

Technical Presentation
Structure diagram, criteria for success.
- The presentation starts with the motivating problem for the research and why it’s being presented.
- Every slide shows something relevant to the motivating problem.
- Every slide shows no more information than necessary to convey the message.
- Slide titles stand on their own; other text supports the visuals.
- The audience takes away the presenter’s desired message .
Identify Your Message and Purpose
Identify your message and goals as a presenter and use them to organize your presentation. Your message is what you wish to convey to the audience, and is your primary goal. Other goals could include eliciting feedback, receiving a job offer, etc. Use your goals to structure your presentation, making it easier for the audience to follow your logic and identify important points that support your goals.
For example, if your goal is to communicate a new scientific result, focus on the results and broader implications rather than your methodology. Specific methods should take a back seat (e.g. “I measured key material properties,” rather than “I found the thermal decomposition temperature and profile”). Spend more time focusing on what the result means, and how it can be used.
Alternatively, if your goal is to elicit feedback from colleagues on an experimental apparatus, focus more on the experimental methods. Compare the advantages and disadvantages to alternatives. Explain your assumptions, base models and why your proposed experimental design will give more useful results than other designs would.
In less formal settings such as lab meetings, you can explicitly tell your audience what you’re looking for (e.g., “I’d appreciate feedback on my experimental methods”).
Analyze Your Audience
Understanding your audience is of paramount importance for a successful presentation. Highlight how your goals overlap with what audience cares about, so they receive your message. A well-designed presentation will steer the audience’s attention such that you can lead them to the exact point that you want them to take away.
Different audiences have different goals for attending a presentation, and therefore pay attention to different things. For example, at the same talk, an engineer may be interested in using your result to solve their problem, a scientist in the broader scientific advance, a venture capitalist in its impact as a novel product, and clinician about how your device could improve their patients’ care. The introduction of your presentation should speak to the range of backgrounds and experiences in your audience.
That being said, often an audience consists of people with similar backgrounds and interests. Therefore, identify whether jargon is appropriate for an audience, and to what extent. Consider whether other methods, such as images or analogies, are more appropriate to convey concepts that would otherwise rely on jargon.
Plan Out the Presentation
Presentations are constrained by the fact that they progress linearly in time, unlike a written piece of communication, where the reader may jump forwards and backwards to get at the information they seek. Outline the content of the entire presentation first, then begin to design the slides, rather than jumping straight into them.
Lay out the order in which the content needs to be presented to achieve your goals, such that your message flows from point to point, topic to topic. This order may be very different from the structure of the journal paper you’ve already written.
Start by motivating your work with a problem that everyone cares about. Then develop your message step by step, from the background to the final message, so the logic flows clearly.
In many cases (depending on the audience), it might be most appropriate to reveal your conclusions up-front, so that the audience can tie everything else in the presentation back to supporting those conclusions. For instance, technology-focused program managers or engineering sponsors are likely most interested in your results, which will determine whether they are interested enough to pay attention to your process and justification. By contrast, certain scientific communities appreciate being taken through your scientific process to develop their own conclusions before you present yours.
Because the audience cannot immediately see a presentation’s structure like they can with a paper, it is often a good idea to provide a high-level roadmap of the presentation early on. At key points throughout the presentation, remind them of where they are on the roadmap.
Connect Your Work Back to the Broader Motivation
At the beginning of your talk, develop the broader context for your work and lay out the motivating questions you aim to answer. The audience should understand how your answers have an impact on the broader context, and why a solution was not immediately possible without your work.
At the next level down, when showing data and results, make sure it’s clear what they contribute to answering the motivating questions.
Anticipate Questions
If your audience is following along with your presentation, they’ll likely have questions about why you made certain decisions or didn’t make others. Sometimes, the questions could arise from what you’ve said and presented. Other times, they’ll arise from a listener’s knowledge of the field and the problem that you’re working on.
While you design your presentation, think about what kinds of questions may come up, and identify how you will address them. For less formal talks, you can anticipate interruptions to discuss these questions, whereas for more formal talks you should make sure that none of the questions are so big that they’ll preoccupy your listeners. For big questions, decide if you’ll explicitly address them in your talk. For smaller ones, consider adding back-up slides that address the issue.
Remember – while you know all of the information that is coming up in your talk, the audience probably does not. If they develop a question that doesn’t get addressed clearly, they could get distracted from the rest of the points you make.
You can use questions to create strong transitions: “seed” the listener’s thought process with the questions you’re about to answer in an upcoming slide. If a listener develops a question, and then you answer it immediately after, your message will stick much better!
Each Slide Should Convey a Single Point
Keep your message streamlined—make a single point per slide. This gives you control over the pace and logic of the talk and keeps everyone in the audience on the same page. Do not be afraid of white space—it focuses your audience’s attention.
The slide title should identify where you are on your roadmap and what topic the question the slide is answering. In other words, the audience should know exactly where in the presentation and what the slide answers just from the slide title.
Strong Titles Tell a Message
Strong titles highlight where on the roadmap you are, and hint at what question the slide is answering. Weak titles tend to be vague nouns that could be used across many slides or presentations. A rule of thumb is your title should be a clear, single-line phrase illustrating the importance of the slide.
Note that different mechanical engineering fields have different preferences for titles that are phrases versus full sentences. In general, design, system, or product-focused presentations tend to have short titles that only highlight what the speaker is saying, allowing audiences to focus more on the body of the slide, which is usually a figure. In other fields, a strong title might instead be a full sentence that states a message.
Emphasize Visuals
When a new slide is presented, most people will shift their attention from what you’re saying to the slide. People can often interpret figures and listen, but not read text and listen simultaneously. The more words on the slide, the less control you have over your audience’s attention. If you are reading words off the slide, you’ve lost the audience’s attention completely—they’ll just read the slide too.
Use brief statements and keywords to highlight and support the slide’s individual point. Slides are a visual medium, so use them for figures, equations, and as few words as possible to convey the meaning of the slide.
If you have a block of text on your slide, ask yourself what the takeaway message is, and what is the necessary supporting material (data, analysis). Then, identify how text can be reduced to still support your point clearly. Consider…
- Replacing text with figures, tables, or lists.
- Eliminating all but key words and phrases, and speaking the bulk of the text instead.
- Breaking up the slide into multiple slides with more visuals.
Replace blocks of text with easy-to-read pictures, tables or diagrams.
Left: The original slide provides specific information as text, but makes it easy for both speaker and audience to read directly off the slide, often leading to a distracted audience.
Right: The improved slide conveys the same information with a simple graphic and keywords, conveying the chronology more clearly, and allowing the reader to speak the same information without reading off the slide.
Simplify Figures
The purpose of a figure is to convey a message visually, whether it be supporting evidence or a main point. Your audience usually gives you the benefit of the doubt and assumes that whatever you show in the figure is important for them to understand. If you show too much detail, your audience will get distracted from the important point you want them to gather.
An effective presentation figure is often not one made for a paper. Unlike you scrutinizing your own data or reading an academic paper, your audience doesn’t have a long time to pore over the figure. To maximize its effectiveness, ask yourself what minimum things need to be shown for the figure to make its point. Remove anything that doesn’t illuminate the point to avoid distraction. Simplify data labels, and add emphasis to key parts using colors, arrows, or labels.
Additionally, presentations offer different opportunities than papers do for presenting data. You can use transitions on your slides to sequentially introduce new pieces of information to your slide, such as adding data to a plot, highlighting different parts of an experiment (or equation), or introducing text concepts as bullets.
Simplify data, simplify labels for emphasis.
Top: Academic referees and peers would prefer to see the complete theoretical model and experimental data (top), so they can interpret it for themselves. In addition, in papers, space is limited, while time to digest is not.
Bottom: But in a presentation, simplifying the data makes it easy to focus on the feature of interests for the presentation, or even at that moment (different regions may be highlighted from slide to slide). Slides provide plenty of space, while time is at a premium. [Adapted from Wind-Willassen et al., Phys. Fluids 25, 082002 (2013); doi:10.1063/1.4817612]
Introduce Your Data
Make sure your audience will be able to understand your data before you show it. They should know what the axes will be, what points in the plot generally represents, and what pattern or signal they’re looking for. If you’re showing a figure common to a specific audience, you may not need to explain as much. But if you show the data before the audience knows how to read it, they’ll stop listening to you, and instead scrutinize the figure, hoping that a knitted brow will help them understand.
If you are worried your audience won’t understand your data, one approach is to show sketches of what the data would should like if your hypothesis were true or false. Then show your real data.
For an audience unfamiliar with cyclic battery testing as a way to measure corrosion, first show a slide explaining how the electrical signal would appear without corrosion ( top ) before showing the slide with the actual data ( bottom ). Use parallel design across the explanation and data slides. This way, the audience is introduced to the logic of the experiments and how to draw conclusions from the data, making them more likely to follow and agree with the point made on the second slide. [Adapted from AAE2]
Be Critical of Visual and Textual Jargon
If there are discipline-accepted symbols, for example in fluid or electrical schematics, using them is an effective tool to simplify your visual for people in your field. However, if these may be unknown to a significant portion of your audience, be sure to add a descriptive keyword, label or legend.
Use simple, consistent visual design
A clean set of slides will minimize visual noise, focus the audience’s attention and improve the continuity between what you’re showing and telling. The graphical design is also important for setting the tone and professionalism of the presentation.
- Are colors related to each other? Do some carry intrinsic meaning (e.g. blue = cold, water, red = hot)?
- Are you using colors that are well-represented when projected?
- Are your color choices appropriate for colorblind members of the audience? Can you textures or line/point styles to differentiate data instead?
- Spread out elements on a slide to use space effectively—don’t be afraid of white space! By limiting the amount of information on a slide, you can control what your audience will focus on at each moment in time.
- Use your software’s alignment and centering features.
- When items are grouped as a list, make sure they actually belong under a helpful unifying theme.
- Make sure all text and figures are legible to the back of the room.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Annotated example 1.
This is a technical presentation given by MechE graduate students for a system design class. 13 MB
Annotated Example 2
This presentation was given by a MechE PhD student during interviews for postdoc positions. 1 MB

