- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

How Apple Is Organized for Innovation
- Joel M. Podolny
- Morten T. Hansen

When Steve Jobs returned to Apple, in 1997, it had a conventional structure for a company of its size and scope. It was divided into business units, each with its own P&L responsibilities. Believing that conventional management had stifled innovation, Jobs laid off the general managers of all the business units (in a single day), put the entire company under one P&L, and combined the disparate functional departments of the business units into one functional organization. Although such a structure is common for small entrepreneurial firms, Apple—remarkably—retains it today, even though the company is nearly 40 times as large in terms of revenue and far more complex than it was in 1997. In this article the authors discuss the innovation benefits and leadership challenges of Apple’s distinctive and ever-evolving organizational model in the belief that it may be useful for other companies competing in rapidly changing environments.
It’s about experts leading experts.
Idea in Brief
The challenge.
Major companies competing in many industries struggle to stay abreast of rapidly changing technologies.
One Major Cause
They are typically organized into business units, each with its own set of functions. Thus the key decision makers—the unit leaders—lack a deep understanding of all the domains that answer to them.
The Apple Model
The company is organized around functions, and expertise aligns with decision rights. Leaders are cross-functionally collaborative and deeply knowledgeable about details.
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to 137,000 employees and $260 billion in revenue in 2019. Much less well-known are the organizational design and the associated leadership model that have played a crucial role in the company’s innovation success.
- Joel M. Podolny is the dean and vice president of Apple University in Cupertino, California. The former dean of the Yale School of Management, Podolny was a professor at Harvard Business School and the Stanford Graduate School of Business.
- MH Morten T. Hansen is a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and a faculty member at Apple University, Apple. He is the author of Great at Work and Collaboration and coauthor of Great by Choice . He was named one of the top management thinkers in the world by the Thinkers50 in 2019. MortentHansen
Partner Center

Designorate
Design thinking, innovation, user experience and healthcare design
Design Thinking Case Study: Innovation at Apple
Apple is one of the leading companies that is renowned for its unique products and brand. A short talk with an Apple user reveals there is an emotional relation between consumers and Apple products , including every “i” product created in the past two decades.
Why are Apple products different from their competitors’ products? How does Apple manage to achieve innovation in its product families? Answering these questions provides interesting insight into Apple’s history and how it survived its most critical time between 1985 and 1997.
When Steve Jobs returned to Apple after being fired, the company share was only worth US $5 and its future was uncertain. Today, in 2016, Apple’s share price is around US $108 and the company achieved revenues of US $233.7 billion in 2015 with net income of US $53.39 billion. This mini case study sheds light on the role that design thinking and innovation played in helping Steve Jobs rescue Apple with his consumer-driven strategy and vision for the company.
The Hard Times at Apple
The early days of Apple (which was cofounded by Steve Jobs on 1976) are characterized by its first personal computer that was delivered with Apple OS. During this time, Apple was dominating the market because there were no other manufacturers of this type of computer as computers were used only by governments or large companies. However, in 1985, Steve Jobs was forced to leave the company. This marked the start of a chaotic era in the company’s strategy and product development.
In the period 1985-1997, Apple struggled to achieve market success, especially after Jobs’s departure and increasing competition from other giants such as IBM, which decided to enter the PC computers market. During this period, Apple faced number of challenges including:
- Unstable strategy due to the change of executive teams
- Unclear vision about Apple’s competitive strategy, especially after IBM entered the PC market
- Unclear vision about selling OS licenses, which would put the company in competition with Windows operating system
- Large number of failed products (such as Newton PDA) and few successful ones (such as PowerBook)
- Products not unique in the market
- Confusion and uncertainty among Apple consumers, resulting from this strategy

Design Thinking to Fuel Innovation
Apple is one of the leading companies in the field of innovation and this couldn’t have happened without the company adopting design thinking . Design thinking is a solution-oriented process that is used to achieve innovation with considerations about the consumer at the heart of all development stages. Tim Brown, president and CEO of IDEO, defines design thinking as follows: “ Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer’s toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success. ”
“Most people make the mistake of thinking design is what it looks like. People think it’s this veneer — that the designers are handed this box and told, ‘Make it look good!’ That’s not what we think design is. It’s not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.” — Steve Jobs
In previous design thinking articles, we explored the different models of design thinking including the IDEO model, d.school model, and IBM design thinking model. Most of these models share the target of achieving innovation through three main factors:
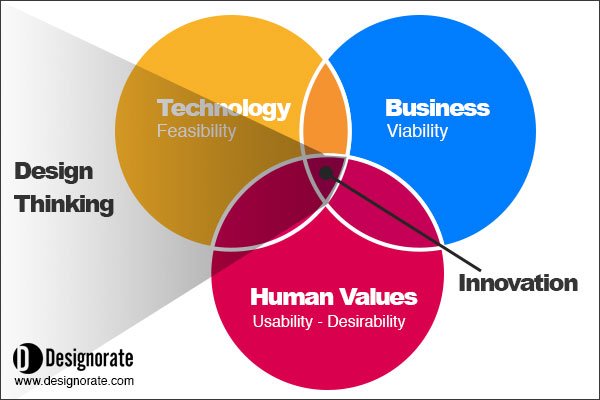
User Desirability . The product should satisfy the consumer’s needs by solving everyday problems through a user-centered process. This can be achieved through a deep understanding of the user and through an empathic design process, which can only be achieved by putting ourselves in the shoes of our consumers (using tools such as an empathic persona map ).
Market Viability . Successful products require an integrated marketing strategy that identifies the target segment and builds the product brand in accordance with this target segment. Tools such as the business model canvas can help our understanding of the project and create a business strategy for it. Also, tools such as the SWOT analysis allows us to understand the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the specified product.
Technology Possibility . Technology provides state-of-art tools for designers to innovate and build products that meet today’s needs. Technology should be adopted through the development process, including the prototyping stage where a visual presentation of the product is made to the team.
Think Different!
After Steve Jobs returned to Apple in 1997 (upon Apple’s acquisition NeXT), he started to apply the design thinking characteristics discussed above, which reflected his vision for Apple products. The vision discussed below was used to form Apple’s strategy from 1997 until today. Steve Jobs applied design thinking by focusing on:
- People’s needs and desires, rather than only the needs of the business
- Building empathy by helping people to love Apple products
- The design rather than the engineering work; designers consider both the form and the function of the product
- Building simple yet user-friendly products rather than complex hard-to-use products
The vision characterized above can be clearly identified in modern Apple products. Although other competitors focus on the features and product capabilities, Apple focuses on a holistic user experience. For example, the iMac is renowned for being quiet, having a quick wake-up, better sound, and a high-quality display. This vision was formed in Apple’s development strategy that includes:

