We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides Brainstorming Examples + Techniques For Problem Solving

Brainstorming Examples + Techniques For Problem Solving
Written by: Krystle Wong Sep 08, 2023

So — you’re faced with a complex problem that seems as daunting as a mountain. You’ve tried all the usual approaches, but the solution remains elusive. What do you do? That’s where a good brainstorming mind map maker comes into play.
This article is your backstage pass to the world of brainstorming. I’m not just going to give you the playbook; I’m going to show you how it’s done with brainstorming examples that will have you saying, “Why didn’t I think of that?”
So, no more beating around the brainstorming bush. Let’s roll up our sleeves and dive into the many effective techniques and examples that will turbocharge your problem-solving game. It’s time to unleash your inner brainstorming genius!
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 4 rules of brainstorming
12+ brainstorming mind map examples for problem solving, 10 effective brainstorming techniques that work, 5 common mistakes to avoid during brainstorming, brainstorming examples faq.
- 5 steps to create a brainstorming mind map with Venngage
The concept of brainstorming was introduced by Alex Osborn, an advertising executive and he outlined four key rules to facilitate effective brainstorming sessions.
These rules are often referred to as the “Four Rules of Brainstorming” and are designed to encourage creativity and a free flow of ideas within a group. Here are the four rules:
No judgment: All ideas are welcomed and accepted without criticism or evaluation during a brainstorming session. This rule encourages participants to feel free to express even unconventional or seemingly impractical ideas.
Quantity over quality: Forget about perfection for now. In brainstorming, it’s like a numbers game – the more ideas, the merrier. Don’t get bogged down in refining each idea to perfection; just get them out there.
Build on the ideas of others: Teamwork makes the dream work. When someone throws out an idea, don’t just nod and move on. Add your spin, build on it or take it in a different direction. It’s all about collaboration and bouncing off each other’s creativity.
Encourage wild and creative ideas: Embrace the weird, the wild and the wacky. Sometimes the most outlandish ideas can be the seeds of genius solutions. So, don’t be shy – let your imagination run wild.
So, the next time you’re in a brainstorming session, remember these rules. They’re not just guidelines; they’re the keys to unlocking your team’s creative potential. With these principles in play, you’ll find yourself reaching new heights of innovation and problem-solving.
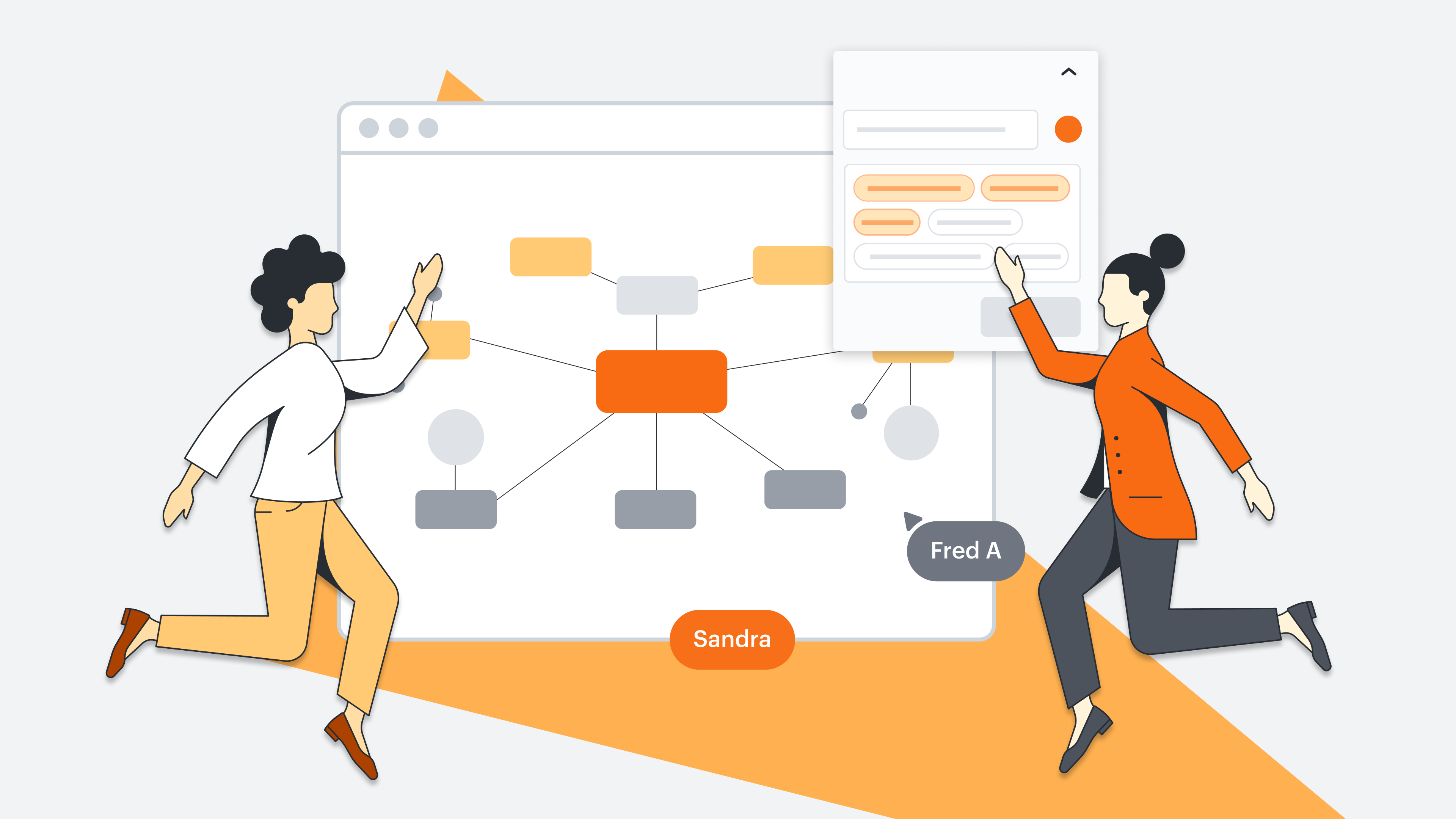
Mind maps are a powerful tool for brainstorming, helping individuals and teams visualize ideas, make connections and unleash their creative potential.
Whether you’re conducting a team retrospective or embarking on a corporate brainstorm, you can significantly enhance idea generation, boost efficient learning and note taking with mind maps . Get started with one of the brainstorming mind map examples below.
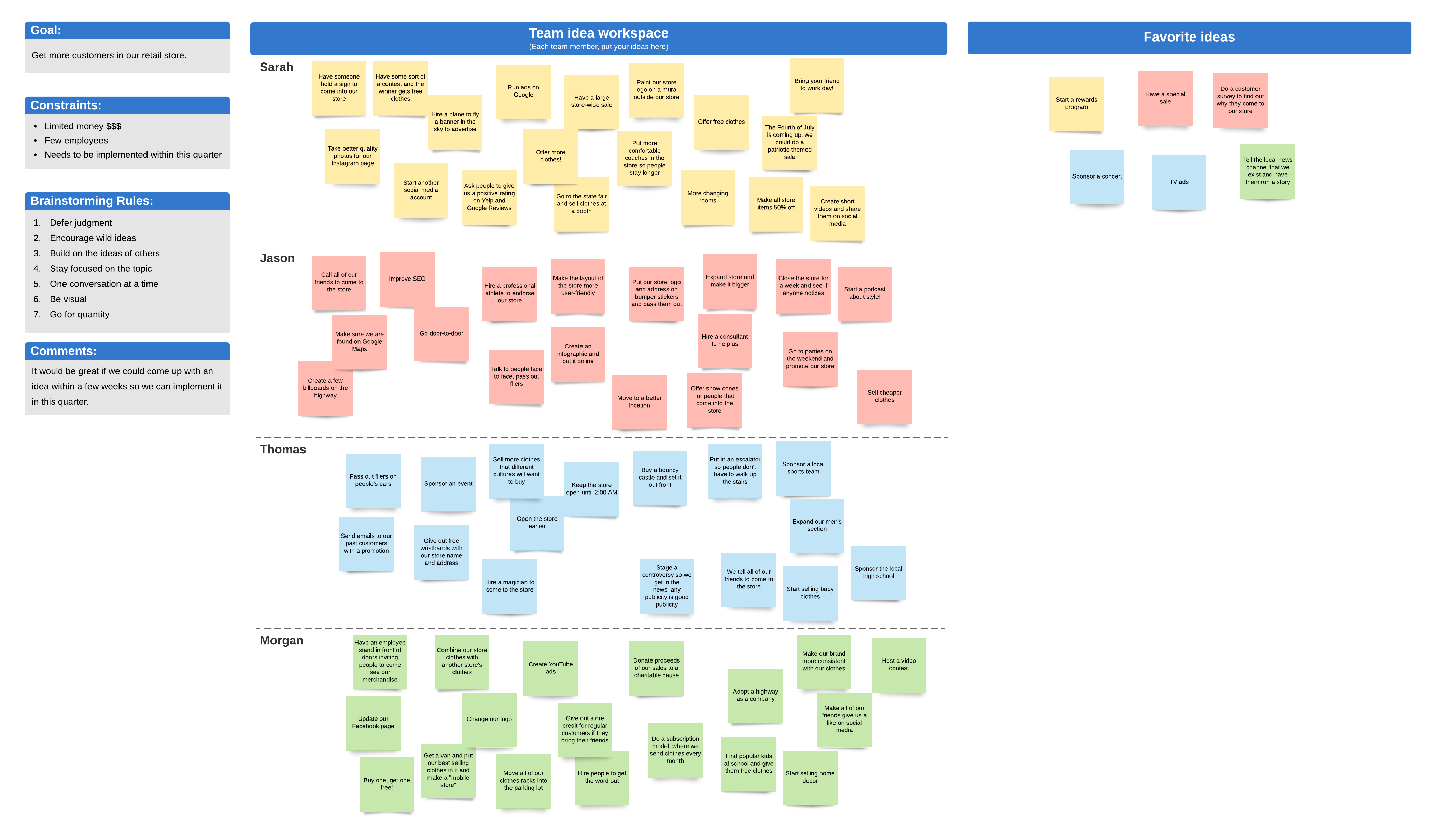
1. Team retrospective board
When creating a mind map for a team retrospective, it’s essential to strike a balance between structure and flexibility.
To achieve this, consider color-coding categories such as “What went well,” “What needs improvement,” and “Action items.” This visual differentiation helps participants quickly identify and prioritize discussion areas.

Additionally, incorporating a timeline element within the mind map can provide a visual representation of the project’s progression, enabling the team to recall specific events and experiences.
You can further enhance the visual appeal and emotional context by using icons or symbols to represent sentiments, such as happy faces for positive experiences and sad faces for challenges.
2. Business model brainstorm
Designing a mind map for brainstorming a business model necessitates a structured approach to represent various model elements coherently.
Incorporate color to cover essential components like value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams and distribution channels. Color coding can help visually organize your ideas and make the map more visually appealing.

To make each component stand out and aid comprehension, incorporate icons or relevant images. For instance, use a dollar sign icon to represent revenue streams. Consistency in color schemes helps differentiate sections and highlights essential elements.

3. Collaborative brainstorm
Collaborative brainstorming often involves multiple participants contributing ideas simultaneously.
To ensure efficient organization and clarity, assign specific branches within the mind map to individual participants. This approach helps maintain ownership of ideas and prevents overlap.
Encourage participants to contribute further context by adding comments or annotations to each branch. Utilize mind mapping software that supports real-time collaboration if the brainstorming session involves remote teams, enabling seamless teamwork and idea exchange.
These collaborative brainstorming examples can be helpful in generating ideas during your next brainstorming process:

4. Product improvement brainstorm
Brainstorming product improvements requires an effective categorization and prioritization of ideas. Organize your mind map by creating branches for different areas of improvement, such as usability enhancements, additional features or performance optimization.
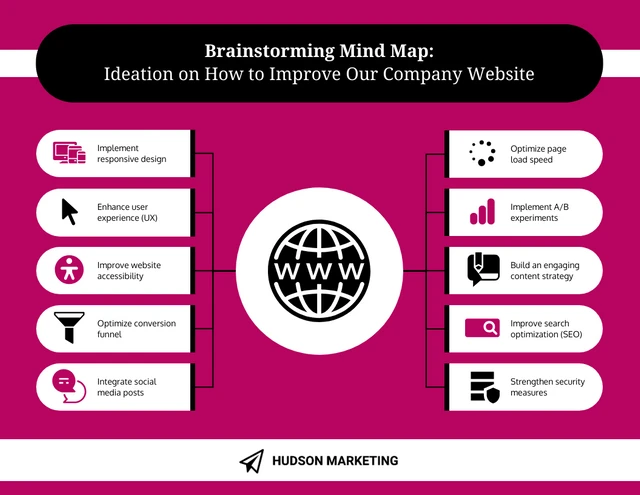
Begin by sharing user feedback, reviews or customer pain points related to the product. This provides context and helps participants understand the existing challenges.
Then, organize your mind map into categories based on different aspects of the product, such as features, user experience, performance or customer support.

Product improvement is an ongoing process so make sure to not limit your brainstorming to a one-time event. Schedule regular sessions to continually enhance the product.
5. Corporate brainstorm
In a corporate brainstorming session, where diverse topics and ideas are on the agenda, systematic organization is crucial.
Divide your mind map into sections and subsections to address various corporate aspects, such as HR, marketing, finance and operations. For example, this mind map on corporate initiative ideas divides the sections into different CSR programs and initiatives that the company can do to enhance public image:
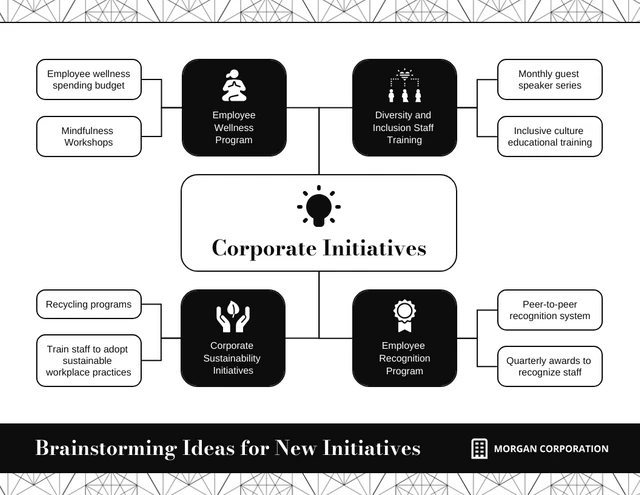
To highlight potential synergies between related ideas from different sections, connect them with clear cross-references. Additionally, for practicality, include action items or tasks linked to specific ideas to facilitate a smooth implementation process within the corporate framework.
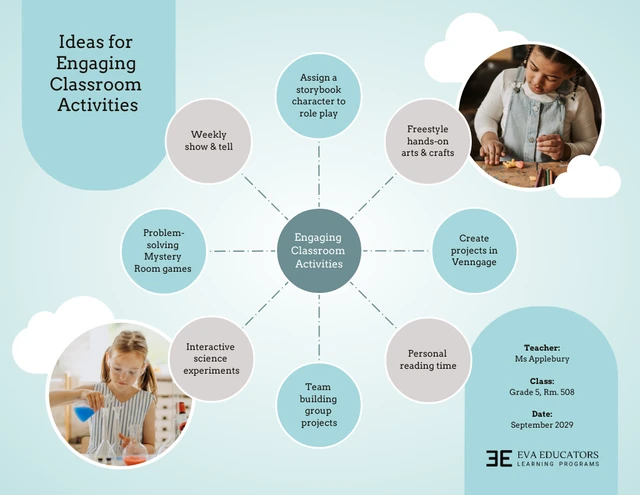
6. Creative brainstorm
Creative brainstorms thrive on spontaneity and inspiration — which is why your mind map design should encourage free-flowing ideas and unconventional thinking.
Opt for a non-linear, organic structure within the mind map, avoiding rigid hierarchies that can stifle creativity. Embrace the use of visuals, such as images, sketches or mood boards, to stimulate creativity and inspiration.
Here’s a brainstorming mind map example that teachers can use to generate exciting classroom activities and keep students engaged:

Allow branches to extend in unexpected directions, reflecting the dynamic and imaginative nature of creative brainstorming. This approach encourages participants to explore unconventional ideas and perspectives, fostering a truly creative atmosphere during the session.
Brainstorming aside, mind maps are versatile tools useful for organizing complex information, creating study aids, structuring project plans and facilitating communication and knowledge sharing in collaborative settings.
Browse our selection of mind map templates or learn about the best mind mapping software to help enhance creativity, solve problems and organize ideas.
Unleashing your team’s creativity through effective brainstorming techniques is a game-changer when it comes to generating new ideas and innovative solutions. Let’s delve into ten creative brainstorming techniques that can breathe life into your brainstorming sessions:
1. Mind mapping
Like concept maps , mind mapping is great for emphasizing the connections and relationships between ideas. You start with a central idea and then let your thoughts branch out like tree branches. Mind mapping is a great way to spot connections you might have missed.

2. Brainwriting
Forget talking — this one’s all about writing your ideas down. Brainwriting lets you pass your ideas around and let your team add their two cents. It’s a great brainstorming strategy for getting everyone involved especially if you’re brainstorming with a large group.
3. SCAMPER Method
SCAMPER stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate and Reverse. This technique encourages participants to explore these strategies for idea generation.
4. Storyboarding
Create a visual narrative or storyboard to explore ideas sequentially. This can help enhance understanding the flow and practicality of concepts, especially in product development or process improvement. Check out our gallery of storyboard templates you could use to generate new ideas.

5. Role storming
Ever tried brainstorming as someone else? In this technique, you put on different thinking caps, like playing pretend. It’s awesome for seeing things from fresh angles.
6. Worst possible idea
This one’s my favorite! Deliberately come up with the crummiest, silliest ideas you can think of. Oddly enough, they can spark some brilliant ones!
7. Round-robin brainstorming
One of my favorite group brainstorming techniques, everyone gets a turn to share their ideas with round-robin brainstorming — no interrupting or dominating the conversation. This technique ensures that everyone has an equal opportunity to contribute.
8. SWOT Analysis
Analyze the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats related to the problem or idea. This structured approach helps identify potential areas for improvement or innovation. Browse our SWOT analysis templates for more inspiration.

9. Random word or image association
Start with something random, like “banana” or “dolphin,” and brainstorm from there. It’s like mental gymnastics and it can lead to some seriously cool ideas.
10. Nominal group technique
For this brainstorming technique, Participants individually generate ideas, which are then anonymously shared and discussed as a group, ensuring balanced participation and minimizing the influence of dominant voices.
To further fuel your brainstorming sessions, you could always consider using a brainstorming tool to facilitate collaboration, structure ideas and provide visual frameworks. From virtual whiteboards to mind maps, here’s a list of brainstorming tools that can cater to various needs and preferences in brainstorming sessions.
Brainstorming sessions can be exhilarating bursts of creativity, but they can also veer off course if not handled with care. Here, we’ll explore five common missteps to steer clear of and conduct a successful brainstorming session.
1. Criticizing ideas too early
When participants criticize or judge ideas too soon in the brainstorming process, it can discourage creativity and stifle the generation of innovative solutions. To avoid this, it’s essential to foster an environment where all ideas are welcomed without immediate criticism.
Solution: Embrace the “No Judgment” rule we mentioned earlier. Encourage a judgment-free zone where all ideas are welcome to generate as many ideas, no matter how unusual or impractical they might seem initially.
2. Groupthink
Ah, groupthink – the silent brainstorming killer. It’s when the desire for harmony within the group overrides critical thinking. Everyone nods along to ideas, not because they believe in them, but to avoid conflict.
Solution: Foster an atmosphere where dissenting opinions are not only tolerated but encouraged. Encourage team members to play devil’s advocate and don’t let conformity hold your brainstorming sessions hostage.
3. Ignoring introverted participants
In the whirlwind of brainstorming, extroverted voices can dominate the conversation, leaving introverts feeling like they’re stranded on the sidelines. Their valuable ideas may get lost in the noise.
Solution: Implement techniques like brainwriting or round-robin brainstorming, which give everyone an equal chance to contribute without the pressure of immediate verbal expression.
4. Prioritizing quantity over quality
Yes, quantity matters in brainstorming, but swinging the pendulum too far toward generating sheer volume can leave you drowning in a sea of mediocre ideas.
Solution: Balance is key. Encourage the generation of many ideas, but once you’ve amassed a list, focus on quality. Sort through them, identify the most promising ones and build upon them collectively.
5. Neglecting follow-up and implementation
Brainstorming is exhilarating, but it’s just the first lap in the race. Failing to follow up on the ideas generated and implementing the best ones is like baking a cake and never eating it.
Solution: Assign responsibility for each idea’s follow-up and implementation. Establish clear timelines and action plans. Make sure the fruits of your brainstorming labor don’t gather dust on the shelf.
By sidestepping these brainstorming bloopers, you’ll be on your way to brilliant solutions and groundbreaking ideas, all while avoiding the pitfalls of the brainstorming jungle.
Ready to kickstart your brainstorming session? These brainstorm presentation templates might come in handy to help spark creativity, ideation and foster collaborative problem-solving within a team.
How does brainstorming help with the writing process
Brainstorming helps the writing process by generating a pool of diverse ideas, facilitating idea organization and overcoming writer’s block. It allows writers to explore different angles and perspectives for their content.
Are there any online tools or software for collaborative brainstorming?
Yes, there are several online tools and software for collaborative brainstorming, such as Miro, Stormboard and Google Jamboard. These platforms enable teams to brainstorm ideas in real-time, regardless of physical location.
What are some brainstorming activities for team building and creativity?
Brainstorming activities for team building and creativity include “Two Truths and a Lie,” “Role Reversal” and “The Six Thinking Hats.” These creative exercises promote trust, collaboration and out-of-the-box thinking among team members to generate creative ideas.
How do I encourage creative thinking during a brainstorming session?
To encourage creative thinking during a brainstorming session, create a non-judgmental environment, encourage wild ideas, use creative prompts and mix up the group dynamics. To facilitate productive brainstorming sessions, reward creativity and emphasize the importance of novelty and innovation.
What role does creativity play in effective brainstorming?
Creativity plays a central role in effective brainstorming as it drives the generation of innovative ideas and solutions. Without creativity, brainstorming sessions can become routine and fail to produce breakthrough concepts.
What are the benefits of using brainstorming examples in a business or creative context?
Using brainstorming examples in a business or creative context can provide tangible illustrations of successful brainstorming outcomes. They can inspire participants, provide a framework for idea generation and demonstrate the practical application of brainstorming techniques. Additionally, they can serve as a reference point for future brainstorming sessions.
5 steps to create a brainstorming mind map with Venngage
In conclusion, mastering the art of brainstorming is like unlocking a treasure chest of solutions to your most challenging problems. By exploring a variety of brainstorming techniques and with the help of the above examples of brainstorming, you’ve gained valuable tools to tackle issues with confidence and creativity.
Now, to bring it all together, consider harnessing the power of visual thinking through a brainstorming mind map. Venngage offers a seamless solution that can transform your brainstorming ideas into organized, inspiring journeys using mind maps . To create a brainstorming mind map with Venngage:
- Sign in or create a free Venngage account.
- Pick a brainstorm mind map template to get started.
- Add your central idea in the central node.
- Create branches and subtopics by clicking, dragging and labeling.
- Customize your mind map with colors, fonts, icons and connectors to make it visually appealing.
Remember, the beauty of brainstorming lies in its boundless potential, always ready to surprise you with fresh perspectives and creative solutions.
So, whether you’re tackling complex business dilemmas or personal puzzles, put your thinking hat on for a productive brainstorming session and let all the ideas roam free.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Brainstorming
What is brainstorming.
Brainstorming is a method design teams use to generate ideas to solve clearly defined design problems. In controlled conditions and a free-thinking environment, teams approach a problem by such means as “How Might We” questions. They produce a vast array of ideas and draw links between them to find potential solutions.
- Transcript loading…
How To Use Brainstorming Best
Brainstorming is part of design thinking . You use it in the ideation phase. It’s extremely popular for design teams because they can expand in all directions. Although teams have rules and a facilitator to keep them on track, they are free to use out-of-the-box and lateral thinking to seek the most effective solutions to any design problem. By brainstorming, they can take a vast number of approaches—the more, the better—instead of just exploring conventional means and running into the associated obstacles. When teams work in a judgment-free atmosphere to find the real dimensions of a problem, they’re more likely to produce rough answers which they’ll refine into possible solutions later. Marketing CEO Alex Osborn, brainstorming’s “inventor”, captured the refined elements of creative problem-solving in his 1953 book, Applied Imagination . In brainstorming, we aim squarely at a design problem and produce an arsenal of potential solutions. By not only harvesting our own ideas but also considering and building on colleagues’, we cover the problem from every angle imaginable.
“It is easier to tone down a wild idea than to think up a new one.” — Alex Osborn
Everyone in a design team should have a clear definition of the target problem. They typically gather for a brainstorming session in a room with a large board/wall for pictures/Post-Its. A good mix of participants will expand the experience pool and therefore broaden the idea space.
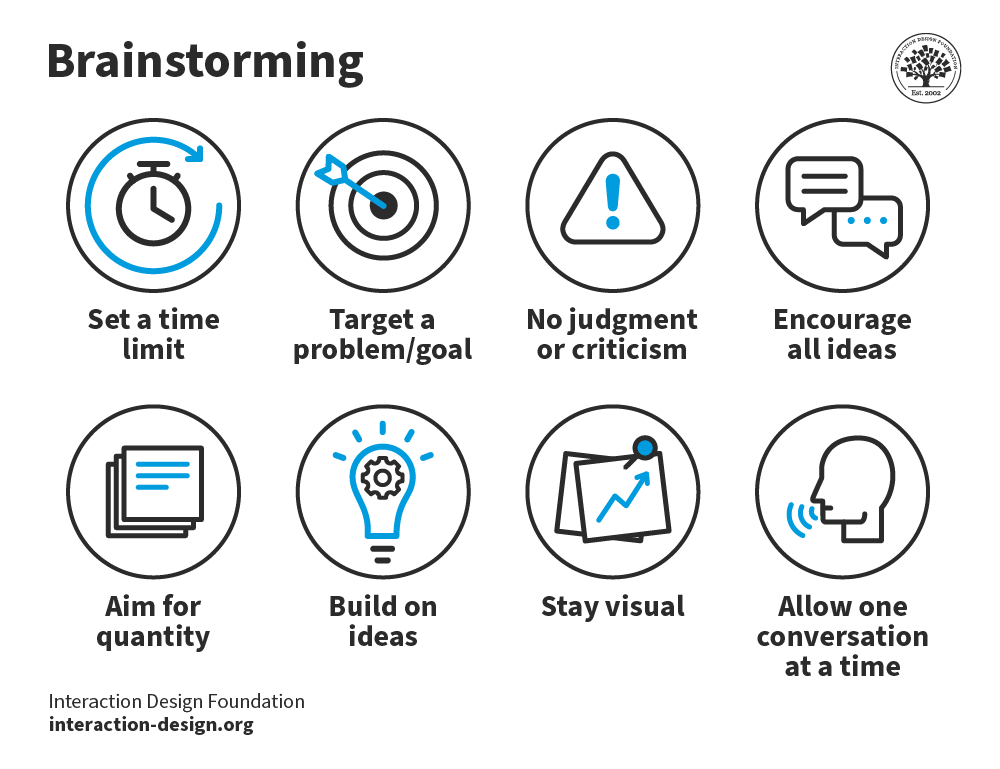
Brainstorming may seem to lack constraints, but everyone must observe eight house rules and have someone acting as facilitator.
Set a time limit – Depending on the problem’s complexity, 15–60 minutes is normal.
Begin with a target problem/brief – Members should approach this sharply defined question, plan or goal and stay on topic.
Refrain from judgment/criticism – No-one should be negative (including via body language) about any idea.
Encourage weird and wacky ideas – Further to the ban on killer phrases like “too expensive”, keep the floodgates open so everyone feels free to blurt out ideas (provided they’re on topic).
Aim for quantity – Remember, “quantity breeds quality”. The sifting-and-sorting process comes later.
Build on others’ ideas – It’s a process of association where members expand on others’ notions and reach new insights, allowing these ideas to trigger their own. Say “and”—rather than discourage with “but”—to get ideas closer to the problem.
Stay visual – Diagrams and Post-Its help bring ideas to life and help others see things in different ways.
Allow one conversation at a time – To arrive at concrete results, it’s essential to keep on track this way and show respect for everyone’s ideas.

To capture everyone’s ideas in a brainstorming session, someone must play “scribe” and mark every idea on the board. Alternatively, write down your own ideas as they come, and share these with the group. Often, design problems demand mixed tactics: brainstorming and its sibling approaches – braindumping (for individuals), and brainwriting and brainwalking (for group-and-individual mixes).
Take Care with Brainstorming
Brainstorming involves harnessing synergy – we leverage our collective thinking towards a variety of potential solutions. However, it’s challenging to have boundless freedom. In groups, introverts may stay quiet while extroverts dominate. Whoever’s leading the session must “police” the team to ensure a healthy, solution-focused atmosphere where even the shiest participants will speak up. A warm-up activity can cure brainstorming “constipation” – e.g., ask participants to list ways the world would be different if metal were like rubber.
Another risk is to let the team stray off topic and/or address other problems. As we may use brainstorming in any part of our design process—including areas related to a project’s main scope—it’s vital that participants stick to the problem relevant to that part (what Osborn called the “Point of View”). Similarly, by framing problems with “How Might We” questions, we remember brainstorming is organic and free of boundaries. Overall, your team should stay fluid in the search for ways you might resolve an issue – not chase a “holy grail” solution someone has developed elsewhere. The idea is to mine idea “ore” and refine “golden” solutions from it later.
How to Supercharge Brainstorming with AI
Learn more about brainstorming.
The Interaction Design Foundation’s course on Design Thinking discusses Brainstorming in depth.
This blog offers incisive insights into Brainstorming workshops .
Jonathan Courtney’s article for Smashing Magazine shows Brainstorming’s versatility .
Literature on Brainstorming
Here’s the entire UX literature on Brainstorming by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Brainstorming
Take a deep dive into Brainstorming with our course Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
Some of the world’s leading brands, such as Apple, Google, Samsung, and General Electric, have rapidly adopted the design thinking approach, and design thinking is being taught at leading universities around the world, including Stanford d.school, Harvard, and MIT. What is design thinking, and why is it so popular and effective?
Design Thinking is not exclusive to designers —all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering and business have practiced it. So, why call it Design Thinking? Well, that’s because design work processes help us systematically extract, teach, learn and apply human-centered techniques to solve problems in a creative and innovative way—in our designs, businesses, countries and lives. And that’s what makes it so special.
The overall goal of this design thinking course is to help you design better products, services, processes, strategies, spaces, architecture, and experiences. Design thinking helps you and your team develop practical and innovative solutions for your problems. It is a human-focused , prototype-driven , innovative design process . Through this course, you will develop a solid understanding of the fundamental phases and methods in design thinking, and you will learn how to implement your newfound knowledge in your professional work life. We will give you lots of examples; we will go into case studies, videos, and other useful material, all of which will help you dive further into design thinking. In fact, this course also includes exclusive video content that we've produced in partnership with design leaders like Alan Dix, William Hudson and Frank Spillers!
This course contains a series of practical exercises that build on one another to create a complete design thinking project. The exercises are optional, but you’ll get invaluable hands-on experience with the methods you encounter in this course if you complete them, because they will teach you to take your first steps as a design thinking practitioner. What’s equally important is you can use your work as a case study for your portfolio to showcase your abilities to future employers! A portfolio is essential if you want to step into or move ahead in a career in the world of human-centered design.
Design thinking methods and strategies belong at every level of the design process . However, design thinking is not an exclusive property of designers—all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering, and business have practiced it. What’s special about design thinking is that designers and designers’ work processes can help us systematically extract, teach, learn, and apply these human-centered techniques in solving problems in a creative and innovative way—in our designs, in our businesses, in our countries, and in our lives.
That means that design thinking is not only for designers but also for creative employees , freelancers , and business leaders . It’s for anyone who seeks to infuse an approach to innovation that is powerful, effective and broadly accessible, one that can be integrated into every level of an organization, product, or service so as to drive new alternatives for businesses and society.
You earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you complete the course. You can highlight them on your resume, CV, LinkedIn profile or your website .
All open-source articles on Brainstorming
Stage 3 in the design thinking process: ideate.

- 1.2k shares
- 4 years ago
14 UX Deliverables: What will I be making as a UX designer?

Introduction to the Essential Ideation Techniques which are the Heart of Design Thinking

- 1.1k shares
- 3 years ago
Learn How to Use the Best Ideation Methods: Brainstorming, Braindumping, Brainwriting, and Brainwalking

Three Ideation Methods to Enhance Your Innovative Thinking

Ideation for Design - Preparing for the Design Race

Transform Your Creative Process with Design Thinking
Start Your UX Journey: Essential Insights for Success

Revolutionize UX Design with VR Experiences

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Better Brainstorming
- Hal Gregersen

Great innovators have long known that the secret to unlocking a better answer is to ask a better question. Applying that insight to brainstorming exercises can vastly improve the search for new ideas—especially when a team is feeling stuck. Brainstorming for questions, rather than answers, helps you avoid group dynamics that often stifle voices, and it lets you reframe problems in ways that spur breakthrough thinking.
After testing this approach with hundreds of organizations, MIT’s Hal Gregersen has developed it into a methodology: Start by selecting a problem that matters. Invite a small group to help you consider it, and in just two minutes describe it at a high level so that you don’t constrain the group’s thinking. Make it clear that people can contribute only questions and that no preambles or justifications are allowed. Then, set the clock for four minutes, and generate as many questions as you can in that time, aiming to produce at least 15. Afterward, study the questions generated, looking for those that challenge your assumptions and provide new angles on your problem. If you commit to actively pursuing at least one of these, chances are, you’ll break open a new pathway to unexpected solutions.
Focus on questions, not answers, for breakthrough insights.
The Problem
Great innovators have always known that the key to unlocking a better answer is to ask a better question—one that challenges deeply held assumptions. Yet most people don’t do that, even when brainstorming, because it doesn’t come naturally. As a result, they tend to feel stuck in their search for fresh ideas.
The Solution
By brainstorming for questions instead of answers, you can create a safe space for deeper exploration and more-powerful problem solving. This brief exercise in reframing—which helps you avoid destructive group dynamics and biases that can thwart breakthrough thinking—often reveals promising new angles and unexpected insights.
About 20 years ago I was leading a brainstorming session in one of my MBA classes, and it was like wading through oatmeal. We were talking about something that many organizations struggle with: how to build a culture of equality in a male-dominated environment. Though it was an issue the students cared about, they clearly felt uninspired by the ideas they were generating. After a lot of discussion, the energy level in the room was approaching nil. Glancing at the clock, I resolved to at least give us a starting point for the next session.
- Hal Gregersen is a Senior Lecturer in Leadership and Innovation at the MIT Sloan School of Management , a globally recognized expert in navigating rapid change, and a Thinkers50 ranked management thinker. He is the author of Questions Are the Answer: A Breakthrough Approach to Your Most Vexing Problems at Work and in Life and the coauthor of The Innovator’s DNA: Mastering the Five Skills of Disruptive Innovators .
Partner Center

When inspiration strikes: 12 effective brainstorming techniques
Reading time: about 9 min
Are you an effective brainstormer? Does the process of brainstorming feel like an opportunity or more like a chore? Chances are if you don’t enjoy the process of brainstorming, you’ve probably been using the wrong brainstorming technique.
That’s right—there are distinct brainstorming methods.
Just as there are different learning styles and different workflow preferences, each of us has a method of brainstorming that works best for us. Whether or not you’re a veteran brainstormer, this article will help you unpack different brainstorming tools, learn the advantages and shortcomings of each, and select a technique for yourself and your team.
12 popular brainstorming methods

Need to take a step back? Learn how to set up a brainstorming session with your team.
Brainwriting
When brainwriting, each group member is told to anonymously write down several ideas on post-it notes or index cards. Keeping ideas anonymous serves two important purposes: First, it prevents idea anchoring and any personality bias that may arise. Second, it provides a way for more introverted teammates to still contribute to ideation.
The result is a broader range of ideas that may not have surfaced if teammates were to brainstorm collectively. Ideas are then shared at random with the rest of the group, who offer feedback and critique each idea. As an alternative, ideas can also be collected and sorted by a team leader or management team. The overlying goal of brainwriting is to separate idea generation from discussion.