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

Chapter 16: Technical Presentations
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 89921
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
One important, but often overlooked, skill in engineering is presenting. From talking with students, I have noticed that a lot of engineering students are intimidated by public speaking. In fact, I have almost a decade of experience lecturing, but I still am a little scared standing in front of a large classroom! It is OK to be a little nervous. I tell students being a little nervous means that you care, and caring is part of successful presentations. This chapter aims to reduce your presentation anxiety by teaching you the skills you need. The main key is to practice, know the format, and be prepared.
Learning Goals
In this chapter we will learn:
- Why it is important to practice and get comfortable presenting technical information.
- What your presentation should entail for the main type of engineering presentations.
- How to present technical information professionally and engagingly.
- What “audience” means and how to use what you know about your audience to your advantage.
- The art of PowerPoint and how to use the features in a non-distracting way.
- What should (and should not) be included in a technical presentation.
Why Learning How to Present Is Important
It is one thing to have a good idea, invent something cool, or develop new technology, but it is a whole other thing to successfully disseminate that information. A lot of people don’t realize that presenting is a skill and like all skills requires practice and study to perfect. It seems like it is easy to slap together a PowerPoint and talk about your project, but if you do not put the time and effort into the presentation to ensure that it impacts your audience, your work will be wasted.
Key Concept: You have to learn how to present in a compelling manner in order to get people to pay attention to your product/idea/report/etc.
For example, I have been an instructor and advisor for several senior design teams. I have seen team projects range from truly impressive to mediocre. I have also seen the impressive teams be dismissed at competitions and the mediocre teams win awards at competitions because of presentation skills alone. What I am trying to convey to you is that presenting can be the “make or break” for a project. No matter how good your project is if you can’t describe to people how good your idea is, no one will care. That being said, the moral of this story is not to do a mediocre project and coast on your presentation skills. Combining a good project with a good presentation should be your goal.
Finally, it should be noted, that engineers have to present a lot . In fact, engineers have to do presentations a lot more than you might think. You might have to present your design idea to your research and development team. You might have to present to the entire company describing how you optimized a system process for efficiency. You might have to present to shareholders the newest technologies your team is working on. You might have to present to future customers on how your technology can improve their productivity. The point is, that engineers are expected to be good presenters and historically, University education in engineering does not explicitly address this skill. Hopefully, this chapter and your subsequent education reverses this.
Presentation Anxiety
Before we jump into some examples and tips, I wanted to take a quick note on presentation anxiety. As I mentioned before, there is no getting around it, you will probably be a little nervous when you present. That is ok! Almost everyone feels a little nervous. However, there are tactics that you can use to reduce your anxiety when stepping up in front of an audience.
One of the biggest keys to reducing your anxiety is preparation . In fact, there is no such thing as “over preparing”. The more you prepare for your presentation the better you will feel because you will be more confident about what you are speaking on.
Here are three tips that should help when it comes to preparation and alleviating anxiety:
Anxiety Reduction Mechanism 1) Rehearse, Rehearse, Rehearse…
Although it might seem self-explanatory or obvious, rehearsing is the most important step in reducing presentation anxiety. In my experience, this is the step that most students spend the least amount of time on even though it is the most important.
Out of all of the time you budget to create your presentation, the majority of time needs to be spent rehearsing.
The more you rehearse, the smoother your delivery will become and the more confident you will feel. Rehearse in front of your roommates. Rehearse in front of your classmates. Rehearse in front of a mirror. Rehearse to your parents (this is a great idea as it will probably impress them about how far you have come in your education and maybe get a few more bucks thrown on your campus cash card!). Rehearse in front of your grandparents (I am sure grandma would love to hear from you anyway). I think you get the idea. Rehearsing is key and the more that you practice your presentation, the more comfortable you will feel. Rehearsing in front of people that aren’t familiar with the course is even better. It will generate questions and make sure that you are explaining things in an optimal manner.
What I suggest to students is, that they time each of the rehearsals of their presentation. The key is to continue to practice rehearsing and practicing until the group can finish the presentation without making any mistakes and when they can finish within +/- 5 seconds of the same time (if it is a 10-minute limit presentation, the team can finish each practice session in 9:50 seconds to 9:55 seconds every time). As you can imagine, this takes a ton of practice but does reflect the level of polish necessary to feel confident about your presentation.
Anxiety Reduction Mechanism 2) Anticipate questions.
The next key to preparation for your presentation is to anticipate the questions you think the audience will ask, and be prepared with answers to those questions. You can’t anticipate every single question that you may get asked, but you can probably think of a few avenues that your audience members’ minds might wander.
For example, let’s imagine that you are giving a presentation on the efficacy of a vaccine. Depending on your audience, you should be prepared to answer the following questions:
- What is a vaccine?
- Specifically, how do vaccines work?
- Do vaccines cause autism? (Spoiler: NO )
- What types of adverse reactions might there be to the vaccine?
- How long will it take to produce 100 million doses of the vaccine?
- Are there specific storage requirements for this vaccine?
Preparing detailed answers to these questions will strengthen your knowledge of your presentation topic and alleviate your anxiety. Since you anticipated the questions your audience will ask, you don’t have to worry as much about looking like a fool on stage. This is also where rehearsing in front of someone who is not familiar with the course or topic can be very beneficial since it will generate a lot of these types of questions that you may have not considered.
Anxiety Reduction Mechanism 3) No one in the audience cares about you.
Sometimes students interpret this incorrectly. I am not saying that no one cares about you. Lots of people do. Your professor does, you have friends in the class, etc. What I mean by this is that it is important to remember that when you give class presentations, often, your classmates and peers have to give presentations as well.
Think back to the last class you were in where you had to present. Think about sitting in your chair, while another team is presenting, waiting for your turn. Be honest. Were you even listening to them? Or were you anxiously awaiting your turn at the presentation? Well, the reality is, everyone else is only thinking about themselves and their presentation while you are presenting . When you make a tiny mistake, no one notices. The only thing they will notice is if you totally bomb the presentation (which you won’t because you rehearsed so much).
So as part of your preparation, relax . The selfish and narcissistic tendencies of your classmates ensure that they won’t be paying as much attention to you as you think they might. Hopefully, that relieves a little bit of the pressure.
Discussion 16.1: How do you feel about presentation anxiety?
What Your Presentation Should Entail
As an engineer, you will typically be presenting on projects you are proposing or presenting data from projects that you have already completed. All of the advice from this chapter (no such thing as over-preparing, etc) will be helpful in reducing stage anxiety but to make sure that your presentation is well received, you need to make sure that the presentation contains the appropriate material.
You will be expected to have the following sections: title, introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. The following example presentation will highlight the most important and standard slides that your presentation should (probably) entail.
To describe each of the required sections (keep in mind that I am showing only one slide for each section but it is likely that you will need multiple slides) I included example slides from a presentation I gave at an American Society for Engineering Education conference in 2019 in which I won the “Best Presentation” award. Note, that the slides shown below are only a subset of the slides that I presented at the conference. For the full slide deck, you can click here.
Title Slide
The title slide is just a place to include the names of all the people that worked on the project and their affiliations. And the title. Duh.
- Keep it simple.
Introduction / Background Slide(s)
The purpose of the introduction slide is to outline your current understanding of the subject. You need to include specific examples of previous work/research.
- Clearly explain the importance of the current project and what the significance of the project will be.
- Justify the merit of your project by presenting significant information.
- End with a specific, clear, and explicit purpose for the project. Some of the projects that you complete during your undergraduate career will be chosen for you. It does not mean that the purpose of the project is “because the professor told me to do it”. Spend some time thinking about the project and what learning outcomes you are expected to gain from it.
Materials and Methods
The purpose of the materials and methods slide is to list the necessary steps for your audience to interpret the results.
- You should include: sample sizes, how the data will be processed, everything that was used in the project, and what statistical tests if any will be used.
- It should be clear how the materials and methods relate to the purpose of the project.
- The audience should feel that presenters fully understand the scope and details of the work (especially if it is a proposal).
The results slide is the place where you describe what you found from your project.
- Present the data from the project. What did you do? What did you find?
- Do not interpret your results yet! Just show what you gathered.
- Visual descriptions of your data are important. Be sure to include figures and tables as appropriate.
Although it might seem like your results are the most important slide, I would argue that it is actually your discussion slide. Whereas in your results section you simply tell your audience what you found, in your discussion section, you need to interpret the results for your audience.
- Interpret the data from the results section.
- Answer the “why” of the data.
- Draw conclusions about the project.
- List any limitations of the project.
- Discuss future work.
Conclusion / Significance
Finally, we get to the conclusion slide. This is another very important slide as it can be an opportunity to reinforce the takeaway message that you want to give your audience.
- Should be a “natural” conclusion. Your presentation should not end abruptly. The audience should feel it coming.
- Summarize the major points from your presentation. Be sure to provide your audience with a take-home message.
- Summarize the weaknesses of the project. It shows that you can critically think about your own work and makes your audience more sympathetic to your position. Admitting what you would change actually strengthens your position.
How To Give a Dynamic Engineering Presentation
There are two main things to worry about when presenting engineering information in a dynamic and interesting way; the content and yourself.
In my opinion, one of the best ways to convey what makes for a dynamic and engaging presentation is to have you look at one of the worst. What follows is one of the worst presentations I could find on the internet. To set the stage for you, it is from a British show in which people pitch their ideas to a group of investors (it is similar to the American show Shark Tank). I chose this particular clip for a few reasons:
It is supposed to be entrepreneurs getting the opportunity of a lifetime to get their dream invested. They should be excited and passionate by default! The following pitch is atrocious but the product is actually kind of an interesting idea. It seems to me that if she had given a more dynamic and engaging pitch, the investors may have been more interested. In fact, one of the investors says as much. With that out of the way, watch the following pitch from Gayle Blanchflower (I couldn’t find out if this spelling was correct). Note: the video should automatically start at 30:12 for you. If it doesn’t you can skip there. Also, be prepared to answer some questions on what you think went wrong with her pitch.
Discussion 16.2: An atrocious presentation
I am truly sorry for putting you through that. However, I hope you agree that it gives you some ideas of what NOT to do when trying to give a dynamic and interesting presentation. Here are some more tips about both the content of your presentations and tips for you.
Know your audience Your audience will dictate what you are presenting. If you are presenting on the efficacy of vaccines to a group of doctors, you can assume that they know what vaccines are and how they work, therefore, you can leave that information out of the presentation. However, if you are giving the same presentation to a group of middle schoolers, it might be a good idea to include that background information. The key is to know your audience and tailor the presentation to their knowledge.
Convey your excitement If you aren’t excited about your project, your audience surely will not be. Get excited and make your presentation exciting the best that you can.
Tell a story This chapter gives you the basic framework (you can think about it like the beginning, middle, climax, end, or a story) but you need to tell it. The more you can make your presentation flow like a story, the better.
Keep it simple (communicate, don’t obfuscate) Every field has jargon and acronyms that make people feel smart for knowing. Don’t lose your audience in the lingo! This is where knowing your audience is critical but in reality, even scientists and engineers appreciate brief definitions of scientific terminologies and processes.
- Set the stage. Clear the podium of distractions. Have whatever tools you need for your presentation ready to go ahead of time.
- Get ready to perform Presentations are performances. Know your subject and know your main talking points. Do not memorize a script! Your rehearsing should have been so extensive you don’t need one anyway.
- Stride up to podium / stage / front of room. Be proud! Don’t sulk.
- Stand tall, keep your chest lifted, and smile. If you aren’t confident by nature, learn to fake it. It goes a long way.
- Pay attention to your teammates when it is their turn to talk. Remember, if you look bored, your audience will interpret that as if they should be bored.
- Speak loudly and project your voice clearly. For some, this is not natural and will take practice. Good thing you rehearsed so much!
- Take your time. A moment or two of silence is a powerful tool.
- Talk to the audience, not the screen.
- Stay on time.
- Rehearse a lot. Remember, there is no such thing as being over-prepared.
PowerPoint Tips
As I stated before for dynamic presentations , I think it is a good idea to look at bad PowerPoint decks to understand what makes the good ones, good. Before moving on, take a look at the slides here: https://www.slideshare.net/Kshivets/...cancer-surgery –4936542. When you have finished looking at those slides, participate in the following discussion prompt before moving on.
Discussion 16.3: A really terrible slide deck
Well after reviewing that horrible slide deck, you should actually probably have a good idea of what makes for a good slide deck. Here are my tips:
- Less is more. Less slides, less text. Trim off the fat and concentrate on the coolest most relevant things.
- Create sections. Title slides to start new sections can help break the presentation into a logical flow. Specifically, you should use the sections that we discussed earlier in the chapter.
- Avoid clutter. 3–5 bullet points per slide at most! Bullets should be keywords, not sentences.
- Make it readable for old people. Sans serif fonts. 28–40 point for headline text, 18–28 point for normal text, and 12–14 point font for references is a good place to start.
- Ensure that there is a clear contrast between the background and all text.
- Use visuals. Steer clear of videos unless completely necessary or exceptionally cool. In my experience, they NEVER work and they take lots of time away from your presentation. Figures are your best bet.
- Triple-check your spelling. A sure-fire way to lose credibility is to have typos in your presentation