Excellence in Execution
In this part, Steve tended to improve the execution process by closing 2 divisions, eliminating 70% of the new products and focusing on the higher potential products, reducing the product lines from 15 to just 3, and shutting facilities to move manufacturing outside the company. Apple also launched a website for direct sale of its products and started to take an interest in materials and how products are manufactured within a consumer-driven culture.
Platform Strategy
Apple streamlined their product portfolio to a family of products that can be produced much more quickly while keeping the existing design elements. Also, the company targeted product that require less repair and maintenance.
Iterative Customer Involvement
The consumer experience should be integrated into the design and development stages through participating in usability testing. Also, the design for interfaces should focus on the user experience.
Beautiful Products
In addition to the function of the product, the form should beautiful, which can be achieved through continuous innovation and development. Apple also focused on the materials and manufacturing process and took a bold approach to trying new ideas rather than sticking with the ordinary design forms.
Apple’s history with innovation provides a clear lesson about how design and innovation can turn company failure to market success and a leading position in a competitive market. Design thinking helped Apple to innovate while placing their consumers at the heart of the process. The period that Steve Jobs was absent from Apple demonstrates that copying others and lacking a clear innovation strategy can lead companies directly from success to failure. On the other hand, innovation can definitely help build a successful business.
Wait, Join my Newsletters!
As always, I try to come to you with design ideas, tips, and tools for design and creative thinking. Subscribe to my newsletters to receive new updated design tools and tips!
Dr Rafiq Elmansy
As an academic and author, I've had the privilege of shaping the design landscape. I teach design at the University of Leeds and am the Programme Leader for the MA Design, focusing on design thinking, design for health, and behavioural design. I've developed and taught several innovative programmes at Wrexham Glyndwr University, Northumbria University, and The American University in Cairo. I'm also a published book author and the proud founder of Designorate.com, a platform that has been instrumental in fostering design innovation. My expertise in design has been recognised by prestigious organizations. I'm a fellow of the Higher Education Academy (HEA), the Design Research Society (FDRS), and an Adobe Education Leader. Over the course of 20 years, I've had the privilege of working with esteemed clients such as the UN, World Bank, Adobe, and Schneider, contributing to their design strategies. For more than 12 years, I collaborated closely with the Adobe team, playing a key role in the development of many Adobe applications.
You May Also Like

How to Use Lego Serious Play in the Design Thinking Process?

The Affinity Diagram: A Practical Case Study

The Six Systems Thinking Steps to Solve Complex Problems

Using the MPPF Method in the Double Diamond Design Process

How to Apply Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework

A Guide to the SCAMPER Technique for Design Thinking
2 thoughts on “ design thinking case study: innovation at apple ”.
these things is very useful and motivation and thinking about ideas to solve the problems
Thanks Ram!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sign me up for the newsletter!
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets & Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Social Impact
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Services
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- Videos, Code & Data
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Get Involved
- Reading Materials
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
The Rise of Apple
Learning objective.

- Priorities for the GSB's Future
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Business Transformation
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships and Prizes
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- Career Advancement
- Career Change
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- Information for Recommenders
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- After You’re Admitted
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- November 2023
- HBS Case Collection
Apple Inc. in 2023
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 26
About The Author
David B. Yoffie
Related work.
- January 2024
- Faculty Research
- Apple Inc. in 2023 By: David B. Yoffie

- International Marketing
Apple’s Global Strategy: Simplicity, Innovation, and Adaptability
- January 19, 2024
Table of Contents
Delving into apple’s global strategy, apple’s core values and the simplicity mantra, apple’s global branding strategy, apple’s global marketing strategy, case studies, apple’s global tax strategy.
- The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strateg
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Apple stands as a beacon of innovation and design, captivating consumers worldwide with its sleek products and user-centric approach. With a global presence spanning over 150 countries and an estimated $383.29 billion in revenue in 2023, according to Statista , Apple’s success is a testament to its astute global strategy , a harmonious blend of differentiation, adaptability, and unwavering commitment to quality.
Apple’s global strategy is rooted in the concept of “differentiation,” a strategic approach that sets it apart from its competitors. By consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation, Apple has carved a niche for itself, offering products that are not only technologically advanced but also aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly . This differentiation has allowed Apple to capture a loyal customer base and establish a strong brand identity across the globe .
Apple’s global strategy has evolved over time, adapting to the changing dynamics of the international market. In its early days, the company focused heavily on innovation, relentlessly pursuing cutting-edge technologies and groundbreaking designs. However, as the company matured, it recognized the importance of customer experience and began placing a greater emphasis on this aspect . Today, Apple’s global strategy is a seamless blend of innovation and customer focus, ensuring that its products and services align with the needs and preferences of consumers worldwide.
At the heart of Apple’s global success lies a set of core values that permeate every aspect of the company’s operations , from product design to marketing campaigns. These values, deeply rooted in the company’s identity, guide Apple’s approach to innovation, customer experience, and global expansion.
- Accessibility: Apple strives to make its products and services accessible to everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. This commitment is evident in features like VoiceOver , which provides spoken feedback for visually impaired users, and AssistiveTouch , which allows users with limited mobility to control devices with gestures.
- Educational Support: Apple recognizes the transformative power of technology in education and actively supports initiatives that promote digital literacy and learning. The company’s initiatives include Apple Teacher certification programs, curriculum resources, and educational apps that enhance teaching and learning.
- Carbon Neutrality: Apple is committed to reducing its environmental impact and is working towards becoming carbon neutral by 2030 . The company has implemented numerous initiatives to minimize its carbon footprint, including transitioning to renewable energy sources, designing energy-efficient products, and recycling materials.
- Inclusive Work Environment: Apple is committed to creating a diverse and inclusive workplace where everyone is valued and respected. The company has implemented policies and programs that promote diversity hiring, provide equal opportunities for advancement, and foster a culture of inclusion.
- Privacy: Apple is a staunch advocate for user privacy and believes that individuals should have control over their personal data. The company has implemented robust privacy protections in its products and services, including encryption, data minimization, and transparency.
- Equity and Justice: Apple is committed to promoting equity and justice in its operations and throughout the world. The company supports initiatives that address social and economic inequalities, promotes human rights, and advocates for environmental sustainability.
- Supplier Responsibility: Apple is committed to ensuring that its suppliers adhere to high ethical standards and treat their workers with respect. The company has established stringent supplier codes of conduct and conducts regular audits to monitor compliance.
These core values, collectively, form the foundation of Apple’s global strategy. They guide the company’s product design, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions , ensuring that Apple delivers products and experiences that are not only technologically advanced but also aligned with its values of simplicity, accessibility, and inclusivity.
Simplicity is a cornerstone of Apple’s design philosophy, evident in the clean aesthetics, intuitive interfaces, and user-friendly features of its products. This emphasis on simplicity has resonated with consumers worldwide , making Apple products accessible to a broad audience and fostering a loyal customer base.
By upholding its core values and embracing simplicity, Apple has not only achieved global success but also established itself as a role model for other companies seeking to build a sustainable and ethical business model.
Apple’s global branding strategy is a delicate balance of standardization and adaptation, ensuring that the company maintains a consistent brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse cultures and markets. On the one hand, Apple strives to project a unified brand image, conveying its core values of innovation, simplicity, and elegance across all its products, marketing campaigns, and customer interactions. This standardization helps reinforce Apple’s reputation for quality and consistency, fostering brand loyalty and recognition worldwide.
On the other hand, Apple recognizes the need to adapt its branding to local markets and cultures. This adaptability is evident in the company’s product offerings, marketing messages, and customer support. For instance, Apple has developed localized versions of its products with features and specifications tailored to specific regions . Additionally, the company’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level.
Apple’s ability to balance standardization and adaptation has been a key factor in its global success. By maintaining a consistent brand identity, the company has built a strong foundation of brand recognition and loyalty . However, by adapting to local markets, Apple has been able to cater to the needs and preferences of consumers in different parts of the world, expanding its reach and deepening its customer base.
Examples of Apple’s Standardization
- Unifying Brand Elements: Apple employs a consistent design language across its products, including clean aesthetics, minimalist interfaces, and sleek silhouettes. This consistent visual language helps establish a cohesive brand identity.
- Global Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns often feature universal themes of innovation, creativity, and personal empowerment, appealing to a global audience.
- Seamless Customer Experience: Apple’s customer support is available in multiple languages, and the company’s online store can be accessed in over 40 countries, ensuring a consistent experience for customers worldwide.

