Modem and Router
Sometime restarting the Internet Modem and Router can fix many minor Internet problems. You can directly cut off the power supply of Modem and Router to turn them off, or manually unplug your modem and router from their respective power sources. After a few minutes, you can turn on your modem and router again, and check if router not connecting to Internet issue is fixed.

Download Urban VPN for Chrome, PC, Android, iOS, etc. to use this free VPN service to access any website in various locations and countries.
Fix 4. Check for Virus/Malware Infection
Malware or virus infection could make your computer work abnormally and cause Internet connection problem. You can use Windows Defender or third-party antivirus software to run a malware/virus scan for your computer.
Fix 5. Reset Your Router to Troubleshoot Internet Connection Problems
Soft reset: If you still can’t connect to Internet, you can perform a router reset. You can perform a soft reset by unplugging and plugging the Power Connector on the front or side of your router.
Hard reset: You can also perform a hard reset to restore the network to its factory settings. This would also factory reset your network name and password. You can press and hold the Reset button on the back of the modem or router for above 30 seconds to reboot the modem/router.
Normally the Reset button is recessed on the back of the modem and router. You can use a pen or some other tools to press this button.
Fix 6. Move Your Computer Closer to the Router
The distance between the device and the wireless access point will affect the performance of WiFi connection. If your device is excluded from the wireless signal range, it can’t connect to the Internet. You can move your device closer to the router and try to connect again.
Fix 7. Contact Your ISP (Internet Service Provider)
If you still can’t connect to Internet or experience slow Internet speed, you can contact your Internet Service Provider for professional help.

This post gives a VeePN review and offers guides on how to download VeePN for Chrome, Edge, Firefox, PC, Mac, Android, iOS, etc. to use this VPN service.
Part 2. How to Fix WiFi Connected But No Internet Connection (Advanced Solutions)
Since some of you may also encounter WiFi connected but no Internet connection problem, below we’ll continue to introduce some advanced solutions to help you fix this issue. You can also try some of these fixes if you can access the web on other devices but not on your PC.
Fix 8. Temporarily Disable Antivirus Software
You can try to temporarily disable or uninstall any third-party antivirus software to see if the WiFi connected but no internet problem can be fixed. Sometimes antivirus can interfere some processes on your computer.
Fix 9. Troubleshoot Your Device Internet Connection Problems
You can click Start -> Settings -> Update & Security -> Troubleshoot . Click Internet Connections and click Run the troubleshooter button. Windows will automatically search and fix detected problems with the connection to the Internet or websites.
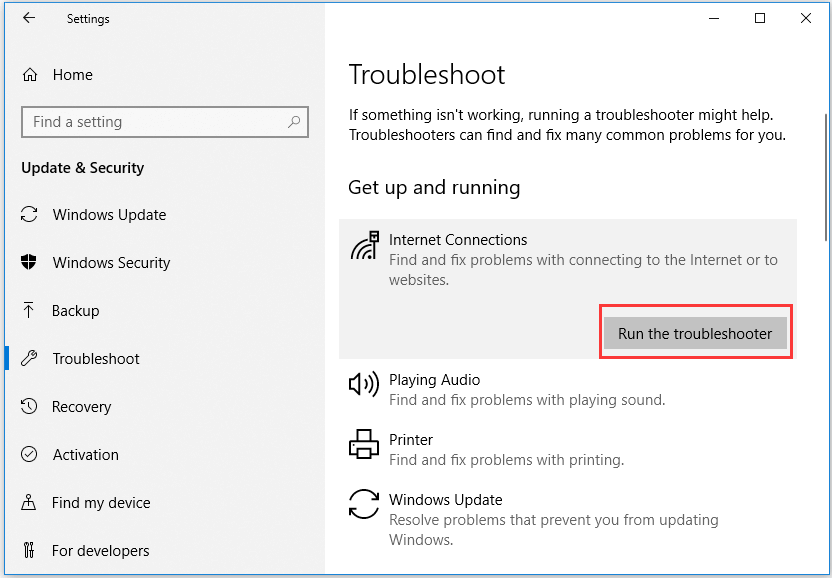
Learn how to download free Browsec VPN for Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Android, iOS, etc. to use it to access restricted content/websites.
Fix 10. Update Network Adapter Drivers
- You can click Start , type device manager , and choose Device Manager to open it.
- Expand Network adapters , and right-click your network device and choose Update driver .
Then you can check if your Windows 10 PC can connect to Internet.
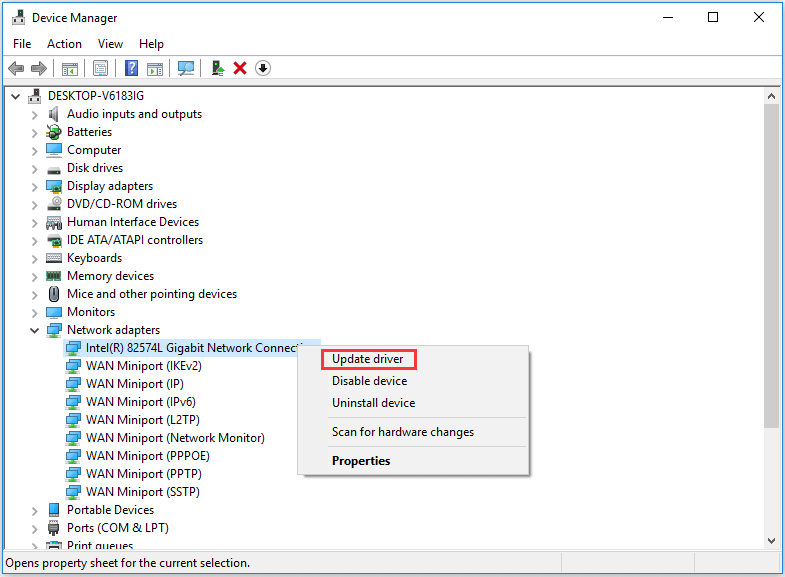
Fix 11. Reset DNS/TCP/IP Settings
You can press Windows + R , type cmd , and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open Command Prompt Windows 10 .
Then you can type the command lines below to reset DNS/TCP/IP.
- ipconfig /release
- ipconfig /all
- ipconfig /flushdns
- ipconfig /renew
- netsh int ip set dns
- netsh winsock reset
This tutorial gathers 11 fixes to help you troubleshoot Internet problems, hope your Internet connection issues like no Internet connection, WiFi connected but no Internet Windows 10, router not connecting to Internet, Internet connected but not working, etc. can be fixed now. If you have better ways to solve Internet connection problems, please do not hesitate to share with us.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
- Accessories
- Entertainment
- PCs & Components
- Wi-Fi & Networks
- Newsletters
- Digital Magazine – Subscribe
- Digital Magazine – Info
- Smart Answers
- Best laptops
- Best antivirus
- Best monitors
- Laptop deals
- Desktop PC deals
When you purchase through links in our articles, we may earn a small commission. This doesn't affect our editorial independence .
Wi-Fi problems? Here’s how to diagnose your router issues

Whenever someone sends me a question about how to fix their Wi-Fi, I wince. It’s not that I dislike helping people with their router problems. In fact, there are few geeky endeavors I find more rewarding than fixing Wi-Fi connection issues at a friend or family member’s home.
But Wi-Fi has always felt more like a dark art than a science, and it’s an art that’s hard to conjure without being physically present. Potential points of failure are everywhere, and what works well in one home might not in another. Even the reviewers of networking gear can reach drastically different conclusions about the very same product.
Wi-Fi is fundamentally at odds, then, with my desire to answer questions with specific recommendations. The best I can do is walk your through how I diagnose Wi-Fi problems myself. That way, you can make better decisions on whether (and how) to upgrade your own gear.
Further reading: The best mesh Wi-Fi routers
Size up the Wi-Fi problem
The first step to solving Wi-Fi issues is to see if the slowdown is coming from your cable modem (which brings internet service into the home) or from the router (which distributes Wi-Fi connectivity throughout the home).
Start by plugging a computer directly into your modem with an ethernet cable and running a speed test. (The easiest way is to do a Google search for “speed test,” then hit the blue “Run Speed Test” button atop the search results.) A USB-to-Ethernet adapter will be necessary for testing on computers that don’t have an ethernet port, but if that’s too much trouble or you don’t have a proper computer at all, you can also try calling your internet provider and asking them to test your internet speed remotely.

Running speed tests throughout the house can help you figure out where the Wi-Fi trouble spots are.
Jared Newman / Foundry
If wired connection speeds are on par with your internet provider’s advertised speeds, the next step is to start running speed tests throughout the house. Measure speeds around the area where connectivity feels slow, then work your way back to where the router is located, running multiple tests in each area as you go.