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
7 Steps to Delivering a Technical Presentation
June 21, 2021 - Dom Barnard
So you want to share the fruits of your technical labor with a presentation? Perhaps, you’re an engineer, a maker, a coder, or a designer, and you’re looking to discuss a research study, explain a process, or demonstrate a product.
Regardless of the agenda, speaking to a group can be intimidating. However, there are steps you can take to deliver an effective technical presentation that gets your point across and appeals to the audience.
Whether you’re presenting in person or via web conferencing software , the following tips and best practices will help you be prepared, feel more confident, and set up the tools you need to conduct your presentation without any issues.
Know your subject matter
A great presentation isn’t about reading a bunch of slides – your attendees are capable of reading much faster on their own.
If you are going to pack your slides with dozens of details and bullet points, you might as well ditch the slides and write an article instead. It’s difficult for the audience to listen to a presenter and read a lot of information at the same time.
Your job as a presenter is to be the expert that your attendees expect you to be. Keep your slides simple and minimal. In fact, 91% of people say that well-designed slides help boost their confidence when giving a presentation.
Remember that your slides are not the star of the show, you are. Help your audience understand and make sense of what they are reading in your slides. To do this, make sure you are using a suitable structure for your presentation.
You can do these things only when you’re well-versed in what you’re presenting. The slides are supposed to be your outline, or simply a table of contents to remind you what to cover during the presentation.
Know your audience
Knowing your audience is crucial for any presentation, but it’s even more important for a technical one. If your audience is as experienced and comfortable with the topic of your presentation as you are, then you don’t want to dumb it down to the extent that it bores them.
On the other hand, you don’t want to give a complex presentation to an audience with no clue of what you’re talking about.
There may also be times when your attendees are people with different levels of technical skill, experience, and interests. Then your job is to make sure that the content of your presentation is relevant and doesn’t alienate any of those segments.
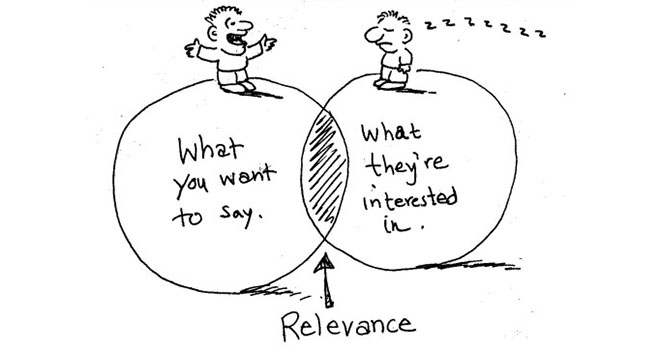
Image Source: Digital Clarity Group
To understand how technical you need to be, consider what your audience might already know and how much is required for them to understand to meet your goal.
If your objective is to acquire funding, for instance, your audience will be more interested in financial benefits than the technical details of your product. The idea is to meet the needs of your audience, not to fuel your passion for engineering.
Configure your IDE
Since you’re delivering a technical presentation, there may be instances where you’ll want to walk your audience through your development environment, code scripts, software demos, or other technical components.
However, you may have adjusted how things look on the screen according to what’s the most convenient for your usual workflow. And what’s good for working in your day-to-day routine may not render well as you go full screen in presentation mode.
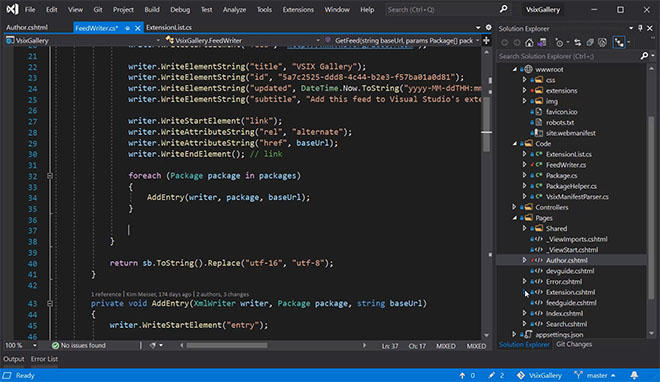
If the attendees can’t decipher what’s on the screen, they’ll get confused and will find it hard to focus on your talk. So it’s important that you customize whatever you’re going to show in your presentation such that it’s easily readable and viewable.
There are several steps you can take to make this happen. First of all, don’t use dark backgrounds. Light-colored backgrounds are easy on the eyes. Second, adjust your font styles and sizes to make sure they’re big enough.
And finally, learn to zoom in on specific areas as required, depending on whether you’re using a Windows PC or a Mac system .
Practice Presentation Skills
Improve your public speaking and presentation skills by practicing them in realistic environments, with automated feedback on performance. Learn More
Minimize distractions
Nothing is more annoying than to keep getting disruptive notifications or popups from in the middle of your presentation. These can be from your operating system (Windows or Mac), or apps such as Slack, Email, Twitter, and more.
At times, these notifications can be personal, embarrassing, or contain confidential information that you don’t want your audience to see.
Therefore, it’s best to make sure in advance that there are no unpleasant surprises. Before you get up to give your presentation, turning off your notifications can go a long way.
This will also reduce the number of processes running on your machine and free up available resources. As a result, the resource-intensive programs that are part of your presentation will run a lot smoother. Here’s how to turn off notifications for Windows , Google Chrome , and Mac .
Get the right equipment
If you want to be a master presenter, you should have the proper tools for the job. The basics include a desktop or laptop machine with good configuration, a big display screen, presentation software (usually MS Powerpoint or Keynote), and a clicker/pointer device.
A clicking device, like the Logitech Wireless Presenter , can help you switch slides from wherever you are in the room, point to a specific part of a slide, and add an overall professional touch to your presentation.
In addition, you should have any cables (HDMI, VGA, USD, etc) and adapters required to connect the devices you are going to use for the presentation.

Conrad Delock USB 3.0 Network adapter
If you have no idea about what will be available at your presentation venue, then carry one piece of each of the commonly used cables and adapters. You’ll thank us later.
Rehearse in advance
Practice your slides and your demo multiple times before the presentation, even if you have presented the exact same thing in the past. Do not make any assumptions about your actual presentation environment based on your practice environment.
Technologies and situations change, and you may find things that catch you off guard. Run through everything at least once the night before just to be sure.

Practice your presentations with interactive exercises .
Even better if you can record yourself during these rehearsal presentations and watch the recordings later to find areas of improvement.
Also, if you’re relying on downloading or doing something in front of the audience that may require a high-speed internet connection, don’t assume you’ll have access to such a network during your presentation. Download and install whatever you need ahead of time.
Finally, enjoy the experience
You’re giving a technical presentation, but that doesn’t mean it has to be boring, or that you have to be serious all the time as you talk.
It’s okay to have fun, crack some jokes, tell a story , ask a rhetorical question or invite participation from the audience when presenting. In fact, a study showed that presentations that don’t let the audience participate see a drop of 14% in engagement.
Don’t worry too much about things going wrong. See every presentation as a dialogue with your attendees and an opportunity to learn and be a better presenter. If you are enjoying yourself, so will your audience.