5 Whys analysis
If you’ve ever been interrogated by a toddler, you know what the 5 Whys might sound like. You give an answer to a question, only for it to be followed by an increasingly urgent series of “Why? Why? Why? Why? Why?”
Truth be told, that toddler is onto something. Created by Taiichi Ohno, the 5 Whys analysis was made popular at Toyota as a standard process for root cause analysis—getting to the heart of a problem.
Less structured than other more traditional problem-solving methods, the 5 Whys is simply what it sounds like: asking why over and over to get to the root of an obstacle or setback. This technique encourages an open dialogue that can trigger new ideas about a problem, whether done individually or with a group. Each why piggybacks off the answer to the previous why.
Both flowcharts and fishbone diagrams can help you track your answers to the 5 Whys.
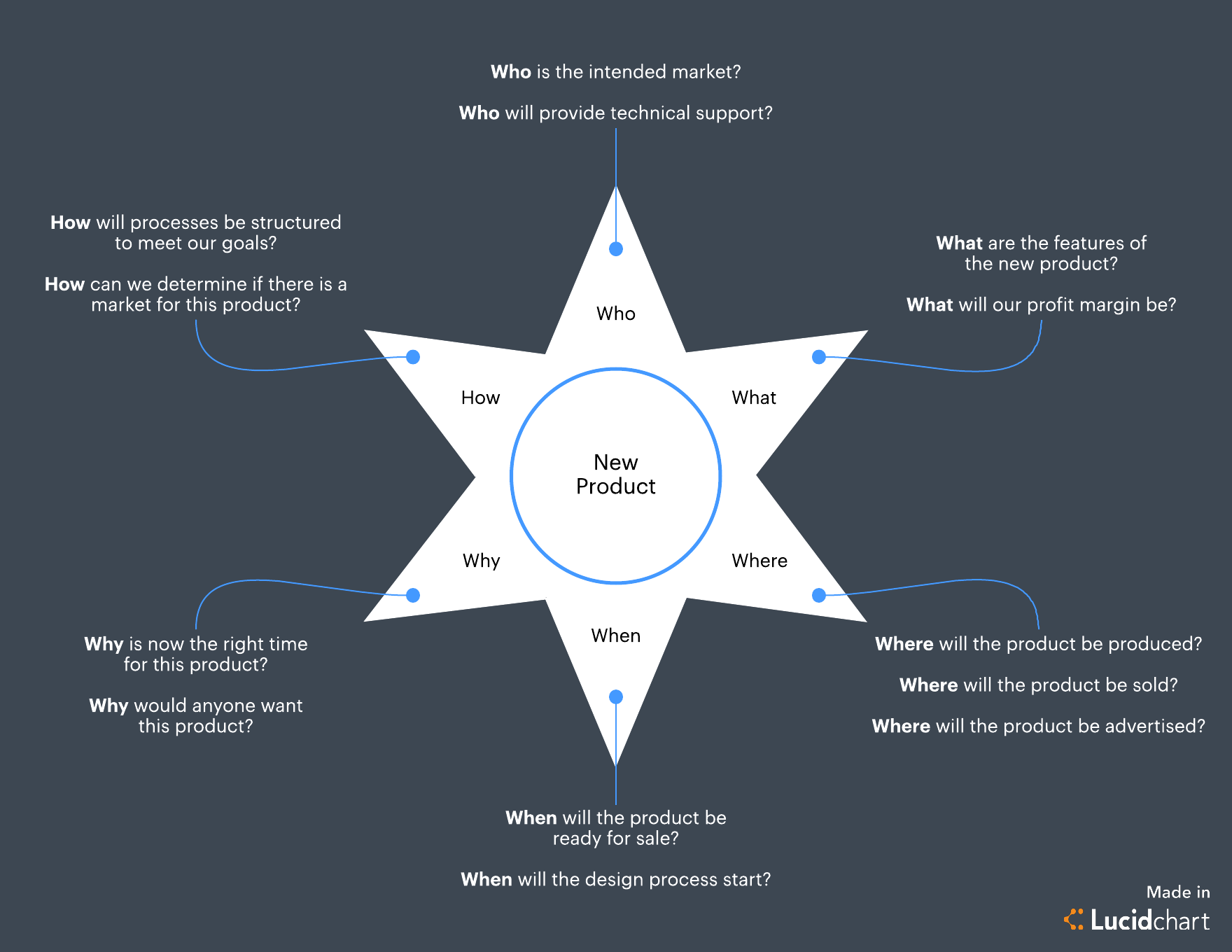
Starbursting
Like a reporter trying to discover the pivotal information to a story, the starbursting method of brainstorming requires you to think about the who, what, where, when, why, and how for any new idea.
Place your main idea at the center of a star diagram, labeling each point of the star with those 5WH questions.
Next, develop a series of questions about your idea for each point. Starbursting is popular among brainstorming methods because of its exploratory nature: One question triggers another question, and before you know it, you have the beginnings of a solid strategy within the answers to those questions.
Mind mapping
Part of the challenge of brainstorming is trying to catch every idea swirling through the air. Mind maps are a creative, non-linear diagram used to capture that influx of ideas so you don’t miss anything. Start with a topic or question in the center of the mind map, and branch off to include every participant’s thoughts. Then use Collaborative AI to generate more in seconds for expanded ideas and an expanded mind.
To create your own mind map online, open the template below or browse through our gallery of additional mind map templates .
Rolestorming/figure storming
Sometimes it’s best to consider someone else’s point of view. Considering how someone else might approach a challenge is the central concept behind rolestorming. A related practice, figure storming asks you to put yourself in the shoes of a famous historical figure.
For example, a legal advocacy group might have teammates ask “How would Mahatma Gandhi solve this problem?” Rolestorming has even made its way into pop culture: Anyone who has ever purchased or even seen the popular rubber WWJD (what would Jesus do?) bracelets has witnessed rolestorming in daily life. Rolestorming or figure storming works best for teams who find themselves coming up with the same ideas for repeating projects.
Gap filling
Gap filling, also known as gap analysis , requires you to identify your current state and your end goal and then find gaps between the two states. It asks the question, “How do we get from here to there?” Gap analysis is especially helpful when it comes to problem solving because it requires you to find workable solutions.
Flowcharts or mind maps can help you grid out your gap analysis. Mark the current state on one end and the ideal state on the other. Then team members will understand what they're working toward and start contributing ideas in the middle to fill the gap.
Brain-netting
Brain-netting has become a popular brainstorming technique in the modern workspace, where virtual collaboration and remote teams are much more common. Email communication can be effective but can take too much time and can be more formal than needed.
With brain-netting, participants use virtual collaboration software to share ideas in real time and can save ideas to a cloud-based storage platform or within the collaboration software itself. The way teams go about virtual collaboration can vary—team leaders may ask a general question like “What do we want our customers to experience?” and have teammates contribute their responses, or teams may engage in other techniques mentioned in this piece including rolestorming, reverse brainstorming, and rapid ideation.
Round robin brainstorming
To engage in this brainstorming technique, begin with having everyone sit in a circle. A team leader or facilitator will then pose a question or offer a request for ideas and have everyone in the circle contribute one by one.
This strategy is great for middle- to large-sized teams who may have quieter team members or for any team with noticeable imbalance in creative contribution. The most important rule for this technique is to treat all ideas with equal weight—give each teammate the same time and attention as they share, and avoid developing any ideas until everyone has had a chance to contribute. If and when a team member says that “Person X already said my idea,” offer them time to come up with a new idea while completing the round robin.
Rapid ideation
Operating within a time limitation can often produce higher quality work. Indeed, Parkinson’s Law teaches us that “work expands so as to fill the time available for its completion.” Rapid ideation uses this phenomenon to its advantage: By setting a time limit on team members to contribute as many ideas or solutions as possible, team managers can maximize productivity and results.
Rapid ideation works well for a few different types of workers—for teams who dislike meetings, or who tend to get sidetracked, rapid ideation is a great way to approach the brainstorming stage of project execution.
A helpful tip to remember: Get silly! Research shows that teams who share funny or embarrassing stories about themselves reported 26% more ideas shared across 15% more categories over teams who kept meetings more formal. Having the space to let down certain social barriers reduces overthinking and produces a greater flow of ideas.
Reverse brainstorming
Most brainstorming techniques ask participants to solve a problem. Reverse brainstorming has participants cause a problem. Rather than forming solutions to a problem, reverse brainstorming has a facilitator ask a question like “How can we cause this problem?” Responses are then recorded and used as springboards to ideate a solution by working through the responses backwards.
Reverse brainstorming is a powerful way to open up new solutions to recurring problems: By challenging participants to work backwards, certain insights that may have been hard to imagine normally become crystal clear from a new perspective.
Stepladder brainstorming
This interesting style of brainstorming was developed in 1992 and involves teammates sharing their ideas individually before being influenced by the group.
The process starts with a facilitator posing a question or problem to the entire group and then having almost every group member exit the room, leaving two members present. These remaining two members share their ideas together while the rest of the team waits outside, until the facilitator directs an outside teammate to join the two inside.
The third and new teammate then shares their idea first, followed by the other two teammates. A fourth group member then enters the room and shares his or her idea first, followed by the other teammates present. The process continues this way until all group members have joined the room and shared their ideas.
Stepladder brainstorming is noted for solving the problem of groupthink by having participants share ideas individually and without influence from the group. It also allows the more shy group members to contribute without being intimidated by a room full of people.
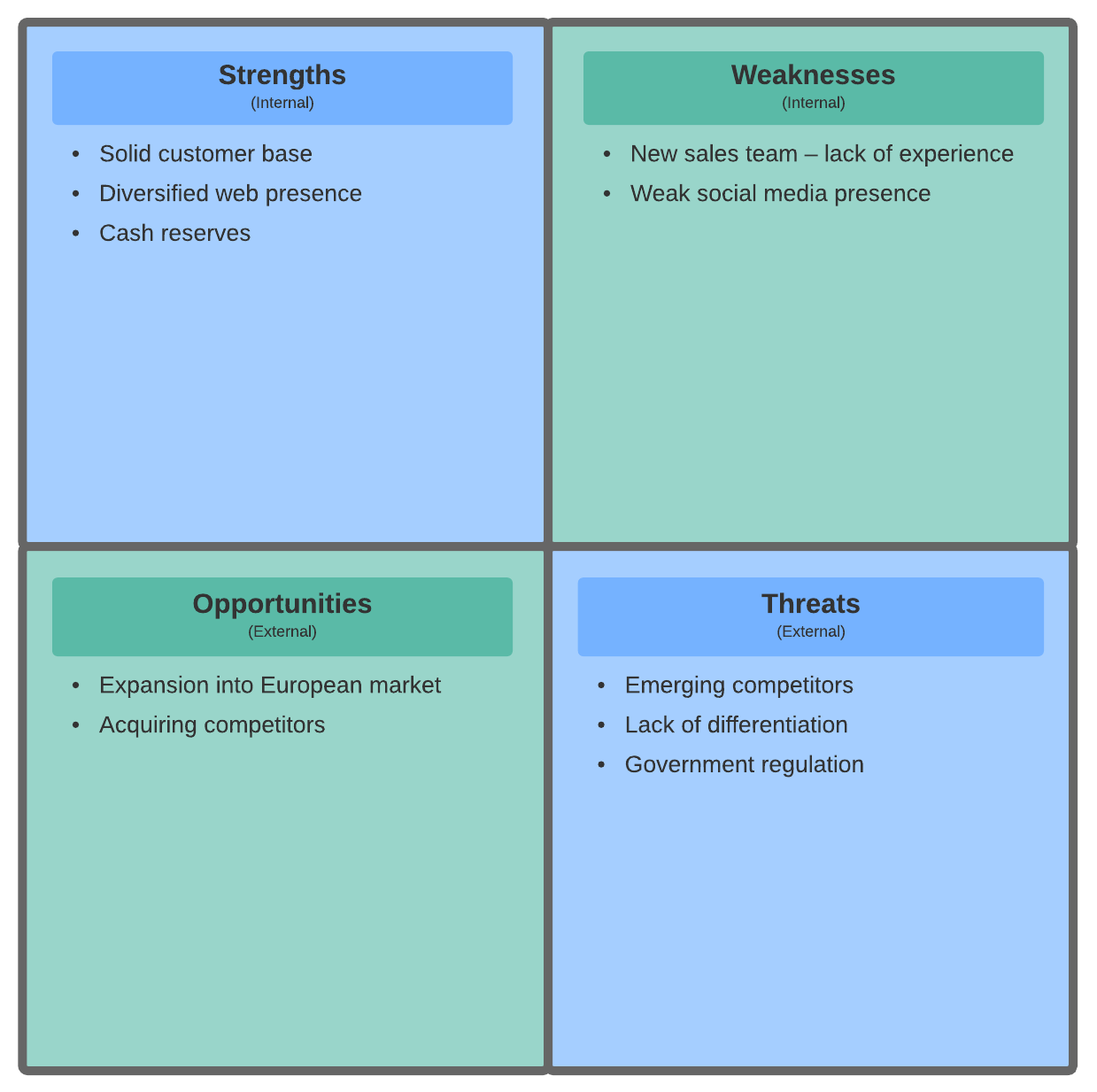
SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis isn't exclusively a brainstorming technique: It's a strategic planning exercise that you can use to evaluate a product, project, person, or business. However, it may be valuable to focus your brainstorm with this mindset. SWOT stands for:
- Strengths: How does the product, project, or business dominate and stand out from its competitors?
- Weaknesses: What are the flaws that can hurt or put the product, project, or business in jeopardy?
- Opportunities: What opportunities could the business capitalize on?
- Threats: What are the possible downfalls lurking for the product, project, or business?
Spend some time in each category and add your teammates' thoughts onto a SWOT matrix.
Choose a brainstorm method and get started
Once you’ve selected your brainstorming technique or techniques, it’s time to get to work. Remember: The first rule of brainstorming is quantity over quality. Encouraging teammates to have the bravery to risk imperfection and contribute ideas is the best way to guide your team toward new ways to approach problems—and often leads to powerful insights.
All these methods can be combined with others, giving you an endless arsenal of brainstorming techniques to continue ideating efficiently.
See our 7 tips for starting a brainstorming meeting with your team.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
Transform teamwork with Confluence. See why Confluence is the content collaboration hub for all teams. Get it free
- The Workstream
- Project collaboration
- Brainstorming best practices
Brainstorming: definition, ground rules, and techniques
Bring on your best ideas
Browse topics
What is brainstorming.
It’s a common scenario: you need to come up with some creative ideas. Maybe you’re trying to find a solution to a complex problem, or perhaps you’re spitballing your team’s next big project.
Either way, you’re feeling the pressure to amp up your innovation and churn out some brilliant suggestions.
What happens now? Well, you might rely on a brainstorming session to get those creative juices flowing.
Before we dig into the ins and outs of how to brainstorm effectively, it’s helpful to take a step back and actually define brainstorming. Merriam-Webster describes brainstorming as “the mulling over of ideas by one or more individuals in an attempt to devise or find a solution to a problem.”
Sounds familiar, right? You can brainstorm on your own, but it’s a technique that’s frequently used in group settings to freely share ideas and build upon them.
Brainstorming is prevalent in today’s working world (you’ve likely been a part of a fair share of sessions yourself), but it has some serious historical roots.
It was first introduced in 1948 by advertising executive Alex F. Osborn in his book "Your Creative Power." As the owner of his own advertising agency, he was looking for ways to pull better ideas out of his employees — something he referred to as “thinking up.” With that objective in mind, he established several principles and characteristics of brainstorming, which we’ll dig into in detail later.
Since that time, brainstorming has gained steam and become a common technique that businesses use to generate creative solutions to a variety of problems.
The importance of brainstorming
While it certainly isn’t without its criticisms and potential pitfalls, there’s a reason this technique has become so popular in the modern working world: it’s effective and is tied to numerous benefits.
Below are just a few of the many advantages of brainstorming that teams can expect to experience.
Brainstorming encourages more creative thinking.
The first benefit is obvious: brainstorming requires an individual or team to think more creatively and without boundaries, which can lead to improved ideas and suggestions. For example, did you know that the idea for the Amazon Echo was reportedly born out of a brainstorming strategy?
Since brainstorming is often done in a group, it forces us to step away from our own biases and consider other perspectives and contributions without offering any upfront criticism.
Beyond that, productive brainstorming exercises challenge us to not only consider other ideas but to build upon them — which leads to an even better end result.
Brainstorming leads to better teamwork and greater group cohesiveness.
All of that working together does more than generate better ideas — it can actually improve our level of teamwork . There’s plenty of research out there that backs this up.
“Groups that focus on both the quantity of ideas and building on the ideas of others significantly increase their cohesiveness,” said David Henningsen , a Northern Illinois University professor and researcher, who co-led a study on brainstorming .
“Brainstorming can be used to help a team buy into and implement a plan of action, or it can be used to simply build cohesiveness, which in turn can lessen employee turnover and increase employee commitment.”
Brainstorming gives everybody a chance to be heard.
How to brainstorm: types, ground rules, and techniques.
When done right, brainstorming offers tons of perks. But that begs the question: how exactly do you do it right?
There’s a bit of strategy involved in pulling off a successful brainstorming session. Here’s the information you need to get the very best ideas out of everyone on your team.
Brainstorming ground rules
Brainstorming techniques.
You have your brainstorming session scheduled and organized. Uhhh...now what? Your team is all just staring at each other slack-jawed. How do you get the conversation rolling?
Below are just a few of the many different tactics that teams can use to get things started and make their brainstorming discussions that much more productive:
- Brainwriting : With this technique, team members share ideas by writing them down independently rather than shouting them out together. It’s especially helpful if you know you have a number of introverts on your team.
- Starting with an embarrassing story : Beginning the conversation with something that’s potentially embarrassing immediately puts everybody in a more vulnerable and open state of mind — which makes them more willing to share ideas.
- Giving ideas time to marinate : Even though the excitement is strong, you might not want to jump into action on an idea right away. Research shows that even a brief break can give you time to strengthen that suggestion even further.
- Figuring storming : This tactic involves putting yourself in the shoes of someone else to think about how they might handle the situation. It can be effective because it challenges us to get away from our own biases and perceptions.
Flex your creative muscles
Brainstorming can be powerful, but it involves more than pulling your team into a room and asking them to share their two cents. It requires a basic understanding to figure out your strategy.
So, the next time you’re trying to figure out how to brainstorm business ideas, return to this overview as your starting resource. It’ll help you lay the foundation for successful brainstorming sessions moving forward, and you’ll be well on your way to getting the very best ideas out of your team.
You may also like
Disruptive brainstorming play.
Come up with a long list of great ideas in a single brainstorming session
Project planning template
Define, scope, and plan milestones for your next project
Enable faster content collaboration for every team with Confluence
Copyright © 2024 Atlassian

10 Brainstorming Techniques for Developing New Ideas
%2520(1).jpeg)
Brainstorming is an essential practice for creative thinking and problem-solving. At its most basic, brainstorming simply means identifying a problem, and then coming up with as many fresh ideas as possible that may help solve that problem. In practice, however, brainstorming needs to be structured to be successful.
No matter which brainstorming method you try, be sure to keep these tips in mind:
- Outline a problem or topic that needs further examination and group feedback for your brainstorming session.
- Use a shared digital space to conduct your brainstorming . This not only makes brainstorming easier, but also ensures you don’t lose any ideas and have a document to refer to in the future.
- Encourage quantity over quality . Participants can often get hung up on having the “best idea” but this often leads to creative blocks. Instead, focus on generating a high number of ideas first. Once you have a lot of ideas, you can start refining the best ones. However, if you have fewer ideas, you’ll have fewer options to choose from.
- You don’t always need a facilitator, but having one can help to have somebody guide a group of people through the ideation process . If needed, assign a team leader or facilitator before the idea generation begins to keep track of time limits and record the most creative ideas.
10 brainstorming techniques for better idea generation
Question brainstorming.
Question brainstorming is a method where participants come up with as many questions about the problem as possible. In this activity, participants should only come up with questions, not answers. This method is great because it helps the group try to understand the problem completely without the pressure to have the single best solution.
How to try this technique:
- Decide on the central topic or problem you want to brainstorm for.
- Each group or individual then takes 10-15 minutes to write as many questions about the topic or problem they have without trying to come up with an answer to any of them.
- After 10-15 minutes, the group gets back together to share, group, and prioritize the questions.
- Go through the full list of questions and start answering each one to better understand the core topic or problem.
Need inspiration? Check out these 25 brainstorming questions for effective brainstorms .
Hybrid brainstorming
The best way to get the most out of your brainstorming efforts is to combine the best of async and real-time idea generation. This technique starts off with individual brainstorming and ends with a collaborative, group brainstorming session.
How to do it:
- Chose the top 5 questions you want the brainstorming session to be based around.
- Have each participant begin brainstorming in their own dedicated space.
- Next, have everyone share their ideas so you have one central repository of all the ideas.
- Go through each question and discuss any questions that arise.
- Vote on the top ideas to focus on.
- Turn the top ideas into action items and celebrate your successful ideation session.

Mind map brainstorming
Using the mind mapping brainstorming technique helps your team use the central focus of your project as a starting point, explore all the potential variables tied to that project, and build an understanding of how those variables relate to the main topic, as well as to one another.
- Add a central topic or question to the center of the mind map.
- Add branches and nodes based on secondary thoughts to the primary topic.
- Keep adding branches and nodes based on additional ideas until you have a satisfactory number of related ideas.

Starbursting
The starbursting method involves asking a series of questions, typically using the 5 W's and 1 H (Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How) to explore the different aspects of the problem or topic. Starbursting is a divergent thinking approach focused on asking questions about the topic in order to generate a wide range of ideas.
How to run a starbursting exercise:
In Mural , Add six sticky notes around a central idea or problem and label them “Who,” “What,” “Where,” “When,” “Why,” and “How.” For each question, encourage participants to generate as many ideas as possible. Alternatively, you can conduct starbursting in Mural by creating a mind map.

Once the ideas have been generated, the facilitator can use other ideation techniques to further refine the ideas and identify potential solutions to the problem. Try clustering similar ideas together, categorizing the ideas into different groups with tags, or prioritizing the ideas based on their potential impact or feasibility.
The 'crazy eights' brainstorming technique is a great way to explore a wide range of ideas by encouraging quantity and time-boxing every exercise for efficiency. Brainstorm 8 different solutions in just 8 minutes. Once you’re ready, you can review the ideas and agree on the most effective solution.
How to do a crazy 8s brainstorm:
- Have each participant take a piece of paper (or use an online whiteboard ) and divide it into eight parts.
- Sketch or detail eight ideas, spending one minute for each panel.
- Have each participant share their own ideas.
- Vote on the top ideas and turn them into actionable next steps.

Round robin brainstorming
A round robin is a great way to encourage your team members to think critically about a problem or challenge, as well as build on one another's ideas. The format calls for dividing your team into small groups, and having each person pass their ideas along to the following teammate, who then offers counterpoints or further suggestions, helping identify potential weaknesses or spurring innovation within the session.
How to run a round robin:
- Set the brainstorming topic or problem you’re looking to solve.
- Divide your group or participants into four teams, or add more panels to accommodate more participants.
- Have each group or participant write down a proposal and move to the next panel
- Looking at what the other group or participant suggested, write down reasons why their proposal might fail then move to the next panel.
- Based on the proposal and weaknesses, have each participant or group craft a final concept using the weaknesses as feedback.

Looking for more instruction? Check out our complete guide on round robin brainstorming with a walkthrough, tips, and variations of the round robin method.
6-3-5 brainwriting
6-3-5 brainwriting is a group brainstorming method that involves creating a lot of ideas and building on the ideas of the other participants to give a total of 108 ideas in a short amount of time.
To run this exercise, you'll need 6 participants to create 3 ideas each within 5 minutes. Run this exercise for 6 rounds for a quick, half-hour brainstorming exercise.
- Have each participant select one panel and begin writing ideas related to the topic or problem statement on the first row of sticky notes.
- After five minutes, participants move to a different panel and do another round of ideation, using the previous row of ideas for inspiration.
- Run four more rounds of this exercise, or stop when you have enough ideas.
- Cluster and vote on the winning ideas with your team.

Brainwriting can be a marked improvment over more conventional brainstorming methods. In addition to reducing the pressure to openly share ideas that might be a bit "out there," brainwriting can help reduce participation inequity and prevent groupthink. Learn more in Mural's guide to brainwriting .
Reverse brainstorming
Reverse brainstorming involves looking at a problem from a different angle for generating ideas. Instead of asking, "What can we do to solve this problem?" the goal becomes, "How can we create this problem or make it worse?"
By focusing on the opposite of the problem or goal, team members can uncover new insights and approaches that they may not have considered otherwise. Once the "reverse" ideas have been generated, participants can then work to flip them around and find ways to turn them into positive solutions.
How to run a reverse brainstorm
- Draft a problem statement or starting topic for your team to brainstorm on
- Instead of posing the question: “How can we fix this?” ask “How can we make this problem worse?
- Participants will instead find more root causes driving the problem that you can start to address and dig deeper into
- Review and prioritize the ideas by severity or impact
Silent circuit
The silent circuit is a quiet brainstorming activity helps groups ideate across multiple topics while still being inclusive for quieter participants. This method is great for large groups, hybrid teams, and teams with introverts. This method is also great for getting different points of view.
How to run a silent circuit:
- Write "how might we" questions or a different prompt at the top of each brainstorming section.
- Set a timer and encourage participants to pan around the canvas and silently add as many ideas on sticky notes as they can under each prompt.
- When time is up, participants return to their original question and share all the ideas for each category.
- Review the questions and create action items for the best ideas.

Brain-netting
Brain-netting is a traditional brainstorming session conducted online. Online brainstorming isn’t a new concept, but recent shifts in remote work and collaboration tools have made this a much more common exercise. The main benefit of a brain-net is that it can be done asynchronously, meaning collaborators don’t have to.
Brain-netting is more common among remote teams, where asynchronous communication and video calls are the norm. However, any team can leverage brain-netting to take a brainstorming activity online, generate innovative ideas, and get the creative juices flowing.
How to run a brain-netting exercise:
- Kickoff the session and warm-up your team with a virtual icebreaker that can be done asynchronously
- Add a problem statement or define a topic to ideate over
- Brainstorm together or set a deadline for when team members should have added their ideas to the brainstorming platform
- Synthesize the ideas together, or summarize them and share the common themes
- Prioritize the ideas, pick a winner, and/or define next steps
Related: How to Facilitate a Brainstorming Session
Why brainstorming is essential for innovation
Brainstorming fosters creative thinking.
If you’re facing a difficult problem, brainstorming can help you to generate potential solutions that you might not have thought of otherwise. The free-flowing nature of brainstorming is meant to encourage exploration and a diversity of ideas — even those suggestions that seem tangential or unrelated at first may wind up forming the basis for effective solutions later on, or as inspiration for new products or features.
Brainstorming puts your best ideas in one place
Brainstorming helps you to organize your team's thoughts and feedback on any project. By structuring your brainstorming sessions so that everyone is engaged and all ideas are recorded, you can later organize your feedback by theme , using tools like tags for sticky notes and filtering. This can help you to better assess which ideas are worth pursuing and which ones are not, and begin to quickly and easily outline actionable next steps.
Types of brainstorming
There are three main types of brainstorming. Each approach has advantages and disadvantages, though hybrid brainstorming (enabled by platforms like Mural) mitigates the issues of by synchronous and async brainstorming.
Asynchronous brainstorming
Individuals are presented with a question or topic to consider on their own. Later, team members contribute their ideas to a shared document for further discussion and organization. The main advantage with asynchronous brainstorming is that it inherently avoids issues like groupthink since each individual completes the exercise independently.
Synchronous brainstorming
A team gathers together to brainstorm in a meeting, with everyone sharing ideas and grouping suggestions by theme. The main advantage of synchronous brainstorming is that it allows your team to build on one another's ideas in real time, making your session potentially more productive and speeding up innovation.
A hybrid approach to brainstorming combines elements of both asynchronous and synchronous ideation. By establishing a basis of psychological safety, as well as taking advantage of modern, cloud-based collaboration tools and features built to avoid groupthink, it's really possible to get the best of both worlds.
Tips for productive brainstorming
Establish an environment of psychological safety.
One of the most important elements in unlocking effective brainstorming is establishing a culture and environment of psychological safety . A brainstorming session should be one where everyone feels comfortable contributing without self-editing — in this phase, ideation shouldn't be interrupted by critiques or pushback. It's simply about collecting as many ideas and different perspectives as possible.
Psychological safety also means you are less likely to be impeded by groupthink — if the brainstorming session is characterized by a wide array of ideas and even constructive disagreement, you will have a much better basis upon which to formulate potential solutions than if everyone agrees or one line of thinking dominates your discussion.
Use private brainstorming within the context of a group meeting
To achieve this, you'll need to make people feel safe to share what they may think are outlandish or controversial ideas, which can be difficult to achieve. If you're not sure how best to begin, tools like Private Mode when using Mural can help you avoid groupthink by hiding the feedback that others are providing. Alternatively, when using a shared digital space like Mural, asynchronous brainstorming is also a viable solution — this allows people to reflect on their own, and bring their unique perspectives without outside influence into the meeting at a later date for discussion and organization.
Related: 7 Key Rules for Brainstorming
Follow-up after the brainstorming session
Brainstorming ideas is only the first step. After the brainstorming session is over, the team moves into the implementation phase. Be sure to define next steps and the roles of each team member so everyone understands the workflow and what’s expected of them. By following up, you ensure that the ideas you captured don’t get forgotten and a solution can be implemented.
Define a strategic goal for your brainstorming meeting
Once you've established the approach for your brainstorm, it helps to give greater context to your ideation by defining an overarching, strategic goal. Are you at the very outset of a problem with a lot of variables, and trying to better understand how they relate to one another? Is the purpose of your meeting to discover new ways to improve user experience for a given product or feature? Each use case requires a different basic framework for your brainstorming meeting.
Use these techniques to run better brainstorming sessions
Brainstorming is an essential part of the innovation process, but it can be difficult to come up with new ideas if you’re not sure where to start. The techniques we’ve outlined in this post should help you structure your brainstorming sessions in a way that makes them more effective and helps you produce actionable insights and takeaways.
If you want to make your brainstorming sessions even more productive, using a shared digital space like Mural not only unlocks visual thinking and online collaboration, but also builds in strategies to combat issues with groupthink and allows for hybrid brainstorming sessions that combine the best of asynchronous and real-time meetings.
Mural offers a host of brainstorming templates to kickstart more effective and meaningful (not to mention fun) sessions. Get started today with a Free Forever plan , and invite unlimited guests so you can build the next great idea together with your whole team.
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts

7 ground rules for brainstorming
.jpeg)
How to Facilitate a Brainstorming Session
.jpg)
How to encourage thinking outside the box
Related blog posts.

Agile vs Waterfall project management: What's the best approach?

What is a Jira Scrum board, and why do you need it?

13 best Agile project management tools
- Brainstorming Tools
- Concept Map Note Taking
- Types of Concept Maps
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Plot Diagrams
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Cynefin Framework
- DACI Framework
- Decision Making Framework
- Decision Making Model
- Decision Making Techniques
- Digital Customer Journey
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Product Portfolio
- Profit & Loss Templates
- RAPID Framework
- Scenario Planning
- SPACE Analysis
- Stakeholder Communication Plan
- Strategic Vs Tactical Planning
- Strategy vs Plan
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Cash Cow Matrix
- Decision Tree Guide
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- Strategy vs Tactics
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Experience Mapping Guide
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Perceptual Maps
- Position Maps
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Visual Note Taking
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Using Creately VIZ
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
The Brainstorming Guide