The goal here is to figure out where your connection troubles are occurring. Consistently slow speeds throughout the house may be a sign of an outdated router, while dead zones or range issues may require a more powerful router or mesh Wi-Fi system. (More on that shortly.)
Find your Wi-Fi router’s 802.11 version
To figure out whether a router needs replacing, it helps to know how old it is. One way to do this to locate the router’s model number—it’s likely printed on the router itself—then search the web for info about which version of Wi-Fi it supports. Here are the major Wi-Fi versions to know about:
- 802.11a/b/g: Extremely old and almost certainly the source of all your Wi-Fi problems.
- 802.11a/b/g/n (or just 802.11n): Outdated at this point and a solid candidate for replacement. Many of these routers only support a single frequency band that’s slower and more congestion-prone, and “dual-band” variants have limited range on the faster 5 GHz frequency band.
- 802.11ac (also marketed as Wi-Fi 5): Not the latest standard, but still widely available even in some high-performance routers.
- 802.11ax (or Wi-Fi 6): Routers using this standard started shipping in late 2020, so your router is likely quite new.
- Wi-Fi 6E: Congrats, you probably just bought a new router .
Wi-Fi versions alone aren’t an indicator of quality—a cheap Wi-Fi 6 router can be worse than a high-end mesh system with Wi-Fi 5—but each successive version has introduced new features that improve connectivity, and we’ve generally seen a push toward better performance over time.
Try some smaller router fixes
Just to rehash a tip I discussed back in July , sometimes changing your router’s channel and bandwidth settings can work wonders for reducing Wi-Fi interference, especially if you’re seeing inconsistent speeds on devices that aren’t too far from the router. By digging into your router’s settings, you can bypass automatic channel selection and find a channel that might be less congested.
You can also try some other little tweaks, like getting your router off the ground and clearing some space around it—but I wouldn’t start rearranging your room for the router’s sake. Chances are the improvements will be minimal. Of course, moving your router to a more central location in the home can help, but that would likely require having the cable company rewire your home internet connection.
Wi-Fi extenders: a last resort

Because replacing a router is a pain, a lot of folks wonder if they can just solve their problems with a Wi-Fi extender or repeater , which take the wireless signal from a router and rebroadcast it farther away. (“Extender” sometimes refers to a device with a wired connection to the router, though I often see both terms used interchangeably.)
My experience with Wi-Fi extenders is hit or miss. Wireless repeaters will always degrade whatever signal they receive, so the benefits can cancel out if you’re trying to address a dead zone or interference from other nearby wireless devices. The same is true with powerline adapters , which send a wired ethernet connection from your router to another part of the house through your wall outlets. Depending on how your house is wired, this approach can give you a weak connection or not work at all.
I don’t tell people to avoid extenders outright, because they can work in some scenarios, but keep your expectations low and be prepared to return the device if it doesn’t help. Here’s how to set up a Wi-Fi extender if you decide to go that route.
Picking a new Wi-Fi router
Once you’ve concluded that it’s time to replace your router, then what?
our favorite mesh wi-fi system
Netgear orbi home wifi system (rbk50).

A mesh Wi-Fi system will be the surest way to solve your Wi-Fi problems, especially in larger homes or ones with lots of dead zones. These systems let you plug in multiple access points throughout the house, creating one big network. They’re better at managing connections than a router with an extender, and systems advertised as “Tri-Band” can connect each access point without congesting the rest of the network.
Such systems might not be necessary, though. If you haven’t replaced your router in a while, even a new standalone router might be enough to power through dead zones if they’re not too far away. Standalone routers are generally less expensive than mesh systems, and some have features that mesh systems lack, such as USB storage support or a large number of ethernet ports.
A supremely powerful gaming router
Tp-link gx90.

Ultimately, though, there’s no way to tell for sure if a new router will work without trying it yourself. You can read all sorts of reviews—PCWorld reviews both Wi-Fi mesh systems and the latest Wi-Fi 6E routers —but even the best advice isn’t one-size-fits-all. Buying a new router will always involve a leap of faith.
A note on modem/router combos
Finally, there’s one more complicating factor: Although cable companies used to distribute internet modems and routers separately—the former bringing in the internet from outside the house, and the latter to distributing Wi-Fi through the home—it’s increasingly common now to get both functions in one box. That makes installation easier for the cable company, but makes router replacement trickier for you.
If you have a combo box and are paying for it in rental fees, consider replacing it with two devices: A new router and a separate cable modem . But be aware that some companies—particularly fiber-optic internet providers such as AT&T and Verizon—make replacing the modem component difficult or impossible.
If replacing the modem isn’t possible or necessary, you can just disable its Wi-Fi features so they don’t interfere with your new router. The instructions for doing so can vary by provider, so expect to do some Googling of “modem mode” or “bridge mode” plus the name of your internet provider.
And if you’re still having Wi-Fi problems after all that, send me an email and I’ll do my best to help. You can also check out my Advisorator newsletter —where a version of this story first appeared—to get more practical tech advice every week.
Editor’s note: This article has been updated with up-to-date product recommendations.
Author: Jared Newman

Jared Newman has been helping folks make sense of technology for over a decade, writing for PCWorld, TechHive, and elsewhere. He also publishes two newsletters, Advisorator for straightforward tech advice and Cord Cutter Weekly for saving money on TV service.
Recent stories by Jared Newman:
- Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E: Which router should you pick?
Connected to Wi-Fi, but No Internet Access in Windows? What to Do
Follow these steps when your router has no internet access.
Quick Links
What does it mean when you're connected with no internet.
- Confirm Other Devices Can't Connect Either
- Reboot Your PC
- Reboot Your Modem and Router
- Disable Any VPN Connections
- Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter
- Check Your IP Address Settings
- Check Your ISP's Status
- Try Networking Command Prompt Tools
- Disable Security Software
- Update Your Wireless Drivers
- Reset Your Network
Seeing the dreaded Windows 10 or Windows 11 internet connection icon proclaiming that you have No Internet Access ? We'll show you the steps to follow when you have no internet access but are still connected to Wi-Fi in Windows.
Before we proceed, we should explain what's happening on your network when you're connected to Wi-Fi but have no internet. This requires knowledge of some home networking basics .
Wireless devices, like a laptop, connect to your router. The router is a device that manages the network connections for the devices in your home. Your router plugs into a modem , a device that bridges the traffic on your home network to the wider internet.
When you see error messages like Connected, no internet access or Connected but no internet on your computer, it means that your computer is connected to the router correctly, but can't reach the internet. Conversely, if you see Not connected, no internet or No internet connection messages, it means that your computer is not connected to a router at all.
This gives you some clues about the issue, as we explain below.
1. Confirm Other Devices Can't Connect Either
Before you do any troubleshooting, it's important to determine whether your PC is the only device with no internet connection. Grab your phone (or another device connected to your Wi-Fi network) and see if it's online—try streaming a YouTube video to check.
On some Android versions, this problem is indicated by an X icon over the Wi-Fi symbol in your status bar (you'll be connected to your mobile network for data). iPhone and iPad users can visit Settings > Wi-Fi and check for a No Internet Connection message under your network name.
If your Windows computer won't connect but other devices will, this is likely due to a misconfigured setting on your PC. But if you have no internet on every device, the problem lies with your network equipment and you can thus skip some of the PC-only steps below, as noted.
Before you proceed, if the problem affects all your devices, you should perform a quick test. Disconnect the Ethernet cable that connects your modem to your router, and use it to connect your PC to the modem directly instead.
If you can get online with this setup, the problem lies with your router. Thus, if you proceed through the following troubleshooting and don't find the fix for your issue, your router is likely faulty.
2. Reboot Your PC
This step isn't necessary if your connection issue is affecting multiple devices.
As with many issues, rebooting your computer is the first troubleshooting step you should try. If you're lucky, you might clear up any temporary bug by restarting, which will fix your PC's network connection issue.
Most of this advice assumes you're using a Wi-Fi connection, since they run into problems more often. However, if you connect your computer to your router with an Ethernet cable, you should also try another cable to confirm that yours isn't faulty.
3. Reboot Your Modem and Router
Since most network issues involve your modem and router, rebooting them is a wise early step. While some routers offer the option to reboot through their web interface, you don't need to do this. Pull the power plug from both devices and leave them unplugged for a few minutes—or use the physical power button if there is one.
Power up the modem again first, letting it fully boot up before you plug in your router again. Wait a few minutes to make sure both are running. While doing this, confirm that your router and modem are working properly. If you don't see any lights on one of the devices, or the lights appear red or flash in an irregular pattern, you may have a bad piece of network hardware.
If your computer says "no internet" even after this, continue—your issue is more complex than a basic reboot.
Note that you're simply rebooting, not resetting, your equipment. Resetting means putting the device back to its factory default settings; you don't need to do that yet!