Craft Effective Technical Presentations: 5 Success Strategies
Dominik Sumer
August 30, 2023 · 8 min read
Technical presentations can be tricky to execute. You know your subject inside out, but is that enough?
How do you ensure your audience stays engaged throughout the presentation, and how do you answer their questions effectively?
This blog post provides modern strategies for crafting effective technical presentations, covering all aspects, from understanding your audience to handling questions and feedback.
You will also learn about the practical parts of technical presentations, including proper tools and examples.
These tips will help you deliver a successful presentation that makes a lasting impact on your audience.
Anyone can use this guide as a checklist , but the following can get huge benefits:
- Software Engineers or Developers
- Tech YouTubers
- Candidates who are presenting in tech interviews
- Social Media Influences like tech on LinkedIn
- Students, Tech Teachers, and much more.
Identify your Audience:

In our previous guide about technical writing , we shared 19 expert tips you should know.
Let me quickly highlight the five most important tips:
- Understand Audience
- Define Purpose
- Always do your research
- Organize thoughts
- Avoid Jargon and Acronyms
Understanding your audience is not a first step but why?
Because first, you need to identify WHO is your target audience.
Question it by yourself, and write down the three closest audiences like:
- JavaScript Developers: Those who want to learn about JavaScript technologies. You can help them learn the tech faster by sharing beautiful code snippets .
- SaaS Owners: Those tech founders who want to learn about the ongoing development progress of their software. Give them tips on how to tackle obstacles in software development by using technical presentation slides .
- Tech Talks: Those interested in code screencasts within the video content like YouTube or TED Talks. You can use rich animated content, like videos created with snappify.
So, identify your audience first and use the smart tools to simplify things for you and the audience.
Use Smart Tools:

So, what are smart tools in the digital world?
Smart Tools are intelligent software applications that help users perform complex tasks more efficiently and effectively.
They simplify processes, improve productivity, and help achieve goals quickly and easily online.
You can learn about our curated list of technical writing tools , which comes with Artificial Intelligence.
Before using your tool for technical presentations, make sure to check these features first:
- Can you create a fully animated slide?
- Is there any feature for Video Export?
- The tool must be user-friendly to avoid presentation disruptions.
- Clear and visually appealing infographics are important for tools with graphs, diagrams, or slides.
Now that you know enough about the features, here is another list of modern tools to help you become a good presenter.
- Snappify: It can help you present code beautifully and has all the features I have mentioned above. It also has pre-made templates to help you create and share snippets faster.
- PowerPoint: A user-friendly software for creating dynamic presentations with text, images, charts, and multimedia elements.
- Google Slides: A web based presentation tool that lets users create basic presentations and save them online.
Let's take a closer look at the Slides and Video Export features of snappify and how it can become your new companion for your technical presentations.
It comes with a Present button at the top of the bar, which can help you show your code snippets in the presentation mode.
In slides, there are several options for animations:
Besides showing your presentation, you can download all slides or export videos to share on social media.
You can follow this tutorial on creating code presentations with snappify .
Video Export : TypeWriter Example
Video showcasing the TypeWriter transition
Structure Your Presentation
To craft an effective technical presentation, it is crucial to structure your content in a clear and logical flow .
Begin with an attention-grabbing introduction that captivates your audience and sets the tone for the presentation.
Organize your content into sections or chapters, making it easier for your audience to comprehend and follow along.
- Divide your presentation into key sections or points.
- Each section should have a clear focus and contribute to your main message.
- Use bullet points and concise text to support each point.
- Transition smoothly between sections to maintain a logical flow.
- Include visuals such as images, charts, graphs, animations , and videos to enhance understanding and engagement.
- Share real-life examples or case studies that illustrate your points.
- Use relevant data and statistics to back up your points and add credibility.
Finally, remember to summarize key points and provide a memorable conclusion to leave a lasting impact.
Create your next presentation
snappify will help you to create stunning presentations and videos.
This video was created using snappify 🤩
Choose a good Font and Color for the Slides

Font and color choices in slides play a key role in shaping the impact and effectiveness of your presentation.
These choices go beyond aesthetics; they influence how your content is perceived, understood, and remembered.
Here are quick tips to make effective font and color choices:
- Readability: Use simple, easy-to-read fonts that can be seen from far away. Avoid fancy or complex fonts that can make reading difficult.
- Consistency: For a professional look, limit your presentation to two font styles: headings and body text.
- Contrast: Use contrasting fonts for headings and body text for better readability. Headings should be in bold or larger font, while body text should be in regular font.
- Hierarchy: Establish hierarchy with color by using bold or contrasting hues for headings and more subdued tones for body text.
- Limit Bright Colors: While bright colors can add visual interest, avoid using too many as they can be distracting and make your presentation look unprofessional.
Remember that your font and color choices should support your technical content and help convey your message effectively.
Test your chosen fonts and colors on different screens to ensure they appear as intended.
Consistency in font and color usage contributes to a polished and visually appealing presentation.
Also take a look at our handcrafted templates to get started with your technical presentations.
Engage with Stories

People remember stories better than facts alone.
Include relatable case studies to illustrate your points and make your presentation more relatable.
Storytelling is a powerful technique that can elevate your technical presentation from informative to captivating.
Humans have been using stories to communicate and connect for centuries, and integrating this approach into your presentation can help you create a deeper and more lasting impact on your audience.
Here's how you can effectively use storytelling to engage your audience during your technical presentation:
Quick Story Example:

Meet Maya, a talented developer on a mission to make her technical presentations truly captivating.
One day, she discovered snappify, a tool rumored to bring code snippets to life .
Maya decided to give it a shot.
With snappify, Maya's code snippets transformed into dynamic visuals that got animated smoothly across the screen.
During her presentation, she used it to break down complex algorithms step by step.
The audience was captivated, effortlessly following along as the code was visually displayed.
Impressed by Maya's presentation, fellow developers asked about snappify.
Maya shared how the tool had elevated her delivery, making code accessible to all.
Afterward, snappify was known for its captivating technical demonstrations.
Developers worldwide used it to transform complex code into interesting visuals, captivating audiences and enhancing code comprehension.
Now, turn your boring code into fancy and beautiful snippets before sharing it on social media or inside your technical presentation.
In conclusion, delivering a successful technical presentation requires technical skills, engaging visuals, and audience interaction.
A compelling story and utilizing effective visuals are crucial for delivering a memorable and impactful presentation.
Following the tips in this comprehensive guide, you can always deliver successful technical presentations for interviews, YouTube videos, tech talks, social media posts, and much more.
How can I adjust my technical presentation to different levels of expertise among the audience?
Adjust technical depth and terminology based on audience familiarity. Provide real-world examples for beginners and deeper insights for experts.
What is the difference between presentation and technical presentation?
Presentations can be either general or technical. General presentations inform or persuade, while technical presentations explain complex concepts to an audience with relevant expertise like engineering, coding, or more.
How do I overcome nervousness before a technical presentation?
Practice is key. Familiarity with your content and great rehearsal can help reduce anxiety during the presentation.
What is most important in technical presentation?
Effectively convey complex concepts with clear explanations, visuals, and relevance to the audience's needs and expertise - that's clarity.
What are the four essential components of a technical presentation?
A technical presentation has four parts: intro, content, conclusion, and Q&A. Introduce, present, summarize, and impress.
How do you engage your audience during a technical presentation?
To keep your audience engaged during a technical presentation, use relatable examples, break down complex information, and include interactive elements like polls or Q&A sessions. Personal stories can also make it more interesting.
Share Article
October 26, 2023
Can't find what you're looking for?
How to Deliver a Memorable Technical Presentation
Master the art of technical presentations, whether it's in your project meeting or an industry conference. Unleash your potential with these invaluable tips to ensure your presentation success.
What's Inside?
Tips to Ace Your Technical Presentation

Let’s say your company launched a SaaS application a few days ago. As head of the team, the onus is on you to spearhead the sales process. And the first step started with drafting a technical presentation explaining the product. Yes, you are a pro who knows all about the technical aspect, and you might be confident too.
But there are several questions you should ponder over
- Who will you be presenting to?
- How well is everyone aware of SaaS products?
- What should be your approach to drive sales and convince people of the product?
The answers to these questions will change the course of your presentation each time because the content will have to be modified accordingly.
Technical presentations are lengthy, specific, and involve complex information/ideas (often dreary and detailed), making them difficult to deliver over non-technical ones. And that’s why they require a different approach, which we have covered in this article.