Examples of Apple’s Adaptation
- Localization of Products: Apple offers localized versions of its products, such as the iPhone and iPad, with features and specifications tailored to specific regions. For instance, the iPhone SE 2020 is optimized for Indian consumers with support for two SIM cards and regional cellular bands.
- Culturally Sensitive Marketing: Apple’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level. For example, the company’s “ Shot on iPhone ” campaign features images captured by photographers from around the world, showcasing the diversity of visual storytelling.
- Localized Customer Support: Apple provides customer support in multiple languages and offers localized resources, such as online FAQs and tutorials, tailored to specific regions. The company also partners with local businesses to offer personalized support services.
Apple’s success in balancing standardization and adaptation is a testament to its understanding of the complexities of global branding. By striking this delicate balance, the company has been able to maintain a strong brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse markets , solidifying its position as one of the world’s most recognizable brands.
Apple’s global marketing strategy is a multifaceted approach that revolves around four key pillars: wide acceptance, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation . These pillars are intertwined, working together to propel Apple’s success in the global marketplace.
Wide Acceptance
Apple’s products have achieved widespread acceptance worldwide, attracting a loyal customer base across diverse demographics and regions . This widespread appeal is attributed to several factors, including:
- Innovative Designs: Apple consistently pushes the boundaries of design, creating products that are both aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. The company’s sleek, minimalist aesthetic has become synonymous with Apple’s brand identity.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Apple’s products are renowned for their intuitive interfaces, making them easy to navigate and use for people of all technical backgrounds.
- Effective Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns are known for their creativity and emotional appeal, resonating with consumers on a personal level. The company often uses storytelling and cultural references to connect with diverse audiences.
Brand Value
Apple has built a strong brand value over the years, characterized by perceptions of quality, innovation, and premium craftsmanship . This brand value has been instrumental in attracting consumers and fostering brand loyalty.
- Reputation for Quality: Apple is consistently rated among the most reliable and durable consumer electronics brands. This reputation for quality has earned the company a loyal following among consumers who value long-lasting products.
- Innovation: Apple is renowned for its pioneering spirit, consistently introducing innovative products that redefine the technological landscape. This focus on innovation has helped maintain Apple’s cutting-edge reputation and attract early adopters.
- Premium Branding: Apple’s products are positioned in the premium segment of the market , commanding higher prices than its competitors. This premium positioning contributes to the company’s brand value and reinforces its image as a luxury brand.
Competitive Advantage
Apple maintains a competitive advantage in the global market through a combination of factors, including:
- Strategic Product Differentiation: Apple differentiates its products from competitors through unique features, design elements, and user experiences. This differentiation strategy has helped the company carve out a distinct niche in the market.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Apple prioritizes customer satisfaction, creating a seamless and personalized experience for its users. This focus on customer experience has helped foster brand loyalty and attract new customers.
- Global Retail Presence: Apple has a strong global retail presence, with over 500 stores in 23 countries, as per Statista . This extensive retail network provides consumers with easy access to Apple products and services.
Low Imitation
Despite facing intense competition from numerous technology giants, Apple has been able to maintain a relatively low level of imitation . This is due to several factors, including:
- Continuous Innovation: Apple’s relentless pursuit of innovation makes it difficult for competitors to replicate its products and services.
- Strengthened Intellectual Property Protection: Apple has a robust intellectual property portfolio, providing legal protection for its innovative designs and technologies.
- Brand Loyalty: Apple’s loyal customer base is less susceptible to imitation, as they are often willing to pay a premium for Apple products due to their brand loyalty and trust in the company.
Apple’s successful global marketing strategy is a testament to its ability to balance innovation, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation. By consistently delivering high-quality products, cultivating a strong brand reputation, and prioritizing customer experience, Apple has cemented its position as one of the world’s leading technology companies .
Apple’s remarkable global success is evident in its ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India. These two countries represent two of the world’s most populous and rapidly growing economies, offering significant opportunities for technology companies. Apple’s success in these markets is a testament to its ability to adapt its global strategy to local conditions and preferences .
China has become Apple’s second-largest market , with over 190 million active iPhones in use as of 2023 ( Statista , 2023). Apple’s success in China can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Pricing Strategy: Apple has adopted a tiered pricing strategy in China, offering a wider range of products at lower price points to cater to a broader range of consumers.
- Distribution Channels: Apple has established a strong network of authorized resellers and retail stores in China, making its products readily available to consumers across the country.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Chinese telecommunications companies, e-commerce platforms, and content providers to expand its reach and customer base.
- Localization: Apple has made sure to localize its products , marketing campaigns, and customer support for the Chinese market, ensuring that they resonate with local consumers.
Despite facing challenges such as piracy and counterfeiting, Apple has successfully established itself as a premium brand in China . The company’s commitment to innovation, design, and customer experience has resonated with Chinese consumers, who are increasingly embracing technology.
India is another key market for Apple, with a growing middle class and increasing smartphone penetration. Apple’s strategy in India has focused on tailoring its products and services to the specific needs and preferences of Indian consumers .
- Price Sensitivity: Apple has introduced more affordable iPhone models in India, such as the iPhone SE, to attract price-conscious consumers.
- Online Sales: Apple has heavily invested in its online presence in India, making it easier for consumers to purchase its products online.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Indian e-commerce platforms, mobile carriers, and banks to expand its distribution reach and payment options.
- Localization: Apple’s localization strategy for the Indian market has included the adaptation of its products, marketing campaigns, and customer support, including the development of Hindi-language versions of its software.
Apple’s success in India has been gradual but steady. The company has faced challenges such as competition from local smartphone brands and a lack of brand recognition in rural areas. However, Apple’s commitment to innovation and adaptation has helped it gain traction in this emerging market .
Apple’s global success has been accompanied by scrutiny over its tax practices, particularly its use of a subsidiary company in Ireland to minimize its global tax liability. This strategy, known as “ Double Irish with a Dutch Sandwich ,” has allowed Apple to shift profits offshore, effectively reducing its tax payments in the United States and other countries .
While Apple has defended its tax strategy, arguing that it complies with all applicable laws, it has faced criticism from governments, tax experts, and consumer advocacy groups . Critics argue that Apple’s tax practices amount to corporate tax avoidance, depriving governments of revenue that could be used for public services.
Advantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has several potential advantages for the company, including:
- Reduced Tax Burden: By shifting profits offshore, Apple can effectively reduce its tax payments, which can boost its profitability and financial returns to shareholders.
- Increased Competitiveness: Lowering tax costs can give Apple a competitive advantage over other companies, allowing it to invest more in research and development, marketing, and product development.
- Enhanced Shareholder Value: By reducing its tax burden and increasing profitability, Apple can improve its financial performance and boost shareholder value.
Disadvantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has also been criticized for several potential disadvantages, including:
- Public Image Concerns: Apple’s tax practices have tarnished its public image, raising concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior.
- Legal Challenges: Governments and tax authorities around the world have been investigating Apple’s tax strategy, and the company faces potential legal challenges that could lead to fines and penalties.
- Political Fallout: Apple’s tax practices have created political tensions, with some countries considering imposing stricter tax laws to prevent multinational corporations from shifting profits offshore.
A Balancing Act
Apple’s global tax strategy has been a source of controversy, highlighting the delicate balance between corporate profitability and societal responsibility . While the company may benefit financially from its tax practices, it also faces reputational risks and potential legal repercussions. Apple must carefully navigate this complex landscape to maintain its global success while addressing concerns about its ethical conduct.
The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strategy
Apple’s journey to becoming one of the world’s most recognizable and successful companies is a testament to its ability to balance simplicity, innovation, and adaptability. From its early days as a niche computer manufacturer to its current status as a global technology powerhouse, Apple has consistently demonstrated its knack for understanding and meeting the evolving needs of consumers worldwide .
Apple’s core values, particularly its emphasis on simplicity, have permeated every aspect of its business. The company’s products are renowned for their user-friendly interfaces and intuitive designs , making them accessible to a wide range of users, regardless of their technical expertise. This commitment to simplicity extends to Apple’s marketing campaigns, which often use storytelling and emotional appeals to resonate with consumers on a personal level.
Apple’s unwavering focus on innovation has been another driving force behind its global success. The company has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, introducing groundbreaking products that have transformed the way people interact with the digital world . From the revolutionary iPhone to the sleek AirPods, Apple has consistently redefined the standards for innovation in the technology industry.
Alongside innovation and simplicity, Apple has also demonstrated remarkable adaptability in its global expansion . The company has successfully tailored its products, marketing strategies, and customer support to suit the unique needs and preferences of different cultures. This adaptability has been crucial in Apple’s ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India, where local competitors pose significant challenges.
Apple’s approach to globalization is not without its critics. The company’s tax strategy, which has been the subject of intense scrutiny, has raised concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior. As Apple continues to expand its global footprint, it will need to address these concerns and demonstrate its commitment to operating responsibly and ethically in all the markets it serves.
Looking to the future, Apple faces a number of challenges and opportunities. The company will need to continue to innovate and adapt to the ever-changing technological landscape . It will also need to navigate the complexities of global markets, ensuring that its products and services remain relevant and appealing to consumers worldwide.
Apple’s journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and interconnected world .
As Apple embarks on the next chapter of its global journey, it remains to be seen how the company will navigate the evolving landscape of technology, consumerism, and globalization. However, one thing is certain: Apple’s commitment to innovation and its ability to understand the needs of consumers worldwide will continue to be key drivers of its success in the years to come.