4. Disable Any VPN Connections
Using a VPN has benefits, but it also adds a layer to your internet connection setup. As a result, what you think is an issue with your home network connection could be a problem with your VPN. Sometimes a VPN will time out if you're connected for too long while your PC is idle, or you could be using an overloaded server that can't handle your connection.
If you're running a VPN, whether through an app, a manual connection in Windows, or on your router, disable it and try to get online again. If that doesn't fix it, keep the VPN turned off for the rest of your troubleshooting to reduce the number of variables.
5. Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter
If you're only having an issue with your Windows PC, something is likely wrong with your computer's network settings. While the built-in Windows troubleshooter usually doesn't fix issues, it's worth a try before you move onto more advanced steps.
To access the network troubleshooter on Windows 10, visit Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Select Network troubleshooter and follow the steps to see if Windows can rectify the problem.
On Windows 11, you'll find this tool at Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters > Network and Internet .
6. Check Your IP Address Settings
Next, you should walk through one of the key steps for diagnosing network issues : confirming that your computer has a valid IP address. In most home networks, under normal circumstances, the router hands out an address to devices when they connect. If your computer's IP settings aren't correct, it can cause this "no internet access" problem or an IP conflict .
Review IP Settings on Windows 10
When using Windows 10, head back to Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Click the Change adapter options entry and then double-click the connection you're using.
Once you have a window open with information about your connection, click the Properties button. Find Internet Protocol Version 4 in the list and double-click that.
There, make sure you have Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically both selected. Setting an IP address manually is for advanced use; chances are if you have something entered here, it's invalid.
Click OK after setting these both to use automatic values, then try to get online again.
Check IP Options on Windows 11
If you're using Windows 11, open Settings again and go to Network & internet . Click Advanced network settings at the bottom of the list, then select the network connection you're using. In the expanded list, choose View additional properties at the bottom.
On the resulting menu, make sure IP assignment and DNS server assignment are both set to Automatic (DHCP) . If not, click the Edit button next to these and change them both to Automatic . Once you confirm this, try connecting again.
7. Check Your ISP's Status
If you still can't get any devices online, it's worth checking if your internet service provider (ISP) is having an issue. Though this is rare, it could explain why you have no internet access across devices.
Use your phone's data connection to see if Xfinity, Verizon, or whatever company provides service for your home has reported outages. DownDetector is a great site for this, as it includes an outage map to show where reports are happening. A quick Google or X search can reveal whether others are having a problem, too.
8. Try Networking Command Prompt Tools
Windows offers several networking commands in the Command Prompt . You should run a few of them if you still have no internet access in Windows. Type cmd into the Start Menu, then right-click on it and choose Run as administrator to open an elevated Command Prompt window.
To reset some of the files Windows keeps to access the internet, use these two commands:
If that doesn't work, try releasing your computer's IP address and obtaining a fresh one from the router with these two commands, one at a time:
Finally, refresh your computer's DNS settings with this command:
It doesn't hurt to reboot your PC again at this point. If you continue to be stuck offline, there are a few more steps to try.
9. Disable Security Software
Another uncommon, but plausible, scenario is that you have security software on your PC preventing access to the internet. Avast and other antivirus suites have had problems where glitched updates block some websites—or even the entire internet—for no good reason.
Disable any third-party antivirus apps you may have installed and see if your connection returns. If it does, you may need to change the settings in your antivirus app or consider using an alternative solution.
While on the topic of security, it's worth running a malware scan with an app like Malwarebytes . While unlikely, a malicious program could have knocked out your internet connection.
10. Update Your Wireless Drivers
Normally, you don't need to update most of your computer drivers, as doing so can cause more problems than it's worth. But if your network connection issue persists, you should check for driver updates for your computer's wireless chip.
If you have a manufacturer update app (like HP Support Assistant or Lenovo System Update) installed on your PC, open that up and check for wireless driver updates. Otherwise, follow our guide to updating your Windows drivers manually.
11. Reset Your Network
If you've proceeded through all these steps and still have the "no internet access but connected" problem, there's not much you can do other than reset your network settings.
If your Windows PC is the only device you can't connect with, you can reset its network configuration on Windows 10 by visiting Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Click the Network reset text at the bottom of the screen, then Reset now . On Windows 11, go to Settings > Network & internet , then click Advanced network settings and choose Network reset .
Following the prompts in these menus will completely remove all network adapters and set all your network settings back to default. You'll have to set everything up again, including VPN software, but it might be the fix you need.
When you can't get online with any devices in your home, your best bet is resetting your router (and modem, if needed). Look for a small pinhole on the back or bottom of your router and hold it in (using a paper clip or similar object) for several seconds to reset it to factory defaults. If there's no physical reset button, you'll need to log in to your router and run a factory reset from there.
With everything reset, you can run through the initial setup and use the factory defaults to see if you can get online again. If you still have no internet connection after this, you likely have faulty equipment and need a replacement. If anything you own is still under warranty, contact the manufacturer.
Hopefully, you don't have to factory reset anything to fix your connection issue. One of the earlier steps should take care of it, but there's no perfect formula for network issues. If you follow all the steps, you've confirmed that your devices are set up correctly and you don't have anything blocking the connection.
It's possible to jump into more comprehensive troubleshooting if you desire. However, it might be worth contacting a network-savvy friend for further help instead.

Internet Down Again? Here Are 5 Possible Causes and How to Fix Them
Internet provider options, vault’s viewpoint on internet issues.
- Internet or WiFi outages disrupt users’ internet connection for work or pleasure, causing inconvenience, frustration and even lost income.
- Rebooting your equipment and using ISP or device troubleshooting tools can resolve most common internet issues.
- Frequent errors and slow connections can require additional investigations.
Resolving Home Internet Outages
According to Pew Research , eight in 10 U.S. adults subscribe to a home broadband internet service. Another 15% are “smartphone-only” internet users, meaning they use a mobile carrier for internet services, not an ISP at home.
Outage frequency and length vary by region and ISP provider. In 2021, Pew Research found that about one in 10 Americans “often have problems connecting to the internet at home.”
Why Isn’t My Internet Working?
Most internet issues stem from equipment problems. Checking cables and rebooting your modem or router can reconnect your service. But what if your wireless connection is intermittent or just crawling at a snail’s pace?
Several factors can impact your home internet, from inclement weather to ISP outages. The remedy and troubleshooting methods differ depending on the potential causes.
Internet issues include the following:
- ISP disruptions: It’s rare for a provider outage to affect only one address. Infrastructure damage, maintenance or failures usually impact dozens or thousands of residents. A neighbor or construction worker can cut through a fiber optic cable or a scheduled upgrade may take longer than planned.
- Basic router or modem errors: Internet equipment is always running. Like other electronic devices, routers and modems have memory storage, download firmware updates and deal with power fluctuations. Each aspect can cause temporary glitches, resulting in an internet or WiFi outage.
- Weather or natural disasters: Signal interference and physical damage can cause your internet to go down. Extreme temperatures disrupt connections and strain equipment, whereas severe conditions prevent services from transferring data efficiently or at all.
- Home network or hardware issues: Ongoing or sudden problems could stem from WiFi dead zones, bandwidth issues or older devices. If the problem doesn’t come from outside the house or is managed by a simple reboot, you should further inspect your network and equipment.
- Cyber incidents: Bad actors can steal your bandwidth, hijack your domain name server (DNS) settings and compromise your home router. Although ISPs have systems to manage distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on their networks, their services may not cover cybersecurity breaches on yours.
How to Fix My Internet Issues Quickly
For many people, their internet has run reliably for ages. Then, one day, it doesn’t. Conversely, some live in regions with more frequent outages. Always start by confirming that you have power, everything’s plugged in and you paid the bill.
Smaller communities or areas with only one internet provider might check their local social media community pages. You’ll learn if the internet is downor if you should troubleshoot further.
Without knowing why your internet isn’t working, you can try the following actions:
- Check your ISP’s website to learn about an outage in your area.
- View Downdetector or Cisco’s Thousand’s Eyes outages map to see service disruptions.
- Unplug your modem and router (or combo unit), count to 30, and restart your equipment.
No Internet Connection? Here Are 5 Solutions
Rebooting your modem doesn’t always work; recurring interruptions could signal a different issue. Think of a household like a business. The more you know about troubleshooting your system efficiently, the better you can make informed decisions and resolve problems.
1. Diagnose an Internet Outage
Depending on where you live (and often how many ISPs serve your area), you may have few to no outages or regular service interruptions—once a month or more. You may hear a boom or nothing at all or most of the lights could go out on your router.
Check out your provider’s support site for an internet outage map. See if you can report an outage online or text and receive SMS alerts when the company resolves the issues. If you’re listed, sit tight. (If you have a home or business cell phone plan, you can use the service to access the internet during a home outage.)