Introduction to Brainstorming
Have you ever encountered a challenge that felt impossible to overcome, dreamt of starting a business from the ground up, wanted to create a solid plan, launch a product, or hoped to write a memorable story? And the good news is that within you, right now, lies the key to unlocking solutions, innovations, and narratives that can transcend boundaries.
Your secret weapon? Brainstorming.
Brainstorming can help you solve problems, start businesses, make plans, or create stories successfully. But here’s the issue: many people don’t know how to brainstorm effectively, whether they’re doing it alone or with others.
Sometimes, people waste a lot of time thinking of repeated and uninteresting ideas that won’t actually work. They believe they’re brainstorming, but they’re not doing it effectively.
What if you could learn the best way to brainstorm and start coming up with really powerful and profitable ideas quickly?
Keep reading to find out how to make the most of brainstorming.
Definition of Brainstorming
We’ll start off with the basics.
Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique that involves generating a large number of ideas or solutions to a particular issue or challenge.
It typically takes place in a group setting, although it can also be done individually. The primary goal of brainstorming is to encourage free thinking and idea generation without immediate criticism or evaluation.
Brainstorming is a valuable tool for generating creative solutions, fostering teamwork, and encouraging innovative thinking. It can be applied to a wide range of contexts, from business strategy and product development to creative writing and problem-solving in everyday life.
Brief History of Brainstorming
If you are interested in learning how brainstorming came to be, here’s a brief history of brainstorming.
Brainstorming was first developed by advertising executive Alex Osborn in the late 1930s. Osborn was seeking ways to improve the creative thinking and idea generation process within his advertising agency, and he formalized the brainstorming method in his book titled “Applied Imagination” in 1953.
Origins in Advertising
Alex Osborn coined the term “brainstorming” to describe a structured approach to idea generation. He believed that traditional meetings often stifled creativity, so he introduced brainstorming as a way to encourage free thinking and open collaboration.
Modern Approaches
In response to some of the limitations of traditional brainstorming, modern variations and techniques have emerged. These include techniques such as mind mapping , brainwriting , and online brainstorming tools , which aim to boost creativity and idea generation in different ways.
Four Rules of Brainstorming
Osborn also established four fundamental rules to guide effective brainstorming sessions. These rules are designed to pave the way for a creative and open-minded atmosphere favorable for idea generation. The four rules of brainstorming are:
- No criticism: During a brainstorming session, participants are explicitly instructed to withhold criticism, judgment, or negative feedback of any kind. The aim is to create a safe and non-threatening environment where everyone feels comfortable sharing their ideas, no matter how unconventional or seemingly impractical they may be.
- Quantity over quality: Participants are encouraged to generate as many ideas as possible within the allotted time frame. The emphasis is on quantity rather than quality in the initial stages of brainstorming. This rule encourages participants to think freely and prevents them from censoring themselves or holding back potentially valuable ideas.
- Build on ideas: Brainstorming sessions thrive on collaboration and the interplay of ideas. Participants are encouraged to build on one another’s suggestions. This means that when someone presents an idea, others should try to expand, modify, or combine it with their own contributions to create new and improved concepts.
- Encourage wild ideas: “Wild” or unconventional ideas are actively welcomed and encouraged in brainstorming. These unusual or seemingly far-fetched ideas can often serve as catalysts for innovative thinking. They may inspire more practical solutions or lead to unique insights.
What are the Benefits of Brainstorming?
Brainstorming offers a range of benefits in various personal, professional, and creative contexts. Some of the key advantages of brainstorming include:
- Idea generation : Brainstorming is a structured approach to generating a large number of ideas in a relatively short time. This is especially valuable when you need creative solutions, innovative concepts, or fresh perspectives.
- Promote creativity : It promotes creative thinking by encouraging participants to think outside the box, explore unconventional ideas, and break free from mental constraints and self-censorship.
- Explore multiple perspectives : Brainstorming sessions often involve multiple participants with different backgrounds, expertise, and viewpoints. This diversity can lead to a broader range of ideas and solutions.
- Foster collaboration : Brainstorming sessions often involve group participation, fostering collaboration and teamwork. Participants can build on each other’s ideas, leading to the development of more refined concepts.
- Identify effective solutions: It is an effective tool for problem-solving. Brainstorming can help identify potential solutions to challenges, enabling better decision-making.
- Inspire innovation : Brainstorming often leads to the generation of innovative and novel ideas, which can be valuable in fields such as product development, marketing, and research.
- Effective meetings : When conducted efficiently, brainstorming can lead to more productive and focused meetings, reducing the likelihood of unproductive discussions and tangents.
- Time efficiency : Brainstorming can lead to quicker problem-solving and idea generation compared to individual or unstructured approaches.
- Adaptability : It can be applied to a wide range of situations, from brainstorming in business to personal decision-making.
Important Brainstorming Factors to Keep in Mind
Despite its benefits, it’s important to note that brainstorming may not always be the most effective method in every scenario. It works best when guided by established principles and adapted to suit the specific needs and goals of a particular project or challenge.
- Group dynamics : Brainstorming may not work well in groups where there is a lack of trust, or where dominant personalities overshadow others. In such cases, alternative methods like individual ideation followed by group evaluation might be more effective.
- Time constraints : If time is limited, traditional brainstorming sessions can be lengthy. In such cases, rapid brainstorming techniques like “brainwriting” may be more time-efficient.
- Complex problems : For highly complex issues, brainstorming alone may not be enough. It might need to be supplemented with other problem-solving techniques, research, or expert consultation.
- Sensitive topics : Some topics may be too sensitive or controversial for traditional brainstorming, as the “no criticism” rule can hinder necessary discussions. In such cases, a more structured and moderated approach may be better.
- Overused technique : If a group frequently relies on brainstorming without variation, it can become less effective due to repetitive thinking. Mixing in different creative techniques can help maintain its effectiveness.
- Large groups : With too many participants, managing a brainstorming session can become unwieldy. Smaller breakout groups or online collaboration tools may be needed to facilitate effective idea generation.
- Clear goals : Brainstorming should always have a clear objective. If the purpose is ill-defined or ambiguous, it can lead to unfocused sessions and ineffective outcomes.
Different Types of Brainstorming
Based on the participants' involvement and the approach used to generate ideas, brainstorming can be divided into different types.
Individual Brainstorming
This involves a single person generating ideas on their own, often in a quiet and reflective setting. It’s suitable for personal projects, introspective thinking, or when group collaboration is impractical.
Group Brainstorming
Group brainstorming involves a team of people coming together to collectively generate ideas. It’s a collaborative approach that benefits from diverse perspectives and is often used in professional settings. Learn more about group brainstorming with our guide to effective group brainstorming strategies .
Analytical Brainstorming
In analytical brainstorming, participants focus on critically evaluating and analyzing existing ideas or problems. The aim is to break down complex issues and generate solutions through systematic analysis.
Quiet Brainstorming
Quiet brainstorming emphasizes a calm and focused environment, ideal for introverted individuals or those who work best in solitude. It allows for deep thinking without the pressure of vocalizing ideas.
Role Play Brainstorming
Participants take on different roles or personas to approach a problem from various perspectives. This technique encourages empathy and creative thinking by viewing the issue through different lenses.
What to Do Before a Brainstorming Session
Preparing for a successful brainstorming session is the first crucial step toward unlocking creativity and innovative solutions. Whether you’re tackling a complex problem, generating fresh ideas, or planning your next project, careful preparation will set the stage for productive collaboration and meaningful outcomes.
Select the right participants
Choose participants carefully based on their expertise, knowledge, and relevance to the topic. Ensure diversity in perspectives if possible, as different viewpoints can lead to richer discussions.
Schedule and communicate
Set a date, time, and location for the session, and communicate this information to all participants well in advance. If it’s conducted online, make sure to send an email invitation with the meeting link prior to the session. Ensure that everyone knows the session’s purpose and what is expected of them.
Provide background information
Share relevant information, data, or research materials with participants ahead of time. This allows participants to come prepared and have a better understanding of the topic or problem.
Prepare materials
Make sure that you have all the necessary materials ready, such as whiteboards, flip charts, markers, sticky notes, or digital tools. This makes it easier to capture and organize ideas during the session.
Assign a facilitator or moderator
If possible, appoint a facilitator or moderator who can guide the session, keep it on track, and enforce the ground rules. This person can also help manage time and encourage participation.
Refreshments and comfort
Depending on the duration of the session, provide refreshments and ensure a comfortable environment. Hungry or uncomfortable participants may not be as engaged or creative.
Backup plan
Have a backup plan in case technical issues arise or if the brainstorming session encounters unexpected challenges. Being prepared for contingencies can prevent disruptions.
Review previous sessions
If this is not the first brainstorming session on the topic, review the outcomes of previous sessions to build on existing ideas and avoid duplication.
How to Run a Productive Brainstorming Session
Define clear objectives.
Clearly articulate the purpose and goals of the brainstorming session. What specific problem are you trying to solve, or what ideas are you seeking to generate? Having a well-defined objective makes sure that the session remains focused.
Set the ground rules
Establish clear ground rules for the brainstorming session . Remind participants of the principles, such as no criticism during idea generation, encouraging wild ideas, and focusing on quantity over quality.
Set a time limit
Determine the duration of the brainstorming session and allocate specific time slots for each stage (ideation, discussion, evaluation, etc.). Adhering to a schedule helps maintain focus and productivity.
Warm-up activity
Consider starting the session with a warm-up activity or icebreaker to help participants get into a creative mindset and build rapport with each other.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Decide on a brainstorming technique
If you prefer a more structured brainstorming approach, you can select a brainstorming technique such as mind mapping, 5 whys, reverse brainstorming, etc. to guide the idea generation process. You can also use sticky notes to write down ideas first and an affinity diagram to group them later based on themes.
Generate ideas
Encourage participants (whether individual or group) to generate a wide range of ideas without self-censorship. Emphasize that all ideas are welcome, no matter how unconventional they may seem.
Capture ideas
Record and document all ideas as they are generated. Use tools like whiteboards, sticky notes, or digital platforms to display and organize the ideas.
Build on ideas
After initial idea generation, invite participants to expand, refine, or combine each other’s ideas. This collaborative process can lead to innovative solutions.
Organize and prioritize
Categorize and group related ideas to identify common themes or patterns. Discuss and evaluate the ideas based on relevant criteria to prioritize the most promising ones.
You can use a prioritization grid to visually evaluate the ideas based on relevant criteria such as feasibility, impact, and relevance to prioritize the most promising ones.
Select the best ideas
Choose the ideas or solutions that align best with your objectives or criteria. Encourage participants to vote on ideas they prefer and you can select ones with the most votes. These are the concepts you will further develop or implement.
Action planning
Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing or exploring the selected ideas.
Document everything
Keep a comprehensive record of all generated ideas, even those not immediately selected. These can serve as a valuable resource for future brainstorming or reference.
Feedback and iteration
Seek feedback from others if applicable, and be open to refining and iterating on your ideas based on input and new insights.
Brainstorming Methods and Templates
Brainstorming methods are valuable tools for individuals and groups seeking to tap into their collective creativity and explore new possibilities. From structured processes like mind mapping and SWOT analysis to more unconventional methods like the 5 Whys and negative brainstorming, these techniques provide a structured framework to inspire fresh thinking and uncover innovative solutions.
- Mind mapping : Creating a visual representation of ideas by branching out from a central concept with related sub-ideas, helping to uncover connections and associations.
- Brainwriting : Participants silently write down their ideas on paper or digital platforms, passing them to others for further development or evaluation.
- Round Robin Brainstorming : In a group, each member takes turns suggesting one idea until everyone has contributed, often fostering more equitable participation.
- Reverse Brainstorming : Identifying ways to create or exacerbate a problem, which can lead to innovative solutions when these negative scenarios are reversed.
- SCAMPER : An acronym for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to Another Use, Eliminate, and Reverse, used to prompt creative thinking by altering existing ideas.
- Storyboarding : Creating a visual narrative of a process, idea, or concept using drawings, images, or sketches to aid in brainstorming and idea development.
Roles Storming : Participants take on different roles or personas to explore a problem or idea from various perspectives.
SWOT Analysis : Evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a topic to generate ideas for improvement or growth.
- Random Word Association : Using randomly generated words or images as prompts to trigger creative thinking and idea generation.
- Card Sorting : Organizing ideas or concepts on physical or digital cards, then rearranging and categorizing them to identify patterns or solutions.
Stepladder Technique : Introducing new members to an ongoing brainstorming group one at a time, allowing fresh perspectives and ideas to emerge gradually.
Six Thinking Hats : Participants wear metaphorical “hats” representing different thinking styles (e.g., creative, critical, optimistic) to explore a topic from multiple angles.
- Lotus Blossom Technique : Expanding on a central idea by creating a diagram with multiple interconnected sub-ideas, allowing for in-depth exploration.
- Starbursting : Ask and answer questions (who, what, where, when, why, how) about a central idea to gain insights and generate new ideas.
- Rapid Ideation : Quickly generate a large quantity of ideas without overthinking, with the understanding that evaluation comes later.
- Plus-Delta Method (Delta+) : Assess past experiences by identifying positives (pluses) and areas for improvement (deltas) to learn and make future improvements.
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa) : Visualize and analyze potential causes of a problem using a branching diagram.
- Affinity Diagram : Organize large amounts of data or ideas into related categories or themes to identify patterns and insights.
Common Brainstorming Mistakes to Avoid
Brainstorming is a valuable tool for generating creative ideas and solutions, but it can be less effective if certain common mistakes are not addressed. Here are some common brainstorming mistakes to avoid:
- Criticism and evaluation : One of the cardinal rules of brainstorming is to defer criticism and judgment during the idea generation phase. Critiquing ideas as they are presented can stifle creativity and make participants hesitant to share. Avoid evaluating or criticizing ideas until the brainstorming session is over.
- Dominance : Allowing one or a few individuals to dominate the discussion can lead to an imbalance of ideas. Ensure that everyone has an equal opportunity to contribute, and encourage quieter participants to speak up.
- Groupthink : Groupthink occurs when participants conform to a consensus or the opinions of a dominant person within the group. It can limit the diversity of ideas. Encourage participants to think independently and express dissenting viewpoints.
- Lack of structure : While brainstorming should be free-flowing, it still benefits from some structure. Without clear guidelines or a well-defined problem statement, brainstorming sessions can become disorganized and unfocused.
- No follow-up : Brainstorming without follow-up actions can result in a lack of accountability and implementation. Ensure that ideas generated in the session are documented, evaluated, and assigned to responsible parties for further action.
- Overthinking : Overthinking and overanalyzing ideas too early in the process can inhibit creativity. Encourage participants to let their thoughts flow freely without worrying about feasibility or practicality at the beginning.
- Staying in the comfort zone : Participants may stick with familiar or safe ideas instead of exploring new or unconventional ones. Encourage thinking outside the box and exploring diverse perspectives.
- Not mixing techniques : Relying solely on one brainstorming technique for all situations may not yield the best results. Experiment with different techniques and approaches depending on the goals and nature of the problem.
- Skipping warm-up activities : Jumping straight into brainstorming without warm-up activities or icebreakers can hinder creativity. Warm-up exercises can help participants get into a creative mindset.
Brainstorming Tips
Whether you’re working individually or in a group, here are some effective brainstorming tips to help you create a conducive environment for creativity, encourage diverse perspectives, and improve the quality of ideas generated.
- Set clear objectives : Clearly define the problem, challenge, or goal that the brainstorming session aims to address. A well-defined objective provides participants with a clear focus and purpose for generating ideas.
- Create a comfortable environment: Ensure the physical environment is comfortable, with ample seating, appropriate lighting, and minimal distractions. Additionally, create a psychologically safe space where participants feel comfortable sharing their ideas without fear of criticism.
- Defer judgment : Emphasize that during the initial idea generation phase, criticism and evaluation should be avoided. This encourages participants to freely express their thoughts without self-censorship.
- Build upon ideas : Encourage participants to listen actively and build on each other’s ideas. Collaboration and idea development can lead to more refined and creative concepts.
- Use visual aids : Utilize visual tools such as whiteboards, sticky notes, or digital collaboration platforms to help participants organize ideas visually and stimulate creative thinking.
- Silent brainstorming : Incorporate silent brainstorming sessions where participants write down their ideas individually before sharing them with the group. This approach can be particularly helpful for introverted participants.
- Change perspectives : Encourage participants to explore the problem or idea from different angles or viewpoints. This can trigger fresh insights and solutions.
- Mindful listening : Promote active and attentive listening during idea sharing. This means allowing others to express their ideas without interruption and acknowledging their contributions.
- Combine and modify ideas : Explore how combining or modifying ideas can lead to entirely new and innovative solutions. Encourage participants to think about how different concepts can complement each other.
- Rotate facilitators : If conducting multiple brainstorming sessions, consider rotating the role of the facilitator. Different facilitators can bring diverse leadership styles and approaches to each session, leading to varied outcomes.
- Celebrate successes : Recognize and celebrate the achievements resulting from successful brainstorming sessions. Acknowledging contributions and successes fosters a culture of innovation and encourages continued creative thinking.
Effective Tips and Tricks to Running Successful Brainstorming Workshops
You can use these tips to improve your brainstorming workshop’s creativity, engagement, and overall effectiveness.
- Have a diverse facilitation team : Assign a co-facilitator or subject matter expert to help the primary facilitator. This allows for different perspectives and expertise to guide the workshop effectively.
- Use idea generation techniques : Try different structured idea generation techniques beyond standard brainstorming, such as mind mapping, SWOT analysis, or the Six Thinking Hats method, to generate multiple ideas.
- Rotate facilitators : If the workshop is lengthy, consider rotating the facilitator role during different phases. This helps to maintain participants' engagement and provide fresh perspectives.
- Use breakout groups : Split participants into smaller breakout groups to work on specific aspects of the problem or to generate ideas independently. Afterward, bring these groups together to share and analyze what they brainstormed.
- Try cross-pollination : Encourage participants from different teams or departments to collaborate, fostering cross-functional thinking and innovation.
- Use silent brainstorming : Silent brainstorming is a technique where participants write down their ideas independently before sharing. This minimizes groupthink and helps generate a wide range of ideas.
- Try role play and simulation : Include role-playing or simulation exercises relevant to the workshop’s theme to encourage creativity and empathy in problem-solving.
- Use physical props : Introduce physical props, visual aids, or prototypes related to the topic to stimulate ideas and inspire innovative solutions.
- Form expert panels : Invite experts or guest speakers to share insights or provide different perspectives during the workshop, inspiring participants with fresh viewpoints.
- Have storytelling sessions : Hold storytelling sessions where participants share personal or relevant stories related to the topic. This can evoke emotions and lead to more creative thinking.
- Use gaming elements : Include gamification elements, such as team challenges or problem-solving games, to make the workshop more engaging and competitive. Here’s how to make virtual brainstorming fun and effective .
- Have feedback loops : Build in periodic feedback loops where participants can reflect on the workshop’s progress and suggest adjustments to the process.
- Use visual documentation : Use visual recording techniques (e.g. graphic facilitation or sketchnoting) to visually capture the workshop’s key points and ideas, creating a dynamic record.
- End with a creative exercise : Wrap up the workshop with a creative exercise or activity that helps participants to unwind and reflect on the day’s accomplishments, reinforcing the creative mindset.
In this guide, we have covered everything about brainstorming, from what it is to how to do it well. We explored methods, gave tips, and pointed out common mistakes to avoid. Whether you’re a business leader, team member, or just interested in brainstorming, this guide has given you the knowledge and tools to succeed.
Remember, brainstorming is not just a process; it’s a way of thinking that encourages open discussion and creative problem-solving. By using the principles and practices mentioned here, you can tap into the full potential of brainstorming to generate creative ideas and find innovative solutions for your personal and professional challenges.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
Our site and app needs some cookies to function and perform better. And we also use them to optimize and improve our product. Could you please set your preferences?
Cookies help us tailor your experience, making it smoother and more intuitive. They also give us insights on how to improve our platform for you and all our users. By accepting cookies, you're saying 'yes' to a better Creately experience. If you want to know more about the cookies we use and the choices you have, check out our Privacy Policy.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The six thinking hats method: how to use it for effective brainstorming
August 10, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Learn how to effectively use the six thinking hats method to foster diverse perspectives and improve decision-making. Discover practical tips and techniques to promote more productive and collaborative thinking in your team!
What is Edward De Bono’s six thinking hats brainstorming method?
Edward De Bono’s six thinking hats is a decision-making and problem-solving method that encourages parallel thinking and creativity.
Parallel thinking is a term coined by De Bono. It’s a collaborative thought process where people explore different perspectives on a topic, enabling a balanced and productive brainstorming environment.
The six thinking hats process involves a facilitator guiding participants through different thinking styles by symbolically wearing different hats. Using these hats, participants explore a topic, one perspective at a time, giving everyone an equal chance to contribute without debate or criticism.
We’ll dive deeper into this later, but for now, here’s a quick breakdown of what each hat represents and its related thinking style:
- White hat: Objective data analysis.
- Red hat: Emotional and intuitive responses.
- Black hat: Critical judgment for identifying risks and flaws.
- Yellow hat: Positive thinking for exploring benefits.
- Green hat: Creative and innovative ideas.
- Blue hat: Facilitation and process control.
In all, the six thinking hats process provides a framework that improves collaboration, decision-making, and problem-solving by leveraging the power of parallel thinking and tapping into group intellect.
The 6 benefits of six thinking hats
There are many benefits of the six thinking hats brainstorming technique that may be of interest when problem-solving and decision-making. Some of these include:
1. Enhanced creativity
The six thinking hats method stimulates creative thinking by encouraging participants to explore various perspectives, generate new ideas, and think outside the box.
By wearing different hats, individuals are encouraged to step out of their comfort zones and explore uncommon ideas. Overall, the method promotes nontraditional thinking and unlocks fresh ideas and possibilities.
2. Balanced thinking
Each of the six hats ensures balanced thinking by considering all angles of a topic, including:
- Facts
- Emotion
- Critical judgments
- Positive thinking
- Creativity
- Process control
When all of these factors are considered, the results are more balanced and fairer. This allows participants to see the topic, idea, or problem comprehensively.
3. Improved collaboration
The structured framework of the six thinking hats facilitates effective collaboration by ensuring that all participants can contribute to the discussion. Furthermore, they have the opportunity to share their viewpoints without conflicts or interruptions.
4. Efficient decision-making
The method enables faster and more efficient decision-making by systematically analyzing different aspects, risks, benefits, and alternative possibilities.
By doing so, the method helps streamline the decision-making process, reducing the time spent on deliberation and enabling timely outcomes. Moreover, the approach minimizes the risk of overlooking important factors, which helps to create solid solutions.
5. Reduced bias and subjectivity
The six thinking hats technique asks participants to temporarily set aside their personal biases and judgments and focus on the specific thinking style that their appointed hat represents.
By encouraging a temporary shift in thinking, individuals can approach a problem or idea with an objective mindset. This enables them to consider perspectives based on logical reasoning rather than personal biases.
6. Increased productivity
The six hats process provides a structured and organized approach to brainstorming , ideation, and planning, which increases productivity.
During a session, discussions remain concentrated on the overall goal. By channeling efforts towards a common objective, participants can streamline their thought processes, eliminate distractions, and maintain focus throughout the session.
This increased clarity contributes to heightened productivity as team members use their collective intelligence to achieve outcomes quickly.
The six thinking hats step-by-step process
The six thinking hats process, developed by Edward De Bono, is a structured method for brainstorming, problem-solving , and decision-making.
The process involves the following steps, participants, facilitation, and tools:
- Define the focus. The session begins by clearly defining the problem, idea, or topic of discussion that requires brainstorming and decision-making.
- Select participants. Select a diverse group of individuals who bring different perspectives, expertise, and roles to the discussion.
- Introduce the six hats. The chosen facilitator introduces the concept of the six thinking hats and explains the meaning and role of each hat color. Participants are briefed on the thinking styles associated with each hat and the purpose they serve during the session.
- Assign hat roles. The facilitator assigns specific hat roles to participants. Each person is responsible for wearing a particular hat for a given period.
- Hat rotation. The session progresses with hat rotation, where participants switch roles by changing hats at designated intervals. This rotation ensures that every participant has the chance to contribute from different perspectives and prevents individuals from becoming fixated on a single thinking style.
- Hat exploration. While wearing a specific hat, participants share their thoughts, ideas, observations, or questions related to the topic. The facilitator guides the discussion, ensuring that the focus remains on the thinking style represented by the current hat.
- Facilitator’s role. The facilitator plays a crucial role in managing the session. They guide the flow of the discussion, enforce hat rotation, encourage active participation, and maintain a balanced and inclusive environment. The facilitator also ensures that all participants have an opportunity to express their views and that the session stays on track.
- Tools and visual aids. The brainstorming process can be supported by visual aids so that participants can jot down key points, ideas, or observations associated with their hat. Visual representations help in organizing thoughts and summarizing outcomes.
- Summarize and analyze. At the end of the session, the facilitator summarizes the key insights, observations, ideas, and conclusions from each thinking style. This summary helps to consolidate the collective understanding, identify patterns, and inform subsequent decision-making processes.
The six thinking hats colors and what they represent
Each hat in the six thinking hats method represents a distinct thinking style. The collective use of these hats during a brainstorming session facilitates the evaluation of ideas and well-rounded decision-making.
Red hat
The red hat represents emotions and intuition. When wearing the red hat, participants can express their feelings, gut instincts, and subjective opinions without the need for justification.
This hat encourages the open sharing of personal perspectives and taps into the intuitive and emotional aspects of decision-making. It helps to foster a more holistic understanding of the topic at hand.
Green hat
The green hat symbolizes creativity and new ideas. Participants wearing the green hat are encouraged to think innovatively, develop fresh ideas, and explore alternative possibilities.
This hat promotes divergent thinking, encourages brainstorming, and stimulates creative solutions. It adds a spark of inventiveness to the session.
Blue hat
The blue hat represents process control and organization. It plays the role of a facilitator in the brainstorming session.
The blue hat wearer manages the overall thinking process, guides the discussion, and ensures the session stays on track. They summarize outcomes, coordinate the contributions of different hats, and keep the session focused and productive.
Yellow hat
The yellow hat signifies positive thinking. Participants wearing the yellow hat focus on exploring the benefits, advantages, and positive aspects of the ideas or proposal.
Yellow hat wearers look for value, prospects, and optimistic perspectives. In addition, they help to create a constructive and forward-thinking atmosphere.
White hat
The white hat is associated with facts and information. It represents a logical and objective thinking style.
Participants wearing the white hat gather and analyze data, facts, and information relevant to the topic. They provide an objective foundation and add evidence-based insights, helping the group make well-informed decisions.
Black hat
The black hat embodies critical judgment. Participants wearing the black hat take a cautious and critical approach.
They identify potential risks, flaws, and negative aspects of ideas or proposals. The black hat thinking style aims to identify pitfalls, challenge assumptions, and encourage careful evaluation.
When to use the six thinking hats method
The six thinking hats method provides a framework for collaborative brainstorming that maximizes the potential of a team’s collective intelligence. As a result, sessions may be more creative and effective.
The six hats thinking method is particularly useful in situations where:
- A team needs to generate new ideas or solutions.
- There are diverse opinions or conflicts among team members.
- A comprehensive evaluation of ideas is required.
- Emotional or intuitive aspects need to be considered alongside logical reasoning.
- The decision-making process needs to be more objective and rational.
Six thinking hats example
To understand the six thinking hats method more fully, here’s an example of how the process may play out in a real-life scenario:
- Team : The marketing team at a tech company.
- Objective : Generate innovative marketing campaign ideas for a new product launch.
- Process : The team leader introduces the six thinking hats method and assigns specific hat roles to each team member.
- Red hat (emotions and intuition): The individual wearing the red hat openly expresses their gut feelings and emotional responses towards the marketing campaign ideas at hand. They discuss their personal inclinations and share their enthusiasm or concerns about specific campaign concepts.
- Green hat (creativity) : The green hat team member freely shares creative marketing campaign ideas without criticism. They generate diverse ideas, such as viral videos, interactive social media campaigns, and experiential events.
- White hat (facts and information): The team transitions to the person wearing the white hat. Here, the individual analyzes the feasibility and gathers data on the market campaign ideas. They consider budget constraints, target audience demographics, and competitor analysis.
- Black hat (critical judgment): Moving to the black hat, this individual critically evaluates the ideas on the table. They identify potential risks, such as legal implications, negative public perception, or budget overruns. They weigh the pros and cons of each idea and highlight any drawbacks or challenges.
- Yellow hat (positive thinking): The person wearing the yellow hat focuses on the positive aspects of the campaign ideas. They discuss potential benefits, advantages, and opportunities for each concept. They also highlight the possible impact on brand awareness, customer engagement, and market differentiation
- Blue hat (process control): This team member takes on the role of session manager. They summarize the key insights and guide the discussion toward the most promising ideas. They also highlight the most feasible concepts from the overall hat discussion.
- Results : The brainstorming session allowed the marketing team to explore various creative marketing campaign ideas. The team considered diverse perspectives, backed by data and discussion.
The session facilitated inclusive participation and balanced the exploration of ideas. As a result, the team identified three promising campaign concepts:
- A gamified social media contest.
- An influencer-driven product launch event.
- An interactive augmented reality experience.
The team left the session with a clear direction for further developing and refining these ideas. This led to a more informed and effective marketing strategy for the new product launch.
Unleash the power of the six thinking hats method for brainstorming and take your ideation sessions to new heights!
Explore the benefits of MindManager®, the ultimate mind mapping tool, to unlock innovative ideas, foster collaboration, and make informed decisions.
Sign up for a free trial today and supercharge your brainstorming sessions with MindManager!
Six thinking hats frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Below are a few commonly asked questions about the six thinking hats brainstorming method:
What is six thinking hats?
The six thinking hats is a method developed by Edward De Bono for structured thinking and decision-making. It involves wearing six metaphorical hats, each representing a specific thinking style.
This technique explores ideas, analyzes information, considers emotions, and facilitates well-rounded and effective discussions.
How do teams use six thinking hats?
Teams use the six thinking hats to develop unique perspectives and ideas. By assigning different hats to each participant, teams can work together to think outside the box and enjoy efficient and productive brainstorming, problem-solving, and decision-making.
What are the benefits of six thinking hats?
The benefits of six thinking hats include:
- Enhanced creativity
- Balanced perspectives
- Improved decision-making
- Efficient collaboration
- Effective problem-solving
- Increased productivity
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Inspire & Impact Collection |
- 29 brainstorming techniques: effective ...
29 brainstorming techniques: effective ways to spark creativity

Bright ideas don’t come as easily as flicking on a light.
When it’s up to one individual to dream up a solution, it can be time-consuming and cause a lot of pressure. And when it comes to a group of people tasked with solving a problem, ideas might clash. Not to mention, everyone has a preferred method for their creative madness, making it difficult to get every team members’ wheels turning in the same direction.
That’s where brainstorming techniques come in. These techniques provide structure for brainstorming sessions, ignite creativity across all brainstormers, and ensure your ideas come to fruition. And luckily, there are lots of effective brainstorming techniques to choose from.
What is brainstorming?
Here’s a general brainstorming definition: it’s an approach taken by an individual or team to solve a problem or generate new ideas for the improvement of a product, organization, or strategy.
No matter your preferred method, most brainstorming techniques involve three steps:
Capture ideas
Discuss and critique the ideas
Choose which ideas to execute
Every brainstorming technique also involves the same ingredients. All you need is an individual or group of people, a problem to solve or an opportunity to address, and time.
Brainstorming challenges
The golden rule of all brainstorming sessions is quantity over quality. The more ideas you have, the better your chances are that one will be worthy of execution. For these reasons, especially in group brainstorming sessions, be sure all team members check their criticisms at the door and let it be known that the only bad ideas are no ideas.
Of course, not every brainstorming session will go off without a hitch. Some common brainstorming challenges include:
Unbalanced conversations, sometimes due to extroverts dominating discussions
The anchoring effect, meaning brainstormers cling to the first few ideas shared and don’t move on to others
Awkward silences, which often occur when participants are not prepared
Perhaps you’ve experienced some of these uncomfortable brainstorming sessions yourself. Thankfully, there are plenty of tried-and-true, and also some unorthodox, brainstorming techniques and tools that tackle just these issues.
Analytic brainstorming techniques
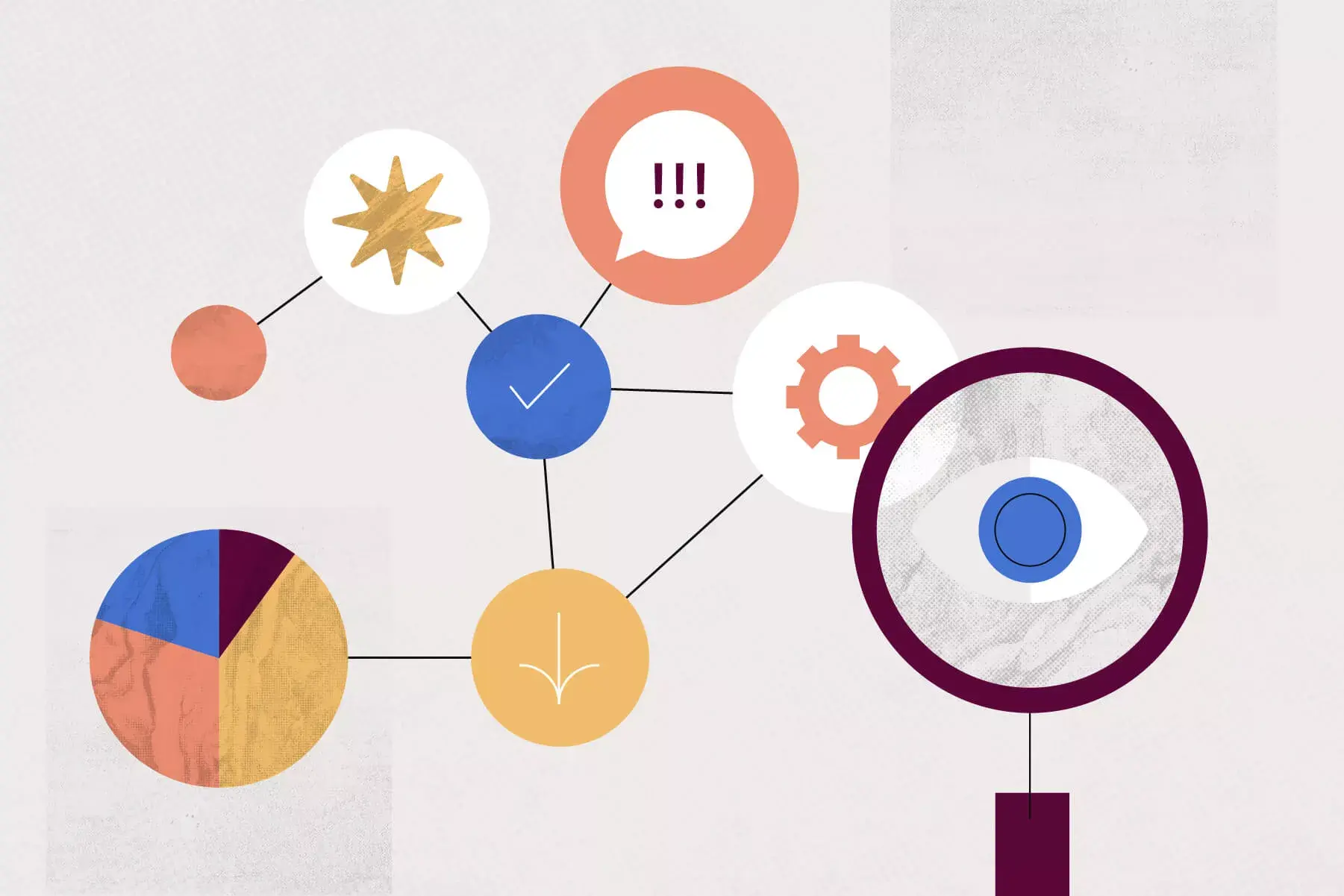
When you need to look at an idea from all angles or vet a problem thoroughly, analytic brainstorming techniques might be worth implementing. Consider the following brainstorming methods and tools to generate and qualify ideas.
1. Starbursting
A visual brainstorming technique, starbursting should be used once you or your team of brainstormers has homed in on a single idea. To begin starbursting, put an idea on the middle of a whiteboard and draw a six-point star around it. Each point will represent a question:
Consider every question and how it might pertain to your idea, such as, “Who will want to buy this product?” or, “When will we need to launch this program?” This will help you explore scenarios or roadblocks you hadn’t considered before.
Best for: large group brainstorms, vetting ideas thoroughly
2. The five whys, a.k.a. why analysis
Similar to starbursting, the five whys brainstorming technique helps you evaluate the strength of an idea. Challenge yourself to ask “why” questions about a topic or idea at least five times and consider what new problems you surface—and, importantly, note how you can address them. To help organize your thoughts, consider using a flowchart or fishbone diagram in hand with this brainstorming technique.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, vetting ideas thoroughly
3. SWOT analysis
You might be familiar with SWOT analysis as it relates to strategic planning , and you might also be surprised to know that this concept can also be applied as a brainstorming exercise to help qualify an idea. The notion? Discuss the following aspects of your topic to determine whether it’s worth executing:
Strengths : how does the idea dominate or stand out from competitors?
Weakness : are there any flaws in the idea that could jeopardize its execution?
Opportunities : what else can you capitalize on based on this idea?
Threats : what are potential downfalls that could arise if the idea is launched?
4. How Now Wow
The How Now Wow brainstorming technique is all about categorizing ideas based on how unique they are and how easy they are to implement. Once you’ve collected several ideas, either individually or from team members, talk through where they fall in the How Now Wow spectrum:
How ideas are ideas that are original but not executable.
Now ideas are unoriginal ideas that are easily executable.
Wow ideas are never-been-pitched before ideas that are also easy to implement.
Obviously, you want as many “Wow” ideas as possible since these are executable but also because they might set you apart from competitors or dispel monotony in a company. To help organize your ideas, consider using a matrix of four squares with difficulty weighted on the Y-axis and innovation on the X-axis.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, homing in on an executable solution
5. Drivers analysis
Just as the name implies, driver analysis is a brainstorming technique that analyzes the drivers or “causes” of a problem. To use this brainstorming technique, simply keep asking yourself or your team of brainstormers: “What’s driving [insert problem]?” and then, “What’s driving [insert answer to the previous question]?” Similar to why analysis, the deeper you dig into a problem, the more well-vetted it will be and the more confident you will be in executing solutions for those problems.
6. Mind mapping
Another visual brainstorming technique, mind mapping addresses the anchoring effect—a common brainstorming challenge where brainstormers fixate on the first ideas instead of coming up with new ones. Mind mapping does this by using the first idea to inspire other ideas.
You’ll need a large piece of paper or whiteboard to do this. Begin by writing down a topic and then drawing lines connecting tangential ideas to it. This essentially helps you paint a picture of your topic at hand and what might impact its execution or even expedite it.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, visual thinkers
7. Gap filling, a.k.a. gap analysis
When you’re struggling with how to execute an idea, that’s where gap filling comes in—to address the obstacles standing in your way. Begin by starting with a statement of where you are and then a statement of where you want to be. For example, “Our company creates smart watches; we want to expand our portfolio to also include fitness trackers.”
It’s worth writing these out on a large piece of paper or a whiteboard for all of your brainstormers to see, perhaps using a flowchart or mind map to do so. Then, list obstacles that are preventing you from getting where you want to be and work through solutions for each of them. By the end of your brainstorming session, you should have a clearer plan of how to get where you want to be.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, visual thinkers, honing in on an executable solution
Quiet async brainstorming techniques

Best for businesses that are crunched for time or teams with more introverted individuals, these quiet brainstorming techniques allow brainstormers to contribute ideas on their own time and often anonymously. Look to the following methods to get your creative juices flowing, especially for remote teams with frequent virtual meetings .
8. Brainwriting, a.k.a. slip writing
A nonverbal and in-person brainstorming technique, brainwriting addresses the brainstorming challenge of unbalanced conversations head-on. That’s because it requires participation and teamwork from every brainstormer, beginning with each person writing down three ideas relating to a topic on three separate slips of paper. Then everyone passes their ideas to the right or left and their neighbor builds on those ideas, adding bullet points and considerations.
The slips of paper continue to be passed around the table until they’ve made it all the way around. Then, the brainstorm facilitator can digest all of the ideas themselves, or the brainstormers can discuss each idea out loud and determine what’s worth pursuing. Pro tip: limit this brainstorming technique to no more than 10 people to not be overwhelmed with ideas or time constraints.
Best for: group brainstorms and introverted team members
9. Collaborative brainwriting
You can think of collaborative brainwriting like a herd of cows grazing in a field, except it’s brainstormers grazing on ideas throughout a week, anonymously jotting down thoughts or ideas. Oftentimes a brainstorming facilitator will kick off this technique by posting a large piece of paper, sticky notes, or sharing a cloud-based document to jot down a few brainstorming ideas.
From there, team members can build off of those ideas on their own time and anonymously provide feedback. Be sure to set a clear deadline of when the brainstorming session closes to ensure all brainstormers have an opportunity to chime in.
Best for: individual brainstorming
10. Brain-netting, a.k.a. online brainstorming
Great for remote teams, brain-netting is essentially a place for a team to brain dump their own ideas, whether that’s a Slack channel, Google Doc, or your project management tool .
The notion is that brainstormers can add ideas whenever inspiration strikes and that the list will be ever-evolving. Of course, the team leader might want to inform their team of brainstormers of any important dates or deadlines when they need solutions to a problem. They may also want to hold a meeting to discuss the ideas. All brainstormers’ identities can be left anonymous even in the meeting.
Best for: group brainstorms, introverted team members, remote teams
11. SCAMPER
The SCAMPER brainstorming technique encourages brainstormers to look at an idea from different angles and it uses its acronym to inspire each lens:
Substitute : consider what would happen if you swapped one facet of a solution for another.
Combine : consider what would happen if you combined one facet of a solution with another.
Adapt : consider how you could adapt an idea or solution in a new context.
Modify : consider how you can modify an idea to make it higher impact.
Put to another use : consider how else you could leverage your idea.
Eliminate : consider what you could remove from the idea or solution so that it’s simplified.
Reverse effective : finally, consider how you could reorganize an idea to make it most effective .
When used in a group brainstorming session, you might want to use templates to track responses or pair the SCAMPER method with a brainwriting session to encourage all brainstormers to evaluate ideas from every angle.
12. Lightning Decision Jam
Known as LDJ for short, the Lightning Decision Jam brainstorming technique requires 40 minutes to one hour to complete. What will you have by the end? Tangible results and buy-in from an entire team of brainstormers.
This brainstorming technique is great for remote team alignment . It all begins with writing down positives about a topic or what’s working regarding the topic, then writing down negatives and identifying what needs to be addressed most urgently. This is followed by a few minutes of reframing problems as questions, then brainstorming solutions for those problems.
Finally, your team uses a matrix to determine how high impact and how high effort your solutions are to decide which ideas are worth pursuing. For a more robust explanation of LDJ, watch this video by design agency AJ&Smart, which created the brainstorming technique.
Best for: group brainstorms, remote workforces, tight deadlines, honing in on an executable solution
13. The idea napkin
Similar to LDJ, the idea napkin is essentially a brainstorming template that distills a broad topic into tangible solutions. How it works: Every brainstormer has an “idea napkin” that they commit one idea to, beginning by writing down their idea, as well as an elevator pitch for it.
The idea napkin also includes a column for who the idea is targeting—meaning who you’re solving a problem for (customers, teammates, etc.)—and a column noting what problems your idea addresses. Brainstormers can fill out their napkins ahead of or during a brainstorming session, each is expected to present or share them. The final ideas will be placed on an impact and effort matrix to determine which are worth pursuing.
Best for: group brainstorms, honing in on an executable solution
Roleplaying brainstorm techniques

Drama lovers rejoice! These roleplay brainstorming techniques encourage brainstormers to figuratively walk in someone else’s shoes or put on their hat—or six hats, in one instance—to address a problem or dream up ideas from a new perspective. An added benefit of this? When brainstormers take on a personality that’s not their own, it lowers inhibitions since it’s technically not their point of view being brought to the table.
14. Six thinking hats
This brainstorming technique requires a minimum of six brainstormers to wear imaginary hats—hence the name— that require them to look solely at an idea from one specific angle. For instance, one brainstormer might be wearing an impact hat and only concern themselves with the impact of an idea and another might be wearing a constraints hat and only looking at the constraints of an idea.
You can pick and choose which angles are most important to your organization. And by the end of the group discussion, the whole brainstorming group should be able to hang their hats feeling confident about the ideas you’ll pursue.
Best for: group brainstorms (six or more people), introverted team members, vetting ideas thoroughly
15. Figure storming
Ever heard the phrase, “What would Abe do?” That’s pretty much the premise of this brainstorming technique in that brainstormers take on the identity of a famous or prominent figure, whether that’s a leader or celebrity, and put themselves in their brain space and how they’d approach an idea.
This helps teams look at a topic through a different lens and, in the case of group brainstorms, alleviates any nervousness that brainstormers will put out bad ideas. Because they’re not putting out their ideas—they’re sharing someone else’s. So go on and give yourself a new job title for the day.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, extroverted team members
16. Role storming
Role storming is similar to figure storming in that brainstormers take on different personalities to dream up ideas, but with one dramatic twist—brainstormers act out those ideas.
Generally, brainstormers are asked to take on the role of an average person who will be affected by the idea or solution in question, whether that’s an employee, client, or another party, and they act out a scenario that could stem from the idea to help them decipher what problems might arise from it. Consider this brainstorming technique for more extroverted teams.
Best for: group brainstorms, extroverted team members
17. Reverse brainstorming
Reverse brainstorming is grounded in a little bit of chaos. It encourages brainstormers to play the role of disruptors by brainstorming problems first and then solutions. To kick off the brainstorming questions, a team leader will usually ask, “How do we cause [insert problem]?”
Once your team has listed the causes, they’ll have a new and different perspective for coming up with solutions to problems.
Best for: group brainstorms, idea generation, problem-solving
18. Reverse thinking
Reverse thinking is a bit of a mashup of the figure storming and six thinking hats brainstorming techniques. It encourages brainstormers to merely ask themselves, “What would someone else do in this situation?” Then, it prompts them to think through why that person’s solution would work or not and if your current solution is more effective.
Best for: group brainstorms, extroverted team members, vetting ideas thoroughly
Group brainstorm techniques

Most brainstorming techniques can be applied to groups of brainstormers, but these specific brainstorming techniques promote (and some even require) participation from everyone. When facilitated well, group brainstorming techniques not only yield more ideas but they can also:
Boost team morale through lighthearted brainstorming games and by involving participation in every step of the brainstorming process
Promote creative thinking, especially when brainstormers are given time to prepare their ideas and a structured approach to solve problems
Bring more diverse ideas together, thanks to the unique perspective each brainstormer has and their individual strengths
All this to say, group brainstorming techniques are all about putting people’s heads together.
19. Eidetic image method
The eidetic image method is grounded in setting intentions, and it begins with group members all closing their eyes to do just that. For example, if a company is setting out to design a new smartwatch, the brainstorming facilitator would encourage all brainstormers to close their eyes and quietly meditate on what smartwatches currently look like.
Then the group would discuss and close their eyes once more and quietly imagine new features to add to the device. They’d all open their eyes and discuss again, essentially layering on the possibilities for enhancing a product. This brainstorming technique is ideal for revamping or building on an existing product or solution.
Best for: visual thinkers, creating an idea anew
20. Rapid ideation
Great for teams that get sidetracked or have difficulty staying focused in meetings, the rapid ideation brainstorming technique encourages brainstormers to race against a clock and come up with as many ideas as possible—and importantly, not take themselves too seriously. This can be done by having brainstormers shout out ideas to a facilitator or write them on a piece of paper. You might find that some of the same ideas keep popping up, which likely means those are worth pursuing.
Best for: extroverted team members, tight deadlines
21. Round-robin brainstorming
Participation is required for the round-robin brainstorming technique. Everyone must contribute at least one idea before the entire group can give feedback or share a second idea.
Given the requirement that everyone must share an idea, it’s best to allow brainstormers time to prepare ideas before each round-robin brainstorming session. This brainstorming technique is great for introverted team members and also for larger groups to ensure everyone can contribute. Moreover, the round-robin brainstorming technique also promotes the notion that the only bad idea is no idea.
Best for: introverted team members and developing a surplus of ideas
22. Step-ladder brainstorming
Ideal for medium-sized groups of five to 15 people, the step-ladder brainstorming technique prevents ideas from being influenced by the loudest brainstormers of a group.
Here’s how it works: A brainstorming facilitator introduces a topic to their group of brainstormers and then dismisses all but two brainstormers from the room. The two brainstormers left in the room discuss their ideas for a few minutes and then one brainstormer is welcomed back into the room and shares their ideas before the original two brainstormers divulge their ideas.
Brainstormers are added back into the room one by one, with each new brainstormer sharing their ideas before the rest of the group divulges theirs, and so forth. Once the entire brainstorming group is back in the room, it’s time to discuss the ideas they’ve built together, step by step.
Best for: introverted team members, vetting ideas thoroughly, honing in on an executable solution
23. Charrette
You might want to book a few rooms for this one. The charette brainstorming technique helps break up a problem into smaller chunks and also breaks up your brainstormers into separate teams to address them.
For instance, you might reserve three rooms, write a topic or problem on a whiteboard, and have three sets of brainstormers walk into those rooms to jot down their ideas. Then, the sets of brainstormers rotate rooms and build off of the ideas of the group that was there before them. Consider it effective teamwork at its best.
Best for: vetting ideas thoroughly, honing in on an executable solution
More brainstorming techniques
For more unconventional approaches to get your individual or your team’s wheels turning, consider adding some of these brainstorming techniques to your arsenal of ways to ideate.
24. ‘What if’ brainstorming
A very off-the-cuff brainstorming technique, “what if” brainstorming is as simple as throwing out as many “what if” questions surrounding a topic as possible, similar to the rapid ideation brainstorming technique. For instance, “what if this problem occurred in a different country,” or, “what if this problem occurred in the 1800s?”
Walking through the scenarios might help spur new obstacles pertaining to your problem. Essentially, the “what if” brainstorming technique helps your team evaluate all the possibilities.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, creating an idea anew, vetting ideas thoroughly
25. Change of scenery
It’s no secret that physical surroundings can impact your team workflow and even creativity. When your brainstorming session is in a rut, consider relocating to another location, perhaps a park, a walking meeting, or even a coffee shop.
Being in a new setting might spur new ideas and even loosen up your brainstormers so that they’re more open to sharing ideas and helping you achieve quantity over quality.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, creating an idea anew
26. Random word picker
As this name implies, this brainstorming technique is a little random. Begin by tossing words into a hat and then pull them out and discuss how they relate to your brainstorming topic at hand. You may want to use a template to keep track of your thoughts and any new ideas the word association sparks.
To further organize your thoughts, consider pairing this brainstorming technique with word banking, meaning categorizing random words together and then drawing associations between their category and the brainstorming topic.
Best for: group brainstorms, creating an idea anew
27. Storyboarding
Turns out, storyboarding isn’t only for television and film. You can also apply this as a brainstorming technique, meaning illustrating or drawing a problem and possible solutions. Consider it another way to put yourself in someone else’s shoes, especially those your solution impacts. It’s also a means to visualize any roadblocks you might experience when executing a solution.
Best for: individual or group brainstorms, problem-solving, vetting ideas thoroughly
28. Wishing
Wishing is as simple as it sounds: You just wish for the solution you want to build. Think: “I wish our company was carbon neutral,” and then think of the possible ways in which you could achieve this, as well as areas that might be impossible to address for this. This will help uncover obstacles you might face and maybe even shed light on what you’re capable of overcoming.
Best for: individual or group brainstorms, creating an idea anew
29. Crazy eights
A short and fun brainstorming technique, crazy eights delivers on quantity by encouraging brainstormers to think quickly using a template that has eight boxes and only eight minutes on the clock to sketch out eight ideas. Once the timer stops, the group discusses their ideas.
For a larger group, consider having each brainstormer narrow in on only three ideas and give them a longer time limit of six minutes to sketch them out in more detail.
Best for: group brainstorms, visual thinkers, developing a surplus of ideas
8 tips for a productive brainstorming session
No matter which brainstorming technique is right for you and your team, consider the following best practices to brainstorm most effectively . Of course, it all begins with the brainstorming facilitator and how they set the tone for the session.
1. Allow time to prep
A brainstorming facilitator isn’t the only one in a brainstorming session who needs time to prepare for a meeting . They also should give brainstormers some context ahead of the session, such as in the form of a meeting agenda , to get in the correct mindset for the brainstorming session.
At least one day is standard but as little as two to 10 minutes is useful. Moreover, brainstorming facilitators should also have a few ideas in their back pocket for any creative ruts that might creep in.
2. Set a clear intention
The more context you can provide brainstormers from the get-go, the more fruitful ideas they can produce. For instance, clearly spell out what types of ideas you’re looking for. Whether it’s quickly executable ones or ones that are entirely pathbreaking, identify specific targets to address.
Additionally, be sure to let brainstormers know of any constraints you or your organization is operating under, including project timelines or budgets, so they’re generating executable ideas.
3. Invite new teammates and ideas
When the same people brainstorm together over and over, they can tend to produce the same ideas over and over. For this reason, consider introducing new people to your brainstorming session to shake up the usual and lend a fresh perspective—and hopefully fresh ideas—to your brainstorming topics. Invitees can be colleagues from different departments, customers or clients for a focus group, or an outside consultant.
4. Promote inclusivity
Every brainstorming session should be considered a safe space to share ideas—even unconventional ones. Remember, the only bad ideas are no ideas, and any idea shared shouldn’t be shot down or judged. In addition, the brainstorm facilitator should ensure every brainstormer is treated equally and given the same amount of time to talk. This might mean setting a timer for each brainstormer to talk and acknowledging those who are dominating conversations. Likewise, every brainstormer should be open and curious to ideas.
5. Think out of the box
Creative thinking begins with not taking ourselves too seriously. Just as you encourage inclusivity, encourage imperfections and out-of-the-box thinking, too. This could include anything from fun team building games to unique icebreaker questions. Hey, even a bevy of silly ideas to build off of is better than no ideas at all. Brainstorming techniques like wishing can encourage team members to open up.
6. Amplify creativity with music
Similar to how a change of scenery can inspire new ideas, even a little background music can promote creativity. Consider putting some on for your brainstorming session, and for the best results ensure it’s:
Instrumental
In a major key
On a fixed tempo and volume
7. Mix and match brainstorming techniques
Just as brainstorming techniques aren’t necessarily one-size-fits-all, they also aren’t all one-type-fits-every-session. Be prepared to pivot your brainstorming technique depending on what your group of brainstormers is most receptive to and also how many ideas you're juggling.
8. Execute your ideas
Coming up with bright ideas is great. But they’re pretty useless unless you effectively execute them. While some brainstorming techniques build the execution process into them, others might require you to follow up with brainstormers using project templates to map out a plan using creative solutions.
Brainstorming is about quantity over quality
When done right, a brainstorming session shouldn’t feel like a chore but rather an opportunity to create something together, especially when your brainstorming technique supports different styles of thinking and expression.
And whether you're operating as an individual or on a team, there’s something uniquely satisfying about seeing your ideas come to fruition. Get the creative ideas flowing, then customize your workflow management tool to turn those ideas into action.
Related resources
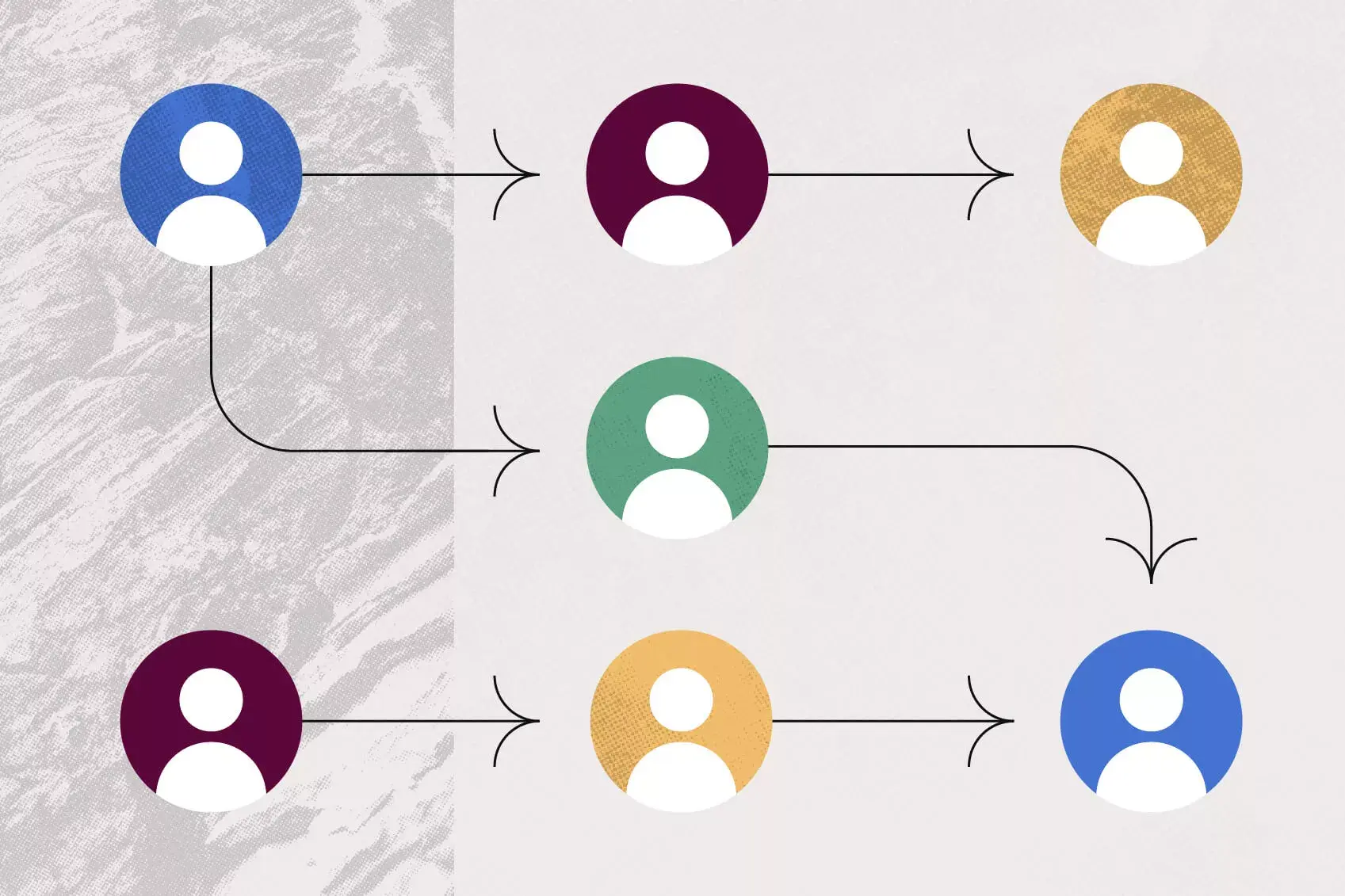
4 ways to establish roles and responsibilities for team success