Privacy Preferences
When you visit our website, it may store information through your browser from specific services, usually in the form of cookies. Here you can change your Privacy preferences. It is worth noting that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our website and the services we are able to offer.

Product details

Apple’s Innovation Strategy
August 21, 2012
Case Description
Apple is perhaps the most innovative company in the world, but how has it achieved such success and what is its approach to design thinking and innovation? This case study highlights the ingredients of Apple’s success and its strategy to innovation.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction – Apple without Steve Jobs
- 2. Background Note
- 3. Consumer Delighting Innovation
- 4. Innovative Business Models
- 4.1. Apple’s innovative value proposition
- 4.2. Innovation Culture, not process driven
- 4.3. Focus Strategy – Apple says ‘no’
- 4.4. Apple’s Mindshare to Marketshare Retail strategy
- 4.4.1. Sony vs. Apple
- 4.4.2. Apple’s Retail Strategy
- 4.4.3. Apple’s Experiential Marketing
- 4.4.4. The Apple Lifestyle
- 4.4.5. Apple Store facts
- 4.4.6. Microsoft vs. Apple
- 4.5. Apple’s Four Quadrant product grid
- 4.6. Attention to Detail and Simplicity in Design
- Bibliography
- Exhibit 1 – Innovations like the iPod, iPhone & iPhone among others have helped propel Apple’s share price from $9 US in 2000 to almost $400 US in 2011
- Exhibit 2 – Apple’s Product Line-up
- Exhibit 3 – Comparison of Google and Apple’s innovation models
- Exhibit 4 – Apple’s Design Process
- Exhibit 5 – Timeline
- Exhibit 6 – Overcoming Barriers to Open Innovation
- Exhibit 7 – Apple’s growth with and without Steve Jobs (1980 – 2010)
- Exhibit 8 – Top 10 World’s most innovative companies
- Exhibit 9 – Five Skills of Disruptive Innovators
Sample Page – Introduction – Apple without Steve Jobs
In August 2011, Steve Jobs (Steve), Apple Inc.’s founder and CEO announced his decision to resign. Stock prices fell more than 5% with Apple’s most recognized person leaving behind a legacy of innovation, a process he had begun after rejoining the company in 1997. Steve’s passion for building great breakthrough products like the iPod, iPhone and iPad with elegant, minimalist design had made Apple an icon for innovation. Without Steve, many felt that the company would struggle while CEO Tim Cook felt that Apple would continue to innovate and not just survive, but also succeed. However, with or without Steve, the challenge that Apple faces will be the same – Innovate and build breakthrough products because customers buy Apple products not because of Steve Jobs, but because they are breakthrough innovations that have translated into sales.
Case Snippets/Updates
- Apple’s R&D spending : Contrary to belief, Apple spends very less on research and development. An estimate suggests that the company spends only 3% of its revenues on R&D. In Q1 2012 as well, Apple spent $758 million on R&D much less than its competitors Microsoft, Nokia and Google.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Apple innovation; a case study

Related Papers
Accounting Forum
William Lazonick
NZ Collection
Journal of the International Academy for Case Studies
TODD A FINKLE
The primary issues in this case involve business startup and management, and are appropriate for entrepreneurship and management courses. A secondary issue demonstrates how personal drive and motivation are critical components of successfully managing and growing a business, thereby making this case appropriate for discussion on the topic of strategic management. The case chronicles the life and passion of entrepreneur, Steve Jobs – illustrating the rise, fall, and current state of the Apple Computer Company. The purpose of this case is to illustrate how individual passion, determination, and innovation is a critical element in business start up success and also to stimulate critical thinking in terms of future direction for a company in a struggling economy.
Dr. İbrahim Atakan Kubilay
Apple Corporation is one of the most profitable, and socially influential companies that ever existed. Its products are in homes, businesses and entertainment venues. It constantly brings out new high-tech tools to the consumer electronics market, the most recent one being the Apple Watch. The creation of this company is more humble, and is the result of a conjuncture of various factors that have converged to create a unique environment. It all started with a group of amateur electronics enthusiasts. Smart individuals, an engineering-oriented social environment, business angels willing to invest in a new start-up company, and the developments in technology appearing at the right time and place have all contributed to this creation. It took engineering knowledge, visionary management and a business outlook to succeed. Individual entrepreneurs and developing countries carefully study the reasons behind the success and influence of Apple, so that they could recreate the conditions for imitating similar successes for themselves and their countries. Especially universities are encouraged to launch start-up companies and dive into the commercial world. Techno-parks are built to imitate the achievements of garage founded companies such as Apple. In this study, the perceived and deducted reasons for Apple’s success are examined using an opinion survey, and accounts of the founders are examined and conclusions are made based on this information. The results show that the perceived and true reasons for Apple’s success may be very different and that a legendary image of the company with an ardent fan base may obscure the true reasons behind its success.
gregory johnson
Scot King , Bruce Holman , Marilyn Gates
International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting Vol 4, No 2 (2014)
Zohaib Babar , Jawwad Jaskani , Tehreem Ilyas
Purpose: This case suggests the development of financial reporting of Apple Inc. in comparison with the industry over the period of 2004 to 2013. This study is helpful for different field of researchers e.g., management, technology, etc. Apple Inc. was found in 1976 by Steve Jobs. In 2007, Apple introduced smartphones and iOS and was the pioneer in this industry. But after the rising competition in this industry Androids snatched the market share from the Apple. Methodology: This study illustrates the reasons and the current performance of the company in the industry. The performance has been measured through actual financial data and through various financial techniques. Findings: This study has found that the company is losing share in the market because of the features in its products whereas the features offered by other competitors are relative consumer friendly and according to their demand. Suggestions: To retain the market share Apple should offer more products that are more affordable for the consumers. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5296/ijafr.v4i2.6079
Samuel Roscoe
The Apple Computer Company is arguably one of the most innovative technology companies to emerge in the last three decades. Apple, Inc. is responsible for bringing to market such products as the Macintosh desktop and the portable computer, iPod and iTunes, and most recently, the iPhone. The success of the company can be traced to the ingenuity of their founder and CEO, Steven Jobs. His philosophy has always been to create products that consumers find easy to use and integrate innovative technology. Throughout Apple’s history it has accomplished these goals. However, with a growing line of products, a competitive market landscape, and an unpredictable technology life cycle curve, the company faces challenges as to the direction of its product lines. The case gives an overview of a tool that is used to analyze a company’s product line portfolio and applies it to Apple, Inc.’s array of products. Questions for discussion are provided to enable students to use critical thinking skills in applying the case material.
RELATED PAPERS
Tetrahedron Letters
Francis Johnson
Gigi Obrecht
BMC Cell Biology
Kaveh Emami
Mariana Calligaro
edwin quiros
Perla Rocío Arellano Salazar
Vuma Dumakude
Katia Morosov Alonso
Gynecologic Oncology
Aaron Wolfson
Revista De Humanidades
Julio César Navarro torres
Fisheries Research
Medicine and Pharmacy Reports
Pedagonal : Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan
Sastra Wijaya
Tạp chí Y học Việt Nam
Đào Thị Thanh Thúy
Cecilia Carril
RAM. Revista de Administração Mackenzie
sandro nascimento
Journal of Biological Engineering
bahram rouz
Dementia & Neuropsychologia
Henrique Guimarães
Journal of Food Science
International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems (IJPEDS)
Yelena Pérez Zamora
CERIA (Cerdas Energik Responsif Inovatif Adaptif)
arXiv (Cornell University)
Interface - Comunicação, Saúde, Educação
Ronaldo Linhares
International Forestry Review
Ganga Dahal
Eveligh Carpio
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
InnovationMain - Creativity And Innovation Driving Business