Otherwise, look for self-service diagnostic tools. Many broadband and fiber optic services have automated troubleshooting systems for the internet and WiFi. These systems test your connection and send reset signals to devices. If the attempt fails, the automated tool often recommends scheduling a tech visit.
2. Restart Your Modem and Router
Rebooting your devices, including leased modems, routers or combo units, can solve common connectivity issues.Of course, if you have the instruction manual or want to find manufacturer-specific guidelines, you can go that route. But you can refresh most hardware with the following steps:
- Unplug the power cord from the back of the modem, router or all-in-one device.
- Ensure the remaining cords are secure while you wait 30 seconds.
- When the time is up, replace the power cord(s) in the hardware.
- Give the modem to power up and for all the lights to come on.
3. Assess Weather-Related Disruptions
Is it raining? No, Seriously. Depending on your location and ISP’s infrastructure, you may feel your internet goes down every time it rains. It’s also possible to experience an outage due to a severe weather event in another town.
This disruption can halt your internet instantly, slow it down or deliver a sporadic connection. Your home internet needs electrical power, so if the power goes out and you don’t have a backup solution, like a generator, you won’t have internet during a storm.
If you have power but no internet, follow the usual steps of checking with your ISP, using diagnostic tools and rebooting your system. If the weather conditions are ongoing, the ISP may take longer to repair the service.
4. Troubleshoot Equipment or Network Errors
You don’t need a total outage to disrupt your life. Suppose your TVs display error messages every time you turn them on, alerting you that they are disconnected from the internet. You may notice more buffering when streaming video or audio. Family members might mention that they can’t connect to the network.
Performance issues require further investigation. Microwaves or Bluetooth devices might interfere with your WiFi network. Alternatively, someone in your home could be monopolizing bandwidth.
Here are a few tips for reducing connection issues:
- Confirm that your router is centrally located, on a higher shelf if possible, and away from potential obstructions.
- Check with household members to see if a wired connection would support their resource-intensive activities better.
- Adjust the number or types of devices per channel, but remember to put devices far from the router on the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band and others on the faster yet shorter-ranged 5 GHz.
- If your router is over a few years old, consider upgrading or requesting a replacement from your ISP.
- WiFi extenders and mesh systems [link to 3-8-24 mesh wifi article] improve connectivity in multi-story homes. They also support smart devices and multiple, simultaneous high-bandwidth activities, like gaming, conferencing and streaming.
5. Consider Cyber Vulnerabilities
An unsecured or compromised wireless network might cause occasional downtime or slow speeds without any reason. It can also result in a DDoS attack that overwhelms your system, preventing internet access.
In addition to thieving your bandwidth and disrupting your services, cybercriminals access private details. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) cautions that “Internet-connected devices may be used by nefarious entities to collect personal information, steal identities, compromise financial data, and silently listen to—or watch—users.”
Restore your home network by:
- Changing your WiFi network password
- Looking at the list of connected devices and removing unknown hardware
- Updating your router’s firmware
- Enabling your router’s encryption and firewall capabilities
- Checking for network logging tools to monitor activity
Frequently Asked Questions
Do i need home internet if i have a smartphone.
A cell phone with an unlimited data plan and a hotspot can handle a few home devices. However, it doesn’t work as well if multiple family members need to use the same hotspot simultaneously.
Should I Connect My Smart TV to WiFi or Ethernet?
A hard-wired connection delivers faster, more consistent speeds than WiFi when streaming on a smart TV. But since it involves cabling, Ethernet is less flexible than WiFi.
Why Is My Internet Down?
Power outages, modem malfunctions and other problems can disrupt services. Rebooting your router and using diagnostic tools from your internet service provider can help.
The post Internet Down Again? Here Are 5 Possible Causes and How to Fix Them first appeared on Newsweek Vault .


Microsoft Learn Q&A needs your feedback! Learn More
May 20, 2024
Microsoft Learn Q&A needs your feedback!
Want to earn $25 for telling us how you feel about the current Microsoft Learn Q&A thread experience? Help our research team understand how to make Q&A great for you.
Find out more!
Contribute to the Windows forum! Click here to learn more 💡
May 10, 2024
Contribute to the Windows forum!
Click here to learn more 💡
Windows 11 Forum Top Contributors: Ramesh Srinivasan - Kapil Arya MVP - neilpzz - RAJU.MSC.MATHEMATICS - _AW_ ✅
Windows 11 Forum Top Contributors:
Ramesh Srinivasan - Kapil Arya MVP - neilpzz - RAJU.MSC.MATHEMATICS - _AW_ ✅
- Search the community and support articles
- Search Community member
Ask a new question
Please fix your internet connection
How do I remove the red error message "please check your internet connection" on top of my Infinix screen when browsing? My network is ok but the error message won't go away
- Subscribe to RSS feed
Report abuse
Reported content has been submitted
Replies (1)
- Microsoft Agent |
Hello, Roger Segawa1
Welcome to the Microsoft Community.
Hello, sorry to hear about your situation, it seems that the top of your computer is prompting “Please check your internet connection”. Can I ask if you are getting this message in edge or in all screens, if you can take a screenshot here and I will check it out for you.
Of course you can try to reset your network first, you can refer to the following steps to reconnect your network after this.
A.Reset Network
1. Search for CMD, open and find the command prompt (, run in administrator mode)
2. In the command box that pops up, enter the following commands (each line runs after the next one)
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /registerdns
netsh int ip reset
netsh winsock reset
netsh winhttp reset proxy
3. Restart the computer to see if the problem can be solved.
B. Reset Network Settings
Tap windows+R, type inetcpl.cpl, open Internet Options, click Advanced, and check “Use SSL 3.0” and “Use TLS 1.0”, “Use TLS 1.1”, “Use TLS 1.2”, reboot the computer after the application to see if the problem can be solved.
C.Reset Proxy Server Settings
Click windows+R, type inetcpl.cpl, open Internet Options, click Connections, click LAN Settings, check whether the Proxy Server column is checked, if so, uncheck it and click OK, restart your computer after applying it to see if the problem can be solved.
D. Change DNS
1. Click windows+R and type ncpa.cpl. 2.
2. Click on the name of the network you are now connected to, open the Network Status window, click Properties, and then double-click Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4) in the Network Properties window.
3. Manually set the DNS servers to “4.2.2.1” and “4.2.2.2” and restart the computer to see if the problem is solved.
Best regards
Bobhe | Microsoft Community Support Specialist
Was this reply helpful? Yes No
Sorry this didn't help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
Thanks for your feedback.
Question Info
- Internet and connectivity
- Norsk Bokmål
- Ελληνικά
- Русский
- עברית
- العربية
- ไทย
- 한국어
- 中文(简体)
- 中文(繁體)
- 日本語
- Compare Providers
- Review Providers
5 Reasons Why Your Internet Keeps Disconnecting—and How You Can Fix It
How to fix a finicky internet connection.
Random internet disconnections and Wi-Fi drops aren’t just frustrating, they’re tricky. Because these issues tend to come and go, the causes are often difficult to pin down—but it’s not impossible if you know where to look. As a former broadband technician, I’ve encountered this problem countless times. Let’s go over the top five reasons why your internet is disconnecting and what you can do about it.
Fed up with internet problems? Check out your other options.
Enter your zip code below to see what’s available in your area.
Jump to: Top 5 reasons for disconnecting internet | How to fix disconnecting internet | Other reasons for disconnecting internet | FAQ
Top 5 reasons for disconnecting internet
We go deeper into each of these potential internet issues and how you can fix them further down the page. Click on an issue to auto-scroll to its solution.
Here are the most common causes of disconnecting internet service:
1. You need to restart your modem and router Always the first step when troubleshooting internet issues, an equipment restart is like internet WD-40; it gets things moving smoothly again by giving the equipment a chance to flush out any glitches.
2. You have a spotty or weak Wi-Fi signal A weak Wi-Fi signal can result from obstructions, a lack of range, or even interference from other Wi-Fi networks and electronic devices.
3. Your home network is congested A congested network usually means you’re trying to do too much with too little. To fix it, you need to either decrease your internet usage or upgrade your internet plan.
4. Your ISP is having intermittent outages and slowdowns Outages are usually the result of infrastructure issues that your ISP needs to resolve. This is entirely dependent on where you live, and there’s no reliable way you can prevent it. If you experience a lot of outages and the situation doesn’t improve, it may be time to switch ISPs.
5. Your network cables are damaged Damaged cables are difficult to spot because the damage isn’t always obvious from looking at the outside of the cable. An ISP technician is usually needed to diagnose the issue and make repairs.
Test your internet speed
Give your connection a quick health check to see if you’re getting the speeds you’re paying for.