Listening to understand: How to practice active listening (with examples)

Unmasking impostor syndrome: 15 ways to overcome it at work

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals
43 brainstorming techniques and games for creating new ideas

Finding new and innovative ideas is a vital part of the growth and success of any team or organization . While brainstorming techniques are rightly perceived as creative and exciting , it’s important to find a framework and idea-generation process that empowers your group to generate meaningful results.
Innovation is important for many businesses, but what brainstorming activities might you use to help make true innovation a reality? Find out in this collection of effective brainstorming techniques!
Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, 54 great online tools for workshops and meetings, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps.
- 18 Free Facilitation Resources We Think You’ll Love
In this post, we’ll explore a host of effective brainstorming techniques in categories such as creative exercises and visual idea generation games, all of which can be used to help your group brainstorm be more effective and gratifying for all involved.
We’ll also explore talk about the benefits of group ideation and share some examples of brainstorming sessions that utilize these methods. Let’s get started!
What are brainstorming techniques?
Brainstorming is a process of enabling people to think freely and creatively when trying to come up with ideas, solutions, or sharing knowledge.
Brainstorming techniques are proven activities and frameworks for coming up with lots of ideas quickly. They’ll often include steps to shift perspective, facilitate team collaboration and refine initial ideas into something even better.
Some examples of brainstorming activities include classic mind mapping and brain writing where you quickly try to generate as many ideas as possible.
Teams often use these techniques to generate creative ideas to tough problems and to explore possible solutions . They can also be used as part of more in-depth brainstorming workshops where team members then refine and choose ideas to put into action.
Some of the core concepts of brainstorming include: reserving judgment, go for quality over quantity, listen to all ideas, and think outside of the box in the pursuit of radical new ideas and creative solutions. Bring these concepts and a proven technique to your session and you’re already on the route to success!
If you’re finding your team with a problem they don’t know how to solve, a technique that encourages creative thinking might be just the ticket! Use these activities as part of a complete workshop process to refine those ideas into something actionable.
In SessionLab, it’s quick an easy to create an effective agenda for a brainstorming workshop in minutes. Drag and drop blocks in the session planner to create your structure. Add timing for each item to ensure you stay on time. Color-code your blocks to get an instant sense of your learning flow.
Core group brainstorming techniques
Brainstorming has been around as long as individuals and teams have tried to find creative and innovative solutions, or come up with new ideas or products. Whether a group is ideating on how to solve an organizational problem or generate ideas for new features or initiatives, getting people together to quickly ideate and come up with something new is time well spent.
In this section, we’ll first explore some of the core techniques that have been used time and again to create meaningful results and great ideas.
| 10 + | 2 – 10 | Low | |
| 10 + | 2 – 10 | Low | |
| 10 – 20 | 6 – 50 | Low | |
| 30 – 45 | 5 – 15 | Low | |
| 10 – 30 | 3 + | Low | |
| 2 – 15 | 2 + | Low | |
| 30 + | 1 + | Low | |
| 20 + | 5 – 20 | Low | |
| 10 – 30 | 8 + | Low | |
| 10 – 20 | 5 + | Low | |
| 120 + | 5 + | Low | |
| 10 – 30 | 2 – 20 | Low | |
| 30 – 60 | 2 – 10 | Low |
Popcorn Brainstorming
One of the classic brainstorming techniques, chances are you’ve done a popcorn brainstorm already. It’s been used by everyone from school teachers to CEOs to generate ideas and create energy around new initiatives – much like the popping of corn in a microwave!
Start by posing a question or problem statement and invite participants to take a minutes silence to think on it. Once the minute is up, start a timer and invite everyone to contribute ideas out-loud and build on each other’s ideas too. Have a single person take notes and encourage quality over quantity: no evaluation, no criticism or discussion yet – just rapid ideation!
Brainstorming – Popcorn and Round Robin #idea generation #brainstorming Simple, classic brainstorming with two variants. Popcorn – where participants speak out-loud and Round Robin – where participants work in silence and pass their ideas to the next person in turn.
Round-Robin Brainstorming
A tried and tested idea generation technique, Round-Robin Brainstorming provides a little more structure and ensures everyone in a group can contribute to a brainstorm by ensuring the discussion isn’t dominated by the loudest voices.
In this group method, seat everyone in a circle and hand them an index card. In silence, everyone writes an idea on their index card before passing it to the person to their left. Each participant then writes an idea based on their neighbour’s card and passes that along.
The result is a more relaxed session that encourages a combination of idea development and co-creation while ensuring everyone is heard. Perfect for teams with big personalities!

SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) is a tried and tested technique that teams often using when planning new initiatives or solving problems. It also happens to be a great tool for generating new ideas while also taking into account potential problems and opportunities.
The act of brainstorming around your weaknesses or threats can result in innovative solutions and ideas you might not have otherwise come up with. Try using each point of the process as a jumping off point for ideation or explore a topic from each of the different angles for best results.
SWOT Analysis #project planning #strategic planning #environmental analysis #planning #issue analysis #online #remote-friendly A SWOT Analysis is used in project planning, strategic planning and other processes where agreement is needed about the current situation of a project, team, department or organization. It stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
Brainwriting
No single person is as smart or as creative as a group. With the brain writing technique, tap into the ideas and approaches of multiple collaborators and co-create effectively.
Start by writing down the topic or area for which you’ll be generating ideas. Have all team members silently write down an idea related to the topic on a card and then, pass that idea to the person to their right. The receiving player reads the card and then adds an idea inspired by the original OR enhances the original idea before passing the card along.
By asking participants to grow and improve on one another’s ideas, Brain writing helps a group ideate effectively and come up with better ideas. You can even bring this to an online brainstorming session by using an online whiteboard and have participants pass post-its to the working spaces of their partners.
Brainwriting #gamestorming #idea generation Some of the best ideas are compilations from multiple contributors. Brainwriting is a simple way to generate ideas, share them, and subsequently build on them within a group. Access to multiple hands, eyes, and minds can yield the most interesting results.
Question storming
Sometimes, shifting perspective and starting from a different angle can generate the best ideas. Q-Storming, or question storming invites participants to brainstorm questions, rather than solutions.
After rounds of gathering qualifying data and assumptions, ask your group to think of all those questions that they still have which might help the team think the matter through. This approach can be really useful at finding ideas your team might not have considered and ensuring that what you come up with is truly going to solve the problem at hand.
Walking Brainstorm
Brainstorming methods come in many forms – you might have a quick-fire session that encourages excitement and verbal exchanges. Alternatively, you might find your group will create better ideas by working together in a more relaxed, introvert-friendly manner.
Walking Brainstorm is designed to help large groups work on idea generation dynamically but without creating scenarios where only the loudest participants are heard.
Create a space where different topics or questions are spread on posters/post-its around a room or virtual space. Silently and individually, each participant is encouraged to walk around and visit each question/topic in turn and add ideas to each. By moving around and working individually, this method helps create a more reflective, dynamic ideation session and can also help ensure group-think doesn’t set in!
Walking Brainstorm #brainstorming #idea generation #remote-friendly This introvert-friendly brainstorming technique helps groups of any size to generate and build on each other’s ideas in a silent but dynamic setting. As the participants keep moving, the exercise is ideal to kick-off a full day workshop or re-energize the group after lunch.
For those who prefer a more organized approach to idea generation, mind mapping is a great activity for creating ideas quickly and effectively.
Begin by writing the key topic in the center of a piece of paper or in an online whiteboard. Invite participants to brainstorm related topics and ideas by adding branches to the central idea and create new nodes or elements. As a facilitator, you’ll want to group ideas by color and also amend the thickness of the branches to show the strength of various ideas and concepts.
When you’re done mind mapping, the result will be a diagram that visually represents your ideas and makes it clear how the various parts interrelate – a great resource for idea development or for future sessions!
Mind map #idea generation #concepts #create #issue analysis #design A mind map is a diagram used to represent a number of ideas or things. Mind maps are methods for analyzing information and relationships.
Brain Netting
The concept of brain netting is to not only take your brainstorming online, but to use online tools and virtual spaces to make the session a truly engaging experience.
The key is to use an online tool that the group is familiar with, can co-create in easily and which works both synchronously or asynchronously. Using an online whiteboard or shared document for brain netting means participants can contribute in both a live online workshop as well as in their own time. This is a unique benefit of online brainstorming, and it’s one we’d recommend taking advantage of with your team!
We’d especially recommend using an online tool that supports easy commenting, images, videos and links – encourage your group to use whatever assets best communicate their ideas!
Six Thinking Hats
Exploring a problem or idea from multiple perspectives is a great way to generate new ideas and inform your brainstorming process. In this brainstorming activity, start by explaining the six different hats and that at various points, each person will wear the different hats to explore your chosen topic. For example, the green hat is for creative thinking while the white hat is all about information and facts.
Invite the group to start with the blue hat, which is to control the process and then move between hats to explore, define, ideate, identify risk and gather information around a topic in a sequence. By asking the group to all wear the same hat at the same time, you can ensure your brainstorm moves forward while also ensure all perspectives are explored.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Rapid writing
Different teams and workshops need different approaches to generating fresh ideas. While a carefully structured approach can be effective, using quick-fire brainstorming techniques like Rapid Writing can help create a sense of energy, urgency, and get heaps of ideas out quickly.
For this method of brainstorming, start by setting a timer and encouraging your participants to get as many ideas out as possible within that time limit. Remember that at this stage in the idea generation process, there is no such thing as a bad idea and by quickly ideating without being critical, your group can be creative without prematurely shutting down possible ideas. Be sure to collect all the ideas and share them without judgment at the end, whether you’re brainstorming online or in person!

Lotus Blossom
Some of the most effective techniques are those that encourage free-thinking and rapid ideation while also having some rules that can keep things structured. Lotus Blossom combines these concepts while also creating a great visual representation of your brainstorming activity.
Lotus Blossom helps facilitate idea generation by working out from a central concept and adding eight additional themes or ideas inspired by the first on sticky notes. Once you have those eight ideas, you then invite participants to take each of those and add another eight and effectively blossom them around the original. By clustering ideas in this way, this ideation method also creates a visual resource you can come back to later and follow the brainstorming process from start to finish.
Lotus blossom #concepts #create #design #idea generation The lotus blossom method is a creativity exercise. It is a framework for idea generation, starting from one central theme. Eight conceptual themes grow out from the main theme and each of them are used as central theme to generate 8 more themes. Explore!
Starbursting
Complete freedom without an ideation framework isn’t always the best way to find and develop ideas. Structured techniques like Starbursting can help guide a team through more effective idea generation and ensure all key elements are considered at an early stage.
To begin, create a six-pointed star on a large piece of paper or online whiteboard. At the tip of each point of the star, write down the words Who, What, Why, Where, When and How. Invite the group to brainstorm ideas and questions related to each of these points in turn.
At this stage, the group only needs to brainstorm questions in each of these sections, leaving answers until later, though creating follow-up questions can also be helpful in effectively ideating on your central concept or problem.
When ideating on solutions to problems, it’s very easy to come to the table with underlying assumptions that can affect the course of the idea generation process. You can avoid this potential pitfall by using The 5 Whys to go further and deeper in a very simple, group-friendly manner.
Kick-off by working as a group to create a problem statement that you’ll work on solving. Once you have a concise statement, ask the group why you have this problem and discuss the answer. After working together to form a cohesive answer, ask the group why you have the problem again. By repeating the process, you and your team can dig deeper and find the root cause of the issue and move past the first, most obvious ideas.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
Creative brainstorming techniques
All brainstorming is creative. Generating ideas and finding solutions often asks groups and teams to find new ways of looking at things but in this next section, we’ll look at techniques that aim to approach the ideation process from a unique or especially creative starting point.
If you’re finding your typical exercises aren’t yielding results or want to try something new, creative games like those below can create space for innovation. Let’s dig in!
| 15 – 60 | 5 – 30 | Low | |
| 15 + | 3 – 6 | Low | |
| 5 – 15 | 3 + | Low | |
| 30 – 45 | 5 – 15 | Low | |
| 15 – 20 | 5 – 10 | Low | |
| 5 – 10 | 2 + | Low | |
| 120 – 240 | 5 + | Low | |
| 30 + | 5 + | Medium |
Imagie-ination
Words are often our primary tool when it comes to starting a brainstorm or kicking off an idea generation workshop. While these kinds of techniques are tried and tested, it can also be useful to try something different that can unlock your team’s creativity.
With Imagie-ination, you’ll use images to help your group generate ideas that go beyond the norm. First, collect an assortment of images for your brainstorm and write down a simple description of the topic you want to generate new ideas around. Have each participant select an image and then come up with as many ideas as they can for how the image relates to the topic.
After the first round, you’ll then cluster ideas together and find an image and title to best illustrate those clusters. This kind of clustering and titling can help refine the ideas your team has generated and move them towards action – a great outcome for any brainstorming session!
Imagie-ination #idea generation #gamestorming Images have the ability to spark insights and to create new associations and possible connections. That is why pictures help generate new ideas, which is exactly the point of this exercise.
Bad idea brainstorming
Idea generation is at its best when groups are encouraged to add their ideas without being self critical or overthinking. Often, individuals involved in ideation can put pressure on themselves to offer only great ideas and so don’t contribute everything that comes to their minds.
Use this brainstorming technique to help free your group’s creativity and encourage them to come up with the absolute worst ideas they can in relation to a central topic or problem. Like reverse brainstorming, this brainstorming technique is a great way to find alternative routes to more creative ideas. Just be sure to use a swot analysis to figure out what should make it into reality!
Bad Idea Brainstorm #brainstorming #creative thinking #idea generation Name all the bad ideas to make room for good ones. Coming up with the perfect solution right off the bat can feel paralyzing. So instead of trying to find the right answer, get unstuck by listing all the wrong ones.
Brainstorm questions instead of solutions
Our first instinct when it comes to problem-solving can often be to jump straight to giving answers and finding solutions. Though this can be effective, when it comes to generating creative ideas, a different tact can be more effective.
With this reverse brainstorming game, challenge participants to offer questions instead of solutions so they can respond to a central concept creatively and from a new angle. If you’re finding your group can become blocked when generating ideas, it might be that your existing questions or frameworks aren’t sufficient. By taking a new ideation approach, you can unblock your team!
Brainstorm questions instead of solutions #questions and answers #brainstorming When we are given a problem our reflex is to find answers. But it can be difficult to leave the comfort zone and to come up with creative answers. This exercise will encourage to think out of the box.
Stakeholder Round Robin Brainstorm
Bringing together groups of different stakeholders with their own areas of expertise is a great idea whether you’re brainstorming or finding solutions. That said, it’s worth noting that in these kinds of mixed groups, participants will be coming from different places and have different priorities and approaches to idea generation.
Start by creating a flipchart or whiteboard space for each stakeholder’s perspective and writing this at the top. Give each stakeholder two minutes to brainstorm on the central idea from their perspective and add those to their flipchart before then inviting each participant to move to the next one and brainstorm from this different perspective. By using this round-robin brainstorming exercise, you can help the group understand the perspectives and insights each member brings to the table while also generating fresh ideas as a result!
Backcasting
A simple change in perspective can have a massive impact on how your team approaches solving a problem. Backcasting is a simple but effective brainstorming exercise where a team is invited to work backwards from an ideal future state in order to come up with concrete actions they can take today.
Start by listing your long term goals in a time frame of 1-20 years. Then work backwards from that state to today, listing every action necessary to achieve that goal state. Collect insights on what difficulties might come up, what steps your team needs to take and what resources you might need in order to brainstorm effectively and find a new way to reach your team’s long term goals!
Backcasting #define intentions #create #design #action Backcasting is a method for planning the actions necessary to reach desired future goals. This method is often applied in a workshop format with stakeholders participating. To be used when a future goal (even if it is vague) has been identified.
Walking Questions
A brainstorming technique with a What if learning style, Walking Questions is a great way of encouraging group members to share knowledge, ask questions to personal problems, and explore a topic dynamically.
Best used at the end of a training session or workshop, each participant writes a question they have on the top of a sheet of paper then hands it to the person to their right. The person receiving the paper then writes any ideas or answers they have underneath and passes it to the next person.
By the end, the original piece of paper will be returned to the owner filled with ideas and answers from the entire group. It’s a great way of generating ideas from a group quickly and efficiently and of utilizing everyone’s expertise in a structured way. Give it a go!
Walking questions #what if learning style #idea generation #learning This is a great facilitation technique to answer open questions of trainees with a “What if” learning style. It prevents the facilitator from answering all questions herself. With this method trainees can: close knowledge gaps find solutions for personal problems imagine themselves using their new knowledge in future and prepare themselves for obstacles
Guided Imagery
Coming up with new ideas doesn’t always have to be boisterous! You can also get the creative juices flowing in a relaxed way by tapping into mindfulness and imagination with this method.
Start by inviting participants to close their eyes and get comfortable. Next, progress through a guided meditation designed to inspire creativity. Afterward, ask your group to reflect on what came up for them in the meditation and use this as the basis for further brainstorming!
Guided Imagery #idea generation #creativity #online facilitation #reflection This can be used for idea generation especially when the group is stuck.
Headlines from the future
Starting from the desired outcome and working backward with a reverse brainstorming technique can be a great way to solve a problem. Thinking into the future can also be inspiring in a way that encourages free thinking and big ideas – a great result for any brainstorming workshop.
In this idea generation game, ask your group to imagine it’s twenty years in the future and that your project or organisation has been a huge success. Invite each participant to draft a headline and sketch an image for a New York Times feature of this reality. Encourage big, bold ideas and debrief by discussing any common themes or ideas before moving onto idea development as a team!
Headlines from the Future #creative thinking #design #idea generation #creativity Get inspired today by a world 20 years away. Sometimes it helps to start from the end. This exercise will help you align with your team on an audacious vision for your project – one that you can work backward from.
Brainstorming techniques for problem solving and refining ideas
When you want to go beyond initial brainstorming and generate more refined ideas, the following complex idea generation techniques can effectively guide you through the process.
These activities combine brainstorming with idea evaluation, idea selection, and then going into concept development to help you come up with the best options. Let’s dig in!
| 25 – 30 | 10 + | Medium | |
| 20 – 30 | 2 – 10 | Low | |
| 60 – 120 | 2 – 40 | Medium | |
| 10 – 15 | 4 + | Low | |
| 20 – 40 | 6 + | Low | |
| 30 – 180 | 1 + | Medium | |
| 30 – 90 | 2 – 20 | Low |
25/10 Crowd Sourcing
Group ideation can be tricky to manage, and not all techniques are up to the task of managing creative input from large groups effectively. 25/10 Crowd Sourcing is a fantastic exercise that not only invites big, bold ideas, but can ensure everyone takes part in generating ideas as a group.
After first inviting participants to write a big, bold idea on an index card, start a timer and invite the group to move around the space and exchange cards without reading. Stop the timer and ask each person to read the idea and give it a score from 1 to 5. Repeat five times so that each idea has a score out of twenty-five and then find and share the top ten ideas with the group.
Group brainstorming techniques with a mix of blind scoring and sharing can be especially useful in avoiding bias and encouraging bold ideas – especially useful when ideating in large groups!
25/10 Crowd Sourcing #idea generation #liberating structures You can help a large crowd generate and sort their bold ideas for action in 30 minutes or less! With 25/10 Crowd Sourcing , you can spread innovations “out and up” as everyone notices the patterns in what emerges. Though it is fun, fast, and casual, it is a serious and valid way to generate an uncensored set of bold ideas and then to tap the wisdom of the whole group to identify the top ten. Surprises are frequent!
3-12-3 Brainstorm
Brainstorming is often associated with fast ideation and energetic idea generation sessions. While many standard techniques can be slowed down and run in different ways, there can be obvious benefits to maintaining energy and proving the value of short working bursts to your ideation group.
The 3-12-3 Brainstorm technique taps into the power of speed to generate great ideas and can help a team generate, develop, and present ideas in just less than twenty minutes. By combining speed and structure, this ideation method can help a group pressed for time use the session effectively, and we love how much ground can be covered by a group with this exercise!
3-12-3 Brainstorm #gamestorming #idea generation This format for brainstorming compresses the essentials of an ideation session into one short format. The numbers 3-12-3 refer to the amount of time in minutes given to each of three activities: 3 minutes for generating a pool of observations, 12 for combining those observations into rough concepts, and 3 again for presenting the concepts back to a group.
Mash-Up Innovation
Some of the best ideas come from taking existing ideas and putting them together. Brainstorming that takes advantage of what your group already knows and loves can really supercharge the idea generation process and this creative exercise is a perfect example of that.
In Mash-Up innovation, first ask your group to brainstorm around three different topics or areas and add them to a shared space or whiteboard. Next, organize your participants into small groups who will spend the next twelve minutes combining and mashing up as many of the elements as possible to make even better ideas. After a short idea presentation, you can even take your group through an idea development stage to really make the most out of this activity. You’ll be surprised at what comes out!
Mash-Up Innovation #hyperisland #innovation #idea generation Mash-ups is a collaborative idea generation method in which participants come up with innovative concepts by combining different elements together. In a first step, participants brainstorm around different areas, such as technologies, human needs, and existing services. In a second step, they rapidly combine elements from those areas to create new, fun and innovative concepts. Mash-ups demonstrates how fast and easy it can be to come up with innovative ideas.
Large group brainstorming can be dynamic, exciting, and productive but without structure and strong facilitation, it can also become disorganized and frustrating. 1-2-4-All is a classic idea generation process that not only helps ideas find space to allow idea development but also ensures the entire group can contribute to the session.
Start by inviting silent self-reflection on a shared challenge or question before then moving to pairs, foursomes, and then entire group ideation. One of the many benefits of this brainstorming technique is that everyone gets a chance to contribute freely and share their ideas in a structured way. In groups where conversation can become dominated by strong personalities or not everyone gets a chance to speak, this method is well worth employing.
1-2-4-All #idea generation #liberating structures #issue analysis With this facilitation technique you can immediately include everyone regardless of how large the group is. You can generate better ideas and more of them faster than ever before. You can tap the know-how and imagination that is distributed widely in places not known in advance. Open, generative conversation unfolds. Ideas and solutions are sifted in rapid fashion. Most importantly, participants own the ideas, so follow-up and implementation is simplified. No buy-in strategies needed! Simple and elegant!
One will get you Ten
Ideas most often spring from other ideas, and the sharing and co-creation of ideas during a brainstorm or idea generation workshop is where the magic really happens. This technique uses the sharing of ideas between teams as a central concept and it’s a great way of having participants communicate and learn from one another’s ideas meaningfully.
After first generating ideas solo and as a team, this ideation game asks team members to pair up with members of another team and share ideas. Each member then returns to their own team and presents two ideas – one of their own, and one from the other team – while the rest of the team guesses whose is whose. It’s interesting to see how participants package and present generated ideas and find ways to improve them organically as part of a rapid ideation.
One will get you Ten #thiagi #idea generation #team If I give you a dollar and you give me a dollar, we both end up where we began. But if I give you an idea and you give me an idea, we end up with two ideas each, benefiting from a 100 percent return on our investment. In One Will Get You Ten, we leverage this principle so that you and all other participants receive a 1000 percent return on your investment on ideas.
The Creativity Dice
When approaching the idea generation process it can be tempting for a team to go with what’s worked in the past and get locked into what appears to be working. Games that challenge the status quo and challenge teams in ways they don’t expect can be especially effective when generating ideas.
The Creative Dice is a brainstorming technique that encourages participants to work in three minute bursts and work on either specification, investigation, ideation, incubation, Iteration or integration based on a roll of the dice. By moving between different modes, this method prevents premature closure of one line of ideation and keeps the session energized and engaging. What’s more, the non-linear thinking can help with idea development too!
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Affinity Map
Using brainstorming techniques to get a large number of ideas together quickly and efficiently is a great first step to developing new solutions or solving problems. But what to do once you’ve generated lots of ideas and want to work on idea development? Affinity Map is a great method for organizing your group’s brainstormed ideas and for both seeing and challenging existing patterns.
Starting with a simple brainstorm, Affinity Map asks that the group collectively organizes the ideas into columns or groups based on relationships. By doing this idea clustering as a group, your team can take ownership of the idea generation process and discover patterns of thinking together! It’s a great way of identifying and improving a group’s natural inclinations while also creating meaningful ideas.
Affinity Map #idea generation #gamestorming Most of us are familiar with brainstorming—a method by which a group generates as many ideas around a topic as possible in a limited amount of time. Brainstorming works to get a high quantity of information on the table. But it begs the follow-up question of how to gather meaning from all the data. Using a simple Affinity Diagram technique can help us discover embedded patterns (and sometimes break old patterns) of thinking by sorting and clustering language-based information into relationships. It can also give us a sense of where most people’s thinking is focused

Fun brainstorming games
Brainstorming is often a fast-paced and engaging process that results in a group having fun. Creative brainstorming games that help participants have fun while generating ideas are also effective ways of loosening folks up and getting into new ways of thinking. If you’re finding your group stuck
In this section, we’ll look at brainstorming games that intentionally take a fun angle as a means to create better ideas.
| 15 – 30 | 5 – 15 | Medium | |
| 20 – 30 | 2 – 10 | Low | |
| 6 + | 3 – 15 | High | |
| 10 – 20 | 4 + | Low | |
| 15 + | 3 + | Low | |
| 60 – 90 | 3 – 12 | High |
Energy, fun, and creativity go hand-in-hand, and brainstorming techniques that encourage these items and generate ideas quickly and effectively – especially with large groups!
In MindSpin, teams of 3-5 participants are challenged to write as many ideas as they can in two five-minute rounds. Whenever a person writes an idea, they slam it down on the table. If they cannot think of one, they can take an idea from the person on their left and hopefully be inspired to write an additional card they also slam on the table. Remember that this brainstorming game is designed to be fast and loud while getting creative juices flowing. Encourage all participants to really slam their ideas down and keep things moving!
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
Figure storming
One potential difficulty when generating ideas is that not everyone feels comfortable sharing or holds back their ideas for fear of judgment. Creative brainstorming is all about removing restrictions or hesitation, and enabling your group to ideate freely – figure storming is a great method for achieving this!
Start by asking the group how a famous person, fictional character or well-known creative would approach the problem or topic at hand. You might ask how Albert Einstein, Elizabeth Bennett or Barack Obama might think about the ideas or concepts at hand. By inhabiting a different person’s perspective, not only can teams and individuals access new ideas, but they can also do so free of judgment. Also, it can be great fun to invite Atilla the Hun or Cleopatra to your creative exercises!
Flip and Rip
Images can often unlock our creativity but when using them to generate ideas, it can sometimes be difficult to know where to start. This visual brainstorming technique places some rules on how a group will both source and use images, and can encourage some really creative ideas!
Start by giving participants two magazines or image sets each. Then, invite each person to tear our whatever images stand out to them or grab their attention. Next, give them a problem statement and encourage them to find the connections between the problem and their chosen images. These unexpected connections between visuals can then be used as the foundation for further ideas! Plus, who doesn’t love the sound and feeling of tearing paper!
Flip and Rip #idea generation #problem solving #creativity #online Creativity through pictures and images
Forced Connections
An important part of the ideation process is giving your team permission to be silly and bring ideas to the table without fear of judgement or inhibitions. Empowering your team to be creative without limiting themselves can massively affect the effectiveness of your brainstorming and so it’s worth spending time to unblock your participants early.
Assemble a collection of random objects or images and invite participants to choose two or more items and brainstorm how they might be used together or connected in some way. Encourage out-of-the-box thinking and unusual ideas by bringing a collection of odd items to the table and you’ll be surprised at all the ideas your team can generate!
The Thing from the Future
Science fiction and speculative thinking about the future has long been a great source of ideas. In this brainstorming exercise, invite groups to co-design their ideal future by creating tangible objects with their imaginations.
Begin by sourcing a heap of prototyping materials and craft supplies. Invite participants to imagine an ideal future state and create an object that has time travelled back to the present. After spending some time creating strange and wonderful objects, participants then present them to the group and tell stories about the objects to inform future strategies and ideas.
If you’re looking for a fun, practical exercise to bring to your brainstorming session and encourage creative thinking, this activity is a great choice!
The Thing from the Future #imagination #storymaking #idea generation #issue analysis Help a group to time-travel and tap their imagination by fictional objects. With tangible objects and the stories your participants make up w/ them you’ll get so much richer inputs and context to inform joint visioning / strategizing: The future doesn’t look that far away when you can pick it off the shelf.
Making Lemonade
Sometimes, the best ideas come from moments of adversity or struggle. This brainstorming exercises leverages the power of positive thinking and attempting to make the best of a bad situation to generate creative ideas.
Start by sharing a couple of negative scenarios that might radically change something in the world. For example, everyone in the world has a cold, it rains constantly or we lost all our customers over night.
Next, ask your group to take something that appears negative and aim to reframe it to be as positive as possible while coming up with ideas of how that change might actually have a positive impact. Rain every day? That might be the end of drought and a boom to umbrella sales!
Making Lemonade #creative thinking #creativity #design #idea generation Try on a relentlessly positive, can-do attitude before tackling the big stuff. The proverb goes “If life gives you lemons, make lemonade.” Practice the art of positive thinking to unlock creative ideas. Use this as a warm-up before brainstorming or to energize your team meetings.
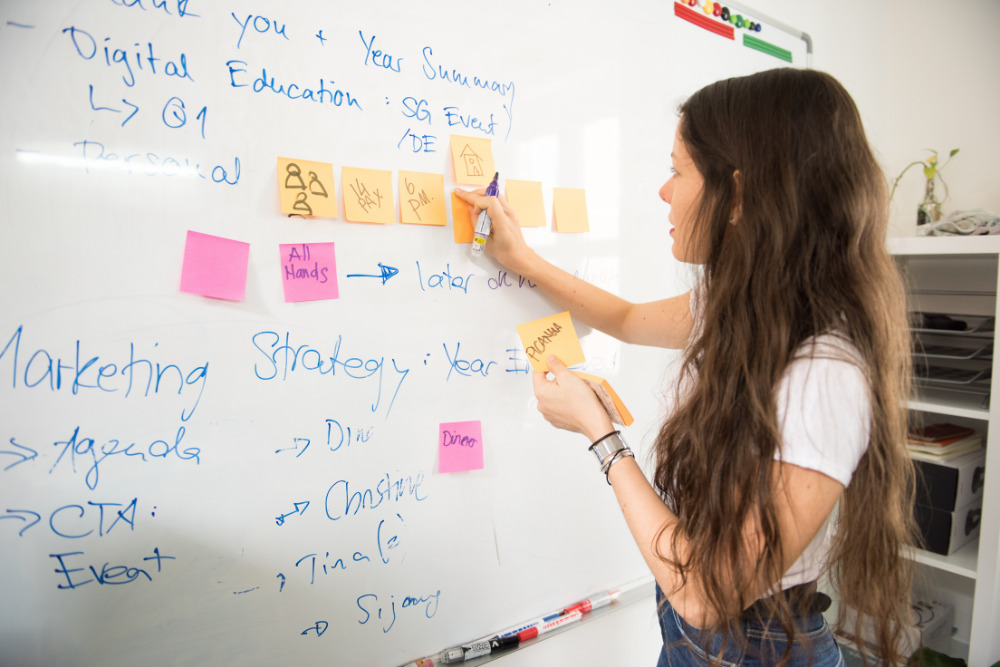

Visual brainstorming techniques
Visual brainstorming is a great way of helping your teams out of creative roadblocks and encouraging fresh ideas. When words fail, images can enliven, invigorate and inspire your process. In this section, we’ll look at some great brainstorming techniques that focus on drawing or creating visual responses when ideating. Let’s take a look!
| 30 – 45 | 2 – 20 | Low | |
| 90 + | 1 – 12 | Low | |
| 30 – 40 | 4 – 20 | Low |
Brainstorming shouldn’t stop when you have your first good idea. Fast iteration and refinement can help your group discover better ideas and develop ideas in record time. With 6-8-5, you can encourage your team to move from brainstorming to idea development in just a few minutes, and by asking participants to draw, you can keep things flowing easily!
Start by inviting your group to sketch 6-8 ideas in response to a central question or topic in five minutes. Encourage your team to be rough and not to worry about finesse at this stage – remember that the first stage of brainstorming works best when it’s free and unrestricted!
After a quick round of presenting ideas, go through the sketching process again and encourage idea development or ideas that have come out of group sharing. The result will be a heap of ideas and sketches you can move forward with too!
6-8-5 #gamestorming #idea generation Part of the reason we end up with under-developed ideas is that we stick with the first good idea we have — rather than taking the time to explore complementary approaches. 6-8-5 is designed to combat this pattern by forcing us to generate lots of ideas in a short period of time. The activity can then be repeated to hone & flesh out a few of the best ideas.
Four Step Sketch
Visual brainstorming techniques can be great right at the start of the process but they can be equally effective later on when it comes to idea development. In this exercise pulled from the design sprint playbook, take your group through a structured ideation process that encourages reflection, quick sketching and a completed idea too.
Begin by reviewing any existing materials or outputs from earlier exercises before then having your group do a round of Crazy 8’s, where they create eight sketched variations on their idea. At this stage, you then invite participants to finesse their idea and create a final polished sketch to share with the team. By mixing reflection, ideation and development, this brainstorming technique offers a structured path towards better ideas!
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
Drawing Together
Visual thinking is a powerful tool for any creative process or brainstorming workshop. This brainstorming game asks teams to tell stories about a personal or group challenge personal by expressing themselves with just five simple symbols drawn on paper. After a first draft, participants are then invited to refine their stories with colour, size and placement before the group interprets them.
By expressing themselves in a novel way, participants can exercise their creative muscles and consider new ways to express ideas nonverbally.
Drawing Together #skills #liberating structures #visual methods You can help people access hidden knowledge such as feelings, attitudes, and patterns that are difficult to express with words. When people are tired, their brains are full, and they have reached the limits of logical thinking, you can help them evoke ideas that lie outside logical, step-by-step understanding of what is possible. Stories about individual or group transformations can be told with five easy-to-draw symbols that have universal meanings. The playful spirit of drawing together signals that more is possible and many new answers are expected. Drawing Together cuts through the culture of overreliance on what people say and write that constrains the emergence of novelty. It also provides a new avenue of expression for some people whose ideas would otherwise not surface.
Brainstorming games for warming up
Generating ideas and thinking creatively isn’t always easy. Finding ways to energize and prepare your group for brainstorming with simple and fun warm-ups can help ensure the success of the workshop or session and introduce key idea generation concepts too.
While these creative games don’t necessarily create ideas in themselves, they are a great way to get teams ready for the next step. Let’s take a look!
| 10 – 15 | 5 + | Low | |
| 15 – 20 | 10 – 50 | Low | |
| 30 – 60 | 2 – 40 | Low |
When it comes to warming people up for an idea generation workshop, simple is best. With Draw Toast, you can introduce your group to visual thinking, working memory and systems thinking, all through the prism of a simple warm-up that works well online or offline!
For this creative exercise, invite your participants to illustrate how to make toast with a sketch or diagram without using any text. Afterward, share observations and insights as a group and outline the fact that there is no right or wrong diagram, and that differing and unique approaches to a problem or concept are all valid and useful. Not only is this a fun, fast brainstorming technique, but it prepares a group for the next stages of idea generation too!
Draw toast #problem solving #opening #design #gamestorming #idea generation You can use the Draw Toast exercise to introduce people to the concepts of visual thinking, working memory, mental models and/or systems thinking. This also works as a nice warm-up exercise to get people engaged with each other and thinking visually. Plus, it’s fun!