LEARN TO INNOVATE
Apple innovation strategy, how did apple, the #1 innovative company in the world until 2011, innovate and create game-changing innovations such as the ipod, itunes, iphone, ipad and more what is apple's secret recipe for innovation success.
What is Apple's Innovation Strategy and Innovation Process? Download these Apple Innovation insights, case study and report, and innovate like Apple... and think like Steve Jobs, the top innovator and CEO of Apple.
" There's an old Wayne Gretzky quote that I love. ' I skate to where the puck is going to be, not where it has been. ' And we've always tried to do that at Apple. Since the very very beginning. And we always will. " —
Steve Jobs , Apple CEO, Co-Founder and Chairman (1955-2011)
Apple innovates through: • Creativity and Innovation • Innovation Process • Innovation in Products • Innovation in Business Model • Innovation in Customer Experience • Innovation and Leadership • Steve Jobs
This Apple Innovation Strategy ebook provides insights, strategy, best practices, process, facts and much more...
Apple's Innovation Strategy has been revised in April 2011 - latest information on the iPad, iPhone 4, Steve Jobs interview and much more!
Apple has built an Innovation Factory – one that harnesses unbridled creativity from its people, stimulating bold & enterprising new ideas, and launching successful, profitable new innovations... time and again! Apple leverages its diverse ecosystem of employees, customers, suppliers, partners & global networks, proven innovation process, and a winning culture that doesn't accept second place - to seize the new opportunities in the marketplace and grow its business... exponentially…
Apple Innovation Strategy eBook details invaluable tools to unlock: Creativity -> Ideas -> Innovations -> Success -> Profits
Table of Contents
Apple in 2000 Apple in 2001 Apple Fast Forward Apple Today
How did Apple do it? Apple’s Innovation Strategy Innovation in Products Innovation in Business Model Innovation in Production Model Innovation in Customer Experience Apple’s Innovative Leadership
Apple iPod iPod made Apple #1 Disruptive Innovation iPod and Apple Revenue iPod Growth Challenges iPod Falling Price / Unit iPod touch iPod Opportunity Can Apple create iPod turnaround?
Apple iTunes iTunes Challenges iTunes Opportunities
Apple Strategic Innovation Shifts
Apple iPhone Apple iPhone Juggernaut Apple iPhone Apps Apple iPhone Innovation
Apple Innovation Leadership How does Apple innovate? Another Apple innovation... the new iPad How Apple Innovates?
Apple Innovation Takeaways Where’s Apple headed?
PAY IT FORWARD
Apple's Innovation Strategy - Learn How Apple Innovates Business Innovation eBook and Report Deployed by 500+ innovators worldwide!
How did Apple do it? • Increase revenue more than 1,200% since 2000 • Increase net profit more than 3,000% since 2000 • Increase market cap more than thirty five times to over $300 billion and counting…
Download Apple's Innovation Strategy and learn to innovate, like Apple and Steve Jobs, today!!
Who should DOWNLOAD?
If you are a product manager , marketer, product marketer , sales operations manager, sales director , sales consultant, business consultant , product designer, brand manager , marketing manager, VP of products , VP of marketing, VP of technology , research & development director , product director, marketing manager , marketing consultant, brand consultant , innovation consultant, chief innovation officer , design engineer, business school professor , business school student, consultant , trainer, management consultant or entrepreneur - this definitive guide is for you! If you are one of the key executives of the company or the CEO, buy this guide for your company!
Pay it forward. Apple's Innovation Strategy is a free download. Check out the insights, and share them with your team or co-workers today.
Download Apple's Innovation Strategy eBook ($29.95 value) for free, and learn how Apple became the #1 innovator by creating successful new innovations including Apple iPod, iTunes, iMac, iPhone, the all new iPad, and created a global phenomenon & following...
HOW APPLE INNOVATES
Apple innovations.
Apple iPod, launched in 2001, made Apple the #1 Innovator in the world, accounting for more than third of Apple's revenue...
Apple iPhone
Apple iPhone is a real example of successful innovation - Apple iPhone sales revenue grew to over 5% of Apple's revenue within just one year of introduction. Apple iPhone contributes more than a third of Apple's revenue today, and made Apple a formidable cell phone company within 1.5 years of launch.
Apple sold over 15 million iPads in 2010, with revenue of over $9.5 billion within the first year of launch.
Copyright © 2021 InnovationMain - Creativity And Innovation Driving Business - All Rights Reserved.
Powered by GoDaddy
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: iPod, Apple’s Best Innovation
Case Study: iPod, Apple’s Best Innovation
Apple had in effect recognized an opening inside the digital music market. They had acknowledged that there was a drop in sales of digital music players due to the goods presently on the market being inadequate. Apple will have believed that the then current crop of music players were insufficient thus prompting them into designing the phenomenon that is the iPod . Due to the success of the Sony Walkman, Apple decided they wanted to enter the music player market. Therefore the company expanded from the core product of computers and software manufacture into many areas including personal music/media players (iPod). The creator of Apples iTunes was Steve Jobs , an in-house software creator. Apple released the first iPod into the market place on 23rd of October 2001. It proved hugely successful due to the software created by Steve Jobs which allows users to download music directly from the internet to the device a first at the time of launch. Today, over 40% of the profits Apple makes come from iPod sales. iTunes was completely invented from “scratch” (new technology emerges) by Apple which was a push to produce iPods. Apple recognized the change in market sentiment and behavior, were other players persist in alternative explanations (CD, mini disc, etc). Apples iPod was a platform innovation created by Sony (The Walkman).
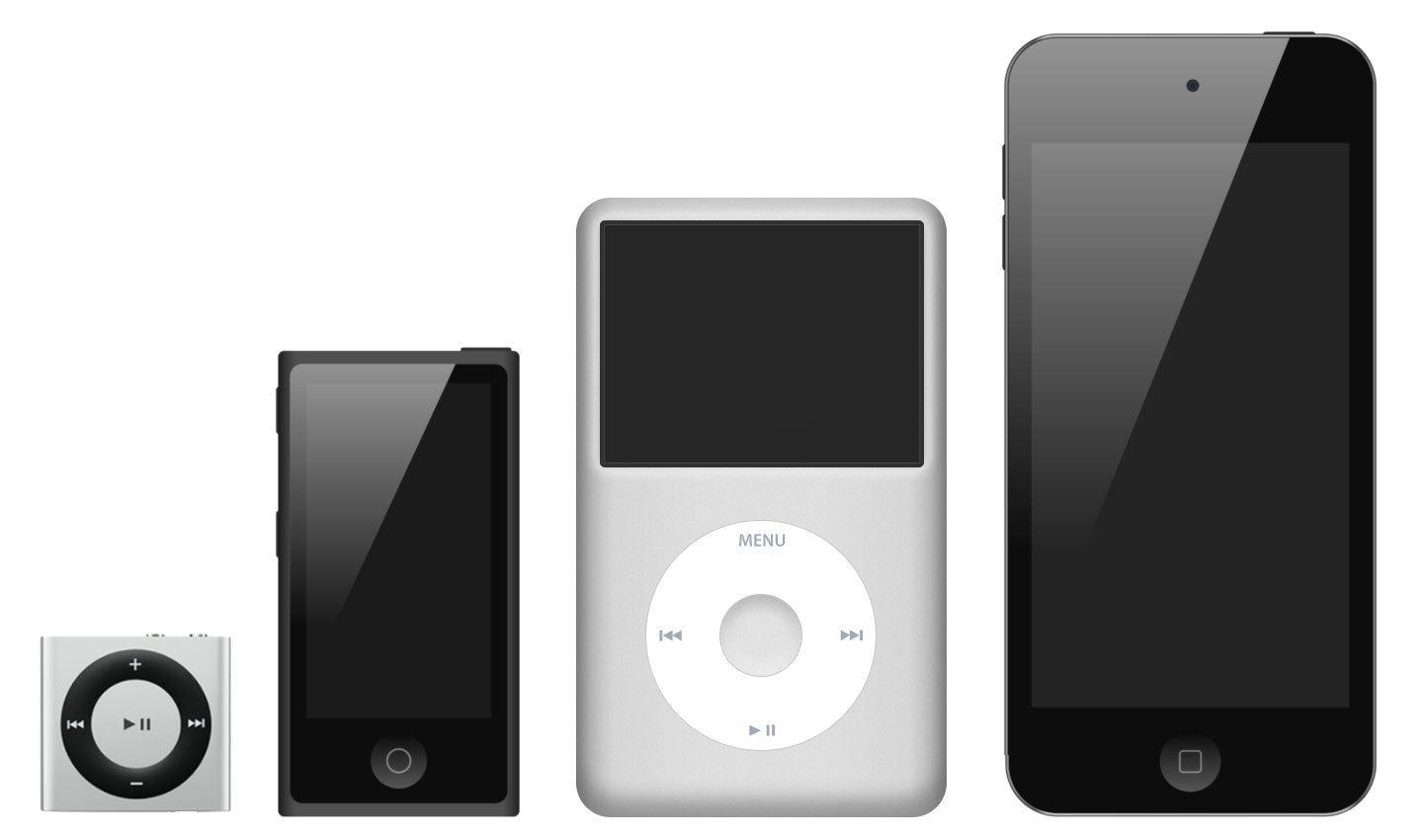