How to Deliver a Winning Technical Presentation?
Here are some pro tips for creating impeccable slides and leaving your mark.
1. What is the core message and purpose of your presentation?
Structure your presentation around the key goal, which could be anything from sharing information and eliciting feedback to getting funding or a job offer, etc.
Organizing your presentation around a core theme will help your audience identify and follow the central points that support your content.
For instance, if your goal is to present a scientific result, include more information about what the result means and how it can be used rather than focusing on your methodology.
Or if your goal is to elicit response/feedback on some experiment, focus more on the methods, i.e., advantages, disadvantages of different models, your assumptions, how your model is more useful, etc.
Tell your audience what you want them to do. Why should they do it, and how?
2. Who is your audience?
Knowing your people (audience analysis) will help you stick to the right chord.
It will also help you know how much technical jargon you can rely on and whether images and analogies would suit the audience better.
Your audience might be diverse (investors, clients, customers, etc.) with different interests, knowledge bases, goals, and concerns. And, mind you, they are as central to your presentation as you are. So, know as much as you can about them and structure your presentation accordingly. Highlight how your message overlaps with what these people care about, and remember to include the diverse backgrounds and experiences in the introductory part. And you will have everyone’s attention right from the start.
3. Define a clear outline
You can divide the content into three sections for clear structure and easy comprehension. The first section gives an outline/summary of the main topic and illustrates why it was important enough to become the subject.
The second part can elaborate on the main subject with its minute technical details and everything that the audience needs to know.
The third section can highlight the resolution, solution, CTA, and course of action to the problem presented.
An effective presentation is not one where you detail every possible information about the topic or include as many issues as possible. It is when you can get people to build understanding and support for your central message.
4. Take help of everything that can explain the concept
For any presentation, words/text are not enough. And it becomes all the more imperative in a technical presentation slide.
According to a survey, people prefer 1/4th of the slide composed of text at most.
Since you will have to use jargon here and there, you can’t rely just on your speech. Use pre-designed PowerPoint templates comprising graphs, diagrams, animations, videos, infographics, etc., to help people understand technical concepts and information clearly. You can also use other experiential methods like prototypes, handmade models, or real-time experiments.
For a better understanding, go through this video showcasing paper prototyping of a mobile application :
5. Remember to be consistent
When your presentation slides differ in size, display, structure, etc., it can distract or confuse people and make them lose attention. Creating a consistent theme is important to help people focus and keep your presentation aligned.
Take the help of these tips to incorporate consistency in your work-
- Go for colors that complement each other, following the preferred color scheme.
- Choose fonts that are easy to read in a presentation or digital content like Serif or Sans-serif.
- Go for the same layout for a similar kind of content. Use one kind of layout for cover slides, one kind for section introduction, and one for content slides. It will help your audience categorize the content and know where to look for what information.
And, of course, don’t forget how immensely it will help you as a presenter.
And yes, keep your presentation short – not more than 10 slides. You can go for the 10/20/30 rule, i.e., 10 slides, 20 minutes, and 30 font size.
6. Leave space for questions and queries
Since your presentation is technical and the audience might be diverse, be prepared to answer questions. The major cause of anxiety before a presentation is a lack of preparation. Being thorough with the subject matter will also aid you in answering any questions being asked, apart from avoiding presentation jitters.
Allocate a well-designated time to interact with the audience. You can also do that during the course of the presentation if it doesn’t interfere with your speech. It will keep people engaged and alert as they get small windows to pose queries throughout.
7. Practice sessions
You might be confident about your content, but when you speak/deliver, your words and ideas might come out in a different way and not as you intend.
It could so happen that you are not too good with voice modulation or at specifying relevant points. That’s why it is imperative that you have multiple practice talks before delivering the presentation.
Keep your practice audience small and diverse so that you get relevant opinions and everyone has something to share.
You can share hard copies and remember to number your slides as well. It will help people annotate them and return them at the end. You can videotape yourself as well to see how you come across and improve accordingly.
8. A few quick tips
Keep in mind where you want to take your audience through the presentation. What perspective shift do you seek?
Do you want them to invest in the product? Or is it just an internal meeting highlighting the attributes of the product?
WIIFY is an acronym for What’s in It for You. Make sure you present it to your audience. For example, in the case of the SAAS application, your WIIFY to your potential investors would be - Investing in our product will get you an excellent ROI.
Let them know the USP of your proposition and the concept you are presenting. For example, you could highlight your USP as the one place for everything from website development to QA testing.
Use a short statement to capture everyone’s attention. It may be anecdotes, statistics, analogies, aphorisms, a question, etc.
For example, you could start with a statement like - Keep track of how many times I shall say ‘if’ when I explain the success of this product.
Or an analogy like - SAAS is like traveling by train where you have assigned routes and co-ride with other passengers.
Do’s and Dont's
- The presentation should start with the motivation, i.e., why this particular thing needs to be presented.
- Every presentation slide should contain only relevant information and not more than that.
- Titles should be enough on their own (self-explanatory); the rest of the text should be there to support the visuals, comprising relevant graphs, charts, histograms, etc.
- And most importantly, the audience properly understands the message the presenter desires to convey. Also, be mindful of overusing jargon.
In a Nutshell
Be thorough about the topic, learn about your audience, take the help of props and visual aids, and structure your presentation well. Don’t forget to interact with your audience as and when you get the chance. Also, make sure your audience knows what to do with the information you shared, i.e., give them a proper course of action.
Keeping these points in mind will help you create a coherent technical presentation that can serve its purpose.

Don't waste your time designing your presentations by yourself!
Type your content and let our platform design your presentations automatically. No more wasting time for your presentations. Use hundreds of presentation templates to impress your audience. This is the only tool you need to prepare presentations. Try our Presentation Builder today >>
Don’t waste your time by trying to make a website for all your content
Place your content links and let our platform design your bio link automatically. No more wasting time for your social content distribution. Use hundreds of presentation biolink to impress your audience. This is the only tool you need to prepare good-looking bio links. Try our Bio Link Builder today >>
Do You Want To Create a Presentation?
Latest Articles

May 27, 2024
Decktopus vs Beautiful.ai: 2023's Best AI Presentation Tool?
In the dynamic realm of AI-powered presentations, Decktopus and Beautiful.AI engage in fierce competition. Both platforms harness the potential of AI to redefine the presentation landscape, offering users instant access to intuitive tools and dynamic features. Decktopus, with its innovative approach, integrat
.jpg)
Exploring Beautiful.ai Alternatives: Competitors and Top Picks
Discover top Beautiful.ai alternatives for your presentations. From WPS Office to Piktochart, Slides, Visme, and more, we've listed the best AI-powered presentation apps to elevate your slides.
.jpg)
Decktopus vs Google Slides: Ultimate 2024 Showdown
Explore a head-to-head comparison of Decktopus vs Google Slides in the 2024 showdown! Get insights on customization, collaboration & innovation features in presentation.
Sign up for our newsletter to stay up-to-date on the latest news and tips from Decktopus.
Let’s create a form here to get visitors’ email addresses.
Ready to dive in? Start your free trial today.
This website is sponsored by the Leonhard Center for the Enhancement of Engineering Education at Penn State.
- Assured PNT
- RF Solutions
- High Vibration
- Space Solutions
- High Performance Oscillators
- Space Oscillators
- Atomic Clocks
- Clocks & Oscillators
- Crystals & Transducers
- Filters & Multiplexers
- Company History
Inside Frequency Control
A quick guide to building effective technical presentations.
As an expert in a technical field, you will occasionally be called upon to give a presentation on your work to people who are not very familiar with your field, such as your company's sales and marketing team. You need to be aware of the proper communication techniques to be able to place highly technical facts before your listeners in a manner they can understand.
Here is a quick guide to building an effective technical presentation:
1. know your audience.
There are a few questions you will need to ask yourself before your technical presentation to determine the type of presentation to prepare. How familiar is the audience with the subject? Are they experts or novices in the field? What style of presentation are they used to sitting through? Will they understand technical terms or do you need to use simpler language? Do they respond better to a lecture or a more interactive learning session?
Once the answers to these questions have been determined, you can set about creating a technical presentation that caters specifically to the tastes and preferences of your audience.
2. Limit Your Subject
Determine beforehand how technical your presentation needs to be in order to get the point across. Only go as deeply into the subject as required, and avoid throwing in terms and references which have nothing to do with the subject at hand.
3. Make an Outline
Now it's time to break down the presentation into smaller chunks that focus on one point at a time. With technical presentations, it is useful to have three sections to a presentation. The first section identifies the main subject and provides a summary of its broad definition and why it has become the subject of the presentation.
The second section goes more deeply into the main subject and provides the minute technical details which the audience needs to understand about the topic. The final section offers a solution or resolution to the problem presented through the presentation. You can also add in a course of action that is being taken or should be taken in the near future at the end of the technical presentation.
4. Use Visual Aids

When dealing with technical jargon, don't just depend on your speech to get the point across to the listeners. Ensure that they truly grasp the meaning of your words with the help of visual aids. Creating a PowerPoint presentation is the most useful tool in this regard since it will allow you to add graphs, statistics, and animation to your technical presentation. But you can also make use of handmade models, working prototypes and other visual aids in your presentation.
5. Approach the Subject from Different Angles
Don't focus only on your work in relation to the subject. Try to present a comprehensive view of the topic which also includes its sales, marketing, and business side. Remember that the audience likely has a different relationship to the subject matter than you do, so try to include content relating to the subject from their point of view as well.
6. Be Prepared for Questions
Finishing your lecture won't be the end of your technical presentation. There is almost always a question and answer session afterward during which the audience will ask you for greater details about the information presented. Do your homework beforehand to prepare for any questions that might be asked.
Keeping these points in mind will help ensure that your knowledge is presented in an attractive and easily understandable manner which will create a positive impression and provide a useful, comprehensive and enlightening technical presentation to the audience.
At Bliley, we often collaborate on projects and presentations. Learn about our favoriate collaboration tools here . What applications do you use to collaborate or prepare presentations? We'd love to hear from you!

Topics: engineering , general

Subscribe... get an eBook!
- crystal oscillators (68)
- RF Technology (63)
- Space & Satellites (43)
- engineering (38)
- general (38)
- Defense & PNT (26)
- General Topics (26)
- Press Release (22)
- Clocks & Crystals (20)
- Military & Defense (17)
- aerospace (17)
- Leadership (16)
- Integrated RF (14)
- GPS & GNSS (9)
- Engineering Equiptment (7)
- Filters & Multiplexers (1)
See What's Popular
Most recent.