The Paper Clip Method
Even established and successful groups have preconceptions about brainstorming or how to generate ideas. Warming up a team by introducing the power of brainstorming practically can prevent stumbling blocks later on and ensure everyone is on the same page when approaching the brainstorming process.
The Paper Clip Method is a creative exercise that challenges your group to brainstorm all possible uses for a paper clip. After some silent brainstorming, debrief by sharing what the group has come up with and highlight how the group has cumulatively come up with a greater quality and quantity of ideas than any single person could.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Apple-Drawing Ideation
Learning how to approach creative brainstorming as a group is a worthwhile way to kick-off your idea generation workshop. In this simple creative game, split your participants into groups and invite them to take it in turns to fill a grid with drawings of apples, with the challenge that no apple can be the same as another.
When the time is done or the grid is full, debrief and highlight some of key concepts for effective brainstorming including the fact quantity is a precursor to quality and that we should try to build on the ideas of others. This brainstorming game is flexible by design and you can use it with something other than apples for a more practical application: e.g., draw 30 logos, write 30 taglines, draw 30 new cars.
Apple-Drawing Ideation #hyperisland #innovation #idea generation The purpose of this simple exercise is to demonstrate three key principles useful for creativity and idea generation: quantity is a condition for quality; building on the ideas of others; the ideas we come up with are usually all the same. The format is simple, with small groups standing and drawing apples. At the end of the exercise, the whole group reflects and draws out learnings and reflections.
Activities to support a brainstorming workshop
We’ve covered everything from fast and fun creative games to in-depth brainstorming techniques, but what about if you’re looking for ways to improve or kick start your brainstorming process? Preparing for a brainstorming workshop with research on inspiration collection can really help your team make the most of the upcoming session.
In this section, we’ll look at some techniques and methods you can use to inform, enable and improve your group brainstorm and bring better quality ideas to the table!
| 5 – 30 | 2 – 40 | Low | |
| 60 – 90 | 2 – 12 | Low | |
| 30 – 60 | 2 – 10 | Low |
Rapid Research
Like all effective workshops, idea generation sessions generally want to limit the number of participants in the room to ensure productivity. That said, ideas and insight can come from anywhere in an organisation and this brainstorming technique can tap into the expertise of people outside of the room.
Start by asking participants to think of a colleague or peer outside the room and call them to get a perspective on the topic or question at hand. For remote teams, you can arrange quick calls or use Slack or other tools to get quick and useful feedback. After collecting input, bring the group back together to share and document insights. You’ll be surprised at how quickly and effectively you can get a wide variety of useful information!
Rapid Research #hyperisland #innovation #idea generation A simple exercise that complements exploratory, discursive, and creative workshops with insights and opinions from outside. Use this exercise when brainstorming ideas, developing a new product or service or creating a strategy or plan that will include others. Participants phone a co-worker and ask them questions relevant to the task. This quickly generates meaningful input from a range of “outside” perspectives. Often, participants will be surprised at how simple it was to solicit this input and how valuable it is to the process.
Lightning Demos
No idea is wholly original. Brainstorming is all about taking existing ideas and learning from others while also bringing our own insights to the table.
With this activity, you and your group will look for inspiration from how other organizations, products or thought leaders have solved or approached the problem or topic at hand. Invite participants to spend a little time gathering 2-3 examples before then presenting ideas back to the group. By the end of the exercise, you’ll have a set of ideas you can use as the basis for further discussion or idea development.
If you’re working online, collect demos in an online whiteboard and even explore the possibility of gathering inspiration before the workshop if your team has a busy schedule.
Lightning Demos #design sprint #innovation #idea generation This is an exercise to inspire your team with products or services that they think they can use as inspiration for their concepts in the next phases of their design sprints.
The Medici Effect
Great ideas can often come from sources outside of your own industry or field. The Medici Effect is inspired by Frans Johansson’s book The Medici Effect, which explores how game-changing ideas and breakthroughs can occur when concepts and ideas from one area are applied to another and used as the basis for innovation.
In this exercise, invite participants to find examples of how individuals from other fields have achieved their goals and come up with great ideas. Think of successful scientists, creatives, business owners, musicians, entrepreneurs, educators etc. have found success and what inspiration you and your team might take from them. If working online, encourage participants to include images, links and quotes so you can create an inspiration wall for further exploration of the problem you are trying to solve!
Brainstorming session templates
Are you looking to run a workshop or meeting where you need a complete group process to come up with ideas and turn those into actions?
Check out the brainstorming session templates below to see how to build upon an initial brainstorming session with appropriate idea selection and prioritization tools to arrive at sound group decisions.!
Ideation Workshop
In this one-day workshop template, follow an entire ideation process from start to finish, going from brainstorming and idea generation through to idea development and pitching. Tap into concepts such as disruptive cases, future tech & trends and opposite thinking to create innovative ideas and empower your team!
One Hour Brain Sprint
Have imited time for group brainstorming? Try the One Hour Brain Sprint to generate ideas quickly and effectively, all while avoiding unproductive discussions and the pitfalls of some brainstorming approaches.
One-hour Brain Sprint
Remote Problem Solving Workshop
Want to solve problems with your remote team? This virtual workshop template includes several stages of ideation and development and provides a great example of how you might utilize lightning demos and research as a basis for experimental ideas and solutions.
Remote problem solving workshop
What are the benefits of group brainstorming ?
While the primary measure of success for a brainstorming workshop will be the quantity and quality of ideas generated, the benefits of this kind of session can go much further.
Establishing an ideation mindset and encouraging creative thinking will benefit your organization in the long term, and finding new ways to push your team in the direction of generating effective ideas has positive effects for your whole organization. Let’s see some of the benefits that can come from bringing team members together for a brainstorming session.
Encourage creativity
Creative games and exercises can yield instant results when it comes to creatively engaging a team and generating ideas but beyond that, regular brainstorming can help participants be more creative in their regular work and find methods of finding new ideas and solutions that work for them. Being creative is a wonderful way to engage a group and getting out of a regular workflow can be the key that unlocks innovation.
Inclusive, easy-to-understand activities
Brainstorming is a simple group activity that is easy to understand and contribute to. Whatever skill level or competency a person has, the first stage of the idea generation process is something that can be involved in with little overhead or difficulty. This can have massive value in helping a team come together toward a shared goal in an inclusive and simple way!
Diverse ideas
Relying on certain teams or individuals to generate ideas alone can lead to stagnation. By pooling together a diverse group of people to contribute to generating and developing ideas, brainstorming can be a great way to find innovative approaches and diverse ways of thinking. Every point of view you bring to the table is another way of approaching the issue and the results generated by diverse groups are often more robust and multi-facted than those made in a silo.
Quantity of ideas
When it comes to brainstorming techniques, quantity often comes before quality. In order to find great ideas, a group first needs to flush out as many ideas as possible and share before moving onto idea development. The best brainstorming exercises encourage the creation of large amounts of ideas in a short period of time, providing a great foundation for the next steps!
Get past creative blocks
Problem solving or idea generation can go around in circles if a team isn’t given the freedom to think creatively and approach things from a new angle. Brainstorming methods like those featured here are great ways to unblock a team’s creative and find new ways to approach stalled conversations.
Improve team morale
Brainstorm sessions are often fun and energetic by their nature, and games and exercises that focus on idea generation allow for everyone to contribute and feel heard as part of their team. These kinds of idea generation activities can really help bring a team together and improve team morale too – everyone wants to take part in developing new ideas and being creative!
Get project buy-in
Involving participants across departments and specialties early in the process by inviting them to contribute to generating and developing ideas can not only lead to great ideas but also ensure that a project is followed through on. Get buy-in early by involving stakeholders in early brainstorming sessions and help that creative energy continue throughout your project!
Kickstart projects with energy
The opening stages of a project can determine the tone for the rest of it, and by kicking off your projects with a fun, energetic brainstorming workshop, you can ensure everyone is energised for the work ahead. Try creative games to help your team approach the project with a sense of creativity and experimentation and use brainstorming techniques that see proven results to help move a team forward effectively.
Brainstorming sessions made simple
An effective brainstorming session means creating a balanced agenda of activities and group discussions while keeping everyone engaged.
With SessionLab, you drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your step-by-step agenda.
Your session timing adjusts automatically as you make changes and when you’re done, you can share a beautiful printout with your colleagues and participants.
Explore how facilitators use SessionLab to design effective workshops that create results or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
Brainstorming can be simple or complex, visual or virtual, but whatever method you choose to use, the results should be the same – great ideas. Finding new ways to facilitate innovation is something we’re passionate about here at SessionLab, and we hope you find the above brainstorming techniques useful!
Did we miss anything? Are there any great brainstorming or idea generation methods you’d like to add? We’d love to hear from you in the comments.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of great workshop tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your life easier and run better workshops and meetings. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
5 brainstorming techniques for efficient problem-solving
Executive Summary:
There are plenty of advantages that come with efficient problem-solving, such as quicker decision-making, overcoming obstacles, gaining a competitive edge, and generating business growth. So, it’s pretty clear that problem-solving is crucial for businesses, and effective brainstorming techniques are vital when it comes to achieving it.
Brainstorming is a method used by individuals or groups to generate innovative ideas or solutions for a specific issue. It encourages free thinking and unrestricted sharing of thoughts, promoting a creative and collaborative atmosphere. Yet, at the end of the day, brainstorming is only part of problem-solving; they aren’t the same thing and here are three reasons why:
- Brainstorm focuses on generating ideas, while problem-solving involves analyzing andimplementing solutions.
- Brainstorming is informal and spontaneous, encouraging creativity and diverse opinions, whereas problem-solving follows a systematic and structured method whereby the outcome is a solution.
- Brainstorming produces multiple ideas, while problem-solving simply seeks one practical and effective solution.
So, as you’re probably realizing, brainstorming is only the starting point for problem-solving. During brainstorming sessions, a wide range of ideas and perspectives are generated. These ideas are then evaluated and selected during the problem-solving phase of the process. By incorporating diverse ideas, problem-solving becomes more innovative and creative, leading to more effective solutions.
To help you reach your goals for efficient problem-solving, here are five examples of brainstorming techniques that you can implement in your company:
- Team Relay : small groups share and build on ideas to foster creativity and initiate new projects.
- Reverse Brainstorming: generating ideas that exacerbate the problem to find unconventional, out-of-the-box solutions.
- Focus Group: small group discussions to generate suggestions and ideas for problem-solving.
- Crazy-8 : fast-paced brainstorming technique to generate ideas within 8 minutes.
- 1-2-4-All: individual and group idea generation to facilitate teamwork and quick idea generation.
If you run a business, you should know one thing.
You’re inevitably going to be faced with challenges.
While no one likes to talk about when things go wrong, there’s no denying that it happens pretty regularly in the world of business. There are always going to be problems and challenges to overcome. But instead of becoming sitting ducks for these challenges, you’ll gain the upper hand if you know how to solve these problems… and how to solve them fast !
Quick problem-solving has many advantages, including quick decision-making , overcoming obstacles, a competitive edge over others , business success/growth, among many more.
That said, all the benefits look great, but there’s one underlying question: how can you solve your company’s problems fast? The answer lies in the concept of efficient brainstorming techniques .
In this article, you’ll find a step-by-step guide, telling you all you need to know about brainstorming to make problem-solving decisions more efficiently, boosting your company's success and promoting efficient teamwork .
Key concepts
What is problem-solving.
Problem-solving is a process that seeks to find solutions to problems or challenges. It includes a series of steps:
- Examining the problem
- Identifying potential solutions
- Assessing them
- And then choosing the optimal solution
But most importantly, you should know that problem-solving follows a structured methodology . It combines critical thinking, creativity, and decision-making abilities , all to reach the goal of a straightforward solution to problems.
Now that that’s sorted, let’s talk about brainstorming .
What is brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a method used by individuals or groups to generate multiple inventive ideas or solutions for a particular issue or subject. The whole concept is based on a cooperative effort and an approach that prompts you and your team members to think freely, articulating any thoughts you have without restriction.
This process aims to build a creative and encouraging atmosphere , where everyone within your company can expand each another's ideas to collaboratively come to creative solutions.
It takes the pressure to come up with one ultimate solution, and shares it out between everyone on the team – as they say, “a problem shared is a problem halved” and the same notion applies here!
You can skip the next section if you’re already confident in differentiating between the two concepts of brainstorming and problem-solving . However, plenty of people tend to mix the two up given their similarities. So, the next section focuses on the differences between them.
What are the differences between problem-solving and brainstorming?
There are three key differences between problem-solving and brainstorming, but that doesn’t mean that you can’t use them in close connection. After this section, we’ll cover how the two concepts work hand-in-hand, but in order to combine them successfully, you also need to understand each of them individually .
The first difference is the focus or the objective . Aside from the fact that brainstorming is simply an initial stage within the problem-solving process, it also has a different objective. The goal of brainstorming techniques is to simply generate ideas. In this phase, there’s no evaluation of their feasibility or efficiency - the goal is simply to come up with as many ideas as possible for solving the problem in question.
Conversely, problem-solving is a more complex process. It entails the analysis of the problem, the evaluation of potential solutions, and the selection of the most suitable way to implement it. It revolves around identifying the best solution from the numerous ideas generated through the brainstorming process. The goal of problem-solving is not to generate ideas, but rather to find the ones that will solve the problem.
Another difference between the two can be found in the approach by which the process is conducted . Brainstorming adopts a more informal approach as participants are encouraged to think freely, to share ideas spontaneously , and to build on each other's suggestions. Of course, there is a need for structure, but there are no boundaries for efficient teamwork.
Then, we have the difference in the emphasis on encouraging creativity and a range of opinions , which isn’t so much the case in problem-solving. The problem-solving process adheres to a systematic and structured methodology, including problem identification, analysis, solution evaluation, and implementation. It relies on an established structure that can guarantee a solution.
The last of the three differences lies in the result — or the outcome, as we often refer to it. Brainstorming sessions produce so many ideas, as they aim to drum up as many options through different creative thinking approaches that can then be further explored. For problem-solving, you’re only looking for one practical and effective solution to the problem.
The success of a problem-solving process doesn’t just depend on how many ideas you can come up with, but rather depends on whether the identified solution is able to adequately address the issue and achieve the desired results.
If you’ve kept up this far, you’ve probably started to realize that the two can work hand-in-hand.
How can brainstorming and problem-solving be complementary for efficient teamwork?
You already know that a brainstorming session is the starting point for a problem-solving process, but that’s not all that there is to it.
You and your team members can generate various ideas, approaches, and perspectives during the brainstorming phase. This uninhibited flow of ideas helps expand everyone’s thinking and thought processes , and to explore multiple potential solutions.
Once the brainstorming phase is complete, you can transition into problem-solving mode . This is when you and your team can evaluate the ideas generated during brainstorming and select the most promising ones for further analysis and development. This evaluation ensures that the chosen ideas align with the problem at hand and are more likely to succeed.
By incorporating the diverse ideas generated during brainstorming, problem-solving becomes more creative and innovative . You and your team can explore unconventional approaches and perspectives that may only have been briefly considered during the brainstorming phase. The result? More effective and efficient solutions.
How can brainstorming help in problem-solving in teams of any size?
You might be thinking, ‘Haven’t we already gone over this?’, but the answer is, not really!
While we have explored the correlation between brainstorming and problem-solving, this section will look into the benefits of brainstorming and which ways it can be the best starting point to guarantee optimally efficient problem-solving process. Here are a few reasons as to why brainstorming is the ultimate solution for efficient problem-solving in your business.
A range of perspectives leading to a broader range of solutions
Brainstorming involves collecting input and ideas from different team members. So, the larger the team, the more diverse perspectives and experiences are likely to be offered up. This diversity can lead to a broader range of ideas and solutions as individuals approach problems from various angles .
Higher chance of unique ideas
Brainstorming encourages free thinking and is conducive to creativity. Purely down to numbers, larger teams have a higher chance of generating unique and innovative ideas. Team members' collective intelligence and creativity can result in unexpected, breakthrough solutions.
Collective intelligence and synergy
Brainstorming facilitates collaboration and encourages active participation from team members. When people come together to generate ideas, they can build on each other's suggestions, expand upon initial concepts, and create synergistic solutions. The whole team can benefit from the collective intelligence and creativity of everyone involved.
Brainstorming facilitates problem-understanding
In a larger team, different individuals bring diverse expertise and knowledge to the table, and brainstorming allows team members to share their insights and understanding of the problem, enabling a more comprehensive analysis. This broader perspective can lead to a deeper understanding of the problem and help uncover underlying factors that may have been previously overlooked.
Increased solution pool
With a larger team, there is a higher likelihood of generating a larger pool of potential solutions. Brainstorming enables the team to explore a wide range of ideas, even if some may initially seem unconventional or unlikely. A larger solution pool enhances the chances of finding an optimal and effective solution .
Increased motivation to find a solution through team accountability
When team members are actively involved in brainstorming sessions, they feel a sense of accountability and engagement to the problem-solving mission. In larger teams, more individuals have the opportunity to contribute and to be heard, leading to higher engagement levels and boosting motivation to find a solution.
Higher chances of making a decision
Brainstorming also helps in narrowing down the options and selecting the most viable solutions . Larger teams can leverage their collective wisdom and diverse perspectives to evaluate and prioritize the ideas generated during brainstorming. This collaborative decision-making process increases the likelihood of selecting the best solution for the problem.
5 brainstorming methods that can help for efficient problem-solving – and how they do it
Team Relay involves working together in small groups to share ideas. It’s just like a relay race; instead of passing on the baton, you pass and build on ideas. Everyone takes turns to put their two cents in, and the ideas continue to evolve within the group . This helps you to work with your team members and come up with lots of creative ideas.
Team Relay is best for teams of about 12 participants , and this method helps you find new ideas by bouncing off what the team says. You can identify and initiate new projects by working as a cohesive team, capitalizing on every idea collectively and elevating your thinking powe r to new heights. If you want to kick things off with the Team Relay method, the Klaxoon visual platform has a readymade template for this brainstorming technique that you can use.
Reverse Brainstorming
Reverse brainstorming is a technique where, instead of generating ideas to solve a problem, you focus on creating ideas that will make the problem worse or that will cause the problem. In other words, you’ll turn the problem upside down to define the worst-case scenario. So, how does this help solve the problem?
This excellent brainstorming tool can be used with your team at the start of a project or when you're stuck at a crossroads with a problem. It helps you t hink outside the box and unleash your imagination . Then, just like magic, the solutions will start to appear on their own! Give this tool a go, and try this template .
Focus group
A focus group is a small group of people (about 6 to 12 participants) who have been selected to meet up and talk or share ideas about a specific problem (strategic development, marketing positioning, etc.).
This selected team works together to generate thoughts and suggestions to help solve the problem or develop new ideas. You can either conduct a qualitative survey on a concept, product, or service, or you can ask the participants to fill in this ready-to-use template .
Crazy 8 is a pretty fast-paced, dynamic technique, so we’ll try to keep up the pace and explain it concisely.
This is a unique strategy that allows you to brainstorm with your team with a key element… speed ! While some brainstorming techniques could simply waste time and drum up an excessive volume of sub-par or irrelevant ideas, this method is all about eyes on the prize, full steam ahead.
With the Crazy 8 methodology, you can generate new ideas as a team in less than 8 minutes ! If you want to know more about this unique technique, head over to the this Klaxoon template .
As the last of the five, we are introducing you to a concept that has proven to be very effective. The 1-2-4-All method is like regular brainstorming but in several steps:
- First, everyone thinks on their own;
- Then, they share their ideas in bigger groups (in pairs, then in groups of 4, and then with everyone).
The goal is to help your team come up with ideas together. With this method, everyone can first think independently , no matter how many people are in the group. Other people can't influence their ideas or make them doubt themselves, and in this uninhibited way, the ideas pile up quickly.
It makes it easier for both you, as the leader, and your team members, to contribute their ideas and progressively confirm their objectivity through the groups’ input. It's a relaxed and pressure-free way to get everyone involved.
Try ready-to-use brainstorming tools and resources
On the Klaxoon visual platform, we have tools that you can use with your team to lead more effective brainstorming sessions . We also provide ready-to-use templates for brainstorming that can be used in different ways for quick problem-solving.
Our visual tools are designed to promote efficient teamwork and collaboration, no matter what kind of business you have. So, if you want to boost your business, hone your problem-solving strategy, and refine your brainstorming techniques , check out our resources and see how the Klaxoon platform can help you.
.png)
Unlock your teamwork potential
Brainstorming: 24 Techniques for Effective Brainstorming [+ How-to]
Home » Brainstorming | 🕑
Gust de Backer
June 25, 2024.

👉🏻 Workshop / Keynote / Consultancy
Every company does brainstorming , but some companies are better at it than others….
So why is that?
I’m going to show you:
- What different brainstorming techniques there are.
- How to prioritize brainstorm ideas.
- And how to be creative during your brainstorming sessions.
Let’s start..
Table of Contents
What is brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a technique for working with a group to find creative ideas for a specific problem.
In short, brainstorming is a method to creatively solve a problem . In this, it is important that everyone has a good understanding of what the problem is in order for people to brainstorm accurate solutions.
Do’s and don’ts
| There is a clear problem-statement and everyone understands what the problem-statement means. | Cracking down on ideas or making fun of them. |
| Write down as many ideas as possible without regard to quality. | Don’t deviate too much from the problem. |
| Encourage wild and unconventional ideas. | Don’t force people to talk or participate in a brainstorm. |
| Combine and improve existing ideas. | Do the brainstorming in the morning, that way people still have enough focus. |
| Go into the brainstorm unbiased and open-minded. | |
| Make sure people can read up on the matter beforehand. | |
| Choose a facilitator to lead the brainstorm. | |
| Build on each other’s ideas. |
Why is brainstorming important?
Creative thinking shows us that there are multiple solutions to a problem and multiple ways to look at a problem.
People are often stuck in their ways of thinking because of the patterns they see, which is extremely bad for innovation.
Creative thinking helps to challenge our assumptions, discover new things, see from new perspectives and keep us mentally sharp.
24 brainstorming techniques
Brainstorming is not about the quality, but about the quantity of ideas.
You’re going to come up with as many ideas for a problem as possible, possibly with a group of people, for a set amount of time.
There are 24 methods you can use to make brainstorming more effective:
1. Brainwriting / Purge
Each member of the group has a certain amount of time to write down all his/her ideas. This has two main advantages:
- Introverts get a chance to share their ideas.
- It ensures that no one or two ideas dominate the brainstorming.
The result is a wide range of ideas that would not have surfaced if a few ideas had been discussed from the beginning.
2. The 5 Why’s Analysis
The 5 why’s analysis has become popular because Toyota used it as a standard process for root-cause analysis.
By asking “why?” 5 times in response to an answer you will get to the root of the problem or solution which allows for a broader perspective and better dialogue.
3. Starbursting
The starbursting technique pushes you to think about the who, what, where, when, why and how of an idea. Place your idea or problem in the center of the star diagram and at the ends put the questions:

4. Mind mapping
You place your problem or idea in the center of the board and start adding to it with new parts:
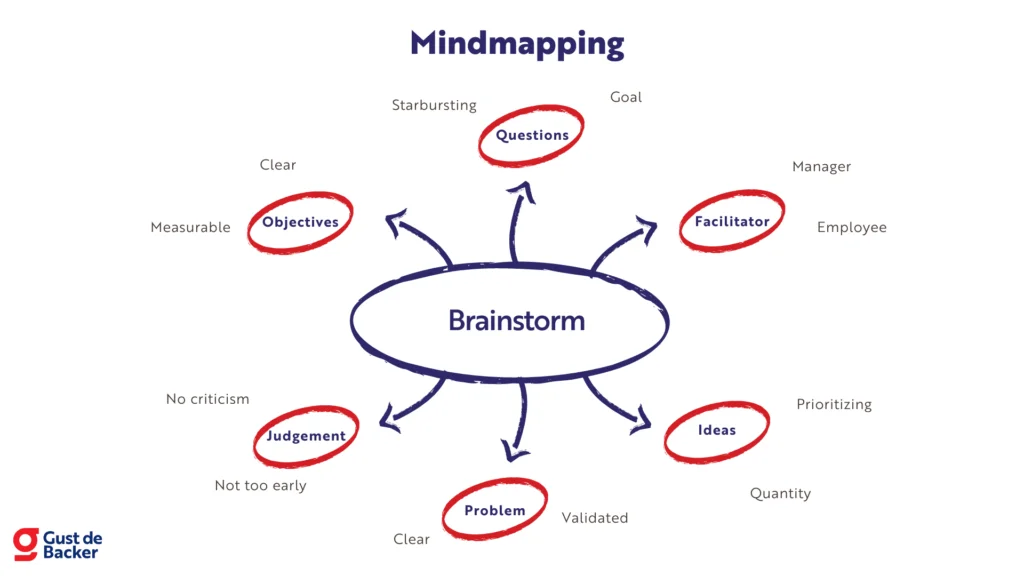
This also directly ensures that there is structure and that everything is broken down into certain topics.
5. Rolestorming
Try to imagine yourself as another person, it may be someone familiar or someone you know from your immediate environment.
If you can imagine yourself to be another person, ask yourself again how that would solve your problem?
6. Gap filling
See what situation you are in now (ready state) and see where you want to go (target state). Then ask yourself the question, how do we go from the ready state to the target state? What is needed for that?
The gap filling way is a good brainstorming technique to get from A to B.
7. Brain-netting
Using online software, write down ideas that belong to a particular problem or issue.
This is especially useful in preparation for a brainstorm so that people have enough time in advance to think about possible solutions without a lot of email traffic.
8. Round robin brainstorming
In round robin brainstorming, there is one person responsible for bringing up a question or several questions…
In this process, everyone must answer one at a time. In doing so, no feedback may be given or a second idea shared until everyone has shared his or her idea.
This brainstorming technique is ideal for medium to large teams where there are introverted team members or where there is a poor balance of creative input.
Tip : If someone shares an idea that has already been, give that person time to come up with a new idea.
9. Rapid ideation
Parkinson’s law shows us that we spend as much time on our work as we have available
Putting a time limit on brainstorming can increase the quality of the brainstorm. This allows team managers to maximize productivity and results.
Especially for teams with little time, who have little desire for meetings, or who are easily distracted, Rapid Ideation can be a good brainstorming technique.
10. Reverse brainstorming
Brainstorming sessions are often aimed at solving a problem. Reverse brainstorming sessions are aimed at causing problems.
Instead of asking “how can we solve this problem?” you ask “how can we make [problem] happen? From the answers you get, you can start to find solutions to possible problems that a concept or idea might pose.
Thinking of problems first ensures that the team then has a better perspective in solving the problems.
11. Stepladder brainstorming
In stepladder brainstorming, a problem is presented to the group where all but one or two people must leave the room….
The one or two people must then share their ideas after which a third person may enter the room to share his or her ideas, then a fourth, then a fifth and that until everyone has been.
The advantage to this brainstorming technique is that it does not involve thinking as a group, but allows everyone to share their own individual unique ideas without being influenced by the group.
12. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is not directly a brainstorming technique, but it can provide additional perspective during brainstorming.
SWOT stands for:
- Strengths : what are the strengths?
- Weaknesses : what are the weaknesses?
- Opportunities : where do the opportunities lie?
- Threats : what are the threats?
The SWOT analysis can also be the basis of brainstorming on how to assess a concept.
13. Eidetic image method
In the Eidetic image method, the group starts by closing their eyes to illustrate the current product in their minds…
Then they can start discussing what it looks like, close their eyes again and start visualizing what an improved version would look like, what features it would contain, what color it is, how big it is, etc.
This brainstorming technique works best when improving an existing product or solution.
14. Change of scenery
If you are constantly brainstorming with the same people in the same space, it can feel like repetition, which is obviously not good for inspiration.
By regularly changing the scenery or space and perhaps also the team composition, it is possible to tap into new sources of inspiration.
15. Drivers analysis
In the drivers analysis brainstorming technique, you focus on the causes of a problem.
Ask yourself or your team of brainstormers, “What causes [problem]?” and then “What causes [answer previous question]?
The deeper you can go the more likely you are to find the root of a problem.
16. Collaborative brainwriting
With this method of brainstorming, there is no need to dedicate a specific session to it….
For example, a facilitator hangs up a large sheet in an office with a problem-statement and possibly already some brainstorming ideas and everyone can contribute ideas in his or her own time.
This way everyone can contribute anonymously, just make sure it is clear to everyone when the deadline is to contribute.
17. SCAMPER
The SCAMPER brainstorming technique helps brainstormers look at a problem from multiple perspectives, SCAMPER is an acronym that stands for:
- Substitute : evaluate what would happen if you swapped one facet or solution for another.
- Combine : evaluate what would happen if you combined one facet or solution with another.
- Adapt : assess what would happen if you placed one idea or solution in a different context.
- Modify : think about how you could change an idea or solution to make even more impact.
- Put to another use : think about how you could still use your idea in other ways.
- Eliminate : assess what can be removed from your idea or solution to make it simpler.
- Reverse effective : finally, you can look at how you can reorganize an idea to make it more effective.
During a brainstorm, it is helpful to use a SCAMPER template:

18. The idea napkin
The Idea Napkin brainstorming technique allows a broad topic to be broken down into tangible solutions.
Each brainstormer has an ‘Idea Napkin’, on which they write one idea and an elevator pitch of that idea. They also write down who they are trying to solve a problem for and what problem they are solving.
When everything is written down, the idea is for everyone to present their ‘Idea Napkin’ to the others, then all ideas are prioritized on an impact and effort matrix to determine which ideas are worthwhile:

19. 6 thinking hats
In the 6 thinking hats brainstorming technique, you need at least 6 people who are going to wear thinking hats. These different ‘thinking hats’ are going to allow them to look at a problem or idea from one specific angle.
There are 6 different thinking hats:
- Blue hat (Conductor’s hat) : manage the decision process, ask for summaries and come to conclusions.
- Green hat (Creative hat) : the green hat comes up with creative ideas and thinks in terms of possibilities.
- Red hat (Hat for the heart) : go out of your feeling and instinct, you don’t necessarily have to think logically.
- Yellow hat (Optimist’s hat) : with the yellow hat you look at problems with an optimistic view, you see advantages in everything.
- Black hat (Judge’s hat) : the black hat is very critical and sees problems in everything, it is important to see risks and dangers quickly.
- White hat (Fact hat) : neutral and objective, shares lots of statistics and facts.
- + Royal hat (Owner hat) : guides the brainstorm, looking for the balance between subjectivity and objectivity.
This brainstorming technique is useful to get an overall picture of one or more ideas.
20. ‘What if’ brainstorming
The ‘What if’ brainstorming technique is a good technique to bring out all possible solutions to a problem.
By asking questions like “What if this problem occurred in the 1800s?” or “What if our president would have to solve this issue?”.
By approaching it this way you can look at the problem and the solutions from different angles.
21. Random word picker
You pick a random word or animal and start brainstorming about how the word or the characteristics of the animal can help you solve your problem.
This brainstorming technique is really about getting new ideas in a creative way.
22. Storyboarding
Storyboarding is a brainstorming technique where you start sketching the problem and possible solutions. In doing so, you are going to visualize different parts of the problem and the solution which works extremely well for physical challenges.
23. Wishing
You start by wishing for something ‘I wish our company would make 10 million euros in profit’ and then you start thinking about how you can achieve this.
Try to set really ambitious goals, this ensures that you start thinking bigger and you will encounter other problems and solutions.
24. Crazy eights
In the crazy eights brainstorming technique, each participant is given a template with 8 empty boxes. The timer is set for 8 minutes during which time each participant must fill the boxes with 8 sketches of possible ideas. Repeat this process so that they can build on each other’s ideas.
How do you prioritize ideas?
There are several ways to prioritize ideas:
1. Dotmocracy
To prioritize ideas, it is possible to give all participants X number of stickers that they can divide on the ideas they have.
You can be creative with this by handing out different colored stickers to also vote on ideas that absolutely should not be implemented or perhaps an order in the ideas based on the colors.
2. How Now Wow
The How Now Wow technique is more about categorizing ideas based on how unique they are and how easy they are to accomplish.
After a team has written down ideas, they can be prioritized in the How Now Wow matrix:

- How ideas : original but difficult to implement.
- Now ideas : unoriginal and easy to execute.
- Wow ideas : unique ideas that are easy to execute.
Obviously, you want to have as many “Wow” ideas as possible because they are unique from the competition.
3. Impact-Effort Matrix
The impact-effort matrix allows you to determine the ratio of effort to results and then prioritize the best ideas:

You can write down where an idea belongs on the matrix or you can give points to ideas and use those points to determine where an idea will be placed.
4. I.C.E. / P.I.E.
ICE and PIE are well-known prioritization frameworks; they are acronyms that stand for…
- Impact : what is the potential impact if the idea works?
- Confidence : how confident are we that the idea will work?
- Ease : how easy is it to set up this idea?
- Potential : how potential is this solution to our problem?
- Importance : how important do we think solving this problem is?
- Ease : how easy is it to implement this solution?
| 6 | 7 | 9 | 7,3 | |
| 2 | 6 | 10 | 6 |
From these scores you can get an average, it is also possible to add a multiplier to certain parts of ICE or PIE that you think are important.
5. Feasibility, Desirability and Viability Scorecard
These 3 pillars are topics on which you can rank an idea:
- Feasibility : is it actually achievable?
- Desirability : how much would we like this solution?
- Viability : how confident are we that this will work?
This is very similar to the ICE / PIE framework, but the questioning changes a little bit.
MoSCoW is a very well known prioritization framework, it is widely used to set up requirements for a particular thing and prioritize them.
MoSCoW is an acronym that stands for:
- Must have : What really needs to be in it?
- Should have : what should actually be included?
- Could have : nice to have, is nice to add, but has no priority.
- Would have / Will not have : we’re not going to do anything with this for now.
7. Multi-criteria Decision Making
In multi-criteria decision making, you write down what you think is important about a solution and prioritize different ideas based on that:
| Idea 1 | Idea 2 | |
| Cost | 3 | 5 |
| Scalability | 5 | 7 |
| Maintenance | 2 | 2 |
| Support | 8 | 3 |
| Average | 4,5 | 4,3 |
8. The Value Matrix
Also called the Value and Effort matrix, this involves weighing the costs against the benefits:

How to brainstorm effectively?
How do you set up the brainstorm effectively?
The better the problem statement is the better the brainstorming will go. It is easier to focus ideas on a situation when that situation is enormously clear.
By just starting to do anything you will probably not find the desired solution. Make sure you have a clear agenda with times when you want to do something exactly. It is also important to make clear in advance what the desired end result of the brainstorm is.
Each brainstorming technique fits a different type of situation, evaluate which brainstorming techniques exist and choose some to come up with solutions from multiple angles.
By just talking and thinking about ideas a lot will be lost, document the ideas so they can be looked back at later.
Not every idea has the same potential to be used, therefore it is important to choose which ideas can be taken up, which ones will be interesting at a later date and which ones can be thrown in the garbage can.
Make sure you have time available in the coming period to start working on good ideas.
What is creativity in brainstorming?
Creativity is the ability to think outside of traditional ways and come up with new, original ideas, methods or objects.
It is often thought that the left part of the brain is for creativity and that the right part of the brain contains analytical ability:

In creativity, it is about the networks between the different parts in the brain. There are 3 types of networks that are important here:
- The executive attention network : allows you to maintain your attention and focus.
- The imagination network : allows you to daydream or imagine yourself in someone else’s shoes.
- The salience network : allows you to identify certain things based on old information stored in your brain.
A video that goes into some detail here:
What types of creative thinking are there?
At work, there are several types of creative thinking you may encounter:
- Divergent Thinking : a brainstorming session where you write down as many solutions as you can think of.
- Convergent Thinking : gathering facts and finding the most used and complete solution to the problem.
- Inspirational Thinking : focus on the best-case scenario to find a new solution to a problem.
- Lateral Thinking : reorganize information to come up with creative solutions to move from the ready state to the target state.
- Aesthetic Thinking : solutions that we actually like, with a focus on structure, knowledge, composition, color and shape.
What is critical thinking in brainstorming?
A critical thinker does not simply assume ideas and assumptions, but will always be looking for more ideas, arguments and insights to get the full picture.
Critical thinkers will identify, analyze and solve problems in a systematic way rather than thinking from intuition or instinct.
A critical thinker is able to:
- Make the connection between ideas and in them determine how important and relevant arguments and ideas are.
- Recognize, build and evaluate arguments.
- Find errors and inconsistencies in reasoning.
- To approach problems in a consistent and systematic way.
- Reflect on his own assumptions, beliefs and values.
Discover your creativity
You are now armed with knowledge to set up the best creative brainstorming sessions….
I’m curious, what do you think is the best brainstorming technique?
Let me know in a comment.
P.S. Want more help? Send an email to [email protected]
Frequently asked questions about brainstorming
A design sprint is a limited-time process that uses design thinking. The goal is to find an answer to a critical business question or a specific problem within that limited timeframe.
During a design sprint, design thinking is used.
To lead a brainstorm session it is important that you understand the problem, that you set a clear agenda, that you use the right brainstorm techniques and that you stimulate new ideas and don’t criticize ‘bad’ ideas.
First come up with a clear problem-statement, then choose matching brainstorm techniques, plan a clear agenda and at the end prioritize the outcomes of the brainstorm session.
There should be a purpose for the brainstorm, it should be with others, you should stimulate each other’s ideas, there should be no criticism of ideas, and make sure there is enough creativity.
Before brainstorming, the right questions should be asked, this can be done using Starbursting. Starbursting asks questions such as: how, what, where, when, who and why.

I try to help business surpass their growth ceiling with my content.
Sounds interesting?
Let’s connect on LinkedIn!
Business Strategy | Change Management | Digital Marketing | Growth Hacking | Marketing and Sales | Organizational Culture | Scrum | Team Management
Gust’s Must-Reads 👇🏼
- TAM SAM SOM
- Value Proposition
- Decision Making Unit
- Product-Market Fit
- North Star Metric
- Market Research
- Customer Development
- Growth Hacking
- Brand Identity
- Customer Journey
- Account-Based Marketing
![brainstorming method of problem solving Customer Journey Map (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Customer-Journey-Map.png)
Customer Journey Map (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]
The Customer Journey is the process your customers go through with your company. This then covers the first to last interaction someone has with your company. Many companies do not have a map of how their customers orient, what they care about or when the company...
![brainstorming method of problem solving Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/151-Cognitive-Biases.png)
Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]
Cognitive biases, there are so many of them... Decisions we make based on emotion, cognitive biases are irrational 'errors' that are programmed into people's brains and affect the decision-making process. Plenty of different articles have been written and an entire...

What is Growth Hacking? (2024): Best Strategy to Grow Your Business
The popularity of Growth Hacking is increasing rapidly, but what is Growth Hacking? Many companies lack a clear strategy for achieving growth and don't know how to manage a (marketing) team in it... Many marketers and entrepreneurs find Growth Hacking the best way to...
Thank you, Khaled!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment

Experiment Canvas
You have successfully subscribed, proven (marketing) management tactics 12x / year.
✔ Discover the secrets of successful companies.
✔ Make better decisions and avoid bad choices.
✔ Never miss out on any growth for your company.
Function Owner C-Level Manager Marketer Sales Student
Thank you! You have successfully subscribed.

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
8 brainstorming techniques to harness the power of teamwork

Jump to section
What is brainstorming?
4 benefits of brainstorming, what are the best brainstorming techniques, 5 steps for brainstorming, what could go wrong, brainstorm your way to team success, empower your team with brainstorming techniques.
Coming up with a solution to a problem always feels like a win. Especially when it’s productive teamwork that has helped you achieve your team goals .
But sometimes, you hit a wall in the problem-solving process. It feels like your team is going around in circles, discussing the same thing.
This kind of mental block isn’t uncommon. And it’s the kind of situation that calls for a group brainstorming session.
Although simple, brainstorming can be a powerful tool for the creation of new ideas . This is especially true when you and your team need to get your creative juices flowing .
Ready to learn about some new and creative brainstorming techniques? Read on to discover how the right brainstorming session can boost your team’s productivity .
Brainstorming is a model for extracting fresh ideas from a group of people.
It’s a method used by everyone from school children to executives. It generates inspiration and imagination in the problem-solving process.
During a brainstorming session, a group of team members comes together, either as equal co-contributors or under the supervision of a facilitator.

The fundamental principle behind different types of brainstorming techniques is that no idea is too wild or too unrealistic. This allows the team to think beyond the structured boundaries of the workplace and truly tap into unique creative potential .
Instead of coming up with a ready-made, perfectly thought-out plan from the get-go, team members are encouraged to think big and then tailor to fit.
Removing conceptual boundaries opens up the potential for the team to be bold and innovative during their collaboration.
Brainstorming has numerous benefits for both individuals and the team.
Let’s take a look at some of the many advantages you can expect from using brainstorming techniques.
1. Promotes teamwork
When left to their own devices, team members tend to become individualistic and wrapped up in their own preferred methods and ideas. They might also be driven by ego . As any effective leader will know, this approach is not conducive to innovation.
It takes a team of dedicated minds to come up with truly unique solutions to problems. All of whom can contribute something slightly different to the process.
The best brainstorming techniques get everyone together in a room with the sole purpose of collaborating.
2. Encourages creative ideas
When conceptualizing solutions to a specific problem, it is easy to get stuck in a mental rut that bears no creative fruit.
The process of brainstorming seeks to actively remove the limitations and boundaries we set in our own minds.

This encourages team members to think outside the lines and put their creative thinking hats on. While not every idea conceived in this spirit will be feasible, there will undoubtedly be at least one or two that show promise.
3. Provides different perspectives
No matter how diligent or accomplished you might be in your field, you need to draw on the experiences and viewpoints of those around you. This helps to get a holistic picture of the needs you are trying to meet.
Bringing people together in the spirit of problem-solving invites input from different walks of life . This ensures that your ideas hold strong from all angles.
4. Generates many ideas in a short amount of time
Throwing creatives in a room together and removing conceptual boundaries might sound like a chaotic way to spend an afternoon. But by the end of it, you are guaranteed to have a whiteboard full of new ideas or directions to pursue.
Again, not all of them will be pure gold, but at least a few of them are bound to show promise.
The number of brainstorming methods to choose from can seem overwhelming. Let’s look at some of the most effective brainstorming techniques for rapid ideation and creative solutions.
1. Mind mapping
Mind mapping is probably one of the most well-known brainstorming techniques. It helps teams visually represent a hierarchy of ideas and how they are interconnected. Generally, you start with a central ‘umbrella’ term and break it down into smaller components.
If you’re unsure where to begin, use a mind map template to help your team visualize the process.

Drawing a mind map helps all team members keep track of the problem’s structure. It also helps them think coherently around a common thread and see theoretical connections in a concrete way.
Studies have shown that mind mapping helps people retain and work with information more effectively.
2. Gap filling
Gap filling is a useful tool in product development. It involves using a timeline to plot past and future actions or realities in order to identify the best course of action for the present. Starting with the past refreshes the mind on how you got where you are and what needs you are trying to meet.
Filling in the future helps you and your team decide on a common goal — what you want reality to look like after your intervention. This way, you can make logical and creative connections between the needs of the past and the goals of the future .
3. Brainwriting
Brainwriting is an effective method for getting ideas out of all members of the group.
Instead of everyone trying to shout over each other, team members have a few minutes to privately write down their ideas on a piece of paper or post-it.
When everyone is done, the group can discuss the raw ideas one by one. This harnesses the potential of each individual and encourages introverts to speak up and contribute .
4. SWOT analysis
‘SWOT’ stands for ‘strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.’
Each category is allocated one quadrant of a page. The team can then break down the elements of an idea into these categories and weigh the pros against the cons to see if it is worthwhile.
5. Rolestorming
Rolestorming is a relatively unusual type of brainstorming technique. It combines role-playing and creative collaboration.
The idea is to help team members overcome the shyness and sensitivity behind their contributions. This is done by presenting ideas from another’s perspective. It also forces the team to consider how important figures might respond to their ideas.
For instance, somebody could role-play a customer or client. This will help them understand their clients’ needs better by adopting their point of view.
6. Starbursting
The structure of the starbursting technique is simple. It focuses on identifying the right questions before trying to come up with solutions.
In this technique, a six-pointed star represents six root questions: who, what, when, where, why, and how? From there, more detailed questions are developed that guide the team in unique directions.
7. The five whys
Although it seems simple, this technique is surprisingly effective at locating the root of a problem. It draws on the power of intellectual curiosity . The idea is to start with the most obvious, surface-level problem and ask why it is a problem.
Establish a factual, robust answer to this, and then repeat the process with the secondary problem. This method helps burrow through the various layers of an issue and eventually reach the underlying root cause.
8. Stop-and-go-brainstorming
This method involves rapid switching between modes of thinking. For a select period of time (usually no longer than ten minutes), the team will focus on idea generation.
After, they will evaluate those ideas and give feedback to determine their potential. Some teams find that this method helps avoid creative fatigue. It gives the brain a chance to exercise different cognitive skills instead of overusing one.
Ready to come up with some great new ideas? Here are the steps to follow for a productive brainstorming session.
1. Prepare the group
The loose structure of most creative brainstorming techniques is essential to their success. However, it can lead to chaos if the group isn’t managed properly .
Take a few minutes to explain the workflow and purpose of the gathering. Outline exactly what you expect from the group for the duration of the exercise.
2. Present the problem or goal
The next step is to familiarize the team with the problem you’re trying to address or the goal you’re trying to achieve .
Give them a foundational understanding of the issue. Inform them of any past attempts to grapple with it and tell them why it’s important.
3. Capture all ideas
Depending on the technique you’ve chosen, make sure all necessary resources are provided for the team to record ideas.