The first iPods were produced with an unambiguous structure and a straightforwardness which proved to have its advantages against their competitors and proved to be their core competencies . Nowadays, however, the hardware fight has grown to be much stronger, predominantly within the “mini” sector which is growing at a rapid pace. Since the iPod was debuted, not one of the changes we have seen have been drastic, we have just seen many refinements, these including:- slicker designs, color screens, camera’s, lesser form factors, updated applications, and slightly modified interfaces. The ‘simpleness’ of the iPod is another competence. Anybody no matter how technologically advanced they may be would be able to use one.
The iTunes is probably one of the reasons the iPod has been such a hit. It allows customers to purchase music and other content on the internet in a downloadable form which is legal. It was the first innovative program that was made specifically for just the one music player, making the iPod the only compatible player to download onto.
The marketing campaign behind the iPod was another reason why it has been so successful. MP3 player technology had already been invented, however apple took the next step with introducing huge memory and a new slick design. They are constantly looking at and finding ways to improve their product so they are always ahead of competitors by redesigning and establishing themselves as the only MP3 to buy. They appeal to a mass audience of all ages, thus breaking into all segments of the market. Apple has made sure the iPod is a household name, and due to this it is hard to find a teen without one. Continual sales figures prove iPod’s success at market development as all their sales figures are streets ahead of any competitor.
The worldwide success of the iPod would suggest that they have a very effective strategy in place. Apple’s COO Tim Cook explained Apple’s iPod strategy at a Goldman Sachs conference: ‘Sell less, make more. Worldwide iPod unit shipments were up 5 percent December-to-December — relatively low growth, thanks to slumping sales of Apple’s cheap Shuffle. But iPod revenue still grew 17 percent’. “Shuffle pulled the units down, the iPod Touch pulled the revenue up. Frankly, it was much more important for us to have a great launch on Touch and to establish that product … than it was on units,” he said.
If you were to ask Apple what the reason behind driving the iPod’s success was, the corporation may flaunt its integration. Undeniably, manufacturing a product with the advantage of firm integration habitually causes you to lose the first-mover benefit. Apple’s integration has seen colossal profit for the iPod and this has happened at a stage whilst digital music has been mystifying and awkward for many listeners and the business is more than likely going to continually uphold an improved lead here than it would in either hardware or software per se.
To conclude, Apple had recognized an opening in an emergent market and they have exploited it successfully by inventing a new products and notion that is appreciated by consumers. The new innovative idea of the iPod was swiftly entered into the market, and all of Apples competitors were unable to match its exceptional design and functionality. New product’s need to be exclusive, advanced and differentiated and the customers need to be able to acknowledge that it is good value for what they are paying for. Every aspect of this criteria is indeed met by the iPod. Apple have a team constantly trying to find ways in which they are able to make the iPod development grow even more so it is able to prolong its market control. It is almost certain that the success of the iPod is liable to persist into the future. Companies achieve competitive advantage through acts of innovation . They approach innovation in its broadest sense, including both new technologies and new ways of doing things.
Related posts:
- Case Study on Apple’s iPod: The Marketing of an Idea Project
- Case Study: Apple iPod Silhouette Ad Campaign
- Case Study: Samsung’s Innovation Strategy
- Case Study of Dyson: Competitive Advantage through Innovation
- Case Study: Business Model Innovation and Customer-Driven Innovation at Dell
- Case Study: Product Innovation at Gillette
- Case Study of Apple: Competitive Advantage Through Innovation
- Case Study of Apple: Strategic Enablers and Barriers to Innovation
- Case Study of Jack Welch: Leadership that Creates Innovation
- Case Study: iTunes Strategic Innovation
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Top 10 Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
1. nasa's mars exploration rover: innovative project management in space exploration., 2. apple's iphone development: delivering revolutionary products with precision., 3. tesla's gigafactory construction: exemplary project execution in renewable energy., 4. netflix's content expansion: agile management in the entertainment industry., 5. amazon's prime air drone delivery: pioneering logistics project management., 6. google's waymo self-driving cars: cutting-edge technology meets project efficiency., 7. mcdonald's digital transformation: adaptive project management in fast food., 8. ikea's sustainable store design: eco-friendly project implementation in retail., 9. unicef's vaccine distribution: humanitarian project management at scale., 10. spacex's starlink satellite network: revolutionizing global connectivity with project prowess., discover more stories.
World Intellectual Property Report 2024: Making Innovation Policy Work for Growth and Development
Geneva, May 2, 2024 PR/2024/916
A new WIPO report probes the intersection of human innovation, economic diversification and industrial policy and finds that the key to sustainable growth for countries is to focus policy making on developing local innovation capabilities.
The biennial World Intellectual Property Report (WIPR) “Making Innovation Policy Work for Development” documents a recent resurgence in industrial policy making, including in many developing and least developed countries, aimed at ensuring a wide and growing economic structure base - and the innovation, creativity and technology required to achieve it.
Photos on Flickr
The WIPR establishes a novel methodology that maps 20 years of innovation capabilities across 150-plus WIPO member states, pinpointing how different countries have boosted their economic diversification in areas of technology, science and exports. Through this, the WIPR results help governments design their policies in a highly dynamic economic and political environment.