Disclosure: This blog contains product affiliate links to help support the blog. We only link trusted, well-rated products.
Epic content.
- Privacy Policy
- Distributors and Reps
© 2024 Bliley | Refund and Return Policy | Privacy Policy | Powered by Piconsulting

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.3 Designing Your Presentation
Suzan Last and Robin L. Potter
How you organize the contents of your presentation and how you design your slide deck will help to determine whether or not your message is conveyed in its most powerful form. This chapter will focus on speech structure and on slide design.
Speech Structure
You are by now familiar with the conventions of technical correspondence and report structure: introduction, background, details, conclusion. This structure forms the backbone for most messaging in technical fields. Many presentations are created using this simple structure as well, often melding the introduction and background together to save on time. The key message would constitute the high point of the presentation, followed by information that supports that point. This “triangle-shaped” structure is used commonly.
To determine how your presentation should be constructed, consider your purpose. In technology, the purpose often falls within the following, according to David McMurrey (1997-2017):
- Informative purpose: A presentation can be primarily informative. For example, as a member of a committee involved in a project to relocate the plant, your job might be to give a presentation on the condition of the building and grounds at one of the sites proposed for purchase. Or, you might be required to go before the city council and report on the success of the new city-sponsored recycling project.
- Instructional purpose: A presentation can be primarily instructional. Your task might be to train new employees to use certain equipment or to perform certain routine tasks.
- Persuasive purpose: A presentation can be primarily persuasive. You might want to convince members of local civic organizations to support a city-wide recycling program. You might appear before city council to persuade its members to reserve certain city-owned lands for park areas, softball and baseball parks, or community gardens.
When creating a presentation that has a persuasive message, you have structural options. You can organize your content using the traditional “triangle” method, or you can use the “what is, what can be” comparative method shared by Nancy Duarte in her presentation below The Secret Structure of Great Talks (2011). In this presentation, which offers a great example of effective persuasive presentation structure and design, Duarte reveals that speeches that have changed society make use of this “what is, what can be” structure, which compares what the current situation is to what the situation can be in its improved form after your great idea is implemented. Keep this structure in your toolbox for times when you want to persuade the reader to implement a new procedure, accept a proposed project, or sell a new product, for example.
Knowledge Check
A Brief Overview of PowerPoint
Even the most dynamic speakers often make use of visual aids to accompany their presentation and help illustrate their ideas. Having well-designed visuals as part of your presentation is one way for presenters to add interest and audience engagement to their talks. Despite much discussion on the pros and cons of this medium, PowerPoint is probably the most common software used to create presentations using visual aids. While many other presentation tools are worthy of your consideration, PowerPoint is a standard, versatile workplace tool, so it would be wise to gain proficiency with it. The key concept to remember is that your visual aids should supplement and illustrate what you want to say to your audience.
When designing a PowerPoint presentation, it is helpful to be familiar with the key terminology used to discuss the various elements.
- Deck : The deck is the entire presentation (all the slides in the presentation; see Figure 9.2.1) .

- Gloss : Gloss is what the speaker says about each slide. The speaker should not simply read what is on the slide. Slides should have minimal text in the form of keywords and short bullet points. It might include key quotations. The speaker should elaborate on what is written or shown on the slide.
- Slide : The slide is one “page” of the presentation ( Figure 9.2.2 shows one slide from the deck above) with the various elements identified. Note the source entry for the image at the bottom of the slide. Even images must be cited!

- Slide Titles : Usually at the top of the slide, the titles acts as “headings” indicating the topic to be discussed in each slide.
- Body Text: Body text is the written text on the slide, often in the form of bullet points or key terms. This text should be kept to a minimum (keywords/phrases; quotations you want to read out loud). Don’t write your “script” in the slide’s body text.
- Exhibits : Exhibits are illustrative graphics on the slides that are glossed in the presentation. You should discuss graphics and explain what is important about them.
- Decorative visuals : Decorative visuals are slide motifs, themes, and other non-essential images that add visual appeal to the slides, but do not illustrate substantive ideas.
- Sources: Citation notes indicating the sources for images.
- Notes : The section underneath the slide where you can write notes you want to cover in your gloss. The audience will not see the “notes” portion.
You may want to view sample presentations: Click on the presentations listed below or take a look at the PowerPoint decks that accompany this textbook to see detailed examples of effective presentation decks.
PowerPoint Presentation on PRESENTATIONS (.ppt)
Definitions in Technical Writing – Sample student presentation (.pdf) (Created by Isaac Morton)
Designing Slides for Technical Information
You will probably be most familiar with the slide design illustrated above, with each slide containing a title and content consisting of bullet points. You will see this design in most of your professors’ lectures. Though it is the most commonly used slide design, it has also been criticized as being too rigid and resulting in poor long-term information retention. When this traditional slide design was compared to the assertion-evidence slide design discussed below, researchers discovered that using assertion-evidence slide structure resulted in deeper learning and understanding (Garner, et al. 2011).
Assertion-evidence slide structure, pioneered by Michael Alley at Penn State University, consists of a statement, or assertion, usually placed where the slide title would normally be placed. Among other types of content, the body of the slide would then include (excerpted from McMurrey, 1997-2017):
- Drawing or diagram of key objects: If you describe or refer to any objects during your presentation, show visuals of them so that you can point to different components or features.
- Tables, charts, graphs: If you discuss statistical data, present them in some form or table, chart, or graph. Many members of your audience may be less comfortable “hearing” such data as opposed to seeing them.
- Other research data or information: Usually presented in text or charts.
Below is a video by Robert Yale (2013) that reviews conventional PowerPoint disadvantages, studies in information retention, and the assertion-evidence structure. If you want to learn how to create slides using this method and see examples, please view this video as it is a good primer.
Visual Rhetoric
PowerPoint is not the only visual medium you might use. Posters, infographics, and other kinds of displays can also work to effectively convey your message if they are well designed. Considering how to present ideas visually can be as important as determining what to say. Here are some resources to help you design visual information in a rhetorically effective way:
Visual Rhetoric page from the Online Writing Lab (OWL) at Purdue University
Rule of Thirds (Wikipedia)
Psychology of Font Choices (The Daily Egg)
Putting It All Together
As you deepen your knowledge of general slide deck design, check out these two texts, which are considered key primers on the topic of presentation design.
- Garr Reynolds, PresentationZen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery provides a clear, easy-to-read set of tips for cutting through the noise and blather of modern life and reaching an audience through simple, pared-down slides and story-telling: two techniques that can help you connect with and inspire your audience in an authentic, genuine way.
- Nancy Duarte, Slideology: T he Art and Science of Creating Great Presentations looks to the role of presentation software in the visualization of ideas and information. Its goal is to turn you into a “visual thinker” so you can design presentation graphics that enable your audience to easily and effectively process data—an especially valuable skill for technical presenters who often have to convey complex data in meaningful ways to non-technical audiences. Review the video below for a video explanation of these principles.
( How to Create Better Visual Presentations , 2014)
____________________________________________________________________
Note: Some of the contents of this chapter have been adapted from David McMurrey (1997-2017), Online Technical Writing: Oral Presentations. https://mcmassociates.io/textbook/oral.html CC by Attribution 4.0
Ally, M. (n.d.). Rethinking presentations in science and engineering . Penn State University Park. https://www.assertion-evidence.com/templates.html
Duarte, N. (2008). Slide:ology: T he art and science of creating great presentations . Duarte.com. https://www.duarte.com/books/slideology/
Duarte, N. (2011, November.) The secret structure of great talks. TEDxEast. https://www.ted.com/talks/nancy_duarte_the_secret_structure_of_great_talks?utm_campaign=tedspread&utm_medium=referral&utm_source=tedcomshare
Duarte, N. (2014) How to Create Better Presentations [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=so9EJoQJc-0&t=2s
Garner, J.K., Alley, M., Sawarynski, L.E., Wolfe, K.L., & Zappe, S.E. (2011). Assertion-evidence slides appear to lead to better comprehension and recall of more complex concepts. American Society of Engineers. PDF.
Garr, R. (2011). PresentationZen: Simple ideas on presentation design and delivery. Toronto: Pearson. http://ptgmedia.pearsoncmg.com/images/9780321811981/samplepages/0321811984.pdf
Hunt, Ted. (2013, July 5). A pro designer shares the psychology of font choices. [Infographic]. The Daily Egg.
Keithonearth, [Bicycle image embedded in slide]. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derailleur_gears#/media/File:Derailleur_Bicycle_Drivetrain.svg . CC BY-SA 3.0.
McMurrey, D. (1997-2017). Online technical writing: Oral presentations. https://mcmassociates.io/textbook/oral.html
Online Writing Lab (OWL). Visual rhetoric. University of Purdue. https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/visual_rhetoric/visual_rhetoric/index.html
Wikipedia. (2021, February 9 edited). Rule of Thirds. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rule_of_thirds
Yale, R. (2013). The Assertion-evidence structure for PowerPoint slide design. YouTube. https://youtu.be/xNW84FUe0ZA
Technical Writing Essentials Copyright © 2019 by Suzan Last and Robin L. Potter is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4.6 Presentations
Presentations are an interesting genre, since they can cover a variety of genres and purposes. Presentations provide the opportunity to present information in a multimodal format, and often require you to condense information for a broad audience. Within the very broad genre of “presentation” many genres fall with more specific conventions and constraints. Some examples include:
- Conference presentations
- Less formal meeting or business presentations (internal)
As technology continues to develop, you might consider other genres under the umbrella of “presentations,” including:
- Youtube videos
In this section, we talk about the specific genre of presentations, but we also focus on taking complex information (such as gathered in a formal report) and reworking, condensing, and remixing that information into a presentation, a website, a poster or infographic, or a podcast.