The best brainstorming techniques are the ones that get ideas on paper, no matter how broad they are. Other tools to capture ideas are whiteboards, notepads, pens, markers, and sticky notes.
Empower your team by giving them the tools they need to get their thoughts down in print.
4. Share and discuss ideas
All ideas should be given their time in the spotlight. Work through each one methodically. Give everyone a chance to speak and contribute. Listen to everyone’s ideas and record changes or revisions as they come up. Just like there are different ways to learn, there are also different ways to listen .
Encourage constructive criticism . Remind the team that 90% of raw ideas will be discarded or revised before they can be implemented. There is no need to feel defensive or spiteful if their ideas are dismissed or criticized.
5. Make an action plan
This is the final step. Once all your ideas have been explored and fleshed out, identify the strongest ones. Take all suggestions into account, and convert them into actionable tasks to be delegated to the right person.
The agile methodology is a great method to help teams stay on task and measure progress. Have a look at our agile methodology guide for more on this popular type of project management.
As with any collaborative effort, brainstorming sometimes doesn’t go according to plan.
Here are some possible hiccups you could experience during the process and how to address them effectively.
1. Brainstorming session is dominated by one person
Sometimes, one or two people at work seem to always want to be the center of attention. Whenever the opportunity arises for them to take center stage, they do so, regardless of whether they are casting a shadow on someone else. This kind of toxic trait could be counterproductive for the brainstorming session.
This is where a skilled facilitator comes in handy. They know how to hold space gently and respectfully for everyone to contribute equally. This may involve asking someone to step back and stop talking over less assertive members of the team .
2. Ideas are criticized by others
Another common problem in brainstorming groups is the tendency of some people to be overly critical without suggesting alternative solutions. In some cases, gaslighting at work is used to belittle others and give them a constant negative narrative about their ideas.
It is important to clarify that constructive criticism and feedback need to be communicated with respect . Encourage team members to come up with suggestions for improving the idea that’s being criticized.
3. Lots of ideas are generated, but no action comes of it
Without eventual action, no number of brilliant ideas is helpful. Including a senior supervisor in the brainstorming session is a good way to combat a lack of action.

Once all the raw ideas have been broken down into actionable tasks, they can delegate responsibilities .
Here are six tips to help you facilitate a better brainstorming session with your team.
1. Encourage out-of-the-box thinking
This is the golden rule of all brainstorming techniques. Don’t limit the creativity of your team. In fact, encourage them to put concerns of practicality out of mind for the duration of the session.
It only takes one idea to revolutionize the way we think about certain problems.
2. Put a time limit on your session
Brainstorming involves dealing with loads of information on a surface level. This means it’s easy to get distracted by rabbit holes of conversation.
Giving your team a set window will prevent time wastage and keep them focused . If necessary, you can schedule a follow-up session to discuss important points that were missed.
Time blocking is an effective method to keep track of time during your brainstorming session. With this time management technique , the team focuses on a single task or a group of similar tasks within a set time block.
3. Guide the discussion
A skilled facilitator knows when to let the conversation flow and when to step in . If the discussion is drifting too far away from the task at hand, the facilitator must be able to bring the focus back gently but assertively.
Experienced facilitators should use the right management styles to guide the brainstorming session. For example, a democratic leadership style will ensure the facilitator is working closely with all team members and building rapport.
4. Focus on quality over quantity
While brainstorming will inevitably give rise to many ideas, not all of them will show merit or warrant further discussion. The facilitator should be able to guide team members into discussions that focus on developing the ideas with more potential and fewer obstacles.
5. Set ground rules
Even the best brainstorming techniques lead to sessions that get out of hand quickly without some basic guidelines.
The discussion should always be kept respectful and professional. Furthermore, irrelevant tangents and anecdotes should be avoided.
6. Recognize and reward input
Putting yourself out there by sharing an idea isn’t always easy, especially for more introverted members of the team. Basic psychology tells us that people will be more willing to contribute when their input is recognized and rewarded .
Acknowledge team members’ contributions and thank them for their participation. This will build confidence quickly and get the conversational momentum going.
Fostering effective collaboration and creativity in the workplace is no easy feat. But it's crucial for your business' success.
With more employees working from home , the brainstorming process can seem even more daunting. But with the right technology and remote working support , online brainstorming (or brain-netting) lets virtual teams brainstorm ideas in real-time.
There are plenty of group brainstorming techniques you and your team could try for your next session. It's just a matter of learning what works for you.
Get access to the most effective techniques by getting in touch with a BetterUp coach . Our robust coaching experience guides teams down the path to a more productive tomorrow.
Cultivate your creativity
Foster creativity and continuous learning with guidance from our certified Coaches.
Maggie Wooll, MBA
Maggie Wooll is a researcher, author, and speaker focused on the evolving future of work. Formerly the lead researcher at the Deloitte Center for the Edge, she holds a Bachelor of Science in Education from Princeton University and an MBA from the University of Virginia Darden School of Business. Maggie is passionate about creating better work and greater opportunities for all.
What’s convergent thinking? How to be a better problem-solver
How different learning styles make a difference at work, 8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems, social learning theory: bandura’s hypothesis (+ examples), 15 inspiring ted talks that just might change your life, how to implement peer to peer learning in the workplace, 6 ai prompt generator tools to boost your creativity, how divergent thinking can drive your creativity, the power of professional learning communities, how experiential learning encourages employees to own their learning, 6 ways to leverage ai for hyper-personalized corporate learning, how to develop critical thinking skills, how to make personalized learning work (and how not to), 6 chatgpt prompts to save time and boost productivity, top-down processing & how to avoid self-limiting behavior, why asynchronous learning is the key to successful upskilling, 18 excellent educational podcasts to fuel your love of learning, the benefits of microlearning: learn big, study small, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Book a Demo
Are you struggling to come up with innovative ideas or solutions? Look no further! In this article, we will explore various brainstorming techniques that can help you unlock your creativity and generate fresh perspectives. By utilizing these techniques, you can break free from the constraints of traditional thinking and tap into the limitless potential of your mind.
So get ready to unleash your imagination as we embark on a journey through various types of brainstorming that will revolutionize the way you think and generate ideas!
Brainstorming: Unleashing Creativity and Problem-Solving Potential
Brainstorming is a powerful technique used by individuals or teams to tackle problems, spur innovation, and generate fresh ideas for enhancing products, organizations, or strategies. Brainstorming can unlock creativity and solve complex challenges by following a structured process.
What is Brainstorming, You Ask?
Brainstorming is a collaborative approach that encourages participants to think freely, share ideas, and build upon each other’s contributions. It fosters an environment where no idea is deemed too outrageous or impractical, promoting a diverse range of perspectives and possibilities.
Three Steps of A Successful Brainstorming Session
Regardless of the chosen method, most brainstorming strategies involve three essential steps:
- Capture ideas: During this phase, participants generate and record as many ideas as possible without judgment or evaluation. The goal is to encourage a free flow of thoughts and maximize the number of suggestions.
- Discuss and critique the ideas: Once a substantial list of ideas has been generated, participants engage in a constructive discussion to examine and evaluate each suggestion. This step allows for clarification, expansion, and refinement of ideas through open communication.
- Choose which ideas to execute: Following the discussion and critique phase, participants collectively determine which ideas have the most potential for implementation. Selection criteria may include feasibility, impact, alignment with objectives, and resource availability.
The Ingredients for Effective Brainstorming
Every successful brainstorming session requires three fundamental elements:
- Individuals or groups: Brainstorming can be performed individually or in a group setting. Individual brainstorming allows for personal reflection and ideation, while group brainstorming harnesses the collective intelligence and diverse perspectives of multiple participants.
- A problem or opportunity: Brainstorming is initiated with a specific problem or opportunity in mind. It could range from addressing a technical issue in a product to finding innovative marketing strategies for a new business venture. Clearly defining the focus ensures a targeted and productive brainstorming session.
- Time: Sufficient time should be allocated to allow participants to engage in thorough idea generation, discussion, and evaluation. Rushing through the process may hinder creativity and limit the quality of the outcomes.
Common Challenges in Brainstorming Sessions and How to Overcome Them
Brainstorming sessions are meant to be a collaborative and dynamic process for generating ideas and solving problems. However, several factors can hinder the effectiveness of a brainstorm, preventing teams from maximizing their creative potential.
Here we explore some common challenges that can derail brainstorming sessions and offers strategies to overcome them.
Unbalanced Conversation
One prevalent issue in brainstorming sessions is when extroverted individuals or quick thinkers dominate the conversation, leaving little room for other team members to contribute. This lack of balance can stifle creativity and hinder the exploration of diverse perspectives.
The Anchoring Effect
The anchoring effect occurs when participants fixate on the initial ideas presented during a brainstorming session. This fixation can limit the generation of new ideas and prevent the team from exploring alternative possibilities.
Overcoming the anchoring effect is crucial for fostering a more expansive and innovative brainstorming environment.
Awkward Silence
A lack of preparation among participants can lead to awkward silence during brainstorming sessions, creating an unproductive atmosphere. Alternatively, the session may be cut short to alleviate the discomfort. These situations hinder the free flow of ideas and impede the overall progress of the session.
Disconnected Teams in Remote Settings
With the rise of remote work during the pandemic, brainstorming sessions have shifted to video conferencing platforms. However, this transition brings its own challenges, such as the difficulty of capturing the creative energy that arises from having everyone physically present in the same room.
Additionally, remote sessions can be prone to interruptions and communication issues, further hindering the brainstorming process.
14 Effective Brainstorming Techniques – Different Types of Brainstorming Explained

Associative Brainstorming
Associative brainstorming is a versatile technique that can be performed individually or in a group. By starting with a single word that captures the essence of an idea, participants jot down associated words that come to mind.
This process is most effective when the mind is allowed to roam freely, generating as many words as possible. The interplay of related words stimulates the brain to make new connections, fostering the emergence of fresh ideas.
The duration of the exercise can be tailored to suit preferences, ranging from 10 minutes to an hour.
Brainwriting: Unleashing Collective Creativity
Brainwriting is a collaborative brainstorming exercise that harnesses the collective creative potential of a team. The exercise begins with a team leader presenting a topic. Each team member writes down three ideas on a piece of paper, which is then passed to another member.
The process continues, with each subsequent participant building upon the ideas presented before them. Once completed, the team gathers to review and refine the generated ideas, discarding some and identifying others that inspire further exploration.
With additional brainstorming, average ideas can be transformed into extraordinary ones.
Freestorming: Capturing the Power of Uninhibited Thinking
Freestorming involves capturing every thought that comes to mind when contemplating an idea. In a quiet setting, individuals immerse themselves in free storming, noting down every relevant and irrelevant, good and bad idea in a notebook or on a computer.
This powerful technique allows for the uninhibited expression of “real and raw” ideas and encourages deep exploration, unveiling hidden possibilities waiting to be discovered.
Virtual Brainstorming: Overcoming Time and Space Barriers
Virtual brainstorming, also known as online brainstorming, has become increasingly popular as teams are often geographically dispersed. With a reliable internet connection, teams can gather on a centralized online platform to initiate and facilitate discussions.
Collaboration tools, such as OneThread , offer a seamless communication and collaboration experience, enabling teams to conduct brainstorming sessions through discussions and capture important insights in the notes section.
Virtual brainstorming eliminates the constraints of time and space, allowing for efficient idea generation.
Rolestorming: Embracing Empathy and Creativity
Rolestorming injects an element of fun and engagement into the brainstorming process. Instead of thinking from their own perspective, participants imagine themselves in someone else’s shoes, such as their boss, mentor, or even prominent figures like Warren Buffett , Steve Jobs, or Barack Obama.

This technique encourages participants to break free from their own limitations and inhibitions, fostering fresh ideas while retaining their authenticity. By adopting the mindset of influential individuals, rolestorming allows for unique insights and a glimpse into the world of the great thinkers.
Rapid Ideation
In this technique, everyone writes down as many ideas as possible within a set time before any ideas are discussed. This prevents premature dismissal of ideas and encourages the sharing of raw thoughts.
Figure Storming
This involves discussing how a well-known figure not present in the room would approach the problem. This can help the team approach the problem from a different perspective and encourages more creative sharing.
Eidetic Image Method
This visualization-based method involves using vivid mental images to build upon an existing design or idea. It’s particularly useful when the goal is to enhance an existing concept rather than reinvent it.
Online Brainstorming (Brain Netting)
This technique involves using a central location, such as a shared document or a chat platform, for team members to write down their ideas. It’s especially useful for remote teams and can help level the playing field.
Round-Robin Brainstorming
In this method, every member contributes one idea in turn. This ensures everyone gets to participate and all ideas are shared before moving on to the critique phase.
Step-Ladder Technique
This complex technique involves introducing team members one by one to the brainstorming session, allowing each person to share their ideas before learning about the ideas already discussed. This helps avoid undue influence from the first few ideas or the loudest voices.
Mind Mapping
Starting with one idea, the group draws lines connecting sub-ideas to the first one. This visual approach can be helpful for those who think visually.
Starbursting
This later-stage technique involves creating a six-point star around an idea, with each point representing a question: who, what, when, where, why, and how. This helps the team examine an idea from every angle.
Change of Scenery
Moving the brainstorming session to a different location can help stimulate new ideas. A new environment can help people think differently and come up with fresh ideas.
Benefits of Team Brainstorming: Enhancing Collaboration and Creativity
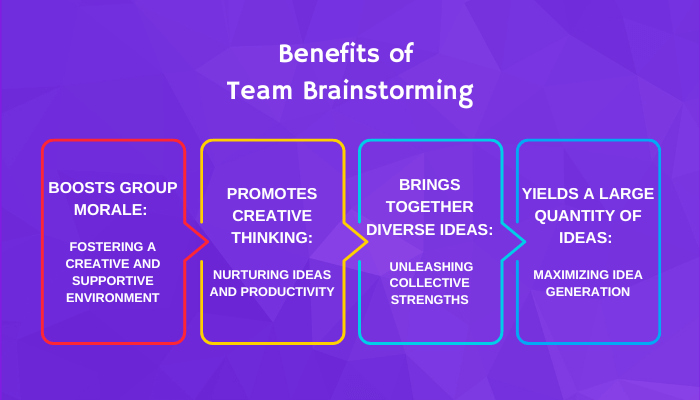
Boosts Group Morale: Fostering a Creative and Supportive Environment
Brainstorming as a team boosts group morale by creating a sense of unity and shared purpose. Collaborating in a creative and supportive setting allows teammates to engage face-to-face, strengthening team bonds.
To reap this benefit, it is crucial to withhold criticisms during the initial idea-capturing phase of the brainstorming process.
Promotes Creative Thinking: Nurturing Ideas and Productivity
Amidst the hustle and bustle of daily tasks, individuals often lack dedicated time for free-flowing idea generation, even in creative fields. Allocating specific time for unrestricted idea exploration without distractions is essential for maintaining creativity.
Furthermore, rallying individuals around a common topic or idea reduces isolation and can significantly enhance productivity. Unlike traditional meetings where preparedness is expected, brainstorms provide a space for half-baked ideas to be shared, serving as catalysts for new insights and building upon each other’s contributions.
Brings Together Diverse Ideas: Unleashing Collective Strengths
The collective brainstorming process surpasses the individual capabilities of team members. By bringing together diverse perspectives and strengths, group brainstorming generates more robust outcomes than solo ideation.
The variety of viewpoints sparks innovation and enables comprehensive problem-solving.
Yields a Large Quantity of Ideas: Maximizing Idea Generation
One of the key advantages of team brainstorming lies in the sheer quantity of ideas produced. While not every idea will be a winner, the abundance of generated ideas ensures a higher likelihood of discovering valuable concepts.
Following a brainstorming session, it is important to conduct a planning session to identify the most promising ideas and develop strategies for implementation.
These team brainstorming benefits can be further enhanced by employing structured brainstorming techniques. To boost creative energy, consider exploring creative quotes that can invigorate you and your team throughout the process.
By incorporating these diverse brainstorming methods into your creative process, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and come up with innovative solutions. Whether you are working on a business project or pursuing personal goals, these methods will help unlock your imagination and generate fresh ideas.
So next time you find yourself in need of inspiration or facing a creative block, remember the power of these brainstorming techniques – they might just lead you to brilliant breakthroughs!

Let's Get Started with Onethread
Onethread empowers you to plan, organise, and track projects with ease, ensuring you meet deadlines, allocate resources efficiently, and keep progress transparent.
By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy .
Giving modern marketing teams superpowers with short links that stand out.
- Live Product Demo
© Copyright 2023 Onethread, Inc

What is Brainstorming: Techniques for Effective Problem Solving
Brainstorming is an invaluable method for generating ideas and solving problems in a creative, collaborative environment. Its essence lies in leveraging the collective thinking of a group, allowing for a diverse range of solutions to emerge from different perspectives. The essence of the Brainstorming Maker method resides in harnessing the collaborative thinking of a group, enabling a wide spectrum of solutions to arise from diverse perspectives. This technique, when executed effectively, can lead to groundbreaking solutions and innovative ideas that might not be discovered through individual efforts alone. In this extensive guide, we'll delve into what brainstorming is, explore various techniques for effective problem-solving, and provide tips for maximizing the benefits of your brainstorming sessions.
Understanding Brainstorming Techniques
Brainstorming, a concept first introduced by advertising executive Alex Osborn in the 1930s, has evolved into a fundamental tool in the arsenal of teams across various disciplines, including the innovative use of Moodboard Maker to facilitate the brainstorming process. The core principle of brainstorming is to generate a large quantity of ideas in order to find a solution to a specific problem, a principle that Moodboard Maker enhances by allowing teams to visualize concepts and themes visually. It operates on the premise that more ideas result in better solutions, underpinned by a non-judgmental and supportive environment that encourages free thought and expression. Moodboard Maker, in this context, serves as a digital canvas for collecting and sharing visual ideas, further enriching the brainstorming experience by making it more dynamic and engaging.
Rules of Brainstorming
The traditional approach to brainstorming is simple: a group of people comes together to think about a problem and suggests as many solutions as possible, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This process is based on four fundamental rules:
- No criticism: Ideas are not to be judged or critiqued during the brainstorming session. This encourages open communication and the flow of ideas.
- Welcome wild ideas: The wilder, the better. Encouraging unconventional thoughts can lead to creative solutions.
- Quantity over quality: The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible. Quality and feasibility are considerations for later.
- Combine and improve ideas: Building on others' ideas can lead to innovative solutions that might not be reached individually.
Why Brainstorming Works
Brainstorming is effective because it taps into the collective experience and creativity of the group, allowing for a broader and more diverse set of ideas than any individual could generate alone. Incorporating a Timeline Infographic Maker into this process can further enhance its effectiveness by visually mapping the development of ideas over time, providing a clear overview of the brainstorming journey. This tool not only encourages a sense of ownership and collaboration among team members, as they are actively involved in the problem-solving process, but also allows them to see the evolution of their collective thoughts, making the brainstorming session more structured and insightful. The use of a Timeline Infographic Maker, therefore, enriches the brainstorming experience, adding a visual dimension to the creative exploration and fostering a deeper understanding of how ideas interconnect and evolve.
Techniques for Effective Problem Solving
While the traditional brainstorming method has its merits, integrating tools like Graph Maker into the process can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your brainstorming sessions. Graph Maker allows teams to visually represent ideas, trends, and relationships between concepts through various forms of graphs, making the evaluation and comparison of brainstormed ideas more accessible and comprehensible. Here are some of the most impactful techniques that, when combined with the visual clarity provided by Graph Maker, can lead to more productive and insightful brainstorming sessions. This approach not only leverages the collective intelligence of the group but also utilizes visual data representation to streamline the decision-making process and highlight key insights that might be overlooked in a purely verbal or textual brainstorming session.
The Stepladder Technique
This method ensures that all members contribute individually before being influenced by the group. It starts with presenting the problem to the team. Then, each member is asked to think about the problem individually. One by one, members are added to the group discussion, sharing their ideas before hearing the others. This technique ensures that each member's initial thoughts are heard, reducing the conformity effect seen in traditional brainstorming.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping, enhanced by the use of the best mind mapping apps , is a visual tool that starts with a central idea or problem. Branches are created from this central idea, representing different aspects or solutions related to the main problem. Utilizing these apps can significantly aid in organizing thoughts, seeing relationships between ideas, and generating new ideas through a visual and structured format. The best mind mapping apps offer intuitive interfaces, collaborative features, and the flexibility to adapt to various brainstorming needs, making the mind mapping process more efficient and engaging. By integrating these applications, individuals and teams can leverage technology to streamline the brainstorming process, ensuring that every aspect and solution related to the main problem is visually mapped out in a comprehensive and accessible manner.
Brainwriting
In brainwriting, participants write down their ideas on paper or digitally before sharing them with the group. This can be particularly effective in ensuring that introverted team members have their ideas seen and heard. After a set period, ideas are shared with the group for discussion and further development.
Role Storming
Role storming encourages participants to take on different personas, such as a customer, a competitor, or even an unrelated third-party, to think about the problem from various perspectives. This can lead to a deeper understanding of the problem and more creative solutions.
Reverse Brainstorming
This technique involves thinking about the problem in reverse. Instead of looking for solutions to the problem, participants seek ways to cause the problem. This can help in understanding the root cause of the problem and, thus, finding innovative solutions by reversing the identified causes.
Brainstorming Examples: Real-World Applications
To further illustrate the power and versatility of brainstorming in solving problems and generating ideas, let's explore a few real-world examples where different brainstorming techniques were applied successfully across various contexts, now enhanced with the integration of an AI Video Generator . This innovative tool can bring brainstormed ideas to life by creating dynamic visual representations, making it easier to understand complex concepts and solutions through engaging video content. By utilizing an AI Video Generator, teams can not only discuss and develop ideas but also visualize them in action, adding a new dimension to the brainstorming process that enriches understanding and engagement across various projects and challenges. This approach underscores the evolving nature of brainstorming, where technology like AI Video Generators plays a crucial role in facilitating more interactive and impactful problem-solving sessions.
Product Development in a Tech Company
A tech company facing stagnation in its product line used brainstorming sessions to ignite creativity and innovation within its development team. By employing the Reverse Brainstorming technique, the team focused on identifying all the potential flaws and problems with their existing products instead of directly seeking improvements. This approach led to a comprehensive understanding of consumer frustrations and, ultimately, to the development of a new product feature that addressed a common user complaint, significantly enhancing user satisfaction and boosting sales.
Healthcare Solutions for Remote Areas
A non-profit organization dedicated to improving healthcare in remote areas used Role Storming to identify innovative solutions for delivering medical services. Team members assumed the roles of patients, doctors, and even logistical support personnel to deeply understand the challenges from multiple perspectives. This brainstorming session led to the idea of mobile health clinics, which could travel to remote areas, providing essential healthcare services that were previously inaccessible to these populations.
Marketing Strategy Overhaul
A medium-sized enterprise struggling to make an impact in a saturated market used Mind Mapping to overhaul its marketing strategy, further enhanced by the incorporation of Timeline Infographic Templates . Starting with the central problem of 'low market visibility,' the marketing team branched out into various strategies, such as social media engagement, influencer partnerships, and community events. This visual and structured brainstorming method, complemented by the clear visual organization provided by Timeline Infographic Templates, helped the team not only to generate a multitude of ideas but also to clearly see how different tactics could work together in a cohesive strategy over time. The templates allowed for a visual representation of the marketing plan’s development, implementation phases, and key milestones, leading to a successful marketing campaign that significantly increased brand awareness. The use of Timeline Infographic Templates in this context provided a strategic overview, ensuring all team members could visualize the sequence and timing of activities, thereby facilitating a more organized and effective approach to increasing market visibility.
Educational Curriculum Development
An educational institution looking to update its curriculum to better prepare students for the future workforce used the Brainwriting technique. Faculty members independently wrote down their ideas on how to integrate technology and critical thinking skills into the curriculum. This approach ensured that even the more introverted educators had their voices heard. The session resulted in a comprehensive plan to incorporate project-based learning and digital literacy across all subjects, enhancing the overall educational experience for students.
Environmental Conservation Efforts
A group dedicated to environmental conservation faced the challenge of increasing community involvement in its efforts. By utilizing the Stepladder Technique, the group ensured that each member could contribute their unique ideas before being influenced by the broader discussion. This led to the development of a community garden project that not only involved the community in conservation efforts but also educated participants on sustainable practices. The project became a model for similar initiatives in other communities, showcasing the impact of well-structured brainstorming on solving complex problems.
Reflecting on Examples
These examples demonstrate the flexibility and effectiveness of brainstorming techniques in various contexts, from business and healthcare to education and environmental conservation, further enriched by the use of tools like an Image Color Picker . By choosing the right technique for the problem at hand and fostering an environment of open communication and respect, organizations can leverage brainstorming to uncover innovative solutions and drive positive change. The Image Color Picker can play a crucial role in this process, especially in projects where visual elements are key, by helping teams select and harmonize colors that best represent their ideas, thereby enhancing the visual communication of concepts. Whether it's developing new products, enhancing services, or solving complex societal issues, brainstorming, complemented by visual and creative tools like the Image Color Picker, remains a powerful tool for creative problem-solving. This integration highlights how the combination of traditional brainstorming methods with digital tools can elevate the brainstorming process, making it more dynamic and effective.
Maximizing the Benefits with Brainstorming Tips
To get the most out of your brainstorming sessions, consider integrating Graph Templates into the process, among the following tips. Graph Templates can help in visually organizing and analyzing ideas, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among the brainstormed concepts. This visual tool complements traditional brainstorming techniques by providing a structured format for presenting data and insights, thereby enhancing the clarity and effectiveness of the session outcomes. By utilizing Graph Templates, teams can more efficiently evaluate the feasibility, impact, and interconnections of ideas, facilitating a more productive and informed decision-making process.
Set Clear Objectives
Before starting, ensure that the problem is clearly defined and that the objectives of the session are clear to all participants, incorporating the use of an AI Image Generator to visually represent these objectives and the problem at hand. This helps in keeping the session focused and productive by providing a visual aid that can make abstract concepts more concrete and understandable for all participants. The AI Image Generator can create images that encapsulate the problem or goals of the session, offering a visual reference point that can stimulate creativity and focus discussions. By integrating this visual tool, you can enhance the clarity and engagement of the brainstorming session, ensuring that everyone is aligned and motivated towards the same objectives.
Create a Supportive Environment
A supportive and open environment is crucial for effective brainstorming. Encourage participation from all members and ensure that ideas are not criticized or dismissed prematurely.
Use a Skilled Facilitator
A skilled facilitator can help guide the session, encourage participation, and keep the discussion on track. They can also help in synthesizing the ideas generated and in moving the group towards a solution.
Brainstorming should not end with the session. Ideas need to be evaluated, refined, and implemented. Ensure there is a clear plan for how ideas will be assessed and acted upon after the session.
Encourage Diversity
Diversity in team composition can enhance creativity and lead to a wider range of ideas. Different backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives can enrich the brainstorming process.
Brainstorming, when executed properly and enhanced with the use of Infographic Templates, can be a powerful tool for creative problem solving. By understanding the principles behind effective brainstorming and employing various techniques, teams can harness the collective creativity and intelligence of their members. Infographic Templates can aid in visually summarizing the brainstorming process, making complex ideas more accessible and understandable. Remember, the key to successful brainstorming lies not just in generating ideas but in creating an environment where all participants feel valued and heard. With the right approach brainstorming can lead to innovative solutions that might otherwise remain undiscovered. This visual aid ensures that the brainstorming outcomes are not only heard but also seen, reinforcing the collaborative effort and enhancing the overall effectiveness of the brainstorming session.
Related Articles
- HQ-Edit: A High-Quality Dataset for Instruction-based Image Editing
- Slicedit: Zero-Shot Video Editing With Text-to-Image Diffusion Models Using Spatio-Temporal Slices
- Dark Blue Color Unveiled for Every Creative
- Machine Learning & Its Application in Our Daily Lives
- Customer First: How to Build Loyalty and Drive Growth with AI Technology
- 9 Excellent Food Photography Ideas that You Can Try at Home
- Effortless Mac Right-Click Techniques & Your Path to Website Building
- Advantages of A/B Testing in Mobile Apps
- How to Delete Blank Rows in Excel
- How To Create A Taxi Booking App Like Uber or Careem?
Most Popular Posts
- 99+ Happy New Year Wishes 2024
- Venmo vs PayPal Integrations: Which One Is Right for You? – A Comparison Guide
- 11 Best Web Developer Portfolios: Stand Out From the Crowd
- 26 Landing Page Design & How to Engage & Convert Your Audience
- B2B Customer Service: A Comprehensive Guide
The ultimate guide: how to use post-it notes for problem solving

We at Miro love post-it notes, actually, we are fans. Recently we were inspired by the book Rapid Problem Solving with Post-It Notes written by David Straker. In this post we explain how to use online post-it notes for problem solving and focus on the methods described in the book: Post-up, Swap Sort, Top-Down Tree and Information Map.
Read our fresh post on how to improve your brainstorming sessions with better techniques, tips and rules.
Use your Miro post-it notes and creativity and go ahead!
- Problem solving part 1. Step-by-Step guide for post-up in Miro
The first technique we are focused on is called Post-up, it provides methods for getting information into chunks. Post-up is based on four methods – Brainstorming , Brainwriting , Nominal group technique and Crawford slip method .
The Post-up method works in several dimensions. First, it allows people to work simultaneously, thus speeding the session and getting everyone engaged at once. It also gets people emotionally engaged as they are writing their own ideas rather than have other people write or interpret them.
Posting up one idea at a time by person ensures equality through the team and also allows that each idea is considered by all team members.
Try Miro for visual exercises – Sign up
Step 1. define the problem.
First of all, you should decide about what are you trying to solve and make the problem visible for everyone. Use text tool and type your session goal. Let’s take ‘How to make an app better’ as the example.

Step 2. Make special sections on your board
Divide your board into several parts using shapes , icons , and text tool :
– Help section for Goals, Constraints, Idea Stimulators. Write them down before the start (we made it grey on the left).
– Participants section – special individual zones where people can post their notes during the ideation process (green section in the middle, divided into 4 parts for 4 different people).
– Workspace for the best ideas (yellow section on the right side).
Try Miro for visual exercises – Sign up free
Step 3. invite your team and explain the rules..
Invite your team to the board. The simplest way is to use “Share with the team” feature (if you have a Team account ). Another way is to send them invites via email or add from friends list.
Tell them how to play:
– First, let people see the Goal and explore the help section.
– The only tool they should use is Post-It (key 7)
– Each post-it note should contain only one idea.
– Use color coding – blue post-its for facts, yellow for opinions, pink for assumptions.
No credit card required.
Step 4. Writing of ideas
Give your team some time to think and brainstorm individually (approx. 7-10 minutes, if you think they need more – give them more). They should not at this time stick their post-its to the common workspace.
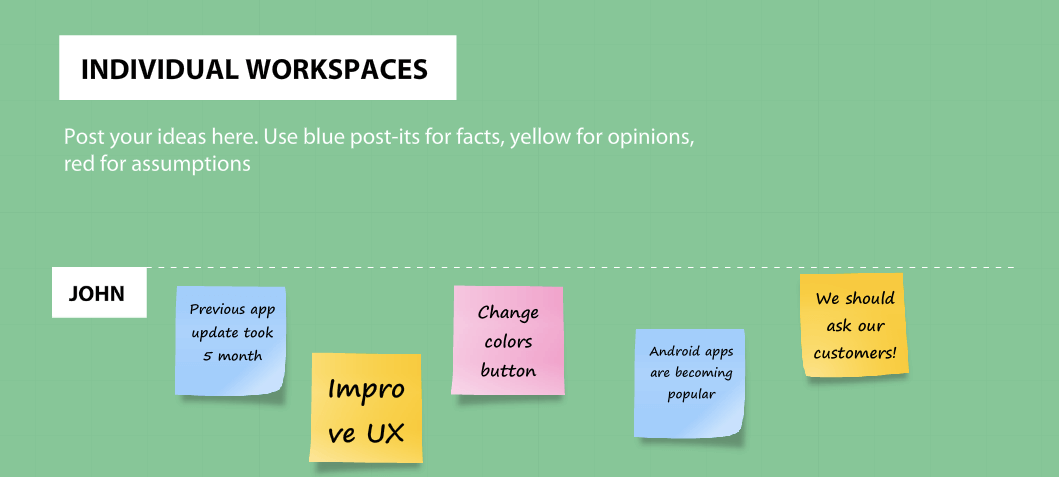
Step 5. Post up ideas
The team then posts up their ideas on the ideas workspace. A good way of doing this is to have each person take turns to post one – the most valuable – idea.
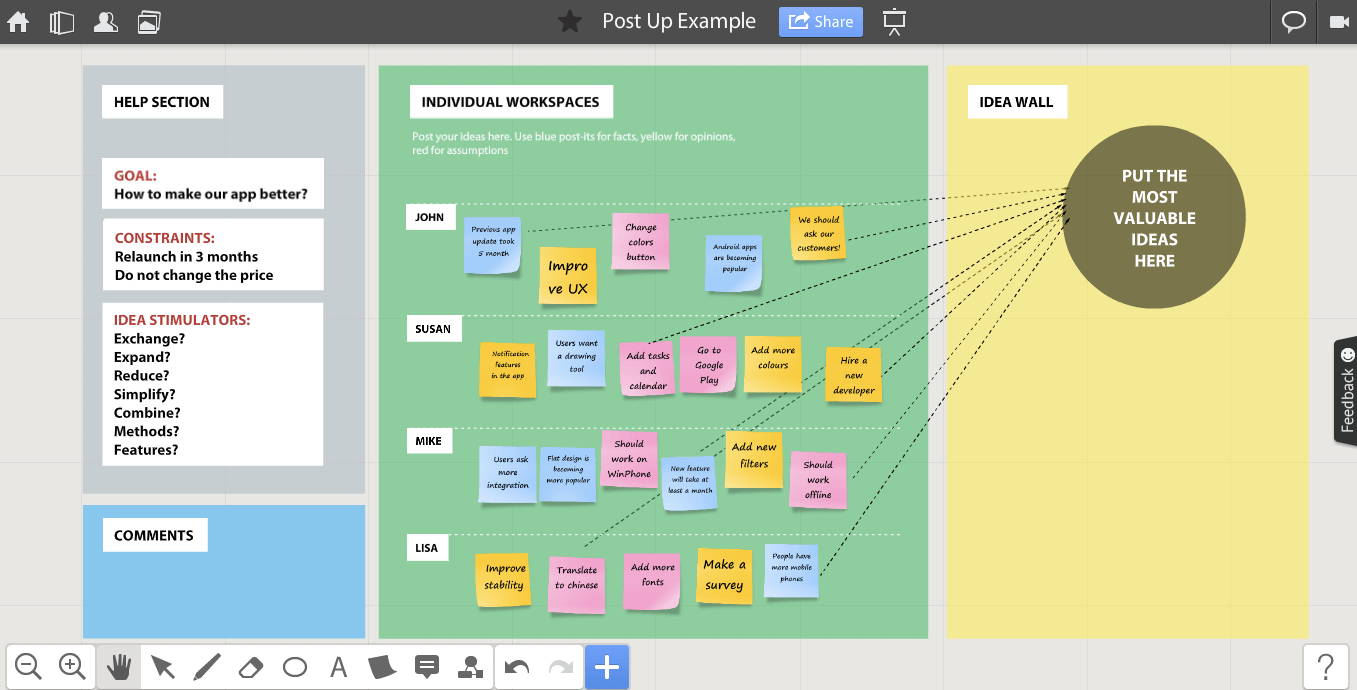
If any idea triggers other ideas for anyone in the team, they can write them on more post-its and add them to their individual section. When all ideas are posted, then you can also use other creative methods to generate even more ideas (we put it into comment section).

- Problem solving part 2. Step-by-step guide for Swap Sort in Miro
This part is devoted to the next technique – Swap Sort, which is based on Bubble sort , Paired comparison and Prioritization matrix . Swap Sort is extremely useful when you need to put a set of ideas into priority order.
Use it only when you have relatively few items to prioritize (not hundreds, really). If too many, it may become a trouble. You can try Post up or other techniques to identify ideas for prioritization.
We always make decisions by comparing and contrasting. Taking two items at a time, as in this swap-sort creates focus and attention on just those two items, making decisions as to which is more important easier.
The pattern of repeated comparisons and exchanges comes from computing, where it is known as a ‘bubble sort’. Swap sort takes the same concept and brings it to the board with post-its.
Step 1. Identify the problem
First of all, explain your team what problem you are trying to solve. We’ll take the previous case devoted to the app improvements. Now our goal is to decide what will be the order of the selected improvements. Take a look at the picture below.
You can continue working on one of your brainstorming boards or use your offline brainstorming results.
Use text tool , shapes , icons and anything that will help you to visualize. You should have the following spaces:
– Help section with the goal and criteria.
– Preparation zone where you put the all the ideas written on post-its.
– Workspace for swap sort and final results.
Step 3. Identify the criteria
Identify the criteria that you are going to be using to prioritize. These should be relatively few. One is just fine. Three is ok. Five is rather a lot.
Write them on Post-it notes and put these into priority order (use help section), using a ‘mini’-swap-sort. Then reference these for every comparison exchange.
Step 4. Invite collaborators
If you had a brainstorming session already, you can continue to develop the ideas and concepts with the same people or invite independent experts.
Use chat or video/voice chat (if you have Team or Pro account) if your team works remotely.
Step 5. Pairwise swapping
Write the items that you want to compare on Post-it notes. Shuffle them so they are not in any ‘leading’ order, then place them out in a line (vertically is often the best, though a horizontal line is just fine).
Now take the first two items and compare them. If the higher one (in a vertical setting) is more important than the lower one, then swap them.
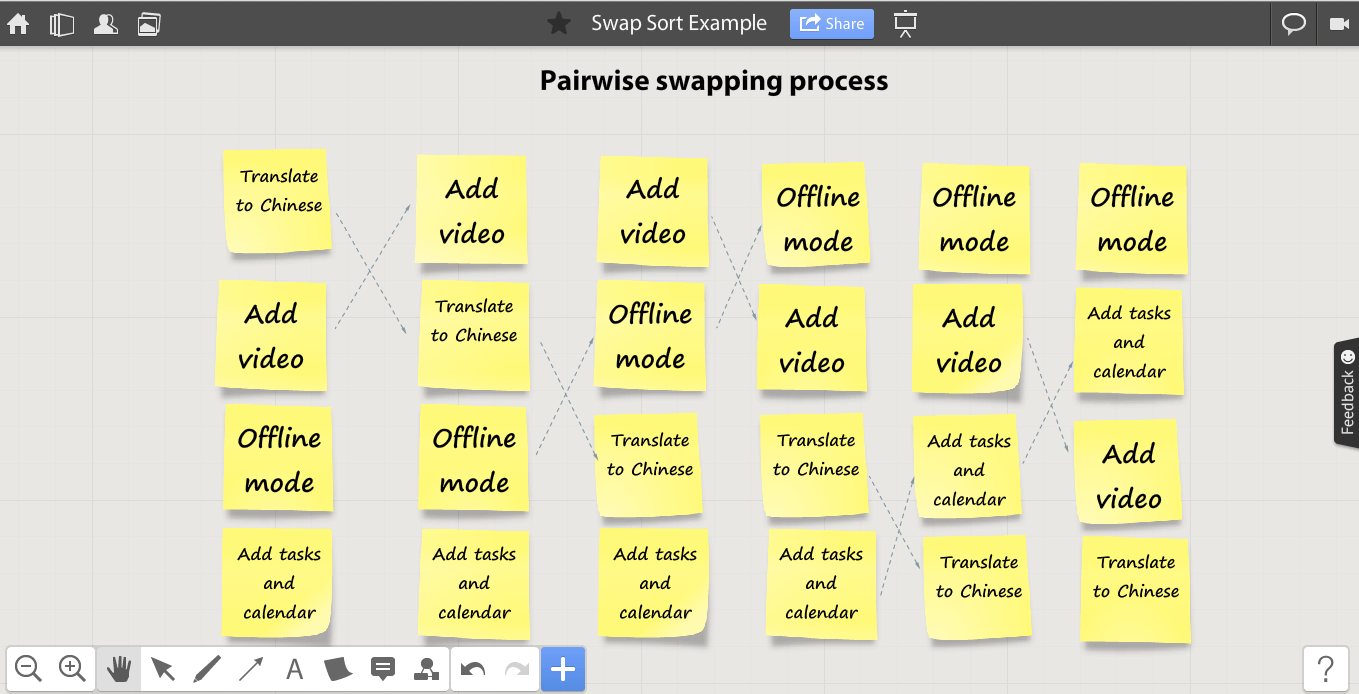
Then repeat this comparison and possible swap with the second pair, third pair and so on until you get to the bottom. Put the result on the right.
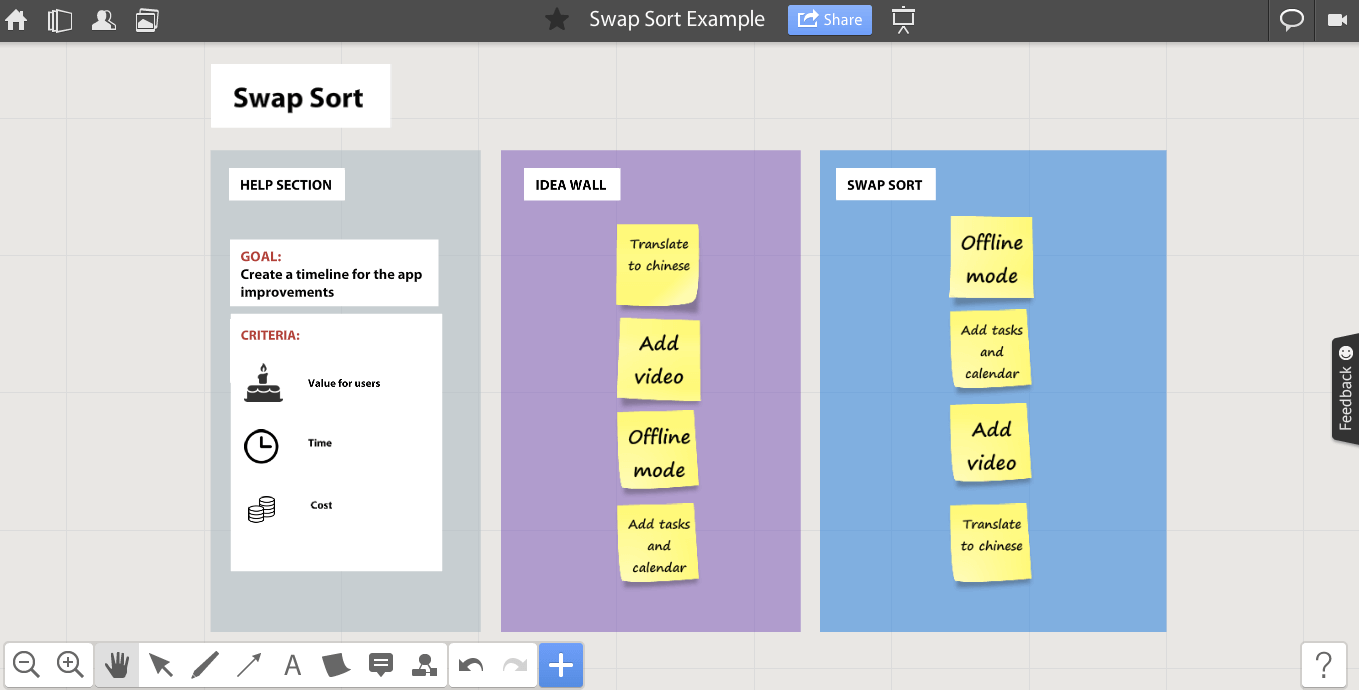
Don’t use color coding or post-its of different size in order to avoid misunderstanding or wrong prioritization.
- Problem solving part 3. Step-by-step guide for Top-down Tree in Miro
This part is devoted to the next problem solving technique – Top-down Tree. This method is based on Tree Diagram , Why-Why Diagram , How-How Diagram and Process Decision Program Chart .
Top-down trees are used to break problems down into constituent parts with increasing levels of detail and are useful when the problems is fairly well known at a broad level, but complex. So, this technique works well when the nature of the problem is unknown and you need to find more details to solve it. Top-down tree is well-structured, that’s the distinctive feature of the method.
- Short glossary
Node – a tree element (one post-it in our case)
Root – the starting node
The names of relationships between nodes are modeled after family relations:
- A node’s “parent” is a node one step higher in the hierarchy (i.e. closer to the root node) and lying on the same branch. “Child” is lower than parent.
- “Sibling” (“brother” or “sister”) nodes share the same parent node.
- A node’s “uncles” are siblings of that node’s parent.
- A node that is connected to all lower-level nodes is called an “ancestor”. The connected lower-level nodes are “descendants” of the ancestor node.
How to visualize trees – different approaches
We consider five of them for top-down trees – top-down, star, comb, right to left and fishbone. Take a look at them.