Download speed 000 Mbps
Upload speed 000 Mbps
Latency (ping) 00 ms
Jitter 00 ms

How to fix disconnecting internet
1. your modem and router need a restart.
The first thing to try when experiencing internet issues is a modem and router restart. It’s super quick, super easy, and super effective. This often solves the problem.
The restart process is the same for a modem, router, or gateway (modem/router combo unit):
Step 1: Unplug the equipment’s power cable from the back.
Step 2: Wait 60 seconds.
Step 3: Plug the power cable back in.
Step 4: Wait while the equipment reboots.
2. You have a spotty Wi-Fi signal
If you’re too far from your router, your internet may cut in and out as Wi-Fi signals struggle to reach your device. Obstructions between your device and router may also cause intermittent disconnections.
Pay attention to your device’s Wi-Fi signal meter to see where your Wi-Fi signal gets weak and disconnects. Take note of areas where you disconnect while moving around, and pay attention to what stands between you and your router in those areas.
Certain materials, like stone, metal, tile, and water are particularly hard on Wi-Fi signals. Try to avoid placing your router or devices in areas that force the Wi-Fi signal to pass through these materials. Some examples of things to avoid are placing your router undeath or behind metal furniture, right next to a tiled bathroom, or near a fish tank. Some electronic devices, such as microwaves, garage door openers, and baby monitors can also interfere with your Wi-Fi signal causing slowdowns and disconnects.
Wi-Fi can get tricky, but there’s a lot you can do to improve your signal. Check out our guides on the best place to put your router and how to improve your Wi-Fi range to get the most out of your Wi-Fi.
3. Your internet plan is too slow
If you’re trying to access more bandwidth than your internet plan allows, you’ll experience slowdowns that may seem like your internet is disconnecting. If your internet issues tend to happen when multiple people in your household are using the web, it’s even more likely you’ve reached the speed limit of your internet plan.
To find out if you need to upgrade your plan, first, find your internet plan’s advertised speed. Then, use our speed test below to see if your connection is as fast as it should be. If you get a speed reading that’s close to your plan’s advertised speed, then it’s probably time to upgrade your internet plan. Use our “How much internet speed do I need?” tool below to discover your household’s ideal internet speed.
How much internet speed do you need?
Use our free tool to discover the ideal internet speed for your household.

4. You’re having internet outages
Internet outages come in all shapes and sizes. Sometimes your connection will be out for hours, other times it may flicker in and out like a dying light bulb. Your randomly disconnecting internet could indeed be caused by outages from your ISP.
You can check for outages via your ISP’s app, or web account, or by simply calling your ISP to ask. You can also ask for information on past outages to see if it really is the cause of your persistent disconnections. Most internet providers keep excellent records of their customers’ internet connections. A technical support representative should be able to see exactly how many outages your address has suffered and exactly when those outages happened. Hopefully, they can give you an estimate of when the service will be back to normal.
If you’re sick of dealing with disconnection issues, it may be time to consider switching ISPs. It’s always good to at least know your options. The internet landscape has been changing rapidly. With new services like fiber and 5G home internet, you may have a few more options than the last time you checked. Enter your zip code below to see which internet providers are in your area.
5. There’s an issue with your networking cables
The network cabling in your home can cause your internet connection to disconnect if it’s damaged, loose, or configured poorly.
Here’s what to look for:
- Damaged cables Check all your networking cables for signs of damage. Look for tears, chew marks, and kinks. Make sure coaxial cables are screwed on snug to the modem and wall outlet. Don’t forget to check the Ethernet cable connecting your modem to your router or computer, too.
- Loose cables Coaxial cables should be screwed on tight, and Ethernet cables should make an audible click when fully inserted. Loose cabling is a common culprit of intermittent internet issues because a loose cable may still pass signal, albeit poorly. But the signal may go out completely under any additional stress—like every time the cable moves slightly. Oftentimes, the springy clip that holds the Ethernet cable firmly in the port breaks or loosens. Ethernet cables should make an audible click when inserted into a port and shouldn’t come out without compressing the clip.
- Unused, but active, coaxial lines When you have an active coaxial line in your home that isn’t connected to any equipment, the open line acts as an antenna that introduces radio interference into your home network. If you get a professional install, always ask your technician to close off any open coaxial outlets. Determining if you have an unused but active coaxial line is difficult without professional equipment.
Fixing cabling problems on your own can be difficult because of the specialized tools and skills required. If you suspect a cabling problem, it may be best to request a technician visit from your ISP.
Other reasons why your internet is disconnecting
If you’re still stumped, don’t worry—there are still plenty of fixes to try.
Restart your device
This works more for PCs than anything else. Restarting your device resets some of the networking which may help flush out stubborn glitches.
Update your device
Our computers and devices need to stay up to date to continue working as planned in the very fast moving world of modern technology. But sometimes, it’s easy to put off updates until something stops working. Before you spend any more time troubleshooting, it’s worth completing any needed updates.
Check if your device is auto-switching between two Wi-Fi networks
Your device may jump between known Wi-Fi networks, which you experience as a temporary loss of signal. When Wi-Fi signals are weak, your device may search for a stronger signal automatically.
Try disabling any Wi-Fi auto-joining or auto-switching functions on your affected devices, and connect to your preferred Wi-Fi network manually.
See if you’re on a crowded Wi-Fi channel
Your router broadcasts Wi-Fi on specific radio frequency channels. They can become overcrowded when too many networks use the same channels near each other. This is especially common in apartment buildings and other situations where multiple routers broadcast within range of one another.
If you have an Android phone or tablet, you can use a Wi-Fi analyzer app, like Netspot , to see all the available channels in your home and the usage on each. You could also log in to your router settings and switch the Wi-Fi channel to see if it fixes your dropping internet.
To change your Wi-Fi channel, you need to log in to your router and adjust the channel settings—you can usually find these settings under a tab labeled “Wi-Fi” or “wireless.”
Check for modem issues with your ISP
If your modem is failing to properly communicate with your ISP, perhaps because of an update or a change in compatibility, you’ll start experiencing all sorts of internet problems. For example, if something isn’t quite right with the registration, the modem or ISP may be continuously trying to authenticate one another, causing slowdowns. You’re more likely to experience these problems if you supply your own modem.
You need to contact your ISP to diagnose and fix these issues. They can check if the modem is successfully checking in and updating, that it’s still compatible, and that it’s properly registered. Sometimes, the customer service reps won’t have the ability to run the appropriate test, in which case you need to request a technician visit or an escalation of your issue up the tech support ladder.
To truly complete this step, you need straight answers to the following questions:
- Is my modem registered?
- Is my modem still compatible with the service?
- Is my modem communicating with the network properly?
Update your network adapter drivers
Your computer’s network adapter (sometimes called a network card) drivers update automatically unless you disabled auto-updates in your operating system. Still, it’s worth checking just to make sure.
Follow these steps to update network adapter drivers in Windows 10:
Step 1: In the Windows search bar, type “device manager,” and press enter.
Step 2: Click “Network adapters” in the list of the devices.
Step 3: In the expanded dropdown menu, right-click your network adapter and select “Update Driver Software.”
Step 4: In the resulting dialog box, select “Search automatically for updated driver software.”
Step 5: Follow the remaining on-screen instructions to complete the update.
Step 6: Restart your PC.
Reset your computer’s network settings
Sometimes, giving your computer a clean networking slate can resolve strange disconnection issues and other hiccups that are difficult to diagnose outright. This is a serious move, though—it makes your computer forget all your network settings, so you have to reinstall all your networking software, like antiviruses and VPNs, and reconnect to your home network. So make sure you have all your login credentials before you continue.
To reset your network settings on Windows 10:
Step 1: Click the Start button.
Step 2: Click Settings.
Step 3: Click Network and Internet.
Step 4: From the Status tab, select Network Reset near the bottom of the menu.
Step 5: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the reset.
Try your computer’s built-in network troubleshooter
Windows PCs have network troubleshooter apps built into the OS. These utilities can help you easily diagnose and solve internet connectivity issues on your computer.
Mac OS has a network utility that you can use to run tests and find info that can help diagnose network problems, but Mac OS has no automated network troubleshooter.
Run the network troubleshooter in Windows 10:
Step 1: Navigate to Settings by typing “settings” into the Windows search bar.
Step 2: In the Settings menu, select Network & Internet.
Step 3: Under the Advanced Network Settings heading, select Network Troubleshooter.
Step 4: Follow the prompts as the troubleshooter as it attempts to diagnose the issue.
Open Network Utility on Mac OS:
Step 1: Open Spotlight Search by pressing command + space bar.
Step 2: Type “network utility,” and press enter.
Investigate your computer’s background processes
Computer programs running in the background of your OS can sometimes slow your internet connection or drop it altogether. This can happen if a program hogs all your bandwidth for a short period or conflicts with your firewall. Cloud backup programs, auto-updater clients (think Adobe), and third-party utilities are notorious troublemakers.