We hope this report will guide policymakers across the world on how to leverage innovation for improved productivity, competitiveness, and development amid global economic shifts, geopolitical tensions and digital acceleration.
Our report shows that countries that leverage on local strengths, build diverse innovation ecosystems and develop deep capabilities are in a better place to win the innovation race.
said WIPO Director General Daren Tang , adding
We hope that policymakers will find the data and insights in this report useful and interesting as they build durable innovation ecosystems that brings real growth over decades.
To help guide policymakers, the report documented:
- Power of local capabilities: Countries often use their existing innovation capabilities as a springboard for diversification. Innovation capabilities based on scientific, technological and production know-how in a particular country or region can be measured by studying the data on scientific publications, patent applications and international trade respectively. For example:
- Economic Specialization and Diversification: Analysis of nearly 40 million patent filings, over 70 million scientific papers and economic activity worth more than 300 trillion dollars in goods and services exports, reveals that innovative outcomes are highly concentrated. Over the past 20 years, for example, the top eight countries account for 50 percent of exports, 60 percent of scientific publications and 80 percent of international patenting. But change is occurring: China, India and the Republic of Korea saw big increases in their technological diversification over the period. China jumped from being specialized in only 16% to 94% of all technological capabilities, the Republic of Korea's technological capabilities went from 40% to 83%, and India saw its technological capabilities double from 9% to 21%.
- Innovation Complexity: Innovation complexity is the knowledge in an economy as expressed in the diversity and sophistication of the science, technologies, and products it generates. Complex capabilities are rare and only diversified innovation ecosystems can make use of them. Of the three types of innovation capabilities, technological capabilities are the most complex and also more likely to generate higher growth.
Case Studies Spotlight
The WIPR focuses on three case studies across eight countries to reveal insights on how innovators and policymakers leveraged and enhanced existing industrial capabilities to create the advanced and sophisticated motorcycles, videogames and agricultural technologies of today.
Motorcycles Industry - full throttle on innovation
The documented evolution of the motorcycle industry is a key example of human innovation and economic diversification, which economists and policymakers can use to spur sustainable, long-term growth across the globe.
The experiences of Italy, Japan and India show how historical ties with closely related sectors - including bicycles, automobiles, and aviation – have allowed them to carve out their own unique specialized trajectories within the same innovative and complex industry.
For instance, Italian motorcycles excel in high-performance and groundbreaking design thanks to vibrant know-how in racing and top of the line craftsmanship; the big four Japanese motorcycles companies (Honda, Yamaha, Kawasaki, Suzuki) dominate the global market by exploiting Japan’s complex innovation capabilities on advanced technologies, product reliability, and sophisticated supply-chain logistics ( keiretsu ) ; and Indian motorcycle companies have emerged as a key global industry player catapulted by India’s capabilities on cost efficient production, particularly prioritizing fuel-efficient engines.
The motorcycle case study provides evidence of strategic implementation of industrial policies, such as those that enhanced the rise of national champions in Japan or faster adoption of electric two- and three-wheelers in India.
Today, the motorcycle industry is in a new and disruptive transformational journey driven by changing consumer preferences, a heightened focus on sustainability and technological shifts. Electrification, artificial intelligence, and enhanced connectivity technologies are revolutionizing the industry.
Agricultural Leveraging Technologies
The agricultural sector is undergoing a spectacular technological transformation as shown by the 239% increase of patent protected agriculture inventions in the last decade. New scientific breakthroughs in genetic engineering and the adoption of frontier robotic and digital technologies are increasing the innovation sophistication of one of the oldest economic activities.
The increase in innovation complexity in the agricultural sector is happening around the world. For instance, scientists in Kenya have leveraged their plant breeding capabilities to create a pest-resistant maize variety successfully being used across the African continent. In Brazil, sugarcane and sugar production capabilities were the standpoint for Brazil's global leadership of ethanol related technologies helping consumers find sustainable fossil-fuel alternatives.
The Rise of the Global Videogame Industry
The videogame case study showcases how seemingly unrelated existing capabilities can be used to create an innovative and sophisticated new industry.
The video game industry is a breeding ground for new businesses, with around 45% of game developers being newly founded companies. This dynamic environment fosters competition and innovation, contributing to the industry's rapid growth.
In addition, the report finds that around 15% of new video games launched each year are based on existing intellectual property (excluding sequels).
The development of the global video game industry has seen regional hubs navigating unique challenges and capitalizing on local strengths. The four video game industry hubs discussed in the chapter demonstrate how local expertise, cultural capital and interconnected industries collectively have influenced the industry's evolution and offer strategic insights for policymakers.
World IP Report 2024: A Guide for Policy Makers
The report provides a new policy toolkit that can help countries replicate these success stories. By identifying over 600 technological, scientific and production capabilities spread around the world, the new framework allow decision takers to design smart policies based on empirical evidence.
Policy makers can see where, when and how to target their innovation policies, either by nurturing their strengths, or by leveraging them to attain new and exciting scientific, technological and production opportunities.
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is the United Nations agency that serves the world’s innovators and creators, ensuring that their ideas travel safely to the market and improve lives everywhere.
We do so by providing services that enable creators, innovators and entrepreneurs to protect and promote their intellectual property (IP) across borders and acting as a forum for addressing cutting-edge IP issues. Our IP data and information guide decisionmakers the world over. And our impact-driven projects and technical assistance ensure IP benefits everyone, everywhere.
- Tel: (+41 22) 338 81 61 / 338 72 24
Brought to you by:

Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple
By: Stefan Thomke, Barbara Feinberg
Describes Apple's approach to innovation, management, and design thinking. For several years, Apple has been ranked as the most innovative company in the world, but how it has achieved such success…
- Length: 14 page(s)
- Publication Date: Jan 9, 2009
- Discipline: Entrepreneurship
- Product #: 609066-EPB-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
Describes Apple's approach to innovation, management, and design thinking. For several years, Apple has been ranked as the most innovative company in the world, but how it has achieved such success remains mysterious because of the company's obsession with secrecy. This note considers the ingredients of Apple's success and its quest to develop, in the words of CEO Steve Jobs, insanely great products. Focuses on: 1) design thinking; 2) product development strategy and execution; 3) CEO as chief innovator; and 4) bold business experimentation.
Learning Objectives
Managing innovation.
Jan 9, 2009 (Revised: May 1, 2012)
Discipline:
Entrepreneurship
Harvard Business School
609066-EPB-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
[Live Training] Case Study: “135% growth in cold call meetings booked month-over-month” Outbound Squad
This episode is the audio from our recent webinar on cold calling. Jason unpacked the process we took a client through to increase their qualified meetings landed from cold calling by 135%. Check out the show notes, more free content, and get coaching at https://outboundsquad.com
- Episode Website
- More Episodes
- © Outbound Squad. All Rights Reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to ...
Dean, Apple University Morten T. Hansen Faculty, Apple University AUTHORS FOR ARTICLE REPRINTS CALL 800-988-0886 OR 617-783-7500, OR VISIT HBR.ORG Harvard Business Review November-December 2020 3 This article is made available to you with compliments of Apple Inc for your personal use. Further posting, copying or distribution is not permitted.
Abstract. Describes Apple's approach to innovation, management, and design thinking. For several years, Apple has been ranked as the most innovative company in the world, but how it has achieved such success remains mysterious because of the company's obsession with secrecy. This note considers the ingredients of Apple's success and its quest ...
Today, in 2016, Apple's share price is around US $108 and the company achieved revenues of US $233.7 billion in 2015 with net income of US $53.39 billion. This mini case study sheds light on the role that design thinking and innovation played in helping Steve Jobs rescue Apple with his consumer-driven strategy and vision for the company.
The Rise of Apple. By William P. Barnett, Debra Schifrin. 2016 | Case No. SM260 | Length 12 pgs. Between 2000 and 2016 Apple introduced a number of new products and services that dramatically expanded the company's scope well beyond its traditional market position in computers. Over that period, the direction of the company changed and ...
Abstract. After a decade as CEO, Tim Cook is facing one of his biggest strategic transitions of his tenure. While Apple had performed spectacularly well under Cook, Apple's core business was maturing. Sales of iPhones, iPads, and Macs were flat or down. However, Apple's new hardware—Apple Watch and Airpods—as well as services were growing ...
Describes Apple's approach to innovation, management, and design thinking. For several years, Apple has been ranked as the most innovative company in the world, but how it has achieved such success remains mysterious because of the company's obsession with secrecy. This note considers the ingredients of Apple's success and its quest to develop, in the words of CEO Steve Jobs, insanely great ...
Abstract. Under CEO Tim Cook, Apple became the first trillion dollar market cap company, the first two trillion dollar company, and the first three trillion dollar company. Since the COVID pandemic, Apple gained over 20% of the world smartphone market and 50% of the U.S. market, making Apple the largest seller of smartphones in 2023.
Abstract. Apple Inc. (Apple), is one of the world's most valuable companies in terms of market capitalization. Apple led the global technology market by creating innovative products such as the Mac, iPod, iPhone, and iPad, all of which redefined their respective markets. This case examines Apple's approach to innovation, and the founder's role ...
Apple's journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and ...
2014, Apple had revenues of $182bn and cash reserves of $155bn. Operating income stood at. 28.7%, and net income at 21.6% (Annual Report, 2014). Apple Inc's financial statements and. sales by ...
This case is designed for use in an MBA program. It is suitable for courses in marketing management, strategic management, and innovation. The key learning objectives of this case study are to understand and consider the conceptual phenomenon of innovation resistance; types of innovation resistance (active versus passive); consumer-centric approaches for managing innovation resistance; and the ...
Apple led the global technology mar ket by creating inno vative pro ducts such as the Mac, iPod, iPhone, and iPad, all of which redef ined their respective markets. This case examines Apple's ...
This case is designed for MBA/MS level students, and is intended to be part of a general management/strategic management curriculum. The case will enable students to: 1) Study Apple's innovation strategy; 2) analyze the key factors which have contributed to the creation of a unique culture focused on innovation and creativity at Apple; 3 ...
Exhibit 1 - Innovations like the iPod, iPhone & iPhone among others have helped propel Apple's share price from $9 US in 2000 to almost $400 US in 2011. Exhibit 2 - Apple's Product Line-up. Exhibit 3 - Comparison of Google and Apple's innovation models. Exhibit 4 - Apple's Design Process. Exhibit 5 - Timeline.
Purpose: This case suggests the development of financial reporting of Apple Inc. in comparison with the industry over the period of 2004 to 2013. This study is helpful for different field of researchers e.g., management, technology, etc. Apple Inc. was found in 1976 by Steve Jobs. In 2007, Apple introduced smartphones and iOS and was the ...
P a g e | 1. Heights of Success. Apple is arguably one of the most innovative and transformative companies in the world. Under. the leadership of Steve Jobs, t he market capitalization of Apple ...
The first enabler is the leader, Steve Jobs who is CEO of Apple and co-founded in 1976. He said "Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower". From this idea, he thought that the innovation is the key to get competitive advantage. Jobs said that the best work always come from the best people working.
Apple's Innovation Strategy, Innovation Process, Insights, Case study, Innovation eBook. Learn how Apple innovates, and creates such innovative game-changers including iPod, iTunes, iMac, iPhone, iPad and more. How did Apple become the top, #1, innovator in the world? Learn to be like Apple, like Steve Jobs, the founder & CEO of Apple.
This case study is about innovation at Apple Inc. (Apple), one of the most valuable companies in the world in terms of market capitalization. Apple led the global technology market by developing innovative products such as the Mac, the iPod, the iPhone, and the iPad which redefined their respective markets. The case discusses Apple's approach ...
Case Study: iPod, Apple's Best Innovation. Apple had in effect recognized an opening inside the digital music market. They had acknowledged that there was a drop in sales of digital music players due to the goods presently on the market being inadequate. Apple will have believed that the then current crop of music players were insufficient ...
Explore top project management case studies of 2024, from Mars exploration to self-driving cars, showcasing innovation and success across industries. Top 10 Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024. 1. NASA's Mars Exploration Rover: Innovative project management in space exploration. ... Apple's iPhone Development: Delivering ...
Geneva, May 2, 2024. PR/2024/916. A new WIPO report probes the intersection of human innovation, economic diversification and industrial policy and finds that the key to sustainable growth for countries is to focus policy making on developing local innovation capabilities. The biennial World Intellectual Property Report (WIPR) "Making ...
Abstract. The essential components of carrying out an organizational analysis (a case study on Apple Inc) include evaluating external factors that can affect the organization's performance as well ...
Describes Apple's approach to innovation, management, and design thinking. For several years, Apple has been ranked as the most innovative company in the world, but how it has achieved such success remains mysterious because of the company's obsession with secrecy. This note considers the ingredients of Apple's success and its quest to develop, in the words of CEO Steve Jobs, insanely great ...
100 episodes. The Private Practice Podcast is a podcast for counsellors, psychologists, social workers, allied health professionals, music, art and play therapists and anyone looking to start or grow a private practice. Each episode includes tip, tools and insights to help you open, navigate or grow your business in a way that's ethical and ...
Apple Podcasts Preview. 1 hr. PLAY [Live Training] Case Study: "135% growth in cold call meetings booked month-over-month" Outbound Squad Careers This episode is the audio from our recent webinar on cold calling. Jason unpacked the process we took a client through to increase their qualified meetings landed from cold calling by 135%.