Diversity, equity, and inclusion
Just like with the other common genres that we’ve discussed so far, presentations are developed for a specific audience. So, you need to consider how your audience might best receive the information that you are working to communicate. Presentations are a great way to reach an audience, and as a communicator you get to explore various communication modes and approaches. As with anything else, what might work for one audience would not work for another audience; think back to the different ways to communicate the process of conducting a Covid-19 nasal test. Each example was effective, but only in the context of their intended audience.
Technical presentations are a specific genre that often take the complex, lengthy information included in a formal report and condenses and translates that information in a way that includes visual and audio communication modes. Consider why it is useful to present information in various ways (as a formal report and as a 5-10 minute presentation). How might presenting information in various ways or formats increase accessibility? How might developing a presentation work towards equity of information access?
When creating a presentation, the principles of universal design are important things to keep in mind. One example might be adding captions if you create a presentation that has any audio component. The captions are essential for any audience members who are hearing impaired, AND they make it easier to absorb content and understand the audio for your entire audience. Remember that universal design means that accessibility of information is an essential part of your presentation: do not think about accessibility after you’ve created your content, but work it in from the beginning and throughout your process.
Technical presentations
Technical presentations can vary quite a bit in length and content, depending on your purpose, audience, and context (remember that the rhetorical situation is always relevant!). Generally speaking, a technical presentation will:
- Condense a longer text, such as a formal report
- Summarize the most important, useful, or meaningful information from that text
- Use visuals, text, and audio together in order to tell a story
Most often, presentations work to inform, to persuade, or both. All the things that we’ve discussed so far are important to consider when you create a presentation, including plain language, document design, and considering diversity, equity, and inclusion. Just as with any other genre, to create an effective presentation, you must understand your audience.
Google Slides
These are only 3 of many free tutorials available online.
When creating effective presentation slides, be sure that you balance the amount of information on each slide. Consider how your audience is interacting with these slides: they are not likely sitting down with so much time to carefully read through each one. Rather, they may only have a minute to take in all the content. So, less is often better than putting too much text on any one slide. It’s also important to use a variety of visual modes–such as graphics and images–along with text.
The text that you choose should summarize key points, and the images should reinforce or illustrate those points. Do not make your audience take in large blocks of text. Instead, summarize key questions, data points, findings, and conclusions. Show them examples that help to illustrate these important points, but do not overwhelm them. You cannot include everything in a presentation that you would include in a lengthy report. Rather, you must choose the most important pieces so that your audience has a clear idea of what you want them to take away from your project.
When planning and creating audio, be sure that you do not simply read the text from our slides. Instead, you can use the audio portion of your presentation to further explain key concepts. Give your reader a bit more detail, but do not overwhelm them. A presentation works to create a narrative or tell a story. The audio and text should complement each other, but not be exactly the same (if you’ve ever attended a presentation where the presenter read each slide out loud, you know how uninteresting that can be!).
Finally, consider accessibility when you design your presentation. Create closed captions or subtitles when recording audio, and be sure to incorporate the principles of universal design. Try to imagine how to make information accessible to your audience in regards to your text, your use of language and terminology, your use of visuals and graphics, and your use of audio.
Message titles
On way to create stronger, more memorable presentations is through the use of message titles rather than subject titles for each slide. It’s important to use strong titles, and a message title delivers a full message to your reader. A subject title is briefer and less specific. An example of the difference between a message title and subject title might be:
Subject title:
Covid-19 prevention
Message title:
How can I protect myself from Covid-19?
A message title is generally more effective for audiences because it provides more information. Further, delivering a full message helps audiences to retain the information presented in that slide and it frames what you cover in that section of your presentation. Remember that audiences must listen to your presentation and read your slides at the same time. Subject titles provide information, but message titles helps audiences place that information into a more specific framework. A message title delivers your message in a more complete way.
Condensing and remixing
While most formal reports use some sort of presentation software and rely on a combination of slides (which contain visuals and text) and audio (which may be spoken live as you present to an audience or may be recorded ahead of time), there are other ways to remix and present information in a condensed and useful way. As technology develops, so does the presentation genre. For example, podcasts, videos, or websites might be useful in place of a technical presentation, again depending on the audience, purpose, and context.
If you are enrolled in WRIT 3562W, you are not asked to create a podcast or website; however, you may come across such genres and want to use them as sources in your own report. And, you will likely want to (or be asked to!) create a website or podcast someday. So how can you begin to take information presented in something like a formal report and revise, translate, and remix it for a completely different medium?
First, consider the rhetorical situation and reflect on your own experiences as a website user or a podcast listener. Which websites do you like best? Which podcasts do you enjoy? Then, do some reflection and analysis and consider the following questions:
- When interacting with a website, what features are most important to you? How are you typically interacting with content (do you want to be able to search for something specific, do you want something easy to skim, do you want to deeply read all the text, etc.)?
- Think of the easiest to navigate website you’ve visited recently; what specific features made it easy to navigate? How did it use text, images, alignment, repetition, contrast, colors, language to help you know how to find and understand information?
- Think of the most difficult to navigate website that you’ve ever visited; what made it difficult? What specific features can you identify or isolate that made it hard to find information?
- Consider your favorite podcast; how does the creator(s) organize the content and present information clearly? How long does it take to listen to? What environment do you usually listen to podcasts in (your car, at home, using headphones, on a speaker while you cook dinner…). What specific features can you identify or isolate that make it enjoyable?
These types of reflection questions help you to make decisions about the texts that you create. They are useful when considering conventions or strengths of specific genres, AND they are useful when you have to create a genre that is completely new to you. Remember that analyzing the rhetorical situation and genre conventions together make it manageable as you approach any new communication task.
Throughout this text, we’ve discussed technical communication as rhetorical, as always concerned with diversity, equity, and inclusion, how we define or set the boundaries for technical communication, and the conventions of common genres. As you continue your education and practice as a technical communicator, or as you approach any new communication situation, keep doing the work of analysis and reflection. Consider how each act of communication engages a specific audience for a specific purpose. Even the most seemingly objective genres require you to make choices: what information do you include, whose voices and experiences do you elevate, how do you take in feedback and revise your texts, how do you approach research in a way that reduces bias and incorporates marginalized experiences–these are all important pieces of the communication process. As technical communication continues to develop and evolve, and as technology and genres also change, keep these considerations in mind.
Activity and Reflection: Presenting information
Together or with a partner, find a presentation (you can search YouTube for technical presentations or Ted Talks). Reflect on the following questions to perform a rhetorical analysis on the presentation:
- Who is the target audience for this presentation? How can you tell?
- What is the main purpose or goal of the presentation? How can you tell?
- What did you like about the presentation (be specific)? What features make it effective?
- What would you change, and why?
- How does the presentation use text and audio together to deliver a message? How do these elements complement each other?
Introduction to Technical and Professional Communication Copyright © 2021 by Brigitte Mussack is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
This website uses cookies. Learn more
How to structure a PowerPoint presentation: A detailed guide
· Create Courses

How do you structure a PowerPoint presentation?
Introduction , the body , the conclusion , powerpoint presentation examples , graphy, the all-in-one course creation platform.
In this blog, you’ll understand the step-by-step guide on how you can structure a PowerPoint presentation effectively.
You might be a great presenter but suck at creating a structured presentation. The idea of outlining, selecting the right templates, and adding transitions is way out of your league.
However, creating a structured presentation is as important as the narration.
When information is presented logically, the retention rate automatically goes up. It becomes easier for a viewer to understand the meaning behind the words and create a flow of information.
Monetize your skills and extertise GOT YOUR CONTENT READY? GRAPHY IS ALL YOU NEED TO GET STARTED!
A report published by Standard Business says that people retain 40% more information when presented structurally.
So, here we are to help you understand how you should structure your PowerPoint presentation to make it likable and easy to digest.
Table of Contents
You can follow this standard structure while creating your PowerPoint presentations. A good presentation is always one that has a good storyline and narration. Let’s dive into detail on how to create a solid PowerPoint structure.
An introduction is the most crucial part of a presentation. It sets the tone for your audience and makes them comfortable. Before you start with your presentation, make sure to
- Introduce yourself
- Explain the purpose of this presentation
- And, what outcomes can your audience expect at the end of it?
This doesn’t have to be super-detailed, but it should build a connection with the person. You can include storytelling to gather attention and further move on to introducing the topic.
Here are some slides that you must include in your introduction:
- The title: Introduce the topic of the presentation and add a brief description
- Challenges/ objectives: Explain the goals or challenges you will target in the presentation. For example, I’ll “compare,” “evaluate,” and “analyze” this topic.
- Outcome: Your audience must know the results they can expect at the end of the presentation. For instance, at the end of this presentation, I hope to provide you with a….
- Table of Content: You can include a table of contents for your audience to know the topic of discussion in the presentation.
In the introduction, you can also tell the length of the talk or whether you want audience participation. Clarifying such small things can make presentations smoother and less awkward.
This is the part where you take your introduction forward and briefly discuss the key topics. You must organize these points to transition smoothly from one topic to another. The body of your presentation needs to be spot-on for your audience to understand the information given.
Here are some tips to consider when creating the body of your presentation:
- The length and structure of your slides are crucial to the body of your presentation. You can use the 5-5-5 and 10-20-30 rules to structure a PowerPoint presentation.
What is the 555 rule in PowerPoint?
The 555 rule says, to use at least
- 5 words on a single line.
- 5 lines of text on every slide
- 5 slides that use the mentioned rules in a row
The purpose of this 555 rule is to create a flow in presenting your information. This rule helps if you have to make a big presentation that requires heavy content and various slides. It will help you structure a presentation well and not overwhelm your audience with the information.
What is the 10 20 30 rule in PowerPoint?
The 10 / 20 / 30 rule in PowerPoint is fairly simple. It says that no PowerPoint presentation should have over 10 slides, be longer than 20 minutes, and have fonts smaller than 30 points.
Each of the rules helps the presenter form a balance between design and explanation. This helps to structure a PowerPoint presentation and create easy-to-digest slides.
- Use images more than words. The human brain processes visual stimuli 60 times faster than text. So, instead of writing lengthy paraphs, add photos or videos. If you think a concept is explainable through a photo, use it.
- Your presentation should be short and crisp. You don’t have to write everything about the topic in your slides. Include a few short-crisp sentences and use narration to explain the topic in depth.
- Try to organize your topics well. List points in order of numbers or alphabets put them in a time frame, or use transition words like next, then, and another for easy understanding. No matter how well you explain concepts, if your presentation lacks the translation to move from one topic to another, then it might not work.
In your conclusion, you can summarise the main points you have made and do a recap of what your audience has learned. Lastly, mention how this new information meets your objective for the presentation.
In conclusion, you must state your sources of information, like books, articles, or interviews with people.
Include a Q&A part to ask questions. This way, there isn’t any open-ended conversation, and your audience is clear about the points you made. If you cannot answer any question because of a lack of time, note it down to provide the solution through mail or phone.
End your presentation by thanking your audience for their precious time and asking for their feedback.
See how simple it is to structure a PowerPoint presentation. Now, look at a few examples of PowerPoint structures for your reference.
Powerpoint presentations are mostly referred to as bland and boring, but that’s not the case. If you structure it well, your presentations will become more like a learning opportunity than an endurance test. Here are some PowerPoint presentation examples you can refer to:
- Teacher education
Look at this slide deck , created for teachers on how to use Google Slides. It’s not overloading with information nor holding it back; it’s simply perfect. Most of the slides are image-oriented with practical examples to help the audience understand the basics of creating presentations in Google Slides.
- Zuroa sales deck
To see how storytelling works in presentation, refer to Zuroa’s sales desk . These slides are a perfect example of how you can make your audience relate to your issues. Including metrics and messages from well-known CEOs makes the slides authoritative.
- Trackmaven research deck
Creating a data-heavy presentation is quite tricky. Your audience can quickly accelerate from engaging to boring. Trackmaven excellently presents its report on the best time to post on social media. The presentation has more graphs than numbers or text. If you are looking for a reference for creating such data extensive topic, then, indeed, check this out.
- Officevibe collaboration examples
This slide deck increases awareness of the problem faced because of a disengaged team. The presentation has bright colors and unique designs that draw attention. Plus, it’s filled with relevant data to ensure the authority and seriousness of the issue.
They are excellent examples of how you can structure a PowerPoint presentation. If you notice, none of them are text-heavy. Instead, they have used visuals or videos to convey most of their information. Thus, the information presented is easy to digest and keeps the audience hooked until the end.
If you are looking to create your online course and sell it with minimum effort and easy-to-use features, then Graphy is the best place for you. Graphy has thousands of active content creators who have created their own online courses and monetized their skills. You can also do the same, and the best thing is that you can start for free.
Graphy offers a load of features that will definitely add stars to your success, features like:
- Branded website and mobile app
- Advanced-level marketing and sales tools and features
- Multi-layer content security
- Rich multimedia
- 24*7 customer support
- Customizable landing/sales pages
- Personalized course completion certificates for your learners
- Integrated payment gateways and country-specific pricing
Isn’t it amazing?
So join Graphy , just like 40,000+ creators.
Course platform
create your online course
online course platform india
PowerPoint presentation
structure a PowerPoint presentation
Top creators use Graphy to sell courses and memberships
Join 100K+ creators who have launched their online knowledge business using Graphy
You may also want to read