Step 1. Define the goal
First of all, think about the problem you are trying to solve and invite the participants. As you can remember from the previous posts, we are trying to find out how to improve the app. The goal of this brainstorming session will be to define the key factors, which affect the app popularity among users.
Step 2. Make special sections on your board and prepare the questions
Use text tool, shapes, icons and anything that will help you to visualize your sections on the whiteboard. You should have the following spaces:
– Help section with the goal and questions.
– Preparation zone where you put the all the ideas written on post-its
– Workspace for top-down tree and final results.
Step 3. Write the key question on the root post-it note
Use the goal from the first step to identify problem. For example, in our case the problem may be “people don’t use our app for entertainment”. Write the problem on a post-it and place it on your workspace. This will be the root node, and all the others will be children. We have chosen the top-down structure and put the root node on the top.
Step 4. Define children nodes
Ask the questions from the help section to identify the children and write them on post-its. You can initially put them on idea wall.
Step 5. Link the nodes
Link the nodes (parents and children) between each other and define families. Now you will be able to see the whole tree structure.
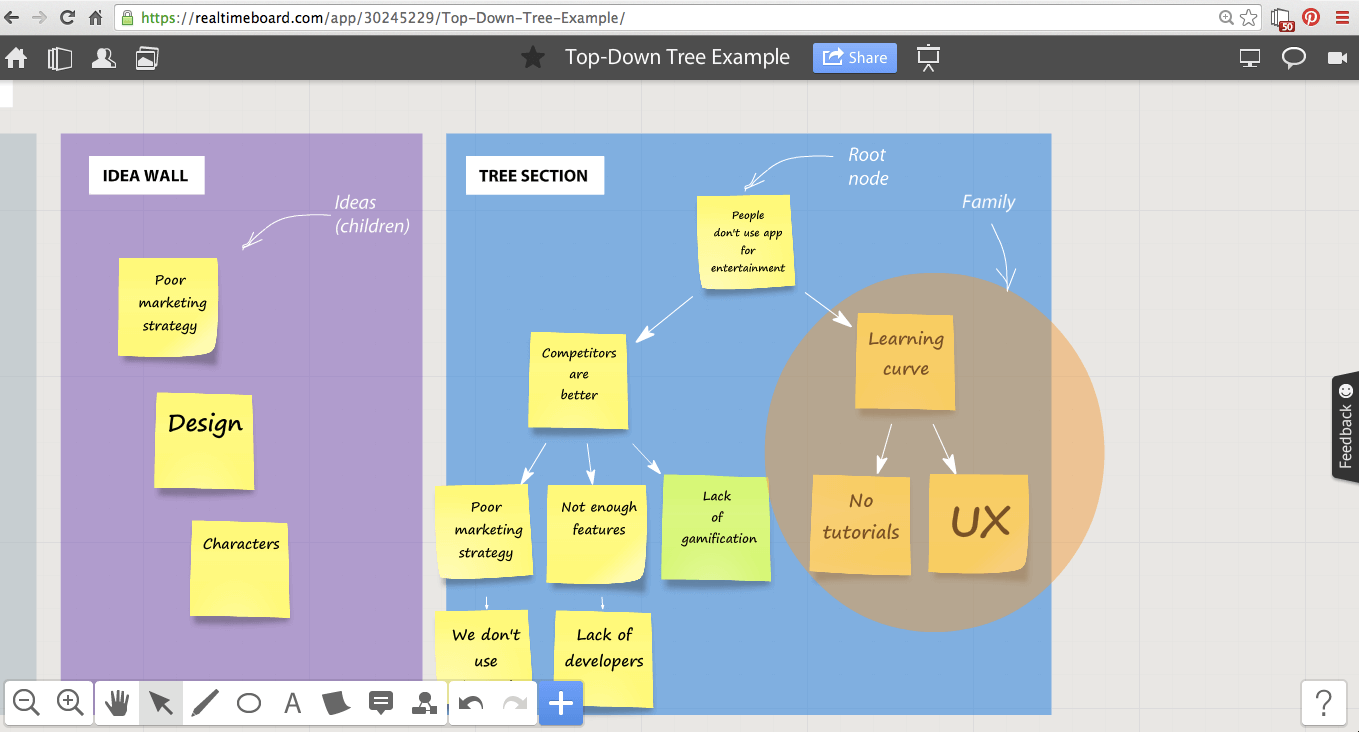
Step 6. Check the whole tree
When you finish the work on your tree, check if it is complete (it answers every question from the help section), clear (relationships between parents and children are obvious), and useful (helps to achieve the initial goal).
Analyze the results and add necessary comments/decisions.
Problem solving part 4. Step-by-step guide for Information map in Miro
We have already reviewed 3 useful methods – Post-up, Swap Sort and Top-Down Tree, which are great for generating ideas and prioritizing them. Now we will talk about Information map. This method is based on Relations Diagram , Mind Maps , Entity-Relation Diagram and State-Transition Diagram .
- How it works
Information map is useful when you need to find interrelations between different elements. Use Information map when you know (or at least suspect) that different elements have interconnections between each other. This tool is extremely useful during creative sessions when you have no strict structure and need to connect the dots.
Information maps can reflect not all the possible interconnections, and in order to discover some hidden but important things you should act consequentially asking the questions which will lead to the goal. Note that maps are not so well-structured as trees.
When you are building interrelations, consider some important points you can face with:
- Chain of post-its with one arrow between each node . This means that the elements have straight connection, and if you exclude the first one, the last will never happen.
- Bottleneck. If one post it has a lot of ‘input’ arrows, and only few of ‘output’ arrows, this means you have a so-called bottleneck, which potentially may cause incidents.
- Source . Post-its which have only output arrows are called sources (these can be information sources, suppliers, etc.)
- Stocks . These are post-its that have only input arrows (i.e. information stocks).
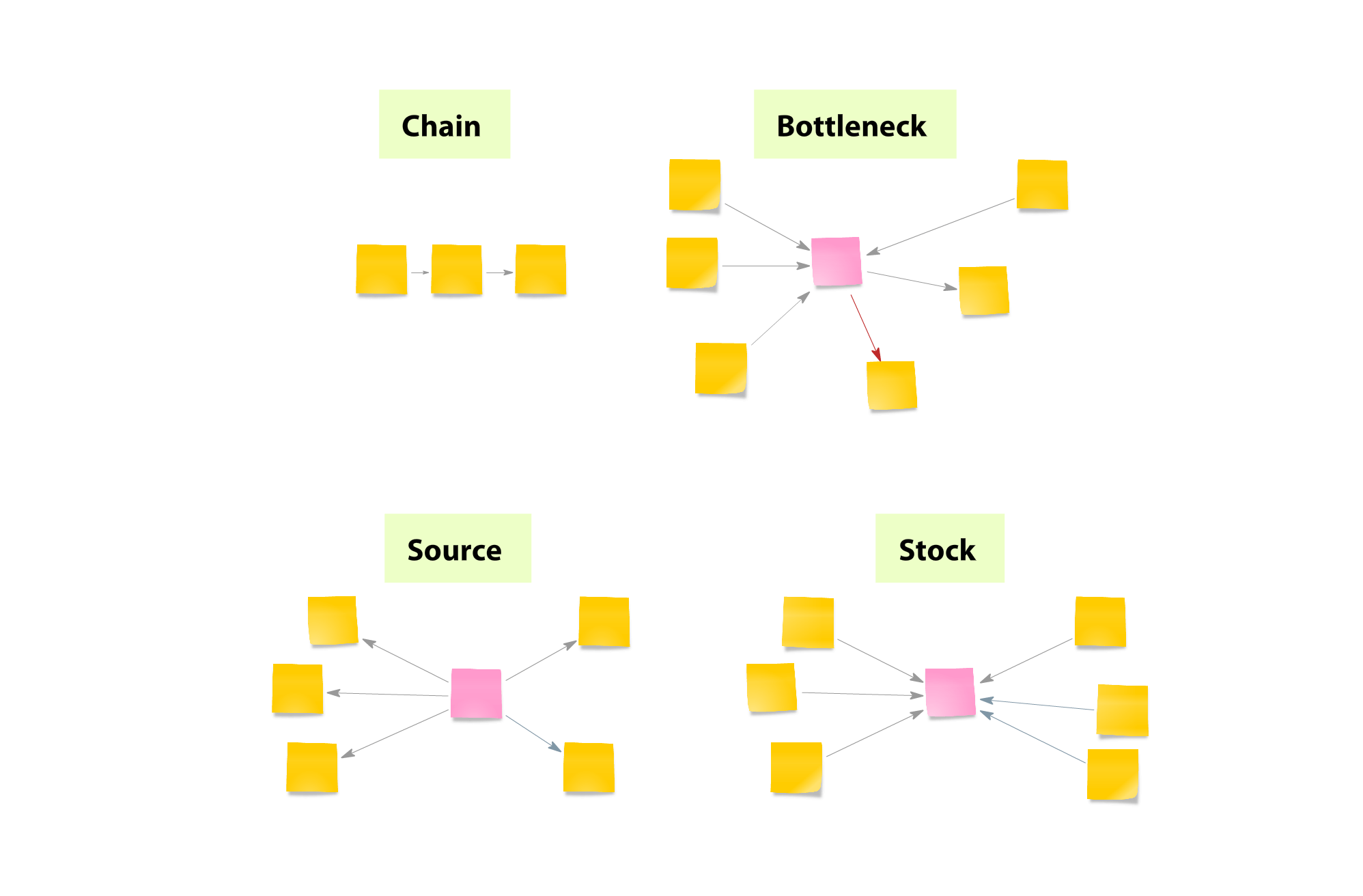
First of all, think about the problem you are trying to solve and invite the participants. As you can remember from the previous posts, we are trying to find out how to improve the app. The goal of this brainstorming session will be to understand the connections between app updates growth of popularity.
Step 2. Define the principles
What question will you use to find related elements? Note that the question should contain a verb, which will describe the characteristics of relations (i.e. induce, connect, improve etc.). Our question is “What factors affect the growth of app popularity?”
Step 3. Make special sections on your board and prepare the questions
Use text tool, shapes, icons and anything that will help you to visualize your sections on the board. You should have the following spaces:
– Workspace where you put the all the ideas written on post-its
– Zone for information map and final results.
Step 4. Find the root post-it
Find the root post-it and put it in the center of your workspace. In our case the root will be ‘Growth of app popularity’. Use another color or mark-up tools to make this post-it special and visible.
Step 5. Find interrelations
Start asking questions to find from the Step 2 to find the related pieces of information. When you collect some, place them around your root post-it note.
Step 6. Repeat the previous step to find more post-its
Repeat the previous step to find more related elements asking the question from step 2. Place the new elements around related post-its. Leave enough space between post-its to add links between them.
Step 7. Add arrows (links) to show the connections
When you are finished with the post-its, add links between them (use the Link tool on the tools panel below. If you see that the elements don’t have straight connection, but one affects another, use another type of the link.
Step 8. Check the map
Check the whole map, review the connections, correct if necessary and be ready to make decisions.
Well, now aftre we have revised for ultimately effective ways to use post-it notes for problem solving, hope you are inspired enough to practice it and solve your problems using Miro’s visual workspace. Don’t forget to invite your team and conduct a real-time brainstorming session to make your problem solving 100% effective.
Miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together.
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
- How to visualize trees – different approaches
- Problem solving part 4. Step-by-step guide for Information map in Miro
16 secrets of engaging remote meetings
How to build a product roadmap that truly works (with Miro)
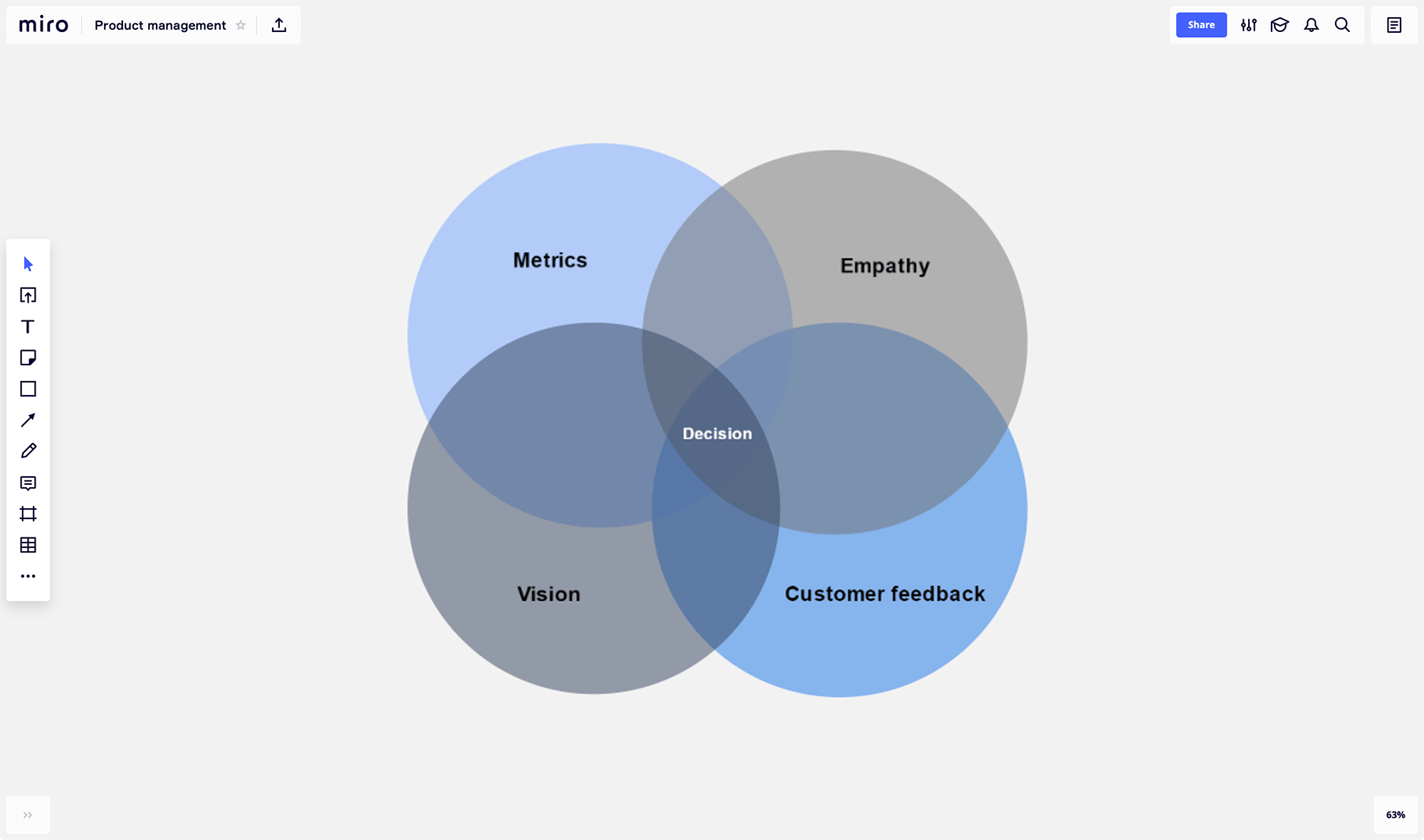
A Problem Solving Method: Brainstorming

| Steps in Brainstorming | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding the problem | To grasp the nature and extent of the problem | Identifying that the company's profits are declining |
| Gathering information | To gather all necessary data and insights regarding the problem | Surveying customers, examining sales data |
| Generating ideas | To create a variety of possible solutions | Suggesting new marketing strategies or improved customer service |
| Evaluating and selecting ideas | To sift through the possible solutions and select the one most likely to succeed | Choosing to implement a new marketing strategy |
| Implementing the best idea | To put the chosen solution into practice | Launching the new marketing campaign |
| Reviewing the results | To assess the effectiveness of the solution | Analyzing sales data post-campaign launch |
| Brainstorming in Business | To generate innovative ideas and solve problems | Creating new products, improving services, exploring new markets |
| Brainstorming in Problem-solving | To generate potential solutions to complex problems | Finding the reason for declining sales |
| Brainstorming in Marketing | To attract new customers and retain current ones | Identifying target audiences, creating marketing campaigns |
| Brainstorming in Interface design | To create user-friendly interfaces | Designing an intuitive app interface |
Brainstorming is a problem solving technique where a problem is broken down into smaller, more manageable parts to develop different solutions for it. The problem can be anything from what to have for dinner, where to go on vacation or which person in the office is stealing from the communal coffee pot.
To brainstorm a problem, problem solvers gather a group of knowledgeable people about that particular problem and ask them questions about it. They then take all of these answers and try to find common themes among them – usually by drawing diagrams or writing lists – these themes will lead them towards finding a solution to their problem. Brainstorming is also used to generate ideas, especially those aimed at creative projects such as problem solving or an interface between two parties.
The problem solvers can be anyone from business consultants to CEOs who problem-solve with their own companies to friends trying to decide where they want to go for dinner. It's also used in marketing problem solving, finding new markets for products/services, marketing strategies, and how target audiences will respond (positively or negatively) to certain types of messaging.
A problem solver will break down the problem into smaller ones that are easier to solve, then define problems until there is one left which they have no idea how the problem might solve. This final problem is used as the basis for an answer. The main steps in brainstorming when problem solving include:
1. Understanding the problem
2. Gathering information about the problem
3. Generating ideas about the problem
4. Evaluating and selecting ideas
5. Implementing the best idea
6. Reviewing the results of the brainstorming session
Brainstorming is used in business, problem-solving, marketing, and interface design contexts. It's a problem solving technique that can be used by anyone with a problem to solve, and it's a great way to get a group of people working together to find a solution. When used correctly, brainstorming will lead you towards finding an answer to your problem.
If you want to learn more problem solving skills , you can join IIENSTITU's problem solving skills course . In addition, you can improve your solving skills with free online courses and certifications . Join us today!
1. What Is The Problem Solving Method Of Brainstorming?
2. What Are The Steps of the Brainstorming Process?
What Is The Problem Solving Method Of Brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a problem solving method that allows you to generate ideas in an uncontrolled environment. Unlike other problem-solving methods, brainstorming does not produce effective results if participants can pass judgment on the ideas presented. This problem-solving method is used for all types of problems, ranging from big decisions like moving cities to smaller ones like what gift to buy your friend for their birthday.
The first step in problem solving with brainstorming is getting participants together and introducing them to the issue at hand through a summary or by showing it directly. Participants should then be told that they will be given time, usually two minutes, before being asked to share any thoughts about potential solutions. After this period of silence, participants are asked to share the ideas they came up with, even if they seem entirely ridiculous. The brainstorming method does not allow for any critique or judgment during the idea-sharing. It is important to accept every idea that participants offer and thank them for their input when people finish speaking.
People may use the problem-solving method in various ways depending on what problem you're trying to solve and who your audience is. For example, if you're planning a surprise birthday party for your husband, brainstorming would help you develop gift ideas that he might like and then schedule a celebration that fits his interests without him knowing about it beforehand. If you need to plan out an entire project at work using this problem solving method, brainstorming will help you develop problem-solving strategies and possible solutions.
The problem-solving method can be used for any problem that needs to be solved, even the ones we don't typically think of as such. For example, problem-solving-oriented brainstorming may help you decide which movie to see this weekend or what ingredients to add to make a fantastic dish. It is also advantageous when planning something like a wedding: problem-solving-oriented brainstorming will help determine how many guests will attend and where the ceremony and reception should occur.
The problem-solving method involves everyone affected by whatever problem is being solved so everyone can hear them and their input considered in the decision-making process. This results in much more creative ideas and a higher chance of finding the best solution. Brainstorming is also a problem solving method that can be used for people who are not used to problem solving. This problem solving method is more relaxed than others and allows for mistakes, which can help people feel more comfortable when brainstorming.
Brainstorming is a problem-solving method used in many different fields and for many other purposes. It is essential to keep an open mind when using this problem solving method and accept all ideas that participants offer, no matter how ridiculous they may seem. With enough time and practice, brainstorming can help you find solutions to any problem.
The problem solving method of brainstorming helps us develop potential solutions by getting input from everyone involved in the issue at hand, without judgment. The problem solving method of brainstorming is used for all sorts of problems, depending on who is using it and what problem they are trying to solve. Still, it only involves problem-solving-oriented brainstorming when there is an objective. It can be applied to any issue that needs to be solved and allows people who may not feel comfortable problem solving with other methods to express themselves freely. This problem solving method requires time and practice before you can use it properly. However, once mastered, it creates a creative environment where everyone's input will be considered equally, leading to better results.
What Are The Steps of the Brainstorming Process?
When it comes to problem solving, brainstorming is one of the most popular methods. But what are the steps involved in this process? Here's a look at what you need to do to get the most out of brainstorming:
1. Define the problem. The first step is to define the problem you're trying to solve clearly. It will help you stay focused and ensure that all ideas generated during the brainstorming session are related to the issue at hand.
2. Encourage creativity. The next step is to encourage creativity among your team members. It means giving them permission to think outside the box and develop unconventional solutions.
3. Generate ideas. Once everyone is feeling creative, you can start generating ideas. Don't be afraid to develop wild concepts, as they might lead to more practical solutions. It's also a good idea to create action items that you feel your team could work on for the problem at hand.
4. Refine ideas and select the best option. Once everyone has shared their ideas, it's time to narrow down your choices to the most viable options available. It will give you a good starting point for problem-solving so you can easily create the next steps for each of these action items.
1. What do you think is the best solution for solving a particular problem?
2. How many ideas do you typically come up with during brainstorming sessions?
3. When should one use brainstorming sessions versus other types of problem-solving methods?
4. Do you find that productivity decreases after completing a brainstorming session?

What are the key factors that contribute to climate change?
Key Factors Contributing to Climate Change
There are several key factors that contribute significantly to climate change. The most significant is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas. When fossil fuels are burned, they release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun, causing global temperatures to rise.
Deforestation is another major factor. Trees absorb and store carbon dioxide. When forests are cleared, that stored carbon is released. Deforestation also reduces the number of trees available to remove carbon dioxide from the air. Between 2015 and 2020, the world lost over 4 million hectares of forest per year.
Intensive livestock farming generates significant greenhouse gas emissions. Cows and sheep produce methane as part of their digestive process. Large scale cattle ranching leads to deforestation too. The livestock sector accounts for around 15% of global emissions.
Other contributors are fertilizers containing nitrogen and the burning of biomass. Overall, human activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases over the last century. To mitigate climate change, we must transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy and prevent further deforestation. We must also reduce emissions from agriculture and other sources.
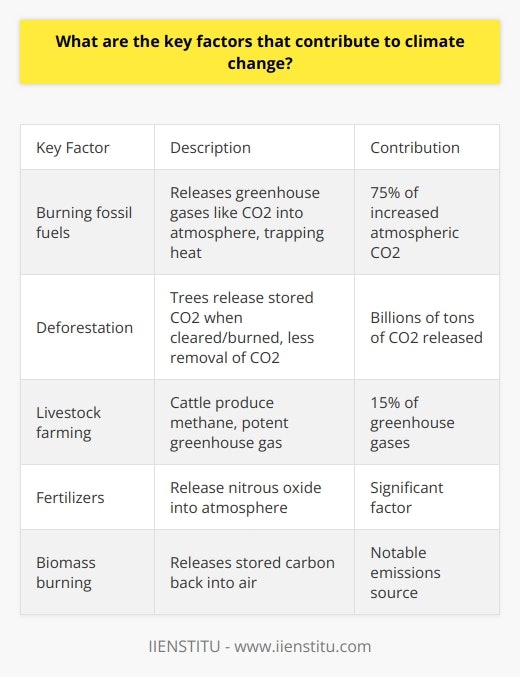
How does gender inequality manifest in different cultures?
Manifestations of Gender Inequality
Gender inequality refers to unequal treatment or perceptions of individuals based on their gender. This manifests in various ways across cultures. In many cultures, traditional gender roles cast women as caregivers and men as leaders. This leads to inequalities in domestic duties, employment, and positions of authority. For example, in parts of South Asia, women spend much more time on unpaid domestic work than men. In Saudi Arabia, strict laws prohibit women from traveling or working without a male guardian's permission.
Gender discrimination in education also perpetuates inequality. In Afghanistan, girls face barriers to attending school including lack of facilities, child marriage, and Taliban restrictions. Only 37% of Afghan girls complete primary education, compared to 66% of boys. This lack of education limits women's ability to participate in society.
Violence against women is another manifestation of gender inequality. Practices like female genital mutilation in parts of Africa, acid attacks in Southeast Asia, and honor killings in the Middle East target and control women. Up to 38% of murders of women worldwide are committed by intimate partners. Laws and enforcement often fail to protect women.
While many cultures have embedded gender inequalities, increased education for women and girls, activism, and legal protections are working to promote equal rights. Achieving gender equality requires changing long-held biases and practices.