On Windows 10, you can see some background programs by clicking the up arrow in the lower left corner of the screen in the taskbar.
You can review all your background processes in the task manager:
Step 1: Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete.
Step 2: Select Task Manager from the menu.
Step 3: Navigate to the Processes tab.
Step 4: Click the Network column to organize the processes by network usage.
Step 5: Investigate any suspicious processes by right-clicking and selecting Properties.
If you find something you suspect may be causing issues, try closing the process’ host program (you can identify the host program in the properties menu from step five). If your internet disconnections stop, you’ve likely found your issue.
Update your antivirus software
Your antivirus software is the gatekeeper to your network. Its main function is to block risky internet traffic, but to do so, it needs to differentiate between good traffic and bad traffic—that means a lot of updates. Most antivirus software have an auto-update option that we recommend keeping switched on.
Temporarily turn off your antivirus
While we definitely don’t recommend spending much time on the web unprotected, the best way to check if antivirus is causing your problem is to temporarily shut it off. Your antivirus could be conflicting with a program and blocking your internet connection.
If turning off the antivirus software fixes your problem, turn it back on and then get in touch with tech support. You may need to disable the conflicting program or process—or try a different antivirus ASAP.
Programs that regularly update or check in with servers in the background are especially prone to creating intermittent internet disconnections. Look out for cloud services and programs suites with update and licensing clients (like Adobe).
Make sure your modem and router have the latest firmware
Your modem and router need regular firmware updates to function properly with your ISP. If your equipment is running on outdated firmware, your internet may periodically disconnect due to glitches or registration issues.
Your ISP automatically updates your modem, but it’s still worth double-checking to make sure the latest firmware is installed. If you have a separate stand-alone router, you should definitely make sure it’s up to date—especially if you didn’t get it from your ISP.
You can check for modem and router updates by logging into each device’s interface via a web browser. If you have a separate modem and router, complete the following steps for each piece of equipment:
Step 1: Open a web browser.
Step 2: Input your equipment’s IP address or login URL—you can usually find this printed on a sticker attached to the back or bottom of the equipment.
Step 3: Enter the username and password—also usually printed on a sticker attached to the back or bottom of the equipment.
Step 4: Find the firmware version number—often labeled and displayed in the upper-right corner of your equipment’s initial settings page.
Step 5: Run a web search or check your equipment manufacturer’s website to make sure your firmware version number matches the version number of the latest update. This is usually as simple as googling your equipment’s manufacturer name and model number followed by the words “latest update.”.
See our more detailed instructions on logging into your router if you’re having trouble accessing your equipment’s settings interface.
Check your router log
Your router keeps a log of significant events on your network. Reviewing this information could lead you to the source of your internet connectivity problems.
You can access your router’s log by logging in to your router’s interface via a web browser. The location of the log will be a little different for different routers:
Step 1: Enter your router’s IP address or login URL into a web browser. You can usually find it on a sticker attached to the back or bottom of your router. See our full guide on how to log into your router for some additional help with this step.
Step 2: Log in with your router admin name and password, commonly on the same sticker as the IP address. If you never set your admin name or password, your login name is probably “admin,” and your password is probably “password.”
Step 3: Navigate to the router log, commonly labeled as “system log” or “network log.” This step is different for different routers, but it’s often under an “advanced” tab.
The log entries are a bit cryptic sometimes, but there’s usually some obvious term that gives away troublesome events. Look for words like “failed,” “malicious,” or “attack.” Google is your friend here—if you see anything suspicious, like the same entry popping up over and over, google it to see what’s going on.
Nothing worked. Now what?
Call your ISP. It’s better equipped to find and solve broadband issues. This might require a technician to come to your home to test the tap on the utility pole, check your signal levels, conduct advanced connectivity tests, and a ton of other things that you can’t do on your own. It’s annoying to schedule and wait for an appointment, but it’s the best way to get your issue resolved permanently.
Why is my internet dropping?
How can i extend my wi-fi range.
You can extend your Wi-Fi range by choosing a central and elevated spot for your router, or by using a Wi-Fi range extender, long-range router, or Wi-Fi mesh network. See our guide on how to extend your Wi-Fi range to learn more.
Additional internet troubleshooting resources
- How to Troubleshoot Internet Issues
- How to Fix Your Slow Internet
- Can I install Internet by Myself?
Author - Austin Aguirre
Austin worked as a broadband technician installing and troubleshooting countless home internet networks for some of the largest ISPs in the U.S. He became a freelance writer in 2020 specializing in software guides. After graduating with a BS in technical communication from Arizona State University, he joined the team at HighSpeedInternet.com where he focuses on home network improvement and troubleshooting.
Editor - Rebecca Lee Armstrong
Rebecca Lee Armstrong has more than six years of experience writing about tech and the internet, with a specialty in hands-on testing. She started writing tech product and service reviews while finishing her BFA in creative writing at the University of Evansville and has found her niche writing about home networking, routers, and internet access at HighSpeedInternet.com. Her work has also been featured on Top Ten Reviews, MacSources, Windows Central, Android Central, Best Company, TechnoFAQ, and iMore.
Related Posts

How-To Geek
How to troubleshoot your internet connection, layer-by-layer.
Broadband is the lifeblood of the modern household and it's incredibly frustrating when your Internet connection is flaky.
Quick Links
Why do i want to do this, troubleshooting your modem, how to troubleshoot your router, how to troubleshoot your devices.
Broadband is the lifeblood of the modern household and it's incredibly frustrating when your Internet connection is flaky. Read on as we walk you through our tried and true troubleshooting techniques so you can pin down exactly where your connectivity problems are coming from.
The obvious answer to why you want to do this is to fix your network problems but actually fixing things in a permanent way involves a bit more troubleshooting than the typical plug and unplug routine. Everyone out there with connectivity/Internet issues wants to fix those issues and they often do so by plugging and unplugging things, turning the power to their devices and networking equipment on and off, and so forth.
Related: Understanding Routers, Switches, and Network Hardware
In most instances those things fix your problems because you force the device software to reload, dump potential errors in the memory, and get (or give) new network assignments but not because you've really isolated what is wrong with your connection. The purpose of this guide is to help you narrow down exactly what is causing the problem so that you have the ability to monitor it in the future and be proactive in keeping your network running smoothly (and, most importantly, so that every time your Wi-Fi gets flaky you aren't stuck in the reboot-everything-in-the-house loop). By narrowing things down you know whether to complain to your ISP to fix a problem beyond your control, troubleshoot your own router, tinker at the device level, or otherwise focus your attention.
"Help me fix my flaky Internet connection" is, by far and away, the most frequent call for help we get here at How-To Geek as well as the top number one request we get from friends and family. As much as we'd love to be able to precisely troubleshoot each of your specific network problems (because we do love fixing geeky problems big and small) that's not something we can, alas, do on a reasonable scale.
What we can do, however, is distill the basics of Internet connection troubleshooting down to a simple workflow that can help anyone, no matter how inexperienced they might be, figure out where the weakest link in their home Internet connection is. The best way to find the weakest link is to start from the biggest of the links in the chain and work from there. Read on as we work from the largest and most critical components of the network down to the individual devices, offering troubleshooting insight as we go.
In addition to working from the biggest link to the smallest link, each section of the tutorial include a "Short Term Fix" and "Long Term Fix" section focused on what to do right now to fix your problem (potentially only temporarily depending on the severity) and what to do to ensure the problem doesn't return (which might include calling the cable guy out to run line tests or replacing your router). In each section we'll list the immediate steps near the top of the section and then further explain why we're performing each step.
Whether your broadband connection is fiber optic, cable, or DSL, the first stop is at the most critical point: the modem. This is the point where your home network is directly linked to the outside world and the last thing within your home you can manage and diagnose before you get into the territory of things that can only be fixed by your ISP (like weak signal strength on the line coming off the utility pole).
If you have no connectivity at the modem level then you're effectively dead in the water until you (or your ISP) resolve it. As such the very first step in any connectivity troubleshooting routine is to establish that the proverbial tap is on and Internet access is flowing into your home.
It Helps to Understand What Your Modem's Lights Mean
One of the most useful troubleshooting tricks, as it requires no particular skill or hassle of connecting or disconnecting equipment, is to simply have documentation on hand that tells you what the diagnostic lights on your modem mean. Whether you look up the modem model number yourself and print the relevant pages from the manual or look it up on your ISP's website and print it from there, having a diagnostic sheet on hand is extremely valuable. It's the difference between "What does the blinking globe mean?" and "The blinking globe means the modem has an established link with my ISP" or what have you.