Top 7 Christmas Marketing Strategies to Boost Sales

9 Telegram Bots Every Telegram Channel Owner Must Have (2024 Updated)

How To Create a Paid Telegram Channel In 2024 (Updated)?

- How to Plan a Technical Presentation
Technical experts – scientists, engineers, and programmers – are being asked more and more frequently to give presentations. And not just to other technical experts. Often they are speaking to people with little or no technical expertise, to people from marketing, sales, and finance.
Here’s how to plan a technical presentation so it is clear and convincing.
1. Limit your Subject If you’re like most technical experts, you probably spend too much time doing research. Then, because you haven’t allowed yourself enough time to pull it all together, you end up cramming everything you know about your subject into your presentation. You produce many more slides than you can possibly do justice to in the allotted time.
With most presentations, you won’t have the time you need to say everything you want to say. So you have to prioritize. It’s your job to know what to say and, just as importantly, what not to say.
While non-technical speakers are often “light” on content, technical presenters more commonly present — or try to present — too much material.
2. Understand your Audience Knowing who you’re talking to – your audience – is as important as knowing what you’re talking about – your subject. Your audience’s knowledge level, experience, learning style, and attitudes will – or should – affect how you shape and present your material.
Find the answers to these questions:
- What does you audience already know about your subject?
- Are they experts like yourself or neophytes?
- How much knowledge can you take for granted?
- How much background will you have to explain?
- Will they understand basic jargon?
- What is their learning style?
- Are they accustomed to sitting through lectures and holding their questions to the end? Or will they expect to interact with you, asking questions throughout your presentation?
- Do they like lots of PowerPoint™ slides and handouts? Or are they expecting you to be more interactive?
- What are their opinions, prejudices, preconceived notions, agendas?
- What is their stake in the subject?
- How will your presentation affect their research or work?
3. Determine your Objective What do you want to accomplish? What do you want your audience to do as a result of your presentation?
Do you want them to
- Challenge your assumptions or data or to confirm them?
- Implement your procedure or technique?
- Renew your grant?
- Approve your proposal?
- Give you the go ahead for the next step of your research?
Once you know what you want them to do, ask yourself what they need to know and to feel in order to do it.
4. Prepare your Outline If possible, break your presentation into three basic sections. (You can divide each section into more, smaller units.)
Here are some 3-section outlines you might find helpful:
- The problem, its causes, and the solution.
- The illness, the symptoms, and the treatment
- The current situation or standard operating procedure, the problems associated with it, and an alternative
- The state of your research, questions raised by your research, and the next steps
- A product, its composition, and its application
Once you’ve “clumped” the various elements of your talk into their major sections – I strongly recommend three sections, but you could have as many as five – add an introduction and conclusion.
5. Create your Slides Now you can turn on PowerPoint™ and begin creating your slides.
See also 10 Tips for Using Visual Aids and How to Improve a Technical Presentation .
Chris Witt, a coach based in San Diego, works with technical experts who want to give more effective presentations. If you’re interested in learning more about how you could benefit from his coaching, contact him for a complimentary call.
10 TIPS TO MAKE YOU A BETTER SPEAKER NOW
- How Leaders Speak
- How to Plan an Oral Proposal
- Take the Listening Quiz
- How to Handle the Q&A Session
- 10 Tips for Using Visual Aids
- How to Develop Confidence in Public Speaking
- Build Rapport with Any Audience
- 7 Principles of Influence
- What to Do When Your Mind Goes Blank
Speaking your way to success
Have you ever been bored by a PowerPoint presentation? Of course you have. The real question is, why can't more people speak in a way that has the power to change the way people think and feel and act?
Technical Presentations - Book 2: Structure - Anatomy of a Successful Presentation
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Technical Presentation. Structure diagram. Criteria for Success. The presentation starts with the motivating problem for the research and why it's being presented. ... Because the audience cannot immediately see a presentation's structure like they can with a paper, it is often a good idea to provide a high-level roadmap of the presentation ...
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
PowerPoint Tips. Figure 16.1: It can be scary looking at a large audience, even for us who do it a lot. One important, but often overlooked, skill in engineering is presenting. From talking with students, I have noticed that a lot of engineering students are intimidated by public speaking.
However, there are steps you can take to deliver an effective technical presentation that gets your point across and appeals to the audience. ... To do this, make sure you are using a suitable structure for your presentation. You can do these things only when you're well-versed in what you're presenting. The slides are supposed to be your ...
Discussion of Example #3. This presentation employs a clear structure of a main assertion and subsequent sub-assertions to lead the audience through the presentation. We can see this represent here visually with an assertion tree: Let's take a look at some other structural elements in this presentation.
A common structure for a technical presentation is the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. In the introduction, you should capture the attention of your audience, introduce your topic and ...
Structure your presentation. To craft an effective technical presentation, it is crucial to structure your content in a clear and logical flow. Begin with an attention-grabbing introduction that captivates your audience and sets the tone for the presentation. Organize your content into sections or chapters, making it easier for your audience to ...
And yes, keep your presentation short - not more than 10 slides. You can go for the 10/20/30 rule, i.e., 10 slides, 20 minutes, and 30 font size. 6. Leave space for questions and queries. Since your presentation is technical and the audience might be diverse, be prepared to answer questions. The major cause of anxiety before a presentation is ...
With these 3 key guidelines, you can be assured of success in technical presentations. In this article I will focus on the first guideline — how to gain a sufficient understanding of your audience to be able to gauge their key concerns, base level of understanding on the topic at hand, and expectations for the presentation you're about to give.
Effective technical presentations are discussed from four perspectives: structure, speech, delivery, and visual aids. Discussion questions are provided to initiate group discussion when watched in a classroom setting or as an assignment. Additionally, there is an Exercises section that provides potential assignments and activities.
Technical presentations are inevitable, especially when conveying knowledge around the fast-evolving technology stack, algorithms, and workflows. ... The need to explain LSTM and the architectural structure simply seems like a mission impossible to me. Needless to say, the audience did not take away anything from the 2 hours session. ...
Determine beforehand how technical your presentation needs to be in order to get the point across. Only go as deeply into the subject as required, and avoid throwing in terms and references which have nothing to do with the subject at hand. 3. Make an Outline. Now it's time to break down the presentation into smaller chunks that focus on one ...
When designing a PowerPoint presentation, it is helpful to be familiar with the key terminology used to discuss the various elements. Deck : The deck is the entire presentation (all the slides in the presentation; see Figure 9.2.1). Figure 9.2.1 PowerPoint Deck. Gloss : Gloss is what the speaker says about each slide.
Technical presentations are a specific genre that often take the complex, lengthy information included in a formal report and condenses and translates that information in a way that includes visual and audio communication modes. Consider why it is useful to present information in various ways (as a formal report and as a 5-10 minute presentation).
Hook, Meat and Payoff. This presentation structure, like The Drama, is deeply founded in the art of storytelling. While the Hero's Journey is more of a literary technique, Hook, Meat and Payoff is more like a spoken-word progression. Source. Create your own graphics with this drag-and-drop tool.
Objectives. This exercise is designed to improve the following skills: The ability to explain and discuss technical material to an engineering audience. The ability to develop and use effectively overhead slides for presentations. The ability to speak effectively and maintain interest before an engineering audience without using notes.
The body of your presentation needs to be spot-on for your audience to understand the information given. Here are some tips to consider when creating the body of your presentation: The length and structure of your slides are crucial to the body of your presentation. You can use the 5-5-5 and 10-20-30 rules to structure a PowerPoint presentation.
Here's how to plan a technical presentation so it is clear and convincing. 1. Limit your Subject. If you're like most technical experts, you probably spend too much time doing research. Then, because you haven't allowed yourself enough time to pull it all together, you end up cramming everything you know about your subject into your ...
A technical expert must not only know, understand and interpret complex data but also present the facts through clear, concise and correct speech. The first step in conveying technical information is to establish a clear understanding of when, where, why, how, what and to whom your information is to be presented. The next step is to structure the presentation. The structure of a presentation ...
The Slide-Structure of a Technical 20-min Presentation By Michalis Faloutsos Thanks to Michael Samidi General guidelines: Expect 1.5-2 minutes per slide on average. However, I have seen people go through faster and slower. which leads us to the next point. Time yourself.
Therefore, we created a lecture targeting computer science students that teaches how to design an effective presentation, especially a technical presentation, with a clear narrative. In this workshop, we will introduce how we designed the lecture, and participants will be involved in a group activity that students did in the lecture to see the ...