What policies can governments implement to reduce poverty?
Policies to Reduce Poverty
Governments can implement several policies to help reduce poverty. One important policy is to increase access to education. Governments can make primary and secondary education free and compulsory. They can also provide subsidies and scholarships to help low-income students attend college or vocational schools. Education gives people the skills needed to obtain better-paying jobs.
Another policy is to create more jobs and improve wages. Governments can invest in infrastructure and green technology to create construction and manufacturing jobs. They can set higher minimum wages and strengthen unions to improve pay. Policies that support small businesses can also lead to more job creation.
Governments can also strengthen social safety net programs. They can provide cash assistance, food stamps, and housing vouchers to help families meet their basic needs. Healthcare subsidies can make insurance more affordable. Increasing funding for childcare, disability, and unemployment benefits further aids those struggling financially.
Lastly, governments can reform tax policies to ease the burden on lower-income households. They can make tax systems more progressive by increasing taxes on the wealthy. Tax credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit can supplement wages for workers. Reducing regressive payroll and sales taxes helps increase take-home pay.
Implementing a mix of education, job creation, safety net, and tax reform policies can significantly reduce poverty. A comprehensive approach addresses both the symptoms and root causes of financial hardship for low-income families and individuals.
What are some examples of effective brainstorming techniques for problem solving?
Brainstorming techniques for problem solving.
Brainstorming is a creative thinking process that generates many ideas to solve a problem. Effective brainstorming techniques encourage people to come up with as many solutions as possible, without judging or filtering ideas initially. This fosters an environment where people feel comfortable sharing unconventional or outlandish solutions that can spark innovative approaches. There are several techniques that can facilitate effective brainstorming sessions.
Individual Brainstorming
Individual brainstorming involves people generating ideas independently before sharing with the group. This allows time for private reflection without influences from others’ opinions. Individuals can freely organize thoughts and build on previous ideas. It prevents prematurely dismissing solutions due to groupthink. Individual brainstorming encourages people to fully develop their own concepts before introducing them to the group.
Round-Robin Brainstorming
The round-robin approach gathers individuals in a group and takes turns sharing ideas one at a time. This gives everyone equal opportunity to contribute. It prevents vocal participants from dominating the discussion. The structured format helps introverts and passive thinkers engage more actively. Individuals can develop on previous ideas or introduce unrelated solutions. Including an object to designate the speaker prevents people from interrupting the current contributor.
Silent Brainstorming
Silent brainstorming sessions utilize writing to generate ideas. Participants silently reflect and write down solutions individually. This removes influence from others’ opinions and encourages independent thinking. It gives introverts space to formulate concepts without pressure to verbalize immediately. Silent brainstorming sessions can then gather all contributions and collectively review the ideas generated. This technique encourages equal participation and develops a robust list of options to evaluate.
Online Brainstorming
Online brainstorming uses technology like video conferencing, shared documents, or brainstorming apps to generate ideas remotely. This provides flexibility for people in different locations to contribute. Online tools allow participants to add ideas simultaneously in a shared platform. This builds on other solutions and spurs new connections in real-time. Online brainstorming often needs more structure and moderation to keep the session focused and productive.
Effective brainstorming encourages creative thinking from all participants. Using individual ideation, round-robin sharing, silent writing, or online tools can produce quality solutions. Keeping an open, judgment-free environment allows innovative ideas to emerge. Evaluating and refining solutions comes after generating an extensive list of options through brainstorming.
How can brainstorming sessions be structured to generate the most creative ideas for solving problems?
Generating creative ideas through effective brainstorming.
Brainstorming is a common technique used to produce creative solutions to problems. Well-structured brainstorming sessions allow groups to maximize their ideation potential. Several methods exist for running effective brainstorming meetings that foster imaginative thinking.
Establishing Ground Rules
Groups should begin by outlining guidelines for the session. Critical judgment of ideas must be avoided to encourage free thinking. Participants should be told to offer any idea that comes to mind, no matter how unrealistic. Quantity of concepts is more important than quality at this stage. Building on others' suggestions is also permitted. All ideas should be captured by a recorder.
Priming Creativity
Simple warm-up exercises can stimulate creative thinking before tackling the main issue. For example, unrelated challenges get people to think outside the box. Allocating a few minutes for individuals to brainstorm alone also primes the pump for innovative ideas.
Taking Turns
A round robin approach allows everyone to voice their ideas before others offer additional suggestions. This prevents a few people from dominating the conversation. It also encourages quieter team members to participate. Periodically cycling back to people inspires new concepts.
Changing Perspectives
Seeing things from different viewpoints sparks imagination. Participants might be asked to conceptualize solutions from the perspective of various stakeholders. Alternately, they can brainstorm while pretending to be a famous inventor or eccentric CEO.
Introducing Stimuli
Introducing various stimuli during the session gets creativity flowing. Listening to music, drawing pictures, or using evocative imagery prompts new connections. Having tactile objects to manipulate also provides inspiration.
Taking Breaks
Taking short breaks periodically re-energizes participants’ minds. During this time, they can engage in relaxing activities like stretching, snacking, or casual conversation. Breaks allow ideas to percolate further.
Reviewing and Refining
After listing all ideas without judgment, the group should review the options and start prioritizing them. Now constructive analysis can shape the solutions. The most promising concepts can be refined and developed. This process turns creative ideas into practical solutions.
Following basic guidelines for effective brainstorming greatly enhances the quantity and originality of concepts generated. Well-run sessions allow teams to harness their collective imagination to devise innovative solutions to problems.
In what ways can brainstorming be used as a tool for collaborative problem solving in an academic setting?
Brainstorming as a Collaborative Problem Solving Tool
Brainstorming is a technique that can be highly effective for collaborative problem solving in academic settings. By bringing together a diverse group of individuals, brainstorming allows for the generation of creative ideas and solutions through the cross-pollination of perspectives and expertise. There are several key ways that brainstorming facilitates collaborative problem solving for students and educators.
Generating Ideas
The primary function of brainstorming is to produce a broad range of ideas, unhindered by judgement or debate. Every participant is encouraged to think freely and suggest as many ideas as possible, no matter how outlandish. This allows the group to maximize its creative potential and identify innovative solutions that may not have emerged through conventional thinking. The sheer volume of ideas generated through brainstorming increases the chances that the group will identify promising solutions.
Incorporating Diverse Viewpoints
Brainstorming brings together people with diverse backgrounds, skill sets, and perspectives. This diversity is a valuable asset when collaboratively solving complex problems. A broad range of expertise allows the group to approach the problem from different angles. Varying viewpoints give rise to fresh insights and prevent groupthink. By incorporating input from individuals with different modes of thinking, brainstorming provides a more holistic understanding of the problem.
Building on Ideas
An effective brainstorming session encourages participants to build on one another's ideas. One idea can spur new associations and directions in creative thinking. Hearing others' ideas may inspire participants to come up with innovative solutions or find clever ways to improve on ideas. This synergistic effect of feeding off one another's ideas is what makes brainstorming a truly collaborative endeavor. The result is a set of solutions that no individual could have developed alone.
Promoting Egalitarian Participation
Brainstorming creates a level playing field where all group members can contribute equally. Status differences and hierarchies are set aside as participants share ideas freely in an open forum. This helps ensure that no single voice or viewpoint dominates the discussion. Bringing different group members into the collaborative process broadens the array of ideas and allows for unique contributions from all participants. By giving everyone an equal chance to brainstorm ideas, the group gains access to perspectives that may otherwise go unheard.
In summary, brainstorming leverages the diversity of perspectives, builds on creative associations, and promotes egalitarian idea generation. This makes it a flexible tool for collaborative problem solving within student project teams, faculty research groups, interdisciplinary task forces, and other academic settings requiring innovation and cooperation.
What are some examples of effective brainstorming methods used in teaching?
Brainstorming is a common technique used by teachers to generate creative ideas and engage students in active thinking. Some examples of effective brainstorming methods used in teaching include:
Think-Pair-Share
In this method, students are first asked to think individually about a topic or question posed by the teacher. They are given a minute or two to jot down their ideas. Next, students pair up and share their thoughts with a partner. Finally, pairs share their ideas with the larger class group. This technique allows all students to participate and builds on individual reflection.
Roundtable Brainstorming
Students are divided into small groups of 4-6 students. Each group sits around a table or cluster of desks. One student starts by sharing an idea, then going around the circle each student contributes. Groups can record ideas on chart paper or digitally on a shared document. This method enables collaboration and equal participation.
Brainwriting
In this silent method, each student has a sheet of paper or digital document. Students write down their ideas individually for 2-3 minutes. Then, they pass their paper to the student on the left. Students read the new paper and add additional ideas. This rotation continues several times. Brainwriting allows all students to actively contribute ideas.
Mind Mapping
Students visually organize and connect ideas around a central topic. Main themes branch out with related sub-topics and details. Mind maps can be created individually or as a class using a projector, whiteboard, or large paper. This activity promotes critical thinking and visual learning.
Brainstorming with Movement
The class stands in a circle or scattered around the room. The teacher asks a question then tosses a ball to a student, who shares an idea before tossing to someone else. Students can also move around the room gathering ideas on post-it notes from classmates. Incorporating physical movement engages kinesthetic learners.
In summary, effective brainstorming in teaching provides opportunities for individual reflection, collaboration with peers, whole-class participation, and movement. Varying brainstorming formats allows teachers to accommodate different learning styles and keep students actively engaged in the learning process.
How can teachers utilize brainstorming techniques to engage students in active learning?
Brainstorming Techniques for Active Student Engagement
Teachers can utilize a variety of brainstorming techniques to get students actively engaged in learning. Brainstorming is a collaborative activity that encourages students to come up with ideas and build on each other's contributions. When students brainstorm together, they take ownership of their learning and get invested in the topics being covered. Here are some effective brainstorming methods teachers can use to promote active participation:
The think-pair-share technique provides an easy way to get all students involved. First, the teacher poses a question or problem and gives students a minute to think independently. Next, students pair up and share their ideas with a partner. Finally, partners share their responses with the whole class. This simple structure gives every student a chance to formulate ideas and voice their thoughts.
Round Robin
In a round robin brainstorm, students go around in a circle sharing ideas. The teacher poses a prompt, and then each student takes a turn adding an idea. Students can pass if needed, but then have a second chance once everyone has gone. A round robin gets many perspectives and keeps all students engaged as they listen and build on their classmates' contributions.
Brainwriting is a good option for shy or hesitant students. Rather than calling out ideas, students write down their thoughts and pass them around. Teachers can use brainwriting to have students list ideas individually, then combine and categorize the ideas as a group. This allows for more equal participation and thoughtful responses.
Online Boards
Digital whiteboards like Padlet or Jamboard provide an online space for students to simultaneously brainstorm ideas. Teachers can create a board for a prompt, then have students add virtual sticky notes with their thoughts. This allows for rapid collection of many ideas that can be displayed, categorized, and prioritized.
Concept Mapping
Concept mapping is a visual brainstorming activity. Students add ideas to a map, connecting them with lines and branches to show relationships. This helps students organize and analyze information to see patterns and themes. Concept mapping activates critical thinking as students categorize concepts and identify connections.
Brainstorming brings several benefits that support active learning. It gets students engaged right away, rather than passively listening to a lecture. It allows teachers to rapidly assess student knowledge and ideas. Most importantly, it empowers students to take charge of their own learning. Implementing regular brainstorming provides a pathway to student-driven education.
In what ways can brainstorming activities encourage creative thinking and problem-solving skills among students?
Encouraging Creative Thinking and Problem-Solving through Brainstorming
Brainstorming activities can be highly effective for developing creative thinking and problem-solving skills in students. Brainstorming involves coming up with as many ideas as possible in a short time period, without judging or analyzing the ideas. This creates an environment where students feel comfortable sharing unconventional or "out there" ideas. Several aspects of brainstorming encourage creative thinking.
First, the rapid pace of brainstorming sessions forces students to think on their feet. They must tap into their knowledge and imagination to quickly produce many ideas. This pushes them outside their normal thought patterns. The sheer volume of ideas generated also increases the chances that original, creative ideas will emerge.
Additionally, since there is no criticism during brainstorming, students feel free to take risks. They do not have to worry about their ideas being judged as silly or unrealistic. This lack of criticism promotes creative leaps. Students can make connections between remote ideas and build off each other's ideas in new ways.
Brainstorming also fosters collaborative creativity. Hearing their peers' ideas prompts students to consider a topic from different angles. Combining multiple viewpoints allows for innovative solutions. Interacting as a team strengthens creativity and idea generation.
When applied to problem-solving, brainstorming removes the pressure students often feel to come up with "the right answer." Generating volumes of ideas allows them to explore many possible solutions. This pushes them to think broadly rather than rigidly focusing on obvious or familiar approaches. Evaluating multiple options encourages critical analysis.
Overall, the free-flowing, non-judgmental format of brainstorming gives students license to tap into their creativity. It exposes them to diverse perspectives and unlocks innovative thinking. By promoting out-of-the-box brainpower, brainstorming readies students to be imaginative problem-solvers.
What are some key elements of effective brainstorming?
Generating Many Ideas One of the most important aspects of effective brainstorming is generating a large quantity of ideas. The goal is to come up with as many ideas as possible without judging or filtering them initially. This allows people to think expansively and tap into their creativity. It's easy to dismiss ideas prematurely before fully exploring their potential. Holding off on evaluation and giving oneself permission to think freely leads to more ideas.
Building on Others' Ideas Brainstorming is often done in groups precisely so participants can build on one another's ideas. When one person shares an idea, it can spark new associations and directions in others. This synergistic effect allows the group to generate more creative solutions together than any one individual could alone. It's important to actively listen to teammates and use their ideas to prompt new ones.
Deferring Judgment To maximize idea generation, evaluation and criticism should be deferred during the brainstorming process. Prematurely rejecting ideas hinders creativity. Participants should feel comfortable sharing any idea without fear of judgment. Analysis comes later when ideas are winnowed down. The initial phase should foster an open, noncritical environment.
Allowing Wild Ideas Some of the most creative ideas seem outlandish at first. Unique associations and unexpected directions sometimes lead to innovative solutions. During brainstorming, no idea is too crazy or impossible. In fact, wild ideas often spur more possibilities by opening up new lines of thinking. Imagination should be encouraged, not restrained.
Focusing on Quantity The goal of brainstorming is to maximize the number of ideas generated. The assumption is that quantity will lead to higher quality solutions. A large pool of ideas provides more options to draw from. Even proposed solutions that don't work can stimulate different approaches. Setting a numeric target for ideas can help participants focus on volume.
Recording All Ideas All ideas should be captured during brainstorming, usually by writing them down or typing them. This prevents good ideas from being forgotten or lost. It also shows participants that all contributions are valued rather than judged or filtered prematurely. Recording provides a master list to evaluate later when identifying the most promising solutions.
How can brainstorming be used to generate creative solutions to problems?
Using brainstorming to generate creative solutions.
Brainstorming is a creative thinking technique that can be used by groups or individuals to generate a broad range of ideas for solving problems. The key principles of brainstorming are:
Generate as many ideas as possible - the focus is on quantity, not quality.
Withhold criticism and evaluation of ideas - this comes later in the creative process.
Build on others' ideas - use associations to spark new ideas.
Encourage wild and exaggerated ideas - this can lead to more creative solutions.
Brainstorming takes advantage of the fact that our minds make free associations. One idea can spark another idea or trigger a new connection. By separating the idea generation from the evaluation, we create an environment where people feel free to think creatively.
There are some guidelines for conducting effective brainstorming sessions:
Have a diverse group - different perspectives give more ideas.
Frame the problem clearly - so everyone understands the goal.
Set a time limit - short sessions spark fast idea generation.
Record all ideas - capture everything so it can be reviewed later.
Establish ground rules - like encouraging wild ideas and prohibiting criticism.
Individual brainstorming can also be effective. Some techniques include free writing, mind mapping, or setting a short time limit to list ideas. The key is to let the mind wander freely and make new connections.
After brainstorming, the ideas need to be evaluated and refined. Look for themes and patterns. Combine related ideas into stronger solutions. Identify the ideas that are most creative, practical, and aligned with the goals. By starting with a broad set of possibilities, brainstorming gives us more options to choose from to create the best solutions.
Brainstorming is commonly used in business, but has many other applications as well. Teachers can use it to develop engaging lessons. Engineers can use it to design products. Writers can use it to overcome writer's block. Nonprofits can use it to create programs that better serve their communities. Whenever we need original ideas and creative solutions, brainstorming is a valuable technique.
The key benefits of brainstorming are that it pushes us to think more broadly, tap into our creativity, leverage group knowledge, and arrive at innovative solutions. By capturing a wide range of ideas before evaluating them, brainstorming lays the groundwork for overcoming challenges with imaginative thinking.
What techniques can improve the productivity of a brainstorming session?
Brainstorming is a common technique used to generate creative ideas and solutions for problems. While brainstorming sessions can lead to innovative thinking, they can also be unproductive if not facilitated properly. There are several techniques that can be used to improve the productivity of brainstorming sessions.
Setting Ground Rules
It is important to establish some basic ground rules at the start of a brainstorming session. Participants should be encouraged to think freely and suggest as many ideas as possible, no matter how unrealistic they may seem. Judgment and analysis of ideas should be withheld during the brainstorming process. Setting these expectations helps participants feel comfortable sharing unconventional concepts.
Having a Facilitator
A facilitator can help guide the brainstorming session. The facilitator should create a relaxed environment, keep the discussion on track, make sure every participant has a chance to contribute, and set time limits for activities. They may also record ideas and encourage participants to build on each other's suggestions.
Using Brainstorming Techniques
Certain techniques can help generate more creative ideas during brainstorming. For example, providing thought-provoking questions, prompts or images to stimulate ideas. Using methods like listing, free association, or mind mapping to explore ideas. Allowing time for individual reflection and small group discussions before sharing ideas with the full group. Alternating between divergent thinking to expand ideas and convergent thinking to refine ideas.
Leveraging Technology
Technology tools can facilitate brainstorming and capture ideas. Using online whiteboards allows simultaneous visual idea mapping. Collaborative documents make it easy to co-create and organize ideas. File sharing and cloud-based applications give access to inspiration materials. Virtual sticky notes enable quick capture of thoughts. These tools boost productivity by streamlining the brainstorming process.
With the right facilitation, techniques and technology, brainstorming sessions can lead to innovative breakthroughs. A productive brainstorming environment allows people to think expansively, build on ideas collectively and capture inspiration effectively.
What are some effective brainstorming techniques that can help students generate ideas?
Brainstorming techniques for students.
Brainstorming is a creative thinking process that helps students generate many ideas. Effective brainstorming techniques get students engaged and allow them to build on each other's ideas. This leads to quality ideas that can be used for writing assignments, projects, and more. There are several techniques students can use to brainstorm effectively.
Freewriting
Freewriting involves writing continuously for a set time period, such as 5-10 minutes. Students should write whatever comes to mind about the topic without stopping. This helps overcome writer’s block and tap into creativity. It’s important not to edit or judge the writing. Freewriting brings ideas to the surface that can then be refined.
Listing is simply writing down all ideas that come to mind about a topic. There is no need to elaborate or explain the ideas. The goal is to generate as many ideas or keywords related to the topic as possible. Listing works well individually or in groups, with students contributing their ideas to one master list.
Mind mapping is a visual technique where students create a diagram of ideas around a central topic. Main themes and ideas branch off the central topic, with sub-topics branching off of those. This spatial arrangement helps students see connections between ideas and stimulates new thoughts.
Group Brainstorming
Group brainstorming allows students to build on each other’s ideas. Ground rules help ensure it’s productive, like avoiding criticism and encouraging wild ideas. Taking turns and giving everyone a chance to contribute is key. Groups can brainstorm verbally or by writing ideas down. A recorder can document the ideas generated.
Using a mix of individual and group techniques engages different learning styles. Brainstorming works best when students focus on quantity over quality of ideas. The goal is to generate a large pool of ideas to select from later. With practice, brainstorming can help students become more flexible, creative thinkers.
How can teachers encourage creative brainstorming in the classroom?
Encouraging creative brainstorming in the classroom.
Brainstorming is a creative thinking technique that involves coming up with as many ideas as possible around a specific topic or question. Teachers can utilize brainstorming in the classroom to engage students, spark creativity, and generate a wide range of ideas and perspectives. There are several methods teachers can use to encourage effective brainstorming.
First, teachers should explain the brainstorming process and set expectations. Clarify that the goal is to produce a large quantity of ideas without any judgment or critique. Encourage students to think broadly and suggest any idea that comes to mind, no matter how outlandish. Frame brainstorming as an opportunity to be creative and innovative.
Second, teachers can use brainstorming prompts or questions that are open-ended yet focused on a specific topic. Narrow prompts give students a direction while still allowing for imagination. Asking "how might we..." questions also sparks divergent thinking. For example, "How might we redesign the cafeteria to make lunchtime more enjoyable?"
Third, teachers should encourage equal participation from all students during brainstorming. Shyer students can be drawn out by using think-pair-share techniques. Calling on students randomly also prevents any one student from dominating. Writing down all ideas anonymously is another way to get broad participation.
Fourth, teachers can set a fun, energetic tone during brainstorming sessions. Upbeat music playing in the background promotes creativity. Teachers can also use timers to encourage fast-paced idea generation. Turning brainstorming into a competition or game, like seeing which group can come up with the most ideas, also engages students.
Fifth, it is important for teachers to withhold any judgment or criticism during the brainstorming process. Every idea should be welcomed. Teachers should encourage students to build on one another's ideas, but there should be no discussion of quality until later. Evaluating ideas comes after brainstorming.
By explaining the brainstorming process, using focused prompts, encouraging broad participation, setting an energetic tone, and withholding judgment, teachers can promote creative and effective brainstorming in the classroom. The variety of perspectives and unfiltered ideas will benefit students as they tackle issues and challenges.
What types of brainstorming activities work well for students just learning this skill?
Brainstorming activities for beginners.
Brainstorming is an important skill for students to learn. It involves coming up with as many ideas as possible on a topic without judging or filtering them. Some effective brainstorming activities for students just learning this skill include free writing, listing, group brainstorming, using prompts, and mind mapping.
Free Writing
Free writing involves setting a timer for 5-10 minutes and writing continuously about a topic. This helps students generate lots of ideas without self-editing. Teachers can provide thought-provoking questions to guide the free writing.
Listing is a simple brainstorming technique where students make a bulleted list of words or phrases related to the topic. Listing works well individually or in groups. Teachers can have students list for a set time to encourage volume of ideas.
Group brainstorming allows students to build on each other's ideas. Teachers can have students share ideas round robin style or sticky note ideas on charts. It helps expose students to diverse perspectives.
Using Prompts
Prompts like photos, quotes, and questions can stimulate students' thinking in new directions. Teachers can provide a variety of thought-provoking prompts to unlock ideas.
Mind mapping involves noting a central idea and branching out related ideas. This visual approach helps students see connections. Mind mapping works for individual and group brainstorming.
The key with any brainstorming activity is to defer judgment and go for quantity and diversity of ideas. Teachers should encourage an open, playful approach. The more students practice brainstorming, the more adept they will become at this valuable skill.
What are the benefits of individual brainstorming?
Generating Many Ideas One of the main benefits of individual brainstorming is that it allows a person to generate many ideas without being influenced or interrupted by others. When brainstorming alone, a person can freely think through and explore an issue from multiple angles and perspectives. This leads to coming up with a large quantity and wide variety of ideas. Individual brainstorming gives a person the time and space to make connections between concepts and follow trains of thought without external distractions.
No Evaluation Another advantage of individual brainstorming is that there is no pressure to evaluate ideas as they emerge. In a group setting, some ideas may be dismissed prematurely before they are fully explored. When brainstorming alone, a person can record any and all ideas without judging them. This separation of the idea generation and evaluation stages allows for greater creativity. Unique, unconventional ideas have a chance to surface when evaluation is deferred.
Convenience Individual brainstorming is often more convenient than group brainstorming. It can be done at any time and place without having to coordinate schedules with others. This makes it easy to incorporate brainstorming sessions into a regular work routine. Individual brainstorming also avoids potential conflicts and complications that can arise when putting together a group. A person can brainstorm productively at their own pace without having to compromise.
No Social Pressures Brainstorming alone eliminates social pressures that can interfere with idea generation in groups. There is no need to worry about judgment or rejection of ideas by others. Shy or introverted individuals may feel more comfortable brainstorming independently rather than in groups. Without the fear of embarrassment or ridicule, a person can be more imaginative and think freely. Individual brainstorming provides a safe space to explore bold, unusual ideas.
Focus Individual brainstorming allows a person to maintain focus on the topic at hand. In group settings there can be distractions, side conversations, and tangents that divert attention and disrupt the flow of ideas. When brainstorming alone, a person can concentrate fully on the brainstorming goal without external interference. This sustained focus facilitates making connections between ideas and drilling down on concepts more deeply.
How can I apply individual brainstorming techniques?
Applying Individual Brainstorming Techniques
Individual brainstorming is a creative thinking technique that can generate many ideas by allowing one person to think freely. When applying individual brainstorming, it is important to create an environment conducive to free-flowing thought. This can be done by finding a comfortable, quiet space free from distractions. It is also helpful to have writing tools available to capture ideas as they arise.
To begin an individual brainstorming session, first identify the problem or topic you want to generate ideas about. Write this down so you can stay focused. Next, set a time limit, usually about 15-30 minutes. This will help drive focused idea generation.
During the session, let your mind wander freely related to the topic. Write down any idea that comes to mind, without judging or analyzing the idea. The key is to record as many ideas as possible. If you get stuck, try prompting further ideas by asking yourself questions like "How can I improve this?" or "What if I changed this?".
After the timed session, review all the ideas you wrote down. Now you can analyze and prioritize the ideas to select the best ones to pursue. For example, you may choose ideas that are the most unique, feasible, or aligned with your goals.
Applying techniques like individual brainstorming can lead to creative solutions and innovations. The free-flowing ideation lets you tap into your imagination. By suspending judgment during idea generation, you give your creative mind more space to make connections. The result can be fresh, unconventional ideas. With focused practice, individual brainstorming can become a productive part of your problem-solving process.
What steps should I follow when using individual brainstorming?
Individual brainstorming is a creative thinking technique that allows a person to generate ideas independently. This method can help stimulate new thoughts and perspectives without influence from others. When using individual brainstorming, there are several steps to follow:
Preparation
First, clearly define the problem, topic, or issue you want to brainstorm. Understanding the scope and parameters will focus your thoughts. Gather any background information that may spark ideas. Have the necessary supplies available like a notepad, whiteboard, recorder, etc. Set a time limit for your brainstorming session.
Idea Generation
During the session, focus solely on coming up with ideas. Write down every thought that comes to mind, without judging or analyzing. Let your mind wander freely through associations, combinations, translations, etc. Build on ideas by finding relationships and modifying concepts. Capture any insight or inspiration in the moment. Silence self-criticism and edit later. Set a goal for the number of ideas to create momentum.
Organization
After the timed session, review all the ideas generated. Group related concepts together. Look for themes and patterns. Eliminate duplicates. Refine ideas by adding detail and merging overlapping thoughts. Rank ideas by criteria like feasibility, novelty, and alignment with goals. Prioritize the strongest ideas for further development. Discard impractical or irrelevant notions.
With the filtered list, critically analyze each idea. Determine pros, cons, and potential obstacles. Look for ways to improve upon ideas. Identify those that align best with objectives. Select the top ideas to pursue further. Consider testing concepts quickly through low-cost experiments. Save unused ideas in case they become relevant later.
Following this deliberate process stimulates creative thinking and produces promising new ideas through individual brainstorming. Separating idea generation from evaluation allows unconstrained ideation. Preparation, organization, and evaluation then transform raw concepts into viable solutions to pursue.
What are the key steps involved in reverse brainstorming?
Reverse brainstorming is a creative thinking technique that involves working backwards from a goal or desired outcome to generate ideas. There are several key steps involved in conducting an effective reverse brainstorming session:
Define the Goal
The first step is to clearly define the goal or desired outcome you want to achieve. This gives the reverse brainstorming process a specific focus and direction. For example, the goal could be developing a new product, improving an existing process, or solving a particular problem.
Identify Obstacles and Barriers
Once the goal is defined, the next step is to identify potential obstacles, issues, or barriers that could prevent you from achieving the goal. The aim is to think of all the things that could possibly go wrong or get in the way of the desired outcome.
Generate Ideas to Overcome Obstacles
With the obstacles and barriers identified, the third step is to generate ideas and solutions for overcoming them. Approach this step with creativity and an open mindset. The aim is to develop strategies, processes, and innovations that could help overcome the identified obstacles to reach the goal.
Refine and Prioritize Ideas
The fourth step involves analyzing and refining the ideas generated in the previous step. Look for ways to combine or improve upon the ideas. Then prioritize the most promising and innovative solutions. Focus on the ideas that seem most likely to overcome the identified barriers.
Develop an Implementation Plan
The final step is to develop an action plan for implementing the best ideas from the session. Determine what resources are needed, who will be responsible for each task, and timelines for rolling out the solutions. This provides a roadmap for applying the output of the reverse brainstorming session.
In summary, reverse brainstorming fosters creative problem solving by working backward from goals to identify and overcome obstacles. Defining the goal, identifying barriers, generating solutions, refining ideas, and developing an implementation plan are the key steps in this productive group thinking technique.
How can reverse brainstorming be used to generate innovative ideas?
Using reverse brainstorming to generate innovative ideas, the reverse brainstorming process, overcoming limiting factors, fostering creative thinking, applications of reverse brainstorming, what are some of the advantages and disadvantages of using reverse brainstorming compared to traditional brainstorming, advantages of reverse brainstorming, disadvantages of reverse brainstorming, how can brainstorming ideas lead to innovative solutions, generating ideas through brainstorming.
Brainstorming is a common technique used to generate creative ideas and solutions. It involves coming up with as many ideas as possible in a short period of time, without judging or analyzing the ideas. Brainstorming taps into a group's collective knowledge and imagination to explore possibilities and alternatives. It encourages people to think freely and suggest any idea that comes to mind, including unconventional or outlandish ideas. Studies show that brainstorming in groups leads to more creative ideas than individuals working alone.
During a brainstorming session, all ideas are welcomed. The goal is to defer judgment and stimulate the flow of ideas. Participants can build on each other's ideas, combining and improving them. One idea can spark another creative connection. Capturing all the ideas provides a large pool of options to draw from. After the brainstorming, the ideas can be analyzed and the most promising solutions identified. Setting a time limit creates a sense of urgency that motivates quick idea generation.
Brainstorming brings together people with diverse backgrounds who can contribute different perspectives. This diversity of experience and knowledge leads to more innovative outcomes. When group members feel psychologically safe to share unconventional ideas without fear of judgment, more creativity emerges. Laughter and humor can foster an open, playful environment that sparks new insights and connections.
Following are some tips for effective brainstorming: Ask open-ended questions to get ideas flowing. Encourage wild and exaggerated ideas. Build on others' ideas. Set a time limit to spur quick thinking. Defer judgment and avoid criticizing ideas during the brainstorm. Capture every idea by writing or drawing them. Appoint someone to record the ideas. Changing locations can stimulate creative thinking. The random mixing of ideas and cross-pollination often produces the most innovative results.
In summary, brainstorming provides an inclusive environment for imaginative idea generation. By leveraging group knowledge and promoting unconventional solutions, brainstorming can lead to innovative outcomes and creative problem solving. The free flow of ideas unhindered by judgment is key to tapping the collective creativity of the group. Evaluation comes later. The synergy of the group, cross-fertilization of perspectives, and spontaneous sparks of insight give brainstorming its power to develop new, original solutions.
What techniques are most effective for brainstorming ideas in a group setting?
Brainstorming techniques for groups.
Brainstorming is a creative technique to generate ideas in a group. It involves suggesting as many ideas as possible without judging them. Effective brainstorming results in a large number of creative ideas. There are several techniques that can improve brainstorming effectiveness in a group setting.
No Criticism
The most important rule in brainstorming is no criticism of ideas. Judgment and analysis at this stage stops idea flow. All ideas should be welcomed. Evaluation comes later. Members must feel comfortable suggesting unusual ideas without fear of criticism.
Encourage Wild Ideas
Wild and exaggerated ideas can lead to creative solutions. Members should be encouraged to think outside the box. Unusual suggestions may spark others to improve on them. Impossible ideas can lead to practical solutions. Welcoming all ideas sets a creative tone.
Build on Other Ideas
Members should be encouraged to build on each other's ideas. This piggyback effect stimulates the group's imagination. Combining and improving ideas leads to even better solutions. Building on others' ideas brings synergy to the group.
Record All Ideas
All ideas should be visible to the group. A whiteboard, flipchart or digital doc allows real-time recording. This encourages members to keep suggesting ideas when they can see them accumulate. Visible recording also enables combining and improving ideas.
Set a Time Limit
A time limit creates a sense of urgency. Members focus on quickly suggesting many ideas instead of elaborating on them. Short 5-10 minute bursts allow rapid fire brainstorming. Time limits keep the session fast-paced and dynamic.
Stay Focused
The brainstorming session should focus on a single, clearly defined issue. Straying from the topic wastes time and dilutes ideas. The leader should re-direct the group if focus is lost. A visible reminder of the issue keeps the group on track.
Using these techniques will produce a wealth of creative options. The ideas can then be analyzed to select the best solutions for implementation. Effective group brainstorming sessions lead to innovation.
How do creative thinkers generate and develop brainstorming ideas?
Generating Brainstorming Ideas Creative thinkers use various techniques to generate initial brainstorming ideas. One approach is free association, where thinkers spontaneously shout out any ideas that come to mind related to the topic without judging or filtering. This encourages divergent thinking and gets past mental blocks. Another technique is making forced connections between the topic and unrelated subjects, which can yield unexpected insights. Thinkers may also gather existing ideas by researching what others have already done. Finally, changing physical and mental perspectives, such as moving to a new location or imagining being someone else, can stimulate new ideas.
Developing Brainstorming Ideas Once creative thinkers have generated initial ideas through brainstorming, they use various strategies to develop the most promising ones. A common technique is to combine ideas together into new hybrid concepts. Building on each other's ideas in a collaborative group setting often produces fresh perspectives. Thinkers also try to find the weaknesses in initial ideas to improve and strengthen them. Setting the ideas aside for a time before revisiting them allows for incubation, yielding natural enhancements. Experimenting with taking ideas to extremes or reversing them also stretches thinking in new directions. Overall, creative thinkers iterate on brainstorming by playing with ideas, testing them, and bouncing them off others.
Assessing Brainstorming Ideas After generating and developing a set of brainstormed ideas, creative thinkers assess the results to identify the solutions with the most potential. They analyze ideas against the goals and criteria of the problem to gauge alignment. Thinkers also get feedback from others, like colleagues, experts, or target users, to help determine the best directions. Prototyping or testing out some ideas on a small scale is another way creative thinkers evaluate brainstorming results. The most promising ideas are those that are original, useful, and feasible to implement. With assessment, creative thinkers determine which brainstorming ideas merit further energy and resources.
Selecting the Best Ideas The final step is to select the top ideas from the brainstorming process for implementation. Creative thinkers compare the pros and cons of the final options. They combine complementary ideas and refine details to strengthen the solutions. Budget, resources, and other constraints are considered to focus on executable ideas. The solutions are prioritized based on which have the greatest potential for impact and success. This narrowing process requires making tough choices to bring the most promising brainstormed ideas to fruition.
In summary, creative thinkers have many techniques for generating ideas through brainstorming, developing the most promising ones, assessing them against goals, and selecting the best to act on. With iteration, collaboration, and evaluation, brainstorming enables thinkers to produce innovative solutions to complex problems.

SHe is a graduate of Akdeniz University, Department of Business Administration. She graduated from the university with a faculty degree. It has contributed to its environment with its social responsibility project. She writes articles about business and its fields.

What are Problem Solving Skills?

How To Develop Problem Solving Skills?

How To Solve The Problems? Practical Problem Solving Skills

What are Leadership Qualities?
How to Use Online Whiteboards for Effective Problem-Solving
- Post author By Jessica Wu
- Post date July 3, 2024

Effective problem-solving is at the heart of innovation and success, especially for agile teams. Teams need to quickly identify issues, brainstorm solutions, implement strategies efficiently, and adopt technology tools to help. Online whiteboards are a popular tool for distributed teams and have revolutionized the way we approach these challenges, helping teams collaborate visually and structure their thoughts in real-time, no matter where they are. Below, we explore how to harness the power of online whiteboards for problem-solving, dive into various problem-solving strategies, and introduce Frameable Whiteboard as a top-tier tool designed for structured thinking.
The Power of Online Whiteboards in Problem-Solving
What is an Online Whiteboard?
An online whiteboard is a digital tool that mimics the functionality of a physical whiteboard but with enhanced features such as real-time collaboration, drawing and annotation tools, and more. These features allow users to brainstorm, organize ideas, and develop solutions in a virtual canvas accessible from anywhere.
Why Use Online Whiteboards?
Online whiteboards bring several advantages to the table, especially when it comes to problem-solving:
- Collaboration: Teams can work together in real-time, regardless of their geographical location.
- Visualization: Concepts and ideas can be illustrated with diagrams, mind maps, and other visual aids.
- Organization: Notes, images, and other resources can be organized on an infinite canvas, making it easier to see the big picture.
- Accessibility: All changes are saved in the cloud, ensuring that the latest version is always available to all team members.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills with Online Whiteboards
Structured Visual Thinking
Effective problem-solving often requires structured visual thinking , which involves organizing and processing information visually to enhance understanding and communication. Online whiteboards excel in facilitating this by offering various templates and tools that help structure thoughts and ideas clearly and logically.
Problem-Solving Strategies
Here are some key problem-solving strategies that can be enhanced through the use of online whiteboards:
- Brainstorming: This initial stage involves generating as many ideas as possible. Online whiteboards provide a collaborative platform where all team members can contribute ideas simultaneously on a blank canvas.
- Mind Mapping : This technique helps in organizing thoughts and ideas around a central concept. By creating a mind map on an online whiteboard, teams can visually explore and connect different aspects of a problem.
- SWOT Analysis : This strategy involves analyzing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem. Online whiteboards can be used to create a structured SWOT analysis chart, to help you identify and comprehensively assess various factors affecting the problem at hand.
Approaching Complex Problems with Online Whiteboards
When it comes to complex problem-solving, structured thinking is crucial. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to approach a complex problem using an online whiteboard as a canvas for organizing your thoughts:
- Define the Problem: Clearly articulate the problem statement. This step should always be followed for effective problem-solving.
- Gather Information: Collect relevant data and insights and add this information to your online whiteboard so everything you need is organized in one place.
- Identify Possible Solutions: Brainstorm potential solutions and create a mind map to explore different ideas. If you’ve never created a mind map, there are plenty of mind map templates to help you get started.
- Evaluate Solutions: Use online whiteboards to create SWOT analysis or decision trees to evaluate the pros and cons of each solution.
- Implement the Solution: Develop an action plan in an online whiteboard and assign tasks to teammates using the whiteboard’s collaborative features such as tags and comments.
- Monitor and Review: Track progress and make necessary adjustments. Online whiteboards allow for unlimited updates and revisions.
Frameable Whiteboard: Built for Structured Thinking
Frameable Whiteboard is a premier online whiteboard designed specifically for structured thinking and problem-solving [link to pillar page]. It offers a suite of features tailored to facilitate complex and effective problem-solving strategies:
Nested Cards: Frameable Whiteboard allows users to create nested cards, which are perfect for breaking down complex problems into manageable parts. This feature supports structured visual thinking by helping users organize information hierarchically.
Templates for Structured Thinking: Frameable Whiteboard provides a variety of templates, including Business Model Canvas, SWOT Analysis, Concept Map, Mind Map, and Decision Tree. These templates are designed to guide users through structured problem-solving processes.
Real-Time Collaboration: Teams can collaborate in real-time, making it easy to brainstorm ideas, develop strategies, and track progress together, regardless of location.
Tips for Maximizing the Use of Online Whiteboards
Establish Clear Objectives
Before diving into a brainstorming or problem-solving session, establish clear objectives. Knowing what you aim to achieve keeps the team focused and ensures that the session is productive. Use the online whiteboard to list these objectives visibly so everyone stays aligned and on-task.
Encourage Participation
To harness the full potential of your team’s creativity and problem-solving skills, encourage participation from all members. Online whiteboards allow for real-time contributions, so ensure that everyone has the opportunity to share their ideas with time-boxed opportunities to do so in these sessions. This inclusive approach can uncover insights that might otherwise be missed.
Utilize Templates
Frameable Whiteboard offers a variety of templates designed for structured thinking. Take advantage of these templates to streamline your problem-solving process. Whether it’s a SWOT analysis or a mind map, these tools provide a structured format that can help organize and visualize your thoughts.
Break Down Problems
Complex problems can often feel overwhelming. Use nested cards on Frameable Whiteboard to break down these problems into smaller, more manageable parts. This hierarchical organization makes it easier to tackle each aspect of the problem methodically and completely.
Track Progress
An effective problem-solving process doesn’t end once a solution is implemented. Continuously track progress and make adjustments as needed. Online whiteboards allow you to update your plans in real time, ensuring that your team stays on track and any new issues are promptly addressed.
Leverage Visual Aids
Visual aids such as arrows and shapes can significantly enhance understanding and communication. Use these features on your online whiteboard to illustrate complex relationships and ideas, making it easier for the team to grasp and analyze information.
Transform Your Problem-Solving Approach
Online whiteboards are powerful tools for enhancing problem-solving skills and strategies. By facilitating structured visual thinking and real-time collaboration, they enable teams to tackle complex problems effectively. Frameable Whiteboard, with its suite of features designed for structured thinking, stands out as an ideal solution for teams looking to enhance their problem-solving processes.
Ready to elevate your problem-solving skills? Get started with Frameable Whiteboard for free and experience the power of structured visual thinking in action. Visit Frameable Whiteboard to sign up and begin your journey towards more effective problem-solving today!
Problem solving made easy with structured-thinking practices
- Tags productivity , remote work , whiteboard

Effective Problem-Solving Techniques in Business
Problem solving is an increasingly important soft skill for those in business. The Future of Jobs Survey by the World Economic Forum drives this point home. According to this report, complex problem solving is identified as one of the top 15 skills that will be sought by employers in 2025, along with other soft skills such as analytical thinking, creativity and leadership.
Dr. Amy David , clinical associate professor of management for supply chain and operations management, spoke about business problem-solving methods and how the Purdue University Online MBA program prepares students to be business decision-makers.
Why Are Problem-Solving Skills Essential in Leadership Roles?
Every business will face challenges at some point. Those that are successful will have people in place who can identify and solve problems before the damage is done.
“The business world is constantly changing, and companies need to be able to adapt well in order to produce good results and meet the needs of their customers,” David says. “They also need to keep in mind the triple bottom line of ‘people, profit and planet.’ And these priorities are constantly evolving.”
To that end, David says people in management or leadership need to be able to handle new situations, something that may be outside the scope of their everyday work.
“The name of the game these days is change—and the speed of change—and that means solving new problems on a daily basis,” she says.
The pace of information and technology has also empowered the customer in a new way that provides challenges—or opportunities—for businesses to respond.
“Our customers have a lot more information and a lot more power,” she says. “If you think about somebody having an unhappy experience and tweeting about it, that’s very different from maybe 15 years ago. Back then, if you had a bad experience with a product, you might grumble about it to one or two people.”
David says that this reality changes how quickly organizations need to react and respond to their customers. And taking prompt and decisive action requires solid problem-solving skills.
What Are Some of the Most Effective Problem-Solving Methods?
David says there are a few things to consider when encountering a challenge in business.
“When faced with a problem, are we talking about something that is broad and affects a lot of people? Or is it something that affects a select few? Depending on the issue and situation, you’ll need to use different types of problem-solving strategies,” she says.
Using Techniques
There are a number of techniques that businesses use to problem solve. These can include:
- Five Whys : This approach is helpful when the problem at hand is clear but the underlying causes are less so. By asking “Why?” five times, the final answer should get at the potential root of the problem and perhaps yield a solution.
- Gap Analysis : Companies use gap analyses to compare current performance with expected or desired performance, which will help a company determine how to use its resources differently or adjust expectations.
- Gemba Walk : The name, which is derived from a Japanese word meaning “the real place,” refers to a commonly used technique that allows managers to see what works (and what doesn’t) from the ground up. This is an opportunity for managers to focus on the fundamental elements of the process, identify where the value stream is and determine areas that could use improvement.
- Porter’s Five Forces : Developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter, applying the Five Forces is a way for companies to identify competitors for their business or services, and determine how the organization can adjust to stay ahead of the game.
- Six Thinking Hats : In his book of the same name, Dr. Edward de Bono details this method that encourages parallel thinking and attempting to solve a problem by trying on different “thinking hats.” Each color hat signifies a different approach that can be utilized in the problem-solving process, ranging from logic to feelings to creativity and beyond. This method allows organizations to view problems from different angles and perspectives.
- SWOT Analysis : This common strategic planning and management tool helps businesses identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT).
“We have a lot of these different tools,” David says. “Which one to use when is going to be dependent on the problem itself, the level of the stakeholders, the number of different stakeholder groups and so on.”
Each of the techniques outlined above uses the same core steps of problem solving:
- Identify and define the problem
- Consider possible solutions
- Evaluate options
- Choose the best solution
- Implement the solution
- Evaluate the outcome
Data drives a lot of daily decisions in business and beyond. Analytics have also been deployed to problem solve.
“We have specific classes around storytelling with data and how you convince your audience to understand what the data is,” David says. “Your audience has to trust the data, and only then can you use it for real decision-making.”
Data can be a powerful tool for identifying larger trends and making informed decisions when it’s clearly understood and communicated. It’s also vital for performance monitoring and optimization.
How Is Problem Solving Prioritized in Purdue’s Online MBA?
The courses in the Purdue Online MBA program teach problem-solving methods to students, keeping them up to date with the latest techniques and allowing them to apply their knowledge to business-related scenarios.
“I can give you a model or a tool, but most of the time, a real-world situation is going to be a lot messier and more valuable than what we’ve seen in a textbook,” David says. “Asking students to take what they know and apply it to a case where there’s not one single correct answer is a big part of the learning experience.”
Make Your Own Decision to Further Your Career
An online MBA from Purdue University can help advance your career by teaching you problem-solving skills, decision-making strategies and more. Reach out today to learn more about earning an online MBA with Purdue University .
If you would like to receive more information about pursuing a business master’s at the Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr. School of Business, please fill out the form and a program specialist will be in touch!
Connect With Us

- Advanced Search
Isogeometric dual reciprocity BEM for solving time-domain acoustic wave problems
New citation alert added.
This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to:
You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited.
To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below.
New Citation Alert!
Please log in to your account
Information & Contributors
Bibliometrics & citations, view options, recommendations, coupling of the improved singular boundary method and dual reciprocity method for multi-term time-fractional mixed diffusion-wave equations.
The main purpose of this work is to present an impressive numerical scheme to solve two-dimensional multi-term time fractional mixed diffusion-wave differential equations (TFMDWE). The proposed method is based on the compact dual ...
Solving Boundary Integral Problems with BEM++
Many important partial differential equation problems in homogeneous media, such as those of acoustic or electromagnetic wave propagation, can be represented in the form of integral equations on the boundary of the domain of interest. In order to solve ...
On Solving an Acoustic Wave Problem Via Frequency-Domain Approach and Tensorial Spline Galerkin Method
In this paper, we introduce a numerical method for solving the dynamical acoustic wave propagation problem with Robin boundary conditions. The method used here is divided into two stages. In the first stage, the equations are transformed, via the ...
Information
Published in.
Pergamon Press, Inc.
United States
Publication History
Author tags.
- Isogeometric BEM
- Non-uniform rational B-splines
- Dual reciprocity method
- Infinite domain
- Time-domain acoustic wave problems
- Research-article
Contributors
Other metrics, bibliometrics, article metrics.
- 0 Total Citations
- 0 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 0
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 0
View options
Login options.
Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.
Full Access
Share this publication link.
Copying failed.
Share on social media
Affiliations, export citations.
- Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ...
We will inform you here when the file is ready.
Your file of search results citations is now ready.
Your search export query has expired. Please try again.

COMMENTS
Unleashing your team's creativity through effective brainstorming techniques is a game-changer when it comes to generating new ideas and innovative solutions. Let's delve into ten creative brainstorming techniques that can breathe life into your brainstorming sessions: 1. Mind mapping.
Whether you're problem-solving, developing a new product, or trying to come up with creative ideas for your business, brainstorming isn't just about gathering your group members together and hoping the innovation sparks fly. There are proven methods, techniques, and tools that can make effective brainstorming easier than ever.
Brainstorming is a method design teams use to generate ideas to solve clearly defined design problems. ... Marketing CEO Alex Osborn, brainstorming's "inventor", captured the refined elements of creative problem-solving in his 1953 book, Applied Imagination. In brainstorming, we aim squarely at a design problem and produce an arsenal of ...
Better Brainstorming. Focus on questions, not answers, for breakthrough insights. Summary. Great innovators have long known that the secret to unlocking a better answer is to ask a better question ...
Definition of brainstorming. Brainstorming is a creative thinking technique for coming up with new ideas and solving problems. Teams use this ideation method to encourage new ways of thinking and collectively generate solutions. Brainstorming encourages free thinking and allows for all ideas to be voiced without judgment, fostering an open and ...
How it works: Unlike the others, this technique is best used ahead of your brainstorming session so that you can set your team up for success. Problem-framing challenges you to pinpoint the core problem that you're solving for (for example, improving collaboration between your marketing and sales teams) and then draft a problem statement.
Starbursting. Like a reporter trying to discover the pivotal information to a story, the starbursting method of brainstorming requires you to think about the who, what, where, when, why, and how for any new idea. Place your main idea at the center of a star diagram, labeling each point of the star with those 5WH questions.
Brainstorming leads to better teamwork and greater group cohesiveness. All of that working together does more than generate better ideas — it can actually improve our level of teamwork. There's plenty of research out there that backs this up. "Groups that focus on both the quantity of ideas and building on the ideas of others ...
Brainstorming combines a relaxd, informal approach to problem solving with lateral thinking. It encourages people to come up with thoughts and ideas that can, at first, seem a bit crazy. ... Online Brainstorming (also known as Brain-netting) - An electronic method of brainstorming, this uses a document stored on a central server, ...
Brainstorming is an essential practice for creative thinking and problem-solving. At its most basic, brainstorming simply means identifying a problem, and then coming up with as many fresh ideas as possible that may help solve that problem. ... 6-3-5 brainwriting is a group brainstorming method that involves creating a lot of ideas and building ...
Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique that involves generating a large number of ideas or solutions to a particular issue or challenge. ... Brainstorming methods are valuable tools for individuals and groups seeking to tap into their collective creativity and explore new possibilities. From structured processes like mind mapping ...
There are many benefits of the six thinking hats brainstorming technique that may be of interest when problem-solving and decision-making. Some of these include: 1. Enhanced creativity . The six thinking hats method stimulates creative thinking by encouraging participants to explore various perspectives, generate new ideas, and think outside ...
Consider the following brainstorming methods and tools to generate and qualify ideas. 1. Starbursting ... The idea napkin also includes a column for who the idea is targeting—meaning who you're solving a problem for (customers, teammates, etc.)—and a column noting what problems your idea addresses. Brainstormers can fill out their napkins ...
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting. ... Problem-solving techniques for brainstorming solutions . Now you have the context and background of the problem you are trying to solving, now comes the time to start ideating and thinking about how ...
Problem solving or idea generation can go around in circles if a team isn't given the freedom to think creatively and approach things from a new angle. Brainstorming methods like those featured here are great ways to unblock a team's creative and find new ways to approach stalled conversations. Improve team morale
Focus Group: small group discussions to generate suggestions and ideas for problem-solving. Crazy-8: fast-paced brainstorming technique to generate ideas within 8 minutes. . 1-2-4-All: individual and group idea generation to facilitate teamwork and quick idea generation. If you run a business, you should know one thing.
Brainstorming is a technique for working with a group to find creative ideas for a specific problem. In short, brainstorming is a method to creatively solve a problem. In this, it is important that everyone has a good understanding of what the problem is in order for people to brainstorm accurate solutions. Do's and don'ts
Establish a factual, robust answer to this, and then repeat the process with the secondary problem. This method helps burrow through the various layers of an issue and eventually reach the underlying root cause. 8. Stop-and-go-brainstorming. This method involves rapid switching between modes of thinking.
Hypothetical brainstorming asks "what if" questions, poses role play scenarios and focuses on creative problem-solving, sometimes in nontraditional ways. Some types of this technique are: 16. "What if" situation With this method of brainstorming, a facilitator presents a central topic and poses a hypothetical scenario. The team presents ...
Brainstorming: Unleashing Creativity and Problem-Solving Potential. Brainstorming is a powerful technique used by individuals or teams to tackle problems, spur innovation, and generate fresh ideas for enhancing products, organizations, or strategies. Brainstorming can unlock creativity and solve complex challenges by following a structured process.
What is Brainstorming: Techniques for Effective Problem Solving. Brainstorming is an invaluable method for generating ideas and solving problems in a creative, collaborative environment. Its essence lies in leveraging the collective thinking of a group, allowing for a diverse range of solutions to emerge from different perspectives. The essence ...
These methods, among others, are vibrant threads in the tapestry of ideation strategies that can be tailored to a myriad of scenarios. B. Suitability of different strategies for different situations. Each brainstorming strategy boasts its unique merits, often making it particularly suitable for specific situations.
Use your Miro post-it notes and creativity and go ahead! Problem solving part 1. Step-by-Step guide for post-up in Miro. The first technique we are focused on is called Post-up, it provides methods for getting information into chunks. Post-up is based on four methods - Brainstorming, Brainwriting, Nominal group technique and Crawford slip method.
The problem solving method of brainstorming is used for all sorts of problems, depending on who is using it and what problem they are trying to solve. Still, it only involves problem-solving-oriented brainstorming when there is an objective. It can be applied to any issue that needs to be solved and allows people who may not feel comfortable ...
Problem-Solving Strategies. Here are some key problem-solving strategies that can be enhanced through the use of online whiteboards: Brainstorming: This initial stage involves generating as many ideas as possible. Online whiteboards provide a collaborative platform where all team members can contribute ideas simultaneously on a blank canvas.
The courses in the Purdue Online MBA program teach problem-solving methods to students, keeping them up to date with the latest techniques and allowing them to apply their knowledge to business-related scenarios. "I can give you a model or a tool, but most of the time, a real-world situation is going to be a lot messier and more valuable than ...
Identify the Correct Problem: Use methods like the 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram to ensure you're solving the right problem. Idea Generation: Employ classic or advanced brainstorming techniques to ...
The fundamental solution of the potential problem is used to establish the boundary-domain integral equation, which avoids the problem of solving the coefficient matrix repeatedly at different times. On the one hand, in order to maintain the dimensionality reduction advantages of the boundary element method, the classical dual reciprocity ...