Diagnostic lights only go so far though and to establish if your modem really is functioning properly it is very useful to directly connect an Ethernet-based device directly to the Ethernet port on your modem. While we would never recommend connecting your computer directly to the modem without some sort of firewall (such as the firewalls built into nearly every commercial router under the sun) for normal use, in this case we're expressly trying to establish that the modem is functioning. You can use your regular computer or laptop, an old beater laptop you keep around just for testing purposes, or even a media device with a network adapter like an Amazon Fire TV, Apple TV, or even a Raspberry Pi.
The goal is to plug your device directly into the modem via the hardline of an Ethernet cable and establish a connection to the greater Internet. If you're using an actual computer, be it a laptop or desktop, it's best to use a very basic connectivity test such as pinging Google's DNS servers. You can do so by opening up a command prompt, "cmd" in the run box, and typing "ping 8.8.8.8". If you get a response then you know your modem is communicating with the outside world. For devices that you can't easily send out a ping request, try performing a simple network connectivity test like prompting the device to check for software updates or loading a streaming video file. While performing the most basic test possible, like a ping, is ideal any method available to you is worthwhile.
The Short Term Fix
If you find that there is no connection between your modem and your ISP (because the connectivity test yields no positive result) the easiest short term solution is to fully disconnect your modem from the power source, the network cables, and the coax/fiber/cable that connects it to the actual utility line or drop attached to your house.
Step 1: Disconnect your modem entirely from the power and network cables (or at least just the power). Step 2: Let the device sit for at least 30-60 seconds. Step 3: Hook up all the network/utility cables and then the power cable.
These are very common directions when you call tech support -- they always want you to leave the device unplugged for at least half a minute. But why?
The short of it is this: devices like modems, routers, and so on, have two types of memory: volatile and non-volatile RAM. The non-volatile RAM (usually referred to a NVRAM) is like a tiny little flash drive inside that stores important stuff like the device operating system and settings. The volatile memory is just like the memory on your computer: used for holding data while the device is in operation but it can't hold data when the power is off. The reason you are told to keep the device off for at least half a minute is because the charge that keeps the little bits of data in the RAM can take that long to full dissipate and the goal is to have the memory totally clean when the device reboots.
When the modem is fully powered up, repeat the above test with your laptop or other Ethernet-enable device to establish that a direct connection between the modem and the greater Internet is possible. If it stays up and active, great. If it loses connectivity make a note of how long it stayed up as this information can be helpful for later troubleshooting.
The Long Term Fix
What if power cycling your modem doesn't immediately solve your problem or the problem quickly returns? There's a good chance something is wrong with your modem or the wiring leading up to the modem. You'll need to contact your ISP and rule out problems on their side.
Step 1: Contact your ISP to determine if your modem needs to be remotely reset/reprovisioned. Step 2: If using a cable modem, determine if the line is split excessively before entering the cable modem. Step 3: Call a support rep out to test the signal strength at your home to determine if the problem is a weak signal or damaged cable. Step 4: Barring any of the aforementioned problems, replace the modem.
They may need to remotely provision your modem, reset it, or make other adjustments (we once had a cable modem for three years that we later found out the cable company had never even formally linked to our account; tech support calls are full of mysteries).
One thing you can do on the street-to-modem side of things that will help is remove extra splitters if you have a cable modem; every time the line is split via splitter the signal strength is diminished by both the number of splitters and the number of splits within the splitter.
If your house was wired for cable in the late 20th century there's a good chance they linked all the cable drops in the house to a monstrous 9-way splitter that is killing the strength of your signal. If you must use such a box to keep the TV signal flowing to various rooms, then we'd recommend using a simple 2-way splitter to branch the cable modem line off before then splitting it with the larger splitting for distribution throughout the house.
If neither you nor the remote support offered by your ISP can put your modem back between the navigational beacons then the next step is to have an ISP representative sent out to check on the actual line and ensure the connection has adequate signal strength at the point it enters your home and, potentially, to replace the modem. If you own your modem ( and you should! ) the replacement cost is on you but at least you know you're getting a superior modem and not paying monthly rental fees. Replacing a modem isn't fun (or cheap) but when our 7 year old cable modem finally bit the dust and we replaced it with a newer one the speed improvements and stability were worth every penny.
If your modem checks out OK but you're still having connectivity issues the next suspect to investigate is your router. You can have the most stable modem in the world but if your router is constant freezing up or rebooting you'll have a very difficult time with any modern broadband applications like gaming, streaming video, and so on.
Router problems are, by far and away, the most frustrating home network problems. Unlike your modem, which is almost always either fully functional or totally offline, routers can be like old cars with a myriad of problems and ghosts in the machine you have to hunt down.
The biggest thing to focus on when troubleshooting your router is to establish what works (starting with the basics like Ethernet-connected computers and working up to Wi-Fi connected devices) and how long they work before issues arise.
Related: Wi-Fi vs. Ethernet: How Much Better Is a Wired Connection?
Can you guess the first step? Grab an Ethernet-enabled device and connect it directly to your router. If you don't have a single Ethernet-capable device in your household, you'll need to conduct the test with Wi-Fi (but we strongly recommend using an Ethernet-based device). Why Ethernet? Wi-Fi is notoriously unstable compared to hardline connections and it's very useful to see if the issue isn't as much your entire router but the Wi-Fi related elements. We've owned and tested many a router over the years where the hardline side of stuff worked just fine but the Wi-Fi was flaky as could be.
Step 1: Connect a device directly to the router via Ethernet. Step 2: Test for connectivity by pinging a common address like Google's 8.8.8.8 DNS server or loading a web page. Step 3: Power cycle router if necessary.
If you can't get a hardline Ethernet connection and/or a wireless Wi-Fi connection, it's time to restart it. Just like the broadband modem your router has volatile and non-volatile RAM. You need to disconnect your device from the power source (not just using the power switch if your router has one) for at least 30 seconds in order to allow all energy in the device to fully dissipate and the volatile memory to completely empty.
Power things back up and see if that restored connectivity. Again, like with your modem, if it loses connectivity after a period of time make a note of how long it was up.
If your router seems to be giving you consistent problems that a simple power cycle didn't iron out, it's time to dig in a little deeper.
Step 1: Check for firmware updates. Step 2: Reset your router (be sure to record the settings first). Step 3: If the previous steps fail to resolve your issue then replace the router.
Your first order of business should be to check the firmware. If you've had your router for years and it doesn't have automatic firmware updating, it's a pretty safe bet that you're firmware is years out of date.
Related: Change Your Wi-Fi Router Channel to Optimize Your Wireless Signal
Not only do you want to update to take advantage of security patches but you want all those missing bug fixes that patch things like memory leaks and instability in the router operating system. Check the control panel of your router and/or the manufacturer website to update the firmware. Most modern routers have a built in check-for-updates function that will download and install the update if you approve it but older routers will require you to download the file yourself and upload it, much like uploading a file to a web site, to the router.
If your problems are Wi-Fi related we'd strongly encourage you to change your Wi-Fi channel. 2.4GHz band Wi-Fi is very congested and if you live in a fairly dense urban area it's quite possible (and outright likely) that your Wi-Fi channel is conflicting with one or more of your neighbors' routers. You can read more about how to change the router's channel here .
The second order of business is to reset your router. This is different from power cycling the device and actually resets it back to the factory settings. While resetting a router is typically not necessary we've run into plenty of situations over the years where a stubborn error was only eradicated via hard reset. Before you perform such a reset, it's important you know what settings were on the router so you can restore them later on. See our guide Clone Your Current Router for a Headache Free Router Upgrade to see what settings you should take the time to write down before performing the reset.
Finally if you find yourself struggling with router problems week after week you might want to consider upgrading to a newer router. We have the privilege of testing a wide range of modern and top-tier routers here at How-To Geek and let us tell you, routers like the Netgear R7000 and the D-Link DIR-890L are astoundingly stable and powerful when compared to the old 2000s-era routers some people are still using.
Here's where things can get a little maddening. Generally speaking it is fairly easy to iron out a modem problem, sort of easy to iron out a router problem, and often quite frustrating to iron out a problem with one particular device on your network. We had an iPhone 6, for example, that hated a particular router we tested. No other device seemed to care one way or the other but that particular iPhone 6 wouldn't stay connected to the Wi-Fi access point for more than a few minutes at a time. Sometimes you simply find particular device is not a fan of your home network.
We can't provide detailed advice on your particular device but we can offer some times for wrangling wayward devices back into the networking pen.
Like in our previous sections, if you can hook a device up via hardline (to avoid any Wi-Fi issues) that's great. We strive to hook as many of our devices up via Ethernet as possible so when and if Wi-Fi issues crop up we can watch our movie in peace or finish our work and deal with the Wi-Fi later.
Step 1: Hook the device up, if possible, directly to the router. Step 2: Restart the device or otherwise force a new address assignment.
Whether connected by Wi-Fi or Ethernet, the first simple step is to restart. The reason restarting a device almost always gets you a short (or even long term) bit of relief from networking problems is thanks almost entirely to DHCP, the dynamic address assignment service used by your router (and the cooperating devices) to get a unique local network IP address. When you reboot the device you force both the router and the device to go through the assignment process and often resolve any issues.
On computers you can force the networking component of the OS to request a new assignment without rebooting. The easiest way to do this in Windows, for example, is to open up the command prompt and enter the command "ipconfig /release" to dump the assigned address and then "ipconfig /renew" to force an update in which the computer will request a new address from the router.
Long Term Device Troubleshooting
Rebooting and forcing DHCP assignment is a short term trick but often times you need to tweak your network a little more permanently. If you're having recurring problems with devices dropping off your network (and you've ruled out Wi-Fi congestion as the source of your headaches) you might find it useful to start assigning static IP addresses to your device. Select an address outside the pool used by the DHCP server (check your router to see what that pool is) and then assign it to the device using your router's control panel.
Step 1: Assign static IP addresses. Step 2: Change the Wi-Fi band the device uses.
Another trick that works well for Wi-Fi devices that can handle both 2.4GHz and 5Ghz bands is to switch the device permanently to the one band or the other (with a preference for the lest congested 5Ghz band). In order to do so you need to assign a unique SSID to each band so you can select one over the other (and force your device to forget the password for the band you don't want it to use). For example if your current SSID is "StevesHouse", leave it as "StevesHouse" for 2.4GHz and rename the 5GHz radio "StevesHouse5G" with a different password. All your devices will still be on the same network but you can segregate them between the two bands more easily.
Troubleshooting network gear isn't exactly fun work but at least with our guide you've got a clear workflow and a clear outcome: stable and enjoyable internet access.
Have a network troubleshooting tip or trick? Jump to our discussion forum with the link below and share your wisdom. Have a question about home networking hardware? Shoot us an email at [email protected].
Image courtesy of Chauncey Davis .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
And clear your browser's cache and cookies. 2. Check the Wi-Fi Settings. (Credit: PCMag / Apple) Check the Wi-Fi settings on your device and make sure you are connected to the proper SSID. If not ...
Loose or damaged cables can cause a wide range of internet issues. Sometimes the fix is as simple as tightening a connection, other times you may need to replace a cable or require the help of a broadband technician. See instructions. 3. Move your router to a better spot If you're using the internet over Wi-Fi, router placement is crucial.
Try Restarting the Problem Device. Ensure That Network Hardware Is Working. Reboot Your Router. Check the Connection Status on Your Router/Modem. Try Another Device to Isolate the Issue. Finally: Contact Your Service Provider. It's useful to have a checklist of things to try when your internet is not working.
Run Get Help to troubleshoot and fix common connection problems. Right click the network icon in the right side of the taskbar and select Diagnose network problems or open Get Help for Network & Internet. Make sure Wi‑Fi is turned on. Select the No internet icon on the right side of the taskbar, and make sure Wi-Fi is turned on.
1. Move closer to the wireless router. Sometimes your computer or smartphone is too far away from the checkpoint to connect to Wi-Fi. Move closer to your router and try to connect again. 2. Position your router antennas upward. If your router has antennas, repositioning them can help create a better signal.
Step 1: Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the lower-right corner of the screen. Step 2: Click "Troubleshoot problems.". Step 3: Select "All network adapters" and click Next. Step 4: Wait while the troubleshooter searches for the problem.
Internet connection problems can be frustrating. Rather than mashing F5 and desperately trying to reload your favorite website when you experience a problem, here are some ways you can troubleshoot the problem and identify the cause. Ensure you check the physical connections before getting too involved with troubleshooting.
The Fix. Many times, restoring your internet connection back is as simple as unplugging your router or modem and plugging it back in. Here's how: Unplug your router and modem from the power source. Wait for one minute. Plug your modem back in and wait 30 seconds. Plug your router back in. Wait five minutes and retry the connection.
Go to Windows Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update. Click Check for Updates. If there are updates available, Windows will download and install them. 8. Open Windows Network Diagnostics. Windows has a tool called Windows Network Diagnostics that lets users troubleshoot connection issues.
Go to Settings. Click Update & Security. Select Troubleshoot on the left-hand side. Select Additional troubleshooters. Select Internet Connection. Now your PC will run an internet connection diagnostic. Wait for the process to finish and see if provides any helpful insight to fix your broadband connection.
Step 2: Wait 60 seconds. Step 3: Plug the power cable back into the back of the equipment. Step 4: Wait for the equipment to reboot (this can take up to 20 minutes). 2. Your home network is congested. Your slow speeds might be the result of trying to do too much at once on your internet connection.
Here's the process: Unplug or power off your router. Wait five more minutes and retry the connection. In most cases, this should fix your issue and allow you to get back online. If you go through these steps and something still isn't working, you may need to contact your internet service provider for assistance.
Get back online with some troubleshooting tips. Quick Links. Double Check the Wi-Fi Password. See if the Connection Requires a Wi-Fi Login Page. Restart Your Connecting Device. "Forget" the Wi-Fi Network and Try Again. Restart Your Wi-Fi Router or Access Point.
The farther away from a Wi-Fi device, the slower the local connection. Wireless signal interference in the area can also limit the range of a Wi-Fi connection. If you can't reach the access point and can't connect to the internet, measure your Wi-Fi signal strength and then boost your Wi-Fi signal.
Reboot your equipment. Unplug your modem and router and plug it back in after 60 seconds. This technique will clear the router cache and improve your internet speed as well. Reset your Wi-Fi ...
Try turning off the Wi-Fi on your device, then re-enabling it — or unplugging and replugging your Wi-Fi dongle. If that doesn't work, restart the device and try again. Then try restarting the ...
Select Start > Settings > Network & internet, then turn on Wi-Fi. Next, select More options ( >) next to Wi-Fi, then select Show available networks. If a network you expect to see appears in the list, select it, then select Connect . Open Wi-Fi settings. See if you can use the Wi-Fi network to get to websites from a different device.
1. On your PC, click the Start button search box and type "CMD," then press Enter. 2. In the Command Prompt window, type "ping Google.com." 3. Wait for the result. If you can see a ping from ...
If the Internet connection problem only happens on one device, then you can focus on fixing no Internet connection problem on that specific machine. You can get some solutions in Part 2. Fix 3. Restart Internet Modem and Router. Sometime restarting the Internet Modem and Router can fix many minor Internet problems.
Size up the Wi-Fi problem. The first step to solving Wi-Fi issues is to see if the slowdown is coming from your cable modem (which brings internet service into the home) or from the router (which ...
To access the network troubleshooter on Windows 10, visit Settings > Network & Internet > Status. Select Network troubleshooter and follow the steps to see if Windows can rectify the problem. On Windows 11, you'll find this tool at Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters > Network and Internet . 6.
Internet Provider Options Vault's Viewpoint on Internet Issues Resolving Home Internet Outages According to Pew Research, eight in 10 U.S. adults subscribe to a home broadband internet service ...
Restart the computer to see if the problem can be solved. B. Reset Network Settings. Tap windows+R, type inetcpl.cpl, open Internet Options, click Advanced, and check "Use SSL 3.0" and "Use TLS 1.0", "Use TLS 1.1", "Use TLS 1.2", reboot the computer after the application to see if the problem can be solved. C.Reset Proxy Server ...
Step 1: In the Windows search bar, type "device manager," and press enter. Step 2: Click "Network adapters" in the list of the devices. Step 3: In the expanded dropdown menu, right-click your network adapter and select "Update Driver Software.".
Here, In This Video I Will Show You how to fix gcash no internet connection problem I Will Show The Easiest Process To fix gcash no internet connection probl...
Step 2: If using a cable modem, determine if the line is split excessively before entering the cable modem. Step 3: Call a support rep out to test the signal strength at your home to determine if the problem is a weak signal or damaged cable. Step 4: Barring any of the aforementioned problems, replace the modem.
how to fix gcash no internet connection problem 2024 | gcash network connection error Here In This Video I will show you [ How To Fix Gcash No Internet Conne...
If you are using Microsoft Edge web browser and want to fix Twitter (X) website opening issue, following steps will help you: STEP 1: Open Twitter or X website in Edge and click on the Lock icon present at the left-side corner of the address bar. STEP 2: Now disable or turn off " Tracking prevention for this site (Strict) " toggle option.
How to Fix GCash App Network Connection Problem (Easy Solution) In this video I will show you How to Fix GCash App Network Connection Problem (Easy Solution)...
Apple Issues iOS 16.7.8 To Fix Already-Exploited Issue Alongside iOS 17.5, Apple has issued iOS 16.7.8, fixing two issues, one of which is already being used in real-life attacks.